Home / Guides / Writing Guides / Writing Tips / How to Brainstorm for an Essay

How to Brainstorm for an Essay
Once you get going on a paper, you can often get into a groove and churn out the bulk of it fairly quickly. But choosing or brainstorming a topic for a paper—especially one with an open-ended prompt—can often be a challenge.
You’ve probably been told to brainstorm ideas for papers since you were in elementary school. Even though you might feel like “brainstorming” is an ineffective method for actually figuring out what to write about, it really works. Everyone thinks through ideas differently, but here are some tips to help you brainstorm more effectively regardless of what learning style works best for you:
Tip #1: Set an end goal for yourself
Develop a goal for your brainstorm. Don’t worry—you can go into brainstorming without knowing exactly what you want to write about, but you should have an idea of what you hope to gain from your brainstorming session. Do you want to develop a list of potential topics? Do you want to come up with ideas to support an argument? Have some idea about what you want to get out of brainstorming so that you can make more effective use of your time.
Tip #2: Write down all ideas
Sure, some of your ideas will be better than others, but you should write all of them down for you to look back on later. Starting with bad or infeasible ideas might seem counterintuitive, but one idea usually leads to another one. Make a list that includes all of your initial thoughts, and then you can go back through and pick out the best one later. Passing judgment on ideas in this first stage will just slow you down.
Tip #3: Think about what interests you most
Students usually write better essays when they’re exploring subjects that they have some personal interest in. If a professor gives you an open-ended prompt, take it as an opportunity to delve further into a topic you find more interesting. When trying to find a focus for your papers, think back on coursework that you found engaging or that raised further questions for you.
Tip #4: Consider what you want the reader to get from your paper
Do you want to write an engaging piece? A thought-provoking one? An informative one? Think about the end goal of your writing while you go through the initial brainstorming process. Although this might seem counterproductive, considering what you want readers to get out of your writing can help you come up with a focus that both satisfies your readers and satisfies you as a writer.
Tip #5: Try freewriting
Write for five minutes on a topic of your choice that you think could be worth pursuing—your idea doesn’t have to be fully fleshed out. This can help you figure out whether it’s worth putting more time into an idea or if it doesn’t really have any weight to it. If you find that you don’t have much to say about a particular topic, you can switch subjects halfway through writing, but this can be a good way to get your creative juices flowing.
Tip #6: Draw a map of your ideas
While some students might prefer the more traditional list methods, for more visual learners, sketching out a word map of ideas may be a useful method for brainstorming. Write the main idea in a circle in the center of your page. Then, write smaller, related ideas in bubbles further from the center of the page and connect them to your initial idea using lines. This is a good way to break down big ideas and to figure out whether they are worth writing about.
Tip #7: Enlist the help of others
Sometimes it can be difficult coming up with paper topics on your own, and family and friends can prove to be valuable resources when developing ideas. Feel free to brainstorm with another person (or in a group). Many hands make light work—and some students work best when thinking through ideas out loud—so don’t be afraid to ask others for advice when trying to come up with a paper topic.
Tip #8: Find the perfect brainstorming spot
Believe it or not, location can make a BIG difference when you’re trying to come up with a paper topic. Working while watching TV is never a good idea, but you might want to listen to music while doing work, or you might prefer to sit in a quiet study location. Think about where you work best, and pick a spot where you feel that you can be productive.
Tip #9: Play word games to help generate ideas
Whether you hate playing word games or think they’re a ton of fun, you might want to try your hand at a quick round of Words With Friends or a game of Scrabble. These games can help get your brain working, and sometimes ideas can be triggered by words you see. Get a friend to play an old-fashioned board game with you, or try your hand at a mobile app if you’re in a time crunch.
Tip #10: Take a break to let ideas sink in
Brainstorming is a great way to get all of your initial thoughts out there, but sometimes you need a bit more time to process all of those ideas. Stand up and stretch—or even take a walk around the block—and then look back on your list of ideas to see if you have any new thoughts on them.
For many students, the most difficult process of paper writing is simply coming up with an idea about what to write on. Don’t be afraid to get all of your ideas out there through brainstorming, and remember that all ideas are valid. Take the time necessary to sort through all of your ideas, using whatever method works best for you, and then get to writing—but don’t be afraid to go back to the drawing board if a new inspiration strikes.
EasyBib Writing Resources
Writing a paper.
- Academic Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- College Admissions Essay
- Expository Essay
- Persuasive Essay
- Research Paper
- Thesis Statement
- Writing a Conclusion
- Writing an Introduction
- Writing an Outline
- Writing a Summary
EasyBib Plus Features
- Citation Generator
- Essay Checker
- Expert Check Proofreader
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tools
Plagiarism Checker
- Spell Checker
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Grammar and Plagiarism Checkers
Grammar Basics
Plagiarism Basics
Writing Basics
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started

Brainstorming
What this handout is about.
This handout discusses techniques that will help you start writing a paper and continue writing through the challenges of the revising process. Brainstorming can help you choose a topic, develop an approach to a topic, or deepen your understanding of the topic’s potential.
Introduction
If you consciously take advantage of your natural thinking processes by gathering your brain’s energies into a “storm,” you can transform these energies into written words or diagrams that will lead to lively, vibrant writing. Below you will find a brief discussion of what brainstorming is, why you might brainstorm, and suggestions for how you might brainstorm.
Whether you are starting with too much information or not enough, brainstorming can help you to put a new writing task in motion or revive a project that hasn’t reached completion. Let’s take a look at each case:
When you’ve got nothing: You might need a storm to approach when you feel “blank” about the topic, devoid of inspiration, full of anxiety about the topic, or just too tired to craft an orderly outline. In this case, brainstorming stirs up the dust, whips some air into our stilled pools of thought, and gets the breeze of inspiration moving again.
When you’ve got too much: There are times when you have too much chaos in your brain and need to bring in some conscious order. In this case, brainstorming forces the mental chaos and random thoughts to rain out onto the page, giving you some concrete words or schemas that you can then arrange according to their logical relations.
Brainstorming techniques
What follows are great ideas on how to brainstorm—ideas from professional writers, novice writers, people who would rather avoid writing, and people who spend a lot of time brainstorming about…well, how to brainstorm.
Try out several of these options and challenge yourself to vary the techniques you rely on; some techniques might suit a particular writer, academic discipline, or assignment better than others. If the technique you try first doesn’t seem to help you, move right along and try some others.
Freewriting
When you freewrite, you let your thoughts flow as they will, putting pen to paper and writing down whatever comes into your mind. You don’t judge the quality of what you write and you don’t worry about style or any surface-level issues, like spelling, grammar, or punctuation. If you can’t think of what to say, you write that down—really. The advantage of this technique is that you free up your internal critic and allow yourself to write things you might not write if you were being too self-conscious.
When you freewrite you can set a time limit (“I’ll write for 15 minutes!”) and even use a kitchen timer or alarm clock or you can set a space limit (“I’ll write until I fill four full notebook pages, no matter what tries to interrupt me!”) and just write until you reach that goal. You might do this on the computer or on paper, and you can even try it with your eyes shut or the monitor off, which encourages speed and freedom of thought.
The crucial point is that you keep on writing even if you believe you are saying nothing. Word must follow word, no matter the relevance. Your freewriting might even look like this:
“This paper is supposed to be on the politics of tobacco production but even though I went to all the lectures and read the book I can’t think of what to say and I’ve felt this way for four minutes now and I have 11 minutes left and I wonder if I’ll keep thinking nothing during every minute but I’m not sure if it matters that I am babbling and I don’t know what else to say about this topic and it is rainy today and I never noticed the number of cracks in that wall before and those cracks remind me of the walls in my grandfather’s study and he smoked and he farmed and I wonder why he didn’t farm tobacco…”
When you’re done with your set number of minutes or have reached your page goal, read back over the text. Yes, there will be a lot of filler and unusable thoughts but there also will be little gems, discoveries, and insights. When you find these gems, highlight them or cut and paste them into your draft or onto an “ideas” sheet so you can use them in your paper. Even if you don’t find any diamonds in there, you will have either quieted some of the noisy chaos or greased the writing gears so that you can now face the assigned paper topic.
Break down the topic into levels
Once you have a course assignment in front of you, you might brainstorm:
- the general topic, like “The relationship between tropical fruits and colonial powers”
- a specific subtopic or required question, like “How did the availability of multiple tropical fruits influence competition amongst colonial powers trading from the larger Caribbean islands during the 19th century?”
- a single term or phrase that you sense you’re overusing in the paper. For example: If you see that you’ve written “increased the competition” about a dozen times in your “tropical fruits” paper, you could brainstorm variations on the phrase itself or on each of the main terms: “increased” and “competition.”
Listing/bulleting
In this technique you jot down lists of words or phrases under a particular topic. You can base your list on:
- the general topic
- one or more words from your particular thesis claim
- a word or idea that is the complete opposite of your original word or idea.
For example, if your general assignment is to write about the changes in inventions over time, and your specific thesis claims that “the 20th century presented a large number of inventions to advance US society by improving upon the status of 19th-century society,” you could brainstorm two different lists to ensure you are covering the topic thoroughly and that your thesis will be easy to prove.
The first list might be based on your thesis; you would jot down as many 20th-century inventions as you could, as long as you know of their positive effects on society. The second list might be based on the opposite claim, and you would instead jot down inventions that you associate with a decline in that society’s quality. You could do the same two lists for 19th-century inventions and then compare the evidence from all four lists.
Using multiple lists will help you to gather more perspective on the topic and ensure that, sure enough, your thesis is solid as a rock, or, …uh oh, your thesis is full of holes and you’d better alter your claim to one you can prove.
3 perspectives
Looking at something from different perspectives helps you see it more completely—or at least in a completely different way, sort of like laying on the floor makes your desk look very different to you. To use this strategy, answer the questions for each of the three perspectives, then look for interesting relationships or mismatches you can explore:
- Describe it: Describe your subject in detail. What is your topic? What are its components? What are its interesting and distinguishing features? What are its puzzles? Distinguish your subject from those that are similar to it. How is your subject unlike others?
- Trace it: What is the history of your subject? How has it changed over time? Why? What are the significant events that have influenced your subject?
- Map it: What is your subject related to? What is it influenced by? How? What does it influence? How? Who has a stake in your topic? Why? What fields do you draw on for the study of your subject? Why? How has your subject been approached by others? How is their work related to yours?
Cubing enables you to consider your topic from six different directions; just as a cube is six-sided, your cubing brainstorming will result in six “sides” or approaches to the topic. Take a sheet of paper, consider your topic, and respond to these six commands:
- Describe it.
- Compare it.
- Associate it.
- Analyze it.
- Argue for and against it.
Look over what you’ve written. Do any of the responses suggest anything new about your topic? What interactions do you notice among the “sides”? That is, do you see patterns repeating, or a theme emerging that you could use to approach the topic or draft a thesis? Does one side seem particularly fruitful in getting your brain moving? Could that one side help you draft your thesis statement? Use this technique in a way that serves your topic. It should, at least, give you a broader awareness of the topic’s complexities, if not a sharper focus on what you will do with it.
In this technique, complete the following sentence:
____________________ is/was/are/were like _____________________.
In the first blank put one of the terms or concepts your paper centers on. Then try to brainstorm as many answers as possible for the second blank, writing them down as you come up with them.
After you have produced a list of options, look over your ideas. What kinds of ideas come forward? What patterns or associations do you find?
Clustering/mapping/webbing:
The general idea:
This technique has three (or more) different names, according to how you describe the activity itself or what the end product looks like. In short, you will write a lot of different terms and phrases onto a sheet of paper in a random fashion and later go back to link the words together into a sort of “map” or “web” that forms groups from the separate parts. Allow yourself to start with chaos. After the chaos subsides, you will be able to create some order out of it.
To really let yourself go in this brainstorming technique, use a large piece of paper or tape two pieces together. You could also use a blackboard if you are working with a group of people. This big vertical space allows all members room to “storm” at the same time, but you might have to copy down the results onto paper later. If you don’t have big paper at the moment, don’t worry. You can do this on an 8 ½ by 11 as well. Watch our short videos on webbing , drawing relationships , and color coding for demonstrations.
How to do it:
- Take your sheet(s) of paper and write your main topic in the center, using a word or two or three.
- Moving out from the center and filling in the open space any way you are driven to fill it, start to write down, fast, as many related concepts or terms as you can associate with the central topic. Jot them quickly, move into another space, jot some more down, move to another blank, and just keep moving around and jotting. If you run out of similar concepts, jot down opposites, jot down things that are only slightly related, or jot down your grandpa’s name, but try to keep moving and associating. Don’t worry about the (lack of) sense of what you write, for you can chose to keep or toss out these ideas when the activity is over.
- Once the storm has subsided and you are faced with a hail of terms and phrases, you can start to cluster. Circle terms that seem related and then draw a line connecting the circles. Find some more and circle them and draw more lines to connect them with what you think is closely related. When you run out of terms that associate, start with another term. Look for concepts and terms that might relate to that term. Circle them and then link them with a connecting line. Continue this process until you have found all the associated terms. Some of the terms might end up uncircled, but these “loners” can also be useful to you. (Note: You can use different colored pens/pencils/chalk for this part, if you like. If that’s not possible, try to vary the kind of line you use to encircle the topics; use a wavy line, a straight line, a dashed line, a dotted line, a zigzaggy line, etc. in order to see what goes with what.)
- There! When you stand back and survey your work, you should see a set of clusters, or a big web, or a sort of map: hence the names for this activity. At this point you can start to form conclusions about how to approach your topic. There are about as many possible results to this activity as there are stars in the night sky, so what you do from here will depend on your particular results. Let’s take an example or two in order to illustrate how you might form some logical relationships between the clusters and loners you’ve decided to keep. At the end of the day, what you do with the particular “map” or “cluster set” or “web” that you produce depends on what you need. What does this map or web tell you to do? Explore an option or two and get your draft going!
Relationship between the parts
In this technique, begin by writing the following pairs of terms on opposite margins of one sheet of paper:
| Whole | Parts |
| Part | Parts of Parts |
| Part | Parts of Parts |
| Part | Parts of Parts |
Looking over these four groups of pairs, start to fill in your ideas below each heading. Keep going down through as many levels as you can. Now, look at the various parts that comprise the parts of your whole concept. What sorts of conclusions can you draw according to the patterns, or lack of patterns, that you see? For a related strategy, watch our short video on drawing relationships .
Journalistic questions
In this technique you would use the “big six” questions that journalists rely on to thoroughly research a story. The six are: Who?, What?, When?, Where?, Why?, and How?. Write each question word on a sheet of paper, leaving space between them. Then, write out some sentences or phrases in answer, as they fit your particular topic. You might also record yourself or use speech-to-text if you’d rather talk out your ideas.
Now look over your batch of responses. Do you see that you have more to say about one or two of the questions? Or, are your answers for each question pretty well balanced in depth and content? Was there one question that you had absolutely no answer for? How might this awareness help you to decide how to frame your thesis claim or to organize your paper? Or, how might it reveal what you must work on further, doing library research or interviews or further note-taking?
For example, if your answers reveal that you know a lot more about “where” and “why” something happened than you know about “what” and “when,” how could you use this lack of balance to direct your research or to shape your paper? How might you organize your paper so that it emphasizes the known versus the unknown aspects of evidence in the field of study? What else might you do with your results?
Thinking outside the box
Even when you are writing within a particular academic discipline, you can take advantage of your semesters of experience in other courses from other departments. Let’s say you are writing a paper for an English course. You could ask yourself, “Hmmm, if I were writing about this very same topic in a biology course or using this term in a history course, how might I see or understand it differently? Are there varying definitions for this concept within, say, philosophy or physics, that might encourage me to think about this term from a new, richer point of view?”
For example, when discussing “culture” in your English, communications, or cultural studies course, you could incorporate the definition of “culture” that is frequently used in the biological sciences. Remember those little Petri dishes from your lab experiments in high school? Those dishes are used to “culture” substances for bacterial growth and analysis, right? How might it help you write your paper if you thought of “culture” as a medium upon which certain things will grow, will develop in new ways or will even flourish beyond expectations, but upon which the growth of other things might be retarded, significantly altered, or stopped altogether?
Using charts or shapes
If you are more visually inclined, you might create charts, graphs, or tables in lieu of word lists or phrases as you try to shape or explore an idea. You could use the same phrases or words that are central to your topic and try different ways to arrange them spatially, say in a graph, on a grid, or in a table or chart. You might even try the trusty old flow chart. The important thing here is to get out of the realm of words alone and see how different spatial representations might help you see the relationships among your ideas. If you can’t imagine the shape of a chart at first, just put down the words on the page and then draw lines between or around them. Or think of a shape. Do your ideas most easily form a triangle? square? umbrella? Can you put some ideas in parallel formation? In a line?
Consider purpose and audience
Think about the parts of communication involved in any writing or speaking act: purpose and audience.
What is your purpose?
What are you trying to do? What verb captures your intent? Are you trying to inform? Convince? Describe? Each purpose will lead you to a different set of information and help you shape material to include and exclude in a draft. Write about why you are writing this draft in this form. For more tips on figuring out the purpose of your assignment, see our handout on understanding assignments .
Who is your audience?
Who are you communicating with beyond the grader? What does that audience need to know? What do they already know? What information does that audience need first, second, third? Write about who you are writing to and what they need. For more on audience, see our handout on audience .
Dictionaries, thesauruses, encyclopedias
When all else fails…this is a tried and true method, loved for centuries by writers of all stripe. Visit the library reference areas or stop by the Writing Center to browse various dictionaries, thesauruses (or other guide books and reference texts), encyclopedias or surf their online counterparts. Sometimes these basic steps are the best ones. It is almost guaranteed that you’ll learn several things you did not know.
If you’re looking at a hard copy reference, turn to your most important terms and see what sort of variety you find in the definitions. The obscure or archaic definition might help you to appreciate the term’s breadth or realize how much its meaning has changed as the language changed. Could that realization be built into your paper somehow?
If you go to online sources, use their own search functions to find your key terms and see what suggestions they offer. For example, if you plug “good” into a thesaurus search, you will be given 14 different entries. Whew! If you were analyzing the film Good Will Hunting, imagine how you could enrich your paper by addressed the six or seven ways that “good” could be interpreted according to how the scenes, lighting, editing, music, etc., emphasized various aspects of “good.”
An encyclopedia is sometimes a valuable resource if you need to clarify facts, get quick background, or get a broader context for an event or item. If you are stuck because you have a vague sense of a seemingly important issue, do a quick check with this reference and you may be able to move forward with your ideas.
Armed with a full quiver of brainstorming techniques and facing sheets of jotted ideas, bulleted subtopics, or spidery webs relating to your paper, what do you do now?
Take the next step and start to write your first draft, or fill in those gaps you’ve been brainstorming about to complete your “almost ready” paper. If you’re a fan of outlining, prepare one that incorporates as much of your brainstorming data as seems logical to you. If you’re not a fan, don’t make one. Instead, start to write out some larger chunks (large groups of sentences or full paragraphs) to expand upon your smaller clusters and phrases. Keep building from there into larger sections of your paper. You don’t have to start at the beginning of the draft. Start writing the section that comes together most easily. You can always go back to write the introduction later.
We also have helpful handouts on some of the next steps in your writing process, such as reorganizing drafts and argument .
Remember, once you’ve begun the paper, you can stop and try another brainstorming technique whenever you feel stuck. Keep the energy moving and try several techniques to find what suits you or the particular project you are working on.
How can technology help?
Need some help brainstorming? Different digital tools can help with a variety of brainstorming strategies:
Look for a text editor that has a focus mode or that is designed to promote free writing (for examples, check out FocusWriter, OmmWriter, WriteRoom, Writer the Internet Typewriter, or Cold Turkey). Eliminating visual distractions on your screen can help you free write for designated periods of time. By eliminating visual distractions on your screen, these tools help you focus on free writing for designated periods of time. If you use Microsoft Word, you might even try “Focus Mode” under the “View” tab.
Clustering/mapping. Websites and applications like Mindomo , TheBrain , and Miro allow you to create concept maps and graphic organizers. These applications often include the following features:
- Connect links, embed documents and media, and integrate notes in your concept maps
- Access your maps across devices
- Search across maps for keywords
- Convert maps into checklists and outlines
- Export maps to other file formats
Testimonials
Check out what other students and writers have tried!
Papers as Puzzles : A UNC student demonstrates a brainstorming strategy for getting started on a paper.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Allen, Roberta, and Marcia Mascolini. 1997. The Process of Writing: Composing Through Critical Thinking . Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Cameron, Julia. 2002. The Artist’s Way: A Spiritual Path to Higher Creativity . New York: Putnam.
Goldberg, Natalie. 2005. Writing Down the Bones: Freeing the Writer Within , rev. ed. Boston: Shambhala.
Rosen, Leonard J. and Laurence Behrens. 2003. The Allyn & Bacon Handbook , 5th ed. New York: Longman.
University of Richmond. n.d. “Main Page.” Writer’s Web. Accessed June 14, 2019. http://writing2.richmond.edu/writing/wweb.html .
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill

The Writing Process
Making expository writing less stressful, more efficient, and more enlightening, search form, you are here.
- Step 1: Generate Ideas
Brainstorming

"It is better to have enough ideas for some of them to be wrong, than to always be right by having no ideas at all." —Edward de Bono
Most people have been taught how to brainstorm, but review these instructions to make sure you understand all aspects of it.

- Don't write in complete sentences, just words and phrases, and don't worry about grammar or even spelling;
- Again, do NOT judge or skip any idea, no matter how silly or crazy it may initially seem; you can decide later which ones are useful and which are not, but if you judge now, you may miss a great idea or connection;
- Do this for 15, 20, or (if you're on a roll) even 30 minutes--basically until you think you have enough material to start organizing or, if needed, doing research.
Below is a sample brainstorm for an argument/research paper on the need for a defense shield around the earth:

Photo: "Brainstorm" ©2007 Jonathan Aguila
- Learn English
- Learn French
- Learn German
- Learn Italian
- Learn Portuguese
- Learn Spanish
- Mission Statement
- Board of Directors
- Meet the Team
- Host a Student
- Volunteer with ILI
Home / News / Academic Writing Tip: 8 Brainstorming Techniques
Academic Writing Tip: 8 Brainstorming Techniques
So, you’ve read and re-read the academic writing assignment that you received from your professor, and now you’re staring at a blank page.
Does your mind feel as blank as the page? Are you Frozen by fear? Rubbing your eyes with exhaustion?
Whether you’re writing an essay for a community college in Boston, Massachusetts or a university in New England, USA, you need to start somewhere. Brainstorming means you use your imagination and prior knowledge to collect thoughts. After gathering a great quantity of ideas, you select the highest quality ideas.
Filling that empty white document can feel like leaping into unknown icy water. Brainstorming is the way to warm up for a deep dive into the EAP topic.
Brainstorming begins with simple questions. What do you know about the topic? What do you want to learn about the topic?
As you brainstorm, you journey farther down the academic writing quest. How do you narrow down a topic into a thesis? How do you gather the examples and evidence necessary for an academic essay?
Here are EAP brainstorming strategies to jumpstart the engine of your creativity.
Brainstorming tip #1: Freewriting
Do you have no ideas? Or the opposite problem—too many ideas?
Freewriting means what it sounds like—you’re free to write whatever comes to mind. The point is not to make it perfect—not even necessarily to make it good—but just to put thoughts on paper—no rules, no revising. You can even write about how you don’t know what to write about.
The only limit you should set for yourself is that you write for a specific period of time—let’s say 30 minutes—or for a specific number of pages—let’s say 2 pages. Non-stop activity gets the juices flowing, and a concrete goal gives you satisfaction. Here’s an example of freewriting:
This essay is supposed to be about the Boston Tea Party but I don’t know anything about US history except that the American Revolution happened a long time ago (when???) somewhere in Massachusetts or maybe I’m wrong. I can’t think of anything else to say and now the clock says two minutes, I’ll keep babbling anyway. Boston, MA, politics, tea. My grandmother used to make tea when I stopped by after my English courses. But that’s not useful for this essay. Or maybe there’s a connection. Hmmm… I remember the professor talked about the taxes in the New English states (colonies?) and my grandmother used to complain about paying high taxes at the market and…
Freewriting stimulates your brain the same way physical exercise wakes up your mind.
Brainstorming tip #2: Making a Cube
Draw a cube in your notebook. Each of the six sides has a task:
Side 1: Describe the topic.
Side 2: Compare the topic.
Side 3: Connect the topic.
Side 4: Classify the topic.
Side 5: Argue for or against the topic.
Side 6: Personalize the topic.
Instead of those 6 tasks, you could replace those verbs with other academic tasks: apply, analyze, question, connect, define, classify, associate, or explain cause and effect—whichever inspire ideas.
Imagine your topic is attending university in the U.S. Next to each point on the cube, you would write words and phrases inspired by the verb at hand:
Side 1: Describe: Exciting, difficult, expensive, growing opportunities, expensive, valuable.
Side 2: Compare: Different from my country. USA = more essay writing, dorms with roommates, critical thinking, fewer standardized exams and lectures, smaller classes.
Side 3: Connect: student visa policies, US immigration law, IELTS, TOEFL iBT, travel restrictions from covid-19, globalization means more English at work.
Side 4: Classify: community colleges (Holyoke, Greenfield), state universities (UMASS Boston), private ivy league (Harvard) graduate schools, MBA, BA, MFA programs.
Side 5: Argue for : opens doors, better jobs, international workplace, investment in future, social networking, broadens horizons.
Side 6: Personalize: my cousin > engineering degree, MIT internship, campus resources help with culture shock (which worries me.) IELTS stresses me out!!!! Way to avoid?
This brainy approach works if you like approaching topics from different angles.
Brainstorming tip #3: Clustering
When you cluster, you draw bubbles and connect words and concepts associated with the topic—anything that comes to mind.
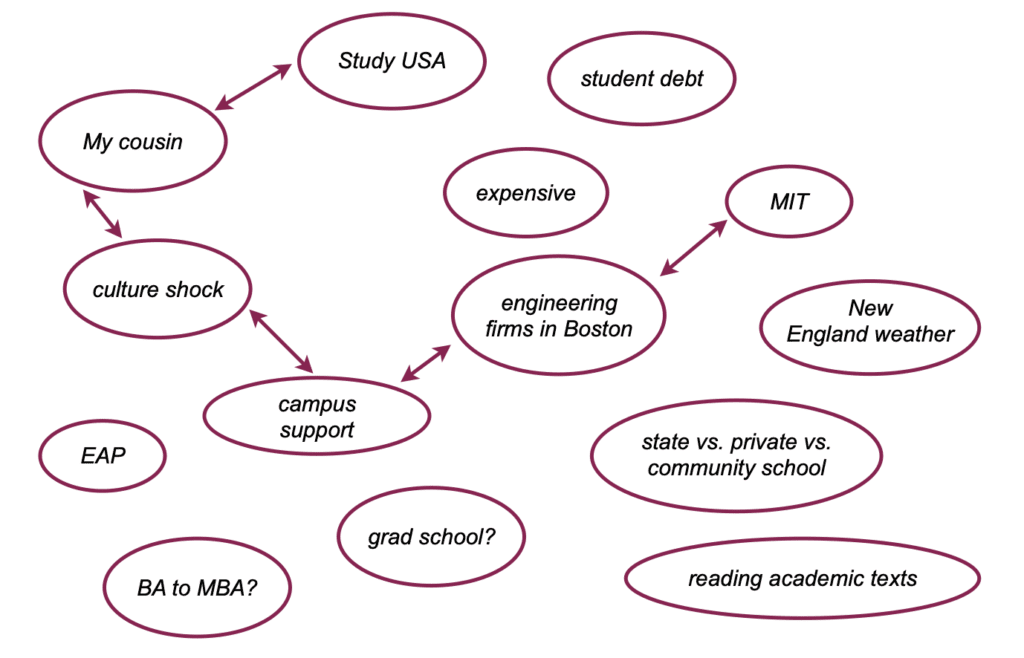
This visual method works when you have a lot of random thoughts and you are trying to “see” connections.
Brainstorming tip #4: Bulleting
With this technique, you make bulleted lists with concepts, terms, and ideas. This can help you narrow down from the first list to a second list. The list on the left contains general bullet points, while the list on the right expands on a single bullet to delve deeper.
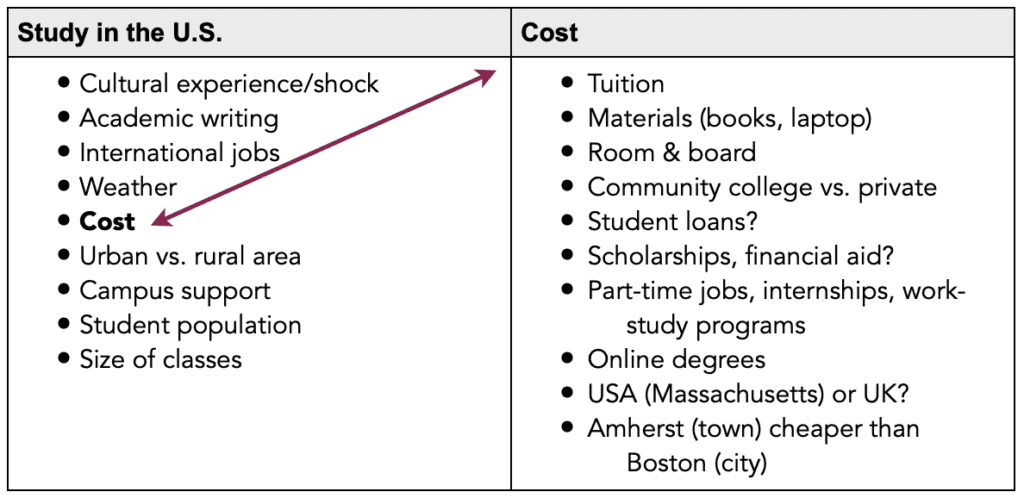
This method works great if you’re an orderly person who likes making lists.
Brainstorming tip #5: Venn Diagram
The famous Venn diagram technique works well for brainstorming differences and similarities between two topics. You draw two intersecting circles and write the qualities they share in the middle where the circles intersect and the qualities that are unique in the left and right spaces. For example, let’s say you’re brainstorming differences and similarities between two cities in Massachusetts, Boston and Northampton.
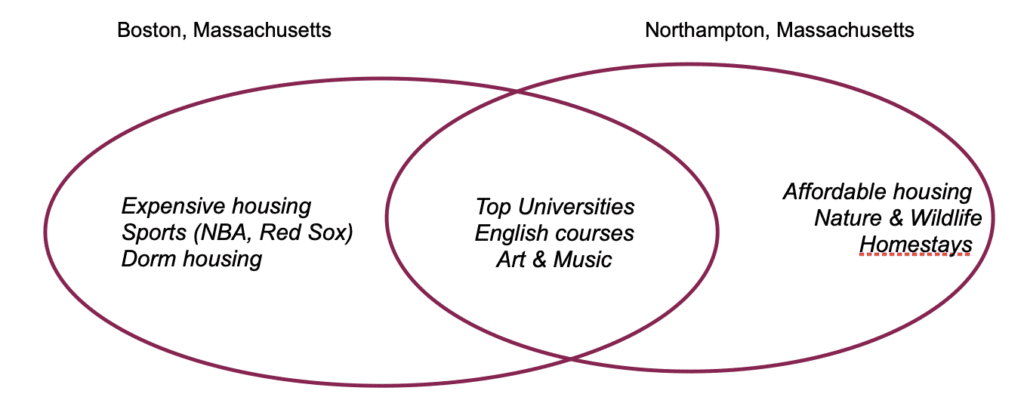
This famous brainstorming method is used in the academic and business worlds because it so clearly shows differences and similarities.
To analyze relationships among three topics, you can make a Venn diagram with three circles. The 3-circle helps visualize and understand complex connections. You brainstorm three basic questions. Which qualities are unique to each? Which traits do any two topics have in common? Which similarities are shared by all three topics?
Brainstorming tip #6: Tree diagram
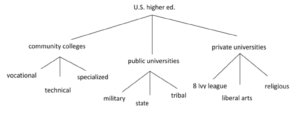
The tree diagram begins with a central idea that branches off into categories or supporting ideas.
Imagine you’re brainstorming different types of schools in US higher education.
Tree diagrams are perfect for brainstorming classification essays. You could also draw tree diagrams to brainstorm effects, starting with a cause at the top and branching off into increasingly specific downstream effects. Pretty cool, huh?
Brainstorming tip #7: Journalist Dice
Dice aren’t just toys for games and gambling–they can be a tool for writing. Rolling journalist dice is a stimulating way to flesh out narrative essays. Each side of the die corresponds to one of the 6 question words. To make the game fun, roll a die, and write down one answer the question every time you roll. Roll at least a dozen times to write down a variety of details and ideas.

In addition to building a narrative essay, this brainstorming technique can help you develop a compelling story for your college application essay. For the tired and uninspired writer, the game element of rolling dice makes the writing process more engaging and enjoyable.
Brainstorming tip #8: T diagram
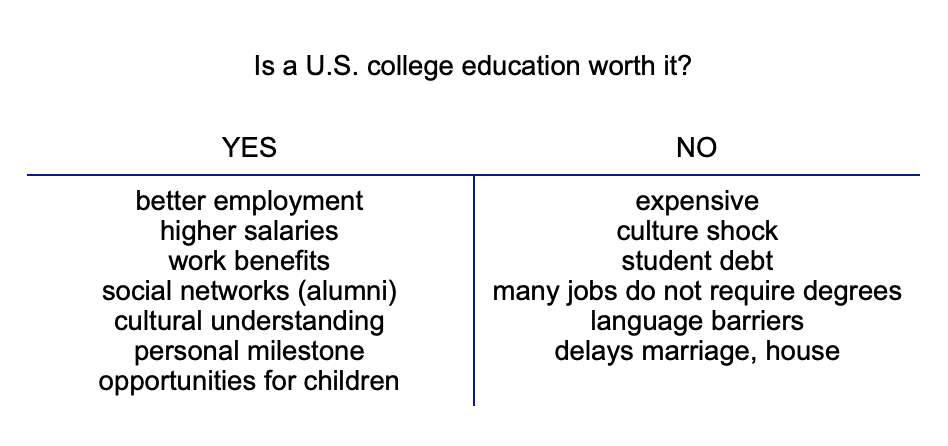
This method works well if you like thinking in terms of opposites. Can you say “On the one hand” and “On the other hand”?
What’s next in the writing process?
After your fast and furious brainstorm, the next step is to create an outline. When you outline, you pick your best and brightest ideas. Then you begin organizing them into a coherent, linear argument. You select and sort supporting points, evidence, examples, and elaboration. To learn more about outlining, click here for the next article in our academic writing series.
The best way to improve your writing is to join an academic or business English course . With guidance from an expert instructor and feedback from a community of peers, you can master the art of academic writing.
Related Articles
- How to improve your academic and business English writing skills
- Why 2021 has skyrocketed the importance of improving your English communication skills for the workplace?
- What is the difference between social and academic English, Part 1
- What is the difference between social and academic English, Part 2
- Top movies to help you learn English and love the language more
- Academic Writing Tip: Making an Outline
Article tags:
Are you seeking one-on-one college counseling and/or essay support? Limited spots are now available. Click here to learn more.
How to Brainstorm a College Essay
June 10, 2024
Brainstorming often gets a bad rap. Many people either find it completely useless or outright hate it. Quick, try it—what do you think of when you hear “brainstorm”? A group of students sitting awkwardly around a whiteboard, waiting for someone else to share their idea first? Staring at a blank page with ever-increasing bewilderment slash terror? Producing a list of ideas, only to think every single one of them is a dumpster fire? Now, it’s time to write your college essay, and word on the street is that you should brainstorm first—but what does that even mean, and do you have to do it? If you’ve ever wondered how college essay brainstorming works or how to brainstorm college essay ideas, we’ll be getting into all that and more in today’s blog.
What is brainstorming?
In general, brainstorming is the process of producing ideas, whether individually or in a group. Although it can be employed in a number of different contexts, from board rooms to PTA meetings, we’re going to focus on its relevance to the college essay writing process in particular.
Why should I brainstorm college essay ideas?
The goal of brainstorming is not to simply transcribe the ideas you already have but to unlock ideas that you didn’t even know you had.
For example, it’s very likely that your brainstorm will reveal forgotten memories or events. It almost always generates surprising connections. And at the very least, it will help you understand why you want to write about a particular topic, which is an essential piece of information to keep in mind as you move forward.
Brainstorming college essay ideas is also a way to overcome a fear of the blank page, which is a legitimate form of writer’s block. Usually, writers either feel like they have no ideas or so many ideas that committing to just one is causing anxiety. Either way, it’s debilitating. Don’t worry, though—a good brainstorming process will either produce at least a few viable ideas or help you pare down your list.
Finally, brainstorming and writing are creative processes, which means we can better understand what goes on in our brains—and develop new ways to spark creativity during both acts—by delving into literature on the subject. For starters, according to many researchers , creativity is often characterized by an interplay between divergent and convergent thinking, or the process of producing as many ideas as possible in a spontaneous, unfiltered way and then narrowing those ideas down in a logical, evaluative way. Fortunately, both types of thinking can be harnessed during the brainstorming process to help you choose your best possible topic.
Do you always have to brainstorm?
Nope! Some students do enter the college essay process with a very clear sense of what they want to write about. This tends to happen when 1) you have an all-consuming passion or 2) you have undergone a significant challenge or life event. In either case, you just can’t imagine writing about anything else but your topic.
For example, when I wrote my college personal statement, I knew right away that I wanted to write about writing. I spent most of my free time seriously crafting and revising fiction, and it was a part of my life that felt indistinguishable from me as a person. To know me, I felt that admissions readers had to know that I loved to write, what my writing meant to me, and how I wanted it to influence my future. Although I spent many hours refining how the essay would begin and unfold, the topic itself felt non-negotiable.
So if you already know your Common App topic, that’s incredible. Check that item off your to-do list!
That said, students who enter the essay process knowing what they want to write about are few and far between. For this reason, we ask all our students to at least humor us with the brainstorming process, even if only to gather potential ideas for future supplemental essays. Moreover, many students are stuck between 2 to 3 potential topics, and engaging in brainstorming exercises tends to clarify the way forward.
How do I brainstorm college essay ideas?
Have a piece of paper or word processing document ready, and let’s begin!
College Essay Brainstorming Step #1: Set the mood.
Before you try to brainstorm college essay ideas, set yourself up for success by evaluating where and how you work best. Do you like being in a quiet space, listening to instrumental music, or being outside? Do you enjoy physically writing your ideas down on a piece of paper, using a digital mind mapping tool, or speaking your ideas into a voice recorder? Maybe you need to be at your desk in your room with some instrumental pop in your headphones and a snack at the ready, or sitting outside at your favorite café with a coffee. Whatever your ideal set-up is, get it ready!
If you need to center yourself before you sit down, try going for a quick walk, doing a meditation, or listening to some music that makes you feel positive or motivated. Feel free to pause and do this again at any point during your brainstorming process if you begin to feel too unfocused.
College Essay Brainstorming Step #2: Iterate.
To kickstart the creative process, you’ll want to activate your DMN, or default mode network, via divergent thinking. Divergent thinking is the process of amassing as many ideas as possible in a spontaneous, non-judgmental way. There is a great deal of freedom at this stage so it’s important not to censor yourself, even if some of your ideas seem far-fetched or unlikely. Why? That far-fetched or unlikely idea will spark even more ideas, some of which may be surprisingly perfect. Bottom line: write down anything (yes, anything!) that comes to mind.
So how do you do this? In our opinion, brainstorming works best when it’s semi-structured. Instead of sitting down in front of a blank Google Doc and waiting for inspiration (spoiler alert: you’ll be there for a while), use targeted brainstorming questions and lists to help, like Nancie Atwell’s Writing Territories or Georgia Heard’s heart maps . Set a timer for each exercise if you’d like–10-15 minutes is usually sufficient, but feel free to go beyond that.
College Essay Brainstorming (Continued)
Still not sure where to start? Try out the following list of questions, inspired by the Common App prompts . Bullet point as many ideas/experiences as possible underneath each, even if they feel silly or “out there.” We also hereby give you permission to doodle, draw, use different colors, go crazy with Post-It notes, or whatever you feel like you need to do to get this first step done.
- When you think of your background (racial, cultural, socioeconomic, family, etc), what comes to mind? What about your background is most important to you?
- When you think of your identity (religious, family, language, sexual, gender, etc.), what comes to mind? What about your identity is most important to you?
- If you had one hobby or interest that you could pursue forever, what would it be?
- Do you have any special talents (artistic, athletic, etc) that you’ve poured a great deal of time and energy into? What are they?
- Have you ever experienced a challenge, setback, or failure? What was it?
- Have you ever questioned or challenged a belief? An idea? Which ones?
- When have you felt deeply happy or thankful? Why?
- What have you accomplished that you are most proud of?
- Have you ever had a realization that made you see the world differently? What was it?
- What topics keep you up at night? What sends you down a Google or Wikipedia rabbit hole? What could you research, write, read, or talk about for hours? Make a list.
Although you might naturally gravitate towards certain types of brainstorming exercises, try to keep an open mind. Sometimes, the strangest brainstorming activities produce the best ideas. In addition, aim to complete more than one exercise—we typically have our students do 2 to 3 exercises in various modalities, such as sketching, drawing, and listing.
College Essay Brainstorming Step #3: Evaluate.
When we underwent Step #2, we eschewed evaluative thinking and tried to let our brains be as “unfiltered” as possible. Now, we want to turn that evaluative thinking back on and start to filter what ideas or topics would be the best possible options for this particular essay. This part of the process stimulates the CCN, or cognitive control network, and is also known as convergent thinking. Before you do this, remind yourself of the point of the Common App essay: t o add dimension to the rest of your application . This will help you evaluate your ideas according to your essay’s purpose.
For example, let’s say you completed Nancie Atwell’s Writing Territories. Under “Pets” you listed “Mr. Sparkles Jr.”, AKA the guppy that made the journey to Fish Heaven when you were seven. This might be a great topic for an essay about a childhood memory, but likely wouldn’t be a good Common App topic. (Unless Mr. Sparkles inspired your love of ichthyology and you now give presentations at your local elementary school about caring for pet fish, in which case, we stand corrected.)
Two ways to engage in evaluative thinking:
- Go back through your exercises and code each of your responses. Circle the responses that you’re most interested in or drawn to. Cross out the responses you don’t want to write about or feel uninterested in. Underline the responses that you’re not sure about.
- Read through your exercises. Highlight your top five ideas. Then, circle your top three.</li></li>
College Essay Brainstorming Step #4: Test your ideas.
When you’ve narrowed your brainstorm down to a few ideas, a great way to decide between them is to do a quick test run. You can do this quickly and easily by freewriting. When freewriting, you write down everything you can think of about this topic—anecdotes, sensory details, connections, people, etc.—for at least 10 minutes without stopping or censoring yourself. You can write in paragraph form or use bullet points. For example, a freewrite about Mr. Sparkles, Jr. might look like this:
Mr. Sparkles Jr was a gift from my godmother. I added him to my tank happily and he soon became my favorite fish because he was different from all the other fish. He was black-and-white striped and I used to sit for hours watching him swim around the tank. I remember coming home from school and my mother told me that he had died, and my dad had already flushed him down the toilet. Devastated, I cried for hours and my godmother even brought me a backpack with fish printed on it, with one that looked like Mr. Sparkles so that I could remember him. I think I still have that backpack somewhere.
Anyway, it was also the first time that I had thought about death. I wondered if Mr. Sparkles had felt anything when he died, or if the other fish in the tank were sad, or whether there was anything I could have done to help him stay alive longer?
After you finish a freewrite for each topic, see which topic satisfies all three of the below conditions:
- The topic feels interesting and/or exciting to you and gives you room to explore.
- The topic shows the reader something positive about you: a trait, a value, a way of thinking, etc.
- The topic is recent, or you are able to draw recent connections (i.e., the essay does not start in first grade and end in third grade, with no connection to present day).
You can do this a few times—there are no rules!
Keep going until you narrow down to one topic or discover that you can combine more than one topic because they have a hidden connection (this is always exciting).
Okay, seriously…what topic should I pick, though?!
If you’re stuck between a few possible topics, you might be wondering “What does it matter what I want to write about? What topic is the strongest one for my college application?!”
Okay, hear us out—the topic that you are most excited to write about, that presents you in a positive light, and that is recent—IS the strongest one for your college application! Not only will the resultant essay be authentic to you and demonstrative of you (which is the whole point) but research suggests that revision is most effective when you are invested in your topic . So if Person in Your Life thinks it would be the best move for you to write about your extensive hand-sewn collection of mini animals and how it showcases your creativity, but you’re like “eh…” listen to that gut feeling! You like your mini animals, sure. But maybe what you really want to write about is how you overcame the fear of learning to scuba dive .
Neither topic is inherently better or worse than the other, and neither will necessarily strengthen your application more than the other. The topic that will strengthen your application is the one that you are excited to write about and feel committed to working on over an extended period of time.
Final step…write!
You can start by creating an outline or writing a 1-2 page (double-spaced) topic exploration draft. This can also be called a zero draft or a brain dump. Call it whatever you want to make it less intimidating.
Final Thoughts — College Essay Brainstorming
Brainstorming college essay ideas doesn’t have to be overly stressful or intimidating. If you do it right, it can actually be (dare we say) low-stress and enlightening.
Want to work with one of College Transitions’ highly skilled essay coaches? Click here to see available packages or schedule a free consultation.
Need more resources? You might consider checking out the following:
- Common App Essay Prompts
- 10 Instructive Common App Essay Examples
- College Application Essay Topics to Avoid
- UC Essay Examples
- 150 Journal Prompts
- How to Start a College Essay
- How to End a College Essay
- “Why This College?” Essay Examples
- Best College Essay Help
- College Essay
Kelsea Conlin
Kelsea holds a BA in English with a concentration in Creative Writing from Tufts University, a graduate certificate in College Counseling from UCLA, and an MA in Teaching Writing from Johns Hopkins University. Her short fiction is forthcoming in Chautauqua .
- 2-Year Colleges
- ADHD/LD/Autism/Executive Functioning
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Search/Knowledge
- College Success
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Data Visualizations
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High School Success
- High Schools
- Homeschool Resources
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Outdoor Adventure
- Private High School Spotlight
- Research Programs
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Teacher Tools
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight
“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.

- Counseling Services Overview
- Online Courses
- For media inquiries
6 Creative Ways to Brainstorm an Essay

The process of brainstorming destroys the barriers to creativity and allows us to generate ideas, find solutions quickly, and do our best work. Brainstorming helps you deal with much of the uncertainty and anxiety around essay writing. The following list of brainstorming methods includes both individual and group approaches that can be applied to choosing an essay pro mpt, developing an essay prompt, establishing a writing approach, and anything else your creative mind can conjure.
Individual Brainstorming Techniques
Brainstorming may give rise to images of groups shooting ideas back and forth. However, you don’t need anyone else to brainstorm with the following techniques. Note: these techniques are not limited to individuals; they will also work in groups.
The word storm technique is about creating groups of word clouds so you can visualize an idea or encourage the process of creative writing to begin. Feel free to use a whiteboard and a marker or a pen and paper. Start with a simple word in the middle of the sheet or board (usually, the one describing the topic of your essay best) and use association to come up with any other word related to it. Finally, group these together based on some connection between them.
Mind Mapping
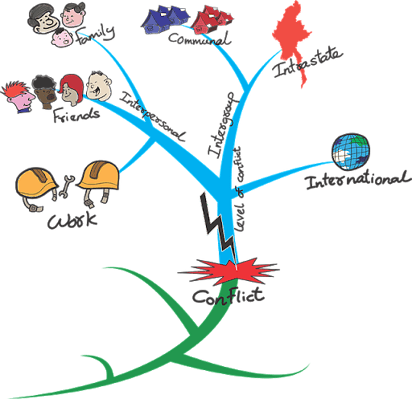
Another way to use associations and organize ideas is by mind mapping. This works better than lists as it emphasizes the visual element, which is proven to help us remember better. Start with a single word/idea again and imagine that any other word you write connected to it is the branch of a tree. This is especially useful with complex essay topics, which you can break down into easy to follow steps.
hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(2405229, 'dbddaf63-c9ab-4cae-9492-52f39e084f6a', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"});
Group brainstorming techniques.
While all of the previous methods can work for either individual or group brainstorming, these next techniques work best with more than one person.
Brain Writing
Gather 2 or more people together and present to them the same problem (the topic of the essay). Each individual will write an idea on a piece of paper or index card. Then everyone passes the index card to their left or right.
After receiving another’s card, you add a comment or improvement to the idea directly below it. Continue this until everyone has commented on each card. After one or more sessions, collect all ideas and write them on a whiteboard. Let the discussion ensue.
Rapid Ideation
Rapid ideation is an intensive session of idea generation that can produce massive results. Experts in all fields have used it to think of big ideas in a short amount of time, and it might be what you’re looking for to proceed with writing your essay. There are many methods connected to this approach, such as SCAMPER (the technique that uses action verbs to help the idea generation process) and gamestorming (for those interested in gamification).
Figure Storming
Figure storming is an unusual technique that involves thinking of a person from history that all people in the group know and trying to figure out what that person would do to solve the problem you’re discussing. This method encourages individuals to explore outside perspectives in a new, fun way.
Brain Netting
Brain netting, a fancy name for online brainstorming, allows a group of people located in different parts of the world to collaborate (which brings extra opinions and resources to the table). The principles of any other brainstorming session are the same, except you are drawing from a larger and more diverse set of people. There are a wide variety of tools at your disposal such as Google Docs. Get connected and get creative.
Brainstorming is a crucial element in the process of writing a good essay. It is the foundation from which you construct your narrative. Use the above techniques to facilitate your creative process and distinguish yourself from the large pools of essays in your classroom or your admissions process. If you are still struggling with your essay, check out our deconstruction of the notorious Costco Essay that got one student into 5 Ivy League schools.

Recommended For You

4 Keys to Ivy League Letters of Recommendation

The Costco Essay Deconstructed

How to Write Yale's Supplement Essay 2018 - 2019
Writing Studio
Invention (aka brainstorming), what is “invention”.
In an effort to make our handouts more accessible, we have begun converting our PDF handouts to web pages. Download this page as a PDF: Invention Return to Writing Studio Handouts
Invention (also referred to as brainstorming) is the stage of the writing process during which writers discover the ideas upon which their essays will focus. During this stage, writers tend to overcome some of the anxiety they might have about writing a paper, and in many cases, actually become excited about it. Although invention usually occurs at the beginning of the writing process, exercises aimed at facilitating invention can be helpful at many stages of writing. Some of the best writers return to this stage a number of times while composing drafts of their essays.
Recommended Invention Techniques
Freewriting.
Read through your assignment and choose a topic, theme, or question that comes to mind. Write for 10-15 minutes in response to this idea – do not lift your pen from the paper or your hands from the keyboard.
When you are finished, read through your draft and underline or circle ideas that might lead you to a thesis for your paper. Consider asking a classmate or friend to read what you’ve written and ask questions about your ideas and topics.
After freewriting, read through what you have written and underline a phrase or sentence that you think is particularly effective or that expresses your ideas most clearly. Write this at the top of a new sheet of paper and use it to guide a new freewrite.
Repeat this process several times. The more you write and select, the more you will be able to refine your ideas.
Talk to Yourself
Some people often find themselves saying, “I know what I want to say. It’s just that I can’t figure out how to put it in writing.” If this is the case for you, try dictating your thoughts on a digital recording device. After several minutes, listen to what you’ve recorded and write down ideas you want to incorporate into your paper.
If you don’t have a recording device, ask a friend to write down some of the main points you make as you talk about your ideas.
List all the ideas you can think of that are connected to the topic or the subject you want to explore. Consider any idea or observation as valid and worthy of listing (go for quantity at this point). List quickly and then set your list aside for a few minutes. Come back and read your list and then do the listing exercise again.
Using Charts or Shapes
Use phrases or words that are central to your topic and try to arrange them spatially in a graph, grid, table, or chart. How do the different spatial representations help you see the relationships among your ideas? If you can’t imagine the shape of a chart at first, just put the words on a page and draw lines between or around them.
Break Down the Assignment
Sometimes prompts are so complicated that they can seem overwhelming. Students often ask: There’s so much to do, where should I start? Try to break the assignment down into its constituent parts:
- The general topic, like “The relationship between tropical fruits and colonial powers.”
- A specific subtopic or required question, like “How did the availability of multiple tropical fruits influence competition among colonial powers trading from the larger Caribbean islands during the 19th century?”
- A single term or phrase that seems to repeat in the material you’ve read or the ideas you’ve been considering. For example, if have you seen the words “increased competition” several times in the class materials you’ve been reading about tropical fruit exports, you could brainstorm variations on the phrase within the context of those readings or focus on variations of each component of the phrase (i.e., “increased” and “competition”).
Once you have identified the major parts of the topic, try to figure out what you are being asked to think about in the assignment. What questions are you expected to answer? Are there related questions that need to be addressed in order to answer the primary questions? If so, what are they?

Defining Terms
In your own words, write definitions for key terms or concepts given in the assignment. Find other definitions of those terms in your course readings, the dictionary, or through conversations and then compare the definitions to your own. Keep these definitions in mind as you begin to write your essay.
Summarizing Positions
Summarize the positions of relevant authors from your course readings or research. Do you agree or disagree with their ideas, methods, or approaches? How do your interests overlap with the positions of the authors in question? Try to be brief in your descriptions. Write a paragraph or up to a page describing a reading or a position.
Get together with a group of classmates and have each person write down her or his tentative topic or thesis at the top of a blank sheet of paper. Pass the sheets around from left to right so that each person can write down a thoughtful question or suggest related ideas to think about.
Compare / Contrast Matrix
If your assignment asks you to compare or contrast two concepts, texts, subjects, etc., try to organize your thoughts in a compare/contrast matrix by focusing on the attributes you will consider in your draft. These attributes should establish the key points of comparison or contrast with which you will deal in your essay.
Last revised: 07/2008 | Adapted for web delivery: 05/2021
In order to access certain content on this page, you may need to download Adobe Acrobat Reader or an equivalent PDF viewer software.

- Dalhousie University Libraries
Writing Centre Online Resource Guide
- Planning: Brainstorming, Outlines & Organization
Brainstorming
Organizing your ideas.
- Drafting: Thesis Statements and Essay Structure
- Punctuation
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- How to Cite
- Critical Thinking
- Architecture & Planning
- Computer Science
- Engineering
- Health Professions
- Interdisciplinary Studies
- Political Science
- Sociology and Social Anthropology
- Social Sciences
- Social Work
- Sustainability
- First Year Students
- Academic Writing
- Group and Collaborative Writing
- Writing Letters and Emails
- Resumes and Job Applications
- Applying to Graduate and Professional Schools
- Theses and Dissertations
- Applying for Grants and Academic Jobs
- Writing for Publication
- English Language Learners
- Resources for Writing Tutors
- Resources for Online Reviews
Dalhousie Writing Centre
The Writing Centre is a free service for students who want to improve their writing skills. Whether you are writing academic, business or personal documents, we can help you articulate ideas and structure your writing plan
- About the Writing Centre
- Make an Appointment
- Seminars and Events
- Academic Integrity Module
- Faculty Support and Consultations
- Writing Centre Resource Guide
Contact us:
- Email: [email protected]
- Phone: (902) 494-1963
- Introduction
- Resources for Brainstorming
After you have undergone the process of working through the expectations of the assignment and selecting a topic, it is time to brainstorm. Brainstorming generates the ideas that will eventually become your thesis statement and supporting points. Developing a clear thesis will help you know what to write and how to organize it. If you have writer’s block or do not know where to begin, brainstorming can be especially helpful.
- Preparing to Write
- Socratic Method of Questioning Try using the Socratic Method of Questioning to help you brainstorm. Although the Socratic method normally involves a dialogue, with one person asking questions and another responding, you could consider using the questions provided in the handout as a guide for developing your arguments. For example, you could go through each of the questions and write down possible answers. From there, you may notice that more information on a topic may be needed; perhaps there exists some controversy around a topic and you want to explore this further; or you may form your own opinion on a topic that you then want to persuade readers to share with you. These are good places to start focusing your argument. (Retrieved from http://tools4sucessnotes.wikispaces.com under the Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike 3.0 License)
- The Academic Phrasebank Manchester University's Academic Phrasebank presents examples of commonly used phrases in academic writing, organized according to the main sections of a research paper. Common phrases used to introduce arguments, critique writing, or write a conclusion, for example, may help prompt your own ideas.
- Organizational Strategy
- Making an Outline
After you have brainstormed, it is necessary to place your ideas into categories and to select an arrangement for these categories. As with every aspect of the writing process, the method of organizing and the type of outline vary depending on individual preferences as informed by the assignment and the discipline.
- Essay Organizer (3 Topics)
- Essay Organizer (5 Topics)
1. What is the subject of your paper?
2. What background information, definitions, or context does the reader require in order to follow your paper?
3. What is the thesis (perspective), or what is your research question/hypothesis?
4. What organizational strategy most effectively conveys your points to the reader? List each point.
a. Create a topic sentence for each point.
b. Determine the evidence required to convince the reader of each point.
5. With what ideas do you want to leave your reader? What ideas should be reinforced? What are the implications of these ideas?
- << Previous: Prewriting
- Next: Drafting: Thesis Statements and Essay Structure >>
- Last Updated: Jul 3, 2024 1:53 PM
- URL: https://dal.ca.libguides.com/writingcentre
How to Brainstorming Essays with 100+ Ideas in 2024
Anh Vu • 03 April, 2024 • 8 min read
We have all been there. Teachers assign us an essay due next week. We tremble. What should we write about? What problems to tackle? Would the essay be original enough? So, how do we brainstorming essays ?
It's like you are venturing into an unexplored abyss. But fret not, because making a brainstorm for essay writing can actually help you plan, execute and nail that A+
Here's how to brainstorm for essays ...
Table of Contents
Engagement tips with ahaslides.
- What is brainstorming?
- Write ideas unconsciously
- Draw a mind map
- Get on Pinterest
- Try a Venn Diagram
- Use a T-Chart
- Online tools
- More AhaSlides Tools
- 14 brainstorming rules to Help You Craft Creative Ideas in 2024
- 10 brainstorm questions for School and Work in 2024

Easy Brainstorm Templates
Get free brainstorming templates today! Sign up for free and take what you want from the template library!
What is Brainstorming?

Every successful creation starts with a great idea, which is actually the hardest part in many cases.
Brainstorming is simply the free-flowing process of coming up with ideas. In this process, you come up with a whole bunch of ideas without guilt or shame . Ideas can be outside of the box and nothing is considered too silly, too complex, or impossible. The more creative and free-flowing, the better.
The benefits of brainstorming can surprise you:
- Increases your creativity : Brainstorming forces your mind to research and come up with possibilities, even unthinkable ones. Thus, it opens your mind to new ideas.
- A valuable skill: Not just in high school or college, brainstorming is a lifelong skill in your employment and pretty much anything that requires a bit of thought.
- Helps organise your essay : At any point in the essay you can stop to brainstorm ideas. This helps you structure the essay, making it coherent and logical.
- It can calm you: A lot of the stress in writing comes from not having enough ideas or not having a structure. You might feel overwhelmed by the hoards of information after the initial research. Brainstorming ideas can help organise your thoughts, which is a calming activity that can help you avoid stress.
Essay brainstorming in an academic setting works a bit differently than doing it in a team. You'll be the only one doing the brainstorming for your essay, meaning that you'll be coming up with and whittling down the ideas yourself.
Learn to use idea board to generate ideas effectively with AhaSlides
Here are five ways to do just that...
Brainstorming Essays - 5 Ideas
Idea #1 - write ideas unconsciously.
In " Blink: The Power of Thinking without Thinking ," Malcolm Gladwell points out how our unconscious is many times more effective than our conscious in decision-making.
In brainstorming, our unconscious can differentiate between relevant and irrelevant information in a split second. Our intuition is underrated. It can often produce better judgments than a deliberate and thoughtful analysis as it cuts through all the irrelevant information and focuses on just the key factors.
Even if the ideas you come up with in essay brainstorming seem insignificant, they might lead you to something great later. Trust yourself and put whatever you think of on paper; if you don't focus on self-editing, you may come up with some ingenious ideas.
That's because writing freely can actually negate writer's block and help your unconscious run wild!
Idea #2 - Draw a Mind Map
Brains love visual communication and mind maps are exactly that.
Our thoughts rarely arrive in easily digestible chunks; they're more like webs of information and ideas that extend forward at any given time. Keeping track of these ideas is tough, but manifesting them all in a mind map can help you get more ideas and both understand and retain them better.
To draw an effective mind map, here are some tips:
- Create a central idea : In the middle of your paper draw a central topic/idea which represents the starting point of your essay and then branch out to different arguments. This central visual will act as visual stimulus to trigger your brain and remind you constantly about the core idea.
- Add keywords : When you add branches to your mind map, you will need to include a key idea. Keep these phrases as brief as possible to generate a greater number of associations and keep space for more detailed branches and thoughts.
- Highlight branches in different colours : Coloured pen is your best friend. Apply different colours to each key idea branch above. This way, you can differentiate arguments.
- Use visual signifiers : Since visuals and colours are the core of a mind map, use them as much as you can. Drawing small doodles works great because it mimics how our mind unconsciously arrives at ideas. Alternatively, if you're using an online brainstorming tool , you can real images and embed them in.
Idea #3 - Get on Pinterest
Believe it or not, Pinterest is actually a pretty decent online brainstorming tool. You can use it to collect images and ideas from other people and put them all together to get a clearer picture of what your essay should talk about.
For example, if you're writing an essay on the importance of college, you could write something like Does college matter? in the search bar. You might just find a bunch of interesting infographics and perspectives that you never even considered before.
Save that to your own idea board and repeat the process a few more times. Before you know it, you'll have a cluster of ideas that can really help you shape your essay!
Idea #4 - Try a Venn Diagram
Are you trying to find similarities between two topics? Then the famous Venn diagram technique could be the key, as it clearly visualises the characteristics of any concept and shows you which parts overlap.
Popularised by British Mathematician John Venn in the 1880s, the diagram traditionally illustrates simple set relationships in probability, logic, statistics, linguistics and computer science.
You start by drawing two (or more) intersecting circles and labelling each one with an idea you're thinking of. Write the qualities of each idea in their own circles, and the ideas they share in the middle where the circles intersect.
For example, in the student debate topic Marijuana should be legal because alcohol is , you can have a circle listing the positives and negatives of marijuana, the other circle doing the same for alcohol, and the middle ground listing the effects they share between them.
Idea #5 - Use a T-Chart
This brainstorming technique works well to compare and contrast, thanks to the fact that it's super simple.
All you have to do is write the title of the essay at the top of your paper then split the rest of it into two. On the left side, you'll write about the argument for and on the right side, you'll write about the argument against .
For example, in the topic Should plastic bags be banned? you can write the pros in the left column and the cons in the right. Similarly, if you're writing about a character from fiction, you can use the left column for their positive traits and the right side for their negative traits. Simple as that.
💡 Need more? Check out our article on How to Brainstorm Ideas Properly !
Online Tools to Brainstorm for Essays
Thanks to technology, we no longer have to rely on just a piece of paper and a pen. There are a plethora of tools, paid and free, to make your virtual brainstorming session easier...
- Freemind is a free, downloadable software for mind mapping. You can brainstorm an essay using different colours to show which parts of the article you're referring to. The color-coded features keep track of your essays as you write.
- MindGenius is another app where you can curate and customise your own mind map from an array of templates.
- AhaSlides is a free tool for brainstorming with others. If you're working on a team essay, you can ask everyone to write down their ideas for the topic and then vote on whichever is their favourite.
- Miro is a wonderful tool for visualising pretty much anything with a lot of moving parts. It gives you an infinite board and every arrow shape under the sun to construct and align the parts of your essay.
More AhaSlides Tools to Make your Brainstorming Sessions Better!
- Use Online Word Cloud Generator to gather more ideas from your crowds and classrooms!
- Host Free Live Q&A to gain more insights from the crowd!
- Gamify engagement with a spin the wheel ! It's a fun and interactive way to boost participation
- Instead of boring MCQ questions, learn how to use online quiz creator now!
- Random your team to gain more fun with AhaSlides random team generator !
Final Say on Brainstorming Essays
Honestly, the scariest moment of writing an essay is before you start but brainstorming for essays before can really make the process of writing an essay less scary. It's a process that helps you burst through one of the toughest parts of essay and writing and gets your creative juices flowing for the content ahead.
💡 Besides brainstorming essays, are you still looking for brainstorming activities? Try some of these !

Tips to Engage with Polls & Trivia
More from AhaSlides

The Importance of Brainstorming in Writing or How to Ease Your Assignment Handling

Having a Plan
It’s a situation that plenty of students have found themselves in: you’re halfway through writing a paper, when you realize that you have no idea what to say next about your topic. This is a very frustrating experience, to say the least. Luckily, when you take some time to brainstorm beforehand, you’ll always have a plan for what to write next. As a result, you won’t find yourself struggling to complete your work as the deadline moves closer.
Making Clear Points
No matter what topic you may be writing about, your teacher or instructor will want you to make clear, relevant points due to it. If you just dive into your work without planning beforehand, odds are good your work will come across as random and unfocused. There’s no way you’re getting the best grade possible with that approach. That’s one of the key reasons why brainstorming is so important. You need time to develop your ideas before beginning the writing process. That way, when you actually sit down to write the essay, you’ll never lose focus on your main arguments.
Being Original
Again, all professors want you to make clear points in your work. Usually, they also want you to make original points. Many essay assignments essentially require you to make an argument about a subject. Too often, students make arguments that are commonplace. To many professors, this is too easy. It’s not difficult to prove a point that others have made several times before. If you want to earn the best grade, you need to show that you can think critically about your topic and explore it in a unique way. Brainstorming gives you the chance to sort through your thoughts and come up with an idea that is truly unique.
Improving Organization
Unless you’re writing a story or poem for a creative writing class, your instructors will expect your work to be concise and organized. Even if you have a strong grasp on language and have an interesting point to make, your work will suffer if it sounds rambling and unclear. Regardless of how a strong writer you may be, you still need to take some time to prepare in order to ensure that your work is properly organized. Students may feel that brainstorming is just an extra step that makes completing an assignment an even longer process than it already is. That’s not the case, though. Brainstorming actually helps save your time by giving you a clear plan to stick to.
Our statistics
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
Where to Begin? 6 Personal Essay Brainstorming Exercises
←8 Do’s and Don’ts for Crafting Your College Essay
Creating the First Draft of Your College Application Essay →

The Common App publishes a list of 7 prompts each year. They ultimately ask for similar types of responses, regardless of slight alterations year-to-year. The Common App prompts provide you with a forum to write about yourself, using whatever anecdote or vehicle you wish in order to communicate something profound and genuine about yourself to adcoms.
If this feat seems daunting or spellbindingly vague to you, you are not alone. For virtually every student applying to college, the moment when you sit down to draft your personal statement is likely the first—and may end up being the only—time in your life when you are pushed to describe your entire identity succinctly and eloquently. So, where to begin?
As with any writing assignment, the best way to approach the personal essay is to brainstorm what it is you want the entire essay to communicate about you to the adcom that will be considering you for admission. Read on for 4 surprising brainstorming exercises that will lead you to an effective personal statement strategy.
1. Consider the four core questions.
When writing your personal statement, there are four questions that your essay should answer:
- “Who am I?”
- “Why am I here?”
- “What is unique about me?”
- “What matters to me?”
These questions are important because they help bring awareness to the kind of person you are and touch on things such as your personality traits, your journey throughout high school, the interests and skills that make you unique, and what’s important to you. Colleges want to understand how you became who you are, and where you’re going (successful alumni reflect well on their school, after all!).
2. Try freeform writing.
To help answer these questions and start brainstorming, freeform writing is a good place to start. Begin by writing down 3-5 aspects of your personality or experiences and spend some time constructing narratives out of these different combinations.
This process of getting some ideas on paper and seeing how they can relate to each other can help you better identify a prompt that works for you. For example, you might note that you enjoy tutoring students in STEM, and are now working with a local school to create a Women in STEM initiative in your school district. You may also have tried previous initiatives that failed. These experiences could be constructed and applied to a number of Common App prompts. You could address a specific identity or interest you have associated with STEM, discuss what you learned from your failed initiatives, explore how you challenged the lack of women in STEM programs in your school district, envision solving for the lack of women involved in the science and mathematics fields, etc.
3. Make a list of opinions you firmly hold and explain them.
This exercise requires you to think about aspects of your identity that you have actively chosen. While exercise #4 asks you to consider what parts of your identity you have struggled to overcome, this exercise asks you to consider what aspects of your identity you are most proud of—those opinions that you hold because you chose to believe in something specific of your own accord.
This is an important brainstorming exercise because it should get you thinking about things you are passionate about. Ultimately, you will want to write your personal statement about something that defines you, gets you excited, and can exhibit your ability to think and speak for yourself. So now, before you start writing, make a list of the things that you care about most, and explain why you feel that way about them.
This list can include everything from your political affiliation to your stance on McDonald’s decision in the past year to serve breakfast for longer. The point of this exercise is that there is no right or wrong way of going about it, no topic that is more worthwhile than any other so long as you are passionate about it.
4. Make a list of your character flaws.
While the ultimate goal of the personal essay is to present yourself in as positive a light as possible to adcoms, the challenge is to do so in a way that is realistic and genuine. To do this, you’ll need to do some serious thinking about what types of character flaws accompany your best traits.
There are two main reasons why we suggest that students not shy away from talking about their own shortcomings as well as their achievements. The first reason is quite simple: a personal statement that paints a picture of its writer as perfect and without flaws will come across as dishonest and unrealistic. Obviously, you want to avoid this at all costs. Second, and even more important, if you are able to write a personal statement that acknowledges your flaws and recognizes that you are imperfect, it will reflect positively on you and vouch for your maturity.
If it feels counterintuitive or scary to dwell on anything other than successes, do not fret: that is the expected reaction to this advice. But if done correctly, acknowledging that you are not perfect can add genuineness to any personal essay. So, how to discuss character flaws? There are several ways to go about this.
One way is to discuss a character flaw that you have always struggled with and worked to improve upon throughout your life. In this scenario, discussing flaws can help introduce a discussion about growth or maturation and give your personal statement a nice narrative arc. Yet another way to discuss your character flaws is to acknowledge how certain struggles or personal shortcomings have shaped your identity, allowing you to go into more detail about the ways in which you were able to better yourself by identifying a flaw in yourself and being willing to fix it.
The thinking here is that students have no difficulty remembering all of the accomplishments, productive experiences, and glowing achievements that they want to include in their personal statements. After all, it is easy to write about these things. It is much harder to force yourself to think about aspects of your identity that rankle, and to think about how these things have shaped you.
5. Reflect on your choices and why you made them.
Another brainstorming exercise that can help you think of a topic is to reflect on what choices you’ve made and why. Once you come up with a list, it will be easier to see what you value and the direction in which you can take your essay.
Think about some of these questions to get the juices flowing:
- Why are they my best friend?
- Under what circumstances did we become friends?
- When did we last fight?
- If I had to spend 10 days doing the same exercise or physical activity, what would I choose? Why?
- Say I had to pick one food, and my three closest friends or family members could only eat that food for one week. What would that food be and why?
- Say I had to start a business selling something, and I would achieve the average level of success (financially, socially, etc) within that business, what would I choose to do?
- What movie would I want to take the place of a character in and which character would I want to play? Why?
- What class or teacher did I like most, and why? What class or teacher did I dislike most, and why?
- If I had to choose between singing, doing standup comedy, or dancing in front of 18,000 people, what would I choose? Why?
6. Make a list of anecdotes, childhood memories, or stories about yourself. Then choose one and make it your “vehicle.”
Finally, you should conclude your brainstorming session by searching for a vehicle: an anecdote that you can use to frame your personal statement.
You can use anecdotes in your personal statement in a number of ways. Some students choose to open with one, others close with one, and still others will use two or three anecdotes in order to add color and rhetorical flair to the points they are trying to make about themselves. The best types of anecdotes are the ones that tell the most about you or give insight into your character.
When we help students write their personal statements, we usually begin by brainstorming a few potential anecdotes to use in your essay. But if you are wondering what the point is of using an anecdote— Why use one at all when I could save words and just talk about myself ?—it’s useful to first understand why telling a story or two makes your personal statement stronger.
Ultimately, you will want your personal statement to communicate something about your character and personality that is unique and appealing to schools. When an adcom reads your personal statement, they are looking to hear about you in general, they are looking to learn something unique or special about you (so they can differentiate you from other applicants), and they are also looking for evidence that you would be a valuable addition to their community. But the fact of the matter is that these are fairly broad and vague directives to write about if you don’t have something specific to focus on.
This is where the anecdotes come in to save the day! They help instigate a conversation about yourself, your personality, your identity, and your character while also giving you something concrete to talk about. This is why we call it a “vehicle”—it can exist in its own right, but it carries with it important information about you as well.
Now that you know what the purpose of this vehicle is, it should be a little easier to brainstorm the anecdote(s) that you choose to frame your personal statement with. If you are not yet sure what to write about in your personal statement, you can start brainstorming anecdotes from your childhood, from favorite family stories to fond memories, from hilarious vacation mishaps to particularly tender moments. Do your parents have favorite stories to tell about you? Write those into your list as well.
Once you have a collection of stories to work with, you may begin to see certain patterns forming. Perhaps all of your favorite stories take place in the same setting—a vacation home that meant a lot to you or in the classroom of your favorite teacher. Maybe, you will realize that all of your fondest memories involve a certain activity or hobby of yours. Or, alternatively, you may notice that one story from your childhood mirrors or foreshadows a like, dislike, or accomplishment that would come to fruition later in your life.
If you already know what you want to say about yourself, you can come at the same exercise from another angle: try to think of several anecdotes that could be potential vehicles for the message about yourself that you want to transmit. If you want to illustrate that you love to learn, try to think pointedly about where that love comes from or what you have done that proves this. In this case, remember that any given anecdote can reveal more than one thing about you.
It is hard to imagine all of the possible personal statements that could come out of this brainstorming session, but it is almost certain that this exercise will help you come up with several concrete points to make about yourself and provide you with a tangible way to say those things.
Final Thoughts
If after doing these six brainstorming exercises, you still don’t feel ready to write your personal statement, fear not! Writing a personal essay is daunting and won’t be done in three steps, or even three days!
For more guidance, check out these blog posts:
How to Write a Personal Statement That Wows Colleges
How to Come Up With an Idea for a Personal Statement
How to Write the Common App Essays
Mastering the Personal Statement
5 Tips for Editing Your College Essays
Want help with your college essays to improve your admissions chances? Sign up for your free CollegeVine account and get access to our essay guides and courses. You can also get your essay peer-reviewed and improve your own writing skills by reviewing other students’ essays.
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

- I nfographics
- Show AWL words
- Subscribe to newsletter
- What is academic writing?
- Academic Style
- What is the writing process?
- Understanding the title
- Brainstorming
- Researching
- First draft
- Proofreading
- Report writing
- Compare & contrast
- Cause & effect
- Problem-solution
- Classification
- Essay structure
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Book review
- Research proposal
- Thesis/dissertation
- What is cohesion?
- Cohesion vs coherence
- Transition signals
- What are references?
- In-text citations
- Reference sections
- Reporting verbs
- Band descriptors
Show AWL words on this page.
Levels 1-5: grey Levels 6-10: orange
Show sorted lists of these words.
| --> |
Any words you don't know? Look them up in the website's built-in dictionary .
|
|
Choose a dictionary . Wordnet OPTED both
Brainstorming Types and methods of brainstorming
After you have understood the title , the next step of the writing process is to generate ideas. The best way to do this is by a process called 'brainstorming'. The page gives information on what brainstorming is , as well as describing three useful brainstorming techniques, namely clustering , listing , and freewriting .
What is brainstorming?

For another look at the same content, check out YouTube or Youku , or the infographic .
Brainstorming is a technique which is used to get as many ideas as you can, as quickly as you can. The words 'many' and quickly' are important. A common mistake students make when brainstorming is to stop after writing down only a few ideas. This is not 'brainstorming'. As the word 'storm' suggests, it is something which should have much energy and power, leading to a flood of ideas. Although brainstorming may take some time, it will save you time in the long run. There is nothing worse than racing confidently into an essay then getting stuck for ideas halfway through (i.e. 'writer's block').
Clustering, also called mind-mapping, is a visual brainstorming technique. It is especially useful for visual learners . The advantage of this technique is that ideas are organised on the page, making it easier to move to the outlining stage of the process. As a result, it is the most popular brainstorming method with students.
Below is an example of the clustering style of brainstorming. This was for a short (250 word) essay, written under exam conditions, with the title: 'Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of the internet'.
Listing, as its name suggests, is a brainstorming technique in which you make a list of ideas. The advantage of this technique is that it enables ideas to be generated more quickly than with clustering, as the ideas can be written in any order.
Below are two examples of the listing style of brainstorming. Both are for the same title as above, namely 'Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of the internet'.

Freewriting
Freewriting is a brainstorming activity in which the writer writes anything they can about a topic, in continuous prose, hoping that one idea will lead to another. The advantage of this technique is that it might enable you to generate ideas when the other methods fail. However, it is not generally favoured by students of academic writing. It takes more time, and the writing you produce will be disorganised and will need to be discarded at the end. It is more useful when writing creative works such as stories. Try this method if you think this will be a good technique for you:
- Write the topic at the top of your paper.
- Write as much as you can about the topic. Include as many supporting facts, details, and examples as you can, but do not worry if you do not have many at this stage.
- After you have run out of ideas, reread your passage and circle/highlight the ideas which seem useful.
- Group the related ideas together, then use them to write an outline . If necessary, generate more ideas first using one of the methods on this page.

GET FREE EBOOK
Like the website? Try the books. Enter your email to receive a free sample from Academic Writing Genres .
Below is a checklist for this section.
| I have used to generate ideas for my writing. | ||
| I have used either , or to brainstorm ideas. |
Next section
Read more about researching to support your ideas.
Previous section
Go back to the previous section about understanding the title .

Author: Sheldon Smith ‖ Last modified: 03 March 2022.
Sheldon Smith is the founder and editor of EAPFoundation.com. He has been teaching English for Academic Purposes since 2004. Find out more about him in the about section and connect with him on Twitter , Facebook and LinkedIn .
Compare & contrast essays examine the similarities of two or more objects, and the differences.
Cause & effect essays consider the reasons (or causes) for something, then discuss the results (or effects).
Discussion essays require you to examine both sides of a situation and to conclude by saying which side you favour.
Problem-solution essays are a sub-type of SPSE essays (Situation, Problem, Solution, Evaluation).
Transition signals are useful in achieving good cohesion and coherence in your writing.
Reporting verbs are used to link your in-text citations to the information cited.
- Free Essays
- Tips for Students
How to Brainstorm for an Essay

Brainstorming for an essay is an essential stage of gathering ideas for an essay. It is one of the prerequisites how to make the paper well-organized and logically structured. If you are interested in getting some valuable tips for brainstorming essay ideas, read the article presented below.
Brainstorming and How to Do It Properly
Brainstorming is vital when you start writing your paper. It does not matter whether you feel that writing is not your passion or consider yourself a super writer, brainstorming helps in creating a brilliant paper. Generally speaking, brainstorming means generating certain ideas on a given subject in order to sort and choose the main concepts. The result of brainstorming is a number of phrases, words or even concepts that are related to the chosen subject or topic .
The Process of Brainstorming for an Essay
- You have to get ready for it. Take a pen and a piece of paper or simply turn on your PC as you will have to write down all your ideas and thoughts. Pay attention to your workplace as it plays a crucial role for the process of brainstorming ideas. Thus it has to be comfortable and clean.
- Setting a deadline is also important. At first, it may seem that if you spend more time on generating ideas, brainstorming will be more effective. However, 20 minutes are usually enough.
- Focus on your topic or subject and try to write down every thought and idea that comes up in your head. Do not try to organize your ideas and thoughts at this stage. It will only have a negative impact on the process. Plain writing has to be done at this stage.
- After you feel that all your thoughts are written down, go through the list. Now you are free to reorganize all your written ideas and thoughts. Select the most important ideas that can help you write an informative essay. Then you have to structure the selected ideas according to their level of importance.
- In case you are sure that the list of ideas and thoughts is sufficient for writing an A-grade essay, begin creating an outline of your future paper.
How to Brainstorm for an Essay?
Still do not know how to brainstorm ideas? We can help you with that as there is a number of techniques used for brainstorming. They help to make the writing process easier. Such techniques are usually divided into those used by a team who work on the same topic or by an individual writer who writes a paper on his/her own. The following are some of the popular brainstorming techniques:
- Mapping the mind. The technique organizes your ideas through using pre-generated thoughts. In order to create a mind map, one has to write down the main idea in the center and circle it around. After that, ideas that refer to the main one should be written down in little circles and connected to the main circle. The same should be done with each smaller idea. Mapping the mind helps in framing all your ideas and identifying their connection.
- Techniques of free writing. While using this method, start writing all your ideas in a free and uncensored way. Stop thinking where your thoughts can lead you. The only task you have to do is to write down everything that comes to your mind. Free writing technique involves writer’s subconsciousness during the creative process.
- Start asking questions. Asking questions about the topic or subject instead of writing on the topic is another useful technique. Ideas for writing the paper will start generating when you answer all your questions.
- The technique of role storming. Try to imagine that you are a different person. It will help you think about the required topic from a different point of view. Sometimes, such technique can be useful for brainstorming strong ideas.
Even though this article mainly deals with team brainstorming, you may still find some effective strategies of brainstorming for an essay. For example, when gathering ideas for the paper, ask yourself what would make the paper appealing to the audience – and then write a list of ideas that might make the paper interesting. Afterwards, ask yourself where you are heading with the idea and try to collect further ideas for making the topic even more engaging. In this way, the brainstorming strategies work. When brainstorming, be sure not to rely merely on books, articles, and other scholarly sources but also on ideas of other people, so do not be afraid or shy to ask about others’ ideas or opinions. After you have gathered the necessary number of ideas, take a break and then switch over to the process of organizing them into a coherent paper.
Remember that brainstorming for an essay is not about perfection, so do not expect to provide an impeccable draft at first. You may just write the ideas into your notebook even when they seem to be illogical. Once you write them all down, you will be able to draw connections between them and find out how they match the paper topic. Some of them may initially seem silly to you but it does not mean that you should stop and wait for some perfect ideas. On the brainstorming stage, write down everything that comes to your mind.
Five Essay Brainstorming Strategies for Writers
Brainstorming writing is effective when you cannot gather enough ideas for your essay writing or, on the contrary, when you have too many ideas to fit them all and develop them in a paper. With the help of brainstorming, you can get a clear and vivid picture of all ideas you have, you can organize them properly, and also decide which of them are worth consideration and which are not. Still, you should remember one of the core brainstorming methods – not just to evaluate the ideas but also enumerate. Read more about the strategies of brainstorming for students:
Just like the cube has six points, you have to explore the paper topic or central idea from six main perspectives or viewpoints. First, provide a description of the topic and define what it is like. Second, compare it with the other subject areas and pinpoint to the differences and similarities between them. Third, provide associations you have with the topic, i.e. what the topic makes you think of. Fourth, provide the topic analysis, for example, what the topic constitutes of. Fifth, pinpoint to the practical application of the topic. Sixth, provide an argument for or against it, i.e. whether you support the topic or oppose it.
Cubing technique for brainstorming is a kind of critical thinking analysis that was developed for students as a means of expressing their opinions in essays. Still, this strategy can also be adjusted to general writing.
A similar technique to cubing is the one that explores only three perspectives:
- description of the topic, its constituents, challenges, and features, as well as its comparison and contrast with the other topics;
- exploration of the topic background or history (i.e. the topic evolution or development);
- analysis of similar topics or the topics that closely relate to your essay topic.
2. Free writing
This is one of the brainstorming steps that is particularly effective when you do not know where to start or what to write about in general. You just need to write anything that comes to your mind even if you do not know how it sounds. When practicing free writing, make sure you have quantitative goals, for example, to write down ideas without stopping for 3 or 5 minutes or to write 300 or 500 words without a pause, etc. When free writing, do not intend to write everything in a flawless way – in other words, do not pay attention to grammar, punctuation or spelling mistakes – just write.
3. Provide lists
If you are working on an essay or a review, you may also use lists as means of gathering ideas. If you are working on creative writing, such as a story, provide a list of ideas or chapters you would like to include. Sometimes, it can be enough to provide a list of keywords and then return to them – they will serve as a notification for the idea you want to develop. If you are working on some creative fiction story, you may jot down names of people, places, ideas or emotions that will enable you to recall the necessary information in the process of writing.
This brainstorming step is also known as webbing or clustering. Unlike the other brainstorming methods, this brainstorming for writing relates to graphic means of gathering ideas. So, take a board or a piece of paper and list the ideas separately. Afterwards, think of what connections they may have between one another. You may use different colors for grouping ideas, circles, underlining, etc.
The process of producing a map depends on your creativity, original thinking, and design skills. The visual representation of the map may differ but make sure that you list down all the possible ideas for your paper.
5. Researching
After you have got the topic for writing, you might as well gather ideas from researching or reviewing literature. Therefore, be sure to devote yourself sufficient time in order to browse through the online libraries and databases. Pay consideration to both primary and secondary sources. Be sure to outline the key points of the topic you plan to look up further.
If you plan to produce some kind of fiction writing, be sure to investigate more information about the place, where the story would take place, the culture, the country, traditions, etc. If it is a historical novel or story, pay specific attention to history, social structure, and general atmosphere. Pay attention to how people dressed, what transport they used, how they looked overall, etc.
Thesis Brainstorming Techniques for Students
When brainstorming for an essay, it is essential to find out what part of brain is active – right or left.
1. Brainstorming for right brains
When it comes to right-brained thinkers, they find it easier to perceive creatively presented information. For example, they like patterns, shapes, diagrams, and tables more than plain text. So, the best brainstorming technique for right-brain thinkers is mind mapping. Therefore, to start the process, it is necessary to take different stickers, pieces of paper, tape, glue, colored pens, highlighters, etc. The process of brainstorming for right brains takes the shape of an artistic performance.
Start brainstorming ideas by putting the central idea in the center of the paper. Afterwards, write down ideas relating to the central issue or topic. Do not try to follow a specific pattern – just jot down the ideas. If it seems to you that there is nothing to write about, start asking yourself specific questions, such as “what,” “who,” “when,” “why,” and “how.” When you do so, it will be more likely to gather a few more ideas. When you gather ideas, do not worry that you may repeat them – just go on with jotting them down. Only when you feel that your brain is really empty for ideas, you may take a break from writing. It is advisable to take a break after brainstorming and return to the writing process later – you will be surprised how the ideas form in some regular patterns. When you notice that a few ideas are repetitive, highlight them in one color – you will definitely know that these ideas are worth considering for the topic sentences as subtopics. When you notice some other repetitive or related ideas, draw them in the other color. Be sure to come up with a specific pattern and use one color for one group of ideas.
In this way, you will form the basis for the paper. Now you can start crafting a well-organized paper from the bunch of disorganized ideas.
2. Brainstorming for left brains
If you have read the description of the brainstorming above and it made you sweat, then you are definitely not a right-brain thinker. Nothing to worry about – it is just that the above-mentioned brainstorming techniques do not work for you. If you are not comfortable with visuals and the chaos that is brought with them, you need to search for some other brainstorming techniques.
So, start with writing down the title of your paper at the top of a piece of paper. Now think of the three or four major topic constituents that can serve as the main arguments for this paper. These ideas can also be chosen as subtopics. If the ideas are to broad, think of the subtopics and the ways of breaking them into smaller sections.
Provide titles of the subtopics and leave space between them. When gathering ideas for each of subtopic or argument, be sure to list them in a numbered or bullet-pointed list. So far, do not worry about the logical connections and transitions between the ideas and paragraphs. Think of the coherence and logical connections within the paper only after you finish collecting the ideas and take a break from work. When you feel that you have written down all ideas, be sure to take a break and only afterward start working on the smooth and coherent essay. This is actually how you produce an outline for your paper.
3. Brainstorming strategy for everyone
Some students like to use the Venn diagram for organizing ideas and thoughts. To follow this brainstorming strategy, you have to draw two circles that intersect. Each circle should be entitled with the name of the topic/ subject that you would like to compare. Afterward, fill the circles (below the title) with the words relating to the ideas that each of the compared subjects possesses. In the intersecting field, please provide words that refer to the mutual characteristics.
Use 15% OFF on 1st order!
- Writing Ideas
- Writing Prompts
- Essay Writing
- Writing Guide
- $item->year, 'month' => $item->month]) }}"> {{ $item->year }} {{ $item->month_name }} {{-- ({{ $item->count }}) --}}

- Career Exploration
- Arts, Communications, & Media
- Education, Nonprofit, & Public Health
- Business, Consulting, Finance, & Marketing
- Government, International Affairs, Law, & Public Policy
- Health Professions Advising
- Career Essentials Resources
- Graduate School
- Application Support
- Short Internship Projects (SHIPs)
- Fellowships for Undergraduates
- Fellowships for Graduates
- Class of 2025 Fellowship Planning
- Fellowships for International Students
- Civic Engagement
Writing a Personal Statement

Preparing to Write
Brainstorming, don't forget, sample prompts.
A personal statement is a narrative essay that connects your background, experiences, and goals to the mission, requirements, and desired outcomes of the specific opportunity you are seeking. It is a critical component in the selection process, whether the essay is for a competitive internship, a graduate fellowship, or admittance to a graduate school program. It gives the selection committee the best opportunity to get to know you, how you think and make decisions, ways in which past experiences have been significant or formative, and how you envision your future. Personal statements can be varied in form; some are given a specific prompt, while others are less structured. However, in general a personal statement should answer the following questions:
- Who are you?
- What are your goals?
- How does this specific program/opportunity help you achieve your goals?
- What is in the future?
A personal statement is not:
- A variation of your college admissions essay
- An academic/research paper
- A narrative version of your resume
- A creative writing piece (it can be creative, though)
- An essay about somebody else
Keep in mind that your statement is only a portion of the application and should be written with this in mind. Your entire application package will include some, possibly all, of the materials listed below. You will want to consider what these pieces of the application communicate about you. Your personal statement should aim to tie everything together and fill in or address any gaps. There will likely be some overlap but be sure not to be too repetitive.
- Personal Statement(s)
- Transcripts
- Letters of recommendations
- Sample of written work
- Research proposal
For a quick overview of personal statements, you might begin by watching this "5 Minute Fellowships" video!
If you are writing your first personal statement or working to improve upon an existing personal statement, the video below is a helpful, in-depth resource.
A large portion of your work towards completing a personal statement begins well before your first draft or even an outline. It is incredibly important to be sure you understand all of the rules and regulations around the statement. Things to consider before you begin writing:
- How many prompts? And what are they? It is important to know the basics so you can get your ideas in order. Some programs will require a general statement of interest and a focused supplementary or secondary statement closely aligned with the institution's goals.
- Are there formatting guidelines? Single or double spaced, margins, fonts, text sizes, etc. Our general guideline is to keep it simple.
- How do I submit my statement(s)? If uploading a document we highly suggest using a PDF as it will minimize the chances of accidental changes to formatting. Some programs may event ask you to copy and paste into a text box.
- When do I have to submit my statement(s)? Most are due at the time of application but some programs, especially medical schools, will ask for secondary statements a few months after you apply. In these instances be sure to complete them within two weeks, any longer is an indication that you aren't that interested in the institution.
Below is a second 5 Minute Fellowships video that can help you get started!
Before you start writing, take some time to reflect on your experiences and motivations as they relate to the programs to which you are applying. This will offer you a chance to organize your thoughts which will make the writing process much easier. Below are a list of questions to help you get started:
- What individuals, experiences or events have shaped your interest in this particular field?
- What has influenced your decision to apply to graduate school?
- How does this field align with your interests, strengths, and values?
- What distinguishes you from other applicants?
- What would you bring to this program/profession?
- What has prepared you for graduate study in this field? Consider your classes at Wellesley, research and work experience, including internships, summer jobs and volunteer work.
- Why are you interested in this particular institution or degree program?
- How is this program distinct from others?
- What do you hope to gain?
- What is motivating you to seek an advanced degree now?
- Where do you see yourself headed and how will this degree program help you get there?
For those applying to Medical School, if you need a committee letter for your application and are using the Medical Professions Advisory Committee you have already done a lot of heavy lifting through the 2017-2018 Applicant Information Form . Even if you aren't using MPAC the applicant information form is a great place to start.
Another great place to start is through talking out your ideas. You have a number of options both on and off campus, such as: Career Education advisors and mentors ( you can set up an appointment here ), major advisor, family, friends. If you are applying to a graduate program it is especially important to talk with a faculty member in the field. Remember to take good notes so you can refer to them later.
When you begin writing keep in mind that your essay is one of many in the application pool. This is not to say you should exaggerate your experiences to “stand out” but that you should focus on clear, concise writing. Also keep in mind that the readers are considering you not just as a potential student but a future colleague. Be sure to show them examples and experiences which demonstrate you are ready to begin their program.
It is important to remember that your personal statement will take time and energy to complete, so plan accordingly. Every application and statement should be seen as different from one another, even if they are all the same type of program. Each institution may teach you the same material but their delivery or focus will be slightly different.
In addition, remember:
- Be yourself: You aren’t good at being someone else
- Tragedy is not a requirement, reflection and depth are
- Research the institution or organization
- Proofread, proofread, proofread
- How to have your personal statement reviewed
The prompts below are from actual applications to a several types of programs. As you will notice many of them are VERY general in nature. This is why it is so important to do your research and reflect on your motivations. Although the prompts are similar in nature the resulting statements would be very different depending on the discipline and type of program, as well as your particular background and reasons for wanting to pursue this graduate degree.
- This statement should illustrate your academic background and experiences and explain why you would excel in the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering (UMass Amherst - M.S. in Civil Engineering).
- Describe your academic and career objectives and how the Yale School of Forestry and Environmental Studies can help you achieve them. Include other considerations that explain why you seek admissions to the Yale School of Forestry and Environmental Studies and your interests in the environmental field (Yale - Master of Environmental Management).
- Please discuss your academic interests and goals. Include your current professional and research interests, as well as your long-range professional objectives. Please be as specific as possible about how your objectives can be met at Clark and do not exceed 800 words (Clark University - M.A. in International Development and Social Change).
- Write a 500- to 700-word statement that describes your work or research. Discuss how you came to focus on the medium, body of work, or academic area you wish to pursue at the graduate level. Also discuss future directions or goals for your work, and describe how the Master of Fine Arts in Studio (Printmedia) is particularly suited to your professional goals (School of the Art Institute of Chicago - MFA in Studio, Printmaking).
- Your statement should explain why you want to study economics at the graduate level. The statement is particularly important if there is something unusual about your background and preparation that you would like us to know about you (University of Texas at Austin - Ph.D in Economics).
- Your personal goal statement is an important part of the review process for our faculty members as they consider your application. They want to know about your background, work experience, plans for graduate study and professional career, qualifications that make you a strong candidate for the program, and any other relevant information (Indiana University Bloomington - M.S.Ed. in Secondary Education).
- Your autobiographical essay/personal statement is a narrative that outlines significant experiences in your life, including childhood experiences, study and work, your strengths and aspirations in the field of architecture, and why you want to come to the University of Oregon (University of Oregon - Master of Architecture).
- Personal history and diversity statement, in which you describe how your personal background informs your decision to pursue a graduate degree. You may refer to any educational, familial, cultural, economic or social experiences, challenges, community service, outreach activities, residency and citizenship, first-generation college status, or opportunities relevant to your academic journey; how your life experiences contribute to the social, intellectual or cultural diversity within a campus community and your chosen field; or how you might serve educationally underrepresented and underserved segments of society with your graduate education (U.C. Davis - M.A. in Linguistics).
- A Personal Statement specifying your past experiences, reasons for applying, and your areas of interest. It should explain your intellectual and personal goals, why you are interested in pursuing an interdisciplinary degree rather than a more traditional disciplinary one, and how this degree fits into your intellectual and personal future (Rutgers University - Ph.D in Women’s and Gender Studies).
- Your application requires a written statement to uploaded into your application and is a critical component of your application for admission. This is your opportunity to tell us what excites you about the field of library and information science, and what problems you want to help solve in this field. Please also tell us how your prior experiences have prepared you for this next step toward your career goals and how this program will help you achieve them (University of North Carolina Chapel Hill - Master of Science in Library Science).
- After watching the video, please describe what strengths and preferences as a learner you have that will facilitate your success in this innovative curriculum. What challenges in our curriculum do you anticipate and what strategies might you use to address these challenges? (MGH Institute of Health Professions PT - They recently redesigned their curriculum)
- Your personal goal statement should briefly describe how you view the future of the field, what your goals are to be part of that future, and what brought you to pursue an advanced education degree in your chosen field. You may include any other information that you feel might be useful. (Northeastern PT)
- Personal Statement: In 500 words or less, describe a meaningful educational experience that affected your professional goals and growth and explain how it impacted you. The educational experience does not need to be related to this degree. Focus on the educational experience and not why you think you would be a good professional in this field. (Simmons PT)
- Personal Statement (500 word minimum): State your reasons for seeking admission to this program at this institution. Include your professional goals, why you want to pursue a career in this field and how admission to this program will assist you in accomplishing those goals. (Regis College Nursing)
- “Use the space provided to explain why you want to go to this type of program.” (AMCAS)
- Address the following three questions(Though there is no set limit, most statements are 1–2 pages, single-spaced.): What are your reasons for pursuing this degree? Why do you wish to pursue your degree at this institution? How do you intend to leverage your degree in a career of this field? (Boston University MPH)
- Please submit a personal statement/statement of purpose of no more than 500 words for the department/degree of choice. Professional degree essays require a clear understanding of the _______ field and how you hope to work within the field. Be sure to proofread your personal statement carefully for spelling and grammar. In your statement, be sure to address the following: what interests you in the field of _____ what interests you in a specific degree program and department at this institution and what interests you in a particular certificate (if applicable). Please also describe how you hope to use your ________ training to help you achieve your career goals. (Columbia PhD in Public Health - Epidemiology)
- Because each Home Program requires significant original research activities in fulfillment of the requirements for the degree, we are interested in obtaining as much information as possible about your previous research experiences. Those who already have such experience are in a better position to know whether they are truly interested in performing ______ research as part of a graduate program. Please include specific information about your research experience in your Statement of Purpose. You may also use the Statement to amplify your comments about your choice of Home Program(s), and how your past experiences and current interests are related to your choice. Personal Statements should not exceed two pages in length (single spaced). Make sure to set your computer to Western European or other English-language setting. We cannot guarantee the ability to access your statement if it is submitted in other fonts. (Stanford Biosciences PhD)
- Your statement of purpose should describe succinctly your reasons for applying to the Department of ____ at ___ University. It would be helpful to include what you have done to prepare for this degree program. Please describe your research interests, past research experience, future career plans and other details of your background and interests that will allow us to evaluate your ability to thrive in our program. If you have interests that align with a specific faculty member, you may state this in your application. Your statement of purpose should not exceed two pages in length (single spaced). (Stanford Bioengineering PhD)
- Statement of purpose (Up to one page or 1,000 words): Rather than a research proposal, you should provide a statement of purpose. Your statement should be written in English and explain your motivation for applying for the course at this institution and your relevant experience and education. Please provide an indication of the area of your proposed research and supervisor(s) in your statement. This will be assessed for the coherence of the statement; evidence of motivation for and understanding of the proposed area of study; the ability to present a reasoned case in English; and commitment to the subject. (Oxford Inorganic Chemistry - DPhil)
Related resources
Still have questions? Leave a comment
Add Comment
Checklist: Dissertation Proposal
Enter your email id to get the downloadable right in your inbox!
Examples: Edited Papers
Need editing and proofreading services, 10 best ai essay outline generators of 2024.

- Tags: Artificial Intelligence , Essay , Writing Tips
Artificial intelligence (AI) has simplified the creation of engaging, information-rich content today. Not only can users create content, images, software code, and the like but also generate ideas about how this content should look and read.
One particular area of writing where outline generators can work wonders is essays. Though AI outline generators are used for different content forms today, we will focus on essay outline generators in this article. Let us begin by discussing what outline generators for essays can do for you.
Editing your essay feels like a challenge? Talk to us! Learn more
What is an essay outline generator?
An essay outline generator is an AI tool designed to help users create a structure and strategy for their essays. Many consider essay writing an uphill task, and AI essay outline generators can help streamline the planning process—the writing approach, style, and structure.
As most websites offer comprehensive content creation services, an essay outline generator is one of the features available to users. These free essay outline generators can help you brainstorm and organize your content.
Using free AI essay outline generators, you can form logically sound and cogent points about the topic you write. If you have an argumentative essay to write, an argumentative essay outline generator will do the trick quite nicely when you give it the right prompt or input.
Ten popular essay outline generators today
Here is a list of some well-known content and outline generators available online:
1. Copylime
This versatile writing tool offers extensive content generation support, covering blogs , articles, essays, cold emails, newsletters, listicles, headlines, conclusions, etc. The essay outline writer asks for the theme or subject, tone, and language.
While the platform offers free writing tools, the paid version costs $29 a month.
2. Perfect Essay Writer
Perfect Essay Writer is another website that provides a host of writing, grammar, plagiarism checking , citations , paragraphs, and other tools. It also offers professional essay writing services tailored to individual needs.
The free plan gives users access to all the tools but with certain word count limitations. The paid versions, Basic, Pro, and Advanced, cost $9.99/month, $14.99/month, and $99.99/year. The Basic plan includes access to “AI Essay Writer” and “AI Essay Outliner”.
Ahrefs is a widely used search engine optimization (SEO) toolset, with multiple features and services being made available to users. While the outline generator looks like it is built for blogs, it can generate outlines for all kinds of content, including academic papers, presentations, etc.
The company focuses on content creation and has 4 different plans—Lite, Standard, Advanced, and Enterprise costing $129/month, $249/month, $449/month, and $14,999/year, respectively.
4. MyEssayWriter.ai
This is an AI-powered essay writing assistant that offers essay outlines tailored to specific topics. The platform offers an artificial intelligence-based essay outline generator.
It is a focused essay outline writing tool that generates essay outlines in minutes. This free outline generator for essays is easy to use.
5. Custom-Writing.org
Custom-Writing.org provides personalized writing services for academic needs, comprising essays, term papers, research papers, reports, letters, etc. You can also get custom essays written on this platform. Their 24/7 customer support makes getting queries resolved easy.
Pricing is based on the complexity and assignment deadline, with rates starting at approximately $12 per page.
6. EssayService.ai
This is a user-friendly platform that offers various tools to improve essay quality. It offers grammar feedback and input on tone and style. It gives multiple essay generation options, with a free essay outline generator for users.
The platform also offers a paid essay writing service.
This is an AI writing tool offering multiple options for content generation, including essay generation. It allows you to create essay outlines and AI-generated essays in no time. Rytr has a paragraph generator, too, which can help with essay outlines.
The free version allows you to generate 10K characters per month. To access advanced features, users will be required to opt for paid services.
8. Writesonic
This is a content-creation tool, but it offers essay-writing features as well. It can generate essay outlines based on your input. The platform assures users that the content it generates is plagiarism-free.
The free version is quite effective as it offers all the features of Writesonic.
9. Writing Lab
Writing Lab’s essay outline generator is a useful essay outline generator. When you input your essay topic, it suggests ideas and creates an organized outline. This is a great tool to brainstorm, structure your thoughts, and save time while submitting time-sensitive assignments.
This essay outline generator also gives you grammar suggestions. The only drawback of using this tool is that it offers limited free services.
This AI outline generator is a user-friendly tool that can help you quickly draft great essays. It can create structured outlines for various content forms, including essays. It is ideal for those struggling with organizing the content in their essays and maintaining consistency in writing.
The “Basic” user plan starts at $49 per user per month, but the free version might just be sufficient if you are a student.
How to use an essay outline generator
Learning how to use an essay outline generator can come in handy, particularly when you need to create a well-thought-out outline and save time while writing.
So here’s a quick step-by-step guide on how to use an essay outline generator:
- Identify the requirements: Outline the requirements to determine the nature and content of your prompt for the tool. Identify the essay type , length, word count, tone, title options, and other topic-specific requirements.
- Choose an AI tool: Now, select an AI essay outline generator. Consider reviews while making this decision. You can select multiple free tools to get essay outline options. Some platforms offer subscription-based services, but free tools will get the job done.
- Input the relevant information: Most platforms ask to input information like essay type, length, purpose, academic level, word count, etc.
- Adjust, modify, or refine the input: Once you generate an outline, check if it meets your needs. If not, change or adjust the input details to create suitable outline ideas.
- Finalize an outline: Study the outline/s and finalize one that incorporates the best ideas. From here, you are all set to start drafting your essay.
Benefits of using an essay outline generator
Essay outline generators familiarize people at various proficiency levels with different essay structures and writing styles . Let us go a little deeper keeping this thought in sight and understand the benefits of using an essay generator.
- New idea generation or incorporation: Using an essay outline generator, you can develop new ideas and make your essay insightful.
- Idea development and review: With a meticulously designed outline and quick reviews, incorporating ideas, research points, facts, and other relevant information is easy.
- Strong premise creation: These tools help you create logical arguments and include well-founded statements, giving your essay a solid body and direction.
- Efficiency: Essay writing becomes efficient with a structure in place.
- Free templates: Essay writing can be simplified further using free templates . You can save the time and effort required to format your document well.
Also read: Compare and Contrast Essay | Quick Guide with Examples
So, these are some reasons why you should consider using an AI essay outline generator online.
There is no doubt that this tool helps write impressive essays. However, it is advisable to use these tools as a writing aid rather than a crutch. We recommend the use of free essay outline generators and essay writers to spruce up the content of your essay that might just help you get that otherwise elusive grade A.
If you think your essay needs a professional review, explore PaperTrue’s essay editing and proofreading services .
You might find the following articles helpful:
- Essential Research Tips for Essay Writing
- Top 10 Essay Editing Services of 2024
- College Essay Format: Tips, Examples, and Free Template
- 100 Best College Essay Topics & How to Pick the Perfect One!
- Guide to Essay Editing: Methods, Tips, & Examples
Frequently Asked Questions
Can an argumentative essay outline generator create a detailed outline with multiple headings, can essay outline generators be used in conjunction with free essay templates, can i customize an outline generated by free ai essay outline generators.
Found this article helpful?
Leave a Comment: Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Your vs. You’re: When to Use Your and You’re
Your organization needs a technical editor: here’s why, your guide to the best ebook readers in 2024, writing for the web: 7 expert tips for web content writing.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Get carefully curated resources about writing, editing, and publishing in the comfort of your inbox.
How to Copyright Your Book?
If you’ve thought about copyrighting your book, you’re on the right path.
© 2024 All rights reserved
- Terms of service
- Privacy policy
- Self Publishing Guide
- Pre-Publishing Steps
- Fiction Writing Tips
- Traditional Publishing
- Additional Resources
- Dissertation Writing Guide
- Essay Writing Guide
- Academic Writing and Publishing
- Citation and Referencing
- Partner with us
- Annual report
- Website content
- Marketing material
- Job Applicant
- Cover letter
- Resource Center
- Case studies

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Tip #6: Draw a map of your ideas. While some students might prefer the more traditional list methods, for more visual learners, sketching out a word map of ideas may be a useful method for brainstorming. Write the main idea in a circle in the center of your page. Then, write smaller, related ideas in bubbles further from the center of the page ...
Brainstorming can help you choose a topic, develop an approach to a topic, or deepen your understanding of the topic's potential. Introduction If you consciously take advantage of your natural thinking processes by gathering your brain's energies into a "storm," you can transform these energies into written words or diagrams that will ...
Most people have been taught how to brainstorm, but review these instructions to make sure you understand all aspects of it. Make a list (or list s) of every idea you can think of about your subject; Don't write in complete sentences, just words and phrases, and don't worry about grammar or even spelling; Again, do NOT judge or skip any idea ...
Brainstorming tip #2: Making a Cube. Draw a cube in your notebook. Each of the six sides has a task: Side 1: Describe the topic. Side 2: Compare the topic. Side 3: Connect the topic. Side 4: Classify the topic. Side 5: Argue for or against the topic. Side 6: Personalize the topic.
In this English writing lesson, you will learn multiple ways to brainstorm ideas for an essay from a college professor, including how to use a T-chart, clust...
Individual vs. group brainstorming. How to brainstorm in 6 steps. Prepare. Capture the main focal points. Write down all your initial ideas. Look for patterns. List the "holes" or unaddressed objectives. Generate new ideas for the missing parts. How to organize ideas after a brainstorming session.
College Essay Brainstorming Step #2: Iterate. To kickstart the creative process, you'll want to activate your DMN, or default mode network, via divergent thinking. Divergent thinking is the process of amassing as many ideas as possible in a spontaneous, non-judgmental way.
Brainstorming is an essential step before outlining the major points needed to create a well-organized essay. Several techniques can be used for brainstorming, including freewriting, listing ...
Brainstorming helps you deal with much of the uncertainty and anxiety around essay writing. The following list of brainstorming methods includes both individual and group approaches that can be applied to choosing an essay pro mpt, developing an essay prompt, establishing a writing approach, and anything else your creative mind can conjure.
A useful brainstorming strategy is to ask yourself questions (perhaps based off of the assignment prompt and/or in relation to your ideas and interests). Write down the answers to your own questions as a way to think through potential ideas. A useful brainstorming strategy is to think aloud. It is productive to brainstorm by having a ...
Brainstorming is the process of generating ideas or topics to write about or discuss. It can be a useful tool when you are starting to write a paper, but it's also an informal process that can be done at any time during the writing process. There is no right or wrong way to brainstorm!
Return to Writing Studio Handouts. Invention (also referred to as brainstorming) is the stage of the writing process during which writers discover the ideas upon which their essays will focus. During this stage, writers tend to overcome some of the anxiety they might have about writing a paper, and in many cases, actually become excited about it.
Brainstorming generates the ideas that will eventually become your thesis statement and supporting points. Developing a clear thesis will help you know what to write and how to organize it. If you have writer's block or do not know where to begin, brainstorming can be especially helpful. ... Essay Organizer (3 Topics)
The first step is to back up. Before you write anything of value, you must first. The first, messiest, least demanding, but perhaps most important stage of pre-writing is . Here's a sample of five brainstorming techniques to get your mind moving and your words flowing as you start to plan your college essays: 1.
Idea #2 - Draw a Mind Map. Brainstorm for essays - Image courtesy of Uyen.vn. Brains love visual communication and mind maps are exactly that. Our thoughts rarely arrive in easily digestible chunks; they're more like webs of information and ideas that extend forward at any given time.
Look at an example topic and outline, and learn the basic components of brainstorming, outlining and reading and analyzing a prompt.
Step 2: Pick one of the things you wrote down, flip your paper over, and write it at the top of your paper, like this: This is your thread, or a potential thread. Step 3: Underneath what you wrote down, name 5-6 values you could connect to this. These will serve as the beads of your essay.
Brainstorming can take many forms, from creating an outline for a paper to keeping a list of ideas and thoughts. The method you choose depends only on what works best for you. ... when you actually sit down to write the essay, you'll never lose focus on your main arguments. Being Original. Again, all professors want you to make clear points ...
Here's a useful way to understand and reframe college essay topics: Essentially, your "topic" (e.g. Home or Light) is just an excuse— your topic is always you. Who you are, what you value, what you bring to a campus and community. So this is the place to fill in the gaps by being personal and specific.
6. Make a list of anecdotes, childhood memories, or stories about yourself. Then choose one and make it your "vehicle.". Finally, you should conclude your brainstorming session by searching for a vehicle: an anecdote that you can use to frame your personal statement. You can use anecdotes in your personal statement in a number of ways.
Brainstorming is a technique which is used to get as many ideas as you can, as quickly as you can. The words 'many' and quickly' are important. A common mistake students make when brainstorming is to stop after writing down only a few ideas. This is not 'brainstorming'. As the word 'storm' suggests, it is something which should have much energy ...
When brainstorming for an essay, it is essential to find out what part of brain is active - right or left. 1. Brainstorming for right brains. When it comes to right-brained thinkers, they find it easier to perceive creatively presented information. For example, they like patterns, shapes, diagrams, and tables more than plain text.
A personal statement is a narrative essay that connects your background, experiences, and goals to the mission, requirements, and desired outcomes of the specific opportunity you are seeking. It is a critical component in the selection process, whether the essay is for a competitive internship, a graduate fellowship, or admittance to a graduate school program.
Writing Lab's essay outline generator is a useful essay outline generator. When you input your essay topic, it suggests ideas and creates an organized outline. This is a great tool to brainstorm, structure your thoughts, and save time while submitting time-sensitive assignments. This essay outline generator also gives you grammar suggestions.
In writing the actual essay, know that proper grammar and punctuation is key. Clarity in your writing and logical organization is also important. ... Also - look for the thread or theme if you observed one in your brainstorming. Make sure that the story of your WHY is the story that comes through. Final Points. Be ready to write multiple ...
Of the 30% who used generative AI for help on their essays, 50% used it for brainstorming ideas, 48% used it for spelling and grammar checks, 47% had it create an essay outline, 32% used it to ...