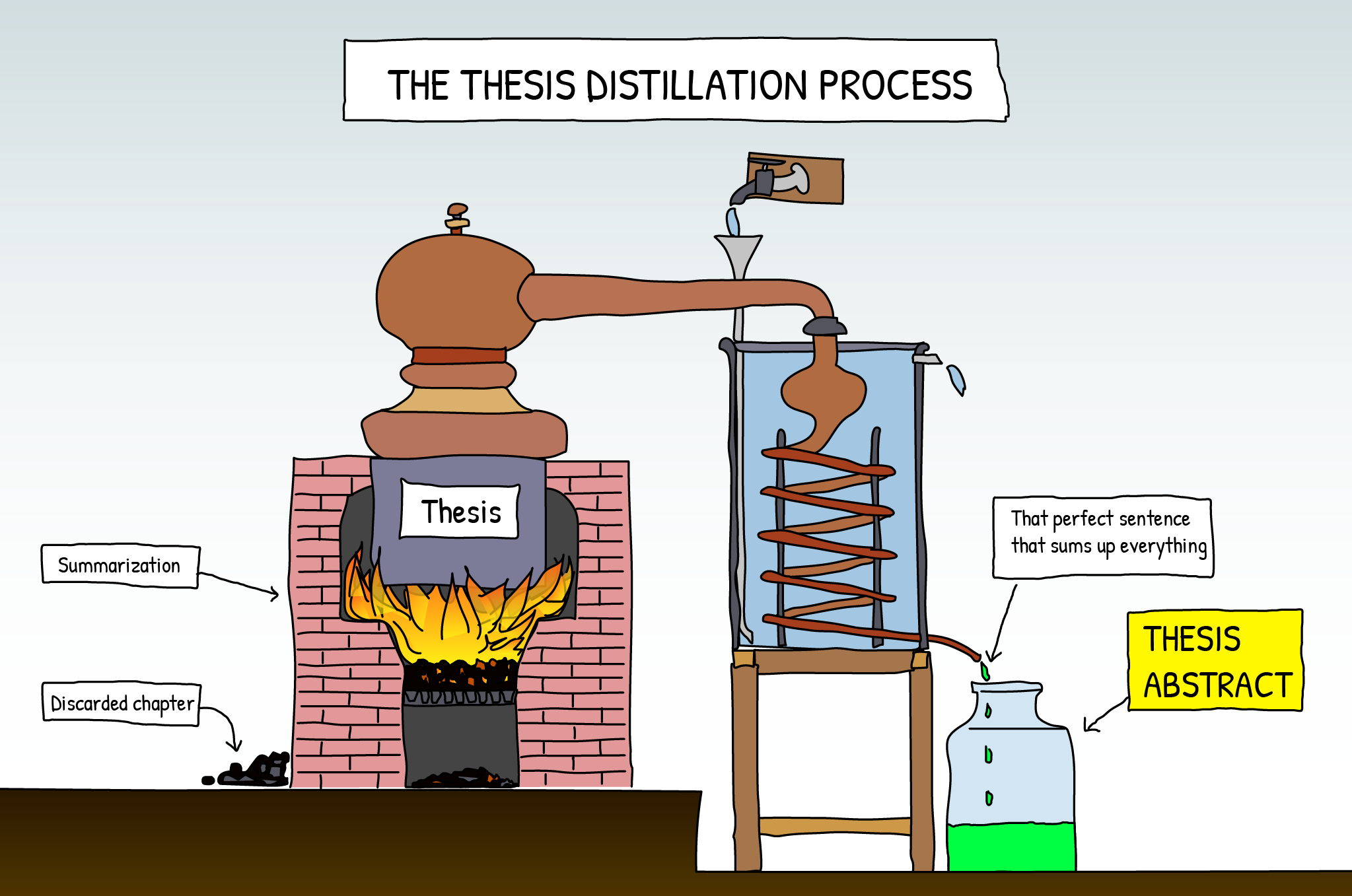
How to Write a Thesis Summary
Your thesis summary is the distilled essence of your thesis: a tool to underline the strengths of your research and make yourself recognizable as a competent scholar.

The importance of writing a good thesis summary is often underestimated and it is not too difficult to understand why. Even in the cases where a student has seriously engaged in writing his thesis, the summary is usually the last thing that gets done. The typical scenario is therefore the following: the bulk of the work has finally been done, the deadline to submit the thesis is imminent. Time is running out and, consequently, when it comes to set the summary down, this is written in a very hasty way… I am pretty sure that you can relate to this situation and – trust me – you are not the only one. Yet, this is a pity! Your thesis summary deserves to be written with a certain care for several good reasons. An effective summary is the best way to impress your readers. It will be the first thing to be read and – as hard as it is to admit – the first impression is what really counts. You should therefore think of the summary as a distilled and concentrated essence of your thesis: a tool to underline the strengths of your research and make yourself recognizable as a competent scholar.
Especially if your thesis is written in another language, setting down an accurate, compelling summary in English can be the first step to internationally disseminate your work. In this regard, keep also in mind that an English summary of your thesis may be required for a job application or a PhD-position. Having said that, how to proceed? Here you are some useful steps to write an effective summary.

Elaborate a thesis statement
The thesis statement . is the most important part. This is a sentence usually placed at the beginning of the summary and it is aimed at clarifying the main research questions of your work. The thesis statement must be clear and concise. MA theses, but also PhD dissertations, usually concern very narrow topics. So, avoid being vague and explain the central idea of your research as specific as possible. Let’s do some practical examples. A sentence like:
“the aim of the present study is to show how English skills can be improved in several ways” is certainly too vague.
Instead, a statement like:
“the aim of the present research is to show how the use of Ludwig can improve English writing skills, by providing reliable texts to get inspiration”
defines a narrower field of research. In addition, as the last example demonstrates, a good thesis statement can be enforced with further arguments.
For example, one could state that:
taking inspiration from a database of 300 million English sentences can indeed help a student to perfect their phrasing, by seeing words in the context of real sentences. A mere automatic correction tool, instead, carries the risk of worsening the student performance, for example by favouring the memorization of wrong phrases and expressions.

Explain the structure of the thesis
Each thesis is usually divided into diverse chapters, such as an introduction, a section dedicated to explaining the terminology, a chapter for the methodology, the discussion of the data, the results of the research etc. A good summary must give a clear idea of how you have organized your research step by step. So be very clear and use sentences like “in the first chapter of my thesis I treated”, “while in the second…”, “the analysis of the data has shown that” etc. And, of course, do not hesitate to use Ludwig if you need examples to take inspiration from. Keep in mind, you may have made the discovery of the century… but if you are not able to explain how you achieved such a result, you will be considered a charlatan.
How to write a thesis summary: a practical example
In this regard, it is good practice to read a number of thesis summaries and to analyse how they are written. Nowadays all the most prestigious universities offer free access to their online repositories, where one can find great inspirational models. See, for example, this website by Cambridge University. Now, let's analyse the structure of one of them:
The Italian giallo film was a type of thriller that was produced in huge numbers between the early 1960s and the late 1980s. This thesis contributes to recent scholarly attempts to situate the giallo within its socio-cultural historical context but resists the critical tendency to read these films as passive and transparent reflections of social attitudes in post-war Italy. Rather, I attend concretely to the form of these films and, specifically, to their critically neglected sound designs . I argue that the giallo’s voice tracks were conditioned by the commercial imperatives of Italy’s post-war popular film industry and that these commercial imperatives were in turn shaped by wider social, economic and political phenomena. By theorising the voice as a mediator between the giallo text and its industrial and social contexts, I show that these films both registered and reified social change. Chapter 1 demonstrates that the anonymous narrator of Mario Bava’s The Girl Who Knew Too Much (1963) adopts a range of sonorous modes throughout the film. Each of these sonorous modes invokes a specific set of intertexts which are vital to tracing both the giallo’s cultural origins and the increasingly globalised socio- cultural landscape from which it emerged. This chapter then shows that Dario Argento’s The Bird with the Crystal Plumage (1970) uses the model of the cinematic voice-over to explore the subjective experience of urban space in post-war Italy. The film suggests that by 1970 the ability to vocally ‘narrate’ and thus control space had become a fundamental assumption of the modern, cosmopolitan subject. Chapter 2 analyses Lucio Fulci’s Don’t Torture a Duckling (1972) and Sergio Martino’s Torso (1973). Both films draw on longstanding Italian cultural stereotypes to pitch the silence of the rural against the vocality of the urban. The films use silence and the voice as ‘cartographic’ tools to delineate the profound socio-economic divisions between Italy’s rural South and its more urban North, but they also illustrate the giallo’s underlying affinities with its silent cinema ancestors and so challenge the assumed temporal borders between cinematic eras. Chapter 3 argues that Argento’s Tenebrae (1982) and Fulci’s The New York Ripper (1982) variously mimic the vocal aesthetics of television. These films lay bare both the increasing dominance of the Italian cultural landscape by imported commercial television in the 1980s and the neoliberal economic project that underpinned that trend. Ultimately, they question the stability of the nation itself, precisely because the voice — now fractured across a global mediascape — is unable to signal national specificity.
The sentences in bold highlight how the author carefully organized the structure of the text. He started with a well elaborate thesis statement. As you can see, the object of the research is well defined and narrow: the study focuses on Italian thrillers , produced during a specific historical period between the early 1960s and the late 1980s. Moreover, the investigation depeens a specific aspect: the use of sounds in this movie genre. Then, the scholar explains in detail how he organized his work step by step, by summarizing the content of each chapter.

Ultimately, we can say that to write a theis summary is a less daunting task than one might imagine at first sight!
Keep in mind why and for whom you are writing
There is a huge difference between writing a summary for the theses database of your university and to write a summary for a more ambitious purpose. As mentioned above, a summary of your thesis may be required for a job application or to get a PhD position. So, if you are facing this kind of situation, you must “use” your summary in a smart way. Are there any points of contact between your thesis and the position you hope to get? If yes which ones? Is it the topic? Or, perhaps, in order to undertake your research, you have used a tool/method/program that could be pertinent with this position? So, tailor your summary in order to highlight what you need to stand out from the crowd and… good luck!
Others from Academic English

MLA, APA, Chicago, IEEE - What’s the best citation style for your paper?

The Fall of the Five-Paragraph Essay

Should I publish it in English? About the role of English in the scientific community

How to write the perfect abstract: do not displease your reviewers and get published
Subscribe to new posts.
How to write a PhD in a hundred steps (or more)
A workingmumscholar's journey through her phd and beyond, concluding the thesis.
I am co-supervising a PhD student who is handing in her thesis for examination in November. She is currently revising her whole thesis, working towards the conclusion (and finally, the introduction). Conclusions can be tricky things to write – pulling something as big as a PhD dissertation together into a final, clear chapter is not easy. It is both an intellectual and an emotional challenge, as conclusion-writing comes towards the very end of the process, and you are so tired, and probably feeling like there are no more coherent words or sentences in your brain. This post reflects a little on what a thesis conclusion is for, with some thoughts on how to construct one that does justice to your meisterwerk .

To begin with, let’s think a bit about what conclusions are for in a piece of written work. In undergraduate studies, students are typically taught that conclusions are summaries . You restate the thesis, or main claim, of your paper, reiterate what each paragraph has said that contributes to that argument, and then bring it all together with a firm final sentence or two that says something about the relevance of the paper, or argument. There should be no new information, just a summing up of what has already been said. Sometimes you are allowed recommendations, depending on the discipline. It makes sense, then, that we progress into postgraduate studies believing that we are writing summaries whenever we conclude (a paper, or a journal article, or a thesis). I have seen many conclusions like this in postgraduate, postdoctoral and early career writing. But, unfortunately, at these levels conclusions that merely summarise a paper the reader has just read are not adequate, or suitable . A shift is needed.
As Pat Thomson usefully argues in this post about writing a thesis conclusion, the conclusion to a thesis (or journal article) is not a summary of the whole . The summary part of a thesis conclusion should ideally be quite brief, and used rather as a springboard to the real work of the conclusion: using the preceding writing and research to show how the study has addressed the research questions, and in so doing, how it has made a valid, and useful, contribution to knowledge .
A strong conclusion shows your readers what your research means within the context of the field you have referenced in your ‘literature review’, and how in answering your research questions you have been able to speak back to this body of research in which you have located your own study. It answers your research questions, succinctly and clearly, so that your readers understand the overall claims of your study, the focus of your argument, the basis upon which you have advanced your argument, and the significance, meaning or value of that argument to your (their) field. It discusses – argues – for the place of your research within your field, and the contribution it is making.

There are a few ways in which you can approach writing such a conclusion (and Pat’s post above is very helpful here). There are also a few guidelines to consider in writing this vital part of your thesis.
To begin with, you do need to bring your reader up to speed with the thesis thus far . Examiners and other readers are unlikely to read your whole PhD in one go, so ending each chapter with a brief summary, and starting the next one with a short section that connects the present chapter to the previous one is a good idea for creating coherent connections between chapters, and is helpful for your readers. Thus, you should begin your conclusion with an overview, or brief summary, of the argument thus far.
Then, consider your research questions : what did you set out to do in this project or study? Your research questions could make useful sub-headings here, at least in a first draft, to help you organise your thoughts. Starting here, you can begin to pull out the answers you have found (in the ‘analysis chapter/s’) so that you can discuss the implications of your findings, their relevance in relation to your overall argument, and the way in which what you have found relates to the body of research to which you have connected your study. No new information : just an analytical discussion of selected aspects of your findings that are useful for answering your research questions, and further consolidating your argument.
Perhaps you have recommendations , on the basis of your findings and their implications for practice, and/or further research. You could include a section on these, discussing a step further the possible implications of your research in relation to your field. Something else that may be relevant to include here could be limitations to the size or scope of your findings: are there any that your readers need to know about, so that they don’t expect your study to have done something other than what it has done? Don’t just list all the things you could have done but didn’t do: think carefully about pertinent limitations that may represent counter-arguments you could defend or mitigate against.
At the end of the end, consider your argument again : what has your thesis claimed and to what end? Try to end your thesis with a paragraph that reiterates not just what your thesis has argued, but WHY this argument has relevance, or import, for your readers. What do you hope the outcome of your research will be? Why are you so passionate about it, and why do you think others should care too? Read a few thesis conclusions to get a sense of different ways of doing this, and check out Pat Thomson’s posts on conclusion writing , too. Then write a draft and share it with your supervisor for feedback.
It’s worth really taking your time and not rushing this chapter, even as it comes at the end when you are tired, and really just want to be done. End on the highest note you can: you owe yourself that much after all your hard work getting there.
Share this:
I am at exactly this point with my thesis so your very helpful suggestions couldn’t have been better timed. Pretty sure I would have most of the mistakes mentioned otherwise, so many thanks!
I’m so pleased that this is helpful – good luck with the conclusion and submission 🙂
You have a great blog! I didn’t reall of the posts, but all the titles of the posts seem to apply to me right now! I’m trying to finish up my PhD, which means, a lot of writing. This is very helpful!
Thanks for the comment, and all the best with the final push!
Timely. Half way through writing mine!
Swapped university with a few years to run on my candidature, got really sick and was struggling. Employed in aviation so COVID-19 has been great fun!
This summary is very timely!
Leave a comment Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar

How to write a PhD thesis: a step-by-step guide
A draft isn’t a perfect, finished product; it is your opportunity to start getting words down on paper, writes Kelly Louise Preece
Kelly Louise Preece

Created in partnership with

You may also like

Popular resources
.css-1txxx8u{overflow:hidden;max-height:81px;text-indent:0px;} Can we really decolonise the university?
Universities need to act now to bridge the gen z gap, school visits are a triple-win for academics, schools and society, why visible senior leadership in sustainability matters, why the search for research funding is like romance.
Congratulations; you’ve finished your research! Time to write your PhD thesis. This resource will take you through an eight-step plan for drafting your chapters and your thesis as a whole.

Organise your material
Before you start, it’s important to get organised. Take a step back and look at the data you have, then reorganise your research. Which parts of it are central to your thesis and which bits need putting to one side? Label and organise everything using logical folders – make it easy for yourself! Academic and blogger Pat Thomson calls this “Clean up to get clearer” . Thomson suggests these questions to ask yourself before you start writing:
- What data do you have? You might find it useful to write out a list of types of data (your supervisor will find this list useful too.) This list is also an audit document that can go in your thesis. Do you have any for the “cutting room floor”? Take a deep breath and put it in a separate non-thesis file. You can easily retrieve it if it turns out you need it.
- What do you have already written? What chunks of material have you written so far that could form the basis of pieces of the thesis text? They will most likely need to be revised but they are useful starting points. Do you have any holding text? That is material you already know has to be rewritten but contains information that will be the basis of a new piece of text.
- What have you read and what do you still need to read? Are there new texts that you need to consult now after your analysis? What readings can you now put to one side, knowing that they aren’t useful for this thesis – although they might be useful at another time?
- What goes with what? Can you create chunks or themes of materials that are going to form the basis of some chunks of your text, perhaps even chapters?
Once you have assessed and sorted what you have collected and generated you will be in much better shape to approach the big task of composing the dissertation.
Decide on a key message
A key message is a summary of new information communicated in your thesis. You should have started to map this out already in the section on argument and contribution – an overarching argument with building blocks that you will flesh out in individual chapters.
You have already mapped your argument visually, now you need to begin writing it in prose. Following another of Pat Thomson’s exercises, write a “tiny text” thesis abstract. This doesn’t have to be elegant, or indeed the finished product, but it will help you articulate the argument you want your thesis to make. You create a tiny text using a five-paragraph structure:
- The first sentence addresses the broad context. This locates the study in a policy, practice or research field.
- The second sentence establishes a problem related to the broad context you have set out. It often starts with “But”, “Yet” or “However”.
- The third sentence says what specific research has been done. This often starts with “This research” or “I report…”
- The fourth sentence reports the results. Don’t try to be too tricky here, just start with something like: “This study shows,” or “Analysis of the data suggests that…”
- The fifth and final sentence addresses the “So What?” question and makes clear the claim to contribution.
Here’s an example that Thomson provides:
Secondary school arts are in trouble, as the fall in enrolments in arts subjects dramatically attests. However, there is patchy evidence about the benefits of studying arts subjects at school and this makes it hard to argue why the drop in arts enrolments matters. This thesis reports on research which attempts to provide some answers to this problem – a longitudinal study which followed two groups of senior secondary students, one group enrolled in arts subjects and the other not, for three years. The results of the study demonstrate the benefits of young people’s engagement in arts activities, both in and out of school, as well as the connections between the two. The study not only adds to what is known about the benefits of both formal and informal arts education but also provides robust evidence for policymakers and practitioners arguing for the benefits of the arts. You can find out more about tiny texts and thesis abstracts on Thomson’s blog.
- Writing tips for higher education professionals
- Resource collection on academic writing
- What is your academic writing temperament?
Write a plan
You might not be a planner when it comes to writing. You might prefer to sit, type and think through ideas as you go. That’s OK. Everybody works differently. But one of the benefits of planning your writing is that your plan can help you when you get stuck. It can help with writer’s block (more on this shortly!) but also maintain clarity of intention and purpose in your writing.
You can do this by creating a thesis skeleton or storyboard , planning the order of your chapters, thinking of potential titles (which may change at a later stage), noting down what each chapter/section will cover and considering how many words you will dedicate to each chapter (make sure the total doesn’t exceed the maximum word limit allowed).
Use your plan to help prompt your writing when you get stuck and to develop clarity in your writing.
Some starting points include:
- This chapter will argue that…
- This section illustrates that…
- This paragraph provides evidence that…
Of course, we wish it werethat easy. But you need to approach your first draft as exactly that: a draft. It isn’t a perfect, finished product; it is your opportunity to start getting words down on paper. Start with whichever chapter you feel you want to write first; you don’t necessarily have to write the introduction first. Depending on your research, you may find it easier to begin with your empirical/data chapters.
Vitae advocates for the “three draft approach” to help with this and to stop you from focusing on finding exactly the right word or transition as part of your first draft.

This resource originally appeared on Researcher Development .
Kelly Louse Preece is head of educator development at the University of Exeter.
If you would like advice and insight from academics and university staff delivered direct to your inbox each week, sign up for the Campus newsletter .
Can we really decolonise the university?
How ai and immersive technology will personalise learning, campus podcast: how to prepare for university leadership, emotions and learning: what role do emotions play in how and why students learn, how a strong network can enhance the phd journey, a diy guide to starting your own journal.
Register for free
and unlock a host of features on the THE site

How To Write A High-Impact Executive Summary
By Derek Jansen | January 2018

In this post, I’ll deconstruct the often-misunderstood executive summary and show you how to develop a high-impact executive summary for your assignment, research report or even your dissertation or thesis.
So, what is an executive summary?
An executive summary (sometimes called an abstract ) is quite simply a summary of summaries. In other words, an executive summary provides a concise summary of each of your assignment or report chapters/sections . More specifically, it should communicate the key points/insights/findings/suggestions from the following chapters:
- Introduction
- Recommendations
- Implementation (if applicable)
- Reflection (if applicable)
I’ll discuss which key points from each section need to be addressed a bit later. On a separate note – if you’re writing an executive summary for a dissertation or thesis, all of the concepts described in this post will still apply to you, however, you’ll include an additional paragraph about your methodology, and you’ll likely spend more word count discussing your analysis findings.
The 4 Important Attributes Of An Exec Summary
Before I discuss what goes into the executive summary, let’s quickly look at 4 attributes that make for a strong executive summary:
#1 – It should be able to stand alone.
The executive summary should be able to stand independently as an informative document . In other words, the reader should be able to grasp your broad argument without having to read the full document. Further reading should be purely for attaining more detail. Simply put, the executive summary should be a “Mini-Me” of the assignment.
This independence means that anything you write in the executive summary will need to be re-stated in the body of your assignment. A common mistake that students make is to introduce key points in the executive summary and then not discuss them again in the document – accordingly, the marker must view the main document as missing these key points. Simply put – make sure you discuss key points in both the executive summary and the main body . It will feel repetitive at times – this is normal.

#2 – It should be written for the intelligent layman.
When crafting your executive summary, its useful to keep the intelligent layman front of mind. What I mean by this is that you should write your summary assuming that your reader (i.e. the marker) will be intelligent but won’t be familiar with your topic and/or industry. This means that you should explain any technical concepts, avoid jargon and explain acronyms before using them.
#3 – It should be concise.
Typically, your executive summary should be a one-pager (one and a half pages at worst). To summarise a 3000 – 5000-word document into one page is no easy task, so you’ll need to:
- Present only the most important information (key insights, recommendations, etc).
- Write concisely – i.e. with brevity and completeness.
To the first point, I’ll explain what the “most important” information is for each chapter shortly. To the second point (writing concisely), there are various ways to do this, including:
- Using simple, straightforward language.
- Using the active voice.
- Removing bloaty adverbs and adjectives.
- Reducing prepositional phrases.
- Avoiding noun strings.
Does this sound like gibberish to you? Don’t worry! The Writing Center at the University of Wisconson-Madison provides a practical guide to writing more concisely, which you can download here.
On a related note, you typically would not include headings, citations or bulleted/numbered lists in your executive summary. These visual components tend to use a lot of space, which comes at a premium, as you know.
#4 – It should be written last.
Given that your executive summary is a summary of summaries, it needs to be written last , only once you’ve identified all your key insights, recommendations and so on. This probably sounds obvious, but many students start writing the summary first (potentially because of its position in the document) and then end up re-writing it multiple times, or they don’t rewrite it and consequently end up with an executive summary which is misaligned with the main document.
Simply put, you should leave this section until everything else is completed. Once your core body content is completed, you should read through the entire document again and create a bullet-point list of all the key points . From this list, you should then craft your executive summary . The approach will also help you identify gaps, contradictions and misalignments in your main document.

So, what goes into an executive summary?
Right, let’s get into the meat of it and consider what exactly should go into your executive summary. As I’ve mentioned, you need to present only the absolutely key point points from each of your chapters, but what does this mean exactly?
Each chapter will typically take the form of 1 paragraph (with no headings) in your executive summary. So, 5 chapters means 5 paragraphs. Naturally, some will be longer than others (let this be informed by the mark allocation), but assuming one page contains 500 words, you’re aiming for roughly 100 words per paragraph (assuming a 5-paragraph structure). See why conciseness is key!
Now, let’s look at what the key points are for each chapter in the case of a typical MBA assignment or report. In the case of a dissertation or thesis, the paragraph structure would still mimic the chapter structure – you’d just have more chapters, and therefore, more paragraphs.
Paragraph 1: Introduction
This paragraph should cover the following points:
- A very brief explanation of the business (what does it do, for whom and where?).
- Clear identification and explanation of the problem or opportunity that will be the focus of the assignment/report.
- A clear statement of the purpose of the assignment (i.e. what research questions will you seek to answer?).
- Brief mention of what data sources were utilised (i.e. secondary research) and any fieldwork undertaken (i.e. primary research ).
In other words, your first paragraph should introduce the business, the problem/opportunity to be addressed, why it’s important, and how you approached your analysis. This paragraph should make it clear to the reader what the assignment is all about at a broad level. Here’s a practical example:
This assignment focuses on ABC Ltd, a XXX business based in XXX, which provides XXX to XXX customers. To date, the firm has relied almost exclusively on XXX marketing channel. Consequently, ABC Ltd has little understanding of consumer segments, wants, and needs. This marketing channel is now under regulatory threat due to XXX. The core challenge, therefore, is that whilst ABC Ltd seeks to grow its market share, it has little understanding of its market characteristics or competitive set, and its sole marketing channel under regulatory threat. Accordingly, the objective of this assignment is XXX. The assignment draws on survey, interview, and industry data.
Paragraph 2: Analysis and findings
In this paragraph, you should discuss the following:
- What exactly did you analyse? For example, you might have analysed the macro context (i.e. PESTLE analysis), followed by the meso (i.e. competitor or industry analysis) and then the micro (i.e. internal organisational analysis).
- What were your key findings in relation to the purpose of the assignment? For example, you may have identified 4 potential causes of a problem and would then state them.
In other words, your second paragraph should concisely explain what you analysed and what your main findings were . An example of this:
Segmentation analysis, consisting of macro, industry and firm-level analyses, revealed a strong segmentation variable in the form of XXX, with distinct needs in each segment. Macro analysis revealed XXX, while industry and firm-level analyses suggested XXX. Subsequently, three potential target segments were established, namely XXX, XXX and XXX. These were then evaluated using the Directional Policy Matrix, and the results indicated XXX.
From a presentation perspective, you might structure this section as:
- Analysis 1, findings from analysis 1.
- Analysis 2, findings from analysis 2.
- Analysis 3, findings from analysis 3.
Importantly, you should only discuss the findings that are directly linked to the research questions (i.e. the purpose of the assignment) – don’t digress into interesting but less relevant findings. Given that the analysis chapter typically counts for a large proportion of marks, you could viably write 2-3 paragraphs for this. Be guided by the mark allocation.
Lastly, you should ensure that the findings you present here align well with the recommendations you’ll make in the next paragraph. Think about what your recommendations are, and, if necessary, reverse engineer this paragraph to create a strong link and logical flow from analysis to recommendations.

Paragraph 3: Recommendations
With the key findings from your analysis presented in the preceding paragraph, you should now discuss the following:
- What are your key recommendations?
- How do these solve the problems you found in your analysis?
- Were there any further conclusions?
Simply put, this paragraph (or two) should present the main recommendations and justify their use (i.e. explain how they resolve the key issue). As mentioned before, it’s critically important that your recommendations tightly align with (and resolve) the key issues that you identified in the analysis. An example:
Based on the Directional Policy Matrix analysis, it is recommended that the firm target XXX segment, because of XXX. On this basis, a positioning of XXX is proposed, as this aligns with the segment’s key needs. Furthermore, a provisional high-level marketing mix is proposed. The key aspects of the marketing mix include XXX, XXX and XXX, as these align with the firm’s positioning of XXX. By adopting these recommendations, the key issue of XXX will be resolved.
Also, note that (typically) the tone changes from past to present tense when you get to the recommendations section.
Paragraph 4: Implementation
If your assignment brief requires an implementation/project plan-type section, this paragraph will typically include the following points:
- Time requirements (how long will it take?)
- People requirements (what skills are needed and where do you find them?)
- Money requirements (what budget is required?)
- How will the project or change be managed? (i.e. project management plan)
- What risks exist and how will these be managed?
Depending on what level of detail is required by your assignment brief, you may need to present more, less or other details in this section. As always, be guided by the assignment brief.
A practical example:
A high-level implementation plan is proposed, including a stakeholder analysis, project plan and business case. Resource requirements are presented, detailing XXX, XXX and XXX requirements. A risk analysis is presented, revealing key risks including XXX, XXX and XXX. Risk management solutions are proposed, including XXX and XXX.

Paragraph 5: Reflection
As with the implementation chapter, the need for a reflection chapter/section will vary between assignments and universities. If your assignment has this requirement, it’s typically good to cover the following points:
- What were your key learnings? What were your ah-ha moments?
- What has changed in the real world as a consequence of these learnings? I.e. how has your actual behaviour and approach to “X” changed, if any?
- What are the benefits and/or disadvantages of this change, if any?
This section is very personal, and so each person’s reflections will be different. Don’t take the above points as gospel.
Time to test it out.
Once you’ve written up your executive summary and feel confident that it’s in good shape, it’s time to test it out on an unsuspecting intelligent layman. This is a critically important step, since you, as the writer, are simply too close to the work to judge whether it all makes sense to a first-time reader. In fact, you are the least suitable person on the planet!
So, find someone who is not familiar with your assignment topic (and ideally, not familiar with your industry), and ask them to have a read through your executive summary. Friends and family will usually tell you its great, regardless of the quality, so you need to test them on their understanding. Do this by asking them to give the details back to you in their own words. Poke and prod – can they tell you what the key issues and recommendations were (in their own words!). You’ll quickly spot the gaps this way, and be able to flesh out any weak areas.
Wrapping up.
In this post, I’ve discussed how to write the all too often undercooked executive summary. I’ve discussed some important attributes of a strong executive summary, as well as the contents that typically go into it. To recap on the key points:
The key attributes of a high-impact executive summary:
- It should be able to stand alone.
- It should be written for the intelligent layman.
- It should be concise.
- It should be written last.
The key contents of a high-impact executive summary:
Each paragraph should cover a chapter from the document. For example, In the case of a typical assignment, it would be something like:
- Summary of the introduction chapter.
- Summary of the analysis chapter.
- Summary of the recommendations and/or conclusions chapter.
- Depending – summary of the implementation and reflection.
Lastly, don’t forget to test out your executive summary on an unsuspecting layman or two. This is probably the most important step of them all!
If you have any questions or suggestions, we’d love to hear from you. Please get in touch here or leave a comment below.
Thanks so much for your methodical process and explanation of Executive Summary. It is exactly what I was researching for.
Regards Saane
It’s a pleasure!
This was really helpful with how to structure my assignment.
Thank you so much for the step by step process. It’s so helpful for beginners like me.
Great! This post is very informative and gives clear guidance on to write an executive summary. Thanks very much for sharing this information, it’s very helpful.
Thanks for the feedback, Anna. Best of luck with your writing 🙂
Thank you for the great article, really helped explain what was needed.
Great insight and tips . Thanks
Thank you so much for sharing this. It was exactly what I was looking for.
Thank you for your help
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- +44 (0) 207 391 9032
Recent Posts
- How to Write a Character Analysis Essay
- Best Colours for Your PowerPoint Presentation: How to Choose
- How to Write a Nursing Essay
- Top 5 Essential Skills You Should Build As An International Student
- How Professional Editing Services Can Take Your Writing to the Next Level
- How to Write an Effective Essay Outline
- How to Write a Law Essay: A Comprehensive Guide with Examples
- What Are the Limitations of ChatGPT?
- How to Properly Write an Essay Outline Using ChatGpt
- Why Presentation Skills Are Important for Students
- Academic News
- Custom Essays
- Dissertation Writing
- Essay Marking
- Essay Writing
- Essay Writing Companies
- Model Essays
- Model Exam Answers
- Oxbridge Essays Updates
- PhD Writing
- Significant Academics
- Student News
- Study Skills
- University Applications
- University Essays
- University Life
- Writing Tips

How to Write a PhD Thesis: A Step-by-Step Guide for Success
Since 2006, oxbridge essays has been the uk’s leading paid essay-writing and dissertation service.
We have helped 10,000s of undergraduate, Masters and PhD students to maximise their grades in essays, dissertations, model-exam answers, applications and other materials. If you would like a free chat about your project with one of our UK staff, then please just reach out on one of the methods below.
Writing a PhD thesis is a complicated and demanding process that involves rigorous research, detailed analysis, and structured writing. This guide provides an extensive overview of each step required to craft a successful PhD thesis, offering essential insights and strategies that benefit novice and seasoned researchers.
Step 1: Understand the Requirements
The initial step in crafting your PhD thesis is to thoroughly understand its specific requirements, which can vary widely between disciplines and institutions. A thesis must contribute new knowledge to its field, necessitating a deep familiarity with the expected structure, depth of analysis, and submission formalities. Your university guidelines should state how many words in a PhD thesis are needed within your discipline—usually ranging from 60,000 to 80,000 words.
Step 2: Choose Your Topic Wisely
Selecting a suitable topic is crucial and should be approached with great care. Your subject should interest you, fill a research gap, and be feasible within your available time and resources. Extensive preliminary reading and discussions with advisors are crucial at this stage to refine your topic and formulate precise research questions.
Step 3: Develop a Detailed Proposal
A detailed proposal acts as your thesis roadmap, outlining your research questions, the study's significance, methodologies, and a preliminary literature review. This document guides your research trajectory and is a reference point throughout your project.
Step 4: Conduct Rigorous Research
The research phase forms the backbone of your thesis. It involves systematic data collection, comprehensive literature review, and meticulous analysis. Effective research methods are crucial, and keeping organised, detailed records during this phase will facilitate a smoother writing process later on.
Step 5: Start Writing Early
Begin writing early in the research process. Starting with less complex sections like the literature review or methodology can help clarify your thoughts and identify gaps in your research. Early writing reduces the burden as the thesis deadline approaches.
Step 6: Structure Your Thesis
A PhD thesis usually has an introduction, a literature review, a methodology, findings, a discussion, a conclusion, and a list of references. Each section serves a distinct purpose: the introduction presents your research question and its significance, while the conclusion synthesises your findings and highlights their importance. But, how long is a PhD thesis typically? It usually ranges from 100 to 300 pages, varying by field and the nature of the research conducted.
Step 7: Seek Feedback Regularly
Regular feedback from your supervisor and peers is invaluable. Sharing drafts of chapters as you complete them ensures you remain on the correct path and integrates diverse perspectives that can enhance your work.
Step 8: Revise Thoroughly
Revision is a critical phase in which good writing is refined into excellent writing. Use feedback to enhance your arguments, clarify points, and refine your prose. Expect multiple rounds of revisions and be prepared to rework sections as needed.
Step 9: Proofread and Edit
Comprehensive proofreading and editing are crucial to ensure your thesis is error-free. Consider employing PhD thesis help from a PhD thesis writing service if needed. These professionals can provide detailed feedback and help polish your document to perfection.
Step 10: Prepare for the Viva
The final step is the viva, where you'll present your research to a panel of experts in your field. Thorough preparation, including a deep understanding of your research and readiness for potential questions, is essential. This presentation is your opportunity to highlight the significance and rigour of your work.
The Importance of a High-Quality PhD Thesis
A high-quality PhD thesis is not just a requirement for completing your doctorate; it significantly contributes to your field of study. Furthermore, it highlights your ability to conduct independent research, contribute original insights, and communicate complex ideas clearly and effectively. The calibre of your thesis can influence your academic and professional future, impacting job opportunities, postdoctoral positions, and the ability to publish your work in reputable journals.
Seeking Professional Help: Sources and Providers
When crafting your PhD thesis, seeking professional help can be a wise decision. Support can come from various sources:
University Resources : Most universities offer writing centres and libraries with professionals skilled in research methodologies, writing, and editing. PhD Thesis Writing Services : Specialised services can provide comprehensive help throughout the writing process. These services employ experienced PhD thesis writers familiar with the nuances of doctoral writing across various disciplines. Independent Consultants : Expert consultants or freelance PhD thesis writers can offer personalised guidance and feedback, focusing on specific areas of your thesis where you need extra help.
The Advantages of Professional PhD Thesis Help
Opting for professional PhD thesis help offers several advantages:
- Expert Guidance : Professional writers and editors bring expertise that can help you improve your thesis. They understand the academic standards and can help ensure your thesis meets them.
- Time Management : With the help of a PhD thesis writing service, you can manage your time more effectively. Professionals can speed up the research, writing, and revision processes, allowing you to focus on other important academic or personal commitments.
- Reduced Stress : The process of writing a PhD thesis can be stressful. Having a professional by your side can alleviate much of this stress by ensuring you are on the right track and providing reassurance through expert feedback.
Key Takeaways
A high-quality PhD thesis is the masterpiece of your academic career, thus requiring meticulous attention to detail and a deep understanding of your research topic. When asking, "How many words are in a PhD thesis?" it's important to note that quality and depth of research often matter more than the word count.
Utilising professional help, whether through university resources, dedicated PhD thesis writing services, or independent consultants, can provide invaluable support. These professionals enhance the quality of your work and help streamline the entire thesis process, allowing you to present a polished, scholarly work that stands out in your field. By investing in professional help, you invest in your academic success and future career prospects.

Is a Thesis Writing Format Easy? A Comprehensive Guide to Thesis Writing

How Much Does It Cost To Write A Thesis? Get Complete Process & Tips

How to Tell if a Source is Reliable
Writing services.
- Essay Plans
- Critical Reviews
- Literature Reviews
- Presentations
- Dissertation Title Creation
- Dissertation Proposals
- Dissertation Chapters
- PhD Proposals
- Journal Publication
- CV Writing Service
- Business Proofreading Services
Editing Services
- Proofreading Service
- Editing Service
- Academic Editing Service
Additional Services
- Marking Services
- Consultation Calls
- Personal Statements
- Tutoring Services
Our Company
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Become a Writer
Terms & Policies
- Fair Use Policy
- Policy for Students in England
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- [email protected]
- Contact Form
Payment Methods
Cryptocurrency payments.

How to plan, structure and write every chapter in your PhD
In this collection, we’ll walk you through each chapter of your thesis. You’ll learn what goes where and how it fits together.

The PhD Discussion Chapter: What It Is & How To Write It
Your PhD discussion chapter is your thesis's intellectual epicenter. Think of it as the scholarly equivalent of a courtroom closing argument, where you summarise the evidence and make your case. Perhaps that’s why it’s so tricky - the skills you need in your...

Everything you wanted to know about structuring your PhD but were too afraid to ask
Understanding how to structure your PhD is tough. It helps to break it down into four distinct sections. In this guide, we explain how.

How to find the thread that runs through your PhD thesis
You probably worry about finding the thread that runs through the PhD thesis. In this guide we walk you through what’s required.

How to edit a PhD thesis (without going mad)
Your thesis takes a lot of time to research, ideate, and write. Here’s how to properly edit a PhD thesis such that you impress your examiners and achieve even greater success.

The 9 most effective ways to achieve PhD success
Writing a PhD is physically, intellectually and emotionally daunting. You may spend each day doubting yourself, not sure if you’re making the right choices and unsure whether you’ve got what it takes. During my life, I’ve helped thousands of PhD students like...

How To Structure A PhD Thesis
Struggling to understand what goes where? Let us walk you through a non-nonsense guide that’ll teach you how to structure a PhD thesis.

The difference between empirical and discussion chapters (and how to write them)
There is a very important distinction that needs to be made between the empirical and discussion sections/chapters. It is a common misconception that the empirical chapters are the place for your analysis. Often this confuses the reader.

Five tips to improve your PhD thesis
Regardless of what stage of the writing process you are at, there are five overarching tips you need to keep in mind if you want to improve your PhD thesis.

What are you doing and how are you doing it? Articulating your aims and objectives.
How long does it take the person reading your thesis to understand what you’re doing and how you’re doing it? If the answer is anything other than ’in the the opening lines of the thesis’, keep reading.

Learn how to write a PhD proposal that will stand out from the rest
When stripped down to its basic components, the PhD proposal explains the what and the why of your research. What it will be about and why it will be important.

Easily understand how to write a PhD thesis introduction
Get the introduction right and the rest of your dissertation will follow. Mess it up and you’ll be struggling to catch up. The introduction is the place to factually recount what it is you will be discussing in the thesis. Learn more in this detailed guide.

Last impressions count – writing your PhD thesis conclusion
The conclusion is the last thing your examiner will read before they write their viva report. You need to make sure it stands out.

What is a dissertation abstract and how do I write one for my PhD?
Don’t underestimate how hard it is to write a PhD thesis abstract. When I wrote mine I though it’d be straightforward. Far from it. It’s tricky. You have to condense hundred of pages and years of work into a few hundred words.

Russian (dolls) to the rescue – how to structure an argument in your PhD
At the core of the PhD are arguments. Lots of them. Some more important and some very specific. When you understand how to structure an argument, your thesis reads clearly and logically. If you don’t the reader ends up confused and your thesis suffers.

Drowning in a sea of authors – How to be critical in a PhD literature review.
Don’t get lost in a sea of authors when you write your PhD literature review. Instead be critical. In this guide we explain how.

Wrestling an elephant into a cupboard: how to write a PhD literature review in nine easy steps
When I was writing my PhD I hated the literature review. I was scared of it. I thought it would be impossible to grapple. So much so that it used to keep me up at night. Now I know how easy it can be and I’m sharing my top tips with you today.

A Template To Help You Structure Your PhD’s Theoretical Framework Chapter
In this guide, I explain how to use the theory framework template. The focus is on the practical things to consider when you’re working with the template and how you can give your theory framework the rockstar treatment.

How To Structure A PhD With Our PhD Writing Template
Our PhD Writing Template allows you to visualise your PhD on one page. Here we explain how to fill it in and how it can help you structure each chapter.

Eureka! When I learnt how to write a theoretical framework
The theoretical framework is so important, but so misunderstood. Here we explain it is in simple terms: as a toolbox.
Explore Other PhD Knowledge Base Collections
Eight collections of free resources to help you along the phd journey.

Mastering your theory and literature review chapters

How to structure and write every chapter of the PhD


How to stay motivated and productive

Techniques to improve your writing and fluency

Advice on maintaining good mental health

Resources designed for non-native English speakers

Explore our back-catalogue of motivational advice
Each week we send out a short, motivational email to over 4,000 students. Here you can sign up and access the archive.

A free one-page PhD structure template
- Write my thesis
- Thesis writers
- Buy thesis papers
- Bachelor thesis
- Master's thesis
- Thesis editing services
- Thesis proofreading services
- Buy a thesis online
- Write my dissertation
- Dissertation proposal help
- Pay for dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help online
- Buy dissertation online
- Cheap dissertation
- Dissertation editing services
- Write my research paper
- Buy research paper online
- Pay for research paper
- Research paper help
- Order research paper
- Custom research paper
- Cheap research paper
- Research papers for sale
- Thesis subjects
- How It Works
Guide On How To Write a Thesis Summary In 2023

So, you just found out that you need to write a thesis summary. In most cases, students who encounter this requirement for the first time start to panic. Frankly, not everyone knows what this thesis summary is. And let’s not forget that most students have no clue how to write one. Don’t worry about it too much though.
What is a thesis summary?
Why use a thesis summary, how to write an effective thesis summary in 2023, master thesis summary example.
A thesis summary is a document that summarizes the points of a longer essay, thesis, or dissertation. Readers will often find a summary to be helpful as it offers a succinct overview of the document’s contents. A Thesis Summary should not be confused with an abstract as they both refer to separate documents that serve different purposes.
The steps involved in writing a Thesis Summary depend on what type of thesis you are summarizing. If you’re summarizing a text-based thesis, then your first step should be to read the Thesis and make note of any major key points and conclusions made by the author(s). You then assemble your notes into one coherent paragraph detailing each one of the major key points. Keep in mind that this initial paragraph will serve as an introduction to your Thesis Summary; therefore, it should not contain the thesis’ main points. Once you’ve completed this step, use these Main Points (identified in your thesis) as a guide for writing the body of your document.
If you’re developing a summary thesis that’s math-related, then you’ll first need to take note of the main conclusions. Second, you must determine how these conclusions were reached by noting each step in the proof. Finally, you’ll have to explain why each step is true using logic statements and definitions from the thesis.
These are the two standard ways to write a thesis summary. However, you can also include your insights, opinions, and comments if you choose.
The steps for writing a ‘ Thesis Summary in 2023’ are just about the same as they’ve always been. They’re pretty much set in stone because this is how students have written thesis summaries for decades.
For both types of thesis summaries, you should include a final paragraph that ties everything together with a brief conclusion. This final paragraph should highlight the key points and conclusions made throughout your document as well as offer a brief statement about why these points matter.
Step 1: Read the Text
The very first thing you’ll want to do is read the entire text. When you’re reading, make note of any major key points and conclusions made by the author(s). If you’re summarizing a text-based thesis, then these major points will form the basis for your introduction paragraph. However, don’t include these points in this introduction.
Step 2: Get to Work
After reading the entire document, it’s time to get started! Begin by taking notes on what you’ve learned from the text and organize them into one coherent paragraph. Make sure that this introduction doesn’t contain the thesis’ main points. Next, use these Main Points (identified in your thesis) as a guide for writing the rest of your thesis summary.
Step 3: Proof it Out
If you’re summarizing a math-related thesis, then you’ll first need to take note of the main conclusions and purposes stated within the document. Next, determine how these conclusions were reached by noting each statement or step in the proof. Finally, complete your Thesis Summary by explaining why each step is true using logical statements and definitions from the thesis.
Step 4: Wrap it Up
Once you’ve finished writing the body of your Thesis Summary, include a final paragraph that ties everything together with a brief conclusion. This final paragraph should highlight the key points and conclusions made throughout your document as well as offer a brief statement about why these points matter.
The best reasons to use a thesis summary are that it will both summarize the relevance of the document and add relevance to an argument. If someone is looking for a specific point or conclusion from the original text, then a Thesis Summary provides them with a quick breakdown of what they can find in the document’s introduction.
You should include a thesis summary in your writings when you believe that there may be too many arguments within your writing. It will help you put together the important points from the different arguments into one concise section.
If you’re summarizing a math-related thesis, they will ensure that you proof every step of the proof given in your paper. It will make sure that you do not miss any details.
There are a few key things that you should keep in mind when writing an effective thesis summary.
- When you’re summarizing a math-related paper, make sure to highlight the main conclusions and how they were arrived at.
- Tell the reader why these conclusions matter by explaining each one with logical statements and definitions from the original document.
- Include a brief conclusion paragraph that ties everything together and highlights the key points covered throughout your work.
- If your thesis is text-based, make sure to include important points throughout the body of your work.
- Last but not least, remember that you are writing a summary so don’t use big words or complex sentence structures! Your goal is to be understood by anyone who reads it in the future.
This Thesis Summary sample is based on a text-based document. Please note, as far as the format and structure are concerned, there’s not much difference between a summary of a bachelor thesis example, an example of a Ph.D. thesis summary, and a thesis chapter summary from a Master thesis summary.
The introduction to the original document should be written as such:
“In this thesis, we’d like to introduce a new framework for understanding how we learn and teach math. The topic of learning and teaching should be the focus of mathematics education.”
Then, point out the main points and conclusions made throughout the body of your work:
“One conclusion that we’ve drawn from our research is that children’s conceptions should be taken into account when designing an appropriate math curriculum for them.”
“A second conclusion that we’ve drawn from our research is that children are more likely to develop their ideas about math if they are encouraged to think critically.”
Finally, make a brief statement about why these points matter using logical statements and definitions from the thesis:
“These conclusions highlight how important it is to focus on children’s conceptions when designing curricula because if we don’t take them into account, we miss out on our student’s potential.”
“These conclusions also show that we need to emphasize critical thinking as a means for children to develop their ideas about math.”
Now, you’ve successfully written an effective thesis summary! Keep in mind that your goal is to highlight the main points and conclusions of the original document as well as boast about their significance. To make this process easier for you, we hope that our tips come in handy.
You should now have a good idea about what a thesis summary or dissertation summary is, why you should use them, and how to write one.
A thesis summary is an overview of the main points and conclusions made in a text-based document or simply put, a summary of the research paper. A Thesis Summary should be included when you believe there are too many arguments within your writing, or if you’re summarizing math-related papers for proofing purposes. Key things to keep in mind while writing one include highlighting important concepts that were previously mentioned, explaining why these new ideas matter with logical statements and definitions from the original work, and providing a brief conclusion paragraph that ties everything together. If you want thesis help with any part of this process from reading or understanding complex texts to organizing them into coherent paragraphs let us know! Our team of thesis writers will be happy to help you complete your thesis summary!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
How to write Master's thesis summary for PhD application
I am currently applying for several PhD programs (in mathematics) and for many of them, it is required to write a short (approx. 2 pages; no more than 10.000 characters) summary of my Master's thesis. It should contain the motivations of the thesis and research, the methods used as well as the results obtained in my research.
Now, the application commitee is probably less interested in the precise topic of my research or in the project itself, but I guess that the aim of this writing in my application is more for them to examine my ability of writing and explaining my research to others, as the latter is one of the key abilities a scientist should probably have, in my opinion.
My questions are now the following:
(1) How detailed should such a writing be? In my specific case, I am appliying for a math PhD and many things which I did in my thesis, which lied in the border of math and physics, are very abstract, so it not always easy to explain them in simple, non-technical, terms (and I guess, this applies for most of the projects done in pure mathematics). So, should I aim in writing this text in a more "popular" science way, or should I "confront" them with full technical details (the middle way is, as written above, hardly possible, as the things are kind of abstract).
(2) Should I aim in writing this stuff more formally, or more from a personal point of view? So, should I, for example, write about my personal reasons for chosing this particular problem, or should I more concentrate on the scientific reasons of why this type of questions are interesting?
- graduate-admissions
- application
- 2 A thesis I'd have supervised (not in math, admittedly) would have a summary/an abstract in the beginning which could be used just like it is for your purpose. Does your thesis not contain an abstract/a short summary? – Snijderfrey Commented May 16, 2022 at 15:05
- 1 Hi, yes my thesis does contain an abstract, but this is rather small (half a page) and really just contains the technical contents and result.... So its written similar in spirit as an abstract of a paper... – B.Hueber Commented May 16, 2022 at 16:19
- 1 @Snijderfrey I'm not sure that's a good advice in generality. Many job applications I see which contain the abstract of the thesis don't look very convincing - this might just be correlations, but just putting the abstract makes a very un-excited impression. And who wants to hire unexcited students? – user151413 Commented May 17, 2022 at 19:17
2 Answers 2
Note that your essay will be read by other mathematicians, but most of them won't be in your specialty. An overly detailed presentation, such as you might present to your advisor won't be the best.
You are probably correct that they are looking for a writing sample, so focus on the writing at least as much as the math.
A personal view of "why" you chose this path is probably not the right focus, though a sentence might be fine.
First, though, what is the most important result in your thesis? It might be a theorem, but it might also be an interesting (thought provoking) proof technique. Talk about that result primarily, and situate it within the mathematical literature. Talk about why it is an important result. If possible, talk about what it might lead to, though you may not yet be sophisticated enough to understand that.
If the work gave you any special "insights" into the wider world of your specialty (or math in general) include a few words about that. Is there follow up research that is indicated?
As to the level, think about how you would explain the thesis to a good upper level undergraduate class. I'm guessing that such a level might be the best, of course, but all of your readers (various mathematicians) would be able to understand it.
The details are in the thesis, of course, and the committee will probably have access to that as well, so a higher level (or lower level, if you like) presentation is probably enough.
- Thanks a lot! Yes indeed, I also uploaded the full thesis in the application. – B.Hueber Commented May 16, 2022 at 16:23
- I join this answer to ask If it could be a good idea to write the MSc thesis summary in the form of a scientific article. Consider the following template provided by springer as a possible example: overleaf.com/latex/templates/… – g_don Commented Aug 13, 2023 at 19:29
Make it in 3 parts
- Synopsis: This is what you have written at the start of your Master's thesis.
- Brief description of your work: Describe what (and how) you did in your Master's project.
- Results: What new goals you achieved in your work.
The whole language is slightly technical, without many complex formulas and equations.
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged phd graduate-admissions thesis application ..
- Featured on Meta
- Bringing clarity to status tag usage on meta sites
- We've made changes to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy - July 2024
- Announcing a change to the data-dump process
Hot Network Questions
- How does the Israeli administration of the Golan Heights affect its current non-Jewish population?
- What is the lowest feasible depth for lightly-armed military submarines designed around the 1950s-60s?
- "Not many can say that is there."
- Shifted accordingly
- How can the Word be God and be with God simultaneously without creating the meaning of two Gods?
- Concise zsh regular expression parameter expansion to replace the last match of a pattern
- Shift right by half a trit
- Do space stations have anything that big spacecraft (such as the Space Shuttle and SpaceX Starship) don't have?
- Unstable output C++: running the same thing twice gives different output
- WW2 Bombers continuing on one of 2 or 4 engines, how would that work?
- Open a url with a custom protocol from the command line
- Large scale structure/Single galaxy simulation on GPU
- Am I allowed to link code licensed under GPL to proprietary libraries?
- Would several years of appointment as a lecturer hurt you when you decide to go for a tenure-track position later on?
- Can light be somehow confined to create a kugelblitz?
- How can the divergence of a cylinder with uniform magnetic field be non-zero?
- Communicate the intention to resign
- Automotive Controller LDO Failures
- Why is "a black belt in Judo" a metonym?
- Combinatorics: Bars and Stars Confusion
- NONODOKU, A new game
- Why is Excel not counting time with COUNTIF?
- efficiently reverse EISH to HSIE
- How to make a case based on factual evidence that my colleague's writing style for submitted manuscripts has got to be overhauled?

- How to Write an Abstract for a Dissertation or Thesis
- Doing a PhD
What is a Thesis or Dissertation Abstract?
The Cambridge English Dictionary defines an abstract in academic writing as being “ a few sentences that give the main ideas in an article or a scientific paper ” and the Collins English Dictionary says “ an abstract of an article, document, or speech is a short piece of writing that gives the main points of it ”.
Whether you’re writing up your Master’s dissertation or PhD thesis, the abstract will be a key element of this document that you’ll want to make sure you give proper attention to.
What is the Purpose of an Abstract?
The aim of a thesis abstract is to give the reader a broad overview of what your research project was about and what you found that was novel, before he or she decides to read the entire thesis. The reality here though is that very few people will read the entire thesis, and not because they’re necessarily disinterested but because practically it’s too large a document for most people to have the time to read. The exception to this is your PhD examiner, however know that even they may not read the entire length of the document.
Some people may still skip to and read specific sections throughout your thesis such as the methodology, but the fact is that the abstract will be all that most read and will therefore be the section they base their opinions about your research on. In short, make sure you write a good, well-structured abstract.
How Long Should an Abstract Be?
If you’re a PhD student, having written your 100,000-word thesis, the abstract will be the 300 word summary included at the start of the thesis that succinctly explains the motivation for your study (i.e. why this research was needed), the main work you did (i.e. the focus of each chapter), what you found (the results) and concluding with how your research study contributed to new knowledge within your field.
Woodrow Wilson, the 28th President of the United States of America, once famously said:
The point here is that it’s easier to talk open-endedly about a subject that you know a lot about than it is to condense the key points into a 10-minute speech; the same applies for an abstract. Three hundred words is not a lot of words which makes it even more difficult to condense three (or more) years of research into a coherent, interesting story.
What Makes a Good PhD Thesis Abstract?
Whilst the abstract is one of the first sections in your PhD thesis, practically it’s probably the last aspect that you’ll ending up writing before sending the document to print. The reason being that you can’t write a summary about what you did, what you found and what it means until you’ve done the work.
A good abstract is one that can clearly explain to the reader in 300 words:
- What your research field actually is,
- What the gap in knowledge was in your field,
- The overarching aim and objectives of your PhD in response to these gaps,
- What methods you employed to achieve these,
- You key results and findings,
- How your work has added to further knowledge in your field of study.
Another way to think of this structure is:
- Introduction,
- Aims and objectives,
- Discussion,
- Conclusion.
Following this ‘formulaic’ approach to writing the abstract should hopefully make it a little easier to write but you can already see here that there’s a lot of information to convey in a very limited number of words.
How Do You Write a Good PhD Thesis Abstract?
The biggest challenge you’ll have is getting all the 6 points mentioned above across in your abstract within the limit of 300 words . Your particular university may give some leeway in going a few words over this but it’s good practice to keep within this; the art of succinctly getting your information across is an important skill for a researcher to have and one that you’ll be called on to use regularly as you write papers for peer review.
Keep It Concise
Every word in the abstract is important so make sure you focus on only the key elements of your research and the main outcomes and significance of your project that you want the reader to know about. You may have come across incidental findings during your research which could be interesting to discuss but this should not happen in the abstract as you simply don’t have enough words. Furthermore, make sure everything you talk about in your thesis is actually described in the main thesis.
Make a Unique Point Each Sentence
Keep the sentences short and to the point. Each sentence should give the reader new, useful information about your research so there’s no need to write out your project title again. Give yourself one or two sentences to introduce your subject area and set the context for your project. Then another sentence or two to explain the gap in the knowledge; there’s no need or expectation for you to include references in the abstract.
Explain Your Research
Some people prefer to write their overarching aim whilst others set out their research questions as they correspond to the structure of their thesis chapters; the approach you use is up to you, as long as the reader can understand what your dissertation or thesis had set out to achieve. Knowing this will help the reader better understand if your results help to answer the research questions or if further work is needed.
Keep It Factual
Keep the content of the abstract factual; that is to say that you should avoid bringing too much or any opinion into it, which inevitably can make the writing seem vague in the points you’re trying to get across and even lacking in structure.
Write, Edit and Then Rewrite
Spend suitable time editing your text, and if necessary, completely re-writing it. Show the abstract to others and ask them to explain what they understand about your research – are they able to explain back to you each of the 6 structure points, including why your project was needed, the research questions and results, and the impact it had on your research field? It’s important that you’re able to convey what new knowledge you contributed to your field but be mindful when writing your abstract that you don’t inadvertently overstate the conclusions, impact and significance of your work.
Thesis and Dissertation Abstract Examples
Perhaps the best way to understand how to write a thesis abstract is to look at examples of what makes a good and bad abstract.
Example of A Bad Abstract
Let’s start with an example of a bad thesis abstract:
In this project on “The Analysis of the Structural Integrity of 3D Printed Polymers for use in Aircraft”, my research looked at how 3D printing of materials can help the aviation industry in the manufacture of planes. Plane parts can be made at a lower cost using 3D printing and made lighter than traditional components. This project investigated the structural integrity of EBM manufactured components, which could revolutionise the aviation industry.
What Makes This a Bad Abstract
Hopefully you’ll have spotted some of the reasons this would be considered a poor abstract, not least because the author used up valuable words by repeating the lengthy title of the project in the abstract.
Working through our checklist of the 6 key points you want to convey to the reader:
- There has been an attempt to introduce the research area , albeit half-way through the abstract but it’s not clear if this is a materials science project about 3D printing or is it about aircraft design.
- There’s no explanation about where the gap in the knowledge is that this project attempted to address.
- We can see that this project was focussed on the topic of structural integrity of materials in aircraft but the actual research aims or objectives haven’t been defined.
- There’s no mention at all of what the author actually did to investigate structural integrity. For example was this an experimental study involving real aircraft, or something in the lab, computer simulations etc.
- The author also doesn’t tell us a single result of his research, let alone the key findings !
- There’s a bold claim in the last sentence of the abstract that this project could revolutionise the aviation industry, and this may well be the case, but based on the abstract alone there is no evidence to support this as it’s not even clear what the author did .
This is an extreme example but is a good way to illustrate just how unhelpful a poorly written abstract can be. At only 71 words long, it definitely hasn’t maximised the amount of information that could be presented and the what they have presented has lacked clarity and structure.
A final point to note is the use of the EBM acronym, which stands for Electron Beam Melting in the context of 3D printing; this is a niche acronym for the author to assume that the reader would know the meaning of. It’s best to avoid acronyms in your abstract all together even if it’s something that you might expect most people to know about, unless you specifically define the meaning first.
Example of A Good Abstract
Having seen an example of a bad thesis abstract, now lets look at an example of a good PhD thesis abstract written about the same (fictional) project:
Additive manufacturing (AM) of titanium alloys has the potential to enable cheaper and lighter components to be produced with customised designs for use in aircraft engines. Whilst the proof-of-concept of these have been promising, the structural integrity of AM engine parts in response to full thrust and temperature variations is not clear.
The primary aim of this project was to determine the fracture modes and mechanisms of AM components designed for use in Boeing 747 engines. To achieve this an explicit finite element (FE) model was developed to simulate the environment and parameters that the engine is exposed to during flight. The FE model was validated using experimental data replicating the environmental parameters in a laboratory setting using ten AM engine components provided by the industry sponsor. The validated FE model was then used to investigate the extent of crack initiation and propagation as the environment parameters were adjusted.
This project was the first to investigate fracture patterns in AM titanium components used in aircraft engines; the key finding was that the presence of cavities within the structures due to errors in the printing process, significantly increased the risk of fracture. Secondly, the simulations showed that cracks formed within AM parts were more likely to worsen and lead to component failure at subzero temperatures when compared to conventionally manufactured parts. This has demonstrated an important safety concern which needs to be addressed before AM parts can be used in commercial aircraft.
What Makes This a Good Abstract
Having read this ‘good abstract’ you should have a much better understand about what the subject area is about, where the gap in the knowledge was, the aim of the project, the methods that were used, key results and finally the significance of these results. To break these points down further, from this good abstract we now know that:
- The research area is around additive manufacturing (i.e. 3D printing) of materials for use in aircraft.
- The gap in knowledge was how these materials will behave structural when used in aircraft engines.
- The aim was specifically to investigate how the components can fracture.
- The methods used to investigate this were a combination of computational and lab based experimental modelling.
- The key findings were the increased risk of fracture of these components due to the way they are manufactured.
- The significance of these findings were that it showed a potential risk of component failure that could comprise the safety of passengers and crew on the aircraft.
The abstract text has a much clearer flow through these different points in how it’s written and has made much better use of the available word count. Acronyms have even been used twice in this good abstract but they were clearly defined the first time they were introduced in the text so that there was no confusion about their meaning.
The abstract you write for your dissertation or thesis should succinctly explain to the reader why the work of your research was needed, what you did, what you found and what it means. Most people that come across your thesis, including any future employers, are likely to read only your abstract. Even just for this reason alone, it’s so important that you write the best abstract you can; this will not only convey your research effectively but also put you in the best light possible as a researcher.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.

Thesis Summary
Ai generator.
Considering that you have finished writing your thesis, it is high time that you started working on your thesis summary or abstract as the last and final part of your research paper before submitting it to your instructor. Writing an abstract is actually the simplest way for your audience, the teachers and the panel of publishers (if you wish for it to be published) to know what your research paper is about without going through the bulk of your paper.
What is an Abstract?
According to an article found in the Simon Fraser University database, the abstract is deemed a critical part of your thesis and it is presented at the beginning of the thesis, as it is a summary of the whole thesis. The thesis summary is a substantive description of your work read by an external examiner by presenting all the major elements of your work in a highly condensed form.
Size and Structure
Normally, a thesis summary would only contain 120 or less (for undergraduate theses), 150 words (for Masters theses) and 350 words (for a doctoral dissertation).
- For doctoral dissertations, it is best to limit it to only 280 words with a format of one double-spaced page, to preserve visual coherence.
- The structure of the abstract should mirror the structure of the whole thesis, and should represent all its major elements.
- For instance, if your thesis has five chapters (rationale, literature review, methodology, results, conclusion), limit each chapter to only a sentence or two for each chapter in order to maximize some parts that need more substantial backing.
Clearly Specify Your Research Questions
- Research questions are important in making sure that the abstract is coherent and logically structured as they form the backbone to which other elements adhere; they should be presented near the beginning of the abstract.
- Depending on the length of your research paper, there is only room for one to three questions. If there are more than three major research questions in your thesis, try to rearrange them by reducing some to subsidiary status.
Don’t Forget the Results
- One of the most common mistakes in writing abstracts is the failure to indicate the results.
- The primary function of your thesis (and by extension your abstract) is not to tell readers what you did, it is to tell them what you discovered. Other information, such as the account of your research methods, is needed mainly to back the claims you make about your results.
- The final part of your thesis should be about summarizing your results as well as interpreting them.
- Although it is sometimes not necessary, you can choose to add keywords below your abstract as the most important terms that can be found in the thesis.
Listed below are some thesis summary examples:
This study aimed to analyze and identify the most frequent news category and rhetoric of the three local English dailies as well as assess whether they align to the readers’ news preference. These factors served as the sources of the data gathered by the researchers: ninety tertiary students, each local publication’s respective editorial board, and banner stories. Findings indicated that even though the editors would usually select their stories based on impact, the banner story content however focused more on news like crime and politics which are mostly conflict-based issues, instead of human interest stories that readers prefer the most. In conclusion, the respective editorial boards of each publication are not presenting the readers with their main interests in the banner story. Keywords: banner stories, news values, news categories, gatekeeping/gatekeepers, and readers’ preference
An example of a summary format The aim or goal or purpose of this graduation thesis (title) is to … (analyse, characterize, compare, examine, illustrate, present, survey, design, reconstruct) … The graduation thesis is composed of five chapters, each of them dealing with different aspect of … Chapter 1 is introductory and (defines, describes, reviews, deals with) … The chapter is subdivided into two parts. Part 1 describes … and explains … . Part 2 deals with … Chapter 2 examines … . The chapter consists of three parts. Part 1 focuses on … . Part 2 investigates … . Part 3 addresses the issue of … . Chapter 3 is subdivided into two parts and provides an outline of relevant … Part 1 illustrates … . Part 2 looks at … . Chapter 4 concentrates on problems resulting from … Part 1 describes …. Part 2 recommends changes to be made in legislation … Conclusions are drawn in Chapter 5. The main aim of the graduation thesis has been reached. The author suggests that …………………… should be changed/introduced/applied.
The aim of this graduation thesis entitled Development of Yamakawa Technologies to Ascertain the Existence of Cheese on the Moon is to test the use of Yamakawa technologies in ascertaining the existence of cheese on the moon. Yamakawa technologies have been successfully used to test the existence of water in Wakanda, but to date no further applications are known. For this reason the author decided to test further applications, with the aim of describing the technology’s suitability for further development. This thesis first examines the testing procedures for the water in Wakanda experiment, and presents the results. In a second stage several adaptations to Yamakawa for the testing of the existence of cheese on the moon are undertaken. Finally the technology is applied to the question of cheese on the moon, within a six-week testing phase. At the end of each week the testing apparatus is fine tuned, and experiment results are charted every twenty-four hours. The results of the experiment show that Yamakawa technologies are well suited to ascertaining the presence of water in Wakanda, but were unable to be sufficiently modified for the purpose of ascertaining the existence of cheese on the moon. The author recommends further modification to the technology before any other uses are considered.
After writing the said abstract in your research paper, then congratulations! You are now ready to move to the next step of your thesis journey, defending it. Just remember this, always know your thesis by heart. Believe me, if you do, you will not have a hard time and eventually, you will learn to enjoy it too. Good luck!
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
maghrebi-studies
end of your doctoral degree program with success
- Avoiding fraud
- Online dissertation database
- How to select a topic
- Getting an abstract sample
- Proofread examples available
- Custom writing assistance
- Getting a degree without dissertation
- Thesis help online
- Writing an introduction
- Watch out for fraud services
- Can I use cheap services?
- How to complete it in a month
- Writing an outline
- Finding dissertation analysis templates
- PhD dissertation writing tips
- Dissertation front page in the MLA style
- Thesis topic ideas on education
- Dissertation proofreading tips
- Master’s thesis paper on ecology
- Choosing a thesis writing service
- Where to get low-cost thesis writing help
- MBA dissertation writing help offline
- How to select a writing company
- Project management thesis cover page
- Buying a dissertation online
- Epidemiology dissertation writing guide
- Completing a thesis hypothesis
- In search of a reliable dissertation writer
- How to write a thesis on domestic violence
- Getting a Master's thesis proposal sample
- Dissertation editing instructions
- How to pass a defense successfully
- Thesis writing help
- PhD thesis writing services
- Situations to avoid
- Organizing the title page
- Working on a thesis abstract
- How to buy a thesis
- Getting a good thesis sample
- Writing a PhD summary
- Finding help with thesis writing
- Topics for an Anthropology thesis
- A thesis and master's degree
- Finding an APA dissertation example
- Economics thesis prompts
- Business dissertation ideas
- Political science thesis writing tips
- Writing a psychology Master's thesis
- Get prepared for a thesis proposal defense
- Law thesis methodology chapter
- Dissertation proposal literature review
- Medical thesis paper writing tips
- Architecture thesis topic ideas
- Developmental psychology thesis paper
- How to use an example of an abstract
- Ordering a thesis on the web
- Completing a history thesis on time
- Finding accounting thesis writing help
- Science dissertation assumptions
- Conclusion for a sociology thesis
- Business management thesis sample
- 15 topics on visual merchandising
- Report format thesis paper
- Completing a thesis on renewable energy

How To Write A Summary For A Doctoral Thesis: Tips And Examples
As you are ready to start working on your doctoral thesis, the foremost component of your paper is obviously the summary. It is an essential introduction or a precise introductory statement that stays right at the beginning of the work. So, you want to create a very powerful first impression of your work among readers? Then, a well-written summary is the best component.
Objectives of the summary:
Before writing the summary, you must figure out its objectives. When you know what purpose the summary is intended to serve, it becomes easier for you to make it an effective part.
- The summary provides your target readers with a concise and precise synopsis of what you are going to state out of your research.
- The summary offers a compelling and substantial reason for readers to continue to read the rest of the thesis.
Hooking your readers:
This is what you should start with.
- The very first sentence of the summary should include a captivating or convincing reason why your reader can keep reading.
- The best way to accomplish this is by indicating a research gap or problem in the current research or its methodology that you promise to put correctly in your study.
- You need to be wary of using your style of writing. Do not use gimmicky or flowery phrasing in your introductory sentence because it is still possible to hook the reader with a straightforward and simple statement.
Restating your statement:
Now, you will move onto the second sentence.
- The second summary sentence needs to recap your thesis statement.
- Using precise language when you reiterate the thesis is always effective.
- You have to assume that your readers are already familiar with the field of your study, and they will follow what you provide them as your premise.
Summarizing research methodology and conclusions:
This is the last part of your summary. This part may contain anywhere from two sentences to five or six sentences.
- Your research methods and objectives should be stated vividly but in a precise manner.
- Do not forget to include the conclusion or significant contributions or outcomes the thesis has to offer to the field of your study.
- It is recommended that you limit technical jargon.
- Although it is allowed to cite influential sources, you must not quote them in the summary section.
Final thoughts:
Your summary should contain somewhere from 100 to 300 words. Also, you should avoid abbreviations which are not explained yet. You can include some relevant keywords, so online accessibility of your doctoral thesis increases.
Easy Guides
- Using the right structure
- Prepare for defense online
- How to write a proposal
- Economics thesis topics
- Topic ideas for a Marketing thesis
- Surviving thesis defense
- Formatting your thesis properly
- If you need some writing help
- Topics for a Physiology dissertation
- Ideas for a science thesis
- Sample Media theses
- 10 Psychology thesis topics
- Hints for creative PhD writing
- Example thesis proposals for MBA
- Picking a dissertation writing agency
- Dissertation title page templates
- Choosing Law dissertation topics
- 3 tips on Graduate thesis writing
- Buying a paper written from scratch
- How to write a thesis
- Finding quality assistance
- Insights for an engineering thesis
- Nursing dissertation topics
- Project management thesis topics
- Sources of MSc thesis samples
- Finding PhD samples for free
- Sample methodology sections
- How to find a realible thesis service
- IT dissertation tips & topics
© maghrebi-studies.org. All rights reserved.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
Published on January 11, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on August 15, 2023 by Eoghan Ryan.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . It usually comes near the end of your introduction .
Your thesis will look a bit different depending on the type of essay you’re writing. But the thesis statement should always clearly state the main idea you want to get across. Everything else in your essay should relate back to this idea.
You can write your thesis statement by following four simple steps:
- Start with a question
- Write your initial answer
- Develop your answer
- Refine your thesis statement
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is a thesis statement, placement of the thesis statement, step 1: start with a question, step 2: write your initial answer, step 3: develop your answer, step 4: refine your thesis statement, types of thesis statements, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
A thesis statement summarizes the central points of your essay. It is a signpost telling the reader what the essay will argue and why.
The best thesis statements are:
- Concise: A good thesis statement is short and sweet—don’t use more words than necessary. State your point clearly and directly in one or two sentences.
- Contentious: Your thesis shouldn’t be a simple statement of fact that everyone already knows. A good thesis statement is a claim that requires further evidence or analysis to back it up.
- Coherent: Everything mentioned in your thesis statement must be supported and explained in the rest of your paper.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The thesis statement generally appears at the end of your essay introduction or research paper introduction .
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts and among young people more generally is hotly debated. For many who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education: the internet facilitates easier access to information, exposure to different perspectives, and a flexible learning environment for both students and teachers.
You should come up with an initial thesis, sometimes called a working thesis , early in the writing process . As soon as you’ve decided on your essay topic , you need to work out what you want to say about it—a clear thesis will give your essay direction and structure.
You might already have a question in your assignment, but if not, try to come up with your own. What would you like to find out or decide about your topic?
For example, you might ask:
After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process .
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Now you need to consider why this is your answer and how you will convince your reader to agree with you. As you read more about your topic and begin writing, your answer should get more detailed.
In your essay about the internet and education, the thesis states your position and sketches out the key arguments you’ll use to support it.
The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education because it facilitates easier access to information.
In your essay about braille, the thesis statement summarizes the key historical development that you’ll explain.
The invention of braille in the 19th century transformed the lives of blind people, allowing them to participate more actively in public life.
A strong thesis statement should tell the reader:
- Why you hold this position
- What they’ll learn from your essay
- The key points of your argument or narrative
The final thesis statement doesn’t just state your position, but summarizes your overall argument or the entire topic you’re going to explain. To strengthen a weak thesis statement, it can help to consider the broader context of your topic.
These examples are more specific and show that you’ll explore your topic in depth.
Your thesis statement should match the goals of your essay, which vary depending on the type of essay you’re writing:
- In an argumentative essay , your thesis statement should take a strong position. Your aim in the essay is to convince your reader of this thesis based on evidence and logical reasoning.
- In an expository essay , you’ll aim to explain the facts of a topic or process. Your thesis statement doesn’t have to include a strong opinion in this case, but it should clearly state the central point you want to make, and mention the key elements you’ll explain.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
Follow these four steps to come up with a thesis statement :
- Ask a question about your topic .
- Write your initial answer.
- Develop your answer by including reasons.
- Refine your answer, adding more detail and nuance.
The thesis statement should be placed at the end of your essay introduction .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, August 15). How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 13, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/thesis-statement/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- Norwegian website
How to write a popular scientific summary
The popular scientific summary is an important part of disseminating your doctoral thesis to the outside world. You yourself write the draft content of the popular scientific summary by using the popular scientific summary form, and the department of communications ensures publication on inn.no and distribution to the press.
Tips for writing a popular scientific summary
A popular scientific summary should contain new information. Explain what your research has to offer people outside your academic field. Think about social benefits. Think about usability. Think of concrete examples.
- Headline: Create a good and short title that captures the interest
- The main thing first: Start with the conclusion – what have you discovered?
- What are the "new" things you do in your doctoral thesis?
- Highlight: Concentrate on one main point, not the entire thesis
- Avoid details: Think key facts – avoid reservations and clarifications
- Active sentences: Use direct language, avoid generalisations and passive forms
- Write succinctly: One-third of a page with single line spacing (max 1500 characters including spaces)
- Write simply: use everyday language, avoid discipline-specific expressions
- Quote yourself: Feel free to use your own wording or quotations from the thesis
Please read aloud the popular scientific summary for a friend who is not an academic. If the text is well suited for reading aloud, it will almost always flow well in written form as well.
Take a look at the public defences overview at inn.no to see how previous articles / popular scientific summaries have been formulated.
- Form for dissemination of PhD Thesis – Popular Scientific Summary
Submission of popular scientific summary form
The form for dissemination of PhD thesis together with an electronic photo (jpg, landscape format and a minimum of 1 MB) of yourself should be sent to [email protected] , with PhD coordinator at your programme on CC, three weeks before the defence.The department of communication will publish an article on INN University's website and will assess how the doctoral thesis can be communicated to other sources approximately two weeks before the public defence.
How to write a popular science summary
The summary of your thesis (see Regulations section 17.1 ) must be popularized and adapted to a broader target group. Here you will find tips on how to do this.
The summary must be sent to the communication adviser at the Faculty 4 weeks prior to the announcement of the disputation. Please use the Faculty’s communication adviser if you want help and guidance during the work on the summary
You will receive feedback on the summary within 4 work days and an offer of help to disseminate your research in the media. The summary will be published in announcements of disputations on UiO’s webpages.
Explain the significance of your research for people unfamiliar with your subject area. Think about the benefits to society and the applicability of the research. What is new? Preferably use concrete examples.
Heading: Think of a brief, catchy title that attracts interest and highlights the message.
Start with the most important thing: Begin with the conclusion – what have you discovered?
Main point: Concentrate on one main point, not the whole thesis.
Avoid detail: Focus on the main features – avoid reservations and definitions.
Active sentences: Use direct language, avoid the use of ’one’ and passive structures.
Write concisely : Maximun 1 1/2 page with single spacing.
Write simply: Use everyday language and avoid specialist terminology.
Quote yourself: Feel free to use apt expressions or quotes from your thesis.
It is advisable to read the press release aloud to a friend who is not an academic. Does he or she understand the content? If the text is well-suited to reading aloud, it will almost invariably flow smoothly in writing as well.
Remember to send a digital high-resolution photograph of yourself. You must check with the photographer that the photograph can be published on the net. Give the name of the photographer together with information about who holds the copyright on the photograph. You can also contact the Faculty’s communication unit for help in having a photograph taken.
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Communication adviser Jorunn Kanestrøm
- Adviser Gøril Arnesen
The dissemination of research to the general public is emphasized in UiO’s strategic plan
Section 17.1 of the Regulations for the Degree of Philosophiae Doctor (PhD) at the University of Oslo.
Study Postgraduate
Phd in chemistry (2022 entry), find out more about our chemistry phd..
The PhD in Chemistry enables you to carry out a unique research project and write an outstanding thesis. You will join a community of leading Chemistry research groups and utilise Warwick’s specialist facilities to produce an original contribution to science.

Course code
3 October 2022
3-4 years full-time; Up to 7 years part-time
Qualification
University of Warwick
About this research graduate course
Course overview.
A PhD in Chemistry will give you an opportunity for you to devote up to four years conducting full time research in an area of your choice, addressing real-world problems. Find a supervisor in the tab below and let us know what areas you’d like to research. You write up a thesis at the end of your studies. In some cases, the project may be carried out in collaboration with an industrial sponsor. Warwick offers comprehensive training in transferable skills, access to taught modules, and a supportive research environment.
To contact the department directly with any questions please email chem-postgraduate at warwick dot ac dot uk .
General entry requirements
Minimum requirements.
2:i undergraduate degree (or equivalent) in Chemistry or a related subject.
English language requirements
You can find out more about our English language requirements . This course requires the following:
- IELTS overall score of 6.5, minimum component scores not below 6.0.
International qualifications
We welcome applications from students with other internationally recognised qualifications.
For more information, please visit the international entry requirements page .
Additional requirements
There are no additional entry requirements for this course.
Our research
The current research themes include:
- Measurement and Modelling
- Materials and Polymers
- Synthesis and Catalysis
- Chemical, Structural and Synthetic Biology
Full details on the current research themes are available on the Chemistry website.
You can also read our general University research proposal guidance.
Find a supervisor
Find your supervisor using the link below and discuss with them the area you’d like to research.
Explore our Chemistry Staff Directory where you will be able to filter by:
- Research Theme
- Research Specialism
- Global Challenge
You can also see our general University guidance about finding a supervisor .
Tuition fees
Tuition fees are payable for each year of your course at the start of the academic year, or at the start of your course, if later. Academic fees cover the cost of tuition, examinations and registration and some student amenities.
Taught course fees Research course fees
Fee Status Guidance
We carry out an initial fee status assessment based on the information you provide in your application. Students will be classified as Home or Overseas fee status. Your fee status determines tuition fees, and what financial support and scholarships may be available. If you receive an offer, your fee status will be clearly stated alongside the tuition fee information.
Do you need your fee classification to be reviewed?
If you believe that your fee status has been classified incorrectly, you can complete a fee status assessment questionnaire. Please follow the instructions in your offer information and provide the documents needed to reassess your status.
Find out more about how universities assess fee status
Additional course costs
As well as tuition fees and living expenses, some courses may require you to cover the cost of field trips or costs associated with travel abroad. Information about department specific costs should be considered in conjunction with the more general costs below, such as:
As well as tuition fees and living expenses, some courses may require you to cover the cost of field trips or costs associated with travel abroad.
For departmental specific costs, please see the Modules tab on the course web page for the list of core and optional core modules with hyperlinks to our Module Catalogue (please visit the Department’s website if the Module Catalogue hyperlinks are not provided).
Associated costs can be found on the Study tab for each module listed in the Module Catalogue (please note most of the module content applies to 2022/23 year of study). Information about module department specific costs should be considered in conjunction with the more general costs below:
- Core text books
- Printer credits
- Dissertation binding
- Robe hire for your degree ceremony
Scholarships and bursaries

Scholarships and financial support
Find out about the different funding routes available, including; postgraduate loans, scholarships, fee awards and academic department bursaries.

Living costs
Find out more about the cost of living as a postgraduate student at the University of Warwick.
Chemistry at Warwick
Do you share our enthusiasm for chemistry and its applications, from medicine to renewable energy?
We are one of the UK’s top chemistry providers, highly ranked for both teaching and research. Our courses will offer you an excellent all-round experience that allows you to explore and follow your curiosity.
The skills you will develop will equip you to seek a future career in a number of industries and employers.
Find out more about us on our website
Our Postgraduate Taught courses
We offer non-accredited and Royal Society of Chemistry accredited course routes, depending on your career aspirations.
- Analytical and Polymer Science (MSc)
- Analytical Sciences and Instrumentation (MSc)
- Chemistry with Scientific Writing (MSc)
- Molecular Analytical Science (MSc)
- Polymer Chemistry (MSc)
- Polymer Science (MSc)
- Scientific Research and Communication (MSc)
Our Postgraduate Research courses
- MSc in Chemistry by Research
- PhD in Chemistry

Taught course applications
Here is our checklist on how to apply for taught postgraduate courses at Warwick.

Research course applications
Here is our checklist on how to apply for research postgraduate degrees at the University of Warwick.

After you’ve applied
Find out how we process your application.

Applicant Portal
Track your application and update your details.

Admissions statement
See Warwick’s postgraduate admissions policy.

Join a live chat
Ask questions and engage with Warwick.
Postgraduate Open Day
Postgraduate fairs.
Throughout the year we attend exhibitions and fairs online and in the UK. These events give you the chance to learn about our Master's and PhD study routes, and the wider context of postgraduate study.
Find out more
Every week, you can connect directly with representatives from Warwick, who will be answering your questions on applying to and studying postgraduate studies at Warwick.
Sign up for Live Chats
Departmental events
Some academic departments hold events for specific postgraduate programmes, these are fantastic opportunities to learn more about Warwick and your chosen department and course.
See our online departmental events
Connect with us
Want to hear more about postgraduate study at Warwick? Register your interest and find out more.
Learn more about Postgraduate study at the University of Warwick.
Why Warwick
Discover why Warwick is one of the best universities in the UK and renowned globally.
6th in the UK (The Guardian University Guide 2022) Link opens in a new window
64th in the world (QS World University Rankings 2023) Link opens in a new window
6th most targeted university by the UK's top 100 graduate employers Link opens in a new window
(The Graduate Market in 2022, High Fliers Research Ltd. Link opens in a new window )
About the information on this page
This information is applicable for 2022 entry. Given the interval between the publication of courses and enrolment, some of the information may change. It is important to check our website before you apply. Please read our terms and conditions to find out more.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
There is a huge difference between writing a summary for the theses database of your university and to write a summary for a more ambitious purpose. As mentioned above, a summary of your thesis may be required for a job application or to get a PhD position.
Writing the summarizing part The summary should consist of updated knowledge from the field of research and should review and summarize the problem areas, findings and conclusions presented in the articles, so that the thesis is presented as a whole. The thesis must be relevant and updated at the time of submission.
As Pat Thomson usefully argues in this post about writing a thesis conclusion, the conclusion to a thesis (or journal article) is not a summary of the whole. The summary part of a thesis conclusion should ideally be quite brief, and used rather as a springboard to the real work of the conclusion: using the preceding writing and research to show how the study has addressed the research ...
Congratulations; you've finished your research! Time to write your PhD thesis. This resource will take you through an eight-step plan for drafting your chapters and your thesis as a whole.
Learn how to write a clear and impactful thesis or dissertation conclusion that summarizes your main findings and highlights the implications for your field.
Learn how to write up a high-quality conclusion chapter for your dissertation or thesis. Step-by-step instructions and free template.
Learn how to write a top-notch dissertation or thesis with Grad Coach's straightforward 8-step guide (including examples and videos).
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program. Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you've ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating ...
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical early steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding the specifics of your dissertation topic and showcasing its relevance to your field.
Our PhD writing template can help with this, as it forces you to write a synopsis of each chapter which you can add together for a summary of the thesis. Note, though, that there's a difference between summarising your thesis and repeating huge tracts of it.
Learn how to develop a high-impact executive summary for your assignment, research report or even your dissertation or thesis.
How to Structure an Abstract Your abstract should be a short summary at the beginning of the thesis that sums up the research, summarises the separate sections of the thesis and outlines the contribution. Above all, your PhD abstract should answer the question: 'So what?' In other words, what is the contribution of your thesis to the field?
Struggling with your PhD thesis? Follow our step-by-step guide to master the process of writing a comprehensive and compelling PhD thesis, from research to final draft.
Use our free tools, guides and templates to learn how to structure your entire PhD thesis. All expertly written and designed to help.
Let's show you how to write the perfect thesis summary for your paper. Learn where you can get a great thesis summary example from.
6 I am currently applying for several PhD programs (in mathematics) and for many of them, it is required to write a short (approx. 2 pages; no more than 10.000 characters) summary of my Master's thesis. It should contain the motivations of the thesis and research, the methods used as well as the results obtained in my research.
The executive summary is a highly condensed version of your thesis. It should be able to stand alone, independent of your thesis. Your executive summary should summarize your purpose, methods, results, conclusions and recommendations to allow someone who can read ONLY that section to walk away with a solid understanding of the overall purpose, scope, methods, and findings of the research. Some ...
The abstract you write for your dissertation or thesis should succinctly explain to the reader why the work of your research was needed, what you did, what you found and what it means. Most people that come across your thesis, including any future employers, are likely to read only your abstract.
Thesis Summary Considering that you have finished writing your thesis, it is high time that you started working on your thesis summary or abstract as the last and final part of your research paper before submitting it to your instructor. Writing an abstract is actually the simplest way for your audience, the teachers and the panel of publishers (if you wish for it to be published) to know what ...
How To Write A Summary For A Doctoral Thesis: Tips And Examples As you are ready to start working on your doctoral thesis, the foremost component of your paper is obviously the summary. It is an essential introduction or a precise introductory statement that stays right at the beginning of the work.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay. It usually comes near the end of your introduction. Your thesis will look a bit different depending on the type of essay you're writing. But the thesis statement should always clearly state the main idea you want to get across.
The popular scientific summary is an important part of disseminating your doctoral thesis to the outside world. You yourself write the draft content of the popular scientific summary by using the popular scientific summary form, and the department of communications ensures publication on inn.no and distribution to the press.
The summary of your thesis (see Regulations section 17.1) must be popularized and adapted to a broader target group. Here you will find tips on how to do this.
The authority on APA Style and the 7th edition of the APA Publication Manual. Find tutorials, the APA Style Blog, how to format papers in APA Style, and other resources to help you improve your writing, master APA Style, and learn the conventions of scholarly publishing.
The PhD in Chemistry enables you to carry out a unique research project and write an outstanding thesis.
New Program Proposal Executive Summary PhD Health Psychology [ CIP Code: 42.2810] Clemson University [Site Code: 50104] ... to articulate critical issues important for developing and implementing a thesis, manuscript, or study within a topic relevant to Health Psychology. ... I am writing to provide a letter of support for the doctorate program ...