- Privacy Policy

Home » Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide

Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
Table of contents.

Definition:
Thesis is a scholarly document that presents a student’s original research and findings on a particular topic or question. It is usually written as a requirement for a graduate degree program and is intended to demonstrate the student’s mastery of the subject matter and their ability to conduct independent research.
History of Thesis
The concept of a thesis can be traced back to ancient Greece, where it was used as a way for students to demonstrate their knowledge of a particular subject. However, the modern form of the thesis as a scholarly document used to earn a degree is a relatively recent development.
The origin of the modern thesis can be traced back to medieval universities in Europe. During this time, students were required to present a “disputation” in which they would defend a particular thesis in front of their peers and faculty members. These disputations served as a way to demonstrate the student’s mastery of the subject matter and were often the final requirement for earning a degree.
In the 17th century, the concept of the thesis was formalized further with the creation of the modern research university. Students were now required to complete a research project and present their findings in a written document, which would serve as the basis for their degree.
The modern thesis as we know it today has evolved over time, with different disciplines and institutions adopting their own standards and formats. However, the basic elements of a thesis – original research, a clear research question, a thorough review of the literature, and a well-argued conclusion – remain the same.
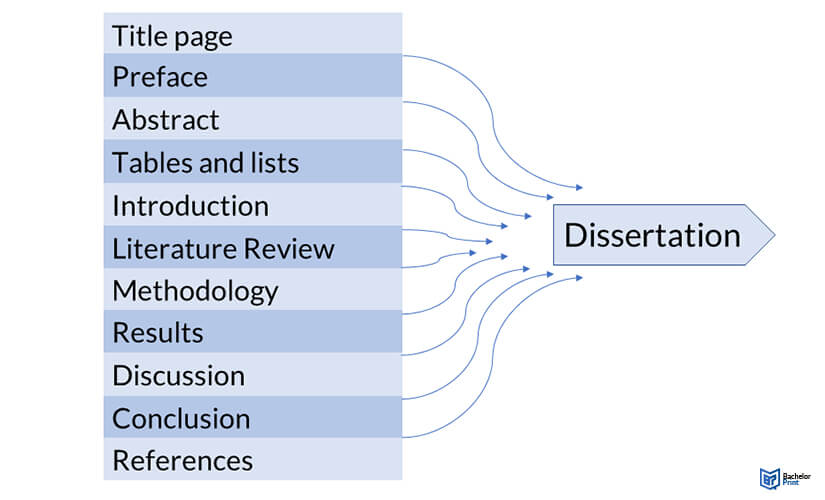
Structure of Thesis
The structure of a thesis may vary slightly depending on the specific requirements of the institution, department, or field of study, but generally, it follows a specific format.
Here’s a breakdown of the structure of a thesis:
This is the first page of the thesis that includes the title of the thesis, the name of the author, the name of the institution, the department, the date, and any other relevant information required by the institution.
This is a brief summary of the thesis that provides an overview of the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions.
This page provides a list of all the chapters and sections in the thesis and their page numbers.
Introduction
This chapter provides an overview of the research question, the context of the research, and the purpose of the study. The introduction should also outline the methodology and the scope of the research.
Literature Review
This chapter provides a critical analysis of the relevant literature on the research topic. It should demonstrate the gap in the existing knowledge and justify the need for the research.
Methodology
This chapter provides a detailed description of the research methods used to gather and analyze data. It should explain the research design, the sampling method, data collection techniques, and data analysis procedures.
This chapter presents the findings of the research. It should include tables, graphs, and charts to illustrate the results.
This chapter interprets the results and relates them to the research question. It should explain the significance of the findings and their implications for the research topic.
This chapter summarizes the key findings and the main conclusions of the research. It should also provide recommendations for future research.
This section provides a list of all the sources cited in the thesis. The citation style may vary depending on the requirements of the institution or the field of study.
This section includes any additional material that supports the research, such as raw data, survey questionnaires, or other relevant documents.
How to write Thesis
Here are some steps to help you write a thesis:
- Choose a Topic: The first step in writing a thesis is to choose a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. You should also consider the scope of the topic and the availability of resources for research.
- Develop a Research Question: Once you have chosen a topic, you need to develop a research question that you will answer in your thesis. The research question should be specific, clear, and feasible.
- Conduct a Literature Review: Before you start your research, you need to conduct a literature review to identify the existing knowledge and gaps in the field. This will help you refine your research question and develop a research methodology.
- Develop a Research Methodology: Once you have refined your research question, you need to develop a research methodology that includes the research design, data collection methods, and data analysis procedures.
- Collect and Analyze Data: After developing your research methodology, you need to collect and analyze data. This may involve conducting surveys, interviews, experiments, or analyzing existing data.
- Write the Thesis: Once you have analyzed the data, you need to write the thesis. The thesis should follow a specific structure that includes an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, conclusion, and references.
- Edit and Proofread: After completing the thesis, you need to edit and proofread it carefully. You should also have someone else review it to ensure that it is clear, concise, and free of errors.
- Submit the Thesis: Finally, you need to submit the thesis to your academic advisor or committee for review and evaluation.
Example of Thesis
Example of Thesis template for Students:
Title of Thesis
Table of Contents:
Chapter 1: Introduction
Chapter 2: Literature Review
Chapter 3: Research Methodology
Chapter 4: Results
Chapter 5: Discussion
Chapter 6: Conclusion
References:
Appendices:
Note: That’s just a basic template, but it should give you an idea of the structure and content that a typical thesis might include. Be sure to consult with your department or supervisor for any specific formatting requirements they may have. Good luck with your thesis!
Application of Thesis
Thesis is an important academic document that serves several purposes. Here are some of the applications of thesis:
- Academic Requirement: A thesis is a requirement for many academic programs, especially at the graduate level. It is an essential component of the evaluation process and demonstrates the student’s ability to conduct original research and contribute to the knowledge in their field.
- Career Advancement: A thesis can also help in career advancement. Employers often value candidates who have completed a thesis as it demonstrates their research skills, critical thinking abilities, and their dedication to their field of study.
- Publication : A thesis can serve as a basis for future publications in academic journals, books, or conference proceedings. It provides the researcher with an opportunity to present their research to a wider audience and contribute to the body of knowledge in their field.
- Personal Development: Writing a thesis is a challenging task that requires time, dedication, and perseverance. It provides the student with an opportunity to develop critical thinking, research, and writing skills that are essential for their personal and professional development.
- Impact on Society: The findings of a thesis can have an impact on society by addressing important issues, providing insights into complex problems, and contributing to the development of policies and practices.
Purpose of Thesis
The purpose of a thesis is to present original research findings in a clear and organized manner. It is a formal document that demonstrates a student’s ability to conduct independent research and contribute to the knowledge in their field of study. The primary purposes of a thesis are:
- To Contribute to Knowledge: The main purpose of a thesis is to contribute to the knowledge in a particular field of study. By conducting original research and presenting their findings, the student adds new insights and perspectives to the existing body of knowledge.
- To Demonstrate Research Skills: A thesis is an opportunity for the student to demonstrate their research skills. This includes the ability to formulate a research question, design a research methodology, collect and analyze data, and draw conclusions based on their findings.
- To Develop Critical Thinking: Writing a thesis requires critical thinking and analysis. The student must evaluate existing literature and identify gaps in the field, as well as develop and defend their own ideas.
- To Provide Evidence of Competence : A thesis provides evidence of the student’s competence in their field of study. It demonstrates their ability to apply theoretical concepts to real-world problems, and their ability to communicate their ideas effectively.
- To Facilitate Career Advancement : Completing a thesis can help the student advance their career by demonstrating their research skills and dedication to their field of study. It can also provide a basis for future publications, presentations, or research projects.
When to Write Thesis
The timing for writing a thesis depends on the specific requirements of the academic program or institution. In most cases, the opportunity to write a thesis is typically offered at the graduate level, but there may be exceptions.
Generally, students should plan to write their thesis during the final year of their graduate program. This allows sufficient time for conducting research, analyzing data, and writing the thesis. It is important to start planning the thesis early and to identify a research topic and research advisor as soon as possible.
In some cases, students may be able to write a thesis as part of an undergraduate program or as an independent research project outside of an academic program. In such cases, it is important to consult with faculty advisors or mentors to ensure that the research is appropriately designed and executed.
It is important to note that the process of writing a thesis can be time-consuming and requires a significant amount of effort and dedication. It is important to plan accordingly and to allocate sufficient time for conducting research, analyzing data, and writing the thesis.
Characteristics of Thesis
The characteristics of a thesis vary depending on the specific academic program or institution. However, some general characteristics of a thesis include:
- Originality : A thesis should present original research findings or insights. It should demonstrate the student’s ability to conduct independent research and contribute to the knowledge in their field of study.
- Clarity : A thesis should be clear and concise. It should present the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions in a logical and organized manner. It should also be well-written, with proper grammar, spelling, and punctuation.
- Research-Based: A thesis should be based on rigorous research, which involves collecting and analyzing data from various sources. The research should be well-designed, with appropriate research methods and techniques.
- Evidence-Based : A thesis should be based on evidence, which means that all claims made in the thesis should be supported by data or literature. The evidence should be properly cited using appropriate citation styles.
- Critical Thinking: A thesis should demonstrate the student’s ability to critically analyze and evaluate information. It should present the student’s own ideas and arguments, and engage with existing literature in the field.
- Academic Style : A thesis should adhere to the conventions of academic writing. It should be well-structured, with clear headings and subheadings, and should use appropriate academic language.
Advantages of Thesis
There are several advantages to writing a thesis, including:
- Development of Research Skills: Writing a thesis requires extensive research and analytical skills. It helps to develop the student’s research skills, including the ability to formulate research questions, design and execute research methodologies, collect and analyze data, and draw conclusions based on their findings.
- Contribution to Knowledge: Writing a thesis provides an opportunity for the student to contribute to the knowledge in their field of study. By conducting original research, they can add new insights and perspectives to the existing body of knowledge.
- Preparation for Future Research: Completing a thesis prepares the student for future research projects. It provides them with the necessary skills to design and execute research methodologies, analyze data, and draw conclusions based on their findings.
- Career Advancement: Writing a thesis can help to advance the student’s career. It demonstrates their research skills and dedication to their field of study, and provides a basis for future publications, presentations, or research projects.
- Personal Growth: Completing a thesis can be a challenging and rewarding experience. It requires dedication, hard work, and perseverance. It can help the student to develop self-confidence, independence, and a sense of accomplishment.
Limitations of Thesis
There are also some limitations to writing a thesis, including:
- Time and Resources: Writing a thesis requires a significant amount of time and resources. It can be a time-consuming and expensive process, as it may involve conducting original research, analyzing data, and producing a lengthy document.
- Narrow Focus: A thesis is typically focused on a specific research question or topic, which may limit the student’s exposure to other areas within their field of study.
- Limited Audience: A thesis is usually only read by a small number of people, such as the student’s thesis advisor and committee members. This limits the potential impact of the research findings.
- Lack of Real-World Application : Some thesis topics may be highly theoretical or academic in nature, which may limit their practical application in the real world.
- Pressure and Stress : Writing a thesis can be a stressful and pressure-filled experience, as it may involve meeting strict deadlines, conducting original research, and producing a high-quality document.
- Potential for Isolation: Writing a thesis can be a solitary experience, as the student may spend a significant amount of time working independently on their research and writing.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and...

Research Questions – Types, Examples and Writing...

Limitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Critical Analysis – Types, Examples and Writing...

Significance of the Study – Examples and Writing...

Data Verification – Process, Types and Examples
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

What is a thesis | A Complete Guide with Examples

Table of Contents
A thesis is a comprehensive academic paper based on your original research that presents new findings, arguments, and ideas of your study. It’s typically submitted at the end of your master’s degree or as a capstone of your bachelor’s degree.
However, writing a thesis can be laborious, especially for beginners. From the initial challenge of pinpointing a compelling research topic to organizing and presenting findings, the process is filled with potential pitfalls.
Therefore, to help you, this guide talks about what is a thesis. Additionally, it offers revelations and methodologies to transform it from an overwhelming task to a manageable and rewarding academic milestone.
What is a thesis?
A thesis is an in-depth research study that identifies a particular topic of inquiry and presents a clear argument or perspective about that topic using evidence and logic.
Writing a thesis showcases your ability of critical thinking, gathering evidence, and making a compelling argument. Integral to these competencies is thorough research, which not only fortifies your propositions but also confers credibility to your entire study.
Furthermore, there's another phenomenon you might often confuse with the thesis: the ' working thesis .' However, they aren't similar and shouldn't be used interchangeably.
A working thesis, often referred to as a preliminary or tentative thesis, is an initial version of your thesis statement. It serves as a draft or a starting point that guides your research in its early stages.
As you research more and gather more evidence, your initial thesis (aka working thesis) might change. It's like a starting point that can be adjusted as you learn more. It's normal for your main topic to change a few times before you finalize it.
While a thesis identifies and provides an overarching argument, the key to clearly communicating the central point of that argument lies in writing a strong thesis statement.
What is a thesis statement?
A strong thesis statement (aka thesis sentence) is a concise summary of the main argument or claim of the paper. It serves as a critical anchor in any academic work, succinctly encapsulating the primary argument or main idea of the entire paper.
Typically found within the introductory section, a strong thesis statement acts as a roadmap of your thesis, directing readers through your arguments and findings. By delineating the core focus of your investigation, it offers readers an immediate understanding of the context and the gravity of your study.
Furthermore, an effectively crafted thesis statement can set forth the boundaries of your research, helping readers anticipate the specific areas of inquiry you are addressing.
Different types of thesis statements
A good thesis statement is clear, specific, and arguable. Therefore, it is necessary for you to choose the right type of thesis statement for your academic papers.
Thesis statements can be classified based on their purpose and structure. Here are the primary types of thesis statements:
Argumentative (or Persuasive) thesis statement
Purpose : To convince the reader of a particular stance or point of view by presenting evidence and formulating a compelling argument.
Example : Reducing plastic use in daily life is essential for environmental health.
Analytical thesis statement
Purpose : To break down an idea or issue into its components and evaluate it.
Example : By examining the long-term effects, social implications, and economic impact of climate change, it becomes evident that immediate global action is necessary.
Expository (or Descriptive) thesis statement
Purpose : To explain a topic or subject to the reader.
Example : The Great Depression, spanning the 1930s, was a severe worldwide economic downturn triggered by a stock market crash, bank failures, and reduced consumer spending.
Cause and effect thesis statement
Purpose : To demonstrate a cause and its resulting effect.
Example : Overuse of smartphones can lead to impaired sleep patterns, reduced face-to-face social interactions, and increased levels of anxiety.
Compare and contrast thesis statement
Purpose : To highlight similarities and differences between two subjects.
Example : "While both novels '1984' and 'Brave New World' delve into dystopian futures, they differ in their portrayal of individual freedom, societal control, and the role of technology."
When you write a thesis statement , it's important to ensure clarity and precision, so the reader immediately understands the central focus of your work.
What is the difference between a thesis and a thesis statement?
While both terms are frequently used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings.
A thesis refers to the entire research document, encompassing all its chapters and sections. In contrast, a thesis statement is a brief assertion that encapsulates the central argument of the research.
Here’s an in-depth differentiation table of a thesis and a thesis statement.
Aspect | Thesis | Thesis Statement |
Definition | An extensive document presenting the author's research and findings, typically for a degree or professional qualification. | A concise sentence or two in an essay or research paper that outlines the main idea or argument. |
Position | It’s the entire document on its own. | Typically found at the end of the introduction of an essay, research paper, or thesis. |
Components | Introduction, methodology, results, conclusions, and bibliography or references. | Doesn't include any specific components |
Purpose | Provides detailed research, presents findings, and contributes to a field of study. | To guide the reader about the main point or argument of the paper or essay. |
Now, to craft a compelling thesis, it's crucial to adhere to a specific structure. Let’s break down these essential components that make up a thesis structure
15 components of a thesis structure
Navigating a thesis can be daunting. However, understanding its structure can make the process more manageable.
Here are the key components or different sections of a thesis structure:
Your thesis begins with the title page. It's not just a formality but the gateway to your research.

Here, you'll prominently display the necessary information about you (the author) and your institutional details.
- Title of your thesis
- Your full name
- Your department
- Your institution and degree program
- Your submission date
- Your Supervisor's name (in some cases)
- Your Department or faculty (in some cases)
- Your University's logo (in some cases)
- Your Student ID (in some cases)
In a concise manner, you'll have to summarize the critical aspects of your research in typically no more than 200-300 words.

This includes the problem statement, methodology, key findings, and conclusions. For many, the abstract will determine if they delve deeper into your work, so ensure it's clear and compelling.
Acknowledgments
Research is rarely a solitary endeavor. In the acknowledgments section, you have the chance to express gratitude to those who've supported your journey.

This might include advisors, peers, institutions, or even personal sources of inspiration and support. It's a personal touch, reflecting the humanity behind the academic rigor.
Table of contents
A roadmap for your readers, the table of contents lists the chapters, sections, and subsections of your thesis.

By providing page numbers, you allow readers to navigate your work easily, jumping to sections that pique their interest.
List of figures and tables
Research often involves data, and presenting this data visually can enhance understanding. This section provides an organized listing of all figures and tables in your thesis.

It's a visual index, ensuring that readers can quickly locate and reference your graphical data.
Introduction
Here's where you introduce your research topic, articulate the research question or objective, and outline the significance of your study.

- Present the research topic : Clearly articulate the central theme or subject of your research.
- Background information : Ground your research topic, providing any necessary context or background information your readers might need to understand the significance of your study.
- Define the scope : Clearly delineate the boundaries of your research, indicating what will and won't be covered.
- Literature review : Introduce any relevant existing research on your topic, situating your work within the broader academic conversation and highlighting where your research fits in.
- State the research Question(s) or objective(s) : Clearly articulate the primary questions or objectives your research aims to address.
- Outline the study's structure : Give a brief overview of how the subsequent sections of your work will unfold, guiding your readers through the journey ahead.
The introduction should captivate your readers, making them eager to delve deeper into your research journey.
Literature review section
Your study correlates with existing research. Therefore, in the literature review section, you'll engage in a dialogue with existing knowledge, highlighting relevant studies, theories, and findings.

It's here that you identify gaps in the current knowledge, positioning your research as a bridge to new insights.
To streamline this process, consider leveraging AI tools. For example, the SciSpace literature review tool enables you to efficiently explore and delve into research papers, simplifying your literature review journey.
Methodology
In the research methodology section, you’ll detail the tools, techniques, and processes you employed to gather and analyze data. This section will inform the readers about how you approached your research questions and ensures the reproducibility of your study.

Here's a breakdown of what it should encompass:
- Research Design : Describe the overall structure and approach of your research. Are you conducting a qualitative study with in-depth interviews? Or is it a quantitative study using statistical analysis? Perhaps it's a mixed-methods approach?
- Data Collection : Detail the methods you used to gather data. This could include surveys, experiments, observations, interviews, archival research, etc. Mention where you sourced your data, the duration of data collection, and any tools or instruments used.
- Sampling : If applicable, explain how you selected participants or data sources for your study. Discuss the size of your sample and the rationale behind choosing it.
- Data Analysis : Describe the techniques and tools you used to process and analyze the data. This could range from statistical tests in quantitative research to thematic analysis in qualitative research.
- Validity and Reliability : Address the steps you took to ensure the validity and reliability of your findings to ensure that your results are both accurate and consistent.
- Ethical Considerations : Highlight any ethical issues related to your research and the measures you took to address them, including — informed consent, confidentiality, and data storage and protection measures.
Moreover, different research questions necessitate different types of methodologies. For instance:
- Experimental methodology : Often used in sciences, this involves a controlled experiment to discern causality.
- Qualitative methodology : Employed when exploring patterns or phenomena without numerical data. Methods can include interviews, focus groups, or content analysis.
- Quantitative methodology : Concerned with measurable data and often involves statistical analysis. Surveys and structured observations are common tools here.
- Mixed methods : As the name implies, this combines both qualitative and quantitative methodologies.
The Methodology section isn’t just about detailing the methods but also justifying why they were chosen. The appropriateness of the methods in addressing your research question can significantly impact the credibility of your findings.
Results (or Findings)
This section presents the outcomes of your research. It's crucial to note that the nature of your results may vary; they could be quantitative, qualitative, or a mix of both.

Quantitative results often present statistical data, showcasing measurable outcomes, and they benefit from tables, graphs, and figures to depict these data points.
Qualitative results , on the other hand, might delve into patterns, themes, or narratives derived from non-numerical data, such as interviews or observations.
Regardless of the nature of your results, clarity is essential. This section is purely about presenting the data without offering interpretations — that comes later in the discussion.
In the discussion section, the raw data transforms into valuable insights.
Start by revisiting your research question and contrast it with the findings. How do your results expand, constrict, or challenge current academic conversations?
Dive into the intricacies of the data, guiding the reader through its implications. Detail potential limitations transparently, signaling your awareness of the research's boundaries. This is where your academic voice should be resonant and confident.
Practical implications (Recommendation) section
Based on the insights derived from your research, this section provides actionable suggestions or proposed solutions.
Whether aimed at industry professionals or the general public, recommendations translate your academic findings into potential real-world actions. They help readers understand the practical implications of your work and how it can be applied to effect change or improvement in a given field.
When crafting recommendations, it's essential to ensure they're feasible and rooted in the evidence provided by your research. They shouldn't merely be aspirational but should offer a clear path forward, grounded in your findings.
The conclusion provides closure to your research narrative.
It's not merely a recap but a synthesis of your main findings and their broader implications. Reconnect with the research questions or hypotheses posited at the beginning, offering clear answers based on your findings.

Reflect on the broader contributions of your study, considering its impact on the academic community and potential real-world applications.
Lastly, the conclusion should leave your readers with a clear understanding of the value and impact of your study.
References (or Bibliography)
Every theory you've expounded upon, every data point you've cited, and every methodological precedent you've followed finds its acknowledgment here.

In references, it's crucial to ensure meticulous consistency in formatting, mirroring the specific guidelines of the chosen citation style .
Proper referencing helps to avoid plagiarism , gives credit to original ideas, and allows readers to explore topics of interest. Moreover, it situates your work within the continuum of academic knowledge.
To properly cite the sources used in the study, you can rely on online citation generator tools to generate accurate citations!
Here’s more on how you can cite your sources.
Often, the depth of research produces a wealth of material that, while crucial, can make the core content of the thesis cumbersome. The appendix is where you mention extra information that supports your research but isn't central to the main text.

Whether it's raw datasets, detailed procedural methodologies, extended case studies, or any other ancillary material, the appendices ensure that these elements are archived for reference without breaking the main narrative's flow.
For thorough researchers and readers keen on meticulous details, the appendices provide a treasure trove of insights.
Glossary (optional)
In academics, specialized terminologies, and jargon are inevitable. However, not every reader is versed in every term.
The glossary, while optional, is a critical tool for accessibility. It's a bridge ensuring that even readers from outside the discipline can access, understand, and appreciate your work.

By defining complex terms and providing context, you're inviting a wider audience to engage with your research, enhancing its reach and impact.
Remember, while these components provide a structured framework, the essence of your thesis lies in the originality of your ideas, the rigor of your research, and the clarity of your presentation.
As you craft each section, keep your readers in mind, ensuring that your passion and dedication shine through every page.
Thesis examples
To further elucidate the concept of a thesis, here are illustrative examples from various fields:
Example 1 (History): Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the ‘Noble Savage’ on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807 by Suchait Kahlon.
Example 2 (Climate Dynamics): Influence of external forcings on abrupt millennial-scale climate changes: a statistical modelling study by Takahito Mitsui · Michel Crucifix
Checklist for your thesis evaluation
Evaluating your thesis ensures that your research meets the standards of academia. Here's an elaborate checklist to guide you through this critical process.
Content and structure
- Is the thesis statement clear, concise, and debatable?
- Does the introduction provide sufficient background and context?
- Is the literature review comprehensive, relevant, and well-organized?
- Does the methodology section clearly describe and justify the research methods?
- Are the results/findings presented clearly and logically?
- Does the discussion interpret the results in light of the research question and existing literature?
- Is the conclusion summarizing the research and suggesting future directions or implications?
Clarity and coherence
- Is the writing clear and free of jargon?
- Are ideas and sections logically connected and flowing?
- Is there a clear narrative or argument throughout the thesis?
Research quality
- Is the research question significant and relevant?
- Are the research methods appropriate for the question?
- Is the sample size (if applicable) adequate?
- Are the data analysis techniques appropriate and correctly applied?
- Are potential biases or limitations addressed?
Originality and significance
- Does the thesis contribute new knowledge or insights to the field?
- Is the research grounded in existing literature while offering fresh perspectives?
Formatting and presentation
- Is the thesis formatted according to institutional guidelines?
- Are figures, tables, and charts clear, labeled, and referenced in the text?
- Is the bibliography or reference list complete and consistently formatted?
- Are appendices relevant and appropriately referenced in the main text?
Grammar and language
- Is the thesis free of grammatical and spelling errors?
- Is the language professional, consistent, and appropriate for an academic audience?
- Are quotations and paraphrased material correctly cited?
Feedback and revision
- Have you sought feedback from peers, advisors, or experts in the field?
- Have you addressed the feedback and made the necessary revisions?
Overall assessment
- Does the thesis as a whole feel cohesive and comprehensive?
- Would the thesis be understandable and valuable to someone in your field?
Ensure to use this checklist to leave no ground for doubt or missed information in your thesis.
After writing your thesis, the next step is to discuss and defend your findings verbally in front of a knowledgeable panel. You’ve to be well prepared as your professors may grade your presentation abilities.
Preparing your thesis defense
A thesis defense, also known as "defending the thesis," is the culmination of a scholar's research journey. It's the final frontier, where you’ll present their findings and face scrutiny from a panel of experts.
Typically, the defense involves a public presentation where you’ll have to outline your study, followed by a question-and-answer session with a committee of experts. This committee assesses the validity, originality, and significance of the research.
The defense serves as a rite of passage for scholars. It's an opportunity to showcase expertise, address criticisms, and refine arguments. A successful defense not only validates the research but also establishes your authority as a researcher in your field.
Here’s how you can effectively prepare for your thesis defense .
Now, having touched upon the process of defending a thesis, it's worth noting that scholarly work can take various forms, depending on academic and regional practices.
One such form, often paralleled with the thesis, is the 'dissertation.' But what differentiates the two?
Dissertation vs. Thesis
Often used interchangeably in casual discourse, they refer to distinct research projects undertaken at different levels of higher education.
To the uninitiated, understanding their meaning might be elusive. So, let's demystify these terms and delve into their core differences.
Here's a table differentiating between the two.
Aspect | Thesis | Dissertation |
Purpose | Often for a master's degree, showcasing a grasp of existing research | Primarily for a doctoral degree, contributing new knowledge to the field |
Length | 100 pages, focusing on a specific topic or question. | 400-500 pages, involving deep research and comprehensive findings |
Research Depth | Builds upon existing research | Involves original and groundbreaking research |
Advisor's Role | Guides the research process | Acts more as a consultant, allowing the student to take the lead |
Outcome | Demonstrates understanding of the subject | Proves capability to conduct independent and original research |
Wrapping up
From understanding the foundational concept of a thesis to navigating its various components, differentiating it from a dissertation, and recognizing the importance of proper citation — this guide covers it all.
As scholars and readers, understanding these nuances not only aids in academic pursuits but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the relentless quest for knowledge that drives academia.
It’s important to remember that every thesis is a testament to curiosity, dedication, and the indomitable spirit of discovery.
Good luck with your thesis writing!
Frequently Asked Questions
A thesis typically ranges between 40-80 pages, but its length can vary based on the research topic, institution guidelines, and level of study.
A PhD thesis usually spans 200-300 pages, though this can vary based on the discipline, complexity of the research, and institutional requirements.
To identify a thesis topic, consider current trends in your field, gaps in existing literature, personal interests, and discussions with advisors or mentors. Additionally, reviewing related journals and conference proceedings can provide insights into potential areas of exploration.
The conceptual framework is often situated in the literature review or theoretical framework section of a thesis. It helps set the stage by providing the context, defining key concepts, and explaining the relationships between variables.
A thesis statement should be concise, clear, and specific. It should state the main argument or point of your research. Start by pinpointing the central question or issue your research addresses, then condense that into a single statement, ensuring it reflects the essence of your paper.
You might also like

Boosting Citations: A Comparative Analysis of Graphical Abstract vs. Video Abstract

The Impact of Visual Abstracts on Boosting Citations

Introducing SciSpace’s Citation Booster To Increase Research Visibility

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Dissertation Overview — Guide With Examples
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

A dissertation (a.k.a. a thesis or final year project ) is a long-form academic essay on a niche subject that requires original, primary research alongside an extensive discussion of existing topical secondary works. Your dissertation grade will usually weigh heavily (40%~70%) on your final award. Ideally, your dissertation needs to be your masterpiece.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Dissertation Overview – In a Nutshell
- 2 Definition: Dissertation overview
- 3 Dissertation overview: Research proposal
- 4 Dissertation overview: The structure
- 5 Dissertation overview: Title page
- 6 Dissertation overview: Preface
- 7 Dissertation overview: Abstract
- 8 Dissertation overview: Tables and lists
- 9 Dissertation overview: Introduction
- 10 Dissertation overview: Literature review
- 11 Dissertation overview: Methodology
- 12 Dissertation overview: Results
- 13 Dissertation overview: Discussion
- 14 Dissertation overview: Conclusion
- 15 Dissertation overview: The final pages
- 16 Dissertation overview: Proofreading and editing
- 17 Dissertation overview: Dissertation defense
Dissertation Overview – In a Nutshell
The following article covers:
- Dissertation overview – General help and guidance
- Dissertation overview – Components, layouts, and structure
- Special features, proofreading , referencing, and polish of a dissertation overview
- Example of dissertations
Definition: Dissertation overview
- The overwhelming majority of undergraduate and postgraduate taught courses require the submission of a dissertation to pass.
- A dissertation will take ca. 6~18 months to complete, usually covering ca. 5000-15,000 words . You can expect to receive your assignment and deadline during the last third of your timetable.
- What you study (within reason) is up to you. Pre-made questions and projects might also be available if sources and inspiration are lacking.
- Your assigned dissertation supervisor will provide valuable input, insight, and advice on structure and substance . Make sure to update them regularly.
- Your deadline will likely coincide with the end of your last academic year . Extensions may be allowed to account for personal setbacks, travel, or complex research projects .
Dissertation research plans are kept deliberately formulaic. Every dissertation develops as so:
- Initial research Potential areas of interest are shortlisted.
- Establishing a question What exactly will the dissertation ask?
- Initial proposal Viability testing and hypothesis fine-tuning.
- Source analysis Collection, exploration, and discussion of sources.
- Writing A dissertation overview begins to form.
- Development Content, polish, detail, and nuance.
- Editing Trimming, referencing, and error checking.
- Submission The dissertation is marked.
There are also slight differences in how British and US academia use the word dissertation. Remember that:
| A dissertation is the final written assignment for a Bachelor's or Master's degree. The text of a PhD is a thesis. | The term "dissertation" is used to refer to a written PhD. |
Dissertation overview: Research proposal
Before you start with the dissertation overview, write a draft dissertation research proposal , refine it, and get it approved by your supervisor(s).
Your draft will broadly cover why you want to research your topic , your plan or methodology , and why your dissertation would benefit academia.
Academic discussion at this stage is critical. Considering constructive advice and ideas from your tutors and field experts helps highlight productive questions.
Better planning usually results in a better end mark.
In practice, your research proposal will be a short paper (ca. 500~2000 words) explaining your ambitions. It contains:
- Introduction: A dissertation overview.
- Background review : A guide to your area of study.
- Literature review : An overview of Existing Sources.
- Methodology : Your main question(s) and research plan.
- Implications : How your research will contribute.
- Conclusion: A summary recap.
Dissertation overview: The structure
Now you can start filling out the skeletal structure of your dissertation overview. Depending on your style, you may find it productive to create extensive notes before ordering them.
Your research will segment by topic, area, purpose, and theme. Your structure will also vary to match your discipline.
- Dissertations in the humanities often read like lengthy essays, building to a central, final argument.
- Dissertations in the sciences tend to divide mechanically. Methodology, experiments, results, and implications place into different, unique chapters.
The University of Leeds (UK) maintains an online public archive of award-winning dissertations. You can browse excellent dissertation overview examples here .
Try these pieces to start:
An Investigation into the Relationship between Early Exposure and Brand
Loyalty (Psychology)
Image Processing and Analysis of Porous Materials (Material Sciences)
Faith, Selfhood and the Blues in the Lyrics of Nick Cave (English and Media)
Dissertation overview: Title page
Every dissertation overview starts with a title page. The front cover provides vital information about who you are and what you’re about.
A dissertation title page includes:
- Your full name
- Your student and submission numbers (If relevant)
- Your course and projected award (e.g., BSc Hons. Biology)
- A full dissertation title
- Your university (or awarding institution)
- Your department and supervisor
- A university logo
- Your date of final submission
Your dissertation title should always be placed at the top.
Dissertation overview: Preface
The preface of a dissertation overview is a special place to acknowledge crucial institutions, individuals, or experts who helped you. You can also dedicate the work to a loved one.
You should always politely acknowledge your supervisor, your personal tutor, and any labs, libraries, or archives used extensively.
Dissertation overview: Abstract
The abstract is a ca. 150~500-word paragraph dissertation overview briefly summarizing your topic, questions, methodology, and conclusions. It reads as a dissertation overview and a formal blurb for your work that advertises it to new readers. An effective abstract requires a complete and flowing thesis to draw on. Writing your abstract should be your absolute last task.
Printing Your Thesis With BachelorPrint
- High-quality bindings with customizable embossing
- 3D live preview to check your work before ordering
- Free express delivery
Configure your binding now!
to the print shop
Dissertation overview: Tables and lists
Good direction, collation, and indexing help keep your dissertation easy to read, reference, and check for errors. An effective dissertation overview consists of the outline of chapters, inserts, and technical terms.
Dissertation overview: Table of contents
The table of contents tells readers which numbered pages link to which segments. It always appears before the main text. This section helps simplifying your dissertation overview.
Your contents table should cover all chapter headings, major subheadings, and other exceptional points of interest. Page numbers should always follow each entry.
Avoid citing every individual subheading, paragraph, or change of topic. Careful curation of milestones is best.
You can easily use Microsoft Word to autogenerate a table of contents. Remember to activate automatic page numbering.
List of Figures and Tables
Likewise, you should cite all relevant figures, tables, and illustrations here. A table list is optional but highly advisable for a dissertation overview.
Write your items in a numbered list in order of appearance. Again, Microsoft Word can autogenerate this via the Insert Caption feature.
List of Abbreviations
Abbreviations help save space in a packed manuscript. However, unexplained, obscure acronyms can confound even experienced readers.
If your dissertation references unusual, new, or technical abbreviations, include an alphabetical guide that explains their exact meanings. Avoid including commonplace abbreviations (e.g. a.k.a.).
You can also add an explanatory glossary of complex technical names and terms to your dissertation overview. Scientific dissertations may find some (optional) exposition particularly useful.
Again, order your entries by first alphabetical initial and avoid common words. Term descriptions should be 1-3 sentences long.
Dissertation overview: Introduction
Your introduction gives a first glance at your topic, purpose, and impact. Think of it as an expanded abstract. Stay clear, relevant, and assertive – this is your first chance to hook the reader.
Your introduction is also a great chance to make the relevant initial points needed to set up discussion, exploration, and argument. In the dissertation overview, you should:
- Clearly state your research question and objectives
- Set your focus and topical limits
- Detail all necessary background information and context
- Argue why your dissertation is relevant
- Outline your broad structure and methodology
Dissertation overview: Literature review
A topical literature review briefly tells the reader about existing material, comments on relevance, and demonstrates gaps in our collective knowledge.
Your literature review often forms the backbone of your broader theoretical framework in the dissertation overview. Primary, secondary, and meta sources (e.g. commentaries) count as literature.
| • Source credibility • Analysis of each source • Any obvious shortcomings (e.g. Bias, length, outdated methodologies) • Recurring patterns and themes • How you will build on your sources | • Simply repeating your source content (as is) • Taking complex, improbable, or controversial sources at face value • Leaving connections unexamined • Not setting clear study objectives • Missing out major works |
Dissertation overview: Methodology
In the dissertation overview, your methodology section describes the methods you used to collect and process your research data . Stating your methodology keeps your research credible, verifiable , and transparent.
Your methodology section should cover how and why you made your choices (e.g. longitudinal-isolated, qualitative-quantitative ), your collection methods, and how, where, and when you collected your primary data. Make a solid case for why this was the best technical approach available and address ethical concerns.
You should expect to write a far lengthier methodology for dissertations in the sciences over literary subjects (e.g. History).
Dissertation overview: Results
The results in the dissertation overview is where you list what you (objectively) discovered. Discuss all results – even if the data didn’t match your expectations.
Tables, graphics, and prose summaries relevant to your hypothesis can all be displayed. Make sure to differentiate between sections with labels and subheadings.
Careful selection and curation are good ways to keep text flowing. If your datasets are too extensive, abridge and move them to an appendix . Likewise, it’s usually worth trimming down transcripts to highlights .
Make sure to stick to the facts here. Discussion, speculation, and context will come later. However, feel free to add referenced secondary context (e.g. Reprinted data tables from earlier papers).
Dissertation overview: Discussion
The penultimate section in the dissertation overview should cover your thoughts on your discoveries and how your results fit into your theoretical framework. It’s also a place to discuss any potential implications in depth.
Include thorough but concise callbacks alongside your commentary. Using questions to self-interrogate works well. Ask:
- Why are these results relevant?
- Where do they apply?
- Are they replicable?
- How do they fit existing secondary literature?
- Are there any limitations or drawbacks?
Dissertation overview: Conclusion
In the dissertation overview, the conclusion is your dissertation’s final answer. In 500~1000 words, you’ll respond directly to your initial question(s).
Don’t include any further speculation, results, or analysis here. Other segments can house last-minute additions.
Include your overall impressions of your results and how your findings change our understanding. Briefly reflect too on any further study you think is advantageous. Try to end on a suitably optimistic yet punchy note.
Dissertation overview: The final pages
Dissertation overview done? It’s time to cite all of your sources. Include a blank end page for the back cover, too.
Dissertation overview: References
Make sure to fully reference all sources used in the footnotes and your bibliography. Clear referencing helps researchers and avoids plagiarism.
Stick to one referencing style (e.g. APA style , Chicago style , MLA ) for the entire dissertation. You can find style guides and reference generators online. Your supervisor can recommend a “best practice” referencing style for your project.
Is anything vital left over that would take up too much room? Use an appendix.
Essential methodological work (such as questionnaire templates) and full data tables too bulky for the main text can always be stored here.
Dissertation overview: Proofreading and editing
Once you’ve created your final draft, read it back and edit it. You’ll likely need to trim and refine your text to showcase your best work.
It’s also essential to remove grammatical, style, factual, or spelling errors before submission. Presentation counts heavily towards your final mark.
Set aside at least 10% of your dissertation schedule for checking and polishing. You can use online checkers or pay professional proofreading and editing services (as long as they don’t write for you) to help.
Dissertation overview: Dissertation defense
You may also have to attend a dissertation defense . The defense is a meeting in which you give a closed presentation to a supervisory panel and your peers. It’s also a chance to reveal exciting discoveries.
You’ll be prepared well in advance by your supervisor to defend any contentious points, arguments, or methodological approaches made. Defenses can be rerun with modifications if you fail the first attempt.
Once the panel accepts your argument, you’ve officially passed your dissertation. Congratulations!
How do you start the dissertation introduction?
Cover your topic’s what, why, where, how, and when. Establishing a foundation for your research is crucial.
How should I format my dissertation?
Stick to uniform, commonly known, and easy-to-read black fonts, font sizes, and graphics. Ring or book binding your finished work is advisable.
Why is proper referencing so important?
Unreferenced dissertations may be accused of plagiarism and annulled – wrecking years of hard work. Always cite where and whenever you can.
Extremely satisfied, excellent deal with delivery in less than 24h. The print...
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Eigentümer dieser Website, |
| Zweck | Speichert die Einstellungen der Besucher, die in der Cookie Box von Borlabs Cookie ausgewählt wurden. |
| Cookie Name | borlabs-cookie |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Bachelorprint |
| Zweck | Erkennt das Herkunftsland und leitet zur entsprechenden Sprachversion um. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | ip-api.com |
| Cookie Name | georedirect |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Playcanvas |
| Zweck | Display our 3D product animations |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | playcanv.as, playcanvas.as, playcanvas.com |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Cookie von Google zur Steuerung der erweiterten Script- und Ereignisbehandlung. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Cookie Name | _ga,_gat,_gid |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 2 Jahre |
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Meta Platforms Ireland Limited, 4 Grand Canal Square, Dublin 2, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Facebook-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .facebook.com |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird zum Entsperren von Google Maps-Inhalten verwendet. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .google.com |
| Cookie Name | NID |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 6 Monate |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Meta Platforms Ireland Limited, 4 Grand Canal Square, Dublin 2, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Instagram-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .instagram.com |
| Cookie Name | pigeon_state |
| Cookie Laufzeit | Sitzung |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Openstreetmap Foundation, St John’s Innovation Centre, Cowley Road, Cambridge CB4 0WS, United Kingdom |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um OpenStreetMap-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .openstreetmap.org |
| Cookie Name | _osm_location, _osm_session, _osm_totp_token, _osm_welcome, _pk_id., _pk_ref., _pk_ses., qos_token |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1-10 Jahre |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Twitter International Company, One Cumberland Place, Fenian Street, Dublin 2, D02 AX07, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Twitter-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .twimg.com, .twitter.com |
| Cookie Name | __widgetsettings, local_storage_support_test |
| Cookie Laufzeit | Unbegrenzt |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Vimeo Inc., 555 West 18th Street, New York, New York 10011, USA |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Vimeo-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | player.vimeo.com |
| Cookie Name | vuid |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 2 Jahre |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um YouTube-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | google.com |
| Cookie Name | NID |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 6 Monate |
Privacy Policy Imprint
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to structure a thesis
A typical thesis structure
1. abstract, 2. introduction, 3. literature review, 6. discussion, 7. conclusion, 8. reference list, frequently asked questions about structuring a thesis, related articles.
Starting a thesis can be daunting. There are so many questions in the beginning:
- How do you actually start your thesis?
- How do you structure it?
- What information should the individual chapters contain?
Each educational program has different demands on your thesis structure, which is why asking directly for the requirements of your program should be a first step. However, there is not much flexibility when it comes to structuring your thesis.
Abstract : a brief overview of your entire thesis.
Literature review : an evaluation of previous research on your topic that includes a discussion of gaps in the research and how your work may fill them.
Methods : outlines the methodology that you are using in your research.
Thesis : a large paper, or multi-chapter work, based on a topic relating to your field of study.
The abstract is the overview of your thesis and generally very short. This section should highlight the main contents of your thesis “at a glance” so that someone who is curious about your work can get the gist quickly. Take a look at our guide on how to write an abstract for more info.
Tip: Consider writing your abstract last, after you’ve written everything else.
The introduction to your thesis gives an overview of its basics or main points. It should answer the following questions:
- Why is the topic being studied?
- How is the topic being studied?
- What is being studied?
In answering the first question, you should know what your personal interest in this topic is and why it is relevant. Why does it matter?
To answer the "how", you should briefly explain how you are going to reach your research goal. Some prefer to answer that question in the methods chapter, but you can give a quick overview here.
And finally, you should explain "what" you are studying. You can also give background information here.
You should rewrite the introduction one last time when the writing is done to make sure it connects with your conclusion. Learn more about how to write a good thesis introduction in our thesis introduction guide .
A literature review is often part of the introduction, but it can be a separate section. It is an evaluation of previous research on the topic showing that there are gaps that your research will attempt to fill. A few tips for your literature review:
- Use a wide array of sources
- Show both sides of the coin
- Make sure to cover the classics in your field
- Present everything in a clear and structured manner
For more insights on lit reviews, take a look at our guide on how to write a literature review .
The methodology chapter outlines which methods you choose to gather data, how the data is analyzed and justifies why you chose that methodology . It shows how your choice of design and research methods is suited to answering your research question.
Make sure to also explain what the pitfalls of your approach are and how you have tried to mitigate them. Discussing where your study might come up short can give you more credibility, since it shows the reader that you are aware of its limitations.
Tip: Use graphs and tables, where appropriate, to visualize your results.
The results chapter outlines what you found out in relation to your research questions or hypotheses. It generally contains the facts of your research and does not include a lot of analysis, because that happens mostly in the discussion chapter.
Clearly visualize your results, using tables and graphs, especially when summarizing, and be consistent in your way of reporting. This means sticking to one format to help the reader evaluate and compare the data.
The discussion chapter includes your own analysis and interpretation of the data you gathered , comments on your results and explains what they mean. This is your opportunity to show that you have understood your findings and their significance.
Point out the limitations of your study, provide explanations for unexpected results, and note any questions that remain unanswered.
This is probably your most important chapter. This is where you highlight that your research objectives have been achieved. You can also reiterate any limitations to your study and make suggestions for future research.
Remember to check if you have really answered all your research questions and hypotheses in this chapter. Your thesis should be tied up nicely in the conclusion and show clearly what you did, what results you got, and what you learned. Discover how to write a good conclusion in our thesis conclusion guide .
At the end of your thesis, you’ll have to compile a list of references for everything you’ve cited above. Ideally, you should keep track of everything from the beginning. Otherwise, this could be a mammoth and pretty laborious task to do.
Consider using a reference manager like Paperpile to format and organize your citations. Paperpile allows you to organize and save your citations for later use and cite them in thousands of citation styles directly in Google Docs, Microsoft Word, or LaTeX:
🔲 Introduction
🔲 Literature review
🔲 Discussion
🔲 Conclusion
🔲 Reference list
The basic elements of a thesis are: Abstract, Introduction, Literature Review, Methods, Results, Discussion, Conclusion, and Reference List.
It's recommended to start a thesis by writing the literature review first. This way you learn more about the sources, before jumping to the discussion or any other element.
It's recommended to write the abstract of a thesis last, once everything else is done. This way you will be able to provide a complete overview of your work.
Usually, the discussion is the longest part of a thesis. In this part you are supposed to point out the limitations of your study, provide explanations for unexpected results, and note any questions that remain unanswered.
The order of the basic elements of a thesis are: 1. Abstract, 2. Introduction, 3. Literature Review, 4. Methods, 5. Results, 6. Discussion, 7. Conclusion, and 8. Reference List.


Thesis Statements
What this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can craft or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence near the beginning of your paper (most often, at the end of the first paragraph) that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I create a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis” that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following :
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question. If the prompt isn’t phrased as a question, try to rephrase it. For example, “Discuss the effect of X on Y” can be rephrased as “What is the effect of X on Y?”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is likely to be “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s okay to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on contemporary communication, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: “Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.” Looking back at your notes, you might start with this working thesis:
Social media impacts public awareness in both positive and negative ways.
You can use the questions above to help you revise this general statement into a stronger thesis.
- Do I answer the question? You can analyze this if you rephrase “discuss the impact” as “what is the impact?” This way, you can see that you’ve answered the question only very generally with the vague “positive and negative ways.”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not likely. Only people who maintain that social media has a solely positive or solely negative impact could disagree.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? No. What are the positive effects? What are the negative effects?
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? No. Why are they positive? How are they positive? What are their causes? Why are they negative? How are they negative? What are their causes?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? No. Why should anyone care about the positive and/or negative impact of social media?
After thinking about your answers to these questions, you decide to focus on the one impact you feel strongly about and have strong evidence for:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
This version is a much stronger thesis! It answers the question, takes a specific position that others can challenge, and it gives a sense of why it matters.
Let’s try another. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
You begin to analyze your thesis:
- Do I answer the question? No. The prompt asks you to analyze some aspect of the novel. Your working thesis is a statement of general appreciation for the entire novel.
Think about aspects of the novel that are important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
- Do I answer the question? Yes!
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not really. This contrast is well-known and accepted.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? It’s getting there–you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation. However, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? Not yet. Compare scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions and anything else that seems interesting.
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?”
After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Ramage, John D., John C. Bean, and June Johnson. 2018. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing , 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Ruszkiewicz, John J., Christy Friend, Daniel Seward, and Maxine Hairston. 2010. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers , 9th ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
How to Write a Thesis Summary
Your thesis summary is the distilled essence of your thesis: a tool to underline the strengths of your research and make yourself recognizable as a competent scholar.

The importance of writing a good thesis summary is often underestimated and it is not too difficult to understand why. Even in the cases where a student has seriously engaged in writing his thesis, the summary is usually the last thing that gets done. The typical scenario is therefore the following: the bulk of the work has finally been done, the deadline to submit the thesis is imminent. Time is running out and, consequently, when it comes to set the summary down, this is written in a very hasty way… I am pretty sure that you can relate to this situation and – trust me – you are not the only one. Yet, this is a pity! Your thesis summary deserves to be written with a certain care for several good reasons. An effective summary is the best way to impress your readers. It will be the first thing to be read and – as hard as it is to admit – the first impression is what really counts. You should therefore think of the summary as a distilled and concentrated essence of your thesis: a tool to underline the strengths of your research and make yourself recognizable as a competent scholar.
Especially if your thesis is written in another language, setting down an accurate, compelling summary in English can be the first step to internationally disseminate your work. In this regard, keep also in mind that an English summary of your thesis may be required for a job application or a PhD-position. Having said that, how to proceed? Here you are some useful steps to write an effective summary.
Elaborate a thesis statement
The thesis statement . is the most important part. This is a sentence usually placed at the beginning of the summary and it is aimed at clarifying the main research questions of your work. The thesis statement must be clear and concise. MA theses, but also PhD dissertations, usually concern very narrow topics. So, avoid being vague and explain the central idea of your research as specific as possible. Let’s do some practical examples. A sentence like:
“the aim of the present study is to show how English skills can be improved in several ways” is certainly too vague.
Instead, a statement like:
“the aim of the present research is to show how the use of Ludwig can improve English writing skills, by providing reliable texts to get inspiration”
defines a narrower field of research. In addition, as the last example demonstrates, a good thesis statement can be enforced with further arguments.
For example, one could state that:
taking inspiration from a database of 300 million English sentences can indeed help a student to perfect their phrasing, by seeing words in the context of real sentences. A mere automatic correction tool, instead, carries the risk of worsening the student performance, for example by favouring the memorization of wrong phrases and expressions.

Explain the structure of the thesis
Each thesis is usually divided into diverse chapters, such as an introduction, a section dedicated to explaining the terminology, a chapter for the methodology, the discussion of the data, the results of the research etc. A good summary must give a clear idea of how you have organized your research step by step. So be very clear and use sentences like “in the first chapter of my thesis I treated”, “while in the second…”, “the analysis of the data has shown that” etc. And, of course, do not hesitate to use Ludwig if you need examples to take inspiration from. Keep in mind, you may have made the discovery of the century… but if you are not able to explain how you achieved such a result, you will be considered a charlatan.
How to write a thesis summary: a practical example
In this regard, it is good practice to read a number of thesis summaries and to analyse how they are written. Nowadays all the most prestigious universities offer free access to their online repositories, where one can find great inspirational models. See, for example, this website by Cambridge University. Now, let's analyse the structure of one of them:
The Italian giallo film was a type of thriller that was produced in huge numbers between the early 1960s and the late 1980s. This thesis contributes to recent scholarly attempts to situate the giallo within its socio-cultural historical context but resists the critical tendency to read these films as passive and transparent reflections of social attitudes in post-war Italy. Rather, I attend concretely to the form of these films and, specifically, to their critically neglected sound designs . I argue that the giallo’s voice tracks were conditioned by the commercial imperatives of Italy’s post-war popular film industry and that these commercial imperatives were in turn shaped by wider social, economic and political phenomena. By theorising the voice as a mediator between the giallo text and its industrial and social contexts, I show that these films both registered and reified social change. Chapter 1 demonstrates that the anonymous narrator of Mario Bava’s The Girl Who Knew Too Much (1963) adopts a range of sonorous modes throughout the film. Each of these sonorous modes invokes a specific set of intertexts which are vital to tracing both the giallo’s cultural origins and the increasingly globalised socio- cultural landscape from which it emerged. This chapter then shows that Dario Argento’s The Bird with the Crystal Plumage (1970) uses the model of the cinematic voice-over to explore the subjective experience of urban space in post-war Italy. The film suggests that by 1970 the ability to vocally ‘narrate’ and thus control space had become a fundamental assumption of the modern, cosmopolitan subject. Chapter 2 analyses Lucio Fulci’s Don’t Torture a Duckling (1972) and Sergio Martino’s Torso (1973). Both films draw on longstanding Italian cultural stereotypes to pitch the silence of the rural against the vocality of the urban. The films use silence and the voice as ‘cartographic’ tools to delineate the profound socio-economic divisions between Italy’s rural South and its more urban North, but they also illustrate the giallo’s underlying affinities with its silent cinema ancestors and so challenge the assumed temporal borders between cinematic eras. Chapter 3 argues that Argento’s Tenebrae (1982) and Fulci’s The New York Ripper (1982) variously mimic the vocal aesthetics of television. These films lay bare both the increasing dominance of the Italian cultural landscape by imported commercial television in the 1980s and the neoliberal economic project that underpinned that trend. Ultimately, they question the stability of the nation itself, precisely because the voice — now fractured across a global mediascape — is unable to signal national specificity.
The sentences in bold highlight how the author carefully organized the structure of the text. He started with a well elaborate thesis statement. As you can see, the object of the research is well defined and narrow: the study focuses on Italian thrillers , produced during a specific historical period between the early 1960s and the late 1980s. Moreover, the investigation depeens a specific aspect: the use of sounds in this movie genre. Then, the scholar explains in detail how he organized his work step by step, by summarizing the content of each chapter.

Ultimately, we can say that to write a theis summary is a less daunting task than one might imagine at first sight!
Keep in mind why and for whom you are writing
There is a huge difference between writing a summary for the theses database of your university and to write a summary for a more ambitious purpose. As mentioned above, a summary of your thesis may be required for a job application or to get a PhD position. So, if you are facing this kind of situation, you must “use” your summary in a smart way. Are there any points of contact between your thesis and the position you hope to get? If yes which ones? Is it the topic? Or, perhaps, in order to undertake your research, you have used a tool/method/program that could be pertinent with this position? So, tailor your summary in order to highlight what you need to stand out from the crowd and… good luck!
Others from Academic English

MLA, APA, Chicago, IEEE - What’s the best citation style for your paper?

The Fall of the Five-Paragraph Essay

Should I publish it in English? About the role of English in the scientific community

How to write the perfect abstract: do not displease your reviewers and get published
Subscribe to new posts.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Tips for Writing Your Thesis Statement
1. Determine what kind of paper you are writing:
- An analytical paper breaks down an issue or an idea into its component parts, evaluates the issue or idea, and presents this breakdown and evaluation to the audience.
- An expository (explanatory) paper explains something to the audience.
- An argumentative paper makes a claim about a topic and justifies this claim with specific evidence. The claim could be an opinion, a policy proposal, an evaluation, a cause-and-effect statement, or an interpretation. The goal of the argumentative paper is to convince the audience that the claim is true based on the evidence provided.
If you are writing a text that does not fall under these three categories (e.g., a narrative), a thesis statement somewhere in the first paragraph could still be helpful to your reader.
2. Your thesis statement should be specific—it should cover only what you will discuss in your paper and should be supported with specific evidence.
3. The thesis statement usually appears at the end of the first paragraph of a paper.
4. Your topic may change as you write, so you may need to revise your thesis statement to reflect exactly what you have discussed in the paper.
Thesis Statement Examples
Example of an analytical thesis statement:
The paper that follows should:
- Explain the analysis of the college admission process
- Explain the challenge facing admissions counselors
Example of an expository (explanatory) thesis statement:
- Explain how students spend their time studying, attending class, and socializing with peers
Example of an argumentative thesis statement:
- Present an argument and give evidence to support the claim that students should pursue community projects before entering college
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
Published on 15 September 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on 25 July 2024.
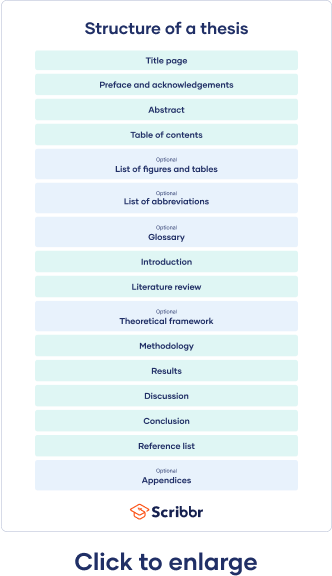
A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a PhD program in the UK.
Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Indeed, alongside a dissertation , it is the longest piece of writing students typically complete. It relies on your ability to conduct research from start to finish: designing your research , collecting data , developing a robust analysis, drawing strong conclusions , and writing concisely .
Thesis template
You can also download our full thesis template in the format of your choice below. Our template includes a ready-made table of contents , as well as guidance for what each chapter should include. It’s easy to make it your own, and can help you get started.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Thesis vs. thesis statement, how to structure a thesis, acknowledgements or preface, list of figures and tables, list of abbreviations, introduction, literature review, methodology, reference list, proofreading and editing, defending your thesis, frequently asked questions about theses.
You may have heard the word thesis as a standalone term or as a component of academic writing called a thesis statement . Keep in mind that these are two very different things.
- A thesis statement is a very common component of an essay, particularly in the humanities. It usually comprises 1 or 2 sentences in the introduction of your essay , and should clearly and concisely summarise the central points of your academic essay .
- A thesis is a long-form piece of academic writing, often taking more than a full semester to complete. It is generally a degree requirement to complete a PhD program.
- In many countries, particularly the UK, a dissertation is generally written at the bachelor’s or master’s level.
- In the US, a dissertation is generally written as a final step toward obtaining a PhD.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
The final structure of your thesis depends on a variety of components, such as:
- Your discipline
- Your theoretical approach
Humanities theses are often structured more like a longer-form essay . Just like in an essay, you build an argument to support a central thesis.
In both hard and social sciences, theses typically include an introduction , literature review , methodology section , results section , discussion section , and conclusion section . These are each presented in their own dedicated section or chapter. In some cases, you might want to add an appendix .
Thesis examples
We’ve compiled a short list of thesis examples to help you get started.
- Example thesis #1: ‘Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the “Noble Savage” on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807’ by Suchait Kahlon.
- Example thesis #2: ‘”A Starving Man Helping Another Starving Man”: UNRRA, India, and the Genesis of Global Relief, 1943-1947’ by Julian Saint Reiman.
The very first page of your thesis contains all necessary identifying information, including:
- Your full title
- Your full name
- Your department
- Your institution and degree program
- Your submission date.
Sometimes the title page also includes your student ID, the name of your supervisor, or the university’s logo. Check out your university’s guidelines if you’re not sure.
Read more about title pages
The acknowledgements section is usually optional. Its main point is to allow you to thank everyone who helped you in your thesis journey, such as supervisors, friends, or family. You can also choose to write a preface , but it’s typically one or the other, not both.
Read more about acknowledgements Read more about prefaces

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
An abstract is a short summary of your thesis. Usually a maximum of 300 words long, it’s should include brief descriptions of your research objectives , methods, results, and conclusions. Though it may seem short, it introduces your work to your audience, serving as a first impression of your thesis.
Read more about abstracts
A table of contents lists all of your sections, plus their corresponding page numbers and subheadings if you have them. This helps your reader seamlessly navigate your document.
Your table of contents should include all the major parts of your thesis. In particular, don’t forget the the appendices. If you used heading styles, it’s easy to generate an automatic table Microsoft Word.
Read more about tables of contents
While not mandatory, if you used a lot of tables and/or figures, it’s nice to include a list of them to help guide your reader. It’s also easy to generate one of these in Word: just use the ‘Insert Caption’ feature.
Read more about lists of figures and tables
If you have used a lot of industry- or field-specific abbreviations in your thesis, you should include them in an alphabetised list of abbreviations . This way, your readers can easily look up any meanings they aren’t familiar with.
Read more about lists of abbreviations
Relatedly, if you find yourself using a lot of very specialised or field-specific terms that may not be familiar to your reader, consider including a glossary . Alphabetise the terms you want to include with a brief definition.
Read more about glossaries
An introduction sets up the topic, purpose, and relevance of your thesis, as well as expectations for your reader. This should:
- Ground your research topic , sharing any background information your reader may need
- Define the scope of your work
- Introduce any existing research on your topic, situating your work within a broader problem or debate
- State your research question(s)
- Outline (briefly) how the remainder of your work will proceed
In other words, your introduction should clearly and concisely show your reader the “what, why, and how” of your research.
Read more about introductions
A literature review helps you gain a robust understanding of any extant academic work on your topic, encompassing:
- Selecting relevant sources
- Determining the credibility of your sources
- Critically evaluating each of your sources
- Drawing connections between sources, including any themes, patterns, conflicts, or gaps
A literature review is not merely a summary of existing work. Rather, your literature review should ultimately lead to a clear justification for your own research, perhaps via:
- Addressing a gap in the literature
- Building on existing knowledge to draw new conclusions
- Exploring a new theoretical or methodological approach
- Introducing a new solution to an unresolved problem
- Definitively advocating for one side of a theoretical debate
Read more about literature reviews
Theoretical framework
Your literature review can often form the basis for your theoretical framework, but these are not the same thing. A theoretical framework defines and analyses the concepts and theories that your research hinges on.
Read more about theoretical frameworks
Your methodology chapter shows your reader how you conducted your research. It should be written clearly and methodically, easily allowing your reader to critically assess the credibility of your argument. Furthermore, your methods section should convince your reader that your method was the best way to answer your research question.
A methodology section should generally include:
- Your overall approach ( quantitative vs. qualitative )
- Your research methods (e.g., a longitudinal study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., interviews or a controlled experiment
- Any tools or materials you used (e.g., computer software)
- The data analysis methods you chose (e.g., statistical analysis , discourse analysis )
- A strong, but not defensive justification of your methods
Read more about methodology sections
Your results section should highlight what your methodology discovered. These two sections work in tandem, but shouldn’t repeat each other. While your results section can include hypotheses or themes, don’t include any speculation or new arguments here.
Your results section should:
- State each (relevant) result with any (relevant) descriptive statistics (e.g., mean , standard deviation ) and inferential statistics (e.g., test statistics , p values )
- Explain how each result relates to the research question
- Determine whether the hypothesis was supported
Additional data (like raw numbers or interview transcripts ) can be included as an appendix . You can include tables and figures, but only if they help the reader better understand your results.
Read more about results sections
Your discussion section is where you can interpret your results in detail. Did they meet your expectations? How well do they fit within the framework that you built? You can refer back to any relevant source material to situate your results within your field, but leave most of that analysis in your literature review.
For any unexpected results, offer explanations or alternative interpretations of your data.
Read more about discussion sections
Your thesis conclusion should concisely answer your main research question. It should leave your reader with an ultra-clear understanding of your central argument, and emphasise what your research specifically has contributed to your field.
Why does your research matter? What recommendations for future research do you have? Lastly, wrap up your work with any concluding remarks.
Read more about conclusions
In order to avoid plagiarism , don’t forget to include a full reference list at the end of your thesis, citing the sources that you used. Choose one citation style and follow it consistently throughout your thesis, taking note of the formatting requirements of each style.
Which style you choose is often set by your department or your field, but common styles include MLA , Chicago , and APA.
Create APA citations Create MLA citations
In order to stay clear and concise, your thesis should include the most essential information needed to answer your research question. However, chances are you have many contributing documents, like interview transcripts or survey questions . These can be added as appendices , to save space in the main body.
Read more about appendices
Once you’re done writing, the next part of your editing process begins. Leave plenty of time for proofreading and editing prior to submission. Nothing looks worse than grammar mistakes or sloppy spelling errors!
Consider using a professional thesis editing service to make sure your final project is perfect.
Once you’ve submitted your final product, it’s common practice to have a thesis defense, an oral component of your finished work. This is scheduled by your advisor or committee, and usually entails a presentation and Q&A session.
After your defense, your committee will meet to determine if you deserve any departmental honors or accolades. However, keep in mind that defenses are usually just a formality. If there are any serious issues with your work, these should be resolved with your advisor way before a defense.
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation shouldn’t take up more than 5-7% of your overall word count.
When you mention different chapters within your text, it’s considered best to use Roman numerals for most citation styles. However, the most important thing here is to remain consistent whenever using numbers in your dissertation .
If you only used a few abbreviations in your thesis or dissertation, you don’t necessarily need to include a list of abbreviations .
If your abbreviations are numerous, or if you think they won’t be known to your audience, it’s never a bad idea to add one. They can also improve readability, minimising confusion about abbreviations unfamiliar to your reader.
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical first steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organise your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
Generally, an outline contains information on the different sections included in your thesis or dissertation, such as:
- Your anticipated title
- Your abstract
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review, research methods, avenues for future research, etc.)
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
George, T. (2024, July 25). What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 21 August 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/thesis-ultimate-guide/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, dissertation & thesis outline | example & free templates, how to write a thesis or dissertation conclusion, how to write a thesis or dissertation introduction.
Thesis and Purpose Statements
Use the guidelines below to learn the differences between thesis and purpose statements.
In the first stages of writing, thesis or purpose statements are usually rough or ill-formed and are useful primarily as planning tools.
A thesis statement or purpose statement will emerge as you think and write about a topic. The statement can be restricted or clarified and eventually worked into an introduction.
As you revise your paper, try to phrase your thesis or purpose statement in a precise way so that it matches the content and organization of your paper.
Thesis statements
A thesis statement is a sentence that makes an assertion about a topic and predicts how the topic will be developed. It does not simply announce a topic: it says something about the topic.
Good: X has made a significant impact on the teenage population due to its . . . Bad: In this paper, I will discuss X.
A thesis statement makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of the paper. It summarizes the conclusions that the writer has reached about the topic.
A thesis statement is generally located near the end of the introduction. Sometimes in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or an entire paragraph.
A thesis statement is focused and specific enough to be proven within the boundaries of the paper. Key words (nouns and verbs) should be specific, accurate, and indicative of the range of research, thrust of the argument or analysis, and the organization of supporting information.
Purpose statements
A purpose statement announces the purpose, scope, and direction of the paper. It tells the reader what to expect in a paper and what the specific focus will be.
Common beginnings include:
“This paper examines . . .,” “The aim of this paper is to . . .,” and “The purpose of this essay is to . . .”
A purpose statement makes a promise to the reader about the development of the argument but does not preview the particular conclusions that the writer has drawn.
A purpose statement usually appears toward the end of the introduction. The purpose statement may be expressed in several sentences or even an entire paragraph.
A purpose statement is specific enough to satisfy the requirements of the assignment. Purpose statements are common in research papers in some academic disciplines, while in other disciplines they are considered too blunt or direct. If you are unsure about using a purpose statement, ask your instructor.
This paper will examine the ecological destruction of the Sahel preceding the drought and the causes of this disintegration of the land. The focus will be on the economic, political, and social relationships which brought about the environmental problems in the Sahel.
Sample purpose and thesis statements
The following example combines a purpose statement and a thesis statement (bold).
The goal of this paper is to examine the effects of Chile’s agrarian reform on the lives of rural peasants. The nature of the topic dictates the use of both a chronological and a comparative analysis of peasant lives at various points during the reform period. . . The Chilean reform example provides evidence that land distribution is an essential component of both the improvement of peasant conditions and the development of a democratic society. More extensive and enduring reforms would likely have allowed Chile the opportunity to further expand these horizons.
For more tips about writing thesis statements, take a look at our new handout on Developing a Thesis Statement.

Writing Process and Structure
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Getting Started with Your Paper
Interpreting Writing Assignments from Your Courses
Generating Ideas for Your Paper
Creating an Argument
Thesis vs. Purpose Statements
Developing a Thesis Statement
Architecture of Arguments
Working with Sources
Quoting and Paraphrasing Sources
Using Literary Quotations
Citing Sources in Your Paper
Drafting Your Paper
Introductions
Paragraphing
Developing Strategic Transitions
Conclusions
Revising Your Paper
Peer Reviews
Reverse Outlines
Revising an Argumentative Paper
Revision Strategies for Longer Projects
Finishing Your Paper
Twelve Common Errors: An Editing Checklist
How to Proofread your Paper
Writing Collaboratively
Collaborative and Group Writing
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
Published on June 7, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on November 21, 2023.
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical early steps in your writing process . It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding the specifics of your dissertation topic and showcasing its relevance to your field.
Generally, an outline contains information on the different sections included in your thesis or dissertation , such as:
- Your anticipated title
- Your abstract
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review, research methods, avenues for future research, etc.)
In the final product, you can also provide a chapter outline for your readers. This is a short paragraph at the end of your introduction to inform readers about the organizational structure of your thesis or dissertation. This chapter outline is also known as a reading guide or summary outline.
Table of contents
How to outline your thesis or dissertation, dissertation and thesis outline templates, chapter outline example, sample sentences for your chapter outline, sample verbs for variation in your chapter outline, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about thesis and dissertation outlines.
While there are some inter-institutional differences, many outlines proceed in a fairly similar fashion.
- Working Title
- “Elevator pitch” of your work (often written last).
- Introduce your area of study, sharing details about your research question, problem statement , and hypotheses . Situate your research within an existing paradigm or conceptual or theoretical framework .
- Subdivide as you see fit into main topics and sub-topics.
- Describe your research methods (e.g., your scope , population , and data collection ).
- Present your research findings and share about your data analysis methods.
- Answer the research question in a concise way.
- Interpret your findings, discuss potential limitations of your own research and speculate about future implications or related opportunities.
For a more detailed overview of chapters and other elements, be sure to check out our article on the structure of a dissertation or download our template .
To help you get started, we’ve created a full thesis or dissertation template in Word or Google Docs format. It’s easy adapt it to your own requirements.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template

It can be easy to fall into a pattern of overusing the same words or sentence constructions, which can make your work monotonous and repetitive for your readers. Consider utilizing some of the alternative constructions presented below.
Example 1: Passive construction
The passive voice is a common choice for outlines and overviews because the context makes it clear who is carrying out the action (e.g., you are conducting the research ). However, overuse of the passive voice can make your text vague and imprecise.
Example 2: IS-AV construction
You can also present your information using the “IS-AV” (inanimate subject with an active verb ) construction.
A chapter is an inanimate object, so it is not capable of taking an action itself (e.g., presenting or discussing). However, the meaning of the sentence is still easily understandable, so the IS-AV construction can be a good way to add variety to your text.
Example 3: The “I” construction
Another option is to use the “I” construction, which is often recommended by style manuals (e.g., APA Style and Chicago style ). However, depending on your field of study, this construction is not always considered professional or academic. Ask your supervisor if you’re not sure.
Example 4: Mix-and-match
To truly make the most of these options, consider mixing and matching the passive voice , IS-AV construction , and “I” construction .This can help the flow of your argument and improve the readability of your text.
As you draft the chapter outline, you may also find yourself frequently repeating the same words, such as “discuss,” “present,” “prove,” or “show.” Consider branching out to add richness and nuance to your writing. Here are some examples of synonyms you can use.
| Address | Describe | Imply | Refute |
| Argue | Determine | Indicate | Report |
| Claim | Emphasize | Mention | Reveal |
| Clarify | Examine | Point out | Speculate |
| Compare | Explain | Posit | Summarize |
| Concern | Formulate | Present | Target |
| Counter | Focus on | Propose | Treat |
| Define | Give | Provide insight into | Underpin |
| Demonstrate | Highlight | Recommend | Use |
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Anchoring bias
- Halo effect
- The Baader–Meinhof phenomenon
- The placebo effect
- Nonresponse bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
When you mention different chapters within your text, it’s considered best to use Roman numerals for most citation styles. However, the most important thing here is to remain consistent whenever using numbers in your dissertation .
The title page of your thesis or dissertation goes first, before all other content or lists that you may choose to include.
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical first steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review , research methods , avenues for future research, etc.)
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, November 21). Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved August 21, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/dissertation-thesis-outline/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, dissertation table of contents in word | instructions & examples, figure and table lists | word instructions, template & examples, thesis & dissertation acknowledgements | tips & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- Skip to Content
- Skip to Main Navigation
- Skip to Search

Indiana University Bloomington Indiana University Bloomington IU Bloomington

- Mission, Vision, and Inclusive Language Statement
- Locations & Hours
- Undergraduate Employment
- Graduate Employment
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Newsletter Archive
- Support WTS
- Schedule an Appointment
- Online Tutoring
- Before your Appointment
- WTS Policies
- Group Tutoring
- Students Referred by Instructors
- Paid External Editing Services
- Writing Guides
- Scholarly Write-in
- Dissertation Writing Groups
- Journal Article Writing Groups
- Early Career Graduate Student Writing Workshop
- Workshops for Graduate Students
- Teaching Resources
- Syllabus Information
- Course-specific Tutoring
- Nominate a Peer Tutor
- Tutoring Feedback
- Schedule Appointment
- Campus Writing Program
Writing Tutorial Services
How to write a thesis statement, what is a thesis statement.
Almost all of us—even if we don’t do it consciously—look early in an essay for a one- or two-sentence condensation of the argument or analysis that is to follow. We refer to that condensation as a thesis statement.
Why Should Your Essay Contain a Thesis Statement?
- to test your ideas by distilling them into a sentence or two
- to better organize and develop your argument
- to provide your reader with a “guide” to your argument
In general, your thesis statement will accomplish these goals if you think of the thesis as the answer to the question your paper explores.
How Can You Write a Good Thesis Statement?
Here are some helpful hints to get you started. You can either scroll down or select a link to a specific topic.
How to Generate a Thesis Statement if the Topic is Assigned How to Generate a Thesis Statement if the Topic is not Assigned How to Tell a Strong Thesis Statement from a Weak One
How to Generate a Thesis Statement if the Topic is Assigned
Almost all assignments, no matter how complicated, can be reduced to a single question. Your first step, then, is to distill the assignment into a specific question. For example, if your assignment is, “Write a report to the local school board explaining the potential benefits of using computers in a fourth-grade class,” turn the request into a question like, “What are the potential benefits of using computers in a fourth-grade class?” After you’ve chosen the question your essay will answer, compose one or two complete sentences answering that question.
Q: “What are the potential benefits of using computers in a fourth-grade class?” A: “The potential benefits of using computers in a fourth-grade class are . . .”
A: “Using computers in a fourth-grade class promises to improve . . .”
The answer to the question is the thesis statement for the essay.
[ Back to top ]
How to Generate a Thesis Statement if the Topic is not Assigned
Even if your assignment doesn’t ask a specific question, your thesis statement still needs to answer a question about the issue you’d like to explore. In this situation, your job is to figure out what question you’d like to write about.
A good thesis statement will usually include the following four attributes:
- take on a subject upon which reasonable people could disagree
- deal with a subject that can be adequately treated given the nature of the assignment
- express one main idea
- assert your conclusions about a subject
Let’s see how to generate a thesis statement for a social policy paper.
Brainstorm the topic . Let’s say that your class focuses upon the problems posed by changes in the dietary habits of Americans. You find that you are interested in the amount of sugar Americans consume.
You start out with a thesis statement like this:
Sugar consumption.
This fragment isn’t a thesis statement. Instead, it simply indicates a general subject. Furthermore, your reader doesn’t know what you want to say about sugar consumption.
Narrow the topic . Your readings about the topic, however, have led you to the conclusion that elementary school children are consuming far more sugar than is healthy.
You change your thesis to look like this:
Reducing sugar consumption by elementary school children.
This fragment not only announces your subject, but it focuses on one segment of the population: elementary school children. Furthermore, it raises a subject upon which reasonable people could disagree, because while most people might agree that children consume more sugar than they used to, not everyone would agree on what should be done or who should do it. You should note that this fragment is not a thesis statement because your reader doesn’t know your conclusions on the topic.
Take a position on the topic. After reflecting on the topic a little while longer, you decide that what you really want to say about this topic is that something should be done to reduce the amount of sugar these children consume.
You revise your thesis statement to look like this:
More attention should be paid to the food and beverage choices available to elementary school children.
This statement asserts your position, but the terms more attention and food and beverage choices are vague.
Use specific language . You decide to explain what you mean about food and beverage choices , so you write:
Experts estimate that half of elementary school children consume nine times the recommended daily allowance of sugar.
This statement is specific, but it isn’t a thesis. It merely reports a statistic instead of making an assertion.
Make an assertion based on clearly stated support. You finally revise your thesis statement one more time to look like this:
Because half of all American elementary school children consume nine times the recommended daily allowance of sugar, schools should be required to replace the beverages in soda machines with healthy alternatives.
Notice how the thesis answers the question, “What should be done to reduce sugar consumption by children, and who should do it?” When you started thinking about the paper, you may not have had a specific question in mind, but as you became more involved in the topic, your ideas became more specific. Your thesis changed to reflect your new insights.
How to Tell a Strong Thesis Statement from a Weak One
1. a strong thesis statement takes some sort of stand..
Remember that your thesis needs to show your conclusions about a subject. For example, if you are writing a paper for a class on fitness, you might be asked to choose a popular weight-loss product to evaluate. Here are two thesis statements:
There are some negative and positive aspects to the Banana Herb Tea Supplement.
This is a weak thesis statement. First, it fails to take a stand. Second, the phrase negative and positive aspects is vague.
Because Banana Herb Tea Supplement promotes rapid weight loss that results in the loss of muscle and lean body mass, it poses a potential danger to customers.
This is a strong thesis because it takes a stand, and because it's specific.
2. A strong thesis statement justifies discussion.
Your thesis should indicate the point of the discussion. If your assignment is to write a paper on kinship systems, using your own family as an example, you might come up with either of these two thesis statements:
My family is an extended family.
This is a weak thesis because it merely states an observation. Your reader won’t be able to tell the point of the statement, and will probably stop reading.
While most American families would view consanguineal marriage as a threat to the nuclear family structure, many Iranian families, like my own, believe that these marriages help reinforce kinship ties in an extended family.
This is a strong thesis because it shows how your experience contradicts a widely-accepted view. A good strategy for creating a strong thesis is to show that the topic is controversial. Readers will be interested in reading the rest of the essay to see how you support your point.
3. A strong thesis statement expresses one main idea.
Readers need to be able to see that your paper has one main point. If your thesis statement expresses more than one idea, then you might confuse your readers about the subject of your paper. For example:
Companies need to exploit the marketing potential of the Internet, and Web pages can provide both advertising and customer support.
This is a weak thesis statement because the reader can’t decide whether the paper is about marketing on the Internet or Web pages. To revise the thesis, the relationship between the two ideas needs to become more clear. One way to revise the thesis would be to write:
Because the Internet is filled with tremendous marketing potential, companies should exploit this potential by using Web pages that offer both advertising and customer support.
This is a strong thesis because it shows that the two ideas are related. Hint: a great many clear and engaging thesis statements contain words like because , since , so , although , unless , and however .
4. A strong thesis statement is specific.
A thesis statement should show exactly what your paper will be about, and will help you keep your paper to a manageable topic. For example, if you're writing a seven-to-ten page paper on hunger, you might say:
World hunger has many causes and effects.
This is a weak thesis statement for two major reasons. First, world hunger can’t be discussed thoroughly in seven to ten pages. Second, many causes and effects is vague. You should be able to identify specific causes and effects. A revised thesis might look like this:
Hunger persists in Glandelinia because jobs are scarce and farming in the infertile soil is rarely profitable.
This is a strong thesis statement because it narrows the subject to a more specific and manageable topic, and it also identifies the specific causes for the existence of hunger.
Produced by Writing Tutorial Services, Indiana University, Bloomington, IN
Writing Tutorial Services social media channels

What Is A Literature Review?
A plain-language explainer (with examples).
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) & Kerryn Warren (PhD) | June 2020 (Updated May 2023)
If you’re faced with writing a dissertation or thesis, chances are you’ve encountered the term “literature review” . If you’re on this page, you’re probably not 100% what the literature review is all about. The good news is that you’ve come to the right place.
Literature Review 101
- What (exactly) is a literature review
- What’s the purpose of the literature review chapter
- How to find high-quality resources
- How to structure your literature review chapter
- Example of an actual literature review
What is a literature review?
The word “literature review” can refer to two related things that are part of the broader literature review process. The first is the task of reviewing the literature – i.e. sourcing and reading through the existing research relating to your research topic. The second is the actual chapter that you write up in your dissertation, thesis or research project. Let’s look at each of them:
Reviewing the literature
The first step of any literature review is to hunt down and read through the existing research that’s relevant to your research topic. To do this, you’ll use a combination of tools (we’ll discuss some of these later) to find journal articles, books, ebooks, research reports, dissertations, theses and any other credible sources of information that relate to your topic. You’ll then summarise and catalogue these for easy reference when you write up your literature review chapter.
The literature review chapter
The second step of the literature review is to write the actual literature review chapter (this is usually the second chapter in a typical dissertation or thesis structure ). At the simplest level, the literature review chapter is an overview of the key literature that’s relevant to your research topic. This chapter should provide a smooth-flowing discussion of what research has already been done, what is known, what is unknown and what is contested in relation to your research topic. So, you can think of it as an integrated review of the state of knowledge around your research topic.

What’s the purpose of a literature review?
The literature review chapter has a few important functions within your dissertation, thesis or research project. Let’s take a look at these:
Purpose #1 – Demonstrate your topic knowledge
The first function of the literature review chapter is, quite simply, to show the reader (or marker) that you know what you’re talking about . In other words, a good literature review chapter demonstrates that you’ve read the relevant existing research and understand what’s going on – who’s said what, what’s agreed upon, disagreed upon and so on. This needs to be more than just a summary of who said what – it needs to integrate the existing research to show how it all fits together and what’s missing (which leads us to purpose #2, next).
Purpose #2 – Reveal the research gap that you’ll fill
The second function of the literature review chapter is to show what’s currently missing from the existing research, to lay the foundation for your own research topic. In other words, your literature review chapter needs to show that there are currently “missing pieces” in terms of the bigger puzzle, and that your study will fill one of those research gaps . By doing this, you are showing that your research topic is original and will help contribute to the body of knowledge. In other words, the literature review helps justify your research topic.
Purpose #3 – Lay the foundation for your conceptual framework
The third function of the literature review is to form the basis for a conceptual framework . Not every research topic will necessarily have a conceptual framework, but if your topic does require one, it needs to be rooted in your literature review.
For example, let’s say your research aims to identify the drivers of a certain outcome – the factors which contribute to burnout in office workers. In this case, you’d likely develop a conceptual framework which details the potential factors (e.g. long hours, excessive stress, etc), as well as the outcome (burnout). Those factors would need to emerge from the literature review chapter – they can’t just come from your gut!
So, in this case, the literature review chapter would uncover each of the potential factors (based on previous studies about burnout), which would then be modelled into a framework.
Purpose #4 – To inform your methodology
The fourth function of the literature review is to inform the choice of methodology for your own research. As we’ve discussed on the Grad Coach blog , your choice of methodology will be heavily influenced by your research aims, objectives and questions . Given that you’ll be reviewing studies covering a topic close to yours, it makes sense that you could learn a lot from their (well-considered) methodologies.
So, when you’re reviewing the literature, you’ll need to pay close attention to the research design , methodology and methods used in similar studies, and use these to inform your methodology. Quite often, you’ll be able to “borrow” from previous studies . This is especially true for quantitative studies , as you can use previously tried and tested measures and scales.

How do I find articles for my literature review?
Finding quality journal articles is essential to crafting a rock-solid literature review. As you probably already know, not all research is created equally, and so you need to make sure that your literature review is built on credible research .
We could write an entire post on how to find quality literature (actually, we have ), but a good starting point is Google Scholar . Google Scholar is essentially the academic equivalent of Google, using Google’s powerful search capabilities to find relevant journal articles and reports. It certainly doesn’t cover every possible resource, but it’s a very useful way to get started on your literature review journey, as it will very quickly give you a good indication of what the most popular pieces of research are in your field.
One downside of Google Scholar is that it’s merely a search engine – that is, it lists the articles, but oftentimes it doesn’t host the articles . So you’ll often hit a paywall when clicking through to journal websites.
Thankfully, your university should provide you with access to their library, so you can find the article titles using Google Scholar and then search for them by name in your university’s online library. Your university may also provide you with access to ResearchGate , which is another great source for existing research.
Remember, the correct search keywords will be super important to get the right information from the start. So, pay close attention to the keywords used in the journal articles you read and use those keywords to search for more articles. If you can’t find a spoon in the kitchen, you haven’t looked in the right drawer.
Need a helping hand?
How should I structure my literature review?
Unfortunately, there’s no generic universal answer for this one. The structure of your literature review will depend largely on your topic area and your research aims and objectives.
You could potentially structure your literature review chapter according to theme, group, variables , chronologically or per concepts in your field of research. We explain the main approaches to structuring your literature review here . You can also download a copy of our free literature review template to help you establish an initial structure.
In general, it’s also a good idea to start wide (i.e. the big-picture-level) and then narrow down, ending your literature review close to your research questions . However, there’s no universal one “right way” to structure your literature review. The most important thing is not to discuss your sources one after the other like a list – as we touched on earlier, your literature review needs to synthesise the research , not summarise it .
Ultimately, you need to craft your literature review so that it conveys the most important information effectively – it needs to tell a logical story in a digestible way. It’s no use starting off with highly technical terms and then only explaining what these terms mean later. Always assume your reader is not a subject matter expert and hold their hand through a journe y of the literature while keeping the functions of the literature review chapter (which we discussed earlier) front of mind.

Example of a literature review
In the video below, we walk you through a high-quality literature review from a dissertation that earned full distinction. This will give you a clearer view of what a strong literature review looks like in practice and hopefully provide some inspiration for your own.
Wrapping Up
In this post, we’ve (hopefully) answered the question, “ what is a literature review? “. We’ve also considered the purpose and functions of the literature review, as well as how to find literature and how to structure the literature review chapter. If you’re keen to learn more, check out the literature review section of the Grad Coach blog , as well as our detailed video post covering how to write a literature review .

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
16 Comments
Thanks for this review. It narrates what’s not been taught as tutors are always in a early to finish their classes.
Thanks for the kind words, Becky. Good luck with your literature review 🙂
This website is amazing, it really helps break everything down. Thank you, I would have been lost without it.
This is review is amazing. I benefited from it a lot and hope others visiting this website will benefit too.
Timothy T. Chol [email protected]
Thank you very much for the guiding in literature review I learn and benefited a lot this make my journey smooth I’ll recommend this site to my friends
This was so useful. Thank you so much.
Hi, Concept was explained nicely by both of you. Thanks a lot for sharing it. It will surely help research scholars to start their Research Journey.
The review is really helpful to me especially during this period of covid-19 pandemic when most universities in my country only offer online classes. Great stuff
Great Brief Explanation, thanks
So helpful to me as a student
GradCoach is a fantastic site with brilliant and modern minds behind it.. I spent weeks decoding the substantial academic Jargon and grounding my initial steps on the research process, which could be shortened to a couple of days through the Gradcoach. Thanks again!
This is an amazing talk. I paved way for myself as a researcher. Thank you GradCoach!
Well-presented overview of the literature!
This was brilliant. So clear. Thank you
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Definition of thesis
Did you know.
In high school, college, or graduate school, students often have to write a thesis on a topic in their major field of study. In many fields, a final thesis is the biggest challenge involved in getting a master's degree, and the same is true for students studying for a Ph.D. (a Ph.D. thesis is often called a dissertation ). But a thesis may also be an idea; so in the course of the paper the student may put forth several theses (notice the plural form) and attempt to prove them.
Examples of thesis in a Sentence
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'thesis.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
in sense 3, Middle English, lowering of the voice, from Late Latin & Greek; Late Latin, from Greek, downbeat, more important part of a foot, literally, act of laying down; in other senses, Latin, from Greek, literally, act of laying down, from tithenai to put, lay down — more at do
14th century, in the meaning defined at sense 3a(1)
Dictionary Entries Near thesis
the sins of the fathers are visited upon the children
thesis novel
Cite this Entry
“Thesis.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/thesis. Accessed 22 Aug. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of thesis, more from merriam-webster on thesis.
Nglish: Translation of thesis for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of thesis for Arabic Speakers
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about thesis
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
Plural and possessive names: a guide, 31 useful rhetorical devices, more commonly misspelled words, absent letters that are heard anyway, how to use accents and diacritical marks, popular in wordplay, 8 words for lesser-known musical instruments, it's a scorcher words for the summer heat, 7 shakespearean insults to make life more interesting, 10 words from taylor swift songs (merriam's version), 9 superb owl words, games & quizzes.


International Student & Scholar Services
Office for global engagement, main navigation, post-completion optional practical training (opt).
Learn about the process of applying for Post-Completion OPT to work after graduation.
Navigate ISSS
- Meet an International Student Advisor
- What Is an I-20
- Full-Time Enrollment
- Receiving an Initial I-20
- Reduced Course Load
- Changing Majors
- I-20 Extension
- Reinstatement
- On-Campus Employment
- Social Security Number
- Curricular Practical Training (CPT)
- Volunteer Work & Unpaid Internships
- Post-Completion Optional Practical Training
- Post-Completion OPT Reporting
- 24 Month STEM OPT Extension
- 24 Month STEM OPT Reporting
- H-1B and Cap-Gap Extension
- F-2 Dependents Invitation Letter
- SEVIS Closure Transfer Out Leave of Absence
Students are not allowed to work on or off-campus, paid or unpaid, after your program end date on your I-20 until you receive your EAD card AND your Post-Completion OPT start date on the EAD has begun.
overview and definition
Post-Completion Optional Practical Training (Post-Completion OPT) is designed to provide graduating students an opportunity to gain temporary employment experience within their program of study for one year after completing their program. Permission for this temporary employment is obtained through the United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS). The employment must be directly related to the student's major field of study and appropriate for the level of education. Students may work anywhere in the United States and are required to report their employment .
icon Please note that this is not an entitled benefit. USCIS has the right to deny any OPT application at their discretion. It is the student's responsibility to ensure they are paying the correct fee and filling out the correct application.
icon OPT Workshop Event Details
Attendance is mandatory to avoid any confusion in the process and ask advisors questions. Registration is required through UAtlas and opens 30 days prior to each workshop. Below is a schedule of dates for the 2024 year.
| Spring | 2 PM to 3:30 PM (MST) | |
| Spring | 2 PM to 3:30 PM (MST) | |
| Summer | 11 AM to 12:30 PM (MST) | |
| Fall | 2 PM to 3:30 PM (MST) | |
| Fall | 2 PM to 3:30 PM (MST) | |
| Fall | 11 AM to 12:30 PM (MST) |
return to top of page
Application Review
Students interested in attending walk-in advising are encouraged to come with specific questions to the application but we will not review the entire application. Please review the " Applying for the Post-OPT I-20 " section below.
Eligibility Requirements
icon Lawful Status
Students must have been lawfully enrolled full-time for at least two consecutive semesters and in active F-1 status immediately prior to finishing your degree and applying for OPT.
icon More information can be found in the Frequently Asked Questions under "General."
icon Program End Date
Students must have an anticipated program end date.
icon Graduate with a Degree
Students must be graduating with a Bachelor's, Masters or Ph.D. degree.
icon Non-degree students, students attending certificate programs, and those doing post-doctoral research are not qualified for OPT.
icon Full-Time CPT (12 Months)
Students must not have accumulated more than 12 months of full-time CPT during the student's current degree level. Students are responsible for tracking their full-time CPT months.
Utah Asia Campus (UAC) Students
Students transitioning to the University of Utah main campus from the Asia Campus must have completed two consecutive full-time semesters at the main (Salt Lake City) campus and must be attending the main campus in their final semester to be eligible to apply for OPT.
Processing Time & Expedited Requests (ISSS)
The Post-Completion OPT I-20 will be processed by ISSS within 10 business days once the application is submitted.
ISSS is not able to expedite any request as we strive to provide fair and equitable service to all students. It is the student's responsibility to ensure they submit their request in a timely manner.
Calling or emailing ISSS to ask for your request to be expedited will slow down the process. We ask that you patiently wait until a decision is made.
OPT I-20 (30 Day Validity)
Student must submit the OPT application to USCIS within 30 days from when the I-20 was issued by ISSS. Contact ISSS immediately if you have not submitted your OPT application to USCIS and your I-20 is older than 30 days.
icon To request a new OPT I-20, students must submit a NEW OPT I-20 request to ISSS and not an I-20 Reprint Request.
90 Days of Unemployment
Students on approved Post-OPT are allowed up to 90 days of unemployment during their authorized OPT. Students must work at least 21 hours per week or more to be considered employed full-time. If students work fewer than 20 hours per week, they will be using up unemployment days.
icon If students use up all of their unemployment days, they are considered out of status. Students do not get an additional grace period, and should leave the U.S. before the end of their unemployment period.
SEVP Portal
Students are responsible for notifying USCIS of their employment within 10 days of starting or ending their job. For more information about the SEVP Portal and reporting employment, students are encouraged to navigate to the Reporting Post-Completion OPT page.
Traveling on Post-Completion OPT can be complicated depending on when the student plans to travel and if the application is pending or approved. More information about traveling can be found in our Frequently Asked Questions section.
graduate thesis students
A graduate thesis student who only has the thesis or equivalent remaining may either apply for Pre-completion OPT or Post-Completion OPT while completing the thesis/dissertation. If a student in this situation applies for Pre-completion OPT , he or she:
- May work full-time. 14 SEVP Policy Guidance 1004-003 Updates to Optional Practical Training
- Is not subject to the unemployment provision, and may receive a program extension.
- May not apply for the 24-month extension from a period of Pre-completion OPT.
- Would not be eligible for the cap gap extension of OPT.
Alternatively, if a student in this situation applies for Post-Completion OPT , he or she:
- May work full-time.
- Would be eligible for the cap-gap extension.
- May apply for the 24-month extension if otherwise eligible.
- Would be subject to the unemployment provisions.
- Would be unable to receive an extension of his or her course of study.
Post-completion opt process
Before submitting an e-form to ISSS, the student must attend the Mandatory OPT Workshop to better understand the process of applying for OPT and when to apply for OPT.
Program End Date
The program completion date or program end date is on the student's I-20. Students will apply for OPT based on the semester the students complete program requirements. ISSS will adjust the program completion date on the student's I-20.
icon The program completion date corresponds with the last day of finals and not necessarily the date of the graduation ceremony or degree conferral date.
Graduate Thesis Students
TA/RA/GA: If you apply for Post Completion OPT based on completion of your dissertation requirements, and that date is prior to the last day of finals for your graduating semester you will not be able to continue your assistantship assignment.
The program completion date could fall under one of following:
- The semester the student finishes all required coursework for their degree and only have the thesis/dissertation remaining in the upcoming semester(s).
icon Students who fall under this must continue to be enrolled in thesis credits (3 credits) while working on their dissertation.
- Example : A student finished up all of his required courses for Spring 2024 and wants to apply for OPT while working on their dissertation. The student's program end date is the last day of the Spring 2024 semester and will continue to enroll in thesis credits.
- The last day of the semester the student will defend.
- The student's thesis defense date.
It is recommended that students consult with an ISSS advisor prior to making a final decision.
Apply as Early as Possible
The OPT application window will open 90 days BEFORE the program end date (more information in the next section.) Students will also have the option to apply for OPT up to 60 days (grace period) AFTER the program end date. Students cannot submit an application to USCIS before the 90 day period or after the 60 day period as it will result in a denial.
icon It is recommended that students apply during the 90 day window in order to submit and receive a decision in a timely manner. For processing time, please see the Processing Times from USCIS.
Choosing an OPT Start Date
Students are not eligible to begin working UNTIL the approved OPT start date as listed on the OPT EAD card. The OPT Start Date is only a request and may change.
Before submitting a request to ISSS for an OPT I-20, students must pick a start date for their OPT. The start date must fall between the program end date on the I-20 and the 60-day grace period that follows.
icon Below are some suggestions to help the student make the right decision when picking a start date:
Choosing an Earlier OPT Start Date
Students will choose an earlier start date if they have a job lined up. If the student chooses an earlier start date and cannot find a job quickly, the student is at risk of losing unemployment days. If the student uses up their entire 90 days of unemployment they will need to leave the U.S.
Choosing a Later OPT Start Date
Most students will choose this option so that they have more time to find a job and have a less chance to be unemployed for 90 days.
Post-Completion OPT Application Timeline

Applying for the post-opt i-20 & Form I-765 (Uscis)
Login to UAtlas
Complete the Post or Pre Completion I-20 Request e-form and indicate "Post-Completion OPT."
A Designated School Official (DSO) from ISSS will review the completed application. Once the DSO receives the completed application, they will process it within 10 business days. DSOs will review the student's application, course enrollment and once the application is approved, the student will receive an email from ISSS.
Receiving the OPT I-20 Once the OPT request is approved, the DSO will send the I-20 electronically through UAtlas. As soon as the student receives the I-20, they must review the information on pages 1 and 2 of the I-20. Pay particular attention to the Program of Study information on page 1 and the OPT information (including requested dates) on page 2. If everything looks accurate, students should immediately print and sign and date at the bottom of page 1 in the Student Attestation section of the I-20 and scan it for the application. icon The OPT I-20 that is issued by ISSS is only valid for 30 days. Students will need to apply for OPT before the OPT I-20 is considered "old." Students who have an old OPT I-20 will need to submit a new request to ISSS. Do NOT file for OPT with USCIS using an OPT I-20 that is more than 30 days old. We recommend that you submit it well before it reaches the 30 day mark. More information can be found in our policy section under OPT I-20 (30 Day Validity) .
Prepare OPT Application for USCIS Students are required to attend an OPT Workshop by ISSS to avoid confusion and filling out the application incorrectly. ISSS will not offer one-on-one application reviews. More information can be found at the top of the page under workshops or can be found in our Events Calendar . Below, students will have the option to either send the application by mail or online. Students cannot do both options: icon F-1 students wanting to avoid Form I-765 Delays are encouraged to review the tip sheet provided by the Office of the Citizenship and Immigraiton Services Ombudsman. HOW F-1 STUDENTS SEEKING OPTIONAL PRACTICAL TRAINING CAN AVOID FORM I-765 DELAYS
Online (Highly Recommended)
Students are required to review our guide on how to fill out an application where we have compiled all the questions taken from the application into one document and provided additional information for each question.
Online application: form i-765 how-to-guide
Collect Documents to mail with the I-765 paper application to USCIS (in the recommended order):
- G -1145 (for paper application only) - Downloadable from https://www.uscis.gov/g-1145 . By completing this form, you are requesting an email or text message to be sent to you when your application arrives at the USCIS office. Place this on the top of your application so they are aware of your request.
- Two U.S. passport type photographs - photos must be taken within the past 30 days and may not be the same photos used for other government requests, such as passport or visa renewals. Print your name and I-94 number clearly on the back of each photo and make sure to not damage the photos. USCIS recommends you use a pencil and write the information lightly but readable. Put the photos in an envelope and attach it to front of I-765 and indicate on the envelope the photos are inside. Ensure the photos meet U.S. passport requirements. Photos from your home country may not be the correct size or may be too old to be used.
- Application Fee - In the form of check or money order, made to the U.S. Department of Homeland Security. You can find the appropriate fee by using the USCIS Fee Calculator https://www.uscis.gov/feecalculator , select “I-765”, “Permission to accept Employment”, “Foreign Students” then “(c)(3)(B)” for Post-Completion OPT. The fee can also be found at https://www.uscis.gov/i-765 .
- Form I-765 - download the form at https://www.uscis.gov/i-765 under "Forms and Document Downloads." Instructions on how to complete this form are in the I-765 Instructions guide. Also use the I-765 webpage to confirm the edition date of your Form I-765 is acceptable to USCIS. You can find a Post-Completion OPT mock I-765 form below:
Paper application opt: sample
- Post-Completion OPT I-20 issued from ISSS with your requested dates (Remember: USCIS must receive it within 30 days from the issue date). Make sure you sign and date your Post-Completion OPT I-20.
- Valid passport identification page (and the expiration date page if it’s on a separate page).
- F-1 Visa - the most recent F-1 visa issued to you.
- I-94 (obtainable at https://i94.cbp.dhs.gov/I94/#/home)
- Previous EAD card , include a copy of the front and back (only if you have been approved for OPT in the past)
Submit Payment
The options are below (This is only a guideline, ISSS is not liable for incorrect payments submitted to USCIS)
- Personal Check - Must be made to "U.S. Department of Homeland Security." Under "For" you will list the SEVIS ID (starts with N, found on your I-20), OPT
- Pay to "U.S. Department of Homeland Security". If the money order asks for the recipient address, you should list the address where you are mailing your application.
- In the Memo/Payment For Section, put "Your SEVIS ID Number, OPT"
- In the bottom right corner, sign your name in the "From" section.
- In the money order asks for your purchaser's address, include your mailing address noted on your I-765 application form.
- Keep the receipt portion of the money order for your records as that is the only way to track your payment.
- Do not sign the back of the money order as it will void the payment.
Mail Documents to USCIS
- Keep copies of everything you mail for your own record.
- Mail all the required documents (listed on page 5) to USCIS. USCIS must receive your application within 30 days from when your Post-Completion OPT I-20 was issued.
- If USCIS receives your packet earlier than 90 days before your program completion date or later than 60 days after your program end date, as listed on the OPT I-20, the packet may be rejected right away or worse, be denied about 3 months later.
- To find the appropriate mailing address, please refer to USCIS website: https://www.uscis.gov/i-765 . Also use the I-765 webpage to confirm the edition date of your Form I-765 is acceptable to USCIS.
- If you receive I-797 receipt, keep it in a safe place as it is proof of your pending Post-Completion OPT application and allows you to remain in the United States after your program has ended.
After receiving approval for post-opT
icon Do not start employment BEFORE receiving the Employment Authorization Document (EAD) Card.
Review the Reporting Requirements for Post-Completion OPT Students are required to understand the requirements to report while on OPT by reviewing the Reporting Requirements for Post-Completion OPT page.
Post-Completion OPT - Frequently Asked Questions
How long will my post-completion opt application take to process.
Applying for Post-Completion OPT is a two-step process. You must first obtain your Post-Completion OPT I-20 from International Student & Scholar Services (ISSS), which has 10 business day processing time, and then mail your application with all the required documents to USCIS to obtain an Employment Authorization Document (EAD) card, which takes an average of 3-5 months to process.
When should I submit my Post-Completion OPT application?
You must apply for Post-Completion OPT no earlier than 90 days before your program end date and no later than 60 days after your program end date. If you send in your Post-Completion OPT application more than 90 days before your program ends or after your 60-day grace period is over, your request will be denied by USCIS.
When is my program end date?
For undergraduate and non-thesis graduate students, the program end date is the last day of your final semester (last day of final exams) meaning the semester that you complete your last classes needed to meet graduation requirements. You cannot continue enrollment or delay graduation once requirements have been met. If you are a double-major, you must seek advising from ISSS to clarify your program end date – you should do this before your last semester. For thesis graduate students, the program completion date can be the last day of your defense semester or your defense date. Graduate thesis students are eligible for Post-Completion OPT after they have defended their thesis. It is not necessary to have graduated or obtained a diploma to apply for Post-Completion OPT.
Is there a deadline for applying to USCIS with my new I-20?
You need to have your complete Post-Completion OPT application received by the appropriate USCIS Service Center within 30 days of the Post-Completion OPT I-20 issue date by ISSS. Applications that arrive after the 30 days will be rejected or denied at a later date. You will miss your opportunity to participate in Post-Completion OPT if you cannot refile before your grace period ends.
I have a job offer but my EAD card has not arrived yet. Can I begin work?
No. You must have received your EAD card to show that you have legal work status. Any employment done before the EAD card has arrived is illegal and may harm Post-Completion OPT as well as your future chances of obtaining an H-1B visa, permanent residency or other types of benefits from immigration. You are not allowed to work on or off-campus, paid or unpaid, after your program end date on your I-20 until you receive your EAD card AND your Post-Completion OPT start date on the EAD has begun.
How can my past CPT participation affect my Post-Completion OPT?
You are not eligible for Post-Completion OPT if you have participated in 12 months or more of full-time CPT. Past participation in part-time CPT or full-time CPT for less than 12 months should not affect your Post-Completion OPT eligibility unless USCIS determines CPT was used to facilitate employment rather than to serve as a temporary internship opportunity.
Can I do CPT during my last semester? Will it affect my OPT?
Students may participate in full or part time CPT in their last semester but they must maintain a physical presence on campus in Salt Lake City and may not participate in CPT in another state. Students approved for CPT may not work past the CPT end date. Graduate thesis students may not participate in CPT once they have defended. Be aware that CPT employment in the last semester should be added to your I-20 before you request an OPT I-20. Requesting CPT after filing for OPT with USCIS can complicate your OPT application and may raise a red flag with immigration. Speak with an ISSS advisor for details. Also, be aware that USCIS forbids using CPT in the last semester as a way to start OPT employment “early” or to otherwise facilitate OPT employment. If you have questions, speak with an ISSS advisor.
What is the 14- month rule for Post-Completion OPT?
Federal regulations state that Post-Completion OPT must be completed within 14 months of your program end date. If you decide to apply for Post-Completion OPT AFTER the completion date of your program, USCIS may still take 90 days to process the I-765 application. The time that USCIS takes to adjudicate your request will be taking time away from when you would have been working on OPT. This means that if the processing time for your Post-Completion OPT goes beyond the 60 days past your program end date on the front of your I-20, this time will be deducted from your 12 months of OPT.
Does the job I have while on OPT have to be paid employment, or can it be unpaid?
For Post-Completion OPT, the employment does NOT have to be paid employment, although it is recommended. Interning or volunteering in a position directly related to the academic field is considered “employment” for the purposes of Post-Completion OPT employment. To apply for the 24-month STEM extension, work must be paid employment with an E-Verify employer at least 21 hours per week.
If I complete one degree program, take 12 months of Post-Completion OPT then begin a second course of study, am I eligible for an additional 12 months of practical training?
After completing one year of Post-Completion OPT, you must complete a higher academic level (Bachelors, Masters, or Ph.D.) before you are eligible for another OPT. If you complete a second degree at the same level and if you already applied and have been approved for Post-Completion OPT at that level, you are not eligible for a second Post-Completion OPT after completing the second degree. If you complete a Ph.D. degree, you may not apply for a Masters level OPT even if you have never participated in the OPT on that level before, rather you must apply for OPT based on your Ph.D. degree.
Do I get a grace period after my Post-Completion OPT?
Yes, your lawful F-1 status expires 60 days after your last day of Post-Completion OPT. During your 60-day grace period, you may not engage in any employment or studies. You are expected to depart the country at the end of the 60 days or else be in pending status for a new degree program or a new visa status or have transferred your SEVIS record out. Note that if you will begin a new program at the University of Utah, your new program I-20 must be issued before your grace period ends or you will be out of status and will need to depart the U.S. If you exit the country during your 60- day grace period, you may not re-enter on your F-1 Post-Completion OPT I-20. Please note that if you decide to end your Post-Completion OPT early or have accrued more than 90 days of unemployment days, you are not eligible for a 60 day grace period and must depart U.S. as soon as possible.
What if I change my mind and I want to cancel my application for Post-Completion OPT? Or what happens if I wasn’t able to graduate?
The answer to this question varies on many factors. Please meet with an ISSS advisor to discuss your options.
What if I have lost or thrown away my old I-20s?
International Student & Scholar Services may have copies of your old I-20s in your file. You can request that ISSS make you copies of your old I-20s by completing the “Request for Document Copies” e-form, but keep in mind that it could take up to a week to process your request. It is always your responsibility to keep your I-20s. Your file may or may not contain copies of the documents you are looking for. It is best if you maintain a well-kept file of your documents in a safe place. Keep in mind you only need to submit I-20s at your current degree level for your OPT application. If you are missing I-20s, please submit what you currently have as including previous I-20s is a recommendation, not a requirement for the OPT application.
Since I need to move and don’t know my new address, can I put a foreign address on I-765 form?
No, USCIS requires you indicate an address in the United States. The address you use may be a friend’s address or a P.O. Box. If you use a friend’s address, you must put their name in the “in care of name” field on page 2 of the I-765. Contact ISSS if you have further questions about your mailing address.
How can I check on the status of my application?
When USCIS sends you your I-797 receipt notice in the mail, you will receive a receipt number. You can use this number to access information about your application at the USCIS Case Status page.
What happens to my dependents, who are on F-2 visas, during the application and Post-Completion OPT process?
If you are granted the Post-Completion OPT work authorization and you are still in legal F-1 immigration status, then your dependents are still in legal F-2 immigration visa status. You will receive new I-20s for yourself and all dependents if you are eligible for the Post-Completion OPT work authorization. If you do not follow F-1 regulations while on Post-Completion OPT and fall out of status, your F-2 dependents automatically fall out of status with you.
Terminated Status
Students who have decided to depart the country and re-enter with a new I-20 in order to reinstate their status will lose any time they have accrued toward qualification for Post-OPT. In other words, students who travel to reinstate are subject to another full academic year (2 full-time semesters) to be eligible for OPT or CPT.
Can I apply for OPT if received a second degree at the same education level?
Students who have been previously approved for Post-Completion OPT in the same degree level cannot re-apply for OPT at that same level.
For example, a student was previously approved for a Bachelor's OPT, afterward the student wanted to get a second Bachelor's degree, they are not eligible to apply for OPT for that second degree since it is the same degree level.
Can I use OPT again if I complete a bachelors degree and use OPT and then complete a masters degree?
Yes, students can apply for OPT once per education degree level.
Can I travel home (or anywhere outside of the U.S.) after I graduate?
The answer to this question depends on if you have applied for Post-Completion OPT and where you are in that process:
Have not applied for Post-Completion OPT
If you have not applied yet, you may leave the U.S. during your grace period but you will not be allowed to return on your F-1 student visa and you also will lose the opportunity to apply for Post-Completion OPT. If you wish to return to the U.S. on your student visa and participate in Post-Completion OPT, you must send in your application and wait for Post-Completion OPT approval before traveling outside of U.S.
Your Post-Completion OPT is pending
If you have a pending Post-Completion OPT application and it is after your program end date, it is very strongly recommended that you do NOT travel until your request has been approved by USCIS If you do depart U.S., please understand that entry into the U.S. is granted at the discretion of the U.S. Customs and Border Protection officer, and you travel at your own risk. If you still wish to travel while your Post-Completion OPT is pending, please speak with an ISSS advisor about the risks involved.
Your Post-Completion OPT has been approved
After you have received your EAD card, your travel documents should include your signed Post-Completion OPT I-20, valid F-1 visa, a passport valid for at least six months, EAD card, and a letter from your employer (if applicable). The letter should state that they have employed you or plan on employing you, and you are coming back to the U.S. to work for them.
Note: When you receive your EAD card it will say, “Not valid for travel”. This means besides your EAD card, you will need your I-20, valid passport, and visa in order to travel.
These same rules apply for both the Post-Completion OPT and the 24 month STEM extension. Please understand that entry into the U.S. is granted at the discretion of the U.S. Customs and Border Protection officer, and you travel at your own risk.
Dependent travel
Since Post-Completion OPT is not noted on dependent I-20s, an F2 dependent must carry copies of the F-1 student’s I-20 with Post-Completion OPT recommendation, EAD card, and proof of employment, in addition to their own F-2 I-20 when traveling
What documents should I travel with?
You should always travel with valid passport, valid F-1 visa, most recent I-20 with a travel signature, EAD card, and if applicable, your job offer letter. Please refer to our Travel page for more information for OPT.
I want to leave the U.S. for a short time while my Post-Completion OPT application is in process, but I need to return before the card will arrive. I have a tourist visa (B2) that is valid for 10 years. Can’t I just enter the U.S. on my tourist visa while I’m waiting to get the EAD card, and then start work with the card once I get it?
NO!! If you intend to continue working on your Post-Completion OPT authorization, NEVER enter in any other immigration status except F-1. If you leave the U.S. and re-enter with any other status than F-1, you will immediately forfeit your F-1 status. This means your Post-Completion OPT will be invalid.
Can I renew my F-1 visa while on Post-Completion OPT?
It is possible and many students on Post-Completion OPT get their F-1 visa stamps renewed. You do have to be careful to demonstrate non-immigrant intent. The risk of denial of an application for a renewed visa stamp for Post-Completion OPT is somewhat higher than while you are in your active student program. The F-1 student visa requires that the applicant must intend to return to the home country at the end of the program, and if the embassy official is not convinced of your intention to return home, the visa application could be denied.
What documents do I need to show at the embassy for a new visa stamp under Post-Completion OPT?
You need to take a valid passport, your EAD card, your Post-Completion OPT I-20 issued by ISSS, and your job offer letter or proof of employment (if applicable). You should also be prepared to discuss how this job experience will apply to the job market in your home country, and how you intend to apply it there. You should find additional information about required documents at your embassy’s website before your visa renewal appointment.
Do I still need a travel signature to travel if I am on Post-Completion OPT?
Yes. During Post-Completion OPT, if you travel outside the U.S., your I-20 must be signed for travel. The current travel signature on page 2 of your I-20 is valid for 6 months. If you return after this date, you may be denied reentry. For more information should check out our Travel page.
How do I report my employment?
You are required to report your employment to SEVP within 10 days of beginning a new job. For more information about reporting are encouraged to review our Reporting Post-Completion OPT page .
How do I get access to the SEVP Portal?
SEVP will send you an email to your UMail account on the date that your Post-Completion OPT employment begins. This email will instruct you on how to register your portal account. You must register your account within 14 days of receiving the email. If you do not receive an email, check your junk or spam folders. For more information about the portal are encouraged to review the Reporting Post-Completion OPT page.
What type of employment can I accept? Does it have to be paid?
Your job must be related to your major. Your employment may or may not be paid while on Post-Completion OPT.
Do I need to have job offer to apply for Post-Completion OPT?
You don’t need a job offer to apply for Post-Completion OPT.
Do I need to have a job while I am on Post-Completion OPT?
Yes, you do need to be employed while on Post-Completion OPT. You are only allowed to have a total of 90 days of unemployment during approved Post-Completion OPT time. This total number of unemployment days applies through the entire period of Post-Completion OPT. If you have already used 30 days of unemployment on Post-Completion OPT and you lost your job 6 months into Post-Completion OPT, you then have 60 days of unemployment days left to find a job. Remember to report all employment changes to the SEVP portal
What if I can’t find a full-time job?
USCIS considers full-time work to be at least 21 hours or more per week. If you are working less than this, it is considered as unemployment time. ISSS strongly recommends students that are nearing the 90 days of unemployment apply for an internship (paid or unpaid) of at least 21 hours per week. Interning or volunteering in a position directly related to your academic field can be considered “employment” for the purpose of Post Completion OPT employment. Keep in mind, however, that you must be working in a paid position for an E-verified employer in order to apply for STEM OPT (if you are otherwise eligible)
Can I work multiple jobs?
Yes, each must be related to the student's major and must be properly reported in the SEVP Portal.
Attending School
I’m finished with my post-completion opt and i want to return to school. what do i need to know.
If you wish to return to school after you finish Post-Completion OPT, you must obtain a new I-20 from the International Admissions Office within 60 days of your OPT end date. You must begin classes within the next available semester or within 5 months, whichever is sooner. If you are changing schools, you must request that we transfer your SEVIS record within 60 days of your Post-Completion OPT end date.
Students are allowed to take classes while on Post-Completion OPT, but these classes must be avocational in nature (for example, a cooking or exercise class) and may not be part of a new degree and will not count towards maintaining your F-1 status. If you are admitted into a new degree program, you will get a new I-20 and your Post-Completion OPT will be canceled.
Can I take classes while remaining on Post-Completion OPT?
Students are allowed to take classes while on Post-Completion OPT, but these classes must be avocational in nature (for example, a cooking or exercise class) and may not be part of a new degree program. If you are admitted into a new degree program, you will need a new I-20 and your Post-Completion OPT will be canceled once the new program begins. Even if you don’t get a new I-20 because you are not transferring your SEVIS record or studying at the University of Utah, USCIS can still see this as a violation of status if you remain on OPT.
Can I take extra classes while on Post-Completion OPT?
Can i transfer to a new school while on post-completion opt.
Students can transfer their SEVIS record to a new school while on Post-Completion OPT. Once you transfer your record to the new school, your Post-Completion OPT will automatically terminate and you will not able to engage in employment until authorized to do so from the new school. Please speak with ISSS advisor if you have any concerns or questions. Students are encouraged to review our Transfer page.
Thesis Students
Can a student in a graduate-level program who has completed all program requirements, aside from thesis or equivalent, apply for either pre-completion opt or post-completion opt.
Yes, a student who only has the thesis or equivalent remaining may either apply for Pre-completion OPT or post-completion OPT while completing the thesis/dissertation. If a student in this situation applies for Pre-completion OPT, he or she:
Alternatively, if a student in this situation applies for Post-Completion OPT, he or she:
If a student does not complete his or her thesis/dissertation during the 12 months of post-completion OPT and are not eligible for STEM Extension, what steps must he or she take?
The student should prepare to change status, change education level and/or transfer, or depart the country prior to the end of the 60 day grace period.
When is my final semester?
Your final semester would be the semester you pass your final defense to meet the graduation requirement. If you have already declared your last semester with ISSS but your plans changed, please reach out to ISSS immediately.
I defended, but my thesis has not yet been approved by the Thesis Office. Can I apply for Post-Completion OPT?
Yes, since you have successfully defended, you are considered to have met the graduation requirement and you should apply for Post-Completion OPT. Please keep in mind that if you are STEM eligible, you are required to show a copy of your diploma when applying for STEM OPT. Therefore, it is recommended that you work with the Thesis Office closely to ensure it is approved before you apply for STEM OPT

IMAGES
COMMENTS
A thesis statement is a very common component of an essay, particularly in the humanities. It usually comprises 1 or 2 sentences in the introduction of your essay, and should clearly and concisely summarize the central points of your academic essay. A thesis is a long-form piece of academic writing, often taking more than a full semester to ...
To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough. Note.
Thesis. Definition: Thesis is a scholarly document that presents a student's original research and findings on a particular topic or question. It is usually written as a requirement for a graduate degree program and is intended to demonstrate the student's mastery of the subject matter and their ability to conduct independent research.
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
A thesis is an in-depth research study that identifies a particular topic of inquiry and presents a clear argument or perspective about that topic using evidence and logic. Writing a thesis showcases your ability of critical thinking, gathering evidence, and making a compelling argument.
A thesis statement is a sentence in a paper or essay (in the opening paragraph) that introduces the main topic to the reader. As one of the first things your reader sees, your thesis statement is one of the most important sentences in your entire paper—but also one of the hardest to write! In this article, we explain how to write a thesis ...
Craft a convincing dissertation or thesis research proposal. Write a clear, compelling introduction chapter. Undertake a thorough review of the existing research and write up a literature review. Undertake your own research. Present and interpret your findings. Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications.
A thesis statement . . . Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic. Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper. Is focused and specific enough to be "proven" within the boundaries of your paper. Is generally located near the end ...
Harvard College Writing Center 1 Thesis Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic. Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim.
Definition: Dissertation overview. The overwhelming majority of undergraduate and postgraduate taught courses require the submission of a dissertation to pass. A dissertation will take ca. 6~18 months to complete, usually covering ca. 5000-15,000 words. You can expect to receive your assignment and deadline during the last third of your timetable.
A typical thesis structure. 1. Abstract. The abstract is the overview of your thesis and generally very short. This section should highlight the main contents of your thesis "at a glance" so that someone who is curious about your work can get the gist quickly. Take a look at our guide on how to write an abstract for more info.
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
Elaborate a thesis statement. The thesis statement. is the most important part. This is a sentence usually placed at the beginning of the summary and it is aimed at clarifying the main research questions of your work. The thesis statement must be clear and concise. MA theses, but also PhD dissertations, usually concern very narrow topics.
An analytical paper breaks down an issue or an idea into its component parts, evaluates the issue or idea, and presents this breakdown and evaluation to the audience.; An expository (explanatory) paper explains something to the audience.; An argumentative paper makes a claim about a topic and justifies this claim with specific evidence. The claim could be an opinion, a policy proposal, an ...
A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a PhD program in the UK. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Indeed, alongside a dissertation, it is the longest piece of writing students typically complete. It relies on your ability to conduct research from start to ...
A good thesis has two parts. It should tell what you plan to argue, and it should "telegraph" how you plan to argue—that is, what particular support for your claim is going where in your essay. Steps in Constructing a Thesis. First, analyze your primary sources. Look for tension, interest, ambiguity, controversy, and/or complication.
A thesis statement makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of the paper. It summarizes the conclusions that the writer has reached about the topic. A thesis statement is generally located near the end of the introduction. Sometimes in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or an entire ...
This is a short paragraph at the end of your introduction to inform readers about the organizational structure of your thesis or dissertation. This chapter outline is also known as a reading guide or summary outline. Tip You can find a thesis and dissertation outline template below, as well as a chapter outline example, and example sentences ...
The kind of thesis statement you write will depend on the type of paper you are writing. Here is how to write the different kinds of thesis statements: Argumentative Thesis Statement: Making a Claim. Analytical Thesis Statement: Analyzing an Issue. Expository Thesis Statement: Explaining a Topic.
A thesis statement should show exactly what your paper will be about, and will help you keep your paper to a manageable topic. For example, if you're writing a seven-to-ten page paper on hunger, you might say: World hunger has many causes and effects. This is a weak thesis statement for two major reasons.
The word "literature review" can refer to two related things that are part of the broader literature review process. The first is the task of reviewing the literature - i.e. sourcing and reading through the existing research relating to your research topic. The second is the actual chapter that you write up in your dissertation, thesis or ...
The meaning of THESIS is a dissertation embodying results of original research and especially substantiating a specific view; especially : one written by a candidate for an academic degree. How to use thesis in a sentence.
overview and definition. Post-Completion Optional Practical Training (Post-Completion OPT) is designed to provide graduating students an opportunity to gain temporary employment experience within their program of study for one year after completing their program. ... graduate thesis students. ... meaning the semester that you complete your last ...
Thesis. Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic. Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore ...
Methodology. Our study involved six countries familiar to our research team (Table 1), allowing investigation of the Thesis by Publication in different national and linguistic contexts and at different stages in terms of acceptance and adoption.For each country, we began by identifying all public universities with doctoral programmes, and determining the presence of a Thesis by Publication ...
Canada's two largest railroads shut down Thursday morning in response to a labor dispute that could quickly have dire consequences for the U.S. economy.