Sustainable HRM and well-being: systematic review and future research agenda
- Published: 14 July 2023

Cite this article

- Faisal Qamar ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4916-8229 1 ,
- Gul Afshan ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0016-5721 1 &
- Salman Anwar Rana 1
1677 Accesses
9 Citations
Explore all metrics
This paper attempts to undertake a systematic literature review to identify ways and means by which sustainable human resource management (HRM) and well-being are linked for better individual and organizational outcomes. Its primary focus is to study whether sustainable HRM predicts well-being at work? If yes, how and when this prediction takes place? Systematic computerized search and review were conducted for articles published until December 2022. A total of 134 research articles were finally selected. It was found that sustainable HRM predicts well-being at work. However, our findings suggest that the area is largely underexplored and empirical work is too rare. Although few moderators and mediators are examined, research is required to propose and test more comprehensive models with more robust research designs and sophisticated theoretical links.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others
Moving beyond the link between hrm and economic performance: a study on the individual reactions of hr managers and professionals to sustainable hrm.

Creating Sustainable Human Resource Management Systems for High-Performance Work Culture

Practitioner’s View on Sustainability and HRM
Explore related subjects.
- Artificial Intelligence
Data availability
Information/data of all the research papers analysed during this study are included in the body of this manuscript and its appendix. Any further information related to earlier research papers considered for this review are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Aboramadan M, Kundi YM, Becker A (2021) Green human resource management in nonprofit organizations: effects on employee green behavior and the role of perceived green organizational support. Pers Rev Ahead-of-Print. https://doi.org/10.1108/PR-02-2021-0078
Article Google Scholar
Adjei-Bamfo P, Bempong B, Osei J, Kusi-Sarpong S (2020) Green candidate selection for organizational environmental management. Int J Manpow 41:1081–1096. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJM-10-2019-0480
Agarwal V, Mathiyazhagan K, Malhotra S, Saikouk T (2021) Analysis of challenges in sustainable human resource management due to disruptions by Industry 4.0: an emerging economy perspective. Int J Manpow. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJM-03-2021-0192
Ahmad I, Umrani WA (2019) The impact of ethical leadership style on job satisfaction. Leadersh Organ Dev J 40:534–547. https://doi.org/10.1108/LODJ-12-2018-0461
Al Kerdawy MMA (2019) The role of corporate support for employee volunteering in strengthening the impact of green human resource management practices on corporate social responsibility in the Egyptian Firms. Eur Manag Rev 16:1079–1095. https://doi.org/10.1111/emre.12310
Al Marzouqi AH, Khan M, Hussain M (2020) Employee social sustainability: prioritizing dimensions in the UAE’s airlines industry. Soc Responsib J 16:349–367. https://doi.org/10.1108/SRJ-07-2018-0166
Alberton A, Kieling AP, Lyra FR, Hoffmann EM, Lopez MPV, Stefano SR (2020) Competencies for sustainability in hotels: insights from Brazil. Empl Relat Int J. https://doi.org/10.1108/ER-01-2019-0093
Alcaraz JM, Susaeta L, Suarez E, Colon C, Gutiérrez-Martínez I, Cunha R, Leguizamón F, Idrovo S, Weisz N, Correia MF (2019) The human resources management contribution to social responsibility and environmental sustainability: explorations from Ibero-America. Int J Hum Resour Manag 30:3166–3189
Almarzooqi AH, Khan M, Khalid K (2019) The role of sustainable HRM in sustaining positive organizational outcomes. Int J Product Perform Manag 68:1272–1292. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJPPM-04-2018-0165
Al-Minhas U, Ndubisi NO, Barrane FZ (2020) Corporate environmental management. Manag Environ Qual Int J 31:431–450. https://doi.org/10.1108/MEQ-07-2019-0161
Alvarez-Risco A, Estrada-Merino A, Perez-Luyo R (2020) Sustainable development goals in hospitality management. In: Ruël H, Lombarts A (eds) Sustainable hospitality management. Emerald Publishing Limited, pp 159–178
Chapter Google Scholar
Amrutha V, Geetha S (2020) A systematic review on green human resource management: Implications for social sustainability. J Clean Prod 247:119131
Anlesinya A, Amponsah-Tawiah K (2020) Towards a responsible talent management model. Eur J Train Dev 44:279–303. https://doi.org/10.1108/EJTD-07-2019-0114
Anlesinya A, Susomrith P (2020) Sustainable human resource management: a systematic review of a developing field. J Glob Responsib
App S, Büttgen M (2016) Lasting footprints of the employer brand: can sustainable HRM lead to brand commitment? Empl Relat 38:703–723. https://doi.org/10.1108/ER-06-2015-0122
Ardichvili A (2012) Sustainability or limitless expansion: paradigm shift in HRD practice and teaching. Eur J Train Dev 36:873–887. https://doi.org/10.1108/03090591211280946
Arnold KA (2017) Transformational leadership and employee psychological well-being: a review and directions for future research. J Occup Health Psychol 22:381
Au WC, Ahmed PK (2014) Sustainable people management through work-life balance: a study of the Malaysian Chinese context. Asia-Pac J Bus Adm 6:262–280. https://doi.org/10.1108/APJBA-02-2014-0024
Aust I, Matthews B, Muller-Camen M (2020a) Common Good HRM: A paradigm shift in Sustainable HRM? Hum Resour Manag Rev 30:100705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr.2019.100705
Aust I, Matthews B, Muller-Camen M (2020b) Common Good HRM: A paradigm shift in Sustainable HRM? Sustain Hum Resour Manag Triple Bottom Line Multi-Stakehold Strateg Concepts Engagem 30:100705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr.2019.100705
Barrena-Martínez J, López-Fernández M, Romero-Fernández PM (2019) Towards a configuration of socially responsible human resource management policies and practices: Findings from an academic consensus. Int J Hum Resour Manag 30:2544–2580
Baum T, Hai NTT (2019) Applying sustainable employment principles in the tourism industry: righting human rights wrongs? Tour Recreat Res 44:371–381
Google Scholar
Beer M, Boselie P, Brewster C (2015) Back to the future: implications for the field of HRM of the multistakeholder perspective proposed 30 years ago. Hum Resour Manage 54:427–438. https://doi.org/10.1002/hrm.21726
Bondarouk T, Brewster C (2016) Conceptualising the future of HRM and technology research. Int J Hum Resour Manag 27:2652–2671
Brannon DW, Burbach R (2021) Sustaining hospitality talent pools through a common pool resource lens. In: Jooss S, Burbach R, Ruël H (eds) Talent management innovations in the international hospitality industry. Emerald Publishing Limited, pp 53–78
Brunetto Y, Farr-Wharton B, Wankhade P, Saccon C, Xerri M (2022) Managing emotional labour: the importance of organisational support for managing police officers in England and Italy. Int J Hum Resour Manag 1–23
Bush JT (2020) Win-Win-Lose? Sustainable HRM and the promotion of unsustainable employee outcomes. Hum Resour Manag Rev 30:100676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr.2018.11.004
Cabral C, Dhar RL (2021) Green competencies: insights and recommendations from a systematic literature review. Benchmark Int J 28:66–105. https://doi.org/10.1108/BIJ-11-2019-0489
Caldana ACF, Eustachio JHPP, Lespinasse Sampaio B, Gianotto ML, Talarico AC, da Batalhão SAC (2021) A hybrid approach to sustainable development competencies: the role of formal, informal and non-formal learning experiences. Int J Sustain High Educ. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJSHE-10-2020-0420
Chams N, García-Blandón J (2019) On the importance of sustainable human resource management for the adoption of sustainable development goals. Resour Conserv Recycl 141:109–122
Chaudhary R (2019) Green human resource management and job pursuit intention: examining the underlying processes. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag 26:929–937. https://doi.org/10.1002/csr.1732
Chaudhary R (2020) Corporate social responsibility and employee performance: a study among indian business executives. Int J Hum Resour Manag 31:2761–2784
Chillakuri B (2020) Understanding generation Z expectations for effective onboarding. J Organ Change Manag 33:1277–1296. https://doi.org/10.1108/JOCM-02-2020-0058
Chillakuri B, Vanka S (2020) Understanding the effects of perceived organizational support and high-performance work systems on health harm through sustainable HRM lens: a moderated mediated examination. Empl Relat Int J Ahead-of-Print. https://doi.org/10.1108/ER-01-2019-0046
Chillakuri B, Vanka S (2021) Examining the effects of workplace well-being and high-performance work systems on health harm: a sustainable HRM perspective. Soc Bus Rev 16:71–93. https://doi.org/10.1108/SBR-03-2020-0033
Christina S, Dainty A, Daniels K, Tregaskis O, Waterson P (2017) Shut the fridge door! HRM alignment, job redesign and energy performance. Hum Resour Manag J 27:382–402. https://doi.org/10.1111/1748-8583.12144
Clarke M (2011) Readings in HRM and Sustainability. Melb Tilde 117–132
Cook DJ, Mulrow CD, Haynes RB (1997) Systematic reviews: synthesis of best evidence for clinical decisions. Ann Intern Med 126:376–380
Cooke FL, Dickmann M, Parry E (2020) IJHRM after 30 years: taking stock in times of COVID-19 and looking towards the future of HR research. Int J Hum Resour Manag 32:1–23
Cooke FL, Xiao M, Chen Y (2021) Still in search of strategic human resource management? A review and suggestions for future research with China as an example. Hum Resour Manage 60:89–118
Cooper B, Wang J, Bartram T, Cooke FL (2019) Well-being-oriented human resource management practices and employee performance in the Chinese banking sector: The role of social climate and resilience. Hum Resour Manage 58:85–97
Csath M (2022) Organizational learning as the best business practice for adaptation in times of great changes: a viewpoint. Dev Learn Organ Int J
Dao V, Langella I, Carbo J (2011) From green to sustainability: information technology and an integrated sustainability framework. Green IT 20:63–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsis.2011.01.002
de Freitas SWR, Caldeira-Oliveira JH, Teixeira AA, Stefanelli NO, Teixeira TB (2020) Green human resource management and corporate social responsibility. Benchmark Int J 27:1551–1569. https://doi.org/10.1108/BIJ-12-2019-0543
de Freitas SWR, Caldeira Oliveira JH, Teixeira AA, Stefanelli NO (2021) Green human resource management, corporate social responsibility and customer relationship management: relationship analysis in the Brazilian context. Int J Product Perform Manag 70:1705–1727. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJPPM-12-2019-0597
De Prins P, Van Beirendonck L, De Vos A, Segers J (2014) Sustainable HRM: bridging theory and practice through the ’respect openness continuity (ROC)’-model. Manag Rev 25:263–284
De Prins P, Stuer D, Gielens T (2020) Revitalizing social dialogue in the workplace: the impact of a cooperative industrial relations climate and sustainable HR practices on reducing employee harm. Int J Hum Resour Manag 31:1684–1704
De Witte H, Pienaar J, De Cuyper N (2016) Review of 30 years of longitudinal studies on the association between job insecurity and health and well-being: Is there causal evidence? Aust Psychol 51:18–31
De-la-Calle-Durán M-C, Rodríguez-Sánchez J-L (2021) Employee engagement and wellbeing in times of COVID-19: a proposal of the 5Cs model. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18:5470
del-Castillo-Feito C, Blanco-González A, Hernández-Perlines F (2022) The impacts of socially responsible human resources management on organizational legitimacy. Technol Forecast Soc Change 174:121274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.121274
Denyer D, Tranfield D (2009) Producing a systematic review
Deshwal P (2015) Green HRM: an organizational strategy of greening people. Int J Appl Res 1:176–181
Di Vaio A, Palladino R, Hassan R, Escobar O (2020) Artificial intelligence and business models in the sustainable development goals perspective: a systematic literature review. J Bus Res 121:283–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.08.019
Diaz-Carrion R, López-Fernández M, Romero-Fernandez PM (2018) Developing a sustainable HRM system from a contextual perspective. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag 25:1143–1153. https://doi.org/10.1002/csr.1528
Diaz-Carrion R, López-Fernández M, Romero-Fernandez PM (2020) Sustainable human resource management and employee engagement: a holistic assessment instrument. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag 27:1749–1760. https://doi.org/10.1002/csr.1921
Diaz-Carrion R, López-Fernández M, Romero-Fernandez PM (2021) Constructing an index for comparing human resources management sustainability in Europe. Hum Resour Manag J 31:120–142. https://doi.org/10.1111/1748-8583.12286
Díez-Martín F, Blanco-González A, Díez-de-Castro E (2021) Measuring a scientifically multifaceted concept. The jungle of organizational legitimacy. Eur Res Manag Bus Econ 27:100131
Dixon-Fowler H, O’Leary-Kelly A, Johnson J, Waite M (2020) Sustainability and ideology-infused psychological contracts: An organizational- and employee-level perspective. Hum Resour Manag Rev 30:100690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr.2019.100690
Donald WE, Baruch Y, Ashleigh MJ (2020) Striving for sustainable graduate careers. Career Dev Int 25:90–110. https://doi.org/10.1108/CDI-03-2019-0079
DuBois CLZ, Dubois DA (2012) Strategic HRM as social design for environmental sustainability in organization. Hum Resour Manage 51:799–826. https://doi.org/10.1002/hrm.21504
Ehnert I, Harry W, Zink KJ (2014) Sustainability and HRM. In: Sustainability and human resource management. Springer, pp 3–32
ElAlfy A, Palaschuk N, El-Bassiouny D, Wilson J, Weber O (2020) Scoping the evolution of corporate social responsibility (CSR) research in the sustainable development goals (SDGs) era. Sustainability 12:5544
Elkington J (1999) Triple bottom-line reporting: looking for balance. Aust CPA 69:18–21
Gardas BB, Mangla SK, Raut RD, Narkhede B, Luthra S (2019) Green talent management to unlock sustainability in the oil and gas sector. J Clean Prod 229:850–862
Ghouri AM, Mani V, Khan MR, Khan NR, Srivastava AP (2020) Enhancing business performance through green human resource management practices: an empirical evidence from Malaysian manufacturing industry. Int J Product Perform Manag 69:1585–1607. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJPPM-11-2019-0520
Gollan PJ (2000) Human resources, capabilities and sustainability
Gould-Williams J (2003) The importance of HR practices and workplace trust in achieving superior performance: a study of public-sector organizations. Int J Hum Resour Manag 14:28–54
Greenwood M, Anderson E (2009) ‘I used to be an employee but now I am a stakeholder’: implications of labelling employees as stakeholders. Asia Pac J Hum Resour 47:186–200
Greve HR (2021) The resource-based view and learning theory: overlaps, differences, and a shared future. J Manag 47:1720–1733
Guerci M, Shani ABR, Solari L (2014) A stakeholder perspective for sustainable HRM. Sustain Hum Resour Manag 205–223
Gutiérrez Crocco F, Martin A (2019) Towards a sustainable HRM in Latin America? Union-management relationship in Chile. Empl Relat Int J. https://doi.org/10.1108/ER-01-2019-0036
Hameed Z, Naeem RM, Hassan M, Naeem M, Nazim M, Maqbool A (2021) How GHRM is related to green creativity? A moderated mediation model of green transformational leadership and green perceived organizational support. Int J Manpow. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJM-05-2020-0244
Hooi LW, Liu M-S, Lin JJJ (2021) Green human resource management and green organizational citizenship behavior: do green culture and green values matter? Int J Manpow Ahead-of-Print. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJM-05-2020-0247
Hu X, Jiang Z (2018) Employee-oriented HRM and voice behavior: a moderated mediation model of moral identity and trust in management. Int J Hum Resour Manag 29:746–771
Jackson SE, Seo J (2010) The greening of strategic HRM scholarship. Organ Manag J 7:278–290
Jang S, Ardichvili A (2020) The role of HRD in CSR and sustainability: a content analysis of corporate responsibility reports. Eur J Train Dev 44:549–573. https://doi.org/10.1108/EJTD-01-2020-0006
Jerónimo HM, de Lacerda TC, Henriques PL (2020) From sustainable HRM to employee performance: a complex and intertwined road. Eur Manag Rev 17:871–884. https://doi.org/10.1111/emre.12402
Jithendran K, Baum T (2000) Human resources development and sustainability—the case of Indian tourism. Int J Tour Res 2:403–421
Kainzbauer A, Rungruang P, Hallinger P (2021) How does research on sustainable human resource management contribute to corporate sustainability: a document co-citation analysis, 1982–2021. Sustainability 13:11745
Kane C (2022) The future workplace: reimagining the office for the twenty-first century. in: european cities after COVID-19. Springer, pp 179–195
Kashyap V, Arora R (2020) Decent work and work–family enrichment: role of meaning at work and work engagement. Int J Product Perform Manag Ahead-of-Print. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJPPM-03-2020-0133
Kassen M (2022) Open data governance as a theoretical concept: a stakeholder and institutional analysis. In: Open data governance and its actors. Springer, pp 1–28
Kelloway EK, Barling J (1991) Job characteristics, role stress and mental health. J Occup Psychol 64:291–304
Kelman I (2021) Words without meaning? Examining sustainable development terminology through small states and territories. Small States Territories 4:231–244
Khan KS, Kunz R, Kleijnen J, Antes G (2003) Five steps to conducting a systematic review. J R Soc Med 96:118–121
Kitchenham B (2004) Procedures for performing systematic reviews. Keele UK Keele Univ 33:1–26
Kowalski TH, Loretto W (2017) Well-being and HRM in the changing workplace. Int J Hum Resour Manag 28:2229–2255
Kramar R (2014) Beyond strategic human resource management: is sustainable human resource management the next approach? Int J Hum Resour Manag 25:1069–1089
Kramar R (2021) Workplace performance: a sustainable approach. Asia Pac J Hum Resour 59:567–581. https://doi.org/10.1111/1744-7941.12289
Kumar Pradhan R, Prasad Panigrahy N, Kesari Jena L (2021) Self-efficacy and workplace well-being: understanding the role of resilience in manufacturing organizations. Bus Perspect Res 9:62–76
Kundu SC, Gahlawat N (2015) Socially responsible HR practices and employees’ intention to quit: The mediating role of job satisfaction. Hum Resour Dev Int 18:387–406
Lange T (2016) Sustainable HRM and employee well-being: an empirical agenda. Int J Manpow 37:918–923
Lansbury RD (2021) Introduction to the symposium ‘transforming our future: a new social contract at work’? Asia Pac J Hum Resour
Lăzăroiu G, Ionescu L, Andronie M, Dijmărescu I (2020) Sustainability management and performance in the urban corporate economy: a systematic literature review. Sustainability 12:7705
Lechuga Sancho MP, Martínez-Martínez D, Larran Jorge M, Herrera Madueño J (2018) Understanding the link between socially responsible human resource management and competitive performance in SMEs. Pers Rev 47:1211–1243. https://doi.org/10.1108/PR-05-2017-0165
Lee H-W (2017) Sustainable leadership: An empirical investigation of its effect on organizational effectiveness. Int J Organ Theory Behav 20:419–453. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOTB-20-04-2017-B001
Lee H-W (2019) How does sustainability-oriented human resource management work?: examining mediators on organizational performance. Int J Public Adm 42:974–984
Lisovskaia A (2022) Implementing well-being practices through russian context: HRD perspective. J East-West Bus 1–16
Lombardi R, Manfredi S, Cuozzo B, Palmaccio M (2020) The profitable relationship among corporate social responsibility and human resource management: a new sustainable key factor. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag 27:2657–2667. https://doi.org/10.1002/csr.1990
Longoni A, Cagliano R (2016) Human resource and customer benefits through sustainable operations. Int J Oper Prod Manag 36:1719–1740. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOPM-11-2014-0564
Lopez-Cabrales A, Valle-Cabrera R (2020) Sustainable HRM strategies and employment relationships as drivers of the triple bottom line. Hum Resour Manag Rev 30:100689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr.2019.100689
Luu TT (2021a) Socially responsible human resource practices and hospitality employee outcomes. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag 33:757–789. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCHM-02-2020-0164
Luu TT (2021b) A tale of two countries: How do employees with disabilities respond to disability inclusive HR practices in tourism and hospitality industry? J Sustain Tour. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2021.1876073
Macini N, Fernandes Rodrigues Alves M, Oranges Cezarino L, Bartocci Liboni L, Cristina Ferreira Caldana A (2020) Beyond money and reputation: sustainable HRM in Brazilian banks. Empl Relat Int J Ahead-of-Print. https://doi.org/10.1108/ER-12-2018-0331
Macke J, Genari D (2019) Systematic literature review on sustainable human resource management. J Clean Prod 208:806–815
Maheshwari M, Samal A, Bhamoriya V (2020) Role of employee relations and HRM in driving commitment to sustainability in MSME firms. Int J Product Perform Manag 69:1743–1764. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJPPM-12-2019-0599
Mak A, Cheung L, Mak A, Leung L (2014) Confucian thinking and the implications for sustainability in HRM. Asia-Pac J Bus Adm 6:173–189. https://doi.org/10.1108/APJBA-02-2014-0029
Malik SY, Hayat Mughal Y, Azam T, Cao Y, Wan Z, Zhu H, Thurasamy R (2021) Corporate social responsibility, green human resources management, and sustainable performance: Is organizational citizenship behavior towards environment the missing link? Sustainability 13:1044
Mariappanadar S (2003) Sustainable human resource strategy. Int J Soc Econ 30:906–923. https://doi.org/10.1108/03068290310483779
Mariappanadar S (2012a) The harm indicators of negative externality of efficiency focused organizational practices. Int J Soc Econ 39:209–220. https://doi.org/10.1108/03068291211199378
Mariappanadar S (2012b) Harm of efficiency oriented HRM practices on stakeholders: an ethical issue for sustainability. Soc Bus Rev 7:168–184. https://doi.org/10.1108/17465681211237628
Mariappanadar S (2013) A conceptual framework for cost measures of harm of HRM practices. Asia-Pac J Bus Adm 5:103–114. https://doi.org/10.1108/17574321311321595
Mariappanadar S (2014) Stakeholder harm index: A framework to review work intensification from the critical HRM perspective. Hum Resour Manag Rev 24:313–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr.2014.03.009
Mariappanadar S (2016) Health harm of work from the sustainable HRM perspective: scale development and validation. Int J Manpow 37:924–944. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJM-12-2015-0204
Mariappanadar S (2020) Do HRM systems impose restrictions on employee quality of life? Evidence from a sustainable HRM perspective. J Bus Res 118:38–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.06.039
Mariappanadar S, Aust I (2017) The dark side of overwork: an empirical evidence of social harm of work from a sustainable HRM perspective. Int Stud Manag Organ 47:372–387
Mariappanadar S, Kramar R (2014) Sustainable HRM: The synthesis effect of high performance work systems on organisational performance and employee harm. Asia-Pac J Bus Adm. https://doi.org/10.1108/APJBA-03-2014-0039
Mariappanadar S, Maurer I, Kramar R, Muller-Camen M (2021) Is it a sententious claim? An examination of the quality of occupational health, safety and well-being disclosures in global reporting initiative reports across industries and countries. Int Bus Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibusrev.2021.101922
Mashhady A, Khalili H, Sameti A (2021) Development and application of a service design-based process for improvement of human resource management service quality. Bus Process Manag J 27:459–485. https://doi.org/10.1108/BPMJ-04-2020-0164
Mowbray PK, Wilkinson A, Tse HHM (2021) High-performance work systems and employee voice behaviour: an integrated model and research agenda. Pers Rev 50:1530–1543. https://doi.org/10.1108/PR-12-2019-0692
Muisyo PK, Qin S, Julius MM, Ho TH, Ho TH (2021) Green HRM and employer branding: the role of collective affective commitment to environmental management change and environmental reputation. J Sustain Tour 1–18
Mujtaba M, Mubarik MS (2021) Talent management and organizational sustainability: role of sustainable behaviour. Int J Organ Anal Ahead-of-Print. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOA-06-2020-2253
Müller-Christ G, Remer A (1999) Environmental economics or business ecology? Preliminary thoughts on a theory of resource management. Oper Environ Manag 21st Century Asp Tasks Perspect 69–87
Nuis JW, Peters P, Blomme R, Kievit H (2021) Dialogues in sustainable HRM: examining and positioning intended and continuous dialogue in sustainable HRM using a complexity thinking approach. Sustainability 13:10853
O’Donohue W, Torugsa N (2016) The moderating effect of ‘Green’HRM on the association between proactive environmental management and financial performance in small firms. Int J Hum Resour Manag 27:239–261
Okoli C, Schabram K (2010) A guide to conducting a systematic literature review of information systems research
Omidi A, Dal Zotto C (2022) Socially responsible human resource management: a systematic literature review and research agenda. Sustainability 14:2116
Onkila T, Sarna B (2021) A systematic literature review on employee relations with CSR: state of art and future research agenda. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag n/a. https://doi.org/10.1002/csr.2210
Parng Y-J, Kurrahman T, Chen C-C, Tseng ML, Minh Hà H, Lin C-W (2021) Visualizing the hierarchical sustainable human resource management under qualitative information and complex interrelationships. Manag Environ Qual Int J 32:1422–1447. https://doi.org/10.1108/MEQ-04-2021-0086
Paulet R, Holland P, Morgan D (2021) A meta-review of 10 years of green human resource management: is Green HRM headed towards a roadblock or a revitalisation? Asia Pac J Hum Resour 59:159–183. https://doi.org/10.1111/1744-7941.12285
Pellegrini C, Rizzi F, Frey M (2018) The role of sustainable human resource practices in influencing employee behavior for corporate sustainability. Bus Strategy Environ 27:1221–1232
Peng L, Liu H, Nie Y, Xie Y, Tang X, Luo P (2020) The transnational happiness study with big data technology. ACM Trans Asian Low-Resour Lang Inf Process TALLIP 20:1–12
Pham DDT, Paillé P (2020) Green recruitment and selection: an insight into green patterns. Int J Manpow 41:258–272. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJM-05-2018-0155
Piwowar-Sulej K (2021a) Human resources development as an element of sustainable HRM: with the focus on production engineers. J Clean Prod 278:124008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124008
Piwowar-Sulej K (2021b) Core functions of Sustainable Human Resource Management. A hybrid literature review with the use of H-Classics methodology. Sustain Dev
Pizzi S, Caputo A, Corvino A, Venturelli A (2020) Management research and the UN sustainable development goals (SDGs): a bibliometric investigation and systematic review. J Clean Prod 276:124033
Pluta A, Rudawska A (2016) Holistic approach to human resources and organizational acceleration. J Organ Change Manag 29:293–309. https://doi.org/10.1108/JOCM-11-2014-0210
Podgorodnichenko N, Akmal A, Edgar F, Everett AM (2020a) Sustainable HRM: toward addressing diverse employee roles. Empl Relat Int J Ahead-of-Print. https://doi.org/10.1108/ER-01-2019-0016
Podgorodnichenko N, Edgar F, McAndrew I (2020b) The role of HRM in developing sustainable organizations: Contemporary challenges and contradictions. Hum Resour Manag Rev 30:100685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr.2019.04.001
Podgorodnichenko N, Edgar F, Akmal A (2021) An integrative literature review of the CSR-HRM nexus: Learning from research-practice gaps. Hum Resour Manag Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr.2021.100839
Poon TS-C, Law KK (2020) Sustainable HRM: An extension of the paradox perspective. Hum Resour Manag Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr.2020.100818
Pradhan RK, Jena LK, Panigrahy NP (2020) Do sustainability practices buffer the impact of self-efficacy on organisational citizenship behaviour? J Indian Bus Res 12:509–528. https://doi.org/10.1108/JIBR-05-2019-0170
Randev KK, Jha JK (2019) Sustainable human resource management: a literature-based introduction. NHRD Netw J 12:241–252
Ranjbari M, Esfandabadi ZS, Zanetti MC, Scagnelli SD, Siebers P-O, Aghbashlo M, Peng W, Quatraro F, Tabatabaei M (2021) Three pillars of sustainability in the wake of COVID-19: A systematic review and future research agenda for sustainable development. J Clean Prod 297:126660
Raub SP, Martin-Rios C (2019) “Think sustainable, act local”—a stakeholder-filter-model for translating SDGs into sustainability initiatives with local impact. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag 31:2428–2447. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCHM-06-2018-0453
Ren S, Jackson SE (2020) HRM institutional entrepreneurship for sustainable business organizations. Hum Resour Manag Rev 30:100691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr.2019.100691
Ribeiro RP, Gavronski I (2021) Sustainable management of human resources and stakeholder theory: a review. Rev Gest Soc E Ambient 15:e02729–e02729
Richards J (2020) Putting employees at the centre of sustainable HRM: a review, map and research agenda. Empl Relat Int J Ahead-of-Print. https://doi.org/10.1108/ER-01-2019-0037
Rincon-Roldan F, Lopez-Cabrales A (2021a) Linking organisational values and sustainability: the role of AMO practices. Pers Rev Ahead-of-Print. https://doi.org/10.1108/PR-06-2020-0414
Rincon-Roldan F, Lopez-Cabrales A (2021b) The impact of employment relationships on firm sustainability. Empl Relat Int J Ahead-of-Print. https://doi.org/10.1108/ER-12-2020-0522
Robinson RN, Martins A, Solnet D, Baum T (2019) Sustaining precarity: critically examining tourism and employment. J Sustain Tour 27:1008–1025
Roca-Puig V (2019) The circular path of social sustainability: an empirical analysis. J Clean Prod 212:916–924
Rubel MRB, Kee DMH, Rimi NN (2021) The influence of green HRM practices on green service behaviors: the mediating effect of green knowledge sharing. Empl Relat Int J 43:996–1015. https://doi.org/10.1108/ER-04-2020-0163
Samimi E, Sydow J (2021) Human resource management in project-based organizations: revisiting the permanency assumption. Int J Hum Resour Manag 32:49–83
Santana M, Lopez-Cabrales A (2019) Sustainable development and human resource management: a science mapping approach. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag 26:1171–1183. https://doi.org/10.1002/csr.1765
Sarvaiya H, Arrowsmith J (2021) Exploring the context and interface of corporate social responsibility and HRM. Asia Pac J Hum Resour n/a. https://doi.org/10.1111/1744-7941.12316
Sathasivam K, Che Hashim R, Abu Bakar R (2021) Automobile industry managers’ views on their roles in environmental sustainability: a qualitative study. Manag Environ Qual Int J 32:844–862. https://doi.org/10.1108/MEQ-09-2020-0194
Schulte P, Vainio H (2010) Well-being at work–overview and perspective. Scand J Work Environ Health 422–429
Secundo G, Ndou V, Del Vecchio P, De Pascale G (2020) Sustainable development, intellectual capital and technology policies: a structured literature review and future research agenda. Technol Forecast Soc Change 153:119917
Shah SMA, Jiang Y, Wu H, Ahmed Z, Ullah I, Adebayo TS (2021) Linking green human resource practices and environmental economics performance: the role of green economic organizational culture and green psychological climate. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18:10953
Sharpley R (2020) Tourism, sustainable development and the theoretical divide: 20 years on. J Sustain Tour 28:1932–1946
Shoaib M, Abbas Z, Yousaf M, Zámečník R, Ahmed J, Saqib S (2021) The role of GHRM practices towards organizational commitment: a mediation analysis of green human capital. Cogent Bus Manag 8:1870798
Silva S, Nuzum A-K, Schaltegger S (2019) Stakeholder expectations on sustainability performance measurement and assessment. a systematic literature review. J Clean Prod 217:204–215
Singh S, Vanka S (2019) Voice matters: Why HR should listen to employee voice? Strateg HR Rev 18:268–271. https://doi.org/10.1108/SHR-04-2019-0026
Singh SK, Pradhan RK, Panigrahy NP, Jena LK (2019) Self-efficacy and workplace well-being: moderating role of sustainability practices. Benchmarking Int J 26:1692–1708. https://doi.org/10.1108/BIJ-07-2018-0219
Sobhani FA, Haque A, Rahman S (2021) Socially responsible HRM, employee attitude, and bank reputation: the rise of CSR in Bangladesh. Sustainability 13:2753
Sorribes J, Celma D, Martínez-Garcia E (2021) Sustainable human resources management in crisis contexts: Interaction of socially responsible labour practices for the wellbeing of employees. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag 28:936–952. https://doi.org/10.1002/csr.2111
Sotome R, Takahashi M (2014) Does the Japanese employment system harm productivity performance? Asia-Pac J Bus Adm 6:225–246. https://doi.org/10.1108/APJBA-02-2014-0031
Southey K (2016) To fight, sabotage or steal: are all forms of employee misbehaviour created equal? Int J Manpow 37:1067–1084. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJM-12-2015-0219
Stahl GK, Brewster CJ, Collings DG, Hajro A (2020) Enhancing the role of human resource management in corporate sustainability and social responsibility: A multi-stakeholder, multidimensional approach to HRM. Sustain Hum Resour Manag Triple Bottom Line Multi-Stakehold Strateg Concepts Engagem 30:100708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr.2019.100708
Stankevičiūtė Ž, Savanevičienė A (2018) Designing sustainable HRM: the core characteristics of emerging field. Sustainability 10:4798
Stankevičiūtė Ž, Savanevičienė A (2019) Can sustainable HRM reduce work-related stress, work-family conflict, and burnout? Int Stud Manag Organ 49:79–98
Teeuwisse V, Brannon DW (2020) A qualititaive exploration of sustainble talent management of hospitality interns’ career intentions based on their pre-, post- and present practical placement experiences. In: Ruël H, Lombarts A (eds) Sustainable hospitality management. Emerald Publishing Limited, pp 63–82
Tworzydło D, Gawroński S, Opolska-Bielańska A, Lach M (2021) Changes in the demand for CSR activities and stakeholder engagement based on research conducted among public relations specialists in Poland, with consideration of the SARS-COV-2 pandemic. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag n/a. https://doi.org/10.1002/csr.2189
Úbeda-García M, Claver-Cortés E, Marco-Lajara B, Zaragoza-Sáez P (2021) Corporate social responsibility and firm performance in the hotel industry. the mediating role of green human resource management and environmental outcomes. J Bus Res 123:57–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.09.055
Van Buren III HJ (2020) The value of including employees: a pluralist perspective on sustainable HRM. Empl Relat Int J Ahead-of-Print. https://doi.org/10.1108/ER-01-2019-0041
Van Dam K, Van Vuuren T, Kemps S (2017) Sustainable employment: the importance of intrinsically valuable work and an age-supportive climate. Int J Hum Resour Manag 28:2449–2472
Vecchi A, Della Piana B, Feola R, Crudele C (2021) Talent management processes and outcomes in a virtual organization. Bus Process Manag J 27:1937–1965. https://doi.org/10.1108/BPMJ-06-2019-0227
Vyas L (2022) “New normal” at work in a post-COVID world: work–life balance and labor markets. Policy Soc 41:155–167
Wellton L, Lainpelto J (2021) The intertwinement of professional knowledge culture, leadership practices and sustainability in the restaurant industry. Scand J Hosp Tour 21:550–566
Westerman JW, Rao MB, Vanka S, Gupta M (2020) Sustainable human resource management and the triple bottom line: Multi-stakeholder strategies, concepts, and engagement. Hum Resour Manag Rev 30:100742
WHO (2021) Comprehensive Mental Health Action Plan 2013–2030
Wikhamn W (2019) Innovation, sustainable HRM and customer satisfaction. Int J Hosp Manag 76:102–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2018.04.009
Wright PM, Steinbach AL (2022) Pivoting after almost 50 years of SHRM research: toward a stakeholder view. Asia Pac J Hum Resour 60:22–40
Xiao Y, Watson M (2019) Guidance on conducting a systematic literature review. J Plan Educ Res 39:93–112
Yang W, Nawakitphaitoon K, Huang W, Harney B, Gollan PJ, Xu CY (2019) Towards better work in China: mapping the relationships between high-performance work systems, trade unions, and employee well-being. Asia Pac J Hum Resour 57:553–576. https://doi.org/10.1111/1744-7941.12205
Ybema JF, van Vuuren T, van Dam K (2020) HR practices for enhancing sustainable employability: implementation, use, and outcomes. Int J Hum Resour Manag 31:886–907
Yong JY, Yusliza M-Y, Jabbour CJC, Ahmad NH (2020) Exploratory cases on the interplay between green human resource management and advanced green manufacturing in light of the ability-motivation-opportunity theory. J Manag Dev 39:31–49. https://doi.org/10.1108/JMD-12-2018-0355
Yusliza M-Y, Norazmi NA, Jabbour CJC, Fernando Y, Fawehinmi O, Seles BMRP (2019) Top management commitment, corporate social responsibility and green human resource management. Benchmarking Int J 26:2051–2078. https://doi.org/10.1108/BIJ-09-2018-0283
Zaugg RJ, Blum A, Thom N (2001) Sustainability in human resource management. Eval Rep Surv Eur Co Inst Arbeitsbericht Inst Für Organ Pers Univ Bern Eidgenöss Pers
Zheng X, Zhu W, Zhao H, Zhang C (2015) Employee well-being in organizations: theoretical model, scale development, and cross-cultural validation. J Organ Behav 36:621–644. https://doi.org/10.1002/job.1990
Zink KJ (2011) The contribution of quality of work to organisational excellence. Total Qual Manag Bus Excell 22:567–585
Download references
Acknowledgements
There are no acknowledgements for this manuscript.
The authors declare that no funds, grants or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Business Administration, Sukkur IBA University, Sukkur, Pakistan
Faisal Qamar, Gul Afshan & Salman Anwar Rana
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Dr. GA and Mr. FQ contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation and analysis were performed by Mr. FQ and Mr. SR. The first draft of the manuscript was prepared by Mr. FQ. Dr. GA and Mr. SR then commented on previous versions of the manuscript. Mr. SR significantly contributed to prepare the final manuscript alongwith Mr. Faisal. Dr. GA supervised the overall work. Finally, all the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Faisal Qamar .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Qamar, F., Afshan, G. & Rana, S.A. Sustainable HRM and well-being: systematic review and future research agenda. Manag Rev Q (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-023-00360-6
Download citation
Received : 16 November 2022
Accepted : 21 June 2023
Published : 14 July 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-023-00360-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Psychological health
- Sustainable HRM
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Hum Resour Health
- PMC10696747

Human resource management research in healthcare: a big data bibliometric study
Xiaoping qin.
1 School of Health Policy and Management, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100730 China
Yu-Ni Huang
2 College of Medical and Health Science, Asia University, Taichung, 41354 Taiwan
Kaiyan Chen
3 Department of Education, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100730 China
4 Department of Innovative Medical Research, Hospital Management Institute, Chinese People’s Liberation Army General Hospital, Beijing, 100853 China
Richard Szewei Wang
5 Affiliation Program of Data Analytics and Business Computing, Stern School of Business, New York University, New York, 10012 United States of America
6 Tsinghua-Berkeley Shenzhen Institute, Tsinghua University, Shenzhen, 518055 China
Bing-Long Wang
Associated data.
All data and materials generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Human resource management (HRM) in healthcare is an important component in relation to the quality and efficiency of healthcare delivery. However, a comprehensive overview is lacking to assess and track the current status and trends of HRM research in healthcare. This study aims to describe the current situation and global trends in HRM research in healthcare as well as to indicate the frontiers and future directions of research. The research methodology is based on bibliometric mapping using scientific visualization software (VOSviewer). The data were collected from the Web of Science(WoS) core citation database. After applying the search criteria, we retrieved 833 publications, which have steadily increased over the last 30 years. In addition, 93 countries and regions have published relevant research. The United States and Australia have made significant contributions in this area. Current research articles focus on topics clustered into performance, hospital/COVID-19, job satisfaction, human resource management, occupational/mental health, and quality of care. The most frequently co-occurring keywords are human resource management, job satisfaction, nurses, hospitals, health services, quality of care, COVID-19, and nursing. There is limited research on compensation management and employee relations management, so the current HRM research field still has not been able to present a complete and systematic roadmap. We propose that our colleagues should consider focusing on these research gaps in the future.
Introduction
Among the many management elements, people are the most dynamic and active element, and they are an important asset in organizations [ 1 ]. The term “human resources” was first coined by the academic Peter F. Drucker in 1954 [ 2 ]. The key function of human resources management (HRM) is to “put the right people in the right jobs at the right time” [ 2 ]. HRM refers to the planned allocation of human resources in accordance with the requirements of organizational development through a series of processes, such as recruitment, training, use, assessment, motivation, and adjustment of employees, to mobilize their motivation, bring into play their potential and create value for the organization [ 1 ]. Ensuring the achievement of the organization’s strategic objectives, HRM activities mainly include human resource strategy formulation, staff recruitment and selection, training and development, performance management, compensation management, staff mobility management, staff relationship management, staff safety and health management, etc. Similarly, modern healthcare management has human resources as the core. The HRM level in hospitals is related to the quality and efficiency of medical services provided by hospitals, which is also the core of internal hospital management and the focus of health macro management [ 3 ].
The World Health Organization (WHO) states that health systems can only work with the help of health workers, and that improving the coverage of health services and realizing the right to the highest standard of health depends on the availability, accessibility, acceptability and quality of health workers [ 4 ]. In response to evolving characteristics in socio-economic development and the human resource market, healthcare system personnel reforms are evident in three key areas: first, decentralization and flexible employment practices grant hospital managers greater decision-making autonomy concerning priorities and access to medical resources. However, they also impose quantitative and functional constraints on physicians' working hours, career planning, and medical payment systems. Second, a focal point is the rational allocation of technical staff to achieve efficiency while controlling labor costs. Finally, hospital organization change and restructuring are prevalent. Many European countries have unionized hospital employees, limiting the ability to establish independent incentives and rewards. In contrast, U.S. hospital employees often do not belong to specific organizations, leading cost control efforts to revolve around adjusting the allocation of technical staff and employee numbers to reduce labor expenses [ 5 – 7 ].
The current global trend in the number of publications on HRM in healthcare is rising. However, there are currently several problems in HRM research. The following issues mainly exist: (1) the expertise and professionalism of HRM managers are limited. (2) Theoretical methods and technical applications are weak. (3) Insufficient regulation of regulations, systems and procedures. (4) Management is mainly at the level of operational work, and functions are too fragmented [ 8 , 9 ]. Although hospitals worldwide generally recognize the importance of HRM, they do not pay sufficient attention to it. The management of human resources is also stuck in the previous understanding that its work is carried out only by transferring positions in hospitals, promoting and reducing the salary of employees and a series of other operations [ 10 ]. Most senior management in hospitals have comprehensive medical knowledge; some are experts in a particular field. Still, they lack expertise in HRM, which makes them work in a transactional way in HRM. There is also currently a general health workforce imbalance in countries worldwide. The lack of well-being of healthcare workers is particularly problematic in foreign healthcare institutions [ 11 ], and to reduce costs, some organizations have reduced staffing levels. In turn, because of lower quality of service, the morale of healthcare providers often suffers. Patient satisfaction may decline [ 12 ]. In the process of data gathering, we found that the literature related to HRM in healthcare is still under-reported and that the research topics are scattered, and there is still a lack of generalization and summary of these literatures [ 13 ]. There is no systematic theoretical support in the current research, which defines the perspective that researchers should take when analyzing and interpreting the data to be collected, leading to biased interpretations of the results, and does not allow other researchers to combine the findings with existing research knowledge and then apply them to practice [ 14 ]. Second, data collection was not rigorous, and the downloading strategy was not appropriate to achieve completeness and accuracy of data. There is also a lack of information and incomplete use of features in the presentation of knowledge maps and visualization results [ 15 ].
Therefore, the aims of this study are the following; first, we provide a new way of viewing the field of healthcare HRM and its associations by examining co-occurrence data. Second, we relate our evolutionary analysis to a comprehensive future research agenda which may generate a new research agenda in healthcare hospital HRM. This review, therefore, focuses on illuminating the research frontiers and future roadmap for healthcare HRM research [ 16 , 17 ].
Materials and methods
This study provides a bibliometric analysis of the HRM research literature in health care over a 30-year period to describe the landscape and trajectory of change in the research field. The methodology used for this overview is based on bibliometric mapping [ 18 , 19 ], a visualization technique that quantitatively displays the landscape and dynamic aspects of the knowledge domain [ 20 ]. Data were collected from the Web of Science (WoS) core citation database. Two Java-based scientific visualization software packages (CiteSpace and VOSviewer), developed by Chaomei Chen and Van Eck and Waltman, were used to analyze the data [ 18 , 21 ].
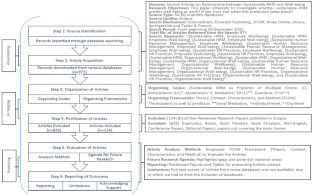
The data for this study were retrieved from the Web of Science on 28 September 2022. Web of Science was chosen as the search engine, because it is the most widely accepted and commonly used database for analyzing scientific publications [ 22 ]. The keywords “human resource management” and “healthcare organization” were used as search topics. First, to get a complete picture of HRM research, we searched all the literature from 1977 to the date of the search.
Eight hundred thirty-three publications on HRM in healthcare organizations were identified (Fig. 1 ). We excluded publications before 1990, because the two documents before 1990 did not include complete information. In addition, articles, review articles, and early access articles were included in the study. To minimize language bias, we excluded literature published in languages other than English. Each publication in WoS contains detailed information, including the year of publication, author, author’s address, title, abstract, source journal, subject category, references, etc. A detailed description of the contents of the database preceded the bibliographic analysis. For example, some authors presented their names in different spellings when submitting articles, so reviewing and integrating the data in detail was necessary. A total of 718 publications were included and exported to VOSviewer and CiteSpace software to analyze the following topics: global publishing trends, countries, journals, authors, research orientations, institutions, and quality of publications.

Research flow chart of the bibliometric analysis
Introduction to CiteSpace and VOSviewer
VOSviewer is a software tool for building and visualizing bibliometric networks. It was developed by Van Eck and Waltman [ 21 ]. In VOSviewer, metric networks can be visualized and analyzed for factors, including journals, researchers, or individual publications. They can be constructed based on citations, bibliographic couplings, co-citations, or co-authorship relationships [ 21 ].
Global publication trends
Number of global trends.
After applying the search criteria, we retrieved a total of 718 articles. Figure 2 a shows the increase in articles from 1 in 1977 to 108 in 2021. To predict future trends, a linear regression model was used to create a time curve for the number of publications throughout the year, and the model fit curve for the growth trend is shown in Fig. 2 b. The trend in the number of publications fitted the time curve well at R 2 = 0.8802. The R-squared value is a measure of how well the trend line fits. This value reflects the degree of fit between the estimated value of the trend line and the corresponding actual data; the better the fit, the more reliable the trend line is [ 23 , 24 ]. Based on the model’s trends, it is also predicted that the number of articles on HRM in healthcare will increase to approximately 300 by 2030, an almost threefold increase compared to 2021.

a Total number of publications related to HRM research. The bars indicate the number of publications per year. b Model fitting curves of global publication trends. c Top 10 countries of total publications. d Distribution world map of HRM research
Country and regional contributions
Figure 2 c, d shows the number of publications and the world distribution of the top 10 countries in total publication numbers. The USA contributed the most publications (172, 24.2%), followed by Australia (86, 12.0%), the UK (83, 11.6%), and China (78, 10.9%).
Total number of citations
The USA had the highest total number of citations of all included publications (5195) (Table (Table1), 1 ), while the UK ranked second (2661), followed by Australia (1960) and the Netherlands (1271). The detailed rankings and numbers are shown in Fig. 3 a and Table Table1 1 .
Contributions in publications of countries
| Country | Publications | Sum of the Times Cited | Average Citations per Item | H-index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA | 172 | 5195 | 30.2 | 36 |
| UNITED KINGDOM | 83 | 2661 | 32.06 | 27 |
| AUSTRALIA | 86 | 1960 | 22.79 | 23 |
| NETHERLANDS | 60 | 1271 | 21.18 | 21 |
| CANADA | 46 | 1248 | 27.13 | 22 |
| CHINA | 78 | 997 | 12.78 | 19 |
| BELGIUM | 19 | 936 | 49.26 | 12 |
| TAIWAN | 36 | 795 | 22.08 | 15 |
| GERMANY | 31 | 596 | 19.23 | 11 |
| IRAN | 27 | 277 | 10.26 | 9 |

a Top 10 countries of average citations for each article. b Average number of citations. c Top 10 countries of the H-index
Average citation frequency
Belgium had the highest average number of citations (49.26), followed by the UK (32.06), the USA (30.2), and Canada (27.13), as shown in Fig. 3 b.
Total citations and the h-index reflect the quality of a country’s publications and academic impact[ 25 ]. Figure 3 c shows the ranking of the h-index, where the top country is the USA (h-index = 36), followed by the UK (h-index = 27), Australia (h-index = 23), and Canada (h-index = 22).
Analysis of publications
Table Table2 2 shows the top 10 journals for publications on HRM in healthcare, with 54 articles published in “International Journal of Human Resource Management”, 44 articles published in “BMJ Open”, 30 articles published in “Journal of Nursing Management”, and 24 articles in “BMC Health Services Research”.
Top 10 journals of publications related to HRM research
| Publications | Times | Percentage( = 718) |
|---|---|---|
| International Journal Of Human Resource Management | 54 | 7.521 |
| Bmj Open | 44 | 6.128 |
| Journal Of Nursing Management | 30 | 4.178 |
| Bmc Health Services Research | 24 | 3.343 |
| Journal Of Advanced Nursing | 18 | 2.507 |
| Health Care Management Review | 16 | 2.228 |
| Human Resources For Health | 16 | 2.228 |
| Human Resource Management | 14 | 1.95 |
| Plos One | 14 | 1.95 |
| Human Resource Management Journal | 11 | 1.532 |
Table Table3 3 shows the top 10 most published authors with 96 articles/reviews in the last decade, representing 13.4% of all literature in the field. Timothy Bartram from Australia has published 19 papers, followed by Sandra Leggat from Australia, Stanton P from the USA, and Townsend K from the UK with 13, 11, and 10 papers, respectively. All researchers listed as authors were included in this term for analysis, regardless of their relative contribution to the study. Notably, we have included all authors in this analysis regardless of their relative contribution to the study.
Top 20 authors of publications
| Author | Publications | Sum of the Times Cited | Average Citations per Item | h-index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bartram T | 19 | 722 | 38 | 12 |
| Leggat SG | 13 | 488 | 37.54 | 9 |
| Stanton P | 11 | 510 | 46.36 | 8 |
| Townsend K | 10 | 210 | 21 | 8 |
| Wilkinson A | 10 | 210 | 21 | 8 |
| Van Rhenen W | 8 | 138 | 17.25 | 5 |
| Paauwe J | 7 | 258 | 36.86 | 4 |
| Boselie P | 6 | 338 | 56.33 | 6 |
| Kellner A | 6 | 87 | 14.5 | 6 |
| Marchal B | 6 | 163 | 27.17 | 6 |
Research orientation
Figure 4 a shows the top 10 research orientations of the 100 research orientations. The most common research orientations were management (193 articles), nursing (107 articles), health policy services (105 articles), and health care sciences services (201 articles).

a Top 10 research orientations and the number of publications in each orientation. b Top 20 institutions with the most publications
Institutions
Figure 4 shows the top 20 institutions with the most published papers. La Trobe University has the highest number of articles with 24, followed by the University of London (23) and Griffith University (18).
Co-occurrence analysis
In the keyword mapping on HRM research in healthcare, the size of the nodes represents the frequency, while the line between the nodes reflects the co-occurrence relationship. A total of 1914 keywords were included, and 59 met the criteria. All keywords were grouped into six clusters: performance (light blue cluster), job satisfaction (red cluster), quality of care (blue cluster), human resource management (brown cluster), occupational/mental health (purple cluster), and hospital/COVID-19 (green cluster) (Fig. 5 ).

Co-occurrence analysis of HRM research in healthcare
The most prominent themes in HRM research in healthcare are as below. In the “Performance” cluster, the keywords which have the greatest co-occurrence strength were “performance”, “systematic review”, “decentralization health system” and “motivation”. The main keywords in the “Job Satisfaction” cluster are “job satisfaction”, “organizational commitment”, “transformational leadership” and “turn over”. In the “Quality of care” cluster, the keywords that stand out are “quality of care”, “patient safety”, “high-performance work system”, “quality management” and “patient satisfaction”. In the “Human resource management” cluster, the prominent keywords include “human resource management”, “health policy”, “public health”, and “education and training”. In the “Occupational/Mental Health” cluster, the prominent keywords are “Occupational health”, “mental health”, “well-being” and “burnout”. The main keywords in the “Hospital/COVID-19” cluster were “hospitals”, “COVID-19” “workforce” and “qualitative research”.
Global trends in HMR in healthcare
Our study of HMR research in healthcare illustrates current and global trends in publications, contributing countries, institutions, and research orientations. The field of HMR research has evolved over the past three decades. However, as this study shows, the number of publications steadily increases yearly, with 93 countries or regions publishing in the field, suggesting that research focusing on HMR research and providing in-depth knowledge will likely increase.
Quality and status of publications worldwide
We find that most publishing countries are developed countries, but developing countries are catching up. The total citation rate and the h-index reflect the quality and scholarly impact of a country’s publications [ 25 ]. According to our study, the US ranks first among other countries in total publications, citations, and h-index, making the most substantial contribution to global HRM research. The UK and Canada also contribute significantly, with impressive total citation frequencies and h-index, especially the UK, which ranks second in average citation frequency. However, some countries, such as Belgium, Canada and Australia, also play an important role, given their high average citation frequency. In developing countries, HRM research has also served as a guide for hospitals to improve the quality of care. The study will serve as a reference for developing countries to learn from the experience of developed countries as their economic development gradually catches up with that of developed countries.
The impact and prestige of the journals can be seen in the number of articles published in the field and the influential journals in healthcare HRM research, including the BMC Health Services Research, the Journal of Nursing Management, the International Journal of Human Resource Management, the Health Care Management Review, and the Journal of Health Organisation and Management. These high-quality journals are thus the main source of information for researchers in this field on the latest developments in HRM in healthcare.
The study shows that almost all of the top 20 institutions come from the top five countries with the most publications, with the majority coming from the US, Australia and the Netherlands, reflecting the great academic influence of these three countries in the field of HRM in healthcare. These institutions play an important role in raising the academic performance of a country. Furthermore, the top 20 authors represent research leaders who are likely to impact the future direction of research significantly. Therefore, more attention should be paid to their work to stay abreast of the latest developments in the field.
Research Focus on HRM
Keywords play a crucial role in research papers as they contain vital information [ 26 ]. A systematic analysis of keywords within a specific research domain offers valuable insights into trends and focal points across various research areas [ 27 ]. Moreover, co-occurrence analysis relies on the number of joint publications to evaluate relationships among the identified keyword domains. As a result, it serves as an effective method for predicting future trends and focal points within the research areas of interest. These findings are expected to inspire more researchers to contribute to the future of HRM research in healthcare [ 28 ].
In this study, a total of six research domains were eventually summarized. Performance, Hospital/COVID-19, Job Satisfaction, Human resource management, Occupational/Mental Health, and Quality of care. By visualizing the analysis results, we can easily further clarify future trends. As the co-occurrence diagram shows, the keywords “Organizational culture”, “Patient safety”, “Nursing”, “Leadership”, “Quality of care” and “Hospitals” are highlighted as larger icons, so that investment and demand for quality research are necessary for the context of these six research directions.
Six modules and research directions in human resources
This study found that the visual clustering results and the keywords that emerged from the clusters were closely related to the HRM module s described in “Human Resources Management: Gaining a Competitive Advantage” by Noe. R . [ 29 ]. The modules have been cited in HRM research and are used as textbooks in universities [ 30 – 33 ]. Some of the keywords in each cluster correspond to human resource planning, performance management, recruitment and staffing, and training and development, respectively. The explanation of the HRM modules is described in the next paragraph. However, there are no explicit keywords in the modules related to employee relations management and compensation management results. This may be due to the private nature of the compensation structure in healthcare organizations during data collection, making it unavailable.
The explanation of the HRM modules [ 29 ]
- Human resource planning is the starting point of HRM. It helps the organization forecast future personnel needs and their basic qualities, primarily through planning.
- Recruitment and staffing, with HR planning as the input, is equivalent to the organization’s blood, nourishing the organization and solving the problem of staffing and staff matching.
- Training and development, with the “education” theme.
- Performance Management is at the heart of the six dimensions. It is also the primary input to the other dimensions.
- Compensation management aims to motivate employees to solve the company’s problems.
- Employee relations management aims to manage people and help the company form an effective cycle of rational human resource allocation.
Human resource planning
Human Resource Plan (HRP) stands for the implementation of the HR development strategy of the enterprise and the accomplishment of the enterprise’s goals, according to the changes in the internal and external environment and conditions of the enterprise, through the analysis and estimation of the future needs and supply of human resources and the use of scientific methods for organizational design, as well as the acquisition, allocation, utilization and maintenance of HR and other aspects of functional planning. HRP ensures that the organization has a balance of HR supply and demand at a needed time and in a required position, and achieves a reasonable allocation of HR and other resources to effectively motivate and develop of employees [ 34 ].
Decentralization health system, organizational culture/structure are high-frequency words in the clustering results related to “human resource management”. It is important to assess the extent to which decentralization can be used as a policy tool to improve national health systems. For policymakers and managers, based on relevant literature and research as well as country experience analysis, the experience of decentralization in relation to the organization and management of healthcare services is considered a forward-looking and pioneering concept capable of achieving optimal allocation of HR and other resources, in addition to the need to focus more on ex-ante and ex-post incentive development to deliver a 1 + 1 > 2 HRM effect [ 35 ]. HRP is the starting point and basis for all specific HRM activities. It directly affects the efficiency of the overall HRM of the enterprise. It is, therefore, taken as the primary job requirement for HR managers [ 36 ]. Organizational culture/structure significantly impacts the healthcare sector, such as excellence in healthcare delivery, ethical values, engagement, professionalism, cost of care, commitment to quality and strategic thinking, which are key cultural determinants of high-quality care delivery [ 37 ]. Therefore, as with other for-profit organizations, healthcare organizations must ensure that their organizational structure functions effectively to achieve their strategic goals. The organization formulates and implements HRM, an important task to achieve the development strategy goals.
Staff recruitment and allocation
Recruitment and staffing are the first steps in hospital HRM activities. Under the guidance of the organization’s human resources development plan, potential staff who meet the development conditions are attracted. Through the scientific selection of outstanding personnel, a platform with guaranteed treatment and development prospects is provided to ensure that the team of the healthcare organization is built solidly and meets the development needs. From the findings of this study, the keywords “workforce” and “workload” appear as high-frequency keywords in the co-occurrence analysis. Still, keywords related to traditional staff recruitment (e.g., analysis of recruitment needs, job analysis, competency analysis, recruitment procedures, and strategies) do not appear often. Recruitment and staffing are the prerequisites of human resources work. They bring a new dynamic source to healthcare organizations while complementing staff, making the organization full of vitality and vigor, facilitating organizational innovation and management innovation and helping improve the healthcare organization’s competitive advantage [ 38 ]. Recruitment and staffing, as a part of HR, directly impact the successful running of daily activities.
Training and development
Human resource training is an important component of quality and safety in the health care system. The keyword “education and training” shows a high frequency of co-occurrence in the clustering results of analysis, corresponding to the module “training and education”. However, it is connected to the keywords “human resource management” and “health policy”, and is in the same cluster with” public health”, “health care management”, and the distance between the lines and dots indicate that these topics are closely related, proving the importance of education and training in the HRM of health systems. Healthcare organizations (especially for non-professionals and caregivers) can improve the performance of their employees by enhancing their capabilities, knowledge and potential through learning and training, so that they can maximize their qualifications to match the demands of their work and advance their performance [ 39 , 40 ].
Performance management
Performance management, the core of the six modules, is also featured in the clustering results. Although this is an important focus for HR professionals, few studies have explored the link between HRM and health sector performance [ 6 ], the results show “performance” and “motivation”. The effectiveness of performance management is an important component of HRM, which effectively improves the quality of care in healthcare organizations/institutions [ 6 ]. Focusing on the effectiveness of performance management is considered to be crucial. First, as an integral part of HRM within an organization, it can help the organization meet its goals. Second, ineffective approaches can lead to negative attitudes among employees (including clinicians, nursing staff, administrators, etc.) and adversely affect performance due to decreased satisfaction among employees and patients. Third, given the increasing quality and cost reduction pressures on healthcare organizations, conducting further research on performance management and effectiveness is critical [ 41 ]. However, it is clear from our results that healthcare organizations have recognized the importance of performance management and are pursuing “high performance”. Although the topic of performance management in HRM in healthcare is one of the research priorities, the number is lacking and more discussion on performance management should be suggested for future research.
Compensation management
Compensation is an important tool to motivate employees to work hard and to motivate them to work hard. The results of the database's bibliographic analysis show that no keywords directly involved compensation. This indicates that “compensation management” has not been considered a hot topic or a research issue over 30 years of available literature. To clarify the content of this module, we further searched the database of 718 articles with keywords, such as compensation, remuneration, salary, etc., and found that only 35 of them mentioned or discussed compensation, and some years (e.g., 2018, 2009) even had no relevant literature being published. However, issues such as fairness of compensation management and employee compensation satisfaction are still important issues of concern to business management academics [ 42 , 43 ]. The actual situation is that it is difficult to conduct research on compensation management. Most organizations keep their employees’ compensation confidential, and when conducting research, HR managers avoid talking about their employees’ compensation or leave it vague, rendering it impossible for researchers to conduct further research.
Employee compensation is one factor that has the greatest impact on organizational performance. In the future, organizations should be encouraged to scientifically structure their compensation management and empower academic research to establish and implement fair compensation management systems based on empirical research while maintaining the privacy and security of organizational information.
Employee relations management
The connotation of employee relations management involves organizational culture and employee relations, as well as the coordination of the relationship between employers and employees. Healthcare organizations have complex structures with employees with varying skills, tasks or responsibilities, and such conflicts are often managed through the communication skills of administrative staff [ 44 ]. Although the keywords related to “employee relations management” did not occur in this study's analysis results, the six HRM modules are closely related. Therefore, this does not mean that no description of employee relations management was completely absent in the retrieved articles. It is clear that there is currently a lack of research on employee relations management in the healthcare field. Still, with the continuous development of the healthcare industry, it faces multiple challenges. If employee relations are not handled properly, healthcare organizations with social responsibility will face great public pressure, which will even affect the quality of healthcare services and performance, so it is especially important to strengthen the research on employee relations management.
This study inevitably has some limitations, the first of which arises from using quantitative methods to review documents in the field of HRM. The review relied on an analysis of the bibliographic data associated with the documents rather than a review of the research findings. The impact of the study was, therefore, limited to the general direction of developments in the field, rather than a synthesis of research findings. As a result, we may have missed some publications due to database bias. Second, most of the publications identified were in English and some articles relevant to other languages have not been included. Third, Since HRM exists in a wide range of industries and research areas, although researchers have set the screening criteria as detailed as possible, there may still be some literature that has not been detected.
This study describes the current state and global trends in HRM research in healthcare. The United States has made significant contributions in this field, establishing itself as a global leader. It is foreseeable that more and more publications will be published in the coming years, which indicates that HRM research in healthcare is booming. The analysis results of this study echoed the modules of HRM. It can be seen that in the current HRM research, many topics have been of interest. However, the focus and hotspots of the research are scattered, and there is presently no systematic research on the content of HRM in healthcare.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Editor-in-Chief and the referees for their helpful comments which help to improve our manuscript significantly.
Author contributions
BW, ZH and LLconceived of the presented idea. BW, developed the theory. BW, YH, RW, KC and XQ collected the data and discussed the results. BW and YH encouraged XQ to investigate the hospital management field and supervised the findings of this work. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
This research was supported by Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, China (Grant number: 2021-RC630-001).
Availability of data and materials
Declarations.
There are no human or animal studies in this manuscript, and no potentially identifiable human images or data are presented in this study.
Not applicable.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Human Resource Management Review
- October 2013
- Human Resource Management Review 23(4):322–325
- 23(4):322–325

- Trinity College Dublin
Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations

- Vini Wiratno Putri

- J Manag Hist

- James H. Macomber
- Marc Cutright
- J WORLD BUS

- MANAGE DECIS

- Hum Resource Manag Rev

- J ORGAN BEHAV
- MIT SLOAN MANAGE REV
- Boris Groysberg

- Hum Resource Manag J

- Gary C. McMahan
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by

So, Human Resources Is Making You Miserable?
Get in line behind the H.R. managers themselves, who say that since the pandemic, the job has become an exasperating ordeal. “People hate us,” one said.

By David Segal
Show of hands: Who’s fed up with human resources?
Maybe you’re irked by the endless flow of memos and forms, many of which need to be filled out, pronto. Maybe you’re irritated by new initiatives that regularly emerge from H.R., which never seems to run out of new initiatives, not all of them necessary or especially wise, in your opinion. Or you’ve got some problem with management and you don’t trust that H.R. representatives will actually help. They sure are friendly, but they get paid by the suits. In a crunch, it’s pretty clear whose side they are on.
The H.R. department bugs a lot of employees and managers, and it seems to have more detractors than ever since the pandemic began. That’s when H.R. began to administer rules about remote work and pay transparency, programs to improve diversity, equity and inclusion and everything else that has rattled and changed the workplace in the last four years.
But if the H.R. department is bothering you, here’s a fact you might find perversely consoling: You are not as aggravated or bummed out as the people who work in H.R.
That was obvious at Unleash, an annual three-day conference and expo held this year at Caesars Forum, an immense convention hall near the Las Vegas Strip. In May, the event brought together some 4,000 H.R. professionals from across the country. It was billed as a place where “global H.R. leaders come to do business and discover inspirational stories.”
It was more like a place where the H.R. department came to complain.
“Everything feels like a fool’s errand,” said Kyle Lagunas, a former H.R. executive at General Motors who now works at Aptitude Research, an H.R. advisory company based in Boston. He had just finished a highly animated presentation about H.R. tech in front of an audience of about 50 people. Now he sat in the designated media room and ranted a bit about the maddening challenges of running H.R. during and after the tumult of the pandemic.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
Performance Management: Meaning, Stages, and Best Practices
by Aleksandra Masionis
Updated on August 9, 2024

Create a culture that means business™
Email address
Managing employee performance ensures that your workforce remains productive, engaged, and motivated. By setting clear expectations, providing regular feedback, and recognizing achievements, organizations can create a culture of high performance that drives business success. But without balancing the need for honest, critical assessments with the need to maintain positive employee morale — and ensuring evaluations are consistent and fair — employees may resist performance management initiatives, perceiving them as punitive, overly bureaucratic, and biased.
The right performance management strategy and tools can address these challenges and transform the process into a positive experience for both managers and employees. Let’s explore what great performance management entails, taking a look at each part of the performance management cycle and how your company can improve productivity and engagement across your entire workforce.
- What is performance management?
Performance management is the process of assessing and improving employee performance. It revolves around setting clear expectations, providing regular feedback, and supporting employee development. When done right, performance management ensures that team members understand what your company expects of them and how their roles contribute to your organization’s success. By establishing a structured process for evaluating and developing performance, organizations can identify their most productive employees and support team members as they grow.
5 stages of the performance management cycle
The performance management cycle consists of five key stages, each of which plays an important role in enhancing employee productivity.
1. Create a performance plan
The planning stage involves setting measurable goals for employees, informed by their professional interests and company goals. Managers and employees should collaborate to define expectations, establish performance criteria, and outline the steps needed to achieve set goals. This cooperative approach helps build a common understanding of employees’ roles and responsibilities, while making it more likely that team members will buy into the performance review process. Managers should also empower employees by outlining the resources, training, and other support needed to meet objectives in the performance plan itself — and then provide everything they’ve promised, so team members can reach their full potential.
2. Monitor employee performance
After developing a plan, managers should monitor employee performance as they make progress towards the established goals. During this stage, leaders should gather data to concretely assess how well employees are performing — as well as how they feel about the performance management process and other key aspects of your company. Managers should also hold regular check-ins with direct reports to discuss performance and provide a channel for honest, two-way feedback .
By maintaining open lines of communication, manager will never lack an opportunity to motivate team members by offering words of encouragement and recognition . They’ll also be able to address issues or challenges that may arise in a timely fashion and provide any guidance needed to ensure employees stay on the track to success.
3. Help employees develop
Explaining what you want team members to do and telling them to “go at it” won’t result in the performance your organization is looking for. Instead, managers should work with employees to build personalized development plans that address specific skill gaps and align with team members’ career aspirations. Identify professional development needs through performance assessments, and then provide training opportunities targeted to meet those needs while matching employees’ individual learning styles. These development initiatives can include coaching initiatives , on-the-job training, and access to online learning resources.
4. Review employee performance
Conducting reviews is a core part of any performance management process. These assessments are an opportunity for managers and employees to reflect on achievements and ensure that both the organization’s and team member’s needs are being met. Managers must evaluate how well employees have met their goals and provide comprehensive feedback — highlighting the positives while discussing areas for improvement. Leaders should base each review on objective data and observations, staying alert for any biases that may impact their judgment.
As noted above, annual performance reviews aren’t sufficient. By the time they occur, much of the feedback from both sides’ will be largely irrelevant, unactionable, and, by extension, mutually frustrating to receive. Setting a relatively frequent cadence of performance-focused, one-on-one meetings with direct reports, supplementing these discussions with more formal reviews held quarterly or twice a year, and establishing a range of open feedback channels will ensure that both employees and managers can adjust their approach before issues become intractable.
Your company can facilitate this environment of continuous improvement by adopting performance management software that allows managers and employees to share feedback instantly, set goals, track progress, and document performance discussions. And don’t forget to adopt an employee engagement platform that lets employees provide feedback anonymously at any time. Otherwise, they’re likely to hold back some of their real thoughts they aren’t comfortable sharing with management directly, and your business will miss out on key ways to improve performance management and the employee experience .
5. Recognize and reward employees
Recognizing employees for their contributions , both large and small, is perhaps the most essential part of performance management — and certainly the one that should be most enjoyable for all parties involved. Recognition can take many forms, from a quick email of thanks, to a well-deserved bonus, to public appreciation during an all-hands meeting. But to make a real impact, your organization needs to streamline and scale its recognition efforts , so every team member can provide meaningful appreciation with the push of a button, no matter where they find themselves. The fastest way to accomplish this is with an employee recognition solution that brings everyone together in a communal space, where they can show thanks and react to others’ moments of appreciation.
- Best practices for setting performance management standards
Effective performance management requires a balance between positive reinforcement and constructive feedback — between helping employees meet their own professional goals and empowering them with the resources and guidance needed to achieve those of your business. Achieving this ideal starts with establishing clear standards to measure employee performance against. There’s no need to reinvent the wheel when it comes to setting tangible objectives, though. Instead, use a popular, easy-to-adopt framework like SMART goals or objectives and key results (OKRs) , both of which facilitate clear communication and accountability on the part of managers and employees.
SMART goals are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. This framework helps employees understand exactly what is expected of them, how their performance will be measured, and the timeline for achieving their objectives. SMART goals provide a roadmap that team members can follow when prioritizing their tasks, and one that managers can use to track employee progress and provide targeted, relevant feedback.
OKRs involve first setting high level objectives and then defining measurable key results that indicate progress toward those goals. They encourage employees to set ambitious goals and keep their focus on outcomes rather than activities. By tracking and regularly reviewing OKRs, organizations gain a valuable, objective yardstick for measuring employee performance while maintaining alignment between individual contributions and shifting business priorities.
- What to look for in a performance management solution
There are many aspects of performance management that can benefit from the right HR technology. First, ensure you’ve taken care of the basics. Look for a performance management solution that lets managers and employees set clear, measurable goals, track progress towards them, and easily conduct frequent reviews to maintain alignment and fast track employee development. It should also provide powerful analytics and reporting capabilities that help HR professionals and leaders gain insights into performance trends, identify high performers, and pinpoint areas for individual improvement.
Your company should also look for an employee engagement solution that provides a real time stream of honest employee feedback. The best engagement platforms offer a range of intuitively designed feedback channels, from focused pulse surveys to intelligent chatbots that are able to prompt employees for input. Leaders and HR professionals can then use built-in reporting capabilities and dashboards to see where their performance management system is working and where employees think it could use some improvement.
Last but not least, adopt an employee recognition and rewards platform that allows for both peer-to-peer and manager-to-employee recognition. Beyond the fundamentals, like a centralized place for all team members to provide public recognition, a mobile-friendly app, and integrations with the tools your employees use every day, select a solution that lets team members tie each recognition to meaningful rewards . This isn’t as difficult as it might sound — with a points-based reward system backed by a marketplace filled with millions of options employees actually want, your company can make every performance win truly memorable.
- Transform performance management at your company
You can take performance management at your company beyond the norm and into the realm of real excellence with the Achievers Employee Experience Platform . It leverages the science of HR to make performance management an engaging and effective process, starting with Achievers Recognize , a comprehensive employee recognition and rewards solution. It provides the incentives needed to keep the performance management cycle running smoothly, with easy-to-use social recognition features and a rewards marketplace filled to bursting with exciting merchandise and experiences.
And thanks to Achievers Listen , your people leaders will never lack real time insights into how employees feel about the performance management process and what they can do to engage them further. By streamlining the collection and analysis of feedback, Listen provides leaders with a deep understanding of what drives team members, so they can make informed decisions that improve employee experience and performance.
See how the Achievers Employee Experience Platform can improve performance management for yourself with a free demo.
Discover the number one reason employees will job hunt in 2024
In this article:
- 5 stages of the performance management cycle 1. Create a performance plan 2. Monitor employee performance 3. Help employees develop 4. Review employee performance 5. Recognize and reward employees

Interested in learning more about Achievers?
We use cookies to help us understand how you use our site so we can show you personalized content and enhance your browsing experience. Learn more by viewing our Privacy Policy
Meet all your HR needs with an all-in-one HRIS.
Automate and simplify payroll processes with payroll software.
Find and onboard top talent to stay competitive in your industry.
Track and analyze employee performance.
Digital learning platforms to teach and train employees.
All-in-one HRMS for workforce management.
Comprehensive HCM for HR excellence.
Track time & attendance accurately.
Elevate talent with top TMS software.
Free Software Match !
Get matched for free with top HR software
Learn how Matchr helps HR professionals streamline their software searches.
- Best HRIS Software
- HRIS Vendor List
- Free HRIS Software List
- HRIS Resources
- Best Payroll Software
- Payroll Vendor List
- Free Payroll Software
- Payroll Resources
- Best ATS Software
- ATS Vendor List
- Free ATS Software
- ATS Resources
- Best LMS Software
- LMS Vendor List
- Free LMS Software
- LMS Resources
- Best Performance Management Software
- Performance Management Vendor List
- Free Performance Software
- Performance Management Resources
- Best HRMS Software
- HRMS Vendor List
- Free HRMS Software
- Best HCM Software
- HCM Vendor List
- Free HCM Software
- Best Time and Attendance Software
- TA Vendor List
- Free TA Software
- Best TMS Software
- TMS Vendor List
- Free TMS Software
- Case Studies
- Scholarship
- Get Software Matches
Key Functions of Human Resources

HR is typically associated with professionals interviewing candidates or conducting employee training. However, there is a lot more to this role. Over the years, it has evolved significantly and encompasses numerous functions. HR professionals are involved in talent management, employee engagement, legal compliance, and more. Each of these functions plays a crucial role in fostering a positive work environment, ensuring employee well-being, and integrating HR initiatives with organizational goals. This multifaceted approach to human resource management is vital for promoting organizational growth and employee satisfaction.
Generalist and Specialist Paths in HR
HR professionals can choose to become either generalists or specialists, depending on their career goals and interests. HR generalists possess a wide range of skills that allow them to manage multiple facets of a company’s HR needs. On the other hand, HR specialists focus on a specific area of HR, developing deep expertise in one field. Specialists bring a high level of knowledge and proficiency to their chosen area, ensuring that the company excels in that particular aspect of HR. Regardless of whether an HR professional is a generalist or a specialist, there are key functions that are essential to the role.
What Are HR Functions?
HR Functions are core responsibilities that include various activities aimed at promoting employee well-being while aligning with the company’s needs. HR departments carry out these functions to ensure that employees are treated in a manner that benefits both the individual and the organization’s overall objectives.
Exploring HR Key Functions
These core HR functions are the main business of the Human Resources department within a company. They include:
- Talent acquisition
- Performance management
- Employee onboarding
- Employee relations
- Compensation and benefits
- Training and development
- Workplace safety
- Legal compliance
- Company culture
- Employee well-being
- Administrative duties
- Technology and data management
By effectively executing these responsibilities, an organization’s HR team contributes to its overall success and growth, ensuring a productive and satisfied workforce.
Recruiting, Hiring, and Retaining Talent
The HR department plays a critical role in sourcing and talent acquisition, ensuring that the organization attracts and retains top talent. This process includes elaborating detailed job descriptions, conducting thorough background checks, and managing the hiring process from start to finish. Effective HR management in these areas ensures that the organization is staffed with skilled and motivated individuals who contribute to its success.
Recruiting Candidates
Finding the right person begins with developing accurate and detailed job descriptions. HR professionals must analyze the job market and establish a competitive salary range before beginning the recruitment process. HR professionals then review and evaluate job applications and determine which candidates are suitable and qualified to proceed to the next stages of the hiring process. This initial screening helps identify the most promising candidates who meet the job requirements and have the potential to succeed in the role. This often involves setting up one or more interviews with employees, managers, and senior leadership.
Hiring Employees
HR managers conduct background checks, onboard new employees, and explain payroll, benefits, and company policies. The hiring process involves significant legal paperwork, recordkeeping, and administrative duties. Ensuring that all information is accurate, complete, and securely stored is crucial for both employee and company security.
Retaining Talent
Employee retention is another critical aspect of HR’s role. According to the Society for Human Resources Management (SHRM), employees identify the following five factors as the leading contributors to job satisfaction: respectful treatment of all employees at all levels, trust between employees and senior management, opportunities to use their skills and abilities at work, competitive compensation and pay, and job security.
Performance Management
Performance management is a key function of human resource management that focuses on evaluating progress and improving employee performance. An employee’s performance includes attitude, efficiency, and effectiveness. This function involves conducting regular performance reviews and appraisals, setting clear performance metrics, and providing feedback and support. HR professionals use assessments and metrics to identify areas for improvement. Implementing effective performance management strategies helps in succession planning and ensures that employees are aligned with the organization’s goals.
Onboarding New Employees
The onboarding process for new employees is a crucial function of human resources that significantly impacts employee retention and satisfaction. Effective onboarding goes beyond orientation. It involves integrating new hires into the company culture, explaining their roles and responsibilities, and providing the tools and resources they need to succeed. HR professionals play a pivotal role in offering support and designing onboarding programs that include initial training and introductions to key team members. By ensuring that new employees feel welcomed, valued, and well-prepared for their roles, HR helps to establish a strong foundation for long-term success and fosters a sense of belonging within the organization.
Employee Relations
Promoting effective communication between employees, HR professionals, and senior leadership is essential for creating a positive work environment. This interaction helps align all of its members with the organization’s goals and values. Improving employee relations involves preventing and resolving workplace disputes. This includes addressing employee issues, conflict resolution, and promoting open communication. By implementing fair company policies that support a healthy work environment, HR ensures that employee concerns are heard and addressed promptly. Strong employer-employee relations enhance staff loyalty and engagement, contributing significantly to overall employee well-being and helping build trust among the workforce.
Compensation and Benefits
Managing compensation and benefits is a critical HR function that directly impacts employee retention and satisfaction. HR professionals are responsible for designing and administering benefits packages, which include health insurance, retirement plans, career development opportunities, and other employee benefits. Retention strategies help maintain employee engagement and reduce turnover rates. This function must also ensure compliance with employment and labor laws, ensuring that all compensation practices are fair and legal. Benefits administration also involves regular reviews and updates to the benefits package to keep it fair and competitive. By offering attractive compensation and benefits, HR helps to attract and retain top talent, contributing to the overall well-being of the workforce.
Training and Development
Training and development are essential HR functions that focus on employee growth and professional development. HR professionals design and implement training programs that enhance skills and competencies, ensuring that employees are well-equipped to perform their roles effectively. These initiatives help employees gain new skills, enhance their performance, and adjust to evolving business requirements. HR professionals identify training needs, develop training programs, and oversee their execution to promote continuous learning and growth within the organization. Ongoing development programs, such as professional development workshops and career development initiatives, support continuous learning and help employees advance in their careers. HR contributes to a knowledgeable and capable workforce by prioritizing training and development.
Workplace Safety
HR professionals must ensure workplace safety and compliance with safety regulations. They implement health and safety programs to protect employees from workplace hazards and promote a safe work environment. This includes conducting regular safety audits, providing training on safety protocols, and ensuring adherence to safety regulations to prevent accidents, injuries, and work-related illnesses. Additionally, HR is responsible for legal compliance, ensuring that the organization follows all employment laws and labor laws. By proactively managing risks, HR helps to create a safe and compliant workplace, reducing the likelihood of accidents and legal issues.
Employment Law and Compliance
Ensuring legal compliance is a fundamental HR function that involves adherence to employment laws, labor laws, and company policies. HR professionals conduct regular audits to ensure that HR practices and procedures are compliant with legal standards and regulations. This includes reviewing employee data, assessing compliance with HR policies, and implementing necessary changes to meet legal requirements. By maintaining legal compliance, HR protects the organization from potential legal disputes and ensures fair and equitable treatment of employees.
Company Culture and Engagement
HR professionals are responsible for creating and maintaining a positive company culture that actively engages employees. This can involve organizing activities that promote participation and networking, such as wellness programs, contests, or office parties. Another method to enhance engagement includes offering incentives or rewards for employee performance or participation in workplace activities. For instance, the company might implement a referral program to enhance hiring efforts and offer rewards for successful candidate referrals. Incentives help employees feel valued and motivated to go to work. By promoting a strong company culture, HR professionals create a supportive workplace where employees feel included and aligned with the organization’s mission and goals.
Employee Well-Being
Promoting employee well-being is a key function of HR that encompasses physical, mental, and emotional health. HR professionals implement wellness programs and initiatives that support employees’ overall health and happiness. This includes offering health insurance, employee assistance programs, and initiatives that promote work-life balance. HR also focuses on creating a positive work environment where employees feel supported and valued. By prioritizing employee well-being, HR helps to reduce stress, increase job satisfaction, and improve overall productivity. A healthy and happy workforce is essential for the organization’s long-term success.
Administrative Duties
HR is responsible for a range of administrative duties essential for an organization’s efficient operation. This includes managing payroll, maintaining employee records, and overseeing HR information systems. HR professionals ensure that all administrative processes are efficient and compliant with legal requirements. They also handle the administration of benefits packages, health insurance, and other employee benefits. By effectively managing administrative tasks, HR supports the overall functionality of the organization and ensures that employees’ needs are met promptly and accurately.
Technology and Data Management
Integrating HR information systems (HRIS) enables HR professionals to manage payroll, benefits administration, performance evaluations, and employee records effectively. By employing technology, HR can automate repetitive tasks, minimize administrative workloads, and increase precision. Furthermore, data analytics offer valuable insights into workforce trends, employee performance, and retention rates, allowing HR to make well-informed decisions and develop strategies that support organizational goals. Efficient use of HR technology not only boosts the efficiency of the HR department but also contributes to the organization’s overall growth.
Why Are These Key Functions Important?
Key HR functions are integral to the role of HR and are essential for ensuring the success of any organization. HR professionals play a crucial role in effectively managing a company’s workforce planning and employee life cycle. Successful human resource planning to fulfill these responsibilities contributes to a productive, satisfied, and engaged workforce. By strategically planning and implementing HR functions, professionals ensure that the workforce is aligned with the company’s goals and objectives.
Strong Execution of HR Functions Enhances Organizational Success
By focusing on these diverse yet interconnected functions, HR professionals drive long-term business success and significantly contribute to organizational growth and employee satisfaction. Effective human resource management ensures that both employees and businesses reach their full potential.
Find the right software match!
Get matched for free with top HR software.
How many employees are in your organization?
Select the software features you need.
We're matching your needs with the software in our database.
By clicking the checkbox I agree to opt-in to receive future emails from Matchr and its software vendor partners. I also accept the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.
Thanks for using our Software Matching service!
Would you like to schedule a 5-10 minute meeting with a Software Advisor right now?
We are sorry, Matchr currently does not offer support to countries outside USA, Canada
Find the Right Software Match

Related Articles
How much should you expect to get paid as an hr professional.
Starting off as an HR professional can be exciting. You have the opportunity to directly influence the way that people are treated within your organization and potentially even on a grander scale in the workforce. While the ideals for starting out as an HR professional are noble, it’s important to consider pay in order to …
Proven Ways to Motivate Employees
Although motivating employees is important for companies, knowing how to motivate employees can be difficult. Different employees have different things that motivate them to work harder and better. Some are motivated by recognition while others are better motivated by financial rewards. What motivates one employee may fail to motivate another. Employee motivation is even more …
5 Ways Employers Can Protect Themselves Against Non-Compete Bans
One of the biggest challenges in HR is being prepared for a change in legislation while also keeping things in place in the event they stay status quo. So how can you prepare for an elimination of these contracts? By diving into the purpose and nature behind non-competes. What Happened? In January of 2024, The …
How Do You Know if Your Employees Are Unhappy?
Every good employer wants to create a workplace where employees feel content and satisfied. In reality, you can’t please everyone all the time — but you may be able to identify unhappy employees and take steps to fix the situation before you lose good employees. By taking a proactive approach to spotting and mitigating unhappiness, …

Looking for a new HRIS? Explore Paycor's HCM solution.

Free tools and downloads to hire, support, and retain talent.
To give you the best possible experience, this site uses cookies. If you continue browsing, you accept our use of cookies. You can review our Privacy Policy to find out more about the cookies we use.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Why Dropping the E in DEI Is a Mistake
- Enrica N. Ruggs
- Oscar Holmes IV

The Society for Human Resource Management’s decision to remove “equity” from its DEI framework sets a dangerous precedent that flies in the face of decades of research.
The Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM) has decided to remove “equity” from its inclusion, equity, and diversity (IE&D) framework, now promoting “inclusion and diversity” (I&D) instead. This decision sets a dangerous precedent that flies in the face of decades of research about DEI in the workplace. It undermines efforts to create equitable workplaces and ignores the vital role of equity in fostering fairness and addressing systemic barriers faced by marginalized groups. Instead of scaling back their focus on equity, companies should: 1) Commit to achievable equity goals; 2) Implement and track evidence-based DEI policies and practices; and 3) Establish accountability and transparency.
Recently, the Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM), a leading voice of HR professionals, announced that it was abandoning the acronym “IE&D” — inclusion, equity, and diversity — in favor of “I&D.”
- Enrica N. Ruggs , PhD is an associate professor of management in the C. T. Bauer College of Business at the University of Houston. She is a workplace diversity scholar who conducts research on reducing discrimination and bias in organizations and improving workplace experiences for individuals with marginalized identities.
- Oscar Holmes IV , PhD, SHRM-SCP is an associate professor of management at Rutgers University-Camden and the creator and host of the podcast Diversity Matters . In his research he examines how leaders can maximize productivity and well-being by fostering more inclusive workplaces.
Partner Center
Ocean Exploration Matters
Seventy percent of Earth is covered by the ocean. Ninety percent of the ocean is considered "deep," with a depth of greater than 200 meters (656 feet). Yet only slightly more than a quarter of the ocean has been mapped at high resolution and just a fraction of that has been visually surveyed and explored. Given this, can we truly say that we “know” our own ocean? And if we don’t, how do we manage or protect it and the resources it holds?
Take a deep dive with us as we look at several of the reasons why exploring our ocean is so important .
To view this video please enable JavaScript, and consider upgrading to a web browser that supports HTML5 video

The deep ocean impacts our very survival, yet remains poorly understood.
The ocean impacts all of us, whether you live in a coastal community or in a landlocked area. The ocean plays a role in everything from the air we breathe , the food we eat, and the transportation of the goods we buy to our daily weather and longer-term climate trends .
Most of our knowledge of the ocean lies in shallower waters. However, deeper waters continue to grow in their importance to our nation. Many fisheries are based in deep waters, providing food, jobs, and livelihoods. The deep ocean holds reserves of oil, gas, precious metals, and rare minerals. Within ocean depths may lie cures to crippling diseases and sources of other natural products with potential as pharmaceuticals, enzymes, cosmetics, and more.
How will we know what is out there if we aren’t even looking for it?

Good management of ocean resources is critical, but we can’t manage what we don’t know.
The ocean is an interconnected network of animals, plants, microorganisms, rocks, and other structures. When a change happens to one component of an ocean ecosystem, it can have dramatic impacts on the ecosystem as a whole. We depend on the ocean for the many services it provides. Yet we can unintentionally set an ecosystem off balance without intending to simply by extracting and using marine resources such as seafood and energy. Resource managers and ocean users alike need environmental information to make good decisions.
We need to be careful and conservative in how we use our ocean and its resources to ensure future generations can do the same. Careful practice requires good management that balances use, enjoyment, and protection. But if we don’t know what’s out there, how can we effectively manage it?
By exploring unknown reaches of the ocean and putting gained knowledge into the hands of management and regulatory communities, exploration helps to ensure that the ocean is not just managed, but managed in a wise and sustainable way.
Ocean exploration knowledge, tools, and technologies can be applied elsewhere, enhancing resilience and recovery.
Oftentimes we don’t think about our limited knowledge of the deep ocean until after disaster strikes and it’s too late. An oil spill or a missing aircraft can quickly demonstrate how little we know about these deepwater environments and how difficult it is to get timely, actionable information about them.
Deep reaches of the ocean are places with near-freezing temperatures , corrosive saltwater, limited or no light , and intense pressure . Not only do we not always know what’s found at ocean depths, we also often are lacking the tools and technology needed to get to and survey these extreme places.
Early ocean explorers used lead lines to map the seafloor, collecting data one laborious cast at a time. Our current technology allows us to deploy ships and other vehicles with increasingly sophisticated systems for mapping the seafloor, measuring ocean characteristics, and sampling the marine environment. Increased use of highly autonomous vehicles is greatly increasing the pace and scope of exploration.
Before, not after, a disaster or crisis strikes—that is when we need knowledge about the environment. Ocean exploration provides the basic environmental information needed to respond appropriately. Additionally, the tools and technologies being developed for exploration can be transferred for use in emergency situations such as response to an oil spill.
Without basic knowledge and technologies, how can we respond in the face of an ocean crisis and how can we know that our response is the right one?
Our ocean is not a static place.
The environment on Earth is constantly changing. Many of those changes are happening faster than ever. The ocean plays a critical role in many of these changes, from the increasing frequency and severity of coastal storms to sea level rise and warming global temperatures. Communities, particularly those in coastal areas, must make increasingly difficult decisions to stay safe, resilient, and economically sound.
Through ocean exploration, from mapping and characterizing previously unseen seafloor to collecting and disseminating data about the water column, we can establish baseline information needed to better understand environmental change.
This baseline knowledge fills gaps in the unknown, delivering the reliable and authoritative science that is foundational to providing foresight about future conditions and informing the decisions we confront every day on this dynamic planet.
While the ocean exploration community continues to grow, despite its importance, the number of people exploring our ocean remains small.
Given the immense breadth and scope of ocean exploration, no single person or organization could ever go it alone. The pooling of resources, expertise, and capabilities through strategic partnerships is paramount to bridging gaps in our understanding of the ocean.
NOAA Ocean Exploration is one organization focused on exploring our unknown ocean. As the only federal organization currently dedicated to ocean exploration, we work closely with government agencies, academic institutions, nonprofit organizations, the private sector, local communities, and others to identify requirements and needs.
We collaborate with stakeholders to build ocean exploration campaigns—multi-partner, multi-ship, multi-year initiatives to map and explore areas of national importance. We provide partnership coordination, funding , staff , tools , and expertise needed to develop exploration missions that deliver rigorous, systematic observations and documentation of biological, chemical, physical, geological, and archaeological aspects of the ocean. We work to get scientists to uncharted areas; to design, test, and implement new deep-sea technologies; and to bring the wonders of ocean exploration to everyone. And, during and after expeditions, our system of data management ensures that collected information arrives quickly – and accurately – into the hands of those who need it to make timely decisions.
Every day, our unique capabilities are helping to advance knowledge and understanding needed to help communities, businesses, and governments make smart choices to protect lives, property, and economic well being.
Published August 13, 2024

COMMENTS
Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles, conference papers, preprints and more on HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT. Find methods information, sources, references or conduct a literature ...
We present a systematic review of 495 empirical studies on 516 HR systems in which we analyze the development of HR systems research over time and identify important trends, explicitly linking conceptualization and measurement of the HR system.
In this fourth annual review issue published by The International Journal of Human Resource Management (IJHRM), we are delighted to present five articles that cover some of the important areas in people management in contemporary work settings. Our review articles cover topics that are less well-researched, compared with some popular themes, as ...
The Human Resource Management Review(HRMR) is a quarterly academic journal devoted to the publication of scholarly conceptual/theoreticalarticles pertaining to human resource management and allied fields (e.g. industrial/organizational psychology, human capital, labor relations, organizational behavior). HRMR welcomes manuscripts that focus on micro-, macro-, or multi-level phenomena relating ...
HR's New Role. Organizational Development Magazine Article. Peter Cappelli. Ranya Nehmeh. Though the human resources function was once a strong advocate for employees, in the 1980s things changed ...
Finally, a variety of descriptive and evaluative conceptualizations have been used. Recommendations and avenues for future research to gain a more comprehensive understanding of employee perceptions of HRM are provided. Keywords: Strategic human resource management employee perceptions of HR practices systematic literature review
Human Resource departments had a difficult job prior to the pandemic. In 2019, more than 50% of HR leaders struggled to ensure that employees had the skills necessary to navigate an increasingly ...
This paper attempts to undertake a systematic literature review to identify ways and means by which sustainable human resource management (HRM) and well-being are linked for better individual and organizational outcomes. Its primary focus is to study whether sustainable HRM predicts well-being at work? If yes, how and when this prediction takes place? Systematic computerized search and review ...
The half-life of knowledge and strategic human capital. Eirik Sjåholm Knudsen, Lasse B. Lien. Article 100989. View PDF. Article preview. Read the latest articles of Human Resource Management Review at ScienceDirect.com, Elsevier's leading platform of peer-reviewed scholarly literature.
Human Resource Management is the leading journal for human resource management studies. Internationally recognised, this HRM journal covers micro to multi-level topics.
This study reviews Human Resource Management (HRM) literature by adopting a hybrid research approach-bibliometric analaysis and content analysis-on 1802 documents from the Scopus database.
Ranya Nehmehis an HR specialist working on topics related to people strategy, human capital, leadership development, and talent management and is the author of The Chameleon Leader: Connecting ...
ISSN: 1053-4822. Read the latest articles of Human Resource Management Review at ScienceDirect.com, Elsevier's leading platform of peer-reviewed scholarly literature.
This article reviews the literature on human resource management in public management and public service delivery, and identifies key research gaps and future directions.
Scholars reviewing research exploring the association between human resource management (HRM) and outcomes have noted a frequent absence of any link between the espoused HRM theory and the HR practices used to measure it.
In this paper the influence of human resource management (HRM) on business performance is analyzed. The main goal was to thoroughly and systematically examine literature in the domain of HRM, and ...
Human Resources New research on human resources from Harvard Business School faculty on issues including organizational design, compensation, incentive plans, hiring practices, and recruitment.
Human resource management (HRM) in healthcare is an important component in relation to the quality and efficiency of healthcare delivery. However, a comprehensive overview is lacking to assess and track the current status and trends of HRM research in healthcare. This study aims to describe the current situation and global trends in HRM ...
Endorsed by the Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development, the Human Resource Management Journal is a global HRM journal covering personnel management, training & more. ... In this systematic literature review, we identified 87 articles related to organisational context factors and female leadership. We mapped these articles onto the ...
The article asks what the main consequences have been for managerial work arising from changes to human resource management (HRM) practices during an era of neoliberal corporate restructuring.
Talking the talk: Considering forced language-switching in the workplace. Stephanie R. Seitz, Sara A. Smith. Article 100833. View PDF. Article preview. Read the latest articles of Human Resource Management Review at ScienceDirect.com, Elsevier's leading platform of peer-reviewed scholarly literature.
Abstract. This paper provides a commentary on the article in this special issue by Meyers, van Woerkom, and Dries on the meaning of the term 'talent' with a particular focus on the extent to ...
This article reviews the body of empirical work on human resource management in times of crisis, including that which was conducted prior to the COVID-19 pandemic and that which has been published ...
In sum, we present a systematic review of existing empirical studies on HR systems and analyze the development of the field over time. We take a comprehensive approach and focus on all choices researchers make when designing a study on HR systems, explicitly linking conceptualization and measurement of the HR system.
Get in line behind the H.R. managers themselves, who say that since the pandemic, the job has become an exasperating ordeal. "People hate us," one said.
You can take performance management at your company beyond the norm and into the realm of real excellence with the Achievers Employee Experience Platform. It leverages the science of HR to make performance management an engaging and effective process, starting with Achievers Recognize, a comprehensive employee recognition and rewards solution ...
Performance management is a key function of human resource management that focuses on evaluating progress and improving employee performance. An employee's performance includes attitude, efficiency, and effectiveness.
The Society for Human Resource Management's decision to remove "equity" from its DEI framework sets a dangerous precedent that flies in the face of decades of research. The Society for Human ...
Read the latest articles of Human Resource Management Review at ScienceDirect.com, Elsevier's leading platform of peer-reviewed scholarly literature.
Resource managers and ocean users alike need environmental information to make good decisions. We need to be careful and conservative in how we use our ocean and its resources to ensure future generations can do the same. Careful practice requires good management that balances use, enjoyment, and protection.