

HeinOnline Blog
The 15 most inspiring presidential speeches in american history.
- By Tara Kibler
- February 15, 2021
- History , Political Science
Over the centuries, millions upon millions of words have been used by U.S. presidents to motivate, caution, reassure, and guide the American people. Whether written in the news, spoken at a podium, or shared on Twitter, all of these words have carried weight, each with the potential to impact the trajectory of our nation. Only a handful of times, however, has the particular arrangement and context of these words been considered truly inspiring.
This Presidents’ Day, join HeinOnline in rediscovering some of the greatest presidential speeches in American history using our U.S. Presidential Library and other sources.
1. Washington’s Farewell Address
Date: September 17th, 1796
Context: Toward the end of his second term as the first U.S. president, George Washington announced his retirement from office in a letter addressed to the American people. Though many feared for a United States without Washington, the address reassured the young nation that it no longer required his leadership. Washington also used the opportunity to offer advice for the prosperity of the country. After witnessing the growing division between the Federalist and Democratic-Republican parties, much of his advice was to warn against political parties, factions, and other animosities (domestic and foreign) that would eventually undermine the integrity and efficacy of the American government.
Notable Quote: “This spirit [of party], unfortunately, is inseparable from our nature, having its root in the strongest passions of the human mind … [but] the disorders and miseries which result gradually incline the minds of men to seek security and repose in the absolute power of an individual; and sooner or later the chief of some prevailing faction, more able or more fortunate than his competitors, turns this disposition to the purposes of his own elevation, on the ruins of public liberty.
“Without looking forward to an extremity of this kind (which nevertheless ought not to be entirely out of sight), the common and continual mischiefs of the spirit of party are sufficient to make it the interest and duty of a wise people to discourage and restrain it. It serves always to distract the public councils and enfeeble the public administration. It agitates the community with ill-founded jealousies and false alarms, kindles the animosity of one part against another, foments occasionally riot and insurrection. It opens the door to foreign influence and corruption, which finds a facilitated access to the government itself through the channels of party passions … A fire not to be quenched, it demands a uniform vigilance to prevent its bursting into a flame, lest, instead of warming, it should consume.”
2. Lincoln’s Gettysburg Address
Date: November 19, 1863
Context: Four months after Union armies defeated Confederates at Gettysburg during the American Civil War, President Lincoln visited the site to dedicate the Soldiers’ National Cemetery. In what were intended to be brief, appropriate remarks for the situation, Lincoln used the moment to offer his take on the war and its meaning. The ten sentences he spoke would ultimately become one of the most famous speeches in American history, an inspiration for notable remarks centuries later, and even a foundation for the wording of other countries’ constitutions.
Notable Quote: “… from these honored dead we take increased devotion to that cause for which they heregave the last full measure of devotion; that we here highly resolve that the dead shall not have died in vain; that the Nation shall under God have a new birth of freedom, and that Governments of the people, by the people and for the people shall not perish from the earth.”
3. Franklin D. Roosevelt’s Inaugural Address
Date: March 4, 1933
Context: The inauguration of Franklin D. Roosevelt was held as the country was in the throes of the Great Depression, and as such, America anxiously awaited what he had to say. Roosevelt did not disappoint, offering 20 minutes of reassurance, hope, and promises for urgent action.
Notable Quote: “So, first of all, let me assert my firm belief that the only thing we have to fear is … fear itself — nameless, unreasoning, unjustified terror which paralyzes needed efforts to convert retreat into advance. In every dark hour of our national life a leadership of frankness and of vigor has met with that understanding and support of the people themselves which is essential to victory. And I am convinced that you will again give that support to leadership in these critical days.”
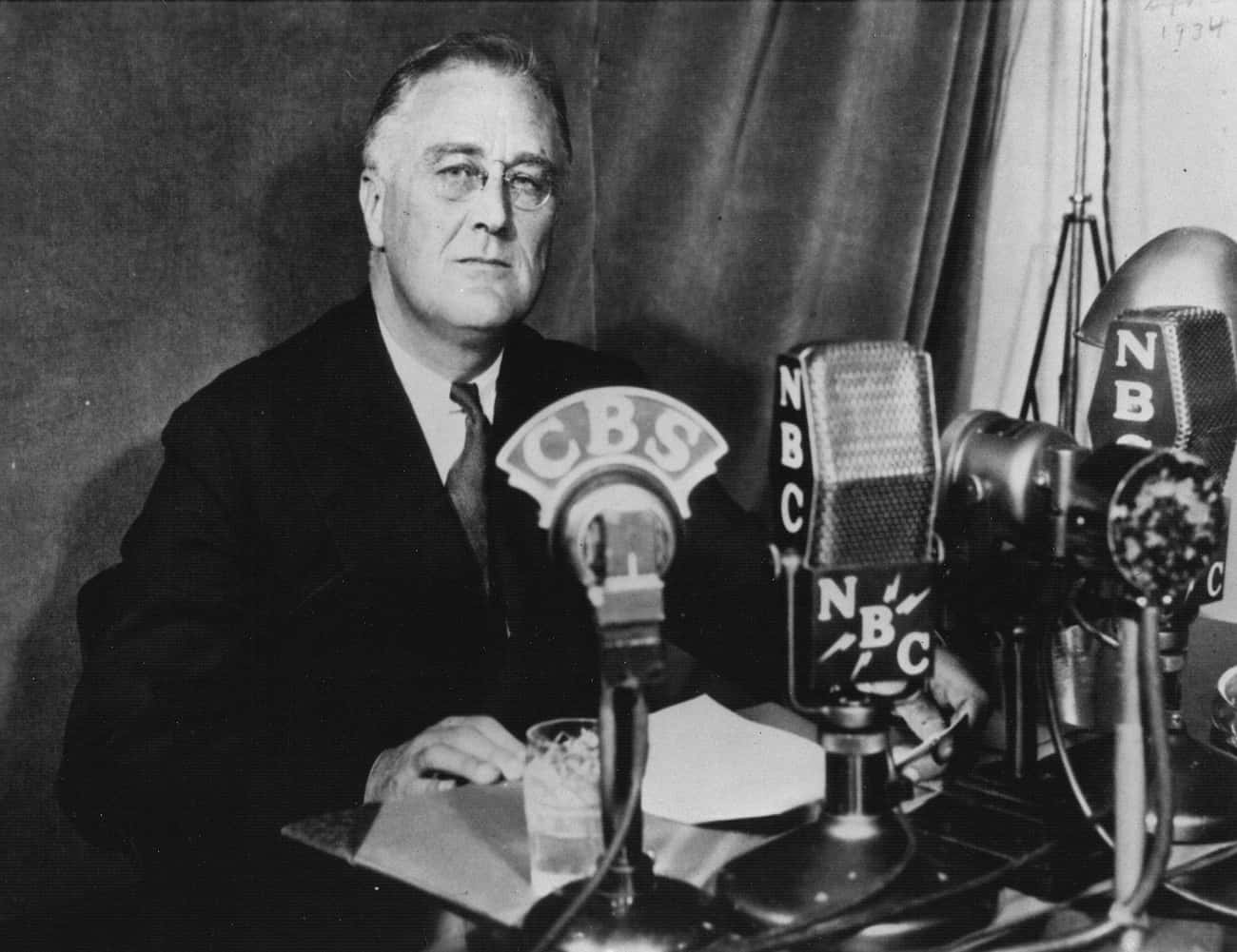
4. Franklin D. Roosevelt’s First Fireside Chat
Date: March 12, 1933
Context: Just a few days after his inauguration, Roosevelt instituted what he called “fireside chats,” using the relatively new technology of radio to enter the living rooms of Americans and discuss current issues. In these moments, he could speak at length, unfiltered and uninterrupted by the press, while also offering a reassuring, optimistic tone that might otherwise have been lost in the written word. In this first fireside chat, he crafted a message to explain the American banking process (and its current difficulties) in a way that the average listener could understand.
Notable Quote: “Confidence and courage are the essentials of success in carrying out our plan. You people must have faith. You must not be stampeded by rumors or guesses. Let us unite in banishing fear. We have provided the machinery to restore our financial system, and it is up to you to support and make it work. It is your problem, my friends. Your problem no less than it is mine. Together, we cannot fail.”
5. Franklin D. Roosevelt’s “Four Freedoms” Speech
Date: January 6, 1941
Context: By 1941, many affected by the Great Depression had experienced economic recovery, but another world-changing phenomenon had reared its head—Hitler and his Nazi regime. World War II was raging in Europe and the Pacific, but the United States had thus far remained largely neutral. In light of the atrocities occurring overseas, Roosevelt sought to change that. He crafted his State of the Union address that January to highlight four freedoms which are deserved by all humans everywhere. The “Four Freedoms” speech, as it was ultimately known, later became the basis for America’s intervention in World War II and significantly influenced American values, life, and politics moving forward.
Notable Quote: “In the future days, which we seek to make secure, we look forward to a world founded upon four essential human freedoms. The first is freedom of speech and expression—everywhere in the world. The second is freedom of every person to worship God in his own way—everywhere in the world. The third is freedom from want—which, translated into world terms, means economic understandings which will secure to every nation a healthy peace of time life for its inhabitants—everywhere in the world. The fourth is freedom from fear—which, translated into world terms, means a world-wide reduction, armaments to such a point and in such a thorough fashion that no nation will be in a position to commit an act of physical aggression against any neighbor—anywhere in the world.”
6. Eisenhower’s “Atoms for Peace” Speech
Date: December 8, 1953
Context: During World War II, Roosevelt formally authorized the Manhattan Project, a top-secret U.S. effort to weaponize nuclear energy. By 1945, America had successfully created the atomic bomb , and President Truman had authorized its detonation in Japan’s Hiroshima and Nagasaki, leveling the two cities and killing hundreds of thousands of people. Following the end of World War II, political and economic differences between the United States and Soviet Union drove the two countries to another war soon after, but this time, the Soviet Union had their own atomic bomb as well. The world was teetering on a frightening ledge built by access to nuclear power, causing President Eisenhower to launch an “emotion management” campaign with this speech to the United Nations about the very real risks but also peaceful uses of nuclear energy.
Notable Quote: “… the whole book of history reveals mankind’s never-ending quest for peace and mankind’s God-given capacity to build. It is with the book of history, and not with isolated pages, that the United States will ever wish to be identified. My country wants to be constructive, not destructive. It wants agreements, not wars, among nations. It wants itself to live in freedom and in the confidence that the peoples of every other nation enjoy equally the right of choosing their own way of life. … The United States knows that if the fearful trend of atomic military build-up can be reversed, this greatest of destructive forces can be developed into a great boon, for the benefit of all mankind.”
7. Eisenhower’s Farewell Address
Date: January 17, 1961
Context: As he came to the end of his term, President Eisenhower found himself in a nation much stronger, much richer, and much more advanced than when he began. Prepared as early as two years in advance, his farewell address acknowledged the pride all should have in these achievements, but also served to ground the American people in sobering reality—that how the United States uses this power and standing will ultimately determine its fate. Like Washington, his address was one of caution against dangers such as massive spending, an overpowered military industry, and Federal domination of scientific progress (or vice versa, the scientific-technological domination of public policy). In all things, he stressed the need to maintain balance as the country moves forward, for the preservation of liberty.
Notable Quote: “Down the long lane of the history yet to be written America knows that this world of ours, ever growing smaller, must avoid becoming a community of dreadful fear and hate, and be, instead, a proud confederation of mutual trust and respect. Such a confederation must be one of equals. The weakest must come to the conference table with the same confidence as do we, protected as we are by our moral, economic, and military strength. That table, though scarred by many past frustrations, cannot be abandoned for the certain agony of the battlefield.”
8. Kennedy’s Inaugural Address
Date: January 20, 1961
Context: A few days after Eisenhower’s farewell speech, he turned over his office to the youngest-ever elected president, John F. Kennedy. Kennedy now found himself faced with the monumental task of strengthening the United States while also quelling American anxieties about the Cold War and avoiding nuclear warfare. His speech thus focused on unity, togetherness, and collaboration both domestically and abroad.
Notable Quote: “In the long history of the world, only a few generations have been granted the role of defending freedom in its hour of maximum danger. I do not shrink from this responsibility—I welcome it. I do not believe that any of us would exchange places with any other people or any other generation. The energy, the faith, the devotion which we bring to this endeavor will light our country and all who serve it—and the glow from that fire can truly light the world.
And so, my fellow Americans: ask not what your country can do for you—ask what you can do for your country. My fellow citizens of the world: ask not what America will do for you, but what together we can do for the freedom of man.”
9. Kennedy’s “We Choose to Go to the Moon” Speech
Date: September 12, 1962
Context: In the name of national security, the United States and USSR set their sights on spaceflight as a top priority during the Cold War. To the surprise (and fear) of people around the globe, the Soviet Union launched the first-ever artificial satellite in 1957, then sent the first human being into space in 1961, signaling to onlookers that its nation was a technological force to be reckoned with. Kennedy was determined to come up with a challenge in space technology that the United States actually stood a chance to win. In the early ’60s, he proposed that America focus on putting a man on the moon. In an uplifting speech at Rice University, Kennedy reminded his listeners of the country’s technological progress so far and of his administration’s determination to continue the pioneering spirit of early America into the new frontier of space.
Notable Quote: “We choose to go to the moon. We choose to go to the moon in this decade and do the other things, not because they are easy, but because they are hard, because that goal will serve to organize and measure the best of our energies and skills, because that challenge is one that we are willing to accept, one we are unwilling to postpone, and one which we intend to win, and the others, too.”
Read about America’s successful moon landing in this blog post.
10. Lyndon B. Johnson’s “Great Society” Speech
Date: May 22, 1964
Context: Lyndon B. Johnson was sworn in as President in 1963, immediately following Kennedy’s assassination . Johnson vowed to continue the former president’s work on poverty, civil rights, and other issues. Inspired in part by FDR’s New Deal, he devised a set of programs intended to completely eliminate poverty and racial injustice. In 1964, he formally proposed some specific goals in a speech to the University of Michigan, where he coined the lofty ideal of a “Great Society.”
Notable Quote: “Your imagination, your initiative, and your indignation will determine whether we build a society where progress is the servant of our needs, or a society where old values and new visions are buried under unbridled growth. For in your time we have the opportunity to move not only toward the rich society and the powerful society, but upward to the Great Society.”
11. Lyndon B. Johnson’s “We Shall Overcome” Speech
Date: March 15, 1965
Context: By the 1960s, blacks in areas of the Deep South found themselves disenfranchised by state voting laws, such as those requiring a poll tax, literacy tests, or knowledge of the U.S. constitution. Furthermore, these laws were sometimes applied subjectively, leading to the prevention of even educated blacks from voting or registering to vote. Inspired (and sometimes joined) by Reverend Martin Luther King, Jr., protests were planned throughout the region. Eight days after racial violence erupted around one of these protests in Selma, Alabama, President Johnson addressed Congress to declare that “every American citizen must have an equal right to vote” and that discriminatory policies were denying African-Americans that right.
Notable Quote: “What happened in Selma is part of a far larger movement which reaches into every section and State of America. It is the effort of American Negroes to secure for themselves the full blessings of American life. Their cause must be our cause too. Because it’s not just Negroes, but really it’s all of us, who must overcome the crippling legacy of bigotry and injustice. And we shall overcome …
“This great, rich, restless country can offer opportunity and education and hope to all, all black and white, all North and South, sharecropper and city dweller. These are the enemies: poverty, ignorance, disease. They’re our enemies, not our fellow man, not our neighbor. And these enemies too—poverty, disease, and ignorance: we shall overcome.”
12. Reagan’s D-Day Anniversary Address
Date: June 6, 1984
Context: During World War II, the Allied forces attacked German troops on the coast of Normandy, France on June 6, 1944. A turning point for the war, the day came to be known as D-Day, and its anniversary is forever acknowledged. On its 40th anniversary, President Ronald Reagan honored the heroes of that day in a speech that also invoked a comparison of World War II’s Axis dictators to the Soviet Union during the ongoing Cold War. This reminder to the Allies that they once fought together against totalitarianism and must continue the fight now helped contribute to the ultimate dissolution of the Soviet Union.
Notable Quote: “We look for some sign from the Soviet Union that they are willing to move forward, that they share our desire and love for peace, and that they will give up the ways of conquest. There must be a changing there that will allow us to turn our hope into action. We will pray forever that some day that changing will come. But for now, particularly today, it is good and fitting to renew our commitment to each other, to our freedom, and to the alliance that protects it. We are bound today by what bound us 40 years ago, the same loyalties, traditions, and beliefs. We’re bound by reality. The strength of America’s allies is vital to the United States, and the American security guarantee is essential to the continued freedom of Europe’s democracies. We were with you then; we are with you now. Your hopes are our hopes, and your destiny is our destiny.”
13. Reagan’s Berlin Wall Speech
Date: June 12, 1987
Context: With the fall of Nazi Germany at the end of World War II, Western powers and the Soviet Union sought to establish systems of government in their respective occupied regions. West Germany developed into a Western capitalist country, with a democratic parliamentary government, while East Germany became a socialist workers’ state (though it was often referred to as communist in the English-speaking world). Many experiencing hunger, poverty, and repression in the Soviet-influenced East Germany attempted to move west, with the City of Berlin their main point of crossing. Ultimately, the Soviet Union advised East Germany to build a wall on the inner German border, restricting movement and emigration by threat of execution for attempted emigrants. Seen as a symbol of Communist tyranny by Western nations, the Berlin Wall persisted for nearly three decades. In 1987, President Ronald Reagan visited West Berlin and called upon Soviet President Mikhail Gorbachev to take down the wall as a symbol of moving forward.
Notable Quote: “We welcome change and openness; for we believe that freedom and security go together, that the advance of human liberty can only strengthen the cause of world peace. There is one sign the Soviets can make that would be unmistakable, that would advance dramatically the cause of freedom and peace. General Secretary Gorbachev, if you seek peace, if you seek prosperity for the Soviet Union and Eastern Europe, if you seek liberalization: Come here to this gate! Mr. Gorbachev, open this gate! Mr. Gorbachev, tear down this wall!”
14. George W. Bush’s Post-9/11 Speech
Date: September 11, 2001
Context: On September 11, 2001, the United States experienced the single worst terrorist attack in human history , where four American planes were hijacked and flown into American buildings, killing nearly 3,000 people. Viewers around the world watched the news as five stories of the Pentagon fell and the World Trade Center buildings collapsed entirely. Later that evening, President George W. Bush addressed the nation with a brief but powerful message that chose to focus not on fear, but on America’s strength in unity.
Notable Quote:
“These acts of mass murder were intended to frighten our nation into chaos and retreat. But they have failed. Our country is strong. A great people has been moved to defend a great nation. Terrorist attacks can shake the foundations of our biggest buildings, but they cannot touch the foundation of America. These acts shatter steel, but they cannot dent the steel of American resolve. America was targeted for attack because we’re the brightest beacon for freedom and opportunity in the world. And no one will keep that light from shining.”
15. Obama’s “More Perfect Union” Speech
Date: March 18, 2008
Context: While campaigning for the presidency in 2008, Barack Obama came under fire for his relationship with pastor Jeremiah Wright, who had been heard to denounce the United States and accuse the government of racial crimes. To officially address the relationship and condemn Wright’s inflammatory remarks, Obama crafted a speech that discussed the history of racial inequality in America as well as the dissonance between that history and America’s ideals of human liberty. Importantly, however, he also highlighted the necessity for a unified American people to effectively combat those issues, rather than more racial division.
Notable Quote: “[T]he remarks that have caused this recent firestorm weren’t simply controversial. They weren’t simply a religious leader’s effort to speak out against perceived injustice. Instead, they expressed a profoundly distorted view of this country—a view that sees white racism as endemic, and that elevates what is wrong with America above all that we know is right with America ….
“[These] comments were not only wrong but divisive, divisive at a time when we need unity; racially charged at a time when we need to come together to solve a set of monumental problems—two wars, a terrorist threat, a falling economy, a chronic health care crisis and potentially devastating climate change; problems that are neither black or white or Latino or Asian, but rather problems that confront us all ….
“The fact is that the comments that have been made and the issues that have surfaced over the last few weeks reflect the complexities of race in this country that we’ve never really worked through—a part of our union that we have yet to perfect. And if we walk away now, if we simply retreat into our respective corners, we will never be able to come together and solve challenges like health care, or education, or the need to find good jobs for every American.”
Read about Barack Obama’s presidency in this blog post.
About the U.S. Presidential Library
As the head of state and government of the United States of America, the president is one of the most influential and noteworthy political figures in the world. The role that each American president has played reflects the evolution of the United States’ government, society, and standing on the world stage.
Research the impact of each president with HeinOnline’s U.S. Presidential Library , a database of nearly 2,000 titles and more than a million pages dedicated to presidential documents. The database includes messages and papers of the presidents, daily and weekly compilations of presidential documents, public papers of the presidents, documents relating to impeachment, Title 3 of the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), and a host of other related works.
Access the database within your subscription via the link below, or evaluate the resource by requesting an organization trial or quote today.
Tara Kibler
- Tags: u.s. presidential library , u.s. presidents

Wounded Knee and the American Indian Movement
In February 1973, Indigenous activists arrived in the town of Wounded Knee, South Dakota, site of the massacre in 1890, kicking off a months-long standoff with federal troops.

The 1889 Johnstown Flood
The 1889 Johnstown Flood was the greatest single-day loss of civilian life in the United States before 9/11. It also helped rewrite the country’s liability law.
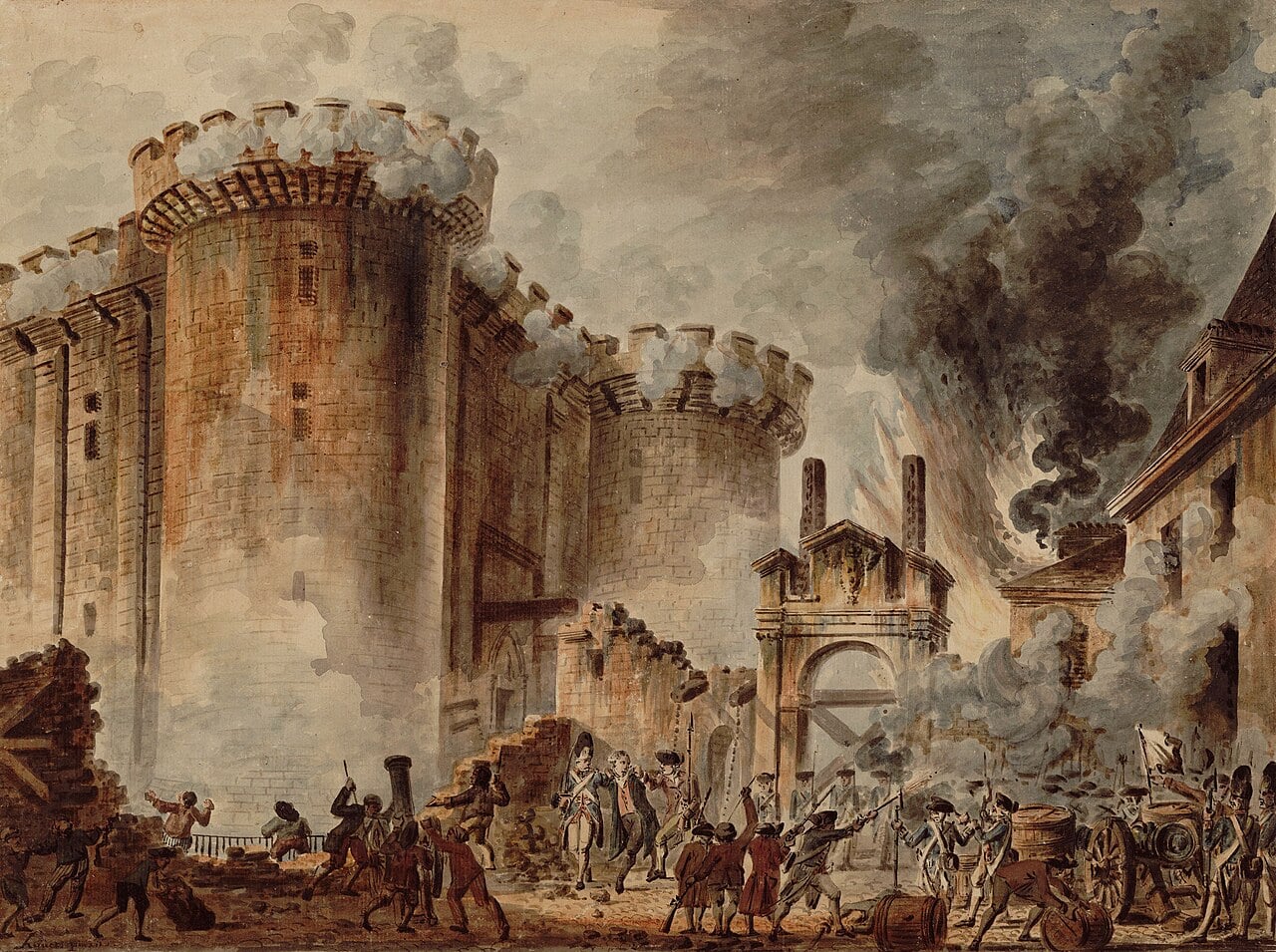

The Storming of the Bastille
Ten days after the Fourth of July, France will celebrate its own national holiday, called Bastille Day, or Fête nationale française. Why is the storming of the Bastille celebrated more than 230 years later? Let’s find out!
Like what you see?
There’s plenty more where that came from! Subscribe to the HeinOnline Blog to receive posts like these right to your inbox.
By entering your email, you agree to receive great content from the HeinOnline Blog. HeinOnline also uses the information you provide to contact you about other content, products, and services we think you’ll love.
Like what you're reading? Subscribe to the blog!
12 Greatest Political Speeches in American History

Pegging 12 of the most important speeches and moments in American politics is no easy feat. From Washington to Lincoln, from Kennedy to Reagan, these are the names, faces and moments that have changed the course of our nation. For good measure, we've included a few lesser-known — but equally significant — ones too.
1. Washington's Farewell Address

The parting words of our first president have stood the test of time in just about every way. Washington forswore another term in office, setting the two-term precedent, and mused on policy fronts from factions and partisanship to foreign entanglements.
His words encompassed the early Federalist Party's credo and were cited in political discourse for years to come. By 1899, it was annually read on Washington's Birthday in both the House and Senate. Though the House had ceased doing so by 1984, the Senate continues the tradition to this day.
2. Andrew Jackson on Nullification
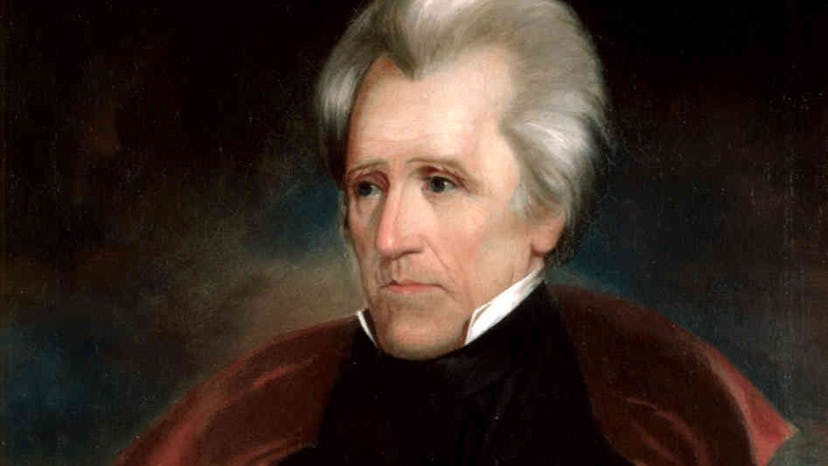

Despite not originating in a speech, one of Andrew Jackson's comments on nullification stands out as one of the defining moments of the seventh president's legacy. At the annual Democratic Jefferson Day dinner on April 13, 1830, Jackson, countering Vice-President John C. Calhou's pronullification rationale that states could nullify whatever feder laws they saw fit, rosefrom his seat and in a thundering voice pronounced : "Our federal union — it must be preserved!"
Two years later, Jackson offered his Proclamation Regarding Nullfication . For many years to follow, the question remained a defining one leading up to the Civil War.
3. Lincoln's Gettysburg Address

There's little left to be said, but Abraham Lincoln's ten sentence missive at Gettysburg is remembered by many as the greatest speech in American political history. Though it was met with a decidedly mixed, even downright mocking, reception at the time, it's far and away outlived Edward Everett's two-hour oratory from the same day. It also recently spawned a very cool project in honor of its 150 year anniverary.
4. William Jennings Bryan's 'Cross of Gold' speech
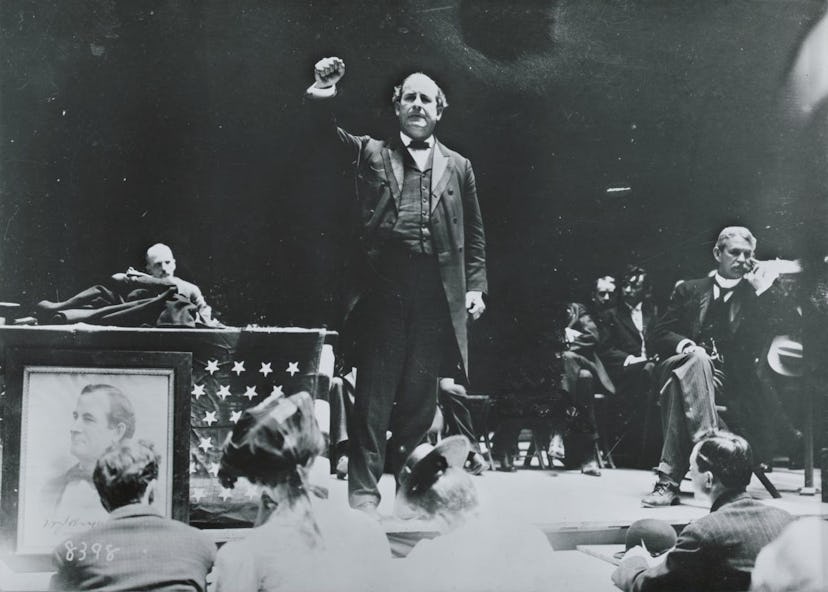

Three times he was the Democratic nominee for president, and three times he came up short. William Jennings Bryan's electoral legacy makes him the Buffalo Bills of American politics, but his influence stands the test of time. He was one of the first national candidates to actually be a national candidate, hitting the speaking circuit at a time when front porch campaigns were considered the more dignified move.
His 1896 address to the Democratic National Convention is what threw him into the national spotlight. Bryan thundered in support of the populist cause of the day, free silver, closing with a cry that "you shall not crucify mankind upon a cross of gold" and holding his arms henceforth. It's remembered to this day as the speech that made him the de facto leader of the Democrats and coalesced populists within their ranks.
5. Calvin Coolidge's 1925 Inaugural Address
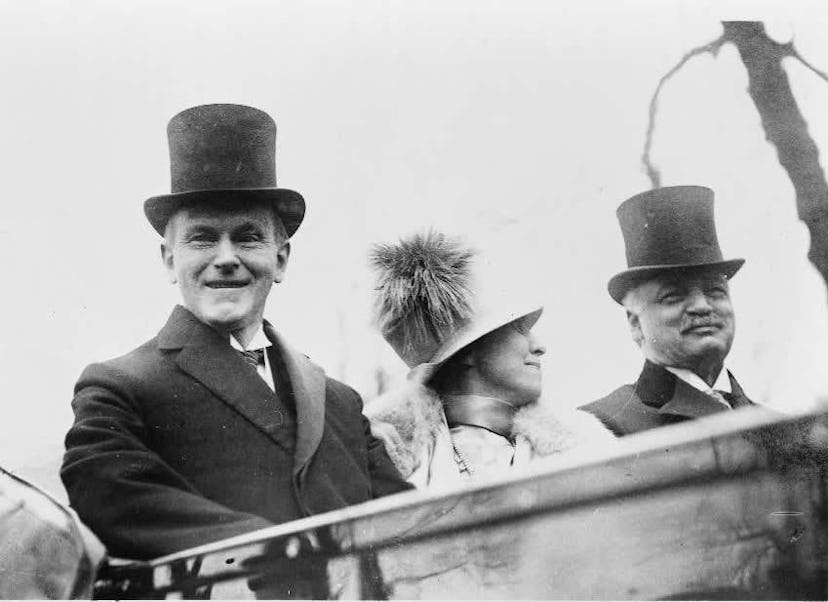

It's easy to generalize Coolidge as the quiet man's president, after all, his nickname was "Silent Cal." But Coolidge remains one of the most consequential presidents in history when it comes to the conservative mindset, and his reputation at the time didn't quite fit the convention wisdom. He held 520 press conferences while in office, a number unmatched both before and since.
His 1925 inaugural address remains remarkably significant in American history because it was the first to be broadcast on radio, enabling more citizens than ever before to actually hear the words of their president.
6. Franklin Roosevelt's 1933 Inaugural Address
"The only thing we have to fear is fear itself," he quipped, offering reassurances to a nation facing the bleakness of the Great Depression.
7. John F. Kennedy's 1961 Inaugural Address
Much like FDR, JFK's inaugural address stands the test of time as one of the most iconic moments in American political history.
"Ask not what your country can do for you, ask what you can do for your country" remains a line cited on both sides of the political aisle, ushering in the era of Camelot and the remarkably consequential 1960s.
8. Martin Luther King Jr.'s 'I Have a Dream' Speech
The only speech on this list not delivered by a president, King's address during the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom is remembered by many as the defining moment of the Civil Rights Movement, coming just shy of 100 years after Lincoln's Gettysburg Address. He was subsequently named Time Magazine ’s Man of the Year, and the spot in which he stood has been enshrined at the Lincoln Memorial in Washington.
9. Ronald Reagan at the Berlin Wall
The Cold War wouldn't end for several more years, but Ronald Reagan's standing in front of the Berlin Wall and challenging Mikhail Gorbachev to tear it down is assuredly in the annals of the most powerful moments in American history.
Much like King's "I Have A Dream" speech, the words speak for themselves more powerfully than I ever could. Reagan's policies encompassed the '80s and the years that were to come, and this was the iconic moment to define the resolve his presidency.
10. Bill Clinton's 1996 State of the Union
Although Bill Clinton may have become the first Democrat to reside in the White House since Jimmy Carter in 1992 by learning to talk like a Republican, the party's liberal agenda cost them heavily in the '94 midterms elections.
Perhaps recognizing that conservatism had won the Reagan Era, Clinton turned a corner with his '96 State of the Union by famously proclaiming: "The era of big government is over." The apparent policy shift may have only been politically motivated, as later that year major welfare reform was passed with his backing.
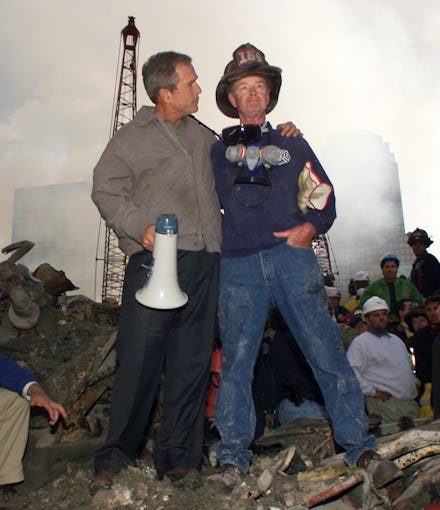
11. George W. Bush's Post-9/11 Bullhorn Speech
Much has been written, and will continue to be written, about George W. Bush's eight years in office, but it's undeniable that his remarks atop the rubble of Ground Zero are powerful to this day. Speaking from a bullhorn to workers and firefighters, with many of them unable to hear him at first, Bush 43 rallied the nation with the promise that "the people who knocked these buildings down will hear all of us soon."
12. Barack Obama's 2009 Inaugural Address
Even though some might disagree with the policies pushed by President Obama, one can still appreciate the significance of his swearing-in. Coming 46 years after Martin Luther King's "I Have A Dream" speech and just over 150 after Lincoln's Gettysburg Address, the first inaugural address of the first African-American president in American history ranks as an iconic moment of the right kind of progress.
Correction: March 4, 2015
Explore the Constitution
- The Constitution
- Read the Full Text
Dive Deeper
Constitution 101 course.
- The Drafting Table
- Supreme Court Cases Library
- Founders' Library
- Constitutional Rights: Origins & Travels

Start your constitutional learning journey
- News & Debate Overview
Constitution Daily Blog
- America's Town Hall Programs
- Special Projects
Media Library

America’s Town Hall
Watch videos of recent programs.
- Education Overview
Constitution 101 Curriculum
- Classroom Resources by Topic
- Classroom Resources Library
- Live Online Events
- Professional Learning Opportunities
- Constitution Day Resources

Explore our new 15-unit high school curriculum.
- Explore the Museum
- Plan Your Visit
- Exhibits & Programs
- Field Trips & Group Visits
- Host Your Event
- Buy Tickets

New exhibit
The first amendment, looking at 10 great speeches in american history.
August 28, 2017 | by NCC Staff
Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have A Dream” speech certainly ranks highly in the pantheon of public speaking. Here is a look at the Dream speech and other addresses that moved people – and history.

King’s “Dream” speech from August 28, 1963 topped the list, followed by John F. Kennedy’s 1961 inaugural address and Franklin Roosevelt’s first inaugural address in 1933. In fact, three of King’s speeches were included in the top 50 speeches listed by the experts.
The eclectic list included public speeches from Barbara Jordan, Richard Nixon, Malcom X and Ronald Reagan in the top 10 of the rankings.
Link : Read The List
Public speaking has played an important role in our country’s story. Here is a quick look at some of the landmark speeches that often pop up in the discussion about public rhetoric.
1. Patrick Henry. “ Give Me Liberty Or Give Me Death .” In March 1775, Henry spoke to a Virginia convention considering a breakaway from British rule. “The war is actually begun. The next gale that sweeps from the north will bring to our ears the clash of resounding arms,” said Henry, who spoke without notes. “I know not what course others may take; but as for me, give me liberty, or give me death!”
2. George Washington’s first inaugural address . In 1789, the First President addressed the First Congress after his inauguration, setting the precedent for all inaugural speeches to follow. Washington enforced the need for the Constitution, concluding that “Parent of the Human Race … has been pleased to favor the American people with opportunities for deliberating in perfect tranquillity, and dispositions for deciding with unparalleled unanimity on a form of government for the security of their union and the advancement of their happiness.”
3. Frederick Douglass. “ The Hypocrisy Of American Slavery .” In 1852, Douglass was invited to speak at a public Fourth of July celebration in Rochester, N.Y. Instead of talking about the celebration, Douglass addressed the issue that was dividing the nation. “I will, in the name of humanity, which is outraged, in the name of liberty, which is fettered, in the name of the Constitution and the Bible, which are disregarded and trampled upon, dare to call in question and to denounce, with all the emphasis I can command, everything that serves to perpetuate slavery,” he said.
4. Abraham Lincoln. “ The Gettysburg Address .” The best known of Lincoln’s speeches was one of his shortest. Lincoln was asked to make a few remarks in November 1863 after featured speaker Edward Everett spoke for about two hours. “Fourscore and seven years ago our fathers brought forth, upon this continent, a new nation, conceived in liberty and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal,” Lincoln said in his opening paragraph. He spoke for two minutes.
5. William Jennings Bryan. “ Cross of Gold Speech .” A lesser-known contender for the Democratic presidential nomination in 1896, Bryan created a sensation with his speech that condemned the gold standard and held the promise of debt relief for farmers. “We shall answer their demands for a gold standard by saying to them, you shall not press down upon the brow of labor this crown of thorns. You shall not crucify mankind upon a cross of gold,” Bryan said with his arms spread in a crucifix-like position.
6. FDR’s first inaugural address . In 1933, the new President faced a nation in the grips of a deep economic recession. “First of all, let me assert my firm belief that the only thing we have to fear is fear itself -- nameless, unreasoning, unjustified terror which paralyzes needed efforts to convert retreat into advance,” Roosevelt said as he opened his powerful speech. The inaugural set the agenda for FDR’s 12 years in office.
7. Richard Nixon’s Checkers speech . Facing controversy as a vice presidential candidate, Nixon showed how television could be used as a powerful communications tool. In a stroke of political genius, Nixon spoke to the nation about his family finances, and then said the only gift he wouldn’t return was Checkers, the family dog.
8. JFK’s first inaugural address . The well-written 1961 speech is considered one of the best inaugural speeches ever. Rhetoric expert Dr. Max Atkinson told the BBC in 2011 what made the Kennedy speech special. “Tt was the first inaugural address by a U.S. president to follow the first rule of speech-preparation: analyze your audience - or, to be more precise at a time when mass access to television was in its infancy, analyze your audiences.”
9. Dr. King’s “I Have A Dream” speech . King’s speech at the Lincoln Memorial in August 1963, in front of 250,000 people, is also one of the most-analyzed speeches in modern history. But King hadn’t included the sequence about the “Dream” in his prepared remarks. Singer Mahalia Jackson yelled for King to speak about “the Dream,” and King improvised based on remarks he had made in earlier speeches.
10. Ronald Reagan in Berlin . President Reagan appeared at the 750 th birthday celebration for Berlin in 1987, speaking about 100 yards away from the Berlin Wall. Reagan first cited President Kennedy’s famous 1963 speech in Berlin, and then asked, “General Secretary Gorbachev, if you seek peace, if you seek prosperity for the Soviet Union and Eastern Europe, if you seek liberalization: Come here to this gate! Mr. Gorbachev, open this gate! Mr. Gorbachev, tear down this wall!” A Reagan speech writer later said the State Department didn’t want Reagan to use the famous line, but Reagan decided to do it anyway.
More from the National Constitution Center

Constitution 101
Explore our new 15-unit core curriculum with educational videos, primary texts, and more.

Search and browse videos, podcasts, and blog posts on constitutional topics.

Founders’ Library
Discover primary texts and historical documents that span American history and have shaped the American constitutional tradition.
Modal title
Modal body text goes here.
Share with Students
- Cool Things a New POTUS Gets to Do
- Biggest Firsts in POTUS History
- Normal Things a POTUS Can't Do
- Cool Facts About the Secret Service
- POTUSes' Most Controversial Pardons, Ranked
- Photos from Their Wedding Days
- Pics Before & After Major Events
- In the Event of an Apocalypse
- Presidents in the Illuminati
- Feuds with Vice Presidents
- Ailments and Medical Problems
- Rules All Former POTUSes Have to Follow
- Sex Scandals Involving 11 US Presidents
- What The Losers Of Presidential Elections Did N...
- What Factors Should Disqualify Someone From Bei...
- Every Permanent Position In The US President’s ...
- What Happens Immediately After An Assassination...
- US Presidents Who Died In Office And What Happe...

- GNU Free Documentation License
The Best Presidential Speeches of All Time
Presidential speeches are often remembered for one great phrase, memorable line, or rhetorical flourish that makes its way into the history books. But they should be seen as more than collections of memorable words - in fact, as documents of their time and place. Great presidential speeches are made in the context of crises, challenges, and times of great peril. But they can also inspire, uplift, and encourage. The truly great speeches manage to do both at once.
What's less well-known about many of the great addresses by presidents that they're short. Maybe the most famous speech in American history, Lincoln's Gettysburg Address, is just over two minutes long. Many others, rather than being long rambles of adjectives and superlatives, are fewer than one thousand words, and lasted just 10 minutes. They didn't need thousands and thousands of words to make their point, just a few well-chosen ones given by a dynamic speaker.
Here are the greatest and most inspiring presidential speeches of all time, be sure to upvote those that inspire you the most!

- George Eastman House
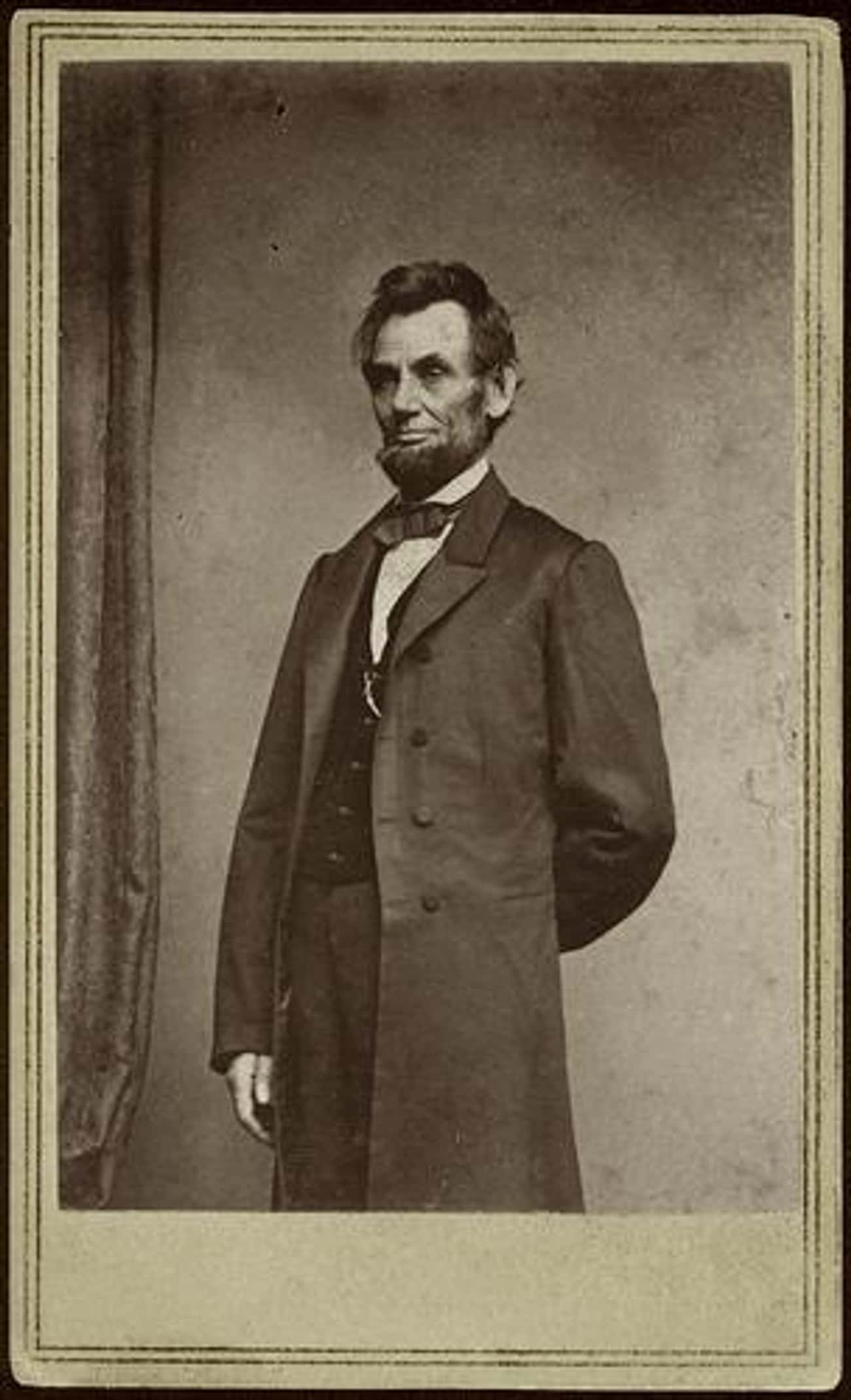
The Gettysburg Address
President Lincoln delivered his most famous speech just five months after the Battle of Gettysburg, at the dedication of the site's military cemetery. There is no existing final copy, and the five surviving manuscripts of the speech all have slightly different word choices. The speech was just 10 sentences long, and took two and a half minutes to deliver.

- White House Photographs
- National Park Service
- Public Domain
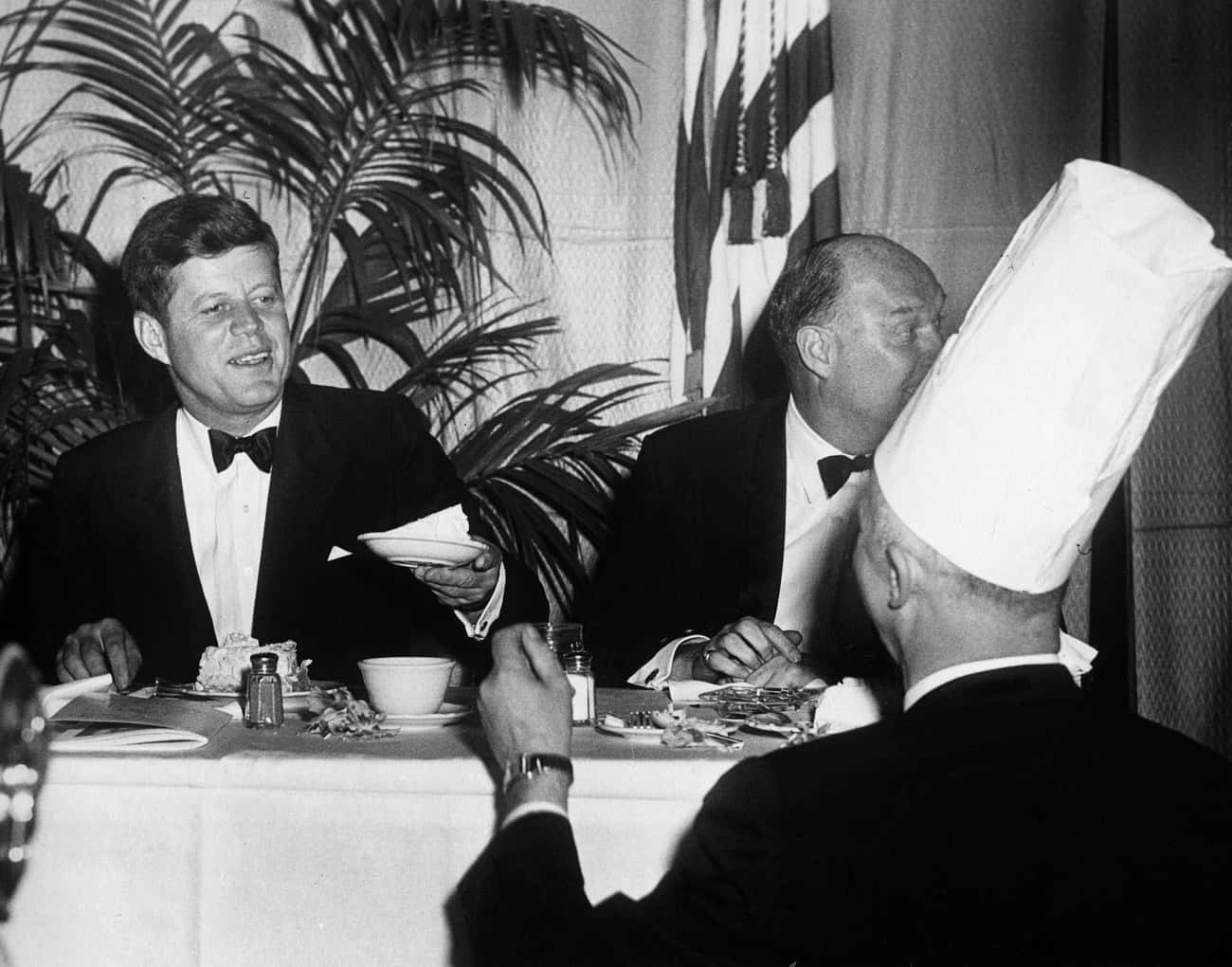
Kennedy's Inaugural Address
President Kennedy's only inaugural address was one of the shortest on record, fewer than 1,400 words and taking only 13 minutes and 42 seconds. But it perfectly encapsulated the social change, economic prosperity, and political upheaval Kennedy was walking into.

- Wally Gobetz
Washington's Farewell Address
President Washington actually wrote a version of his farewell to the American people after his first term, but decided to run for a second given the precarious state of the country. It was first published in the American Daily Advertiser newspaper, then in papers and pamphlets around the country. Washington never actually gave the address as a speech.

- NASA on The Commons
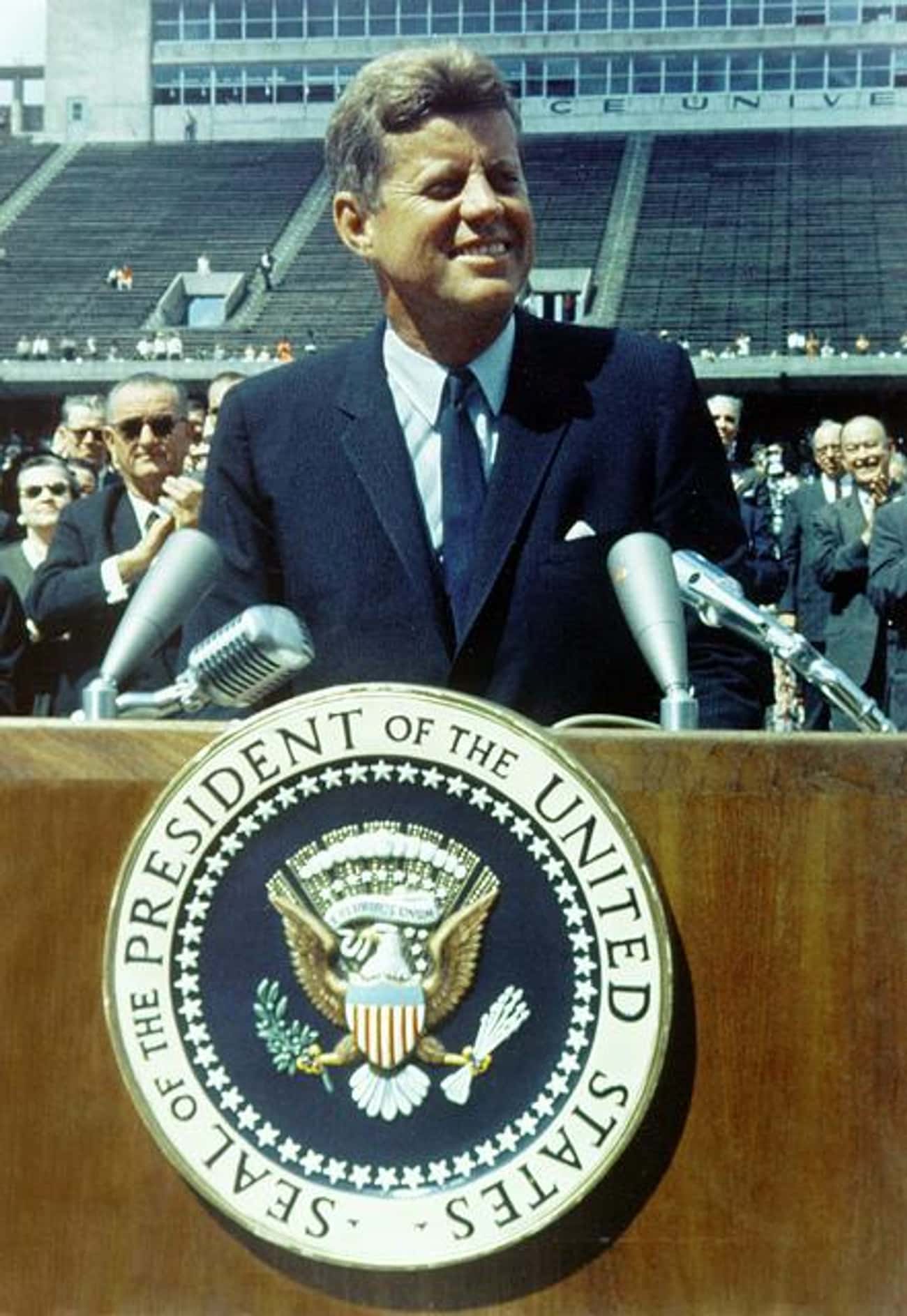
Kennedy's "We Choose to Go to the Moon" Speech
While President Kennedy had declared the United States's intention to put a man on the Moon in May 1961, the idea didn't truly resonate with the American people until his speech in September of the next year. In front of a massive crowd at Rice University, Kennedy managed to make Americans enthusiastic about spending billions of dollars on a prospect with no guarantee of success.

- Brett Gullborg
Lincoln's Second Inaugural Address
President Lincoln gave his second inaugural address on March 4, 1865, as the Civil War was reaching its bloody conclusion. With reconstruction between the North and South looming, Lincoln paused to take stock of what had been lost, and what could be gained. It was just 700 words long, and took around five minutes to deliver.

- FDR Presidential Library & Museum
FDR's Infamy Speech
President Roosevelt's speech to a Joint Session of Congress the day after the attack on Pearl Harbor served to emphasize the idea of America as the victim of a cowardly sneak attack, rather than as a player in a complicated geopolitical struggle. Lasting just seven minutes, the speech let it be known that isolationism was no longer an option - and less than an hour later, the US declared war on Japan.
Help inform the discussion
- X (Twitter)
The Presidency / Presidential Speeches
Famous presidential speeches.
Use the "Filter" button to select a particular president and find the speech you want

Famous speeches from every US president
Presidential speeches have been an invaluable part of U.S. democracy since Washington's inaugural address on April 30, 1789. While much of the oral tradition has remained unchanged, the evolution of mass communication has turned speeches into conversations. Using historical documents, government and political science websites, and news articles, Stacker curated a gallery of famous speeches from every U.S. president.
Whether presented as an inaugural address, a message to Congress, a State of the Union, or a response to a national event, presidential speeches are snapshots of the nation's values and challenges at a given point in time. They have been used to unite what seemed like an irrevocably divided country. They hold Americans accountable to the country's founding values and signal the adoption of new ones.
In the throes of crises, death, scandal, and disillusionment, presidents have had to find the right words to quell fears, assert changes, and heal morale. In peacetime and moments of relative prosperity, presidents have used speeches to celebrate or to galvanize the country behind a greater good, a call to action, or a reason for hope.
Each speech, especially in moments of tribulation, marks the evolution of America. They are important not just for what they communicate in the moment, but for what they communicate about that moment when viewed retroactively through the lens of history.
Presidents throughout history have found new ways to communicate with the country. From the regular use of radio with Franklin D. Roosevelt's Fireside Chats to Kennedy's first live, unedited television broadcast to constant and immediate communication enabled by social media, technology has shaped presidential correspondence with the nation.
It has also empowered Americans to gauge accuracy and transparency. Real-time fact-checking, whether by organizations like FactCheck.org or by individuals, is becoming synonymous with presidential rhetoric.
Read on to understand what these speeches were about and how they relate to particular moments in U.S. history.
You may also like: Experts rank the best U.S. presidents of all time
George Washington
- Speech name: Farewell address - Date delivered: Sept. 19, 1796
One of the greatest things Washington ever did for the office of the presidency was quit. By refusing to serve as president for a third term, Washington established a precedent for limiting executive power and signaled the value of the transition of power. Washington's farewell address , which was printed in papers, not delivered in person, cautioned against "pretended patriotism," political divisions, and permanent foreign alliances. Washington questioned whether his words would have an enduring impact, but it's easy to appreciate their timeless relevance even two centuries later.
- Speech name: Inaugural address - Date delivered: March 4, 1797
Second in a long line of inaugural addresses that praised the principles of the Constitution, Adams' speech also warns against losing perspective on the nation's hard-won liberties. Corruption, fraud, and terror are among the evils that threaten the Constitution and those who lead by it.
Thomas Jefferson
- Speech name: First inaugural address - Date delivered: March 4, 1801
In his first inaugural address , Jefferson presented his goals for the presidency and objectives for the nation. This included unifying Republicans and Federalists, establishing equal rights, and upholding the tenets of the Constitution.
James Madison
- Speech name: Special message to Congress on the foreign policy crisis—war message - Date delivered: June 1, 1812
In this message, Madison asks Congress to declare war against Great Britain, citing four justifications, including impressment, illegal blockades, the Orders in Council, and British responsibility for inciting warfare among Native Americans. The House of Representatives voted 79-49 in favor of war . While the British revoked the Orders in Council in an attempt to avoid war, word reached the United States too late. June 18 marked the beginning of the War of 1812.
James Monroe
- Speech name: Seventh annual message - Date delivered: Dec. 2, 1823
Layered into a routine annual message to Congress , Monroe outlined the philosophy and tenets for what would eventually be known as the Monroe Doctrine . This doctrine—named after Monroe but written by then-Secretary of State John Quincy Adams—established the United States as a sphere of influence in the Western Hemisphere and warned against European colonization in the New World. Monroe also asserted that any encroachment on the Western Hemisphere would be considered "dangerous to our peace and safety" and acted upon accordingly. Since this speech, the Monroe Doctrine has largely shaped U.S. foreign policy.
John Quincy Adams
- Speech name: Speech to the U.S. House of Representatives on Foreign Policy - Date delivered: July 4, 1821
John Quincy Adams' most referenced speech was actually delivered when he served as the secretary of state, not the U.S. president. He praised America's dedication to freedom and peace—not just her own, but of those around the world. "She goes not abroad, in search of monsters to destroy. She is the well-wisher to the freedom and independence of all." Considered to be, at best, ineffective and at worst, a failure, Adams' legacy is defined more so by his diplomatic success before and after his presidency—including his facilitation of America's expansion west to the Pacific, and his vocal opposition to slavery—than his time in office.
Andrew Jackson
- Speech name: Second annual message to Congress - Date delivered: Dec. 6, 1830
The United States was fervently embracing an attitude of territorial expansion when Andrew Jackson took office in 1829. A champion of the cultural shift toward frontier life, Jackson initiated the Indian Removal Act of 1830 , allowing the government to remove Native Americans, at times forcibly, from territories within state borders in exchange for unsettled land west of the Mississippi. Just several months after signing and enacting the Indian Removal Act, Jackson delivered his "Second Annual Message to Congress" in which he defends the policy, lauds its early success, and reinforces the belief that all parties involved stood to benefit from it.
Martin Van Buren
- Speech name: Inaugural address - Date delivered: March 4, 1837
Van Buren, the first president born an American citizen, used his inaugural address to assure the nation that he could represent and serve everyone. He talked about the country's growth over the last 50 years and celebrated unique success. He delineated the roles of state and federal government. He also vowed to maintain the status quo of slavery in the country, appealing to skeptical constituents in the South.
William Henry Harrison
- Speech name: Inaugural address - Date delivered: March 4, 1841
At just over two hours, William Henry Harrison's inaugural address—and the only speech he gave as president of the United States—is the longest in history. Harrison's presidential tenure, however, is the briefest in history, cut short when he died from pneumonia 31 days into his term. Invoking parallels to Roman emperors and immovable European monarchies, Harrison spoke of the dangers of the presidency and called for term limits to avoid corruption. The most prescient forewarning in Harrison's inaugural address, which was delivered 20 years before the start of the American Civil War, comments on the dangers of disunion among the states.
- Speech name: Address upon assuming the office of president of the United States - Date delivered: April 9, 1841
John Tyler became the first vice president to assume the office of the president after William Henry Harrison's death in 1841, establishing the precedent for presidential succession. Instead of an inaugural address, Tyler delivers a statement to Congress acknowledging the novelty of the situation and vows to uphold the ideal of his predecessor.
James K. Polk
- Speech name: Inaugural address - Date delivered: March 4, 1845
Polk's inaugural address aptly captures the spirit of the nation at that point in time, which was growing rapidly with an appetite for more. He celebrates the annexation of Texas and of the opportunities that Oregon will afford. Besides celebrating expansion, he also outlines his opposition to a national bank. Polk reestablished the Independent Treasury system, which remained in place until 1913.
Zachary Taylor
- Speech name: Inaugural address - Date delivered: March 5, 1849
Zachary Taylor died just 16 months into his term. Like his predecessors, Taylor expressed his gratitude to the country, his reverence for the office of the presidency, and his determination to uphold the values outlined in the Constitution.
Millard Fillmore
- Speech name: Message regarding compromise with Texas - Date delivered: Aug. 6, 1850
In this message to Congress , Fillmore expressed his support of the Compromise of 1850 . He recommended that Congress overturn the Wilmot Proviso, making Texas open to slavery. Fillmore also asked that Texas be paid to give up parts of New Mexico. Congress paid Texas $10 million for the territory.
Franklin Pierce
- Speech name: Message regarding disturbances in Kansas - Date delivered: Jan. 24, 1856
The Kansas-Nebraska Act of 1854 allowed citizens of Kansas and Nebraska, rather than the federal government, to decide whether to permit or prohibit slavery within the boundaries of those territories. As a result, pro-slavery and anti-slavery advocates fought to establish political dominance in the state. Clashes grew more violent, and in 1856, Pierce addressed Congress on the extent of the civil unrest.
James Buchanan
- Speech name: Message to Congress transmitting the constitution of Kansas - Date delivered: Feb. 2, 1858
James Buchanan is widely regarded as one of the worst presidents of all time, in many cases earning the title of worst. His message to Congress regarding the recent elections in Kansas helps to illustrate why. It was well-known that voter fraud was rampant —in favor of pro-slavery factions—in the recent vote on whether Kansas should be a slave state. Despite knowing this, Buchanan supported the vote and the territory's new Constitution. He urged Congress to approve the controversial legislation, looking for the fastest way to make the conflict in Kansas disappear.
Abraham Lincoln
- Speech name: Gettysburg Address - Date delivered: Nov. 19, 1863
It's possible that no speech has done more with less. Lincoln's speech at Gettysburg is regarded as one of the most influential in American history, and he wasn't even the top-billed speaker that day. Edward Everett, a politician from Massachusetts, delivered the program's official two-hour Gettysburg address. But it was Lincoln's two-minute remarks , in which he spoke of the country's unique founding values of liberty and equality for all and the need to protect and unite the nation under those values, that have resonated throughout history.
Andrew Johnson
- Speech name: Veto message on civil rights legislation - Date delivered: March 27, 1866
In the wake of the Civil War, Congress proposed the Civil Rights Act to provide newly freed slaves with federal citizenship and expand the impact of the pre-existing Freedmen's Bureau . Johnson vetoed the legislation reasoning in his message to Congress that it operated "in favor of the colored and against the white race." Johnson's veto message challenged the whole necessity of citizenship for newly freed slaves and even questioned if they were worthy of that privilege. Congress overrode Johnson's veto on April 9, 1866, enacting legislation that would take over 100 years fully actualize.
Ulysses S. Grant
- Speech name: Announcement of Fifteenth Amendment ratification - Date delivered: March 30, 1870
In this speech, Grant announced the ratification of the Fifteenth Amendment , which established universal black male suffrage. Grant called the 15th Amendment the greatest civil change and most important event since the birth of the nation. He warned those privileged citizens who have long enjoyed the country's freedoms and the right to express their opinions through voting not to stand in the way of the newly enfranchised. Grant also referenced Washington's belief that a successful government can only be sustained by an enlightened populace. Grant challenged everyone "to see to it that all who possess and exercise political rights shall have the opportunity to acquire the knowledge which will make their share in the Government a blessing and not a danger."
Rutherford B. Hayes
- Speech name: Prohibition of federal employees' political involvement - Date delivered: June 22, 1877
In 1877, to stifle corruption and dismantle the spoils system, Hayes issued an executive order barring federal employees from involvement in political activities such as the management of political organizations, campaigns, conventions, or caucuses. Additionally, those in office could not be removed for political reasons. The order marked a significant moment for civil service reform and laid the groundwork for the Pendleton Civil Service Reform Act of 1883.
James A. Garfield
- Speech name: Inaugural address - Date delivered: March 4, 1881
Garfield was shot four months into his term by Charles J. Guiteau. Guiteau sought to exact retribution against the president for not being appointed a consulship in Europe. Succumbing to his wounds two months later, after a total of just six months in office, Garfield's most memorable speech is his inaugural address . Garfield celebrated the rights of African Americans now written into the Constitution but rebuked persistent attempts being made in parts of the country to prevent them from exercising these rights. "Freedom can never yield its fullness of blessings," Garfield stated, "so long as the law or its administration places the smallest obstacle in the pathway of any virtuous citizen."
Chester A. Arthur
- Speech name: Veto of the Chinese Exclusion Act - Date delivered: April 4, 1882
The Chinese Exclusion Act was the first prohibitive immigration law passed in the United States. Laborers on the West Coast blamed Chinese immigrant workers for their economic hardships even though they comprised less than 1% of the population . The Chinese Exclusion Act initially proposed to suspend Chinese immigration for 20 years. To the dismay of American laborers, Arthur vetoed the first bill , concerned that 20 years was too long and could prove to be permanently damaging to trade relations with China. Arthur eventually signed a bill that suspended immigration for 10 years and denied citizenship for current Chinese residents.
Grover Cleveland
- Speech name: Message regarding U.S. labor force - Date delivered: April 22, 1886
Cleveland asserted that laborers were an indispensable part of the country's strength and prosperity. In considering their contributions to the growth of the U.S., Cleveland proposed the creation of a government committee that would operate under the Bureau of Labor to resolve disputes between labor and capital. Cleveland stated that a laborer's demands "should be met in such a spirit of appreciation and fairness as to induce a contented and patriotic cooperation in the achievement of a grand national destiny."
Benjamin Harrison
- Speech name: Message regarding Valparaiso incident - Date delivered: Jan. 25, 1892
During a period of escalating tension between the United States and Chile, beginning with the Itata incident and reaching its peak with the Valparaiso incident , both countries were inching closer to waging war. Harrison sent a special message to Congress , urging them to take "appropriate actions" against Chile, expressing support for war and severing diplomatic relations. War was averted after Chile agreed to terms of a U.S. ultimatum.
- Speech name: Message regarding Venezuelan-British dispute - Date delivered: Dec. 17, 1895
The United States got involved in an ongoing boundary dispute between Venezuela and Britain during Cleveland's second presidential term. Venezuela appealed to the U.S. to intervene in the territorial dispute for nearly two decades before Cleveland made his appeal to Congress regarding the matter. In this message , he invoked the Monroe Doctrine as justification for involvement, specifically to create a commission that would assess and enforce their findings "by every means." The U.S. established itself internationally as a power in the Western Hemisphere, willing to use the Monroe Doctrine to preserve that status.
William McKinley
- Speech name: Speech in Buffalo, New York - Date delivered: Sept. 5, 1901
On Sept. 5, 1901, six months into his second term, McKinley spoke at the Pan American Exposition in Buffalo, New York. His remarks , shaped by his first term spent navigating foreign policy and fighting the Spanish American War, focus on progress in business, avoidance of war, and building goodwill internationally. "The period of exclusiveness is past. The expansion of our trade and commerce is the pressing problem." McKinley was shot the next day and died from his wounds eight days later.
Theodore Roosevelt
- Speech name: Message regarding meatpacking plants - Date delivered: June 4, 1906
Many experts regard Theodore Roosevelt as one of the greatest presidents in U.S. history . Among his many enduring accomplishments, his advocacy for consumer protection endures. In 1906, after revelations of the dangerous and unsanitary conditions of stockyards and meatpacking plants , Roosevelt addressed Congress , calling for immediate legislation to regulate the industry. Later that month, Roosevelt signed the Meat Inspection Act and the Pure Food and Drug Act, which required transparent product labeling and federal inspection of all plants engaged in interstate commerce.
William H. Taft
- Speech name: Message regarding income tax - Date delivered: June 16, 1909
In this speech , Taft proposed two tax-related pieces of legislation. First, that Congress ratify the Sixteenth Amendment to the Constitution, permitting the collection of personal federal income tax. This was viewed by supporters as a better way to generate income instead of relying heavily on tariffs. Second, that all corporations, except banks, pay a 2% tax on net income.
Woodrow Wilson
- Speech name: Wilson's Fourteen Points - Date delivered: Jan. 8, 1918
Wilson's famous "Fourteen Points" outlined his plan for peace to end World War I, albeit in broad terms. Recognizing that America's prosperity would come to rely more substantially on international relations, Wilson's "Fourteen Points" served as a framework for ensuring international cooperation. He believed his most important point was the development of a League of Nations —a governing body of united nations tasked with mitigating war by solving disputes between countries. The United Nations replaced the League of Nations at the end of World War II.
Warren G. Harding
- Speech name: Opening speech of the Conference on the Limitation of Armament - Date delivered: Nov. 12, 1921
In 1921, building on pursuing peace in the wake of World War I, Harding convened a disarmament conference in Washington. In attendance were military powers, including Belgium, China, Great Britain, Italy, France, the Netherlands, Portugal, and Japan. In his opening remarks, Harding asked the group to collectively commit to peacetime and quell the fears of the post-war world with a reduction in firepower. The results were several disarmament treaties signed by those world powers present that day.
Calvin Coolidge
- Speech name: First annual message - Date delivered: Dec. 6, 1923
Coolidge's first annual message was the first speech to be broadcast via radio to the entire nation, making advantageous use of the medium's rapidly growing popularity. It is estimated that 2.5 million radios existed in the U.S. at that time , while a mere 5,000 existed just three years prior. Coolidge paid homage to his predecessor William G. Harding who died in office six months earlier, expressed his support of prohibition and pushed for continued restrictions on immigration.
Herbert Hoover
- Speech name: Message regarding the Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act - Date delivered: June 16, 1930
A year into the Great Depression, against the advice of economists, Hoover signed the Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act, which raised tariffs in an attempt to generate revenue for the federal government. In his message to Congress , Hoover states that no tariff bill is or will ever be perfect, but this particular one is necessary to combat the economic crisis gripping the nation. As economists had warned, trade partners retaliated by raising their own tariffs, halting international trade, and driving the U.S. into an even deeper economic depression.
Franklin D. Roosevelt
- Speech name: Fireside Chat 1: On the Banking Crisis - Date delivered: March 12, 1933
Roosevelt's presidency spanned an unprecedented three terms (and election to a fourth he did not live to to see the end of). In those 12 years, he gave many influential speeches that shaped the nation and the world. His inaugural address is well-known for his affirmation that "the only thing we have to fear is fear itself." Just as familiar is his designation of Dec. 8, 1941, as "a day that will live in infamy." But perhaps most notable is FDR's first Fireside Chat . Speaking directly to the American public at one of the lowest points in the nation's history, FDR used the power of mass communication to calm fears, explain politics, inform, update, and uplift. It was a novel way of leading the country, and Roosevelt hosted 30 fireside chats in total.
Harry S. Truman
- Speech name: Statement by the president announcing the use of the A-bomb at Hiroshima - Date delivered: Aug. 6, 1945
Sixteen hours after the first atomic bomb was dropped on Hiroshima, Truman addressed the nation , explaining its unprecedented power and the need to keep the technology behind this new weapon secret. "The Japanese began the war from the air at Pearl Harbor. They have been repaid many fold. And the end is not yet," Truman warned. Three days later, a second atomic bomb was dropped on Nagasaki.
Dwight D. Eisenhower
- Speech name: Chance for Peace - Date delivered: April 16, 1953
Following the death of Joseph Stalin, Eisenhower delivered his "Chance for Peace'' speech, also referred to as the "Cross of Iron" speech. Eisenhower spoke of the dangers of an arms race with the Soviet Union, stating "every gun that is made, every warship launched, every rocket fired signifies, in the final sense, a theft from those who hunger and are not fed, those who are cold and are not clothed... under the cloud of threatening war, it is humanity hanging from a cross of iron."
John F. Kennedy
- Speech name: Address on the space effort - Date delivered: Sept. 12, 1962
Seventeen months after Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin became the first man in space, Kennedy outlined a plan to put a man on the moon . He galvanized the country with a desire for greatness, the likes of which the world had never seen. He reminded everyone that Americans do things like go to the moon, "not because they are easy, but because they are hard." It is those hard things, Kennedy attested, that the entrepreneurial spirit of America was best suited to achieve.
Lyndon B. Johnson
- Speech name: Speech before Congress on voting rights - Date delivered: March 15, 1965
In the wake of violence against civil rights protesters in Selma, Alabama, Johnson addressed Congress requesting their help to pass voting legislation that would allow all citizens to register and cast a vote free from harassment and discrimination. Johnson expressed that pervasive discrimination and constitutional infringements were not a regional problem, but a problem the whole country shared responsibility in correcting. "It is wrong—deadly wrong—to deny any of your fellow Americans the right to vote in this country. There is no issue of states' rights or national rights. There is only the struggle for human rights," Johnson urged.
Richard M. Nixon
- Speech name: Address to the nation announcing decision to resign the office of president - Date delivered: Aug. 8, 1974
Less than a month after the House Judiciary Committee voted for three articles of impeachment, Nixon announced his resignation on national television. "I have never been a quitter. To leave office before my term is completed is abhorrent to every instinct in my body." Nixon stated. "But as President, I must put the interests of America first." It was the first time in U.S. history that a president resigned, affirming that no person was above the law.
Gerald R. Ford
- Speech name: Remarks in Helsinki - Date delivered: Aug. 1, 1975
Ford signed the controversial Helsinki Accords on Aug. 1, 1975. Among other things, the accords were a vehicle by which the U.S. and the Soviet Union could further pursue détente . In his remarks that day , Ford spoke about U.S. commitment to human rights, fundamental freedoms, and restoring diplomacy. "If the Soviet Union and the United States can reach agreement so that our astronauts can fit together the most intricate scientific equipment, work together, and shake hands 137 miles out in space, we as statesmen have an obligation to do as well on Earth."
Jimmy Carter
- Speech name: Crisis of Confidence - Date delivered: July 15, 1979
In the midst of the energy crisis , America, Carter believed, was also suffering from a crisis of confidence. The country's trust in the government was eroded. Belief in the American way of life wavered. Faith that the future would be better than the present waned. Carter reminded Americans over a television broadcast of his "Crisis of Confidence" speech that this was the country that put a man on the moon and fought for civil rights. He assured the nation that overcoming the energy crisis would be another milestone in a long history of American resilience.
Ronald Reagan
- Speech name: Address on the Space Shuttle Challenger - Date delivered: Jan. 28, 1986
At times, presidents throughout history needed to play the role of spiritual advisor. While some called upon their own religious beliefs to offer words of healing, at the core of these messages was a universal, human connection and expression of compassion. The Space Shuttle Challenger disaster was one such moment for Reagan . He commended on the bravery of the crew, noting that their lives and ultimately their sacrifices, which would never be forgotten, were part of a sacred tradition of pioneering and exploration. Reagan also spoke directly to the children of the country, reminding them to have courage and understand that Americans bear great risks in pursuit of greater rewards.
George H. W. Bush
- Speech name: Address to the nation on the invasion of Iraq - Date delivered: Jan. 16, 1991
After five months of failed negotiations with Saddam Hussein and following Iraq's invasion of neighboring Kuwait, Bush announced the aerial invasion of Iraq . His goals were outlined clearly: restore peace to Kuwait upon ousting Hussein and his forces and ensure Iraq's compliance with U.N. resolutions. This marked the beginning of the Persian Gulf War that would last 42 days but impact relations in the region for decades to come .
Bill Clinton
- Speech name: State of the Union Address - Date delivered: Jan. 27, 1998
What makes Clinton's 1998 State of the Union Address impressive is that it came just one day after his response to allegations about his sexual misconduct with then-intern Monica Lewinsky. On the heels of the infamous "I did not have sexual relations with that woman," Clinton showcased his persuasive speaking skills and delivered a thoughtful, focused State of the Union on preparing the country for prosperity in the 21st century.
George W. Bush
- Speech name: Address on the U.S. response to the attacks of Sept. 11 - Date delivered: Sept. 22, 2001
Bush addressed the nation after the attacks on Sept. 11, 2001—the deadliest terror attack on U.S. soil. His message focused on helping and healing and invoked sentiments of the enduring strength of the country. Eleven days later, Bush addressed Congress proposing the War on Terror to defeat Al Qaeda and defend the American way of life: "These measures are essential. But the only way to defeat terrorism as a threat to our way of life is to stop it, eliminate it, and destroy it where it grows."
Barack Obama
- Speech name: Remarks at the 50th anniversary of the Selma marches - Date delivered: March 7, 2015
From announcing the death of Osama Bin Laden to honoring the victims of the Sandy Hook shooting, Obama's legacy is largely defined by the poignant speeches he delivered. Historian Douglas Brinkley said of Obama : "I don't know of any president who has put that kind of work into his speeches." Experts rank his remarks at the 50th Anniversary of the Selma march among the most influential speeches of his presidency. He asserted that one of the greatest forms of patriotism, as demonstrated at Selma 50 years earlier, is to believe that America can always evolve and to hold it to newer, higher standards.
Donald J. Trump
- Speech name: Speech Urging Supporters to Go Home - Date delivered: January 6, 2021
Before Congress certified Joe Biden as the next president of the United States and the rightful winner of the 2020 election, Donald Trump spoke to his followers at a "Save America" rally to present evidence of how the election was "stolen." "We will never concede; it doesn't happen. You don't concede when there's theft involved," he said. In the hour-long speech laden with violent, combative rhetoric, Trump made a single early reference to peaceful protestation. He concluded the rally by encouraging his supporters to "fight like hell" and to march down Pennsylvania Avenue. Hours later, thousands of insurrectionists stormed and breached the U.S. Capitol building. Instead of admonishing the mob's actions, Trump's speech urging his supporters to leave struck an empathetic tone; he told them he loved them and thought they were very special. In this speech lasting just under a minute, Trump again reiterated his belief that the election was fraudulent.
- Speech name: Remarks on the Continued Battle for the Soul of the Nation - Date delivered: September 1, 2022
This speech, delivered two months before the 2022 midterm elections, was Biden's appeal to the American public to uphold the core tenets of democracy—what he describes as the soul of the nation . In a rare bit of presidential rhetoric, Biden explicitly names a group of American citizens—Donald Trump and MAGA Republicans—as a direct threat to democracy. This plea to not only preserve but win the battle for America's soul came at a time when more than 70% of Republicans believed Biden did not legitimately win the 2020 presidential election. Throughout the speech, Biden repeatedly refers to political violence—an ever-present threat amid the political climate of his first term. These mentions are references to the Jan. 6 attack on the U.S. Capitol building and a warning against future politically motivated violence instigated by extremists, which experts say is on the rise.
Trending Now
100 best 'snl' episodes.

Best sitcoms of all time

50 best crime TV shows of all time

50 best space movies of all time
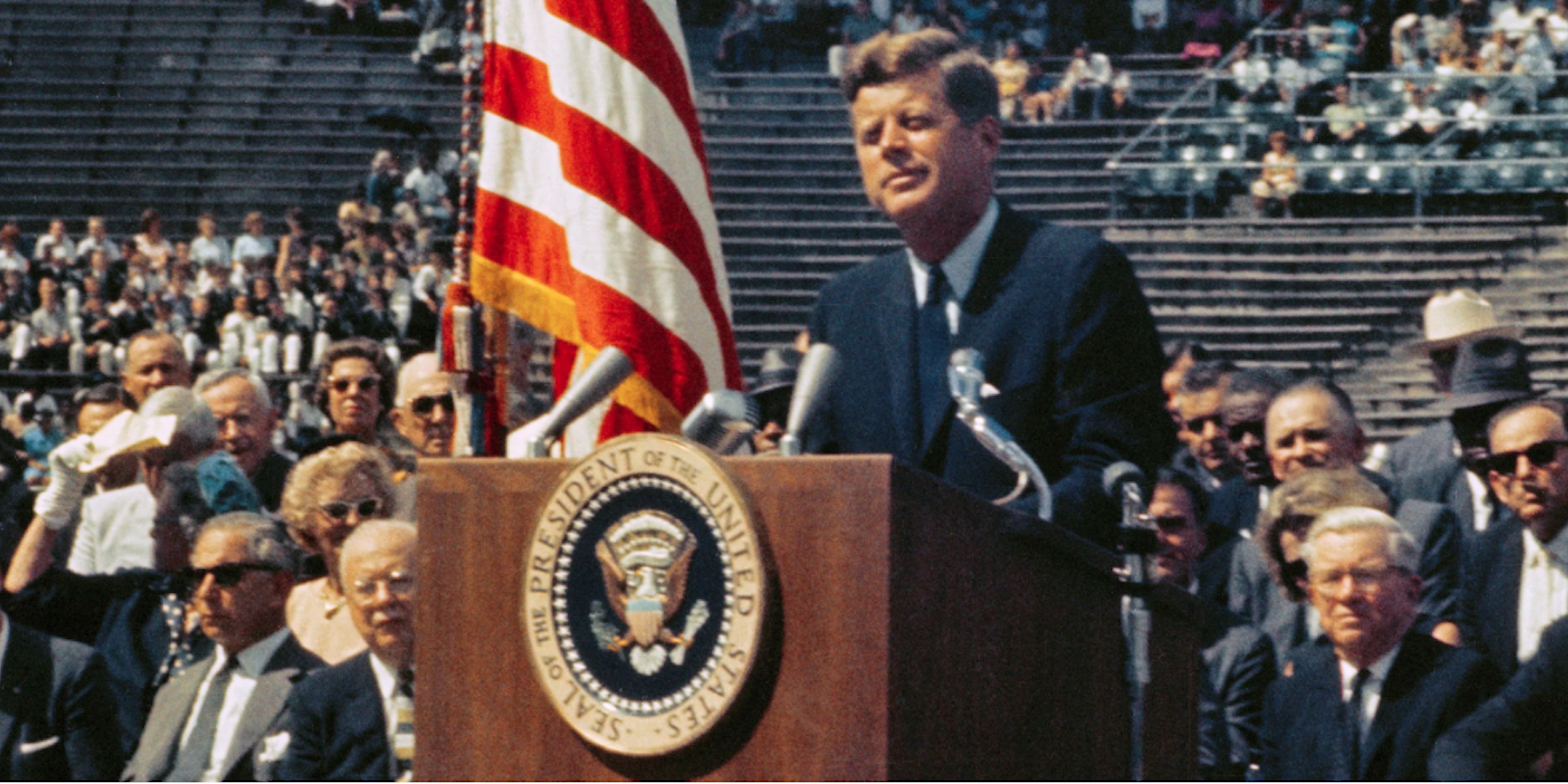


Photo via NASA on the Commons/Flickr
Celebrate Presidents Day with these 10 historic speeches
Reflecting back on our nation’s greatest leaders..
Kristen Hubby
Posted on Feb 20, 2017 Updated on May 24, 2021, 11:27 pm CDT
Presidents Day is time to reflect and show appreciation for our nation’s greatest leaders, those who have led the country and lifted the people up with their inspiring words and courageous actions. Acast , the Swedish podcast platform, recently released a new series, Presidents’ Day Collection , highlighting the most influential presidential speeches. The collection, which was done in collaboration with the National Archives, dates back to JFK’s memorable inaugural address in 1961.
“We thought, let’s do something political, but what everyone can feel good about, which is reminding people how powerful the U.S. presidents and the presidential post is,” said Caitlin Thompson, Acast’s U.S. director of content. “That this can be a clarion call to be optimistic and get people to work together.”
Listed below are Acast’s 10 most influential speeches from former U.S. presidents in the past 50 years to rouse inspiration and positivity that is sometimes forgotten.
1) John F. Kennedy

Screengrab via Presidents’ Day Collection/Acast
Former President John F. Kennedy was sworn in as president Jan. 20, 1961, as the 35th president of the United States. His inaugural address was memorable for many reasons, including his use of the phrase “my fellow citizens,” which was last issued by George Washington and rejected by former presidents due to its informal nature.
Here’s the final thrust of the address .
In the long history of the world, only a few generations have been granted the role of defending freedom in its hour of maximum danger. I do not shrink from this responsibility–I welcome it. I do not believe that any of us would exchange places with any other people or any other generation. The energy, the faith, the devotion which we bring to this endeavor will light our country and all who serve it–and the glow from that fire can truly light the world. And so, my fellow Americans: ask not what your country can do for you–ask what you can do for your country. My fellow citizens of the world: ask not what America will do for you, but what together we can do for the freedom of man. Finally, whether you are citizens of America or citizens of the world, ask of us here the same high standards of strength and sacrifice which we ask of you. With a good conscience our only sure reward, with history the final judge of our deeds, let us go forth to lead the land we love, asking His blessing and His help, but knowing that here on earth God’s work must truly be our own.
2) Richard Nixon

President Richard Nixon delivered his first inauguration address Jan. 20, 1969. Nixon’s presidency was, of course, one of the most controversial, resulting in resignation. Despite the Nixon administration continuing the war in Vietnam in 1973, his inauguration address talked of peace and solidarity.
We are caught in war, wanting peace. We are torn by division, wanting unity. We see around us empty lives, wanting fulfillment. We see tasks that need doing, waiting for hands to do them. To a crisis of the spirit, we need an answer of the spirit. And to find that answer, we need only look within ourselves.
- The number of executive orders by every U.S. president
- What’s stopping Elizabeth Warren from running for president in 2020?
- Will Beto O’Rourke run for president in 2020?
3) Jimmy Carter
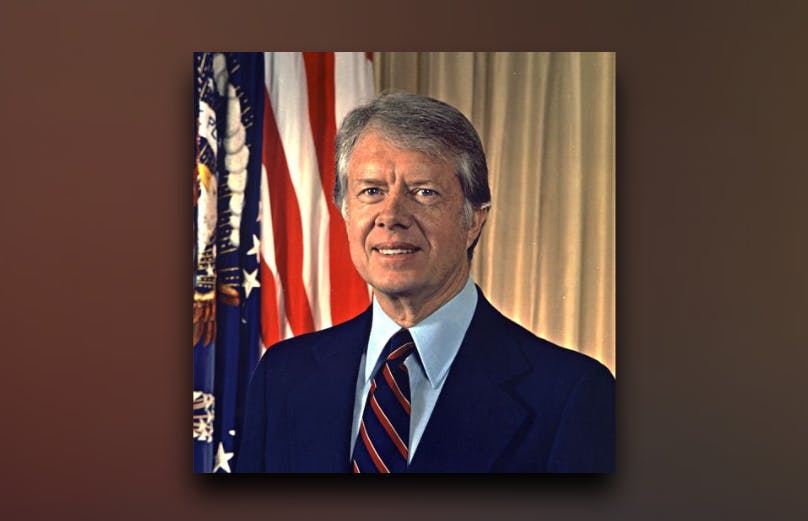

Jimmy Carter was sworn in as the 39th president of the United States on Jan. 20, 1977. However, his inaugural address was not the pick for the podcast series. Instead, they chose his famous “Crisis of Confidence” address to the nation that was televised on July 15, 1979.
Little by little we can and we must rebuild our confidence. We can spend until we empty our treasuries, and we may summon all the wonders of science. But we can succeed only if we tap our greatest resources — America’s people, America’s values, and America’s confidence. I have seen the strength of America in the inexhaustible resources of our people. In the days to come, let us renew that strength in the struggle for an energy secure nation.
4) George H.W. Bush

President George H.W. Bush’s inaugural address on Jan. 20, 1989, carried on his campaign’s promise for a “kinder, gentler” nation and also emphasized the need to tackle the federal budget deficit.
Some see leadership as high drama and the sound of trumpets calling, and sometimes it is that. But I see history as a book with many pages, and each day we fill a page with acts of hopefulness and meaning. The new breeze blows, a page turns, the story unfolds. And so, today a chapter begins, a small and stately story of unity, diversity, and generosity — shared, and written, together.
5) George W. Bush

President George W. Bush gave one of the most memorable speeches at the Islamic Center of Washington, D.C., on Sept. 17, 2001, six days after the terrorist attacks of Sept. 11 on the World Trade Center, the Pentagon, and a failed hijacking that resulting in a deadly crash in Pennsylvania.
In his speech, Bush stated “Islam is peace,” that the millions of Muslims in the U.S. are an “incredibly valuable contribution to our country,” and that American’s should treat each other with respect. In a time of crisis, Bush gave the speech to comfort the wounded country and bring the people together.
Jenna Bush, his daughter, recently shared the text of the speech after President Trump issued his controversial travel ban.
“This is not the America I know…” just a reminder this am to teach acceptance and love to our kids for all races, all religions.. pic.twitter.com/32XohAGMv7 — Jenna Bush Hager (@JennaBushHager) January 31, 2017
6) Lyndon B. Johnson

President Lydon B. Johnson, or LBJ, was the 36th president of the United States. His speech on the Voting Rights Act before Congress on March 15, 1965, was one week after Bloody Sunday, where peaceful protestors were beaten in the famous walk from Selma, Alabama, to Montgomery. His speech stated there “is only an American problem” when it comes to segregation and racism, delivering notes of unity, stating all Americans have the right to vote.
This was the first nation in the history of the world to be founded with a purpose. The great phrases of that purpose still sound in every American heart, North and South: “All men are created equal”—”government by consent of the governed”—”give me liberty or give me death.” Well, those are not just clever words, or those are not just empty theories. In their name Americans have fought and died for two centuries, and tonight around the world they stand there as guardians of our liberty, risking their lives. Those words are a promise to every citizen that he shall share in the dignity of man. This dignity cannot be found in a man’s possessions; it cannot be found in his power, or in his position. It really rests on his right to be treated as a man equal in opportunity to all others. It says that he shall share in freedom, he shall choose his leaders, educate his children, and provide for his family according to his ability and his merits as a human being.
7) Gerald Ford

Gerald Ford was the 38th president of the United States, serving from 1974 to 1977. His inaugural remarks speech on Aug. 9, 1974, was impactful in the way he addressed the nation as “a straight talk among friends.”
As we bind up the internal wounds of Watergate, more painful and more poisonous than those of foreign wars, let us restore the golden rule to our political process, and let brotherly love purge our hearts of suspicion and of hate.
8) Ronald Reagan

The 40th president of the United States, Ronald Reagan, made iconic remarks at the Brandenburg Gate in West Berlin on June 12, 1987. Reagan addressed the leader of the Soviet Union, Mikhail Gorbachev, to open up the Berlin Wall in 1987 saying, “Tear down this wall! “Tear down this wall!”
9) Bill Clinton

The 42nd president of the United States, Bill Clinton, became the first Democrat to serve as president in more than a decade when he took the oath of office. Clinton delivered his inaugural address on Jan. 20, 1993, focusing on “American renewal.” Maya Angelou recited a poem, becoming the first poet at an inauguration address since Robert Frost spoke during John F. Kennedy’s address in 1961.
Today we do more than celebrate America. We rededicate ourselves to the very idea of America, an idea born in revolution and renewed through two centuries of challenge; an idea tempered by the knowledge that, but for fate, we, the fortunate, and the unfortunate might have been each other; an idea ennobled by the faith that our Nation can summon from its myriad diversity the deepest measure of unity; an idea infused with the conviction that America’s long, heroic journey must go forever upward.
10) Barack Obama

President Barack Obama made history as the first black president of the United States, and his first inaugural address on Jan.ry 20, 2009, recognized the financial crisis the nation was facing.
We are a nation of Christians and Muslims, Jews and Hindus — and nonbelievers. We are shaped by every language and culture, drawn from every end of this Earth; and because we have tasted the bitter swill of civil war and segregation, and emerged from that dark chapter stronger and more united, we cannot help but believe that the old hatreds shall someday pass; that the lines of tribe shall soon dissolve; that as the world grows smaller, our common humanity shall reveal itself; and that America must play its role in ushering in a new era of peace.
“Whether you like any one of those presidents or not, you can’t deny the fact that their words were sort of filled with hope and optimism, and some leadership,” said Thompson. “I think, you know, we felt like it was a good time to remember that this Presidents Day.”
Share this article
Kristen Hubby is a tech and lifestyle reporter. Her writing focuses on sex, pop culture, streaming entertainment, and social media, with an emphasis on major platforms like Snapchat, YouTube, and Spotify. Her work has also appeared in Austin Monthly and the Austin American-Statesman, where she covered local news and the dining scene in Austin, Texas.
Uncategorized
40 famous persuasive speeches you need to hear.
Written by Kai Xin Koh

Across eras of calamity and peace in our world’s history, a great many leaders, writers, politicians, theorists, scientists, activists and other revolutionaries have unveiled powerful rousing speeches in their bids for change. In reviewing the plethora of orators across tides of social, political and economic change, we found some truly rousing speeches that brought the world to their feet or to a startling, necessary halt. We’ve chosen 40 of the most impactful speeches we managed to find from agents of change all over the world – a diversity of political campaigns, genders, positionalities and periods of history. You’re sure to find at least a few speeches in this list which will capture you with the sheer power of their words and meaning!
1. I have a dream by MLK
“I have a dream that one day down in Alabama, with its vicious racists, with its governor having his lips dripping with the words of interposition and nullification – one day right there in Alabama little black boys and black girls will be able to join hands with little white boys and white girls as sisters and brothers. I have a dream today. I have a dream that one day every valley shall be exalted, and every hill and mountain shall be made low, the rough places will be made plain, and the crooked places will be made straight, and the glory of the Lord shall be revealed and all flesh shall see it together. This is our hope. This is the faith that I go back to the South with. With this faith we will be able to hew out of the mountain of despair a stone of hope. With this faith we will be able to transform the jangling discords of our nation into a beautiful symphony of brotherhood. With this faith we will be able to work together, to pray together, to struggle together, to go to jail together, to stand up for freedom together, knowing that we will be free one day. This will be the day, this will be the day when all of God’s children will be able to sing with new meaning “My country ’tis of thee, sweet land of liberty, of thee I sing. Land where my father’s died, land of the Pilgrim’s pride, from every mountainside, let freedom ring!”
Unsurprisingly, Martin Luther King’s speech comes up top as the most inspiring speech of all time, especially given the harrowing conditions of African Americans in America at the time. In the post-abolition era when slavery was outlawed constitutionally, African Americans experienced an intense period of backlash from white supremacists who supported slavery where various institutional means were sought to subordinate African American people to positions similar to that of the slavery era. This later came to be known as the times of Jim Crow and segregation, which Martin Luther King powerfully voiced his vision for a day when racial discrimination would be a mere figment, where equality would reign.
2. Tilbury Speech by Queen Elizabeth I
“My loving people, We have been persuaded by some that are careful of our safety, to take heed how we commit our selves to armed multitudes, for fear of treachery; but I assure you I do not desire to live to distrust my faithful and loving people. Let tyrants fear. I have always so behaved myself that, under God, I have placed my chiefest strength and safeguard in the loyal hearts and good-will of my subjects; and therefore I am come amongst you, as you see, at this time, not for my recreation and disport, but being resolved, in the midst and heat of the battle, to live and die amongst you all; to lay down for my God, and for my kingdom, and my people, my honour and my blood, even in the dust. I know I have the body of a weak, feeble woman; but I have the heart and stomach of a king, and of a king of England too, and think foul scorn that Parma or Spain, or any prince of Europe, should dare to invade the borders of my realm; to which rather than any dishonour shall grow by me, I myself will take up arms, I myself will be your general, judge, and rewarder of every one of your virtues in the field. I know already, for your forwardness you have deserved rewards and crowns; and We do assure you on a word of a prince, they shall be duly paid. In the mean time, my lieutenant general shall be in my stead, than whom never prince commanded a more noble or worthy subject; not doubting but by your obedience to my general, by your concord in the camp, and your valour in the field, we shall shortly have a famous victory over these enemies of my God, of my kingdom, and of my people.”
While at war with Spain, Queen Elizabeth I was most renowned for her noble speech rallying the English troops against their comparatively formidable opponent. Using brilliant rhetorical devices like metonymy, meronymy, and other potent metaphors, she voiced her deeply-held commitment as a leader to the battle against the Spanish Armada – convincing the English army to keep holding their ground and upholding the sacrifice of war for the good of their people. Eventually against all odds, she led England to victory despite their underdog status in the conflict with her confident and masterful oratory.
3. Woodrow Wilson, address to Congress (April 2, 1917)
“The world must be made safe for democracy. Its peace must be planted upon the tested foundations of political liberty. We have no selfish ends to serve. We desire no conquest, no dominion. We seek no indemnities for ourselves, no material compensation for the sacrifices we shall freely make. We are but one of the champions of the rights of mankind. We shall be satisfied when those rights have been made as secure as the faith and the freedom of nations can make them. Just because we fight without rancor and without selfish object, seeking nothing for ourselves but what we shall wish to share with all free peoples, we shall, I feel confident, conduct our operations as belligerents without passion and ourselves observe with proud punctilio the principles of right and of fair play we profess to be fighting for. … It will be all the easier for us to conduct ourselves as belligerents in a high spirit of right and fairness because we act without animus, not in enmity toward a people or with the desire to bring any injury or disadvantage upon them, but only in armed opposition to an irresponsible government which has thrown aside all considerations of humanity and of right and is running amuck. We are, let me say again, the sincere friends of the German people, and shall desire nothing so much as the early reestablishment of intimate relations of mutual advantage between us—however hard it may be for them, for the time being, to believe that this is spoken from our hearts. We have borne with their present government through all these bitter months because of that friendship—exercising a patience and forbearance which would otherwise have been impossible. We shall, happily, still have an opportunity to prove that friendship in our daily attitude and actions toward the millions of men and women of German birth and native sympathy who live among us and share our life, and we shall be proud to prove it toward all who are in fact loyal to their neighbors and to the government in the hour of test. They are, most of them, as true and loyal Americans as if they had never known any other fealty or allegiance. They will be prompt to stand with us in rebuking and restraining the few who may be of a different mind and purpose. If there should be disloyalty, it will be dealt with with a firm hand of stern repression; but, if it lifts its head at all, it will lift it only here and there and without countenance except from a lawless and malignant few. It is a distressing and oppressive duty, gentlemen of the Congress, which I have performed in thus addressing you. There are, it may be, many months of fiery trial and sacrifice ahead of us. It is a fearful thing to lead this great peaceful people into war, into the most terrible and disastrous of all wars, civilization itself seeming to be in the balance. But the right is more precious than peace, and we shall fight for the things which we have always carried nearest our hearts—for democracy, for the right of those who submit to authority to have a voice in their own governments, for the rights and liberties of small nations, for a universal dominion of right by such a concert of free peoples as shall bring peace and safety to all nations and make the world itself at last free. To such a task we can dedicate our lives and our fortunes, everything that we are and everything that we have, with the pride of those who know that the day has come when America is privileged to spend her blood and her might for the principles that gave her birth and happiness and the peace which she has treasured. God helping her, she can do no other.”
On April 2, 1917, President Woodrow Wilson of the USA delivered his address to Congress, calling for declaration of war against what was at the time, a belligerent and aggressive Germany in WWI. Despite his isolationism and anti-war position earlier in his tenure as president, he convinced Congress that America had a moral duty to the world to step out of their neutral observer status into an active role of world leadership and stewardship in order to liberate attacked nations from their German aggressors. The idealistic values he preached in his speech left an indelible imprint upon the American spirit and self-conception, forming the moral basis for the country’s people and aspirational visions to this very day.
4. Ain’t I A Woman by Sojourner Truth
“That man over there says that women need to be helped into carriages, and lifted over ditches, and to have the best place everywhere. Nobody ever helps me into carriages, or over mud-puddles, or gives me any best place! And ain’t I a woman? Look at me! Look at my arm! I have ploughed and planted, and gathered into barns, and no man could head me! And ain’t I a woman? I could work as much and eat as much as a man – when I could get it – and bear the lash as well! And ain’t I a woman? I have borne thirteen children, and seen most all sold off to slavery, and when I cried out with my mother’s grief, none but Jesus heard me! And ain’t I a woman? … If the first woman God ever made was strong enough to turn the world upside down all alone, these women together ought to be able to turn it back , and get it right side up again! And now they is asking to do it, the men better let them.”
Hailing from a background of slavery and oppression, Sojourner Truth was one of the most revolutionary advocates for women’s human rights in the 1800s. In spite of the New York Anti-Slavery Law of 1827, her slavemaster refused to free her. As such, she fled, became an itinerant preacher and leading figure in the anti-slavery movement. By the 1850s, she became involved in the women’s rights movement as well. At the 1851 Women’s Rights Convention held in Akron, Ohio, she delivered her illuminating, forceful speech against discrimination of women and African Americans in the post-Civil War era, entrenching her status as one of the most revolutionary abolitionists and women’s rights activists across history.
5. The Gettsyburg Address by Abraham Lincoln
“Fondly do we hope, fervently do we pray, that this mighty scourge of war may speedily pass away. Yet, if God wills that it continue until all the wealth piled by the bondsman’s two hundred and fifty years of unrequited toil shall be sunk, and until every drop of blood drawn with the lash shall be paid by another drawn with the sword, as was said three thousand years ago, so still it must be said “the judgments of the Lord are true and righteous altogether.” With malice toward none, with charity for all, with firmness in the right as God gives us to see the right, let us strive on to finish the work we are in, to bind up the nation’s wounds, to care for him who shall have borne the battle and for his widow and his orphan, to do all which may achieve and cherish a just and lasting peace among ourselves and with all nations.”
President Abraham Lincoln had left the most lasting legacy upon American history for good reason, as one of the presidents with the moral courage to denounce slavery for the national atrocity it was. However, more difficult than standing up for the anti-slavery cause was the task of unifying the country post-abolition despite the looming shadows of a time when white Americans could own and subjugate slaves with impunity over the thousands of Americans who stood for liberation of African Americans from discrimination. He urged Americans to remember their common roots, heritage and the importance of “charity for all”, to ensure a “just and lasting peace” among within the country despite throes of racial division and self-determination.
6. Woman’s Rights to the Suffrage by Susan B Anthony
“For any State to make sex a qualification that must ever result in the disfranchisement of one entire half of the people is to pass a bill of attainder, or an ex post facto law, and is therefore a violation of the supreme law of the land. By it the blessings of liberty are for ever withheld from women and their female posterity. To them this government has no just powers derived from the consent of the governed. To them this government is not a democracy. It is not a republic. It is an odious aristocracy; a hateful oligarchy of sex; the most hateful aristocracy ever established on the face of the globe; an oligarchy of wealth, where the right govern the poor. An oligarchy of learning, where the educated govern the ignorant, or even an oligarchy of race, where the Saxon rules the African, might be endured; but this oligarchy of sex, which makes father, brothers, husband, sons, the oligarchs over the mother and sisters, the wife and daughters of every household–which ordains all men sovereigns, all women subjects, carries dissension, discord and rebellion into every home of the nation. Webster, Worcester and Bouvier all define a citizen to be a person in the United States, entitled to vote and hold office. The only question left to be settled now is: Are women persons? And I hardly believe any of our opponents will have the hardihood to say they are not. Being persons, then, women are citizens; and no State has a right to make any law, or to enforce any old law, that shall abridge their privileges or immunities. Hence, every discrimination against women in the constitutions and laws of the several States is today null and void, precisely as in every one against Negroes.”
Susan B. Anthony was a pivotal leader in the women’s suffrage movement who helped to found the National Woman Suffrage Association with Elizabeth Cady Stanton and fight for the constitutional right for women to vote. She courageously and relentlessly advocated for women’s rights, giving speeches all over the USA to convince people of women’s human rights to choice and the ballot. She is most well known for her act of righteous rebellion in 1872 when she voted in the presidential election illegally, for which she was arrested and tried unsuccessfully. She refused to pay the $100 fine in a bid to reject the demands of the American system she denounced as a ‘hateful oligarchy of sex’, sparking change with her righteous oratory and inspiring many others in the women’s suffrage movement within and beyond America.
7. Vladimir Lenin’s Speech at an International Meeting in Berne, February 8, 1916
“It may sound incredible, especially to Swiss comrades, but it is nevertheless true that in Russia, also, not only bloody tsarism, not only the capitalists, but also a section of the so-called or ex-Socialists say that Russia is fighting a “war of defence,” that Russia is only fighting against German invasion. The whole world knows, however, that for decades tsarism has been oppressing more than a hundred million people belonging to other nationalities in Russia; that for decades Russia has been pursuing a predatory policy towards China, Persia, Armenia and Galicia. Neither Russia, nor Germany, nor any other Great Power has the right to claim that it is waging a “war of defence”; all the Great Powers are waging an imperialist, capitalist war, a predatory war, a war for the oppression of small and foreign nations, a war for the sake of the profits of the capitalists, who are coining golden profits amounting to billions out of the appalling sufferings of the masses, out of the blood of the proletariat. … This again shows you, comrades, that in all countries of the world real preparations are being made to rally the forces of the working class. The horrors of war and the sufferings of the people are incredible. But we must not, and we have no reason whatever, to view the future with despair. The millions of victims who will fall in the war, and as a consequence of the war, will not fall in vain. The millions who are starving, the millions who are sacrificing their lives in the trenches, are not only suffering, they are also gathering strength, are pondering over the real cause of the war, are becoming more determined and are acquiring a clearer revolutionary understanding. Rising discontent of the masses, growing ferment, strikes, demonstrations, protests against the war—all this is taking place in all countries of the world. And this is the guarantee that the European War will be followed by the proletarian revolution against capitalism”
Vladimir Lenin remains to this day one of the most lauded communist revolutionaries in the world who brought the dangers of imperialism and capitalism to light with his rousing speeches condemning capitalist structures of power which inevitably enslave people to lives of misery and class stratification. In his genuine passion for the rights of the working class, he urged fellow comrades to turn the “imperialist war” into a “civil” or class war of the proletariat against the bourgeoisie. He encouraged the development of new revolutionary socialist organisations, solidarity across places in society so people could unite against their capitalist overlords, and criticised nationalism for its divisive effect on the socialist movement. In this speech especially, he lambasts “bloody Tsarism” for its oppression of millions of people of other nationalities in Russia, calling for the working class people to revolt against the Tsarist authority for the proletariat revolution to succeed and liberate them from class oppression.
8. I Have A Dream Speech by Mary Wollstonecraft
“If, I say, for I would not impress by declamation when Reason offers her sober light, if they be really capable of acting like rational creatures, let them not be treated like slaves; or, like the brutes who are dependent on the reason of man, when they associate with him; but cultivate their minds, give them the salutary, sublime curb of principle, and let them attain conscious dignity by feeling themselves only dependent on God. Teach them, in common with man, to submit to necessity, instead of giving, to render them more pleasing, a sex to morals. Further, should experience prove that they cannot attain the same degree of strength of mind, perseverance, and fortitude, let their virtues be the same in kind, though they may vainly struggle for the same degree; and the superiority of man will be equally clear, if not clearer; and truth, as it is a simple principle, which admits of no modification, would be common to both. Nay, the order of society as it is at present regulated would not be inverted, for woman would then only have the rank that reason assigned her, and arts could not be practised to bring the balance even, much less to turn it.”
In her vindication of the rights of women, Mary Wollstonecraft was one of the pioneers of the feminist movement back in 1792 who not only theorised and advocated revolutionarily, but gave speeches that voiced these challenges against a dominantly sexist society intent on classifying women as irrational less-than-human creatures to be enslaved as they were. In this landmark speech, she pronounces her ‘dream’ of a day when women would be treated as the rational, deserving humans they are, who are equal to man in strength and capability. With this speech setting an effective precedent for her call to equalize women before the law, she also went on to champion the provision of equal educational opportunities to women and girls, and persuasively argued against the patriarchal gender norms which prevented women from finding their own lot in life through their being locked into traditional institutions of marriage and motherhood against their will.

9. First Inaugural Speech by Franklin D Roosevelt
“So, first of all, let me assert my firm belief that the only thing we have to fear is…fear itself — nameless, unreasoning, unjustified terror which paralyzes needed efforts to convert retreat into advance. In every dark hour of our national life a leadership of frankness and of vigor has met with that understanding and support of the people themselves which is essential to victory. And I am convinced that you will again give that support to leadership in these critical days. … More important, a host of unemployed citizens face the grim problem of existence, and an equally great number toil with little return. Only a foolish optimist can deny the dark realities of the moment. Our greatest primary task is to put people to work. This is no unsolvable problem if we face it wisely and courageously. There are many ways in which it can be helped, but it can never be helped merely by talking about it. We must act and act quickly. … I am prepared under my constitutional duty to recommend the measures that a stricken Nation in the midst of a stricken world may require. These measures, or such other measures as the Congress may build out of its experience and wisdom, I shall seek, within my constitutional authority, to bring to speedy adoption. But in the event that the Congress shall fail to take one of these two courses, and in the event that the national emergency is still critical, I shall not evade the clear course of duty that will then confront me. I shall ask the Congress for the one remaining instrument to meet the crisis — broad Executive power to wage a war against the emergency, as great as the power that would be given to me if we were in fact invaded by a foreign foe.”
Roosevelt’s famous inaugural speech was delivered in the midst of a period of immense tension and strain under the Great Depression, where he highlighted the need for ‘quick action’ by Congress to prepare for government expansion in his pursuit of reforms to lift the American people out of devastating poverty. In a landslide victory, he certainly consolidated the hopes and will of the American people through this compelling speech.
10. The Hypocrisy of American Slavery by Frederick Douglass
“What to the American slave is your Fourth of July? I answer, a day that reveals to him more than all other days of the year, the gross injustice and cruelty to which he is the constant victim. To him your celebration is a sham; your boasted liberty an unholy license; your national greatness, swelling vanity; your sounds of rejoicing are empty and heartless; your shouts of liberty and equality, hollow mock; your prayers and hymns, your sermons and thanksgivings, with all your religious parade and solemnity, are to him mere bombast, fraud, deception, impiety, and hypocrisy – a thin veil to cover up crimes which would disgrace a nation of savages. There is not a nation of the earth guilty of practices more shocking and bloody than are the people of these United States at this very hour. Go search where you will, roam through all the monarchies and despotisms of the Old World, travel through South America, search out every abuse and when you have found the last, lay your facts by the side of the everyday practices of this nation, and you will say with me that, for revolting barbarity and shameless hypocrisy, America reigns without a rival.”
On 4 July 1852, Frederick Douglass gave this speech in Rochester, New York, highlighting the hypocrisy of celebrating freedom while slavery continues. He exposed the ‘revolting barbarity and shameless hypocrisy’ of slavery which had gone unabolished amidst the comparatively obscene celebration of independence and liberty with his potent speech and passion for the anti-abolition cause. After escaping from slavery, he went on to become a national leader of the abolitionist movement in Massachusetts and New York with his oratory and incisive antislavery writings. To this day, his fierce activism and devotion to exposing virulent racism for what it was has left a lasting legacy upon pro-Black social movements and the overall sociopolitical landscape of America.
11. Still I Rise by Maya Angelou
“You may write me down in history With your bitter, twisted lies, You may trod me in the very dirt But still, like dust, I’ll rise. Does my sassiness upset you? Why are you beset with gloom? ’Cause I walk like I’ve got oil wells Pumping in my living room. Just like moons and like suns, With the certainty of tides, Just like hopes springing high, Still I’ll rise. Did you want to see me broken? Bowed head and lowered eyes? Shoulders falling down like teardrops, Weakened by my soulful cries? Does my haughtiness offend you? Don’t you take it awful hard ’Cause I laugh like I’ve got gold mines Diggin’ in my own backyard. You may shoot me with your words, You may cut me with your eyes, You may kill me with your hatefulness, But still, like air, I’ll rise. Does my sexiness upset you? Does it come as a surprise That I dance like I’ve got diamonds At the meeting of my thighs? Out of the huts of history’s shame I rise Up from a past that’s rooted in pain I rise I’m a black ocean, leaping and wide, Welling and swelling I bear in the tide. Leaving behind nights of terror and fear I rise Into a daybreak that’s wondrously clear I rise Bringing the gifts that my ancestors gave, I am the dream and the hope of the slave. I rise I rise I rise.”
With her iconic poem Still I Rise , Maya Angelou is well-known for uplifting fellow African American women through her empowering novels and poetry and her work as a civil rights activist. Every bit as lyrical on the page, her recitation of Still I Rise continues to give poetry audiences shivers all over the world, inspiring women of colour everywhere to keep the good faith in striving for equality and peace, while radically believing in and empowering themselves to be agents of change. A dramatic reading of the poem will easily showcase the self-belief, strength and punch that it packs in the last stanza on the power of resisting marginalization.
12. Their Finest Hour by Winston Churchill
“What General Weygand called the Battle of France is over. I expect that the Battle of Britain is about to begin. Upon this battle depends the survival of Christian civilization. Upon it depends our own British life, and the long continuity of our institutions and our Empire. The whole fury and might of the enemy must very soon be turned on us. Hitler knows that he will have to break us in this Island or lose the war. If we can stand up to him, all Europe may be free and the life of the world may move forward into broad, sunlit uplands. But if we fail, then the whole world, including the United States, including all that we have known and cared for, will sink into the abyss of a new Dark Age made more sinister, and perhaps more protracted, by the lights of perverted science. Let us therefore brace ourselves to our duties, and so bear ourselves that, if the British Empire and its Commonwealth last for a thousand years, men will still say, “This was their finest hour.””
In the darkest shadows cast by war, few leaders have been able to step up to the mantle and effectively unify millions of citizens for truly sacrificial causes. Winston Churchill was the extraordinary exception – lifting 1940 Britain out of the darkness with his hopeful, convicted rhetoric to galvanise the English amidst bleak, dreary days of war and loss. Through Britain’s standalone position in WWII against the Nazis, he left his legacy by unifying the nation under shared sacrifices of the army and commemorating their courage.
13. A Room of One’s Own by Virginia Woolf
“Life for both sexes – and I looked at them (through a restaurant window while waiting for my lunch to be served), shouldering their way along the pavement – is arduous, difficult, a perpetual struggle. It calls for gigantic courage and strength. More than anything, perhaps, creatures of illusion as we are, it calls for confidence in oneself. Without self-confidence we are babes in the cradle. And how can we generate this imponderable quality, which is yet so invaluable, most quickly? By thinking that other people are inferior to oneself. By feeling that one has some innate superiority – it may be wealth, or rank, a straight nose, or the portrait of a grandfather by Romney – for there is no end to the pathetic devices of the human imagination – over other people. Hence the enormous importance to a patriarch who has to conquer, who has to rule, of feeling that great numbers of people, half the human race indeed, are by nature inferior to himself. It must indeed be one of the great sources of his power….Women have served all these centuries as looking-glasses possessing the magic and delicious power of reflecting the figure of man at twice its natural size. Without that power probably the earth would still be swamp and jungle. The glories of all our wars would be on the remains of mutton bones and bartering flints for sheepskins or whatever simple ornament took our unsophisticated taste. Supermen and Fingers of Destiny would never have existed. The Czar and the Kaiser would never have worn their crowns or lost them. Whatever may be their use in civilised societies, mirrors are essential to all violent and heroic action. That is why Napoleon and Mussolini both insist so emphatically upon the inferiority of women, for if they were not inferior, they would cease to enlarge. That serves to explain in part the necessity that women so often are to men. And it serves to explain how restless they are under her criticism; how impossible it is for her to say to them this book is bad, this picture is feeble, or whatever it may be, without giving far more pain and rousing far more anger than a man would do who gave the same criticism. For if she begins to tell the truth, the figure in the looking-glass shrinks; his fitness in life is diminished. How is he to go on giving judgment, civilising natives, making laws, writing books, dressing up and speechifying at banquets, unless he can see himself at breakfast and at dinner at least twice the size he really is?”
In this transformational speech , Virginia Woolf pronounces her vision that ‘a woman must have money and a room of her own if she is to write fiction’. She calls out the years in which women have been deprived of their own space for individual development through being chained to traditional arrangements or men’s prescriptions – demanding ‘gigantic courage’ and ‘confidence in oneself’ to brave through the onerous struggle of creating change for women’s rights. With her steadfast, stolid rhetoric and radical theorization, she paved the way for many women’s rights activists and writers to forge their own paths against patriarchal authority.
14. Inaugural Address by John F Kennedy
“In the long history of the world, only a few generations have been granted the role of defending freedom in its hour of maximum danger. I do not shrink from this responsibility–I welcome it. I do not believe that any of us would exchange places with any other people or any other generation. The energy, the faith, the devotion which we bring to this endeavor will light our country and all who serve it–and the glow from that fire can truly light the world. And so, my fellow Americans: ask not what your country can do for you–ask what you can do for your country. My fellow citizens of the world: ask not what America will do for you, but what together we can do for the freedom of man. Finally, whether you are citizens of America or citizens of the world, ask of us here the same high standards of strength and sacrifice which we ask of you. With a good conscience our only sure reward, with history the final judge of our deeds, let us go forth to lead the land we love, asking His blessing and His help, but knowing that here on earth God’s work must truly be our own.”
For what is probably the most historically groundbreaking use of parallelism in speech across American history, President JFK placed the weighty task of ‘asking what one can do for their country’ onto the shoulders of each American citizen. Using an air of firmness in his rhetoric by declaring his commitment to his countrymen, he urges each American to do the same for the broader, noble ideal of freedom for all. With his crucial interrogation of a citizen’s moral duty to his nation, President JFK truly made history.
15. Atoms for Peace Speech by Dwight Eisenhower
“To pause there would be to confirm the hopeless finality of a belief that two atomic colossi are doomed malevolently to eye each other indefinitely across a trembling world. To stop there would be to accept helplessly the probability of civilization destroyed, the annihilation of the irreplaceable heritage of mankind handed down to us from generation to generation, and the condemnation of mankind to begin all over again the age-old struggle upward from savagery towards decency, and right, and justice. Surely no sane member of the human race could discover victory in such desolation. Could anyone wish his name to be coupled by history with such human degradation and destruction?Occasional pages of history do record the faces of the “great destroyers”, but the whole book of history reveals mankind’s never-ending quest for peace and mankind’s God-given capacity to build. It is with the book of history, and not with isolated pages, that the United States will ever wish to be identified. My country wants to be constructive,not destructive. It wants agreements, not wars, among nations. It wants itself to live in freedom and in the confidence that the peoples of every other nation enjoy equally the right of choosing their own way of life. So my country’s purpose is to help us to move out of the dark chamber of horrors into the light, to find a way by which the minds of men, the hopes of men, the souls of men everywhere, can move forward towards peace and happiness and well-being.”
On a possibility as frightful and tense as nuclear war, President Eisenhower managed to convey the gravity of the world’s plight in his measured and persuasive speech centred on the greater good of mankind. Using rhetorical devices such as the three-part paratactical syntax which most world leaders are fond of for ingraining their words in the minds of their audience, he centers the discourse of the atomic bomb on those affected by such a world-changing decision in ‘the minds, hopes and souls of men everywhere’ – effectively putting the vivid image of millions of people’s fates at stake in the minds of his audience. Being able to make a topic as heavy and fraught with moral conflict as this as eloquent as he did, Eisenhower definitely ranks among some of the most skilled orators to date.
16. The Transformation of Silence into Language and Action by Audre Lorde
“I was going to die, if not sooner then later, whether or not I had ever spoken myself. My silences had not protected me. Your silence will not protect you. But for every real word spoken, for every attempt I had ever made to speak those truths for which I am still seeking, I had made contact with other women while we examined the words to fit a world in which we all believed, bridging our differences. What are the words you do not have yet? What do you need to say? What are the tyrannies you swallow day by day and attempt to make your own, until you will sicken and die of them, still in silence? Perhaps for some of you here today, I am the face of one of your fears. Because I am a woman, because I am black, because I am myself, a black woman warrior poet doing my work, come to ask you, are you doing yours?”
Revolutionary writer, feminist and civil rights activist Audre Lorde first delivered this phenomenal speech at Lesbian and Literature panel of the Modern Language Association’s December 28, 1977 meeting, which went on to feature permanently in her writings for its sheer wisdom and truth. Her powerful writing and speech about living on the margins of society has enlightened millions of people discriminated across various intersections, confronting them with the reality that they must speak – since their ‘silence will not protect’ them from further marginalization. Through her illuminating words and oratory, she has reminded marginalized persons of the importance of their selfhood and the radical capacity for change they have in a world blighted by prejudice and division.
17. 1965 Cambridge Union Hall Speech by James Baldwin
“What is dangerous here is the turning away from – the turning away from – anything any white American says. The reason for the political hesitation, in spite of the Johnson landslide is that one has been betrayed by American politicians for so long. And I am a grown man and perhaps I can be reasoned with. I certainly hope I can be. But I don’t know, and neither does Martin Luther King, none of us know how to deal with those other people whom the white world has so long ignored, who don’t believe anything the white world says and don’t entirely believe anything I or Martin is saying. And one can’t blame them. You watch what has happened to them in less than twenty years.”
Baldwin’s invitation to the Cambridge Union Hall is best remembered for foregrounding the unflinching differences in white and African Americans’ ‘system of reality’ in everyday life. Raising uncomfortable truths about the insidious nature of racism post-civil war, he provides several nuggets of thought-provoking wisdom on the state of relations between the oppressed and their oppressors, and what is necessary to mediate such relations and destroy the exploitative thread of racist hatred. With great frankness, he admits to not having all the answers but provides hard-hitting wisdom on engagement to guide activists through confounding times nonetheless.
18. I Am Prepared to Die by Nelson Mandela
“Above all, My Lord, we want equal political rights, because without them our disabilities will be permanent. I know this sounds revolutionary to the whites in this country, because the majority of voters will be Africans. This makes the white man fear democracy. But this fear cannot be allowed to stand in the way of the only solution which will guarantee racial harmony and freedom for all. It is not true that the enfranchisement of all will result in racial domination. Political division, based on colour, is entirely artificial and, when it disappears, so will the domination of one colour group by another. The ANC has spent half a century fighting against racialism. When it triumphs as it certainly must, it will not change that policy. This then is what the ANC is fighting. Our struggle is a truly national one. It is a struggle of the African people, inspired by our own suffering and our own experience. It is a struggle for the right to live. During my lifetime I have dedicated my life to this struggle of the African people. I have fought against white domination, and I have fought against black domination. I have cherished the ideal of a democratic and free society in which all persons will live together in harmony and with equal opportunities. It is an ideal for which I hope to live for and to see realised. But, My Lord, if it needs be, it is an ideal for which I am prepared to die.”
Apartheid is still considered one of these most devastating events of world history, and it would not have ended without the crucial effort and words of Nelson Mandela during his courageous political leadership. In this heartbreaking speech , he voices his utter devotion to the fight against institutionalised racism in African society – an ideal for which he was ‘prepared to die for’. Mandela continues to remind us today of his moral conviction in leading, wherein the world would likely to be a better place if all politicians had the same resolve and genuine commitment to human rights and the abolition of oppression as he did.
19. Critique on British Imperialism by General Aung San
“Do they form their observations by seeing the attendances at not very many cinemas and theatres of Rangoon? Do they judge this question of money circulation by paying a stray visit to a local bazaar? Do they know that cinemas and theatres are not true indicators, at least in Burma, of the people’s conditions? Do they know that there are many in this country who cannot think of going to these places by having to struggle for their bare existence from day to day? Do they know that those who nowadays patronise or frequent cinemas and theatres which exist only in Rangoon and a few big towns, belong generally to middle and upper classes and the very few of the many poor who can attend at all are doing so as a desperate form of relaxation just to make them forget their unsupportable existences for the while whatever may be the tomorrow that awaits them?”
Under British colonial rule, one of the most legendary nationalist leaders emerged from the ranks of the thousands of Burmese to boldly lead them towards independence, out of the exploitation and control under the British. General Aung San’s speech criticising British social, political and economic control of Burma continues to be scathing, articulate, and relevant – especially given his necessary goal of uniting the Burmese natives against their common oppressor. He successfully galvanised his people against the British, taking endless risks through nationalist speeches and demonstrations which gradually bore fruit in Burma’s independence.
20. Nobel Lecture by Mother Teresa
“I believe that we are not real social workers. We may be doing social work in the eyes of the people, but we are really contemplatives in the heart of the world. For we are touching the Body Of Christ 24 hours. We have 24 hours in this presence, and so you and I. You too try to bring that presence of God in your family, for the family that prays together stays together. And I think that we in our family don’t need bombs and guns, to destroy to bring peace–just get together, love one another, bring that peace, that joy, that strength of presence of each other in the home. And we will be able to overcome all the evil that is in the world. There is so much suffering, so much hatred, so much misery, and we with our prayer, with our sacrifice are beginning at home. Love begins at home, and it is not how much we do, but how much love we put in the action that we do. It is to God Almighty–how much we do it does not matter, because He is infinite, but how much love we put in that action. How much we do to Him in the person that we are serving.”
In contemporary culture, most people understand Mother Teresa to be the epitome of compassion and kindness. However, if one were to look closer at her speeches from the past, one would discover not merely her altruistic contributions, but her keen heart for social justice and the downtrodden. She wisely and gracefully remarks that ‘love begins at home’ from the individual actions of each person within their private lives, which accumulate into a life of goodness and charity. For this, her speeches served not just consolatory value or momentary relevance, as they still inform the present on how we can live lives worth living.
21. June 9 Speech to Martial Law Units by Deng Xiaoping
“This army still maintains the traditions of our old Red Army. What they crossed this time was in the true sense of the expression a political barrier, a threshold of life and death. This was not easy. This shows that the People’s Army is truly a great wall of iron and steel of the party and state. This shows that no matter how heavy our losses, the army, under the leadership of the party, will always remain the defender of the country, the defender of socialism, and the defender of the public interest. They are a most lovable people. At the same time, we should never forget how cruel our enemies are. We should have not one bit of forgiveness for them. The fact that this incident broke out as it did is very worthy of our pondering. It prompts us cool-headedly to consider the past and the future. Perhaps this bad thing will enable us to go ahead with reform and the open policy at a steadier and better — even a faster — pace, more speedily correct our mistakes, and better develop our strong points.”
Mere days before the 4 June 1989 Tiananmen Square uprising, Chinese Communist Party leader Deng Xiaoping sat with six party elders (senior officials) and the three remaining members of the Politburo Standing Committee, the paramount decision-making body in China’s government. The meeting was organised to discuss the best course of action for restoring social and political order to China, given the sweeping economic reforms that had taken place in the past decade that inevitably resulted in some social resistance from the populace. Deng then gave this astute and well-regarded speech, outlining the political complexities in shutting down student protests given the context of reforms encouraging economic liberalization already taking place, as aligned with the students’ desires. It may not be the most rousing or inflammatory of speeches, but it was certainly persuasive in voicing the importance of taking a strong stand for the economic reforms Deng was implementing to benefit Chinese citizens in the long run. Today, China is an economic superpower, far from its war-torn developing country status before Deng’s leadership – thanks to his foresight in ensuring political stability would allow China to enjoy the fruits of the massive changes they adapted to.
22. Freedom or Death by Emmeline Pankhurst
“You won your freedom in America when you had the revolution, by bloodshed, by sacrificing human life. You won the civil war by the sacrifice of human life when you decided to emancipate the negro. You have left it to women in your land, the men of all civilised countries have left it to women, to work out their own salvation. That is the way in which we women of England are doing. Human life for us is sacred, but we say if any life is to be sacrificed it shall be ours; we won’t do it ourselves, but we will put the enemy in the position where they will have to choose between giving us freedom or giving us death. Now whether you approve of us or whether you do not, you must see that we have brought the question of women’s suffrage into a position where it is of first rate importance, where it can be ignored no longer. Even the most hardened politician will hesitate to take upon himself directly the responsibility of sacrificing the lives of women of undoubted honour, of undoubted earnestness of purpose. That is the political situation as I lay it before you today.”
In 1913 after Suffragette Emily Davison stepped in front of King George V’s horse at the Epsom Derby and suffered fatal injuries, Emmeline Pankhurst delivered her speech to Connecticut as a call to action for people to support the suffragette movement. Her fortitude in delivering such a sobering speech on the state of women’s rights is worth remembering for its invaluable impact and contributions to the rights we enjoy in today’s world.
23. Quit India by Mahatma Gandhi
“We shall either free India or die in the attempt; we shall not live to see the perpetuation of our slavery. Every true Congressman or woman will join the struggle with an inflexible determination not to remain alive to see the country in bondage and slavery. Let that be your pledge. Keep jails out of your consideration. If the Government keep me free, I will not put on the Government the strain of maintaining a large number of prisoners at a time, when it is in trouble. Let every man and woman live every moment of his or her life hereafter in the consciousness that he or she eats or lives for achieving freedom and will die, if need be, to attain that goal. Take a pledge, with God and your own conscience as witness, that you will no longer rest till freedom is achieved and will be prepared to lay down your lives in the attempt to achieve it. He who loses his life will gain it; he who will seek to save it shall lose it. Freedom is not for the coward or the faint-hearted.”
Naturally, the revolutionary activist Gandhi had to appear in this list for his impassioned anti-colonial speeches which rallied Indians towards independence. Famous for leading non-violent demonstrations, his speeches were a key element in gathering Indians of all backgrounds together for the common cause of eliminating their colonial masters. His speeches were resolute, eloquent, and courageous, inspiring the hope and admiration of many not just within India, but around the world.
24. 1974 National Book Award Speech by Adrienne Rich, Alice Walker, Audre Lorde
“The statement I am going to read was prepared by three of the women nominated for the National Book Award for poetry, with the agreement that it would be read by whichever of us, if any, was chosen.We, Audre Lorde, Adrienne Rich, and Alice Walker, together accept this award in the name of all the women whose voices have gone and still go unheard in a patriarchal world, and in the name of those who, like us, have been tolerated as token women in this culture, often at great cost and in great pain. We believe that we can enrich ourselves more in supporting and giving to each other than by competing against each other; and that poetry—if it is poetry—exists in a realm beyond ranking and comparison. We symbolically join together here in refusing the terms of patriarchal competition and declaring that we will share this prize among us, to be used as best we can for women. We appreciate the good faith of the judges for this award, but none of us could accept this money for herself, nor could she let go unquestioned the terms on which poets are given or denied honor and livelihood in this world, especially when they are women. We dedicate this occasion to the struggle for self-determination of all women, of every color, identification, or derived class: the poet, the housewife, the lesbian, the mathematician, the mother, the dishwasher, the pregnant teen-ager, the teacher, the grandmother, the prostitute, the philosopher, the waitress, the women who will understand what we are doing here and those who will not understand yet; the silent women whose voices have been denied us, the articulate women who have given us strength to do our work.”
Adrienne Rich, Audre Lorde, and Alice Walker wrote this joint speech to be delivered by Adrienne Rich at the 1974 National Book Awards, based on their suspicions that the first few African American lesbian women to be nominated for the awards would be snubbed in favour of a white woman nominee. Their suspicions were confirmed, and Adrienne Rich delivered this socially significant speech in solidarity with her fellow nominees, upholding the voices of the ‘silent women whose voices have been denied’.
25. Speech to 20th Congress of the CPSU by Nikita Khruschev
“Considering the question of the cult of an individual, we must first of all show everyone what harm this caused to the interests of our Party. Vladimir Ilyich Lenin had always stressed the Party’s role and significance in the direction of the socialist government of workers and peasants; he saw in this the chief precondition for a successful building of socialism in our country. Pointing to the great responsibility of the Bolshevik Party, as ruling Party of the Soviet state, Lenin called for the most meticulous observance of all norms of Party life; he called for the realization of the principles of collegiality in the direction of the Party and the state. Collegiality of leadership flows from the very nature of our Party, a Party built on the principles of democratic centralism. “This means,” said Lenin, “that all Party matters are accomplished by all Party members – directly or through representatives – who, without any exceptions, are subject to the same rules; in addition, all administrative members, all directing collegia, all holders of Party positions are elective, they must account for their activities and are recallable.””
This speech is possibly the most famed Russian speech for its status as a ‘secret’ speech delivered only to the CPSU at the time, which was eventually revealed to the public. Given the unchallenged political legacy and cult of personality which Stalin left in the Soviet Union, Nikita Khruschev’s speech condemning the authoritarian means Stalin had resorted to to consolidate power as un-socialist was an important mark in Russian history.
26. The Struggle for Human Rights by Eleanor Roosevelt
“It is my belief, and I am sure it is also yours, that the struggle for democracy and freedom is a critical struggle, for their preservation is essential to the great objective of the United Nations to maintain international peace and security. Among free men the end cannot justify the means. We know the patterns of totalitarianism — the single political party, the control of schools, press, radio, the arts, the sciences, and the church to support autocratic authority; these are the age-old patterns against which men have struggled for three thousand years. These are the signs of reaction, retreat, and retrogression. The United Nations must hold fast to the heritage of freedom won by the struggle of its people; it must help us to pass it on to generations to come. The development of the ideal of freedom and its translation into the everyday life of the people in great areas of the earth is the product of the efforts of many peoples. It is the fruit of a long tradition of vigorous thinking and courageous action. No one race and on one people can claim to have done all the work to achieve greater dignity for human beings and great freedom to develop human personality. In each generation and in each country there must be a continuation of the struggle and new steps forward must be taken since this is preeminently a field in which to stand still is to retreat.”
Eleanor Roosevelt has been among the most well-loved First Ladies for good reason – her eloquence and gravitas in delivering every speech convinced everyone of her suitability for the oval office. In this determined and articulate speech , she outlines the fundamental values that form the bedrock of democracy, urging the rest of the world to uphold human rights regardless of national ideology and interests.
27. The Ballot or The Bullet by Malcolm X
“And in this manner, the organizations will increase in number and in quantity and in quality, and by August, it is then our intention to have a black nationalist convention which will consist of delegates from all over the country who are interested in the political, economic and social philosophy of black nationalism. After these delegates convene, we will hold a seminar; we will hold discussions; we will listen to everyone. We want to hear new ideas and new solutions and new answers. And at that time, if we see fit then to form a black nationalist party, we’ll form a black nationalist party. If it’s necessary to form a black nationalist army, we’ll form a black nationalist army. It’ll be the ballot or the bullet. It’ll be liberty or it’ll be death.”
Inarguably, the revolutionary impact Malcolm X’s fearless oratory had was substantial in his time as a radical anti-racist civil rights activist. His speeches’ emancipatory potential put forth his ‘theory of rhetorical action’ where he urges Black Americans to employ both the ballot and the bullet, strategically without being dependent on the other should the conditions of oppression change. A crucial leader in the fight for civil rights, he opened the eyes of thousands of Black Americans, politicising and convincing them of the necessity of fighting for their democratic rights against white supremacists.
28. Living the Revolution by Gloria Steinem
“The challenge to all of us, and to you men and women who are graduating today, is to live a revolution, not to die for one. There has been too much killing, and the weapons are now far too terrible. This revolution has to change consciousness, to upset the injustice of our current hierarchy by refusing to honor it, and to live a life that enforces a new social justice. Because the truth is none of us can be liberated if other groups are not.”
In an unexpected commencement speech delivered at Vassar College in 1970, Gloria Steinem boldly makes a call to action on behalf of marginalized groups in need of liberation to newly graduated students. She proclaimed it the year of Women’s Liberation and forcefully highlighted the need for a social revolution to ‘upset the injustice of the current hierarchy’ in favour of human rights – echoing the hard-hitting motto on social justice, ‘until all of us are free, none of us are free’.
29. The Last Words of Harvey Milk by Harvey Milk
“I cannot prevent some people from feeling angry and frustrated and mad in response to my death, but I hope they will take the frustration and madness and instead of demonstrating or anything of that type, I would hope that they would take the power and I would hope that five, ten, one hundred, a thousand would rise. I would like to see every gay lawyer, every gay architect come out, stand up and let the world know. That would do more to end prejudice overnight than anybody could imagine. I urge them to do that, urge them to come out. Only that way will we start to achieve our rights. … All I ask is for the movement to continue, and if a bullet should enter my brain, let that bullet destroy every closet door…”
As the first openly gay elected official in the history of California, Harvey Milk’s entire political candidature was in itself a radical statement against the homophobic status quo at the time. Given the dangerous times he was in as an openly gay man, he anticipated that he would be assassinated eventually in his political career. As such, these are some of his last words which show the utter devotion he had to campaigning against homophobia while representing the American people, voicing his heartbreaking wish for the bullet that would eventually kill him to ‘destroy every closet door’.
30. Black Power Address at UC Berkeley by Stokely Carmichael
“Now we are now engaged in a psychological struggle in this country, and that is whether or not black people will have the right to use the words they want to use without white people giving their sanction to it; and that we maintain, whether they like it or not, we gonna use the word “Black Power” — and let them address themselves to that; but that we are not going to wait for white people to sanction Black Power. We’re tired waiting; every time black people move in this country, they’re forced to defend their position before they move. It’s time that the people who are supposed to be defending their position do that. That’s white people. They ought to start defending themselves as to why they have oppressed and exploited us.”
A forceful and impressive orator, Stokely Carmichael was among those at the forefront of the civil rights movement, who was a vigorous socialist organizer as well. He led the Black Power movement wherein he gave this urgent, influential speech that propelled Black Americans forward in their fight for constitutional rights in the 1960s.
31. Speech on Vietnam by Lyndon Johnson
“The true peace-keepers are those men who stand out there on the DMZ at this very hour, taking the worst that the enemy can give. The true peace-keepers are the soldiers who are breaking the terrorist’s grip around the villages of Vietnam—the civilians who are bringing medical care and food and education to people who have already suffered a generation of war. And so I report to you that we are going to continue to press forward. Two things we must do. Two things we shall do. First, we must not mislead the enemy. Let him not think that debate and dissent will produce wavering and withdrawal. For I can assure you they won’t. Let him not think that protests will produce surrender. Because they won’t. Let him not think that he will wait us out. For he won’t. Second, we will provide all that our brave men require to do the job that must be done. And that job is going to be done. These gallant men have our prayers-have our thanks—have our heart-felt praise—and our deepest gratitude. Let the world know that the keepers of peace will endure through every trial—and that with the full backing of their countrymen, they are going to prevail.”
During some of the most harrowing periods of human history, the Vietnam War, American soldiers were getting soundly defeated by the Vietnamese in guerrilla warfare. President Lyndon Johnson then issued this dignified, consolatory speech to encourage patriotism and support for the soldiers putting their lives on the line for the nation.
32. A Whisper of AIDS by Mary Fisher
“We may take refuge in our stereotypes, but we cannot hide there long, because HIV asks only one thing of those it attacks. Are you human? And this is the right question. Are you human? Because people with HIV have not entered some alien state of being. They are human. They have not earned cruelty, and they do not deserve meanness. They don’t benefit from being isolated or treated as outcasts. Each of them is exactly what God made: a person; not evil, deserving of our judgment; not victims, longing for our pity people, ready for support and worthy of compassion. We must be consistent if we are to be believed. We cannot love justice and ignore prejudice, love our children and fear to teach them. Whatever our role as parent or policymaker, we must act as eloquently as we speak else we have no integrity. My call to the nation is a plea for awareness. If you believe you are safe, you are in danger. Because I was not hemophiliac, I was not at risk. Because I was not gay, I was not at risk. Because I did not inject drugs, I was not at risk. The lesson history teaches is this: If you believe you are safe, you are at risk. If you do not see this killer stalking your children, look again. There is no family or community, no race or religion, no place left in America that is safe. Until we genuinely embrace this message, we are a nation at risk.”
Back when AIDS research was still undeveloped, the stigma of contracting HIV was even more immense than it is today. A celebrated artist, author and speaker, Mary Fisher became an outspoken activist for those with HIV/AIDS, persuading people to extend compassion to the population with HIV instead of stigmatizing them – as injustice has a way of coming around to people eventually. Her bold act of speaking out for the community regardless of the way they contracted the disease, their sexual orientation or social group, was an influential move in advancing the human rights of those with HIV and spreading awareness on the discrimination they face.
33. Freedom from Fear by Aung San Suu Kyi
“The quintessential revolution is that of the spirit, born of an intellectual conviction of the need for change in those mental attitudes and values which shape the course of a nation’s development. A revolution which aims merely at changing official policies and institutions with a view to an improvement in material conditions has little chance of genuine success. Without a revolution of the spirit, the forces which produced the iniquities of the old order would continue to be operative, posing a constant threat to the process of reform and regeneration. It is not enough merely to call for freedom, democracy and human rights. There has to be a united determination to persevere in the struggle, to make sacrifices in the name of enduring truths, to resist the corrupting influences of desire, ill will, ignorance and fear. Saints, it has been said, are the sinners who go on trying. So free men are the oppressed who go on trying and who in the process make themselves fit to bear the responsibilities and to uphold the disciplines which will maintain a free society. Among the basic freedoms to which men aspire that their lives might be full and uncramped, freedom from fear stands out as both a means and an end. A people who would build a nation in which strong, democratic institutions are firmly established as a guarantee against state-induced power must first learn to liberate their own minds from apathy and fear.”
Famous for her resoluteness and fortitude in campaigning for democracy in Burma despite being put under house arrest by the military government, Aung San Suu Kyi’s speeches have been widely touted as inspirational. In this renowned speech of hers, she delivers a potent message to Burmese to ‘liberate their minds from apathy and fear’ in the struggle for freedom and human rights in the country. To this day, she continues to tirelessly champion the welfare and freedom of Burmese in a state still overcome by vestiges of authoritarian rule.
34. This Is Water by David Foster Wallace
“Our own present culture has harnessed these forces in ways that have yielded extraordinary wealth and comfort and personal freedom. The freedom all to be lords of our tiny skull-sized kingdoms, alone at the centre of all creation. This kind of freedom has much to recommend it. But of course there are all different kinds of freedom, and the kind that is most precious you will not hear much talk about much in the great outside world of wanting and achieving…. The really important kind of freedom involves attention and awareness and discipline, and being able truly to care about other people and to sacrifice for them over and over in myriad petty, unsexy ways every day. That is real freedom. That is being educated, and understanding how to think. The alternative is unconsciousness, the default setting, the rat race, the constant gnawing sense of having had, and lost, some infinite thing.”
Esteemed writer David Foster Wallace gave a remarkably casual yet wise commencement speech at Kenyon College in 2005 on the importance of learning to think beyond attaining a formal education. He encouraged hundreds of students to develop freedom of thought, a heart of sacrificial care for those in need of justice, and a consciousness that would serve them in discerning the right choices to make within a status quo that is easy to fall in line with. His captivating speech on what it meant to truly be ‘educated’ tugged at the hearts of many young and critical minds striving to achieve their dreams and change the world.
35. Questioning the Universe by Stephen Hawking
“This brings me to the last of the big questions: the future of the human race. If we are the only intelligent beings in the galaxy, we should make sure we survive and continue. But we are entering an increasingly dangerous period of our history. Our population and our use of the finite resources of planet Earth are growing exponentially, along with our technical ability to change the environment for good or ill. But our genetic code still carries the selfish and aggressive instincts that were of survival advantage in the past. It will be difficult enough to avoid disaster in the next hundred years, let alone the next thousand or million. Our only chance of long-term survival is not to remain inward-looking on planet Earth, but to spread out into space. The answers to these big questions show that we have made remarkable progress in the last hundred years. But if we want to continue beyond the next hundred years, our future is in space. That is why I am in favor of manned — or should I say, personned — space flight.”
Extraordinary theoretical physicist, cosmologist, and author Stephen Hawking was a considerable influence upon modern physics and scientific research at large, inspiring people regardless of physical ability to aspire towards expanding knowledge in the world. In his speech on Questioning the Universe, he speaks of the emerging currents and issues in the scientific world like that of outer space, raising and answering big questions that have stumped great thinkers for years.
36. 2008 Democratic National Convention Speech by Michelle Obama
“I stand here today at the crosscurrents of that history — knowing that my piece of the American dream is a blessing hard won by those who came before me. All of them driven by the same conviction that drove my dad to get up an hour early each day to painstakingly dress himself for work. The same conviction that drives the men and women I’ve met all across this country: People who work the day shift, kiss their kids goodnight, and head out for the night shift — without disappointment, without regret — that goodnight kiss a reminder of everything they’re working for. The military families who say grace each night with an empty seat at the table. The servicemen and women who love this country so much, they leave those they love most to defend it. The young people across America serving our communities — teaching children, cleaning up neighborhoods, caring for the least among us each and every day. People like Hillary Clinton, who put those 18 million cracks in the glass ceiling, so that our daughters — and sons — can dream a little bigger and aim a little higher. People like Joe Biden, who’s never forgotten where he came from and never stopped fighting for folks who work long hours and face long odds and need someone on their side again. All of us driven by a simple belief that the world as it is just won’t do — that we have an obligation to fight for the world as it should be. That is the thread that connects our hearts. That is the thread that runs through my journey and Barack’s journey and so many other improbable journeys that have brought us here tonight, where the current of history meets this new tide of hope. That is why I love this country.”
Ever the favourite modern First Lady of America, Michelle Obama has delivered an abundance of iconic speeches in her political capacity, never forgetting to foreground the indomitable human spirit embodied in American citizens’ everyday lives and efforts towards a better world. The Obamas might just have been the most articulate couple of rhetoricians of their time, making waves as the first African American president and First Lady while introducing important policies in their period of governance.
37. The Audacity of Hope by Barack Obama
“I’m not talking about blind optimism here — the almost willful ignorance that thinks unemployment will go away if we just don’t think about it, or the health care crisis will solve itself if we just ignore it. That’s not what I’m talking about. I’m talking about something more substantial. It’s the hope of slaves sitting around a fire singing freedom songs; the hope of immigrants setting out for distant shores; the hope of a young naval lieutenant bravely patrolling the Mekong Delta; the hope of a millworker’s son who dares to defy the odds; the hope of a skinny kid with a funny name who believes that America has a place for him, too. Hope — Hope in the face of difficulty. Hope in the face of uncertainty. The audacity of hope! In the end, that is God’s greatest gift to us, the bedrock of this nation. A belief in things not seen. A belief that there are better days ahead.”
Now published into a book, Barack Obama’s heart-capturing personal story of transformational hope was first delivered as a speech on the merits of patriotic optimism and determination put to the mission of concrete change. He has come to be known as one of the most favoured and inspiring presidents in American history, and arguably the most skilled orators ever.
38. “Be Your Own Story” by Toni Morrison
“But I’m not going to talk anymore about the future because I’m hesitant to describe or predict because I’m not even certain that it exists. That is to say, I’m not certain that somehow, perhaps, a burgeoning ménage a trois of political interests, corporate interests and military interests will not prevail and literally annihilate an inhabitable, humane future. Because I don’t think we can any longer rely on separation of powers, free speech, religious tolerance or unchallengeable civil liberties as a matter of course. That is, not while finite humans in the flux of time make decisions of infinite damage. Not while finite humans make infinite claims of virtue and unassailable power that are beyond their competence, if not their reach. So, no happy talk about the future. … Because the past is already in debt to the mismanaged present. And besides, contrary to what you may have heard or learned, the past is not done and it is not over, it’s still in process, which is another way of saying that when it’s critiqued, analyzed, it yields new information about itself. The past is already changing as it is being reexamined, as it is being listened to for deeper resonances. Actually it can be more liberating than any imagined future if you are willing to identify its evasions, its distortions, its lies, and are willing to unleash its secrets.”
Venerated author and professor Toni Morrison delivered an impressively articulate speech at Wellesley College in 2004 to new graduates, bucking the trend by discussing the importance of the past in informing current and future ways of living. With her brilliance and eloquence, she blew the crowd away and renewed in them the capacity for reflection upon using the past as a talisman to guide oneself along the journey of life.
39. Nobel Speech by Malala Yousafzai
“Dear brothers and sisters, the so-called world of adults may understand it, but we children don’t. Why is it that countries which we call “strong” are so powerful in creating wars but so weak in bringing peace? Why is it that giving guns is so easy but giving books is so hard? Why is it that making tanks is so easy, but building schools is so difficult? As we are living in the modern age, the 21st century and we all believe that nothing is impossible. We can reach the moon and maybe soon will land on Mars. Then, in this, the 21st century, we must be determined that our dream of quality education for all will also come true. So let us bring equality, justice and peace for all. Not just the politicians and the world leaders, we all need to contribute. Me. You. It is our duty. So we must work … and not wait. I call upon my fellow children to stand up around the world. Dear sisters and brothers, let us become the first generation to decide to be the last. The empty classrooms, the lost childhoods, wasted potential-let these things end with us.”
At a mere 16 years of age, Malala Yousafzai gave a speech on the severity of the state of human rights across the world, and wowed the world with her passion for justice at her tender age. She displayed tenacity and fearlessness speaking about her survival of an assassination attempt for her activism for gender equality in the field of education. A model of courage to us all, her speech remains an essential one in the fight for human rights in the 21st century.
40. Final Commencement Speech by Michelle Obama
“If you are a person of faith, know that religious diversity is a great American tradition, too. In fact, that’s why people first came to this country — to worship freely. And whether you are Muslim, Christian, Jewish, Hindu, Sikh — these religions are teaching our young people about justice, and compassion, and honesty. So I want our young people to continue to learn and practice those values with pride. You see, our glorious diversity — our diversities of faiths and colors and creeds — that is not a threat to who we are, it makes us who we are. So the young people here and the young people out there: Do not ever let anyone make you feel like you don’t matter, or like you don’t have a place in our American story — because you do. And you have a right to be exactly who you are. But I also want to be very clear: This right isn’t just handed to you. No, this right has to be earned every single day. You cannot take your freedoms for granted. Just like generations who have come before you, you have to do your part to preserve and protect those freedoms. … It is our fundamental belief in the power of hope that has allowed us to rise above the voices of doubt and division, of anger and fear that we have faced in our own lives and in the life of this country. Our hope that if we work hard enough and believe in ourselves, then we can be whatever we dream, regardless of the limitations that others may place on us. The hope that when people see us for who we truly are, maybe, just maybe they, too, will be inspired to rise to their best possible selves.”
Finally, we have yet another speech by Michelle Obama given in her final remarks as First Lady – a tear-inducing event for many Americans and even people around the world. In this emotional end to her political tenure, she gives an empowering, hopeful, expressive speech to young Americans, exhorting them to take hold of its future in all their diversity and work hard at being their best possible selves.
Amidst the bleak era of our current time with Trump as president of the USA, not only Michelle Obama, but all 40 of these amazing speeches can serve as sources of inspiration and hope to everyone – regardless of their identity or ambitions. After hearing these speeches, which one’s your favorite? Let us know in the comments below!
Article Written By: Kai Xin Koh
You may also like….

How To Prepare An Awesome Business Presentation
by Kai Xin Koh
Business presentations are inescapable in today’s world, where entrepreneurship and innovation are at the heart of businesses. With limited...
Sign Up for Winning With Stories!
- First Name *
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.

- Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
- Terms & Conditions
- Write For Us

Best Diplomats
14 best presidential speeches in history.
- Post author: Oleksandra Mamchii
- Post published: October 23, 2023
- Post category: Blog / History
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Words have value. Therefore, one of the main indicators of a strong leader is their capacity to persuade others of their goals and ideas, inspire them, and direct them toward a shared objective.
Here are some illustrious presidential quotes from the past, ranging from Abraham Lincoln’s “Gettysburg Address” to Ronald Reagan’s “Tear Down This Wall” and Emmanuel Macron’s 2018 speech at the US Congress.
Presidents throughout history have influenced the populace and the country through their words. There have only been a few occasions when the words said by the presidents over the previous 200 years have been exploited to their full potential.
Also Read: List of Presidents of the United States: Washington to Biden
1) Abraham Lincoln’s 1863 “Gettysburg Address”
Following the Battle of Gettysburg, President Abraham Lincoln delivered a two-minute address at a cemetery dedication for the Union War on November 19, 1983. Lincoln delivered a brief speech on the “New Birth of Freedom” and wasn’t even the event’s keynote speaker, but it has since grown to be considered one of the most powerful and unforgettable in American history.
“Four hundred and seven years ago, our fathers brought forth, on this continent, a new nation, conceived in liberty and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal,” Lincoln said, in part.
2) Franklin D. Roosevelt’s ‘Day Of Infamy’ Speech In 1941
The day after the Japanese bombed Pearl Harbor and precipitated the United States’ entry into World War II, on December 8, 1941, President Franklin D. Roosevelt delivered a well-known speech to a joint session of Congress. The opening sentence is frequently the one that is most frequently quoted, “Yesterday, December 7, 1941—a date which will live in infamy—the United States of America was suddenly and deliberately attacked by naval and air forces of the Empire of Japan.”
3) John F. Kennedy’s 1961 Inauguration Address
In 1961, during his first 14-minute address as commander in chief, President John F. Kennedy used the memorable phrase “My fellow Americans: ask not what your country can do for you—ask what you can do for your country” to motivate both children and adults to engage in volunteer work and civic engagement. The group Kennedy addressed was what he described as “a new generation of Americans—born in this century, tempered by war, disciplined by a hard and bitter peace, proud of our ancient heritage.”
4) John F. Kennedy’s Space Effort Address
Kennedy said, “We chose to undertake the other things in this decade, not because they are simple, but because they are difficult… Prior generations ensured that our nation saw the first waves of the Industrial Revolution, the first waves of modern invention, and the first waves of nuclear power. And this generation does not plan to flounder in the wake of the new space age; rather, we aspire to participate in it and lead it.”
We were in a new era of technology and space exploration, which is why it was significant. Americans were given the impression by President Kennedy that there was nothing they couldn’t accomplish or a difficulty they couldn’t overcome. Before Vietnam, Watergate, the passing of our heroes like Jack and Bobby Kennedy and Martin Luther King, Jr., and before any of these events, there was a time when they all believed that, if they worked together, they could achieve their loftiest aspirations.
5) The “We Shall Overcome” Speech By Lyndon B. Johnson In 1965
Civil rights activist John Lewis and more than 500 marchers were assaulted on March 7, 1965, a day that came to be known as “Bloody Sunday,” as they prepared to march from Selma to Montgomery to register African Americans to vote. Eight days later, President Lyndon B. Johnson spoke before a joint session of Congress to call for the adoption of legislation that would ensure everyone’s access to the polls.
Johnson said that “every American citizen must have an equal right to vote” and that “what happened in Selma is part of a far larger movement that reaches into every section and state of America,” while borrowing the slogan “We Shall Overcome” from black leaders battling for equal rights. On August 6, 1965, Johnson subsequently signed the Voting Rights Act of 1965 into law.
6) The 1987 “Tear Down This Wall” Address By Ronald Reagan
In 1987, President Ronald Reagan visited Berlin, Germany, to mark the city’s 750th anniversary. At the time, the Berlin Wall had been severing the city in half for almost 26 years, acting as both a physical barrier and a powerful symbol of the divide between the communist Soviet bloc and the democratic capitalist bloc. The most well-known words of Reagan’s presidency are perhaps those he spoke when standing barely 100 yards from the barrier during a speech: “Mr. Gorbachev, tear down this wall.”
7) George W. Bush’s Speech Following The 9/11 Terrorist Attacks
On the morning of the September 11, 2001, terrorist attacks, President George W. Bush was in Florida visiting an elementary school. He ultimately took Air Force One back to Washington, D.C., determined to get back to the White House, and delivered a detailed prime-time speech from the Oval Office to a terrified nation.
“Today, our fellow citizens, our way of life, and our very freedom came under attack in a series of deliberate and deadly terrorist acts,” Bush stated. “Evil, disgusting acts of terror abruptly terminated thousands of lives. We were shocked by the images of aircraft crashing into buildings, fires raging, and enormous structures falling. We also felt deep grief and a calm, uncompromising rage. The purpose of these mass murders was to send our country into an uproar and cause it to flee. However, they fell short because our nation is robust,” he added.
8) Dwight Eisenhower’s ‘Atoms For Peace’ Address To The United Nations
Eisenhower said, “I feel compelled to talk in a vocabulary that is, in a way, fresh today. One that I would have hoped to never use, having spent so much of my life in the military. The language of nuclear conflict is that new language. The United States wants to project more than just might against the ominous backdrop of the atomic bomb; it also wants to convey a desire and hope for peace. The United States commits before you, and hence before the rest of the world, that it will do everything in its power to assist in resolving the terrifying nuclear problem.”
Despite his belief in the political potency of nuclear weapons, Eisenhower discusses their perils in this address. He stresses the need to stop the spread of nuclear weapons and suggests that the US and the USSR work together to shrink their nuclear arsenals. Remember that in 1953, there were only 1,300 nuclear weapons worldwide, but there are now more than seven times as many.
9) Ronald Reagan’s Remarks at D-Day’s 40th Anniversary Ceremony
Reagan said, “The rangers glanced up and saw the enemy soldiers at the edge of the cliffs firing down at them and hurling grenades, and the American rangers started to ascend. They launched rope ladders over the cliff’s face and started to haul themselves up. A replacement ranger would step in after one fell. A ranger would grab another rope after cutting the first one, then start climbing once more. They ascended, fired back, and maintained their balance. The rangers eventually pushed themselves over the top one by one, and by taking control of the hard soil at the top of these cliffs, they started to retake control of Europe. You all understood that certain things are worth dying for (for veterans). A person should die for their nation, and democracy is the most morally upright form of governance that has ever been created.”
Reiterating his call for the West to “renew our commitment to each other, to our freedom, and to the alliance that protects it” at the conclusion of that speech, President Reagan told our Allies that “we were with you then, and we are with you now,” which helped to forge the alliance that would ultimately defeat the Soviet Union and bring an end to the Cold War. In many respects, the “boys of Pointe du Hoc” rescued the world more than once.
10) Ronald Reagan’s Speech On The Challenger Space Shuttle Disaster
Reagan said, “The bold, not the weak-hearted, will inherit the future. We were being pulled into the future by the Challenger crew, and we’ll keep doing that. By the way they lived their lives, the Challenger crew of the space shuttle honored us. As they said farewell and got ready for their journey this morning, slipping the shackles of Earth to meet the face of God, we will never forget them or the last time we saw them.”
We frequently consider presidents to be partisan leaders in the current climate of political polarization. The president’s position as “comforter in chief” is nonetheless one of his or her most significant duties. The best presidents are characterized by their capacity to put politics aside in times of sorrow in order to soothe a nation and remind us that, in the end, we are all Americans, whatever our differences.
11) Barack Obama’s ‘A More Perfect Union’ Speech
Obama said, “I have never been so naive to imagine that we can move past our racial differences on a single election cycle or with a single candidate, particularly a candidacy as flawed as mine, contrary to the contention of some of my detractors, black and white. However, I have made it clear that I really believe that through working together, we can heal some of our old racial scars and that there is really no other option—a belief steeped in my trust in God and my confidence in the American people. If we want to keep moving toward a more ideal marriage, we have no choice but to. America can change, as we have seen and know. That is the real brilliance of our country. We have the boldness to aspire for what we can and must do tomorrow because of what we have already accomplished.”
Why It Was Important: According to conventional thinking, speaking about race is not advised. But Obama embraced the challenge rather than avoiding it. Being uniquely positioned to do so, he invited listeners to places many have never been—a predominantly black church, an awkward conversation with a beloved relative of a different race, the kitchen tables of white Americans who feel resentful and left behind—and he recounted Americans’ frequently differing perspectives.
In order to understand the current structural injustices experienced by African Americans and other people of color, he encouraged us to be open and honest about our past. Obama thought that most Americans were prepared to hear the truth and make a decision, to get over the racial impasse, face our difficulties, and respond appropriately. He was direct, honest, and nuanced in his approach.
12) The Farewell Address Of George Washington
This address was actually a letter that was printed and reproduced in national newspapers. Many of the points made by Washington were noteworthy. Even though many people at the time wanted the Big Man to hold the position for the rest of his life, he first declared that he would not run for a third term. It was a magnificent act of humility and wisdom that put an end to any remaining notions of American monarchy and established a genuinely republican atmosphere for the country.
Washington also forewarned against the emergence of factions, or what we euphemistically refer to as political parties today, as well as engaging in a number of other unsavory activities that his successors nevertheless engaged in. However, the speech demonstrated why George Washington is still regarded as our greatest president.
13) Abraham Lincoln’s Second Inaugural Address
Lincoln was a skilled raconteur and public speaker. He could tell a joke or tale quickly, and he was also a fantastic speaker. Lincoln frequently kept his remarks brief and to the point, which is uncommon and appreciated among politicians. In that sense, his second inaugural address, which he gave only a few weeks before being assassinated, was typical, but it also showed the strength of his leadership in the way he tried to chart a route for a post-Civil War America.
By the time Lincoln delivered this address, the outcome of the war was all but certain, and he was already considering the difficult, protracted road that lay ahead for the country as a whole to recover from its wounds.
“Let us strive on to finish the work we are in, to bind up the nation’s wounds, to care for him who shall have borne the battle and for his widow and orphan, to do all that may achieve and cherish a just and lasting peace among ourselves and with all nations,” the Apostle Paul said. “With malice toward none, with charity for all, with firmness in the right as God gives us to see the right,
“Let us strive on to finish the work we are in to bind up the nation’s wounds, to care for him who shall have borne the battle and for his widow and his orphan, to do all that may achieve and cherish a just and lasting peace among ourselves and with all nations,” the Declaration of Independence reads. “With malice toward none, with charity for all, with firmness in the right, as God gives us to see the right,”
14) French President Emmanuel Macron’s 2018 Speech at US Congress
On April 25, 2018, French President Emmanuel Macron spoke in front of the US Congress. Macron emphasized the strong historical bonds between France and the US that are founded on a commitment to equality, tolerance, and freedom.
Regarding current global issues, including terrorism, nuclear proliferation, and climate change, Macron voiced worry. He argued in favor of a robust global strategy to deal with these problems and emphasized the significance of upholding democracy and battling false news.
He urged for the transition to a low-carbon economy and emphasized the need to preserve the environment for future generations. In particular, in the Sahel area, Macron lauded the cooperation between French and American forces in fending off shared dangers.
Macron continued by reiterating the strength of the bond between France and the United States and his belief in their capacity to work together to overcome obstacles.
Also Read: Top 5 Reasons Why USA is Still in Syria
In conclusion, the greatest presidential addresses in history have transcended the constraints of their eras to stand as timeless examples of the hopes, resiliency, and values of the country. These speeches have had a profound impact on the American spirit, from the somber reflections of Abraham Lincoln during the Civil War to the visionary appeals for exploration and unity made by John F. Kennedy, and from the passionate resolve of Franklin D. Roosevelt in the face of adversity to the unwavering dedication of Lyndon B. Johnson to civil rights.
These speeches also serve as examples of the value of leadership during times of crisis and transformation. They serve as a reminder that the proper words, when said with passion and empathy, have the power to mend broken hearts, spark hope, and unite a nation to face its toughest obstacles.
As we think back on these inspiring speeches, we are reminded that a country’s path is characterized not only by its landmarks but also by the knowledge and inspiration that its leaders have shared. We discover the tenacity, bravery, and lasting spirit that characterize the American experience in these verbally preserved events. These speeches act as lighthouses, pointing the path toward a more equitable and prosperous future while asking us to embrace the principles that have created the country and guided us through the difficulties of history.
What Famous Speeches Altered the Course of History?
In addition to many others, notable speeches include Franklin Delano Roosevelt’s “Only thing we have to fear is fear itself” (1933), Winston Churchill’s “Blood, Sweat, and Tears” (1940), Martin Luther King’s “I Have a Dream” (1963), Harvey Milk’s “Hope Speech” (1978), Margaret Thatcher’s “The Lady’s Not for Turning” (1980), and Nelson Mandela’s upon his release from prison in 1990.
Which Eminent Speeches Still Hold True Today?
We are still motivated by those remarks today. Abraham Lincoln’s Gettysburg Address and Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” address both continue to have an impact on people today. Less well-known talks like Nora Ephron’s graduation speech and Hillary Clinton’s “Human Rights Are Women’s Rights” are seen as motivational.
Which Speech In History Has Garnered The Most Notoriety?
One of the greatest speeches in human history is the “I Have a Dream” address given by the Reverend Martin Luther King, Jr., on August 28, 1963.
Oleksandra Mamchii
You might also like.

7 Identified Behaviors to Become a Reliable Leader in 2024

Top 5 Practices of Exemplary Leadership for Long-Term Success

The Uses of Diplomatic Instruments In Diplomatic Missions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Best Diplomats having its headquarters in New York is a Diplomatic Simulation Organizer dedicated to inculcating the skills of Diplomacy among Youth
Quick Links
Destinations, let's have a word.
© 2023. All Rights Reserved | Privacy Policy
| Compiled by researchers at the University of Wisconsin-Madison and Texas A & M University, this list reflects the opinions of 137 leading scholars of American public address. ( .) |

10 of the Most Famous and Inspirational Speeches from History
By Dr Oliver Tearle (Loughborough University)
What makes a great and iconic speech? There are numerous examples of brilliant orators and speechmakers throughout history, from classical times to the present day. What the best speeches tend to have in common are more than just a solid intellectual argument: they have emotive power, or, for want of a more scholarly word, ‘heart’. Great speeches rouse us to action, or move us to tears – or both.
But of course, historic speeches are often also associated with landmark, or watershed, moments in a nation’s history: when Churchill delivered his series of wartime speeches to Britain in 1940, it was against the backdrop of a war which was still in its early, uncertain stages. And when Martin Luther King stood in front of the Lincoln Memorial in 1963, he was addressing a crowd who, like him, were marching for justice, freedom, and civil rights for African Americans.
Let’s take a closer look at ten of the best and most famous speeches from great moments in history.
Abraham Lincoln, ‘ Gettysburg Address ’ (1863).
The Gettysburg Address is one of the most famous speeches in American history, yet it was extremely short – just 268 words, or less than a page of text – and Abraham Lincoln, who gave the address, wasn’t even the top billing .
The US President Abraham Lincoln gave this short address at the dedication of the Soldiers’ National Cemetery in Gettysburg, Pennsylvania on 19 November 1863. At the time, the American Civil War was still raging, and the Battle of Gettysburg had been the bloodiest battle in the war, with an estimated 23,000 casualties.
Lincoln’s speech has been remembered while Edward Everett’s – the main speech delivered on that day – has long been forgotten because Lincoln eschewed the high-flown allusions and wordy style of most political orators of the nineteenth century. Instead, he addresses his audience in plain, homespun English that is immediately relatable and accessible.
Sojourner Truth, ‘ Ain’t I a Woman? ’ (1851).
Sometimes known as ‘Ar’n’t I a Woman?’, this is a speech which Sojourner Truth, a freed African slave living in the United States, delivered in 1851 at the Women’s Convention in Akron, Ohio. The women in attendance were being challenged to call for the right to vote.
In her speech, Sojourner Truth attempts to persuade the audience to give women the vote . As both an ex-slave and a woman, Sojourner Truth knew about the plight of both groups of people in the United States. Her speech shows her audience the times: change is coming, and it is time to give women the rights that should be theirs.
John Ball, ‘ Cast off the Yoke of Bondage ’ (1381).
The summer of 1381 was a time of unrest in England. The so-called ‘Peasants’ Revolt’, led by Wat Tyler (in actual fact, many of the leaders of the revolt were more well-to-do than your average peasant), gathered force until the rebels stormed London, executing a number of high-ranking officials, including the Archbishop of Canterbury and Lord Chancellor, Simon Sudbury.
Alongside Tyler, the priest John Ball was an important leading figure of the rebellion. His famous couplet, ‘When Adam delved and Eve span, / Who was then the gentleman?’ sums up the ethos of the Peasants’ Revolt: social inequality was unheard of until men created it.
Winston Churchill, ‘ We Shall Fight on the Beaches ’ (1940).
Winston Churchill had only recently assumed the role of UK Prime Minister when he gave the trio of wartime speeches which have gone down in history for their rhetorical skill and emotive power. This, for our money, is the best of the three.
Churchill gave this speech in the House of Commons on 4 June 1940. Having brought his listeners up to speed with what has happened, Churchill comes to the peroration of his speech : by far the most famous part. He reassures them that if nothing is neglected and all arrangements are made, he sees no reason why Britain cannot once more defend itself against invasion: something which, as an island nation, it has always been susceptible to by sea, and now by air.
Even if it takes years, and even if Britain must defend itself alone without any help from its allies, this is what must happen. Capitulation to the Nazis is not an option. The line ‘if necessary for years; if necessary, alone’ is sure to send a shiver down the spine, as is the way Churchill barks ‘we shall never surrender!’ in the post-war recording of the speech he made several years later.
William Faulkner, ‘ The Agony and the Sweat ’ (1950).
This is the title sometimes given to one of the most memorable Nobel Prize acceptance speeches: the American novelist William Faulkner’s acceptance of the Nobel Prize for Literature at Stockholm in 1950.
In his speech, Faulkner makes his famous statement about the ‘duty’ of writers: that they should write about ‘the human heart in conflict with itself’, as well as emotions and themes such as compassion, sacrifice, courage, and hope. He also emphasises that being a writer is hard work, and involves understanding human nature in all its complexity. But good writing should also remind readers what humankind is capable of.
Emmeline Pankhurst, ‘ The Plight of Women ’ (1908).
Pankhurst (1858-1928) was the leader of the British suffragettes, campaigning – and protesting – for votes for women. After she realised that Asquith’s Liberal government were unlikely to grand women the vote, the Women’s Social and Political Union, founded by Pankhurst with her daughter Christabel, turned to more militant tactics to shift public and parliamentary opinion.
Her emphasis in this speech is on the unhappy lot most women could face, in marriage and in motherhood. She also shows how ‘man-made’ the laws of England are, when they are biased in favour of men to the detriment of women’s rights.
This speech was given at the Portman Rooms in London in 1908; ten years later, towards the end of the First World War, women over 30 were finally given the vote. But it would be another ten years, in 1928 – the year of Pankhurst’s death – before the voting age for women was equal to that for men (21 years).
Franklin Roosevelt, ‘ The Only Thing We Have to Fear Is Fear Itself ’ (1933).
This is the title by which Roosevelt’s speech at his inauguration in 1933 has commonly become known, and it has attained the status of a proverb. Roosevelt was elected only a few years after the Wall Street Crash of 1929 which ushered in the Great Depression.
Roosevelt’s famous line in the speech, which offered hope to millions of Americans dealing with unemployment and poverty, was probably inspired by a line from Henry David Thoreau, a copy of whose writings FDR had been gifted shortly before his inauguration. The line about having nothing to fear except fear itself was, in fact, only added into the speech the day before the inauguration took place, but it ensured that the speech went down in history.
Marcus Tullius Cicero, ‘ Among Us You Can Dwell No Longer ’ (63 BC).
Of all of the great classical orators, perhaps the greatest of all was the Roman statesman, philosopher, and speechmaker, Cicero (whose name literally means ‘chickpea’).
This is probably his best-known speech. At the Temple of Jupiter in Rome, Cicero addressed the crowd, but specifically directed his comments towards Lucius Catiline, who was accused of plotting a conspiracy to set fire to the capital and stage and insurrection. The speech was considered such a fine example of Roman rhetoric that it was a favourite in classrooms for centuries after, as Brian MacArthur notes in The Penguin Book of Historic Speeches .
Queen Elizabeth I, ‘ The Heart and Stomach of a King ’ (1588).
Queen Elizabeth I’s speech to the troops at Tilbury is among the most famous and iconic speeches in English history. On 9 August 1588, Elizabeth addressed the land forces which had been mobilised at the port of Tilbury in Essex, in preparation for the expected invasion of England by the Spanish Armada.
When she gave this speech, Elizabeth was in her mid-fifties and her youthful beauty had faded. But she had learned rhetoric as a young princess, and this training served her well when she wrote and delivered this speech (she was also a fairly accomplished poet ).
She famously tells her troops: ‘I know I have the body but of a weak and feeble woman; but I have the heart and stomach of a king, and of a king of England too’. She acknowledged the fact that her body was naturally less masculine and strong than the average man’s, but it is not mere physical strength that will win the day. It is courage that matters.
Martin Luther King, ‘ I Have a Dream ’ (1963).
Let’s conclude this selection of the best inspirational speeches with the best-known of all of Martin Luther King’s speeches. The occasion for this piece of oratorical grandeur was the march on Washington , which saw some 210,000 men, women, and children gather at the Washington Monument in August 1963, before marching to the Lincoln Memorial. King reportedly stayed up until 4am the night before he was due to give the speech, writing it out.
King’s speech imagines a collective vision of a better and more equal America which is not only shared by many Black Americans, but by anyone who identifies with their fight against racial injustice, segregation, and discrimination.
Discover more from Interesting Literature
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Type your email…
1 thought on “10 of the Most Famous and Inspirational Speeches from History”
- Pingback: Top Motivational Speeches That Shook the World - Kiiky
Comments are closed.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
What Makes a Great Political Speech?
The best political speeches aren't always the ones that are well-written or well-delivered, says Michael Cohen, author of Live from the Campaign Trail: The Greatest Presidential Campaign Speeches of the Twentieth Century and How They Shaped Modern America .
Copyright © 2008 NPR. All rights reserved. Visit our website terms of use and permissions pages at www.npr.org for further information.
NPR transcripts are created on a rush deadline by an NPR contractor. This text may not be in its final form and may be updated or revised in the future. Accuracy and availability may vary. The authoritative record of NPR’s programming is the audio record.
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
Abraham Lincoln’s Most Enduring Speeches and Quotes
By: Aaron Randle
Updated: February 7, 2024 | Original: January 26, 2022

There’s perhaps no better way to grasp Abraham Lincoln ’s outsized American legacy than through his writing.
From his time as a 20-something political hopeful to his tragic death, Lincoln was a voluminous writer, authoring hundreds of letters, speeches, debate arguments and more.
Despite very little formal schooling, the 16th president was an avid reader who from a young age understood the transformative power of words. “Words were Lincoln’s way up and out of the grinding poverty into which he had been born,” wrote historian and author Geoffrey Ward. “If the special genius of America was that it provided an environment in which ‘every man can make himself,’ as Lincoln believed, pen and ink were the tools with which he did his self-carpentering.”
While he often expressed himself with humor and folksy wisdom, Lincoln wasn’t afraid to wade into lofty territory. His writings show how his thoughts on the thorny issues of the day—like slavery, religion and national discord—evolved over time. He penned some of America’s most monumental expressions of statecraft, such as the Gettysburg Address , widely hailed for its eloquence and clarity of thought. His prose, infused with his deep love of poetry, helped him in his efforts to reach—and heal—a fractured nation.
Here are a few excerpts of Lincoln’s writings, both famous and lesser-known.
On the Fractured Nation
The ‘House Divided’ Speech: As America expanded West and fought bitterly over whether new territories could extend the practice of slavery, Lincoln spoke out about what he saw as a growing threat to the Union. Many criticized this speech as radical, believing—mistakenly—that Lincoln was advocating for war.
The 'Better Angels of Our Nature' speech: By the time Lincoln was first sworn into office , seven states had already seceded from the Union. During his first address as president, he tried to assure the South that slavery would not be interfered with, and to quiet the drumbeat of war by appealing to “the better angels of our nature.”

Was Abraham Lincoln an Atheist?
As a young man, Lincoln openly admitted to his lack of faith. As a politician, he spoke about God but refused to say he was a Christian.
Lincoln‑Douglas Debates
Background and Context for the Debates As the architect of the Kansas‑Nebraska Act, Douglas was one of the most prominent politicians in the country and seen as a future presidential contender. The controversial 1854 law repealed the Missouri Compromise and established the doctrine of popular sovereignty, by which each new territory joining the Union would […]
The Gettysburg Address: Hailed as one of the most important speeches in U.S. history, Lincoln delivered his brief, 272-word address at the dedication of the Gettysburg battlefield , the site of more than 50,000 casualties. By alluding to the Declaration of Independence , he redefined the war as a struggle not just to preserve the Union, but for the fundamental principle of human freedom.
On Religion
During his younger years, the future President remained notoriously noncommittal on the topic of religion—so much so that even his close friends were unable to verify his personal faith. At times, wrote Lincoln scholar Allen Guelzo, “He would actually be aggressive on the subject of unbelief,” asserting that the Bible was just a book or that Jesus was an illegitimate child.
This lack of clarity on his beliefs—Was he an atheist? A skeptic?—proved a political liability early on. After failing to win election to the U.S. House of Representatives in 1843, a worried Lincoln expressed fears that his lack of religiosity might have been to blame:
Lincoln won that House seat three years later, but not without his opponent, a revivalist preacher, accusing him of being a religious scoffer. Instead of dismissing the allegation, as he might have before, the future President wrote a public message directly to his constituency to deny any disrepect, while still avoiding pinning himself down to one personal faith:
By his first inauguration, Lincoln had evolved to making full-throated avowals of faith, even declaring that adherence to Christianity was critical to the Union's survival.
On Racial Inequality
It might seem that the author of the Emancipation Proclamation , the president hailed as “the Great Liberator,” would have clear and consistent views on racial justice and equality. Not exactly.
From the onset, Lincoln always opposed the idea and existence of slavery . As early as 1837, when addressing Congress as a newly-elected member of the Illinois General Assembly, the 28-year-old Lincoln proclaimed the institution to be “founded on both injustice and bad policy.”
Nearly two decades later, he continued to reject it on moral and political grounds:
Nonetheless, despite his deep opposition to slavery, Lincoln did not believe in racial equality. He made this point clear during his famed debates against rival Stephen A. Douglas during their race for the U.S. Senate seat from Illinois:
Lincoln struggled to articulate a vision for how free Black Americans could integrate into white-dominated U.S. society. Under constant political pressure to offset his push for emancipation, Lincoln frequently floated the idea of resettling African Americans elsewhere —to Africa, the Caribbean or Central America. As early as 1854, he articulated this idea:
Lincoln’s views on race equality continued to evolve until his death. In his last public address, just four days before his assassination, Lincoln seemed to denounce a future in which newly freed Black Americans were barred from a chance at equal access to the American dream.
In that same speech, Lincoln also teased the idea of Black suffrage , particularly maddening one attendee. Listening from the crowd, Confederate sympathizer John Wilkes Booth heard the assertion and remarked, “That is the last speech he will make.”
Lincoln’s Humor
An essential facet of Lincoln the man—and a huge contributor to his political success—was his witty, folksy humor and his talent for mimicry. An inveterate storyteller, Lincoln skillfully spun up puns, jokes, aphorisms and yarns to offset dicey social and political situations, ingratiate himself with hostile audiences, endear himself with the common man and separate himself from political opponents.
As a lawyer , Lincoln always made a point to speak plainly to the judge and jury, avoiding obscure or high-minded legal jargon. One day in court, another lawyer quoted a legal maxim in Latin, then asked Lincoln to affirm it. His response: “If that’s Latin, you had better call another witness.”
So captivating and engaging was Lincoln’s banter that even his vaunted Senate opponent Stephen A. Douglas begrudgingly acknowledged its effectiveness. Douglas likened it to "a slap across my back. Nothing else—not any of his arguments or any of his replies to my questions—disturbs me. But when he begins to tell a story, I feel that I am to be overmatched."
Humor played a key role, historians say, in Lincoln’s victory over Douglas in their famed 1858 debates. In one instance, he colorfully undercut Douglas’s arguments for the Dred Scott Supreme Court decision as “as thin as the homeopathic soup that was made by boiling the shadow of a pigeon that had starved to death.”
And when hecklers followed a Douglas jibe by calling Lincoln “two-faced,” the future president famously defused the attack with his famed self-deprecating humor:
“If I were two-faced, would I be wearing this one?”

HISTORY Vault: Abraham Lincoln
A definitive biography of the 16th U.S. president, the man who led the country during its bloodiest war and greatest crisis.

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
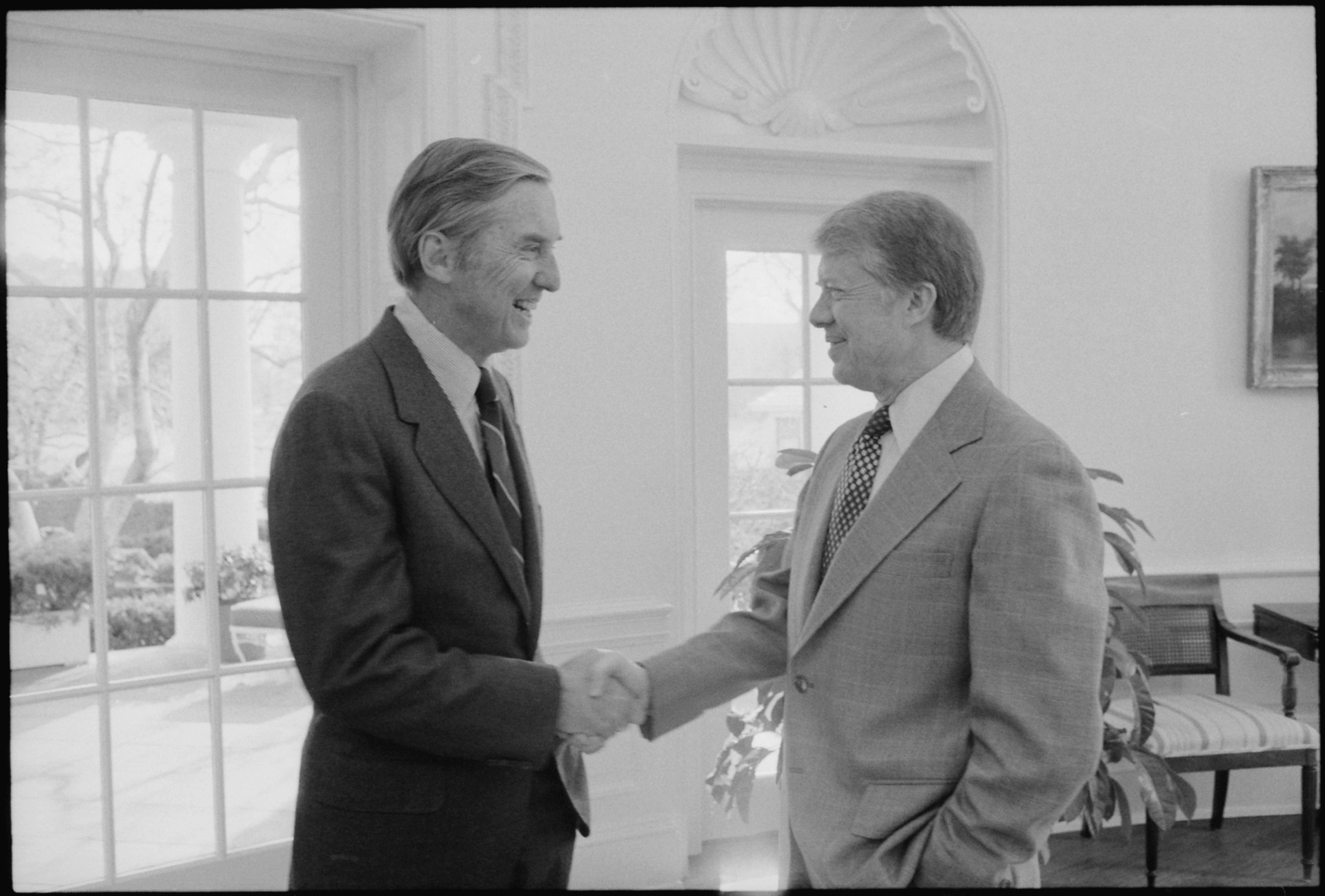
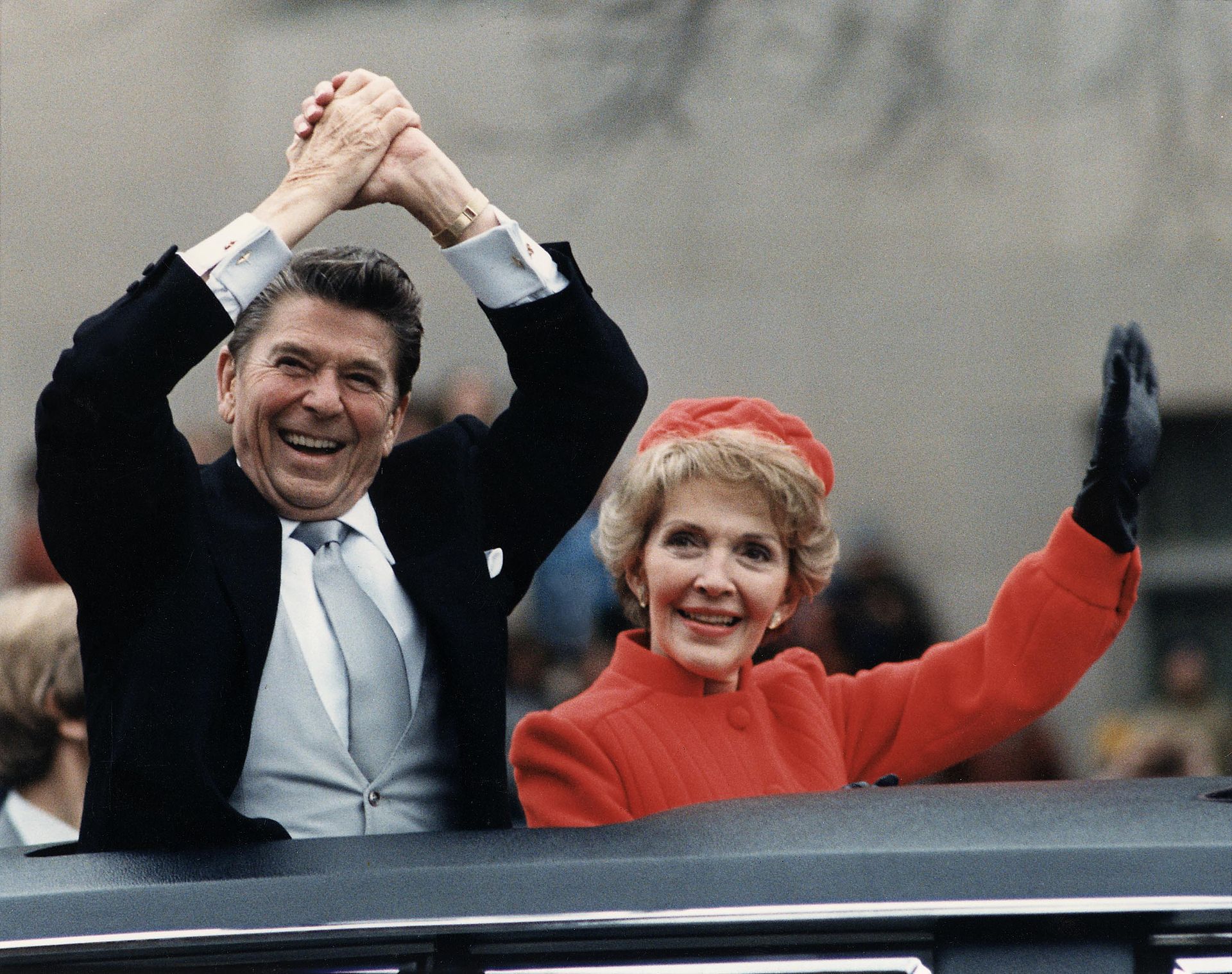
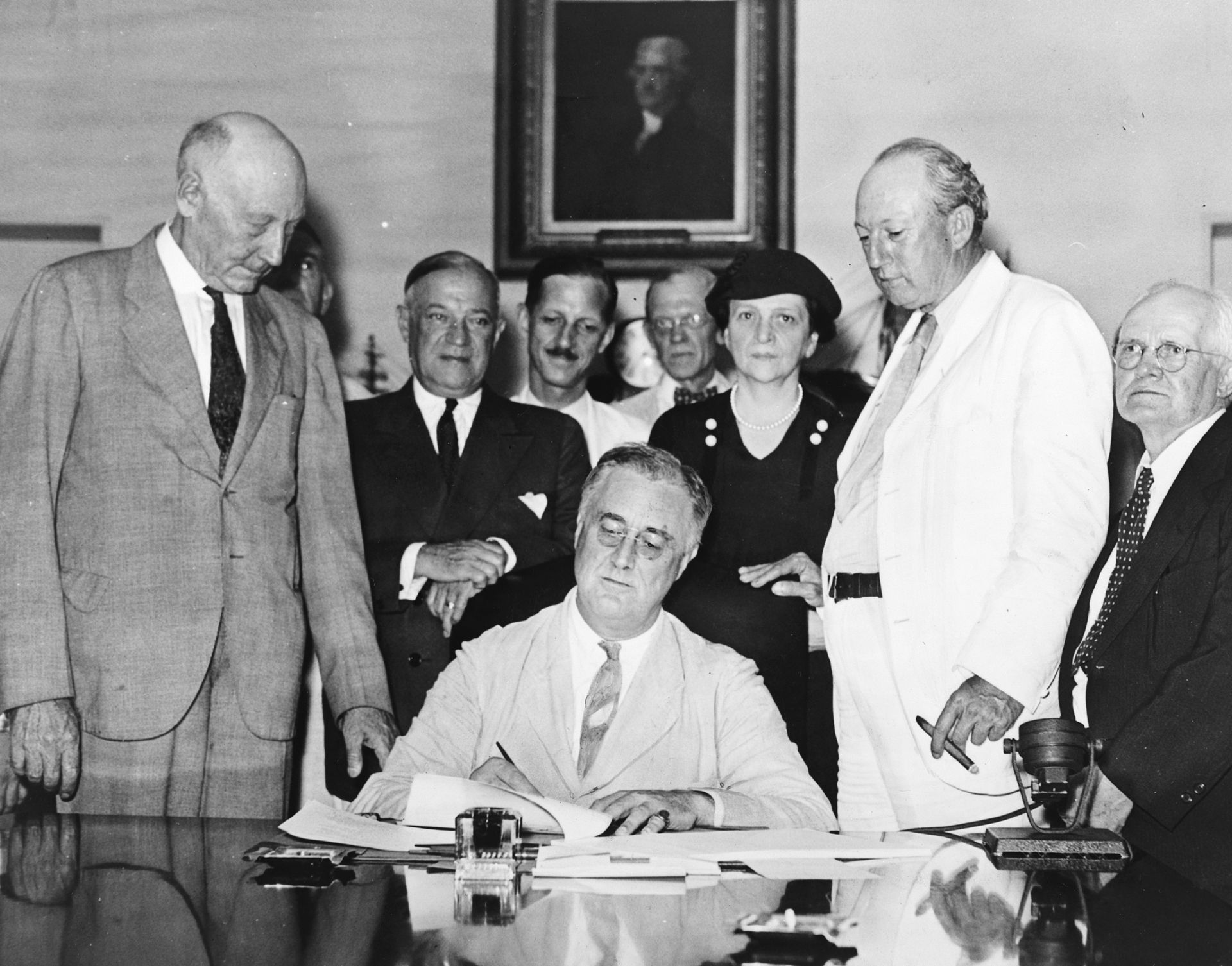
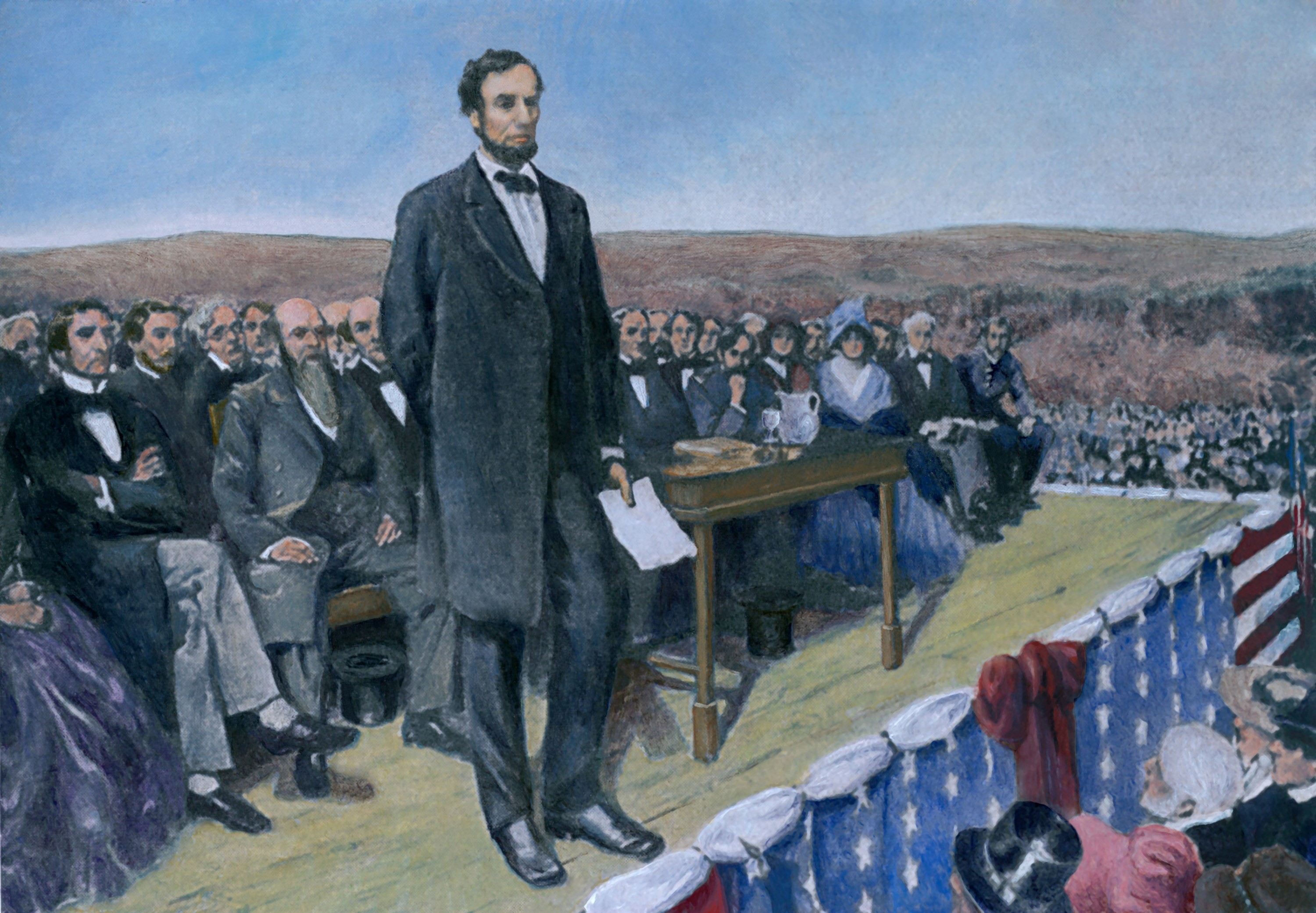
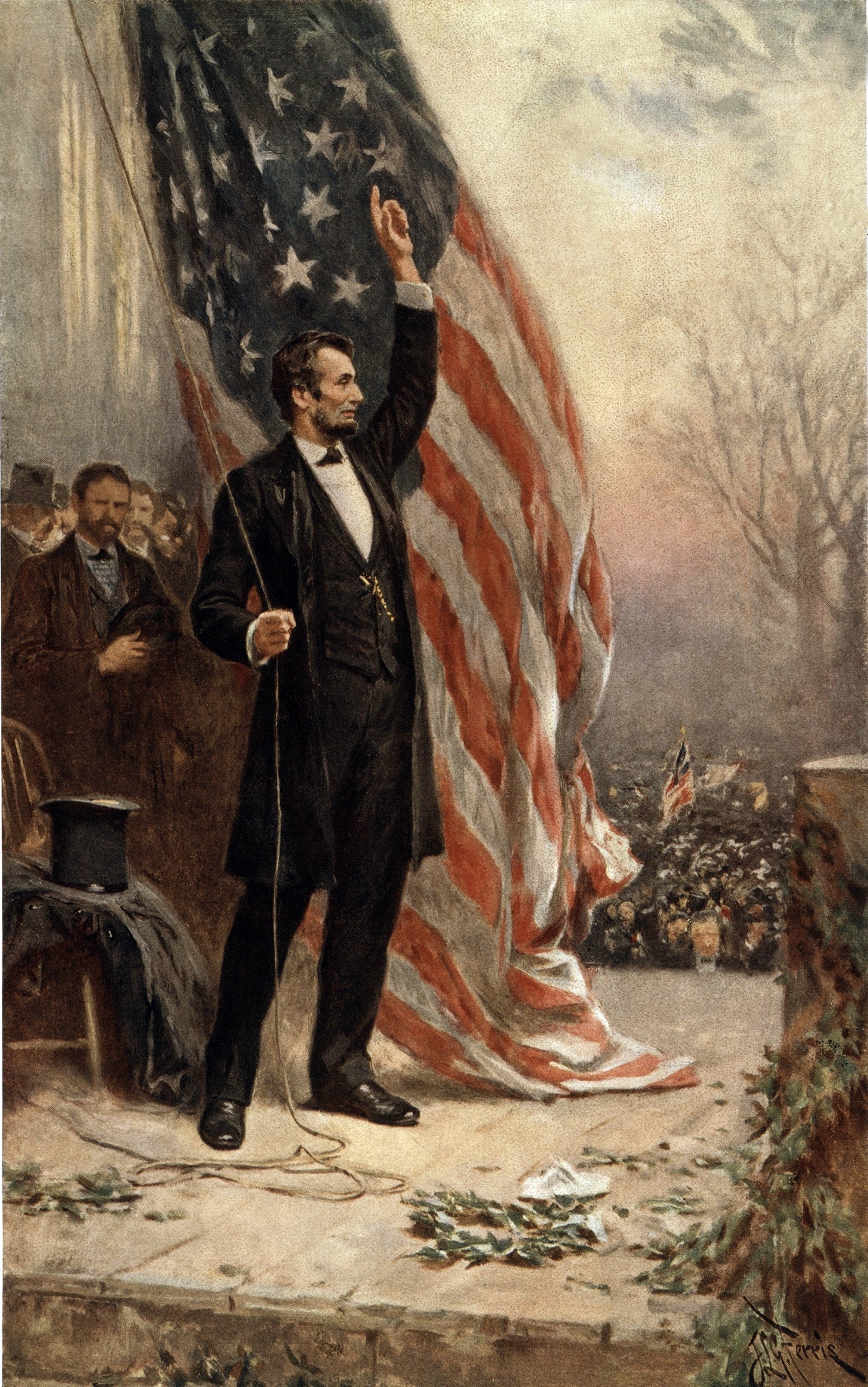















































IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
5. Franklin D. Roosevelt's "Four Freedoms" Speech. Date: January 6, 1941 Context: By 1941, many affected by the Great Depression had experienced economic recovery, but another world-changing phenomenon had reared its head—Hitler and his Nazi regime.World War II was raging in Europe and the Pacific, but the United States had thus far remained largely neutral.
7. John F. Kennedy's 1961 Inaugural Address. Much like FDR, JFK's inaugural address stands the test of time as one of the most iconic moments in American political history. "Ask not what your ...
4. Dwight Eisenhower's Farewell Address. President Dwight D. Eisenhower presenting his farewell address to the nation. (Credit: Ed Clark/The LIFE Picture Collection/Getty Images) When: 1961 ...
Here is a look at the Dream speech and other addresses that moved people - and history. In 1999, a survey of 137 public speaking and political scholars ranked the 100 most-important political speeches of the 21 st Century. The academics evaluated speeches on the basis of their social and political impact, and rhetorical artistry.
THE TOP 100 SPEECHES is an index to and substantial database of full text transcriptions of the 100 most significant American political speeches of the 20th century, according to a list compiled by Professors Stephen E. Lucas and Martin J. Medhurst.Dr. Lucas is Evjue-Bascom Professor in the Humanities and Professor of Communication Arts at the University of Wisconsin at Madison.
Famous quote: "With slight shades of difference, you have the same religion, manners, habits, and political principles. You have in a common cause fought and triumphed together; the independence and liberty you possess are the work of joint counsels, and joint efforts of common dangers, sufferings, and successes." 556 votes.
Famous presidential speeches. Use the "Filter" button to select a particular president and find the speech you want. Animate Background. Off. President. George Washington. ... Search Presidential Speeches. May 31, 2024: Remarks on the Middle East. video icon audio icon transcript icon. March 7, 2024: State of Union Address.
Using historical documents, government and political science websites, and news articles, Stacker curated a gallery of famous speeches from every U.S. president. Whether presented as an inaugural address, a message to Congress, a State of the Union, or a response to a national event, presidential speeches are snapshots of the nation's values ...
Full text, audio, and video database of the 100 most significant American political speeches of the 20th century, according to 137 leading scholars of American public address, as compiled by Stephen E. Lucas (University of Wisconsin-Madison) and Martin J. Medhurst (Baylor University). Discover who made the cut and experience the power of rhetorical eloquence in this provocative list of "who's ...
In this political year, Jon Meacham, the Pulitzer Prize-winning historian, has a podcast about American speeches called "It Was Said." (SOUNDBITE OF MONTAGE) MARTIN LUTHER KING JR: We've got some ...
5) George W. Bush. President George W. Bush gave one of the most memorable speeches at the Islamic Center of Washington, D.C., on Sept. 17, 2001, six days after the terrorist attacks of Sept. 11 ...
17. 1965 Cambridge Union Hall Speech by James Baldwin. "What is dangerous here is the turning away from - the turning away from - anything any white American says. The reason for the political hesitation, in spite of the Johnson landslide is that one has been betrayed by American politicians for so long.
5) The "We Shall Overcome" Speech By Lyndon B. Johnson In 1965. Civil rights activist John Lewis and more than 500 marchers were assaulted on March 7, 1965, a day that came to be known as "Bloody Sunday," as they prepared to march from Selma to Montgomery to register African Americans to vote.
America's major events told through the words of its leaders, since the widespread adoption of the film camera as a communication tool. Through the speeches ...
Top 100 American speeches of the 20th century ... ("The Great Silent Majority") Richard M. Nixon 3 Nov 1969 Washington, DC 22 "Ich bin ein Berliner" John F. Kennedy 26 June 1963 West Berlin, Germany 23 Plea for Mercy at the Trial of Leopold and Loeb Clarence Darrow 22, 23, and 25 Aug 1924 ...
The Gettysburg Address is one of the most famous speeches in American history, yet it was extremely short - just 268 words, or less than a page of text - and Abraham Lincoln, who gave the address, wasn't even the top billing. The US President Abraham Lincoln gave this short address at the dedication of the Soldiers' National Cemetery in Gettysburg, Pennsylvania on 19 November 1863.
MIKE PESCA, host: When we think of great presidential rhetoric, we might think of Washington's farewell, Roosevelt's four freedoms, and John F. Kennedy in 1960. Here's JFK accepting - he gave the ...
William Jennings Bryan's "Cross of Gold," 1896. When former Rep. William Jennings Bryan of Nebraska addressed the Democratic convention the major issue of the day was whether silver as well ...
Biden said this: "When we talk about American democracy, we often talk about the ideals of life, liberty, pursuit of happiness. What we don't talk about is how hard it is.". He said the ...
From his time as a 20-something political hopeful to his tragic death, Lincoln was a voluminous writer, authoring hundreds of letters, speeches, debate arguments and more. ... both famous and ...
Speech Bank: Top 100 Speeches: Great New Speeches: Obama Speeches: GWB Speeches: Movie Speeches: Rhetorical Figures: Christian Rhetoric: 9/11 Speeches: News and Research: For Scholars: Rhetoric Defined: Corax v. Tisias: Plato on Rhetoric: Aristotle on Rhetoric: Comm Journals: Comm Associations: Cool Exercises: Rodman & de Ref: Speech Quiz #1 ...
Great speeches go down in the history books, but it's those short, pithy one-liners that turn politicians into legends. Their off-the-cuff (and fine, probably scripted) remarks don't always have to be funny. Sometimes a political one-liner is inspiring, sometimes it's unintentionally ironic, sometimes it's not even just one line.
Martin Luther King's "I Have a Dream" Speech. "I have a dream" speech by Martin Luther King Jr., which was delivered on 28 August, 1963 at the steps of the Lincoln Memorial during the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom, was a path-breaking moment for the Civil Rights Movement in America. Given to an audience of more than 200,000 ...
The following is a transcript of his speech, as recorded by The New York Times. ... We are a great nation because we are a good people. ... President Joe Biden, U.S. Politics, 2024 Elections ...
Donald Trump falsely suggested Kamala Harris had misled voters about her race as the former president appeared before the National Association of Black Journalists in Chicago Wednesday in an ...
Some famous "white dudes" — including the guy who played "The Dude" — rallied in support of Vice President Kamala Harris, who would be the first female president if elected, in the ...
In fact, Shapiro might be the most visibly Jewish elected official in America: He keeps kosher, has weekly Shabbat dinner with his family, and even quotes Jewish scripture in his political speeches.
D onald Trump arrived an hour late to a rally in the battleground state of Pennsylvania on Wednesday then delivered another 90-minute speech that focused on attacking Kamala Harris.
Former President Donald Trump has revived his four-year-old false claim about how he and Democratic Minnesota Gov. Tim Walz handled the civil unrest that followed the murder of George Floyd by a ...