- How it works


Sample PHD Education and Teaching Dissertation Proposal
Here is a sample that showcases why we are one of the world’s leading academic writing firms. This assignment was created by one of our expert academic writers and demonstrated the highest academic quality. Place your order today to achieve academic greatness.
View a different grade
Using Sustainable ICT in Education: A Phenomenological Case Study of Professional Development Experiences of ELT Faculty at Tertiary Level in the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
Aims and objectives.
The proposed study’s primary aim is to examine how ICT deployments in educational institutions can be made sustainable to aid ELT instructors in English language instruction in the UAE. To achieve this aim, the proposed study has developed the following primary research question;
How can ICT efforts in tertiary level education be made sustainable for English language training?
The primary research question is accompanied by the following secondary research questions answered in the proposed study.
1. What is the extent of educational technology integration in English language teaching at the Tertiary Level in the UAE, and what factors contributed to the adoption of educational technologies to facilitate ELT practices?
2. Has the use of technology improved the overall English language learning experiences of the students?
3. What is the impact of using educational technology on teachers; what are their experiences, and how has this changed their perceptions, attitudes, and beliefs about the teaching and learning process?
4. What is the future of educational technology as a strategy for enhancing English learning processes in the UAE?
The research question and aim will be achieved through achieving the following objectives;
1. Use primary and secondary research to collect data and information on the proposed topic of study.
2. Examine how ICT can be made sustainable in cost, policy, resources, and re-purpose.
3. Analyse the instructor’s experience of using ICT in English language training.
4. Examine factors that facilitated the adoption of educational technologies to promote ELT practice in the tertiary level English language learning institutions in the UAE
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) is placed strategically for trade, allowing multiple languages to thrive in its vicinity. English medium instruction is one of the core concepts upheld in federally funded tertiary education institutes (Rogier, 2012). To extend and provide improved English instruction, it is essential to incorporate ICT and other technologies for teaching and learning the English language.
Sustainability is often described as an education ecosystem’s ability to maintain scholastic processes, functions, diversity, and productivity into the future. To look at it at a practical level, ELT faculty needs to introduce information and communication technologies in existing educational ecosystems so that they may absorb it and own the change (Howard et al., 2016).
As per the current understanding, no literature examines sustainable technology integration in English language training in the UAE (Howard et al., 2016). The current status of technology/ICT can be reviewed at the tertiary level to recommend strategies that further its beneficial use by conducting the proposed study. It is also essential to investigate how ELT faculty in the UAE can use ICT for training students in the English language.
Hire an Expert Dissertation Proposal Writer
Orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in the academic style
- 100% Plagiarism-free & 100% Confidential
- Never resold
- Include unlimited free revisions
- Completed to match exact client requirements
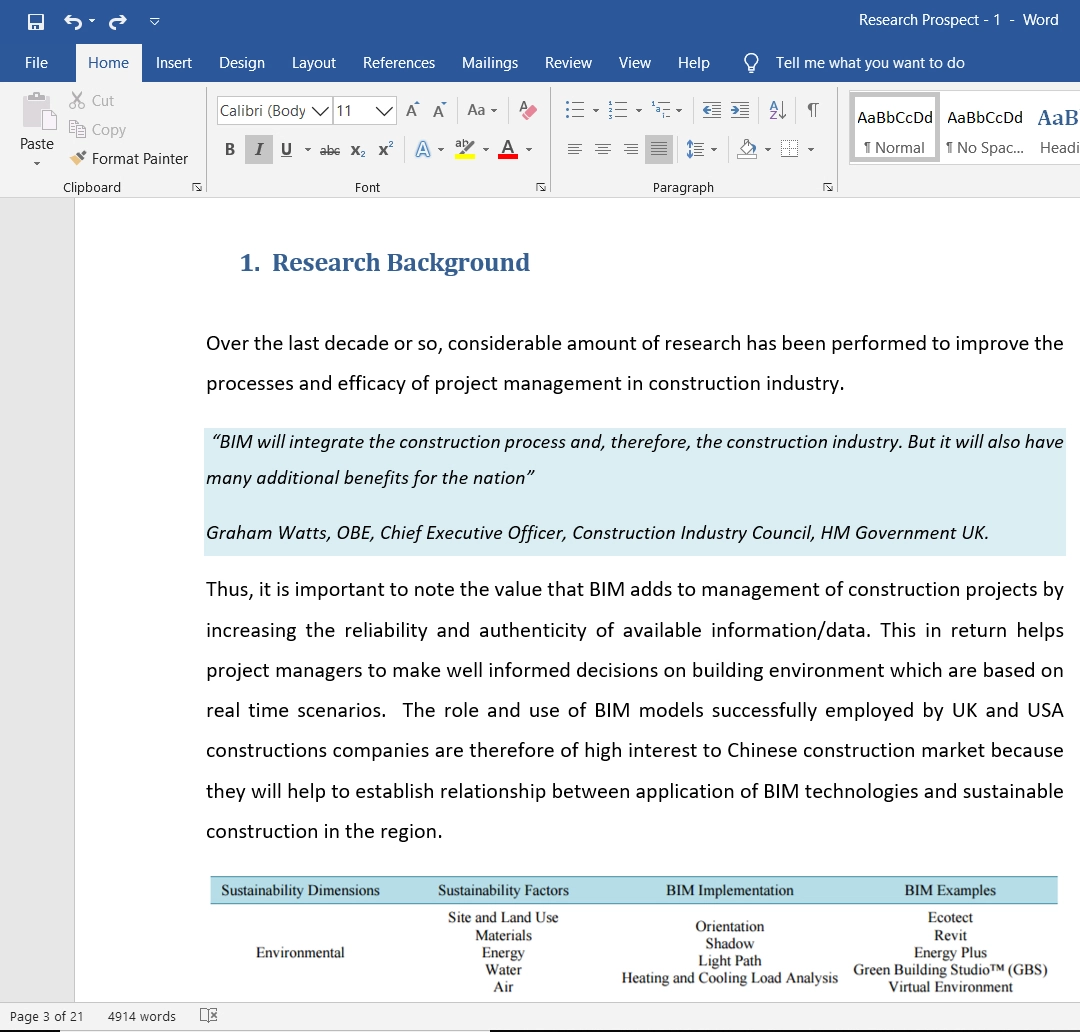
Methodology
Research design.
The proposed research looks to adopt a qualitative phenomenological case study approach. The phenomenological method is used to understand the topic of interest from the everyday knowledge and perceptions of specific respondent groups (Vinke et al., 1998). By using this approach, researchers have an initial understanding of the topic. They are interested in developing an in-depth comprehension or clarification of potentially conflicting or equivocal information from previous data (Stake, 1995).
Denscombe (2004) argues that it is not primarily concerned with explaining the causes of things; instead, it describes how things are experienced first-hand by the typical world. Yin (2003) argues that the case study is a particular style of educational research appropriate for investigating professional development instructors and teachers’ concepts. Stake (1995) asserts the benefit of using a qualitative case study methodology, which arises from emphasising each case’s uniqueness and the educator’s subjective experience.
Data Collection
The proposed research intends to explore the different perspectives of professionals in teaching at the tertiary level in the UAE regarding their experiences as ELT faculty and how technology and ICT use in education can enhance English language learning. The focus group interview will be used in the current study to collect data from a diverse group of people.
Freebody (2004) asserts that the use of focus groups in education research gives opportunities to compare and contrast interpretations, develop unforeseen findings, and aids in exploring findings that would either be considered anomalous or disconfirming of initial impressions. Lindlof and Taylor (2002) argue that group discussions produce data and insight that would be less accessible without interaction in group settings. Listening to others verbalise experiences stimulates memories, ideas, and experiences in those participating.
The proposed study looks to use purposive sampling when choosing the school and the focus group participants, a strategy used by Punch (2005). The tertiary school selected for the proposed research will be chosen based on the staff experience in working as ELT faculty and having experience with using technology for education. Recommendations for selecting the school will also be taken by several tertiary level teachers working at institutions in the UAE.
The study proposes to have ten focus group interviews that will last one hour. Based on the availability of participants, the total number of people interviewed will be determined. However, it is proposed to use fifty (50) participants to take part in the groups. Participants will be included in the focus group if they are ELT faculty at the education institution and have had experience using technology/ICT for English language instruction, particularly in UAE.
Data Analysis
The proposed study will use thematic analysis to evaluate the data obtained. Thematic analysis is used to identify, analyse, and report patterns or themes within data (Braun and Clarke, 2006). The analysis technique minimally organises and describes the data set in rich detail. It further interprets various aspects of the research topic (Braun and Clarke, 2006).
Bibliography
Denscombe, M. (2004) The Good Research Guide For Small Scale Social Research Projects. (2nd Edn) Berkshire: Open University Press.
Freebody, P. (2004) Qualitative Research in Education-Interaction and Practice. London: Sage Publishers.
Howard, A., Basurto-Santos, N. M., Gimenez, T., Moncada, A. M. G., McMurray, M., and Traish, A. (2016). A comparative study of English language teacher recruitment, in-service education, and retention in Latin American and the Middle East. British Council. ELT Research Papers 16.02, 3-72.
Lindlof, T. R., & Taylor, B. C. (2002). Qualitative Communication Research Methods, 2nd Edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Punch, K. (2005) Introduction to Social Research: Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches. London: Sage Publishers.
Rogier, D. (2012). The effects of English-Medium instruction on the language proficiency of students enrolled in higher education in the UAE. Exeter University, student dissertation.
Stake, R.E. (1995). The Art Of Case Study Research. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Vinke, A.A., Snippe, J., & Jochems, W. (1998). English-medium content courses in non-English higher education: A study of lecturer experiences and teaching behaviours. Teaching in Higher Education, 3(3), 383-394.
Yin, R.K. (2003). Case Study Research: Design and Methods. Thousand Oaks, CA; London: Sage Publications
Frequently Asked Questions
How to write a phd dissertation proposal.
To write a Ph.D. dissertation proposal:
- Choose a research topic.
- Develop a clear problem statement.
- Outline objectives and methodology.
- Review literature.
- Present a timeline.
- Seek feedback from advisors.
- Revise and finalize the proposal before submission.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
17 Research Proposal Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process

A research proposal systematically and transparently outlines a proposed research project.
The purpose of a research proposal is to demonstrate a project’s viability and the researcher’s preparedness to conduct an academic study. It serves as a roadmap for the researcher.
The process holds value both externally (for accountability purposes and often as a requirement for a grant application) and intrinsic value (for helping the researcher to clarify the mechanics, purpose, and potential signficance of the study).
Key sections of a research proposal include: the title, abstract, introduction, literature review, research design and methods, timeline, budget, outcomes and implications, references, and appendix. Each is briefly explained below.
Watch my Guide: How to Write a Research Proposal
Get your Template for Writing your Research Proposal Here (With AI Prompts!)
Research Proposal Sample Structure
Title: The title should present a concise and descriptive statement that clearly conveys the core idea of the research projects. Make it as specific as possible. The reader should immediately be able to grasp the core idea of the intended research project. Often, the title is left too vague and does not help give an understanding of what exactly the study looks at.
Abstract: Abstracts are usually around 250-300 words and provide an overview of what is to follow – including the research problem , objectives, methods, expected outcomes, and significance of the study. Use it as a roadmap and ensure that, if the abstract is the only thing someone reads, they’ll get a good fly-by of what will be discussed in the peice.
Introduction: Introductions are all about contextualization. They often set the background information with a statement of the problem. At the end of the introduction, the reader should understand what the rationale for the study truly is. I like to see the research questions or hypotheses included in the introduction and I like to get a good understanding of what the significance of the research will be. It’s often easiest to write the introduction last
Literature Review: The literature review dives deep into the existing literature on the topic, demosntrating your thorough understanding of the existing literature including themes, strengths, weaknesses, and gaps in the literature. It serves both to demonstrate your knowledge of the field and, to demonstrate how the proposed study will fit alongside the literature on the topic. A good literature review concludes by clearly demonstrating how your research will contribute something new and innovative to the conversation in the literature.
Research Design and Methods: This section needs to clearly demonstrate how the data will be gathered and analyzed in a systematic and academically sound manner. Here, you need to demonstrate that the conclusions of your research will be both valid and reliable. Common points discussed in the research design and methods section include highlighting the research paradigm, methodologies, intended population or sample to be studied, data collection techniques, and data analysis procedures . Toward the end of this section, you are encouraged to also address ethical considerations and limitations of the research process , but also to explain why you chose your research design and how you are mitigating the identified risks and limitations.
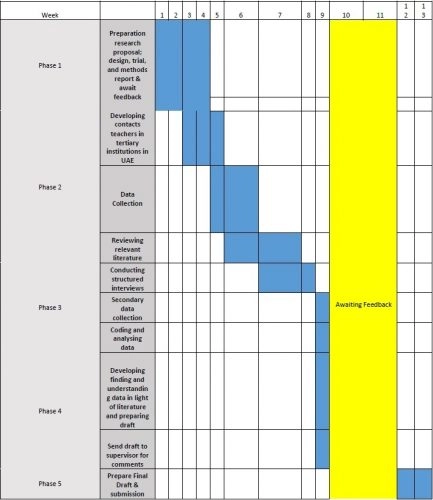
Timeline: Provide an outline of the anticipated timeline for the study. Break it down into its various stages (including data collection, data analysis, and report writing). The goal of this section is firstly to establish a reasonable breakdown of steps for you to follow and secondly to demonstrate to the assessors that your project is practicable and feasible.
Budget: Estimate the costs associated with the research project and include evidence for your estimations. Typical costs include staffing costs, equipment, travel, and data collection tools. When applying for a scholarship, the budget should demonstrate that you are being responsible with your expensive and that your funding application is reasonable.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: A discussion of the anticipated findings or results of the research, as well as the potential contributions to the existing knowledge, theory, or practice in the field. This section should also address the potential impact of the research on relevant stakeholders and any broader implications for policy or practice.
References: A complete list of all the sources cited in the research proposal, formatted according to the required citation style. This demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the relevant literature and ensures proper attribution of ideas and information.
Appendices (if applicable): Any additional materials, such as questionnaires, interview guides, or consent forms, that provide further information or support for the research proposal. These materials should be included as appendices at the end of the document.
Research Proposal Examples
Research proposals often extend anywhere between 2,000 and 15,000 words in length. The following snippets are samples designed to briefly demonstrate what might be discussed in each section.
1. Education Studies Research Proposals
See some real sample pieces:
- Assessment of the perceptions of teachers towards a new grading system
- Does ICT use in secondary classrooms help or hinder student learning?
- Digital technologies in focus project
- Urban Middle School Teachers’ Experiences of the Implementation of
- Restorative Justice Practices
- Experiences of students of color in service learning
Consider this hypothetical education research proposal:
The Impact of Game-Based Learning on Student Engagement and Academic Performance in Middle School Mathematics
Abstract: The proposed study will explore multiplayer game-based learning techniques in middle school mathematics curricula and their effects on student engagement. The study aims to contribute to the current literature on game-based learning by examining the effects of multiplayer gaming in learning.
Introduction: Digital game-based learning has long been shunned within mathematics education for fears that it may distract students or lower the academic integrity of the classrooms. However, there is emerging evidence that digital games in math have emerging benefits not only for engagement but also academic skill development. Contributing to this discourse, this study seeks to explore the potential benefits of multiplayer digital game-based learning by examining its impact on middle school students’ engagement and academic performance in a mathematics class.
Literature Review: The literature review has identified gaps in the current knowledge, namely, while game-based learning has been extensively explored, the role of multiplayer games in supporting learning has not been studied.
Research Design and Methods: This study will employ a mixed-methods research design based upon action research in the classroom. A quasi-experimental pre-test/post-test control group design will first be used to compare the academic performance and engagement of middle school students exposed to game-based learning techniques with those in a control group receiving instruction without the aid of technology. Students will also be observed and interviewed in regard to the effect of communication and collaboration during gameplay on their learning.
Timeline: The study will take place across the second term of the school year with a pre-test taking place on the first day of the term and the post-test taking place on Wednesday in Week 10.
Budget: The key budgetary requirements will be the technologies required, including the subscription cost for the identified games and computers.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: It is expected that the findings will contribute to the current literature on game-based learning and inform educational practices, providing educators and policymakers with insights into how to better support student achievement in mathematics.
2. Psychology Research Proposals
See some real examples:
- A situational analysis of shared leadership in a self-managing team
- The effect of musical preference on running performance
- Relationship between self-esteem and disordered eating amongst adolescent females
Consider this hypothetical psychology research proposal:
The Effects of Mindfulness-Based Interventions on Stress Reduction in College Students
Abstract: This research proposal examines the impact of mindfulness-based interventions on stress reduction among college students, using a pre-test/post-test experimental design with both quantitative and qualitative data collection methods .
Introduction: College students face heightened stress levels during exam weeks. This can affect both mental health and test performance. This study explores the potential benefits of mindfulness-based interventions such as meditation as a way to mediate stress levels in the weeks leading up to exam time.
Literature Review: Existing research on mindfulness-based meditation has shown the ability for mindfulness to increase metacognition, decrease anxiety levels, and decrease stress. Existing literature has looked at workplace, high school and general college-level applications. This study will contribute to the corpus of literature by exploring the effects of mindfulness directly in the context of exam weeks.
Research Design and Methods: Participants ( n= 234 ) will be randomly assigned to either an experimental group, receiving 5 days per week of 10-minute mindfulness-based interventions, or a control group, receiving no intervention. Data will be collected through self-report questionnaires, measuring stress levels, semi-structured interviews exploring participants’ experiences, and students’ test scores.
Timeline: The study will begin three weeks before the students’ exam week and conclude after each student’s final exam. Data collection will occur at the beginning (pre-test of self-reported stress levels) and end (post-test) of the three weeks.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: The study aims to provide evidence supporting the effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions in reducing stress among college students in the lead up to exams, with potential implications for mental health support and stress management programs on college campuses.
3. Sociology Research Proposals
- Understanding emerging social movements: A case study of ‘Jersey in Transition’
- The interaction of health, education and employment in Western China
- Can we preserve lower-income affordable neighbourhoods in the face of rising costs?
Consider this hypothetical sociology research proposal:
The Impact of Social Media Usage on Interpersonal Relationships among Young Adults
Abstract: This research proposal investigates the effects of social media usage on interpersonal relationships among young adults, using a longitudinal mixed-methods approach with ongoing semi-structured interviews to collect qualitative data.
Introduction: Social media platforms have become a key medium for the development of interpersonal relationships, particularly for young adults. This study examines the potential positive and negative effects of social media usage on young adults’ relationships and development over time.
Literature Review: A preliminary review of relevant literature has demonstrated that social media usage is central to development of a personal identity and relationships with others with similar subcultural interests. However, it has also been accompanied by data on mental health deline and deteriorating off-screen relationships. The literature is to-date lacking important longitudinal data on these topics.
Research Design and Methods: Participants ( n = 454 ) will be young adults aged 18-24. Ongoing self-report surveys will assess participants’ social media usage, relationship satisfaction, and communication patterns. A subset of participants will be selected for longitudinal in-depth interviews starting at age 18 and continuing for 5 years.
Timeline: The study will be conducted over a period of five years, including recruitment, data collection, analysis, and report writing.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: This study aims to provide insights into the complex relationship between social media usage and interpersonal relationships among young adults, potentially informing social policies and mental health support related to social media use.
4. Nursing Research Proposals
- Does Orthopaedic Pre-assessment clinic prepare the patient for admission to hospital?
- Nurses’ perceptions and experiences of providing psychological care to burns patients
- Registered psychiatric nurse’s practice with mentally ill parents and their children
Consider this hypothetical nursing research proposal:
The Influence of Nurse-Patient Communication on Patient Satisfaction and Health Outcomes following Emergency Cesarians
Abstract: This research will examines the impact of effective nurse-patient communication on patient satisfaction and health outcomes for women following c-sections, utilizing a mixed-methods approach with patient surveys and semi-structured interviews.
Introduction: It has long been known that effective communication between nurses and patients is crucial for quality care. However, additional complications arise following emergency c-sections due to the interaction between new mother’s changing roles and recovery from surgery.
Literature Review: A review of the literature demonstrates the importance of nurse-patient communication, its impact on patient satisfaction, and potential links to health outcomes. However, communication between nurses and new mothers is less examined, and the specific experiences of those who have given birth via emergency c-section are to date unexamined.
Research Design and Methods: Participants will be patients in a hospital setting who have recently had an emergency c-section. A self-report survey will assess their satisfaction with nurse-patient communication and perceived health outcomes. A subset of participants will be selected for in-depth interviews to explore their experiences and perceptions of the communication with their nurses.
Timeline: The study will be conducted over a period of six months, including rolling recruitment, data collection, analysis, and report writing within the hospital.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: This study aims to provide evidence for the significance of nurse-patient communication in supporting new mothers who have had an emergency c-section. Recommendations will be presented for supporting nurses and midwives in improving outcomes for new mothers who had complications during birth.
5. Social Work Research Proposals
- Experiences of negotiating employment and caring responsibilities of fathers post-divorce
- Exploring kinship care in the north region of British Columbia
Consider this hypothetical social work research proposal:
The Role of a Family-Centered Intervention in Preventing Homelessness Among At-Risk Youthin a working-class town in Northern England
Abstract: This research proposal investigates the effectiveness of a family-centered intervention provided by a local council area in preventing homelessness among at-risk youth. This case study will use a mixed-methods approach with program evaluation data and semi-structured interviews to collect quantitative and qualitative data .
Introduction: Homelessness among youth remains a significant social issue. This study aims to assess the effectiveness of family-centered interventions in addressing this problem and identify factors that contribute to successful prevention strategies.
Literature Review: A review of the literature has demonstrated several key factors contributing to youth homelessness including lack of parental support, lack of social support, and low levels of family involvement. It also demonstrates the important role of family-centered interventions in addressing this issue. Drawing on current evidence, this study explores the effectiveness of one such intervention in preventing homelessness among at-risk youth in a working-class town in Northern England.
Research Design and Methods: The study will evaluate a new family-centered intervention program targeting at-risk youth and their families. Quantitative data on program outcomes, including housing stability and family functioning, will be collected through program records and evaluation reports. Semi-structured interviews with program staff, participants, and relevant stakeholders will provide qualitative insights into the factors contributing to program success or failure.
Timeline: The study will be conducted over a period of six months, including recruitment, data collection, analysis, and report writing.
Budget: Expenses include access to program evaluation data, interview materials, data analysis software, and any related travel costs for in-person interviews.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: This study aims to provide evidence for the effectiveness of family-centered interventions in preventing youth homelessness, potentially informing the expansion of or necessary changes to social work practices in Northern England.
Research Proposal Template
Get your Detailed Template for Writing your Research Proposal Here (With AI Prompts!)
This is a template for a 2500-word research proposal. You may find it difficult to squeeze everything into this wordcount, but it’s a common wordcount for Honors and MA-level dissertations.
| Section | Checklist |
|---|---|
| Title | – Ensure the single-sentence title clearly states the study’s focus |
| Abstract (Words: 200) | – Briefly describe the research topicSummarize the research problem or question – Outline the research design and methods – Mention the expected outcomes and implications |
| Introduction (Words: 300) | – Introduce the research topic and its significance – Clearly state the research problem or question – Explain the purpose and objectives of the study – Provide a brief overview of |
| Literature Review (Words: 800) | – Gather the existing literature into themes and ket ideas – the themes and key ideas in the literature – Identify gaps or inconsistencies in the literature – Explain how the current study will contribute to the literature |
| Research Design and Methods (Words; 800) | – Describe the research paradigm (generally: positivism and interpretivism) – Describe the research design (e.g., qualitative, quantitative, or mixed-methods) – Explain the data collection methods (e.g., surveys, interviews, observations) – Detail the sampling strategy and target population – Outline the data analysis techniques (e.g., statistical analysis, thematic analysis) – Outline your validity and reliability procedures – Outline your intended ethics procedures – Explain the study design’s limitations and justify your decisions |
| Timeline (Single page table) | – Provide an overview of the research timeline – Break down the study into stages with specific timeframes (e.g., data collection, analysis, report writing) – Include any relevant deadlines or milestones |
| Budget (200 words) | – Estimate the costs associated with the research project – Detail specific expenses (e.g., materials, participant incentives, travel costs) – Include any necessary justifications for the budget items – Mention any funding sources or grant applications |
| Expected Outcomes and Implications (200 words) | – Summarize the anticipated findings or results of the study – Discuss the potential implications of the findings for theory, practice, or policy – Describe any possible limitations of the study |
Your research proposal is where you really get going with your study. I’d strongly recommend working closely with your teacher in developing a research proposal that’s consistent with the requirements and culture of your institution, as in my experience it varies considerably. The above template is from my own courses that walk students through research proposals in a British School of Education.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 101 Hidden Talents Examples
8 thoughts on “17 Research Proposal Examples”
Very excellent research proposals
very helpful
Very helpful
Dear Sir, I need some help to write an educational research proposal. Thank you.

Hi Levi, use the site search bar to ask a question and I’ll likely have a guide already written for your specific question. Thanks for reading!
very good research proposal
Thank you so much sir! ❤️
Very helpful 👌
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Postgraduate
Research degrees
- Examples of Research proposals
- Find a course
- Accessibility
Examples of research proposals
How to write your research proposal, with examples of good proposals.
Research proposals
Your research proposal is a key part of your application. It tells us about the question you want to answer through your research. It is a chance for you to show your knowledge of the subject area and tell us about the methods you want to use.
We use your research proposal to match you with a supervisor or team of supervisors.
In your proposal, please tell us if you have an interest in the work of a specific academic at York St John. You can get in touch with this academic to discuss your proposal. You can also speak to one of our Research Leads. There is a list of our Research Leads on the Apply page.
When you write your proposal you need to:
- Highlight how it is original or significant
- Explain how it will develop or challenge current knowledge of your subject
- Identify the importance of your research
- Show why you are the right person to do this research
- Research Proposal Example 1 (DOC, 49kB)
- Research Proposal Example 2 (DOC, 0.9MB)
- Research Proposal Example 3 (DOC, 55.5kB)
- Research Proposal Example 4 (DOC, 49.5kB)
Subject specific guidance
- Writing a Humanities PhD Proposal (PDF, 0.1MB)
- Writing a Creative Writing PhD Proposal (PDF, 0.1MB)
- About the University
- Our culture and values
- Academic schools
- Academic dates
- Press office
Our wider work
- Business support
- Work in the community
- Donate or support
Connect with us
York St John University
Lord Mayor’s Walk
01904 624 624
York St John London Campus
6th Floor Export Building
1 Clove Crescent
01904 876 944
- Policies and documents
- Module documents
- Programme specifications
- Quality gateway
- Admissions documents
- Access and Participation Plan
- Freedom of information
- Accessibility statement
- Modern slavery and human trafficking statement
© York St John University 2024
Colour Picker
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Dui id ornare arcu odio.
Felis bibendum ut tristique et egestas quis ipsum. Et netus et malesuada fames ac turpis egestas. Faucibus pulvinar elementum integer enim neque volutpat ac. Hac habitasse platea dictumst vestibulum rhoncus.
Nec ullamcorper sit amet risus nullam eget felis eget. Eget felis eget nunc lobortis mattis aliquam faucibus purus.
Research proposal - template, PhD programme in Educational Sciences for Teacher Education
Template for research proposals in connection with applications for a PhD position or admission to the PhD programme in Educational Sciences for Teacher Education at the Faculty of Education and international Studies.
All research proposals must be based on this template. Research proposals must be between 8- 10 pages including a reference list.
Title of the project
1. main objective and summary of the project.
(Present the main objective of your project and a brief summary, explaining how you intend to attain this goal. The purpose is to give the reader sufficient information to decide whether the project is of interest. You need to be clear and precise in formulating the project objectives. )
2. Background to the project
(Provide a brief account of the existing knowledge in the field the project is part of and show how the project will contribute to new knowledge. Explain how your project is relevant to the research at the Faculty of Education and International Studies – for individual researchers, research groups or projects.)
3. Theoretical framework
(Outline the theoretical foundation of the project and the reasons you have chosen this particular foundation.)
4. Research question(s) and expected findings (hypothesis)
(Describe the question(s) you want to answer through your project, and briefly outline what answer(s) you expect to find or what outcomes you might expect on the basis of previous research and theoretical background. Your research questions or hypotheses should focus and delimit the topic.)
(Give an account of the methodological foundation for your project and any research-ethical problems linked to the project. Describe the underlying data, source material and sampling approaches that will be used and how these will be collected and analyzed)
6. Proposed dissemination
(Outline your proposed outputs: your plans for communicating / publishing your doctoral project – articles, monographs, lectures, etc.)
7. Progress plan
(Outline briefly how you intend to organize your doctoral work over six semesters, including any planned or anticipated periods of study outside OsloMet and/or field work. We do not expect you to know about individual courses, seminars, etc. that will be included in the training component, but you should include course work in your overall timeframe.)
Total: no more than 8-10 pages in Times New Roman, 12 point type, with one and a half line spacing (including reference list. The reference list must be sorted alphabetically by author.). It is up to you to decide how they are distributed among the different sections of the research proposal.
Some general guidelines
A PhD proposal is generally developed when applying for a funded PhD position. This same proposal is used for applying for admission to the PhD program in Educational Sciences for Teacher Education at the Faculty of Education and international Studies. You need to keep in mind, both with regard to proposals for funding and admission to the PhD program, that you will need to convince the reader that the proposed research and the research objective(s) are important and in some way original or move beyond the current research. How will your proposed study make a contribution to the research field? You also need to be aware of the time limit in doing a PhD and that you cannot be overly ambitious, in total you have three years to complete the work and the reader needs to see that you will be able to complete the study within this time limit.
Make sure to use enough space in the proposal to discuss your research design, research methods, sampling and so forth. Here you need to reference the relevant and up to date literature regarding research methods and research design. Be specific in terms of what you are planning to do and how you will obtain the data you seek. What are the sampling procedures you will use and how will you recruit your participants. Also, think about any ethical issues as well as how you might analyze the data. Be as specific as possible in this section.
You will also need a realistic time plan, which should include the research process, fieldwork/data collection, analysis writing up, and dissemination plan as well as course work, all within the space of three years.
Oslo 13.08.2019,
Professor Halla B. Holmarsdottir, Vice-Dean of Research at the Faculty of Education and International Studies, OsloMet - Oslo Metropolitan University
- Accessibility statement
- Cookies policy
- Employee directory
- Employee website
- Student website
- Upcoming events
- Work for us
- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff

- Current Students Hub

Doctoral handbook
You are here
- Dissertation Proposal
On this page:
Proposal Overview and Format
Proposal committee, proposal hearing or meeting.
- Printing Credit for Use in School of Education Labs
Students are urged to begin thinking about a dissertation topic early in their degree program. Concentrated work on a dissertation proposal normally begins after successful completion of the Second-Year Review, which often includes a “mini” proposal, an extended literature review, or a theoretical essay, plus advancement to doctoral candidacy. In defining a dissertation topic, the student collaborates with their faculty advisor or dissertation advisor (if one is selected) in the choice of a topic for the dissertation.
The dissertation proposal is a comprehensive statement on the extent and nature of the student’s dissertation research interests. Students submit a draft of the proposal to their dissertation advisor between the end of the seventh and middle of the ninth quarters. The student must provide a written copy of the proposal to the faculty committee no later than two weeks prior to the date of the proposal hearing. Committee members could require an earlier deadline (e.g., four weeks before the hearing).
The major components of the proposal are as follows, with some variations across Areas and disciplines:
- A detailed statement of the problem that is to be studied and the context within which it is to be seen. This should include a justification of the importance of the problem on both theoretical and educational grounds.
- A thorough review of the literature pertinent to the research problem. This review should provide proof that the relevant literature in the field has been thoroughly researched. Good research is cumulative; it builds on the thoughts, findings, and mistakes of others.
- its general explanatory interest
- the overall theoretical framework within which this interest is to be pursued
- the model or hypotheses to be tested or the research questions to be answered
- a discussion of the conceptual and operational properties of the variables
- an overview of strategies for collecting appropriate evidence (sampling, instrumentation, data collection, data reduction, data analysis)
- a discussion of how the evidence is to be interpreted (This aspect of the proposal will be somewhat different in fields such as history and philosophy of education.)
- If applicable, students should complete a request for approval of research with human subjects, using the Human Subjects Review Form ( http://humansubjects.stanford.edu/ ). Except for pilot work, the University requires the approval of the Administrative Panel on Human Subjects in Behavioral Science Research before any data can be collected from human subjects.
Registration (i.e., enrollment) is required for any quarter during which a degree requirement is completed, including the dissertation proposal. Refer to the Registration or Enrollment for Milestone Completion section for more details.
As students progress through the program, their interests may change. There is no commitment on the part of the student’s advisor to automatically serve as the dissertation chair. Based on the student’s interests and the dissertation topic, many students approach other GSE professors to serve as the dissertation advisor, if appropriate.
A dissertation proposal committee is comprised of three academic council faculty members, one of whom will serve as the major dissertation advisor. Whether or not the student’s general program advisor serves on the dissertation proposal committee and later the reading committee will depend on the relevance of that faculty member’s expertise to the topic of the dissertation, and their availability. There is no requirement that a program advisor serve, although very often they do. Members of the dissertation proposal committee may be drawn from other area committees within the GSE, from other departments in the University, or from emeriti faculty. At least one person serving on the proposal committee must be from the student’s area committee (CTE, DAPS, SHIPS). All three members must be on the Academic Council; if the student desires the expertise of a non-Academic Council member, it may be possible to petition. After the hearing, a memorandum listing the changes to be made will be written and submitted with the signed proposal cover sheet and a copy of the proposal itself to the Doctoral Programs Officer.
Review and approval of the dissertation proposal occurs normally during the third year. The proposal hearing seeks to review the quality and feasibility of the proposal. The Second-Year Review and the Proposal Hearing are separate milestones and may not occur as part of the same hearing or meeting.
The student and the dissertation advisor are responsible for scheduling a formal meeting or hearing to review the proposal; the student and proposal committee convene for this evaluative period. Normally, all must be present at the meeting either in person or via conference phone call.
At the end of this meeting, the dissertation proposal committee members should sign the Cover Sheet for Dissertation Proposal and indicate their approval or rejection of the proposal. This signed form should be submitted to the Doctoral Programs Officer. If the student is required to make revisions, an addendum is required with the written approval of each member of the committee stating that the proposal has been revised to their satisfaction.
After submitting the Proposal Hearing material to the Doctoral Programs Officer, the student should make arrangements with three faculty members to serve on their Dissertation Reading Committee. The Doctoral Dissertation Reading Committee form should be completed and given to the Doctoral Programs Officer to enter in the University student records system. Note: The proposal hearing committee and the reading committee do not have to be the same three faculty members. Normally, the proposal hearing precedes the designation of a Dissertation Reading Committee, and faculty on either committee may differ (except for the primary dissertation advisor). However, some students may advance to Terminal Graduate Registration (TGR) status before completing their dissertation proposal hearing if they have established a dissertation reading committee. In these cases, it is acceptable for the student to form a reading committee prior to the dissertation proposal hearing. The reading committee then serves as the proposal committee.
The proposal and reading committee forms and related instructions are on the GSE website, under current students>forms.
Printing Credit for Use in GSE Labs
Upon completion of their doctoral dissertation proposal, GSE students are eligible for a $300 printing credit redeemable in any of the GSE computer labs where students are normally charged for print jobs. Only one $300 credit per student will be issued, but it is usable throughout the remainder of her or his doctoral program until the balance is exhausted. The print credit can be used only at the printers in Cubberley basement and CERAS, and cannot be used toward copying.
After submitting the signed dissertation proposal cover sheet to the Doctoral Programs Officer indicating approval (see above), students can submit a HELP SU ticket online at helpsu.stanford.edu to request the credit. When submitting the help ticket, the following should be selected from the drop-down menus for HELP SU:
Request Category : Computer, Handhelds (PDAs), Printers, Servers Request Type : Printer Operating System : (whatever system is used by the student, e.g., Windows XP.)
The help ticket will be routed to the GSE's IT Group for processing; they will in turn notify the student via email when the credit is available.
- Printer-friendly version
Handbook Contents
- Timetable for the Doctoral Degree
- Degree Requirements
- Registration or Enrollment for Milestone Completion
- The Graduate Study Program
- Student Virtual and Teleconference Participation in Hearings
- First Year (3rd Quarter) Review
- Second Year (6th Quarter) Review
- Committee Composition for First- and Second-Year Reviews
- Advancement to Candidacy
- Academic Program Revision
- Dissertation Content
- Dissertation Reading Committee
- University Oral Examination
- Submitting the Dissertation
- Registration and Student Statuses
- Graduate Financial Support
- GSE Courses
- Curriculum Studies and Teacher Education (CTE)
- Developmental and Psychological Sciences (DAPS)
- Learning Sciences and Technology Design (LSTD)
- Race, Inequality, and Language in Education (RILE)
- Social Sciences, Humanities, and Interdisciplinary Policy Studies in Education (SHIPS)
- Contact Information
- Stanford University Honor Code
- Stanford University Fundamental Standard
- Doctoral Programs Degree Progress Checklist
- GSE Open Access Policies
PhD students, please contact

MA POLS and MA/PP students, please contact

EDS, ICE/IEPA, Individually Designed, LDT, MA/JD, MA/MBA students, please contact

Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou
Improving lives through learning

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .

- Schools & departments

Writing your PhD research proposal
Find guidance on how to write your PhD research proposal and a template form for you to use to submit your research proposal.
By asking you for an outline research proposal we hope to get a good picture of your research interests and your understanding of what such research is likely to entail.
The University's application form is designed to enable you to give an overview of your academic experience and qualifications for study at postgraduate level. Your outline research proposal then gives us an idea of the kind of research you want to undertake. This, together with information from your referees, will help us assess whether the Moray House School of Education and Sport would be the appropriate place for you to pursue your research interests.
At the application stage, you are unlikely to be in a position to provide a comprehensive research proposal; the detailed shaping up of a research plan would be done in conjunction with your supervisor(s). But it is important for us to appreciate what you are hoping to investigate, how you plan to carry out the research, and what the results might be expected to contribute to current knowledge and understanding in the relevant academic field(s) of study. In writing your proposal, please indicate any prior academic or employment experience relevant to your planned research.
In your research proposal, please also ensure that you clearly identify the Moray House research cluster your proposal falls under, as well as two to three staff members with expertise in this area. We also encourage you to contact potential supervisors within your area of proposed research before submitting your application to gauge their interest and availability.
How to write your research proposal
The description of your proposed research should consist of 4-5 typed A4 sheets. It can take whatever form seems best, but should include some information about the following:
- The general area within which you wish to conduct research, and why (you might find it helpful to explain what stimulated your interest in your chosen research field, and any study or research in the area that you have already undertaken)
- The kind of research questions that you would hope to address, and why (in explaining what is likely to be the main focus of your research, it may be helpful to indicate, for example, why these issues are of particular concern and the way in which they relate to existing literature)
- The sources of information and type of research methods you plan to use (for example, how you plan to collect your data, which sources you will be targeting and how you will access these data sources).
In addition to the above, please include any comments you are able to make concerning:
- The approach that you will take to analyse your research data
- The general timetable you would follow for carrying out and writing up your research
- Any plans you may have for undertaking fieldwork away from Edinburgh
- Any problems that might be anticipated in carrying out your proposed research
Please note: This guidance applies to all candidates, except those applying to conduct PhD research as part of a larger, already established research project (for example, in the Institute for Sport, Physical Education & Health Sciences).
In this case, you should provide a two- to three-page description of a research project you have undertaken, to complement information in the application form. If you are in any doubt as to what is appropriate, please contact us:
Email: Education@[email protected]
All doctoral proposals submitted as part of an application will be run through plagiarism detection software.
Template form for your research proposal
All applicants for a PhD or MSc by Research must submit a research proposal as part of their application. Applicants must use the template form below for their research proposal. This research proposal should then be submitted online as part of your application. Please use Calibri size 11 font size and do not change the paragraph spacing (single, with 6pt after each paragraph) or the page margins.
- How to Write a Great PhD Research Proposal | FindAPhD.com
How to Write a Great PhD Research Proposal
Written by Mark Bennett
You'll need to write a research proposal if you're submitting your own project plan as part of a PhD application. A good PhD proposal outlines the scope and significance of your topic and explains how you plan to research it.
It's helpful to think about the proposal like this: if the rest of your application explains your ability to do a PhD, the proposal demonstrates the actual PhD you plan to do. Of course, being able to effectively plan and explain a research project is one of the key qualifications for being able to complete one, which is why the proposal is such an important part of the PhD application process.
Thankfully, the secret to writing a good research proposal isn't complicated. It's simply a case of understanding what the proposal is for, what it needs to do and how it needs to be put together.
On this page
What is a phd research proposal.
First things first, do you need a research proposal for your PhD? It depends on the kind of project you want to do:
- If your PhD is advertised by a university, you probably won't need to submit a research proposal for it. The broad aims and objectives for your PhD will already be defined: you just need to prove you're the right person to do it.
- But, if you're proposing your own research topic to research within a university's PhD programme, you will need to write a proposal for it (the clue is in the word "proposing")
As a rule, advertised PhDs are very common in STEM subjects, whereas Arts, Humanities and Social Science students are more likely to propose their own PhDs.
Some PhD programmes actually wait and ask students to develop their research proposal during the degree (usually after they've completed some initial training). This is normal in the USA , but it's becoming more common for some UKRI-funded UK PhDs.
For the purposes of this guide we're going to assume that you do need to write a good research proposal for your PhD application. So let's explore what's involved in that.
Pick the right programme for you
There are lots of choices, let us help you to make the right one. Sign up to our weekly newsletter for the latest advice and guidance from our team of experts.
What should a research proposal for PhD admission include?
It's natural to be a little intimidated at the thought of structuring a PhD proposal, particularly if you've never written anything like this before.
But here's the thing: a research proposal isn't a fiendish test designed to catch you out and stop you ever doing a PhD. It's actually much more boring than that.
All a research proposal really is is a document that demonstrates three things:
- Your PhD is worthwhile
- Your PhD is feasible
- You are capable of completing it at this university
Or to put it even more simply: the PhD is worth doing, it's doable and you can do it.
Demonstrate your PhD is worthwhile (the what and the why)
A successful PhD project has to make a significant original contribution to knowledge. If it doesn't, it won't meet the criteria for a doctoral degree and will probably fail the viva exam .
Your PhD proposal itself doesn't have to meet those criteria (or pass a viva!) but it does need to indicate that your PhD project eventually will.
It does that by first demonstrating that your research topic is original. That means nobody else has studied this same topic (or one very similar) before.
There are all sorts of ways a PhD can be original. You might examine new data or primary sources, to look at existing material from a fresh perspective, or deal with the impact of new events. It doesn't matter how your project is original, so long as your proposal is really specific about what makes it original.
You also need to explain why your proposed research will be academically significant. To do this properly, you'll need to acknowledge relevant existing scholarship and explain how your research will relate to it. You don't need to be exhaustive at this point, but you should be able to show how your PhD will contribute to its field and – ideally – indicate some of the gaps in knowledge it will aim to fill.
The final step in demonstrating your PhD is worthwhile is to suggest what will become possible as a result of your research. How could other researchers use or build upon your results? What might closing those gaps in academic knowledge mean for audiences outside the unviversity?
Demonstrate your PhD is feasible (the how)
It isn't enough just to show that your research is worth doing; it also needs to actually be doable.
The length of a full-time PhD is around three to four years in most countries (it's longer in for a PhD in the USA , but you don't spend all that time doing research).
Three years may seem like a long time, but researching a PhD is a lot of work and you'll probably spend at least some of your time on other activities like teaching, conference presentations or even publication.
So, one of the things your proposal needs to do is demonstrate that your project is feasible: that it fits within the scope of a PhD.
The most important criteria for this is to be clear about what you plan to do. It should be obvious from your proposal what the scope of your project is – what is and isn't included within it.
You also need to outline how you plan to go about your research. Where will you start and what order do you expect to proceed in? Is the logic for that obvious? If not, it's probably a good idea to explain it.
Finally, you need to explain the methodology you plan to use. This could include techniques for collecting data and sources, theoretical perspectives for analysing them – or both. You may also need to detail specific equipment you expect to use or fieldwork you'll need to undertake (including trips to archives or other external resources).
None of this needs to be exact or completely final. The key word here is 'plan' – but you do need to have one.
Demonstrate that you can complete it at this university (the who and the where)
So far we've thought about the project itself: what makes it worth doing and how it's going to get done. But your proposal also needs to address the who and the where: why are you the right person to carry out this research, and why do you want to do it at this particular university?
The first part of this is easier than it probably looks. Writing a good research proposal demonstrates enthusiasm for your project much more convincingly than simply saying you're very interested in it (a classic case of 'show, don't tell').
You also don't need to repeat your grades and academic achievements (other parts of your PhD application will cover those). Instead, try to underline experiences that relate to this project. Has a particular module or Masters dissertation topic prepared you with useful subject knowledge or methodological skills? If so, highlight it.
It's also fine, within reason, to be honest about the skills you don't have and to identify your training needs. This shows you're being practical about your project and thinking seriously about what it will require. Just make sure you can realistically acquire the skills and training you need within the time available (this goes back to the feasibility).
Showing your project is a good fit for the university is also relatively simple. There should already be some reasons why you've chosen this university for your PhD so make sure you explain what they are. Perhaps there's a particular supervisor you'd like to work with , or facilities and resources your research could use. The key is to emphasise the fit between the project and the university – so don't just say you want to research there because it's highly ranked .
PhD research proposal structure
Hopefully the above sections have given you a few ideas for the things your proposal needs to include. Let's be honest though, the scariest thing about a proposal isn't deciding what to include: it's actually writing it.
But, if we flip that on its head, we remember that all a research proposal really is is a piece of writing that follows a pretty standard format. And that's a lot less scary.
Research proposal structure
Because proposals for PhD all have to do the same things, they mostly follow a similar structure. Yours will probably go something like this:
- Title – Keep it simple and descriptive: the clever alliteration and quotes can come later when you write up your thesis. For now, you just want the person reading this to know exactly what your research is about and, perhaps, which prospective supervisor to send it to.
- Overview – Start by defining your research question (the what) and explaining how it contributes to current work in your field (the why). This is also a good place to reference one or two pieces of scholarship: the full literature review can wait until your PhD begins, but you should show that you have some understanding of relevant academic research.
- Methodology – Make sure the reader understands the practical and / or theoretical approaches you'll take to your research. What data will you collect, how will you collect it and how will you analyse it? Ideally refer to relevant research methods and models. It's also a good idea to provide some sort of roadmap for how you'll go about things. Don't worry, you can change it later (and you will).
- Outcomes and impact – What will exist as a result of your research (other than just another PhD on a library shelf) and what will it make possible? You don't need to identify every specific outcome from your project (blue sky research is fine) but you should think about what some potential outcomes might be.
You probably won't need to include a specific conclusion - it should be obvious, by now, what your project is doing, how you're going to do it and why that matters. A quick summary sentence is fine though, if you think it will help.
Writing tips
Being able to effectively communicate academic concepts, ideas and results is a key skill for PhD research in all subjects . Think of your proposal as a chance to demonstrate this.
The good news is that the key principles of good proposal writing aren't that different from other work you've probably done as a Bachelors or Masters student:
- Be clear – The person reading your research proposal should know exactly what it is you're proposing to research, with no room for ambiguity and confusion. This is important on a practical level (they need to know where to send it) but it's also important to the success of your application: a confusing proposal suggests a confused project. Try having a friend read it and ask them "do you know what it is I'm proposing to do here?" (even if they don't understand the details).
- Be concise – You will have more ideas than you can include in your proposal. That's fine. Choose the best ones and leave the others for your interview .
- be coherent – Follow something like the structure above. Don't start with your methodology, then say what it is you want to research.
How long should a PhD research proposal be?
Honestly? As long as the university asks for it to be. Most will have guidelines and you should follow them closely if so.
If you honestly can't find a suggested word count for your proposal, then consider asking a prospective supervisor . If you still aren't sure, aim for somewhere between 1,000-2,000 words .
As a very general rule, Arts, Humanities and Social Sciences are a bit longer than STEM proposals (and a lot of STEM students don't have to write one anyway, as we've explained).

Research proposal for PhD admission - dos and don'ts
Research proposals are a popular topic over on the FindAPhD blog , where we've shared stories of how students wrote theirs , along with mistakes to avoid and a counter-intuitive look at the things a PhD proposal doesn't actually need to do .
Here are a few general tips and mistakes to avoid:
#1 Give yourself enough time to do a good job
Preparing to write a PhD proposal takes time and effort. None of this is wasted as the process of evaluating and framing your ideas for a proposal will improve your project plan immensely. So will the need to decide which ideas to include.
But you need time and space to do that, so make sure you get it. How long it will take to write your PhD proposal is heavily dependent on your personal working style, but you'll likely need to give yourself at least a few weeks to do a good job.
#2 Set out to impress
A good proposal isn't a begging letter. You're approaching the university with a great idea that's going to contribute to and enhance their research. Be honest, be realistic, but don't be unnecessarily humble. They should want you and your project.
#3 Demonstrate original thinking!
You may not need to present original research findings yet, but your proposal does need to present original ideas – and it should be clear why and how those ideas are original.
Make sure you indicate how your project is going to expand, enhance or even correct existing work in your field. Remember that making an "original contribution to knowledge" is a key part of what a PhD is .
#1 Send the same proposal to several universities
A good proposal needs to explain why you want to do your research at a particular university. That's a big part of the feasibility (the fit between project, person and place) and methodology (how are you going to use this university's equipment and archives; when and where will you need to travel).
It's OK to apply to more than one university in parallel, but, in that case, you're writing research proposals .
#2 Use online proposal templates (without evaluating them first!)
It can be tempting to search for PhD proposal samples on the internet, but make sure you evaluate what you find. Some websites may host old proposals from previous PhD students, but there's no way of knowing how relevant these are to your subject and university – or if they were even successful! More 'generic' research proposal examples can offer guidance, but they won't be tailored to your specific project.
The best place to look for a PhD proposal sample is your university. Consider asking your supervisor if they can share a good proposal from a previous student in your subject – or put you in touch with a current student you can ask.
#3 Confuse the proposal with the PhD
We've covered this on the blog , but it's simple enough to include here too.
You're setting out to do a PhD, but you (probably!) haven't done one yet. So you don't need to include research findings, in-depth analysis or a comprehesive literature review. You need to make a case for the research and analysis you want to do.
#4 Ignore your university's help and guidance
The advice on this page is necessarily quite general. We're considering adding guides to writing PhD proposals in specific subjects in future but, for now, the best place to get specific advice for your academic field is probably the university you're applying to.
See if you can get some subject-specific tips by contacting a supervisor , or just checking with the admissions team for your department.
And remember: if they give you a structure and a word count, stick to it.
Ready to apply for a PhD?
Find out what PhD opportunities are currently available with our FindAPhD course listings .
Our postgrad newsletter shares courses, funding news, stories and advice
You may also like....

We've answered some of the most frequently asked questions about PhDs, covering course types, applications, funding and the benefits of further study.

Getting ready to apply for a PhD? Our guides explain research proposals, references and entry tests for doctoral programmes.

Our guide explains how to contact a potential PhD supervisor to discuss your proposal or ideas with them before applying.

A checklist of the things you'll need to do when making an international PhD application, from meeting the entry requirements to sorting out your visa.
FindAPhD. Copyright 2005-2024 All rights reserved.
Unknown ( change )
Have you got time to answer some quick questions about PhD study?
Select your nearest city
You haven’t completed your profile yet. To get the most out of FindAPhD, finish your profile and receive these benefits:
- Monthly chance to win one of ten £10 Amazon vouchers ; winners will be notified every month.*
- The latest PhD projects delivered straight to your inbox
- Access to our £6,000 scholarship competition
- Weekly newsletter with funding opportunities, research proposal tips and much more
- Early access to our physical and virtual postgraduate study fairs
Or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
*Offer only available for the duration of your active subscription, and subject to change. You MUST claim your prize within 72 hours, if not we will redraw.

Do you want hassle-free information and advice?
Create your FindAPhD account and sign up to our newsletter:
- Find out about funding opportunities and application tips
- Receive weekly advice, student stories and the latest PhD news
- Hear about our upcoming study fairs
- Save your favourite projects, track enquiries and get personalised subject updates

Create your account
Looking to list your PhD opportunities? Log in here .

Research Proposal Example/Sample
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template
If you’re getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals , you’ve come to the right place.
In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals , one for a Master’s-level project, and one for a PhD-level dissertation. We also start off by unpacking our free research proposal template and discussing the four core sections of a research proposal, so that you have a clear understanding of the basics before diving into the actual proposals.
- Research proposal example/sample – Master’s-level (PDF/Word)
- Research proposal example/sample – PhD-level (PDF/Word)
- Proposal template (Fully editable)
If you’re working on a research proposal for a dissertation or thesis, you may also find the following useful:
- Research Proposal Bootcamp : Learn how to write a research proposal as efficiently and effectively as possible
- 1:1 Proposal Coaching : Get hands-on help with your research proposal

PS – If you’re working on a dissertation, be sure to also check out our collection of dissertation and thesis examples here .
FAQ: Research Proposal Example
Research proposal example: frequently asked questions, are the sample proposals real.
Yes. The proposals are real and were approved by the respective universities.
Can I copy one of these proposals for my own research?
As we discuss in the video, every research proposal will be slightly different, depending on the university’s unique requirements, as well as the nature of the research itself. Therefore, you’ll need to tailor your research proposal to suit your specific context.
You can learn more about the basics of writing a research proposal here .
How do I get the research proposal template?
You can access our free proposal template here .
Is the proposal template really free?
Yes. There is no cost for the proposal template and you are free to use it as a foundation for your research proposal.
Where can I learn more about proposal writing?
For self-directed learners, our Research Proposal Bootcamp is a great starting point.
For students that want hands-on guidance, our private coaching service is recommended.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
14 Comments
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a PhD in Management at Altantic International University. I checked on the coaching services, but it indicates that it’s not available in my area. I am in South Sudan. My proposed topic is: “Leadership Behavior in Local Government Governance Ecosystem and Service Delivery Effectiveness in Post Conflict Districts of Northern Uganda”. I will appreciate your guidance and support
GRADCOCH is very grateful motivated and helpful for all students etc. it is very accorporated and provide easy access way strongly agree from GRADCOCH.
Proposal research departemet management
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a masters in Analysis of w heat commercialisation by small holders householdrs at Hawassa International University. I will appreciate your guidance and support
please provide a attractive proposal about foreign universities .It would be your highness.
comparative constitutional law
Kindly guide me through writing a good proposal on the thesis topic; Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Financial Inclusion in Nigeria. Thank you
Kindly help me write a research proposal on the topic of impacts of artisanal gold panning on the environment
I am in the process of research proposal for my Master of Art with a topic : “factors influence on first-year students’s academic adjustment”. I am absorbing in GRADCOACH and interested in such proposal sample. However, it is great for me to learn and seeking for more new updated proposal framework from GRADCAOCH.
Kindly help me write a research proposal on the effectiveness of junior call on prevention of theft
kindly assist me in writing the proposal in psychology education
Please,Kindly assist my in my phd thesis writing on personal and socio cultural factors as determinate of family planning adoption
I’m interested to apply for a mhil program in crop production. Please need assistance in proposal format.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
How to write a research proposal
What is a research proposal.
A research proposal should present your idea or question and expected outcomes with clarity and definition – the what.
It should also make a case for why your question is significant and what value it will bring to your discipline – the why.
What it shouldn't do is answer the question – that's what your research will do.
Why is it important?
Research proposals are significant because Another reason why it formally outlines your intended research. Which means you need to provide details on how you will go about your research, including:
- your approach and methodology
- timeline and feasibility
- all other considerations needed to progress your research, such as resources.
Think of it as a tool that will help you clarify your idea and make conducting your research easier.
How long should it be?
Usually no more than 2000 words, but check the requirements of your degree, and your supervisor or research coordinator.
Presenting your idea clearly and concisely demonstrates that you can write this way – an attribute of a potential research candidate that is valued by assessors.
What should it include?
Project title.
Your title should clearly indicate what your proposed research is about.
Research supervisor
State the name, department and faculty or school of the academic who has agreed to supervise you. Rest assured, your research supervisor will work with you to refine your research proposal ahead of submission to ensure it meets the needs of your discipline.
Proposed mode of research
Describe your proposed mode of research. Which may be closely linked to your discipline, and is where you will describe the style or format of your research, e.g. data, field research, composition, written work, social performance and mixed media etc.
This is not required for research in the sciences, but your research supervisor will be able to guide you on discipline-specific requirements.
Aims and objectives
What are you trying to achieve with your research? What is the purpose? This section should reference why you're applying for a research degree. Are you addressing a gap in the current research? Do you want to look at a theory more closely and test it out? Is there something you're trying to prove or disprove? To help you clarify this, think about the potential outcome of your research if you were successful – that is your aim. Make sure that this is a focused statement.
Your objectives will be your aim broken down – the steps to achieving the intended outcome. They are the smaller proof points that will underpin your research's purpose. Be logical in the order of how you present these so that each succeeds the previous, i.e. if you need to achieve 'a' before 'b' before 'c', then make sure you order your objectives a, b, c.
A concise summary of what your research is about. It outlines the key aspects of what you will investigate as well as the expected outcomes. It briefly covers the what, why and how of your research.
A good way to evaluate if you have written a strong synopsis, is to get somebody to read it without reading the rest of your research proposal. Would they know what your research is about?
Now that you have your question clarified, it is time to explain the why. Here, you need to demonstrate an understanding of the current research climate in your area of interest.
Providing context around your research topic through a literature review will show the assessor that you understand current dialogue around your research, and what is published.
Demonstrate you have a strong understanding of the key topics, significant studies and notable researchers in your area of research and how these have contributed to the current landscape.
Expected research contribution
In this section, you should consider the following:
- Why is your research question or hypothesis worth asking?
- How is the current research lacking or falling short?
- What impact will your research have on the discipline?
- Will you be extending an area of knowledge, applying it to new contexts, solving a problem, testing a theory, or challenging an existing one?
- Establish why your research is important by convincing your audience there is a gap.
- What will be the outcome of your research contribution?
- Demonstrate both your current level of knowledge and how the pursuit of your question or hypothesis will create a new understanding and generate new information.
- Show how your research is innovative and original.
Draw links between your research and the faculty or school you are applying at, and explain why you have chosen your supervisor, and what research have they or their school done to reinforce and support your own work. Cite these reasons to demonstrate how your research will benefit and contribute to the current body of knowledge.
Proposed methodology
Provide an overview of the methodology and techniques you will use to conduct your research. Cover what materials and equipment you will use, what theoretical frameworks will you draw on, and how will you collect data.
Highlight why you have chosen this particular methodology, but also why others may not have been as suitable. You need to demonstrate that you have put thought into your approach and why it's the most appropriate way to carry out your research.
It should also highlight potential limitations you anticipate, feasibility within time and other constraints, ethical considerations and how you will address these, as well as general resources.
A work plan is a critical component of your research proposal because it indicates the feasibility of completion within the timeframe and supports you in achieving your objectives throughout your degree.
Consider the milestones you aim to achieve at each stage of your research. A PhD or master's degree by research can take two to four years of full-time study to complete. It might be helpful to offer year one in detail and the following years in broader terms. Ultimately you have to show that your research is likely to be both original and finished – and that you understand the time involved.
Provide details of the resources you will need to carry out your research project. Consider equipment, fieldwork expenses, travel and a proposed budget, to indicate how realistic your research proposal is in terms of financial requirements and whether any adjustments are needed.
Bibliography
Provide a list of references that you've made throughout your research proposal.
Apply for postgraduate study
New hdr curriculum, find a supervisor.
Search by keyword, topic, location, or supervisor name
- 1800 SYD UNI ( 1800 793 864 )
- or +61 2 8627 1444
- Open 9am to 5pm, Monday to Friday
- Student Centre Level 3 Jane Foss Russell Building Darlington Campus
Scholarships
Research areas.
Our breadth of expertise across our faculties and schools is supported by deep disciplinary knowledge. We have significant capability in more than 20 major areas of research.
Research facilities

- Faculty of Social Sciences
- School of Education
- Research degrees
Writing a research proposal
As part of the process of applying for a research degree, you will need to prepare an outline of your proposed research. This must be 5-10 pages long (font 11pt minimum) excluding the bibliography.
Please see our guidance on what to include below:
| Key elements | Content |
|---|---|
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
- Student Services Online
- Class search
- Student email
- Change my password
- MyCDES+ (job board)
- Course outlines
- Learning essentials
- Libraries and Learning Services
- Forms, policies and guidelines
- Campus Card
- Enrol in courses
- Postgraduate students
- Summer school
- AskAuckland
- Student Hubs
- Student IT Hub
- Student Health and Counselling
- Harassment, bullying, sexual assault and other violence
- Complaints and incidents
- Career Development and Employability Services (CDES)
- Ratonga Hauātanga Tauira | Student Disability Services (SDS)
- Rainbow support
- Emergency information
- Report concerns, incidents and hazards
- Health and safety topics
- Staff email
- Staff intranet
- ResearchHub
- PeopleSoft HR
- Forms register
- Careers at the University
- Education Office
- Early childhood centres
- University Calendar
- Opportunities
- Update your details
- Make a donation
- Publications
- Photo galleries
- Video and audio
- Career services
- Virtual Book Club
- Library services
- Alumni benefits
- Office contact details
- Alumni and friends on social media
- No events scheduled for today You have no more events scheduled for today
- Next event:
- Show {0} earlier events Show {0} earlier event
- Event_Time Event_Name Event_Description
- My Library Account
- Change Password
- Edit Profile
- My GPA Grade Point Average About your GPA GPA not available Why can't I see my GPA?
- My Progress
- Points Required Completed points My Progress Progress not available All done!
- Student hubs
- Health and counselling
- All support
- Health, safety and well-being
Breadcrumbs List.
- Education and Social Work
- Study with us
- Study options
- Doctoral programmes
- You are currently on: Research proposal guidelines
Research proposal guidelines
Read our guidelines for how to plan and structure your PhD research proposal during your provisional year.
Research proposal facts Length : 20-30 pages (not more than 10,000 words) Due date : 9-10 months from your registration date Reviewed by : Two academics appointed by your supervisor
What is a research proposal?
A full research proposal contains the following sections:
- A summary or abstract of the proposal
- A statement of the issue, problem, question or hypothesis and its importance and significance
- A review of significant prior research (Literature Review)
- Methods for data collection and analysis
- Ethical considerations
- Limitations
- Key assumptions
- References used in the proposal
Different academic disciplines have different styles in how they structure this material.
For a detailed breakdown of each section, visit Structuring your research proposal .
Please check with your supervisors as to the template they want you to use.
For more details about the research proposal development please read the Generic Guidelines for Full Doctoral Research Proposals .
Building your ideas
A research proposal is not simply a list of good ideas worth researching. It should detail:
- Why the idea is good
- How it fits with previous research
- How it will contribute to knowledge
- How you will explore your ideas (your planned research approach, methodologies and analysis techniques)
The transition from thesis idea to well-defined proposal is often difficult. It may take several months or more. During this period, you should:
- Explore your field of interest
- Read extensively around the area
- Select possible topics
- Formulate research questions
This is independent study that may not require strong or direct supervision. However, once you have identified the key questions you want to explore, it’s time to write the research proposal. For this, you should work closely with your supervisor.
More than a plan
Your proposal is your research and thesis writing roadmap. It also provides your supervisor and other faculty staff with information they can review, suggest improvements (if needed) and approve.
If your proposal is detailed and explicit, this will put you on the right path to conducting proper research, documenting it clearly and producing a final thesis with a high chance of acceptance.
Be aware that your first proposal is often not your final one. You will undergo a process of refining and revision, incorporating critical comments and suggestions from your supervisors and other academic staff. These revised drafts will be further reviewed before final submission to the faculty.
Think about your final thesis
When developing your proposal, it’s useful to remind yourself of what the examiners will be looking for in the final completed thesis.
A good thesis will contain the following elements:
- A distinct contribution to knowledge
- Evidence of the discovery of new knowledge or the exercise of independent judgement
- Literary presentation
- Original work of merit worth of publication
- Evidence of competence in independent research
- Understanding of concepts, issues, techniques and methodology
- Critical use of published work and source materials
Write for a broader audience
All doctorate research topics must be related to one or more specialist areas, including published literature and established methodologies.
However, that does not mean you should write for an informed niche audience. Since the proposal must receive the approval of the Faculty of Education and Social Work, it should contain enough detail to be understood by members of staff whose expertise may not be in the literature and methodology areas you have selected.
Related links
- Doctoral policies and guidelines

Info for Morgan State University
- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty & Staff
- Parents & Families
- Alumni & Friends
- For the Media
Search Morgan State University
Commonly searched pages.
- Payment Plan
- Housing Application
- Comptroller
- Advanced Studies, Leadership, and Policy
- Assessment, Evaluation, and Research
- Community College Leadership
- Comparative and International Education
- Higher Education and Student Affairs
- Mathematics & Science Education
- Urban Educational Leadership
- PhD in Education - Overview
- Program Delivery
The Ph.D. in Education equips students to systematically examine the theoretical and practical challenges evident across the P-20 educational pipeline to address the issue of inequity. The degree program will prepare individuals for careers in academia, research, and policy centers, as well as for high-level administration and curricular positions at educational institutions and agencies.
The program offers seven concentrations:
- Comparative and International Education
- Higher Education Leadership
- Mathematics Education
- Science Education
The educational objectives for the PhD in Education are the following:
- To advance research on inequity issues within the full P-20 educational pipeline.
- To prepare students to use original and existing research to transform educational practice.
- To equip future educational researchers with innovative teaching experience and cutting-edge transdisciplinary research experience to become attractive job candidates on the academic market.
- To prepare candidates to create a collaborative learning community that integrates all the various educational contexts.
- To prepare candidates to be critical thinkers who focus on leadership, policy, ethics, and social justice.
Candidates for the PhD in Education degree must complete a minimum of 54 academic credit hours, pass the comprehensive exam, and submit and successfully defend a research-based dissertation. All students in the program will be expected to complete academic core and research courses of 27 credits and concentration courses of 27 credits. The concentration courses are presented on the the relevant pages and in the PhD Program Handbook .
The Core 27 credits consist of the following:
Academic Core (9 Credits):
- ASLP 600 Introduction to Doctoral Studies and Academic Writing (3)
- ASLP 640 Race and Public Policy in Education (3)
- ASLP 642 Equity and Social Justice in Education (3)
Research (15 Credits)
- ASLP 620 Introduction to Educational Research (3)
- ASLP 700 Methods of Inquiry (3)
- ASLP 710 Quantitative Research Methods (3)
- ASLP 712 Qualitative Research Methods (3)
- *Students will complete an additional 3 credits of advanced research electives related to their chosen methodology.
Dissertation (3 credits)
- ASLP 997/998 (3)
The department offers different delivery options for each concentration. For a full listing please click here .
Students in concentration areas that offer both the High and Low Residency option will be required to select their delivery mode upon admission into the program. Students who wish to switch their delivery option will need to make a formal request to the program direction with an acceptable reason.
Prospective students should complete this brief interest form to be connected to a faculty member for more information.
Admissions Deadlines:
- Priority deadline for those seeking graduate student funding : January 15
- Assessment, Evaluation, and Research: March 1
- Community College Leadership: July 1
- Comparative and International Education: March 1
- Higher Education Leadership: March 1
- Mathematics Education: July 1
- Science Education: July 1
- Urban Educational Leadership: March 1
The School of Graduate Studies coordinates the application process.
Our program offers three types of funding:
- Graduate Research Assistantships
- Graduate Teaching Assistantships
- Tuition Awards
Many of our students also leverage their Tuition Remission benefits from local institutions like the USM schools , JHU , or Morgan State . Tuition Remission is determined and coordinated by your institution. We encourage you to speak with your HR representative about how to use these benefits.
Contact Information
Dr. Frimpomaa Ampaw Chair Department of Advanced Studies, Leadership and Policy Banneker Building #315J
P: (443) 885-1908 E: [email protected]
Interested in Our Programs? Please contact us: https://forms.gle/YU6U6CcEDYyhSraj8

- Research Beacons
- Research Community
- Research Institutes and Centres
- Spotlight on Research
- Research News & Events
- Graduate Research Academy
- Research Development Office
- MaynoothWorks
- Researcher Directory
Undergraduate Studies
- Level 8 Degrees
- Open Days | Events
- Guidance Counsellors
- Visit Maynooth University
- How to Apply | CAO
- A Maynooth Education
- Prospectus & Booklets
- Scholarships
- Certificates and Short Courses
Postgraduate Studies
- Taught Master's, Diplomas and Certificates
- Research Programmes
- Micro-credentials
- Springboard Courses
- Fees, Funding & Scholarships
- How to Apply for a Postgraduate Programme
International
- The Maynooth Student Experience
- Exchange Incoming (ERASMUS and Study Abroad)
- Study Abroad Incoming
- Summer and Tailored Programmes
- Prospective Full Degree Students
- Go Abroad with Maynooth
- Pre-Arrival & Orientation
Search form
Maynooth university department of education.
- Education /
- Our Courses
Qualification : PHILOSOPHIAE DOCTOR DEGREE
Award Type and NFQ level : RESEARCH PH.D. (10)
CAO/PAC code : MH02G (FT), MH03G (PT)
CAO Points :
Closing Date : 30 June 2024
View FETAC details

- Entry Requirements
- Research Interest
- Course Structure
- Career Options
- How to Apply
The Structured PhD in Education is a research degree that supports students in engaging in research at the highest academic level. Students work with their supervisors to develop a substantive piece of research that makes an original contribution to knowledge in the field and tradition of educational research.
Minimum 2.1 degree (BA or MA/M.Ed ) or international equivalent in Education or a cognate area, and a proposal for original research that is accepted by the Department. Students undertake 30 credits of modules that support their research. Generally, students without a Masters undertake 60 credits of modules. Studies can be undertaken on a part-time or full-time basis, and credit requirements are the same for both pathways.
IELTS: 6.5 minimum overall score
TOEFL (Paper based test): 585
TOEFL (Internet based test): 95
PTE (Pearson): 62
Maynooth Universitys TOEFL code is 8850
Course Duration: 3-4 years full-time, 5-6 years part-time
The Department of Education at Maynooth University is an exciting place in which to do postgraduate research. We have an excellent international profile and we are part of a wider research community that engages in research right across the educational continuum. Our staff and students also engage in inter-disciplinary and inter-institutional research. We have a large postgraduate research community, and the diversity of approaches and interests and our pluralistic and collaborative ethos makes it a welcoming and dynamic space for students. The atmosphere is one of intellectual vibrancy and creativity, grounded in excellent research. You can learn more about staff's interests here and about our postgraduate community here .
Students are free to take up research in any area of educational research that interests them. However, a member of staff with relevant expertise must be available to supervise the project. Students may find it helpful to reflect on a research question and locate a provisional area for research prior to contacting the Programme Director/PhD Programme Co-Ordinator. Inter-disciplinary PhDs are also welcomed and cross-departmental co-supervisory arrangements can be negotiated.
The purpose of PhD study is to develop a work of independent and original research. To support this, and ensure that students are part of a wider community of knowledge exchange, research, scholarship and dialogue, Maynooth University research degrees area. Structured PhD students must register for a minimum of 30 credits in pass/fail modules. 15 credits will be in subject-specific modules (2 of which are mandatory in the first year) and 15 credits will be in generic/transferable skills modules. These are selected in close consultation with the students supervisor. Students will write a thesis of approximately 90,000-100,000 words.
Course duration:3-4 years full-time, 5-6 years part-time
Course duration: 3-4 years Full-time, 5-6 years Part-time
More detail in Course Finder