Home ➔ Essay Structure ➔ Body Paragraphs ➔ Topic Sentence ➔ What is a bridge sentence in an essay?

What is a bridge sentence in an essay?
A bridge in an essay is a tool that helps the author to connect ideas and to transition smoothly from one point to another. It can be used to clarify a point that has been made, to introduce a new idea, or to sum up the main points of the essay. A well-written bridge can help keep the reader’s attention focused on the essay and make the writing style more fluid.
Let’s refresh our memory a bit regarding the essay structure :
The first section is the introductory paragraph , in which you present your thesis statement or main argument. The body paragraphs are where you develop your argument, and each body paragraph should focus on a single point. The conclusion is where you wrap up your essay, and it should rephrase your thesis statement.
A bridge sentence —also known as a bridge statement—is a type of topic sentence typically found and used at the start of a body paragraph. The key functions of this transition sentence are to show the direction of the paragraph’s main idea and how it is related to the previous paragraph.
There are a few things to keep in mind when writing a bridge sentence:
- Make sure the bridge is relevant to the two ideas or concepts you are connecting.
- Keep the bridge brief and to the point.
- Use such words and phrases that will help create a smooth transition between ideas.
Bridge sentence types and examples
Among bridge sentences, three main types are usually used: a classic bridge sentence, a question-answer bridge, and a complication bridge. They all have three things in common:
- The use of a “pointer” word that directs the reader’s attention to the previous paragraph
- A part of the sentence that serves as a reference to that previous point
- And a part that is related to the topic of the current paragraph
These three things are the main elements of most bridge sentences.
Now let’s look at each type’s examples to see the common points and the differences. First, we will present the last sentence of a previous paragraph and then a color-coded bridge of each type.
Let’s consider this as the last sentence of our previous paragraph of an essay that discusses various printers:
The inkjet printer is the most popular type of printer for home use. It is less expensive than a laser printer and produces good-quality prints.
Here’s an example of a classic bridge sentence:
This advantage makes an inkjet printer one of the best choices for home offices. But besides reasonable prices and printing quality , it is also worth mentioning how easy it is to use inkjet printers .
We start by pointing to the previous passage (this advantage) and then introduce the topic for a new paragraph (how easy it is to use).
Here’s an example of a question-answer bridge:
But does this price and quality advantage make inkjet printers the best choice? Surely not, because laser printers would not be on the market in such a case. When comparing the two, inkjet printers lose in terms of printing speed and ink usage .
This example has a question that serves as the “pointer” to the previous paragraph. And the answer to this question introduces the main point of the current paragraph.
And here’s an example of a complication bridge:
Such an advantage of inkjet printers might be decisive for many; however, inkjet printers are not as fast as laser printers, and they use more ink .
As you can see, the example above has a “pointer” word (such) that refers to the previous paragraph. It has a transition word (however) that signals to the reader that it is not that simple. Then, it also provides a reference to the previous paragraph (the inkjet printer’s better price advantage), and it states the main point of the current paragraph (laser printers are faster and more economical).
Ways of making logical connections and transitions
There are many ways in which you can connect two ideas. It depends on the essay types : whether you are comparing, arguing, classifying things, etc. Let’s take a look at some schematic examples:
- Making an example: (The next point) clearly illustrates that (the previous point) by…
- Showing cause-effect relationship: (The previous point) led to / has allowed/ directly caused / was the reason / results in (the next point)…
- Giving a counterexample: Even though (the previous) is normally the case, (the next point)…
- Emphasizing a point: (The previous point) is essential / is vital / cannot be omitted because (the next point)…
- Contrasting: (The previous point) differs from (the next point) in how…
- Comparing: (The previous point) is similar to / can be compared with / has some similarities with (the next point)…
- Sequencing: (The previous point) comes before / comes after / is the next (the next point)…
- Proving: (The previous point) means / indicates / proves / implicates that (the next point)…
- Complicating: Yes, (the previous point), but because of that, (the next point)…
- Adding precision: The researchers explain in more detail (the previous point) in their paper regarding (the next point)…
- Clarifying: Yes, (the previous point) is sometimes the case, but it doesn’t mean (the next point)…
Transitional keywords to use
Words that can help you introduce the next paragraph are called “transitional keywords.” Here is a list of some common transitional keywords:
- accordingly, as a result, consequently, for this reason, hence, subsequently, therefore
- according to, as previously stated, before, initially, formerly, earlier, previously
- finally, in conclusion, in brief, in sum, in summary, on the whole, thus, in short
- also, similarly to, likewise, in the same way, as well as, too, much like
- conversely, alternatively, on the other hand, by contrast, in contrast, on the contrary, in contrast to, opposite to, but, however
- for instance, for example, such as, take the case of, to illustrate, imagine, to show you what I mean, suppose that
- according to, as a result of, because, due to, for this reason, since, therefore, thus
- after, afterward, before, subsequently, then, while, whenever
- above, adjacent, below, beyond, here, in front of, nearby, opposite
Key takeaways
- When writing an essay , it is crucial to ensure a logical connection and a smooth flow between the paragraphs.
- This logical connection can be created in various ways, for example, by using a bridge statement.
- A bridge is an opening statement that connects two ideas by “pointing” to the previous paragraph and introducing the topic of the next paragraph.
- There are many ways to create a logical connection between two ideas, and it depends on the type of essay you are writing.
Now that you know what a bridge sentence is and how to use it, try incorporating it into your next essay!
- California State University Northridge – Transitional Words and Phrases
- The College of Saint Rose – Transition Sentences
- University of Colorado – Transitions: Building Bridges Between Ideas
Was this article helpful?

Bridge Sentences
Ai generator.
Imagine a world without bridges, and we mean the bridges that connect pieces of land together for us to travel from one place to another. The bridge could be as short as those build over rivers or as long as the Golden Gate Bridge along the Pacific, yet their purpose remains the same. In a similar sense, bridge sentences in writing and speech serve as transitions to connect two similar or opposing ideas together. In this article, we will discuss the basic function of bridge sentences in communication.
What are Bridge Sentences – Defining
A bridge sentence, also known as a paragraph bridge, is a type of topic sentence that helps connect an old paragraph or idea to a new one. It conveys what the new paragraph is about and how it relates to the one introduced prior to it. The trick to doing so is to create a smooth shift of thoughts by bringing these ideas closer together. If the bridge isn’t constructed properly, then it will fail to convey the right message to its readers. These transitions can sometimes be found in the first line of the paragraph, but you can also find them at the end of a paragraph in some cases.
Short Bridge Sentences
- Moving from historical context to current applications, it’s clear that this technology has evolved significantly.
- On a related note, this brings us to another significant aspect.
- However, this perspective changes when we look at the situation from a different angle.
- Furthermore, this development has implications for both our short-term strategies and long-term goals.
- Conversely, critics argue that this approach may overlook some fundamental concerns.
- Building upon this point, we can see how it directly influences other trends in the field.
- Despite these advancements, several challenges remain unresolved.
- Next, let’s turn our attention to the effects of these changes.
- To better understand this phenomenon, a closer examination of the data is necessary.
Simple Bridge Sentences
- Let’s now consider another aspect of the same issue.
- This leads us to the next point.
- Similarly, we see a related pattern emerging in other areas.
- Contrasting with this idea, another perspective highlights a different issue.
- With this in mind, we can further explore the implications.
- This sets the stage for understanding the broader impact.
- Moreover, this connection is crucial for our discussion.
- This example clearly illustrates the main point.
- Turning to a different example, we can see how this applies in other contexts.
- To delve deeper, let’s examine a specific case.
Words to Start Bridge Sentences
| Additionally | Furthermore | Moreover | Conversely | Similarly |
| As a result | Subsequently | Therefore | Thus | Hence |
| On the other hand | Consequently | Nevertheless | However | Next |
| Following this | Meanwhile | Then | Accordingly | To illustrate |
| In contrast | On a similar note | Leading on from | In addition to | Before moving on |
| Finally | Initially | In conclusion | As previously stated | Moreover |
What is the Purpose of Bridging Paragraphs?
While writing an essay or any academic or business paper, using transitional devices such as bridge sentences is essential in connecting similar thoughts together. This serves as an escort from a previous topic being discussed to a new one.

For example, the bridge sentence of an introductory paragraph is typically found between the ‘hook’ and the thesis statement . The hook is crafted to draw attention, while the bridge sentence is used to slowly introduce the thesis statement to readers. They serve as a clue for readers to understand what was being mentioned in a given article or study, what will be discussed next, and how the two topics relate to one another.
The function of a bridge sentence within multiple paragraphs of an essay writing is also similar to the one previously stated. But, instead of starting each paragraph with a topic sentence, the bridge is used to create a smooth transition of thoughts. Here, the speaker briefly discusses the previous point given in order to tie it to a new point.
Types of Transitions
When it comes to writing a paper, bridge sentences are generally referred to as transitional statements. These statements may consist of a few words or they can make up a whole sentence outline or paragraph. But, keep in mind that these transitions would depend on the relationship being conveyed in the write-up. To understand the proper use of these transitions, you can study the following types:
- Sequential Transitions – Bridge sentences with sequential transitions that demonstrate a logical flow of ideas in a write-up. For example, words such as ‘thus’, ‘therefore’, and ‘then’ show a relationship between the past and the current point being discussed.
- Comparative Transitions – This type of transitional words and phrases can come in handy, especially when the relationship between two ideas isn’t so obvious. These words serve as an effective instrument in drawing analogies that are difficult to comprehend at first. Examples of such include words and phrases like ‘also’, ‘just as’, ‘like’, and ‘similarly’.
- Contrastive Transitions – For instances when you’re neither looking at similarities nor describing relationships but instead focusing on contrasting qualities, these transitions can be extremely useful. Not only can these transitions help emphasize central ideas in a compare-and-contrast essay, but they can also help debunk a claim or point out the opposite side of an issue. Examples that fall under this category include ‘though’, ‘but’, ‘however’, ‘nevertheless’, ‘nonetheless’, ‘then again’, ‘on the other hand’, and ‘at the same time’. You may also see Short Sentence Example .
- Summing Up Transitions – After proving your point, you’d want to throw in that one last thought, to sum up, every important detail provided. To ensure that readers don’t miss the main idea of your paragraph or article, these transitional sentences can help in introducing your final thought in a quick yet appropriate manner. Transitional words in this category include ‘essentially’, ‘basically’, ‘ultimately’, ‘in short’, and ‘in other words’.
Examples of Bridge Sentences
Listed below are brief samples of paragraphs consisting of bridge sentences. The bridge sentence in these examples have been italicized for your reference: You may also see Cumulative Sentence Example .
Sandra and her father played out in the rain despite the strong protest coming from her mother. They danced to the tune of the rain and watched as each droplet fell from the dark skies. She smiled, thinking of the days when she and her father listened helplessly to the endless rants of her mother as their soaking bodies form small puddles of water inside the house. You may also see Balanced Sentence Examples .
Now, thirty years later, Sandra looks back to these memories with tears filling her baby blues.
The documentary concluded its feature with North Korean soldiers dumping corpses onto a military truck.
Why would any news program carry such gruesome footage? Surely they knew what the consequences were for doing so… Instead, representatives from the news network considered it newsworthy because the clips featured exclusive content and startling visual images that viewers were interested in . You may also see Complex Sentence Example .
The World Health Organization began forming a highly-classified group of scientists to study the outpouring origins and effects of disease X. Though the disease remains unknown to society, it is likely to be a hybrid of past diseases that have been carried by animals. The team of scientists was tasked to discover the possible symptoms of the disease, along with the regions it is likely to spread in first. You may also see Compound Sentence Examples .
In other words, disease X is an existing, scientifically-generated epidemic that is yet to sweep a mass number of the earth’s population in the near future.

Ultimately, the main objective of a bridge sentence is to help promote clear communication. By defining the relationship between two separate ideas, readers are able to grasp the connection that exists between them. This creates a smooth flow of thoughts to provide an exceptional reading experience for individuals. You may also see Parallel Sentence Example .
Bridge Sentences for Class 1
- Now, let’s talk about something else.
- Next, we are going to learn about…
- Let’s move on to our next fun fact.
- After that, we did… Now, we will do…
- First we learned about A, now let’s look at B.
- Do you remember what we did yesterday? Today, we’re going to learn more about it.
- We finished our story, now let’s draw a picture of our favorite part.
- We counted apples before. Now, let’s count oranges.
- Let’s put away our books and get out our art supplies.
- We sang a song about the weather, now let’s look outside to see what the weather is doing today.
Bridge Sentences for Class 2
- We just read about animals. Now, let’s write our own story about a lion.
- We finished our math worksheet. Next, we’ll use blocks to show what we learned.
- We learned how plants grow. Let’s draw pictures of a plant’s life cycle.
- After playing our counting game, now we will count all the chairs in our classroom.
- We talked about the weather yesterday. Today, we’ll make a weather chart.
- First, we learned about addition. Now, let’s try some subtraction problems.
- Now that we’ve cleaned up our area, let’s gather around for story time.
- We’ve just finished learning our new words. Let’s use them in sentences now.
- We colored pictures in the morning; now, let’s write about the pictures after lunch.
- We talked about healthy foods; next, we will cut out pictures of foods to make our own healthy meal.
Bridge Sentences for Class 3
- Now that we’ve read about dinosaurs, let’s compare them to animals living today.
- We just learned about multiplication. Let’s apply it by calculating how many apples are in these baskets.
- After discussing the water cycle, let’s create a mini water cycle model in class.
- We’ve written our own fairy tales. Now, let’s read them aloud to the class.
- We’ve explored maps of our country. Next, let’s look at maps of other countries and find the differences.
- Now that we know how to measure length, let’s find objects around the classroom to practice measuring.
- We learned about ancient Egypt; now let’s write a day in the life of an Egyptian child.
- After our lesson on planets, let’s use balls of different sizes to create a model of the solar system.
- We discussed the importance of recycling; now, let’s sort these materials into recyclables and non-recyclables.
- We’ve practiced fractions with pizza slices; next, let’s use the same idea with a chocolate bar.
Types of Bridge Sentences
1. continuation bridges.
- These sentences extend the thought from the previous paragraph or introduce additional information that complements the preceding ideas.
- Example: “Furthermore, continuing this program will not only benefit current participants but also future generations.”
2. Contrast Bridges
- Used to introduce a contrasting or opposing viewpoint to the one just discussed, helping to highlight differences.
- Example: “However, despite the previous success of the initiative, recent reports suggest a decline in its effectiveness.”
3. Cause and Effect Bridges
- These bridge sentences explain the cause and effect relationships between ideas, showing how one event leads to another.
- Example: “Consequently, the sudden drop in temperature last winter caused significant damage to the crop yields.”
4. Similarity Bridges
- They draw parallels between two ideas, emphasizing similarities and connections.
- Example: “Similarly, the economic policies of Country X have mirrored the early stages of economic development seen in Country Y.”
5. Clarification Bridges
- These are used to clarify or further explain a point or idea that might not have been fully understood.
- Example: “To clarify, the new policy does not replace the old one but rather expands upon the existing regulations.”
6. Emphasis Bridges
- Emphasis bridges are employed to stress the importance or critical nature of a point just discussed.
- Example: “Indeed, this evidence highlights the urgent need for reform within the sector.”
7. Conclusion Bridges
- Used to signal that a conclusion or summary is forthcoming, wrapping up the discussion.
- Example: “In conclusion, the multiple benefits of this approach clearly outweigh its drawbacks.”
8. Time Sequence Bridges
- These help organize narratives or processes by marking the progression of time or steps.
- Example: “Subsequently, after the initial trials were successful, the next phase of the project commenced.”
How to Write Bridge Sentences
1. understand the purpose of bridge sentences.
- Transition: Bridge sentences help readers move from one paragraph or section to another seamlessly.
- Prediction: They can set the stage for what is coming next, preparing the reader for a shift in tone, argument, or topic.
- Reflection: Bridge sentences can also reflect on the content just covered, making a connection between the previous information and new ideas.
2. Identify the Connection
- Start by clearly understanding the content of both the preceding and following paragraphs.
- Identify the key elements that connect these two paragraphs. This could be a shared theme, a contrasting point, or a cause-and-effect relationship.
3. Choose the Right Type of Transition
- Continuation transitions (furthermore, moreover, additionally) are used when adding similar information or expanding on a point.
- Contrast transitions (however, on the other hand, conversely) introduce an opposing viewpoint or a shift in direction.
- Cause and effect transitions (therefore, as a result, thus) demonstrate the relationship between actions and outcomes.
- Chronological transitions (next, then, after) are useful in narrative or process writing to show the progression of time or steps.
4. Craft the Sentence
- Keep the bridge sentence concise and to the point.
- Use it to gently guide the reader from one idea to the next, ensuring the sentence fits the tone and style of your writing.
- Make sure it incorporates key terms or concepts that are central to both paragraphs, enhancing the thematic continuity of your text.
5. Evaluate its Effectiveness
- After writing your bridge sentence, read the transition aloud to see if it naturally guides you from one idea to the next.
- Check if the bridge sentence helps clarify the relationship between paragraphs. If the connection still feels jarring or abrupt, consider revising the sentence.
Why are bridge sentences used?
Bridge sentences connect paragraphs or sections, ensuring a smooth transition in writing, aiding coherence, and guiding readers from one idea to another seamlessly.
What is a bridge sentence in analogies?
In analogies, a bridge sentence explains the relationship between two seemingly unrelated topics, clarifying how one idea or example parallels or contrasts with another.
How to use the verb bridge in a sentence?
The verb “bridge” denotes the act of making connections or overcoming gaps; e.g., “This meeting aims to bridge the communication gap between departments.”
What are good bridge sentences?
Good bridge sentences effectively link ideas, clarify transitions, and maintain the flow of text, often incorporating transitional phrases like ‘furthermore’, ‘however’, or ‘consequently’.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

what is a Bridge in Essay: Examples?
A pivotal skill for any essay writer is mastering the art of transitioning seamlessly between ideas. Transitions are the linguistic bridges that connect disparate thoughts, enhancing the flow and coherence of your narrative.
A particularly potent tool in your essay arsenal is the bridge sentence .
This type of sentence acts as a connector between paragraphs or sections, effectively summarizing what has been discussed and hinting at what’s to come. Not only can it counter potential objections, but it also opens the door to new viewpoints.Utilizing bridge sentences can fortify the structure of your essay and smoothly lead your reader through your arguments.
Need help doing your assignment?
Understanding the Concept of a Bridge in Essay Writing
A bridge sentence is a type of transition that connects two ideas or paragraphs in a logical and smooth way. It can help you create a strong structure for your essay and guide your reader through your argument.
Definition of a Bridge
A bridge sentence, also known as a paragraph bridge or a bridge statement, is a sentence that links two paragraphs or sections of an essay. It usually appears at the beginning of a new paragraph, and it serves as a summary of the previous point and a preview of the next point. It can also address a counterargument or introduce a new perspective.
A bridge sentence can be composed of three elements: a pointer word that directs the reader’s attention to the previous paragraph, a part that refers to the previous point, and a part that relates to the current point. For example, consider this bridge sentence:This advantage makes an inkjet printer one of the best choices for home offices. But besides reasonable prices and printing quality, it is also worth mentioning how easy it is to use inkjet printers.The pointer word “this” points to the previous paragraph, where the advantage of an inkjet printer was discussed.
The part “makes an inkjet printer one of the best choices for home offices” summarizes the previous point. The part “but besides reasonable prices and printing quality, it is also worth mentioning how easy it is to use inkjet printers” introduces the topic of the current paragraph, which is the ease of use of inkjet printers.
The Purpose of a Bridge in an Essay
The purpose of a bridge sentence in an essay is to help the writer connect ideas and transition smoothly from one point to another. A bridge sentence can have several benefits for the essay and the reader, such as :
- It can clarify a point that has been made, by restating it in a different way or providing more details.
- It can introduce a new idea, by showing how it is related to the previous idea or how it differs from it.
- It can sum up the main points of the essay, by highlighting the most important arguments or evidence.
- It can keep the reader’s attention focused on the essay, by creating a logical flow of ideas and avoiding abrupt changes of topic.
- It can make the writing style more fluid and coherent, by using words and phrases that create a smooth transition between ideas.
Examples of Bridges in Different Types of Essays
Whether you are composing a rhetorical analysis essay , a double spaced essay , a problem and solution essay , or any other genre, the incorporation of a bridge sentence is elemental in its function and purpose. Subsequent examples will illustrate their usage in different contexts.
Argumentative Essays
Rooted in debate, the argumentative essay forwards a claim, backing it with solid evidence and logical reasoning . Its ultimate goal? To sway the reader toward the writer’s perspective or spur them into action.
Take this bridge sentence as an example: “While social media serves as a formidable platform for communication and learning, it’s not without its drawbacks on mental health and personal well-being.” This sentence acknowledges social media’s benefits before transitioning to its adverse effects, the essay’s primary focus. It even suggests moderation and responsible use as potential remedies, paving the way for further discussion.
Expository Essays
The expository essay enlightens its audience, offering a clear, factual account of its subject. It’s the educator among essays.
A bridge sentence here might encapsulate the preceding paragraph’s main point, link two related concepts, or unveil a new topic. For instance: “The Golden Gate Bridge, an engineering wonder, stands as an iconic beacon across the San Francisco Bay, bridging the gap between San Francisco and Marin County.” This sentence transitions smoothly from discussing the bridge’s construction to its emblematic value, maintaining the informative tone crucial to expository essays.
Narrative Essays
A narrative essay’s charm lies in its storytelling, inviting readers into the writer’s personal experiences and associating them with the emotional journey detailed.
Consider this bridge sentence for generating anticipation or segueing scenes: “Crossing the narrow bridge, the stunning view below—sunlit river, rustling trees—filled me with an elation, blissfully ignorant of the impending peril beyond.” It not only builds suspense but also serves as a seamless transition, enriching the narrative flow.
Descriptive Essays
Descriptive essays paint a picture, detailing subjects so vividly that readers can visually experience the discussed topic. A bridge sentence in this form sharpens focus, draws comparisons, or highlights transitions.
For example: “Beside the ancient, graffiti-laden bridge, a testament to years passed, stood its modern counterpart—sleek, shimmering, an architectural marvel—promising a new era.” This bridge sentence contrasts the two structures effectively, using evocative language to kindle the readers’ imagination while signaling a transition in time and technology.
How to Craft an Effective Bridge: Tips and Techniques
A bridge sentence can help you create a strong connection between your hook and your thesis statement, ensure a smooth transition and cohesion between your paragraphs, and avoid some common mistakes that can weaken your essay.
Linking the Hook and the Thesis Statement
A hook is the first sentence of your essay that grabs the reader’s attention and makes them want to read more. A thesis statement is the last sentence of your introduction that states the main argument or purpose of your essay.
A bridge sentence can help you link these two elements by summarizing the hook and introducing the thesis statement. For example, consider this hook, bridge, and thesis statement: Hook: Have you ever wondered why some people are afraid of spiders, while others are fascinated by them? Bridge: Spiders are among the most diverse and intriguing creatures on the planet, but they also evoke different emotions and reactions from humans. Thesis statement: In this essay, I will explore the reasons behind the fear of spiders, the benefits of overcoming this phobia, and the ways to cope with it. The bridge sentence connects the hook and the thesis statement by providing some background information on spiders and their relationship with humans. It also creates a smooth transition from a general question to a specific topic.
Ensuring Smooth Transition and Cohesion
A smooth transition and cohesion between your paragraphs can make your essay more clear and logical. A bridge sentence can help you achieve this by linking the main idea of the previous paragraph to the main idea of the next one.
You can use different types of transitions, such as sequential, contrastive, causal, or additive, depending on the relationship between your ideas. You can also use words and phrases that create a smooth transition, such as but, and, besides, even so, further, moreover, nevertheless, still, therefore, thus, although, and yet . For example, consider this bridge sentence: Although the fear of spiders is a common and natural response, it can also have negative consequences for the individual and the society. This bridge sentence uses a contrastive transition ( although ) to show the difference between the previous paragraph, which explained the causes of the fear of spiders, and the next one, which will discuss the effects of this fear.
Common Mistakes to Avoid when Writing a Bridge
When writing a bridge sentence, you should avoid some common mistakes that can weaken your essay and confuse your reader. Here are some of them :- Do not repeat the same idea or information that you have already stated in the previous paragraph or the thesis statement.
Instead, restate it in a different way or provide more details.- Do not introduce a new idea or topic that is not related to the previous or the next paragraph. Instead, focus on the connection between the two ideas or topics.- Do not make the bridge too long or too short.
A good bridge should be brief and to the point, but also clear and informative.- Do not use vague or ambiguous words or phrases that can confuse the reader or create a weak transition. Instead, use specific and precise words or phrases that create a strong transition .
How do you write a bridge in an essay?
To write a bridge in an essay, it’s important to connect the main idea of the previous paragraph with the main idea of the next paragraph . This is achieved by employing a pointer word or phrase that references the previous point, followed by introducing the new point with a relevant word or phrase.
For example: “The inkjet printer is the most popular type of printer for home use. It is less expensive than a laser printer and produces good-quality prints.”
This advantage makes an inkjet printer an excellent choice for home offices. Besides reasonable prices and printing quality , it’s also essential to highlight the ease of use of inkjet printers. Here, the bridge sentence uses “ this advantage ” to reference the previous paragraph, while “ but besides reasonable prices and printing quality, it is also worth mentioning ” introduces the new point.
What is an example of a bridge sentence?
An example of a bridge sentence connects two paragraphs or ideas by summarizing the previous one and introducing the next. For instance, “ While the inkjet printer is a popular choice for home use, it has some drawbacks that make it unsuitable for large-scale printing. ”
How is the word bridge used in the essay?
The word bridge in an essay refers to a transitional device that connects two ideas or paragraphs . It aids the author in maintaining a smooth flow of thoughts and in illustrating the relationship between points.
What is a bridge used for in writing?
In writing, a bridge is used to link two separate ideas together and to ensure a smooth transition between them. A bridge can manifest as a sentence or a phrase that summarizes the previous idea, introduces the new idea, or contrasts the two ideas .
Homework Help Service: Help for Homework
As the best homework help service available, we at helpforhomework pride ourselves on delivering top-notch essays that guarantee success. Our team of experienced writers is dedicated to providing you with high-quality, well-researched, and custom-written papers that meet your unique requirements. Whether you need assistance with a challenging topic or a tight deadline, HelpForHomework is here to support you every step of the way. Don’t settle for mediocre results – place your order with us today and experience the difference of working with the best homework help service for all your essay needs.
Recent Posts
- Methods to Indent Paragraphs in Microsoft Word
- Best AI Discussion Reply Generator That Boosted Engagement in 2024
- Is it Possible to Cheat on Proctored Exams like ProctorU and ProctorIO?
- Academic Writing Tips for University Success
- Descriptive Essay Examples: How to Write and Use Them Effectively
You cannot copy content of this page
What Is a Bridge Sentence and How to Write a Transition in an Essay
- Icon Calendar 18 May 2024
- Icon Page 3028 words
- Icon Clock 14 min read
Bridge sentences are important in connecting two independent phrases, expressions, word combinations, or arguments in a paragraph or an essay. Basically, this guideline on how to write a good bridge sentence in an essay or a research article is worth reading because it entails practical ways to write connecting statements. Moreover, the article entails examples of various types of bridge statements, which mean linking phrases that provide concise information on how to ensure a proper flow of ideas in any paper using connecting statements. They allow writers to communicate effectively throughout their essays. The different types of bridge statements include topic, transitional, and concluding sentences with pointers. In this case, topic phrases introduce the main ideas in a passage, while transitional statements create a unique connection between ideas or thoughts. Besides, concluding sentences contain a clear flow of concepts and link them to other sections. However, one must select appropriate transitioning words to create appropriate bridge sentences.
General Aspects of How to Write an Outstanding Bridge Sentence in an Essay
Good essays must have a permanent quality to their content, with a unique flow of ideas and concepts. In this case, bridge sentences are useful in connecting two independent clauses, phrases, word combinations, statements, or claims. Hence, the guideline focuses on how to write a bridge sentence with its definition and meaning and provides clear examples that one can follow to create different types of essays. In turn, people should bother reading this guideline as it focuses on crucial aspects of creating various types of papers, reports, and articles. Because essays are central to advancing knowledge, one must use bridge sentences effectively to ensure effective communication.

Definition of a Bridge Sentence and Its Meaning
From a simple definition, a bridge sentence is a general term that refers to a set of phrases that link ideas and create a smooth transition between concepts in an essay or a research paper. Some examples of bridging phrases include topic, transitional, concluding statements, and pointers. In turn, a single essay or research paper may contain all these types of connecting phrases. Hence, a bridge sentence means many phrases that enable readers to relate all ideas presented in a paper because of an enhanced flow of information and logical order of ideas. A deeper explanation of different types of bridge sentences includes:
- Topic Sentence : Topic sentences reveal the main message explained in a single paragraph and its relationship to a central thesis statement. Every paragraph must begin with a single topic sentence that relates to an initial argument of a paper as a sub-theme. This bridge sentence must contain a single main concept discussed in the section.
- Transitional Sentence: Transitional sentences create a smooth connection between ideas presented in one passage. A good paragraph in an essay should have a chronological and logical flow of ideas. These bridge sentences allow a sequential presentation of thoughts.
- Concluding Sentence: Concluding sentences summarize information and provide a link between two paragraphs, such as a current passage and a next one. In this case, good paragraphs contain a clear summary of all presented ideas. A concluding statement should appear at the end of a single passage as a bridge sentence to tie all the thoughts together.
- Pointer Sentence : Pointers are useful in clarifying the main claim by guiding readers through the structure and argument of an essay or a research paper. For example, pointers refer readers to the previous claim, paragraph, argument, or thesis statement. In this case, they allow the audience to relate concepts and gain better insights into the presented ideas.
Experience a seamless writing process with Wr1ter Team, where plagiarism is never a concern.
Unique Features of Writing Bridge Sentences in Essays or Research Papers & Examples
Bridge sentences are different, with unique features. What comes after a hook in an essay introduction is a transitional word. For example, a scholarly article or an academic essay may have various connecting statements. Their features depend on the purpose and location within a particular passage. Besides, authors may choose linking phrases to invoke unique thoughts or create desirable emotions. The following are descriptions and examples of different bridge sentences.
🔹 Transitional Sentences & Bridge Example
Transition sentences are unique because they show readers how different sections of an essay connect. Transition sentences are useful in linking the college essay introduction, body, and conclusion paragraphs to create a well-organized flow of information. Placing this bridge claim at the beginning of a new paragraph helps to link it to the previous one. An example of a transition sentence is:
Further evidence supporting the hypothesis is that psychological well-being promotes student performance due to increased concentration levels.
This sentence contains information that complements the previous paragraph by providing more support for the same concept.
🔹 Topic Sentences & Bridge Example
Topic sentences are unique because they indicate the paragraph’s subject and central point. Every paragraph in an essay must begin with a topic sentence. This opening statement in a paragraph may provide a connection between the main ideas and indicate how they connect to one of three themes of a 3-point thesis. Besides, this bridge sentence forms the foundation of the supporting evidence. An example of a topic sentence is:
Existing research has consistently shown that the meat industry is unsustainable due to its detrimental environmental impacts.
This phrase introduces the passage’s main point and focuses on the meat industry’s negative environmental impacts, like other thesis statement examples. The entire paragraph should expound on this issue by using and citing credible sources.
🔹 Concluding Sentences & Bridge Example
A concluding sentence is unique because it acts as an indicator that a specific paragraph is coming to an end. This bridge sentence contains a summary of the information presented in a section. However, a conclusion does not include any new information. A practical example of a concluding statement to end a paragraph in an essay is:
Evidently, the meat industry contributes to greenhouse emissions due to methane released from animal manure.
This assertion summarizes the facts presented in a single paragraph on how the meat industry affects the environment.
🔹 Pointers & Bridge Example
Pointers refer to information that enables readers to understand a situation or a piece of information. These bridge statements work as topic sentences for entire sections of an essay or a research paper. In this case, they inform readers that a paper is taking a turn in its core argument. For instance, a pointer may indicate that the writer is delving into a related topic, like a counterargument, stepping up its claims with complex details, or pausing to give important historical or scholarly background. Moreover, these bridge sentences remind readers about what an essay is about and why it is written. An example of a pointer is:
For people to understand the causes of riots, it would be useful to apply sociological theories, like psychoanalytical social contagion.
This sentence points the readers to a change in the explanation strategy to include sociological theories to understand the main subject.
🔹 Classical Bridge Sentences & Bridge Example
A classic bridge sentence is unique because it helps authors to point to previous paragraphs and introduce the topics for a new paragraph. This bridge statement is useful when writing texts with multiple passages having related information. An example of a classic bridge sentence structure is:
This advantage makes transformational leadership effective in promoting employee collaboration. However, besides enhancing communication and cooperation, it is important to mention that transformational leadership allows people to set goals and higher expectations, eventually achieving higher performances.
This phrase, which consists of two sentences, points to the previous paragraph by mentioning the advantage of transformational leadership. Furthermore, this bridge claim introduces the theme for the next passage by mentioning how this leadership style empowers employees to create achievable goals.
🔹 Question-Answer Sentences & Bridge Example
Question-answer bridge is unique because it points to the previous paragraph and introduces the main argument of the next passage. In this case, questions serve as the pointer to the previous section, and the answer connects and introduces the theme for the current passage. An example of a question-answer bridge sentence structure is:
But does transformational leadership promote employee collaboration? Surely yes, because this leadership enhances communication and cooperation among employees. When comparing transformational leadership to other management strategies, it allows people to set goals and higher expectations to achieve higher performances.
🔹 Reiteration Sentence & Bridge Example
A reiteration bridge sentence is unique because it allows writers to use repetition to transition between ideas. This type of bridge statement allows people to emphasize important concepts that the audience should acknowledge in an essay. For instance, a reiteration bridge sentence may involve the incorporation of opposite meanings. An example of a reiteration bridge is:
Demonstrations and picketing lead to unity and victory on the one hand and defeat and loss of life on the other.
This bridge sentence has phrases with contrasting meanings that point to the previous passage and provide a link to the current one. The first part points to the previous passage on the advantages of protests and strikes. The second part introduces the information presented in the current paragraph, which relates to the negative impacts of the dissent march.
🔹 Complication Sentence & Bridge Example
A complication bridge sentence is unique since it contains a pointer, a transition word, a reference to a previous paragraph, and states the main point of the current paragraph. An example of this bridge sentence structure is:
Such advantages of transformational leadership encourage employees to cooperate in making important decisions; however, it is not as effective in democratic governance in enabling leaders to engage their subordinates in addressing emerging and existing issues.
This example has a pointer, “such,” as a bridge claim that refers to the previous paragraph. The transition word, “however,” signals to readers that transformational leadership is ineffective compared to other governance styles. Finally, it references the previous paragraph and states the main argument for the current passage that democratic leadership is better.
Schematic Examples for Writing Purposeful Bridge Sentences in an Essay
- Making an example: (The next idea) clearly illustrates / indicates / suggests / means / underlines that (the previous idea) by / in / from / on / with / within … (explanation).
Enhanced employee productivity clearly illustrates that management by walking around is better than autocratic governance because it enables leaders to identify and address problems.
- Showing a cause-effect relationship: (The previous idea) led to / results in / has allowed / improved / significantly impacted / directly caused / was the reason / (the next idea) … (explanation).
Implementing peer support to new employees improved department cooperation and innovation .
- Giving a counterexample: Even though / although / even if (the previous idea) is ‘describing the situation,’ (the next idea ) … (explanation).
Even though rewarding employees is the accepted way to enhance productivity, allowing them free time to work on interesting concepts promotes innovativeness and efficiency.
- Emphasizing a point: (The previous idea) is important / significant / crucial / essential / vital / or cannot be omitted / denied / ignored because / since (the next idea) … (explanation).
Engaging workers in identifying and addressing problems is essential in management because it enables them to feel acknowledged by the company’s top leadership.
- Contrasting: (The previous idea) differs from / can be contrasted with / is not the same as (the next idea) in how / because / since … (explanation).
Disciplining children through corporal punishment differs from empowering them because it instills fear instead of encouraging them to engage in constructive behaviors.
- Comparing: (The previous idea) is similar to / can be compared with / is the same as / has some vivid similarities with (the next idea) because / since … (explanation).
Brachytherapy resembles external beam radiotherapy because it mainly aims to shrink cancerous tumors.
- Bridge sequencing: (The previous idea) comes before / starts with / comes after (the next idea) … (explanation).
Establishing strategic goals for a company comes before performance appraisals and signing performance contracts.
- Proving: (The previous idea) means / suggests / indicates / proves / states / implicates that (the next idea) … (explanation).
Declining academic performance among adolescents indicates an inability to cope with emerging social challenges.
- Complicating: Yes / sure / arguably / indeed, (the previous idea), but because of that / however / on the other hand, (the next idea) … (explanation).
Yes, academic advancements among staff members should lead to promotions, but because of that, many people may obtain academic papers fraudulently.
- Adding a bridge precision: The researchers / authors / scholars / experts / professionals explain in more detail / provide more insight / analyzed / included (the previous idea) in their paper / article / work / investigation / study / research regarding (the next idea ) … (explanation).
The authors explain in more detail that using renewable energy sources lowers the cost of manufacturing products in their paper regarding sustainable management.
- Clarifying: Yes / sure / arguably / indeed, (the previous idea) is sometimes ‘describing the situation,’ but this aspect / feature / concept / element / characteristic doesn’t mean / work / result in (the next point) … (explanation).
Poor prognosis is sometimes the case in chemotherapy and radiotherapy treatments, but this aspect does not mean cancer is incurable.
Get professional writing assistance that ensures your paper stands out among the rest.
Writing Types of Transition Elements in Bridge Sentences
💠 sequential bridge transitions.
Bridge sentences that contain statements on order and sequence of information should have sequential transitions. These transitioning words or bridge phrases allow one to organize essays or research papers by numerical sequence. Moreover, they indicate a continuation of thoughts or actions by referring to previously mentioned information, indicating excursions, and concluding or summing up ideas. Sequential connecting words allow readers to understand the logical development of concepts presented in an essay. Some examples of sequential transitions include:
- further on,
- consequently,
- incidentally.
💠 Comparative Bridge Transitions
Comparison transition words in an essay establish a relationship between things or ideas. In this case, comparative bridge words and phrases are essential in explaining what two things have in common. Writers can use comparison words to demonstrate similarities between thoughts, objects, or concepts. Moreover, these bridge elements focus on similitudes only as opposed to variations in a sentence. Some examples of comparative transitions include:
- in the same way,
- regardless,
- at the same time,
- in like manner,
- compared to,
- nonetheless.
💠 Contrastive Bridge Transitions
Contrastive bridge words indicate the difference between ideas or objects. These bridge sentence transitions are important when presenting polar, different, or conflicting ideas. Contrastive transitions allow authors to connect opposing ideas and thoughts understandably. Including conflicting thoughts or ideas in an essay can enhance its quality by allowing readers to evaluate them critically. In an essay, contrastive bridge elements become crucial in presenting contradictory thoughts and opinions. Some examples of contrastive transitions include:
- in contrast,
- conversely,
- dissimilarly,
- on the contrary,
- nevertheless,
- on the one hand,
- contrasted with,
- even though,
- alternatively.
💠 Summing-Up Bridge Transitions
Summing-up bridge transitions are useful in drawing the reader’s attention to the main argument. In this case, one must use appropriate transitions to summarize a discussion or a paragraph. For instance, outstanding essays should have a summary of the main ideas in their conclusions. Summing-up bridge sentences are common when writers use statements to conclude a paragraph or summarize an essay. Some examples of summing-up transitions include:
- essentially,
- in conclusion,
- summing up,
- in other words,
- the main point is,
- this boils down to,
- in this case,
- as a result,
- for that reason,
- conclusively.
Examples of Transition Elements
- Introduce the next idea: as such, essentially, therefore, for instance, basically, in particular, notably, hence.
- Referring to the previous idea: indeed, moreover, furthermore, also, according to, additionally, so.
- Introducing a conclusion paragraph: in summary, in conclusion, thus, summing up, to conclude.
- Showing a similarity: in like manner, equally, likewise, at the same time.
- Showing a contrast : contrarywise, opposite to, dissimilarly, nonetheless, but, instead.
- Giving an example: such as, perhaps, for example, to demonstrate, to suppose, to consider.
- Showing a bridge causation: consistent with, because of, owing to, by reason of, subsequently, given that.
- Showing time relations: subsequently, then, later, next, formerly, each time, whereas.
- Showing space relations: directly above, flanking, under, outside, at this point, opposite, neighboring, reverse.
Summing Up on How to Write a Perfect Bridge Sentence in an Essay or a Research Paper
- Bridge sentences help to connect two independent phrases, expressions, or arguments.
- Writers must provide concise information to ensure the organic flow of information in an essay using connecting sentences.
- Effective use of bridge statements allows writers to communicate effectively throughout their essays or research papers.
- Topic sentences reveal the main message explained in a single paragraph and its relationship to a central thesis statement.
- Transitional sentences create a smooth connection between ideas presented in one passage.
- Concluding sentences summarize information and provide a link between two paragraphs.
- Bridge sentences require an appropriate selection of transitioning words for writing an essay.
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles

Causes and Effects of Climate Change on Global Food Production
- Icon Calendar 18 August 2023
- Icon Page 828 words

How Does Animal Behavior Inform Human Psychology?
- Icon Calendar 17 August 2023
- Icon Page 843 words
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Transition sentences | Tips & examples for clear writing
Transition Sentences | Tips & Examples for Clear Writing
Published on June 9, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
Clear transitions are crucial to clear writing: They show the reader how different parts of your essay, paper, or thesis are connected. Transition sentences can be used to structure your text and link together paragraphs or sections.
… In this case, the researchers concluded that the method was unreliable.
However , evidence from a more recent study points to a different conclusion . …
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Transitioning between paragraphs, transitioning to a new section, transitions within a paragraph, other interesting articles.
When you start a new paragraph , the first sentence should clearly express:
- What this paragraph will discuss
- How it relates to the previous paragraph
The examples below show some examples of transition sentences between paragraphs and what they express.
| Transition sentence | This paragraph… |
|---|---|
| evidence in support of is provided by Smith (2019). | … the previous one, providing more support for . |
| , Patel’s arguments are on the matter. | … the previous one by presenting related to the previous discussion. |
| the relationship between these factors, to draw conclusions about the broader process. | …treats the preceding point as on which to more general arguments. |
Placement of transition sentences
The beginning of a new paragraph is generally the right place for a transition sentence. Each paragraph should focus on one topic, so avoid spending time at the end of a paragraph explaining the theme of the next one.
The first dissenter to consider is …
However, several scholars dissent from this consensus. The first one to consider is …
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
While transitions between paragraphs are generally a single sentence, when you start a new section in a longer text, you may need an entire transition paragraph. Transitioning to a new section involves summarizing the content of the previous section and expressing how the new one will build upon or depart from it.
For example, the following sentences might be an effective transition for a new section in a literary analysis essay.
Having established that the subjective experience of time is one of Mann’s key concerns in The Magic Mountain , it is now possible to explore how this theme facilitates the novel’s connection with World War I. The war itself is not narrated in the book, but rather hinted at as something awaiting Castorp beyond the final pages. In this way, Mann links his protagonist’s subjective experience of time to more than just his illness; it is also used to explore the period leading up to the outbreak of war.
As in academic writing generally, aim to be as concise as you can while maintaining clarity: If you can transition to a new section clearly with a single sentence, do so, but use more when necessary.
It’s also important to use effective transitions within each paragraph you write, leading the reader through your arguments efficiently and avoiding ambiguity.
The known-new contract
The order of information within each of your sentences is important to the cohesion of your text. The known-new contract , a useful writing concept, states that a new sentence should generally begin with some reference to information from the previous sentence, and then go on to connect it to new information.
In the following example, the second sentence doesn’t follow very clearly from the first. The connection only becomes clear when we reach the end.
By reordering the information in the second sentence so that it begins with a reference to the first, we can help the reader follow our argument more smoothly.
Note that the known-new contract is just a general guideline. Not every sentence needs to be structured this way, but it’s a useful technique if you’re struggling to make your sentences cohere.
Transition words and phrases
Using appropriate transition words helps show your reader connections within and between sentences. Transition words and phrases come in four main types:
- Additive transitions, which introduce new information or examples
- Adversative transitions, which signal a contrast or departure from the previous text
- Causal transitions, which are used to describe cause and effect
- Sequential transitions, which indicate a sequence
The table below gives a few examples for each type:
| Type | Example sentence | Transition words and phrases |
|---|---|---|
| Additive | We found that the mixture was effective. , it appeared to have additional effects we had not predicted. | furthermore, moreover, for example, in regard to x, similarly, in other words |
| Adversative | The novel does deal with the theme of family. , its central theme is more broadly political … | however, although, nevertheless, regardless, above all, (or) at least |
| Causal | Hitler failed to respond to the British ultimatum, France and the UK declared war on Germany. | because, therefore, consequently, if, provided that, so that, to |
| Sequential | This has historically had several consequences: , the conflict is not given the weight of other conflicts in historical narratives. , its causes are inadequately understood. , … | first, second, third, initially, subsequently, finally, lastly, to return/returning to x, as previously mentioned, in conclusion |
Grouping similar information
While transition words and phrases are essential, and every essay will contain at least some of them, it’s also important to avoid overusing them. One way to do this is by grouping similar information together so that fewer transitions are needed.
For example, the following text uses three transition words and jumps back and forth between ideas. This makes it repetitive and difficult to follow.
Rewriting it to group similar information allows us to use just one transition, making the text more concise and readable.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). Transition Sentences | Tips & Examples for Clear Writing. Scribbr. Retrieved August 12, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/transition-sentences/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, transition words & phrases | list & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Topic sentences and signposts make an essay's claims clear to a reader. Good essays contain both. Topic sentences reveal the main point of a paragraph. They show the relationship of each paragraph to the essay's thesis, telegraph the point of a paragraph, and tell your reader what to expect in the paragraph that follows. Topic sentences also establish their relevance right away, making clear why the points they're making are important to the essay's main ideas. They argue rather than report. Signposts , as their name suggests, prepare the reader for a change in the argument's direction. They show how far the essay's argument has progressed vis-ˆ-vis the claims of the thesis.
Topic sentences and signposts occupy a middle ground in the writing process. They are neither the first thing a writer needs to address (thesis and the broad strokes of an essay's structure are); nor are they the last (that's when you attend to sentence-level editing and polishing). Topic sentences and signposts deliver an essay's structure and meaning to a reader, so they are useful diagnostic tools to the writer—they let you know if your thesis is arguable—and essential guides to the reader
Forms of Topic Sentences
Sometimes topic sentences are actually two or even three sentences long. If the first makes a claim, the second might reflect on that claim, explaining it further. Think of these sentences as asking and answering two critical questions: How does the phenomenon you're discussing operate? Why does it operate as it does?
There's no set formula for writing a topic sentence. Rather, you should work to vary the form your topic sentences take. Repeated too often, any method grows wearisome. Here are a few approaches.
Complex sentences. Topic sentences at the beginning of a paragraph frequently combine with a transition from the previous paragraph. This might be done by writing a sentence that contains both subordinate and independent clauses, as in the example below.
Although Young Woman with a Water Pitcher depicts an unknown, middle-class woman at an ordinary task, the image is more than "realistic"; the painter [Vermeer] has imposed his own order upon it to strengthen it.
This sentence employs a useful principle of transitions: always move from old to new information. The subordinate clause (from "although" to "task") recaps information from previous paragraphs; the independent clauses (starting with "the image" and "the painter") introduce the new information—a claim about how the image works ("more than Ôrealistic'") and why it works as it does (Vermeer "strengthens" the image by "imposing order").
Questions. Questions, sometimes in pairs, also make good topic sentences (and signposts). Consider the following: "Does the promise of stability justify this unchanging hierarchy?" We may fairly assume that the paragraph or section that follows will answer the question. Questions are by definition a form of inquiry, and thus demand an answer. Good essays strive for this forward momentum.
Bridge sentences. Like questions, "bridge sentences" (the term is John Trimble's) make an excellent substitute for more formal topic sentences. Bridge sentences indicate both what came before and what comes next (they "bridge" paragraphs) without the formal trappings of multiple clauses: "But there is a clue to this puzzle."
Pivots. Topic sentences don't always appear at the beginning of a paragraph. When they come in the middle, they indicate that the paragraph will change direction, or "pivot." This strategy is particularly useful for dealing with counter-evidence: a paragraph starts out conceding a point or stating a fact ("Psychologist Sharon Hymer uses the term Ônarcissistic friendship' to describe the early stage of a friendship like the one between Celie and Shug"); after following up on this initial statement with evidence, it then reverses direction and establishes a claim ("Yet ... this narcissistic stage of Celie and Shug's relationship is merely a transitory one. Hymer herself concedes . . . "). The pivot always needs a signal, a word like "but," "yet," or "however," or a longer phrase or sentence that indicates an about-face. It often needs more than one sentence to make its point.
Signposts operate as topic sentences for whole sections in an essay. (In longer essays, sections often contain more than a single paragraph.) They inform a reader that the essay is taking a turn in its argument: delving into a related topic such as a counter-argument, stepping up its claims with a complication, or pausing to give essential historical or scholarly background. Because they reveal the architecture of the essay itself, signposts remind readers of what the essay's stakes are: what it's about, and why it's being written.
Signposting can be accomplished in a sentence or two at the beginning of a paragraph or in whole paragraphs that serve as transitions between one part of the argument and the next. The following example comes from an essay examining how a painting by Monet, The Gare Saint-Lazare: Arrival of a Train, challenges Zola's declarations about Impressionist art. The student writer wonders whether Monet's Impressionism is really as devoted to avoiding "ideas" in favor of direct sense impressions as Zola's claims would seem to suggest. This is the start of the essay's third section:
It is evident in this painting that Monet found his Gare Saint-Lazare motif fascinating at the most fundamental level of the play of light as well as the loftiest level of social relevance. Arrival of a Train explores both extremes of expression. At the fundamental extreme, Monet satisfies the Impressionist objective of capturing the full-spectrum effects of light on a scene.
The writer signposts this section in the first sentence, reminding readers of the stakes of the essay itself with the simultaneous references to sense impression ("play of light") and intellectual content ("social relevance"). The second sentence follows up on this idea, while the third serves as a topic sentence for the paragraph. The paragraph after that starts off with a topic sentence about the "cultural message" of the painting, something that the signposting sentence predicts by not only reminding readers of the essay's stakes but also, and quite clearly, indicating what the section itself will contain.
Copyright 2000, Elizabeth Abrams, for the Writing Center at Harvard University
Understanding Transition Sentences (For Essays and Writing with Examples)

What are transition sentences? And how do they work? Is there a correct way to use them? And an incorrect way? Understanding transition sentences is critical when writing essays, articles, or any type of logical flow.
Learn what transitional sentences are in this short guide…
What are transition sentences?
When you write an article, essay (or anything), you’ll want to write it in a logical sequence. You start with an introduction, highlight your points, and then end with a conclusion. Throughout your writing, you would be using sentences to express your thought. To make your writing effective, you need to link the sentences together in a logical way .
This is where transition sentences can be helpful.
As the name suggests, a transition sentence links the thoughts you are expressing in your writing. They make use of words and phrases that act as a bridge between different parts of your writing.
Transition sentences allow your reader to move smoothly from one section to another. Without transition sentences, your reader might not be able to understand the link between different parts of your writing.
What makes a good transition sentence?
Look at this example:
The CEO was very clear that productivity and efficiency were the two key things he would focus on. However , the legacy systems followed by the company acted as a detriment. Tech modernization was the solution that would enhance productivity and efficiency.
Sentences one and three make sense by themselves. But it is important to establish a relationship between the two. This is what the second sentence does . It acts as a bridge (or transition) between the first and third sentences. By doing so, it helps the writer communicate their ideas more effectively.
A good transition sentence would bring clarity by linking ideas expressed in the sentences before and after it. Words and phrases like ‘however,’ ‘in contrast,’ ‘for instance,’ ‘in fact,’ and ‘therefore’ can get used to help make the transition.

Many transition words are available to use. Choose the appropriate word for the situation.
For example, if you want to show the sequence between two sentences, you can use a word like ‘then’ or ‘after.’ If you want to emphasize a point through the transition, you can use ‘indeed,’ ‘especially,’ or ‘particularly.’
Transition words can be used at the start of the sentence ( e.g. , Surely , you are not going to go now!). It can also be used within the sentence (e.g., I rejected the job offer because the salary was lesser than my present pay ).
Here are a few tips that will help you use transition words correctly:
- When sentences within a paragraph sound abrupt or awkward, you need to use transition words to link them.
- Choose the correct transition word that is appropriate to the situation. A wrong selection can make your reader confused.
- When moving from one idea to another, use a transition word to let the reader know.
- Don’t make the mistake of overusing transition words. Too many transition words can end up making your writing look messy.
List of words for transition sentences
Some common words used in transition sentences are:
- Furthermore
- Nevertheless
- Specifically
List of phrases for transition sentences
Transition sentences would use both words and phrases as the bridge. A few phrases that are used include:
- In other words
- On the contrary
- As a result
- In the long run
- As you can see
- In the following
- In the previous
- Having established
- Most importantly
- For example/instance
- By the time
5 Examples of Transitions (Types of Transitions)
Conjunctive adverbs can be used to establish the logical link between ideas. They can be classified under five heads. It must be noted some words appear in multiple categories.
Of addition
- Additionally
- In addition
- In the same way
The following example will make this clear.
First , put a pan on the stove and heat it. Next , add oil to the pan.
In the above, first and next act as the transition and are adding on to what is being said previously.
Of contrast
These words establish a contrast or difference while making the transition.
- In contrast
- Even though
- At any rate
- In spite of that
- On the other hand
The island was not the paradise we were hoping for. On the contrary , it was dirty, noisy, and had unmanageable traffic.
The above example brings out a contrast between expectations and reality.
Of comparison
- By comparison
- In the same manner
Jonathan is crazy about chess. His daughter is similarly a big fan of the board game.
In this example, the word similarly shows a comparison between father and daughter. You may note the transition word need not be at the start of the sentence. It can be placed anywhere.
These transition words are indicative of a result. It shows the result of the previous sentence/idea.
- Consequently
Their star player was suffering from a hamstring injury and could not play. Hence , their team faced a humiliating defeat on match day.
The star player’s absence resulted in the team’s defeat. The transition word ‘Hence’ in the example is the bridge between the cause/event and the result.
Some transition words show relationships in time. They include:
- Simultaneously
- Subsequently
The speaker will be a bit late for the talk. Meanwhile , let’s ask the participants to share their views on the program .
As the speaker will be late, there is time left. So, the participants are asked to share their views and opinions. In this example, ‘Meanwhile’ is a transition word that shows relationship to time.
Subordinating conjunctions and transition sentences
You can use a subordinating conjunction in a sentence to join a dependent clause to an independent clause .
Example: When the postman came, my dog greeted him with a volley of barks.
In this example, the word ‘when’ is the subordinating conjunction that joins ‘the postman came’ and ‘my dog greeted him …’
The subordinating conjunction serves a special purpose here. It acts as a transition between two ideas. The use of the coordinating conjunction provides a logical flow.
Example: He is smarter than you are.
In this example, “than” is the subordinating conjunction that connects ‘He is smarter’ and ‘you are.’ It provides the bridge or transition between the two clauses .
Let’s look at another example to understand this. There are two clauses – ‘The spring arrives’ and ‘my hay fever gets aggravated. A subordinating conjunction can link the two. We can use ‘As’ here. So, the sentence would now read – ‘ As the spring arrives, my hay fever gets aggravated.’
Correlative conjunctions and transition sentences
The correlative conjunction shows a correlation between two words or phrases within a sentence. They play a key role in transition sentences. The use of a correlative conjunction ensures a smooth flow between two sentences or ideas.
Example: My boss totally ignored my work. Neither my hard work nor my punctuality impressed him. So, I decided to move on and look for a new job.
In the above example, sentences one and three are independent and convey the meaning clearly. However, the second sentence acts as a transition explaining why sentence one leads to sentence two.
In the second sentence, we see the use of neither … nor. This combination of words acts as correlative conjunctions in this example.
Some other words that work as correlative conjunctions are:
- Either … or
- Neither … nor
- Whether … or
- Not only … Also
Whether you want to have dinner or prefer to skip it is entirely left to you.
The above example uses Whether … or as correlative conjunctions in the sentence.
Examples of transition sentences
Examples of transition sentences:
Communicate similarities
To communicate similarities, you can use transitional words like:
Examples of sentences where the transition word communicates similarities:
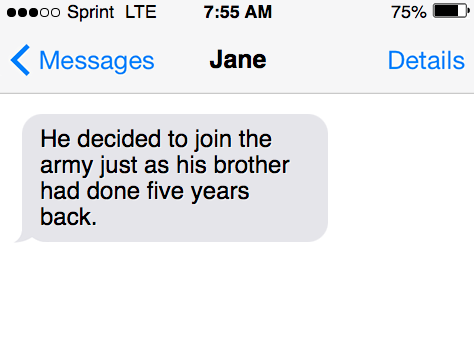
- He decided to join the army just as his brother had done five years back.
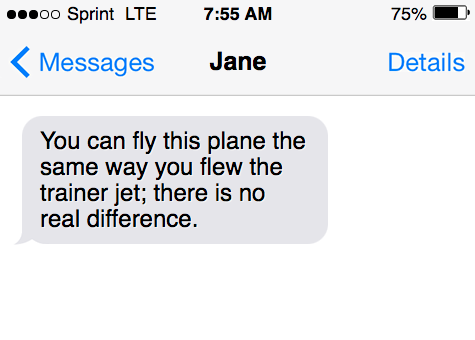
- You can fly this plane the same way you flew the trainer jet; there is no real difference.
- All the employees in the Production department come from the neighboring town . Similarly , the store staff is also from that town.
Express emphasis
Words like ‘especially,’ ‘above all,’ ‘particularly’, ‘indeed,’ in fact,’ and ‘in particular’ can be used to express emphasis. When used in transition sentences, they emphasize the idea express previously.
- She was overweight. In fact , it won’t be wrong to say she was grossly obese.
- I liked the blue dress in particular .
- Indeed , it won’t be wrong to say that her arrogance led to the engagement’s breakup.
- There is a lot of focus on improving public services, especially education.
Cause and effect
Transition sentences can be very helpful in showing cause and effect or result. The following words can be used for this:
- Accordingly
- At that time
- They spent the entire semester binge-watching shows. Consequently , they failed to obtain pass marks on any of the papers.
- There are just ten items left in stock. Hence , it would be better if we suspend taking new orders at present.
- The tests revealed that his blood pressure and cholesterol levels were very high. As a result , the doctor decided that he had to increase the dosage of his medicines.
Position or place can be indicated through the use of transition words like:
- At the back
Here are some example sentences:
- Walk towards the bookshelf. Adjacent to the shelf is a table, that’s where you will find the money.
- The house was located a few yards from the river. Next to the house was the scary-looking tree.
- You will see the building with the red flag. The storeroom is at the back of this building.
Describe a sequence
Transition words are perfect to use while describing a sequence. The words that can be used are:
- Followed by
- First , write down all the numbers in the form of a list. Next , add all the numbers. Finally , write down the total.
- Initially , three employees were working on the project. Subsequently , the project grew the numbers rise to twenty.
- The private plane owned by the CEO was the first to land. This was followed by the helicopter containing the crew.

To show examples
Transition words can be used to show examples or illustrate a particular point. Some words to use are:
- For example
- For instance
- Illustrated by
- As an example
- In this case
- On this occasion
- To illustrate
- To demonstrate
- The speaker displayed the blueprint of the equipment on the screen. To illustrat e its working, he showed a video.
- There are seven tools you can use to solve this problem. As an example , I will talk about the fishbone diagram.
- Different essential oils can help you feel relaxed. For instance , using lavender oil makes you feel refreshed and rejuvenated.
How to use transition sentences between paragraphs
Transition sentences can get used within a paragraph. It also can get used between paragraphs.
This is important since the transition sentence provides a flow between paragraphs . It allows the readers to understand the relationship between the ideas expressed in those two different paragraphs.
When you start writing a paragraph , show a link to the previous paragraph in the first sentence. This establishes a bridge between both paragraphs.
Here’s an example:
There is no doubt that the effects of pollution by industries. This is why activists call for a ban on industries to stop pollution.
Despite the previous argument , we must also think about the economy. Banning industries will bring the economy to a standstill.
This example, ‘despite the previous argument’ is used to transition between the two paragraphs.
In contrast, the first part calls for a ban on industries, and the second discusses the economic effect. Using a transition allows for a smooth flow between the two.
Examples of transition sentences for essays
The use of transitions is very important in essays. An essay is written to convey an idea, opinion, or viewpoint. To ensure its effectiveness, transition sentences are needed at different parts of the essay. Transition sentences are needed between sentences, between sections, and at the conclusion of the essay.
A few examples of this:
- Having established that a large majority of students have internet access, we can conclude t hat e-learning is a distinct possibility.
- All the employees have a smartphone. In fact , most of them connect to the company’s Wi-Fi using their phone.
Examples of transition words for concluding sentences
Transition sentences are used throughout a write-up. It is imperative that the conclusion also has a transition. Your write-up needs to end with a summary of what you are trying to say. Or with a call-to-action. Using transition words in the conclusion can help you achieve this.
A few transition words you can consider using are:
- In conclusion
- As shown above
- On the whole
- Generally speaking
- To summarize
- To summarize , sustained use of this medicine offers significant benefits to patients.
- In summary, democracy has many limitations but no other acceptable alternative.
- Ultimately , it all boils down to the decision taken by the customer.
- In short , the best option available is to get funds from a new investor.
Sentence structure
More on sentence structure:
- Dangling modifier
- Transition sentences
- Active voice
- Passive voice
- Adverbial clause
- Parallelism
- Transition Sentences Tips and Examples for Clear Writing
- Transitional devices
- How to Use Transition Sentences for Smoother Writing
- Transition Words: Examples in Sentences, Paragraphs & Essays
Inside this article
Fact checked: Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.

About the author
Dalia Y.: Dalia is an English Major and linguistics expert with an additional degree in Psychology. Dalia has featured articles on Forbes, Inc, Fast Company, Grammarly, and many more. She covers English, ESL, and all things grammar on GrammarBrain.
Core lessons
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Active Sentence
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Body Paragraph
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- Equivocation Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Gerund Phrase
- Genitive Case
- Helping Verb
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Indicative Mood
- Juxtaposition
- Linking Verb
- Misplaced Modifier
- Nominative Case
- Noun Adjective
- Object Pronoun
- Object Complement
- Order of Adjectives
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Quotation Marks
- Relative Pronoun
- Reflexive Pronoun
- Reciprocal Pronoun
- Subordinating Conjunction
- Simple Future Tense
- Stative Verb
- Subjunctive
- Subject Complement
- Subject of a Sentence
- Sentence Variety
- Second Conditional
- Superlative Adjective
- Slash Symbol
- Topic Sentence
- Types of Nouns
- Types of Sentences
- Uncountable Noun
- Vowels and Consonants
Popular lessons

Stay awhile. Your weekly dose of grammar and English fun.

The world's best online resource for learning English. Understand words, phrases, slang terms, and all other variations of the English language.
- Abbreviations
- Editorial Policy

The Barker Underground
Writing advice from the harvard college writing center tutors, building bridges between your paragraphs.
by Kenneth Mai
Your essay doesn’t flow. Add some transitions.
Those words – along with comments such as “Needs better transitions,” “Where’s the transition?,” or simply “TRANSITION!!!” – plague many a paper that may perhaps otherwise be brilliant.
See, it’s like this. Pretend that the many ideas you’re churning out within a paper are islands in the ocean. (That’s a metaphor! Sometimes metaphors work nicely in papers! ) Some islands are bigger than others. Some are closer to each other, whilst some may seem to be drifting off far away from all the others. Similarly, some ideas are smaller bits a cohesive whole, while others require a bit more effort to reel in. Your task is to gather these islands into a sort of kingdom that you rule. But in order to make sure that you have full control over everything, you need to connect the islands to each other. Now, it’s fine that each island isn’t directly connected to every other island, especially when they’re far enough away from each other to not really be related at all. But ultimately you want all the islands connected to make up a unified whole. So what do you do?
You build bridges!
In the context of writing a paper, these bridges are your transitions. You have two ideas that are related— islands that are close enough that you can build a bridge between them—but ultimately distinct. In order to help your readers across that gulf, then, you need to put in a transition.
But what exactly is a transition? Is it one of the sequential words – “first,” “second,” “finally,” etc. – that were the gold standard of midde school writing? Well…perhaps. But you have many more options now. The kind of transition you use depends on the relationship that you’re trying to build between two ideas, and those relationships can be quite complex. Transitions can be as short as a word or a couple of words to something as long as a sentence or even an entire paragraph. What’s important isn’t so much the shape of the transition as the underlying connection that is being made.
Here are a few useful types of transitions to keep in mind.
- Sequential Transitions: Here, we’re not talking so much about “first, second, third.” Rather, this kind of transition points more towards the ideas that logically follow each other. Words such as “therefore” or “then,” or phrases like “This indicates that…”, show a relationship between the ideas. These transitions are used when one idea is the premise on which the next idea depends or when the second idea comes as a deduction from the first. Examples: Thus, Therefore, Then; It follows that, This indicates that, This implies that; From this we can see that, What this means is that…
- Comparative Transitions : Sometimes, it’s not so much that one idea is derivative of another, but rather that they share some sort of property. This is especially useful when the relationship between the two ideas isn’t obvious. This type of transition is useful in comparative essays (for obvious reasons) but also instrumental when you are using analogies to make a point about some sort of topic (such as talking about islands to make a point about transitions!) Examples: Like, Also, Similarly; Just as, In the same vein; This idea can also be seen in…, A similar phenomenon is found in …
- Contrastive Transitions: There are times when you’re neither describing premise-conclusion relationships nor looking at similarities, but instead focusing on contrasts: “This author says this, but that author says that.” “This appears to be the case, but in reality, it’s something else.” These transitions are useful not only in compare-and-contrast essays, but also whenever you’re trying to debunk a claim or to show another side of an issue. These words can also help you to move on to an entirely different issue. Examples: But, Though, However, Nevertheless/Nonetheless; Then again, On the other hand, At the same time; This ignores, It’s not…but rather, The difference between…and…is that…
- Summing Up Transitions : You’ve established an idea and thrown lots of brilliant evidence our way. Now what? In order to make sure your readers won’t miss important information, it’s a good idea provide the quick and dirty version of the ideas you just laid out before introducing your big, final insight. Examples: Essentially, Basically, Ultimately; In short, In other words, That is to say; This boils down to, The main point is…
Ultimately, the goal of these tools is to bring a sense of cohesion to your paper by showing the logical progression of your thoughts; they’re signposts telling your reader which bridge to cross and what the two islands linked by that bridge have to do with each other. These signposts ought to be everywhere within your paper, moving your reader between phrases and sentences in addition to paragraphs or larger chunks. Sometimes multiple signposts are needed to guide a reader across the bridge, because of the complex relationship of those two ideas. The primary goal to keep in mind, though, is to make sure your reader has a smooth trip. That’s how you make your paper flow.
In my next post, I’ll offer some examples of transitional sentences and paragraphs.
Share this:
Leave a comment.

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar

What Is a Bridge Statement in English Homework?

How to Write a Thesis & Introduction for a Critical Reflection Essay
A writer uses a bridge statement, or bridge sentence, to link one idea to another and create a smooth transition between ideas. John Trimble explains in "Writing with Style: Conversations on the Art of Writing" that essays should maintain a steady flow by "bridging" ideas for the reader. Instead of starting each paragraph with a topic sentence, you can use a bridge sentence to show how the previous idea relates to the idea your article is about to introduce.
Using Bridge Statements
One of the most important bridge statements in an essay, within the introductory paragraph, sets the scene for the reader. The opening statement usually functions as a "hook" or attention grabber to draw in the reader. After this comes your bridge statement, which explains how the opening is relevant to the thesis. The last sentence of the introductory paragraph contains the thesis statement, which demonstrates or sets the stage for what the reader can expect from the rest of your paper.
Paragraph Bridges
Instead of starting with a topic sentence for each paragraph, the writer uses a bridge to make a smooth transition into a new paragraph. Also called a transition idea or transition sentence, it usually discusses the previous point and how it ties in to the new point. The goal is to weave words and ideas together to create a seamless rhetorical tapestry. Your essay should not be a patchwork quilt of jumbled ideas. Bridge sentences provide the chain link between one concept and the next.
Purpose of Bridge Sentences
Bridge sentences resemble topic sentences in the essay structure. They clue in the reader to what the article just mentioned and what will come up next, and how the two topics relate to each other. Expository essays -- the most common essay assigned to students -- inform the reader or give an explanation of a topic based on fact. Persuasive or argumentative essays aim to convince the reader to agree with your point of view by addressing both sides of an argument and refuting the opposition, often in a bridge statement. All essay types make use of bridge statements. For instance, bridge statements in expository essays build a foundation of knowledge by slowly adding on to what has already been presented. Persuasive essays may use bridge statements to introduce a counter argument to hold the reader's attention.
Transitional Keywords
The words you use in your bridge sentences help define the relationship between the paragraphs or ideas you seek to connect. Words such as "consequentially," "therefore" or "accordingly" demonstrate a cause-effect relationship. Words like "whereas," "although" or "nevertheless" establish a contrast between concepts, while "furthermore," "in addition" or "similarly" help you further expand an idea.
Related Articles

How to Write an Introduction to a Reflective Essay
How to write an essay with a thesis statement.

The Functions of Conjunctions in English Argumentative Writing

Ideas for an Imaginative Essay

Comparative Phrases for Essays

How to Write an Introduction to an Analytical Essay

What Is a Diagnostic Paragraph?

How to Write a Comparative Analytical Essay
- Writing Center at Harvard University; Topic Sentences and Signmosting; Elizabeth Abrams; 2000
- The University of Oklahoma: Bridge Sentences
- Long Beach City College: Writing Introductory Paragraphs For Essays
- Purdue University Online Writing Laboratory: Writing Transitions
- DeAnza College: Writing with Style by John R. Trimble

Hooking Things Together With Bridges
essaypop bridge 0
“In the moment of crises, the wise build bridges and the foolish build dams.” – Nigerian Proverb
Mini bridges to introduce research details.
Bridges are like the glue that connects everything in the essay together. Bridges create order and cohesion and allow phrases and ideas to transition together. Without bridges, your writing would feel stiff and awkward. Bridges are often very short; some are just a brief phrase; some are a single word.
In the short response, there are two types of bridges: The first is the simple bridge phrase that connects the thesis statement to the first research detail and, thereafter, research details to accompanying interpretations . Sentence starters that provide these bridge phrases are available via the pull-down curtains located in the bottom-left of each writing frame. Bridge phrases such as, “Consider the following” and “According to” allow writers to smoothly transition into their quotes, facts, and other evidence. Without them, research details land gracelessly and awkwardly onto the paper. Not pretty.
Introducing such information without a bridge would make this information seem abruptly placed and would disrupt the flow of the essay. A basic short response with just one research detail will just have this one transitional bridge. Keep in mind that you don’t need to add a new bridge writing frame in this circumstance because, again, you access it for the research detail frame.
Including additional Bridges
Responses that feature more than one research detail or interpretation usually require another short bridge. In this case, you may want to add a new bridge writing frame using the action icon. Again, without some transition, the flow of the paper will be compromised and the new information will seem awkwardly placed.
One option the writer has in this situation is to simply begin with a research detail sentence starter, using the pull-down described earlier. Just choose a starter that you like and then proceed with the new evidence or commentary. In this case, adding the extra bridge writing frame is not necessary.
If, however, you wish to include a more extensive bridge, you can do so by clicking on the action icon and adding a bridge. This will cause a bridge writing frame to appear and you can write as much as you would like in the box (although we recommend that you keep your bridges to one or two sentences).
Keep in mind that if you feel the need to add more than two or three additional bridges, then you are probably going to want to add a paragraph break or two. Again, this is easily done by adding a paragraph break available in the action icon. What’s ironic is that your “short response” can quickly grow to 750 to 1,000 if you have a lot to say. If you do begin a new paragraph, adding a quick bridge is a great way to start the transition.
Also, keep in mind that if you feel you are moving away from short response territory and moving into writing a more complicated paper, want to consider creating a multiple-paragraph essay instead of a short response.
Bridge Models
These first models feature a short transitional bridge located just after the thesis statement and just before the research detail. The bridges These bridges are shown in context and are in bold underlined text. Keep in mind that these bridges do not require you to open a separate bridge writing frame because they are selected from the sentence starters that are accessed from the research detail writing frame.
Type of essay: short response / response to literature The prompt: In Denise Levertov’s poem, “Moon Tiger”, what is the moon tiger really? Use textual evidence to justify your answer.
…In her poem, “Moon Tiger”, Denise Levertov provides the reader with some very interesting clues as to the true and literal identity of the work’s creeping tiger. Consider the following lines from the poem : “Look. Its white stripes/ In the light that slid/Through the jalousies”. Levertov is inviting us to…
The transitional bridge, “Consider the following lines from the poem” is taken directly from the sentence starter menu located in the pulldown menu of the research detail writing frame.
Type of essay: Expository / Argument The prompt: We just read the Atlantic Monthly article, “How Two Common Medications Became One $455 Million Specialty Pill” by Marshall Allen. In a 300-500 word short essay, discuss whether you believe the Horizon Pharmaceutical Company is justified in selling the drug Vimovo at the price that they do.
…Marshall Allen’s Atlantic monthly article, “How Two Common Medications Became One $455 Million Specialty Pill” brings up two fairly balanced perspectives regarding the cost of their drug, Vimovo. After careful consideration, however, it seems clear that there is no way to justify this company charging such exorbitant prices for this drug . According to this journalist , It seems that Horizon simply takes two very common medications, a pain reliever, and a stomach-upset medicine, and combines them into one pill, because pain relievers cause some people stomach discomfort. Not a bad idea I guess, but at what cost? “Of course I did the math”, says the Allen. “You can walk into your local drugstore and buy a month’s supply of Aleve and Nexium for about $40. For Vimovo, the pharmacy billed my insurance company $3,252.” This is a staggering markup in price. And what’s worse is…
Type of essay: Expository / Argument / Short Response The prompt: We just read the Atlantic Monthly article, “How Two Common Medications Became One $455 Million Specialty Pill” by Marshall Allen. In a 300-500 word short essay, discuss whether you believe the Horizon Pharmaceutical Company is justified in selling the drug Vimovo at the price that they do.
…$455 Million Specialty Pill” brings up two fairly balanced perspectives regarding the cost of their drug, Vimovo. After careful consideration, however, it seems clear that there is no way to justify this company charging such exorbitant prices for this drug. According to this journalist, it seems that Horizon simply takes two very common medications, a pain reliever and a stomach-upset medicine, and combines them into one pill, because pain relievers cause some people stomach discomfort. Not a bad idea I guess, but at what cost? “Of course I did the math”, says the Allen. “You can walk into your local drugstore and buy a month’s supply of Aleve and Nexium for about $40. For Vimovo, the pharmacy billed my insurance company $3,252.” This is a staggering markup in price. And what’s worse is they seem to be getting away with it. Vimovo, according to Allen, has netted the company $455 million since 2014 and shows no signs of slowing down. They seem to be able to get away with this with a series of sales tricks and backroom deals with insurance companies that the doctors and patients prescribing and using the drugs are seldom aware of. And they don’t stop there.
Based on Allen’s research, Vimovo isn’t Horizon’s only such drug. It has brought in an additional $465 million in net sales from Duexis , a similar convenience drug that combines ibuprofen and famotidine, aka Advil and Pepcid. So, they’ve taken a successful…
This is an augmented version of model 2. Two research details are included and both are bridged into with phrases taken from the research-detail-writing-frame sentence starter menu in the respective research writing frames. Here they are both underlined and in bold. The writer chose to indent the second transitional bridge as it is a somewhat new thought.
Adding an Additional Bridge
Sometimes transitions between essay elements require a bit more context and elaboration than a sentence starter allows for. When this is the case, it is sometimes advisable to add a new and distinct bridge. This is easily done using the action icon. The following models feature more elaborate bridges. For ease of identification, these added bridges are highlighted in darker blue .
Type of essay: expository/ argument The prompt: Based on the documents we reviewed in class today that assign blame for the Titanic tragedy to several different individuals, who, in your opinion, is most responsible for the sinking of the RMS Titanic and the deaths of over 1,500 passengers?
…Certainly, many people played a role in the tragedy, but one person seems more culpable than all the others. Based on the documents we have reviewed, it seems clear that Captain Edward J. Smith is the individual most responsible for the sinking of the Titanic and the deaths of all of those unfortunate passengers. Robert Ballard, who is considered one the most-renowned Titanic experts confirms this in his research. Consider the following evidence taken from Ballard’s “Exploring the Titanic”: “In all Captain Smith received seven ice warnings the afternoon and evening of the disaster. Of those, only 3 were posted for anyone to see.” (367) Ignoring this many ice warnings just seems like a recipe for disaster. To use a car/driver analogy, this would be like…
This bridge begins by providing some important contextual information about Robert Ballard; it is important that we know why Mr. Ballard is worthy of listening to. The bridge then transitions to the sentence starter, “Consider the following evidence…”. Together, these create a smooth transition into the research detail.
Type of essay: research/expository The prompt: Are rattlesnakes a bane or a benefit to mankind? Respond in a structured, evidence-based short constructed response that is 300-350 words in length.
… According to the Queensland Department of Environment, “The feeding habits of rattlesnakes act as a natural form of pest control. Snakes are predators and feed on a variety of creatures. Small snakes feed on many harmful bugs and insects. Larger ones eat mice, rats, and other small mammals that can destroy crops or damage personal property.” (Dept. of Environment) It is clear that if we were to eliminate rattlesnakes from our environment to make ourselves “safe”, we would inadvertently and ironically create the opposite effect. An increase in insects and rodents would most certainly lead to such adverse effects as bites, feces in food supplies and the diseases that accompany these conditions. So as you can see, these creatures do have some beneficial qualities Recent research by other scientists supports this idea. In fact, “New research by a team of University of Maryland biologists shows the timber rattlesnake indirectly benefits humankind by keeping Lyme disease in check.” (Kabay) Lyme disease is a very deadly illness that can…
The first transitional bridge beginning with the phrase, “According to…”, comes directly from the research detail sentence starter menu. The second bridge, highlighted in darker blue , sets up the next research detail. Since it is a bit longer, the writer added a bridge writing frame to the mix using the action icon. This bridge allows the next research detail and subsequent interpretation to flow smoothly within the paper. The sentence starter, “In fact”, is used here as well.
Type of Essay: response to literature The prompt: In a multiple-paragraph composition analyze and compare the recurring theme about the nature of love that can be found in William Shakespeare’s “Sonnet 130” and Rodgers and Hart’s jazz classic, “My Funny Valentine”.
…What if instead of being sarcasm or even a celebration of a lover’s “perfect imperfections”, these words were literal descriptions of loved ones who are ill and at the end of their days? As an illustration of this, take these lines from Shakespeare’s Sonnet 130: “I have seen roses damasked, red and white/But no such roses see I in her cheeks;/And in some perfumes is there more delight/Than in the breath that from my mistress reeks”. One could easily read these words as sarcastic jesting or a loving acknowledgment of a few physical flaws. One the other hand, they can also be construed as true depictions of illness and age. The cheeks lose their color because of some sickness and the breath becomes malodorous due to internal disease. Meanwhile, the speaker can only observe helplessly as his lover slowly fades away. Rodgers and Hart seem to be on the same page as the bard, and we see this dark possibility again in “My Funny Valentine” when the singer mournfully asks, “Is your figure less than Greek?/Is your mouth a little weak?/ When you open it to speak, are you smart?” Again, these rhetorical questions could easily be…
The first transitional bridge beginning with the phrase, “As an illustration of this…”, comes directly from the research detail sentence starter menu. The second bridge, highlighted in darker blue , sets up the next research detail. Since it is a bit longer, the writer added a bridge writing frame to the mix using the action icon. This bridge allows the next research detail and subsequent interpretation to flow smoothly within the paper.
Related Posts

Style Guide
What is a Short Response Essay?

Closer – Let’s Land This Thing!

Mastering the Short Response Hook
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
The Enlightened Mindset
Exploring the World of Knowledge and Understanding
Welcome to the world's first fully AI generated website!
What is a Bridge in Writing? A Comprehensive Guide to Crafting Effective Writing Bridges
By Happy Sharer

Introduction
Writing bridges are an essential tool for connecting ideas and creating transitions in your written work. A bridge in writing is a sentence or phrase that links two separate ideas together. They can also be used to emphasize the importance of one idea over another, or to add emphasis to an argument. Writing bridges can help to make your writing clear, concise, and captivating.
A Comprehensive Guide to Writing Bridges
Writing bridges can be used to connect ideas within a single sentence, between sentences, or even between paragraphs. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to use them effectively:
How to Use Bridges to Connect Ideas in Your Writing
When writing a bridge, you want to start by identifying the two ideas you want to link together. Once you’ve identified the two ideas, you can begin crafting your bridge. To create an effective bridge, you should consider the following:
- The purpose of your bridge: Is it to emphasize an idea? To introduce a new idea? To provide a contrast between two ideas?
- The tone of your bridge: Will it be formal or informal? Will it be lighthearted or serious?
- The structure of your bridge: Should it be a single sentence or multiple sentences? Should it include a rhetorical question?
Crafting Creative and Effective Writing Bridges
Once you’ve considered the purpose, tone, and structure of your bridge, it’s time to start crafting it. Here are some tips for crafting creative and effective writing bridges:
- Start with a strong transition word or phrase: Transition words and phrases can help to make your writing more fluid and help to emphasize the connection between two ideas. Examples of transition words and phrases include “in contrast,” “on the other hand,” “similarly,” and “nevertheless.”
- Provide a summary of the previous idea: Summarizing the previous idea can help to make your bridge more effective and will help to remind readers of the context. This can be done in a single sentence or with a few sentences.
- Introduce the new idea: After summarizing the previous idea, you can then introduce the new idea. This can be done in a single sentence or with a few sentences.
- Conclude with a strong statement: Finally, conclude your bridge with a strong statement. This will help to emphasize the connection between the two ideas and will leave readers with an impactful impression.
Examples of Writing Bridges Used in Literature
Now that you’re familiar with how to craft effective writing bridges, let’s take a look at some examples of writing bridges used in literature. These examples will help to illustrate the different types of writing bridges and how they can be used in your own writing.
Three Types of Bridges and How to Use Them in Writing
There are three main types of writing bridges: explicit bridges, implicit bridges, and rhetorical bridges. Explicit bridges are direct statements that explicitly state the relationship between two ideas. Implicit bridges use language to imply the relationship between two ideas. Rhetorical bridges use questions or statements to draw attention to a particular idea or to emphasize an argument.
Bridging the Gap: Writing Bridges for Smooth Transitions
Writing bridges can also be used to create smooth transitions in your writing. When transitioning from one idea to another, it’s important to provide a bridge that clearly states the connection between the two ideas. This will help to ensure that readers understand the context and follow the flow of your writing.
Harnessing the Power of Writing Bridges to Enhance Your Storytelling
Finally, writing bridges can be used to enhance your storytelling. By using bridges to emphasize key points, add tension, and create suspense, you can take your storytelling to the next level. Doing so will keep readers engaged and will help to create a captivating story.
Writing bridges are a powerful tool for connecting ideas and creating smooth transitions in your writing. They can be used to emphasize the importance of one idea over another, to add emphasis to an argument, and to enhance your storytelling. By following the tips outlined in this guide, you can craft effective writing bridges and use them to improve your writing.
With practice, you can learn to use writing bridges to capture your readers’ attention and engage them in your work.
(Note: Is this article not meeting your expectations? Do you have knowledge or insights to share? Unlock new opportunities and expand your reach by joining our authors team. Click Registration to join us and share your expertise with our readers.)
Hi, I'm Happy Sharer and I love sharing interesting and useful knowledge with others. I have a passion for learning and enjoy explaining complex concepts in a simple way.
Related Post
Unlocking creativity: a guide to making creative content for instagram, embracing the future: the revolutionary impact of digital health innovation, the comprehensive guide to leadership consulting: enhancing organizational performance and growth, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Expert Guide: Removing Gel Nail Polish at Home Safely
Trading crypto in bull and bear markets: a comprehensive examination of the differences, making croatia travel arrangements, make their day extra special: celebrate with a customized cake.

Home » Writers-House Blog » English Homework: Bridge Statements
English Homework: Bridge Statements
Writers use bridge sentences, or bridge statements, to connect ideas and to create a smooth transition between them. To make an essay easy to read, you need to connect your ideas, ensuring a smooth flow. Bridge sentences can be used instead of topic sentences at the beginning of a paragraph to explain how previous ideas relate to the new idea that you’re going to introduce in the next paragraph. Learn more about bridge statements with WritersHouse expert opinion.
How to Use Bridge Statements
A bridge statement in the introductory paragraph is especially important because it sets the context for your readers. Usually, the opening statement acts as a hook that grabs attention and makes your audience want to read more. A bridge statement follows the hook, explaining why the opening is relevant to your thesis statement. The last sentence of the introduction must contain the thesis statement, explaining what your readers should expect from the rest of the paper.
Paragraph Bridges
You can start each paragraph with a topic sentence, or you can use a bridge to create a smooth transition to the next paragraph. It is also called a transition sentence or transition idea. Usually, it focuses on the previous point and leads readers to the next point, connecting them logically. Your goal is to make a seamless transition so that your essay will look natural and be easy to read. Bridge sentences help connect different concepts so that you can make sure that your essay makes sense.
The Purpose of Bridge Sentences
Bridge sentences are similar to topic sentences because they perform the same functions in the essay structure. They help readers remember what the writer has mentioned before, connecting this information to the new facts and ideas that will come up next. Simply put, these sentences help explain how different topics relate to each other. Bridge sentences can be used in different essays. For example, expository essays are one of the most common types of writing assignments that are aimed to inform readers or to explain a certain topic based on facts. Argumentative or persuasive essays should convince the audience to agree with the author’s opinion by addressing different perspectives and refuting the opposite opinion. Quite often, writers do it in a bridge statement. When writing an expository essay, your bridge statement may simply add some new information to what you have already presented. In persuasive essays, bridge statements can address a counterargument.
Transitional Keywords
Various transitional words can help you indicate the relationship between different ideas. For example, such words as “accordingly,” “therefore,” and “consequently” illustrate a cause-effect relationship. “Similarly,” “in addition,” and “furthermore” can help you expand your idea, while “nevertheless,” “although,” and “whereas” can establish a contrast.
Leave a Reply
Be the First to Comment!
Place your order
- Essay Writer
- Essay Writing Service
- Term Paper Writing
- Research Paper Writing
- Assignment Writing Service
- Cover Letter Writing
- CV Writing Service
- Resume Writing Service
- 5-Paragraph Essays
- Paper By Subjects
- Affordable Papers
- Prime quality of each and every paper
- Everything written per your instructions
- Native-speaking expert writers
- 100% authenticity guaranteed
- Timely delivery
- Attentive 24/7 customer care team
- Benefits for return customers
- Affordable pricing
- Generating Ideas
- Drafting and Revision
- Sources and Evidence
- Style and Grammar
- Specific to Creative Arts
- Specific to Humanities
- Specific to Sciences
- Specific to Social Sciences
- CVs, Résumés and Cover Letters
- Graduate School Applications
- Other Resources
- Hiatt Career Center
- University Writing Center
- Classroom Materials
- Course and Assignment Design
- UWP Instructor Resources
- Writing Intensive Requirement
- Criteria and Learning Goals
- Course Application for Instructors
- What to Know about UWS
- Teaching Resources for WI
- FAQ for Instructors
- FAQ for Students
- Journals on Writing Research and Pedagogy
- University Writing Program
- Degree Programs
- Graduate Programs
- Brandeis Online
- Summer Programs
- Undergraduate Admissions
- Graduate Admissions
- Financial Aid
- Summer School
- Centers and Institutes
- Funding Resources
- Housing/Community Living
- Clubs and Organizations
- Community Service
- Brandeis Arts Engagement
- Rose Art Museum
- Our Jewish Roots
- Mission and Diversity Statements
- Administration
- Faculty & Staff
- Alumni & Friends
- Parents & Families
- Campus Calendar
- Directories
- New Students
- Shuttle Schedules
- Support at Brandeis
Writing Resources
Constructing effective body paragraphs.
This handout is available for download in DOCX format and PDF format .
A paragraph is a collection of related sentences dealing with a single topic. This handout breaks the paragraph down into its conceptual and structural components.
The conceptual components— direction , movement , and bridges —form the logical makeup of any effective paragraph. The structural elements— topic sentence , transitions , evidence , analysis , and conclusion —are identifiable parts of strong body paragraphs.
Conceptual Components
It is useful to envision body paragraphs as links in the chain of reasoning that forms the overall argument of your essay. In order to get to the next link, each paragraph must establish a claim that moves your overall argument one step closer to its ultimate goal (i.e., proving its thesis). Though the topic sentence will announce your paragraph’s direction, the movement of your analysis within the paragraph will consist of pushing this claim from being unproven at the outset of the paragraph to logically compelling at the end.
Bridges establish the coherence that makes the movement between your ideas easily understandable to the reader. Logical bridges ensure that the same idea is carried over from sentence to sentence. Verbal bridges use language — repetition of keywords and synonyms, use of transitions, etc. — that makes the logical connections between your ideas clear to your reader.
Structural Components
Topic sentence.
The first sentence in a paragraph should clearly announce the thesis of the paragraph (i.e., its direction), the claim that will be supported by the content of the paragraph. Effective topic sentences will often link this local claim back to the overall thesis of the essay.
Transitions (Movement)
Transitions are verbal bridges that use language to make the logical movement and structure of an essay clear to the reader. The topic sentence will often contain a transition that links the argument of the paragraph to the one made in the previous paragraph. This is most often accomplished by opening the paragraph with a prepositional phrase or by retaining some important language from the previous paragraph. The final sentence of a paragraph may also suggest a logical link to the argument to come. Transitions do not always link adjacent paragraphs. Good writers will refer back to relevant points made several paragraphs earlier. Especially long or complex papers will often contain several sentences (even entire paragraphs) of transitional material summarizing what the essay has sought to establish up to that point.
Quotations, examples, data, testimony, etc. should be cited as evidence in support of your paragraph’s central claim. In order to avoid generalization, you should strive to use evidence that is as specific as possible. Evidence should be preceded by an introduction to its source and relevance and followed by analysis of its significance to your overall argument.
Evidence alone does not make your argument for you. Evidence requires analysis to make it relevant to an argument. Analyzing effectively requires showing or explaining how the evidence you have cited actually supports the larger claims your essay is making, both on the paragraph level and the thesis level. Because analytical sections are the places where your essay does real argumentative work, they should constitute the bulk of your paragraph (and essay).
Example Body Paragraph
Here is an example of a body paragraph that we will analyze sentence by sentence:
Swift undermines Gulliver's negative view of humankind by making his hero devolve, in the grip of that view, into an irrational and sadly comic character, unable to appreciate acts of genuine human goodness. Upon leaving the Houyhnhnms at the end of the story, Gulliver's disillusionment with humanity and desire for withdrawal seem, at first, understandable, if not darkly humorous. He wants to find some "small Island uninhabited" in which to isolate himself from human society, "so horrible was the Idea ... of returning to live in the Society and under the Government of Yahoos" (248). But this disillusionment escalates to sociopathia. When he returns home to his wife and children, "the Sight of them filled [him] only with Hatred, Disgust, and Contempt; and the more, by reflecting on the near alliance [he] had to them" (253). Just as Gulliver is disgusted with humanity, by this point Swift is clearly disgusted with Gulliver. Once affably curious, after his departure from the Houyhnhnms, Gulliver loses touch with natural human feelings, values, and priorities. His wife welcomes him home with love, patience, and forbearance, taking him "in her arms and kiss[ing]" him (253). Instead of embracing her in return, Gullivers falls into a "Swoon" for having been touched by an "odious Animal" (253) — a shameful epithet for a loved one. Rather than trying to integrate himself into human society, Gulliver pathologically withdraws from human contact and spends his time talking to a pair of stable horses (254). Here Swift shows us the danger of an excessive sensitivity to human feelings.







COMMENTS
Bridge sentence types and examples. Among bridge sentences, three main types are usually used: a classic bridge sentence, a question-answer bridge, and a complication bridge. They all have three things in common: The use of a "pointer" word that directs the reader's attention to the previous paragraph. A part of the sentence that serves ...
What is the Purpose of Bridging Paragraphs? While writing an essay or any academic or business paper, using transitional devices such as bridge sentences is essential in connecting similar thoughts together. This serves as an escort from a previous topic being discussed to a new one. For example, the bridge sentence of an introductory paragraph is typically found between the 'hook' and the ...
A bridge sentence, also known as a paragraph bridge or a bridge statement, is a sentence that links two paragraphs or sections of an essay. It usually appears at the beginning of a new paragraph, and it serves as a summary of the previous point and a preview of the next point. It can also address a counterargument or introduce a new perspective ...
Transition sentences, as their name implies, express the transitions between thoughts that link them together. They're the segues that communicate the how, when, where, why, and other relationships you explore in your writing as you move from the introduction to the conclusion, incorporating all relevant supporting points along the way.
From a simple definition, a bridge sentence is a general term that refers to a set of phrases that link ideas and create a smooth transition between concepts in an essay or a research paper. Some examples of bridging phrases include topic, transitional, concluding statements, and pointers. In turn, a single essay or research paper may contain ...
Abruptly switching topics in essays can be jarring; however, transition words can smooth the change for the convenience of the reader.Moreover, you can use essay transition words to start a paragraph, sentence, or clause more naturally.Additionally, essay transition words can connect new information to the previous statement so you don't have to say everything at once.
Clear transitions are crucial to clear writing: They show the reader how different parts of your essay, paper, or thesis are connected. Transition sentences can be used to structure your text and link together paragraphs or sections. Example of a transition sentence for a new paragraph. In this case, the researchers concluded that the method ...
Topic sentences and signposts make an essay's claims clear to a reader. Good essays contain both. ... Bridge sentences indicate both what came before and what comes next (they "bridge" paragraphs) without the formal trappings of multiple clauses: "But there is a clue to this puzzle." Pivots. Topic sentences don't always appear at the beginning ...
This is what the second sentence does. It acts as a bridge (or transition) between the first and third sentences. By doing so, it helps the writer communicate their ideas more effectively. ... Examples of transition sentences for essays. The use of transitions is very important in essays. An essay is written to convey an idea, opinion, or ...
These signposts ought to be everywhere within your paper, moving your reader between phrases and sentences in addition to paragraphs or larger chunks. Sometimes multiple signposts are needed to guide a reader across the bridge, because of the complex relationship of those two ideas. The primary goal to keep in mind, though, is to make sure your ...
Bridge Sentences. A bridge sentence is a special kind of topic sentence. In addition to signaling what the new paragraph is about, it shows how that follows from what the old paragraph said. The key to constructing good bridges is briefly pointing back to what you just finished saying. Paragraph 3 à.
See the full course at http://crwnow.comTranscript: The first paragraph in your essay is the introduction. After you write your introductory hook you have to...
A writer uses a bridge statement, or bridge sentence, to link one idea to another and create a smooth transition between ideas. John Trimble explains in "Writing with Style: Conversations on the Art of Writing" that essays should maintain a steady flow by "bridging" ideas for the reader. Instead of starting each paragraph with a topic sentence ...
Bridges are like the glue that connects everything in the essay together. Bridges create order and cohesion and allow phrases and ideas to transition together. Without bridges, your writing would feel stiff and awkward. Bridges are often very short; some are just a brief phrase; some are a single word. In the short response, there are two types ...
A bridge in writing is a sentence or phrase that links two separate ideas together. They can also be used to emphasize the importance of one idea over another, or to add emphasis to an argument. Writing bridges can help to make your writing clear, concise, and captivating.
Bridge Sentences. The first sentence of a new paragraph has a great deal of work to do. Not only is it a "topic sentence" signaling what this new paragraph will do, it must also be a "bridge sentence," guiding the reader from what you've just said to the next step in your reasoning.
Writers use bridge sentences, or bridge statements, to connect ideas and to create a smooth transition between them. To make an essay easy to read, you need to connect your ideas, ensuring a smooth flow. Bridge sentences can be used instead of topic sentences at the beginning of a paragraph to explain how previous ideas relate to the new idea ...
The essay introduction is the first part of an essay, and it contains a hook, a bridge, and a thesis.It also functions to provide an overview of the rest of the essay. It might not be the most ...
Logical bridges ensure that the same idea is carried over from sentence to sentence. Verbal bridges use language — repetition of keywords and synonyms, use of transitions, etc. — that makes the logical connections between your ideas clear to your reader. ... Like the conclusion to the essay as a whole, the final sentence of a paragraph is a ...
Bridging words create narrative flow. They connect two separate ideas with some sort of relationship. They can be used to connect separate clauses or sentences, or even paragraphs, with more flexibility than a simple conjunction. They got to the station on time, but the train had left early. They got to the station on time.
Tools like the Aithor essay writer can improve your essays, but learning these rules yourself will help you use these tools better and improve your essay writing skills in the long run. 5. Write a Compelling Introduction. The introduction sets the mood for your whole essay and is your chance to get the reader interested.
A bridge, also known as a transition sentence or transition sentence, acts as a link between ideas or paragraphs in your essay. ... So, the next time you do an essay, remember to build strong connections between your ideas and guide your readers on a smooth journey from start to finish. Share Add a Comment. Be the first to comment
Cllaassssiicc iAAnnaallooggyy BBrriddggeess. foreveryone.orgClassic Analogy Bridges The best strategy to use when completing analogi. s problems is the bridge sentence strategy. Bridge sentences are helpful because they enable the student to instantly recognize the answer pair by plugging it into the bridge.
That's the magic of good sentence flow. It's not always easy to do, but it's important. No matter what you're writing — an essay, a blog post, or a story — how to make your writing flow can really change how people enjoy it. Let's look at some ways to improve a sentence and make your sentences flow better. 1.
In an essay, a bridge is a transitional statement or phrase that connects one idea or paragraph to another. It helps to create a smooth flow and cohesion within the essay, allowing the reader to follow the writer's train of thought. For example, the bridge sentence could be used to introduce a new topic, provide clarification, or establish a ...
Develop a Strong Thesis: Your thesis statement is the main argument of your essay and the most important sentence you'll write. Make it clear and compelling, setting the stage for your entire essay. ... This background information should bridge the gap between your hook and your thesis statement. Explain why your topic matters, touch on recent ...
Expository Essay. On the other hand, the thesis statement for an expository essay aims to explain or describe the topic in a neutral way and is not argumentative. It provides the reader with a clear view of what the essay is going to talk about or analyze since it contains purely factual information, providing insight into the subject matter.
Officials had braced for more unrest on Wednesday, but the night's anti-immigration protests were smaller, with counterprotesters dominating the streets instead.
James Nelson, 18, from Victoria Road, Horwich, Bolton, is thought to be the first person to receive a prison sentence in relation to the unrest If you'd like to continue reading about this story ...