How to write a research plan: Step-by-step guide
Last updated
30 January 2024
Reviewed by
Short on time? Get an AI generated summary of this article instead
Today’s businesses and institutions rely on data and analytics to inform their product and service decisions. These metrics influence how organizations stay competitive and inspire innovation. However, gathering data and insights requires carefully constructed research, and every research project needs a roadmap. This is where a research plan comes into play.
Read this step-by-step guide for writing a detailed research plan that can apply to any project, whether it’s scientific, educational, or business-related.
- What is a research plan?
A research plan is a documented overview of a project in its entirety, from end to end. It details the research efforts, participants, and methods needed, along with any anticipated results. It also outlines the project’s goals and mission, creating layers of steps to achieve those goals within a specified timeline.
Without a research plan, you and your team are flying blind, potentially wasting time and resources to pursue research without structured guidance.
The principal investigator, or PI, is responsible for facilitating the research oversight. They will create the research plan and inform team members and stakeholders of every detail relating to the project. The PI will also use the research plan to inform decision-making throughout the project.
- Why do you need a research plan?
Create a research plan before starting any official research to maximize every effort in pursuing and collecting the research data. Crucially, the plan will model the activities needed at each phase of the research project .
Like any roadmap, a research plan serves as a valuable tool providing direction for those involved in the project—both internally and externally. It will keep you and your immediate team organized and task-focused while also providing necessary definitions and timelines so you can execute your project initiatives with full understanding and transparency.
External stakeholders appreciate a working research plan because it’s a great communication tool, documenting progress and changing dynamics as they arise. Any participants of your planned research sessions will be informed about the purpose of your study, while the exercises will be based on the key messaging outlined in the official plan.
Here are some of the benefits of creating a research plan document for every project:
Project organization and structure
Well-informed participants
All stakeholders and teams align in support of the project
Clearly defined project definitions and purposes
Distractions are eliminated, prioritizing task focus
Timely management of individual task schedules and roles
Costly reworks are avoided
- What should a research plan include?
The different aspects of your research plan will depend on the nature of the project. However, most official research plan documents will include the core elements below. Each aims to define the problem statement , devising an official plan for seeking a solution.
Specific project goals and individual objectives
Ideal strategies or methods for reaching those goals
Required resources
Descriptions of the target audience, sample sizes , demographics, and scopes
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
Project background
Research and testing support
Preliminary studies and progress reporting mechanisms
Cost estimates and change order processes
Depending on the research project’s size and scope, your research plan could be brief—perhaps only a few pages of documented plans. Alternatively, it could be a fully comprehensive report. Either way, it’s an essential first step in dictating your project’s facilitation in the most efficient and effective way.
- How to write a research plan for your project
When you start writing your research plan, aim to be detailed about each step, requirement, and idea. The more time you spend curating your research plan, the more precise your research execution efforts will be.
Account for every potential scenario, and be sure to address each and every aspect of the research.
Consider following this flow to develop a great research plan for your project:

Define your project’s purpose
Start by defining your project’s purpose. Identify what your project aims to accomplish and what you are researching. Remember to use clear language.
Thinking about the project’s purpose will help you set realistic goals and inform how you divide tasks and assign responsibilities. These individual tasks will be your stepping stones to reach your overarching goal.
Additionally, you’ll want to identify the specific problem, the usability metrics needed, and the intended solutions.
Know the following three things about your project’s purpose before you outline anything else:
What you’re doing
Why you’re doing it
What you expect from it
Identify individual objectives
With your overarching project objectives in place, you can identify any individual goals or steps needed to reach those objectives. Break them down into phases or steps. You can work backward from the project goal and identify every process required to facilitate it.
Be mindful to identify each unique task so that you can assign responsibilities to various team members. At this point in your research plan development, you’ll also want to assign priority to those smaller, more manageable steps and phases that require more immediate or dedicated attention.
Select research methods
Once you have outlined your goals, objectives, steps, and tasks, it’s time to drill down on selecting research methods . You’ll want to leverage specific research strategies and processes. When you know what methods will help you reach your goals, you and your teams will have direction to perform and execute your assigned tasks.
Research methods might include any of the following:
User interviews : this is a qualitative research method where researchers engage with participants in one-on-one or group conversations. The aim is to gather insights into their experiences, preferences, and opinions to uncover patterns, trends, and data.
Field studies : this approach allows for a contextual understanding of behaviors, interactions, and processes in real-world settings. It involves the researcher immersing themselves in the field, conducting observations, interviews, or experiments to gather in-depth insights.
Card sorting : participants categorize information by sorting content cards into groups based on their perceived similarities. You might use this process to gain insights into participants’ mental models and preferences when navigating or organizing information on websites, apps, or other systems.
Focus groups : use organized discussions among select groups of participants to provide relevant views and experiences about a particular topic.
Diary studies : ask participants to record their experiences, thoughts, and activities in a diary over a specified period. This method provides a deeper understanding of user experiences, uncovers patterns, and identifies areas for improvement.
Five-second testing: participants are shown a design, such as a web page or interface, for just five seconds. They then answer questions about their initial impressions and recall, allowing you to evaluate the design’s effectiveness.
Surveys : get feedback from participant groups with structured surveys. You can use online forms, telephone interviews, or paper questionnaires to reveal trends, patterns, and correlations.
Tree testing : tree testing involves researching web assets through the lens of findability and navigability. Participants are given a textual representation of the site’s hierarchy (the “tree”) and asked to locate specific information or complete tasks by selecting paths.
Usability testing : ask participants to interact with a product, website, or application to evaluate its ease of use. This method enables you to uncover areas for improvement in digital key feature functionality by observing participants using the product.
Live website testing: research and collect analytics that outlines the design, usability, and performance efficiencies of a website in real time.
There are no limits to the number of research methods you could use within your project. Just make sure your research methods help you determine the following:
What do you plan to do with the research findings?
What decisions will this research inform? How can your stakeholders leverage the research data and results?
Recruit participants and allocate tasks
Next, identify the participants needed to complete the research and the resources required to complete the tasks. Different people will be proficient at different tasks, and having a task allocation plan will allow everything to run smoothly.
Prepare a thorough project summary
Every well-designed research plan will feature a project summary. This official summary will guide your research alongside its communications or messaging. You’ll use the summary while recruiting participants and during stakeholder meetings. It can also be useful when conducting field studies.
Ensure this summary includes all the elements of your research project . Separate the steps into an easily explainable piece of text that includes the following:
An introduction: the message you’ll deliver to participants about the interview, pre-planned questioning, and testing tasks.
Interview questions: prepare questions you intend to ask participants as part of your research study, guiding the sessions from start to finish.
An exit message: draft messaging your teams will use to conclude testing or survey sessions. These should include the next steps and express gratitude for the participant’s time.
Create a realistic timeline
While your project might already have a deadline or a results timeline in place, you’ll need to consider the time needed to execute it effectively.
Realistically outline the time needed to properly execute each supporting phase of research and implementation. And, as you evaluate the necessary schedules, be sure to include additional time for achieving each milestone in case any changes or unexpected delays arise.
For this part of your research plan, you might find it helpful to create visuals to ensure your research team and stakeholders fully understand the information.
Determine how to present your results
A research plan must also describe how you intend to present your results. Depending on the nature of your project and its goals, you might dedicate one team member (the PI) or assume responsibility for communicating the findings yourself.
In this part of the research plan, you’ll articulate how you’ll share the results. Detail any materials you’ll use, such as:
Presentations and slides
A project report booklet
A project findings pamphlet
Documents with key takeaways and statistics
Graphic visuals to support your findings
- Format your research plan
As you create your research plan, you can enjoy a little creative freedom. A plan can assume many forms, so format it how you see fit. Determine the best layout based on your specific project, intended communications, and the preferences of your teams and stakeholders.
Find format inspiration among the following layouts:
Written outlines
Narrative storytelling
Visual mapping
Graphic timelines
Remember, the research plan format you choose will be subject to change and adaptation as your research and findings unfold. However, your final format should ideally outline questions, problems, opportunities, and expectations.
- Research plan example
Imagine you’ve been tasked with finding out how to get more customers to order takeout from an online food delivery platform. The goal is to improve satisfaction and retain existing customers. You set out to discover why more people aren’t ordering and what it is they do want to order or experience.
You identify the need for a research project that helps you understand what drives customer loyalty . But before you jump in and start calling past customers, you need to develop a research plan—the roadmap that provides focus, clarity, and realistic details to the project.
Here’s an example outline of a research plan you might put together:
Project title
Project members involved in the research plan
Purpose of the project (provide a summary of the research plan’s intent)
Objective 1 (provide a short description for each objective)
Objective 2
Objective 3
Proposed timeline
Audience (detail the group you want to research, such as customers or non-customers)
Budget (how much you think it might cost to do the research)
Risk factors/contingencies (any potential risk factors that may impact the project’s success)
Remember, your research plan doesn’t have to reinvent the wheel—it just needs to fit your project’s unique needs and aims.
Customizing a research plan template
Some companies offer research plan templates to help get you started. However, it may make more sense to develop your own customized plan template. Be sure to include the core elements of a great research plan with your template layout, including the following:
Introductions to participants and stakeholders
Background problems and needs statement
Significance, ethics, and purpose
Research methods, questions, and designs
Preliminary beliefs and expectations
Implications and intended outcomes
Realistic timelines for each phase
Conclusion and presentations
How many pages should a research plan be?
Generally, a research plan can vary in length between 500 to 1,500 words. This is roughly three pages of content. More substantial projects will be 2,000 to 3,500 words, taking up four to seven pages of planning documents.
What is the difference between a research plan and a research proposal?
A research plan is a roadmap to success for research teams. A research proposal, on the other hand, is a dissertation aimed at convincing or earning the support of others. Both are relevant in creating a guide to follow to complete a project goal.
What are the seven steps to developing a research plan?
While each research project is different, it’s best to follow these seven general steps to create your research plan:
Defining the problem
Identifying goals
Choosing research methods
Recruiting participants
Preparing the brief or summary
Establishing task timelines
Defining how you will present the findings
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 6 February 2023
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 April 2023
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you’re on board with our cookie policy

- A Research Guide
- Research Paper Guide
How to Write a Research Plan
- Research plan definition
- Purpose of a research plan
- Research plan structure
- Step-by-step writing guide
Tips for creating a research plan
- Research plan examples
Research plan: definition and significance
What is the purpose of a research plan.
- Bridging gaps in the existing knowledge related to their subject.
- Reinforcing established research about their subject.
- Introducing insights that contribute to subject understanding.
Research plan structure & template
Introduction.
- What is the existing knowledge about the subject?
- What gaps remain unanswered?
- How will your research enrich understanding, practice, and policy?
Literature review
Expected results.
- Express how your research can challenge established theories in your field.
- Highlight how your work lays the groundwork for future research endeavors.
- Emphasize how your work can potentially address real-world problems.
5 Steps to crafting an effective research plan
Step 1: define the project purpose, step 2: select the research method, step 3: manage the task and timeline, step 4: write a summary, step 5: plan the result presentation.
- Brainstorm Collaboratively: Initiate a collective brainstorming session with peers or experts. Outline the essential questions that warrant exploration and answers within your research.
- Prioritize and Feasibility: Evaluate the list of questions and prioritize those that are achievable and important. Focus on questions that can realistically be addressed.
- Define Key Terminology: Define technical terms pertinent to your research, fostering a shared understanding. Ensure that terms like “church” or “unreached people group” are well-defined to prevent ambiguity.
- Organize your approach: Once well-acquainted with your institution’s regulations, organize each aspect of your research by these guidelines. Allocate appropriate word counts for different sections and components of your research paper.
Research plan example

- Writing a Research Paper
- Research Paper Title
- Research Paper Sources
- Research Paper Problem Statement
- Research Paper Thesis Statement
- Hypothesis for a Research Paper
- Research Question
- Research Paper Outline
- Research Paper Summary
- Research Paper Prospectus
- Research Paper Proposal
- Research Paper Format
- Research Paper Styles
- AMA Style Research Paper
- MLA Style Research Paper
- Chicago Style Research Paper
- APA Style Research Paper
- Research Paper Structure
- Research Paper Cover Page
- Research Paper Abstract
- Research Paper Introduction
- Research Paper Body Paragraph
- Research Paper Literature Review
- Research Paper Background
- Research Paper Methods Section
- Research Paper Results Section
- Research Paper Discussion Section
- Research Paper Conclusion
- Research Paper Appendix
- Research Paper Bibliography
- APA Reference Page
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography vs Works Cited vs References Page
- Research Paper Types
- What is Qualitative Research

Receive paper in 3 Hours!
- Choose the number of pages.
- Select your deadline.
- Complete your order.
Number of Pages
550 words (double spaced)
Deadline: 10 days left
By clicking "Log In", you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We'll occasionally send you account related and promo emails.
Sign Up for your FREE account
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
How to Create a Structured Research Paper Outline | Example
Published on August 7, 2022 by Courtney Gahan . Revised on August 15, 2023.

A research paper outline is a useful tool to aid in the writing process , providing a structure to follow with all information to be included in the paper clearly organized.
A quality outline can make writing your research paper more efficient by helping to:
- Organize your thoughts
- Understand the flow of information and how ideas are related
- Ensure nothing is forgotten
A research paper outline can also give your teacher an early idea of the final product.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Research paper outline example, how to write a research paper outline, formatting your research paper outline, language in research paper outlines.
- Definition of measles
- Rise in cases in recent years in places the disease was previously eliminated or had very low rates of infection
- Figures: Number of cases per year on average, number in recent years. Relate to immunization
- Symptoms and timeframes of disease
- Risk of fatality, including statistics
- How measles is spread
- Immunization procedures in different regions
- Different regions, focusing on the arguments from those against immunization
- Immunization figures in affected regions
- High number of cases in non-immunizing regions
- Illnesses that can result from measles virus
- Fatal cases of other illnesses after patient contracted measles
- Summary of arguments of different groups
- Summary of figures and relationship with recent immunization debate
- Which side of the argument appears to be correct?
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

Follow these steps to start your research paper outline:
- Decide on the subject of the paper
- Write down all the ideas you want to include or discuss
- Organize related ideas into sub-groups
- Arrange your ideas into a hierarchy: What should the reader learn first? What is most important? Which idea will help end your paper most effectively?
- Create headings and subheadings that are effective
- Format the outline in either alphanumeric, full-sentence or decimal format
There are three different kinds of research paper outline: alphanumeric, full-sentence and decimal outlines. The differences relate to formatting and style of writing.
- Alphanumeric
- Full-sentence
An alphanumeric outline is most commonly used. It uses Roman numerals, capitalized letters, arabic numerals, lowercase letters to organize the flow of information. Text is written with short notes rather than full sentences.
- Sub-point of sub-point 1
Essentially the same as the alphanumeric outline, but with the text written in full sentences rather than short points.
- Additional sub-point to conclude discussion of point of evidence introduced in point A
A decimal outline is similar in format to the alphanumeric outline, but with a different numbering system: 1, 1.1, 1.2, etc. Text is written as short notes rather than full sentences.
- 1.1.1 Sub-point of first point
- 1.1.2 Sub-point of first point
- 1.2 Second point
To write an effective research paper outline, it is important to pay attention to language. This is especially important if it is one you will show to your teacher or be assessed on.
There are four main considerations: parallelism, coordination, subordination and division.
Parallelism: Be consistent with grammatical form
Parallel structure or parallelism is the repetition of a particular grammatical form within a sentence, or in this case, between points and sub-points. This simply means that if the first point is a verb , the sub-point should also be a verb.
Example of parallelism:
- Include different regions, focusing on the different arguments from those against immunization
Coordination: Be aware of each point’s weight
Your chosen subheadings should hold the same significance as each other, as should all first sub-points, secondary sub-points, and so on.
Example of coordination:
- Include immunization figures in affected regions
- Illnesses that can result from the measles virus
Subordination: Work from general to specific
Subordination refers to the separation of general points from specific. Your main headings should be quite general, and each level of sub-point should become more specific.
Example of subordination:
Division: break information into sub-points.
Your headings should be divided into two or more subsections. There is no limit to how many subsections you can include under each heading, but keep in mind that the information will be structured into a paragraph during the writing stage, so you should not go overboard with the number of sub-points.
Ready to start writing or looking for guidance on a different step in the process? Read our step-by-step guide on how to write a research paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Gahan, C. (2023, August 15). How to Create a Structured Research Paper Outline | Example. Scribbr. Retrieved August 12, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-paper/outline/
Is this article helpful?
Courtney Gahan
Other students also liked, research paper format | apa, mla, & chicago templates, writing a research paper introduction | step-by-step guide, writing a research paper conclusion | step-by-step guide, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

How to Write a Research Paper Outline (with Examples)
Writing a research paper is an essential part of an academic career. However, the task can be quite challenging especially for early career researchers unfamiliar with the nuances of academic research and writing. Creating an impactful research paper demands meticulous attention to detail, an in depth understanding of the topic and research methodology, and the ability to communicate the findings in an accurate and easy to understand way. This is where a research paper outline becomes useful. Writing a research paper can be made simpler and more efficient with a well-organized plan. A well-structured research paper outline offers the fundamental foundation on which researchers can construct their narratives logically, ensuring that the study report is well-presented and interesting for readers.
Table of Contents
This article takes a look now at the benefits of having a good research paper outline and also provides guidance on creating one.
4 steps to create a well-structured research paper outline
List the key components .
To begin with, researchers must list down the key components that should be included in the research paper outline . Start with identifying your research question. Organize your key ideas and thoughts so that you are able to clearly convey the various aspects of your research question or thesis statement. Create separate points for the introduction, literature review, methodology, results, significance of your research along with its limitations. These sections will help you organize your thoughts and ensure that all relevant information is included in your research manuscript.
Structure the outline logically
As you create your outline, make sure that there is logical flow of ideas and arguments. Think through the sequence in which you will present your topic and ideas. Structure the research paper outline in a way that allows a clear and continuous narrative that is easy to understand. For example, the introduction must be concise and engaging and must clearly introduce the research topic. The main paragraphs must focus on the research problem and arguments with supporting evidence. Experts suggest using headings and sub-heads to help organize ideas and data into sub-groups. The concluding section should have a summary of your study’s main points and key takeaways with recommendations for future research.
Provide supporting evidence
It is important to provide adequate supporting evidence and examples that underpin your key idea or argument. This helps to fit your study into the larger context of your subject area. It may be a good idea to collect all your data and relevant sources right from the start. Experts suggest providing at last three supporting evidences for each of your main ideas and including appropriate and accurate citations in the research paper outline .
Review and edit
Finally, take time to review the outline and make necessary modifications as you come across new data and information. To do so, you must have sufficient knowledge of the existing and current literature on the topic. Make sure that your ideas are in a logical order, and you have not missed out anything from your research notes.
3 tips to draft a great research paper outline
- Be concise and clear: Avoid adding unnecessary details to your research paper outline . Try instead, to focus only on the key ideas, information and supporting evidence for your study. Experts suggest avoiding the use of lengthy sentences and recommend the use of short phrases, sub-heads, and bullet points to outline ideas.
- Stay consistent with formatting: To ensure consistency in formatting, researchers can choose from different kinds of research paper outline templates. The most commonly used ones are:
- The alpha-numerical template where the points are written as short sentences,
- The full sentence format where whole sentences are written with specific points
- The decimal format where the main point is presented as a whole number (1, 2) and sub-points are given as decimal points (1.1, 1.2).
- Seek feedback from supervisors: Once you have completed the outline, it is a good idea to share it with your supervisors and mentors and seek their insights. Their inputs will help ensure that your research paper outline is on track.
Research paper outline example
Given below is a research paper outline example that you can use as a starting point.
I. Introduction
- Background and context of the research topic
- Problem statement and research question
- Significance of the study
II. Literature Review
- Overview of relevant literature
- Discussion of previous research and findings
- Identification of gaps and areas for further exploration
III. Methodology
- Explanation of the research design
- Description of data collection methods
- Discussion of data analysis techniques
IV. Results
- Presentation of research findings
- Data visualization (tables, graphs, charts, etc.)
- Explanation of key results
V. Discussion
- Interpretation of the results
- Comparison with existing literature
- Addressing limitations and implications of the study
VI. Conclusion
- Summary of the research paper
- Final remarks and suggestions for future research
Researcher.Life is a subscription-based platform that unifies the best AI tools and services designed to speed up, simplify, and streamline every step of a researcher’s journey. The Researcher.Life All Access Pack is a one-of-a-kind subscription that unlocks full access to an AI writing assistant, literature recommender, journal finder, scientific illustration tool, and exclusive discounts on professional publication services from Editage.
Based on 21+ years of experience in academia, Researcher.Life All Access empowers researchers to put their best research forward and move closer to success. Explore our top AI Tools pack, AI Tools + Publication Services pack, or Build Your Own Plan. Find everything a researcher needs to succeed, all in one place – Get All Access now starting at just $17 a month !
Related Posts

What are the Best Research Funding Sources

What are Experimental Groups in Research

- Research Guides
- Begin Your Research
- Outline and Plan
Begin Your Research: Outline and Plan
- Research Process
- Background Info
- Research Questions
Outlining and Planning Ahead: Confining or Comforting?
Creating a plan and outline before starting your research paper can lead to a more successful and satisfying writing process. Contrary to concerns about stifling creativity, planning ahead actually frees your mind from cluttered thoughts and allows for creativity to flourish within the boundaries of your rough plan. Just like various aspects of the natural and man-made world, successful creations often begin with some form of structure or boundary. Outlines serve as recipes for your paper, while research plans function as shopping lists, helping you organize your ideas and check your progress once you've completed your work.
Why Create an Outline?
According to the Purdue OWL's Writing Process guide , using an outline is helpful when wanting to "show the hierarchical relationship or logical ordering of information. For research papers, an outline may help you keep track of large amounts of information." Outlines even help those that are preparing a speech or presentation to deliver in front of an audience. Therefore, an outline has many benefits in aiding your writing, organizing your thoughts, keeping your material in logical structures, and giving your writing a boundary within which to keep focus. Making any kind of outline, no matter how rough or polished, will benefit you.
What is an Outline?
An outline is a structured document that lists the main parts of your research paper, essay, presentation, or report. It provides a roadmap for your planned writing, utilizing numbered lists to indicate the larger and nested structures.
- You can further divide your subtopics as needed using Arabic numerals, but there should always be more than one.
- Further subdivision
- Subtopic of First Part (more specific in relationship to the First Part heading)
- Subtopic of First Part (more specific in relationship to the heading above)
- Subtopic of First Part (there should always be more than one subtopic of each main part)
Unless required to use a certain outline template, you have the freedom to choose the type of outline that suits you best, whether it is rough or structured with full sentences, phrases, and alphanumeric ordered lists. Any kind of outline can be effective in aiding your writing process. In conclusion, outlining is a valuable tool for successful writing, allowing you to organize your thoughts and achieve your goals efficiently. By creating a clear plan, you can enhance your creativity and produce a more cohesive and well-structured piece of work.
Please open Purdue OWL's Writing Process guide or separate PDF which provides examples of full sentence and alphanumeric outlines.
- Research Outline Template (RTF file)
- Research Outline Template (PDF File)

Creating a Research Plan
Your final step in the beginning stages of your research journey is making a plan for the rest of your research and writing steps. Treat it like a schedule or shopping list, utilizing a short to-do list or a detailed schedule. Remember, this plan you devise is not restrictive; it's a guide to set achievable goals within one overall process. Here's what to include:
What should you include in a research plan?
As stated above, you don't need to fill out an entire research plan right now, *but as you learn more throughout this "How to Research" guide series. The following items are recommended items to put in your research plan:
- The research topic you have chosen and explored
- The research question or thesis statement you have drafted
- Any important assignment due dates, especially if you have to turn anything in at different stages (topic selection, annotated bibliography, rough draft, final draft)
- The kind of information you are interested in including (supporting or contrasting perspectives, definitions, analysis, facts, background, or statistics)*
- The search terms you have brainstormed and planned in the form of keywords, phrases, or search strings*
- The places you will go to look for information (library searchable databases, websites, physical libraries)*
- If there are any limitations or prohibited sources (no website or encyclopedias, for example)
You can use the provided templates to create your research plan as you progress through the "How to Research" guide series.
- Research Plan Template (RTF File)
- Research Plan Template (PDF File)
Congratulations on completing the initial steps of your research journey, and now you're ready to explore different types of information and sources.
- Learn the Types of Research Sources
- Find Research Sources
Image Source
Unless otherwise indicated, all images are courtesy of Adobe Stock. Paul J. Meyer quote image made in Canva, courtesy of Kristen Cook. The Research Outline Template was adapted from EasyBib.com.
- << Previous: Research Questions
- Next: Need Help? >>
- Last Updated: Jul 9, 2024 11:24 AM
- URL: https://mclennan.libguides.com/Begin
© McLennan Community College
1400 College Drive Waco, Texas 76708, USA
+1 (254) 299-8622

What (Exactly) Is A Research Proposal?
A simple explainer with examples + free template.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020 (Updated April 2023)
Whether you’re nearing the end of your degree and your dissertation is on the horizon, or you’re planning to apply for a PhD program, chances are you’ll need to craft a convincing research proposal . If you’re on this page, you’re probably unsure exactly what the research proposal is all about. Well, you’ve come to the right place.
Overview: Research Proposal Basics
- What a research proposal is
- What a research proposal needs to cover
- How to structure your research proposal
- Example /sample proposals
- Proposal writing FAQs
- Key takeaways & additional resources
What is a research proposal?
Simply put, a research proposal is a structured, formal document that explains what you plan to research (your research topic), why it’s worth researching (your justification), and how you plan to investigate it (your methodology).
The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your research supervisor, committee or university that your research is suitable (for the requirements of the degree program) and manageable (given the time and resource constraints you will face).
The most important word here is “ convince ” – in other words, your research proposal needs to sell your research idea (to whoever is going to approve it). If it doesn’t convince them (of its suitability and manageability), you’ll need to revise and resubmit . This will cost you valuable time, which will either delay the start of your research or eat into its time allowance (which is bad news).

What goes into a research proposal?
A good dissertation or thesis proposal needs to cover the “ what “, “ why ” and” how ” of the proposed study. Let’s look at each of these attributes in a little more detail:
Your proposal needs to clearly articulate your research topic . This needs to be specific and unambiguous . Your research topic should make it clear exactly what you plan to research and in what context. Here’s an example of a well-articulated research topic:
An investigation into the factors which impact female Generation Y consumer’s likelihood to promote a specific makeup brand to their peers: a British context
As you can see, this topic is extremely clear. From this one line we can see exactly:
- What’s being investigated – factors that make people promote or advocate for a brand of a specific makeup brand
- Who it involves – female Gen-Y consumers
- In what context – the United Kingdom
So, make sure that your research proposal provides a detailed explanation of your research topic . If possible, also briefly outline your research aims and objectives , and perhaps even your research questions (although in some cases you’ll only develop these at a later stage). Needless to say, don’t start writing your proposal until you have a clear topic in mind , or you’ll end up waffling and your research proposal will suffer as a result of this.
Need a helping hand?
As we touched on earlier, it’s not good enough to simply propose a research topic – you need to justify why your topic is original . In other words, what makes it unique ? What gap in the current literature does it fill? If it’s simply a rehash of the existing research, it’s probably not going to get approval – it needs to be fresh.
But, originality alone is not enough. Once you’ve ticked that box, you also need to justify why your proposed topic is important . In other words, what value will it add to the world if you achieve your research aims?
As an example, let’s look at the sample research topic we mentioned earlier (factors impacting brand advocacy). In this case, if the research could uncover relevant factors, these findings would be very useful to marketers in the cosmetics industry, and would, therefore, have commercial value . That is a clear justification for the research.
So, when you’re crafting your research proposal, remember that it’s not enough for a topic to simply be unique. It needs to be useful and value-creating – and you need to convey that value in your proposal. If you’re struggling to find a research topic that makes the cut, watch our video covering how to find a research topic .

It’s all good and well to have a great topic that’s original and valuable, but you’re not going to convince anyone to approve it without discussing the practicalities – in other words:
- How will you actually undertake your research (i.e., your methodology)?
- Is your research methodology appropriate given your research aims?
- Is your approach manageable given your constraints (time, money, etc.)?
While it’s generally not expected that you’ll have a fully fleshed-out methodology at the proposal stage, you’ll likely still need to provide a high-level overview of your research methodology . Here are some important questions you’ll need to address in your research proposal:
- Will you take a qualitative , quantitative or mixed -method approach?
- What sampling strategy will you adopt?
- How will you collect your data (e.g., interviews , surveys, etc)?
- How will you analyse your data (e.g., descriptive and inferential statistics , content analysis, discourse analysis, etc, .)?
- What potential limitations will your methodology carry?
So, be sure to give some thought to the practicalities of your research and have at least a basic methodological plan before you start writing up your proposal. If this all sounds rather intimidating, the video below provides a good introduction to research methodology and the key choices you’ll need to make.
How To Structure A Research Proposal
Now that we’ve covered the key points that need to be addressed in a proposal, you may be wondering, “ But how is a research proposal structured? “.
While the exact structure and format required for a research proposal differs from university to university, there are four “essential ingredients” that commonly make up the structure of a research proposal:
- A rich introduction and background to the proposed research
- An initial literature review covering the existing research
- An overview of the proposed research methodology
- A discussion regarding the practicalities (project plans, timelines, etc.)
In the video below, we unpack each of these four sections, step by step.
Research Proposal Examples/Samples
In the video below, we provide a detailed walkthrough of two successful research proposals (Master’s and PhD-level), as well as our popular free proposal template.
Proposal Writing FAQs
How long should a research proposal be.
This varies tremendously, depending on the university, the field of study (e.g., social sciences vs natural sciences), and the level of the degree (e.g. undergraduate, Masters or PhD) – so it’s always best to check with your university what their specific requirements are before you start planning your proposal.
As a rough guide, a formal research proposal at Masters-level often ranges between 2000-3000 words, while a PhD-level proposal can be far more detailed, ranging from 5000-8000 words. In some cases, a rough outline of the topic is all that’s needed, while in other cases, universities expect a very detailed proposal that essentially forms the first three chapters of the dissertation or thesis.
The takeaway – be sure to check with your institution before you start writing.
How do I choose a topic for my research proposal?
Finding a good research topic is a process that involves multiple steps. We cover the topic ideation process in this video post.
How do I write a literature review for my proposal?
While you typically won’t need a comprehensive literature review at the proposal stage, you still need to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the key literature and are able to synthesise it. We explain the literature review process here.
How do I create a timeline and budget for my proposal?
We explain how to craft a project plan/timeline and budget in Research Proposal Bootcamp .
Which referencing format should I use in my research proposal?
The expectations and requirements regarding formatting and referencing vary from institution to institution. Therefore, you’ll need to check this information with your university.
What common proposal writing mistakes do I need to look out for?
We’ve create a video post about some of the most common mistakes students make when writing a proposal – you can access that here . If you’re short on time, here’s a quick summary:
- The research topic is too broad (or just poorly articulated).
- The research aims, objectives and questions don’t align.
- The research topic is not well justified.
- The study has a weak theoretical foundation.
- The research design is not well articulated well enough.
- Poor writing and sloppy presentation.
- Poor project planning and risk management.
- Not following the university’s specific criteria.
Key Takeaways & Additional Resources
As you write up your research proposal, remember the all-important core purpose: to convince . Your research proposal needs to sell your study in terms of suitability and viability. So, focus on crafting a convincing narrative to ensure a strong proposal.
At the same time, pay close attention to your university’s requirements. While we’ve covered the essentials here, every institution has its own set of expectations and it’s essential that you follow these to maximise your chances of approval.
By the way, we’ve got plenty more resources to help you fast-track your research proposal. Here are some of our most popular resources to get you started:
- Proposal Writing 101 : A Introductory Webinar
- Research Proposal Bootcamp : The Ultimate Online Course
- Template : A basic template to help you craft your proposal
If you’re looking for 1-on-1 support with your research proposal, be sure to check out our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the proposal development process (and the entire research journey), step by step.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
51 Comments
I truly enjoyed this video, as it was eye-opening to what I have to do in the preparation of preparing a Research proposal.
I would be interested in getting some coaching.
I real appreciate on your elaboration on how to develop research proposal,the video explains each steps clearly.
Thank you for the video. It really assisted me and my niece. I am a PhD candidate and she is an undergraduate student. It is at times, very difficult to guide a family member but with this video, my job is done.
In view of the above, I welcome more coaching.
Wonderful guidelines, thanks
This is very helpful. Would love to continue even as I prepare for starting my masters next year.
Thanks for the work done, the text was helpful to me
Bundle of thanks to you for the research proposal guide it was really good and useful if it is possible please send me the sample of research proposal
You’re most welcome. We don’t have any research proposals that we can share (the students own the intellectual property), but you might find our research proposal template useful: https://gradcoach.com/research-proposal-template/
Cheruiyot Moses Kipyegon
Thanks alot. It was an eye opener that came timely enough before my imminent proposal defense. Thanks, again
thank you very much your lesson is very interested may God be with you
I am an undergraduate student (First Degree) preparing to write my project,this video and explanation had shed more light to me thanks for your efforts keep it up.
Very useful. I am grateful.
this is a very a good guidance on research proposal, for sure i have learnt something
Wonderful guidelines for writing a research proposal, I am a student of m.phil( education), this guideline is suitable for me. Thanks
You’re welcome 🙂
Thank you, this was so helpful.
A really great and insightful video. It opened my eyes as to how to write a research paper. I would like to receive more guidance for writing my research paper from your esteemed faculty.
Thank you, great insights
Thank you, great insights, thank you so much, feeling edified
Wow thank you, great insights, thanks a lot
Thank you. This is a great insight. I am a student preparing for a PhD program. I am requested to write my Research Proposal as part of what I am required to submit before my unconditional admission. I am grateful having listened to this video which will go a long way in helping me to actually choose a topic of interest and not just any topic as well as to narrow down the topic and be specific about it. I indeed need more of this especially as am trying to choose a topic suitable for a DBA am about embarking on. Thank you once more. The video is indeed helpful.
Have learnt a lot just at the right time. Thank you so much.
thank you very much ,because have learn a lot things concerning research proposal and be blessed u for your time that you providing to help us
Hi. For my MSc medical education research, please evaluate this topic for me: Training Needs Assessment of Faculty in Medical Training Institutions in Kericho and Bomet Counties
I have really learnt a lot based on research proposal and it’s formulation
Thank you. I learn much from the proposal since it is applied
Your effort is much appreciated – you have good articulation.
You have good articulation.
I do applaud your simplified method of explaining the subject matter, which indeed has broaden my understanding of the subject matter. Definitely this would enable me writing a sellable research proposal.
This really helping
Great! I liked your tutoring on how to find a research topic and how to write a research proposal. Precise and concise. Thank you very much. Will certainly share this with my students. Research made simple indeed.
Thank you very much. I an now assist my students effectively.
Thank you very much. I can now assist my students effectively.
I need any research proposal
Thank you for these videos. I will need chapter by chapter assistance in writing my MSc dissertation
Very helpfull
the videos are very good and straight forward
thanks so much for this wonderful presentations, i really enjoyed it to the fullest wish to learn more from you
Thank you very much. I learned a lot from your lecture.
I really enjoy the in-depth knowledge on research proposal you have given. me. You have indeed broaden my understanding and skills. Thank you
interesting session this has equipped me with knowledge as i head for exams in an hour’s time, am sure i get A++
This article was most informative and easy to understand. I now have a good idea of how to write my research proposal.
Thank you very much.
Wow, this literature is very resourceful and interesting to read. I enjoyed it and I intend reading it every now then.
Thank you for the clarity
Thank you. Very helpful.
Thank you very much for this essential piece. I need 1o1 coaching, unfortunately, your service is not available in my country. Anyways, a very important eye-opener. I really enjoyed it. A thumb up to Gradcoach
What is JAM? Please explain.
Thank you so much for these videos. They are extremely helpful! God bless!
very very wonderful…
thank you for the video but i need a written example
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper Outline – Types, Example, Template
Research Paper Outline – Types, Example, Template
Table of Contents

By creating a well-structured research paper outline, writers can easily organize their thoughts and ideas and ensure that their final paper is clear, concise, and effective. In this article, we will explore the essential components of a research paper outline and provide some tips and tricks for creating a successful one.
Research Paper Outline
Research paper outline is a plan or a structural framework that organizes the main ideas , arguments, and supporting evidence in a logical sequence. It serves as a blueprint or a roadmap for the writer to follow while drafting the actual research paper .
Typically, an outline consists of the following elements:
- Introduction : This section presents the topic, research question , and thesis statement of the paper. It also provides a brief overview of the literature review and the methodology used.
- Literature Review: This section provides a comprehensive review of the relevant literature, theories, and concepts related to the research topic. It analyzes the existing research and identifies the research gaps and research questions.
- Methodology: This section explains the research design, data collection methods, data analysis, and ethical considerations of the study.
- Results: This section presents the findings of the study, using tables, graphs, and statistics to illustrate the data.
- Discussion : This section interprets the results of the study, and discusses their implications, significance, and limitations. It also suggests future research directions.
- Conclusion : This section summarizes the main findings of the study and restates the thesis statement.
- References: This section lists all the sources cited in the paper using the appropriate citation style.
Research Paper Outline Types
There are several types of outlines that can be used for research papers, including:
Alphanumeric Outline
This is a traditional outline format that uses Roman numerals, capital letters, Arabic numerals, and lowercase letters to organize the main ideas and supporting details of a research paper. It is commonly used for longer, more complex research papers.
I. Introduction
- A. Background information
- B. Thesis statement
- 1 1. Supporting detail
- 1 2. Supporting detail 2
- 2 1. Supporting detail
III. Conclusion
- A. Restate thesis
- B. Summarize main points
Decimal Outline
This outline format uses numbers to organize the main ideas and supporting details of a research paper. It is similar to the alphanumeric outline, but it uses only numbers and decimals to indicate the hierarchy of the ideas.
- 1.1 Background information
- 1.2 Thesis statement
- 1 2.1.1 Supporting detail
- 1 2.1.2 Supporting detail
- 2 2.2.1 Supporting detail
- 1 2.2.2 Supporting detail
- 3.1 Restate thesis
- 3.2 Summarize main points
Full Sentence Outline
This type of outline uses complete sentences to describe the main ideas and supporting details of a research paper. It is useful for those who prefer to see the entire paper outlined in complete sentences.
- Provide background information on the topic
- State the thesis statement
- Explain main idea 1 and provide supporting details
- Discuss main idea 2 and provide supporting details
- Restate the thesis statement
- Summarize the main points of the paper
Topic Outline
This type of outline uses short phrases or words to describe the main ideas and supporting details of a research paper. It is useful for those who prefer to see a more concise overview of the paper.
- Background information
- Thesis statement
- Supporting detail 1
- Supporting detail 2
- Restate thesis
- Summarize main points
Reverse Outline
This is an outline that is created after the paper has been written. It involves going back through the paper and summarizing each paragraph or section in one sentence. This can be useful for identifying gaps in the paper or areas that need further development.
- Introduction : Provides background information and states the thesis statement.
- Paragraph 1: Discusses main idea 1 and provides supporting details.
- Paragraph 2: Discusses main idea 2 and provides supporting details.
- Paragraph 3: Addresses potential counterarguments.
- Conclusion : Restates thesis and summarizes main points.
Mind Map Outline
This type of outline involves creating a visual representation of the main ideas and supporting details of a research paper. It can be useful for those who prefer a more creative and visual approach to outlining.
- Supporting detail 1: Lack of funding for public schools.
- Supporting detail 2: Decrease in government support for education.
- Supporting detail 1: Increase in income inequality.
- Supporting detail 2: Decrease in social mobility.
Research Paper Outline Example
Research Paper Outline Example on Cyber Security:
A. Overview of Cybersecurity
- B. Importance of Cybersecurity
- C. Purpose of the paper
II. Cyber Threats
A. Definition of Cyber Threats
- B. Types of Cyber Threats
- C. Examples of Cyber Threats
III. Cybersecurity Measures
A. Prevention measures
- Anti-virus software
- Encryption B. Detection measures
- Intrusion Detection System (IDS)
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
- Security Operations Center (SOC) C. Response measures
- Incident Response Plan
- Business Continuity Plan
- Disaster Recovery Plan
IV. Cybersecurity in the Business World
A. Overview of Cybersecurity in the Business World
B. Cybersecurity Risk Assessment
C. Best Practices for Cybersecurity in Business
V. Cybersecurity in Government Organizations
A. Overview of Cybersecurity in Government Organizations
C. Best Practices for Cybersecurity in Government Organizations
VI. Cybersecurity Ethics
A. Definition of Cybersecurity Ethics
B. Importance of Cybersecurity Ethics
C. Examples of Cybersecurity Ethics
VII. Future of Cybersecurity
A. Overview of the Future of Cybersecurity
B. Emerging Cybersecurity Threats
C. Advancements in Cybersecurity Technology
VIII. Conclusion
A. Summary of the paper
B. Recommendations for Cybersecurity
- C. Conclusion.
IX. References
A. List of sources cited in the paper
B. Bibliography of additional resources
Introduction
Cybersecurity refers to the protection of computer systems, networks, and sensitive data from unauthorized access, theft, damage, or any other form of cyber attack. B. Importance of Cybersecurity The increasing reliance on technology and the growing number of cyber threats make cybersecurity an essential aspect of modern society. Cybersecurity breaches can result in financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities. C. Purpose of the paper This paper aims to provide an overview of cybersecurity, cyber threats, cybersecurity measures, cybersecurity in the business and government sectors, cybersecurity ethics, and the future of cybersecurity.
A cyber threat is any malicious act or event that attempts to compromise or disrupt computer systems, networks, or sensitive data. B. Types of Cyber Threats Common types of cyber threats include malware, phishing, social engineering, ransomware, DDoS attacks, and advanced persistent threats (APTs). C. Examples of Cyber Threats Recent cyber threats include the SolarWinds supply chain attack, the Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack, and the Microsoft Exchange Server hack.
Prevention measures aim to minimize the risk of cyber attacks by implementing security controls, such as firewalls, anti-virus software, and encryption.
- Firewalls Firewalls act as a barrier between a computer network and the internet, filtering incoming and outgoing traffic to prevent unauthorized access.
- Anti-virus software Anti-virus software detects, prevents, and removes malware from computer systems.
- Encryption Encryption involves the use of mathematical algorithms to transform sensitive data into a code that can only be accessed by authorized individuals. B. Detection measures Detection measures aim to identify and respond to cyber attacks as quickly as possible, such as intrusion detection systems (IDS), security information and event management (SIEM), and security operations centers (SOCs).
- Intrusion Detection System (IDS) IDS monitors network traffic for signs of unauthorized access, such as unusual patterns or anomalies.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) SIEM combines security information management and security event management to provide real-time monitoring and analysis of security alerts.
- Security Operations Center (SOC) SOC is a dedicated team responsible for monitoring, analyzing, and responding to cyber threats. C. Response measures Response measures aim to mitigate the impact of a cyber attack and restore normal operations, such as incident response plans (IRPs), business continuity plans (BCPs), and disaster recovery plans (DRPs).
- Incident Response Plan IRPs outline the procedures and protocols to follow in the event of a cyber attack, including communication protocols, roles and responsibilities, and recovery processes.
- Business Continuity Plan BCPs ensure that critical business functions can continue in the event of a cyber attack or other disruption.
- Disaster Recovery Plan DRPs outline the procedures to recover from a catastrophic event, such as a natural disaster or cyber attack.
Cybersecurity is crucial for businesses of all sizes and industries, as they handle sensitive data, financial transactions, and intellectual property that are attractive targets for cyber criminals.
Risk assessment is a critical step in developing a cybersecurity strategy, which involves identifying potential threats, vulnerabilities, and consequences to determine the level of risk and prioritize security measures.
Best practices for cybersecurity in business include implementing strong passwords and multi-factor authentication, regularly updating software and hardware, training employees on cybersecurity awareness, and regularly backing up data.
Government organizations face unique cybersecurity challenges, as they handle sensitive information related to national security, defense, and critical infrastructure.
Risk assessment in government organizations involves identifying and assessing potential threats and vulnerabilities, conducting regular audits, and complying with relevant regulations and standards.
Best practices for cybersecurity in government organizations include implementing secure communication protocols, regularly updating and patching software, and conducting regular cybersecurity training and awareness programs for employees.
Cybersecurity ethics refers to the ethical considerations involved in cybersecurity, such as privacy, data protection, and the responsible use of technology.
Cybersecurity ethics are crucial for maintaining trust in technology, protecting privacy and data, and promoting responsible behavior in the digital world.
Examples of cybersecurity ethics include protecting the privacy of user data, ensuring data accuracy and integrity, and implementing fair and unbiased algorithms.
The future of cybersecurity will involve a shift towards more advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and quantum computing.
Emerging cybersecurity threats include AI-powered cyber attacks, the use of deepfakes and synthetic media, and the potential for quantum computing to break current encryption methods.
Advancements in cybersecurity technology include the development of AI and machine learning-based security tools, the use of blockchain for secure data storage and sharing, and the development of post-quantum encryption methods.
This paper has provided an overview of cybersecurity, cyber threats, cybersecurity measures, cybersecurity in the business and government sectors, cybersecurity ethics, and the future of cybersecurity.
To enhance cybersecurity, organizations should prioritize risk assessment and implement a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy that includes prevention, detection, and response measures. Additionally, organizations should prioritize cybersecurity ethics to promote responsible behavior in the digital world.
C. Conclusion
Cybersecurity is an essential aspect of modern society, and organizations must prioritize cybersecurity to protect sensitive data and maintain trust in technology.
for further reading
X. Appendices
A. Glossary of key terms
B. Cybersecurity checklist for organizations
C. Sample cybersecurity policy for businesses
D. Sample cybersecurity incident response plan
E. Cybersecurity training and awareness resources
Note : The content and organization of the paper may vary depending on the specific requirements of the assignment or target audience. This outline serves as a general guide for writing a research paper on cybersecurity. Do not use this in your assingmets.
Research Paper Outline Template
- Background information and context of the research topic
- Research problem and questions
- Purpose and objectives of the research
- Scope and limitations
II. Literature Review
- Overview of existing research on the topic
- Key concepts and theories related to the research problem
- Identification of gaps in the literature
- Summary of relevant studies and their findings
III. Methodology
- Research design and approach
- Data collection methods and procedures
- Data analysis techniques
- Validity and reliability considerations
- Ethical considerations
IV. Results
- Presentation of research findings
- Analysis and interpretation of data
- Explanation of significant results
- Discussion of unexpected results
V. Discussion
- Comparison of research findings with existing literature
- Implications of results for theory and practice
- Limitations and future directions for research
- Conclusion and recommendations
VI. Conclusion
- Summary of research problem, purpose, and objectives
- Discussion of significant findings
- Contribution to the field of study
- Implications for practice
- Suggestions for future research
VII. References
- List of sources cited in the research paper using appropriate citation style.
Note : This is just an template, and depending on the requirements of your assignment or the specific research topic, you may need to modify or adjust the sections or headings accordingly.
Research Paper Outline Writing Guide
Here’s a guide to help you create an effective research paper outline:
- Choose a topic : Select a topic that is interesting, relevant, and meaningful to you.
- Conduct research: Gather information on the topic from a variety of sources, such as books, articles, journals, and websites.
- Organize your ideas: Organize your ideas and information into logical groups and subgroups. This will help you to create a clear and concise outline.
- Create an outline: Begin your outline with an introduction that includes your thesis statement. Then, organize your ideas into main points and subpoints. Each main point should be supported by evidence and examples.
- Introduction: The introduction of your research paper should include the thesis statement, background information, and the purpose of the research paper.
- Body : The body of your research paper should include the main points and subpoints. Each point should be supported by evidence and examples.
- Conclusion : The conclusion of your research paper should summarize the main points and restate the thesis statement.
- Reference List: Include a reference list at the end of your research paper. Make sure to properly cite all sources used in the paper.
- Proofreading : Proofread your research paper to ensure that it is free of errors and grammatical mistakes.
- Finalizing : Finalize your research paper by reviewing the outline and making any necessary changes.
When to Write Research Paper Outline
It’s a good idea to write a research paper outline before you begin drafting your paper. The outline will help you organize your thoughts and ideas, and it can serve as a roadmap for your writing process.
Here are a few situations when you might want to consider writing an outline:
- When you’re starting a new research project: If you’re beginning a new research project, an outline can help you get organized from the very beginning. You can use your outline to brainstorm ideas, map out your research goals, and identify potential sources of information.
- When you’re struggling to organize your thoughts: If you find yourself struggling to organize your thoughts or make sense of your research, an outline can be a helpful tool. It can help you see the big picture of your project and break it down into manageable parts.
- When you’re working with a tight deadline : If you have a deadline for your research paper, an outline can help you stay on track and ensure that you cover all the necessary points. By mapping out your paper in advance, you can work more efficiently and avoid getting stuck or overwhelmed.
Purpose of Research Paper Outline
The purpose of a research paper outline is to provide a structured and organized plan for the writer to follow while conducting research and writing the paper. An outline is essentially a roadmap that guides the writer through the entire research process, from the initial research and analysis of the topic to the final writing and editing of the paper.
A well-constructed outline can help the writer to:
- Organize their thoughts and ideas on the topic, and ensure that all relevant information is included.
- Identify any gaps in their research or argument, and address them before starting to write the paper.
- Ensure that the paper follows a logical and coherent structure, with clear transitions between different sections.
- Save time and effort by providing a clear plan for the writer to follow, rather than starting from scratch and having to revise the paper multiple times.
Advantages of Research Paper Outline
Some of the key advantages of a research paper outline include:
- Helps to organize thoughts and ideas : An outline helps to organize all the different ideas and information that you want to include in your paper. By creating an outline, you can ensure that all the points you want to make are covered and in a logical order.
- Saves time and effort : An outline saves time and effort because it helps you to focus on the key points of your paper. It also helps you to identify any gaps or areas where more research may be needed.
- Makes the writing process easier : With an outline, you have a clear roadmap of what you want to write, and this makes the writing process much easier. You can simply follow your outline and fill in the details as you go.
- Improves the quality of your paper : By having a clear outline, you can ensure that all the important points are covered and in a logical order. This makes your paper more coherent and easier to read, which ultimately improves its overall quality.
- Facilitates collaboration: If you are working on a research paper with others, an outline can help to facilitate collaboration. By sharing your outline, you can ensure that everyone is on the same page and working towards the same goals.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Results Section – Writing Guide and...

Informed Consent in Research – Types, Templates...

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Context of the Study – Writing Guide and Examples

Appendices – Writing Guide, Types and Examples

Future Research – Thesis Guide
FLEET LIBRARY | Research Guides
Rhode island school of design, create a research plan: research plan.
- Research Plan
- Literature Review
- Ulrich's Global Serials Directory
- Related Guides
A research plan is a framework that shows how you intend to approach your topic. The plan can take many forms: a written outline, a narrative, a visual/concept map or timeline. It's a document that will change and develop as you conduct your research. Components of a research plan
1. Research conceptualization - introduces your research question
2. Research methodology - describes your approach to the research question
3. Literature review, critical evaluation and synthesis - systematic approach to locating,
reviewing and evaluating the work (text, exhibitions, critiques, etc) relating to your topic
4. Communication - geared toward an intended audience, shows evidence of your inquiry
Research conceptualization refers to the ability to identify specific research questions, problems or opportunities that are worthy of inquiry. Research conceptualization also includes the skills and discipline that go beyond the initial moment of conception, and which enable the researcher to formulate and develop an idea into something researchable ( Newbury 373).
Research methodology refers to the knowledge and skills required to select and apply appropriate methods to carry through the research project ( Newbury 374) .
Method describes a single mode of proceeding; methodology describes the overall process.
Method - a way of doing anything especially according to a defined and regular plan; a mode of procedure in any activity
Methodology - the study of the direction and implications of empirical research, or the sustainability of techniques employed in it; a method or body of methods used in a particular field of study or activity *Browse a list of research methodology books or this guide on Art & Design Research
Literature Review, critical evaluation & synthesis
A literature review is a systematic approach to locating, reviewing, and evaluating the published work and work in progress of scholars, researchers, and practitioners on a given topic.
Critical evaluation and synthesis is the ability to handle (or process) existing sources. It includes knowledge of the sources of literature and contextual research field within which the person is working ( Newbury 373).
Literature reviews are done for many reasons and situations. Here's a short list:
| to learn about a field of study to understand current knowledge on a subject to formulate questions & identify a research problem to focus the purpose of one's research to contribute new knowledge to a field personal knowledge intellectual curiosity | to prepare for architectural program writing academic degrees grant applications proposal writing academic research planning funding |
Sources to consult while conducting a literature review:
Online catalogs of local, regional, national, and special libraries
meta-catalogs such as worldcat , Art Discovery Group , europeana , world digital library or RIBA
subject-specific online article databases (such as the Avery Index, JSTOR, Project Muse)
digital institutional repositories such as Digital Commons @RISD ; see Registry of Open Access Repositories
Open Access Resources recommended by RISD Research LIbrarians
works cited in scholarly books and articles
print bibliographies
the internet-locate major nonprofit, research institutes, museum, university, and government websites
search google scholar to locate grey literature & referenced citations
trade and scholarly publishers
fellow scholars and peers
Communication
Communication refers to the ability to
- structure a coherent line of inquiry
- communicate your findings to your intended audience
- make skilled use of visual material to express ideas for presentations, writing, and the creation of exhibitions ( Newbury 374)
Research plan framework: Newbury, Darren. "Research Training in the Creative Arts and Design." The Routledge Companion to Research in the Arts . Ed. Michael Biggs and Henrik Karlsson. New York: Routledge, 2010. 368-87. Print.
About the author
Except where otherwise noted, this guide is subject to a Creative Commons Attribution license
source document
Routledge Companion to Research in the Arts
- Next: Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Aug 15, 2024 1:29 AM
- URL: https://risd.libguides.com/researchplan

How to Write a Research Proposal: (with Examples & Templates)

Table of Contents
Before conducting a study, a research proposal should be created that outlines researchers’ plans and methodology and is submitted to the concerned evaluating organization or person. Creating a research proposal is an important step to ensure that researchers are on track and are moving forward as intended. A research proposal can be defined as a detailed plan or blueprint for the proposed research that you intend to undertake. It provides readers with a snapshot of your project by describing what you will investigate, why it is needed, and how you will conduct the research.
Your research proposal should aim to explain to the readers why your research is relevant and original, that you understand the context and current scenario in the field, have the appropriate resources to conduct the research, and that the research is feasible given the usual constraints.
This article will describe in detail the purpose and typical structure of a research proposal , along with examples and templates to help you ace this step in your research journey.
What is a Research Proposal ?
A research proposal¹ ,² can be defined as a formal report that describes your proposed research, its objectives, methodology, implications, and other important details. Research proposals are the framework of your research and are used to obtain approvals or grants to conduct the study from various committees or organizations. Consequently, research proposals should convince readers of your study’s credibility, accuracy, achievability, practicality, and reproducibility.
With research proposals , researchers usually aim to persuade the readers, funding agencies, educational institutions, and supervisors to approve the proposal. To achieve this, the report should be well structured with the objectives written in clear, understandable language devoid of jargon. A well-organized research proposal conveys to the readers or evaluators that the writer has thought out the research plan meticulously and has the resources to ensure timely completion.
Purpose of Research Proposals
A research proposal is a sales pitch and therefore should be detailed enough to convince your readers, who could be supervisors, ethics committees, universities, etc., that what you’re proposing has merit and is feasible . Research proposals can help students discuss their dissertation with their faculty or fulfill course requirements and also help researchers obtain funding. A well-structured proposal instills confidence among readers about your ability to conduct and complete the study as proposed.
Research proposals can be written for several reasons:³
- To describe the importance of research in the specific topic
- Address any potential challenges you may encounter
- Showcase knowledge in the field and your ability to conduct a study
- Apply for a role at a research institute
- Convince a research supervisor or university that your research can satisfy the requirements of a degree program
- Highlight the importance of your research to organizations that may sponsor your project
- Identify implications of your project and how it can benefit the audience
What Goes in a Research Proposal?
Research proposals should aim to answer the three basic questions—what, why, and how.
The What question should be answered by describing the specific subject being researched. It should typically include the objectives, the cohort details, and the location or setting.
The Why question should be answered by describing the existing scenario of the subject, listing unanswered questions, identifying gaps in the existing research, and describing how your study can address these gaps, along with the implications and significance.
The How question should be answered by describing the proposed research methodology, data analysis tools expected to be used, and other details to describe your proposed methodology.
Research Proposal Example
Here is a research proposal sample template (with examples) from the University of Rochester Medical Center. 4 The sections in all research proposals are essentially the same although different terminology and other specific sections may be used depending on the subject.

Structure of a Research Proposal
If you want to know how to make a research proposal impactful, include the following components:¹
1. Introduction
This section provides a background of the study, including the research topic, what is already known about it and the gaps, and the significance of the proposed research.
2. Literature review
This section contains descriptions of all the previous relevant studies pertaining to the research topic. Every study cited should be described in a few sentences, starting with the general studies to the more specific ones. This section builds on the understanding gained by readers in the Introduction section and supports it by citing relevant prior literature, indicating to readers that you have thoroughly researched your subject.
3. Objectives
Once the background and gaps in the research topic have been established, authors must now state the aims of the research clearly. Hypotheses should be mentioned here. This section further helps readers understand what your study’s specific goals are.
4. Research design and methodology
Here, authors should clearly describe the methods they intend to use to achieve their proposed objectives. Important components of this section include the population and sample size, data collection and analysis methods and duration, statistical analysis software, measures to avoid bias (randomization, blinding), etc.
5. Ethical considerations
This refers to the protection of participants’ rights, such as the right to privacy, right to confidentiality, etc. Researchers need to obtain informed consent and institutional review approval by the required authorities and mention this clearly for transparency.
6. Budget/funding
Researchers should prepare their budget and include all expected expenditures. An additional allowance for contingencies such as delays should also be factored in.
7. Appendices
This section typically includes information that supports the research proposal and may include informed consent forms, questionnaires, participant information, measurement tools, etc.
8. Citations

Important Tips for Writing a Research Proposal
Writing a research proposal begins much before the actual task of writing. Planning the research proposal structure and content is an important stage, which if done efficiently, can help you seamlessly transition into the writing stage. 3,5
The Planning Stage
- Manage your time efficiently. Plan to have the draft version ready at least two weeks before your deadline and the final version at least two to three days before the deadline.
- What is the primary objective of your research?
- Will your research address any existing gap?
- What is the impact of your proposed research?
- Do people outside your field find your research applicable in other areas?
- If your research is unsuccessful, would there still be other useful research outcomes?
The Writing Stage
- Create an outline with main section headings that are typically used.
- Focus only on writing and getting your points across without worrying about the format of the research proposal , grammar, punctuation, etc. These can be fixed during the subsequent passes. Add details to each section heading you created in the beginning.
- Ensure your sentences are concise and use plain language. A research proposal usually contains about 2,000 to 4,000 words or four to seven pages.
- Don’t use too many technical terms and abbreviations assuming that the readers would know them. Define the abbreviations and technical terms.
- Ensure that the entire content is readable. Avoid using long paragraphs because they affect the continuity in reading. Break them into shorter paragraphs and introduce some white space for readability.
- Focus on only the major research issues and cite sources accordingly. Don’t include generic information or their sources in the literature review.
- Proofread your final document to ensure there are no grammatical errors so readers can enjoy a seamless, uninterrupted read.
- Use academic, scholarly language because it brings formality into a document.
- Ensure that your title is created using the keywords in the document and is neither too long and specific nor too short and general.
- Cite all sources appropriately to avoid plagiarism.
- Make sure that you follow guidelines, if provided. This includes rules as simple as using a specific font or a hyphen or en dash between numerical ranges.
- Ensure that you’ve answered all questions requested by the evaluating authority.
Key Takeaways
Here’s a summary of the main points about research proposals discussed in the previous sections:
- A research proposal is a document that outlines the details of a proposed study and is created by researchers to submit to evaluators who could be research institutions, universities, faculty, etc.
- Research proposals are usually about 2,000-4,000 words long, but this depends on the evaluating authority’s guidelines.
- A good research proposal ensures that you’ve done your background research and assessed the feasibility of the research.
- Research proposals have the following main sections—introduction, literature review, objectives, methodology, ethical considerations, and budget.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. How is a research proposal evaluated?
A1. In general, most evaluators, including universities, broadly use the following criteria to evaluate research proposals . 6
- Significance —Does the research address any important subject or issue, which may or may not be specific to the evaluator or university?
- Content and design —Is the proposed methodology appropriate to answer the research question? Are the objectives clear and well aligned with the proposed methodology?
- Sample size and selection —Is the target population or cohort size clearly mentioned? Is the sampling process used to select participants randomized, appropriate, and free of bias?
- Timing —Are the proposed data collection dates mentioned clearly? Is the project feasible given the specified resources and timeline?
- Data management and dissemination —Who will have access to the data? What is the plan for data analysis?
Q2. What is the difference between the Introduction and Literature Review sections in a research proposal ?
A2. The Introduction or Background section in a research proposal sets the context of the study by describing the current scenario of the subject and identifying the gaps and need for the research. A Literature Review, on the other hand, provides references to all prior relevant literature to help corroborate the gaps identified and the research need.
Q3. How long should a research proposal be?
A3. Research proposal lengths vary with the evaluating authority like universities or committees and also the subject. Here’s a table that lists the typical research proposal lengths for a few universities.
| Arts programs | 1,000-1,500 | |
| University of Birmingham | Law School programs | 2,500 |
| PhD | 2,500 | |
| 2,000 | ||
| Research degrees | 2,000-3,500 |
Q4. What are the common mistakes to avoid in a research proposal ?
A4. Here are a few common mistakes that you must avoid while writing a research proposal . 7
- No clear objectives: Objectives should be clear, specific, and measurable for the easy understanding among readers.
- Incomplete or unconvincing background research: Background research usually includes a review of the current scenario of the particular industry and also a review of the previous literature on the subject. This helps readers understand your reasons for undertaking this research because you identified gaps in the existing research.
- Overlooking project feasibility: The project scope and estimates should be realistic considering the resources and time available.
- Neglecting the impact and significance of the study: In a research proposal , readers and evaluators look for the implications or significance of your research and how it contributes to the existing research. This information should always be included.
- Unstructured format of a research proposal : A well-structured document gives confidence to evaluators that you have read the guidelines carefully and are well organized in your approach, consequently affirming that you will be able to undertake the research as mentioned in your proposal.
- Ineffective writing style: The language used should be formal and grammatically correct. If required, editors could be consulted, including AI-based tools such as Paperpal , to refine the research proposal structure and language.
Thus, a research proposal is an essential document that can help you promote your research and secure funds and grants for conducting your research. Consequently, it should be well written in clear language and include all essential details to convince the evaluators of your ability to conduct the research as proposed.
This article has described all the important components of a research proposal and has also provided tips to improve your writing style. We hope all these tips will help you write a well-structured research proposal to ensure receipt of grants or any other purpose.
References
- Sudheesh K, Duggappa DR, Nethra SS. How to write a research proposal? Indian J Anaesth. 2016;60(9):631-634. Accessed July 15, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5037942/
- Writing research proposals. Harvard College Office of Undergraduate Research and Fellowships. Harvard University. Accessed July 14, 2024. https://uraf.harvard.edu/apply-opportunities/app-components/essays/research-proposals
- What is a research proposal? Plus how to write one. Indeed website. Accessed July 17, 2024. https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/research-proposal
- Research proposal template. University of Rochester Medical Center. Accessed July 16, 2024. https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/MediaLibraries/URMCMedia/pediatrics/research/documents/Research-proposal-Template.pdf
- Tips for successful proposal writing. Johns Hopkins University. Accessed July 17, 2024. https://research.jhu.edu/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/Tips-for-Successful-Proposal-Writing.pdf
- Formal review of research proposals. Cornell University. Accessed July 18, 2024. https://irp.dpb.cornell.edu/surveys/survey-assessment-review-group/research-proposals
- 7 Mistakes you must avoid in your research proposal. Aveksana (via LinkedIn). Accessed July 17, 2024. https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/7-mistakes-you-must-avoid-your-research-proposal-aveksana-cmtwf/
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
How to write a phd research proposal.
- What are the Benefits of Generative AI for Academic Writing?
- How to Avoid Plagiarism When Using Generative AI Tools
- What is Hedging in Academic Writing?
How to Write Your Research Paper in APA Format
The future of academia: how ai tools are changing the way we do research, you may also like, dissertation printing and binding | types & comparison , what is a dissertation preface definition and examples , how to write your research paper in apa..., how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide), maintaining academic integrity with paperpal’s generative ai writing..., research funding basics: what should a grant proposal..., how to write an abstract in research papers..., how to write dissertation acknowledgements.
Reference management. Clean and simple.
Getting started with your research paper outline
Levels of organization for a research paper outline
First level of organization, second level of organization, third level of organization, fourth level of organization, tips for writing a research paper outline, research paper outline template, my research paper outline is complete: what are the next steps, frequently asked questions about a research paper outline, related articles.
The outline is the skeleton of your research paper. Simply start by writing down your thesis and the main ideas you wish to present. This will likely change as your research progresses; therefore, do not worry about being too specific in the early stages of writing your outline.
A research paper outline typically contains between two and four layers of organization. The first two layers are the most generalized. Each layer thereafter will contain the research you complete and presents more and more detailed information.
The levels are typically represented by a combination of Roman numerals, Arabic numerals, uppercase letters, lowercase letters but may include other symbols. Refer to the guidelines provided by your institution, as formatting is not universal and differs between universities, fields, and subjects. If you are writing the outline for yourself, you may choose any combination you prefer.
This is the most generalized level of information. Begin by numbering the introduction, each idea you will present, and the conclusion. The main ideas contain the bulk of your research paper 's information. Depending on your research, it may be chapters of a book for a literature review , a series of dates for a historical research paper, or the methods and results of a scientific paper.
I. Introduction
II. Main idea
III. Main idea
IV. Main idea
V. Conclusion
The second level consists of topics which support the introduction, main ideas, and the conclusion. Each main idea should have at least two supporting topics listed in the outline.
If your main idea does not have enough support, you should consider presenting another main idea in its place. This is where you should stop outlining if this is your first draft. Continue your research before adding to the next levels of organization.
- A. Background information
- B. Hypothesis or thesis
- A. Supporting topic
- B. Supporting topic
The third level of organization contains supporting information for the topics previously listed. By now, you should have completed enough research to add support for your ideas.
The Introduction and Main Ideas may contain information you discovered about the author, timeframe, or contents of a book for a literature review; the historical events leading up to the research topic for a historical research paper, or an explanation of the problem a scientific research paper intends to address.
- 1. Relevant history
- 2. Relevant history
- 1. The hypothesis or thesis clearly stated
- 1. A brief description of supporting information
- 2. A brief description of supporting information
The fourth level of organization contains the most detailed information such as quotes, references, observations, or specific data needed to support the main idea. It is not typical to have further levels of organization because the information contained here is the most specific.
- a) Quotes or references to another piece of literature
- b) Quotes or references to another piece of literature
Tip: The key to creating a useful outline is to be consistent in your headings, organization, and levels of specificity.
- Be Consistent : ensure every heading has a similar tone. State the topic or write short sentences for each heading but avoid doing both.
- Organize Information : Higher levels of organization are more generally stated and each supporting level becomes more specific. The introduction and conclusion will never be lower than the first level of organization.
- Build Support : Each main idea should have two or more supporting topics. If your research does not have enough information to support the main idea you are presenting, you should, in general, complete additional research or revise the outline.
By now, you should know the basic requirements to create an outline for your paper. With a content framework in place, you can now start writing your paper . To help you start right away, you can use one of our templates and adjust it to suit your needs.
After completing your outline, you should:
- Title your research paper . This is an iterative process and may change when you delve deeper into the topic.
- Begin writing your research paper draft . Continue researching to further build your outline and provide more information to support your hypothesis or thesis.
- Format your draft appropriately . MLA 8 and APA 7 formats have differences between their bibliography page, in-text citations, line spacing, and title.
- Finalize your citations and bibliography . Use a reference manager like Paperpile to organize and cite your research.
- Write the abstract, if required . An abstract will briefly state the information contained within the paper, results of the research, and the conclusion.
An outline is used to organize written ideas about a topic into a logical order. Outlines help us organize major topics, subtopics, and supporting details. Researchers benefit greatly from outlines while writing by addressing which topic to cover in what order.
The most basic outline format consists of: an introduction, a minimum of three topic paragraphs, and a conclusion.
You should make an outline before starting to write your research paper. This will help you organize the main ideas and arguments you want to present in your topic.
- Consistency: ensure every heading has a similar tone. State the topic or write short sentences for each heading but avoid doing both.
- Organization : Higher levels of organization are more generally stated and each supporting level becomes more specific. The introduction and conclusion will never be lower than the first level of organization.
- Support : Each main idea should have two or more supporting topics. If your research does not have enough information to support the main idea you are presenting, you should, in general, complete additional research or revise the outline.


Write Your Research Plan
In this part, we give you detailed information about writing an effective Research Plan. We start with the importance and parameters of significance and innovation.
We then discuss how to focus the Research Plan, relying on the iterative process described in the Iterative Approach to Application Planning Checklist shown at Draft Specific Aims and give you advice for filling out the forms.
You'll also learn the importance of having a well-organized, visually appealing application that avoids common missteps and the importance of preparing your just-in-time information early.
While this document is geared toward the basic research project grant, the R01, much of it is useful for other grant types.
Table of Contents
Research plan overview and your approach, craft a title, explain your aims, research strategy instructions, advice for a successful research strategy, graphics and video, significance, innovation, and approach, tracking for your budget, preliminary studies or progress report, referencing publications, review and finalize your research plan, abstract and narrative.
Your application's Research Plan has two sections:
- Specific Aims —a one-page statement of your objectives for the project.
- Research Strategy —a description of the rationale for your research and your experiments in 12 pages for an R01.
In your Specific Aims, you note the significance and innovation of your research; then list your two to three concrete objectives, your aims.
Your Research Strategy is the nuts and bolts of your application, where you describe your research rationale and the experiments you will conduct to accomplish each aim. Though how you organize it is largely up to you, NIH expects you to follow these guidelines.
- Organize using bold headers or an outline or numbering system—or both—that you use consistently throughout.
- Start each section with the appropriate header: Significance, Innovation, or Approach.
- Organize the Approach section around your Specific Aims.
Format of Your Research Plan
To write the Research Plan, you don't need the application forms. Write the text in your word processor, turn it into a PDF file, and upload it into the application form when it's final.
Because NIH may return your application if it doesn't meet all requirements, be sure to follow the rules for font, page limits, and more. Read the instructions at NIH’s Format Attachments .
For an R01, the Research Strategy can be up to 12 pages, plus one page for Specific Aims. Don't pad other sections with information that belongs in the Research Plan. NIH is on the lookout and may return your application to you if you try to evade page limits.
Follow Examples
As you read this page, look at our Sample Applications and More to see some of the different strategies successful PIs use to create an outstanding Research Plan.
Keeping It All In Sync
Writing in a logical sequence will save you time.
Information you put in the Research Plan affects just about every other application part. You'll need to keep everything in sync as your plans evolve during the writing phase.
It's best to consider your writing as an iterative process. As you develop and finalize your experiments, you will go back and check other parts of the application to make sure everything is in sync: the "who, what, when, where, and how (much money)" as well as look again at the scope of your plans.
In that vein, writing in a logical sequence is a good approach that will save you time. We suggest proceeding in the following order:
- Create a provisional title.
- Write a draft of your Specific Aims.
- Start with your Significance and Innovation sections.
- Then draft the Approach section considering the personnel and skills you'll need for each step.
- Evaluate your Specific Aims and methods in light of your expected budget (for a new PI, it should be modest, probably under the $250,000 for NIH's modular budget).
- As you design experiments, reevaluate your hypothesis, aims, and title to make sure they still reflect your plans.
- Prepare your Abstract (a summary of your Specific Aims).
- Complete the other forms.
Even the smaller sections of your application need to be well-organized and readable so reviewers can readily grasp the information. If writing is not your forte, get help.
To view writing strategies for successful applications, see our Sample Applications and More . There are many ways to create a great application, so explore your options.
Within the character limit, include the important information to distinguish your project within the research area, your project's goals, and the research problem.
Giving your project a title at the outset can help you stay focused and avoid a meandering Research Plan. So you may want to launch your writing by creating a well-defined title.
NIH gives you a 200 character limit, but don’t feel obliged to use all of that allotment. Instead, we advise you to keep the title as succinct as possible while including the important information to distinguish your project within the research area. Make your title reflect your project's goals, the problem your project addresses, and possibly your approach to studying it. Make your title specific: saying you are studying lymphocyte trafficking is not informative enough.
For examples of strong titles, see our Sample Applications and More .
After you write a preliminary title, check that
- My title is specific, indicating at least the research area and the goals of my project.
- It is 200 characters or less.
- I use as simple language as possible.
- I state the research problem and, possibly, my approach to studying it.
- I use a different title for each of my applications. (Note: there are exceptions, for example, for a renewal—see Apply for Renewal for details.)
- My title has appropriate keywords.
Later you may want to change your initial title. That's fine—at this point, it's just an aid to keep your plans focused.
Since all your reviewers read your Specific Aims, you want to excite them about your project.
If testing your hypothesis is the destination for your research, your Research Plan is the map that takes you there.
You'll start by writing the smaller part, the Specific Aims. Think of the one-page Specific Aims as a capsule of your Research Plan. Since all your reviewers read your Specific Aims, you want to excite them about your project.
For more on crafting your Specific Aims, see Draft Specific Aims .
Write a Narrative
Use at least half the page to provide the rationale and significance of your planned research. A good way to start is with a sentence that states your project's goals.
For the rest of the narrative, you will describe the significance of your research, and give your rationale for choosing the project. In some cases, you may want to explain why you did not take an alternative route.
Then, briefly describe your aims, and show how they build on your preliminary studies and your previous research. State your hypothesis.
If it is likely your application will be reviewed by a study section with broad expertise, summarize the status of research in your field and explain how your project fits in.
In the narrative part of the Specific Aims of many outstanding applications, people also used their aims to
- State the technologies they plan to use.
- Note their expertise to do a specific task or that of collaborators.
- Describe past accomplishments related to the project.
- Describe preliminary studies and new and highly relevant findings in the field.
- Explain their area's biology.
- Show how the aims relate to one another.
- Describe expected outcomes for each aim.
- Explain how they plan to interpret data from the aim’s efforts.
- Describe how to address potential pitfalls with contingency plans.
Depending on your situation, decide which items are important for you. For example, a new investigator would likely want to highlight preliminary data and qualifications to do the work.
Many people use bold or italics to emphasize items they want to bring to the reviewers' attention, such as the hypothesis or rationale.
Detail Your Aims
After the narrative, enter your aims as bold bullets, or stand-alone or run-on headers.
- State your plans using strong verbs like identify, define, quantify, establish, determine.
- Describe each aim in one to three sentences.
- Consider adding bullets under each aim to refine your objectives.
How focused should your aims be? Look at the example below.
Spot the Sample
Read the Specific Aims of the Application from Drs. Li and Samulski , "Enhance AAV Liver Transduction with Capsid Immune Evasion."
- Aim 1. Study the effect of adeno-associated virus (AAV) empty particles on AAV capsid antigen cross-presentation in vivo .
- Aim 2. Investigate AAV capsid antigen presentation following administration of AAV mutants and/or proteasome inhibitors for enhanced liver transduction in vivo .
- Aim 3. Isolate AAV chimeric capsids with human hepatocyte tropism and the capacity for cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) evasion.
After finishing the draft Specific Aims, check that
- I keep to the one-page limit.
- Each of my two or three aims is a narrowly focused, concrete objective I can achieve during the grant.
- They give a clear picture of how my project can generate knowledge that may improve human health.
- They show my project's importance to science, how it addresses a critical research opportunity that can move my field forward.
- My text states how my work is innovative.
- I describe the biology to the extent needed for my reviewers.
- I give a rationale for choosing the topic and approach.
- I tie the project to my preliminary data and other new findings in the field.
- I explicitly state my hypothesis and why testing it is important.
- My aims can test my hypothesis and are logical.
- I can design and lead the execution of two or three sets of experiments that will strive to accomplish each aim.
- As much as possible, I use language that an educated person without expertise can understand.
- My text has bullets, bolding, or headers so reviewers can easily spot my aims (and other key items).
For each element listed above, analyze your text and revise it until your Specific Aims hit all the key points you'd like to make.
After the list of aims, some people add a closing paragraph, emphasizing the significance of the work, their collaborators, or whatever else they want to focus reviewers' attention on.
Your Research Strategy is the bigger part of your application's Research Plan (the other part is the Specific Aims—discussed above.)
The Research Strategy is the nuts and bolts of your application, describing the rationale for your research and the experiments you will do to accomplish each aim. It is structured as follows:
- Significance
- You can either include this information as a subsection of Approach or integrate it into any or all of the three main sections.
- If you do the latter, be sure to mark the information clearly, for example, with a bold subhead.
- Possible other sections, for example, human subjects, vertebrate animals, select agents, and others (these do not count toward the page limit).
Though how you organize your application is largely up to you, NIH does want you to follow these guidelines:
- Add bold headers or an outlining or numbering system—or both—that you use consistently throughout.
- Start each of the Research Strategy's sections with a header: Significance, Innovation, and Approach.
For an R01, the Research Strategy is limited to 12 pages for the three main sections and the preliminary studies only. Other items are not included in the page limit.
Find instructions for R01s in the SF 424 Application Guide—go to NIH's SF 424 (R&R) Application and Electronic Submission Information for the generic SF 424 Application Guide or find it in your notice of funding opportunity (NOFO).
For most applications, you need to address Rigor and Reproducibility by describing the experimental design and methods you propose and how they will achieve robust and unbiased results. The requirement applies to research grant, career development, fellowship, and training applications.
If you're responding to an institute-specific program announcement (PA) (not a parent program announcement) or a request for applications (RFA), check the NIH Guide notice, which has additional information you need. Should it differ from the NOFO, go with the NIH Guide .
Also note that your application must meet the initiative's objectives and special requirements. NIAID program staff will check your application, and if it is not responsive to the announcement, your application will be returned to you without a review.
When writing your Research Strategy, your goal is to present a well-organized, visually appealing, and readable description of your proposed project. That means your writing should be streamlined and organized so your reviewers can readily grasp the information. If writing is not your forte, get help.
There are many ways to create an outstanding Research Plan, so explore your options.
What Success Looks Like
Your application's Research Plan is the map that shows your reviewers how you plan to test your hypothesis.
It not only lays out your experiments and expected outcomes, but must also convince your reviewers of your likely success by allaying any doubts that may cross their minds that you will be able to conduct the research.
Notice in the sample applications how the writing keeps reviewers' eyes on the ball by bringing them back to the main points the PIs want to make. Write yourself an insurance policy against human fallibility: if it's a key point, repeat it, then repeat it again.

The Big Three
So as you write, put the big picture squarely in your sights. When reviewers read your application, they'll look for the answers to three basic questions:
- Can your research move your field forward?
- Is the field important—will progress make a difference to human health?
- Can you and your team carry out the work?
Add Emphasis
Savvy PIs create opportunities to drive their main points home. They don't stop at the Significance section to emphasize their project's importance, and they look beyond their biosketches to highlight their team's expertise.
Don't take a chance your reviewer will gloss over that one critical sentence buried somewhere in your Research Strategy or elsewhere. Write yourself an insurance policy against human fallibility: if it's a key point, repeat it, then repeat it again.
Add more emphasis by putting the text in bold, or bold italics (in the modern age, we skip underlining—it's for typewriters).
Here are more strategies from our successful PIs:
- While describing a method in the Approach section, they state their or collaborators' experience with it.
- They point out that they have access to a necessary piece of equipment.
- When explaining their field and the status of current research, they weave in their own work and their preliminary data.
- They delve into the biology of the area to make sure reviewers will grasp the importance of their research and understand their field and how their work fits into it.
You can see many of these principles at work in the Approach section of the Application from Dr. William Faubion , "Inflammatory cascades disrupt Treg function through epigenetic mechanisms."
- Reviewers felt that the experiments described for Aim 1 will yield clear results.
- The plans to translate those findings to gene targets of relevance are well outlined and focused.
- He ties his proposed experiments to the larger picture, including past research and strong preliminary data for the current application.
Anticipate Reviewer Questions
Our applicants not only wrote with their reviewers in mind they seemed to anticipate their questions. You may think: how can I anticipate all the questions people may have? Of course you can't, but there are some basic items (in addition to the "big three" listed above) that will surely be on your reviewers' minds:
- Will the investigators be able to get the work done within the project period, or is the proposed work over ambitious?
- Did the PI describe potential pitfalls and possible alternatives?
- Will the experiments generate meaningful data?
- Could the resulting data prove the hypothesis?
- Are others already doing the work, or has it been already completed?
Address these questions; then spend time thinking about more potential issues specific to you and your research—and address those too.
For applications, a picture can truly be worth a thousand words. Graphics can illustrate complex information in a small space and add visual interest to your application.
Look at our sample applications to see how the investigators included schematics, tables, illustrations, graphs, and other types of graphics to enhance their applications.
Consider adding a timetable or flowchart to illustrate your experimental plan, including decision trees with alternative experimental pathways to help your reviewers understand your plans.
Plan Ahead for Video
If you plan to send one or more videos, you'll need to meet certain standards and include key information in your Research Strategy now.
To present some concepts or demonstrations, video may enhance your application beyond what graphics alone can achieve. However, you can't count on all reviewers being able to see or hear video, so you'll want to be strategic in how you incorporate it into your application.
Be reviewer-friendly. Help your cause by taking the following steps:
- Caption any narration in the video.
- Choose evocative still images from your video to accompany your summary.
- Write your summary of the video carefully so the text would make sense even without the video.
In addition to those considerations, create your videos to fit NIH’s technical requirements. Learn more in the SF 424 Form Instructions .
Next, as you write your Research Strategy, include key images from the video and a brief description.
Then, state in your cover letter that you plan to send video later. (Don't attach your files to the application.)
After you apply and get assignment information from the Commons, ask your assigned scientific review officer (SRO) how your business official should send the files. Your video files are due at least one month before the peer review meeting.
Know Your Audience's Perspective
The primary audience for your application is your peer review group. Learn how to write for the reviewers who are experts in your field and those who are experts in other fields by reading Know Your Audience .
Be Organized: A B C or 1 2 3?
In the top-notch applications we reviewed, organization ruled but followed few rules. While you want to be organized, how you go about it is up to you.
Nevertheless, here are some principles to follow:
- Start each of the Research Strategy's sections with a header: Significance, Innovation, and Approach—this you must do.
The Research Strategy's page limit—12 for R01s—is for the three main parts: Significance, Innovation, and Approach and your preliminary studies (or a progress report if you're renewing your grant). Other sections, for example, research animals or select agents, do not have a page limit.
Although you will emphasize your project's significance throughout the application, the Significance section should give the most details. Don't skimp—the farther removed your reviewers are from your field, the more information you'll need to provide on basic biology, importance of the area, research opportunities, and new findings.
When you describe your project's significance, put it in the context of 1) the state of your field, 2) your long-term research plans, and 3) your preliminary data.
In our Sample Applications , you can see that both investigators and reviewers made a case for the importance of the research to improving human health as well as to the scientific field.
Look at the Significance section of the Application from Dr. Mengxi Jiang , "Intersection of polyomavirus infection and host cellular responses," to see how these elements combine to make a strong case for significance.
- Dr. Jiang starts with a summary of the field of polyomavirus research, identifying critical knowledge gaps in the field.
- The application ties the lab's previous discoveries and new research plans to filling those gaps, establishing the significance with context.
- Note the use of formatting, whitespace, and sectioning to highlight key points and make it easier for reviewers to read the text.
After conveying the significance of the research in several parts of the application, check that
- In the Significance section, I describe the importance of my hypothesis to the field (especially if my reviewers are not in it) and human disease.
- I also point out the project's significance throughout the application.
- The application shows that I am aware of opportunities, gaps, roadblocks, and research underway in my field.
- I state how my research will advance my field, highlighting knowledge gaps and showing how my project fills one or more of them.
- Based on my scan of the review committee roster, I determine whether I cannot assume my reviewers will know my field and provide some information on basic biology, the importance of the area, knowledge gaps, and new findings.
If you are either a new PI or entering a new area: be cautious about seeming too innovative. Not only is innovation just one of five review criteria, but there might be a paradigm shift in your area of science. A reviewer may take a challenge to the status quo as a challenge to his or her world view.
When you look at our sample applications, you see that both the new and experienced investigators are not generally shifting paradigms. They are using new approaches or models, working in new areas, or testing innovative ideas.
After finishing the draft innovation section, check that
- I show how my proposed research is new and unique, e.g., explores new scientific avenues, has a novel hypothesis, will create new knowledge.
- Most likely, I explain how my project's research can refine, improve, or propose a new application of an existing concept or method.
- Make a very strong case for challenging the existing paradigm.
- Have data to support the innovative approach.
- Have strong evidence that I can do the work.
In your Approach, you spell out a few sets of experiments to address each aim. As we noted above, it's a good idea to restate the key points you've made about your project's significance, its place in your field, and your long-term goals.
You're probably wondering how much detail to include.
If you look at our sample applications as a guide, you can see very different approaches. Though people generally used less detail than you'd see in a scientific paper, they do include some experimental detail.
Expect your assigned reviewers to scrutinize your approach: they will want to know what you plan to do and how you plan to do it.
NIH data show that of the peer review criteria, approach has the highest correlation with the overall impact score.
Look at the Application from Dr. Mengxi Jiang , "Intersection of polyomavirus infection and host cellular responses," to see how a new investigator handled the Approach section.
For an example of an experienced investigator's well-received Approach section, see the Application from Dr. William Faubion , "Inflammatory cascades disrupt Treg function through epigenetic mechanisms."
Especially if you are a new investigator, you need enough detail to convince reviewers that you understand what you are undertaking and can handle the method.
- Cite a publication that shows you can handle the method where you can, but give more details if you and your team don't have a proven record using the method—and state explicitly why you think you will succeed.
- If space is short, you could also focus on experiments that highlight your expertise or are especially interesting. For experiments that are pedestrian or contracted out, just list the method.
Be sure to lay out a plan for alternative experiments and approaches in case you get negative or surprising results. Show reviewers you have a plan for spending the four or five years you will be funded no matter where the experiments lead.
See the Application from Drs. Li and Samulski , "Enhance AAV Liver Transduction with Capsid Immune Evasion," for a strong Approach section covering potential. As an example, see section C.1.3.'s alternative approaches.
Here are some pointers for organizing your Approach:
- Enter a bold header for each Specific Aim.
- Under each aim, describe the first set of experiments.
- If you get result X, you will follow pathway X; if you get result Y, you will follow pathway Y.
- Consider illustrating this with a flowchart.
Trim the fat—omit all information not needed to make your case. If you try to wow reviewers with your knowledge, they'll find flaws and penalize you heavily. Don't give them ammunition by including anything you don't need.
As you design your experiments, keep a running tab of the following essential data on a separate piece of paper:
- Who. A list of people who will help you for your Key Personnel section later.
- What. A list of equipment and supplies for the experiments you plan.
- Time. Notes on how long each step takes. Timing directly affects your budget as well as how many Specific Aims you can realistically achieve.
Jotting this information down will help you Create a Budget and complete other sections later.
After finishing a draft Approach section, check that
- I include enough background and preliminary data to give reviewers the context and significance of my plans.
- They can test the hypothesis (or hypotheses).
- I show alternative experiments and approaches in case I get negative or surprising results.
- My experiments can yield meaningful data to test my hypothesis (or hypotheses).
- As a new investigator, I include enough detail to convince reviewers I understand and can handle a method. I reviewed the sample applications to see how much detail to use.
- If I or my team has experience with a method, I cite it; otherwise I include enough details to convince reviewers we can handle it.
- I describe the results I anticipate and their implications.
- I omit all information not needed to state my case.
- I keep track of and explain who will do what, what they will do, when and where they will do it, how long it will take, and how much money it will cost.
- My timeline shows when I expect to complete my aims.
If you are applying for a new application, include preliminary studies; for a renewal or a revision (a competing supplement to an existing grant), prepare a progress report instead.
Describing Preliminary Studies
Your preliminary studies show that you can handle the methods and interpret results. Here's where you build reviewer confidence that you are headed in the right direction by pursuing research that builds on your accomplishments.
Reviewers use your preliminary studies together with the biosketches to assess the investigator review criterion, which reflects the competence of the research team.
Give alternative interpretations to your data to show reviewers you've thought through problems in-depth and are prepared to meet future challenges. If you don't do this, the reviewers will!
Though you may include other people's publications, focus on your preliminary data or unpublished data from your lab and the labs of your team members as much as you can.
As we noted above, you can put your preliminary data anywhere in the Research Strategy that you feel is appropriate, but just make sure your reviewers will be able to distinguish it. Alternatively, you can create a separate section with its own header.
Including a Progress Report
If you are applying for a renewal or a revision (a competing supplement to an existing grant), prepare a progress report instead of preliminary studies.
Create a header so your program officer can easily find it and include the following information:
- Project period beginning and end dates.
- Summary of the importance of your findings in relation to your Specific Aims.
- Account of published and unpublished results, highlighting your progress toward achieving your Specific Aims.
Note: if you submit a renewal application before the due date of your progress report, you do not need to submit a separate progress report for your grant. However, you will need to submit it, if your renewal is not funded.
After finishing the draft, check that
- I interpret my preliminary results critically.
- There is enough information to show I know what I'm talking about.
- If my project is complex, I give more preliminary studies.
- I show how my previous experience prepared me for the new project.
- It's clear which data are mine and which are not.
References show your breadth of knowledge of the field. If you leave out an important work, reviewers may assume you're not aware of it.
Throughout your application, you will reference all relevant publications for the concepts underlying your research and your methods.
Read more about your Bibliography and References Cited at Add a Bibliography and Appendix .
- Throughout my application I cite the literature thoroughly but not excessively, adding citations for all references important to my work.
- I cite all papers important to my field, including those from potential reviewers.
- I include fewer than 100 citations (if possible).
- My Bibliography and References Cited form lists all my references.
- I refer to unpublished work, including information I learned through personal contacts.
- If I do not describe a method, I add a reference to the literature.
Look over what you've written with a critical eye of a reviewer to identify potential questions or weak spots.
Enlist others to do that too—they can look at your application with a fresh eye. Include people who aren't familiar with your research to make sure you can get your point across to someone outside your field.
As you finalize the details of your Research Strategy, you will also need to return to your Specific Aims to see if you must revise. See Draft Specific Aims .
After you finish your Research Plan, you are ready to write your Abstract (called Project Summary/Abstract) and Project Narrative, which are attachments to the Other Project Information form.
These sections may be small, but they're important.
- All your peer reviewers read your Abstract and narrative.
- Staff and automated systems in NIH's Center for Scientific Review use them to decide where to assign your application, even if you requested an institute and study section.
- They show the importance and health relevance of your research to members of the public and Congress who are interested in what NIH is funding with taxpayer dollars.
Be sure to omit confidential or proprietary information in these sections! When your application is funded, NIH enters your title and Abstract in the public RePORTER database.
Think brief and simple: to the extent that you can, write these sections in lay language, and include appropriate keywords, e.g., immunotherapy, genetic risk factors.
As NIH referral officers use these parts to direct your application to an institute for possible funding, your description can influence the choice they make.
Write a succinct summary of your project that both a scientist and a lay person can understand (to the extent that you can).
- Use your Specific Aims as a template—shorten it and simplify the language.
- In the first sentence, state the significance of your research to your field and relevance to NIAID's mission: to better understand, treat, and prevent infectious, immunologic, and allergic diseases.
- Next state your hypothesis and the innovative potential of your research.
- Then list and briefly describe your Specific Aims and long-term objectives.
In your Project Narrative, you have only a few sentences to drive home your project's potential to improve public health.
Check out these effective Abstracts and Narratives from our R01 Sample Applications :
- Application from Dr. Mengxi Jiang , "Intersection of polyomavirus infection and host cellular responses"
- Application from Dr. William Faubion , "Inflammatory cascades disrupt Treg function through epigenetic mechanisms"
- My Project Summary/Abstract and Project Narrative (and title) are accessible to a broad audience.
- They describe the significance of my research to my field and state my hypothesis, my aims, and the innovative potential of my research.
- My narrative describes my project's potential to improve public health.
- I do not include any confidential or proprietary information.
- I do not use graphs or images.
- My Abstract has keywords that are appropriate and distinct enough to avoid confusion with other terms.
- My title is specific and informative.
Previous Step
Have questions.
A program officer in your area of science can give you application advice, NIAID's perspective on your research, and confirmation that your proposed research fits within NIAID’s mission.
Find contacts and instructions at When to Contact an NIAID Program Officer .
Students & Educators —Menu
- Educational Resources
- Educators & Faculty
- College Planning
- ACS ChemClub
- Project SEED
- U.S. National Chemistry Olympiad
- Student Chapters
- ACS Meeting Information
- Undergraduate Research
- Internships, Summer Jobs & Coops
- Study Abroad Programs
- Finding a Mentor
- Two Year/Community College Students
- Social Distancing Socials
- Grants & Fellowships
- Career Planning
- International Students
- Planning for Graduate Work in Chemistry
- ACS Bridge Project
- Graduate Student Organizations (GSOs)
- Standards & Guidelines
- Explore Chemistry
- Science Outreach
- Publications
- ACS Student Communities
- LEADS Conference
- ChemMatters
- You are here:
- American Chemical Society
- Students & Educators
Writing the Research Plan for Your Academic Job Application
By Jason G. Gillmore, Ph.D., Associate Professor, Department of Chemistry, Hope College, Holland, MI
A research plan is more than a to-do list for this week in lab, or a manila folder full of ideas for maybe someday—at least if you are thinking of a tenure-track academic career in chemistry at virtually any bachelor’s or higher degree–granting institution in the country. A perusal of the academic job ads in C&EN every August–October will quickly reveal that most schools expect a cover letter (whether they say so or not), a CV, a teaching statement, and a research plan, along with reference letters and transcripts. So what is this document supposed to be, and why worry about it now when those job ads are still months away?
What Is a Research Plan?
A research plan is a thoughtful, compelling, well-written document that outlines your exciting, unique research ideas that you and your students will pursue over the next half decade or so to advance knowledge in your discipline and earn you grants, papers, speaking invitations, tenure, promotion, and a national reputation. It must be a document that people at the department you hope to join will (a) read, and (b) be suitably excited about to invite you for an interview.
That much I knew when I was asked to write this article. More specifics I only really knew for my own institution, Hope College (a research intensive undergraduate liberal arts college with no graduate program), and even there you might get a dozen nuanced opinions among my dozen colleagues. So I polled a broad cross-section of my network, spanning chemical subdisciplines at institutions ranging from small, teaching-centered liberal arts colleges to our nation’s elite research programs, such as Scripps and MIT. The responses certainly varied, but they did center on a few main themes, or illustrate a trend across institution types. In this article I’ll share those commonalities, while also encouraging you to be unafraid to contact a search committee chair with a few specific questions, especially for the institutions you are particularly excited about and feel might be the best fit for you.
How Many Projects Should You Have?

While more senior advisors and members of search committees may have gotten their jobs with a single research project, conventional wisdom these days is that you need two to three distinct but related projects. How closely related to one another they should be is a matter of debate, but almost everyone I asked felt that there should be some unifying technique, problem or theme to them. However, the projects should be sufficiently disparate that a failure of one key idea, strategy, or technique will not hamstring your other projects.
For this reason, many applicants wisely choose to identify:
- One project that is a safe bet—doable, fundable, publishable, good but not earthshaking science.
- A second project that is pie-in-the-sky with high risks and rewards.
- A third project that fits somewhere in the middle.
Having more than three projects is probably unrealistic. But even the safest project must be worth doing, and even the riskiest must appear to have a reasonable chance of working.
How Closely Connected Should Your Research Be with Your Past?
Your proposed research must do more than extend what you have already done. In most subdisciplines, you must be sufficiently removed from your postdoctoral or graduate work that you will not be lambasted for clinging to an advisor’s apron strings. After all, if it is such a good idea in their immediate area of interest, why aren’t they pursuing it?!?
But you also must be able to make the case for why your training makes this a good problem for you to study—how you bring a unique skill set as well as unique ideas to this research. The five years you will have to do, fund, and publish the research before crafting your tenure package will go by too fast for you to break into something entirely outside your realm of expertise.
Biochemistry is a partial exception to this advice—in this subdiscipline it is quite common to bring a project with you from a postdoc (or more rarely your Ph.D.) to start your independent career. However, you should still articulate your original contribution to, and unique angle on the work. It is also wise to be sure your advisor tells that same story in his or her letter and articulates support of your pursuing this research in your career as a genuinely independent scientist (and not merely someone who could be perceived as his or her latest "flunky" of a collaborator.)
Should You Discuss Potential Collaborators?
Regarding collaboration, tread lightly as a young scientist seeking or starting an independent career. Being someone with whom others can collaborate in the future is great. Relying on collaborators for the success of your projects is unwise. Be cautious about proposing to continue collaborations you already have (especially with past advisors) and about starting new ones where you might not be perceived as the lead PI. Also beware of presuming you can help advance the research of someone already in a department. Are they still there? Are they still doing that research? Do they actually want that help—or will they feel like you are criticizing or condescending to them, trying to scoop them, or seeking to ride their coattails? Some places will view collaboration very favorably, but the safest route is to cautiously float such ideas during interviews while presenting research plans that are exciting and achievable on your own.
How Do You Show Your Fit?
Some faculty advise tailoring every application packet document to every institution to which you apply, while others suggest tweaking only the cover letter. Certainly the cover letter is the document most suited to introducing yourself and making the case for how you are the perfect fit for the advertised position at that institution. So save your greatest degree of tailoring for your cover letter. It is nice if you can tweak a few sentences of other documents to highlight your fit to a specific school, so long as it is not contrived.
Now, if you are applying to widely different types of institutions, a few different sets of documents will certainly be necessary. The research plan that you target in the middle to get you a job at both Harvard University and Hope College will not get you an interview at either! There are different realities of resources, scope, scale, and timeline. Not that my colleagues and I at Hope cannot tackle research that is just as exciting as Harvard’s. However, we need to have enough of a niche or a unique angle both to endure the longer timeframe necessitated by smaller groups of undergraduate researchers and to ensure that we still stand out. Furthermore, we generally need to be able to do it with more limited resources. If you do not demonstrate that understanding, you will be dismissed out of hand. But at many large Ph.D. programs, any consideration of "niche" can be inferred as a lack of confidence or ambition.
Also, be aware that department Web pages (especially those several pages deep in the site, or maintained by individual faculty) can be woefully out-of-date. If something you are planning to say is contingent on something you read on their Web site, find a way to confirm it!
While the research plan is not the place to articulate start-up needs, you should consider instrumentation and other resources that will be necessary to get started, and where you will go for funding or resources down the road. This will come up in interviews, and hopefully you will eventually need these details to negotiate a start-up package.
Who Is Your Audience?
Your research plan should show the big picture clearly and excite a broad audience of chemists across your sub-discipline. At many educational institutions, everyone in the department will read the proposal critically, at least if you make the short list to interview. Even at departments that leave it all to a committee of the subdiscipline, subdisciplines can be broad and might even still have an outside member on the committee. And the committee needs to justify their actions to the department at large, as well as to deans, provosts, and others. So having at least the introduction and executive summaries of your projects comprehensible and compelling to those outside your discipline is highly advantageous.
Good science, written well, makes a good research plan. As you craft and refine your research plan, keep the following strategies, as well as your audience in mind:
- Begin the document with an abstract or executive summary that engages a broad audience and shows synergies among your projects. This should be one page or less, and you should probably write it last. This page is something you could manageably consider tailoring to each institution.
- Provide sufficient details and references to convince the experts you know your stuff and actually have a plan for what your group will be doing in the lab. Give details of first and key experiments, and backup plans or fallback positions for their riskiest aspects.
- Hook your readers with your own ideas fairly early in the document, then strike a balance between your own new ideas and the necessary well referenced background, precedents, and justification throughout. Propose a reasonable tentative timeline, if you can do so in no more than a paragraph or two, which shows how you envision spacing out the experiments within and among your projects. This may fit well into your executive summary
- Show how you will involve students (whether undergraduates, graduate students, an eventual postdoc or two, possibly even high schoolers if the school has that sort of outreach, depending on the institutions to which you are applying) and divide the projects among students.
- Highlight how your work will contribute to the education of these students. While this is especially important at schools with greater teaching missions, it can help set you apart even at research intensive institutions. After all, we all have to demonstrate “broader impacts” to our funding agencies!
- Include where you will pursue funding, as well as publication, if you can smoothly work it in. This is especially true if there is doubt about how you plan to target or "market" your research. Otherwise, it is appropriate to hold off until the interview to discuss this strategy.
So, How Long Should Your Research Plan Be?

Learn more on the Blog
Here is where the answers diverged the most and without a unifying trend across institutions. Bottom line, you need space to make your case, but even more, you need people to read what you write.
A single page abstract or executive summary of all your projects together provides you an opportunity to make the case for unifying themes yet distinct projects. It may also provide space to articulate a timeline. Indeed, many readers will only read this single page in each application, at least until winnowing down to a more manageable list of potential candidates. At the most elite institutions, there may be literally hundreds of applicants, scores of them entirely well-suited to the job.
While three to five pages per proposal was a common response (single spaced, in 11-point Arial or 12-point Times with one inch margins), including references (which should be accurate, appropriate, and current!), some of my busiest colleagues have said they will not read more than about three pages total. Only a few actually indicated they would read up to 12-15 pages for three projects. In my opinion, ten pages total for your research plans should be a fairly firm upper limit unless you are specifically told otherwise by a search committee, and then only if you have two to three distinct proposals.
Why Start Now?
Hopefully, this question has answered itself already! Your research plan needs to be a well thought out document that is an integrated part of applications tailored to each institution to which you apply. It must represent mature ideas that you have had time to refine through multiple revisions and a great deal of critical review from everyone you can get to read them. Moreover, you may need a few different sets of these, especially if you will be applying to a broad range of institutions. So add “write research plans” to this week’s to do list (and every week’s for the next few months) and start writing up the ideas in that manila folder into some genuine research plans. See which ones survive the process and rise to the top and you should be well prepared when the job ads begin to appear in C&EN in August!

Jason G. Gillmore , Ph.D., is an Associate Professor of Chemistry at Hope College in Holland, MI. A native of New Jersey, he earned his B.S. (’96) and M.S. (’98) degrees in chemistry from Virginia Tech, and his Ph.D. (’03) in organic chemistry from the University of Rochester. After a short postdoctoral traineeship at Vanderbilt University, he joined the faculty at Hope in 2004. He has received the Dreyfus Start-up Award, Research Corporation Cottrell College Science Award, and NSF CAREER Award, and is currently on sabbatical as a Visiting Research Professor at Arizona State University. Professor Gillmore is the organizer of the Biennial Midwest Postdoc to PUI Professor (P3) Workshop co-sponsored by ACS, and a frequent panelist at the annual ACS Postdoc to Faculty (P2F) Workshops.
Other tips to help engage (or at least not turn off) your readers include:
- Avoid two-column formats.
- Avoid too-small fonts that hinder readability, especially as many will view the documents online rather than in print!
- Use good figures that are readable and broadly understandable!
- Use color as necessary but not gratuitously.
Accept & Close The ACS takes your privacy seriously as it relates to cookies. We use cookies to remember users, better understand ways to serve them, improve our value proposition, and optimize their experience. Learn more about managing your cookies at Cookies Policy .
1155 Sixteenth Street, NW, Washington, DC 20036, USA | service@acs.org | 1-800-333-9511 (US and Canada) | 614-447-3776 (outside North America)
- Terms of Use
- Accessibility
Copyright © 2024 American Chemical Society
LYNN SANTELMANN Assistant Professor, Applied Linguistics Portland State University [email protected] Outline for Research Project Proposal (adapted from Course Materials for Psycholinguistics) When writing, please use section headings to indicate where the information can be found. Subheadings need not be used, though in long sections they may facilitate organization. 1. Introduction Explain the issue you are examining and why it is significant. Describe the general area to be studied Explain why this area is important to the general area under study (e.g., psychology of language, second language acquisition, teaching methods )
Summarize what is already known about the field. Include a summary of the basic background information on the topic gleaned from your literature review (you can include information from the book and class, but the bulk should be outside sources) Discuss several critical studies that have already been done in this area(cite according to APA style). Point out why these background studies are insufficient. In other words, what question(s) do they leave unresolved that you would like to study? Choose (at least) one of these questions you might like to pursue yourself. (Make sure you do not choose too many questions)
- List the specific question(s) that you are exploring.
- Explain how these research questions are related to the larger issues raised in the introduction.
- Describe what specific claim, hypothesis, and/or model of psycholinguistics you will evaluate with these questions.
- Explain what it will show about the psychology of language if your hypothesis is confirmed.
- Explain what it will suggest about the psychology of language if your hypothesis is disconfirmed.
Describe the general methodology you choose for your study, in order to test your hypothesis(es). Explain why this method is the best for your purposes. Participants: Who would you test and why? Describe the sample you would test and explain why you have chosen this sample. Include age, and language background and socio-economic information, if relevant to the design. Are there any participants you would exclude? Why, why not?
Describe what kinds of manipulations/variations you would make or test for in order to test your hypothesis(es). Describe the factors you would vary if you were presenting a person with stimulus sentences. Explain how varying these factors would allow you to confirm or disconfirm your hypotheses. Explain what significant differences you would need to find to confirm or disconfirm your hypothesis(es). In particular, how could your hypothesis(es) be disconfirmed by your data? Controls: What kinds of factors would you need to control for in your study? Describe what types of effects would be likely to occur which would make your results appear to confirm, or to disconfirm your hypothesis(es). Describe how you can by your design rule out or control for apparent effects.
How are you going to present the stimuli? What is the participant in the experiment going to do?
How will you analyze the results? What kind of results would confirm your hypothesis? What kind of results would disconfirm your hypothesis
Filter by Keywords
10 Free Research Plan Templates for Teams and Professionals
February 13, 2024
Start using ClickUp today
- Manage all your work in one place
- Collaborate with your team
- Use ClickUp for FREE—forever
Starting a new research project from scratch can feel overwhelming. Without the right tools and templates, you’re left with a blank page and no direction. With them, starting a new project or organizing an existing one feels like a breeze.
That’s why you need to build a library of the best research plan templates. And we’re here to help you do it.
Stick with us as we run through the benefits of using a research plan template and share some of our favorites—all designed to help make your research projects run like magic.
What is a Research Plan Template?
What makes a good research plan template, 1. clickup user research plan template, 2. clickup market research template, 3. clickup research whiteboard template, 4. clickup equity research report template, 5. clickup seo research & management template, 6. clickup research report template, 7. clickup data analysis findings template, 8. clickup personal swot analysis template, 9. clickup case study template, 10. clickup investigation report template, how to write a research plan.
A research plan template is a document that’s designed to help you build the best research management plan possible. Instead of starting from scratch with a blank screen, a research plan document gives you the building blocks to fill in—so you won’t miss anything important.
There are a lot of solid research plan documents out there—covering everything from UX research (user experience) to case study templates . These templates can be helpful for any team, whether you’re working on product development prototypes or research objectives for a marketing project. They’re especially helpful for product design , UX research, and project management teams.
Some of the most popular research plan templates include:
- UX research plan templates
- Usability testing research templates
- Data analysis findings templates
- Project proposal templates
- Case study templates
- Research process templates
- Market research templates
- Competitive analysis templates
- Request for proposal templates
Each is there to guide you towards collecting, reviewing, and reporting on your research in a more strategic and organized way. Think of the research plan as your helpful research buddy—there to make things easier, provide guidance, and help you ace your project execution .
We’re all looking for something different when it comes to project templates. You might favor simplicity and order, while another team might prefer a more creative approach with lots of color and prompts.
Even though your needs are unique, there are some elements that almost always make a research plan template stand out above all the rest.
The best research plan templates:
- Keep you and your product team organized
- Help you standardize the research process and research method you use
- Keep you focused on the key project goals and deliverables
- Give you suggestions for metrics to record and analyze
- Help you keep your research questions in one place
- Help you stay on target with your project timeline
- Give you a defined place to store your thoughts and research findings
There’s no one perfect template for any individual or team. Consider what your purpose or goal is, what your project management workstreams look like, and which areas you need the most support or guidance in. This will help you choose which templates to feature and how you can use wiki software to build a collection of your go-to templates.
10 Research Plan Templates to Use in 2024
There are hundreds of research plan templates out there, but they’re not all alike. Some of them bring out the best of your project management skills , while others hinder them.
We’ve brought together the best of the best, to share with you the ultimate list of research plan templates to add to your workflow this year. Want to know what’s even better? You don’t need to get buy-in for an expensive pricing plan—these templates are all free!
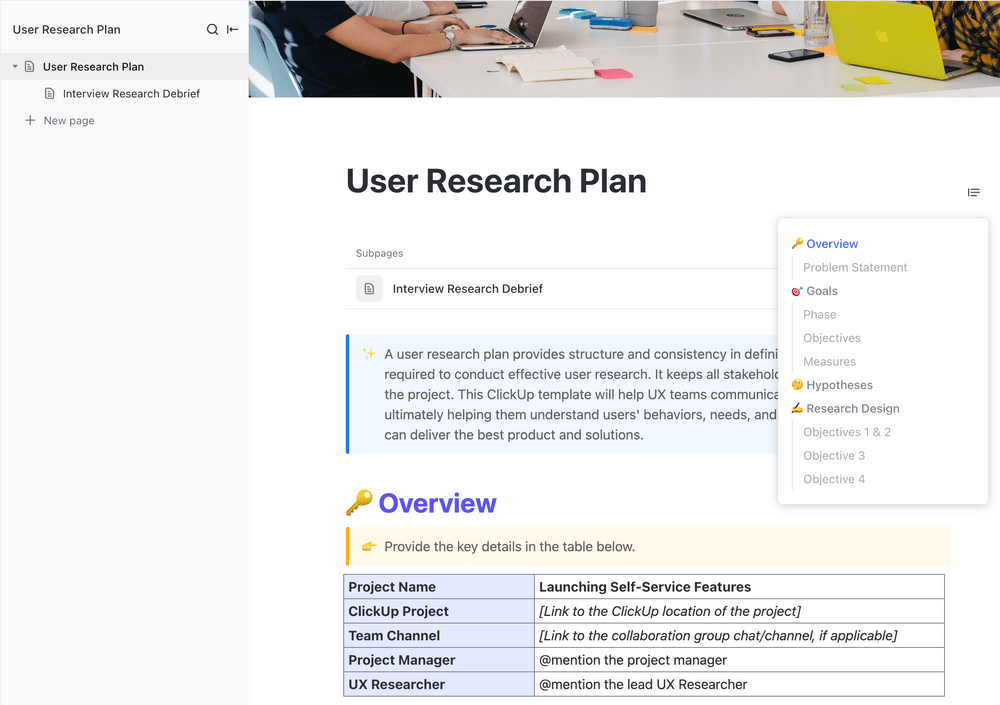
One of the first things that comes to mind when you say “research plan template” is user research. For development and project teams, this is one step of the process where strategy and staying organized is essential.
The User Research Plan Template by ClickUp makes it easy for you to achieve that and more. There’s space to share your project overview and research goals, research objectives, hypotheses, and more—plus a bonus Interview Research Debrief doc.
This template acts as a central resource for all the stakeholders. Use it to bring your team together, reaffirm your goals and objectives, and stay on track as you execute your qualitative research project.
Bonus: UX design tools !
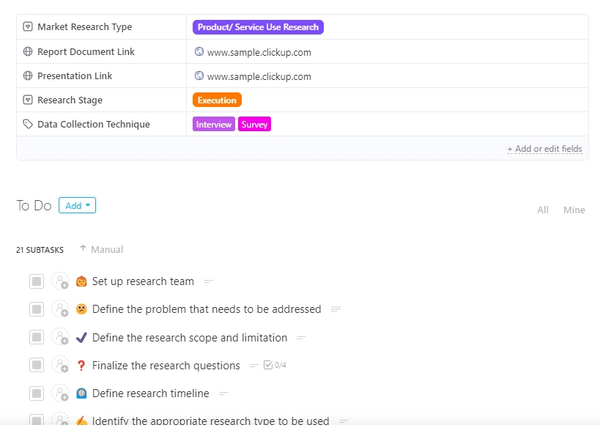
Planning your market research is a must-have if you want to get the best possible data. Give your team everything they need in one place and it helps your process run smoothly.
To help keep your team informed and ready to go, we developed the Market Research Template by ClickUp . It’s a Task template that brings you key information, all in one place.
Our Market Research Template features five custom fields—a research presentation link, market research type, report document link, data collection technique, and research stage. Add your clickable links, and use the dropdowns to assign the correct stage or type as you progress.

You can collect user research in so many ways. Questionnaires, user interviews, focus groups, user research sessions, or social media. Another super engaging way to do this is with a whiteboard.
Collaboration and user research feels interactive and fun with the Research Whiteboard Template by ClickUp . Encourage your team to share the insights they’ve collected in this highly visual template, with digital sticky notes instead of empty white boxes.
Use this ClickUp whiteboard template as a more engaging way to view your user research. You can also use this as a tool for internal research projects—invite your stakeholders by link and ask them to comment directly.
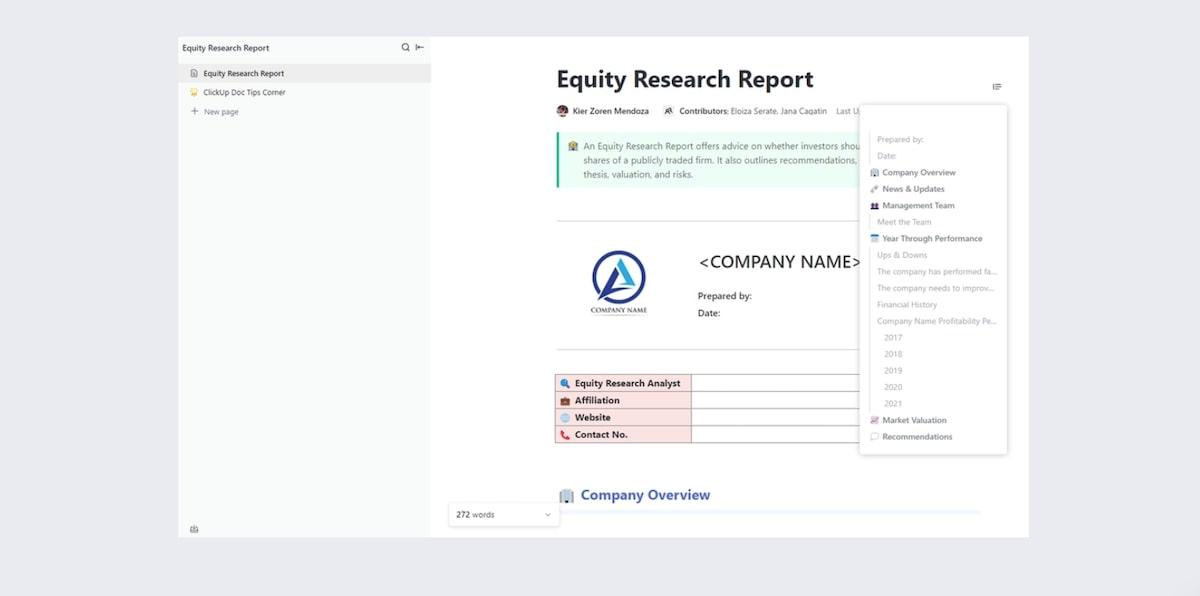
If you’re in the business of advising investors on what to do with their money, an equity report is a must-have. Instead of manually writing a new report every time, a research plan template can help you shortcut the process and get straight to the details.
Enter the Equity Research Report Template by ClickUp . It’s designed to help you share what you know in a more strategic way. Share an insight into the company overview, management team, performance, market valuation, and recommendations.
This research plan template has everything you need to present your findings to investors in an organized and effective way. Look like a pro to your investor clients and partners, and store all your data in a meaningful way to reflect on later.
Staying on top of your company’s SEO performance is no easy task. There are so many moving parts, tools, projects, goals, and team members that you need a way to stay organized and productive.
Luckily for you, the SEO Research & Management Template by ClickUp is here to help simplify the process—and make you look good to your boss. This Folder template gives you a dedicated place to work on your SEO goals, with SEO-related custom fields and plenty of custom task types to help your team communicate progress and see roadblocks in your research plan.
Use this template to see at a glance where your SEO projects are, so you can be more proactive about how your team is working. You can also dive in to details and understand time estimates, publish dates, and where your rankings are at.
Check out these AI SEO Tools !
There’s no need to start from scratch every time you’re asked to put a research report together—instead use a template to make all your research questions and study reports as impressive as the last one.
Shortcut your way to success with the Research Report Template by ClickUp . There are sections for your executive summary, introduction, research method and techniques, results & discussion, references, and appendices. Add a report author and contributors, so you can recognize everyone that contributed to the report.
Share your research methods, approach, and findings with stakeholders and clients with this impressive template. It’s a useful foundation to help your team get organized and find a better way to update stakeholders on progress.

The Data Analysis Findings Template by ClickUp helps you present your data to everyone in a more meaningful way. Instead of presenting numbers and graphs, this template can help you go deeper into the problem statement, scope, analysis and research method, findings, and conclusion.
Use this template to help you organize your thoughts and communicate the results of your study in a transparent and easy-to-read way. Explain the context and background information alongside your approach, so your stakeholders can fully understand what the data shows.

A personal SWOT analysis can help you understand your (or your team’s) strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This information can not only help you work better, but it means you can be more intentional about your impact on the wider company.
The Personal SWOT Analysis Template by ClickUp can help you remember to work on your SWOT analysis. Find your strengths, weaknesses or pain points, opportunities, and threats. This Task template features several custom fields designed to help you monitor your progress—including your objective, timeline, and completion rate.
This template can be a helpful reminder to focus on your personal SWOT analysis, so you can be more intentional and aware of how you contribute to your team and company’s goals and objectives. Use your personal SWOT to help you set professional goals for work and make a bigger impact.

Case studies give you a powerful insight into what your brands, clients, or competitors are doing. They’re an in-depth look into a specific area of the business, based on your personal research and findings.
Simplify the process of building your case studies with the Case Study Template by ClickUp . This template gives you a strong foundation for presenting clear, insightful case studies with your team, stakeholders, or clients. Introduce the company, your case study objective, solutions and statistics, and your insights.
Use this template to help you create case studies at scale. Present your data in a clear and concise way, with all the context your team or stakeholders need to extract the most value from the case study as possible.
Often our research helps us understand the market, our competitors, or what our own company is doing. Sometimes, it’s to help us understand incidents and challenges instead.
That’s where the Investigation Report Template by ClickUp comes in. This template is designed to help you report on accidents, complaints, incidents, and violations. Explain the case details including a summary and evidence, then move into cross-examination with space for interview questions and answers, and your conclusion.
This template is a must-have for teams and companies that want to demonstrate how they overcome challenges or handle incidents. It’s great for transparency and trust-building, and serves as a useful way to document a trail of evidence for when you need it.
Now that you have a template for your research plan, let’s dive into the details of how to write one. Follow these steps to create an effective research plan that will guide your research and help you achieve your goals.
Step 1: Identify Your Research Question
The first step in writing a research plan is to clearly define your research question or topic. This will serve as the foundation for all of your research and help guide your methods and analysis. Make sure your question is specific, relevant, and achievable within the scope of your project.
Step 2: Outline Your Objectives
Next, you should outline the specific objectives or goals of your research. These objectives should be aligned with your research question and provide a clear roadmap for your project. Be sure to make them measurable and achievable.
Step 3: Choose Your Research Methods
Based on your research question and objectives, you can now determine the appropriate methods for gathering data and conducting analysis. This may include surveys, experiments, interviews, or literature reviews. It’s important to choose methods that are suitable for your research topic and will provide reliable and accurate results.
Step 4: Create a Timeline
A research plan should include a detailed timeline for each stage of the project. This will help you stay on track and ensure that you have enough time to complete each task. Be realistic with your timeline and build in some buffer time for unexpected delays or challenges.
Step 5: Consider Ethical Implications
When conducting research, it’s important to consider any potential ethical implications. This may include obtaining consent from participants, ensuring privacy and confidentiality, or following ethical guidelines set by your institution or governing body.
Step 6: Anticipate Potential Outcomes
As with any research project, there are always potential outcomes that can arise. These could be both positive and negative, and it’s important to anticipate and plan for them. This will help you be prepared for any potential challenges or changes that may occur during your research.
Step 7: Revise and Refine Your Plan
Once you have completed the previous steps, it’s essential to review and revise your research plan as needed. It’s common for plans to change as the project progresses, so be open to making adjustments and tweaking your methods or timeline as needed.
Stay Organized with the Best Research Plan Templates
Nobody likes a disorganized project—especially a research project. Let your team breathe a sigh of relief and make your stakeholders smile when they realize you’ve got it all under control.
Use these free research plan templates to help you get organized, streamline your workflows, and keep everyone informed. Build a collection of templates that work for your projects, and make them a central part of the way you work as a team. Standardize, simplify, and get productive.
All of these research plan templates are available right now, for free, inside our template library . Get access to these user-friendly templates, 100MB of storage, 1,000+ integrations, and more with ClickUp—free now, and forever!
Questions? Comments? Visit our Help Center for support.
Receive the latest WriteClick Newsletter updates.
Thanks for subscribing to our blog!
Please enter a valid email
- Free training & 24-hour support
- Serious about security & privacy
- 99.99% uptime the last 12 months
Newly Launched - AI Presentation Maker

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

AI PPT Maker
Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 10 Research Plan Templates with Samples and Examples

Mohammed Sameer
"Research is creating new knowledge."- Neil Armstrong
When we dwell on what we enjoy most about our work — what excites us, what inspires us, what sparks the next big "a-ha" moment — we seldom consider processes or documentation.
But when we reflect on what frustrates us about our work—"next steps" that get delayed, projects that feel unfocused, minor details that obstruct our plans—we frequently blame processes and documentation.
To figure a way out of the dilemma, consider using a research plan to structure your work.
Even if you don't use a research plan on a regular basis or are unaware of what it means, it can help your next project run more smoothly.
This blog shows you how to write a research plan in a jiffy (with templates) that can save you hours of work, on balance.
A research plan template is a concise reference point for your project's timeline, goals, key players, and objectives.
Research plan templates provide an overview of the initiative and serve as a project kick-off document. Its beauty lies in its ability to keep your team on track, to ensure that overarching goals are well-defined and agreed upon, and to ensure that the research meets those goals.
Let's explore our top 10 research plan templates .
Template 1: Business Research Plan PPT Template
Framing a successful business research plan involves dealing with many headaches. A well-structured PPT Template is the answer in all cases. SlideTeam presents a business research plan design that explains project context and objectives, a plan of action, and a timeline to track progress. Download now.

Download this template
Template 2: Business Marketing Research Plan PPT Framework
Here’s a six-step business marketing research plan that every company needs. It helps you:
- Know your Business
- Identify your Target Market
- Analyze Competitors
- Outline Strategy
- Set a Budget
Download it now.

Get this template
Template 3: Timeframe for Business Research Plan
Construct a relevant timeframe for your business research plan using this illustrative template. It has multiple stages, including Industry Profiling, Market Assessment, Customer Persona, and Market Entry Strategies. Each stage is allotted a time frame (in weeks) to ensure your research plan is progressing. Get it now.

Grab this template
Template 4: Marketing Research Plan PPT Design
Using our template, perform an in-depth examination of how your product or service will perform in a specified area. It facilitates an analysis of the market and an assessment of the demand for your product or service. With the help of the template, you can even get to evaluate competitors. Get it now.
Template 5: Customer Research Plan PPT Template
Building a customer research plan from scratch will seem like a mountain to climb. With this PPT Template, you can avoid this struggle. It has five detailed steps that encompass the core of a customer research plan:
- Identify the Problem
- Develop the Research Plan
- Conduct Research
- Analyze and Report Findings
- Take Action in terms of Budget, Personnel, etc.
Grab it now.

Template 6: Developing the Research Plan Timeline PPT Template
Developing the research plan timeline is a methodical process that necessitates keen attention and effort. Our template makes it easy. From developing the research plan, collecting information, presenting findings, and analyzing information, our template covers every conceivable scenario. Get it now.
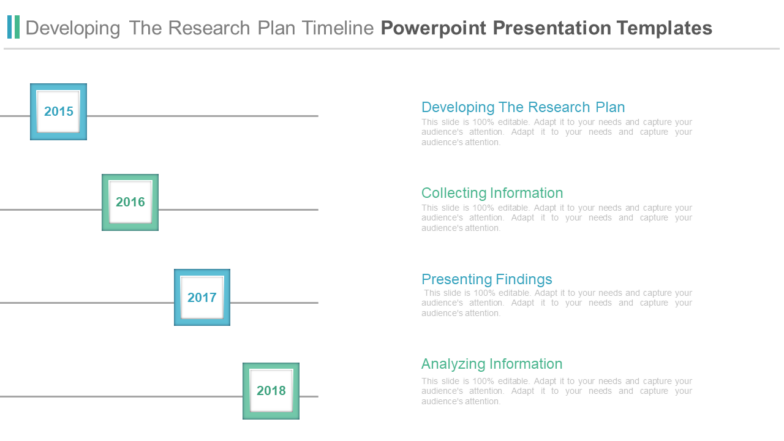
Template 7: Our Market Research Plan PPT Template
Present your organization’s month-wise activities concerning the market research plan. It is designed to foster simplicity and highlights how your market research activities are performing against set targets. You can assign colors to individual activities, which eliminates the risk of duplicacy. Grab it now.
Template 8: Business Marketing Research Plan PPT Template
Business marketing research plans can be troublesome to prepare. With our predesigned PPT Template, you can breathe easy knowing everything concerning your research plan is in place. It helps you build a robust infrastructure of your research plan and reevaluate every critical piece to ensure ideal results. Get it now.
Template 9: Shopper Journey Need Desire Research Plan
This predesigned PowerPoint Presentation helps you prepare an inclusive flowchart encompassing the shoppers’ journey giving special attention to their needs and desires. It also emphasizes the importance of loyalty and experience throughout the journey of these shoppers. This template offers you insights you need to build your research plan. Download it now.
Template 10: Market Research Business Plan Diagram
This four-phase market research business plan is a must-have for every enterprise. This is a four-stage process: Exploration, Design and Development, Planning, and Implementation. Each phase has a space for writing a brief where you can highlight points for your audience. The goal of this template is to allow you to conduct market research and make it easier to comprehend the viability of your plans. Download now.
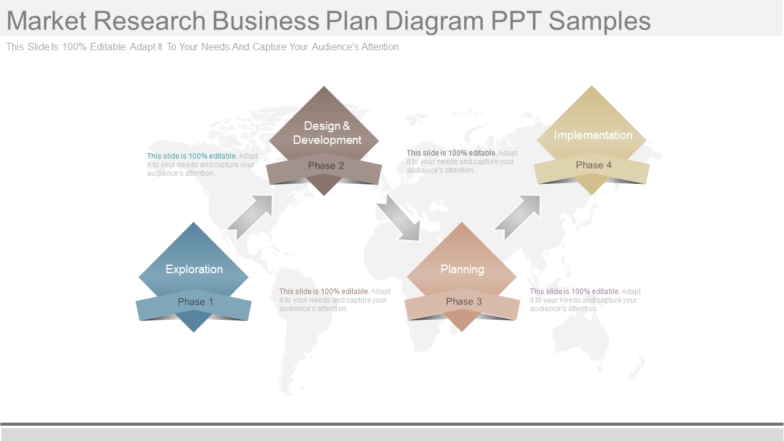
Summing It Up
Your user research plan is a blueprint for your research project. It's the most straightforward way to set expectations, solicit feedback, and generate enthusiasm and support for your research.
A solid research plan can go a long way toward ensuring a solid research project, whether it actively guides your interviews or provides an active structure for organizing your thoughts.
FAQs on Research Plan Templates
What is a research plan.
A research plan is a framework that outlines your approach to your topic. A written outline, a narrative, a visual/concept map, or a timeline are all examples of plans. It is a living document that evolves as you conduct your research.
Components of a research plan:
- Research conceptualization - presents your research question.
- Research methodology - describes how you intend to approach the research question.
- Literature review, critical evaluation, and synthesis - a methodical approach to locating, reviewing, and evaluating relevant work (texts, exhibitions, critiques, etc.)
- Communication - directed at a specific audience, demonstrating evidence of your investigation
How do you write a research plan?
Steps to writing a research plan:
- Define the project's goal
- Determine individual objectives
- Choose a research method
- Organize participants and assign tasks
- Create a project synopsis
- Make a realistic timetable
- Determine how you will present your findings
What are the 5 elements of research?
The systematic investigation of discovering new knowledge or contributing to generalized knowledge is known as research. It adheres to a specific structure that is specified in the research design. For research to be successful, elements that aid in problem-solving must be included. Here are some examples of good research design elements that produce excellent results:
- Statement of purpose
- Methods of data collection
- Techniques for analyzing research data
- Methodologies of research
- Research difficulties
- Prerequisites for conducting research
- The appropriate time for the research study
- Analysis measurement
What is the difference between a research proposal and a research report?
A research proposal is a medium by which a researcher introduces the research problem and communicates the need for research. It is imperative in the application process. It provides a snapshot of the questions that the researcher hopes to answer using the research. It specifies the researcher's methodology during the research process.
On the other hand, a research report is the culmination of the research effort. It's an excellent way to explain the research and its findings to a group of people. It is the result of a study conducted during the research process.
Related posts:
- How to Design the Perfect Service Launch Presentation [Custom Launch Deck Included]
- Quarterly Business Review Presentation: All the Essential Slides You Need in Your Deck
- [Updated 2023] How to Design The Perfect Product Launch Presentation [Best Templates Included]
- 99% of the Pitches Fail! Find Out What Makes Any Startup a Success
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 10 Research Proposal Introduction Templates With Examples and Samples (Free PDF Attached)

Top 10 Research Paper Proposal Templates with Samples and Examples
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

--> Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

--> Sales funnel results presentation layouts
--> 3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

--> Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

--> Future plan powerpoint template slide

--> Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

--> Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

--> Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

--> Agenda powerpoint slide show

--> Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

--> Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

--> Meet our team representing in circular format

Proposal Outlining: A Guide for Getting Started

Have you ever felt the sting of presenting a project proposal only to watch it fall flat? Despite pouring your heart and soul into it, all you get back are crickets and cleared throats. The reality is that crafting a proposal that captivates and convinces isn't a matter of effort alone—it's about strategy. And that strategy starts with a well-structured outline.
In this article, we'll unlock the secrets of an effective proposal outline and explore the elements that make a proposal not just good but remarkable. This first step will help you to align your ideas with your client's needs.
Key takeaways
- A good proposal outline can help you organize your ideas and the key points you need to make to persuade your prospect.
- Each part of the proposal outline should serve a specific purpose
- You might want to share your proposal outline with a peer or even your prospect to ensure it covers all of the critical information your proposal will need
What is a proposal outline?
A proposal outline is a framework that organizes your ideas and pitches into a coherent structure, ensuring every crucial element of your proposal is considered and clearly presented. It’s the backbone of your proposal, guiding you from the introduction to the conclusion, ensuring a logical flow and that no key points are missed.
A well-crafted proposal outline consists of several parts, each serving a specific purpose:
- Introduction : Sets the stage, introduces the problem or need, and captures interest.
- Problem Statement : Clearly defines the issue that your proposal aims to solve.
- Solution Overview : Outlines your proposed solution and its benefits.
- Deliverables and Timelines : Specifies what will be delivered and when .
- Cost Estimate : Provides a clear and detailed breakdown of costs associated with the proposal.
- Conclusion : Summarizes the proposal, reinforcing the value and feasibility of your solution.
By using a proposal outline, you ensure your proposal is not only complete but also tailored to directly address the needs and concerns of your clients. There is also a good selection of proposal software (and even proposal templates ) to help you futher speed up and scale the process here. In fact, we might know a few people ourselves…
Importance of outlining
Why spend extra time on a proposal outline? Well, outlining isn't just about organizing your thoughts—it's about setting a strategic foundation for your proposal. Here’s why it’s absolutely crucial:
- Enhances clarity and focus : An outline keeps your proposal focused on the client’s needs and your solution. It prevents you from veering off-topic and ensures every part of the proposal pushes toward the end goal—securing approval.
- Saves time in the long run : It might seem like extra work at the start, but having a clear outline actually speeds up the writing process. You know exactly what to write about in each section, cutting down on revisions and rewrites.
- Improves persuasiveness : A structured proposal is a persuasive proposal. With all points logically flowing from one to the next, your argument builds momentum- and with it, a compelling case to your client.
- Facilitates collaboration : When working in a team, an outline acts as a shared plan. Everyone knows their part, reducing overlap and ensuring all necessary points are covered.
- Makes a professional impression : A well-organized proposal reflects professionalism and attention to detail. It shows potential clients that you are thorough and capable, boosting their confidence in your abilities.
In short, an outline isn’t just a planning tool—it’s a critical element that elevates the quality and effectiveness of your proposal. By taking the time to outline, you're paving the way for a smoother, more impactful presentation that aligns perfectly with your client's expectations.
Key elements of a detailed project proposal outline
Crafting a project proposal is like telling a story where you're the hero who can solve the client's problem. To tell this story effectively, you need several key elements, communicating your understanding, plan, and commitment to the project's success. These elements are:
- Introduction
Kick off your proposal by grabbing attention. Introduce the problem and hint at the solution, making sure to connect emotionally (and logically) with your potential client.
- Problem statement
Dive deep into the problem. Demonstrate your understanding of the client's needs and challenges. Show empathy and expertise, making it clear why this issue needs resolution.
- Solution overview
This is where you shine. Outline your proposed solution and the unique benefits it offers. Be clear and concise , using simple terms that convey value and feasibility.
- Objectives and goals
Define what success looks like. Detail the objectives your solution aims to achieve, aligning them closely with the client’s requirements.
- Methodology and approach
Explain how you plan to achieve the outlined objectives. This section should reassure the client of your method's effectiveness and your team's capability.
- Deliverables
Specify what you will deliver, including tangible products, reports, and results. This sets clear expectations and helps avoid scope creep.
Map out the project timeline. Include key milestones and deadlines to demonstrate your project management skills and realistic approach.
- Cost estimate
Provide a detailed breakdown of the project cost. Transparency here builds trust and helps the client understand the value they are getting.
Wrap up with a strong conclusion that reiterates the benefits of your proposal. Encourage the client to take action, and make it easy for them to say Yes.
By including these elements, your proposal will not only be comprehensive but also tailored to clearly communicate how you are the best choice for the project.
How to create the perfect proposal outline (then fill it in)
Creating the perfect proposal outline is like preparing a recipe that’s tailored to taste—it needs the right ingredients, a pinch of creativity, and a good understanding of who's going to enjoy it! Here’s a simple, effective way to put it all together:
Step 1: Understand the client’s needs
Begin by thoroughly researching your client’s industry, challenges, and specific needs. The more you know, the better you can tailor your proposal to speak directly to them. Dive into their company reports, read relevant industry news, and analyze their competitors. This groundwork enables you to address their unique pain points with precision.
Step 2: Define the project scope
Clearly define what the proposal will cover and- importantly- what it won’t. Setting these boundaries early prevents misunderstandings and keeps your proposal laser-focused.
Step 3: Gather your data
Collect all the necessary information, data, and resources that will support your solution. This could include case studies, testimonials, or relevant statistics that reinforce your points. Solid data not only backs up your claims but also builds credibility, showing that your solution is grounded in proven results and sound research.
Step 4: Draft the structure
Using the key elements outlined above, start drafting your proposal. Arrange the sections in a logical order that tells a compelling story, from problem to solution. Each section should naturally lead into the next, creating a seamless narrative that keeps the reader engaged and makes your argument compelling.
Step 5: Write the details
Fill in each section with detailed information. Ensure your writing is clear, persuasive, and directly addresses how you will solve the client’s problem. Use active language, avoid jargon, and be specific about the benefits of your solution. Remember, the goal here is to make it easy for the client to understand and see the value in your proposal.
Step 6: Review and refine
Step back and review your proposal as a whole. Does it flow logically? Is it persuasive? Ask a colleague to proofread it for clarity and coherence. A fresh set of eyes can catch errors you might have missed and provide valuable feedback to improve the overall quality of the proposal.
Step 7: Customize your presentation
Tailor the final document to the client’s preferences. Consider their company culture and the decision-maker’s personal style when finalizing the format and tone. Customization shows you’ve taken the time to understand their business and care about their unique context, making your proposal stand out from more generic submissions.
Step 8: Include a Call To Action
End with a clear, compelling call to action. What do you want the client to do next? Make it easy for them to take the next step, whether it’s scheduling a meeting, signing a contract, or simply getting in touch. A strong CTA helps to turn interest into action, guiding the client towards a positive decision.
By following these steps, you’ll create a proposal outline that not only meets the client’s needs but also highlights your capabilities and understanding of their challenges.
6 Top tips for outlining proposals
Here are some top tips to ensure your proposal outlines set you up for success:

Tip 1: Start with a strong hook
Capture your reader's attention from the outset. Use a compelling fact, question, or statement that speaks directly to the reader's interests or pain points.
Tip 2: Keep the client central
Always tailor your proposal outline with the client in mind. Every section should reflect an understanding of their needs, goals, and preferences.
Tip 3: Use clear, concise language
Avoid jargon and complex language. Your proposal should be easy to understand, making the client feel confident about what you’re offering. Simple language helps to ensure your message is clear.
Tip 4: Visualize the flow
Before writing detailed content, visualize how each section flows into the next. A logical, intuitive flow keeps the reader engaged and makes your arguments more persuasive.
Tip 5: Highlight key benefits
While detailing the features of your solution is important, focusing on the benefits for the client can be even more persuasive. Make it clear how your proposal will solve their problems or improve their situation.
Tip 6: Be realistic and honest
Set realistic expectations about what you can deliver and when. Honesty builds trust and reduces the chance of client dissatisfaction down the line.
By implementing these tips, your outlines will lay the foundations for a proposal that is hard to resist.
SaaS Proposal Template
Propel your business forward with our SaaS Proposal Template – present a persuasive case for adopting your solution to prospects.

Final thoughts
We've delved into the nitty-gritty of creating a persuasive proposal outline, focusing on clarity , structure , and a client-centered approach. Your proposal's true power lies in how effectively it addresses your client's needs and highlights your unique solution.
But why stop there? With Qwilr's innovative tools and templates , you can transform your outlines into visually stunning, interactive documents that captivate and convince. If you’re ready to gain a competitive edge and make your proposals irresistible, check out what Qwilr can do for you.
About the author

Marissa Taffer | Founder & President of M. Taffer Consulting
Marissa Taffer is the Founder & President of M. Taffer Consulting. She brings over 15 years of sales and marketing experience across various industries to a broad range of clients.
Frequently asked questions
What's the ideal length for a proposal.
The length of your proposal should be determined by the complexity of the project and the client’s requirements. Generally, aim for clarity and concision.
How much detail should I include about costs?
Provide a detailed breakdown of costs, including all relevant expenses. Transparency here is crucial—clients appreciate knowing exactly what they are paying for and why.
Can I reuse parts of an old proposal for a new client?
While you can reuse generic sections like your company overview, always tailor the proposal to each client’s specific needs and circumstances to show that you’ve crafted a solution just for them. Proposal automation software can help speed up the more generic aspects.
What if the client asks for changes to the proposal?
Be open to feedback and willing to make adjustments. This flexibility can often strengthen the client relationship and lead to a more successful partnership.
How often should I follow up after submitting a proposal?
Follow up within a week of submission to show your enthusiasm and commitment. If you haven’t received a response, a gentle reminder every few weeks can keep your proposal top of mind.
Related articles
- All articles
- Sales management
- Sales techniques
- Sales enablement
- Customer success
- Product updates


Research Plan

Plans, of any kind, help people keep anticipate the things they need to do in the future. For example, a business needs to devise a business plan so that they may be able to foresee their business goals, and the methods that need to be done in accomplishing each of their smart goals .
Most people believe in the ability of small business plans to avoid disaster and chaos especially when hosting events. Researchers are among those people. When doing a research, most researchers plan for the whole course of their research in order to avoid circumstances which may negatively affect their research.
Market Research Plan Template

- Google Docs
- Apple Pages
Size: 19 KB
Legal Research Plan Template

Size: 17 KB
Research Action Plan Template

Size: 63 KB
Quantitative Research Plan Template

Size: 152 KB
Research Development Plan Template

Size: 40 KB
Simple Project Plan Template

Marketing Plan Template

Work Plan Word Template

Strategic Plan Template

Editable Action Plan Template

Full Research Plan Example

Size: 20 kB
Student Research Plan
Size: 53 kB
Strategic Research Plan Sample

Size: 775 kB
Proposed Research Plan

Size: 155 kB
What Is a Research Plan?
Research plan, as the name says, is a plan intended to anticipate a potential research project or study, and the potential course of action for the said research.
Research plans usually include the details of the proposed research including a detailed description of the research, the necessary materials and methods to include in the research, desired outcomes or results, proposed funding for the research, and other important details of the various processes the researchers plan on accomplishing for the research project plan or study.
Importance of a Research Plan
Research plans, basically, describe or propose a potential research.
Like other plans, a strategic plan keeps the researchers organized while doing the research. The researchers will also be able to craft a timeline for the duration of their research and allocate their time properly. Another thing to consider is that research plans constantly remind the researchers of their goals and what they need to do in order to reach those goals. With research plans, researchers will be able to foresee the things that might go wrong and plan for the necessary steps in managing such things.
So basically, if you want your research to go smoothly without sacrificing much time and resources, you need to have a research plan.
Preliminary Research Plan Sample

Size: 31 kB
College Research Plan

Action Research Plan Example

Size: 11 kB
How to Write a Research Plan
If you’re a researcher, how you write your research plan will be entirely up to you. But for beginners, here are some tips which might be useful when writing your research plan:
- Identify the purpose of your research plan. You just need to answer the question: What do I want to achieve in creating a research plan?
- Plan the strategies of attaining your goals. What do researchers usually do in a research? List the things you need to do in order for your research to be successful. Find the best strategies to fit your research plan.
- Organize your strategies. Create an outline of the things you want to do. Create a timeline and allocate enough time for each strategy to be done.
- Keep it specific. Only include things that are related to the simple business plan . Do not include unnecessary ones which may just cause you confusion.
- Keep it concise. You need to keep your plan as concise as you can. Sure you might need a few pages, but maybe not more than three.
- Be realistic. Do not include unrealistic expectations and desired outcomes. Keep your feet on the ground.
- Revise and improve your plan. You don’t need to do much—just check for errors and maybe things to add, and you’re done!
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a study plan for final exams in high school
Develop a project timeline for a middle school science fair.

Title Page Setup
A title page is required for all APA Style papers. There are both student and professional versions of the title page. Students should use the student version of the title page unless their instructor or institution has requested they use the professional version. APA provides a student title page guide (PDF, 199KB) to assist students in creating their title pages.
Student title page
The student title page includes the paper title, author names (the byline), author affiliation, course number and name for which the paper is being submitted, instructor name, assignment due date, and page number, as shown in this example.
Title page setup is covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Section 2.3 and the Concise Guide Section 1.6
Related handouts
- Student Title Page Guide (PDF, 263KB)
- Student Paper Setup Guide (PDF, 3MB)
Student papers do not include a running head unless requested by the instructor or institution.
Follow the guidelines described next to format each element of the student title page.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Paper title | Place the title three to four lines down from the top of the title page. Center it and type it in bold font. Capitalize of the title. Place the main title and any subtitle on separate double-spaced lines if desired. There is no maximum length for titles; however, keep titles focused and include key terms. |
|
| Author names | Place one double-spaced blank line between the paper title and the author names. Center author names on their own line. If there are two authors, use the word “and” between authors; if there are three or more authors, place a comma between author names and use the word “and” before the final author name. | Cecily J. Sinclair and Adam Gonzaga |
| Author affiliation | For a student paper, the affiliation is the institution where the student attends school. Include both the name of any department and the name of the college, university, or other institution, separated by a comma. Center the affiliation on the next double-spaced line after the author name(s). | Department of Psychology, University of Georgia |
| Course number and name | Provide the course number as shown on instructional materials, followed by a colon and the course name. Center the course number and name on the next double-spaced line after the author affiliation. | PSY 201: Introduction to Psychology |
| Instructor name | Provide the name of the instructor for the course using the format shown on instructional materials. Center the instructor name on the next double-spaced line after the course number and name. | Dr. Rowan J. Estes |
| Assignment due date | Provide the due date for the assignment. Center the due date on the next double-spaced line after the instructor name. Use the date format commonly used in your country. | October 18, 2020 |
|
| Use the page number 1 on the title page. Use the automatic page-numbering function of your word processing program to insert page numbers in the top right corner of the page header. | 1 |
Professional title page
The professional title page includes the paper title, author names (the byline), author affiliation(s), author note, running head, and page number, as shown in the following example.
Follow the guidelines described next to format each element of the professional title page.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Paper title | Place the title three to four lines down from the top of the title page. Center it and type it in bold font. Capitalize of the title. Place the main title and any subtitle on separate double-spaced lines if desired. There is no maximum length for titles; however, keep titles focused and include key terms. |
|
| Author names
| Place one double-spaced blank line between the paper title and the author names. Center author names on their own line. If there are two authors, use the word “and” between authors; if there are three or more authors, place a comma between author names and use the word “and” before the final author name. | Francesca Humboldt |
| When different authors have different affiliations, use superscript numerals after author names to connect the names to the appropriate affiliation(s). If all authors have the same affiliation, superscript numerals are not used (see Section 2.3 of the for more on how to set up bylines and affiliations). | Tracy Reuter , Arielle Borovsky , and Casey Lew-Williams | |
| Author affiliation
| For a professional paper, the affiliation is the institution at which the research was conducted. Include both the name of any department and the name of the college, university, or other institution, separated by a comma. Center the affiliation on the next double-spaced line after the author names; when there are multiple affiliations, center each affiliation on its own line.
| Department of Nursing, Morrigan University |
| When different authors have different affiliations, use superscript numerals before affiliations to connect the affiliations to the appropriate author(s). Do not use superscript numerals if all authors share the same affiliations (see Section 2.3 of the for more). | Department of Psychology, Princeton University | |
| Author note | Place the author note in the bottom half of the title page. Center and bold the label “Author Note.” Align the paragraphs of the author note to the left. For further information on the contents of the author note, see Section 2.7 of the . | n/a |
|
| The running head appears in all-capital letters in the page header of all pages, including the title page. Align the running head to the left margin. Do not use the label “Running head:” before the running head. | Prediction errors support children’s word learning |
|
| Use the page number 1 on the title page. Use the automatic page-numbering function of your word processing program to insert page numbers in the top right corner of the page header. | 1 |

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Here's an example outline of a research plan you might put together: Project title. Project members involved in the research plan. Purpose of the project (provide a summary of the research plan's intent) Objective 1 (provide a short description for each objective) Objective 2. Objective 3.
If you want to learn how to write your own plan for your research project, consider the following seven steps: 1. Define the project purpose. The first step to creating a research plan for your project is to define why and what you're researching. Regardless of whether you're working with a team or alone, understanding the project's purpose can ...
A research plan is a comprehensive documented outline of your entire project, encompassing the research process and the anticipated outcomes. This strategic document aids in defining objectives, summarizing the necessary steps to achieve them, and detailing the requirements for obtaining conclusive results.
A research plan is a comprehensive document that outlines the entirety of your research project. It details the research process, from defining the problem statement and research objectives to selecting the research method and outlining the expected outcomes. This plan serves as a blueprint for your research activities, ensuring a focused and ...
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management".
A research paper outline is a useful tool to aid in the writing process, providing a structure to follow with all information to be included in the paper clearly organized. A quality outline can make writing your research paper more efficient by helping to: Organize your thoughts;
Here is an explanation of each step: 1. Title and Abstract. Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research. Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal. 2.
This is where a research paper outline becomes useful. Writing a research paper can be made simpler and more efficient with a well-organized plan. A well-structured research paper outline offers the fundamental foundation on which researchers can construct their narratives logically, ensuring that the study report is well-presented and ...
Creating a plan and outline before starting your research paper can lead to a more successful and satisfying writing process. Contrary to concerns about stifling creativity, planning ahead actually frees your mind from cluttered thoughts and allows for creativity to flourish within the boundaries of your rough plan.
What is a research proposal? Simply put, a research proposal is a structured, formal document that explains what you plan to research (your research topic), why it's worth researching (your justification), and how you plan to investigate it (your methodology). The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your ...
Research Paper Outline. Research paper outline is a plan or a structural framework that organizes the main ideas, arguments, and supporting evidence in a logical sequence. It serves as a blueprint or a roadmap for the writer to follow while drafting the actual research paper. Typically, an outline consists of the following elements:
A research plan is a framework that shows how you intend to approach your topic. The plan can take many forms: a written outline, a narrative, a visual/concept map or timeline. It's a document that will change and develop as you conduct your research. Components of a research plan. 1. Research conceptualization - introduces your research question.
Before conducting a study, a research proposal should be created that outlines researchers' plans and methodology and is submitted to the concerned evaluating organization or person. Creating a research proposal is an important step to ensure that researchers are on track and are moving forward as intended. A research proposal can be defined as a detailed plan or blueprint for the proposed ...
If you are writing the outline for yourself, you may choose any combination you prefer. First level of organization. This is the most generalized level of information. Begin by numbering the introduction, each idea you will present, and the conclusion. The main ideas contain the bulk of your research paper's information.
Organize using bold headers or an outline or numbering system—or both—that you use consistently throughout. Start each section with the appropriate header: Significance, Innovation, or Approach. Organize the Approach section around your Specific Aims. Format of Your Research Plan. To write the Research Plan, you don't need the application ...
A quality example of a research proposal shows one's above-average analytical skills, including the ability to coherently synthesize ideas and integrate lateral and vertical thinking. Communication skills. The proposal also demonstrates your proficiency to communicate your thoughts in concise and precise language.
A research plan is a thoughtful, compelling, well-written document that outlines your exciting, unique research ideas that you and your students will pursue over the next half decade or so to advance knowledge in your discipline and earn you grants, papers, speaking invitations, tenure, promotion, and a national reputation.
The 7 core components of a user research plan: The background of the research project detailing why we are conducting this study. This can also include the internal stakeholders involved. The objectives and goals of the research, what the teams want to learn from the research, or what they would like the outcome to be.
How to plan a UX research study. This is a step-by-step guide to planning user research. It explains the process by which a research plan comes together into a shareable document (like the one above) that enables team alignment, accountability, and efficiency throughout your study. 1. Identify your research goals.
A research plan or proposal is a document that describes a research project, including its purpose, methods, objectives, timeline, budget, participants, expected outcomes, and preliminary studies. This proposal usually outlines what the researcher wants to achieve, explore, or corroborate and explains the importance of the project.
Outline for Research Project Proposal. (adapted from Course Materials for Psycholinguistics) When writing, please use section headings to indicate where the information can be found. Subheadings need not be used, though in long sections they may facilitate organization. 1. Introduction Explain the issue you are examining and why it is significant.
1. ClickUp User Research Plan Template. ClickUp User Research Plan Template. One of the first things that comes to mind when you say "research plan template" is user research. For development and project teams, this is one step of the process where strategy and staying organized is essential.
Template 1: Business Research Plan PPT Template. Framing a successful business research plan involves dealing with many headaches. A well-structured PPT Template is the answer in all cases. SlideTeam presents a business research plan design that explains project context and objectives, a plan of action, and a timeline to track progress.
In short, an outline isn't just a planning tool—it's a critical element that elevates the quality and effectiveness of your proposal. By taking the time to outline, you're paving the way for a smoother, more impactful presentation that aligns perfectly with your client's expectations. Key elements of a detailed project proposal outline
Create an outline of the things you want to do. Create a timeline and allocate enough time for each strategy to be done. Keep it specific. Only include things that are related to the simple business plan. Do not include unnecessary ones which may just cause you confusion. Keep it concise. You need to keep your plan as concise as you can.
For a professional paper, the affiliation is the institution at which the research was conducted. Include both the name of any department and the name of the college, university, or other institution, separated by a comma. Center the affiliation on the next double-spaced line after the author names; when there are multiple affiliations, center ...
The plan's future Project 2025 is backed by a $22m (£17m) budget and includes strategies for implementing policies immediately after the presidential inauguration in January 2025.
Promoting Inclusive and Equitable Research (PIER) Plans. Beginning in FY 2023, all Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science Funding Opportunity Announcements (FOAs) and DOE National Lab Announcements and other funding solicitations will require applicants to submit a Promoting Inclusive and Equitable Research (PIER) Plan as an appendix to their proposal narrative.
Research is shedding light on different chromosomal make-ups and what advantages they may bring to sport.
President Joe Biden on Tuesday announced a new $150 million research grant initiative as part of the "Cancer Moonshot" program.. The "Cancer Moonshot" program began under the Obama administration ...