
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
1. WHAT IS TECHNICAL COMMUNICATION?

1.4 Case Study: The Cost of Poor Communication
No one knows exactly how much poor communication costs business, industry and government each year, but estimates suggest billions. In fact, a recent estimate claims that the cost in the U.S. alone are close to $4 billion annually! [1] Poorly-worded or inefficient emails, careless reading or listening to instructions, documents that go unread due to poor design, hastily presenting inaccurate information, sloppy proofreading — all of these examples result in inevitable costs. The problem is that these costs aren’t usually included on the corporate balance sheet at the end of each year; if they are not properly or clearly defined, the problems remain unsolved.
You may have seen the Project Management Tree Cartoon before ( Figure 1.4.1 ); it has been used and adapted widely to illustrate the perils of poor communication during a project.

The waste caused by imprecisely worded regulations or instructions, confusing emails, long-winded memos, ambiguously written contracts, and other examples of poor communication is not as easily identified as the losses caused by a bridge collapse or a flood. But the losses are just as real—in reduced productivity, inefficiency, and lost business. In more personal terms, the losses are measured in wasted time, work, money, and ultimately, professional recognition. In extreme cases, losses can be measured in property damage, injuries, and even deaths.
The following “case studies” show how poor communications can have real world costs and consequences. For example, consider the “ Comma Quirk ” in the Rogers Contract that cost $2 million. [3] A small error in spelling a company name cost £8.8 million. [4] Examine Edward Tufte’s discussion of the failed PowerPoint presentation that attempted to prevent the Columbia Space Shuttle disaster. [5] The failure of project managers and engineers to communicate effectively resulted in the deadly Hyatt Regency walkway collapse. [6] The case studies below offer a few more examples that might be less extreme, but much more common.
In small groups, examine each “case” and determine the following:
- Define the rhetorical situation : Who is communicating to whom about what, how, and why? What was the goal of the communication in each case?
- Identify the communication error (poor task or audience analysis? Use of inappropriate language or style? Poor organization or formatting of information? Other?)
- Explain what costs/losses were incurred by this problem.
- Identify possible solution s or strategies that would have prevented the problem, and what benefits would be derived from implementing solutions or preventing the problem.
Present your findings in a brief, informal presentation to the class.
Exercises adapted from T.M Georges’ Analytical Writing for Science and Technology. [7]
CASE 1: The promising chemist who buried his results
Bruce, a research chemist for a major petro-chemical company, wrote a dense report about some new compounds he had synthesized in the laboratory from oil-refining by-products. The bulk of the report consisted of tables listing their chemical and physical properties, diagrams of their molecular structure, chemical formulas and data from toxicity tests. Buried at the end of the report was a casual speculation that one of the compounds might be a particularly safe and effective insecticide.
Seven years later, the same oil company launched a major research program to find more effective but environmentally safe insecticides. After six months of research, someone uncovered Bruce’s report and his toxicity tests. A few hours of further testing confirmed that one of Bruce’s compounds was the safe, economical insecticide they had been looking for.
Bruce had since left the company, because he felt that the importance of his research was not being appreciated.
CASE 2: The rejected current regulator proposal
The Acme Electric Company worked day and night to develop a new current regulator designed to cut the electric power consumption in aluminum plants by 35%. They knew that, although the competition was fierce, their regulator could be produced more affordably, was more reliable, and worked more efficiently than the competitors’ products.
The owner, eager to capture the market, personally but somewhat hastily put together a 120-page proposal to the three major aluminum manufacturers, recommending that the new Acme regulators be installed at all company plants.
She devoted the first 87 pages of the proposal to the mathematical theory and engineering design behind his new regulator, and the next 32 to descriptions of the new assembly line she planned to set up to produce regulators quickly. Buried in an appendix were the test results that compared her regulator’s performance with present models, and a poorly drawn graph showed the potential cost savings over 3 years.
The proposals did not receive any response. Acme Electric didn’t get the contracts, despite having the best product. Six months later, the company filed for bankruptcy.
CASE 3: The instruction manual the scared customers away
As one of the first to enter the field of office automation, Sagatec Software, Inc. had built a reputation for designing high-quality and user-friendly database and accounting programs for business and industry. When they decided to enter the word-processing market, their engineers designed an effective, versatile, and powerful program that Sagatec felt sure would outperform any competitor.
To be sure that their new word-processing program was accurately documented, Sagatec asked the senior program designer to supervise writing the instruction manual. The result was a thorough, accurate and precise description of every detail of the program’s operation.
When Sagatec began marketing its new word processor, cries for help flooded in from office workers who were so confused by the massive manual that they couldn’t even find out how to get started. Then several business journals reviewed the program and judged it “too complicated” and “difficult to learn.” After an impressive start, sales of the new word processing program plummeted.
Sagatec eventually put out a new, clearly written training guide that led new users step by step through introductory exercises and told them how to find commands quickly. But the rewrite cost Sagatec $350,000, a year’s lead in the market, and its reputation for producing easy-to-use business software.
CASE 4: One garbled memo – 26 baffled phone calls
Joanne supervised 36 professionals in 6 city libraries. To cut the costs of unnecessary overtime, she issued this one-sentence memo to her staff:
After the 36 copies were sent out, Joanne’s office received 26 phone calls asking what the memo meant. What the 10 people who didn’t call about the memo thought is uncertain. It took a week to clarify the new policy.
CASE 5: Big science — Little rhetoric
The following excerpt is from Carl Sagan’s book, The Demon-Haunted World: Science as a Candle in the Dark, [8] itself both a plea for and an excellent example of clear scientific communication:
The Superconducting Supercollider (SSC) would have been the preeminent instrument on the planet for probing the fine structure of matter and the nature of the early Universe. Its price tag was $10 to $15 billion. It was cancelled by Congress in 1993 after about $2 billion had been spent — a worst of both worlds outcome. But this debate was not, I think, mainly about declining interest in the support of science. Few in Congress understood what modern high-energy accelerators are for. They are not for weapons. They have no practical applications. They are for something that is, worrisomely from the point of view of many, called “the theory of everything.” Explanations that involve entities called quarks, charm, flavor, color, etc., sound as if physicists are being cute. The whole thing has an aura, in the view of at least some Congresspeople I’ve talked to, of “nerds gone wild” — which I suppose is an uncharitable way of describing curiosity-based science. No one asked to pay for this had the foggiest idea of what a Higgs boson is. I’ve read some of the material intended to justify the SSC. At the very end, some of it wasn’t too bad, but there was nothing that really addressed what the project was about on a level accessible to bright but skeptical non-physicists. If physicists are asking for 10 or 15 billion dollars to build a machine that has no practical value, at the very least they should make an extremely serious effort, with dazzling graphics, metaphors, and capable use of the English language, to justify their proposal. More than financial mismanagement, budgetary constraints, and political incompetence, I think this is the key to the failure of the SSC.
CASE 6: The co-op student who mixed up genres
Chris was simultaneously enrolled in a university writing course and working as a co-op student at the Widget Manufacturing plant. As part of his co-op work experience, Chris shadowed his supervisor/mentor on a safety inspection of the plant, and was asked to write up the results of the inspection in a compliance memo . In the same week, Chris’s writing instructor assigned the class to write a narrative essay based on some personal experience. Chris, trying to be efficient, thought that the plant visit experience could provide the basis for his essay assignment as well.
He wrote the essay first, because he was used to writing essays and was pretty good at it. He had never even seen a compliance memo, much less written one, so was not as confident about that task. He began the essay like this:
On June 1, 2018, I conducted a safety audit of the Widget Manufacturing plant in New City. The purpose of the audit was to ensure that all processes and activities in the plant adhere to safety and handling rules and policies outlined in the Workplace Safety Handbook and relevant government regulations. I was escorted on a 3-hour tour of the facility by…
Chris finished the essay and submitted it to his writing instructor. He then revised the essay slightly, keeping the introduction the same, and submitted it to his co-op supervisor. He “aced” the essay, getting an A grade, but his supervisor told him that the report was unacceptable and would have to be rewritten – especially the beginning, which should have clearly indicated whether or not the plant was in compliance with safety regulations. Chris was aghast! He had never heard of putting the “conclusion” at the beginning . He missed the company softball game that Saturday so he could rewrite the report to the satisfaction of his supervisor.
- J. Bernoff, "Bad writing costs business billions," Daily Beast , Oct. 16, 2016 [Online]. Available: https://www.thedailybeast.com/bad-writing-costs-businesses-billions?ref=scroll ↵
- J. Reiter, "The 'Project Cartoon' root cause," Medium, 2 July 2019. Available: https://medium.com/@thx2001r/the-project-cartoon-root-cause-5e82e404ec8a ↵
- G. Robertson, “Comma quirk irks Rogers,” Globe and Mail , Aug. 6, 2006 [Online]. Available: https://www.theglobeandmail.com/report-on-business/comma-quirk-irks-rogers/article1101686/ ↵
- “The £8.8m typo: How one mistake killed a family business,” (28 Jan. 2015). The Guardian [online]. Available: https://www.theguardian.com/law/shortcuts/2015/jan/28/typo-how-one-mistake-killed-a-family-business-taylor-and-sons ↵
- E. Tufte, The Cognitive Style of PowerPoint , 2001 [Online]. Available: https://www.inf.ed.ac.uk/teaching/courses/pi/2016_2017/phil/tufte-powerpoint.pdf ↵
- C. McFadden, "Understanding the tragic Hyatt Regency walkway collapse," Interesting Engineering , July 4, 2017 [Online]: https://interestingengineering.com/understanding-hyatt-regency-walkway-collapse ↵
- T.M. Goerges (1996), Analytical Writing for Science and Technology [Online], Available: https://www.scribd.com/document/96822930/Analytical-Writing ↵
- C. Sagan, The Demon-Haunted World: Science as a Candle in the Dark, New York, NY: Random House, 1995. ↵
Technical Writing Essentials Copyright © 2019 by Suzan Last is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Help Center
5 Internal Communication Case Studies and Best Practices To Follow
Alex Cleary
on Aug 21, 2024
in Internal Communications
From employee engagement to workplace culture to change management, businesses often face similar challenges to each other even if those businesses are radically different. While the specifics of these challenges may differ, how other businesses solve these challenges can give you new insights into addressing your own.
We’re always interested in how our customers use ContactMonkey to solve their internal communications challenges, which is why we publish customer case studies. Learn how other businesses solve their communication challenges and get inspiration on ways you can improve your business by using an internal communications tool .
Get to know your team beyond clicks and opens
Decode employee patterns with real-time analytics., what is an internal communication case study.
An internal communication case study examines how a company addressed a specific problem facing their organization, or achieved a specific goal. Communication is crucial for every business, and communication challenges can manifest in all kinds of situations.
An effective internal communication case study will clearly outline the problem, solution, and result of the business’ efforts to reach their goal. An internal communication case study should also outline best practices that were developed in this process, and how those best practices serve the business going forward.
Why are internal communication case studies important?
A good internal communication case study should not only explain the circumstances around a specific business’ problems and solution. It should also help others develop new ways to approach their own internal communication challenges , and shed light on common communication pitfalls that face a majority of businesses.
Whenever you’re facing a particular communication problem at your workplace, we recommend searching out a relevant internal communication case study about businesses facing similar issues. Even though the particulars may be different, it’s always important to see how internal communications problems are solved .
Featured Resource: Internal Email Benchmark Report 2023
5 Best Internal Communications Case Studies
We put together this list of our favourite ContactMonkey case studies that best demonstrate the many problems our internal communications software can be used to solve. If you want to learn more about any of these customers and see other case studies, check out our Customers page .
Easiest internal emails: drag, drop, and you’re done!
1. mettler toledo saves days on their internal communications with contactmonkey.
When Kate Kraley began as Mettler Toledo’s Marketing Communications Specialist, she wanted to use internal communications to increase engagement and improve communication with employees.
But Mettler Toledo —a global manufacturer of precision instruments for various industries—had a confusing and ineffective array of internal communications channels . Here’s how Kate took charge of internal communications at Mettler Toledo with ContactMonkey.
Kate came to an internal communications department tasked with reaching employees through a number of channels. Email was the main focus of their approach, but this encompassed many forms of communication based on email like employee newsletters, eNews, and quarterly email updates.
Kate wanted to improve the quality of their internal communications. She used a variety of tools to create their newsletters, including using Mailchimp and online HTML template builder. But because Mailchimp is not for internal communications , Kate and her team found themselves spending over 8 hours a week building their internal communications:
“We faced challenges with Mailchimp. Since we had to leave Outlook to use Mailchimp, we found it was double the work to maintain distribution lists in both Outlook and Mailchimp. The HTML builder in Mailchimp was also difficult to use as it didn’t work well with older versions of Outlook, compromising the layout.”
Kate also needed a way to determine whether Mettler Toledo employees were actually reading her internal communications. She used Mailchimp to track open rate, but wanted more in-depth measures of engagement. That’s when she switched to ContactMonkey.
Kate found ContactMonkey via the IABC Hub in 2018, and began testing it out. ContactMonkey’s all-in-one internal communications software removed the need to switch from tool to tool. Using our email template builder , Kate now builds visually stunning email newsletters and templates without having to navigate away from Outlook:
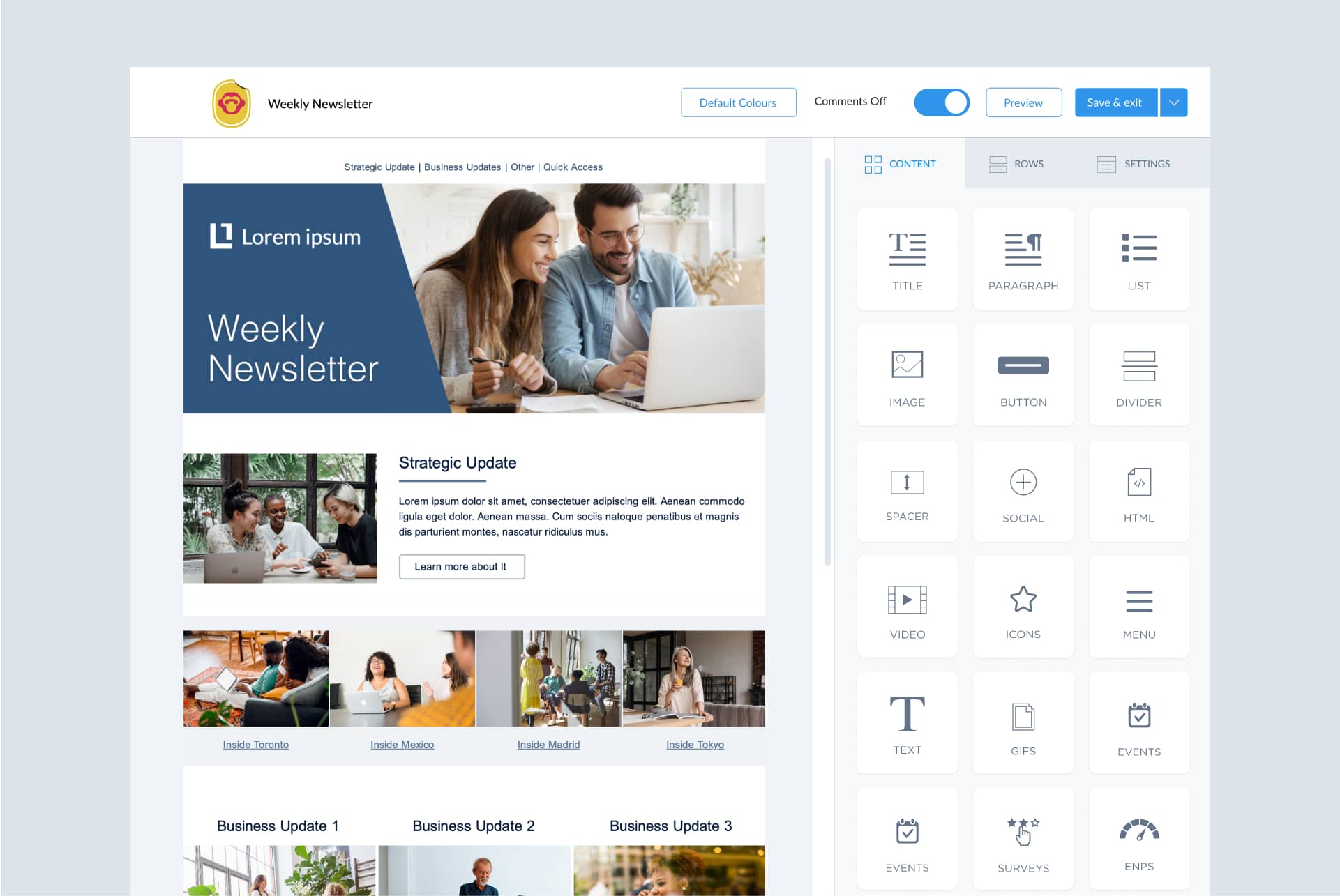
She also now has access to her own analytics dashboard . Kate analyzes numerous email metrics like open rate, click-through rate, read time, opens by device and location, and more to see which communications are driving the most engagement. With this new centralized approach, Kate knew she had found the right solution:
“Once I started using ContactMonkey, I realized I was able to save 4 hours of work a week, which translated to 25 days saved per year! ContactMonkey has helped us understand what employees are interested in!”
2. BASF Manages Their Remote Workforce with ContactMonkey
Mark Kaplan is the Global Communications Manager at BASF’s Agricultural Group —a department of the German chemical company BASF SE. Because BASF has offices and production sites around the world, Mark coordinates with other internal communicators across the company to drive employee engagement.
With the success of any business comes new challenges, and BASF isn’t any different. While Mark knew he had to keep others informed of the latest news from the BASF Agricultural Group, he was aware employees would be receiving news from other parts of the company as well.
With many different departments sending their own internal communications, Mark faced a difficult task: keeping employees engaged while being careful not to overwhelm them with countless emails and updates.
“We try to be very strategic with what we’re sending out because people are already getting a lot.”
Not only did Mark have to find a solution that made his email communications more engaging, but he also had to prove the value of whatever solution he chose to management. How could Mark show that he was increasing employee engagement while avoiding tuning out from oversaturation?
Mark began using ContactMonkey to create better internal communications for BASF employees. Using our drag-and-drop email template builder, he designs emails that maximized communication and minimized distractions, keeping information to just what his recipients needed to know.
Mark uses ContactMonkey’s email template library to save time on his email design process. He also uses the easy drag-and-drop format of the email template builder to add multimedia into his email communications to save space and increase their effectiveness:
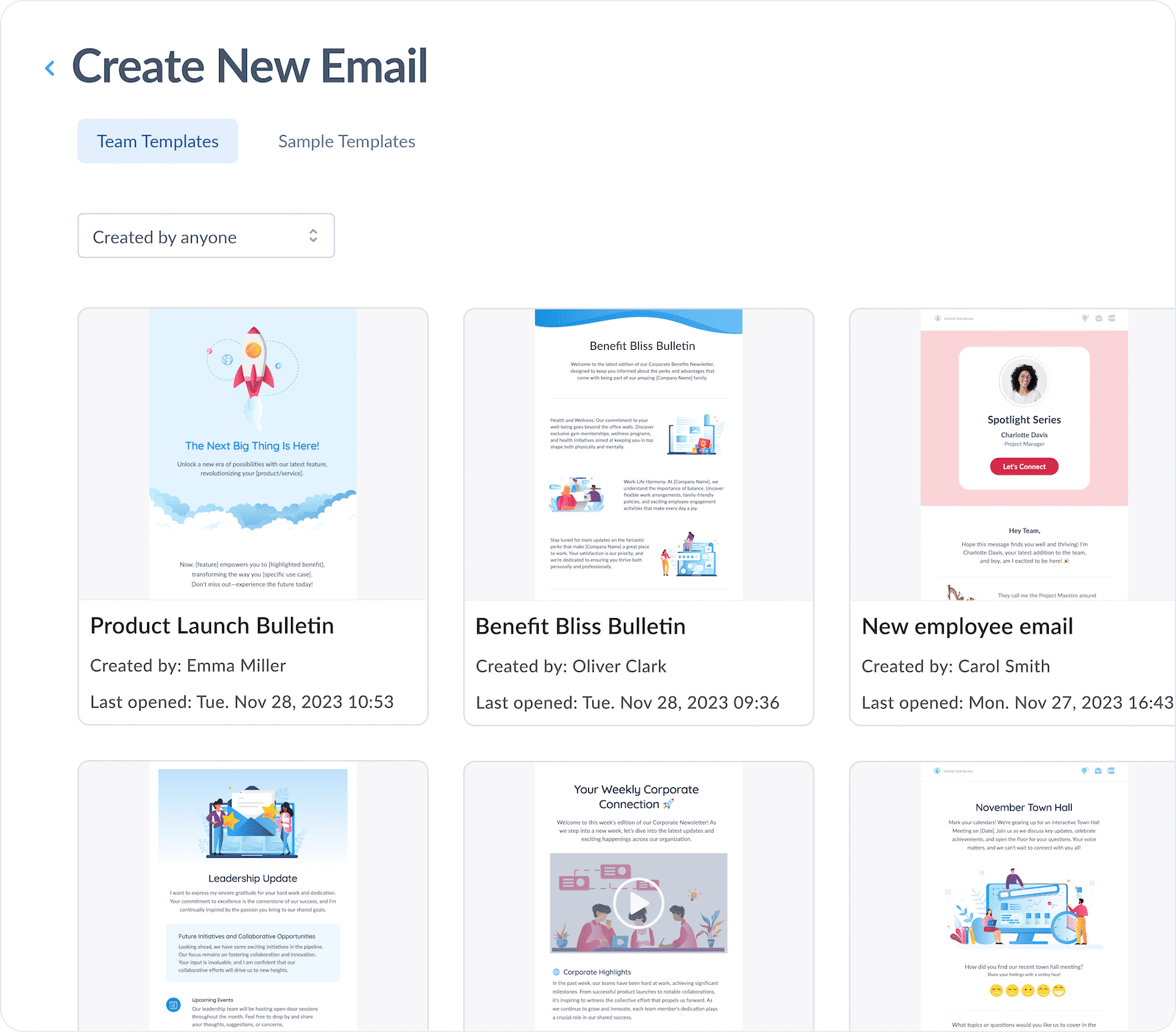
Mark uses the email analytics provided by ContactMonkey to determine the best times to send internal emails . Not only does email analytics help Mark increase engagement on his employee emails, but he now has hard data he can show management to prove the value of his internal communications.
“ContactMonkey has been great in that I can download a report, attach it to an email, and send it to our top leadership and say, ‘Oh, wow. 88% of the organization opened this in the last 24 hours, I think we should do more of this.’ It’s that little extra credibility.”
See ContactMonkey in action
3. alnylam drives remote employee engagement using contactmonkey.
Employee engagement is crucial for ongoing productivity and growth, and Alnylam’s Brendon Pires wanted to leverage their internal communications to increase engagement.
Brendon is an internal communications specialist at Alnylam —the world’s leading RNAi therapeutics company—and is tasked with keeping their 2000+ employees engaged and informed. But Brendon’s existing internal communications process was leading to issues all over the place.
Like many companies, Alnylam shifted to remote work when the COVID-19 pandemic hit. Brendon knew that employees would be relying on his emails to stay up-to-date on the latest company news and announcements, but their existing internal communications tool wasn’t up to the task:
- Scheduled emails were prevented from being sent out.
- Email design was a chore with a difficult-to-use email builder.
- Intranet traffic was down and Brendon’s emails weren’t driving traffic to it.
- Email tracking was limited as many internal emails were being flagged by their tracking software’s firewall.
“We were having consistent issues and it had been going on for like a couple of months. It was one issue after the other, between emails not sending because they were getting caught in our firewall, and then tracking not being consistent. So at the end of the day it was kind of like that’s really important, you know? Obviously if I can’t send that email that’s a problem. So that’s what really drove us to look at other solutions like ContactMonkey”
Brendon and Alnylam use Outlook for their employee emails, so he began looking for alternatives to his current software. That’s when Brendon found ContactMonkey.
Right away Brendon had a much easier time creating internal emails using our email template builder. He can create stellar internal emails and email templates that drive more engagement.
Brendon also uses ContactMonkey’s embedded star ratings to let Alnylam employees rate the emails they’re receiving. This helps Brendon and his team zero-in on their most engaging email content. He also uses our email analytics to measure engagement via open rate and click-through rate. He maximizes his results on these metrics by using ContactMonkey’s scheduled email sending:
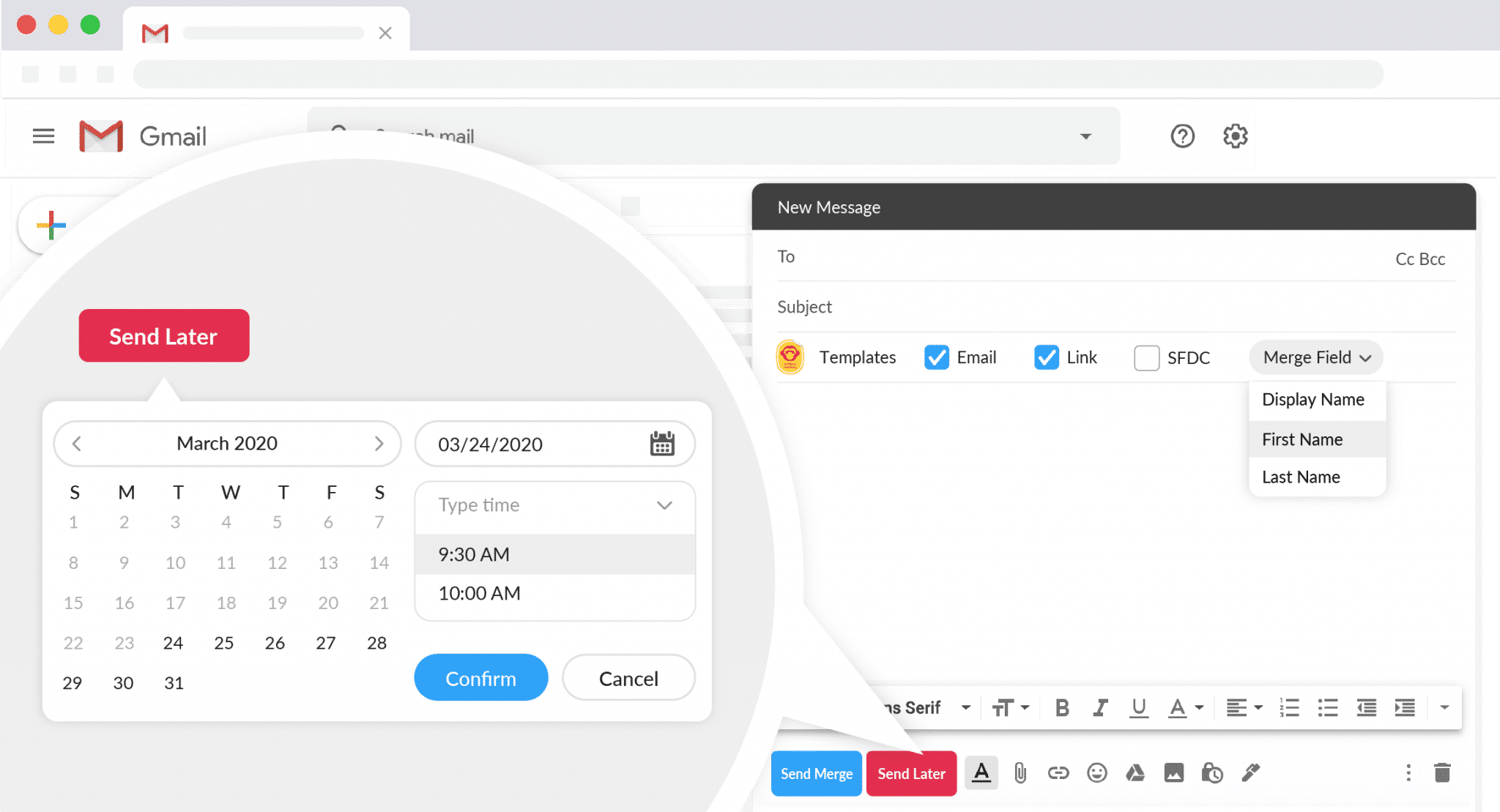
Using ContactMonkey, Brendon was able to increase email engagement and drive traffic to Alnylam’s internal intranet . He now sends emails without worry of encountering sending errors that can hinder engagement—like Outlook not rendering HTML emails .
“ContactMonkey is really easy to use and allows me to create really nice content. There’s enough customization so we can do what we really want and have some creative freedom.”
4. Travel Counsellors Ltd. Stays Connected with Remote Employees Using ContactMonkey
In an economy deeply impacted by COVID-19, countless companies had to adapt to new challenges. As Community Manager at Travel Counsellors , Dave Purcell experienced firsthand the effects on morale and engagement his over 1,900 partners experienced as result of the quarantine and resulting societal changes.
Dave wanted to regularly check-in on Travel Counsellors franchisees’ wellbeing, and measure their engagement over time. But Dave’s current method of checking-in on an audience of over 1,900 was not up to the task.
Using their existing email software, Dave encountered all sorts of problems when trying to gauge wellness and drive email engagement. He and his team were unable to create personalized internal communications , as they were told it just wasn’t possible with their existing “solution”. They also experienced numerous tracking issues, as they were receiving tracking numbers that didn’t make any sense.
“The stats we had previously were unusable and that’s the easiest way I can put it. I was getting 200% open rates, which was just impossible.”
Realizing that email tracking and personalization were must-have features for him and his team, Dave sought a new email software that could deliver what he was looking for.
With the aim of sending personalized emails and tracking wellness in his organization, Dave was immediately impressed by ContactMonkey. “I stumbled across ContactMonkey, and everything just screamed: ‘This is the right platform for us’. It’s pretty fantastic.”
Dave uses ContactMonkey’s merge tags to create personalized subject lines and body copy based on the recipient:
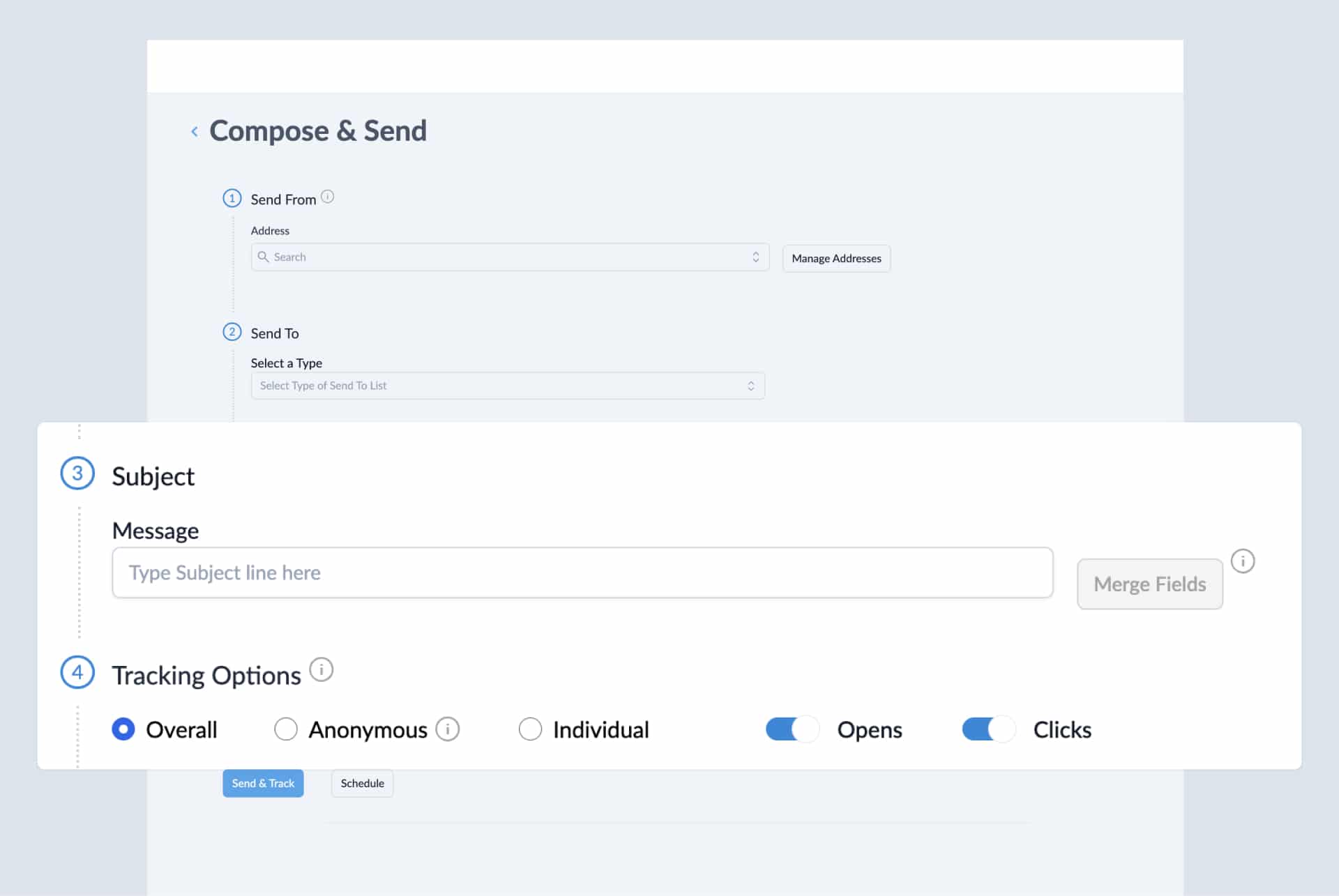
He also began using emoji reactions on his weekly employee newsletters , using them as a pulse check survey for his audience.
“Mindset and wellbeing have always been a big part of what we do. It’s even more so now. Our franchisees craved that personal interaction. ‘Welcome to a Brand New Week’ checks in with them on a Monday, sees how they’re feeling with emoji reactions. And we do the same on a Friday.”
In addition to customization and surveys, Dave uses our email template builder’s custom employer branding options to save time on creating his email newsletters. All of this is driven by email analytics that help Dave and his team determine which content is generating the greatest engagement.
“Our commercial team is looking at what people are engaging with in terms of link clicks and what they’re not engaging with and changing our tactic depending on that. We also send an update from our CEO and we can now track this more accurately. We’re getting a 90% open rate within two days.”
5. Exemplis Boosts Internal Communications Engagement with ContactMonkey
When Corey Kachigan arrived at Exemplis as Engagement and Communications Lead, she knew she had her work cut out for her. Exemplis—the largest volume manufacturer of office seating in North America—was experiencing rapid growth but did not have any sort of internal communications strategy . Corey knew if she wanted to properly manage Exemplis’ ongoing growth, she’d need to make internal communications an indispensable part of the business.
Before Corey arrived, Exemplis’ existing internal communications consisted only of random announcements and update emails. They had no defined approach for sending internal communications, which lead to emails that can cause employees to tune out.
“Our receptionist would email: ‘Hey, whoever left their coffee mug in the sink, please clean it and take it back to your desk.’ And it’s like, okay, that just went to 200 people.”
Corey and her team knew they had to harness their email resources better, and wanted a way to measure what employees actually wanted to see.
“We need some metrics to gauge whether this is working or not. We’re rolling out all these things, but we can’t tell if employees are even clicking these emails. Our team is inundated with hundreds of emails a day. How do we know they are reading these and how do we know they find it valuable? We have no idea.”
They also wanted to use emails to align their ever-growing employee base with Exemplis’ core values and vision. Using Mailchimp—an external marketing email tool—resulted in more problems than solutions. Corey experienced issues with importing and tracking emails within Outlook. She realized that Mailchimp is not for internal communications , and set out to find a new solution to power her employee emails.
So Corey began searching for a new email software for internal communications. Creating a definite approach to internal communications was just one priority of hers; she also wanted to prove the value of internal communications to management using hard data.
What first stood out to Corey about ContactMonkey was the crisp layout and that it worked with Exemplis’ existing Outlook system. ContactMonkey uses your company’s existing email services, and this meant Corey would no longer encounter internal email problems caused by an external tool like Mailchimp.
Corey now uses email metrics and employee feedback to inform her internal communications approach. She features pulse surveys on her internal emails, and uses the results in combination with email metrics to pinpoint what Exemplis employees want to see.
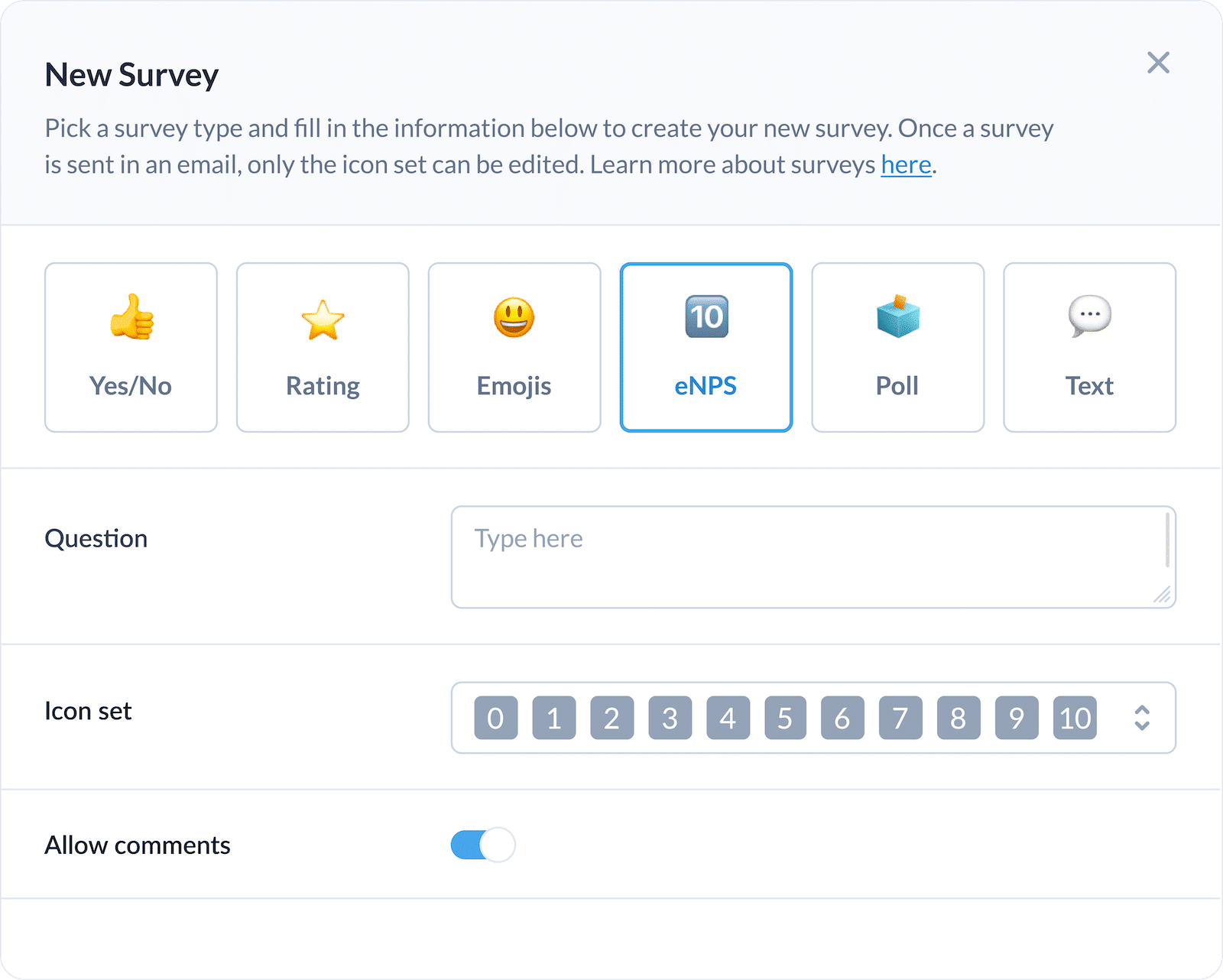
With ContactMonkey’s email analytics, Corey can point to real engagement data to back up her internal communications objectives.
“The thing I love about ContactMonkey is that it allows us to communicate more consistently with our team, but also be able to have the data to back it up. When we used to send out newsletters, we didn’t really have a way to see who did or didn’t open it, who clicked what and they couldn’t interact with the communication besides reply to me, which was super cumbersome.”
Pulse surveys that actually engage employees
Turn emails into conversations., achieve your internal communications goals with contactmonkey.
Although internal communications is a common aspect of all businesses, everyone approaches it differently. Finding out the best email practices that work for your employees is a crucial step in the quest for increased engagement.
Read even one internal communication case study and you’ll see how ContactMonkey stands out among other internal communications tools. You can create, send, and track internal emails, and collect employee feedback and email metrics to develop innovative internal communication tactics .
Whether you’re a seasoned internal communicator or new to the field, ContactMonkey can turn your internal communications into a powerful driver of productivity and growth at your organization.
Unmissable employee comms
Always get your message across with contactmonkey..
Want to see ContactMonkey in action? Book a free demo to see how our internal communications software can transform your employee emails:
Related articles

5 Best Crisis Communication Case Studies and Examples

Top Internal Communications Trends for 2024
10 Best Internal Collaboration Tools to Unlock Your Team’s Productivity
- Design for Business
- Most Recent
- Presentations
- Infographics
- Data Visualizations
- Forms and Surveys
- Video & Animation
- Case Studies
- Digital Marketing
- Design Inspiration
- Visual Thinking
- Product Updates
- Visme Webinars
- Artificial Intelligence
15 Real-Life Case Study Examples & Best Practices

Written by: Oghale Olori

Case studies are more than just success stories.
They are powerful tools that demonstrate the practical value of your product or service. Case studies help attract attention to your products, build trust with potential customers and ultimately drive sales.
It’s no wonder that 73% of successful content marketers utilize case studies as part of their content strategy. Plus, buyers spend 54% of their time reviewing case studies before they make a buying decision.
To ensure you’re making the most of your case studies, we’ve put together 15 real-life case study examples to inspire you. These examples span a variety of industries and formats. We’ve also included best practices, design tips and templates to inspire you.
Let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
What is a case study, 15 real-life case study examples, sales case study examples, saas case study examples, product case study examples, marketing case study examples, business case study examples, case study faqs.
- A case study is a compelling narrative that showcases how your product or service has positively impacted a real business or individual.
- Case studies delve into your customer's challenges, how your solution addressed them and the quantifiable results they achieved.
- Your case study should have an attention-grabbing headline, great visuals and a relevant call to action. Other key elements include an introduction, problems and result section.
- Visme provides easy-to-use tools, professionally designed templates and features for creating attractive and engaging case studies.
A case study is a real-life scenario where your company helped a person or business solve their unique challenges. It provides a detailed analysis of the positive outcomes achieved as a result of implementing your solution.
Case studies are an effective way to showcase the value of your product or service to potential customers without overt selling. By sharing how your company transformed a business, you can attract customers seeking similar solutions and results.
Case studies are not only about your company's capabilities; they are primarily about the benefits customers and clients have experienced from using your product.
Every great case study is made up of key elements. They are;
- Attention-grabbing headline: Write a compelling headline that grabs attention and tells your reader what the case study is about. For example, "How a CRM System Helped a B2B Company Increase Revenue by 225%.
- Introduction/Executive Summary: Include a brief overview of your case study, including your customer’s problem, the solution they implemented and the results they achieved.
- Problem/Challenge: Case studies with solutions offer a powerful way to connect with potential customers. In this section, explain how your product or service specifically addressed your customer's challenges.
- Solution: Explain how your product or service specifically addressed your customer's challenges.
- Results/Achievements : Give a detailed account of the positive impact of your product. Quantify the benefits achieved using metrics such as increased sales, improved efficiency, reduced costs or enhanced customer satisfaction.
- Graphics/Visuals: Include professional designs, high-quality photos and videos to make your case study more engaging and visually appealing.
- Quotes/Testimonials: Incorporate written or video quotes from your clients to boost your credibility.
- Relevant CTA: Insert a call to action (CTA) that encourages the reader to take action. For example, visiting your website or contacting you for more information. Your CTA can be a link to a landing page, a contact form or your social media handle and should be related to the product or service you highlighted in your case study.

Now that you understand what a case study is, let’s look at real-life case study examples. Among these, you'll find some simple case study examples that break down complex ideas into easily understandable solutions.
In this section, we’ll explore SaaS, marketing, sales, product and business case study examples with solutions. Take note of how these companies structured their case studies and included the key elements.
We’ve also included professionally designed case study templates to inspire you.
1. Georgia Tech Athletics Increase Season Ticket Sales by 80%

Georgia Tech Athletics, with its 8,000 football season ticket holders, sought for a way to increase efficiency and customer engagement.
Their initial sales process involved making multiple outbound phone calls per day with no real targeting or guidelines. Georgia Tech believed that targeting communications will enable them to reach more people in real time.
Salesloft improved Georgia Tech’s sales process with an inbound structure. This enabled sales reps to connect with their customers on a more targeted level. The use of dynamic fields and filters when importing lists ensured prospects received the right information, while communication with existing fans became faster with automation.
As a result, Georgia Tech Athletics recorded an 80% increase in season ticket sales as relationships with season ticket holders significantly improved. Employee engagement increased as employees became more energized to connect and communicate with fans.
Why Does This Case Study Work?
In this case study example , Salesloft utilized the key elements of a good case study. Their introduction gave an overview of their customers' challenges and the results they enjoyed after using them. After which they categorized the case study into three main sections: challenge, solution and result.
Salesloft utilized a case study video to increase engagement and invoke human connection.
Incorporating videos in your case study has a lot of benefits. Wyzol’s 2023 state of video marketing report showed a direct correlation between videos and an 87% increase in sales.
The beautiful thing is that creating videos for your case study doesn’t have to be daunting.
With an easy-to-use platform like Visme, you can create top-notch testimonial videos that will connect with your audience. Within the Visme editor, you can access over 1 million stock photos , video templates, animated graphics and more. These tools and resources will significantly improve the design and engagement of your case study.
Simplify content creation and brand management for your team
- Collaborate on designs , mockups and wireframes with your non-design colleagues
- Lock down your branding to maintain brand consistency throughout your designs
- Why start from scratch? Save time with 1000s of professional branded templates
Sign up. It’s free.

2. WeightWatchers Completely Revamped their Enterprise Sales Process with HubSpot

WeightWatchers, a 60-year-old wellness company, sought a CRM solution that increased the efficiency of their sales process. With their previous system, Weightwatchers had limited automation. They would copy-paste message templates from word documents or recreate one email for a batch of customers.
This required a huge effort from sales reps, account managers and leadership, as they were unable to track leads or pull customized reports for planning and growth.
WeightWatchers transformed their B2B sales strategy by leveraging HubSpot's robust marketing and sales workflows. They utilized HubSpot’s deal pipeline and automation features to streamline lead qualification. And the customized dashboard gave leadership valuable insights.
As a result, WeightWatchers generated seven figures in annual contract value and boosted recurring revenue. Hubspot’s impact resulted in 100% adoption across all sales, marketing, client success and operations teams.
Hubspot structured its case study into separate sections, demonstrating the specific benefits of their products to various aspects of the customer's business. Additionally, they integrated direct customer quotes in each section to boost credibility, resulting in a more compelling case study.
Getting insight from your customer about their challenges is one thing. But writing about their process and achievements in a concise and relatable way is another. If you find yourself constantly experiencing writer’s block, Visme’s AI writer is perfect for you.
Visme created this AI text generator tool to take your ideas and transform them into a great draft. So whether you need help writing your first draft or editing your final case study, Visme is ready for you.
3. Immi’s Ram Fam Helps to Drive Over $200k in Sales

Immi embarked on a mission to recreate healthier ramen recipes that were nutritious and delicious. After 2 years of tireless trials, Immi finally found the perfect ramen recipe. However, they envisioned a community of passionate ramen enthusiasts to fuel their business growth.
This vision propelled them to partner with Shopify Collabs. Shopify Collabs successfully cultivated and managed Immi’s Ramen community of ambassadors and creators.
As a result of their partnership, Immi’s community grew to more than 400 dedicated members, generating over $200,000 in total affiliate sales.
The power of data-driven headlines cannot be overemphasized. Chili Piper strategically incorporates quantifiable results in their headlines. This instantly sparks curiosity and interest in readers.
While not every customer success story may boast headline-grabbing figures, quantifying achievements in percentages is still effective. For example, you can highlight a 50% revenue increase with the implementation of your product.
Take a look at the beautiful case study template below. Just like in the example above, the figures in the headline instantly grab attention and entice your reader to click through.
Having a case study document is a key factor in boosting engagement. This makes it easy to promote your case study in multiple ways. With Visme, you can easily publish, download and share your case study with your customers in a variety of formats, including PDF, PPTX, JPG and more!

4. How WOW! is Saving Nearly 79% in Time and Cost With Visme
This case study discusses how Visme helped WOW! save time and money by providing user-friendly tools to create interactive and quality training materials for their employees. Find out what your team can do with Visme. Request a Demo
WOW!'s learning and development team creates high-quality training materials for new and existing employees. Previous tools and platforms they used had plain templates, little to no interactivity features, and limited flexibility—that is, until they discovered Visme.
Now, the learning and development team at WOW! use Visme to create engaging infographics, training videos, slide decks and other training materials.
This has directly reduced the company's turnover rate, saving them money spent on recruiting and training new employees. It has also saved them a significant amount of time, which they can now allocate to other important tasks.
Visme's customer testimonials spark an emotional connection with the reader, leaving a profound impact. Upon reading this case study, prospective customers will be blown away by the remarkable efficiency achieved by Visme's clients after switching from PowerPoint.
Visme’s interactivity feature was a game changer for WOW! and one of the primary reasons they chose Visme.
“Previously we were using PowerPoint, which is fine, but the interactivity you can get with Visme is so much more robust that we’ve all steered away from PowerPoint.” - Kendra, L&D team, Wow!
Visme’s interactive feature allowed them to animate their infographics, include clickable links on their PowerPoint designs and even embed polls and quizzes their employees could interact with.
By embedding the slide decks, infographics and other training materials WOW! created with Visme, potential customers get a taste of what they can create with the tool. This is much more effective than describing the features of Visme because it allows potential customers to see the tool in action.
To top it all off, this case study utilized relevant data and figures. For example, one part of the case study said, “In Visme, where Kendra’s team has access to hundreds of templates, a brand kit, and millions of design assets at their disposal, their team can create presentations in 80% less time.”
Who wouldn't want that?
Including relevant figures and graphics in your case study is a sure way to convince your potential customers why you’re a great fit for their brand. The case study template below is a great example of integrating relevant figures and data.
This colorful template begins with a captivating headline. But that is not the best part; this template extensively showcases the results their customer had using relevant figures.
The arrangement of the results makes it fun and attractive. Instead of just putting figures in a plain table, you can find interesting shapes in your Visme editor to take your case study to the next level.
5. Lyte Reduces Customer Churn To Just 3% With Hubspot CRM

While Lyte was redefining the ticketing industry, it had no definite CRM system . Lyte utilized 12–15 different SaaS solutions across various departments, which led to a lack of alignment between teams, duplication of work and overlapping tasks.
Customer data was spread across these platforms, making it difficult to effectively track their customer journey. As a result, their churn rate increased along with customer dissatisfaction.
Through Fuelius , Lyte founded and implemented Hubspot CRM. Lyte's productivity skyrocketed after incorporating Hubspot's all-in-one CRM tool. With improved efficiency, better teamwork and stronger client relationships, sales figures soared.
The case study title page and executive summary act as compelling entry points for both existing and potential customers. This overview provides a clear understanding of the case study and also strategically incorporates key details like the client's industry, location and relevant background information.
Having a good summary of your case study can prompt your readers to engage further. You can achieve this with a simple but effective case study one-pager that highlights your customer’s problems, process and achievements, just like this case study did in the beginning.
Moreover, you can easily distribute your case study one-pager and use it as a lead magnet to draw prospective customers to your company.
Take a look at this case study one-pager template below.

This template includes key aspects of your case study, such as the introduction, key findings, conclusion and more, without overcrowding the page. The use of multiple shades of blue gives it a clean and dynamic layout.
Our favorite part of this template is where the age group is visualized.
With Visme’s data visualization tool , you can present your data in tables, graphs, progress bars, maps and so much more. All you need to do is choose your preferred data visualization widget, input or import your data and click enter!
6. How Workato Converts 75% of Their Qualified Leads

Workato wanted to improve their inbound leads and increase their conversion rate, which ranged from 40-55%.
At first, Workato searched for a simple scheduling tool. They soon discovered that they needed a tool that provided advanced routing capabilities based on zip code and other criteria. Luckily, they found and implemented Chili Piper.
As a result of implementing Chili Piper, Workato achieved a remarkable 75–80% conversion rate and improved show rates. This led to a substantial revenue boost, with a 10-15% increase in revenue attributed to Chili Piper's impact on lead conversion.
This case study example utilizes the power of video testimonials to drive the impact of their product.
Chili Piper incorporates screenshots and clips of their tool in use. This is a great strategy because it helps your viewers become familiar with how your product works, making onboarding new customers much easier.
In this case study example, we see the importance of efficient Workflow Management Systems (WMS). Without a WMS, you manually assign tasks to your team members and engage in multiple emails for regular updates on progress.
However, when crafting and designing your case study, you should prioritize having a good WMS.
Visme has an outstanding Workflow Management System feature that keeps you on top of all your projects and designs. This feature makes it much easier to assign roles, ensure accuracy across documents, and track progress and deadlines.
Visme’s WMS feature allows you to limit access to your entire document by assigning specific slides or pages to individual members of your team. At the end of the day, your team members are not overwhelmed or distracted by the whole document but can focus on their tasks.
7. Rush Order Helps Vogmask Scale-Up During a Pandemic

Vomask's reliance on third-party fulfillment companies became a challenge as demand for their masks grew. Seeking a reliable fulfillment partner, they found Rush Order and entrusted them with their entire inventory.
Vomask's partnership with Rush Order proved to be a lifesaver during the COVID-19 pandemic. Rush Order's agility, efficiency and commitment to customer satisfaction helped Vogmask navigate the unprecedented demand and maintain its reputation for quality and service.
Rush Order’s comprehensive support enabled Vogmask to scale up its order processing by a staggering 900% while maintaining a remarkable customer satisfaction rate of 92%.
Rush Order chose one event where their impact mattered the most to their customer and shared that story.
While pandemics don't happen every day, you can look through your customer’s journey and highlight a specific time or scenario where your product or service saved their business.
The story of Vogmask and Rush Order is compelling, but it simply is not enough. The case study format and design attract readers' attention and make them want to know more. Rush Order uses consistent colors throughout the case study, starting with the logo, bold square blocks, pictures, and even headers.
Take a look at this product case study template below.
Just like our example, this case study template utilizes bold colors and large squares to attract and maintain the reader’s attention. It provides enough room for you to write about your customers' backgrounds/introductions, challenges, goals and results.
The right combination of shapes and colors adds a level of professionalism to this case study template.

8. AMR Hair & Beauty leverages B2B functionality to boost sales by 200%

With limits on website customization, slow page loading and multiple website crashes during peak events, it wasn't long before AMR Hair & Beauty began looking for a new e-commerce solution.
Their existing platform lacked effective search and filtering options, a seamless checkout process and the data analytics capabilities needed for informed decision-making. This led to a significant number of abandoned carts.
Upon switching to Shopify Plus, AMR immediately saw improvements in page loading speed and average session duration. They added better search and filtering options for their wholesale customers and customized their checkout process.
Due to this, AMR witnessed a 200% increase in sales and a 77% rise in B2B average order value. AMR Hair & Beauty is now poised for further expansion and growth.
This case study example showcases the power of a concise and impactful narrative.
To make their case analysis more effective, Shopify focused on the most relevant aspects of the customer's journey. While there may have been other challenges the customer faced, they only included those that directly related to their solutions.
Take a look at this case study template below. It is perfect if you want to create a concise but effective case study. Without including unnecessary details, you can outline the challenges, solutions and results your customers experienced from using your product.
Don’t forget to include a strong CTA within your case study. By incorporating a link, sidebar pop-up or an exit pop-up into your case study, you can prompt your readers and prospective clients to connect with you.

9. How a Marketing Agency Uses Visme to Create Engaging Content With Infographics

SmartBox Dental , a marketing agency specializing in dental practices, sought ways to make dental advice more interesting and easier to read. However, they lacked the design skills to do so effectively.
Visme's wide range of templates and features made it easy for the team to create high-quality content quickly and efficiently. SmartBox Dental enjoyed creating infographics in as little as 10-15 minutes, compared to one hour before Visme was implemented.
By leveraging Visme, SmartBox Dental successfully transformed dental content into a more enjoyable and informative experience for their clients' patients. Therefore enhancing its reputation as a marketing partner that goes the extra mile to deliver value to its clients.
Visme creatively incorporates testimonials In this case study example.
By showcasing infographics and designs created by their clients, they leverage the power of social proof in a visually compelling way. This way, potential customers gain immediate insight into the creative possibilities Visme offers as a design tool.
This example effectively showcases a product's versatility and impact, and we can learn a lot about writing a case study from it. Instead of focusing on one tool or feature per customer, Visme took a more comprehensive approach.
Within each section of their case study, Visme explained how a particular tool or feature played a key role in solving the customer's challenges.
For example, this case study highlighted Visme’s collaboration tool . With Visme’s tool, the SmartBox Dental content team fostered teamwork, accountability and effective supervision.
Visme also achieved a versatile case study by including relevant quotes to showcase each tool or feature. Take a look at some examples;
Visme’s collaboration tool: “We really like the collaboration tool. Being able to see what a co-worker is working on and borrow their ideas or collaborate on a project to make sure we get the best end result really helps us out.”
Visme’s library of stock photos and animated characters: “I really love the images and the look those give to an infographic. I also really like the animated little guys and the animated pictures. That’s added a lot of fun to our designs.”
Visme’s interactivity feature: “You can add URLs and phone number links directly into the infographic so they can just click and call or go to another page on the website and I really like adding those hyperlinks in.”
You can ask your customers to talk about the different products or features that helped them achieve their business success and draw quotes from each one.
10. Jasper Grows Blog Organic Sessions 810% and Blog-Attributed User Signups 400X
Jasper, an AI writing tool, lacked a scalable content strategy to drive organic traffic and user growth. They needed help creating content that converted visitors into users. Especially when a looming domain migration threatened organic traffic.
To address these challenges, Jasper partnered with Omniscient Digital. Their goal was to turn their content into a growth channel and drive organic growth. Omniscient Digital developed a full content strategy for Jasper AI, which included a content audit, competitive analysis, and keyword discovery.
Through their collaboration, Jasper’s organic blog sessions increased by 810%, despite the domain migration. They also witnessed a 400X increase in blog-attributed signups. And more importantly, the content program contributed to over $4 million in annual recurring revenue.
The combination of storytelling and video testimonials within the case study example makes this a real winner. But there’s a twist to it. Omniscient segmented the video testimonials and placed them in different sections of the case study.
Video marketing , especially in case studies, works wonders. Research shows us that 42% of people prefer video testimonials because they show real customers with real success stories. So if you haven't thought of it before, incorporate video testimonials into your case study.
Take a look at this stunning video testimonial template. With its simple design, you can input the picture, name and quote of your customer within your case study in a fun and engaging way.
Try it yourself! Customize this template with your customer’s testimonial and add it to your case study!

11. How Meliá Became One of the Most Influential Hotel Chains on Social Media

Meliá Hotels needed help managing their growing social media customer service needs. Despite having over 500 social accounts, they lacked a unified response protocol and detailed reporting. This largely hindered efficiency and brand consistency.
Meliá partnered with Hootsuite to build an in-house social customer care team. Implementing Hootsuite's tools enabled Meliá to decrease response times from 24 hours to 12.4 hours while also leveraging smart automation.
In addition to that, Meliá resolved over 133,000 conversations, booking 330 inquiries per week through Hootsuite Inbox. They significantly improved brand consistency, response time and customer satisfaction.
The need for a good case study design cannot be over-emphasized.
As soon as anyone lands on this case study example, they are mesmerized by a beautiful case study design. This alone raises the interest of readers and keeps them engaged till the end.
If you’re currently saying to yourself, “ I can write great case studies, but I don’t have the time or skill to turn it into a beautiful document.” Say no more.
Visme’s amazing AI document generator can take your text and transform it into a stunning and professional document in minutes! Not only do you save time, but you also get inspired by the design.
With Visme’s document generator, you can create PDFs, case study presentations , infographics and more!
Take a look at this case study template below. Just like our case study example, it captures readers' attention with its beautiful design. Its dynamic blend of colors and fonts helps to segment each element of the case study beautifully.

12. Tea’s Me Cafe: Tamika Catchings is Brewing Glory

Tamika's journey began when she purchased Tea's Me Cafe in 2017, saving it from closure. She recognized the potential of the cafe as a community hub and hosted regular events centered on social issues and youth empowerment.
One of Tamika’s business goals was to automate her business. She sought to streamline business processes across various aspects of her business. One of the ways she achieves this goal is through Constant Contact.
Constant Contact became an integral part of Tamika's marketing strategy. They provided an automated and centralized platform for managing email newsletters, event registrations, social media scheduling and more.
This allowed Tamika and her team to collaborate efficiently and focus on engaging with their audience. They effectively utilized features like WooCommerce integration, text-to-join and the survey builder to grow their email list, segment their audience and gather valuable feedback.
The case study example utilizes the power of storytelling to form a connection with readers. Constant Contact takes a humble approach in this case study. They spotlight their customers' efforts as the reason for their achievements and growth, establishing trust and credibility.
This case study is also visually appealing, filled with high-quality photos of their customer. While this is a great way to foster originality, it can prove challenging if your customer sends you blurry or low-quality photos.
If you find yourself in that dilemma, you can use Visme’s AI image edit tool to touch up your photos. With Visme’s AI tool, you can remove unwanted backgrounds, erase unwanted objects, unblur low-quality pictures and upscale any photo without losing the quality.
Constant Contact offers its readers various formats to engage with their case study. Including an audio podcast and PDF.
In its PDF version, Constant Contact utilized its brand colors to create a stunning case study design. With this, they increase brand awareness and, in turn, brand recognition with anyone who comes across their case study.
With Visme’s brand wizard tool , you can seamlessly incorporate your brand assets into any design or document you create. By inputting your URL, Visme’s AI integration will take note of your brand colors, brand fonts and more and create branded templates for you automatically.
You don't need to worry about spending hours customizing templates to fit your brand anymore. You can focus on writing amazing case studies that promote your company.
13. How Breakwater Kitchens Achieved a 7% Growth in Sales With Thryv

Breakwater Kitchens struggled with managing their business operations efficiently. They spent a lot of time on manual tasks, such as scheduling appointments and managing client communication. This made it difficult for them to grow their business and provide the best possible service to their customers.
David, the owner, discovered Thryv. With Thryv, Breakwater Kitchens was able to automate many of their manual tasks. Additionally, Thryv integrated social media management. This enabled Breakwater Kitchens to deliver a consistent brand message, captivate its audience and foster online growth.
As a result, Breakwater Kitchens achieved increased efficiency, reduced missed appointments and a 7% growth in sales.
This case study example uses a concise format and strong verbs, which make it easy for readers to absorb the information.
At the top of the case study, Thryv immediately builds trust by presenting their customer's complete profile, including their name, company details and website. This allows potential customers to verify the case study's legitimacy, making them more likely to believe in Thryv's services.
However, manually copying and pasting customer information across multiple pages of your case study can be time-consuming.
To save time and effort, you can utilize Visme's dynamic field feature . Dynamic fields automatically insert reusable information into your designs. So you don’t have to type it out multiple times.
14. Zoom’s Creative Team Saves Over 4,000 Hours With Brandfolder

Zoom experienced rapid growth with the advent of remote work and the rise of the COVID-19 pandemic. Such growth called for agility and resilience to scale through.
At the time, Zoom’s assets were disorganized which made retrieving brand information a burden. Zoom’s creative manager spent no less than 10 hours per week finding and retrieving brand assets for internal teams.
Zoom needed a more sustainable approach to organizing and retrieving brand information and came across Brandfolder. Brandfolder simplified and accelerated Zoom’s email localization and webpage development. It also enhanced the creation and storage of Zoom virtual backgrounds.
With Brandfolder, Zoom now saves 4,000+ hours every year. The company also centralized its assets in Brandfolder, which allowed 6,800+ employees and 20-30 vendors to quickly access them.
Brandfolder infused its case study with compelling data and backed it up with verifiable sources. This data-driven approach boosts credibility and increases the impact of their story.
Bradfolder's case study goes the extra mile by providing a downloadable PDF version, making it convenient for readers to access the information on their own time. Their dedication to crafting stunning visuals is evident in every aspect of the project.
From the vibrant colors to the seamless navigation, everything has been meticulously designed to leave a lasting impression on the viewer. And with clickable links that make exploring the content a breeze, the user experience is guaranteed to be nothing short of exceptional.
The thing is, your case study presentation won’t always sit on your website. There are instances where you may need to do a case study presentation for clients, partners or potential investors.
Visme has a rich library of templates you can tap into. But if you’re racing against the clock, Visme’s AI presentation maker is your best ally.

15. How Cents of Style Made $1.7M+ in Affiliate Sales with LeadDyno

Cents of Style had a successful affiliate and influencer marketing strategy. However, their existing affiliate marketing platform was not intuitive, customizable or transparent enough to meet the needs of their influencers.
Cents of Styles needed an easy-to-use affiliate marketing platform that gave them more freedom to customize their program and implement a multi-tier commission program.
After exploring their options, Cents of Style decided on LeadDyno.
LeadDyno provided more flexibility, allowing them to customize commission rates and implement their multi-tier commission structure, switching from monthly to weekly payouts.
Also, integrations with PayPal made payments smoother And features like newsletters and leaderboards added to the platform's success by keeping things transparent and engaging.
As a result, Cents of Style witnessed an impressive $1.7 million in revenue from affiliate sales with a substantial increase in web sales by 80%.
LeadDyno strategically placed a compelling CTA in the middle of their case study layout, maximizing its impact. At this point, readers are already invested in the customer's story and may be considering implementing similar strategies.
A well-placed CTA offers them a direct path to learn more and take action.
LeadDyno also utilized the power of quotes to strengthen their case study. They didn't just embed these quotes seamlessly into the text; instead, they emphasized each one with distinct blocks.
Are you looking for an easier and quicker solution to create a case study and other business documents? Try Visme's AI designer ! This powerful tool allows you to generate complete documents, such as case studies, reports, whitepapers and more, just by providing text prompts. Simply explain your requirements to the tool, and it will produce the document for you, complete with text, images, design assets and more.
Still have more questions about case studies? Let's look at some frequently asked questions.
How to Write a Case Study?
- Choose a compelling story: Not all case studies are created equal. Pick one that is relevant to your target audience and demonstrates the specific benefits of your product or service.
- Outline your case study: Create a case study outline and highlight how you will structure your case study to include the introduction, problem, solution and achievements of your customer.
- Choose a case study template: After you outline your case study, choose a case study template . Visme has stunning templates that can inspire your case study design.
- Craft a compelling headline: Include figures or percentages that draw attention to your case study.
- Work on the first draft: Your case study should be easy to read and understand. Use clear and concise language and avoid jargon.
- Include high-quality visual aids: Visuals can help to make your case study more engaging and easier to read. Consider adding high-quality photos, screenshots or videos.
- Include a relevant CTA: Tell prospective customers how to reach you for questions or sign-ups.
What Are the Stages of a Case Study?
The stages of a case study are;
- Planning & Preparation: Highlight your goals for writing the case study. Plan the case study format, length and audience you wish to target.
- Interview the Client: Reach out to the company you want to showcase and ask relevant questions about their journey and achievements.
- Revision & Editing: Review your case study and ask for feedback. Include relevant quotes and CTAs to your case study.
- Publication & Distribution: Publish and share your case study on your website, social media channels and email list!
- Marketing & Repurposing: Turn your case study into a podcast, PDF, case study presentation and more. Share these materials with your sales and marketing team.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of a Case Study?
Advantages of a case study:
- Case studies showcase a specific solution and outcome for specific customer challenges.
- It attracts potential customers with similar challenges.
- It builds trust and credibility with potential customers.
- It provides an in-depth analysis of your company’s problem-solving process.
Disadvantages of a case study:
- Limited applicability. Case studies are tailored to specific cases and may not apply to other businesses.
- It relies heavily on customer cooperation and willingness to share information.
- It stands a risk of becoming outdated as industries and customer needs evolve.
What Are the Types of Case Studies?
There are 7 main types of case studies. They include;
- Illustrative case study.
- Instrumental case study.
- Intrinsic case study.
- Descriptive case study.
- Explanatory case study.
- Exploratory case study.
- Collective case study.
How Long Should a Case Study Be?
The ideal length of your case study is between 500 - 1500 words or 1-3 pages. Certain factors like your target audience, goal or the amount of detail you want to share may influence the length of your case study. This infographic has powerful tips for designing winning case studies
What Is the Difference Between a Case Study and an Example?
Case studies provide a detailed narrative of how your product or service was used to solve a problem. Examples are general illustrations and are not necessarily real-life scenarios.
Case studies are often used for marketing purposes, attracting potential customers and building trust. Examples, on the other hand, are primarily used to simplify or clarify complex concepts.
Where Can I Find Case Study Examples?
You can easily find many case study examples online and in industry publications. Many companies, including Visme, share case studies on their websites to showcase how their products or services have helped clients achieve success. You can also search online libraries and professional organizations for case studies related to your specific industry or field.
If you need professionally-designed, customizable case study templates to create your own, Visme's template library is one of the best places to look. These templates include all the essential sections of a case study and high-quality content to help you create case studies that position your business as an industry leader.
Get More Out Of Your Case Studies With Visme
Case studies are an essential tool for converting potential customers into paying customers. By following the tips in this article, you can create compelling case studies that will help you build trust, establish credibility and drive sales.
Visme can help you create stunning case studies and other relevant marketing materials. With our easy-to-use platform, interactive features and analytics tools , you can increase your content creation game in no time.
There is no limit to what you can achieve with Visme. Connect with Sales to discover how Visme can boost your business goals.
Easily create beautiful case studies and more with Visme

Trusted by leading brands
Recommended content for you:

Create Stunning Content!
Design visual brand experiences for your business whether you are a seasoned designer or a total novice.
About the Author
Internal Communication Case Studies: The Terrible & The Terrific
It’s a question that often comes up: ‘How do other businesses do this?’. Whether you’re implementing a new sales structure or updating your software systems, it’s always helpful to consider how similar companies approached the issue. This is particularly relevant for internal communications , where there is no one-size-fits-all solution. Each organisation has its own unique set of challenges and needs to tailor its internal communication strategy accordingly. Internal communication case studies can help you evaluate your approach, by exploring comparable situations and their outcomes.
In this blog, we’ve selected some of the best internal communication examples from the world of business. Not all were successful. In fact, some were complete disasters. But these failures, along with the success stories, are great examples of internal communication in action. When you’re looking for the answers to effective internal communication , nothing speaks more clearly than real-life examples.
We have grouped the following internal communication case study examples under the ‘seven golden rules’. These rules were proposed by Fitzpatrick in his ground-breaking publication Internal Communications: A Manual for Practitioners. These fundamental rules of internal communication best practices help us to categorise the relative successes and failures of these examples.

Rule 1: Activity means nothing without results
The starting point for every IC has to be: “What do we want people to do?” Being busy and generating a constant stream of campaigns, videos and newsletters is a waste of time if nothing changes as a result. When you’re looking at improving internal communications , always keep track of the outcome as well as the action. This is where the true significance lies.
Case Study 1 - Nationwide Building Society
Background: Nationwide Building Society ran an award-winning five-week BIG Conversation, gathering ideas from all its 18,000 employees in a company-wide collaboration. The aim was directed to reinvigorating Nationwide’s sense of purpose.
Approach: The activity included TalkBack events, online surveys and a huge listening exercise to give staff and members the chance to contribute to its future. By implementing a company-wide internal communications survey , Nationwide opened up a free-flowing conversation with its workforce.
Outcome: The result has been a refreshed strategy and a marketing campaign based on the new concept of ‘building society, nationwide’ – helping people improve the quality of their lives. This business communication case study demonstrates the power of actively listening and acting on employee’s suggestions.
Verdict: Success
Rule 2: Value benefits the business
You will only be adding real value if your employee communication links directly to the business needs of your organisation and helps to achieve a defined strategy or a specific project. The benefits of good internal communication only become apparent when you define your desired outcomes and set actual targets.
Case Study 2 – XPO Transport and Logistics
Background: XPO wanted to leverage great ideas from its colleagues across its 104 UK sites to help its customers improve productivity and reduce costs. Its large, flexible and hard-to-reach workforce (from drivers for Asda to B&Q warehouse contractors) don’t usually have a company phone or laptop. Of all the case studies on communication in the workplace, this large-scale exercise is remarkable in its scope.
Approach: To spark engagement, Talkfreely developed the Ideas Matter App, which every employee was able to download to their personal phone. An internal communications app is the ideal way to connect with remote workers and hard-to-reach employees.
Outcome: Linked directly to business needs, the internal communications platform proved to be exceptional value. The generation of ideas has been significant; 1 in 4 of all ideas submitted are being put into practice. In addition, it showed a remarkable return on investment of 6.5:1 with £156,000 of savings in the first year alone.
Rule 3: In the thick of it
When you’re looking for new ideas, trying to work out what your employees are really thinking or wondering why a previous internal communications plan went wrong, don't sit pondering at your desk or researching online. Leave your office and start talking. Once you talk and listen to your employees, you will begin to understand what motivates them, what concerns them and how they feel about the company. Of all the internal communication ideas , this one is key if you want to keep track of engagement levels.
Case Study 3 – AOL
Background: AOL announced it was slashing its Patch local news network by a third. This was a large-scale change affecting many employees across the company and required careful handling in its communication.
Approach: CEO Tim Armstrong set up a conference call with 1,000 employees with the aim of boosting morale across the workforce. As Armstrong talked, Patch Creative Director Abel Lenz began taking pictures of him. He was immediately sacked, in front of the 1,000 staff on the conference call.
Outcome: Perhaps Armstrong did not know that Lenz’s job included photographing meetings with key leaders for the Patch intranet, for the benefit of remote workers. But he should have. If he had been in touch with his workforce, he would have been fully aware of the roles of individual employees. This employee communication case study gives a clear indication of the importance of understanding your employee’s job roles.
Verdict: Failure
Rule 4: Shut up and listen
Communicating with employees should be a two-way street. The megaphone approach is never going to work best because people only feel connected and motivated if they are part of a conversation. It’s vital to put internal communication channels in place that allow employees to comment on the messages coming down from the top. Listen to what they have to say … and learn.
Case Study 4 – PayPal
Background: The digital payment company needed to address an internal report that revealed not all their employees were not using the PayPal app. The President, David Marcus, wrote a company-wide memo to all staff regarding the problem.
Approach: David Marcus took a heavy-handed approach to the matter. He told his staff to use the product or quit: “If you are one of the folks who refused to install the PayPal app or if you can’t remember your PayPal password, do yourself a favor, go find something that will connect with your heart and mind elsewhere”.
A better policy would have been to find out why his employees weren’t using the payment app, whether they felt competitor products had better features and ask for their suggestions.
Outcome: The memo was leaked to the press. It generated widespread coverage across the media and left customers wondering what was wrong with an app that PayPal’s own staff wouldn't use. Internal communications best practice case studies demonstrate that opening a two-way channel for feedback will improve both internal and external communication .

Rule 5 – I did it their way
Understand the working methods of those you need to convince. If leaders seem bound up in stats and spreadsheets, give them what they want. Gather data to prove your ideas work, show them a process, outline a clear outcome and they’ll soon be on your side. Measuring internal communications will help to provide the rationale behind your ideas. Equally, if the types of internal communication you are using don’t seem to be connecting with your employees, don’t be afraid to try a different approach.
Case Study 5 – Seymour House
Background: Seymour House runs ten outstanding childcare nurseries and wanted to get staff across the group engaging better with each other to share great practice. They needed to identify the best methods of internal communication that would resonate with their unique team-based workforce.
Approach: Talkfreely innovated with an internal communications app called Community. Community replaces static web pages and posts with highly personalised, bite-sized chunks of information presented on boards displaying relevant cards. These communicate quick stories and are far better at connecting people across teams.
Outcome: The Seymour House teams instantly connected with the Community app. Engagement levels took an immediate uplift as the communication and understanding between teams and individuals improved. This internal communications case study shows how crucial it is to connect with employees in a way that suits their style of interaction.
Rule 6: Make the most of managers
Your leadership team are crucial to the success of your strategy. However big or small your organisation, line managers and local leaders are your allies. They are essential to motivating employees and getting them on board: through discussion, allaying fears and leading by example. When you’re pulling together your internal communication definition , make sure leadership is one of the key points.
Case Study 6 – Yahoo
Background: The tech pioneer defined a need for remote workers return to the office environment. There was no longer a role for staff working from home and all employees needed to be office-based moving forward. The job of communicating this message was handed to the HR department.
Approach: Yahoo’s Head of HR sent out a motivational memo full of praise for the company’s “positive momentum”, “the buzz and energy in our offices”, “remarkable progress” and promising “the best is yet to come”. At the end of this message was the directive that all staff working from home must move back into the office or quit.
Outcome: A communication of this importance should have come from the head of the business. By trying to hide the order as a motivational HR message, it failed to provide a strategic business rationale. This is where the CEO needed to be a visible presence, sharing the reasoning behind this unpopular decision. Internal communication case study examples show time after time that leadership visibility is an essential element, especially when communicating change .
Rule 7: There is no silver bullet
We’d love to be able to reveal the secret to implementing that perfect internal communication strategy. Social media, the employee intranet , digital screens, email – they have all at some stage promised to revolutionise internal communications and make everything else redundant. But it hasn’t happened, which means the role of the internal communicator remains absolutely pivotal. Cut yourself slack in how you judge success, because every organisation has a different set of challenges and issues to overcome.
Case Study 7 – West Sussex County Council
Background: West Sussex Country Council has a workforce of over 6,000 staff spread across a wide geographic area in a variety of locations. In addition, around 25% of staff members have limited access to IT equipment and/or limited IT knowledge. The channels of internal communication in operation were outmoded and ineffective, leading to misinterpretation and inconsistencies.
Approach: Talkfreely developed a bespoke internal communications app designed to connect the disparate council workforce. Called ‘The Big Exchange’, the app allowed for real-time communication over a variety of digital platforms. Available 24 hours a day, 365 days a year, it allowed for flexibility in work patterns, increasing its appeal for all employees.
Outcome: By the end of the first quarter, a third of the employee base were actively using the app. In some sectors, 33% would be a pretty modest engagement score. For West Sussex Country Council however, it has connected with those hard-to-reach employees for the very first time. In addition, it proved that there is a real council workforce appetite to get involved. For example - there were 25,200 page views in the first month which means on average, each active user visited over 25 pages of content per month. Read the full case study .
“The TalkFreely app has helped improve, beyond recognition, the way we communicate with our 6000 strong workforce, many of whom are hard to reach. This has become even more evident over the last few weeks in our local response to the coronavirus crisis, helping us to get critical, time-sensitive information out to staff quickly and easily wherever they are across the county.” William Hackett, Communications & Engagement Lead, West Sussex County Council
Final thoughts
It’s clear, when looking at this selection of communication case studies, that not every internal communication is destined for success. And, if handled incorrectly, a poorly targeted message can actually do more harm than good. Internal communication mistakes are very costly, to both morale and the bottom line. However, if you take the time to plan carefully, the positive impact of a good internal communication exchange can be considerable. When assessing internal communications case studies, it’s also vital to consider the arena in which the company is operating before judging the relative success of the campaign. Ultimately, every organisation will need to take a different approach, tailored to suit their unique set of circumstances.

Engage every employee with your own branded Internal Comms App

Featured Resources

The big book of employee engagement ideas
If you are looking to improve employee engagement, this guide is a great place to start. Packed with 44 pages of ideas, insights and inspiration to help you engage your workforce.

How to choose the right employee engagement solution
Navigating the world of employee engagement solutions can be overwhelming. Download our guide to help you choose the best option for you, your employees and your business.

Try Talkfreely for FREE
Explore Talkfreely FREE for 14 days.
Get access to all our employee engagement tools plus support to help you get the most from your trial.
*Trial limited to one trial per person. Each trial will provide unlimited access to all features for 14 days.
Internal communication: everything you need to know.
With so many potential benefits to both employer and employee, this eBook details everything decision-makers and business leaders need to know about internal communication.

Tasked with improving employee engagement
Find out how an employee engagement app can play a pivotal role in delivering an employee engagement strategy.
You might also like...

12 Simple Hacks to Improve Internal Communication

Your Internal Communication Plan: 5 Do’s and 5 Don’ts

- Desktop Pop-up Alert
- Desktop Scrolling Ticker
- Panic Button
- Corporate Screensaver
- Corporate Wallpaper
- Corporate Lockscreen
- SMS Notification
- Emergency Alert
- Digital Signage
- Email Notification
- Extended Reports
- RSVP Invitation
- Video Alert
- Skin Editor
- Mobile Client App
- Technical Support
- Professional Services
- Annual Maintenance
- Engineering
- Hospitality
- Manufacturing
- Oil and Gas
- Change Management
- Email Overload
- Employee Engagement
- Emergency Communications
- Remote Communications
- Compliance Communications
- Internal Communication System
- Crisis Communications
- HR Communications
- Product Overview
- System Requirements
- Templates Library
- Knowledge Base
- AD Integration
- SSO Integration
- API Integration
- Automated Incident Notifications
- MS Teams Integration
- Case Studies
- Become a Partner
- Our Partners
Internal Communication Case Study

When you’re looking to make improvements to your internal communications, you don’t always have to reinvent the wheel. Looking at what other successful organizations have done in this space and learning from their successes can provide inspiration for your company’s internal communications planning.
While your organization will have its unique issues, you may face similar challenges to other businesses. DeskAlerts publishes case studies examples in corporate communication from its clients in different industries to help others to get insights into how to solve similar issues they may be facing.
What is an internal communication case study?
An internal communication case study looks at the way a company has handled a specific problem or achieved a specific outcome or goal so that people reading it can use it to guide their own approach to solving similar problems.

Workplace case study examples for communication should:
- Explain what the problem was, including the circumstances and any challenges the organization faced
- Explain the solution that was implemented
- Explain about any results achieved.
Organizational communication case study examples
This list of case studies in organizational communication from some of our clients at DeskAlerts has been put together to demonstrate how our internal communications software solution can assist you to overcome common communication challenges, no matter what industry you’re in.
1. A dedicated emergency communications channel in a crisis
CHU Saint Pierre is a university hospital in Brussels, Belgium. They were looking for a dedicated communications channel for both everyday staff communications, as well as one that they could turn to in the event of an emergency .
The hospital turned to DeskAlerts to ensure that it had a channel that would be able to be used even when other systems like emails and phone were overloaded .
The system was put to the test in 2016 when a series of terror attacks rocked Brussels and put an enormous strain on the city’s hospitals, which were operating in a state of emergency. The hospital’s telephone system became overloaded as a result. DeskAlerts was deployed to inform staff about using SMS messaging to take the strain off internal phone systems, and was then used throughout the crisis to provide critical updates.
2. A dedicated channel for IT updates
St George’s, University of London, is a tertiary institution dedicated to medical and health sciences, training, research and education. The university needed to find a dedicated channel to keep people informed about IT updates and to help take pressure off its IT helpdesk.
DeskAlerts was selected for the task as it was found to be easy to set up, implement and deploy as well as being value for money.
The University uses DeskAlerts to send tailored notifications that inform internal clients about updates to IT services. In doing so, it pre-empts unnecessary calls to the IT help desk.
3. As a way to communicate important information in manufacturing
KRKA is a pharmaceutical company headquartered in Slovenia that sells products to more than 70 countries around the world. The organization had the unique challenge of needing to communicate to both employees and manufacturing line operators on a range of topics. Not everyone they needed to communicate with accessed information in the same way: some used standalone terminals while others had access to the company intranet.
By implementing DeskAlerts, the company was able to keep people up-to-date on important topics such as system maintenance, system failures, system upgrades and other important events.
The result was that not only were people better informed, but there were various other efficiencies achieved. Staff spent less time having to manually contact people to bring important information to their attention, there were less calls to the tech help desk and staff were able to plan their work around known outages.
4. As a way to mitigate significant data and money loss
Weizmann Institute of Science in Israel is one of the world’s largest multidisciplinary research facilities. Many of the systems that are used by researchers at the institute cannot be interrupted otherwise it will result in significant data loss. Certain processes need to be fully completed before any kind of IT maintenance can be performed – and this can take many days and cost thousands of dollars.
The Institute’s IT department found this challenging as it has a lot of systems it needs to maintain, and needed people to be aware of planned maintenance so they didn’t begin running a lengthy process at the wrong time.
The IT department set about looking for a solution that could send information about maintenance, outages, server downtime and other IT announcements that also had a feature where recipients would verify and acknowledge that they had received and read the information sent.
DeskAlerts was chosen as a reliable channel to send these important IT announcements. It has a guaranteed open rate of 100% and a user acknowledgment function. The IT department is now able to do proactive maintenance and create maintenance windows when all users are aware that systems will be unavailable.
5. As a way to streamline all corporate communications
NewPage is a specialty paper manufacturer headquartered in the United States of America. The company’s approach to internal communications was ad hoc and not at all streamlined. For example, the company still relied on pagers and the HR department spent a lot of time sending email notifications.
By implementing DeskAlerts, the company has been able to save time and money and better target its communications . DeskAlerts has replaced pagers for emergency communications , and general communication messages can now be sent quickly and easily to targeted employees.
There are many different ways to use DeskAlerts to solve internal communications challenges. If your issue isn’t featured here, have a look through our other internal communication case study examples to find out how others have solved a similar issue. You can also get in touch with our internal communication experts to find a tailored solution to your internal communication needs.
Frequently asked questions
What is a communication case study.
An internal communications case study is a way of demonstrating the usefulness and value of a particular service by providing the reader with real-life examples.
What are examples of internal communication?
There are several main types of internal communication:
- Communication generated by leadership
- Communication generated by employees
- Peer to peer communications
- Communication about change or campaigns
- Information
- Culture-related communication
- Crisis and emergency communication
What is the importance of communication in case study?
Communicating case studies on communication in the workplace is an important way to engage and inspire an audience while also passing on important information. You can show the value of your work by presenting evidence and telling a story based on facts.
Send urgent notifications to any corporate devices: PCs, phones, tablets, etc.
The high visibility combined with our 100% delivery rate guarantee. Bypass information overload. Deliver key information even if the computer is on screensaver mode, locked or sleeping.

Posts by Tag
- Alert Software (43)
- Best Practices (13)
- Business Continuity (9)
- Change Management (22)
- Communication in finance (6)
- Communications Feedback Solutions (27)
- Construction Industry (5)
- Corporate Communication Strategy (28)
- Corporate Communication Tools (28)
- Corporate compliance (6)
- Corporate lockscreen (3)
- Corporate screensaver (4)
- Corporate wallpaper (5)
- COVID-19 (30)
- Crisis Communications (6)
- Cybersecurity (25)
- Desktop Alerts (16)
- Desktop Alerts Software (28)
- Digital signage (5)
- duty of care (4)
- Education (10)
- Email overload (17)
- Emergency Alert System (69)
- Emergency communications (19)
- Employee Communication (25)
- Employee Communication Channels (15)
- Employee Engagement (43)
- Employee quiz (2)
- Employee survey (4)
- Executive communications (6)
- Government Industry (6)
- Health and Safety Training (4)
- Healthcare (22)
- Helpdesk (26)
- Hospitality (1)
- HR Communications (57)
- Improve Corporate Communication (428)
- Internal Communication Best Practices (118)
- Internal Communication Channels (29)
- Internal Communication Plan (12)
- Internal Communication Strategy (26)
- Internal Communication Tools (50)
- Internal Communications (46)
- Internal marketing communications (4)
- Internet Security (41)
- IT communications (15)
- IT Issues (23)
- IT Outage (23)
- Manufacturing (5)
- Mass notification (28)
- Mobile App (2)
- MS Teams (2)
- New Release (1)
- Organizational culture (9)
- Pharmaceutical industry (1)
- Pop-up alerts (7)
- RSVP alert (3)
- Safety Culture (7)
- Security Awareness Training (18)
- SMS Notifications (1)
- Staff training (5)
- Strategy-Internal Communication Tools (2)
- Telecom (1)
- Video Alert (3)
- Workplace Safety (5)

16 min read
What Is Business Communication and How Can It Benefit Your Company?
What Is business communication? Business communication is something that every organization does every single day - sometimes well, and sometimes...

9 New Employee Announcement Ideas
When a new employee joins your company, sending an email to the rest of the organization can help to ease the new recruit into their position by...

10 min read
Safety Communications In The Workplace: 10 Best Strategies For 2024
Creating a safe workplace for your employees isn’t something that just happens by osmosis. Instead, it takes a concerted effort from management to...
Communication Case Studies
As part of MastersinCommunications.com dedication to helping students research graduate programs and careers in the field of communication, we created a section dedicated to communication case studies so that students can learn more about real projects completed by communication professionals. We hope this section will help students understand both the diverse array of projects that fall under the field of communication and the skills associated with each type of project.
Business Communication Case Studies

Crisis Communication for a Public Employee Retirement System
This case study explores the creation of a crisis communication plan and how it was used to handle a delicate situation regarding changes to an employee retirement fund. It involves strategic use of public relations, content creation, teamwork, and more.

Human Resources Communication and an Integrity Pledge
This case study examines a company HR strategy that created deep divisions throughout the organization and was ultimately unsuccessful. It deals with the creation and implementation of an Integrity Pledge meant to address issues plaguing a small business.

Strategic Communication for Floodplain Education
In this case study, a communication specialist helps spearhead a strategic communication project for a non-profit conservation collective. Their work entails collaborative project planning and evaluation, content creation, event management, and public relations.
Health Communication Case Studies

Manual for Cancer Patients
This case study follows the creation of a printed manual containing information on cancer treatments. The design process involved gathering data from treatment facilities, as well as finding the right layout to optimize patient experience.

Public Health Communications for Measles Outbreak
When a measles outbreak hits a small rural community, health professionals must figure out how to inform the public about potential risks and prevention strategies. This case study examines how the local health department responded to the crisis.

Risk Communication and Social Media Campaigns
This case study details how one risk communication organization uses social media to provide up-to-date information during a natural disaster. It includes a breakdown of the strategy employed amidst such events, as well as the training involved to prepare.
Technical Communication Case Studies

Mountain Bike Race Guide
In order to help riders navigate the logistical issues involved in an international mountain bike race, as well as the course itself, a technical writer and a usability tester research and develop a detailed guide to the event.

New Employee Training
This case study explores the creation of onboarding materials for new employees hired by a growing non-profit organization. It discusses scope and goals of the project, along with the skills needed to complete the training program.

Online Help Tool
In this case study, a technical writer is tasked with building an online tool to help employees use a new software system. This project involved interviewing staff members, designing the tool’s interface, and writing step-by-step instructions.
Case Studies in Strategic Communication
An online, peer-reviewed, open access journal.
To cite this article Young, C. L., & Flowers, A. (2012). Fight viral with viral: A case study of Domino’s Pizza’s crisis communication strategies. Case Studies in Strategic Communication, 1 , article 6. Available online: http://cssc.uscannenberg.org/cases/v1/v1art6
Access the PDF version of this article
Fight Viral with Viral: A Case Study of Domino’s Pizza’s Crisis Communication Strategies
Cory L. Young Arhlene Flowers Ithaca College
Domino’s Pizza was embroiled in a viral crisis situation when two rogue employees posted videos of adulterated food on YouTube in April 2009. Tim McIntyre, Vice President of Communications, was part of the internal team that delivered the company’s crisis communication plan through Twitter and YouTube. What makes this story so compelling is the social media aspect of both the crisis itself and the strategy for managing the crisis. Using a case study approach, this paper assesses Domino’s decision to integrate the same medium that sparked the crisis into the strategies to manage the situation, and it questions the efficacy of best practices and principles of crisis management in the age of social media.
Keywords : Domino’s Pizza; crisis communication; social media; YouTube; Twitter; case study; public relations
Overview and Background
The way in which companies communicate with stakeholders during a crisis event is rapidly changing with the 24-hour access provided by the Internet, Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube. Public relations practitioners and other communication executives are struggling to craft messages and maintain control of the flow of messages within this dynamic landscape. As Schiller (2007) explains, in “times of crisis, while corporate communication executives are preparing manicured statements, customers are [simultaneously] blogging, e-mailing and posting photos out of rage and desperation because the very people who should be listening to them aren’t” (p. 16). Bell (2010) asserts that stakeholders become “interpretive communities in organizational crisis contexts,” capable of cultivating an organization’s reputation through information they receive in cyberspace (p. 148). Social media allow stakeholders to control when, where, and how “reputational meanings are born and disseminated” as “an organization’s reputation is built on the stories formed by stakeholders and spread within networks” (Aula, 2011, p. 28, 30). Nowhere is this dynamic between organizations and their publics more apparent than on video sharing sites, such as YouTube, that encourage citizens and bloggers to be the co-producers of messages.
Burgess and Green (2009) explain that YouTube users engage with this medium “as if it is a space specifically designed for them and that should therefore serve their own particular interests” (p. vii). This can have enormous positive or negative impacts for organizations involved in crisis management, including but not limited to the inability of boundary spanners to monitor the vastness of this space; malicious users who might create a crisis; and the leveraging capabilities of this platform to enhance a brand during a crisis. Just as consumers can use this social medium to create a crisis for a company and interpret an organization’s reputation throughout, so too can an organization use this medium to manage a crisis and improve its reputation. Patrick Doyle, President of Domino’s Pizza, would come to understand this dynamic as his brand suffered a devastating blow when two employees uploaded a vulgar video demonstrating their grotesque adulteration of food.
Bob Garfield (2010), a writer for Ad Age Blogs , recounts in an online article how this incident began. On Easter Sunday in April 2009, two Domino’s employees who were bored “working in a North Carolina store figured it would be just hilarious to post a video of themselves, defiling sandwich ingredients” (para. 2). The duo created five videos in total, one of which showed an individual sticking mozzarella cheese up his nose and then blowing the cheese on a sandwich, among other unsanitary and stomach-turning activities. An estimated 1 million people viewed these videos before they were pulled two days later.
During the first 24 hours, Tim McIntyre, Vice President of Corporate Communications, surveyed the situation and determined that the videos were not a hoax. He then began to communicate internally and externally with “relevant audiences at that time [including] our social media people, our head of security, senior management team,” according to Amy Jacques (2009) in an article published in The Public Relations Strategist (para. 4, 7). McIntyre collaborated with the consumer watchdog organization GoodAsYou.org , which first alerted Domino’s of the employee video, to identify the rogue employees as Kristy Hammond and Michael Setzer. By Tuesday, according to McIntyre, the company was responding to customers’ queries on Twitter about whether the company knew about the situation, what the company was doing, and why the company had not issued an official statement (Jacques, 2009). By Wednesday, Patrick Doyle, President of Domino’s Pizza, recorded an apology that was then uploaded onto YouTube.
During this event, bloggers and journalists alike captured this crisis in articles and case studies, offering step-by-step timelines [1] (Jacques, 2009; Peeples & Vaughn, 2010) and criticisms of Domino’s responses (Beaubien, 2009; Esterline, 2009; Gregory, 2009; Vogt, 2009; Weiss, 2009; York, 2009). What follows in this case study is an analysis of Domino’s crisis communication strategies, using a blend of best practices for crisis management from the principles of public relations management crafted by Arthur W. Page and from an academic perspective as the framework for analysis. From a communication perspective, according to Jaques (2008), case studies “are generally a narrative of events which are critically examined in relation to recognized public relations theories and models in order to fully appreciate what happened and to consider alternative strategies and outcomes” (p. 194), and are written to provide practical value to managers and practitioners alike who are struggling to manage and control the flow of messages in the viral/digital landscape (Coombs, 2008; “How Social Media,” 2009; Oneupweb, 2007).
The Arthur W. Page Society is a professional organization for executives in the public relations and communication industries. Named after one of the first public relations executives to work for a Fortune 500 corporation (AT&T), this organization is charged with the goal of “embracing the highest professional standards; advancing the way communications is understood, practiced and taught; and providing a collegial and dynamic learning environment” (“Vision, Mission & Goals,” n.d., para. 2). According to the Society’s website, the following principles are designed to guide public relations practitioners’ actions and behaviors and exemplify Page’s philosophy of public relations management: (1) Tell the truth ; (2) Prove it with action ; (3) Listen to the customer ; (4) Manage for tomorrow ; (5) Conduct public relations as if the whole company depends on it ; (6) Realize a company’s true character is expressed by its people ; and lastly, (7) Remain calm, patient and good-humored (“The Page Principles,” n.d.).
These principles are similar to the 10 best crisis communication practices Seeger (2006) generated, based on the work of communication scholars and expert practitioners:
- Process approaches and policy development ;
- Pre-event planning ;
- Partnership with the public ;
- Listen to the public’s concerns and understand the audience ;
- Honesty, candor, and openness ;
- Collaborate and coordinate with credible sources ;
- Meet the needs of the media and remain accessible ;
- Communicate with compassion, concern and empathy ;
- Accept uncertainty and ambiguity ; and
- Messages of self-efficacy .
Veil, Buehner, and Palenchar (2011) extend Seeger’s best practices, incorporating social media tools by making social media engagement a part of risk and crisis management policies and procedures; incorporating social media when scanning the environment; being a part of rumor management to determine appropriate channels; and using social media to communicate updates in an interpersonal manner (pp. 119-120).
Compiling and synthesizing these practices is not an easy task as “crises and disasters are relatively unique in nature, inherently dynamic, and unpredictable” (Bell, 2010, p. 151). These practices, according the Seeger (2006) “do not constitute a plan, but are the principles or processes that underlie an effective crisis communication plan and effective crisis response” (p. 242). Given the nature of crises, these practices will unfold and evolve differently within each situation.
Taking a situational approach to crisis communication, Coombs (2004) offers the Situational Crisis Communication Theory as an explanation for how organizations select a crisis response strategy. Essentially, a crisis triggers attributions of responsibility to the organization from stakeholders, along three dimensions: 1) whether the crisis has happened before or will likely happen again; 2) whether the event was controllable or uncontrollable by an individual or the organization; and 3) whether the crisis occurs within the organization or external to it. In this case, Domino’s as an organization was not directly responsible for this crisis, as the event occurred internally at the hands of employees, and this type of crisis had never happened before.
Based on stakeholder attributions, an organization will respond communicatively by cycling through a four step process: 1) observe events; 2) interpret information for accuracy and relevance; 3) choose a strategy among alternatives; and 4) implement the solution (Hale, Dulek, & Hale, 2005). Ideally, the strategy chosen will be aligned with the best practices and principles articulated above and will follow the four step process. Did Domino’s follow the best practices outlined by Seeger and the Page principles? What were the brand’s overall actions, decisions, and strategies for managing the crisis? In the case of Domino’s, it was not the consumers’ attributions of responsibility to Domino’s that triggered the strategy. Rather, what triggered Patrick Doyle’s decision to deliver a video apology on YouTube was the medium itself, which begs the questions, How did social media impact or influence the decision making process?, and What crisis communication lessons were learned in the process?
Strategies and Execution
This first Page principle—Tell the truth—begs a series of questions about whose truth needs to be told and about what in particular. In crisis situations, multiple truths or social constructions of the event(s) are vying for attention simultaneously: in general, customers, the company, its employees, and the media. In the case of Domino’s, particular watchdog organizations like GoodAsYou.org and Consumerist.com were also constructing versions of the event. The truth that Tim McIntyre, VP of Communications, wanted to convey was that this incident was “a rogue act of two individuals who thought they were being funny. That they do not represent this brand. That they do not represent the 100,000 people who work every day at Domino’s Pizza all over the world” (Flandez, 2009, para. 6). The truth that Patrick Doyle wanted to articulate was that “We didn’t do this. We’re sorry. And we want to earn your trust back” (Peeples & Vaughn, 2010, p. 3).
However, in wanting to be honest, open and candid (Seeger, 2006) about the situation, Domino’s needed to take responsibility. However, taking responsibility had the potential of exposing the organization to lawsuits and other legal vulnerabilities (Claeys & Cauberghe, 2012), including freedom of speech and copyright claims. In order to mitigate the consequences of being truthful and minimize the damage to the organization’s reputation, the company collaborated and coordinated with credible sources (the watch dog organizations and local authorities) and partnered with the public to observe and interpret the events , so as to not “act too hastily and alert more consumers to the situation it was attempting to contain” (York, 2009, para. 5), and to not “add fuel to the online fire” (Levick, 2009, para. 5). Unfortunately, a consequence of following the principles and best practices was that a 24 hour lag occurred. Because Domino’s hesitated, customers began tweeting about whether the company actually knew what was happening and questioning what it was going to do about the videos. Veil, Buehner, and Palenchar (2011) point to the fact that “The power to communicate remains with the communicating organization and their behaviors and narrative content, not in the technology” (p. 120).
A second challenge in telling the truth in the digital age hinges on additional questions (Roberts, 2010): Where in cyber and virtual spaces does an organization tell the truth and with what social medium or platform? York (2009) brought this to our attention in her online article, asking “why Domino’s has been lambasted for a lack of social media presence. After all . . . the brand is on MySpace, Twitter, YouTube and most visibly on Facebook with nearly 300,000 fans” (para. 18). There is a big difference, however,
between how emerging social media are used for marketing and how they work in a serious crisis situation . . . Companies that fail to integrate their marketing efforts with their online crisis response plans before a crisis hits are letting their antagonists have free reign. (Levick, 2009, para. 2-4)
The first message acknowledging the crisis was uploaded onto the corporate website on the day after the offending videos had been posted, but the message hardly yielded any hits. Domino’s did not reach its most popular audience through this social medium.
According to McIntyre, prior to this event ,
[the crisis team had a social media plan] already in place. We didn’t want to just jump in without a strategy. We wanted to do it right. So the irony for us was that we have a plan and we were going to implement it only a week later, so we ended up having to jump in [during] a crisis, which was the opposite of how we wanted to do it. (quoted in Jacques, 2009, para. 10)
However, after listening to the customers/publics’ tweets , the company was compelled to speed up the implementation of the social media plan. A decision was made to
[change] course and [respond] with a viral video . . . [that] featured all the elements of effective crisis communication. The company president apologized. He thanked the online community for bringing the issue to his attention. He separated the company from wrongdoers and announced their prosecution. And he outlined steps that Domino’s was taking to deal with the issue to make sure it never happens again (Levick, 2009, para. 6).
This strategy and decision to fight the crisis’ viral nature using YouTube was the tipping point that allowed the company “to cull user-generated content from social networking sites and use the platform for distributing information back to users” in order to prove itself with action and to communicate with passion, concern and empathy (Veil et al., 2011, p. 114). Levick (2009), in an online article for Bloomberg Businessweek , stipulated that “Domino’s not only demonstrated concern for its customers, but also an understanding of the critical importance of reaching out to a target audience on its own terms and in its own preferred space” (para. 7). This strategy and decision also suggests that Domino’s has the ability to manage the crisis for tomorrow : “This crisis happened online. It had to be dealt with online. By learning that lesson under fire Domino’s broke new ground and opened a new chapter in the ongoing evolution of crisis communications” (Levick, 2009, para. 7).
Evaluation & Discussion
Arthur W. Page advocated for public relations practitioners to tell the truth, a laudable goal to aspire to, but nonetheless one that is increasingly challenging in today’s digital era. Initially, Domino’s relied on its traditional technology (the Internet) to upload a video response on its corporate website to tell the public the truth about the situation. However, the number of people who viewed this video paled in comparison to the number of YouTube viewers who watched the employee prank videos—over one million within 24 hours. This realization accelerated and expedited the implementation of Domino’s social media plan that was still in development.
The crucial lesson to be learned about crisis communication comes in the form of extending and aligning the Situational Crisis Communication Theory with best practices for the integrating of social media (Veil et al, 2011). Coombs (2004) stipulated that a crisis triggers stakeholders’ attributions regarding the organization’s level of responsibility. These attributions, in turn, influence the strategy that an organization will use to lessen the damaging effects. In this case, however, it was not stakeholder attributions that dictated Domino’s strategy, but rather it was the social medium in which the crisis occurred that shaped the company’s decision to respond on YouTube as well as its overall strategy.
The only way to combat and lessen the impact of a social media generated crises like what Domino’s experienced is to integrate social media into crisis communication strategies and to create strategies for monitoring social media dialogue (Tinker, Fouse, & Currie, 2009). Schiller (2007) agrees that “Brands that get it right will be the ones that will use the same online tools as their customers” (p. 16). Further, Peeples and Vaughn (2010) concluded that Domino’s “effectively leveraged social media – the same channel used by the pranksters – to transparently communicate the company’s efforts to address the situation” (p. 1).The end result was that Domino’s emerged from this vulnerability criticized, yet knowledgeable about the reality of crisis communication in the age of social media.
The reality of crisis communication today is complex and contradictory. The speed at which consumers generate information about organizations is surpassing the speed by which public relations practitioners can monitor and verify the validity of such content, in order to respond before, during, and after a crisis incident. Because social media users can instantaneously create visual and textual dialogue with an organization, there is a corresponding expectation that organizations should respond just as quickly throughout all phases of a crisis incident. But taking the time to verify information and craft appropriate and effective responses is necessary to avoid legal issues and other complications. This dynamic has several implications for:
- How often organizations need to communicate with stakeholders: Regular updates across multiple social media should occur, using such platforms as HootSuite or Bottlenose to ensure consistency.
- How far and wide organizations need to span the boundaries of cyberspace and social media for potential crises and for potential stakeholder groups that can be impacted and affected: Johnson, Bazaa, and Chen (2011) conducted a study on boundary spanning, concluding that “organizations should focus on recruiting, attracting, and nurturing those online users with high levels of enduring involvement and social identity,” i.e., highly engaged social media users (p. 15).
- How organizations can manage their online reputations through search engine optimization (SEO).
- How new principles and best practices need to be developed to determine what messages or images from which stakeholder groups will tip towards a crisis.
As organizations grapple with these new directions, employees and consumers will need to learn how to accept uncertainty and ambiguity , and remain calm, patient and good humored.
Discussion Questions
- What impact does social media have on public relations practices, particularly crisis communications and reputation management? How significant is it for organizations today to monitor content on social media sites, including hash tags and other signs of internal and external dialogue?
- How should crisis communications preparedness plans address the proliferation of social media outlets?
- From the perspective of crisis communicators concerned with social media, what else could Domino’s have done or said to prove with action that its key messages are sincere? What other messages could Domino’s have delivered?
- What other types of traditional media and social media could Domino’s have used to reach its stakeholders?
- What other challenges do you think that PR practitioners, marketers, or corporate communicators could have in telling the truth in the digital age?
- How important is speed of response rate in a digital world, particularly when an organization is facing a crisis situation?
- Are there any other conclusions that you can draw from this incident?
Learning Activities
- According to its website, Media Curves “is the leader in public perception of topical issues.” This communications research company uses its patent pending technology to evaluate the “believability” of a particular video, such as the apology posted on YouTube by Domino Pizza’s President Patrick Doyle. To see how Media Curves’ technology captured people’s perceptions of Doyle’s apology video, watch Doyle’s apology video here: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uFiXWboPD5A . Discuss the specific moments in the video that people found most believable and least believable and what public relations practitioners can learn from studies like this. Visit the Media Curves website to watch other assessments of video apologies.
- Using the framework presented in this article, apply the Arthur W. Page Society’s principles (“Vision, Mission & Goals,” n.d.), Seeger’s (2006) best practices, and Veil, Buehner, and Palenchar’s (2011) suggestions for integrating social media to United Airlines and its handling of Dave Carroll’s “United Breaks Guitar Video” or to Providence Renaissance and its handling of “Joey Quits” video . What lessons can be learned about social media and crisis communication from analyzing these organizations’ strategies?
- To see how Domino’s has dealt with this crisis, consider some background information about its Pizza Turnaround campaign . How does this compare with the best practices? How did tweets like #newpizza help?
[1] A visual timeline of the first four days is available on the Arthur W. Page’s website: http://www.awpagesociety.com/insights/winning-case-studies/2010/
Aula, P. (2011). Meshworked reputation: Publicists’ views on the reputational impacts of online communication. Public Relations Review, 37 , 28-36.
Beaubien, G. (2009, April 21). Domino’s YouTube flap: ‘A landmark event in crisis management.’ Public Relations Tactics . Retrieved December 31, 2012, from http://www.prsa.org/SearchResults/view/7978/105/Domino_s_YouTube_flap_a_landmark_event_in_crisis_m
Bell, L. M. (2010). Crisis communication: The praxis of response. The Review of Communication, 10 (2), 142-155.
Burgess, J., & Green, J. (2009). YouTube: Online video and participatory culture . Malden, MA: Polity Press.
Claeys, A., & Cauberghe, V. (2012). Crisis response and crisis timing strategies, two sides of the same coin. Public Relations Review, 38 , 83-88.
Coombs, W. T. (2004). Impact of past crises on current crisis communication: Insights from Situational Crisis Communication Theory. Journal of Business Communication, 41 (3), 265-289.
Coombs, W. T. (2008, April 2). Crisis communication and social media. Institute for Public Relations . Retrieved December 31, 2012, from http://www.instituteforpr.org/topics/crisis-communication-and-social-media/
Esterline, R. M. (2009, April 25). Case study: Domino’s YouTube video . Retrieved December 31, 2012, from http://crisiscomm.wordpress.com/2009/04/25/case-study-dominos
Flandez, R. (2009, April 20). Domino’s response offers lessons in crisis management. The Wall Street Journal . Retrieved December 31, 2012, from http://blogs.wsj.com/independentstreet/2009/04/20/dominos-response-offers-lessons-in-crisis-management
Garfield, B. (2010, January 11). Domino’s does itself a disservice by coming clean about its pizza: We like apologies and honesty, but there are limits. Just ask Ford. Ad Age Blogs . Retrieved December 31, 2012, from http://adage.com/article/ad-review/advertising-domino-s-a-disservice-ads/141393
Gregory, S. (2009, April 18). Domino’s YouTube crisis: Five ways to fight back. Time Magazine . Retrieved December 31, 2012, from http://www.time.com/time/nation/article/0,8599,1892389,00.html
Hale, J. E., Dulek, R. E., & Hale, D. P. (2005). Crisis response communication challenges: Building theory from qualitative data. Journal of Business Communication, 42 (2), 112-134.
How social media are changing crisis communications—for better and worse. (2009, November 1). Security Director’s Report, 9 (11), 2-5.
Jacques, A. (2009, August 17). Domino’s delivers during crisis: The company’s step-by-step response after a vulgar video goes viral. The Public Relations Strategist . Retrieved December 31, 2012, from http://www.prsa.org/Intelligence/TheStrategist/Articles/view/8226/102/Domino_s_delivers_during_crisis_The_company_s_step
Jaques, T. (2008). A case study approach to issue and crisis management: Schadenfreude or an opportunity to learn? Journal of Communication Management, 12 (3), 192-203.
Johnson, P. R., Bazaa, U., & Chen, L. (2011, May). The new boundary spanners: Social media users, engagement, and public relations outcomes . Paper presented at the annual meeting of the International Communication Association, Boston, MA. Retrieved December 31, 2012, from http://www.icavirtual.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/05/FULL-PAPER-SUBMISSION-TEMPLATE-EK1.pdf
Levick, R. S. (2009, April 21). Domino’s discovers social media. Bloomberg Businessweek . Retrieved December 31, 2012, from http://www.businessweek.com/print/managing/content/apr2009/ca20090421_555468.htm
Oneupweb. (2007). Principles of crisis management in a viral age: Integrating the tools and lessons of search 2.0 into a comprehensive crisis response [White paper]. Traverse City, MI: Oneupweb. Retrieved December 31, 2012, from http://internetetopinion.files.wordpress.com/2008/01/crisis_management.pdf
The Page principles. (n.d.). Arthur W. Page Society . Retrieved December 31, 2012, from http://www.awpagesociety.com/about/the-page-principles/
Peeples, A. & Vaughn, C. (2010). Domino’s “special” delivery: Going viral through social media (Parts A & B). Arthur W. Page Society case study competition in corporate communications . Retrieved December 31, 2012, from http://www.awpagesociety.com/insights/winning-case-studies/2010
Roberts, J. (2010, March 18). Bringing your brand back from the brink. Marketing Week . Retrieved December 31, 2012, from http://www.marketingweek.co.uk/bringing-your-brand-back-from-the-brink/3011206.article
Schiller, M. (2007, March 5). Crisis and the web: How to leverage the Internet when a brand takes a hit. Adweek, 48 (10), 16.
Seeger, M. W. (2006). Best practices in crisis communication: An expert panel process. Journal of Applied Communication Research, 34 (3), 232-244.
Tinker, T., Fouse, D. (Eds.), & Currie, D. (Writer). (2009). Expert round table on social media and risk communication during times of crisis: Strategic challenges and opportunities [Report]. Washington, DC: American Public Health Association. Retrieved December 31, 2012, from http://www.apha.org/NR/rdonlyres/47910BED-3371-46B3-85C2-67EFB80D88F8/0/socialmedreport.pdf
Veil, S. R., Buehner, T., & Palenchar, M. J. (2011). A work-in-progress literature review: Incorporating social media in risk and crisis communication. Journal of Contingencies and Crisis Management, 19 (2), 110-122.
Vision, mission & goals. (n.d.). Arthur W. Page Society . Retrieved December 31, 2012, from http://www.awpagesociety.com/about/vision-misson-goals/
Vogt, P. (2009, April 24). Brands under attack: Marketers can learn from Domino’s video disaster. Forbes . Retrieved December 31, 2012, from http://www.forbes.com/2009/04/24/dominos-youtube-twitter-leadership-cmo-network-marketing.html
Weiss, T. (2009, April 22). Crisis management—Domino’s case study research. Trendsspotting Blog . Retrieved December 31, 2012, from http://www.trendsspotting.com/blog/?p=1061
York, E. B. (2009, April 20). What Domino’s did right–and wrong–in squelching hubbub over YouTube video. Advertising Age [Online]. Retrieved December 31, 2012, from http://adage.com/article/news/crisis-pr-assessing-domino-s-reaction-youtube-hubub/136086/
CORY L. YOUNG, Ph.D. , is an associate professor of communication management and design in the Department of Strategic Communication, Roy H. Park School of Communications, at Ithaca College in Ithaca, New York, where she teaches courses in corporate communication. Email: youngc[at]ithaca.edu.
ARHLENE FLOWERS is an associate professor of integrated marketing communications in the Department of Strategic Communication, Roy H. Park School of Communications, at Ithaca College in Ithaca, New York, where she teaches courses in public relations. Email: aflowers[at]ithaca.edu.
Acknowledgments
This manuscript was made possible in part by a James B. Pendleton grant from the Roy H. Park School of Communications at Ithaca College. A version of this paper was presented at the International Communication Association’s pre-conference hosted in Tokyo, Japan, June 2010. Additionally, the following graduate assistants need to be acknowledged for their research contributions: Rui Liu, Savitha Ranga, Nate (Zheli) Ren, and Danielle Clarke.
Editorial history Received November 4, 2011 Revised April 9, 2012 Accepted June 12, 2012 Published December 31, 2012 Handled by editor; no conflicts of interest
15 thoughts on “ ”
Pingback: Bibliography | areyousocialmediaware
Pingback: The Donald Sterling Racism Scandal - CommPRO.biz
Pingback: ORGASM pizza and Domino’s Crisis Communications | Kat Powers
Pingback: Syllabus for Social Media Course at McGill | Proper Propaganda - Inbound Marketing and Public Relations Agency
Pingback: Timing, Honesty, & Location – Crisis Management on Social Media | Andrew Cevasco
Pingback: DOMINO’S PIZZA, BUY MORE PIZZA, HAVE MORE FUN | 6klowns
Pingback: Crisis Communication Strategies | PR Movement
Pingback: Social media: risks and rewards in the public relations industry | A digital jigsaw
Pingback: Effective Crisis Management | digitalmarketingsixteen
Pingback: Crisis management materials overview- GlobalUni advice « GlobalUni
Pingback: Social media as a double-edged sword | SMU Social Media Singapore
Pingback: 15 Ways to Grow Your Business Through Social Listening
Pingback: How to manage companies’ reputation by using social media? – Geer Jin
Pingback: Why PR Crises Occur? | prcrisesblog
Pingback: Online Bigbang! — Never forget to check your organisation online! – Taylor Huang
Comments are closed.
Your browser is ancient! Upgrade to a different browser or install Google Chrome Frame to experience this site.
Master of Advanced Studies in INTERCULTURAL COMMUNICATION

Case Studies in Intercultural Communication
Welcome to the MIC Case Studies page.

Here you will find more than fifty different case studies, developed by our former participants from the Master of Advanced Studies in Intercultural Communication. The richness of this material is that it contains real-life experiences in intercultural communication problems in various settings, such as war, family, negotiations, inter-religious conflicts, business, workplace, and others.
Cases also include renowned organizations and global institutions, such as the United Nations, Multinationals companies, Non-Governmental Organisations, Worldwide Events, European, African, Asian and North and South America Governments and others.
Intercultural situations are characterized by encounters, mutual respect and the valorization of diversity by individuals or groups of individuals identifying with different cultures. By making the most of the cultural differences, we can improve intercultural communication in civil society, in public institutions and the business world.
How can these Case Studies help you?
These case studies were made during the classes at the Master of Advanced Studies in Intercultural Communication. Therefore, they used the most updated skills, tools, theories and best practices available. They were created by participants working in the field of public administration; international organizations; non-governmental organizations; development and cooperation organizations; the business world (production, trade, tourism, etc.); the media; educational institutions; and religious institutions. Through these case studies, you will be able to learn through real-life stories, how practitioners apply intercultural communication skills in multicultural situations.
Why are we opening our "Treasure Chest" for you?
We believe that Intercultural Communication has a growing role in the lives of organizations, companies and governments relationship with the public, between and within organizations. There are many advanced tools available to access, analyze and practice intercultural communication at a professional level. Moreover, professionals are demanded to have an advanced cross-cultural background or experience to deal efficiently with their environment. International organizations are requiring workers who are competent, flexible, and able to adjust and apply their skills with the tact and sensitivity that will enhance business success internationally. Intercultural communication means the sharing of information across diverse cultures and social groups, comprising individuals with distinct religious, social, ethnic, and educational backgrounds. It attempts to understand the differences in how people from a diversity of cultures act, communicate and perceive the world around them. For this reason, we are sharing our knowledge chest with you, to improve and enlarge intercultural communication practice, awareness, and education.
We promise you that our case studies, which are now also yours, will delight, entertain, teach, and amaze you. It will reinforce or change the way you see intercultural communication practice, and how it can be part of your life today. Take your time to read them; you don't need to read all at once, they are rather small and very easy to read. The cases will always be here waiting for you. Therefore, we wish you an insightful and pleasant reading.
These cases represent the raw material developed by the students as part of their certification project. MIC master students are coming from all over the world and often had to write the case in a non-native language. No material can be reproduced without permission. © Master of Advanced Studies in Intercultural Communication , Università della Svizzera italiana, Switzerland.
| : Catholic, Convert, Ethnocentrism, Family, Judaism, Marriage, Mediation, Mexico, Religion, Stereotypes, Stigmatisation, Values | |
| : Cultural Dimensions, Cultural Values, Culture Shock, Erasmus, Finland, France, Integration, Proximity, Studying Abroad, Time Orientation | |
| : Cultural Dimensions, Cultural Values, Finland, International Collaboration, Italy, Miscommunication, Task Vs Social Orientation, Time Orientation | |
| : Economics, Intercultural Negotiations, Iran, Media, Politics, Public Relations, Switzerland | |
| : Africa, Critical Incident, Gender, Generation, High Context/Low Context, Individualism/Collectivism, Nigeria, Public Position, Religion, Time Orientation | |
| : Business, China, Directness, East-West, Individualism/Collectivism, Intercultural Collaboration, Miscommunication, Temporality | |
| : Cultural Prejudice, Generalisation, National Identity, National Past, Offence, Stereotypes, Swiss Banks, Switzerland, WWII | |
| : Christianity, Christmas, Education, Foreign Influence, Islam, Mediation, Parents, Religious Freedom, Schools, Switzerland, Tolerance | |
| : Airport, Awkward Feeling, Burka, Clothing, Critical Incident, International Setting, Local Customs, Neutral Setting, Stereotypes, Travel | |
| : Collaboration, Company, Employees, Face Loss, Gender, Intercultural Collaboration, Mediation, Turkey | |
| : Africa, Competence, In-Country Diversity, Nigeria, Religious Conflicts, Representations, Social Capital, Stereotypes | |
| : Collaboration, Culture Shock, Ethnocentrism, Integration, International Organizations, Management Styles, Mexico, Working Relationship, Working Styles | |
| : China, Cultural Adaptation, Culture Shock, Developmental Model, Going Abroad, Living Conditions, Stages Of Culture Shock, Studying Abroad, Unhappiness | |
| : Bureaucracy, Collaboration, Critical Incident, Cultural Etiquette, Netherlands, Rules And Procedure, Saudi Arabia, Status And Hierarchy, Western Vs Oriental | |
| : (Reverse) Culture Shock, Attire, Clothing, Cultural Configuration, Dress Code, Formality, Job Interviews, Non-Verbal Communication, Work Setting, Working Culture | |
| : Bosnia-Herzegovina, Collaboration, Cultural Perception, Employees, Hierarchy, Individualism/Collectivism, Power Distance, Time Perception | |
| : Arbitration, Cultural Presupposition, Discrimination, Ethnocentrism, Mediation, Rumania, Torture, Trauma, Xenophobia | |
| : Ramadan, Religion, Workplace, Conflict, Mediation Strategies, Inter-Religious Dialogue, Professional Environment | |
| : Christianity, Church, Equality, Finland, Gender, Gender Equality, Media, Religion, Religious Beliefs | |
| : Afghanistan, Critical Incident, Cultural Assumptions, Gender Relations, Hierarchy, Islam, Religion, Work Abroad | |
| : Agnostic, Atheist, Baptism, Christianity, Cultural Norm, Education, Mediation, Parents, Personal Choice, Switzerland, Upbringing | |
| : Geert Wilders, Immigration, Immigration Policy, Islam, Netherlands, Politics, Religion, Religious Stereotypes, Terrorism | |
| : Britain, Culture Of Origin, Expat, Going Abroad, Language, Multiple Identities, Stranger, Switzerland, Two Cultures, Values | |
| : Culture Of Origin, Identity, Identity Shock, Immigration, Language, Stranger, Switzerland | |
| : Collaboration, Cultural Dimensions, Egypt, Employees, Intercultural Competence, Management Styles, Working Abroad | |
| : Adaptation, Culture Shock, Exchange Year, Expectations, Host Family High School, Stereotypes, Study, Teenager, USA, Way Of Life | |
| : African Immigrant, Culture Shock, Immigration, Monoculturality Vs Multiculturality, Multicultural Environment, Multiple Identities, Saudi Arabia, Studying Abroad | |
| : Business Culture, Collaboration, Communication, Compensation, Complaint, Individualism/Collectivism, Local Market Knowledge, Translation, Turkey | |
| : Discrimination, Islamophobia, Mediation, Minarets, Religion, Right-Wing Politics, Stereotypes, Switzerland | |
| : Africa, Ethnic Communities, Genocide, Intercultural Competence, Mediation, Peace Building, Rwanda, Stakeholders | |
| : Bosnia-Herzegovina, Cultural Values, Ex-Yugoslavia, Mediation, Peace Building, Perception, Religion, Religious Belief | |
| : Choice Of Register, Common Ground, Development Cooperation, Ecuador, Indigenous People, Intercultural Negotiations, Negotiation, Non-Verbal Communication, United Nations | |
| : Collaboration, Cultural Dimensions, Intercultural Awareness, Intercultural Competence, Portugal, Stereotypes, United Kingdom, Working Styles | |
| : Communication, Cultural Dimensions, Germany, Immigration, Language, Linguistic Register, Politeness, Switzerland | |
| : Forum, Gender, Homosexuality, International Setting, Islam, Mediation, Politics, Polygamy, Values, Western Vs Oriental, Youth | |
| : Collaboration, Language, Mediation, Neat, Röstigraben, Stereotype, Switzerland, Tunnel | |
| : Archeology, Cultural History, Isreal, Mediation, Middle-East Conflict, Palestine, Religion, Religious Symbols | |
| : Acculturation, China, Cultural Pressure, Family Expectations, Generation, Italy, Marriage, Overseas-Chinese, Parents, Traditions, Two Cultures | |
| : Awkward Feeling, Critical Incident, Cultural Values, Discrimination, Gender, Immigration, Individualism/Collectivism, Intercultural Competence, Money, Politeness, Social Reflex, Stereotypes | |
| : Apartheid, Colonialism, Cultural History, Intra-National Diversity, Minorities, Names, South Africa, Symbols | |
| : Islam, Mediation, Offence, Religion, Religious Belief, Stereotypes, Vatican, Violence, Western Vs Oriental | |
| : Assumptions, Business Meeting, Critical Incident, Etiquette, Gender Relations, Islam, Pakistan, Public Event | |
| : Inter-Religious Dialogue, Islam, Media, Mediation, Minarets, Muslim Communities, Norms, Public Opinion, Religion, Switzerland, Symbol, Values, Vote | |
| : Collaboration, Critical Incident, Eating Habits, Hierarchy, India, Mediation, Non-Verbal Communication, Outsourcing | |
| : Islam, Mediation, Minarets, Religion, Religious Symbols, Religious Values And Identity, Switzerland, Symbol, Vote | |
| : Critical Incident, Dancing, Intercultural Relationship, Meeting The Parents, National Symbol, Non-Verbal Communication, Stereotypes, Turkey, Western Vs Oriental | |
| : Asylum, Conflict Resolution, Denmark, Education, Immigration, Islam, Mediation, Parents, Religion, Stereotypes, Veil | |
| : Collaboration, Critical Incident, Going Abroad, International Setting, Linguistic Meaning, Management, Miscommunication, Philippines, Stress, Time Orientation, Working Style | |
| : Australia, Being Different, Discrimination, Generalisation, Hostility, Immigration, South-East Asian Immigrants, Stereotypes, Two Cultures |
Subscribe Us
If you want to receive our last updated case studies or news about the program, leave us your email, and you will know in first-hand about intercultural communication education and cutting-edge research in the intercultural field.
Undergraduate Research Opportunities Center
Present or publish your research or creative activity, effective communication: case study, three types of communication.
| Type | Meaning for presenter | Meaning for audience |
|---|---|---|
| Verbal | What we are saying | Listening to the presenter and understanding their purpose |
| Non-verbal | How we are saying it | Observing a person and inferring what their purpose is |
| Written | Writing it: Letters, emails, internet, other media | Reading their meaning |
Communicating with your audience is more than giving a handful of information, it is the use of clear language that is factual and logical to depict to the audience that the message is essential to their lives and their future.
The biggest communication problem is we do not listen to understand. We listen to reply.
Here is a video depicting why it is important to tailor to your audience's needs
Communicating to a Diverse Demographic Audience
This video depicts the importance of communication to different demographic audience members. Making sure that your presentation is understood by all individuals is a valuable communication tool
Remember that no matter the audience, everyone should understand and enjoy the information you are presenting.
Thanks for helping us improve csumb.edu. Spot a broken link, typo, or didn't find something where you expected to? Let us know. We'll use your feedback to improve this page, and the site overall.
Online resources available. Physical building closed due to inclement weather

Take the Library Survey and enter to win a prize!
Communication.
- Introduction to Communication
- Find Articles
- Streaming Films & TV
- Speeches and Current Topics
- Spartan Article Search
Finding Case Studies in the Communications Field
Databases with case studies, open educational resources, open access journals & association reports, examples of case studies.
- Recommended Websites
- Media Centers/News
- Organizations
Spartan Articles Search
Journal Title Search (Example: Chronicle of Higher Education or JAMA)
In the databases, use terms like "case study" or "case method." Keep the terms in quotes to force the results to only return that phrase. Combine with terms like "social media," "education," "public relations," "market research," etc.
Begin by cross-searching most of the library databases. You may have more luck using one of the specialty databases listed below.
For more information on case studies, see the Case Study Research Guide .
Search company and industry information in the Industry Profiles Guide .
Company and industry information, company fundamentals, investment research reports, industry ranking, company profiles, SWOT reports, and financial reports. along with scholarly and general business periodicals.
- Case Studies in Strategic Communication (CSSC) "CSSC is dedicated to the study of strategic communication through the case study form. Case studies illustrate the strategies, tactics, and execution of communication campaigns through in-depth coverage of a single situation. CSSC is a peer-reviewed online publication housed at the University of Southern California’s Annenberg School for Communication & Journalism.
- Institute for Public Relations "These studies are composed of IPR’s best-in-class research, gold standard papers and other signature research that exemplify IPR’s mission of bringing relevant research to the public relations practice."
- Public Relations Council Case Studies The PR Council Association collects case studies from various agencies and PR firms.
- Strategies & Tactics Published by the Public Relations Society of America (PRSA), "Strategies & Tactics is a modern newspaper that helps you stay up-to-date with the latest news, best practices and information about everything from crisis communications to social media to reputation management."
Depending on the company or industry you are targeting, there is an abundance of case studies in the library databases. Here are two examples. The first discusses the effective use of social media in PR campaigns. The second explores brand management decisions concerning the terroir product of an authentic beer brand.
Allagui, I., & Breslow, H. (2016). Social media for public relations: Lessons from four effective cases. Public Relations Review , 42 (1), 20–30. https://doi-org.esearch.ut.edu/10.1016/j.pubrev.2015.12.001
Melewar, T. C., & Skinner, H. (2020). Territorial brand management: Beer, authenticity, and sense of place. Journal of Business Research, 116 , 680-689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2018.03.038
- << Previous: Speeches and Current Topics
- Next: Recommended Websites >>
- Last Updated: Sep 9, 2024 11:57 AM
- URL: https://utopia.ut.edu/communication
Macdonald-Kelce Library - The University of Tampa - 401 W. Kennedy Blvd. - Tampa, FL 33606 - 813 257-3056 - [email protected] - Accessibility


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
1.10 Case Studies: The Cost of Poor Communication
This chapter is adapted from Technical Writing Essentials – H5P Edition by Suzan Last licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Learning Objectives
- Apply your understanding of context, purpose, audience, and channel in case studies.
No one knows exactly how much poor communication costs business, industry and government each year, but estimates suggest billions. In 2017, Josh Bernoff claimed that the cost of poor communication was nearly $4 billion per year: “American workers spend 22 percent of their work time reading; higher compensated workers read more… America is spending 6 percent of total wages on time wasted attempting to get meaning out of poorly written material. Every company, every manager, every professional pays this tax, which consumes $396 billion of our national income” (Meier, 2017).
Poorly-worded or inefficient emails, careless reading or listening to instructions, documents that go unread due to poor design, hastily presenting inaccurate information, sloppy proofreading — all of these examples result in inevitable costs. In one tragic case, a lack of communication between contractors and engineers resulted in a walkway collapse that killed 114 people at the Hyatt Regency .
The waste caused by imprecisely worded regulations or instructions, confusing emails, long-winded memos, ambiguously written contracts, and other examples of poor communication is not as easily identified as the losses caused by a bridge collapse. But the losses are just as real—in reduced productivity, inefficiency, and lost business. In more personal terms, the losses are measured in wasted time, work, money, and ultimately, professional recognition. In extreme cases, losses can be measured in property damage, injuries, and even deaths.
The following cases show how poor communications can have real world costs and consequences.
A . Read “Case 1: The Unaccepted Current Regulator Proposal”. Then, answer the 5 questions in the quiz set.
CASE 1: Acme Electric Company
The Acme Electric Company worked day and night to develop a new current regulator designed to cut the electric power consumption in aluminum plants by 35%. They knew that, although the competition was fierce, their regulator could be produced more cheaply, was more reliable, and worked more efficiently than the competitors’ products.
The owner, eager to capture the market, personally but somewhat hastily put together a 120-page proposal to the three major aluminum manufacturers, recommending that their regulators be installed at all company plants.
The first 87 pages of the proposal were devoted to the mathematical theory and engineering design behind the new regulator, and the next 32 pages to descriptions of a new assembly line to produce regulators quickly. Buried in an appendix were the test results that compared her regulator’s performance with present models and a poorly drawn graph showed how much the dollar savings would be.
Acme Electric didn’t get the contracts, despite having the best product. Six months later, the company filed for bankruptcy.
B . In small groups, examine one of the following cases and complete the following :
- Define the rhetorical situation : Who is communicating to whom about what, how, and why? What was the goal of the communication in each case?
- Identify the communication error (poor task or audience analysis? Use of inappropriate language or style? Poor organization or formatting of information? Other?)
- Explain what costs/losses were incurred by this problem.
- Identify possible solution s or strategies that would have prevented the problem, and what benefits would be derived from implementing solutions or preventing the problem.
Present your findings in a brief, informal presentation to the class.
CASE 2: Petro-chemical company report
Cameron (he/him), a research chemist for a major petro-chemical company, wrote a dense report about some new compounds he had synthesized in the laboratory from oil-refining by-products. The bulk of the report consisted of tables listing their chemical and physical properties, diagrams of their molecular structure, chemical formulas and computer printouts of toxicity tests. Buried at the end of the report was a casual speculation that one of the compounds might be a particularly effective insecticide.
Seven years later, the same oil company launched a major research program to find more effective but environmentally safe insecticides. After six months of research, someone uncovered Cameron’s report and his toxicity tests. A few hours of further testing confirmed that one of Cameron’s compounds was the safe, economical insecticide they had been looking for.
Cameron had since left the company because he felt that the importance of his research was not being appreciated.
CASE 3: Novaware instruction manual
As one of the first to enter the field of office automation, Novaware, Inc. had built a reputation for designing high-quality and user-friendly database and accounting programs for business and industry. When they decided to enter the word-processing market, their engineers designed an effective, versatile, and powerful program that Novaware felt sure would outperform any competitor.
To be sure that their new word-processing program was accurately documented, Novaware asked the senior program designer to supervise writing the instruction manual. The result was a thorough, accurate and precise description of every detail of the program’s operation.
When Novaware began marketing its new word processor, cries for help flooded in from office workers who were so confused by the massive manual that they couldn’t even find out how to get started. Then several business journals reviewed the program and judged it “too complicated” and “difficult to learn.” After an impressive start, sales of the new word processing program plummeted.
Novaware eventually put out a new, clearly written training guide that led new users step by step through introductory exercises and told them how to find commands quickly. But the rewrite cost Novaware $350,000, a year’s lead in the market, and its reputation for producing easy-to-use business software.
CASE 4: Policy memo
Nhi (they/them) supervised 36 professionals in 6 city libraries. To cut the costs of unnecessary overtime, they issued this one-sentence memo to their staff:
After the 36 copies were sent out, Nhi’s office received 26 phone calls asking what the memo meant. What the 10 people who didn’t call about the memo thought is uncertain. It took a week to clarify the new policy.
CASE 5: “Nerds gone wild”
The following excerpt is from Carl Sagan’s book, The Demon-Haunted World: Science as a Candle in the Dark, itself both a plea for and an excellent example of clear scientific communication:
The Superconducting Supercollider (SSC) would have been the preeminent instrument on the planet for probing the fine structure of matter and the nature of the early Universe. Its price tag was $10 to $15 billion. It was cancelled by Congress in 1993 after about $2 billion had been spent — a worst of both worlds outcome. But this debate was not, I think, mainly about declining interest in the support of science. Few in Congress understood what modern high-energy accelerators are for. They are not for weapons. They have no practical applications. They are for something that is, worrisomely from the point of view of many, called “the theory of everything.” Explanations that involve entities called quarks, charm, flavor, color, etc., sound as if physicists are being cute. The whole thing has an aura, in the view of at least some Congresspeople I’ve talked to, of “nerds gone wild” — which I suppose is an uncharitable way of describing curiosity-based science. No one asked to pay for this had the foggiest idea of what a Higgs boson is. I’ve read some of the material intended to justify the SSC. At the very end, some of it wasn’t too bad, but there was nothing that really addressed what the project was about on a level accessible to bright but skeptical non-physicists. If physicists are asking for 10 or 15 billion dollars to build a machine that has no practical value, at the very least they should make an extremely serious effort, with dazzling graphics, metaphors, and capable use of the English language, to justify their proposal. More than financial mismanagement, budgetary constraints, and political incompetence, I think this is the key to the failure of the SSC.
CASE 6: Same topic, different genres
Rowan (she/her) was simultaneously enrolled in a university writing course and working as a co-op student at the New Minas Boat Manufacturing plant. As part of her co-op work experience, Rowan shadowed her supervisor/mentor on a safety inspection of the plant, and was asked to write up the results of the inspection in a compliance memo . In the same week, Rowan’s writing instructor assigned the class to write a narrative essay based on some personal experience. Rowan, trying to be efficient, thought that the plant visit experience could provide the basis for her essay assignment as well.
She wrote the essay first because she was used to writing essays and was pretty good at it. She had never even seen a compliance memo, much less written one, so was not as confident about that task. She began the essay like this:
On June 1, 2018, I conducted a safety audit of the New Minas Boat Manufacturing plant. The purpose of the audit was to ensure that all processes and activities in the plant adhere to safety and handling rules and policies outlined in the Workplace Safety Handbook and relevant government regulations. I was escorted on a 3-hour tour of the facility by…
Rowan finished the essay and submitted it to her writing instructor. She then revised the essay slightly, keeping the introduction the same, and submitted it to her co-op supervisor. She “aced” the essay, getting an A grade, but her co-op supervisor told her that the report was unacceptable and would have to be rewritten – especially the beginning, which should have clearly indicated whether or not the plant was in compliance with safety regulations. Rowan was aghast! She had never heard of putting the “conclusion” at the beginning . She missed the company softball game that Saturday so she could rewrite the report to the satisfaction of her supervisor.
Meier, C. (2017, January 14). The Exorbitant Cost of Poor Writing (About $400 Billion). Medium . https://medium.com/@MeierMarketing/the-exorbitant-cost-of-poor-writing-about-400-billion-973b5a4f0096
Sagan, C. (1995). The Demon-Haunted World: Science as a Candle in the Dark. Random House.
Exercises adapted from T.M Georges’ Analytical Writing for Science and Technology. T.M. Goerges (1996), Analytical Writing for Science and Technology [Online], Available: https://www.scribd.com/document/96822930/Analytical-Writing
1.10 Case Studies: The Cost of Poor Communication Copyright © 2021 by Suzan Last is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Internal communication
- Business management
- Corporate communications
- Crisis communication
- Public relations

How to Avoid the Churn That Comes with Agility
- Ron Ashkenas
- September 20, 2023

5 Reasons Your Employees Don’t Understand Your Company’s Vision
- Sabina Nawaz
- September 07, 2021

3 Ways to Clearly Communicate Your Company’s Strategy
- Constantinos C. Markides
- Andrew McLennan
- May 24, 2024

The New Science of Building Great Teams
- Alex "Sandy" Pentland
- From the April 2012 Issue

The Challenges of Becoming a Less Hierarchical Company
- Eric M. Anicich
- Michael Y. Lee
- Juan Pablo Sánchez Celi
- March 21, 2024

The Science of Strong Business Writing
- Bill Birchard
- From the July–August 2021 Issue
Better Risk Communication
- Ndubuisi Ekekwe
- May 11, 2011

When Discussing Uncertainty, Highlight Opportunities for Your Employees
- David Lancefield
- December 12, 2023

Change Is Hard. Here's How to Make It Less Painful.
- Erika Andersen
- April 07, 2022

The Two Biggest Communication Blunders During a Reorg
- Stephen Heidari-Robinson
- Suzanne Heywood
- October 20, 2016
New Study: How Communication Drives Performance
- John Baldoni
- November 19, 2009

Create a Culture of Generosity and Communication in Your Family Business
- Christina R. Wing
- Rohit K Gera
- May 18, 2020

What Demographics Forms Say About Inclusivity at Your Company
- Devon Proudfoot
- March 27, 2024

Preparing to Announce Layoffs in a Virtual Meeting
- Kathryn Janicek
- January 26, 2023

Need a Favor? Research Suggests It's Best to Ask In Person.
- Mahdi Roghanizad
- Vanessa Bohns
- December 20, 2021
Eight Communication Traps That Foil Innovation
- Georgia Everse
- January 12, 2011

Why Leadership Teams Fail
- Thomas Keil
- Marianna Zangrillo
- From the September–October 2024 Issue

GenAI Could Make Online Conversations More Civil
- March 20, 2024

Reducing Information Overload in Your Organization
- Dorian Cundick
- May 01, 2023
How to Communicate Clearly During Organizational Change
- Elsbeth Johnson
- June 13, 2017

Geosoft Inc.: Leading Across Cultures
- Darren Meister
- Chitra P. Reddin
- May 04, 2017
Dovercourt Recreation Centre - Healing a Rift
- August 12, 2014

The Change Management Collection: Lead a Successful Change Initiative Inside Your Organization
- Harvard Business Review
- April 02, 2024
DBS: Transforming the Culture of an Asian Bank
- May 17, 2014
McGregor's Ltd. Department Store
- Thomas J.C. Raymond
- Alison Eadie
- November 01, 1978

Virtual EI (HBR Emotional Intelligence Series)
- Amy C. Edmondson
- Mark Mortensen
- Heidi K. Gardner
- Amanda Sinclair
- April 26, 2022
UAE Exchange: The RACE to Positive Organizational Change
- Wayne Baker
- Thomas Joseph
- Raina Chhajer
- April 12, 2018

HBR Guide to Better Business Writing
- Bryan A. Garner
- January 29, 2013
Anti-LGBT2Q+ University Values: Should an Innovative Experiential Exercise be Cancelled?
- Benjamin Bigio
- Jana Seijts
- September 06, 2022
Navigating SheaMoisture through a Racial Awakening: Cara Sabin's Authentic Leadership
- Stephanie Robertson
- Jeremy Petranka
- July 26, 2022
Infection Control at Massachusetts General Hospital (Abridged)
- Robert S. Huckman
- Nikolaos Trichakis
- August 30, 2017
Gemini Edibles and Fats India: In Pursuit of Growth
- Ira Acharya
- January 26, 2018
Popular Topics
Partner center.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Weak communication and misunderstandings during virtual meetings can give way to resentment and rifts when the cameras turn off. Research by Leslie Perlow probes the nuances of digital communication. ... who tackles tricky scenarios in a series of case studies and offers his advice from the field.
In fact, a recent estimate claims that the cost in the U.S. alone are close to $4 billion annually! [1] Poorly-worded or inefficient emails, careless reading or listening to instructions, documents that go unread due to poor design, hastily presenting inaccurate information, sloppy proofreading — all of these examples result in inevitable costs.
An internal communication case study examines how a company addressed a specific problem facing their organization, or achieved a specific goal. Communication is crucial for every business, and communication challenges can manifest in all kinds of situations. An effective internal communication case study will clearly outline the problem ...
Case studies help attract attention to your products, b. We've put together 15 real-life case study examples to inspire you. ... The use of dynamic fields and filters when importing lists ensured prospects received the right information, while communication with existing fans became faster with automation.
Internal communication case study examples show time after time that leadership visibility is an essential element, especially when communicating change. Verdict: Failure. Rule 7: There is no silver bullet. We'd love to be able to reveal the secret to implementing that perfect internal communication strategy.
Weak communication and misunderstandings during virtual meetings can give way to resentment and rifts when the cameras turn off. Research by Leslie Perlow probes the nuances of digital communication. She offers advice for improving remote teamwork. ... The Cold Call podcast celebrate its five-year anniversary with a classic case study. Harvard ...
Five communications lessons from the biggest corporate turnaround. ... This three-part case-study illustrates key concepts and lessons about leading adaptive change in organizations in the context ...
An internal communication case study looks at the way a company has handled a specific problem or achieved a specific outcome or goal so that people reading it can use it to guide their own approach to solving similar problems. Workplace case study examples for communication should:
Even without managers' regular engagement in problem-solving, communication about its importance can promote more problem-solving among frontline workers. By explaining some of the variation in responsiveness to operational failures, this study empowers managers to adjust their approach to stimulate more problem-solving among frontline workers.
Crisis Communication for a Public Employee Retirement System. This case study explores the creation of a crisis communication plan and how it was used to handle a delicate situation regarding changes to an employee retirement fund. It involves strategic use of public relations, content creation, teamwork, and more.
According to the study, "effective internal communications can keep employees engaged in the business and help companies retain key talent, provide consistent value to customers, and deliver superior financial performance to shareholders" to the tune of a "47% higher return to shareholders over a five-year period (mid-2004 to mid-2009).".
A Case Study of Domino's Pizza's Crisis Communication Strategies. Abstract. Domino's Pizza was embroiled in a viral crisis situation when two rogue employees posted videos of adulterated food on YouTube in April 2009. Tim McIntyre, Vice President of Communications, was part of the internal team that delivered the company's crisis ...
accompanying case study teaching plans addressing issues in intercultural and organizational communication and conflict resolution. Case studies are interactive and engaging ways to approach analysis of real world interpersonal and intercultural conflicts. While factual knowledge of theories and concepts is essential in learning about ...
Welcome to the MIC Case Studies page. Here you will find more than fifty different case studies, developed by our former participants from the Master of Advanced Studies in Intercultural Communication. The richness of this material is that it contains real-life experiences in intercultural communication problems in various settings, such as war, family, negotiations, inter-religious conflicts ...
Communication Case Study. Rashmi Menon; 5.00. View Details. This case is part of a series of four integrated cases about The Empowerment Plan (TEP), a Detroit-based nonprofit that worked to break ...
Case studies can be a useful pedagogical tool to illustrate complex organizational situations and how organizational communication concepts can be applied to them (Alvarez et al., 2015; May, 2017). However, the narrative nature of case studies can make it difficult for students to identify the course concept(s) that the case aims to illustrate.
Communication Case Study. June A. West; Jenny Craddock; 11.95. View Details. In October 2016, Timothy Sloan, the newly appointed CEO of American banking giant Wells Fargo, faced a massive public ...
Communicating with your audience is more than giving a handful of information, it is the use of clear language that is factual and logical to depict to the audience that the message is essential to their lives and their future. The biggest communication problem is we do not listen to understand. We listen to reply.
Case studies illustrate the strategies, tactics, and execution of communication campaigns through in-depth coverage of a single situation. CSSC is a peer-reviewed online publication housed at the University of Southern California's Annenberg School for Communication & Journalism. Institute for Public Relations.
In one tragic case, a lack of communication between contractors and engineers resulted in a walkway collapse that killed 114 people at the Hyatt Regency. The waste caused by imprecisely worded regulations or instructions, confusing emails, long-winded memos, ambiguously written contracts, and other examples of poor communication is not as ...
7. Slack. Slack is one of the most popular instant communication chat tools available right now, and especially after everyone had to work from home during the pandemic, we're guessing a large ...
It's been 100 years since Harvard Business School began using the case study method. Beyond teaching specific subject matter, the case study method excels in instilling meta-skills in students.
Attention During Podcast-Listening. Audio media in general are often used for multitasking (Jeong & Fishbein, Citation 2007).Where radio is really the classic background medium in many cases (see, e.g., Inthorn, Citation 2020), podcasts can play a dual role in this respect: Perks and Turner (Citation 2019) show in their study, that where on the one hand people listen to podcasts as their main ...
John Baldoni. [For more, visit the Communication Insight Center.] "Courage, innovation and discipline help drive company performance especially in tough economic times. Effective internal ...