Speech vs. presentation: What’s the difference?
- Written by: Joby Blume
- Categories: Visual communication , Industry insights
- Comments: 6

What’s the difference between a presentation and a speech? Many people use the words interchangeably, but there are two main areas of difference according to the dictionary definitions. Whether one accepts the dictionary definition is another matter – my four year-old daughter sometimes refuses – but that makes further discussion pretty difficult.
According to the Oxford English Dictionary (OED), a speech is defined as:
a formal address or discourse delivered to an audience
According to the Scrabble fan’s choice – the Collins English Dictionary – a speech is:
a talk or address delivered to an audience
Note that in the Collins definition, the part about being formal is missing.

Presentation
Both the Oxford English and Collins dictionaries define presentation as including some sort of visual element. The OED definition is:
a speech or talk in which a new product, idea, or piece of work is shown and explained to an audience
Note that this includes the word ‘shown’. The Collins definition is even clearer in explicitly mentioning the use of illustrative material:
a verbal report presented with illustrative material, such as slides, graphs, etc
The Collins Dictionary also notes how the word presentation is used more generally to talk about how things are shown – ‘ the manner of presenting, esp the organization of visual details to create an overall impression’.
Presentations and speeches
Does the distinction hold perfectly? No. Firstly, people use the terms interchangeably, so of course the real world is full of speeches that are called presentations and presentations that are called speeches. Which leads to a natural blurring of the boundaries. Second, some presentations are very formal indeed, and some set-piece speeches (e.g. The State of the Union Address ) can have visuals added to them but without the orator interacting with them.
The boundaries aren’t sharp. But, according to the definition, a speech is a talk or address, and a presentation is a talk with the use of some sort of visual aid.
Speech vs. presentation
Why does this matter? Because giving a speech – for a lot of people – seems harder than giving a presentation. Bad slides are actually worse than no slides . But the reason so many speakers want slides or props is because they find it too hard to deliver speeches, and because effective visual aids makes it easier for them to get their points across.
Effective visuals – that support a speaker – make delivering presentations easier than delivering speeches for most people. Not everyone feels they can hold an audience with simply the sound of their own voice.
Great speeches are, well… great. But they aren’t the same as presentations, and shouldn’t be held up as examples of what those giving presentations should emulate.
P.S. For more on words and definitions, see Meaning and Necessity by Saul Kripke.

Related articles
Presentation agency or marketing agency.
- Industry insights
In the agency world, it’s fair to say that PowerPoint design sits somewhere at the bottom of the pile. Working with a specialist presentation design company will generally deliver better results, with less effort, and typically at lower cost. So why do some companies still not use presentation agencies for slide design?

How to make the ULTIMATE sales presentation
- Sales presentations / Sales messaging / Visual communication
- Comments: 8
Sales presentations are the cornerstone of many companies’ sales efforts, yet so often they aren’t given the time and attention they deserve. Thrown together at the last-minute, often your sales reps stand up in front of a sales presentation that's nothing more than a glorified page of notes. Read this article for everything you need to make the ultimate sales presentation.

Choosing a presentation design agency
- PowerPoint design / Visual communication / Industry insights
- Comments: 2
Choosing a presentation design agency for your enterprise is a lot harder than buying a product. With presentation design services, you don’t know what you’re going to get until the project is nearly finished. What you get from the studio isn’t the exact same thing as what any other business ends up with. So how do you choose the right presentation design firm for your company?

This is very interesting. I do appreciate it.
well… i found this information very useful,,,, thanks
This has helped me with my assignment thanks a lot
It is useful information it helps me doing anassignment.thanks
Deference between speech and presentation
Speech Vs Presentation Vs Debate Compitation? Speech: Speech Eleborate In Your Ideas That You Have Crammed(Ratafication). Presetation:To Suggest Anything Infront Of All Student By Using Your Slides Its Own Way That You Have Worked For Project. Debate Compitation:To Disscuss Your Ideas With One Another..
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
Join the BrightCarbon mailing list for monthly invites and resources
Thank you for today’s PowerPoint productivity masterclass. I’ve learned so much from BrightCarbon when it comes to PowerPoint. If there isn’t a BrightCarbon fan club already, I’ll be happy to start one! Kimm Babo Wegmans Food Markets

Oratory Club
Public Speaking Helpline
Speech Vs Presentation: Get The Main Difference In 2023
In the world of communication, there are different ways we express ourselves: through speeches and presentations. But wait, what’s the difference between a speech and a presentation? Let’s break it down!
Imagine you’re standing in front of an audience, sharing your thoughts and ideas. That’s a speech! It’s like having a conversation with a large group of people, where you have the stage all to yourself.
On the other hand, a presentation is like a visual aid that accompanies your speech. It can include slides, videos, and other multimedia elements that help to enhance your message and make it more engaging. So, while a speech relies mainly on your words, a presentation adds that extra visual element.
Now that we know the basics, let’s dive deeper into the world of speeches and presentations and uncover their unique features and purposes. Get ready to conquer the stage and captivate any audience with your powerful words and eye-catching visuals!
Looking to communicate effectively? While both speech and presentation are forms of conveying information, they differ in style and purpose.
- Speech: Typically delivered orally with a focus on storytelling and engaging the audience.
- Presentation: Visual aids such as slideshows accompany the speaker’s message to enhance understanding.
- Speech emphasizes the spoken word, while presentations provide a visual component.
- Speeches often involve more improvisation, while presentations are carefully planned and structured.
- Ultimately, the choice between speech and presentation depends on the context and desired impact on the audience.

Table of Contents
Principales puntos clave
1. Una presentación es cuando muestras visualmente información mientras hablas, mientras que un discurso se enfoca principalmente en transmitir información verbalmente. 2. Las presentaciones pueden incluir diapositivas, gráficos o videos, mientras que los discursos se basan principalmente en el habla. 3. En una presentación, el objetivo es captar la atención del público de manera visual, mientras que en un discurso, el objetivo es transmitir el mensaje de manera clara y persuasiva. 4. En una presentación, las habilidades de diseño gráfico y el uso efectivo de multimedia son importantes, mientras que en un discurso, las habilidades de oratoria y la organización del contenido son fundamentales. 5. Tanto las presentaciones como los discursos requieren práctica y preparación, pero el enfoque principal de cada uno es diferente: visual para las presentaciones y verbal para los discursos.
Comparing Speech vs. Presentation
Speech and presentation are two different methods of communication that serve distinct purposes and have their own unique characteristics. While both involve conveying information to an audience, they differ in terms of format, delivery, and overall objectives. In this article, we will compare speech and presentation, exploring their key features, user experience, pros and cons, price points, and ultimately determine which is better suited for different situations.
Overview of Speech
Speech, in its simplest form, is the act of delivering a spoken message to an audience. It is typically performed by a speaker using their voice, body language, and gestures to convey their ideas and connect with the listeners. Whether it’s a formal address, an inspirational talk, or a persuasive argument, speeches are designed to engage, inform, entertain, and influence.
In a speech, the focus is primarily on the speaker’s delivery and their ability to captivate the audience. The content of the speech is often carefully crafted, incorporating rhetorical devices, storytelling techniques, and persuasive elements to create an impactful message. Public speaking skills, such as voice modulation, articulation, and stage presence, are essential for delivering a compelling speech.
Overview of Presentation
A presentation, on the other hand, is a visual and auditory communication tool used to convey information in a structured and visually appealing format. It typically involves the use of slides, graphics, videos, and other multimedia elements to support the speaker’s message. Presentations can be created using software like Microsoft PowerPoint or Apple Keynote, allowing the presenter to showcase data, visuals, and key points in a streamlined manner.
The emphasis in a presentation lies not only on the speaker’s delivery but also on the visual aids and supporting materials used. Presentations often follow a clear structure, with an introduction, main body, and conclusion, allowing the audience to easily follow the flow of information. The visual elements in a presentation can enhance understanding, clarify complex topics, and make the content more engaging for the audience.
Key Features Compared
Speech and presentation have distinct features that set them apart in terms of their format, delivery, and overall impact. Let’s explore these key features and compare the two:
Speech: A speech is primarily an oral presentation delivered by a speaker, relying on their voice, body language, and facial expressions to convey the message. The content of a speech is usually written down and rehearsed, but the delivery can be more spontaneous and interactive.
Presentation: A presentation is a visual and auditory communication tool that incorporates slides, visuals, and multimedia elements to support the speaker’s message. The content of a presentation is organized into a structured format, often using software programs, and relies on both the speaker’s delivery and the visual aids.
Speech: The delivery of a speech is focused on the speaker’s voice, tone, and overall stage presence. The speaker’s ability to connect with the audience through their delivery plays a crucial role in the impact of the speech. However, there is often less emphasis on the visual aspects of the presentation.
Presentation: In a presentation, the delivery encompasses both the speaker’s verbal communication and their ability to effectively utilize visual aids and technology. The presenter must synchronize their speech with the slides, ensuring a cohesive and engaging delivery that incorporates the visual elements.
Speech: The primary objective of a speech is often to inform, persuade, or inspire the audience. Whether it’s a motivational speech, an educational lecture, or a persuasive argument, the goal is to captivate the listeners and convey a compelling message.
Presentation: Presentations are commonly used for informative purposes, such as sharing research findings, giving product demonstrations, or delivering business proposals. The objective is to present information in a visually appealing and organized manner that enhances audience understanding.
Visual Elements
Presentations typically include various visual elements that enhance the delivery and understanding of information. These elements can include:
– Slides: Slides are the backbone of a presentation, containing text, images, charts, graphs, and other visual representations of information. They provide a structure and guide the presenter and audience through the content.
– Multimedia: Presentations often incorporate multimedia elements, such as videos and audio clips, to add variety and enhance engagement. These elements can help illustrate concepts, provide real-life examples, or showcase product demonstrations.
– Animations: Animations and transitions can be used to add visual interest and create seamless transitions between slides or elements within a slide. When used effectively, they can enhance the overall flow and engagement of the presentation.
– Graphics and Icons: Visual elements like icons, illustrations, and infographics can simplify complex information, making it more accessible and visually appealing to the audience.
Interactivity
Speech: Speeches can often involve a level of interactivity with the audience, depending on the style and purpose of the speech. This can include engaging in a question-and-answer session, encouraging audience participation, or incorporating interactive activities.
Presentation: Interactivity in presentations can vary depending on the delivery method and audience. In some cases, presentations may include interactive elements, such as polls, quizzes, or audience participation through live feedback systems. However, presentations are generally more structured and less interactive compared to speeches.
User Experience
Speech: The user experience of a speech largely depends on the speaker’s ability to deliver a captivating message and engage the audience. A successful speech should leave the audience feeling inspired, informed, or moved by the speaker’s words.
Presentation: The user experience of a presentation is influenced by the visual appeal, organization, and clarity of the content. Well-crafted presentations that effectively convey information and engage the audience can leave a positive impression and enhance the overall user experience.
Pros and Cons
Pros: – Powerful delivery: A well-delivered speech has the potential to captivate and move the audience through the speaker’s voice, gestures, and stage presence. – Personal connection: A speech allows the speaker to establish a personal connection with the audience, as they can see and hear the speaker in real-time. – Flexibility: Speeches can be tailored to different audiences and occasions, allowing for adaptability and customization.
Cons: – Limited visual aids: Speeches rely primarily on the speaker’s delivery and the power of their words, which may limit the use of visuals and multimedia elements. – Less structured format: Speeches can be more spontaneous and less rigid in terms of structure, which can sometimes lead to less clarity or organization in the content. – Lack of visual appeal: As speeches focus on the spoken word, they may not offer the same level of visual appeal or engagement as presentations.
Presentation
Pros: – Visual impact: Presentations leverage visual elements to enhance the delivery of information, making it more engaging and memorable for the audience. – Clarity and organization: Presentations often follow a structured format, making it easier for the audience to follow the flow of information and understand complex concepts. – Multimedia integration: Presentations allow for the seamless integration of multimedia elements, such as videos, charts, and images, which can enhance audience understanding.
Cons: – Dependency on technology: Presentations rely heavily on technology and visual aids, which can be subject to technical glitches or equipment failures. – Potential for information overload: If a presentation is poorly designed or overloaded with information, it can overwhelm the audience and make the content difficult to absorb. – Less personal connection: Compared to speeches, presentations may have a less personal and intimate connection with the audience, as they primarily focus on the visual and auditory aspects of communication.
Price Comparison
When it comes to the cost of implementing speech and presentations, several factors come into play. Here are some considerations for price comparison:
– Software: The cost of presentation software can vary depending on the provider and the specific features included in the package. Popular presentation software options include Microsoft PowerPoint, Apple Keynote, and Google Slides. – Equipment: To deliver a presentation or speech effectively, certain equipment may be required, such as a laptop, projector, microphone, and speakers. The cost of these equipment items can range depending on the brand, quality, and features. – Professional services: If you require assistance with presentation creation, design, or speechwriting, you may need to consider the cost of hiring professionals or consultants who specialize in these areas.
It’s important to note that the cost comparison will vary depending on individual needs, preferences, and the scale of the presentation or speech. It’s advisable to research and consider different options to determine the most cost-effective solution for your specific requirements.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Speech | Presentation | |——————–|—————————–|————————| | Visual Elements | Limited visuals | Multimedia integration | | Delivery | Focus on speaker | Speaker and visuals | | Interactivity | Potential for Q&A | Level of interactivity | | User Experience | Impactful delivery | Visual appeal | | Pros and Cons | Pros and cons of speech | Pros and cons of presentation | | Price Points | Cost considerations for speech | Cost considerations for presentation |
Which is Better – Speech or Presentation?
When deciding whether a speech or presentation is better suited for a particular situation, several factors need to be considered, including the objectives, audience, and context. Here are three reasons why one might be preferred over the other:
1. Information delivery: If the primary goal is to convey a message in a highly personalized and engaging manner, a speech may be the better choice. A well-delivered speech can establish a strong emotional connection with the audience and leave a lasting impact.
2. Visual impact: If the content to be presented relies on visual aids, such as data, graphics, or multimedia elements, a presentation would be more suitable. Presentations allow for the seamless integration of visuals, enhancing the audience’s understanding and engagement with the information.
3. Structure and organization: If the content needs to be presented in a clear and organized manner, with a predefined structure and flow, a presentation is the better option. The structured format of a presentation ensures that information is presented in a logical and digestible manner, making it easier for the audience to follow and comprehend.
Ultimately, the choice between a speech and a presentation depends on the specific objectives, audience, and context of the communication. Both methods have their strengths and can be highly effective when used appropriately. It is essential to consider the key features, pros, and cons of each to determine the best approach for your specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are you confused about the differences between a speech and a presentation? Don’t worry, we’ve got you covered! Check out these commonly asked questions to gain a better understanding of speech versus presentation.
1. What is the main difference between a speech and a presentation?
A speech and a presentation are both forms of communication, but they differ in their intent and delivery style. A speech is typically a verbal address given by one person, often without visual aids, and is more focused on delivering a message or conveying emotions. On the other hand, a presentation combines speech with visual aids, such as slides or graphics, and is more concerned with sharing information or persuading an audience.
Think of a speech as a heartfelt talk meant to inspire or motivate, while a presentation is a more structured and informative way to convey facts or ideas.
2. When should I use a speech and when should I use a presentation?
The choice between using a speech or a presentation depends on your purpose and audience. Use a speech when you want to connect on a deeper emotional level, such as during a graduation ceremony or a motivational event. The lack of visual aids allows for a stronger emphasis on your words and delivery style.
On the other hand, use a presentation when you need to present information in a clear and organized manner. This is useful in educational settings, business meetings, or conferences where you want to enhance audience understanding using visual aids and slides. Additionally, a presentation can be helpful when you need to convince or persuade others by illustrating key points with supporting visuals.
3. How should I prepare for a speech?
To prepare for a speech, start by identifying your main message and purpose. Think about the emotions you want to convey and the impact you want to make on your audience. Craft a clear and concise outline, organizing your speech into an introduction, body, and conclusion.
Practice delivering your speech aloud, paying attention to your tone, pacing, and body language. Use personal stories or anecdotes to engage and connect with your audience. It can also be helpful to rehearse in front of a mirror or record yourself to identify areas for improvement and build confidence in your delivery.
4. How should I prepare for a presentation?
To prepare for a presentation, start by clarifying your main objective and identifying the key points you want to convey. Create visually appealing slides that support your message, using clear and concise text, relevant images, and graphs or charts if necessary.
Practice your presentation multiple times to ensure a smooth and confident delivery. Pay attention to your tone of voice, body language, and eye contact with the audience. Familiarize yourself with the technology or equipment you will be using, such as a projector or microphone, to avoid any technical difficulties during your presentation.
5. How can I engage my audience during a speech or presentation?
To engage your audience during a speech or presentation, consider using storytelling techniques to make your content relatable and memorable. Incorporate interactive elements, such as asking questions or encouraging audience participation, to create a sense of involvement.
Additionally, maintain eye contact with your audience, vary your vocal tone and gestures to keep their attention, and use visual aids effectively to support your message. Encouraging questions or discussion after your speech or presentation also allows for further engagement and interaction with your audience.

Differences between a speech and a presentation (With examples)
In a nutshell, speeches and presentations both involve talking to an audience, but there are some key differences between them. A speech is typically longer and more formal, like the kind you might give at a special event or ceremony. Presentations, on the other hand, are shorter and often involve visual aids like slides or props. They are usually given in a business or educational setting.
When giving a speech, it’s important to use clear and concise language, as well as to connect with the audience on an emotional level. This helps to capture their attention and make your message memorable. In contrast, presentations rely on visual elements to support the information being shared. This can include graphs, pictures, or even videos. These visual aids help to make complex ideas easier to understand.
Remember, whether you’re giving a speech or a presentation, practice is key. The more you rehearse, the more confident and comfortable you’ll feel in front of an audience. Don’t forget to maintain eye contact, speak clearly, and engage with your listeners. By following these tips, you’ll be well on your way to becoming a confident and effective speaker or presenter.
Similar Posts

How to Present a Digital Poster Presentation?
To present a digital poster presentation, use a visually engaging layout and concise text to convey key information effectively. Give attention to design elements, such as font choice and color schemes, that complement the content and enhance its readability. Remember to use clear visuals and graphics, as well as limited text, to keep the audience…
Types of Presentation You Need to Know
Presentations come in various forms, each tailored to suit different purposes, audiences, and content. Here are some common types of presentations: Each type of presentation requires a tailored approach in terms of content, structure, and delivery to effectively achieve its goals and engage the intended audience. More Details of the Types of Presentations The above…

How to Own The Stage in Presentation?
To own the stage in a presentation, maintain a confident presence, engage the audience through storytelling, and deliver a clear message with enthusiasm. A powerful and engaging presentation captures the attention and interest of the audience, leaving a lasting impression. By mastering the art of stage presence and incorporating effective communication techniques, you can create…
What is the Difference between PPT And Slides?
Ppt and Slides are the same thing; they are different file extensions used by Microsoft PowerPoint for saving presentations. In today’s digital age, presentations play a crucial role in various sectors such as education, business, and marketing. PowerPoint, a popular presentation software, offers different formats for saving presentations, including Ppt and Slides. Ppt and Slides…

Things to Carry in A Presentation
For a successful presentation, it is crucial to carry essential items such as slides, notes, a laptop, a clicker, and handouts. A well-prepared presenter will have all the necessary materials readily available to deliver an engaging and informative presentation. Delivering a successful presentation requires careful preparation, and part of that preparation involves knowing what essential…

How to Make a Conference Presentation Fun?
To make a conference presentation fun, use interactive elements like icebreakers, video clips, non-linear structure, Q&A sessions, interactive quizzes, props, storytelling, audio narration, polls, discussion questions, audience movement, hashtags for social interaction, music, and transitions. Additionally, you can make your PowerPoint presentation more interesting by adding context, using the translation technique, shifting perspectives, and joining…
The Differences Between Speech and Presentation You May Not Know

Have you ever thought about the difference between speech and presentation? It might seem like those things look the same, but you should understand the huge differences between them. And once you know it, you will excel at both of them.
Many people still seem to confuse those two things and use the words interchangeably without knowing they are different. So, for example, we checked the meaning of those words in the Merriam-Webster dictionary and discovered two different meanings.
While speech is described as “a formal talk that a person gives to an audience,” a presentation is “a meeting at which something, especially a new product or idea, or piece of work, is shown to a group of people.”
From the definition alone, you can see that one says ‘talk’ and the other says ‘shown.’ But what’s the meaning of those words? To make things clearer, here are the differences between speech and presentation.
Memorizing the material
The first difference between speech and presentation is the way you present the information. Even though they look the same, you indeed feel the differences between speech and presentation by your own experience.
Let’s start with the most subtle difference between speech and presentation: how we present the material based on what we memorize. We tend to make everything so clear to the audience during presentations, which requires a lot of memorization.
The same thing may apply during speeches, but because speeches are not made to tell every single detail of the thing that you want to explain, you might not need to memorize every detail in the fabric.
Fact is, you may even expand your topic during speeches, but not in presentation. So, for example, during your speech on the importance of trees, you may expand to include what’s happening to our environment.
However, if you talk about a specific topic during a presentation, you may want to put further details in it instead of expanding the topic. So, during a presentation, you may memorize more details.
While in speeches, you may memorize the related topics that can support your point. In this case, we may talk about the second difference between those things. In this case, we may speak of the second difference between those things.
Visual aids
There is a reason why both of them use visual aids, and we will show you the difference between each use. The first is about speech. During a lesson, as mentioned above, you need to master your topic to the rate that you can expand it further.
What’s the connection between that and visual aids? Speeches mainly use visual aids to help themselves remember the points they want to talk about. While in presentation, the use of visual aids is to help the audiences understand.
In this case, we can expand the difference between the two. While in speeches, the visual aid design is not that important, the design in presentation is highly regarded. Not all lessons use visual aids because of that reason.
However, it doesn’t mean that visual aids are not crucial in speeches. One of the examples is a video or picture to tell the audience about a story. It surely will help the audience understand what you are talking about.
But in presentation, frequently, your visual aids alone can help the audiences understand what you are talking about. This is why your visual aids, such as PowerPoint presentations, need to be as clear as possible and as attractive as possible.
How visual aids help us in both speeches and presentations is intended to make the following difference clearer. And the next difference is how you share your vision about the topic you are delivering to the audience.
Sharing your vision
Have you ever seen a debate competition? In that competition, you might not see someone presenting their arguments with a well-designed PowerPoint presentation slide. Instead, they speak in front of the adjudicators and the audience with a small paper as a note.
We are not talking about the visual aids here, but we may look at the speaker’s notes. There, they mostly write only about the points that they want to deliver. But what’s the difference between the notes and the presentation handouts that we bring?
In presentation handouts, we also write notes, but our messages are primarily about what the speaker wants to highlight. However, the notes in a debate are about things they want to convince the audience.
Yes, the difference comes from how we speak about the topic in front of the audience. A speaker in speeches wants to convince the audience about their view or stance. They want to spread their vision about things.
While a presenter might not care much about their vision, speakers usually include the advantages, disadvantages, resolutions, plans, or generally accepted things. For example, take a look at how salesmen or saleswomen in their sales.
The ones who do speeches would tell inspiring, motivating, or heartwarming things to sell their products. While the ones presenting their sales would focus more on the advantages, disadvantages, or their products’ unique features.
Preparation time between speech and presentation
This one difference is exciting and a little bit controversial. Why? Because what we want to tell you might shake your view about the differences between those two. What is it? It is about how you prepare for the upcoming speech/presentation.
Supported by Art of Presentation, it says that presenting is a well-prepared action. So it would help if you worked very well in preparing the things you want to deliver to the audience to make sure you can give as well as possible.
You might need to fact-check everything, create PowerPoint presentation slides , getting things correlated with one another. You might also at least practice how you will present to make sure you will nail the presentation.
But with speeches, you may not need to practice anything or prepare for the things you want to deliver. It is because speeches are more like art than just telling people about things. See how we differentiate an excellent orator from a bad one?
Good orators may talk about things as they will, and people will still get their point. However, some good people may not even prepare anything except their own story created spontaneously in the venue.
The difference in stories to deliver between speech and presentation
From the distinction above, you might be able to guess what’s the following difference. While speeches are more about the speaker’s creativity, preservations are more about how you process information and deliver almost the same thing in a descriptive way.
A good orator needs to have a million ways to deliver the information to the audience. On the other hand, a good presenter needs to find the best descriptive way to show the presentation without getting their stories out of context.
You can train yourself into a good orator by collecting exciting stories and experiences to tell your future audiences. This way, you can show a million stories based on things you have collected in your speeches and get the audience to understand your points.
On the other hand, you can train yourself into a good presenter by trial and error in presenting. Then, later on, you can choose the best descriptive way to make them get your points and always use that in your future presentations to get the same result.
That is because your presentation is helped a lot by the visual aids we mentioned above. In addition, you can always correlate your presentation with visual aids.
Detailed information versus convincing words
If you are presenting something, you will primarily use more accurate data. And when someday you are giving a speech to other people, you mostly will tell them stories you created or experienced.
Again, the way we speak in a presentation is different from how we say in a speech. We don’t need to make things too strict in a lesson, but we need to be as professional as possible during a presentation.
But looking deeper into the reasons, we have different ‘languages’ in delivering those things. For example, while presenting something, we tend to give detailed information without trying to make up words or explanations.
Things are different with speeches when we can be as creative in our stories as possible. In this case, our words do not need to be very detailed. The reason for that is because our primary mission is to convince the audiences no matter what.
Now, can you imagine a huge gap between presenting descriptively with detailed information about the thing you want to talk about and how to make a convincing story no matter what? Yes, that huge gap is going to tell you the difference between speech and presentation.
Those are the differences we can easily spot between speech and presentation. We hope it will help you understand what you want to do next before doing any of those things.
Author bio:
This article is written by Ulfah, an SEO & Content Manager, and is currently working for RRGraph Design. Say hello through her LinkedIn .

At SlideBazaar, we help you create engaging and memorable presentations. Choose from our collection of professional templates or opt for our custom design services for a personalized touch. Your presentations deserve to be elevated to new heights, and we’re here to help you achieve just that!
BROWSE BY CATEGORY
- PowerPoint Templates
- Keynote Presentations
- Infographic
- Free slides
QUICK LINKS
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- DMCA Policy
EMAIL NEWSLETTER
Get updates of our PowerPoint templates and slide designs before anyone else.

9 Differences between Presentation and Public Speaking?
By: Author Shrot Katewa

People often confuse presentation with public speaking. After all, both require you to speak in front of an audience. But, there are subtle and important differences between a presentation and public speaking. It is better to understand this difference so that we can prepare accordingly and get the best results!
So, in this article, I will be sharing with you a few key differences between a presentation and public speaking. So, let’s get started!
1. Communication Format
Traditionally, Public Speaking is giving a speech face to face to a live audience. It comprises various forms of spoken communication skills ranging from imparting a speech or debate to motivational speaking to storytelling to Ted talks to entertaining such as a standup comedian.
However, with technological advancements, such as video conferencing, the concept evolved. In modern times, public speaking can be defined as any form of speaking between the speaker and the audience.
On the other hand, a presentation comprises spoken and visual communication. It may be a slide show or an audiovisual presentation. The topic is presented not only verbally but also by displaying content in writing supported with charts, tables, images, or text.
2. Skills Required

Public speaking is the act of presenting a topic verbally. It is often used as a medium to transfer information, but most importantly, to motivate and encourage the audience.
That said, the only input that goes into public speaking is the speaker, his or her verbal talent and style of communication, all elements displayed collectively as a package.
Whereas presentation requires the presenter to combine verbal and written content and to work with visual presentation programs such as Microsoft power point or Google slides.
3. Time for Preparation
Public speaking is more of an art than just a skill. While you are expected to do a good job when you have time at hand, but a good orator is the one who has the skills to resonate with the audience even when he or she is put on the spot!
At times public speaking may be spontaneous such as extempore. Extempore is a speech that is delivered without preparation. The speaker is given a topic on the spot and is given a minute or two to prepare on the same.
Compared with this presentation is a prepared act. Before the presentation, the presenter is ready with all the required information and facts intertwined in a pre-defined sequence. More often than not, a presentation is on a specific topic and the presenter is given ample amount of time for preparation.
4. Creativity Index
Public speaking is an art that is creative. It may be formal or informal in nature. The style of delivery of every individual is different from others. Every speaker possesses few unique qualities and has complete freedom to design his or her communication style.
Presentation is usually a formal offering. It is a form or act that has to be delivered according to certain pre-set instructions and guidelines. The presenter has limited scope and freedom to divert and add creativity to the presentation. For instance, the most common scope of limitation is the amount of time available to deliver a presentation.
5. Purpose of the Speaker

One of the forms of public speaking is debate. In a debate, every participant speaks either in favor or against the topic. The participant has to convince the audience to agree with his stance – whether right or wrong!
Most forms of public speaking work in a similar fashion. The purpose of the speaker is to convince the audience to agree with the stance of the speaker.
However, in a presentation, a topic is presented comprehensively. The topic is explained in detail highlighting various related points such as advantages, disadvantages, improvement areas, resolution plan, targets, or rewards. The primary aim of the presenter is to educate the audience on the topic, and perhaps drive a call to action.
6. Elements for Effectiveness
Effective public speaking requires the speaker to deliver so efficiently that at the end the audience stands out thrilled, amazed, and persuaded.
An impressive delivery secures more marks than intelligent content. A number of elements such as spontaneity, presence of mind, voice modulations, facial expressions, eye contact, or body language go into the making of an effective speaker. For example, in a singing reality show a participant is judged not only on the basis of his voice quality but also on the way he presents himself while singing, popularly known as the X factor.
Unlike public speaking, a presentation focuses more on content rather than on communication style. The key responsibility of the presenter is to provide the audience with detailed information on the topic covering all its aspects.
An example that may be quoted is that of an author narrating a story through a kid’s YouTube video. In the video, the author narrates the story using various voice modulations to make it entertaining for the kids and to make them feel every emotion of the characters. This case portrays the modern form of public speaking where face-to-face interaction has been eliminated.
At the same time the author presents the story using text, pictures, animations or effects in the video to make the kids visualize the characters and understand the flow of the story.
7. Size of the Audience
In public speaking, a speaker can address an audience ranging from a group of few people to a large gathering with thousands or millions of people. An interview wherein two people are in conversation with each other or a motivational speaker addressing a huge crowd may both be considered examples of public speaking.
On the other hand, a presentation is made to a defined set of people organized together in a small or mid-sized group with a limited number of members. To cite an example, students presenting a case study to the classmates or an advertising agency presenting to its prospective client.
Most large forms of presentations won’t usually exceed an audience that can fill an auditorium often limited to a few hundreds. Whereas, for public speaking, the audience can be a large gathering of thousands of people in a ground!
8. Type of Audience

Generally speaking, the type of audience present during a public speaking event is usually a group or a mass of unknown people. The speaker is neither acquainted with the audience nor related to it in any way. For instance, when a spiritual speaker addresses a group of people he is not familiar with the members of the audience.
As against it, in case of presentation the audience comprises a set of people who are familiar with the speaker. Citing the example of a business presentation, say a supervisor presenting to his team the road map to be followed to meet the annual targets, the presenter and every individual in the audience are connected to each other in professional capacity.
9. Motive of the Audience
In public speaking, the people listening to the speaker do not have a common vested interest and every individual in the audience has his own personal motive to fulfill. To elaborate, using the prior example of a spiritual speaker, it is possible that one individual may have resorted to spirituality to overcome his condition of depression and another individual may be listening to the speaker to learn how to control his anger.
Contrary to the above, in the case of a presentation, all the members participating in the presentation and the speaker have a common vested interest towards which they all intend to work collectively. Drawing from the prior example of a business presentation, the supervisor and all the team members have a common goal of achieving the annual targets.
More Related Topics
- How Much Do Public Speaking Classes Cost? A Quick Guide!
- What is the Difference Between TED and TEDx?
- Why Can’t People Give Presentations? [And How to Get Over it!]
- Toastmasters – Is it Worth it? A Comprehensive Guide!
- Does Taking Xanax Help Before a Presentation? The SURPRISING Truth!
What Is the Difference Between a Speech & a Presentation?
by Barbara Bean-Mellinger
Published on 22 Oct 2018
Many people use the words "speech" and "presentation" interchangeably since both involve speaking in front of a group. It's true that both can be dreaded for that very reason. Others note the difference is that speakers in a presentation use visual aids, while those in a speech typically don't. While that's true enough, there are many other distinct differences between the two.
Formal or Not So Formal
Don't tell the speaker giving a presentation in front of the company CEO and other bigwigs that it isn't a formal occurrence. His sweaty palms say otherwise. But, nervousness aside, presentations are given many times throughout the year in business, from sales meetings to conferences, while speeches are reserved for high profile, public events and special occasions like retirement parties and company mergers. Because of this, speeches are more formal. Not that the speaker has to wear formal attire; if only it were that simple to pull off a great speech! Also, the audience is more interested in what your presentation will show them, than they are in you and how you present. Whereas in a speech, it’s just you up there, so all eyes and ears are on you.
Emotional or Just the Facts?
If you think speeches tug at the listeners' emotions while presentations present the facts with visual backup, you're partially right. Speeches make use of anecdotes that pull you in. As you listen you may be thinking, "That's happened to me too!" Or, if the story is unique or outlandish, it leaves you feeling amazed that such a thing happened to the speaker. Stories people can relate to can help presentations, too, but they're not as critical and they can even be distracting. You're already talking and showing visuals; adding stories can seem like too much of a diversion.
Caring Versus Passion
Caring about your work always makes it better. But in a presentation, you can and should dazzle people with your visuals. They're not your backup; they're as critical to your presentation as your explanations. It's a lot like show-and-tell. Without the things to show, you'd have nothing to tell. If you make sure all the charts and graphs you show are easy to understand, your audience will get your messages. A speech, on the other hand, is just you. This is where your passion really comes through, or your lack of it turns your speech into a dud. It's important to decide what your speech's core message is, then build out from that with quotes, anecdotes and humor to convey your message in a memorable way.
Speech and Presentation and More
You may be wondering about other types of public speaking. What's the difference between a seminar and a presentation; or a speech and a lecture? How about the difference between a speech and a debate?
A seminar is different from a presentation in that it's more interactive. While a presentation is given by one person, a seminar involves the participants in some way. It could include small group discussions or a panel. Since seminars are typically several hours in length, they often have many parts that vary in structure to keep people interested.
A lecture is similar to a speech because both are rather formal and one person is doing the talking. Lectures are more often used to teach something, particularly in a college class. Since lectures are typically given during every class period, they aren't expected to be as dramatic or dynamic as a speech, though it might be more motivating if they were!
A debate differs from both a speech and a presentation because it's between two sides that are equally involved. Each side usually takes an opposing view on the debate question or subject. It's often like a contest where, at the end of it, a vote is taken to decide who won the debate.

So you’ve been asked to give a speech. Or was it “remarks”? And what’s the difference, anyway? Here at Spring Green Communications, we are experts at drafting speeches and remarks for our clients — oh, and presentations, too. Here’s what you need to know if you’re asked to deliver any of them.
Speech :
WHAT IT IS: A speech is the most formal of these three types of public speaking, and it tends to be the longest and most carefully scripted. Speeches are often given to an external audience on a planned occasion, and they frequently cover “big ideas” about which you or your company are considered experts.
TO BE SUCCESSFUL:
- Consider your audience, the venue and the occasion before you get started. Your communications team should track down answers to logistical questions in advance.
- Will there be a podium and microphone (and what kind of mic)? Will there be water available? Will the speech be livestreamed or recorded?
- What are the main points you need to hit?
- What’s your time limit? For most people, a 10-minute speech will run about 1,500 words.
- Practice. Read it aloud in a normal cadence to make sure you’re comfortable and it sounds like you.
- Will there be time for questions? If so, consider “planting” a question with an audience member to get the session started.
- Have a printout of the speech in large font, because technology sometimes fails.
Remarks :
WHAT IT IS: Remarks tend to be shorter than speeches and more informal. You may be introducing someone else, or giving or receiving an award.
- You can SOUND impromptu, but you should BE scripted and in your intended “voice.” Don’t let the informality fool you — you need to prepare in advance.
- Again, consider the venue. Will you need to climb up to a podium and back down again? Make sure the space is accessible if this will be a challenge.
- Two minutes of remarks is only about 250-300 words, so make them count.
- Consider putting your main points on a notecard in case you lose track of your thoughts — but don’t read straight from the cards!
Presentation :
WHAT IT IS: A presentation typically uses slides to make a specific point for both internal and external audiences. It can be long or short — but it gives you the opportunity to draw in (or lose) your audience visually.
- Don’t just slap your words onto a few PowerPoint slides and call it a day. We work with clients to design slides that are visually appealing but don’t allow the audience to read ahead.
- Both the words and the visuals must be scripted to fit your intended voice.
- What’s your point? Make sure you have a beginning, middle and end so your audience can follow your story.
- Will you be advancing the slide deck yourself, or will someone else be doing it on your cue? Your comms team can find this out for you. They should also work with the event organizers to download your presentation and run through it in advance at the venue.
- How big is the room? Will your slides be visible to everyone in the room? Will any video clips you want to drop in be both seen and heard?
If this sounds like a lot of work, well, we won’t lie: It is! But if you want to make a name for yourself and your company, you need to get comfortable telling your story in an intentional way in all sorts of settings and to a wide variety of audiences. We have experience with all these types of storytelling, so if you need help putting together a speech, presentation or remarks, reach out. Together, we can tell your story.
by Donna Gorman

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7

Difference Between Public Speaking And Presentation: Explained
Delve into the world of Difference Between Public Speaking and Presentation. Gain insights into the fundamental distinctions between public speaking and presentation skills. Explore the nuances of each, uncover the key differences, and highlight the surprising similarities. Discover strategies to master both public speaking and presentation skills.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Effective Communication Skills
- English Speaking Course
- Assertiveness Skills Training
- Executive Communication Training
- Interpersonal Skills Training Course

So, by gaining a deeper understanding of the Difference Between Public Speaking and Presentation, you can leverage these skills appropriately in various scenarios. But how are they different, and how can they enhance your ability to influence others? Worry no more.
Read this blog to learn about the Difference Between Public Speaking and Presentation. Also, explore the key elements and techniques that make each of these unique.
Table of contents
1) Understanding Public Speaking
2) Exploring Presentation skills
3) Public Speaking and Presentation Skills – Key differences
4) Similarities between Public Speaking and Presentations
5) How can you master Public Speaking and Presentation skills?
6) Conclusion
Understanding Public Speaking
Public Speaking is a powerful form of communication that allows individuals to deliver a message, express their thoughts and ideas, and engage with an audience. It is a skill that plays a significant role in various aspects of life, from personal relationships to professional success.
Public Speaking is the act of speaking to a group of people in a formal or informal setting to convey information, persuade, inspire, or entertain. It involves effectively delivering a message through verbal communication, utilising language, tone, and body language to captivate and engage the listeners.
Importance of Public Speaking Skills
Developing strong Public Speaking Skills is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it empowers individuals to articulate their ideas confidently and clearly. Delivering a Presentation in the workplace, speaking at a conference, or even expressing oneself in social settings, the ability to communicate effectively can greatly impact how ideas are perceived and understood.
Secondly, Public Speaking Skills are essential for professional growth and success. Many leadership positions require individuals to be able to address and inspire teams, present ideas to clients, and represent their organisations in public forums. Mastering the art of Public Speaking can significantly enhance career prospects and open doors to new opportunities.
Elements of Effective Public Speaking
To become an effective Public Speaker, several elements should be considered:
a) Clear and concise message delivery: A successful Public Speaker communicates their message clearly, ensuring the audience understands the main points and takeaways.
b) Engaging storytelling techniques: Storytelling captivates an audience and helps them connect emotionally with the speaker's message. Incorporating anecdotes, examples, and narratives can make the speech more memorable and impactful.
c) Effective use of vocal variety and body language: Public Speaking is not just about words; it’s about how they are delivered. Skilful use of the vocal variety, such as tone, pace, and emphasis, can add depth and meaning to the speech. Similarly, utilising appropriate body language, such as gestures and facial expressions, enhances the speaker’s credibility and engagement with the audience.

Exploring Presentation skills
Presentations are a common and essential form of communication in various professional and educational settings. It can be defined as a structured communication process that involves delivering information to an audience using visual communication such as slides, charts, or multimedia.
It serves as a tool to enhance understanding, engage listeners visually, and support the speaker’s message. Further, Presentations can occur in boardrooms, classrooms, conferences, or any setting where information needs to be effectively communicated.
Importance of Presentation skills
Developing strong Presentation skills is essential in today’s fast-paced and visually-oriented world. Whether in business, academia, or other professional fields, the ability to deliver compelling Presentations can make a significant impact.
Effective Presentation skills enable individuals to organise content, engage the audience, and leave a memorable impression. To deliver an impactful Presentation, several components should be considered:
a) Clear structure and organisation: A well-structured Presentation follows a logical flow, with a clear introduction, main points, and conclusion. It allows the audience to follow along easily and comprehend the key ideas being presented.
b) Engaging visual design and layout: Visual design plays a crucial role in capturing the audience's attention and conveying information effectively. Using consistent colour schemes, appropriate fonts, and visually appealing layouts can enhance the visual impact of the Presentation.
c) Effective use of multimedia elements : Integrating multimedia elements such as images, videos, or audio clips can enhance understanding and engage the audience on multiple sensory levels. These elements should be relevant, well-timed, and used sparingly to avoid overwhelming the audience.
d) Skillful delivery and timing: A successful Presentation requires effective delivery skills. This includes maintaining eye contact, speaking clearly and audibly, and utilising appropriate pacing and pauses. The timing of the Presentation should be well-managed to ensure audience engagement throughout.
Public Speaking and Presentation Skills – Key differences
While Public Speaking and Presentations are related forms of communication, they have distinct characteristics that set them apart. Understanding these differences can help individuals navigate various communication scenarios effectively. Let’s explore the key differences between Public Speaking and Presentations:
|
|
|
|
| Format | Speech delivered to an audience | Visual display of information |
| Audience interaction | Limited, mostly one-way communication | Can involve interactive discussions |
| Delivery | Verbal and non-verbal communication | Primarily visual communication |
| Purpose | Inform, persuade, entertain | Inform, educate, or demonstrate |
| Time frame | Can vary in length (short to long) | Usually time-bound (short to medium) |
| Use of visual aids | Minimal, if any | Essential for supporting information |
| Engagement | Establishing a connection with the audience | Captivating attention through visuals and delivery |
Level of interactivity
One significant Difference Between Public Speaking and Presentations lies in the level of interactivity with the audience. In Public Speaking, there is often direct engagement with the audience, allowing for questions, discussions, and active participation. The speaker may seek audience feedback, encourage dialogue, or facilitate interactive activities to foster engagement.
Presentations, on the other hand, typically have a more one-way communication style. While there might be opportunities for questions at the end, the focus is primarily on delivering the content in a structured manner. Presenters often rely on visual aids and slides to support their message, aiming to inform or educate the audience rather than actively engage them in a dialogue.
Time frame and structure
Public Speaking engagements can vary significantly in terms of duration. They can range from brief speeches delivered in a few minutes to longer keynote addresses that span an hour or more. Public Speakers have the flexibility to adapt their content and delivery style based on the time allotted and the specific needs of the audience. Learning how to improve public speaking skills can help manage this adaptability effectively.
Presentations, on the other hand, are typically more time-bound and follow a structured format. They often have a designated time limit, requiring presenters to plan and organise their content within that timeframe carefully. Presentations commonly follow a clear beginning, middle, and end, with a predefined agenda or outline to guide the flow of information.
Use of visual aids
Visual aids are crucial in Presentations, supporting the content being delivered. Presenters often rely on slides, charts, graphs, or other visual elements to enhance understanding and engage the audience visually. These visual aids serve as a complementary tool, reinforcing key points and visual representation of data or concepts.
In Public Speaking, the use of visual aids is not as prevalent. While speakers may incorporate visual elements sparingly, the focus is primarily on the verbal delivery and the speaker’s ability to captivate the audience through storytelling, rhetoric, or personal connection. Public Speakers rely more on their communication skills and the power of their words to convey their message effectively.
Emphasis on persuasion vs. information
Another Difference Between Public Speaking and Presentations lies in the emphasis on persuasion versus information. Public Speaking often aims to persuade and influence the audience. Whether it’s convincing them to adopt a certain viewpoint, take action, or change their perspective, Public Speakers utilise persuasive techniques such as rhetoric, emotional appeals, and logical arguments to sway the audience’s opinions or attitudes.
Presentations, on the other hand, primarily focus on providing information and delivering content clearly and concisely. While there may be elements of persuasion involved, such as influencing the audience’s understanding or decision-making process, the primary goal of a Presentation is to convey information accurately and effectively.
Degree of formality
Public Speaking and Presentations also differ in terms of formality. Public Speaking can encompass a wide range of settings, from formal events such as conferences or academic lectures to more informal gatherings or impromptu speeches. The level of formality may vary depending on the context and the expectations of the audience.
On the other hand, presentations tend to be more structured and formal. They often involve preparing and delivering information professionally, such as in business meetings, educational settings, or corporate Presentations. Presenters are expected to adhere to certain guidelines and standards of professionalism in their delivery.
Sign up for our Assertiveness Skills Training and start commanding respect in every conversation.
Similarities between Public Speaking and Presentations
While Public Speaking and Presentations have distinct characteristics, they also share several similarities that contribute to effective communication. Understanding these commonalities can help individuals enhance their skills in both areas. So, Let’s learn about the similarities between Public Speaking and Presentations:
Effect on the audience
Both Public Speaking and Presentations can be measured in terms of their effectiveness. In both scenarios, the speaker's ability to engage the audience, convey the intended message clearly, and leave a lasting impact are crucial factors.
Evaluating the audience's response, feedback, and level of understanding can provide insights into the effectiveness of both Public Speaking and Presentations.
Communication skills
Effective communication skills are vital in both Public Speaking and Presentations. Clear articulation, proper use of body language, tone of voice, and the ability to engage the audience are essential elements for success. Whether it's capturing the attention of the listeners during a Public Speaking engagement or delivering a compelling Presentation, honing communication skills is critical in both scenarios.
Audience size
The size of the audience can vary in both Public Speaking and Presentations. While Public Speaking often involves addressing a larger audience, such as in conferences or seminars, Presentations can range from small groups to larger gatherings. In both cases, speakers need to adapt their communication style, engage the audience, and tailor their content to meet the expectations and needs of the listeners.
Creativity window
Both Public Speaking and Presentations provide an opportunity for speakers to showcase their creativity. Whether using storytelling techniques, incorporating visual aids, or employing rhetorical devices, creativity plays a significant role in capturing the audience’s attention and conveying the message effectively. The ability to think outside the box and present ideas in an engaging and innovative manner can elevate both Public Speaking and Presentations.
The overall goal of the speaker
While the specific objectives may vary, the overall goal of the speaker remains consistent in both Public Speaking and Presentations. It is to effectively communicate a message, share knowledge, influence opinions, or inspire action. Whether it's delivering a motivational speech or presenting a business proposal, the speaker aims to engage the audience, leave an impact, and achieve the desired outcome.
Gain in-depth knowledge of communicating through interactive diagrams with our Visual Communication Training .
How to master Public Speaking and Presentation skills?
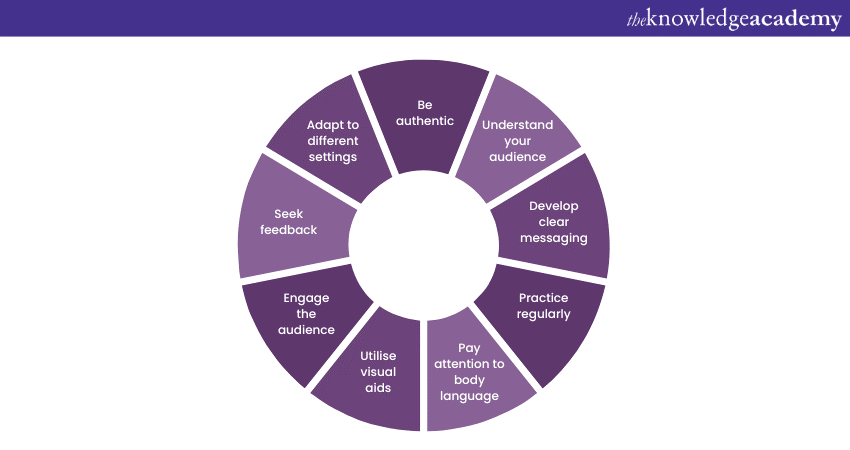
a) Research and analyse your audience to tailor your content and delivery to their interests and needs.
b) Craft concise messages that are easy to understand, avoiding jargon or complex language.
c) Rehearse your speech or Presentation multiple times to build confidence and improve delivery.
d)Use appropriate gestures, maintain eye contact, and control your vocal tone to enhance communication.
e) Incorporate visual elements such as slides or props to enhance understanding and engagement.
f) Encourage interaction, ask rhetorical questions, or use storytelling techniques to captivate the audience.
g) Be flexible in adapting your communication style to different formal or informal settings.
h) Be yourself and let your passion and enthusiasm shine through in your delivery.
Understanding why is public speaking important can further motivate and guide your efforts in mastering these skills.
Conclusion
Understanding the Difference Between Public Speaking and Presentation skills is a valuable asset that can greatly enhance your communication abilities. By understanding these differences, you can become a confident and compelling communicator, making a lasting impact on your personal and professional endeavours. Learn how to communicate effectively and become a catalyst of change with our Communication Skills Training .
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming business skills resources batches & dates.
Fri 25th Oct 2024
Fri 27th Dec 2024
Fri 28th Feb 2025
Fri 11th Apr 2025
Fri 27th Jun 2025
Fri 22nd Aug 2025
Fri 24th Oct 2025
Fri 28th Nov 2025
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest summer sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.
Speech vs. Presentation: Know the Difference
Key Differences
Comparison Chart
Primary focus, engagement style, typical context, preparation, audience interaction, speech and presentation definitions, presentation, repeatedly asked queries, what are the key elements of a presentation, how do speech and presentation differ in audience engagement, do presentations always require technology, what is a speech, is a speech always scripted, what skills are essential for an effective presentation, what settings are typical for presentations, can a speech include visual aids, what's the role of storytelling in speeches, how important is body language in a speech, how can technology enhance a presentation, what's the difference in preparation time for speeches vs. presentations, is it necessary to memorize a speech, what are common mistakes in presentations, how can nervousness be managed during a speech, how do you prepare for a speech, can anyone give a speech, how do you handle questions during a presentation, what makes a presentation successful, are there different types of presentations, share this page.

Popular Comparisons

Trending Comparisons
Featured Comparisons

New Comparisons

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What It Takes to Give a Great Presentation
- Carmine Gallo

Five tips to set yourself apart.
Never underestimate the power of great communication. It can help you land the job of your dreams, attract investors to back your idea, or elevate your stature within your organization. But while there are plenty of good speakers in the world, you can set yourself apart out by being the person who can deliver something great over and over. Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired together are more memorable); don’t underestimate the power of your voice (raise and lower it for emphasis); give your audience something extra (unexpected moments will grab their attention); rehearse (the best speakers are the best because they practice — a lot).
I was sitting across the table from a Silicon Valley CEO who had pioneered a technology that touches many of our lives — the flash memory that stores data on smartphones, digital cameras, and computers. He was a frequent guest on CNBC and had been delivering business presentations for at least 20 years before we met. And yet, the CEO wanted to sharpen his public speaking skills.
- Carmine Gallo is a Harvard University instructor, keynote speaker, and author of 10 books translated into 40 languages. Gallo is the author of The Bezos Blueprint: Communication Secrets of the World’s Greatest Salesman (St. Martin’s Press).
Partner Center

Believe It Or Not, They’re Very Similar
What do public speakers and presenters have in common? Well, in the first instance, they face the same challenges. Overcoming ‘ stage fright ,’ pitching their voice at the right level, understanding their audience, and researching content to ensure their facts are correct, are just some of the skills needed for anyone interested in public speaking or building presentations.
Overall, though, the ambitions of the two are almost identical; and so it stands to reason that the novice public speaker will benefit from attending courses originally designed with the professional presenter in mind.
Read more: 5 Pitching & Presentation Tips
What Are The Similarities?
If you are considering – or perhaps even practicing – public speaking, then you already have one thing in common with the person looking to learn presentation skills: an audience . The remaining similarities are a little more complex – but certainly not difficult to understand or learn given the right mentor and learning environment.
The points we’ve outlined below have been taken directly from some of our best-selling presentation courses and underline the extent to which they overlap with the objectives of an aspiring public speaker:
1. You Need An Objective
Whether you’re selling, explaining – or just want to improve your self-confidence – you’ll need to have an aim. This could be teaching your audience something new, pitching a product or service, or even telling them a funny story. Public speakers, like presenters, must, therefore, structure their dialogue around this central ‘theme’ to ensure they get their point across clearly.

2. Who Are You Presenting To?
This dovetails in with the above point. In fact, arguably, this should be your first consideration. Before you agree on your core objective you need to ask yourself whether it’s thematically compatible with the audience coming to listen to you speak. Will your choice of the topic be relevant – and, above all, interesting to them? Will it grab their attention? Building presentations effectively as a public speaker in this manner is extremely important.
3. How Will You Get Their Attention?
Just as with the delivery of presentations, you’ll be faced with the alarming prospect of walking into a roomful of people who’ll be expecting you to deliver something clear, powerful, and memorable. The repeated use of key phrases will help re-enforce the central theme of your speech and find common ground with your audience – a skill that’s essential to building presentations too.
What Are The Differences?
There are, in fact, very few discrepancies to be found when comparing public speaking with the delivery of presentations. The primary challenge faced when considering this transition is that of the environment: as a presenter, you’ll often be sitting down with people you know in an intimate setting where you can share your ideas openly.
A public speaker will, conversely, find themselves in larger settings and talking to their audience, with little interaction occurring until the very end when the speech is curtailed (and your efforts hopefully rewarded by a healthy round of applause). The other difference is that the public speaker will be judged on the timbre and cadence of their voice, which will be on display for a longer period of time than with the professional presenter.
Get in the driver’s seat and Connect with potential customers with PeaksLead .
Written By: Philip Andrews
Recent posts.

How to Get More Appointments in Sales?

The Ultimate Mobile Marketing Statistics

The Ultimate Affiliate Marketing Statistics

The Ultimate Webinar Statistics

The Ultimate Email Marketing Statistics
Follow us on.

Discover peaksLead Sales, Marketing, and Lead Generation Topics & Articles.
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Center
Copyright © 2024 PeaksLead . All rights reserved.
Privacy Overview
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Public Speaking and Presentations

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Public Speaking and Presentations: Tips for Success
This resource includes tips and suggestions for improving your public speaking skills.
Even if you’ve never spoken in front of a large group before, chances are you will encounter public speaking sometime during your life. Whether you’re giving a presentation for your classmates or addressing local politicians at a city council meeting, public speaking allows you to convey your thoughts and feelings in clear ways. Having the right tools can prepare you for successful public speaking and equip you with high-quality communication skills.
Know Your Audience
Different audiences require different modes of public speaking. How you address a room full of preschoolers will vary from how you address a group of professors at an academic conference. Not only will your vocabulary change, but you might alter your pacing and tone as well.
Knowing your audience also helps you decide the content of your speech. For example, if you’re presenting research to a group of scientists, you might not need to define all your scientific language. However, if you present that same research to a group of individuals who are unfamiliar with your scientific field, you may need to define your terms or use simpler language.
Recognizing the extent to which your audience is familiar with your topic helps you center your presentation around the most important elements and avoid wasting time on information your audience either 1) already knows or 2) does not need to know for the purpose of your speech.
Knowing your audience also means tailoring your information to them. Try to keep things straight and to the point; leave out extraneous anecdotes and irrelevant statistics.
Establish Your Ethos and Feel Confident in Your Subject
It’s important to let your audience know what authority you have over your subject matter. If it’s clear you are familiar with your subject and have expertise, your audience is more likely to trust what you say.
Feeling confident in your subject matter will help establish your ethos. Rather than simply memorizing the content on your PowerPoint slides or your note cards, consider yourself a “mini expert” on your topic. Read up on information related to your topic and anticipate questions from the audience. You might want to prepare a few additional examples to use if people ask follow-up questions. Being able to elaborate on your talking points will help you stay calm during a Q & A section of your presentation.
Stick to a Few Main Points
Organizing your information in a logical way not only helps you keep track of what you’re saying, but it helps your audience follow along as well. Try to emphasize a few main points in your presentation and return to them before you conclude. Summarizing your information at the end of your presentation allows your audience to walk away with a clear sense of the most important facts.
For example, if you gave a presentation on the pros and cons of wind energy in Indiana, you would first want to define wind energy to make sure you and your audience are on the same page. You might also want to give a brief history of wind energy to give context before you go into the pros and cons. From there, you could list a few pros and a few cons. Finally, you could speculate on the future of wind energy and whether Indiana could provide adequate land and infrastructure to sustain wind turbines. To conclude, restate a few of the main points (most likely the pros and cons) and end with the most important takeaway you want the audience to remember about wind energy in Indiana.
Don't be Afraid to Show Your Personality
Delivering information without any sort of flourish or style can be boring. Allowing your personality to show through your speaking keeps you feeling relaxed and natural. Even if you’re speaking about something very scientific or serious, look for ways to let your personality come through your speech.
For example, when Jeopardy! host Alex Trebek announced in March of 2019 that he had stage 4 pancreatic cancer, he still let his trademark dignity and professionalism set the tone for his address. He began his announcement by saying “it’s in keeping with my long-time policy of being open and transparent with our Jeopardy! fan base.” Later, he joked that he would need to overcome his illness in order to fulfill his contract, whose terms required him to host the show for three more years. Though the nature of Trebek's announcement could easily have justified a grim, serious tone, the host instead opted to display the charm that has made him a household name for almost thirty-five years. In doing so, he reminded his audience precisely why he is so well-loved.
Use Humor (When Appropriate)
Using humor at appropriate moments can keep your audience engaged and entertained. While not all occasions are appropriate for humor, look for moments where you can lighten the mood and add some humor.
For example, just two months after the assassination attempt on Ronald Reagan, Reagan was in the middle of giving a speech when a balloon loudly popped while he was speaking. Reagan paused his speech to say “missed me,” then immediately continued speaking. This off-the-cuff humor worked because it was appropriate, spontaneous, and did not really distract from his message.
Similarly, at the end of his final White House Correspondents Dinner, Barack Obama concluded his speech by saying “Obama out” and dropping the mic. Once again, the humor did not distract from his message, but it did provide a light-hearted shift in his tone.
Don't Let Visual Aids Distract From Your Presentation
Visual aids, such as PowerPoints or handouts, often go alongside presentations. When designing visual aids, be sure they do not distract from the content of your speech. Having too many pictures or animations can cause audience members to pay more attention to the visuals rather than what you’re saying.
However, if you present research that relies on tables or figures, having many images may help your audience better visualize the research you discuss. Be aware of the ways different types of presentations demand different types of visual aids.
Be Aware of Your Body Language
When it comes to giving a presentation, nonverbal communication is equally as important as what you’re saying. Having the appropriate posture, gestures, and movement complement the spoken element of your presentation. Below are a few simple strategies to make you appear more confident and professional.
Having confident posture can make or break a presentation. Stand up straight with your shoulders back and your arms at your sides. Slouching or crossing your arms over your chest makes you appear smaller and more insecure. However, be sure you’re not too rigid. Just because you’re standing up tall does not mean you cannot move around.
Eye contact
Making eye contact with your audience not only makes them feel connected to you but it also lets you gauge their response to you. Try to look around the room and connect with different audience members so you’re not staring at the same people the whole time. If you notice your audience starting to nod off, it might be a good time to change your tone or up your energy.
Avoid distracting or compulsive gestures
While hand gestures can help point out information in a slide or on a poster, large or quick gestures can be distracting. When using gestures, try to make them feel like a normal part of your presentation.
It’s also easy to slip into nervous gestures while presenting. Things like twirling your hair or wringing your hands can be distracting to your audience. If you know you do something like this, try to think hard about not doing it while you’re presenting.
Travel (if possible)
If you are presenting on a stage, walking back and forth can help you stay relaxed and look natural. However, be sure you’re walking slowly and confidently and you’re using an appropriate posture (described above). Try to avoid pacing, which can make you appear nervous or compulsive.
Rehearse (if Possible)
The difference between knowing your subject and rehearsing comes down to how you ultimately present your information. The more you rehearse, the more likely you are to eliminate filler words such as like and um . If possible, try practicing with a friend and have them use count the filler words you use. You can also record yourself and play back the video. The more you rehearse, the more confident you will feel when it comes time to actually speak in front of an audience.
Finally, Relax!
Although public speaking takes time and preparation, perhaps one of the most important points is to relax while you’re speaking. Delivering your information in a stiff way prevents you from appearing natural and letting your personality come through. The more relaxed you feel, the more confident your information will come across.

Speech vs. Presentation — What's the Difference?
Difference Between Speech and Presentation
Table of contents, key differences, comparison chart, primary focus, skills required, evaluation criteria, compare with definitions, presentation, common curiosities, why is audience engagement important in both speeches and presentations, how can one improve their speech delivery, are there different types of speeches, what is the main difference between a speech and a presentation, how do visual aids enhance a presentation, is public speaking the same as giving a speech, how do you organize a speech, what makes a presentation memorable, can a speech include visual aids, can a presentation be effective without visual aids, what technology is commonly used in presentations, what role does storytelling play in speeches and presentations, can a presentation be interactive, how important is the closing of a speech or presentation, how can feedback improve a speech or presentation, share your discovery.

Author Spotlight
Popular Comparisons

Trending Comparisons

New Comparisons

Trending Terms


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
13.1 Functions of the Presentation to Inform
Learning objectives.
- Describe the functions of the speech to inform.
- Explain the difference between exposition and interpretation.
Informative presentations focus on helping the audience to understand a topic, issue, or technique more clearly. You might say, “Is that all?” and the answer is both yes and no. An affirmative response underscores the idea that informative speeches do not seek to motivate the audience to change their minds, adopt a new idea, start a new habit, or get out there and vote. They may, however, inform audiences on issues that may be under consideration in an election or referendum. On the other hand, a negative response reaffirms the idea that to communicate a topic, issue, or subject clearly is a challenge in itself and shouldn’t be viewed as a simplistic process. There are distinct functions inherent in a speech to inform, and you may choose to use one or more of these functions in your speech. Let’s take a look at the functions and see how they relate to the central objective of facilitating audience understanding.
The basic definition of communication highlights the process of understanding and sharing meaning. An informative speech follows this definition in the aspect of sharing content and information with an audience. You won’t be asking the audience to actually do anything in terms of offering a response or solving a problem. Instead you’ll be offering to share with the audience some of the information you have gathered relating to a topic. This act of sharing will reduce ignorance, increase learning, and facilitate understanding of your chosen topic.
Increase Understanding
How well does your audience grasp the information? This should be a guiding question to you on two levels. The first involves what they already know—or don’t know—about your topic, and what key terms or ideas might be necessary for someone completely unfamiliar with your topic to grasp the ideas you are presenting. The second involves your presentation and the illustration of ideas. A bar chart, a pie graph, and a video clip may all serve you and the audience well, but how will each ingredient in your speech contribute to their understanding? The audience will respond to your attention statement and hopefully maintain interest, but how will you take your speech beyond superficial coverage of content and effectively communicate key relationships that increase understanding? These questions should serve as a challenge for your informative speech, and by looking at your speech from an audience-oriented perspective, you will increase your ability to increase the audience’s understanding.
Change Perceptions
How you perceive stimuli has everything to do with a range of factors that are unique to you. We all want to make sense of our world, share our experiences, and learn that many people face the same challenges we do. Many people perceive the process of speaking in public as a significant challenge, and in this text, we have broken down the process into several manageable steps. In so doing, we have to some degree changed your perception of public speaking. When you present your speech to inform, you may want to change the audience member’s perceptions of your topic. You may present an informative speech on air pollution and want to change common perceptions such as the idea that most of North America’s air pollution comes from private cars, or that nuclear power plants are a major source of air pollution. You won’t be asking people to go out and vote, or change their choice of automobiles, but you will help your audience change their perceptions of your topic.
Gain Skills
Just as you want to increase the audience’s understanding, you may want to help the audience members gain skills. If you are presenting a speech on how to make salsa from fresh ingredients, your audience may thank you for not only the knowledge of the key ingredients and their preparation but also the product available at the conclusion. If your audience members have never made their own salsa, they may gain a new skill from your speech. In the same way, perhaps you decide to inform your audience about eBay, a person-to-person marketplace much like a garage sale in which items are auctioned or available for purchase over the Internet. You may project onto a screen in class the main Web site and take the audience through a step-by-step process on how to sell an item. The audience may learn an important skill, clean out the old items in their garage, and buy new things for the house with their newfound skills. Your intentions, of course, are not to argue that salsa is better than ketchup or that eBay is better than Amazon, but to inform the audience, increasing their understanding of the subject, and in this case, gaining new skills.
Exposition versus Interpretation
When we share information informally, we often provide our own perspective and attitude for our own reasons. But when we set out to inform an audience, taking sides or using sarcasm to communicate attitude may divide the audience into groups that agree or disagree with the speaker. The speech to inform the audience on a topic, idea, or area of content is not intended to be a display of attitude and opinion. Consider the expectations of people who attend a formal dinner. Will they use whatever fork or spoon they want, or are there expectations of protocol and decorum? In any given communication context there are expectations, both implicit and explicit. If you attend a rally on campus for health care reform, you may expect the speaker to motivate you to urge the university to stop investing in pharmaceutical companies, for example. On the other hand, if you enroll in a biochemistry course, you expect a teacher to inform you about the discipline of biochemistry—not to convince you that pharmaceutical companies are a good or bad influence on our health care system.
The speech to inform is like the classroom setting in that the goal is to inform, not to persuade, entertain, display attitude, or create comedy. If you have analyzed your audience, you’ll be better prepared to develop appropriate ways to gain their attention and inform them on your topic. You want to communicate thoughts, ideas, and relationships and allow each listener specifically, and the audience generally, to draw their own conclusions. The speech to inform is all about sharing information to meet the audience’s needs, not your own. While you might want to inform them about your views on politics in the Middle East, you’ll need to consider what they are here to learn from you and let your audience-oriented perspective guide you as you prepare.
This relationship between informing as opposed to persuading your audience is often expressed in terms of exposition versus interpretation. Exposition means a public exhibition or display, often expressing a complex topic in a way that makes the relationships and content clear. Expository prose is writing to inform; you may have been asked to write an expository essay in an English course or an expository report in a journalism course. The goal is to communicate the topic and content to your audience in ways that illustrate, explain, and reinforce the overall content to make your topic more accessible to the audience. The audience wants to learn about your topic and may have some knowledge on it as you do. It is your responsibility to consider ways to display the information effectively.
Interpretation and Bias
Interpretation involves adapting the information to communicate a message, perspective, or agenda. Your insights and attitudes will guide your selection of material, what you focus on, and what you delete (choosing what not to present to the audience). Your interpretation will involve personal bias. Bias is an unreasoned or not-well-thought-out judgment. Bias involves beliefs or ideas held on the basis of conviction rather than current evidence. Beliefs are often called “habits of the mind” because we come to rely on them to make decisions. Which is the better, cheapest, most expensive, or the middle-priced product? People often choose the middle-priced product and use the belief “if it costs more it must be better” (and the opposite: “if it is cheap it must not be very good”). The middle-priced item, regardless of actual price, is often perceived as “good enough.” All these perceptions are based on beliefs, and they may not apply to the given decision or even be based on any evidence or rational thinking.
By extension, marketing students learn to facilitate the customer “relationship” with the brand. If you come to believe a brand stands for excellence, and a new product comes out under that brand label, you are more likely to choose it over an unknown or lesser-known competitor. Again, your choice of the new product is based on a belief rather than evidence or rational thinking. We take mental shortcuts all day long, but in our speech to inform, we have to be careful not to reinforce bias.
Bias is like a filter on your perceptions, thoughts, and ideas. Bias encourages you to accept positive evidence that supports your existing beliefs (regardless of whether they are true) and reject negative evidence that does not support your beliefs. Furthermore, bias makes you likely to reject positive support for opposing beliefs and accept negative evidence (again, regardless of whether the evidence is true). So what is positive and what is negative? In a biased frame of mind, that which supports your existing beliefs is positive and likely to be accepted, while that which challenges your beliefs is likely to be viewed as negative and rejected. There is the clear danger in bias. You are inclined to tune out or ignore information, regardless of how valuable, useful, or relevant it may be, simply because it doesn’t agree with or support what you already believe.
Point of View
Let’s say you are going to present an informative speech on a controversial topic like same-sex marriage. Without advocating or condemning same-sex marriage, you could inform your audience about current laws in various states, recent and proposed changes in laws, the number of same-sex couples who have gotten married in various places, the implications of being married or not being able to marry, and so on. But as you prepare and research your topic, do you only read or examine information that supports your existing view? If you only choose to present information that agrees with your prior view, you’ve incorporated bias into your speech. Now let’s say the audience members have different points of view, even biased ones, and as you present your information you see many people start to fidget in their seats. You can probably anticipate that if they were to speak, the first word they would say is “but” and then present their question or assertion. In effect, they will be having a debate with themselves and hardly listening to you.
You can anticipate the effects of bias and mitigate them to some degree. First, know the difference between your point of view or perspective and your bias. Your point of view is your perception of an idea or concept from your previous experience and understanding. It is unique to you and is influenced by your experiences and also factors like gender, race, ethnicity, physical characteristics, and social class. Everyone has a point of view, as hard as they may try to be open-minded. But bias, as we’ve discussed previously, involves actively selecting information that supports or agrees with your current belief and takes away from any competing belief. To make sure you are not presenting a biased speech, frame your discussion to inform from a neutral stance and consider alternative points of view to present, compare and contrast, and diversify your speech. The goal of the speech to inform is to present an expository speech that reduces or tries to be free from overt interpretation.
This relates to our previous discussion on changing perceptions. Clearly no one can be completely objective and remove themselves from their own perceptual process. People are not modern works of minimalist art, where form and function are paramount and the artist is completely removed from the expression. People express themselves and naturally relate what is happening now to what has happened to them in the past. You are your own artist, but you also control your creations.
Objectivity involves expressions and perceptions of facts that are free from distortion by your prejudices, bias, feelings or interpretations. For example, is the post office box blue? An objective response would be yes or no, but a subjective response might sound like “Well, it’s not really blue as much as it is navy, even a bit of purple, kind of like the color of my ex-boyfriend’s car, remember? I don’t care for the color myself.” Subjectivity involves expressions or perceptions that are modified, altered, or impacted by your personal bias, experiences, and background. In an informative speech, your audience will expect you to present the information in a relatively objective form. The speech should meet the audience’s need as they learn about the content, not your feelings, attitudes, or commentary on the content.
Here are five suggestions to help you present a neutral speech:
- Keep your language neutral and not very positive for some issues while very negative for others.
- Keep your sources credible and not from biased organizations. The National Rifle Association (NRA) will have a biased view of the Second Amendment, for example, as will the American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU) on civil rights.
- Keep your presentation balanced. If you use a source that supports one clear side of an issue, include an alternative source and view. Give each equal time and respectful consideration.
- Keep your audience in mind. Not everyone will agree with every point or source of evidence, but diversity in your speech will have more to offer everyone.
- Keep who you represent in mind: Your business and yourself.
Key Takeaways
- The purpose of an informative speech is to share ideas with the audience, increase their understanding, change their perceptions, or help them gain new skills.
- An informative speech incorporates the speaker’s point of view but not attitude or interpretation.
- Consider the courses you have taken in the past year or two, and the extent to which each class session involved an informative presentation or one that was more persuasive. Do some disciplines lend themselves more to informing rather than interpretation and attitude? Discuss your findings with your classmates.
- Visit a major network news Web site and view a video of a commentator such as Rachel Maddow or Keith Olbermann (MSNBC) or Glenn Beck or Bill O’Reilly (Fox News). Identify the commentator’s point of view. If you were giving a presentation to inform, would you express your point of view in a similar style?
- On the same network news Web site you used for Exercise no. 2, view a video reporting a news event (as opposed to a commentator’s commentary). Do you feel that the reporter’s approach conveys a point of view, or is it neutral? Explain your feelings and discuss with your classmates.
- What is the difference between an informative presentation and a persuasive one? Provide an example in your response.
- Consider a sample speech to inform on a topic where you have a strong opinion. In what ways would you adjust your key points so as not to persuade your listeners? Discuss your ideas with a classmate.
Business Communication for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
More From Forbes
The 5 differences between a pitch and a presentation.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Persuade me. If you can.
“Tell me a little bit about yourself.”
“Pitch me your business idea.”
“Why should I do business with you?”
Where, exactly, does the story begin? In order to pitch your ideas - or your job skills - effectively, it’s important to understand the fundamental differences between a presentation and a pitch. Because a pitch is more than just an informational presentation. Beyond the constructs of the various TV shows, like Shark Tank , a pitch doesn’t necessarily inform. A good pitch compels . In other words, a pitch inspires action.
Persuasion Creates Opportunity, inside Your Pitch
That’s right, “inspires”. Because if all you want to do is instruct, like an informational presentation, that’s not a pitch. True, your audience might get smarter. But are you getting any richer? What does “good” look like, when it comes to your pitch? Maybe it looks like a new job . A new promotion. Or a new initiative that’s delivered (persuasively) by none other than you. Would you invest in that pitch?
Consider these five key differences between a presentation and a pitch:
- You Don’t Have to Go it Alone : it’s easy to fall into the trap that you’re alone on an island when it comes to your pitch - and that’s why you better talk fast, right? Wrong. A presentation is about information. A pitch is about connection . Slow down, and stop trying to lift the world by yourself. Instead, connect your message to the people you wish to influence most: your investors, your potential new employer, your boss. Stop focusing on yourself and consider the puts and takes for the person right in front of you. You may not be facing off with Mr. Wonderful, but if you can find a way to connect to your audience, you’re making wonderful progress. How does your pitch impact the person you’re trying to influence? Are you clear on their outcomes, not just your own?
- Outcomes, Not Obstacles : there are four words that need to be a part of any persuasive conversation or pitch. Here they are: “I’ve thought this through”. Thinking things through means looking beyond the details. Zoom out and see if you see the big picture - have you thought things through? After all, a pitch is persuasive. It’s not a how-to. You’re not there to instruct, you’re there to inspire. Thinking things through points towards outcomes . What is the outcome of your business idea? What’s the outcome of you being hired by this firm? Stop focusing on your past experience and knowledge (Your background and resumé won’t disappear, when you make this shift). Turn your experience into outcomes for your audience. That way, you create an experience for your investor (or potential employer). Sharing outcomes starts by answering this simple question: “What’s the biggest promise you can keep?”
- What’s Your Log Line? Brant Pinvidic has sold over 300 different vehicles to various studios in Hollywood, including reality TV shows like Pawn Stars and Bar Rescue . In his book, The 3-Minute Rule, he explains how it can be useful to have a “log line”. He defines a log line as “the single most valuable element of your offering...in a single sentence or phrase.” He explains how he sold the idea of The Biggest Loser, the most successful show his company has produced so far: “Overweight contestants compete to lose weight; the winner is the biggest loser.” Simplicity wins, when it comes to your pitch.
- Use Leadership Language - Not Just Description: If you want a pitch that’s a winner, consider the difference between language that describes and language that creates. The language of description is all around us - in news reports, white papers and web pages. The language of creation, however, focuses on what we might be able to make, build or do together. Leadership language emphasizes creation: creating partnerships, opportunities, options and outcomes. Which do you think is more important in a pitch, description or creation? If an investor can take a quiz on your business idea, describe it, and earn an “A”, you might just be the biggest loser. Because if your audience is smarter, but they’re not co-creating a new solution with you, what have you won? Do you want to get a grade, or to get paid?
- Close Like You Know: a compelling pitch is, at its core, is a series of “yeses”. A pitch always finds a way to “yes”. How do you know if your pitch is going well? When you hear these three words from your audience: tell me more . Can you share ideas that are inarguable? Ideas and concepts that inspire agreement instead of inviting argument? These paths lead to yes. And then, at the end of your pitch, offer the easiest thing in the world to say “yes” to. And what is the easiest thing in the world to say “yes” to? No, it’s not free beer. It’s an invitation . What is the invitation you can offer? An invitation that’s logical and actionable and measurable. An invitation to co-create the next step - the step that just might get you into the winner’s circle. Or that new job you’ve been hoping for.
You don’t have to watch Shark Tank in order to see the value in a persuasive conversation. That’s right: a pitch is simply a conversation, if it’s done right. A conversation that’s compelling, clear and guided, so that your audience sees your vision. A vision that’s presented in a way that makes people say “yes”. Using the language of creation, a pitch builds to a “tell me more”, based on a story that gets your audience involved and connected with your vision. So, if you’re looking for a new job, or a new way to get your ideas across, consider how you might be able to create the one thing that every pitch needs: a connection to your audience. Instead of focusing intently on your background, your struggle, or your hero’s journey, consider instead how you can make your audience the hero. That kind of language just might help you create what’s missing. So, you’re invited to change the conversation - and change your results - whenever you’re ready to win.
Best Travel Insurance Companies
Best covid-19 travel insurance plans.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Marketing How To Start a Presentation: 15 Ways to Set the Stage
How To Start a Presentation: 15 Ways to Set the Stage
Written by: Krystle Wong Jul 25, 2023

The opening moments of your presentation hold immense power – it’s your opportunity to make a lasting impression and captivate your audience.
A strong presentation start acts as a beacon, cutting through the noise and instantly capturing the attention of your listeners. With so much content vying for their focus, a captivating opening ensures that your message stands out and resonates with your audience.
Whether you’re a startup business owner pitching a brilliant idea, a seasoned presenter delivering a persuasive talk or an expert sharing your experience, the start of your presentation can make all the difference. But don’t fret — I’ve got you covered with 15 electrifying ways to kickstart your presentation.
The presentation introduction examples in this article cover everything from self-introduction to how to start a group presentation, building anticipation that leaves the audience eager to delve into the depths of your topic.
Click to jump ahead:
How to start a presentation introduction
15 ways to start a presentation and captivate your audience, common mistakes to avoid in the opening of a presentation, faqs on how to start a presentation, captivate the audience from the get-go.
Presentations can be scary, I know. But even if stage fright hits, you can always fall back on a simple strategy.
Just take a deep breath, introduce yourself and briefly explain the topic of your presentation.
To grab attention at the start, try this opening line: Hello everyone. I am so glad you could join me today. I’m very excited about today’s topic. I’m [Your Name] and I’ll be talking about [Presentation Topic]. Raise your hand if you’ve ever felt overwhelmed by [Challenge related to your topic]. Many of us might have faced challenges with [Challenge related to your topic]. Today, we’ll explore some strategies that’ll help us [Solution that you’re presenting].
Regardless of your mode of presentation , crafting an engaging introduction sets the stage for a memorable presentation.
Let’s dive into some key tips for how to start a presentation speech to help you nail the art of starting with a bang:
Understand your audience
The key to an engaging introduction is to know your audience inside out and give your audience what they want. Tailor your opening to resonate with their specific interests, needs and expectations. Consider what will captivate them and how you can make your presentation relevant to their lives or work.
Use a compelling hook
Grab the audience’s attention from the get-go with a compelling hook. Whether it’s a thought-provoking question, a surprising fact or a gripping story, a powerful opening will immediately pique their curiosity and keep them invested in what you have to say.

State your purpose
Be crystal clear about your subject matter and the purpose of your presentation. In just a few sentences, communicate the main objectives and the value your audience will gain from listening to you. Let them know upfront what to expect and they’ll be more likely to stay engaged throughout.
Introduce yourself and your team
Give a self introduction about who you are such as your job title to establish credibility and rapport with the audience.
Some creative ways to introduce yourself in a presentation would be by sharing a brief and engaging personal story that connects to your topic or the theme of your presentation. This approach instantly makes you relatable and captures the audience’s attention.
Now, let’s talk about — how to introduce team members in a presentation. Before introducing each team member, briefly explain their role or contribution to the project or presentation. This gives the audience an understanding of their relevance and expertise.
Group presentations are also a breeze with the help of Venngage. Our in-editor collaboration tools allow you to edit presentations side by side in real-time. That way, you can seamlessly hare your design with the team for input and make sure everyone is on track.
Maintain enthusiasm
Enthusiasm is contagious! Keep the energy levels up throughout your introduction, conveying a positive and upbeat tone. A vibrant and welcoming atmosphere sets the stage for an exciting presentation and keeps the audience eager to hear more.
Before you think about how to present a topic, think about how to design impactful slides that can leave a lasting impression on the audience. Here are 120+ presentation ideas , design tips, and examples to help you create an awesome slide deck for your next presentation.
Captivating your audience from the get-go is the key to a successful presentation. Whether you’re a seasoned speaker or a novice taking the stage for the first time, the opening of your presentation sets the tone for the entire talk.
So, let’s get ready to dive into the 15 most creative ways to start a presentation. I promise you these presentation introduction ideas will captivate your audience, leaving them hanging on your every word.
Grab-attention immediately
Ask a thought-provoking question.
Get the audience’s wheels turning by throwing them a thought-provoking question right out of the gate. Make them ponder, wonder and engage their critical thinking muscles from the very start.
Share a surprising statistic or fact
Brace yourself for some wide eyes and dropped jaws! Open your presentation with a jaw-dropping statistic or a mind-blowing fact that’s directly related to your topic. Nothing captures attention like a good ol’ dose of shock and awe.

State a bold statement or challenge
Ready to shake things up? Kick off with a bold and daring statement that sets the stage for your presentation’s epic journey. Boldness has a way of making ears perk up and eyes widen in anticipation!
Engage with a poll or interactive activity
Turn the audience from passive listeners to active participants by kicking off with a fun poll or interactive activity. Get them on their feet, or rather — their fingertips, right from the start!
Venngage’s user-friendly drag-and-drop editor allows you to easily transform your slides into an interactive presentation . Create clickable buttons or navigation elements within your presentation to guide your audience to different sections or external resources.
Enhance engagement by incorporating videos or audio clips directly into your presentation. Venngage supports video and audio embedding, which can add depth to your content.

Begin with an opening phrase that captures attention
Use opening phrases that can help you create a strong connection with your audience and make them eager to hear more about what you have to say. Remember to be confident, enthusiastic and authentic in your delivery to maximize the impact of your presentation.
Here are some effective presentation starting words and phrases that can help you grab your audience’s attention and set the stage for a captivating presentation:
- “Imagine…”
- “Picture this…”
- “Did you know that…”
- “Have you ever wondered…”
- “In this presentation, we’ll explore…”
- “Let’s dive right in and discover…”
- “I’m excited to share with you…”
- “I have a confession to make…”
- “I want to start by telling you a story…”
- “Before we begin, let’s consider…”
- “Have you ever faced the challenge of…”
- “We all know that…”
- “This is a topic close to my heart because…”
- “Over the next [minutes/hours], we’ll cover…”
- “I invite you to journey with me through…”
Build connection and credibility
Begin with a personal connection .
Share a real-life experience or a special connection to the topic at hand. This simple act of opening up creates an instant bond with the audience, turning them into your biggest cheerleaders.
Having the team share their personal experiences is also a good group presentation introduction approach. Team members can share their own stories that are related to the topic to create an emotional connection with your audience.

Tell a relevant story
Start your presentation with a riveting story that hooks your audience and relates to your main message. Stories have a magical way of captivating hearts and minds. Organize your slides in a clear and sequential manner and use visuals that complement your narrative and evoke emotions to engage the audience.
With Venngage, you have access to a vast library of high-quality and captivating stock photography, offering thousands of options to enrich your presentations. The best part? It’s entirely free! Elevate your visual storytelling with stunning images that complement your content, captivate your audience and add a professional touch to your presentation.

Use a powerful quote
Sometimes, all you need is some wise words to work wonders. Begin with a powerful quote from a legendary figure that perfectly fits your presentation’s theme — a dose of inspiration sets the stage for an epic journey.
Build anticipation
Provide a brief outline.
Here’s a good introduction for presentation example if you’re giving a speech at a conference. For longer presentations or conferences with multiple speakers especially, providing an outline helps the audience stay focused on the key takeaways. That way, you can better manage your time and ensure that you cover all the key points without rushing or running out of time.
Pose a problem and offer a solution
A great idea on how to start a business presentation is to start by presenting a problem and offering a well-thought-out solution. By addressing their pain points and showcasing your solution, you’ll capture their interest and set the stage for a compelling and successful presentation.
Back up your solution with data, research, or case studies that demonstrate its effectiveness. This can also be a good reporting introduction example that adds credibility to your proposal.
Preparing a pitch deck can be a daunting task but fret not. This guide on the 30+ best pitch deck tips and examples has everything you need to bring on new business partners and win new client contracts. Alternatively, you can also get started by customizing one of our professional pitch deck templates for free.
Incite curiosity in the audience
Utilize visuals or props.
Capture your audience’s gaze by whipping out captivating visuals or props that add an exciting touch to your subject. A well-placed prop or a stunning visual can make your presentation pop like a fireworks show!
That said, you maybe wondering — how can I make my presentation more attractive. A well-designed presentation background instantly captures the audience’s attention and creates a positive first impression. Here are 15 presentation background examples to keep the audience awake to help you get inspired.
Use humor or wit
Sprinkle some humor and wit to spice things up. Cracking a clever joke or throwing in a witty remark can break the ice and create a positively charged atmosphere. If you’re cracking your head on how to start a group presentation, humor is a great way to start a presentation speech.
Get your team members involved in the fun to create a collaborative and enjoyable experience for everyone. Laughter is the perfect way to break the ice and set a positive tone for your presentation!
Invoke emotion
Get those heartstrings tugging! Start with a heartfelt story or example that stirs up emotions and connects with your audience on a personal level. Emotion is the secret sauce to a memorable presentation.
Aside from getting creative with your introduction, a well-crafted and creative presentation can boost your confidence as a presenter. Browse our catalog of creative presentation templates and get started right away!
Use a dramatic pause
A great group presentation example is to start with a powerful moment of silence, like a magician about to reveal their greatest trick. After introducing your team, allow a brief moment of silence. Hold the pause for a few seconds, making it feel deliberate and purposeful. This builds anticipation and curiosity among the audience.
Pique their interest
Share a fun fact or anecdote.
Time for a little fun and games! Kick-off with a lighthearted or fascinating fact that’ll make the audience go, “Wow, really? Tell me more!” A sprinkle of amusement sets the stage for an entertaining ride.
While an introduction for a presentation sets the tone for your speech, a good slide complements your spoken words, helping the audience better understand and remember your message. Check out these 12 best presentation software for 2023 that can aid your next presentation.

The opening moments of a presentation can make or break your entire talk. It’s your chance to grab your audience’s attention, set the tone, and lay the foundation for a successful presentation. However, there are some common pitfalls that speakers often fall into when starting their presentations.
Starting with Apologies
It might be tempting to start with a preemptive apology, especially if you’re feeling nervous or unsure about your presentation. However, beginning with unnecessary apologies or self-deprecating remarks sets a negative tone right from the start. Instead of exuding confidence and credibility, you’re unintentionally undermining yourself and your message.
Reading from Slides
One of the most common blunders in the opening of a PowerPoint presentation is reading directly from your slides or script. While it’s crucial to have a well-structured outline, reciting word-for-word can lead to disengagement and boredom among your audience. Maintain eye contact and connect with your listeners as you speak. Your slides should complement your words, not replace them.

Overwhelming with Information
In the excitement to impress, some presenters bombard their audience with too much information right at the beginning.
Instead of overloading the audience with a sea of data, statistics or technical details that can quickly lead to confusion and disinterest, visualize your data with the help of Venngage. Choose an infographic template that best suits the type of data you want to visualize. Venngage offers a variety of pre-designed templates for charts, graphs, infographics and more.
Ignoring the Audience
It’s easy to get caught up in the content and forget about the people in front of you. Don’t overlook the importance of acknowledging the audience and building a connection with them. Greet them warmly, make eye contact and maintain body language to show genuine interest in their presence. Engage the audience early on by asking a show of hands question or encourage audience participation.
Lack of Clarity
Your audience should know exactly what to expect from your presentation. Starting with a vague or unclear opening leaves them guessing about the purpose and direction of your talk. Clearly communicate the topic and objectives of your presentation right from the beginning. This sets the stage for a focused and coherent message that resonates with your audience.
Simplicity makes it easier for the audience to understand and retain the information presented. Check out our gallery of simple presentation templates to keep your opening concise and relevant.

Skipping the Hook
The opening of your presentation is the perfect opportunity to hook your audience’s attention and keep them engaged. However, some presenters overlook this crucial aspect and dive straight into the content without any intrigue. Craft an attention-grabbing hook that sparks curiosity, poses a thought-provoking question or shares an interesting fact. A compelling opening is like the key that unlocks your audience’s receptivity to the rest of your presentation.
Now that you’ve got the gist of how to introduce a presentation, further brush up your speech with these tips on how to make a persuasive presentation and how to improve your presentation skills to create an engaging presentation .
How can I overcome nervousness at the beginning of a presentation?
To overcome nervousness at the beginning of a presentation, take deep breaths, practice beforehand, and focus on connecting with your audience rather than worrying about yourself.
How long should the opening of a presentation be?
The opening of a presentation should typically be brief, lasting around 1 to 3 minutes, to grab the audience’s attention and set the tone for the rest of the talk.
Should I memorize my presentation’s opening lines?
While it’s helpful to know your opening lines, it’s better to understand the key points and flow naturally to maintain authenticity and flexibility during the presentation.
Should I use slides during the opening of my presentation?
Using slides sparingly during the opening can enhance the message, but avoid overwhelming the audience with too much information early on.
How do I transition smoothly from the opening to the main content of my presentation?
Transition smoothly from the opening to the main content by providing a clear and concise outline of what’s to come, signaling the shift and maintaining a logical flow between topics.
Just as a captivating opening draws your audience in, creating a well-crafted presentation closing has the power to leave a lasting impression. Wrap up in style with these 10 ways to end a presentation .
Presenting virtually? Check out these tips on how to ace your next online presentation .
Captivating your audience from the very beginning is crucial for a successful presentation. The first few moments of your talk can set the tone and determine whether your audience remains engaged throughout or loses interest.
Start with a compelling opening that grabs their attention. You can use a thought-provoking question, a surprising statistic or a powerful quote to pique their curiosity. Alternatively, storytelling can be a potent tool to draw them into your narrative. It’s essential to establish a personal connection early on, whether by sharing a relatable experience or expressing empathy towards their needs and interests.
Lastly, be mindful of your body language and vocal delivery. A confident and engaging speaker can captivate an audience, so make eye contact, use appropriate gestures and vary your tone to convey passion and sincerity.
In conclusion, captivating your audience from the very beginning requires thoughtful preparation, engaging content and a confident delivery. With Venngage’s customizable templates, you can adapt your presentation to suit the preferences and interests of your specific audience, ensuring maximum engagement. Go on and get started today!
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
The Presentation of Speech, Writing and Thought
- First Online: 04 October 2023
Cite this chapter

- Jane Lugea 3 &
- Brian Walker 4
206 Accesses
In this chapter, we turn our attention to the presentation of speech, thought and writing in a text—or Discourse Presentation as it is also known. The presentation of what characters or other people said, wrote or thought is an essential component of both fiction and non-fiction. The model of Discourse Presentation we describe in this chapter is based on Short ( Language and Literature 21:18–32, 2012), which is a development of the original model introduced by Leech and Short ( Style in Fiction: A Linguistic Introduction to English Fictional Prose. Longman, 2007 [1981]). In this chapter, we first explain what is meant by Discourse Presentation and then describe the model using examples mainly drawn from the HUM19UK corpus of nineteenth-century novels. We then demonstrate one way in which corpus methods can be used in the analysis of speech, writing and thought in prose fiction.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Bortolussi, M. and Dixon, P. 2002. Psychonarratology: Foundations for the Empirical Study of Literary Response .
Google Scholar
Bray, J. 2007a. The Effects of Free Indirect Discourse: Empathy Revisited. In Contemporary Stylistics , eds. M. Lambrou and P. Stockwell, 56–67. London: Continuum.
Bray, J. 2007b. The “Dual Voice” of Free Indirect Discourse: A Reading Experiment. Language and Literature 16, 1: 37–52.
Busse, B. 2010. Speech, Writing and Thought Presentation in a Corpus of Nineteenth-Century English Narrative Fiction . Bern: University of Bern.
Cohn, D. H. 1978. Transparent Minds: Narrative Modes for Presenting Consciousness in Fiction . Princeton University Press.
Cruikshank, T. and Lahey, E. 2010. Building the Stages of Drama: Towards a Text World Theory Account of Dramatic Play-Texts. Journal of Literary Semantics 39, 1: 67–91.
Crystal, D. 2008. Dictionary of Linguistics and Phonetics . John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated.
Fludernik, M. 1993. The Fictions of Language and the Languages of Fiction: The Linguistic Representation of Speech and Consciousness . London: Routledge.
Gavins, J. 2007. Text World Theory: An Introduction . Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press.
Genette, G. 1980. Narrative Discourse: An Essay in Method . Trans. J. E. Lewin. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
Ikeo, R. 2009. An Elaboration of Faithfulness Claims in Direct Writing. Journal of Pragmatics 41: 999–1016.
Ikeo, R. 2012. Misleading Speech Report in the Media with a Special Reference to an Australian Defamation Case. Journal of Pragmatics 44: 1183–1205.
Jucker, A. H. 2006. ‘But ‘tis Believed That …’: Speech and Thought Presentation in Early English Newspapers. In News Discourse in Early Modern Britain. Selected Papers of CHINED 2004 , ed. N. Brownlees, 105–125. Bern: Peter Lang.
Kilroy, C. 2009. All Names Have Been Changed . London: Faber and Faber.
Leech, G. and Short, M. 2007. Style in Fiction: A Linguistic Introduction to English Fictional Prose . 2nd ed. London and New York: Longman.
Lugea, J. 2013. Embedded Dialogue and Dreams: The Worlds and Accessibility Relations of Inception. Language and Literature 22, 2: 133–153.
McHale, B. 1978. Free Indirect Discourse A Survey of Recent Accounts. PTL A Journal for Descriptive Poetics and Theory of Literature 3: 248–287.
McIntyre, D. and Walker, B. 2011. Discourse Presentation in Early Modern English Writing: A Preliminary Corpus-Based Investigation. International Journal of Corpus Linguistics 16, 1: 101–130.
McIntyre, D. and Walker, B. 2019. Corpus Stylistics: Theory and Practice. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press.
McIntyre, D., Bellard-Thomson, C., Heywood, J., McEnery, A., Semino, E. and Short, M. 2004. Investigating the Presentation of Speech, Writing and Thought in Spoken British English: A Corpus-Based Approach. ICAME Journal 28: 49–76.
Ruano, P. 2018. A Corpus-Based Approach to Charles Dickens’s Use of Direct Thought Presentation. Corpora 13, 3: 319–345.
Rundquist, E. 2014. How Is Mrs Ramsay thinking? The Semantic Effects of Consciousness Presentation Categories Within Free Indirect Style. Language and Literature 23, 2: 159–174.
Scott, M. 2020. WordSmith Tools version 8 . Stroud: Lexical Analysis Software.
Semino, E. and Short, M. 2004. Corpus Stylistics: Speech, Writing and Thought Presentation in a Corpus of English Writing . London: Routledge.
Short, M. 1988. Speech Presentation, the Novel and the Press. In The Taming of the Text , ed. W. van Peer. London: Routledge.
Short, M. 1996. Exploring the Language of Poems, Plays and Prose . Harlow: Longman.
Short, M. 2007. Thought Presentation Twenty-Five Years on. Style 41, 2: 227–257.
Short, M. 2012. Discourse Presentation of Speech (and Writing but not Thought) Summary. Language and Literature 21, 1: 18–32.
Short, M., Semino, E. and Wynne, M. 2002. Revisiting the Notion of Faithfulness in Discourse Presentation Using a Corpus Approach. Language and Literature 11, 4: 325–355.
Sotirova, V. 2004. Connectives in Free Indirect Style: Continuity or Shift? Language and Literature 13, 3: 216–234.
Sternberg, M. 1982. Proteus in Quotation-Land: Mimesis and the Forms of Reported Discourse. Poetics Today 3, 2: 107–156.
Thompson, G. 1996. Voices in the Text: Discourse Perspectives on Language Reports. Applied Linguistics 17, 4: 501–530.
Walker, B. and Karpenko-Seccombe, T. 2017. Speech Presentation and Summary in the BBC News Online Coverage of a Russian TV Interview with Vladimir Putin. CADAAD Journal 9, 2: 79–96.
Waugh, E. 1967. Mr. Loveday’s Little Outing. In The Penguin Book of English Short Stories, ed. C. Dolley, 293–301. Harmondsworth, Middlesex, England: Penguin Books Ltd.
Werth, P. 1999. Text Worlds: Representing Conceptual Space in Discourse . London: Longman.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Arts, English and Languages, Queen’s University Belfast, Belfast, UK
Independent Scholar, Inverness, Scotland
Brian Walker
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jane Lugea .
4.1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (PDF 195 kb)
Supplementary file2 (pdf 1105 kb), rights and permissions.
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Lugea, J., Walker, B. (2023). The Presentation of Speech, Writing and Thought. In: Stylistics. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-10422-0_4
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-10422-0_4
Published : 04 October 2023
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-10421-3
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-10422-0
eBook Packages : Social Sciences Social Sciences (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
How old is Tim Walz? A brief biography of Kamala Harris' running mate

Democratic presidential nominee Vice President Kamala Harris has chosen her running mate. On Tuesday, she selected Minnesota Governor Tim Walz to be the vice president on her 2024 campaign ticket.
The Minnesota governor had been speculated to be Harris' pick, among a short list of other contenders, such as Pennsylvania Gov. Josh Shapiro , Arizona Sen. Mark Kelly , Kentucky Gov. Andy Beshear and Secretary of Transportation Pete Buttigieg .
Alongside Harris, Walz is expected to make an appearance at a campaign rally Tuesday in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
Here's a brief biography of Tim Walz.
Tim Walz is Kamala Harris' VP pick: Minnesota governor named running mate: Live updates
How old is Tim Walz?
Gov. Tim Walz is 60 years old, born on April 6, 1964.
He was born in West Point, Nebraska, and grew up in Valentine, Nebraska. He joined the National Guard at 17 and served for 24 years. He earned a social science degree at Chadron State College in 1989 and a Master of Science in educational leadership from Minnesota State University, Mankato in 2001.
After college, he taught abroad in China and returned to the States to serve full-time in the National Guard. He also taught social studies and coached at a school where he would meet his future wife, Gwen Whipple.
He served as a U.S. Representative for Minnesota's first district, serving six terms in the House from 2007 to 2019. He was elected Minnesota's 41st governor and his tenure began in 2019.
Minnesota Gov. Tim Walz is Harris' VP. Who is his family?
Sign up for Your Vote: Text the USA TODAY elections team your political questions and get breaking news updates .
How old is Kamala Harris?
Vice President Kamala Harris is 59 years old, born Oct. 20, 1964.
When she was sworn in at age 56 in 2021, Harris became the first woman, the first Black American and the first South Asian American to hold the role of vice president.
Just Curious for more? We've got you covered.
USA TODAY is exploring the questions you and others ask every day. From " What are the requirements to be president? " to " Who was the youngest president ever? " to " Who was the first woman elected to Congress? " – we're striving to find answers to the most common questions you ask every day. Head to our Just Curious section to see what else we can answer for you.
Advertisement
Supported by
An Olympics Scene Draws Scorn. Did It Really Parody ‘The Last Supper’?
Some church leaders and politicians have condemned the performance from the opening ceremony for mocking Christianity. Art historians are divided.
- Share full article

By Yan Zhuang
A performance during the Paris Olympics’ opening ceremony on Friday has drawn criticism from church leaders and conservative politicians for a perceived likeness to Leonardo da Vinci’s depiction of a biblical scene in “The Last Supper,” with some calling it a “mockery” of Christianity.
The event’s planners and organizers have denied that the sequence was inspired by “The Last Supper,” or that it intended to mock or offend.
In the performance broadcast during the ceremony, a woman wearing a silver, halo-like headdress stood at the center of a long table, with drag queens posing on either side of her. Later, at the same table, a giant cloche lifted, revealing a man, nearly naked and painted blue, on a dinner plate surrounded by fruit. He broke into a song as, behind him, the drag queens danced.
The tableaux drew condemnation among people who saw the images as a parody of “The Last Supper,” the New Testament scene depicted in da Vinci’s painting by the same name. The French Bishops’ Conference, which represents the country’s Catholic bishops, said in a statement that the opening ceremony included “scenes of mockery and derision of Christianity,” and an influential American Catholic, Bishop Robert Barron of Minnesota, called it a “gross mockery.”
The performance at the opening ceremony, which took place on and along the Seine on Friday, also prompted a Mississippi-based telecommunications provider, C Spire, to announce that it would pull its advertisements from Olympics broadcasts. Speaker Mike Johnson described the scene as “shocking and insulting to Christian people.”
The opening ceremony’s artistic director, Thomas Jolly, said at the Games’ daily news conference on Saturday that the event was not meant to “be subversive, or shock people, or mock people.” On Sunday, Anne Descamps, the Paris 2024 spokeswoman, said at the daily news conference, “If people have taken any offense, we are, of course, really, really sorry.”
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Auto Racing
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Wesley Bell defeats ‘Squad’ member Cori Bush. A pro-Israel group spent $8.5 million to help oust her
St. Louis County Prosecuting Attorney Wesley Bell has defeated U.S. Rep. Cori Bush in a Democratic primary in St. Louis, marking the second time this year that one of the party’s incumbents has been ousted in an expensive contest that reflected deep divisions over the war in Gaza.
Wesley Bell takes a video of his supporters as he takes the stage as the winner of the Democratic congressional primary against incumbent U.S. Rep. Cori Bush on Tuesday, Aug. 6, 2024, in St. Louis. (Robert Cohen/St. Louis Post-Dispatch via AP)
- Copy Link copied
Wesley Bell supporter Shawntelle Fisher takes a call learning of the victory of Bell in the Democratic congressional primary against incumbent U.S. Rep. Cori Bush on Tuesday, Aug. 6, 2024, in St. Louis. (Robert Cohen/St. Louis Post-Dispatch via AP)
U.S. Rep. Cori Bush embraces her father, Errol Bush, on Tuesday, Aug. 6, 2024, while addressing her supporters at a watch party in St. Louis. (Christian Gooden/St. Louis Post-Dispatch via AP)
Wesley Bell supporter Shawntelle Fisher cheers for Bell as he wins the Democratic congressional primary against incumbent U.S. Rep. Cori Bush on Tuesday, Aug. 6, 2024 at the Marriott Grand Hotel in downtown St. Louis. (Robert Cohen/St. Louis Post-Dispatch via AP)
Wesley Bell greets supporters from the stage after winning the Democratic congressional primary against incumbent U.S. Rep. Cori Bush on Tuesday, Aug. 6, 2024 at the Marriott Grand Hotel in downtown St. Louis. (Robert Cohen/St. Louis Post-Dispatch via AP)
U.S. Rep. Cori Bush, center, waits to be introduced to supporters on Tuesday, Aug. 6, 2024, before acknowledging her defeat at a watch party at Chevre Events in downtown St. Louis. (Christian Gooden/St. Louis Post-Dispatch via AP)
ST. LOUIS (AP) — St. Louis County Prosecuting Attorney Wesley Bell has defeated U.S. Rep. Cori Bush in a Democratic primary in St. Louis, marking the second time this year that one of the party’s incumbents has been ousted in an expensive contest that reflected deep divisions over the war in Gaza.
Bush, a member of the progressive congressional group known as the “Squad,” was seeking a third term in Missouri’s 1st Congressional District, which includes St. Louis city and part of St. Louis County. Bell is heavily favored to carry this overwhelmingly Democratic district in November, when his party is aiming to retake control of the U.S. House.
“I am committed to serving the St. Louis region in Congress with integrity, transparency, and dedication,” Bell said in a statement. “Together, we will tackle the challenges ahead and build a community where everyone has the opportunity to thrive.”
Bush, in a fiery concession speech, said she still has work to do, even if she’ll no longer be in Congress.
“At the end of the day, whether I’m a congresswoman or not, I’m still taking care of my people,” Bush said.
Bell’s campaign received a big boost from the American Israel Public Affairs Committee, whose super political action committee, United Democracy Project, spent $8.5 million to oust Bush. She was targeted after repeated criticism of Israel’s response to the Oct. 7 Hamas attack .
It was a gameplan that worked earlier this year in New York. In June, United Democracy Project spent $15 million to defeat another Squad member — U.S. Rep. Jamaal Bowman. Bowman lost to George Latimer, a pro-Israel centrist.
A statement from United Democracy Project said the wins by Bell and Latimer, along with John McGuire’s defeat of U.S. Rep. Bob Good in a Republican primary last week in Virginia, “is further proof that being pro-Israel is good policy and good politics on both sides of the aisle. UDP will continue our efforts to support leaders working to strengthen the U.S.-Israel alliance while countering detractors in either political party.”
Bush, in her concession speech, said she won’t change.
“We will keep supporting a free Palestine,” Bush said. A crowd member answered back: “Free, free Palestine.”
In October, Bush called the Israeli retaliation an “ethnic cleansing campaign.” Soon after the Hamas attack, Bush wrote on social media that Israel’s “collective punishment against Palestinians for Hamas’s actions is a war crime.”
Her comments prompted backlash , even among some supporters in her district. Bell, who had been planning a Senate run against incumbent Republican Josh Hawley, instead opted to challenge Bush. He told The Associated Press last month that Bush’s comments about Israel were “wrong and offensive.”
Bush responded by saying that the donors behind AIPAC support former President Donald Trump and other Republicans.
“This is only the beginning,” Bush told the AP. “Because if they can unseat me, then they’re going to continue to come after more Democrats.”
Bush and Bell both honed their leadership skills in Ferguson, Missouri, in the unrest that followed Michael Brown’s death at the hands of a police officer in 2014. Friday marks the 10th anniversary of Brown’s death.
Brown, a Black 18-year-old, was walking with a friend on Aug. 9, 2014, when a white officer, Darren Wilson, confronted them. Wilson said he fired in self-defense because Brown was so enraged. Some witnesses said Brown, who was unarmed, had his hands up in surrender. Wilson was cleared of wrongdoing and resigned, and Brown’s death led to months of protests.
What to know about the 2024 Election
- Today’s news: Follow live updates from the campaign trail from the AP.
- Ground Game: Sign up for AP’s weekly politics newsletter to get it in your inbox every Monday.
- AP’s Role: The Associated Press is the most trusted source of information on election night, with a history of accuracy dating to 1848. Learn more.
Bush, 48, became a protest leader. She was outspoken and critical of how police in Ferguson and other parts of the St. Louis region treated Black people. Her activism prompted an unsuccessful run against longtime incumbent 1st District Democrat William Lacy Clay in 2018, before she defeated him in 2020. She easily won reelection in 2022.
Bell, 49, began hosting conversations about community policing after Brown’s death. The lawyer, who previously served as a municipal prosecutor and judge, ran successfully for a seat on the Ferguson City Council before defeating seven-term incumbent St. Louis County Prosecuting Attorney Bob McCulloch in the August 2018 Democratic primary.
As prosecutor, Bell reopened an examination into Brown’s death. He announced in July 2020 that while the investigation didn’t exonerate Wilson, there wasn’t enough evidence to charge him.
“My heart breaks” for Brown’s parents, Bell said at the time. “I know this is not the result they were looking for and that their pain will continue forever.”
Brown’s father, Michael Brown Sr., was featured in an ad for Bush.
“He used my family for power,” Brown says of Bell in the ad. “And now he’s trying to sell out St. Louis.”
Bush’s campaign focused on what she’s accomplished for St. Louis. She said her efforts have brought $2 billion to the 1st District and that it was her protest on the steps of the Capitol in 2021 that helped extend the federal eviction moratorium as part of the COVID-19 pandemic, aiding thousands of St. Louisans.
Bell touted his own progressive credentials. He noted that as a prosecutor he has said he will not prosecute any abortion cases in a state that bans the procedure in most instances. He created diversion programs to point people with mental health and substance abuse problems toward treatment instead of jail. And his office has expanded efforts to examine potential cases of wrongful convictions.
In Missouri’s 3rd District, which stretches from the western outskirts of the St. Louis region through central Missouri, the candidate with Trump’s endorsement won. Bob Onder, a physician and also a former state senator, defeated former state Sen. Kurt Schaefer.
Trump wrote on Truth Social last month that Onder was “an incredible America First Patriot.” The former president wrote that Schaefer “is WEAK ON MAGA,” adding, “That’s all you have to know!”
The 3rd District is heavily Republican, and Onder will be favored against Democrat Bethany Mann, a political newcomer, in November. ___
This story has been updated to correct that Onder won in Missouri’s 3rd District, not Schaefer
Summer Ballentine in Columbia, Missouri, contributed to this report.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Because giving a speech - for a lot of people - seems harder than giving a presentation. Bad slides are actually worse than no slides. But the reason so many speakers want slides or props is because they find it too hard to deliver speeches, and because effective visual aids makes it easier for them to get their points across. Effective ...
Speech emphasizes the spoken word, while presentations provide a visual component. Speeches often involve more improvisation, while presentations are carefully planned and structured. Ultimately, the choice between speech and presentation depends on the context and desired impact on the audience.
Speeches mainly use visual aids to help themselves remember the points they want to talk about. While in presentation, the use of visual aids is to help the audiences understand. In this case, we can expand the difference between the two. While in speeches, the visual aid design is not that important, the design in presentation is highly ...
It is better to understand this difference so that we can prepare accordingly and get the best results! So, in this article, I will be sharing with you a few key differences between a presentation and public speaking. So, let's get started! 1. Communication Format. Traditionally, Public Speaking is giving a speech face to face to a live audience.
A debate differs from both a speech and a presentation because it's between two sides that are equally involved. Each side usually takes an opposing view on the debate question or subject. It's often like a contest where, at the end of it, a vote is taken to decide who won the debate. A speech and a presentation are two very different things.
Speech: WHAT IT IS: A speech is the most formal of these three types of public speaking, and it tends to be the longest and most carefully scripted. Speeches are often given to an external audience on a planned occasion, and they frequently cover "big ideas" about which you or your company are considered experts.
Level of interactivity. One significant Difference Between Public Speaking and Presentations lies in the level of interactivity with the audience. In Public Speaking, there is often direct engagement with the audience, allowing for questions, discussions, and active participation. The speaker may seek audience feedback, encourage dialogue, or ...
Speech and presentation have become synonyms for many. Here I share what the difference really is, so you can be confident you're using the right term.
Speech refers to the act of verbally expressing information to an audience, while a presentation encompasses both visual and verbal methods of delivering information to an audience. Key Differences A speech primarily focuses on verbal communication, emphasizing the speaker's language and rhetoric.
Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired ...
In this video, the difference between speeches and presentations is explained. #publicspeaking #presentationskills #speech #presentation, #publicspeaking, #p...
Key Takeaways. There are four main kinds of speech delivery: impromptu, extemporaneous, manuscript, and memorized. Impromptu speaking involves delivering a message on the spur of the moment, as when someone is asked to "say a few words.". Extemporaneous speaking consists of delivering a speech in a conversational fashion using notes.
The other difference is that the public speaker will be judged on the timbre and cadence of their voice, which will be on display for a longer period of time than with the professional presenter. Get in the driver's seat and Connect with potential customers with PeaksLead. Written By: Philip Andrews. TAGS : Personal Development Public Speaking.
Public Speaking and Presentations: Tips for Success. This resource includes tips and suggestions for improving your public speaking skills. Even if you've never spoken in front of a large group before, chances are you will encounter public speaking sometime during your life. Whether you're giving a presentation for your classmates or ...
A speech is typically judged on the clarity of its message, the effectiveness of its delivery, and the emotional impact on the audience. A presentation's success, however, also includes the effectiveness of visual aids, the clarity of data presentation, and the seamless integration of technology and verbal narration.
CREATE THIS PRESENTATION. 2. Persuasive presentation. If you've ever been swayed by a passionate speaker armed with compelling arguments, you've experienced a persuasive presentation . This type of presentation is like a verbal tug-of-war, aiming to convince the audience to see things from a specific perspective.
Describe the functions of the speech to inform. Explain the difference between exposition and interpretation. Informative presentations focus on helping the audience to understand a topic, issue, or technique more clearly. ... The speech to inform is like the classroom setting in that the goal is to inform, not to persuade, entertain, display ...
Wrong. A presentation is about information. A pitch is about connection. Slow down, and stop trying to lift the world by yourself. Instead, connect your message to the people you wish to influence ...
Use humor or wit. Sprinkle some humor and wit to spice things up. Cracking a clever joke or throwing in a witty remark can break the ice and create a positively charged atmosphere. If you're cracking your head on how to start a group presentation, humor is a great way to start a presentation speech.
Because of the difference in the importance of body language, the value of the presenter's voice is greater when it comes to online presentations. As mentioned, the giver of an online presentation is likely to dedicate most of the screen time to sharing visual content that illustrates the main points of the talk.
The main difference between an essay and a presentation is that an essay is written, while a presentation is given verbally. Presentations involve live audiences and incorporate non-verbal ...
The model we introduce in this chapter, which is summarised in Table 4.1, provides a framework for the analysis of Discourse Presentation in texts.It comprises three parallel clines for speech, writing and thought, which are ordered according to the extent the narrator is involved in presenting the discourse of a character and the amount of access we have to the original.
Tim Walz's selection as Kamala Harris' running mate underscores both the power of social media and of being relatively affable and nondivisive.
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF SPEECH-LANGUAGE PATHOLOGY (AJSLP) JOURNAL OF SPEECH, LANGUAGE, AND HEARING RESEARCH (JSLHR) ... , a systematic review was carried out to investigate the differences in perceived VF in a variety of cultural-linguistic contexts, based on a standard self-assessment instrument—the Vocal Fatigue Index (VFI), as translated in ...
CNN's Alayna Treene fact-checks JD Vance's claims about Tim Walz's military service.
Vance, Trump, has taken a hard stance on immigration, referring to a crisis on the southern border. Recently, Vance visited the U.S.-Mexico border and criticized the Joe Biden and Harris ...
How old is Tim Walz? Gov. Tim Walz is 60 years old, born on April 6, 1964. He was born in West Point, Nebraska, and grew up in Valentine, Nebraska. He joined the National Guard at 17 and served ...
Some church leaders and politicians have condemned the performance from the opening ceremony for mocking Christianity. Art historians are divided.
St. Louis County Prosecuting Attorney Wesley Bell has defeated U.S. Rep. Cori Bush in a Democratic primary in St. Louis. Tuesday's results mark the second time this year that one of the party's incumbents has been ousted in an expensive contest that reflected deep divisions over the war in Gaza.
Good morning or afternoon, my name is _____, and in today's presentation we will discuss Williamson Act contracts, Agricult\൵ral Preserves, and Farmland Security Zones, and the difference between them.\爀屲At the bottom of the screen, you will see the st對aff members associated with the Williamson Act program.\爀屲We are glad to answer ...