Ford Motor Company Case Study
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Looking for Ford industry analysis? Find it here! We’ve prepared Ford Motor Company case study that contains analysis of the company’s financial condition and provides recommendations to its management.

Introduction
- Industry Analysis
- Environmental Scan
- Financial Condition
- Recommendations
Works Cited
The current report provides an in-depth analysis of the motor vehicle industry based on the Ford Motor Company case study. It also analyzes Ford Motor Company using SWOT analytical tool. Moreover, strategies that could be adopted by Ford Motor Company for the next five years have been provided. The study is divided in several sections with the first section being the motor vehicle industry analysis.
The industry analysis explores the industry structure, major environmental changes, competitors, and Ford’s competitive position in the industry. The second section gives an environmental scan with major focus on the major opportunities and threats. The third section explores the company’s key strengths and weaknesses. The last section gives viable strategic recommendations which can be adopted for the next five years.
Ford Industry Analysis
The motor vehicle industry is very competitive and characterized by changes in vehicles design and technology (CLLES 7. Just like any other industry, the motor vehicle industrial structure and landscape have been changing and reshaping operationally, functionally, and geographically.
The increase in competition has been as a result of new emerging automotive and vehicle industries in South American, Eastern and Central European, and Asian countries (CLLES 7). The industry’s major structures are the motor vehicle and the motor vehicle parts sections.
These two sections provide employment to more than one million people in U.S. The motor vehicle industry is a loosely connected industry and diversified in terms of supply chain structure, employment levels and compensation. Lastly, the market is characterized with excess capacity which is a major structural problem.
The industry was highly affected by the 2007/2008 global financial crisis. Major players such as Chrysler and General Motor were majorly affected that it took the intervention of the government to bail them out.
However, based on the case study, Ford Motor Company was the only major company which was not affected by the financial crisis. The company has been described by as the only automaker company which has survived the major crises that have hit the motor industry without financial bailout by the government (The New York Times 2012).
The major competitors of Ford Motor Company are BMW, Chrysler, Toyota, General Motors, Honda, Nissan, Mercedes Benz, and Hyundai-Kia among others. In U.S, General Motors (GM), Toyota, and Honda are the main competitors of Ford (Canis and Yacobucci 6). Different automakers use different strategies to increase their competitive advantage.
Based on the case study, Toyota uses lean production to increase its effectiveness and efficiency in production. Toyota’s lean production encourages just-in-time scheduling, flexible production, teamwork, and quality production. In addition, the company avoids material wastage and inventories. Another company like Hyundai produces quality products to meet the demands outside Korea.
For instance, the company has recently established a production line in Alabama, U.S to near KIA to benefit from economies of scale (Canis and Yacobucci 6). In addition, the company offers the longest warranties which are geared towards the attraction of customers from the Japanese and US cars. In general, all the major competitors have brand product portfolio which are part of product diversification and cost differentiation.
General Motors which is the largest competitor of Ford Company has adopted a new strategy which has been borrowed from Toyota Company (Ferrell & Hartline 30). The new strategy is based on new auto designs which meet the expectations and demands of emerging market segments.
The company has acquired the Toyota’s design which involves synchronization of production, platforms, and parts from different parts of the world. This new globalization strategy encourages flexible manufacturing. Based on checks and benchmarking carried by Henry (91), the competitors in the automobile industry are grouped in four groups.
The first group is of high price and low range automobiles and it consists of Rolls Royce and Bentley. The second group comprises of Ferrari, Ashton Martin and Porsche while the third group contains BMW, Mercedes, and Lexus. The last group is composed of Ford, Renault, Honda, Volkswagen, GM, Nissan, Toyota, and Daimler Chrysler (Henry 91).
The Lexus, BMW and Mercedes group produces highly priced and quality products but of a lower product range. The Last group produces a broad range of products which have considerably low prices and quality compared to other groups. In this group, competitors compete in the market based on reliability, price, and the design of their products (Henry 92).
Ford is the second largest automaker after General Motor. The American automaker has found its niche in car and truck production. The company has a strong brand which has improved its competitive advantage. Product diversification has been the major competitive advantage thus increasing its competitive position in the industry.
To maintain its competitive position, Ford brands product portfolio comprises of Ford Ikon, Ford Fiesta, Ford, Fusion, Ford Endeavor, and Ford Figo. Its survival under numerous financial crises has increased the confidence and trust from different stakeholders especially consumers (The New York Times 2012). In North America, Ford remains as the largest market shareholder.
However, the company receives high competition in new emerging markets in Asia and Europe. Nonetheless, the American automaker has continued to defend its position in the industry and in 2008, it closed the gap that existed between itself and Toyota. The company was able to sell over 55,301 vehicles compared to Toyota in 2009 (Canis and Yacobucci 6).
Based on the current statistics, Ford has a market share of 15.5% after GM which has a market share of 19.8 percent (Canis and Yacobucci 6). The fall of GM and Chrysler was beneficial to Ford as many buyers between 2008 and 2009 preferred Ford cars thus increasing its financial and competitive position in the market.
As other companies market shares declined, that of Ford increased. To remain competitive, the company has provided new models which are affordable, competitive, and environmentally friendly.
Ford Company Analysis: Environmental Scan
Environmental scan has been carried through the use of SWOT analysis to give the major opportunities and threats that Ford Company has.
| Most important opportunities | Most important threats |
Company analysis
| Key Strengths | Key Weaknesses |
Ford Company Analysis: Financial Condition
The company is in a better financial position compared to other players such as Chrysler and GM. In 2008, the company survived the U.S and Europe financial crises (The New York Times 2012). In addition, as other companies’ market share reduced, Ford’s market share increased to 15.5% while that of GM’s dropped to 19.8 % (Canis and Yacobucci 6). In 2009, Ford increased its sales by 55,301 vehicles compared to Toyota.
In 2011, Ford increased its small cars sales in U.S by 25 percent (Ford Motor Company 2012). The annual operating profits of Ford increased in 2011 and as a result, the company announced an operating pre-tax profit of $8.8 billion (Ford Motor Company 2012).
In a third year in a row, the company has announced improved annual operating profits which show that the company is in a better financial position. According to Ford Motor Company 2011 annual sustainability report, the company has increased its annual automotive gross cash which is a sign of financial progress (Ford Motor Company 2012).
The revenues of Ford have grown from USD 119.3 billion in 2011 to USD 128.2 billion in 2012 (Bloomberg Businessweek 2012). In addition, the company has reduced its sales pegged on income tax expense to -0.90% from -0.505 thus leading to a bottom line growth of USD 20.2 billion from USD 6.6 billion (Bloomberg Businessweek 2012).
Because of its financial position, the automaker plans to invest $16 billion in the U.S production plants with the objective of designing, engineering and producing upgraded vehicle components. Therefore, Ford Motor Company financial position is strong despite the recession and economic downturns.
Ford Case Study: Recommendations
Based on the industry and company analysis, some suggestions have been provided which can be applied for the next 5 years as part of strategic plan management. First, Ford needs to expand its market operations in emerging economies in Africa, Middle East, and Asia so as to reduce overreliance of the U.S market. This would expand its market share and meet new demand in new market segments.
Second, the company needs to diversify its products to meet the demands and expectations of consumers in the 21 st century. Ford needs to carry out market and consumer demand research to determine the major emerging market trends and patterns. Product diversification can be achieved through the production of more fuel efficient and environmentally clean cars which are small in size.
This would meet the demand in the new segment of environmentally sustainable and green fuel motor vehicles. Ford can adopt the strategy adopted by Toyota of producing a variety of cars annually which fit different market segments. For example, it can design cars that meet the income capacity of consumers in developing nations.
Drawing from the case study analysis, Ford is the second largest American based automaker in the world. In addition, the company operates in a very competitive and saturated market. As a result, the company faces high level of competition from major players such as BMW, GM, Toyota, Honda, Chrysler, and Mercedes Benz among others.
When grouped, Ford lie at the lowest group which produces broadest range of cars which affordable prices. The company is a strong brand which is globally known. Its financial capacity and presence has increased its market share. The major weakness of the company is that it highly depends on the U.S market. Financial crisis in Europe and U.S have threatened its performance and market share.
Financially, Ford is stable and in a better position. The company has increased in sales and revenues as well as pre-tax operating profits in a consecutive period of three years. it has been recommended that the company ought to increase its presence in emerging markets and produce diversified products
Canis, Bills and Brent D. Yacobucci. “The U.S. Motor Vehicle Industry: Confronting a New Dynamic in the Global Economy.” Congressional Research Service 26 Mar. 2010: 1-66. Print.
CLLES. Benchmarking Analysis for the Motor Vehicle Industry. Center for Lean Logistics and Engineered Systems. University of North Carolina, 2009. Print.
Bloomberg Businessweek. “Ford Motor Co (F: New York).” Bloomberg Businessweek 6 Dec. 2012: 1. Print.
Ferrell, O C, and Michael D. Hartline. Marketing Strategy . Mason, OH: Thomson South-Western, 2008. Print.
Ford Motor Company. “ Financial Health – Sustainability 2011/12 .” PDF file. 7 Dec. 2012. < https://corporate.ford.com/homepage.html >.
Henry, Anthony. Understanding Strategic Management . Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2008. Print.
Schwed, Joel. Ford: History and Corporate Profile . 12 Dec. 2011. Web. < http://www.valueline.com/Stocks/Highlight.aspx?id=12047 >.
The New York Times. “Ford Motor Company.” The New York Times 30 Oct. 2012: 1. Print.
- Emirates Airlines Company Financial Analysis
- Michael Eisner's Disney
- Chrysler’s Speed Merchant and Marchionne’s Leadership
- GM Executive Summary: Major Markets for GM Brands
- Microeconomics of Ford, General Motors, Chrysler
- Saudi Basic Industries Corporation (SABIC)
- The Emirates Airline Company
- Amazing Cars Market Position
- Mitsubishi Motors
- Adam Aircraft Industries Challenges
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, May 31). Ford Motor Company Case Study. https://ivypanda.com/essays/company-analysis-ford-motor-company/
"Ford Motor Company Case Study." IvyPanda , 31 May 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/company-analysis-ford-motor-company/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'Ford Motor Company Case Study'. 31 May.
IvyPanda . 2019. "Ford Motor Company Case Study." May 31, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/company-analysis-ford-motor-company/.
1. IvyPanda . "Ford Motor Company Case Study." May 31, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/company-analysis-ford-motor-company/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Ford Motor Company Case Study." May 31, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/company-analysis-ford-motor-company/.
FORD MOTOR COMPANY CASE STUDY
Emrah Aydın
1.INTRODUCTION
Ford Motor Company was started by Henry Ford in 1903 and the company went public in 1956. It is one of the most rooted and long-established automotive companies. It may be said that it is the pioneer of innovations in many areas like the first modern auto assembly line. The company has 2 major businesses which are automotive and financial services. Ford is known with its strong brand recognition, strong financial and marketing network and its innovative products. Mustang, Escort, Model T, Taurus and Explorer and SUVs models of Ford’s were quite influential.
Ford was the most profitable automaker in 1998 and its stock price increased by 130 percent from 1996 to 1999. Then, Jacques Nasser had worked as CEO of the company during 1999–2001. He applied some beneficial strategies like; diversification strategy which bought Kwik-fit to implement this strategy. Also he applied some strategies which brought detrimental consequences to the company. There was the recall of vehicles because of a tire problem and that recall cost $3 billion to Ford. Moreover, there was also dividing between Jacques Nasser and Bill Ford. Then, Bill Ford became CEO in 2001.
This company, which has been operating for many years, has had its ups and downs. The company had a rough time in the early 2000s. This case study is about Ford Motor Company’s strategic analysis which covers the years 1999 and 2003.
2. STRATEGIC ANALYSIS
2.1.General Environment (PESTEL framework)
Ford Motor Company is one of the five big automakers in the world and ranked in the top twenty American-based companies overall based on its global revenues. As a recognized brand, Ford has its plants spread around the world which makes it bound for many factors — this makes PESTEL analysis a must to understand the company’s environment in comprehension and the change of leadership in the midst of Ford’s fall makes this even more important. Though the company is profoundly bounded by PESTEL factors, the company has no or little control over all despite its global size and influence in the automotive industry. This analysis aims to pinpoint and emphasize the potential impacts of political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors affecting the company as a whole.
Political Factors Affecting Ford Motor Company
We should analyse political factors on both international and local levels for Ford Motor Company. The company has lots of plants and initiatives across the globe, thus it is exposed and bound to different political settings. For example, Ford has an added-value business operation for its distribution network in Great Britain, Kwik-Fit, which makes the company affected potentially by the trade agreements both between the US and the Europe, and European and Britain countries– and at large affecting the value chain of Ford Motor Company in European region. Any significant change in these regions could force the company to redesign the value chain and make necessary changes.
Also, the terrorist attacks on September 11 and ties with the Asian countries are counted as political factors for the company. On the local level, the policy interest rates and monetary policies of central banks should be monitored especially for developing countries because in these countries, economy and politics are closely tied. This affects the buying power of individuals in a country especially in times of an economic crisis caused by a pandemic.
As Japanese companies have a substantial market share in the U.S., any political incident or issue between Japan and the U.S. could affect both parts. The company should closely watch the developing relationships between these parties and also for critical countries where Japanese companies penetrate the automotive industry.
Economic Factors Affecting Ford Motor Company
Back then in the late 90s and early 2000s, the economy was soft and interest rates were increased, with the incidents in 2001 and the recession, sales started to decrease dramatically. This resulted in automotive companies to seek growth outside the country: European countries and other continents showed promise for ample growth in sales and market share. However, it proposes a challenge for the company to adjust the value offerings and the designs in line with European or other foreign consumers’ preferences. The company is a renowned brand that showed great resilience in coming out of crisis situations.
Incidents like September 11 cause consumers to buy less, consume less and save more. This resulted in increased price-competition and increased discount & incentive schemes in the automotive industry. The durable nature of cars causes consumers to wait for replacing their current vehicles and this is valid for the whole economy as well — the growth in economy slows and consumer spending decreases significantly.
Ford Motor Company should review business cycle stages in countries as well — this may show differences in different kinds of countries like underdeveloped and developing etc. Although counted as a political factor above, monetary policy of countries interchangeably has an economic impact on the company.
Inflation rates, interest rates, the income levels of household, labor costs, economic stage and growth rate of a country, the situation of financial markets should be observed as economic factors.
Social Factors Affecting Ford Motor Company
Consumers have a huge impact on companies and industries — and especially in the automotive industry we see a rising interest in technology solutions on vehicles, and the power of consumers is only increasing. This is of course bound to the economic and cultural level of consumers and markets as a whole, but the global trends should be observed for insights in varying countries.
Factors like September 11, also changes the social environment in the country — people tend to decrease socialization and leisure activities, limit their spending, and distrust the government and such bodies. This resulted in decreased demand for the industry — this could have been overcome with marketing communications that focus on solidarity and rebuilding trust and relationships with consumers.
Other social factors include class structure, population growth and demographics, family size and structures, lifestyle trends and shared values. The social analysis of the consumer base is crucial for companies like Ford Motor Company, because the automotive industry codes the cars according to the family size and structure, the lifestyle of the family or the individual, the demographics of the target audience and especially the socioeconomic class that they belong to. The company should review social factors imperatively — because cars introduced to the market are positioned accordingly. Demographics, culture and education level of consumers also play a role in the cars introduced and also in the communication choices of the company.
Technological Factors Affecting Ford Motor Company
Today, the technological capabilities and advancement of vehicles play a key role in consumers’ preferences. Although the company introduces the same model of a car with different qualities and technological packages, the consumers’ technology-savviness should be observed. The company is proven to be a leader in the technological capabilities and improvement in the field but with the economic and social factors in mind, the knowledge and capabilities of consumers affect the vehicles’ packages in the particular market.
Ford Motor Company, however, was challenged by the Japanese brands as they had superior design and quality in their vehicles and Ford was lagging behind. Other vehicle brands exploited several segments in the market and they designed accordingly, while Ford failed to do so. Ford’s key focus was to broaden and ease the financing options for consumers rather than serving better models and quality with technological aspects.
Other car makers were exploiting newer hybrid technologies to produce more environment-friendly cars for example. The company, should it want to retain the market share and leadership, must closely watch technological changes and fast-changing consumer preferences. The company could produce pilot units and test the units to introduce the new cars.
Legal Factors Affecting Ford Motor Company
Amidst the fall of Ford, the legal case between Firestone and the company has resulted in bad publicity and loss of consumer trust. The market share should have been affected by this situation where Ford and Firestone could not manage the publicity and the case backfired for both parties. Ford had to recall vehicles that had these tires on.
Also, infringements in patents and intellectual property laws, employment and health & safety laws for employees and e-commerce laws of countries should be observed.
International cases with other automotive companies and other companies could impact the company’s image across the globe, thus the company should manage the PR practices along with the case.
The company should also keep an eye on for legal frameworks and changing regulations on the local level in countries. Because the company has plants all over the world, employee benefits that are implied to be mandatory by the government and work legislations could also have impact on the company as well.
Environmental Factors Affecting Ford Motor Company
Over time the customer base started to show interest in environment friendly solutions in many areas. Vehicles are a big part of this trend, and thus brands in the U.S. started to explore ways to develop more environmentally friendly vehicles for consumers. If the company lags behind the other brands to develop green alternatives, it should focus on benchmarking and follow the competition in this area.
Availability of certain non-renewable energy sources like gas and oil have a huge role in the automotive industry. As the oil sources continue to decrease, automotive companies should look for alternatives — and in this case, green alternatives seem to be the best solutions as consumers become aware of climate change and pollution. Bill Ford is known as “tree hugger” which makes the company focus on the environmental alternatives supported by the top management.
All PESTEL factors should be monitored on both the international and local levels as Ford Motor Company is a global automotive manufacturer with its operations spread across the globe. The company has potential growth areas for the future and threats that can have impact on its business operations if not watched closely.
2.2.Porter Five Forces Analysis: Ford Motor Company
Threats of New Entrants
· Required capital costs and investments are high (weak force)
· Building brand equity is costly (weak force)
· Economy in turmoil (weak force)
Automotive industry is a rather stable one as new entrants are not common. However, when new entrants come into play, they bring innovation, new aspects and fields to improve that the incumbents somehow ignored. New entrants cause challenges like reducing prices and costs, value propositions that are not offered by incumbents.
Ford Motor Company should continue to innovate relentlessly to attract new segments of customers and should improve the brand equity and positioning in the eyes of customers. The company also should give a reason for old Ford drivers to buy new ones.
There are several tools for Ford to use when new entrants start to challenge the market including building economies of scale that the new entrant could not achieve the same reduced costs, improving R&D processes and attracting the talent in the market to keep innovating.
Companies like Ford impose a huge cost to enter the market as the company has lots of plants and employees, has a huge business operation going on all over the world and a brand equity almost impossible to undermine. As the economy is in a bad situation and going through a recession, new players cannot penetrate the market because of the increased interest rates. In times like these, consumers demand incentives and discounts even more and new players do not have the adequate strength to provide these demands. The automotive industry’s high costs of capital, conducting the business and developing a brand equity in fact show prominent weak force for new entrants.
Rivalry Among Existing Competitors
· Competitive aggressiveness of brands (strong force)
· Price competition (strong force)
· High exit barrier for companies in the industry (strong force)
· Moderate number of firms (moderate force)
Facing tough competition around the globe, Ford should both innovate disrupting the market and should show a sustainable innovation to keep the cutting-edge technology the best in the consumers’ eyes. To do so, the company even acquired Volvo to expand its luxury car segment substantially.
The U.S. automotive industry is highly competitive and a cyclical business that is known for overproducing vehicles. In this environment, the company should position itself as one of the top players, and thus should take top players like General Motors, Volvo and Toyota as competition. Because the automotive industry requires high costs and investments, the companies in the industry will pursue competition rather than leaving the industry; this is a strong force that affects the company. The competition will proceed and thus Ford should take its competitive advantage to the maximum.
Ford was lagging behind Toyota and General Motors in producing best-class vehicles, and in January 2004, Toyota surpassed Ford and took its place in the market. Especially in the late 90s, General Motors was challenging the market leader position of Ford.
The rivalry amongst these companies was based on product quality and design, and Ford has focused on delivering incentives and discount schemes to customers. As Japanese had great design and quality, they also introduced such schemes to steal market share even more — this is a huge mistake of Ford as price strategies could be easily replicated, when product quality and technology behind design is more complex and hard to replicate.
In terms of acquiring raw materials, we see that GM and other companies have successfully hedged their risks on purchases of precious materials and Ford has failed to do so due to issues regarding the internal communication — this poses another growth area for the top management. Highly competitive consumer financing offers have caused profit margins to decrease, and companies started to look for growth without profitability — this is coupled with Japanese and other companies’ excellence in delivering product design and quality.
The company has strong ties with marketing and financial networks, although it has gone through conflicts with some partners. Once a leader across multiple fronts, Ford should tighten these relationships to overcome the competition.
In the automotive industry, competition is derived from the product quality and lean production — although Ford has been the leader in the production methods, the company stumbled to keep this sustainable advantage and gave the rein to its competitors. Compared to its competitors, Ford’s time to produce is higher and thus creating much more cost for the company, squeezing its profit margins even more.
Bargaining Power of Buyers
· Moderate substitution cost (moderate force)
· Moderate size of purchase for individuals and families (moderate force)
· Moderate substitutes (moderate force)
As consumers and product makers co-create value propositions, the bargaining power of buyers dramatically increased for the automotive industry as well. With minimum prices in their minds, consumers are demanding a lot from vehicle manufacturers. To balance this force, the company should grow a large customer base among its middle and lower segments, and innovate new products at large — this lowers the discount demands of customers while reducing the effect of competition among the customer base.
Ford has strong brand recognition, however buyers can still significantly influence the way Ford does its business, and a small change can cause the company a great loss. The best option here is to increase customer satisfaction among the customer base across all segments and increase their switching costs. The switching cost is not only the price, it could be the peripheral aspects of being a Ford driver, thus the company should conduct a marketing communication that increases the brand equity and its luxurious associations with the brand. Acquisition of Volvo, in this sense, plays a key role in building brand equity and loyalty among the target audience in this segment.
Threats of Substitutes
· High switching costs (weak force)
· High performance and design of substitutes (strong force)
When the customer base of a segment is faced with a new offering by another company, profitability may suffer — thus, Ford should position itself in a uniquely differentiated way. The company may become a service oriented one instead of a product-oriented; technological capabilities of the company can play a huge role here.
Because vehicles are oftenly bought with loans, the switching costs here are huge for the customer, and other substitutes have little or no added-value aspects compared to Ford. Should the company understand the needs of the customers and deep-dive into it, it may both increase the switching cost and threat of being substituted.
As other brands like General Motors and Toyota provide its customers with constant innovation, Ford is less preferred by customers. Lean production methods help save funds to keep the innovation going for other brands, while Ford focuses on price-based strategies and providing customers with financing options. This results in a damaged brand equity, and customers start to prefer other brands that provide innovative solutions with great design over discounts.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
· Moderate supplies for automotive industry (moderate force)
· Moderate number of suppliers (moderate force)
Vehicle manufacturers buy their raw materials from different suppliers — and in the case of Ford, this is imperative as the company has operations spread across the world. Because the increased power of suppliers may decrease the profit margins of Ford, the company should build a value chain that is constituted from multiple suppliers; using various raw materials to produce the same part of vehicles, as they may change the raw material if necessary, and arranging agreements with suppliers that their businesses depend solely on Ford — which will increase the bargaining power of the company.
2.3.Competitive Profile Matrix (CPM)
In the external and internal environment, there are some positive and some negative aspects for the organization.
The CPM rating represents the company’s response to the crucial performance variables.
In CPM, there are some significant points related to ranking. Rating for each factor is applied as;
· The response is poor represented by 1.0
· The response is average is represented by 2.0
· The response is above average represented by 3.0
· The response is superior represented by 4.0
The weight attribute in CPM shows the relative importance of the factor in the company’s business being efficient. The weight range from 0.0 means not important and 1.0 means important, the total of all weight allocated to variables must be equal to 1.0 otherwise it would not be considered right to quantify.
The result obtained after multiplying each factor rating with the weight, is the weighted score value. Furthermore, the sum of the weighted score is equal to the weighted total score,
For the CPM matrix, the average weighted score is 2.5 The total weighted score of the business higher than 2.5 is considered to be good in the area. The other dimension of CPM is the business with the higher total weighted score considered among the competitors as the winner.
Ford Motor company has two important competitors in the market which are, General Motors and Toyota. Seven critical success factors were determined to see Ford’s place in the market.product quality, Financial position and Brand Recognition are the most crucial success factors.
According to the competitive profile matrix General Motors had the highest weighted score with respect to Ford and Toyota.
2.4.Value chain analysis
Primary Activities:
Inbound and Outbound logistics:
Ford’s manufacturing network is spread globally. Ford had production facilities on six continents and was selling its products worldwide. Logistics played an integral part in Ford’s supply chain’s effective and profitable service. The role of logistics, whether inbound or outbound, is integral to preserving productivity in the supply chain.
Operations :
Ford is a multinational brand and in virtually every corner, it has sales across the globe. It works internationally with its headquarters, assembly plants and dealerships. Manufacturing and manufacturing plants, distribution centers, stores, sales or administration buildings, and engineering centers are among the key assets. Based on the geographic region of operation, with the automotive industry entering global motorization, the markets of Asia, Middle and South America and central and Eastern Europe had a good area for Ford.It has achieved success in environmentally friendly vehicles produced with new hybrid technologies.Ford uses technology to drive higher productivity in its manufacturing and supply chain network. He made unique designs using technological developments with Ford engineers’ teams.
Marketing and sales:
Marketing and sales practices at Ford emphasize innovativeness and quality of the brand, as well as, offer appropriate financing options to the customer. The company sells cars, SUVs, and trucks in global markets. Ford has implemented a strategy for retailing and the recovery of scraps, where Ford can sell and market all aspects of the automobile business, except for production sales in the automotive field. The Premier Automotive Group (PAG) established a corporate division within the Ford Motor Corporation in 1999 to manage the business affairs of the high-end automotive products of Ford.
The automotive industry is highly competitive and, as workers can be a significant source of competitive advantage for any brand, firms want primarily on carefully handling them to ensure their job advancement. When Bill Ford became CEO of Ford Motor Company in October 2001, he brought in a new management team to use this strategy. Bill Ford had a pro-employee, even pro-union reputation. The important effect of this situation increased the trust of the company employees and strengthened their loyalty to the job. Thus the service provided by company employees has improved positively. A wide variety of goods and services have been introduced to the market by Ford. It has continued to develop its product range through a continuous focus on research, development, and production systems. It achieved its strategy in retailing and scrap purchasing by purchasing Kwik-Fit, a service network of 20,000 automobile service centers in the UK. With this strategy, both the sales-marketing area has expanded and has gained great upward momentum in the field of service. Ford also provides financial services through Ford Motor Credit Company LLC (“Ford Credit”).
2.5.Financial analysis
Note: Above ratio calculations may be subject to rounding errors.
a. Liquidity
It seems that Ford Motor Company’s liquidity is with up and down as the current, acid-test and cash ratios indicate. It is clear that Ford Motor Company’s ability to fulfill its short-term debt obligations and to pay its short-term obligations when they are due is not fully met. It shows how many times short-term debt obligations are met by cash and liquid assets. And those values are always smaller than 1 means the short term obligations are not fully covered. So, the company is not in a very good financial situation and it may fall into financial difficulties. When it is reviewed the balance sheet, it is observed that the cash balance has increased creating more liquidity within the total current assets. The most important problem at the base is increasing in current liabilities over time while the current assets are unstable. Ford Motor Company’s cash and cash equivalents, marketable debt securities may be sufficient to meet their liquidity needs. The company may need cash and may need to raise funds via available liquidity and cash flows from operations and future debt issuances.
b. Turnover Ratios
It seems that the company’s total asset turnover is decreasing from 1999 to 2003. It means that Ford Motor Company’s efficiency of using its assets decreased during 1999 to 2003. In the relevant period, there was a peak for inventory turnover in 2001. Then again it was decreasing and it was in the lowest level in 2003. As it seems, the most efficient year according to inventory management is 2001. It is the same for the days’ sales in inventory. Also, the receivable turnover was unstable in relevant years. The peak receivable ratio is in 2002, so the company fastest collected its money in 2002 and the average collection period increased while the inventory turnover actually increased.
While the assets increased, the debt ratio also increased significantly. It seems that the company runs up debts more short term debt than long term debt. Times interest earned are increasing 2000 to 2003 which means the Ford Motor Company’s ability of covering the interest payments for its debts are increasing. From 2000 to 2003, the cash coverage of the company showed the same reaction with times interest earned, so the company was increasing its ability to generate cash from operations.
d. Profitability
After Income Statement check, it is seen that during 2001 and 2002, net income was minus. When it is considered that net income is revenue minus cost of goods sold and other expenses, the company has lost in 2001 and 2002. After that company has increased its net income and again it could have profit. Total asset turnover is decreasing which means the company doesn’t perform well because lower ratios show that the company’s assets generate less revenue per dollar. Other measures for profitability are operating profit margin and gross profit margin. In this five-year period, it is observed that operating profit margin increased until 9.77% but in 2003 it dropped to 8.19%. On the other hand, there is an decrease in gross profit margin that depends on gross profit and sales. This shows that the income coming from operating activities are decreasing whereas non operating income is decreasing. In order to solve this problem, operating expenses should be decreased.
e. Market value
Earnings per share were negative in 2002 and 2001. It means Ford Motor Company has negative earnings in these 2 years. It may be because of environmental factors that are out of the company’s control. In 2003, earning per share became positive so the companies could generate sufficient profit and eliminate the risk of bankruptcy. The highest market to book value is in 1999. However all of the markets to book values are quite under the 1, so the company couldn’t succeed in creating value for stockholders during 1999 to 2003.
2.6.SWOT analysis
1)Strengths
Ford Motor company had an extremely strong brand awareness, a strong financial and marketing network, and also was known for its innovative products in the sector. Many of its products were particularly well known and in great demand. Throughout the history of the company, it has pioneered many firsts. The company made the difference by establishing the first modem auto assembly line that allowed the Model T Class to be manufactured at a cost within the reach of the masses. And others it has been the world’s largest truck manufacturer. Apart from Ford’s popular brands Taurus and Explorer, it has also been in the sports utility vehicles market. With its sporty off-road vehicle, it has gained a contemporary place in this market as well. Ford Credit and Hertz Corporation, two subsidiaries of Ford Motor Company, have had significant success. With the expansion of Ford Credit, it created a greater profit margin than the main automotive sector. Ford didn’t just benefit its own vehicles and it also benefited all brands in the changing times.
2) Weaknesses
Ford has had a lack of focus in some particular areas. Ford’s key focus wasn’t on competing with better models and quality. The key focus on financing options for its customers. It also lacked focus on core areas of product development, manufacturing systems, and finance. Ford Motor company failed to protect the risks on precious metal purchases in January 2002. The lack of communication between the procurement, research and treasury departments within the company caused huge losses. The quality problems of Ford’s automobiles caused its reliability in the market to decrease. As a result of this problem, both companies are blaming each other and leading to bad impressions. Ford had to recall all its vehicles with this tire on the market. Other quality problems that he generally experienced in his vehicles continued. In the survey that measured vehicle durability in 2003, in Exhibit 5 is in the eighth place as can be seen. Ford’s teams of engineers each put a lot of effort into creating unique equipment, and as a result, they created an over-engineered design, but it was a costly vehicle and consumed a lot of time compared to its competitors.
There are three elements that threaten the Ford company. New entrants to the market, cost constraints in the competitive market and the strengths of foreign competitors. Ford’s product that maintained its superiority until that time remained behind with the products released by General Motor in 2001, soon lost its leadership position to General Motors. Another major threat Ford faces in the aftermath were powerful newcomers in this developed market of the auto industry. There were many foreign competitors who are fighting fiercely for market share and producing a wide variety of tools to meet customers’ demand. In 2004, the strength of its competitors and the quality problems it experienced caused a loss of economic power. Even Ford’s newest models were only sold with incentives and discounts. To turn this into an opportunity, its daily competitors took an aggressive way to lower their credit ratings. Finally, if Ford and the auto industry face an increase in raw materials or a continuation of low credit rating, then they will have to increase vehicle prices and operating profits will be thwarted.
4) Opportunities
One of the possibilities Ford used was that the automotive industry in the United States was competitive. The number of cars and trucks sold to retail buyers in the country, or the industry demand, was increasing. Whatever the reasons for the increase, this created an opportunity in the market for the company. The volume of growth was challenging in the US market, where automobile manufacturers were intense and diverse. But the markets of Asia, Central and South America, and central and eastern Europe were hope for cars. A new era of the automobile industry was beginning, and this “global motorization” was a great opportunity for Ford.
2.7.SPACE matrix
The SPACE Matrix consists of four areas which are ,Competitive Advantage (X axis), Financial Strength (Y axis), Industry Strength (X axis) and Environmental stability (Y axis).
CA Average is = -2,5
IS Average is = 3,75
FS Average is = 1,75
ES Average is = -2,75
Vector Coordinates;
X axis= -2,5 +3,75=1,25
Y axis= -2,75+1,75= -1
As a result of the SPACE Matrix Ford company must improve its competitive skills.
2.8.TOWS matrix
Ford Motor Company
1. The reputation of Ford in managing a lot of successes and firsts, such as creating the first modern assembly line
2. Ford is the world’s largest truck manufacturer.
3. The expansion of the Ford Credit created more profit margins than the core automotive sector.
4. Ford had good brand awareness and a strong network for financial and marketing. The organization was praised for its creative goods.
5. In the market for sport utility vehicles, Ford managed to obtain a strong hold.
6. The achievements of Ford Motor Company’s subsidiaries, Ford Credit and Hertz Corporation.
1. In some particular areas, the lack of focus
2. The lack of coordination between the departments of purchasing and treasury
3. There are quality problems at Ford’s automobile models
4. Consumption of too much time to design goods that raise prices and are over-engineered.
Opportunities
1. Depending on the general economic environment, the variability of the automotive industry in the United States, the cost of buying and running cars and trucks, the availability of credit and fuel.
2. The automotive industry has entered the “global motorization” era.
1. Increase marketing to attract customers to spend. (S4, O1)
2. Produce vehicles capable of supporting new technologies. (S1, O2).
3. Market products at low prices by offering more competitive credit options. (S3, S6, O1)
1. Restore facilities to increase product quality. (W3, O2)
1. New entrants coming into the market
2. Cost pressures
3. Foreign rivals’ strength.
1. Use a strong distribution network to reach out the customers and eliminate new entrants in the market. (S4, T1)
2. Invest in intellectual property rights. This would help competing better in the market. (S1, T1, T3)
1. Reduce threat of competition by developing flexible product line (W3, T1, T3)
2. Improve fuel consumption (W4, T2)
3. Focus on cost effective strategies. (W1, T2)
2.9.QSPM analysis
Strategy -1 : Ford should improve its product quality.
Strategy -2: Ford should establish a more flexible manufacturing system.
Strategy-3: Increase the efficiency of Ford Finance.
(Attractiveness Score: 1 = not acceptable; 2 = possibly acceptable; 3 = probably acceptable; 4 = most acceptable; 0 = not relevant)
As a result of QSPM, it is clear that strategy-1 is the best option for Ford Motor Company while the others are close to each other’s.
3.CONCLUSION
In that case study, Ford Motor Company’s strategic analysis was made which covers the years 1999 and 2003. We have covered; General Environment (PESTEL framework), Porter’s five-forces analysis, Competitive Profile Matrix (CPM), Value chain analysis, Financial analysis, SWOT analysis, SPACE matrix, TOWN matrix, QSPM analysis.
Political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors should be considered on both the international and local sides because Ford Motor Company is a global automotive maker with its operations spread to six continents. The company should watch closely its business operations to see potential growth areas for the future and threats. because it is affected by the political and economic conditions of the countries where it operates. Also it should catch up with new environment friendly trends and new technological improvements to better compete with other automakers.
It seems that although Ford is a very old and well-established company and a pioneer of many innovations, it fell into the background compared to its competitors. It can be seen in the competitive profile matrix, too. Because General Motors has a higher score than Ford.
Ford had production facilities on six continents and was selling its products worldwide. So, it has a huge impact of having effective and profitable supply chain service. Ford could manage good operations in Asia, middle and South America and central and Eastern Europe. Also, Ford is good at emphasizing innovativeness and quality of the brand, moreover Ford offers appropriate financing options to the customer. Selling cars, SUVs, and trucks in global markets is also an asset for the company. Ford developed its product range through a continuous focus on research, development, and production systems. By purchasing Kwik-Fit both the sales-marketing area has expanded and has gained great upward momentum in the field of service.
After Ford became the most profitable automaker in 1998, its stock price rose by 130 percent. Unfortunately, the company had started to face financial difficulties in the early 2000’s. The company had a cash problem and it was long term borrowed. The company couldn’t balance its finance and it has a negative income which means Ford took a loss. It is maybe because of recalls of many cars, or unnecessary stock of valuable metal. And also non-effective and long-time production style was more costly than other automaker companies. Then, the new CEO, Bill Ford, managed to improve Ford’s financial situation a little. It was able to increase the negative profits and raise the company’s share value, if not as much as before.
Ford Motor had extremely strong brand awareness, a strong financial and marketing network, and also was known for its innovative products in the sector. However Ford’s key focus wasn’t on competing with better models and quality. The key focus was financing options for its customers. It also lacked focus on core areas of product development, manufacturing systems, and finance which are quite important for a manufacturer. So, new entrants to the market, cost constraints in the competitive market and the strengths of foreign competitors were badly affecting Ford. Besides tough competition between American automakers, also ford was affected by Japanese company’s market share. Hard competition could be an advantage to growth in the markets of Asia, Central and South America, and central and Eastern Europe and this “global motorization” was a great opportunity for Ford. Also in order to deal with that hard competition Ford company must improve its competitive skills like; brand image, innovation, market share and product quality.
It seems that Ford needed to increase marketing activities to attract customers to spend. It was beneficial to produce vehicles capable of supporting new technologies. Also it was helpful of market products at low prices by offering more competitive credit options. Ford was also needed to restore facilities to increase product quality and invest in intellectual property rights. Moreover, developing flexible product lines, improving fuel consumption and focusing on cost effective strategies would reduce threats. Finally, improving its product quality, establishing a more flexible manufacturing system and increasing the efficiency of Ford Finance would be important for Ford.
Emrah Aydin, Secil Kara, Bugra Kaya, Gonca Turna, Ilayda Cevik

Written by Emrah Aydın
Data Analytics Contractor in London | Supervisory Board Member and Volunteer of SACB | Master's Degree in Big Data Analytics
Text to speech
- Harvard Business School →
- Faculty & Research →
- March 1999 (Revised December 2001)
- HBS Case Collection
Ford Motor Company: Supply Chain Strategy
- Format: Print
More from the Author
- September 2009
- Academy of Management Learning & Education
The Technology Manager's Journey: An Extended Narrative Approach to Educating Technical Leaders
- June 2009 (Revised June 2009)
- Faculty Research
iPremier (C): Denial of Service Attack (Graphic Novel Version)
Ipremier (b): denial of service attack (graphic novel version).
- The Technology Manager's Journey: An Extended Narrative Approach to Educating Technical Leaders By: Robert D. Austin, Richard L. Nolan and Shannon O'Donnell
- iPremier (C): Denial of Service Attack (Graphic Novel Version) By: Robert D. Austin, Richard Nolan and Michael Parent
- iPremier (B): Denial of Service Attack (Graphic Novel Version) By: Richard Nolan, Robert D. Austin and Michael Parent

- Order Status
- Testimonials
- What Makes Us Different
Ford Motor Co.: Supply Chain Strategy Harvard Case Solution & Analysis
Home >> Supply Chain Management Cases >> Ford Motor Co.: Supply Chain Strategy

Ford Supply Chain Strategy
There are several operations that are accounted for in Ford’s current strategy that needs to be evaluated in order to lay groundwork. Ford motor is present in a dynamic and complex automotive industry that accounts for various levels of suppliers as well as other partnering firms; which complicates the operations and therefore calls for strategic restructuring. Ford management is evaluating strategic options for its utilization of internet resources in order to capitalize on the current operations so that it can stay ahead of their competition. It is primarily important as other competitors pose serious threat in regional level due to their long history of presence as well as marginally lower level of competitors merging together in order to gain position in market. Ford has been utilizing the internet technology in its recent operational management, which is evident in its suppliers using external data interchange to access Ford however it is not applicable to all of the suppliers due to lack of resources. Another instance where Ford undertaken the usage of technology is its production system which has made it possible to marginally reduce the delivery time to 15 days from a 60+ time frame. This leads to possible implications for further operational efficiencies in supply chain strategy to remain productive and leads the market position through useful implementation of internet technology.
Problem identification
The management is evaluating strategic consideration on implementing ‘virtual integration in supply chain’. The virtual integration accounts for integrating the various supplier bases with the management production as well as procurement department in order to tactfully reduce the operational load on procurement and production units in terms of maintaining the inventory and accounting for the inventory required for assembly and production. The presence of virtually integrated mechanism will entail retail network as well as high number of suppliers that form the basis of production of Ford’s various lines of vehicles. This accounts for the problems associated with collaborating various levels of partners into single system as the complications and level of operations are highly complicated as that of Dell which is being compared to the firm mentioned in the given case. Therefore the problem for management is to evaluate the implementation of virtual integration system in its supply chain.
The implementation decision has to be backed by supporting conclusion from the various associated factors. A strategic evaluation will account for the conclusion to implement the decision; which will be suitable for Ford in maintaining its position in market.
There are multiple layers of suppliers which are in control of providing the sub-units to Ford. These suppliers make-up the last layer of supplier base which is followed by more extensive layers of sub suppliers, these goes up to as extensive as 8 layers of sub-suppliers which are responsible for delivering the raw material or the sub-units to Ford for its production (Corporate Ford, 2014). The suppliers in Ford’s case are crucial players as this firm is operating in the automotive industry. The suppliers account for a strategic role due to the complex units involved in production and the position of Ford in market makes it important for the management to keep in track their suppliers and sub-supplier’s performance in order to prevent any possible blow to the process; which may result in financial loss as well as losing the market position (Brehm, 2013). These factors present the need to identify potential measures in order to induce the suppliers to a par level; through which information flow will enable the management from both sides to access the desired information in order to conduct the activities.
The process of virtually integrating these suppliers in extensive manner remain a pressing issue as the current IT system will eventually be obsolete therefore; raising the needs of introducing a more advanced IT solution that will encompass various levels and activities of the firm in order to maintain the market position. There are certain options available for the management. These are as follows....................
This is just a sample partial case solution. Please place the order on the website to order your own originally done case solution.
Ford describes the examination of its supply chain, to assess whether the company has "virtually integrated" model Dell Computers. "Hide by Robert D. Austin Source: HBS Premier Case Collection 9 pages. Publication Date: Mar 03, 1999. Prod. #: 699198-PDF-ENG
Related Case Solutions & Analyses:

Hire us for Originally Written Case Solution/ Analysis
Like us and get updates:.
Harvard Case Solutions
Search Case Solutions
- Accounting Case Solutions
- Auditing Case Studies
- Business Case Studies
- Economics Case Solutions
- Finance Case Studies Analysis
- Harvard Case Study Analysis Solutions
- Human Resource Cases
- Ivey Case Solutions
- Management Case Studies
- Marketing HBS Case Solutions
- Operations Management Case Studies
- Supply Chain Management Cases
- Taxation Case Studies
More From Supply Chain Management Cases
- VF Brands: Global Supply Chain Strategy
- Managing Risk to Avoid Supply-Chain Breakdown
- Northwest Newsprint Inc. (A)
- E-Enabled Closed-Loop Supply Chains
- TSC Stores: Supply Chain Management for Profitable Growth
- Social Media? Get Serious! Understanding the Functional Building Blocks of Social Media
- Supply Chain Management at World Co. Ltd.
Contact us:

Check Order Status

How Does it Work?
Why TheCaseSolutions.com?

Launching a Flawless Fiesta: Ford Motor Company
Ford Motor Company is one of the largest automakers in the United States, producing millions of automobiles each year at 70 plants worldwide. According to J. D. Power and Associates Initial Quality Survey, Ford has received more top rankings than any other automaker since 2007. It’s no surprise that high quality standards have kept Ford an industry leader since 1903. And Ford knows that quality begins at a vehicle’s launch. When a cosmetic problem with the vehicle’s carpet threatened the impending launch of the 2011 Ford Fiesta, the company’s Body Interior Six Sigma team saw a clear opportunity for quality improvement through proven optimization methods. In their quest to maintain high customer satisfaction and performance, the team used Minitab Statistical Software to help them eliminate the carpet defect and achieve a successful launch.
The Challenge
The launch date for the Fiesta was quickly approaching when Ford determined that the appearance of brush marks on vehicle carpets would be unacceptable to customers. Ford’s Body Interior Six Sigma team, led by Six Sigma Master Black Belt Scott Sterbenz, began by working with the supplier to analyze the process used to manufacture the automotive carpet. They found that the settings of a machine called a needler were the likely cause of the diminished product quality.

Ford Motor Company improved the quality of the carpets in the Ford Fiesta with the help of Minitab Statistical Software.
But the manufacturer worried that altering the needler’s settings also would affect the plushness of the carpet. The team needed to find process improvements that would eliminate brush marks while maintaining the plushness, and they also needed to consider other critical qualities, like the carpet’s durability and stain resistance. As they set out to complete the daunting task of improving carpet quality in the Fiesta, the quality improvement experts turned to the Design of Experiment (DOE) tools in Minitab Statistical Software.
How Minitab Helped
In statistics, DOE refers to the creation of a series of experimental runs, or tests, that provide insight into how multiple variables affect an outcome, or response. In a designed experiment, investigators change more than one factor at a time, and then use statistical analysis to determine what factors are important and identify the optimum levels for these factors. It’s an efficient and economical way to improve almost any process.
With time running out, Ford’s improvement team needed to design an experiment that assessed the effects of the six needler settings on the carpet’s brush markings and plushness levels. The experiment had to satisfy a difficult balance: it needed to be rigorous and reliable, but also needed to minimize the cost of materials and disruption to the supplier’s production schedule. Their challenge was to find an experimental design that would gather sufficient data to optimize the needler settings in as few runs as possible.
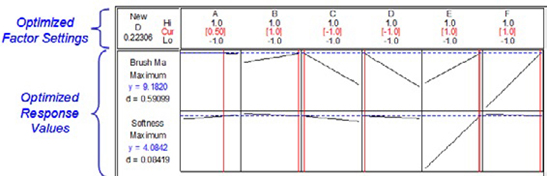
Experimenters used the Minitab Response Optimizer to determine the optimal configurations for eliminating brush marks and maintaining carpet plushness at the same time.
Minitab’s DOE tools can be used to create and analyze many different kinds of experiments, and can help investigators identify the best experimental design for their situation, based on the number of variables being studied and other conditions. Using Minitab’s DOE tools, the Ford team created a fractional factorial design with center points that would give them the information they needed in only 34 runs.
For each of the experimental runs, a team of evaluators compared the new product to the current carpet, and their ratings were averaged and analyzed. The experimenters also performed a Gage R&R study in Minitab to verify that any changes in the assessed quality of the carpet were a direct result of the factors changed in the experiment, and not due to a variation in the opinions of evaluators.
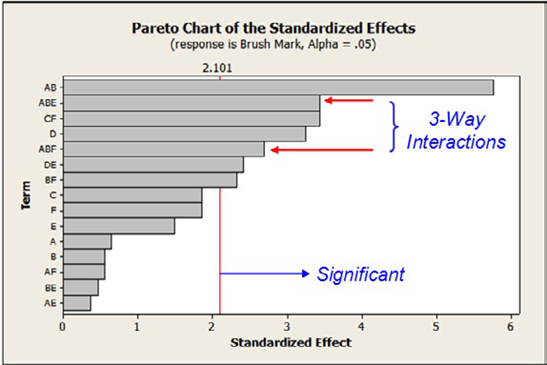
A Pareto chart created in Minitab clearly shows the three-way interactions that had a significant impact on carpet quality.
When data from the 34 runs were analyzed in Minitab, the results for each response revealed complex interactions between the different needler settings. The interactions explained why previous adjustments to individual needler settings had failed to find a way to eliminate brush markings.
The designed experiment not only provided the team with a list of significant variables and interactions, but also with equations to show how the inputs affected the responses. Even better, the results showed that optimization settings for eliminating brush marks did not have an adverse effect on the plushness.
In response to feedback from both the manufacturer and the Fiesta development team, Sterbenz used Minitab’s Response Optimizer tool to fine-tune the optimal settings identified in the initial DOE. Using the results identified in the DOE as a starting point, the Response Optimizer let Sterbenz and his team modify the settings to consider other practical concerns from the manufacturer and the development team.
After the new carpet from the confirmation runs received favorable ratings by the initial evaluators, samples were sent to Ford’s Research and Engineering Center for final assessment. The samples passed all tests for durability, stain resistance, and color and sheen, and the experiment was deemed a major success by all.
The entire project took 12 days, from the time the problem was defined to the point where the solution was in place and the process was under control. Besides a complete elimination of brush marking and an unexpected improvement in the softness of the carpet in the Fiesta, the experimenters achieved a better understanding of the entire manufacturing process.
Minitab helped Ford discover and implement a solution to find the optimum needler settings to eliminate brush marks and simultaneously maintain the plushness of the carpet. The 2011 Ford Fiesta enjoyed a highly successful launch just a few months later, and marked another milestone in Ford’s commitment to excellence and quality improvement.
Access Minitab Case Study
Provide some additional information to view the case study.

Organization
Ford Motor Company
- Founded in 1903
- Headquartered in Dearborn, Mich. with 70 plants worldwide
- More than 164,000 employees
Identify and fix the manufacturing process of carpets to eliminate brush marks
Products Used
Minitab ® Statistical Software
- A complete elimination of brush markings
- An unexpected improvement in the softness of the carpet
- A successful, high-quality launch of the Ford Fiesta
- Trust Center
© 2024 Minitab, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Cookie Settings
You are now leaving minitab.com.
Click Continue to proceed to:

FORD MOTOR COMPANY Case Solution & Answer
Home » Case Study Analysis Solutions » FORD MOTOR COMPANY
FORD MOTOR COMPANY Case Solution
The company also needs to decide on how it should maintain its supply chain processes by using the emerging information technology and ideas which would help the company in attracting the suppliers of the company which help the company in improving its market share in the economy. Most of the researchers argued that if Ford implements new technologies in its business models then it would help in redesigning its supply chain activities with lower market risk. Moreover, the company also faced intense competition in the market; the main competitor of Ford is Dell. In order to improve the supply chain activities, the company copied the strategies of Dell which helped the company in achieving its targeted goals.
The senior management of the company has taken the ONE FORD initiatives that consist of a single plane and a single team work which would help the company in achieving its common business goals in the auto industry as well as deliver profitable growth to the company. For achieving growth for the company and for the employees, the company tookfew initiatives which include few steps regarding the ONE PLAN. The main issues that the company faced arehow the company will attain profitability in the existing and new locations as well ashow will the company embrace new innovative technologies and remain competitive in the market by focusing on the relative core business strategies. Moreover, the market is saturated along with powerful competitors.
The future profitability of the company is entirely dependent on the capabilities and skills of the Ford that how well the company would use its capabilities and skills in order to increase in market share in the foreign and domestic market through refining the economic features of the company. The market share of Ford in the Canadian market is 8.3% and 13% market share acquired by the Honda Company. In order to remain competitive in the market the company focus on the key drivers of the company. Â The key driving forces help the company in maintaining its position in the market as well as provide them opportunities to seize the market share in the development countries. Lower labor cost in the development countries help the auto manufacturers to develop or establish plant and contribute to the economic development of different regions. The intercontinental approach of ford was prosperous in china however, demonstrations weak enactment in the European Market. Due to the weak performance in the European market, the company decided that it would re-engineer the overall process of the company and will follow the ONE FORD or single plan strategy which would help the company in achieving its competitive advantage in the local and international market.
Ford follows the strategy of catering the different demographic regions which would minimizing the efficiency and increase production cost of the auto industry. The company also expected that the growth rate would increase if the demand and population growth increase. Moreover, if the company wants to implement the new technologies and strategies in the economy then it is necessary for the company to focus on the attitude, lifestyle and social concerns which would help the company in implementing a better research and development technologies in the auto industry. The company also improves the productivity of the future vehicles by implementing these forces as they are considered as important forces. Furthermore, the technological changes would also help the company to improve its productivity in the market as well as help them in maintaining its profitability and growth in the competitive market.
1.       MOtivation
- The company focuses on its core business activities which helps the company in achieving its competitive edge in the highly competitive market.
- The company maintains good relationship with the suppliers, which helps the company in improving the quality of the product and services as well as reduced the cycle times. By maintaining good relationship with the suppliers, the company gotthe market share of the international market as well as maintain its stable presence in the foreign competitive market.
- The company improves the control cost of supply chain. It also deals with the customers’ responsiveness of time which would help the company in improving its steady business growth in the international and domestic market.
- The company also improves the shareholders’ value as they know that if they improve the shareholder value then it would them in competing against their competitor in the market.
As compared to Ford, Dell has done a good job in maintain the supply chain management in the organization. In order to improve the supply chain management in Ford, the company copy the strategy of Dell. In the short term, the company improves the technology system of the vehicles first and then enhance the estimate demand of the customers. In the long term planning, the company globalize its processes and operation to the international market. The company also change the marketing and sales strategies of the company and shift the operations from push to pull system. For achieving the long term growth, the company’s re engineered the initiative by implementing the order to delivery services which improved the order process and reduced the lead time from 60 days to 30 days. The company also enhanced automotive exchange network system as well as company keep strong relationship with the small number of suppliers who deal with the customers directly and provide them satisfactory products.
FORD PRODUCTION SYSTEM
The main purpose of the Ford Production system is that it looked at the internal and external expertise of the operations worldwide. The main aim of the project is to make the operations of the company leaner, efficient and more responsive. It focuses on the key attributes of the production system which involve, pull based system, aspiring to level production, stability, continuous flow, and synchronized production process. The company maintains good relationship with its suppliers which help them in acquiring the international and domestic market with single plan and single flow……………….
This is just a sample partial case solution. Please place the order on the website to order  your own originally done case solution
Related Case Solutions:

LOOK FOR A FREE CASE STUDY SOLUTION
Don't have an account? Sign up now
Already have an account login, get 10% off on your next order.
Subscribe now to get your discount coupon *Only correct email will be accepted
(Approximately ~ 0.0 Page)
Total Price
Thank you for your email subscription. Check your email to get Coupon Code.
Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios Case Analysis and Case Solution
Posted by Peter Williams on Aug-09-2018
Introduction of Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios Case Solution
The Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios case study is a Harvard Business Review case study, which presents a simulated practical experience to the reader allowing them to learn about real life problems in the business world. The Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios case consisted of a central issue to the organization, which had to be identified, analysed and creative solutions had to be drawn to tackle the issue. This paper presents the solved Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios case analysis and case solution. The method through which the analysis is done is mentioned, followed by the relevant tools used in finding the solution.
The case solution first identifies the central issue to the Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios case study, and the relevant stakeholders affected by this issue. This is known as the problem identification stage. After this, the relevant tools and models are used, which help in the case study analysis and case study solution. The tools used in identifying the solution consist of the SWOT Analysis, Porter Five Forces Analysis, PESTEL Analysis, VRIO analysis, Value Chain Analysis, BCG Matrix analysis, Ansoff Matrix analysis, and the Marketing Mix analysis. The solution consists of recommended strategies to overcome this central issue. It is a good idea to also propose alternative case study solutions, because if the main solution is not found feasible, then the alternative solutions could be implemented. Lastly, a good case study solution also includes an implementation plan for the recommendation strategies. This shows how through a step-by-step procedure as to how the central issue can be resolved.

Problem Identification of Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios Case Solution
Harvard Business Review cases involve a central problem that is being faced by the organization and these problems affect a number of stakeholders. In the problem identification stage, the problem faced by Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios is identified through reading of the case. This could be mentioned at the start of the reading, the middle or the end. At times in a case analysis, the problem may be clearly evident in the reading of the HBR case. At other times, finding the issue is the job of the person analysing the case. It is also important to understand what stakeholders are affected by the problem and how. The goals of the stakeholders and are the organization are also identified to ensure that the case study analysis are consistent with these.
Analysis of the Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios HBR Case Study
The objective of the case should be focused on. This is doing the Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios Case Solution. This analysis can be proceeded in a step-by-step procedure to ensure that effective solutions are found.
- In the first step, a growth path of the company can be formulated that lays down its vision, mission and strategic aims. These can usually be developed using the company history is provided in the case. Company history is helpful in a Business Case study as it helps one understand what the scope of the solutions will be for the case study.
- The next step is of understanding the company; its people, their priorities and the overall culture. This can be done by using company history. It can also be done by looking at anecdotal instances of managers or employees that are usually included in an HBR case study description to give the reader a real feel of the situation.
- Lastly, a timeline of the issues and events in the case needs to be made. Arranging events in a timeline allows one to predict the next few events that are likely to take place. It also helps one in developing the case study solutions. The timeline also helps in understanding the continuous challenges that are being faced by the organisation.
SWOT analysis of Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios
An important tool that helps in addressing the central issue of the case and coming up with Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios HBR case solution is the SWOT analysis.
- The SWOT analysis is a strategic management tool that lists down in the form of a matrix, an organisation's internal strengths and weaknesses, and external opportunities and threats. It helps in the strategic analysis of Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios.
- Once this listing has been done, a clearer picture can be developed in regards to how strategies will be formed to address the main problem. For example, strengths will be used as an advantage in solving the issue.
Therefore, the SWOT analysis is a helpful tool in coming up with the Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios Case Study answers. One does not need to remain restricted to using the traditional SWOT analysis, but the advanced TOWS matrix or weighted average SWOT analysis can also be used.
Porter Five Forces Analysis for Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios
Another helpful tool in finding the case solutions is of Porter's Five Forces analysis. This is also a strategic tool that is used to analyse the competitive environment of the industry in which Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios operates in. Analysis of the industry is important as businesses do not work in isolation in real life, but are affected by the business environment of the industry that they operate in. Harvard Business case studies represent real-life situations, and therefore, an analysis of the industry's competitive environment needs to be carried out to come up with more holistic case study solutions. In Porter's Five Forces analysis, the industry is analysed along 5 dimensions.
- These are the threats that the industry faces due to new entrants.
- It includes the threat of substitute products.
- It includes the bargaining power of buyers in the industry.
- It includes the bargaining power of suppliers in an industry.
- Lastly, the overall rivalry or competition within the industry is analysed.
This tool helps one understand the relative powers of the major players in the industry and its overall competitive dynamics. Actionable and practical solutions can then be developed by keeping these factors into perspective.
PESTEL Analysis of Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios
Another helpful tool that should be used in finding the case study solutions is the PESTEL analysis. This also looks at the external business environment of the organisation helps in finding case study Analysis to real-life business issues as in HBR cases.
- The PESTEL analysis particularly looks at the macro environmental factors that affect the industry. These are the political, environmental, social, technological, environmental and legal (regulatory) factors affecting the industry.
- Factors within each of these 6 should be listed down, and analysis should be made as to how these affect the organisation under question.
- These factors are also responsible for the future growth and challenges within the industry. Hence, they should be taken into consideration when coming up with the Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios case solution.
VRIO Analysis of Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios
This is an analysis carried out to know about the internal strengths and capabilities of Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios. Under the VRIO analysis, the following steps are carried out:
- The internal resources of Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios are listed down.
- Each of these resources are assessed in terms of the value it brings to the organization.
- Each resource is assessed in terms of how rare it is. A rare resource is one that is not commonly used by competitors.
- Each resource is assessed whether it could be imitated by competition easily or not.
- Lastly, each resource is assessed in terms of whether the organization can use it to an advantage or not.
The analysis done on the 4 dimensions; Value, Rareness, Imitability, and Organization. If a resource is high on all of these 4, then it brings long-term competitive advantage. If a resource is high on Value, Rareness, and Imitability, then it brings an unused competitive advantage. If a resource is high on Value and Rareness, then it only brings temporary competitive advantage. If a resource is only valuable, then it’s a competitive parity. If it’s none, then it can be regarded as a competitive disadvantage.
Value Chain Analysis of Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios
The Value chain analysis of Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios helps in identifying the activities of an organization, and how these add value in terms of cost reduction and differentiation. This tool is used in the case study analysis as follows:
- The firm’s primary and support activities are listed down.
- Identifying the importance of these activities in the cost of the product and the differentiation they produce.
- Lastly, differentiation or cost reduction strategies are to be used for each of these activities to increase the overall value provided by these activities.
Recognizing value creating activities and enhancing the value that they create allow Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios to increase its competitive advantage.
BCG Matrix of Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios
The BCG Matrix is an important tool in deciding whether an organization should invest or divest in its strategic business units. The matrix involves placing the strategic business units of a business in one of four categories; question marks, stars, dogs and cash cows. The placement in these categories depends on the relative market share of the organization and the market growth of these strategic business units. The steps to be followed in this analysis is as follows:
- Identify the relative market share of each strategic business unit.
- Identify the market growth of each strategic business unit.
- Place these strategic business units in one of four categories. Question Marks are those strategic business units with high market share and low market growth rate. Stars are those strategic business units with high market share and high market growth rate. Cash Cows are those strategic business units with high market share and low market growth rate. Dogs are those strategic business units with low market share and low growth rate.
- Relevant strategies should be implemented for each strategic business unit depending on its position in the matrix.
The strategies identified from the Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios BCG matrix and included in the case pdf. These are either to further develop the product, penetrate the market, develop the market, diversification, investing or divesting.
Ansoff Matrix of Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios
Ansoff Matrix is an important strategic tool to come up with future strategies for Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios in the case solution. It helps decide whether an organization should pursue future expansion in new markets and products or should it focus on existing markets and products.
- The organization can penetrate into existing markets with its existing products. This is known as market penetration strategy.
- The organization can develop new products for the existing market. This is known as product development strategy.
- The organization can enter new markets with its existing products. This is known as market development strategy.
- The organization can enter into new markets with new products. This is known as a diversification strategy.
The choice of strategy depends on the analysis of the previous tools used and the level of risk the organization is willing to take.
Marketing Mix of Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios
Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios needs to bring out certain responses from the market that it targets. To do so, it will need to use the marketing mix, which serves as a tool in helping bring out responses from the market. The 4 elements of the marketing mix are Product, Price, Place and Promotions. The following steps are required to carry out a marketing mix analysis and include this in the case study analysis.
- Analyse the company’s products and devise strategies to improve the product offering of the company.
- Analyse the company’s price points and devise strategies that could be based on competition, value or cost.
- Analyse the company’s promotion mix. This includes the advertisement, public relations, personal selling, sales promotion, and direct marketing. Strategies will be devised which makes use of a few or all of these elements.
- Analyse the company’s distribution and reach. Strategies can be devised to improve the availability of the company’s products.
Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios Blue Ocean Strategy
The strategies devised and included in the Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios case memo should have a blue ocean strategy. A blue ocean strategy is a strategy that involves firms seeking uncontested market spaces, which makes the competition of the company irrelevant. It involves coming up with new and unique products or ideas through innovation. This gives the organization a competitive advantage over other firms, unlike a red ocean strategy.
Competitors analysis of Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios
The PESTEL analysis discussed previously looked at the macro environmental factors affecting business, but not the microenvironmental factors. One of the microenvironmental factors are competitors, which are addressed by a competitor analysis. The Competitors analysis of Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios looks at the direct and indirect competitors within the industry that it operates in.
- This involves a detailed analysis of their actions and how these would affect the future strategies of Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios.
- It involves looking at the current market share of the company and its competitors.
- It should compare the marketing mix elements of competitors, their supply chain, human resources, financial strength etc.
- It also should look at the potential opportunities and threats that these competitors pose on the company.
Organisation of the Analysis into Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios Case Study Solution
Once various tools have been used to analyse the case, the findings of this analysis need to be incorporated into practical and actionable solutions. These solutions will also be the Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios case answers. These are usually in the form of strategies that the organisation can adopt. The following step-by-step procedure can be used to organise the Harvard Business case solution and recommendations:
- The first step of the solution is to come up with a corporate level strategy for the organisation. This part consists of solutions that address issues faced by the organisation on a strategic level. This could include suggestions, changes or recommendations to the company's vision, mission and its strategic objectives. It can include recommendations on how the organisation can work towards achieving these strategic objectives. Furthermore, it needs to be explained how the stated recommendations will help in solving the main issue mentioned in the case and where the company will stand in the future as a result of these.
- The second step of the solution is to come up with a business level strategy. The HBR case studies may present issues faced by a part of the organisation. For example, the issues may be stated for marketing and the role of a marketing manager needs to be assumed. So, recommendations and suggestions need to address the strategy of the marketing department in this case. Therefore, the strategic objectives of this business unit (Marketing) will be laid down in the solutions and recommendations will be made as to how to achieve these objectives. Similar would be the case for any other business unit or department such as human resources, finance, IT etc. The important thing to note here is that the business level strategy needs to be aligned with the overall corporate strategy of the organisation. For example, if one suggests the organisation to focus on differentiation for competitive advantage as a corporate level strategy, then it can't be recommended for the Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios Case Study Solution that the business unit should focus on costs.
- The third step is not compulsory but depends from case to case. In some HBR case studies, one may be required to analyse an issue at a department. This issue may be analysed for a manager or employee as well. In these cases, recommendations need to be made for these people. The solution may state that objectives that these people need to achieve and how these objectives would be achieved.
The case study analysis and solution, and Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios case answers should be written down in the Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios case memo, clearly identifying which part shows what. The Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios case should be in a professional format, presenting points clearly that are well understood by the reader.
Alternate solution to the Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios HBR case study
It is important to have more than one solution to the case study. This is the alternate solution that would be implemented if the original proposed solution is found infeasible or impossible due to a change in circumstances. The alternate solution for Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios is presented in the same way as the original solution, where it consists of a corporate level strategy, business level strategy and other recommendations.
Implementation of Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios Case Solution
The case study does not end at just providing recommendations to the issues at hand. One is also required to provide how these recommendations would be implemented. This is shown through a proper implementation framework. A detailed implementation framework helps in distinguishing between an average and an above average case study answer. A good implementation framework shows the proposed plan and how the organisations' resources would be used to achieve the objectives. It also lays down the changes needed to be made as well as the assumptions in the process.
- A proper implementation framework shows that one has clearly understood the case study and the main issue within it.
- It shows that one has been clarified with the HBR fundamentals on the topic.
- It shows that the details provided in the case have been properly analysed.
- It shows that one has developed an ability to prioritise recommendations and how these could be successfully implemented.
- The implementation framework also helps by removing out any recommendations that are not practical or actionable as these could not be implemented. Therefore, the implementation framework ensures that the solution to the Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios Harvard case is complete and properly answered.
Recommendations and Action Plan for Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios case analysis
For Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios, based on the SWOT Analysis, Porter Five Forces Analysis, PESTEL Analysis, VRIO analysis, Value Chain Analysis, BCG Matrix analysis, Ansoff Matrix analysis, and the Marketing Mix analysis, the recommendations and action plan are as follows:
- Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios should focus on making use of its strengths identified from the VRIO analysis to make the most of the opportunities identified from the PESTEL.
- Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios should enhance the value creating activities within its value chain.
- Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios should invest in its stars and cash cows, while getting rid of the dogs identified from the BCG Matrix analysis.
- To achieve its overall corporate and business level objectives, it should make use of the marketing mix tools to obtain desired results from its target market.
Baron, E. (2015). How They Teach the Case Method At Harvard Business School. Retrieved from https://poetsandquants.com/2015/09/29/how-they-teach-the-case-method-at-harvard-business-school/
Bartol. K, & Martin, D. (1998). Management, 3rd edition. Boston: Irwin McGrawHill.
Free Management E-Books. (2013a). PESTLE Analysis. Retrieved from http://www.free-management-ebooks.com/dldebk-pdf/fme-pestle-analysis.pdf
Gupta, A. (2013). Environment & PEST analysis: an approach to the external business environment. International Journal of Modern Social Sciences, 2(1), 34-43.
Hambrick, D. C., MacMillan, I. C., & Day, D. L. (1982). Strategic attributes and performance in the BCG matrix—A PIMS-based analysis of industrial product businesses. Academy of Management Journal, 25(3), 510-531.
Hill, C., & Jones, G. (2010). Strategic Management Theory: An Integrated Approach, Ninth Ed. Mason, OH: South-Western, Cengage Learning.
Hussain, S., Khattak, J., Rizwan, A., & Latif, M. A. (2013). ANSOFF matrix, environment, and growth-an interactive triangle. Management and Administrative Sciences Review, 2(2), 196-206.
IIBMS. (2015). 7 Effective Steps to Solve Case Study. Retrieved from http://www.iibms.org/c-7-effective-steps-to-solve-case-study/
Kim, W. C., & Mauborgne, R. (2004). Blue ocean strategy. If you read nothing else on strategy, read thesebest-selling articles., 71.
Kotler, P., & Armstrong, G. (2010). Principles of marketing. Pearson education.
Kulkarni, N. (2018). 8 Tips to Help You Prepare for the Case Method. Retrieved from https://www.hbs.edu/mba/blog/post/8-tips-to-help-you-prepare-for-the-case-method
Lin, C., Tsai, H. L., Wu, Y. J., & Kiang, M. (2012). A fuzzy quantitative VRIO-based framework for evaluating organizational activities. Management Decision, 50(8), 1396-1411.
Nixon, J., & Helms, M. M. (2010). Exploring SWOT analysis – where are we now?: A review of academic research from the last decade. Journal of Strategy and Management, 3(3), 215-251.
Panagiotou, G. (2003). Bringing SWOT into Focus. Business Strategy Review, 14(2), 8-10.
Pickton, D. W., & Wright, S. (1998). What's swot in strategic analysis? Strategic Change, 7(2), 101-109.
Porter, M. E. (2001). The value chain and competitive advantage. Understanding Business Processes, 50-66.
Porter, M. E. (1985). Competitive advantage: creating and sustaining superior performance (Vol. 2). New York: Free Press.
Porter, M.E. (1979, March). Harvard Business Review: Strategic Planning, How Competitive Forces Shape Strategy. Retrieved July 7, 2016, from https://hbr.org/1979/03/how-competitive-forces-shape-strategy
Rastogi, N., & Trivedi, M. K. (2016). PESTLE Technique–a Tool to Identify External Risks in Construction Projects. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET), 3(1), 384-388.
Rauch, P. (2007). SWOT analyses and SWOT strategy formulation for forest owner cooperations in Austria. European Journal of Forest Research, 126(3), 413-420.
Warning! This article is only an example and cannot be used for research or reference purposes. If you need help with something similar, please submit your details here .
9416 Students can’t be wrong
PhD Experts
Norina Huba
I had no issues with the questions that the expert worked out. Thank you so much!
It was the best suggestion of the Zhang to me to hire this service. I appointed it and am very thankful to it. Thank you!
Massimo Sergio
This was my first experience with this site and it made it possible to submit the assignment to the teacher on time. Thanks! I’ll order you guys again if I obtain good marks.
Margus Dominik
Good job because the assignment was free from mistakes and plagiarism. This service is really helpful!
Calculate the Price
(approx ~ 0.0 page), total price €0, next articles.
- EuropaCorp SA: A Second Attempt At A Turnaround Case Analysis
- B2B Partnerships In The Carbonated Soft Drink Industry Printable Role Sheets Supplement Case Analysis
- AMC Networks Inc: The Walking Dead Problem Case Analysis
- Cabalonga SA: Seeking Sustainability And Self Sufficiency Case Analysis
- Carpenter Tan Handicrafts Co Ltd: Franchisee Satisfaction Case Analysis
- Dami Technology Co Ltd: A Smart Kitchen Ecosystem Case Analysis
- Foxcore Retail (A) And (B) Case Analysis
- Rise And Fall Of AIG Case Analysis
- Spanx Inc: Growth Dilemma For A Shapewear Leader Case Analysis
- Pathfinder Career System Inc: Designing A Growth And Financing Strategy Case Analysis
Previous Articles
- Konica Minolta Business Solutions (HK) Ltd: Pioneering Corporate Social Entrepreneurship Case Analysis
- Ziwo Agricultural Service Co Ltd: Vertical Integration Case Analysis
- Worldwide Equipment (China) Ltd: A Sales Performance Dilemma Case Analysis
- The Career Choice Of Ms Linlin Chen Case Analysis
- China Minmetals Corporation And Noranda Inc Case Analysis
- BMW Mini: Big Decisions Under The Brexit Cloud Case Analysis
- Farro Biomed: Effective Oversight When Leader Character Is A Risk Case Analysis
- Vertu: Last Call For British Luxury Mobile Phone Maker? Case Analysis
- Strategic Marketers Should Sit At The Board Table Case Analysis
- Who Owns Your Banking Data? Case Analysis
Be a great writer or hire a greater one!
Academic writing has no room for errors and mistakes. If you have BIG dreams to score BIG, think out of the box and hire Case48 with BIG enough reputation.

Our Guarantees
Zero plagiarism, best quality, qualified writers, absolute privacy, timely delivery.
Interesting Fact
Most recent surveys suggest that around 76 % students try professional academic writing services at least once in their lifetime!
Allow Our Skilled Essay Writers to Proficiently Finish Your Paper.
We are here to help. Chat with us on WhatsApp for any queries.
Customer Representative
- Silver Bee Group
- [email protected]

- NEW SOLUTION
- Top Visitors
- Popular Topics
- Newest Members
- Newest Papers
- Top Donators
Ford Motor Company
| Word (s) : | 1390 |
|---|---|
| Pages (s) : | 6 |
| View (s) : | 1737 |
| Rank : | 0 |

- University Login
| Google+ | |
| or Login with Email | |
Recent Topics
New entries.
- Quality Parts Company
- Lincoln Electric
- Vêtements Ltée
- Google Case Analysis
Most Recent Request
- oilwell cable comp
- research methods
- human resource sho
- toyota adopts a st
Ease your MBA workload and get more time for yourself

Provide details on what you need help with along with a budget and time limit. Questions are posted anonymously and can be made 100% private.

Studypool matches you to the best tutor to help you with your question. Our tutors are highly qualified and vetted.

Your matched tutor provides personalized help according to your question details. Payment is made only after you have completed your 1-on-1 session and are satisfied with your session.

- Homework Q&A
- Become a Tutor
All Subjects
Mathematics
Programming
Health & Medical
Engineering
Computer Science
Foreign Languages
Access over 35 million academic & study documents
Ford motor company case study.
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Slovenščina
- Science & Tech
- Russian Kitchen
Kolomna: An ancient citadel transformed to center of culture

Kolomna kremlin (fortress). Kolomna (Marinka) Tower. August 19, 2003.
At the beginning of the 20th century, Russian chemist and photographer Sergey Prokudin-Gorsky developed a complex process for vivid, detailed color photography. His vision of photography as a form of education and enlightenment was demonstrated with special clarity through his photographs of architectural monuments in historic sites throughout the Russian heartland.

Old Golutvin Epiphany Monastery, west view. From left: northwest corner tower, bell tower, NE corner tower, Epiphany Cathedral & St. Sergius Church, SE corner tower, SW corner tower. Foreground: railroad & potato field. Summer 1912.
Among the sites visited by Prokudin-Gorsky in 1912 was the Epiphany-Golutvin Monastery (known after 1800 as the Old Golutvin Monastery) near Kolomna, located some 115 km south of Moscow in the direction of Ryazan. Although Kolomna is one of the most appealing of Russia’s provincial cities, there is no record that Prokudin-Gorsky photographed the town itself, just to the north of the Old Golutvin Monastery.
Kolomna’s rich history

Kolomna. Church of the Conception of John the Baptist at Gorodishche. South view. October 12, 1992.
Picturesquely situated at the confluence of the Kolomenka and Moscow rivers, Kolomna (with a population of around 135,000) has a rich history and distinctive regional identity. Its monasteries, which grace the approaches to the town center, have been restored and some of its merchant houses from the early 19th century have preserved their neoclassical charm.
The earliest mention of Kolomna in medieval chronicles refers to a clash in 1177 between Vsevolod the Great Nest, grand prince of Vladimir, and rival prince Gleb of Ryazan. Such local struggles were frequent among Russian princes in the 12th and early 13th centuries, but they were soon to be followed by the far more devastating Mongol invasion of 1237-41. Kolomna was overwhelmed in January 1238, despite fierce resistance. Kulkan, the youngest son of Genghis Khan, was killed during the battle for Kolomna.

Left: Equestrian monument to Dmitry Donskoy. Background: Kolomna kremlin wall. Right: Kolomna kremlin. Spassky (Savior) Gate, also called Pyatnitsky Gate. Southwest view. May 23, 2007.
From the beginning of the 14th century, Moscow’s princes valued Kolomna as a strategic citadel guarding its southern border. Located not far from the point where the Moscow River flows into the Oka River (the major western tributary of the Volga), Kolomna was traversed by trading routes from much of central Russia. This movement of goods and livestock through the town would create the basis for an enduring merchant culture.
Gorodishche

Kolomna. Church of Dormition of the Virgin, Brusensky Dormition Convent, south view. August 18, 2011.
Despite its increasing prosperity, Kolomna experienced serious challenges in the 14th century, including an outbreak of plague in 1363 and looting by the army of Tatar khan Tokhtamysh in August 1382. Yet, in the same period, Kolomna proved its resilience with the construction in 1379 of its first large church, dedicated to the Dormition of the Virgin. It was in the shadow of this church - completely rebuilt in the 17th century - that Moscow’s grand prince Dmitry Donskoi held a prayer service in preparation for the eventual great victory against Tatar khan Mamai at Kulikovo Pole in September 1380.

Kolomna. Wooden houses on Lazhechnikov Street. Background: Cathedral of the Elevation of the Cross, Brusensky Dormition Convent. August 18, 2011.
The earliest stone church from this period, dedicated to John the Baptist at Gorodishche, is located on the outskirts of Kolomna and has been dated to the late 14th century. The place name of this remarkable structure comes from an ancient earthen fort (aka gorodishche ) on the left bank of the Kolomenka River, but, by the time of the church’s construction, the village of Gorodishche belonged to the local bishop.

Kolomna. Unveiling of monument to Sts. Kirill & Methodius. Background: Bell tower & Cathedral of the Dormition. May 23, 2007.
Although much rebuilt, the church's lower walls - of worn limestone - reveal the early stages of recovery of masonry architecture after the cataclysmic Mongol invasion. Apart from these intact lower walls, which include one block with a carving of a unicorn, the basic structure of the Church of John the Baptist dates from the early sixteenth century. The present bell tower was erected in 1780, as, apparently, was the wide refectory. At the beginning of this century, the light gray, roughly textured walls were covered with bright white paint. Fortunately, I was able to photograph the structure in the fall of 1992, when the picturesque texture of its walls was still untouched.
Solidifying Middle Ages

Cathedral of the Dormition. Interior, view toward west wall. December 21, 2003.
During the 16th century, Kolomna benefited from the largess of Moscow’s Grand Prince Basil III (1479-1533), who replaced its log fortress with massive brick walls that signaled the town’s importance as a citadel on Muscovy’s southern flank. Built between 1525 and 1531 to a total length of two kilometers, these walls bear comparison with those of the Moscow Kremlin.

Kolomna panorama. From left: Church of Resurrection in the Fortress, Church of Tikhvin Icon of the Virgin, Bell tower & Dormition Cathedral, School No. 3, bell tower of New Golutvin Trinity Convent, Church of Intercession at New Golutvin Convent. May 24, 2007.
Of the original sixteen towers, seven remain, including one gate tower. The southwest range of the walls was anchored by the massive Kolomna, or Marina, Tower. The last serious military ordeal faced by Kolomna occurred in the early 17th century, when the town was assaulted by various factions during a period of dynastic chaos known as the ‘Time of Troubles’.

Church of Intercession at New Golutvin Convent, southwest view. May 23, 2007.
Within the Kolomna walls is the Brusensky Dormition Monastery, converted into a convent after the devastation of the Time of Troubles. Its distinctive mid-16th-century Church of the Dormition of the Virgin was erected in the 1550s to commemorate Ivan the Terrible’s 1552 conquest of Kazan - as was St. Basil’s in Moscow . Adjacent to the Dormition Church is the brightly painted Cathedral of the Elevation of the Cross, built exactly three centuries later (1852-55) in the Russo-Byzantine style.

Church of the Resurrection at Posad (Church of St. Nicholas Posadsky). South view. May 23, 2007.
A few paces beyond, along an attractive pedestrian street, stands Kolomna’s main cathedral, also dedicated to the Dormition. Rebuilt between 1672 and 1682, its structure follows the traditional design of large Russian churches, with six columns supporting the interior space and five onion domes above. The interior has been well preserved, with a late baroque iconostasis from the 1770s and an impressive set of wall paintings in a late academic style executed in oil during the 1880s and based on an earlier set from 1804.

Bell tower of Church of St. John the Divine, flanked by trading arcade. View from Lazhechnikov House. July 11, 2009.
Adjacent to the cathedral is a massive bell tower, built in 1692. Across from the Dormition Cathedral are the walls and bell tower of the New Golutvin Convent, with its brightly painted Church of the Trinity (1705).
Monumental rivalry

Lazhechnikov House. August 18, 2011.
Kolomna also has numerous parish churches. The most picturesque of these is the Church of the Resurrection “na Posade”, also known as the Church of Saint Nicholas Posadsky, which was originally built in 1716, then substantially modified in the 1790s, before being restored to its earlier form in the 1970s. This distinctive structure, with its decorative gables, represents an echo of ornamented church architecture in Moscow during the 17th century. Nearby is the Museum of Pastila, an apple confectionery for which Kolomna is widely known.

Ozerov House, Red Army Street 2. May 23, 2007.
Kolomna rivals Torzhok with its array of neoclassical monuments. The most visible of these is the Church of St. John the Divine, located on the town’s main square and originally built in 1733-58. The church gained its imposing neoclassical facades in 1829-35. Its soaring bell tower (1826-46) became the center of a trading arcade that enveloped the church structure—an ingenious combination of commercial and religious architecture.
In addition to its churches and bell towers, Kolomna has historic districts with houses from the 19th century. Among the neoclassical houses restored in the town center, the most notable is the Lazhechnikov House, now a museum devoted to one of Russia’s early nineteenth-century novelists.

Log house with lilac in bloom, corner of Ivanov Street 6 & Grazhdansky Street. May 24, 2007.
Also preserved in Kolomna are large numbers of wooden houses, many of them with ornate window surrounds. Some of these houses near the kremlin are associated with 20th-century writers such as Boris Pilnyak and Anna Akhmatova.
Soviet era & now

Kolomna Central Regional Hospital, October Revolution Street 318. Excellent example of Constructivist architecture (completed 1930). December 26, 2003.
During the Soviet period new forms of housing appeared, particularly for workers at the Kolomna Factory, founded in 1863 and subsequently a major producer of locomotives. Examples of housing projects sponsored by the Kolomna Factory in the 1920s can still be seen on the main thoroughfare, October Revolution Street. However, many workers preferred to live in wooden houses with a small garden plot, and such houses continued to be built throughout the Soviet period. Kolomna also has interesting examples of avant-garde Constructivist architecture, built in support of the industrialization campaign of the early Soviet period.

Old Golutvin Epiphany Monastery. South wall & towers in Gothic Revival style. December 26, 2003.
On the outskirts of the town are two additional monastic ensembles, both apparently established by Dmitry Donskoy in the 1380s. The Epiphany-Golutvin Monastery, known after 1800 as the Old Golutvin Monastery , is located near the confluence of the Moscow and Oka Rivers. The most colorful feature of the Old Golutvin Monastery is its wall towers, Gothic Revival fantasies built of red brick with limestone details in the late 1770s. The Pseudo-Gothic style appeared in Russia during the reign of Catherine the Great as a reflection of the empress’s Anglomania and her interest in medieval Russian culture.
Across the Moscow River and to the north of the Kolomna Kremlin is the Bobrenev-Nativity Monastery. Although founded in the late 14th century, its current churches date from the late 18th and 19th centuries. It, too, is enclosed with Gothic Revival walls from the 1790s.

Old Bobrenevo. Bobrenev Nativity of the Virgin Monastery, southwest view. From left: walls & corner towers in Gothic Revival style, abbott's residence, bell tower & Cathedral of Nativity of the Virgin, Church of the St. Theodore Icon of the Virgin. December 26, 2003.
Contemporary Kolomna’s most notable landmark is popularly called the Ice Palace, a community center and modern arena for ice sports. The choice of site was controversial - down the slope from the kremlin. The architects attempted to mitigate the visual clash by designing the arena with a suspended membrane roof whose low silhouette is nestled at the bottom of the river terrain.
The construction of a bypass highway has relieved the historic Kolomna center of through traffic on the way to the city of Ryazan. Like many other Russian towns, Kolomna is seeking a balance between economic development and the preservation of its rich architectural heritage.

Ice Racing Arena on Kolomenka River. Background: Bell tower & Cathedral of the Dormition. May 24, 2007.
In the early 20th century, Russian photographer Sergey Prokudin-Gorsky developed a complex process for color photography. Between 1903 and 1916 he traveled through the Russian Empire and took over 2,000 photographs with the process, which involved three exposures on a glass plate. In August 1918, he left Russia and ultimately resettled in France where he was reunited with a large part of his collection of glass negatives, as well as 13 albums of contact prints. After his death in Paris in 1944, his heirs sold the collection to the Library of Congress. In the early 21st century the Library digitized the Prokudin-Gorsky Collection and made it freely available to the global public. A few Russian websites now have versions of the collection. In 1986 the architectural historian and photographer William Brumfield organized the first exhibit of Prokudin-Gorsky photographs at the Library of Congress. Over a period of work in Russia beginning in 1970, Brumfield has photographed most of the sites visited by Prokudin-Gorsky. This series of articles juxtaposes Prokudin-Gorsky’s views of architectural monuments with photographs taken by Brumfield decades later.
If using any of Russia Beyond's content, partly or in full, always provide an active hyperlink to the original material.
to our newsletter!
Get the week's best stories straight to your inbox
- William Brumfield: The American who made Russia’s architectural heritage famous abroad
- U.S. professor continues photographic legacy of Prokudin-Gorsky in new book
- Khmelita: the resurrected estate linked to a brilliant, yet tragic Russian playwright
This website uses cookies. Click here to find out more.
- NORTH AMERICA
- MIDDLE EAST
- INDO-PACIFIC
- SOUTH AMERICA
Don't forget to sign up!
Sukhoi superjet 100 crashes, kolomna, moscow oblast.
Update (1128 EST): The first photos from the crash site have emerged.

Update (0925 EST): The Russian Investigative Committe has opened an investigation into the crash.
At approximately 0850 EST, initial reports indicated that a Sukhoi Superjet 100 had sent out a distress signal before crashing near Kolomna, Moscow Oblast, Russian Federation. By 0855 EST, Russian Telegram outlets began to report that the aircraft had crashed.
?? ? Ein Passagierflugzeug ist in einem Vorort von #Moskau abgestürzt. rosZMI schreibt über den Absturz, wahrscheinlich des Passagierflugzeugs „ #Suchoi Superjet-100“, in der Gegend von #Kolomna . Russische Flugabwehr, wie geht’s dir? pic.twitter.com/Q1jjeM6xwR — ?? ???Haymo#Solidarität (@HaymoDemokrat) July 12, 2024
By 0900 EST, reports emerged that the commercial aircraft was conducting a test flight after repair work was done by Gazprom-Avia. Emergency services confirmed that three crew members were killed in the crash.

This is developing.
The Sukhoi Superjet 100 or SSJ100 is a regional jet designed by Russian aircraft company Sukhoi Civil Aircraft, a division of the United Aircraft Corporation. With development starting in 2000, it made its maiden flight on 19 May 2008 and its first commercial flight on 21 April 2011 with Armavia

What started out of passion and interest, has turned into a necessity. Atlas has and always will be a place that readers can trust for quality news that's unbiased and unfiltered.
- Terms Of Use
- Privacy Policy
Todays Recap
Eswatini launches nuclear energy initiative, south africa blocked delivery of artillery shells to poland, polish press claims, sabina shoal incident indicates china expanding conflict points in south china sea.
© ATLAS NEWS. All Rights Reserved.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
FORD MOTOR COMPANY Case Study Solution. CASE OVERVIEW. The Ford Motor company was founded by Henry Ford in 1903, and it produced approximately 260 million vehicles since its inception. The company is also considered as the second largest automobile industry in the world with $144 billion revenue.
The current report provides an in-depth analysis of the motor vehicle industry based on the Ford Motor Company case study. It also analyzes Ford Motor Company using SWOT analytical tool. Moreover, strategies that could be adopted by Ford Motor Company for the next five years have been provided. The study is divided in several sections with the ...
25 min read. ·. Aug 3, 2022. 1.INTRODUCTION. Ford Motor Company was started by Henry Ford in 1903 and the company went public in 1956. It is one of the most rooted and long-established automotive ...
Ford Motor Company Struggle in India Case Study Solution & Analysis. Steps for Case Study Solution & Analysis: 1. Introduction of Ford Motor Company Struggle in India Case Solution The Ford Motor Company Struggle in India case study is a Harvard Business Review case study, which presents a simulated practical experience to the reader allowing them to learn about real life problems in the ...
Austin, Robert D. "Ford Motor Company: Supply Chain Strategy." Harvard Business School Case 699-198, March 1999. (Revised December 2001.)
What. Case study: Ford Motor Company. Read the case study and exhibits. You are an analyst working for John Smith, an asset manager and investor in Ford Motor Company. It is January 2018 and your boss has asked you to assess the situation at Ford and propose the next investment strategy. Specifically, he has asked you:
Ford Case Study - solution - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Ford faced several issues including declining sales, high losses, and falling stock prices as newer competitors introduced electric, autonomous, and shared mobility technologies. The company addressed these challenges by developing new strategies focused on vehicle ...
Ford Motor Company Ford Motor Company is the world's largest producer of trucks, and the second largest producer of cars and trucks combined. Ford has manufacturing, assembly or sales affiliates in 34 countries and Ford companies employed 337,800 people world-wide in 1996. Ford has manufacturing facilities in 22 countries on 5 continents, with 87
This is just a sample partial case solution. Please place the order on the website to order your own originally done case solution. Ford describes the examination of its supply chain, to assess whether the company has "virtually integrated" model Dell Computers. "Hide by Robert D. Austin Source: HBS Premier Case Collection 9 pages.
Ford Motor Company is one of the largest automakers in the United States, producing millions of automobiles each year at 70 plants worldwide. ... Minitab helped Ford discover and implement a solution to find the optimum needler settings to eliminate brush marks and simultaneously maintain the plushness of the carpet. The 2011 Ford Fiesta ...
The market share of Ford in the Canadian market is 8.3% and 13% market share acquired by the Honda Company. In order to remain competitive in the market the company focus on the key drivers of the company. Â The key driving forces help the company in maintaining its position in the market as well as provide them opportunities to seize the ...
The Value chain analysis of Ford Motor Company Basic Financial Ratios helps in identifying the activities of an organization, and how these add value in terms of cost reduction and differentiation. This tool is used in the case study analysis as follows: The firm's primary and support activities are listed down.
With a history of relying on survey data analysis tracing back for more than 50 years, Ford has purchased and developed many analytical solutions for managing and analyzing the wide array of survey data collected over the years and across the globe. In the past 10 years, facing increasing competitive pressure and global overcapacity, Ford has ...
Challenge Case Study Solution Analysis Answers Ford Motor Company Electrification Challenge Case Study Solution Analysis. Our tutors are available 24/7 to assist in your academic stuff, Our Professional writers are ready to serve you in services you need. Every Case Study Solution & Analysis is prepared from scratch, top quality, plagiarism ...
Case Study. Ford Motor Company: will the company ' Summarize the company ' s competitive strategies. Complete analysis of external environment [ industry], and internal resources / capabilities using appropriate tools such as Five Forces, PESTEL, SWOT, Value Chain, etc. Analyze financial data using ratio analysis.
Ford Motor Company Supply Chain Strategy Background In 1913, Henry Ford revolutionized product manufacturing by introducing the first assembly line to the automotive industry. Ford's hallmark of achievement proved to be a key competence for the motor company as the low cost of the Model T attracted a broader, new range of prospective car-owners.
Ford Motor Company, one of the world's largest automotive manufacturers, has worked with Penske on several Six Sigma initiatives. As its lead logistics provider (LLP), Penske's quality team of associates are trained in Six Sigma practices and work closely with Ford to streamline operations and create and maintain a more centralized ...
1 Ford Motor Company Case Study Student's Name Institutional Affiliation Course Name Instructor's Name Submission Date 2 Ford Motor Company Case Study History and Background of the Company The starting of Ford was modest, just like the majority of great enterprises. ... you will need to choose the form that is most appropriate to fit the ...
All photos by William Brumfield. The earliest mention of Kolomna in medieval chronicles refers to a clash in 1177 between Vsevolod of the Big Nest, grand prince of Vladimir, and his rival prince ...
May 23, 2007. A few paces beyond, along an attractive pedestrian street, stands Kolomna's main cathedral, also dedicated to the Dormition. Rebuilt between 1672 and 1682, its structure follows ...
Kolomna is a traditional gathering place for Russian troops before military campaigns to the southeast. On August 26, 1380, Grand Duke Dmitry Ivanovich of Moscow arranged a review of Russian squads on the Maiden's Field near Kolomna before going to the Kulikovo field. According to historians, separate princely squads left Kolomna on the ...
The Sukhoi Superjet 100 or SSJ100 is a regional jet designed by Russian aircraft company Sukhoi Civil Aircraft, a division of the United Aircraft Corporation. With development starting in 2000, it made its maiden flight on 19 May 2008 and its first commercial flight on 21 April 2011 with Armavia. Facebook. Twitter. Linkedin. WhatsApp. ReddIt.