Definition of Antithesis
Examples of antithesis in everyday speech, common examples of antithesis from famous speeches, examples of proverbs featuring antithesis, utilizing antithesis in writing, antithesis and parallelism, antithesis and juxtaposition, use of antithesis in sentences , examples of antithesis in literature.
Antithesis is an effective literary device and figure of speech in which a writer intentionally juxtaposes two contrasting ideas or entities. Antithesis is typically achieved through parallel structure, in which opposing concepts or elements are paired in adjacent phrases , clauses , or sentences. This draws the reader’s attention to the significance or importance of the agents being contrasted, thereby adding a memorable and meaningful quality to the literary work.

Example 1: Hamlet (William Shakespeare)
Give every man thine ear, but few thy voice ; Take each man’s censure, but reserve thy judgment.
Example 2: Paradise Lost (John Milton)
Here at least We shall be free; the Almighty hath not built Here for his envy, will not drive us hence: Here we may reign secure, and in my choice To reign is worth ambition though in Hell: Better to reign in Hell, than serve in Heaven.
Example 3: Fire and Ice (Robert Frost)
Some say the world will end in fire, Some say in ice. From what I’ve tasted of desire I hold with those who favor fire. But if it had to perish twice, I think I know enough of hate To say that for destruction ice Is also great And would suffice.
In his poem, Frost utilizes antithesis to contrast fire and ice as elements with devastating and catastrophic potential to end the world. Frost effectively demonstrates the equal powers for the destruction of these elements, despite showcasing them as opposing forces. In this case, the poet’s antithesis has a literal as well as figurative interpretation. As the poem indicates, the world could literally end in the fire as well as ice. However, fire and ice are contrasting symbols in the poem as well. Fire represents “desire,” most likely in the form of greed, the corruption of power, domination, and control. Conversely, ice represents “hate” in the form of prejudice, oppression, neglect, and isolation.
Example 4: The Gettysburg Address by Abraham Lincoln
We have come to dedicate a portion of that field, as a final resting place for those who here gave their lives so that nation might live.
The brave men, living and dead, who struggled here, have consecrated it, far above our poor power to add or detract.
The world will little note, nor long remember what we say here, but it can never forget what they did here.
Function of Antithesis
Synonyms of antithesis, post navigation.

- Ask LitCharts AI
- Discussion Question Generator
- Essay Prompt Generator
- Quiz Question Generator

- Literature Guides
- Poetry Guides
- Shakespeare Translations
- Literary Terms

Antithesis Definition
What is antithesis? Here’s a quick and simple definition:
Antithesis is a figure of speech that juxtaposes two contrasting or opposing ideas, usually within parallel grammatical structures. For instance, Neil Armstrong used antithesis when he stepped onto the surface of the moon in 1969 and said, "That's one small step for a man, one giant leap for mankind." This is an example of antithesis because the two halves of the sentence mirror each other in grammatical structure, while together the two halves emphasize the incredible contrast between the individual experience of taking an ordinary step, and the extraordinary progress that Armstrong's step symbolized for the human race.
Some additional key details about antithesis:
- Antithesis works best when it is used in conjunction with parallelism (successive phrases that use the same grammatical structure), since the repetition of structure makes the contrast of the content of the phrases as clear as possible.
- The word "antithesis" has another meaning, which is to describe something as being the opposite of another thing. For example, "love is the antithesis of selfishness." This guide focuses only on antithesis as a literary device.
- The word antithesis has its origins in the Greek word antithenai , meaning "to oppose." The plural of antithesis is antitheses.
How to Pronounce Antithesis
Here's how to pronounce antithesis: an- tith -uh-sis
Antithesis and Parallelism
Often, but not always, antithesis works in tandem with parallelism . In parallelism, two components of a sentence (or pair of sentences) mirror one another by repeating grammatical elements. The following is a good example of both antithesis and parallelism:
To err is human , to forgive divine .
The two clauses of the sentence are parallel because each starts off with an infinitive verb and ends with an adjective ("human" and "divine"). The mirroring of these elements then works to emphasize the contrast in their content, particularly in the very strong opposite contrast between "human" and "divine."
Antithesis Without Parallelism
In most cases, antitheses involve parallel elements of the sentence—whether a pair of nouns, verbs, adjectives, or other grammar elements. However, it is also possible to have antithesis without such clear cut parallelism. In the Temptations Song "My Girl," the singer uses antithesis when he says:
"When it's cold outside , I've got the month of May ."
Here the sentence is clearly cut into two clauses on either side of the comma, and the contrasting elements are clear enough. However, strictly speaking there isn't true parallelism here because "cold outside" and "month of May" are different types of grammatical structures (an adjective phrase and a noun phrase, respectively).
Antithesis vs. Related Terms
Three literary terms that are often mistakenly used in the place of antithesis are juxtaposition , oxymoron , and foil . Each of these three terms does have to do with establishing a relationship of difference between two ideas or characters in a text, but beyond that there are significant differences between them.
Antithesis vs. Juxtaposition
In juxtaposition , two things or ideas are placed next to one another to draw attention to their differences or similarities. In juxtaposition, the pairing of two ideas is therefore not necessarily done to create a relationship of opposition or contradiction between them, as is the case with antithesis. So, while antithesis could be a type of juxtaposition, juxtaposition is not always antithesis.
Antithesis vs. Oxymoron
In an oxymoron , two seemingly contradictory words are placed together because their unlikely combination reveals a deeper truth. Some examples of oxymorons include:
- Sweet sorrow
- Cruel kindness
- Living dead
The focus of antithesis is opposites rather than contradictions . While the words involved in oxymorons seem like they don't belong together (until you give them deeper thought), the words or ideas of antithesis do feel like they belong together even as they contrast as opposites. Further, antitheses seldom function by placing the two words or ideas right next to one another, so antitheses are usually made up of more than two words (as in, "I'd rather be among the living than among the dead").
Antithesis vs. Foil
Some Internet sources use "antithesis" to describe an author's decision to create two characters in a story that are direct opposites of one another—for instance, the protagonist and antagonist . But the correct term for this kind of opposition is a foil : a person or thing in a work of literature that contrasts with another thing in order to call attention to its qualities. While the sentence "the hare was fast, and the tortoise was slow" is an example of antithesis, if we step back and look at the story as a whole, the better term to describe the relationship between the characters of the tortoise and the hare is "foil," as in, "The character of the hare is a foil of the tortoise."
Antithesis Examples
Antithesis in literature.
Below are examples of antithesis from some of English literature's most acclaimed writers — and a comic book!
Antithesis in Charles Dickens' A Tale of Two Cities
In the famous opening lines of A Tale of Two Cities , Dickens sets out a flowing list of antitheses punctuated by the repetition of the word "it was" at the beginning of each clause (which is itself an example of the figure of speech anaphora ). By building up this list of contrasts, Dickens sets the scene of the French Revolution that will serve as the setting of his tale by emphasizing the division and confusion of the era. The overwhelming accumulation of antitheses is also purposefully overdone; Dickens is using hyperbole to make fun of the "noisiest authorities" of the day and their exaggerated claims. The passage contains many examples of antithesis, each consisting of one pair of contrasting ideas that we've highlighted to make the structure clearer.
It was the best of times , it was the worst of times , it was the age of wisdom , it was the age of foolishness , it was the epoch of belief , it was the epoch of incredulity , it was the season of Light , it was the season of Darkness , it was the spring of hope , it was the winter of despair , we had everything before us, we had nothing before us, we were all going direct to Heaven , we were all going direct the other way —in short, the period was so far like the present period, that some of its noisiest authorities insisted on its being received, for good or for evil, in the superlative degree of comparison only.
Antithesis in John Milton's Paradise Lost
In this verse from Paradise Lost , Milton's anti-hero , Satan, claims he's happier as the king of Hell than he could ever have been as a servant in Heaven. He justifies his rebellion against God with this pithy phrase, and the antithesis drives home the double contrast between Hell and Heaven, and between ruling and serving.
Better to reign in Hell than serve in Heaven.
Antithesis in William Shakespeare's Othello
As the plot of Othello nears its climax , the antagonist of the play, Iago, pauses for a moment to acknowledge the significance of what is about to happen. Iago uses antithesis to contrast the two opposite potential outcomes of his villainous plot: either events will transpire in Iago's favor and he will come out on top, or his treachery will be discovered, ruining him.
This is the night That either makes me or fordoes me quite .
In this passage, the simple word "either" functions as a cue for the reader to expect some form of parallelism, because the "either" signals that a contrast between two things is coming.
Antithesis in William Shakespeare's Hamlet
Shakespeare's plays are full of antithesis, and so is Hamlet's most well-known "To be or not to be" soliloquy . This excerpt of the soliloquy is a good example of an antithesis that is not limited to a single word or short phrase. The first instance of antithesis here, where Hamlet announces the guiding question (" to be or not to be ") is followed by an elaboration of each idea ("to be" and "not to be") into metaphors that then form their own antithesis. Both instances of antithesis hinge on an " or " that divides the two contrasting options.
To be or not to be , that is the question: Whether 'tis nobler in the mind to suffer The slings and arrows of outrageous fortune Or to take arms against a sea of troubles, And by opposing end them ...
Antithesis in T.S. Eliot's "Four Quartets"
In this excerpt from his poem "Four Quartets," T.S. Eliot uses antithesis to describe the cycle of life, which is continuously passing from beginning to end, from rise to fall, and from old to new.
In my beginning is my end . In succession Houses rise and fall , crumble, are extended, Are removed, destroyed, restored, or in their place Is an open field, or a factory, or a by-pass. Old stone to new building , old timber to new fires ...
Antithesis in Green Lantern's Oath
Comic book writers know the power of antithesis too! In this catchy oath, Green Lantern uses antithesis to emphasize that his mission to defeat evil will endure no matter the conditions.
In brightest day , in blackest night , No evil shall escape my sight. Let those who worship evil's might Beware my power—Green lantern's light!
While most instances of antithesis are built around an "or" that signals the contrast between the two parts of the sentence, the Green Lantern oath works a bit differently. It's built around an implied "and" (to be technical, that first line of the oath is an asyndeton that replaces the "and" with a comma), because members of the Green Lantern corps are expressing their willingness to fight evil in all places, even very opposite environments.
Antithesis in Speeches
Many well-known speeches contain examples of antithesis. Speakers use antithesis to drive home the stakes of what they are saying, sometimes by contrasting two distinct visions of the future.
Antithesis in Patrick Henry's Speech to the Second Virginia Convention, 1775
This speech by famous American patriot Patrick Henry includes one of the most memorable and oft-quoted phrases from the era of the American Revolution. Here, Henry uses antithesis to emphasize just how highly he prizes liberty, and how deadly serious he is about his fight to achieve it.
Is life so dear, or peace so sweet, as to be purchased at the price of chains and slavery? Forbid it, Almighty God! I know not what course others may take: but as for me, give me liberty or give me death .
Antithesis in Martin Luther King Jr.'s Oberlin Commencement Address
In this speech by one of America's most well-known orators, antithesis allows Martin Luther King Jr. to highlight the contrast between two visions of the future; in the first vision, humans rise above their differences to cooperate with one another, while in the other humanity is doomed by infighting and division.
We must all learn to live together as brothers —or we will all perish together as fools .
Antithesis in Songs
In songs, contrasting two opposite ideas using antithesis can heighten the dramatic tension of a difficult decision, or express the singer's intense emotion—but whatever the context, antithesis is a useful tool for songwriters mainly because opposites are always easy to remember, so lyrics that use antithesis tend to stick in the head.
Antithesis in "Should I Stay or Should I Go" by The Clash (1981)
In this song by The Clash, the speaker is caught at a crossroads between two choices, and antithesis serves as the perfect tool to express just how confused and conflicted he is. The rhetorical question —whether to stay or to go—presents two opposing options, and the contrast between his lover's mood from one day (when everything is "fine") to the next (when it's all "black") explains the difficulty of his choice.
One day it's fine and next it's black So if you want me off your back Well, come on and let me know Should I stay or should I go ? Should I stay or should I go now? Should I stay or should I go now? If I go, there will be trouble If I stay it will be double ...
Antithesis in "My Girl" by the Temptations (1965)
In this song, the singer uses a pair of metaphors to describe the feeling of joy that his lover brings him. This joy is expressed through antithesis, since the singer uses the miserable weather of a cloudy, cold day as the setting for the sunshine-filled month of May that "his girl" makes him feel inside, emphasizing the power of his emotions by contrasting them with the bleak weather.
I've got sunshine on a cloudy day When it's cold outside I've got the month of May Well I guess you'd say, What can make me feel this way? My girl, my girl, my girl Talkin' bout my girl.
Why Do Writers Use Antithesis?
Fundamentally, writers of all types use antithesis for its ability to create a clear contrast. This contrast can serve a number of purposes, as shown in the examples above. It can:
- Present a stark choice between two alternatives.
- Convey magnitude or range (i.e. "in brightest day, in darkest night" or "from the highest mountain, to the deepest valley").
- Express strong emotions.
- Create a relationship of opposition between two separate ideas.
- Accentuate the qualities and characteristics of one thing by placing it in opposition to another.
Whatever the case, antithesis almost always has the added benefit of making language more memorable to listeners and readers. The use of parallelism and other simple grammatical constructions like "either/or" help to establish opposition between concepts—and opposites have a way of sticking in the memory.
Other Helpful Antithesis Resources
- The Wikipedia page on Antithesis : A useful summary with associated examples, along with an extensive account of antithesis in the Gospel of Matthew.
- Sound bites from history : A list of examples of antithesis in famous political speeches from United States history — with audio clips!
- A blog post on antithesis : This quick rundown of antithesis focuses on a quote you may know from Muhammad Ali's philosophy of boxing: "Float like a butterfly, sting like a bee."

- Climax (Figure of Speech)
- Figure of Speech
- Juxtaposition
- Parallelism
- Protagonist
- Rhetorical Question
- Figurative Language
- Climax (Plot)
- Slant Rhyme
- Tragic Hero
- Personification
- Extended Metaphor
- Rising Action
- Foreshadowing
- Red Herring
- Understatement

- Quizzes, saving guides, requests, plus so much more.
- Literary Terms
- Definition & Examples
- How to Use Antithesis
I. What is an Antithesis?
“Antithesis” literally means “opposite” – it is usually the opposite of a statement, concept, or idea. In literary analysis, an antithesis is a pair of statements or images in which the one reverses the other. The pair is written with similar grammatical structures to show more contrast. Antithesis (pronounced an-TITH-eh-sis) is used to emphasize a concept, idea, or conclusion.
II. Examples of Antithesis
That’s one small step for a man – one giant leap for mankind . (Neil Armstrong, 1969)
In this example, Armstrong is referring to man walking on the moon. Although taking a step is an ordinary activity for most people, taking a step on the moon, in outer space, is a major achievement for all humanity.
To err is human ; to forgive , divine . (Alexander Pope)
This example is used to point out that humans possess both worldly and godly qualities; they can all make mistakes, but they also have the power to free others from blame.
The world will little note , nor long remember , what we say here, but it can never forget what they did (Abraham Lincoln, The Gettysburg Address )
In his speech, Lincoln points out that the details of that moment may not be memorable, but the actions would make history, and therefore, never entirely forgotten.
Antithesis can be a little tricky to see at first. To start, notice how each of these examples is separated into two parts . The parts are separated either by a dash, a semicolon, or the word “but.” Antithesis always has this multi-part structure (usually there are two parts, but sometimes it can be more, as we’ll see in later examples). The parts are not always as obvious as they are in these examples, but they will always be there.
Next, notice how the second part of each example contains terms that reverse or invert terms in the first part: small step vs. giant leap; human vs. divine; we say vs. they do. In each of the examples, there are several pairs of contrasted terms between the first part and the second, which is quite common in antithesis.
Finally, notice that each of the examples contains some parallel structures and ideas in addition to the opposites. This is key! The two parts are not simply contradictory statements. They are a matched pair that have many grammatical structures or concepts in common; in the details, however, they are opposites.
For example, look at the parallel grammar of Example 1: the word “one,” followed by an adjective, a noun, and then the word “for.” This accentuates the opposites by setting them against a backdrop of sameness – in other words, two very different ideas are being expressed with very, very similar grammatical structures.
To recap: antithesis has three things:
- Two or more parts
- Reversed or inverted ideas
- (usually) parallel grammatical structure
III. The Importance of Verisimilitude
Antithesis is basically a complex form of juxtaposition . So its effects are fairly similar – by contrasting one thing against its opposite, a writer or speaker can emphasize the key attributes of whatever they’re talking about. In the Neil Armstrong quote, for example, the tremendous significance of the first step on the moon is made more vivid by contrasting it with the smallness and ordinariness of the motion that brought it about.
Antithesis can also be used to express curious contradictions or paradoxes. Again, the Neil Armstrong quote is a good example: Armstrong is inviting his listeners to puzzle over the fact that a tiny, ordinary step – not so different from the millions of steps we take each day – can represent so massive a technological accomplishment as the moon landing.
Paradoxically, an antithesis can also be used to show how two seeming opposites might in fact be similar.
IV. Examples of Verisimilitude in Literature
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({}); Forgive us this day our trespasses as we forgive those who trespass against us . (The Lord’s Prayer)
The antithesis is doing a lot of work here. First, it shows the parallel between committing an evil act and being the victim of one. On the surface, these are opposites, and this is part of the antithesis, but at the same time they are, in the end, the same act from different perspectives. This part of the antithesis is basically just an expression of the Golden Rule.
Second, the antithesis displays a parallel between the speaker (a human) and the one being spoken to (God). The prayer is a request for divine mercy, and at the same time a reminder that human beings should also be merciful.
All the joy the world contains has come through wanting happiness for others . All the misery the world contains has come through wanting pleasure for yourself . (Shantideva, The Way of the Bodhisattva )
The antithesis here comes with some pretty intense parallel structure. Most of the words in each sentence are exactly the same as those in the other sentence. (“All the ___ the world contains has come through wanting ____ for ____.”) This close parallel structure makes the antithesis all the more striking, since the words that differ become much more visible.
Another interesting feature of this antithesis is that it makes “pleasure” and “happiness” seem like opposites, when most of us might think of them as more or less synonymous. The quote makes happiness seem noble and exalted, whereas pleasure is portrayed as selfish and worthless.
The proper function of man is to live , not to exist . I shall not waste my days in trying to prolong (Jack London, Credo )
The opening antithesis here gets its punch from the fact that we think of living and existing as pretty similar terms. But for London, they are opposites. Living is about having vivid experiences, learning, and being bold; simply existing is a dull, pointless thing. These two apparently similar words are used in this antithesis to emphasize the importance of living as opposed to mere existing.
The second antithesis, on the other hand, is just the opposite – in this case, London is taking two words that seem somewhat opposed (waste and prolong), and telling us that they are in fact the same . Prolonging something is making it last; wasting something is letting it run out too soon. But, says London, when it comes to life, they are the same. If you try too hard to prolong your days (that is, if you’re so worried about dying that you never face your fears and live your life), then you will end up wasting them because you will never do anything worthwhile.
V. Examples of Verisimilitude in Pop Culture
Everybody doesn’t like something, but nobody doesn’t like Sara Lee. (Sara Lee pastry advertisement)
This classic ad uses antithesis to set up a deliberate grammatical error. This is a common technique in advertising, since people are more likely to remember a slogan that is grammatically incorrect. (Even if they only remember it because they found it irritating, it still sticks in their brain, which is all that an ad needs to do.) The antithesis helps make the meaning clear, and throws the grammatical error into sharper relief.
What men must know , a boy must learn . (The Lookouts)
Here’s another example of how parallel structure can turn into antithesis fairly easily. (The structure is noun-“must”-verb. ) The antithesis also expresses the basic narrative of The Lookouts , which is all about kids learning to fend for themselves and become full-fledged adults.
Shut Your Mouth and Open Your Eyes (the band “AFI” – album title)
The antithesis here is a juxtaposition of two different actions (opening and shutting) that are actually part of the same sort of behavior – the behavior of somebody who wants to understand the world rather than be the center of attention. It’s basically a restatement of the old adage that “those who speak the most often have the least to say.”
VI. Related Terms
- Juxtaposition
Antithesis is basically a form of juxtaposition . Juxtaposition, though, is a much broader device that encompasses any deliberate use of contrast or contradiction by an author. So, in addition to antithesis, it might include:
- The scene in “The Godfather” where a series of brutal murders is intercut with shots of a baptism, juxtaposing birth and death.
- “A Song of Ice and Fire” (George R. R. Martin book series)
- Heaven and Hell
- Mountains and the sea
- Dead or alive
- “In sickness and in health”
Antithesis performs a very similar function, but does so in a more complicated way by using full sentences (rather than single words or images) to express the two halves of the juxtaposition.
Here is an antithesis built around some of the common expressions from above
- “ Sheep go to Heaven ; goats go to Hell .”
- “Beethoven’s music is as mighty as the mountains and as timeless as the sea .”
- “In sickness he loved me; in health he abandoned ”
Notice how the antithesis builds an entire statement around the much simpler juxtaposition. And, crucially, notice that each of those statements exhibits parallel grammatical structure . In this way, both Juxtaposition and parallel structures can be used to transform a simple comparison, into antithesis.
List of Terms
- Alliteration
- Amplification
- Anachronism
- Anthropomorphism
- Antonomasia
- APA Citation
- Aposiopesis
- Autobiography
- Bildungsroman
- Characterization
- Circumlocution
- Cliffhanger
- Comic Relief
- Connotation
- Deus ex machina
- Deuteragonist
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Dramatic irony
- Equivocation
- Extended Metaphor
- Figures of Speech
- Flash-forward
- Foreshadowing
- Intertextuality
- Literary Device
- Malapropism
- Onomatopoeia
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Point of View
- Polysyndeton
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Rhetorical Device
- Rhetorical Question
- Science Fiction
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
- Synesthesia
- Turning Point
- Understatement
- Urban Legend
- Verisimilitude
- Essay Guide
- Cite This Website
What Is Antithesis, and How Do You Use It in Writing?

Antithesis is a literary device that positions opposite ideas parallel to each other. Think heroes and villains, hot and cold, bitter and sweet. Antithesis enhances your writing by illuminating differences and making your point more persuasive.
What is antithesis?
Antithesis (pronounced an-TITH-uh-sis) deals in opposites. The Merriam-Webster definition of antithesis is “the direct opposite,” and in Greek the meaning is “setting opposite.” As a tool for writing, antithesis creates a juxtaposition of qualities using a parallel grammatical structure. In other words, it’s setting opposites next to each other using the same terms or structure. This creates a stark contrast that highlights dramatic qualities and creates a rhythm that’s interesting to the reader.
What is the function of antithesis?
The repetition of structure in antithesis makes writing more memorable, and its juxtapositions make writing more convincing.
Take, for example, the opening lines of Charles Dickens’s A Tale of Two Cities : “It was the best of times, it was the worst of times . . . ” You’re probably familiar with this line even if the name Dr. Manette means nothing to you. Dickens took two contrasting qualities (best/worst) and linked them by using a parallel structure (it was . . . of times / it was . . . of times). The contrast is clear, and the sentiment is intriguing. The reader is hooked.
In rhetoric , antithesis calls attention to the differences between two options. For example, in a speech in Saint Louis in 1964, Martin Luther King Jr. said: “We must learn to live together as brothers or perish together as fools.” King is obviously in favor of the former option: living together as brothers. He uses antithesis, placing opposite actions (live/perish) in a parallel structure (. . . together as brothers / . . . together as fools) to make his claim even more convincing.
How to use antithesis in writing
Contrast and parallel structure are the two most important elements for you to think about as you begin using antithesis in your own writing.
Contrast: The main tool of antithesis is its contrast of ideas. Ideally, the two concepts are direct opposites. However, sometimes you can get away with contrasting differences or implied opposites, which are forms of juxtaposition. (We’ll talk about the difference between antithesis and juxtaposition later.) The greater the difference between the two things, the clearer their contrast. Antithesis is more powerful than juxtaposition as it deals in stronger contrasts.
Parallel structure: Parallel structure in writing, also known as parallelism , creates a rhythm that draws attention to your contrast. Think about the famous Dickens line we talked about before: “It was the best of times, it was the worst of times . . .” Notice how memorable that rhythm is. If we remove the parallel structure, you end up with something like: “It was the best of times, but not always. It was also the worst of times.” Same sentiment, not nearly as beautiful.
Be careful not to overuse antithesis though. Its effectiveness depends on grabbing your reader’s attention. Used too often, it can change from noteworthy to annoying.
Antithesis vs. juxtaposition
Antithesis, parallelism, and juxtaposition are closely related literary devices that overlap with each other. Just as antithesis reveals two contrary ideas’ qualities by contrasting them, learning the differences between these devices will help you understand each individually.
Juxtaposition means placing two objects side by side to highlight their differences. It is a broader category than antithesis. Antithesis is a type of juxtaposition. Antithesis means placing direct opposites side by side, while juxtaposition uses any sort of difference. Other forms of juxtaposition are foils (differences between specific characters) and oxymorons (seemingly illogical expressions that use contradictory words).
Antithesis vs. parallelism
This may sound familiar because we just wrote about how antithesis uses parallelism to make its point. Parallelism has to do with syntax , or the structure of the sentence. Put simply, it’s two or more clauses that have the same grammatical structure. For example, the expression “hope for the best, prepare for the worst” uses the same grammatical structure twice in a row. The difference between antithesis and parallelism is that parallelism does not have to deal in opposites, while antithesis does. Furthermore, antithesis refers to both the content and the structure of a statement, whereas parallelism is just a structure.
Antithesis examples
Once you know what to look for, you’ll see antithesis examples everywhere. Below are some selections that we found in literature, poetry, speeches, music, and advertising.
Antithesis in literature
“It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, it was the epoch of belief, it was the epoch of incredulity, it was the season of Light, it was the season of Darkness . . .” —Charles Dickens, A Tale of Two Cities
“. . . me and you, we got more yesterday than anybody. We need some kind of tomorrow.” —Toni Morrison, Beloved
Antithesis in poetry
“Some say the world will end in fire, Some say in ice” —Robert Frost, “Fire and Ice”
Antithesis in speech
“We observe today not a victory of party, but a celebration of freedom, symbolizing an end as well as a beginning, signifying renewal as well as change.” —John F. Kennedy, presidential inaugural speech
Antithesis in music
“’Cause you’re hot then you’re cold / you’re yes then you’re no / you’re in then you’re out / you’re up then you’re down” —Katy Perry, “Hot N Cold”
Antithesis in advertising
“Everybody doesn’t like something, but nobody doesn’t like Sara Lee.” —Sara Lee slogan
Antithesis phrases
Easy come, easy go. Get busy living or get busy dying. “Float like a butterfly, sting like a bee.” —Muhammad Ali, 1964
Antithesis FAQs
Antithesis is a literary device that places opposite words, ideas, or qualities parallel to each other. The contrast between them creates greater emphasis and clarity. Their parallel structure provides a memorable rhythm.
When is antithesis used?
The effect of antithesis is useful in all kinds of writing and speech, including literature, advertising, rhetoric, and music. It’s best used to make an emphatic point in a catchy way.
How is antithesis used in writing?
In writing, antithesis combines juxtaposition and parallelism. The pattern created by antithesis allows writers to highlight differences, emphasize qualities, and generate rhythm.


What is Antithesis? Examples of Antithesis in Literature and Speech
Antithesis is a rhetorical device that has been used for centuries to create contrast and emphasize ideas in speech and writing. It involves placing two contrasting ideas side by side, often using parallel grammatical structures, to highlight their differences. This technique can be used for various purposes, such as to create emphasis, create balance, or to make a point.
Table of Contents
Definition of Antithesis
Antithesis is a literary device that involves contrasting two opposing ideas or concepts in a sentence or passage in order to create a dramatic or rhetorical effect. The word “antithesis” comes from the Greek word “antithenai,” which means “to oppose.”
Antithesis can be used in a variety of ways, including through contrasting words, phrases, or clauses. This technique is often used in poetry, prose, and speeches to create a sense of tension and to emphasize the differences between two ideas.
In antithesis, two contrasting ideas are placed side by side in order to highlight their differences. This technique is often used to create a sense of balance in a sentence or passage. For example, consider the following sentence: “To be or not to be, that is the question.” In this sentence, the opposing ideas of existence and non-existence are contrasted in order to create a sense of tension and to emphasize the importance of the decision at hand.
Examples of Antithesis
Antithesis is a literary device that involves the use of contrasting ideas, words, or phrases in a parallel structure. Here are some examples of antithesis in literature, speeches, and advertising.
Antithesis in Literature
Antithesis is commonly used in literature to highlight the contrast between two opposing ideas or themes. One of the most famous examples of antithesis in literature is found in Charles Dickens’ A Tale of Two Cities . The opening lines of the novel read:
“It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, it was the epoch of belief, it was the epoch of incredulity, it was the season of Light, it was the season of Darkness, it was the spring of hope, it was the winter of despair, we had everything before us, we had nothing before us, we were all going direct to Heaven, we were all going direct the other way – in short, the period was so far like the present period, that some of its noisiest authorities insisted on its being received, for good or for evil, in the superlative degree of comparison only.”
The contrasting ideas of “best” and “worst,” “wisdom” and “foolishness,” “belief” and “incredulity,” and others are used to emphasize the stark differences between the two cities.
Antithesis in Speeches
Antithesis is also commonly used in speeches to create a memorable impact on the audience. One of the most famous examples of antithesis in a speech is from Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech:
“We must learn to live together as brothers or perish together as fools.”
The contrasting ideas of “live together” and “perish together” are used to emphasize the importance of unity and brotherhood.
Antithesis in Advertising
Antithesis is also used in advertising to create memorable slogans and taglines. One example is the slogan for the car company BMW:
“The ultimate driving machine.”
The contrasting ideas of “ultimate” and “driving machine” are used to emphasize the high quality and performance of BMW cars.
In conclusion, antithesis is a powerful literary device that can be used in a variety of contexts to create memorable and impactful statements.
Antithesis vs. Juxtaposition
Antithesis and juxtaposition are two rhetorical devices that are often used in literature and speech. While they may seem similar, there are distinct differences between the two.
Antithesis is a rhetorical device that involves placing two contrasting ideas side by side in a sentence or phrase. The purpose of antithesis is to create a stark contrast between the two ideas, often to emphasize a point or to create a sense of tension or conflict.
For example, one famous example of antithesis comes from Charles Dickens’ “A Tale of Two Cities”: “It was the best of times, it was the worst of times.” This sentence contrasts two opposing ideas, highlighting the extreme differences between them.
Antithesis is often used in speeches and persuasive writing to create a memorable and impactful statement. However, it can also be used in more subtle ways to add depth and complexity to a piece of writing.
Juxtaposition
Juxtaposition, on the other hand, involves placing two ideas or objects next to each other in order to highlight their differences or similarities. Unlike antithesis, the two ideas or objects may not necessarily be opposing or contrasting.
For example, a writer might use juxtaposition to describe two characters in a story. By placing their descriptions side by side, the writer can highlight their differences and create a more vivid picture of each character.
Juxtaposition can also be used to create irony or humor. By placing two unlikely ideas or objects next to each other, a writer can create a sense of surprise or amusement.
In conclusion, while antithesis and juxtaposition are both rhetorical devices that involve placing two ideas or objects next to each other, they serve different purposes. Antithesis is used to create a contrast or conflict between two opposing ideas, while juxtaposition is used to highlight the differences or similarities between two ideas or objects.
Antithesis in Communication
Antithesis is a powerful tool in communication that can be used to emphasize contrast, create memorable phrases, and strengthen arguments. By juxtaposing two opposing ideas, antithesis can help to clarify and highlight the differences between them, making them more easily understood and remembered. In this section, we will explore the importance of antithesis in communication and how it can be used effectively.
Emphasizing Contrast
One of the primary functions of antithesis is to emphasize contrast. By placing two opposing ideas side by side, antithesis can draw attention to their differences and make them more apparent. This can be especially useful in situations where it is important to distinguish between two similar but distinct concepts. For example, in political discourse, antithesis can be used to highlight the differences between two competing policy proposals or ideologies.
Creating Memorable Phrases
Another important function of antithesis is to create memorable phrases. By using contrasting ideas in a sentence or phrase, antithesis can create a sense of balance and rhythm that can make the words more memorable. This can be seen in famous quotes such as “To be or not to be” from Shakespeare’s Hamlet, which uses antithesis to create a memorable phrase that encapsulates the play’s central theme.
Strengthening Arguments
Finally, antithesis can be used to strengthen arguments. By using contrasting ideas, antithesis can help to make an argument more persuasive by highlighting the strengths of one idea while pointing out the weaknesses of another. This can be especially useful in situations where it is important to make a convincing case, such as in a legal argument or a political debate.
In conclusion, antithesis is an important tool in communication that can be used to emphasize contrast, create memorable phrases, and strengthen arguments. By using contrasting ideas, antithesis can help to clarify and highlight the differences between two concepts, making them more easily understood and remembered. Whether in literature, politics, or everyday conversation, antithesis can be a powerful tool for effective communication.
Overall, antithesis is a valuable tool for writers and speakers who want to create a sense of contrast and emphasize their point. When used effectively, it can make writing or speech more memorable and impactful. However, it is important to use it in moderation and not rely on it too heavily. By understanding how to use antithesis effectively, writers and speakers can take their communication skills to the next level.
Related Links
- Verbal Irony
Antithesis Definition Antithesis, which literally means “opposite,” is a rhetorical device wherein opposite thoughts are prepare in a sentence to obtain a contrasting effect. Antithesis emphasizes the idea of assessment through parallel structures of the contrasted terms or clauses. The structures of terms and clauses are similar, so that it will draw the attention of the listeners or readers. For example: “Setting foot on the moon may be a small step for a person but a giant step for mankind.” The use of contrasting thoughts, “a small step” and “a massive step,” within the sentence above emphasizes the importance of one of the most important landmarks of human history. Common Antithesis Examples Some well-known antithetical statements have become part of our everyday speech, and are regularly used in arguments and discussions. Below is a listing of some commonplace antithetical statements: Give every man thy ear, however few thy voice. Man proposes, God disposes. Love is a really perfect thing, marriage a actual thing. Speech is silver, but silence is gold. Patience is bitter, however it has a sweet fruit. Money is the foundation of all evil: poverty is the fruit of all goodness. You are smooth on the eyes, but tough on the heart. Examples of Antithesis in Literature In literature, writers rent antithesis not simplest in sentences, but additionally in characters and events. Thus, its use is extensive. Below are a few examples of antithesis in literature: Example #1: A Tale of Two Cities (By Charles Dickens) The establishing lines of Charles Dickens’ novel A Tale of Two Cities provides an unforgettable antithesis example: “It become the first-class of times, it become the worst of times, it became the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, it become the epoch of belief, it turned into the epoch of incredulity, it changed into the season of Light, it was the season of Darkness, it changed into the spring of hope, it was the wintry weather of despair, we had everything before us, we had nothing earlier than us, we were all going direct to Heaven, we were all going direct the opposite way.” The contrasting thoughts, set in parallel structures, markedly spotlight the battle that existed within the time discussed in the novel. Example #2: Julius Caesar (By William Shakespeare) In William Shakespeare’s Julius Caesar, we note antithesis within the characters of Mark Antony and Marcus Brutus. Brutus is portrayed as the “noblest of Romans,” near Caesar, and someone who cherished Rome and Caesar. Antony, at the contrary, is proven as a person with the evil intentions of harming Caesar, and taking charge of Rome. These antithetical characters spotlight the battle inside the play. Example #3: An Essay on Criticism (By Alexander Pope) Alexander Pope, in his An Essay on Criticism, says: “To err is human; to forgive divine.” Fallibility is a trait of humans, and God – the Creator – is most forgiving. Through those antithetical thoughts, Pope exhibits the simple nature of human beings. He wants to say that God is forgiving because his creation is erring. Example #4: Community (By John Donne) We find antithesis in John Donne’s poem Community: “Good we must love, and must hate ill, For unwell is ill, and correct desirable still; But there are things indifferent, Which we may neither hate, nor love, But one, and then another prove, As we shall discover our fancy bent.” Two contrasting words “love” and “hate” are combined within the above lines. It emphasizes that we love right due to the fact it is always top, and we hate bad due to the fact it's far always bad. It is a matter of desire to love or hate things that are neither good nor bad. Example #5: Paradise Lost (By John Milton) John Milton, in Paradise Lost, says: “Better to reign in Hell than serve in Heav’n.” The contrasting thoughts of reign/serve, and Hell/Heav’n are positioned on this sentence to acquire an antithetical effect. Function of Antithesis A literary tool, like antithesis, makes use of phrases to convey ideas in exceptional methods from the commonplace words and expressions of daily life. Thus, it conveys meaning greater vividly than regular speech. When contrasting thoughts are brought together, the concept is expressed extra emphatically. As a literary device, antithesis makes contrasts in an effort to observe pros and cons of a subject below discussion, and facilitates to bring on judgment on that precise subject.
- Alliteration
- Anachronism
- Antimetabole
- Aposiopesis
- Characterization
- Colloquialism
- Connotation
- Deus Ex Machina
- Didacticism
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Flash Forward
- Foreshadowing
- Internal Rhyme
- Juxtaposition
- Non Sequitur
- Onomatopoeia
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Poetic Justice
- Point of View
- Portmanteau
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Superlative
- Synesthesia
- Tragicomedy
- Tragic Flaw
- Verisimilitude
an-tith-uh-sis
Antithesis occurs when two contrasting ideas are put together to achieve a desired outcome.
E.g. The speaker's use of antithesis , contrasting freedom with captivity and knowledge with ignorance, added a compelling layer of depth to the philosophical debate.
Related terms: Juxtaposition , oxymoron , conflict , irony
The two opposites are accompanied by a parallel structure used to help unite the two phrases. When this rhetorical device is used, the reader should immediately become aware that this line is of particular importance. It allows the writer to emphasize something they know needs to be said to the best possible effect.
A common example is: “You are easy on the eyes , but hard on the heart .” With this phrase, anyone should be able to come to the conclusion that the “you” in these lines is someone the speaker cares for and thinks is attractive, but is also often emotionally hurt by. Through the use of this structure, one is also able to break down complex feelings into something easier to understand.

Explore Antithesis
- 1 Definition of Antithesis
- 2 Examples of Antithesis in Literature
- 3 Antithesis and Juxtaposition
- 4 Antithesis and Oxymoron
- 5 Related Literary Terms
- 6 Other Resources
Definition of Antithesis
Antithesis is used in everyday speech , novels , poems, short stories , plays, and more. The rhetorical device can be used in very different ways in order to achieve varied outcomes.
Parallelism is an important part of antithesis. The structure of the words around the contrasting ideas is usually identical, at least in part. This allows the juxtaposed words to be as powerful as possible.
The word “antithesis” comes from the Greek “anithenai,” meaning “to oppose.”
Examples of Antithesis in Literature
Paradise lost by john milton.
In John Milton’s ‘ Paradise Lost,’ there is a great example of antithesis in the first book. Satan was up in Hell, imprisoned alongside a fiery lake, and he uses these words:
Here we may reign secure, and in my choyce To reign is worth ambition though in Hell: Better to reign in Hell , then serve in Heav’n
While speaking to Beelzebub, he says that it’s better to “reign in Hell, then serve in Heav’n.” Through this clever turn of phrase, he’s suggesting that he’d rather fulfill his role as “the devil” and control his own destiny than be under God’s thumb in Heaven. It’s important to remember when considering this quote that Satan was cast out of Heaven for questioning God. He craves the leeway his position in Hell affords him.
Read more John Milton poems .
A Tale of Two Cities by Charles Dickens
Charles Dickens’ famous novel , A Tale of Two Cities, has a wonderful example of antithesis at the beginning of the first chapter. Here is an excerpt from the novel that demonstrates, in several different ways, how the device might be used.
It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom , it was the age of foolishness , it was the epoch of belief , it was the epoch of incredulity , it was the season of Light , it was the season of darkness, it was the spring of hope , it was the winter of despair , we had everything before us, we had nothing before us, we were all going direct to Heaven , we were all going direct the other way .
The examples of antithesis are seen through the bolded words. “Best” contrasts with “worst” and “everything” with “nothing.” Through the use of this technique, Dickens is able to highlight the different perspectives and conflicts that are going to arise in the following pages.
This excerpt is also a good example of how parallel structures are used. He says, “It was the best of times” and “it was the worst of times.” The phrase “it was the” is used in both instances. The same can be said for the following example in which he uses “it was the age of” to refer to “foolishness” and “wisdom.”
Explore Charles Dickens’ poetry .
Community by John Donne
In this lesser-known Donne poem, the poet includes the following lines:
Good we must love, and must hate ill, For ill is ill, and good good still; But there are things indifferent, Which we may neither hate, nor love, But one, and then another prove, As we shall find our fancy bent.
He presents “love” alongside “hate” in addition to “good” alongside “ill.” By showing the reader both sides, he’s able to emphasize why “we” love what we love and why we hate what we hate. He goes on, to state that, in contrast , it is a matter of choice whether one hates or loves the “things indifferent.”
Read more of John Donne’s famous poems .
Hamlet by William Shakespeare
The famous soliloquy from Hamlet is a good example of how antithesis can be used. In the “To be or not to be” speech, he uses the following lines:
To be or not to be , that is the question: Whether ’tis nobler in the mind to suffer The slings and arrows of outrageous fortune Or to take arms against a sea of troubles,
In the first lines of this excerpt, he presents “to be or not to be” as an example of antithesis. The two opposites hinge on the use of “or” in between them. As the passage goes on, Shakespeare uses antithesis again with “to suffer” or “to take arms.”
Discover William Shakespeare’s poetry .
Antithesis and Juxtaposition
Antithesis is similar to juxtaposition in that they are both concerned with opposites and contrasting terms. When two ideas are juxtaposed, they are placed next to one another but not necessarily to create a relationship between the two. They may not have a more important meaning other than to add interest to the text.
Antithesis and Oxymoron
Antithesis is also often confused with an oxymoron. The latter occurs when two words that contradict one another are placed together in order to reveal a deeper truth. For example, “sweet sorrow” or “living dead.” These are stand-alone statements in which two words that don’t seem to belong together are placed next to one another and then make sense.
In contrast, antithesis does not usually use two contrasting words next to one another. They’re usually more spread out, playing into the importance of parallelism.
Related Literary Terms
- Oxymoron : a kind of figurative language in which two contrasting things are connected together.
- Juxtaposition : a literary technique that places two unlike things next to one another.
- Simile : a comparison between two unlike things that uses the words “like” or “as”.
Other Resources
- Listen: Antithesis—Why Opposites Attract
- Watch: Oxymoron Definition and Examples
- Watch: ‘To be or not to be’ Hamlet Speech
Home » Figurative Language » Antithesis
The Definitive Literary Glossary Crafted by Experts
All terms defined are created by a team of talented literary experts, to provide an in-depth look into literary terms and poetry, like no other.
Cite This Page
Baldwin, Emma. "Antithesis". Poem Analysis , https://poemanalysis.com/figurative-language/antithesis/ . Accessed 30 August 2024.

Help Center
Request an Analysis
(not a member? Join now)
Poem PDF Guides
PDF Learning Library
Beyond the Verse Podcast
Poetry Archives
Poetry Explained
Poet Biographies
Useful Links
Poem Explorer
Poem Generator
Poem Solutions Limited, International House, 36-38 Cornhill, London, EC3V 3NG, United Kingdom
(and discover the hidden secrets to understanding poetry)
Get PDFs to Help You Learn Poetry
250+ Reviews
Literary Devices
Literary devices, terms, and elements, definition of antithesis, difference between antithesis and juxtaposition, common examples of antithesis, significance of antithesis in literature, examples of antithesis in literature.
HAMLET: To be, or not to be, that is the question— Whether ’tis Nobler in the mind to suffer The Slings and Arrows of outrageous Fortune, Or to take Arms against a Sea of troubles, And by opposing, end them?
Arguably the most famous six words in all of Shakespeare’s work are an example of antithesis. Hamlet considers the important question of “to be, or not to be.” In this line, he is considering the very nature of existence itself. Though the line is quite simple in form it contrasts these very important opposite states. Hamlet sets up his soliloquy with this antithesis and continues with others, including the contrast between suffering whatever fortune has to offer or opposing his troubles. This is a good example of Shakespeare using antithesis to present to the audience or readers Hamlet’s inner life and the range of his thinking.
It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, it was the epoch of belief, it was the epoch of incredulity, it was the season of Light, it was the season of Darkness, it was the spring of hope, it was the winter of despair, we had everything before us, we had nothing before us, we were all going direct to Heaven, we were all going direct the other way…
The opening paragraph of Charles Dickens’s A Tale of Two Cities employs many different literary devices all at once. There are many examples of antithesis back-to-back, starting with the first contrast between “the best of times” and “the worst of times.” Each pair of contrasting opposites uses a parallel structure to emphasize their differences. Dickens uses these antithetical pairs to show what a tumultuous time it was during the setting of his book. In this case, the use of antithesis is a rhetorical device that foreshadows the conflicts that will be central to the novel.
There was only one catch and that was Catch-22, which specified that a concern for one’s own safety in the face of dangers that were real and immediate was the process of a rational mind. Orr was crazy and could be grounded. All he had to do was ask; and as soon as he did, he would no longer be crazy and would have to fly more missions. Orr would be crazy to fly more missions and sane if he didn’t, but if he was sane he had to fly them. If he flew them he was crazy and didn’t have to; but if he didn’t want to he was sane and had to. Yossarian was moved very deeply by the absolute simplicity of this clause of Catch-22 and let out a respectful whistle.
In Joseph Heller’s classic anti-war novel Catch-22 , Heller uses a specific type of humor in which antithetical statements show the true absurdity of war. This very famous quote explains the concept of the “Catch-22,” which became a popular idiomatic expression because of the book. In fact, this example is not so much an antithetical statement but instead an antithetical situation. That is to say, the two possible outcomes for Orr are opposite: either he’s deemed crazy and would thus not be forced to fly any more combat missions, or he’s sane and then would indeed have to fly them. However, the one situation negates the possibility of the other, as only a sane man would be clear-headed enough to ask not to fly more missions.
This case is not a difficult one, it requires no minute sifting of complicated facts, but it does require you to be sure beyond all reasonable doubt as to the guilt of the defendant.
( To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee)
Test Your Knowledge of Antithesis
1. What is the correct antithesis definition? A. Using two very similar concepts and showing their subtle differences. B. Setting up a contrast between two opposite ideas or phrases in a balanced grammatical structure. C. Using words to convey an opposite meaning to their literal sense. [spoiler title=”Answer to Question #1″] Answer: B is the correct answer. A is one possible definition of juxtaposition, while C is one possible definition of irony.[/spoiler]
WITCHES: Fair is foul, and foul is fair: Hover through the fog and filthy air.
MACBETH: Is this a dagger which I see before me, The handle toward my hand?
WITCHES: Something wicked this way comes.
4. Which of the following quotes from Heller’s Catch-22 contains an example of antithesis? A. There are now fifty or sixty countries fighting in this war. Surely so many counties can’t all be worth dying for. B. He had decided to live forever or die in the attempt, and his only mission each time he went up was to come down alive. C. You’re inches away from death every time you go on a mission. How much older can you be at your age? [spoiler title=”Answer to Question #4″] Answer: B is the correct answer.[/spoiler]

What is Antithesis? Definition, Examples of Antitheses in Writing
Home » The Writer’s Dictionary » What is Antithesis? Definition, Examples of Antitheses in Writing
Antithesis definition: Antithesis is a literary and rhetorical device where two seemingly contrasting ideas are expressed through parallel structure.
What is Antithesis?
What does antithesis mean? An antithesis is just that—an “anti” “thesis.” An antithesis is used in writing to express ideas that seem contradictory.
An antithesis uses parallel structure of two ideas to communicate this contradiction.
Example of Antithesis:
- “Float like a butterfly, sting like a bee.” –Muhammad Ali

First, the structure is parallel. Each “side” of the phrase has the same number of words and the same structure. Each uses a verb followed by a simile.
Second, the contracting elements of a butterfly and a bee seem contradictory. That is, a butterfly is light and airy while a bee is sharp and stinging. One person (a boxer, in this case) should not be able to possess these two qualities—this is why this is an antithesis.
However, Ali is trying to express how a boxer must be light on his feet yet quick with his fist.
Modern Examples of Antithesis

- “That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind.”
Through parallel structure, this quotation presents an antithesis. It seems contradictory that one action could be a “small step” and a “giant leap.”
However, this contradiction proposes that the action of landing on the moon might have just been a small physical step for the man Neil Armstrong, but it was a giant leap for the progress of mankind.
The Function of Antithesis

An antithesis stands out in writing. Because it uses parallel structure, an antithesis physically stands out when interspersed among other syntactical structures. Furthermore, an antithesis presents contrasting ideas that cause the reader or audience to pause and consider the meaning and purpose.
Oftentimes, the meaning of an antithesis is not overtly clear. That is, a reader or audience must evaluate the statement to navigate the meaning.
Writers utilize antitheses very sparingly. Since its purpose is to cause an audience to pause and consider the argument, it must be used with purpose and intent.
Antithesis Example from Literature

- “It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, it was the epoch of belief, it was the epoch of incredulity…”
From the beginning, Dickens presents two contradictory ideas in this antithesis.
How can it be the “best” and the “worst” of times? These two “times” should not be able to coexist.
Similarly, how can the setting of this novel also take place during an “age of wisdom” and an “age of foolishness?”
The antithesis continues.
Dickens opens his with these lines to set the tone for the rest of the novel. Clearly, there are two sides to this story, two tales of what is the truth. These two “sides” should not function peacefully. And, in fact, they do not. That, after all, is the “tale of two cities.”
Dickens sets up this disparity to set the tone for his novel, which will explore this topic.
Summary: What is an Antithesis?
Define antithesis: An antithesis consists of contrasting concepts presented in parallel structure.
Writers use antithesis to create emphasis to communicate an argument.
- Note: The plural form of antithesis is antitheses.

Antithesis is a literary device that pairs contrasting ideas together in a sentence to highlight their differences. This technique emphasizes the distinction between the ideas, making their unique characteristics more noticeable and impactful. By using antithesis, writers can draw attention to specific traits and enhance the clarity of their message.
What is an Antithesis?
Types of antithesis, conceptual antithesis.
Conceptual antithesis involves contrasting abstract ideas or theories, such as “freedom vs. slavery” or “truth vs. lies,” to emphasize ideological differences.
Structural Antithesis
This type uses parallel grammatical structures to emphasize the contrast between two opposing words or clauses, enhancing the rhythm and balance of the sentence.
Verbal Antithesis
Verbal antithesis contrasts specific words within a statement, like “best of times, worst of times,” focusing on the immediate linguistic juxtaposition.
Figurative Antithesis
Figurative antithesis employs metaphors or similes to contrast two unlike but related concepts, deepening the poetic quality and imagery of the text.
100+ Antithesis Examples

Antithesis examples illustrate how contrasting ideas can be juxtaposed to create a striking effect in language. This literary device is used by writers to emphasize differences by placing opposing concepts in close proximity within their sentences. The result is a clearer and more powerful expression of each idea.
- “Give every man thy ear, but few thy voice.”
- “Many are called, but few are chosen.”
- “You are easy on the eyes, but hard on the heart.”
- “Patience is bitter, but it has a sweet fruit.”
- “We must learn to live together as brothers or perish together as fools.”
- “Money is the root of all evils: poverty is the fruit of all goodness.”
- “Love is an ideal thing, marriage a real thing.”
- “Speech is silver, silence is golden.”
- “It’s not the men in my life, but the life in my men.”
- “Man proposes, God disposes.”
- “They promised freedom but provided slavery.”
- “Ask not what your country can do for you – ask what you can do for your country.”
- “Let’s agree to disagree.”
- “He was too honest to be a politician and too political to be honest.”
- “She’s the sunshine of my life, but sometimes it rains.”
- “That’s one small step for a man, one giant leap for mankind.”
- “You can’t teach an old dog new tricks, but you can learn a lot from them.”
- “War is peace. Freedom is slavery. Ignorance is strength.”
- “It’s not about what it is, it’s about what it can become.”
- “I am a dreamer but not the only one.”
- “We must adjust to changing times and still hold to unchanging principles.”
- “I know one thing; that I know nothing.”
- “The world is a comedy to those that think; a tragedy to those that feel.”
- “He who has a why to live can bear almost any how.”
- “All animals are equal, but some animals are more equal than others.”
- “There is no saint without a past, no sinner without a future.”
- “Fair is foul, and foul is fair.”
- “The more you know, the more you realize you know nothing.”
- “To err is human; to forgive, divine.”
- “She’s as happy as she is sad.”
- “You have to be cruel to be kind.”
- “Better late than never, but never late is better.”
- “The child is the father of the man.”
- “History is written by the victors but read by the survivors.”
- “To lead the people, walk behind them.”
- “He who does not understand your silence will probably not understand your words.”
- “The pen is mightier than the sword.”
- “Actions speak louder than words, but words are often easier.”
- “What we achieve inwardly will change outer reality.”
- “We shape our buildings; thereafter, they shape us.”
- “Prejudice is the reason of fools.”
- “The purpose of life is a life of purpose.”
- “Freedom is not worth having if it does not include the freedom to make mistakes.”
- “The only thing we have to fear is fear itself.”
- “Success is not final, failure is not fatal: It is the courage to continue that counts.”
- “A joke is a very serious thing.”
- “Wisdom is knowing what to do next; virtue is doing it.”
- “The first casualty when war comes is truth.”
- “An eye for an eye only ends up making the whole world blind.”
- “A man who wants to lead the orchestra must turn his back on the crowd.”
- “Life can only be understood backwards; but it must be lived forwards.”
- “Not all those who wander are lost.”
- “The darkest places in hell are reserved for those who maintain their neutrality in times of moral crisis.”
- “If you want to make an omelette, you must be willing to break a few eggs.”
- “In the middle of difficulty lies opportunity.”
- “You must be the change you wish to see in the world.”
- “Every beginning has an end and every end is a new beginning.”
- “It’s better to be hated for what you are than to be loved for what you are not.”
- “He who laughs last laughs best.”
- “Truth is stranger than fiction.”
- “I can resist everything except temptation.”
- “The road to hell is paved with good intentions.”
- “United we stand, divided we fall.”
- “The course of true love never did run smooth.”
- “He who fears being conquered is sure of defeat.”
- “The future belongs to those who believe in the beauty of their dreams.”
- “Youth is wasted on the young.”
- “I must be cruel only to be kind.”
- “Good fences make good neighbors.”
- “He who would learn to fly one day must first learn to stand and walk and run and climb and dance; one cannot fly into flying.”
- “Nothing ventured, nothing gained.”
- “When the going gets tough, the tough get going.”
- “It is always the best policy to speak the truth, unless, of course, you are an exceptionally good liar.”
- “Every exit is an entry somewhere else.”
- “The only source of knowledge is experience.”
- “There is nothing permanent except change.”
- “The only way to have a friend is to be one.”
- “One must be poor to know the luxury of giving.”
- “Injustice anywhere is a threat to justice everywhere.”
- “The only thing more expensive than education is ignorance.”
- “To improve is to change; to be perfect is to change often.”
- “Everything has its beauty, but not everyone sees it.”
- “If you tell the truth, you don’t have to remember anything.”
- “Sometimes you have to be silent to be heard.”
- “Change is the law of life and those who look only to the past or present are certain to miss the future.”
- “The heart has its reasons of which reason knows nothing.”
- “The journey of a thousand miles begins with one step.”
- “He who knows others is wise; he who knows himself is enlightened.”
- “Hope is the dream of a waking man.”
- “A room without books is like a body without a soul.”
- “Courage is not the absence of fear, but rather the judgement that something else is more important than fear.”
- “A person often meets his destiny on the road he took to avoid it.”
- “The best way out is always through.”
- “In theory, there is no difference between theory and practice. But, in practice, there is.”
- “You can do anything, but not everything.”
- “Silence is argument carried out by other means.”
- “Life is what happens when you’re busy making other plans.”
- “The only true wisdom is in knowing you know nothing.”
- “Simplicity is the ultimate sophistication.”
- “Love all, trust a few, do wrong to none.”
- “Happiness is not an ideal of reason, but of imagination.”
Famous Antithesis Examples
Antithesis can be found across classic and modern texts, bringing vivid contrast and memorable clarity to writing. Famous works often use this literary device to draw stark differences between ideas, increasing the impact of their messages.
Antithesis Examples in the Bible
The Bible frequently uses antithesis to emphasize moral contrasts and spiritual dilemmas:
- “For you are all children of light, children of the day; we are not of the night or of the darkness.” — 1 Thessalonians 5:5
- “Whoever exalts himself will be humbled, and whoever humbles himself will be exalted.” — Matthew 23:12
Antithesis Examples in Letter from Birmingham Jail
Martin Luther King Jr.’s “Letter from Birmingham Jail” uses antithesis to highlight the differences between just and unjust laws, as well as the moral gap between actions and inactions:
- “We know through painful experience that freedom is never voluntarily given by the oppressor; it must be demanded by the oppressed.”
Antithesis Examples in I Have a Dream Speech
In his iconic speech, Martin Luther King Jr. used antithesis to emphasize the disparity between the American dream and the American reality:
- “One hundred years later, the Negro is still languished in the corners of American society and finds himself an exile in his own land.”
- “I have a dream that my four little children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin but by the content of their character.”
Antithesis Examples For Kids
Antithesis can also be simplified for children to help them understand opposites in a memorable way:
- “The hero was brave, the villain was cowardly.”
- “She was as quiet as a mouse, he was as loud as a lion.”
How to Use Antithesis
Identify opposing concepts.
Start by identifying two ideas that contrast sharply with each other. These could be qualities, actions, philosophies, or characters.
Create Parallel Structures
Structure your sentence in a way that parallels the opposing ideas. This symmetry helps to highlight the contrast and makes the sentence easier to follow.
Choose Concise Language
Use clear and concise language to express each idea. The sharper the wording, the more effective the antithesis.
Place for Emphasis
Use antithesis in parts of your writing where you want to create a strong, memorable impact, such as in conclusions, thesis statements, or key arguments.
Balance the Sentence
Ensure that both halves of the antithesis are balanced in terms of length and syntactic structure to maintain a rhythmic flow and enhance readability.
Tips for Using Antithesis
- Understand Your Ideas Fully : Before creating an antithesis, make sure you fully understand the ideas or themes you want to contrast. Clear understanding allows for sharper distinctions.
- Use Parallel Structure : Employ parallelism in your sentences when using antithesis. This means keeping the grammatical structures of the contrasting parts similar, which not only emphasizes the contrast but also makes your sentence more rhythmic and easier to understand.
- Keep It Balanced : Ensure that the contrasting elements in the antithesis are balanced in terms of length and syntactic complexity. A balanced structure increases the impact of the contrast.
- Select Appropriate Context : Use antithesis in contexts where highlighting a contrast can strengthen your argument or enhance the poetic quality of your writing. It’s particularly effective in speeches, persuasive essays, and poetry.
- Focus on Clarity : While it’s tempting to use elaborate language, clarity should always be your priority. Choose words that make the contrasting ideas clear and accessible, especially if your audience is broad or diverse.
- Practice Moderation : Although antithesis can be very effective, using it too frequently in a piece of writing can become overwhelming or reduce its impact. Use it sparingly to ensure that each instance stands out and serves a specific purpose.
- Revise for Impact : After writing a sentence with antithesis, revise it to see if the contrast could be stronger or the wording more precise. Editing allows you to refine the structure and wording for maximum impact.
How to pronounce antithesis?
Antithesis is pronounced as an- TITH -eh-sis.
What is a synonym for the word antithesis?
A synonym for antithesis is opposition .
What is an example of an antithesis in a movie?
In “The Dark Knight,” Batman and Joker represent antithesis: order versus chaos.
What is the purpose of using antithesis?
The purpose of using antithesis is to make the differences between two opposing ideas more vivid, enhancing the effectiveness of the message or argument.
Can antithesis be used in everyday conversation?
Yes, antithesis can be used in everyday conversation to emphasize a point or clarify the distinction between two contrasting ideas.
What are common examples of antithesis?
Common examples include phrases like “It was the best of times, it was the worst of times” or “Speech is silver, but silence is golden.”
How does antithesis affect the reader?
Antithesis captures the reader’s attention by creating a stark contrast, making the text more memorable and persuasive.
Is antithesis only used in literature?
No, antithesis is used in various forms of writing and speech, including literature, speeches, advertising, and everyday dialogue.
How can antithesis enhance persuasive writing?
Antithesis sharpens the contrasts in persuasive writing, making arguments clearer and more compelling by highlighting the stakes and choices.
What should be avoided when using antithesis?
Avoid overusing antithesis or forcing unnatural contrasts, as this can make writing seem contrived or unclear. Keep the contrasts relevant and impactful.
AI Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Grammar Palette

- Writing Tips
- Plural Nouns
- Language Devices

Antithesis vs Juxtaposition: What’s the Difference?
When it comes to writing, knowing antithesis vs juxtaposition is really important. These are two tools that writers use to create contrast, but they do it in different ways. Let’s take a closer look at each of them to see how they help writers express their ideas and make their writing more interesting.
Table of Contents
What is Antithesis?
Antithesis is a literary technique that involves placing contrasting ideas, words, or phrases close together to highlight their differences. It’s like putting opposites side by side to make a point more strongly. For example, if someone writes, “To err is human, to forgive divine,” they’re using antithesis to contrast the human tendency to make mistakes with the divine quality of forgiveness. This technique helps writers emphasize contrasts and add depth to their writing.
Examples of Antithesis
- “Darkness cannot drive out darkness; only light can do that. Hate cannot drive out hate; only love can do that.” This quote contrasts darkness with light and hate with love to emphasize the transformative power of positivity.
- “It was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness.” This sentence contrasts wisdom with foolishness to depict the contrasting characteristics of a particular time period.
- “The pen is mightier than the sword.” This phrase contrasts the power of the written word with the power of physical force to highlight the influence of language and ideas.
- “All’s fair in love and war.” This statement contrasts the concepts of fairness and unfairness to suggest that in certain situations, anything goes.
- “United we stand, divided we fall.” This expression contrasts unity with division to underscore the importance of solidarity in achieving success or overcoming challenges.
Origins of Antithesis
The origins of antithesis can be traced back to ancient Greek rhetoric and literary devices. The term itself is derived from the Greek words “anti,” meaning “against,” and “thesis,” meaning “position” or “proposition.” In ancient Greek philosophy and oratory, antithesis was used as a rhetorical device to juxtapose contrasting ideas or statements for persuasive effect. This technique was employed by figures such as Aristotle and Cicero in their writings and speeches to emphasize arguments, provoke thought, and engage audiences. Over time, antithesis became a prominent feature in various forms of literature, including poetry, drama, and prose, where it continues to be utilized to create vivid contrasts and convey deeper meanings.
What is Juxtaposition?
Juxtaposition is a literary technique that involves placing two or more contrasting elements side by side to highlight their differences or create a vivid comparison. It’s like putting things together to emphasize their distinct qualities. For example, in a poem, juxtaposing images of light and darkness can enhance the reader’s understanding of the themes of hope and despair. This technique allows writers to create depth, complexity, and layers of meaning in their works by presenting contrasting ideas, images, or characters in close proximity.
Examples of Juxtaposition
- In a painting, a vibrant, colorful garden is juxtaposed with a dark, ominous sky, creating a stark contrast between beauty and foreboding.
- In a novel, a character who is wealthy and successful lives in a luxurious mansion, but is depicted as lonely and unhappy, juxtaposing material wealth with emotional emptiness.
- In a photograph, a delicate butterfly rests on a rough, weathered surface, juxtaposing fragility with strength.
- In a poem, images of bustling city life are juxtaposed with serene, untouched nature, highlighting the contrast between urban chaos and natural tranquility.
- In a poem, the tranquility of a peaceful lake at dawn is juxtaposed with the chaos of a bustling city at rush hour, illustrating the contrast between natural serenity and urban busyness.
Origins of Juxtaposition
The origins of juxtaposition can be traced back to ancient rhetorical and literary practices, where writers and speakers would strategically place contrasting elements side by side to enhance their message or argument. This technique was commonly employed in ancient Greek and Roman literature, as well as in classical rhetoric, where it was used to create vivid imagery, emphasize contrasts, and provoke thought. Over time, juxtaposition became a fundamental aspect of various literary genres, including poetry, prose, drama, and visual arts, where it continues to be utilized to convey complex ideas, evoke emotions, and engage audiences.
You will like: Oxymoron vs Antithesis
Antithesis vs Juxtaposition: The Differences
Antithesis and juxtaposition, while both serving to highlight contrasts, diverge in their methods and intents. Antithesis, exemplified by phrases like “to be or not to be” or “love is an ideal thing, marriage a real thing,” places opposing concepts or words in close proximity to underscore their differences and provoke thought. It serves as a rhetorical device to emphasize a point or argument through stark contrast. In contrast, juxtaposition involves the placement of contrasting elements side by side to illuminate their disparities or draw a comparison. For instance, juxtaposing images of wealth and poverty in a narrative reveals societal inequalities. While antithesis aims to accentuate differences for rhetorical impact, juxtaposition seeks to create visual or thematic contrasts to deepen understanding or evoke emotion. Understanding these distinctions equips writers with versatile tools to enrich their prose and engage readers effectively.
| Aspect | Antithesis | Juxtaposition |
|---|---|---|
| Contrasting ideas or words placed in close proximity | Contrasting elements placed side by side | |
| Emphasize differences, provoke thought | Highlight disparities, create comparisons | |
| “To be or not to be” | Images of wealth and poverty side by side | |
| Rhetorical device in prose, poetry, speeches | Common in literature, visual arts, photography | |
| Creates rhetorical impact, emphasizes a point or argument | Deepens understanding, evokes emotion | |
| Enhances rhetoric, makes arguments compelling | Enriches narrative, creates visual or thematic contrasts |
How To Use Antithesis and Juxtaposition In Sentences
- Identify contrasting concepts, ideas, or words that you want to emphasize in your sentence.
- Place these contrasting elements in close proximity to each other, typically within the same sentence or clause.
- Ensure that the contrast is clear and meaningful, helping to highlight the differences between the two elements.
- Use antithesis to make your writing more persuasive, engaging, or thought-provoking.
Example: “He is not only my boss but also my mentor.” Here, the contrast between “boss” and “mentor” emphasizes the multifaceted relationship between the two roles.
Juxtaposition
- Select two or more contrasting elements, such as images, ideas, or characters, that you want to juxtapose.
- Place these contrasting elements side by side in your sentence to create a vivid comparison or highlight their differences.
- Use juxtaposition to evoke strong imagery, convey thematic contrasts, or deepen the meaning of your writing.
- Ensure that the juxtaposed elements enhance each other and contribute to the overall message or theme of your sentence.
Example: “The bustling city streets contrast sharply with the peaceful countryside.” Here, the juxtaposition of urban chaos with rural tranquility creates a vivid contrast and emphasizes the differences between the two settings.
Combining Antithesis and Juxtaposition
- Identify contrasting elements: Begin by selecting two or more contrasting concepts, ideas, images, or characters that you want to highlight or compare.
- Create antithetical pairs: Use antithesis to juxtapose these contrasting elements by placing them in close proximity within your sentence or passage. This juxtaposition serves to emphasize the differences between the paired elements while also creating a vivid comparison.
- Ensure coherence and clarity: Make sure that the combined use of antithesis and juxtaposition enhances the overall coherence and clarity of your writing. The contrasts and comparisons should contribute to the deeper meaning or theme of your work without causing confusion or ambiguity.
- Experiment with structure and language: Explore different ways to structure your sentences or passages to effectively combine antithesis and juxtaposition. Experiment with language choices, such as contrasting vocabulary or imagery, to further enhance the impact of your writing.
- Revise and refine: After incorporating antithesis and juxtaposition into your writing, revise and refine your work to ensure that the combined effects are achieving the desired impact. Pay attention to the balance between the contrasting elements and the overall flow of your prose.
Example: “In the heart of the bustling city, amidst the chaos and cacophony of urban life, she found solace in the serene simplicity of a solitary flower blooming defiantly against the cold, gray concrete—a juxtaposition of fragility and resilience, of noise and silence, that captured the essence of her existence.”
In this example, antithesis and juxtaposition are seamlessly combined to contrast the bustling city with the serenity of nature, while also juxtaposing fragility with resilience and noise with silence. This creates a rich and evocative depiction that adds depth and complexity to the writing.
You will like: Juxtaposition vs Paradox
Examples Of Antithesis and Juxtaposition Used In Sentences
Antithesis examples.
- “She was the epitome of grace, yet her words cut like a knife.”
- “His actions spoke volumes, but his silence screamed louder.”
- “In the darkness of night, she found the light of her soul.”
- “Their love was a battlefield, where passion clashed with reason.”
- “The company’s profits soared, while its reputation plummeted.”
Juxtaposition Examples
- “The delicate flower bloomed amidst the thorns, a symbol of resilience in adversity.”
- “The bustling city streets echoed with laughter, while the abandoned alleyways whispered tales of sorrow.”
- “The sun-kissed beach stood in stark contrast to the stormy sea, a juxtaposition of tranquility and turbulence.”
- “His wardrobe was a mishmash of vintage classics and modern trends, a juxtaposition of old and new.”
- “The painting depicted a serene landscape against a backdrop of industrial pollution, a stark juxtaposition of beauty and decay.”
Combined Examples
- “In the heart of the bustling city, where skyscrapers tower over crowded streets, lies a tranquil park, an oasis of calm amidst the urban chaos.”
- “Her laughter echoed through the empty halls, a stark contrast to the silence that enveloped the abandoned mansion.”
- “The old man’s wrinkled face told the story of a lifetime, where joy and sorrow mingled like colors on a canvas, creating a portrait of resilience and wisdom.”
- “In the depths of winter, when the world is cloaked in frost and snow, the flame of hope burns brightest, warming even the coldest hearts.”
- “The towering mountains loomed over the tranquil valley below, a majestic spectacle of nature’s power and serenity.”
- “His charming smile masked the pain in his eyes, a facade of happiness concealing inner turmoil.”
- “The vibrant city skyline faded into the horizon, a testament to both progress and the passage of time.”
- “Amidst the chaos of the carnival, the girl sat quietly on the bench, a beacon of serenity in a sea of excitement.”
Common Mistakes to Avoid when using Antithesis and Juxtaposition
When using antithesis and juxtaposition in writing, there are some common mistakes to avoid to ensure effectiveness:
- Overusing : Using antithesis and juxtaposition too frequently can make your writing feel forced or unnatural. It’s essential to use these techniques judiciously and only when they enhance the meaning or impact of your writing.
- Lack of Clarity : Failing to make the contrast clear can confuse readers. Ensure that the opposing elements in your antithesis or the contrasting elements in your juxtaposition are clearly presented and easily understood.
- Weak Contrast : Weak or insignificant contrasts diminish the effectiveness of antithesis and juxtaposition. Make sure the differences between the paired elements are substantial enough to create impact and provoke thought.
- Mismatched Pairings : Pairing elements that don’t naturally contrast or juxtapose can result in awkward or illogical sentences. Ensure that the elements you’re comparing or contrasting are appropriate and relevant to the context.
- Ignoring Context : Antithesis and juxtaposition should serve the broader context of your writing. Failing to consider the overall theme, tone, or purpose of your piece can lead to disjointed or irrelevant use of these techniques.
- Forced Symmetry : Trying to force symmetry or balance between the contrasting elements can feel contrived. Allow for natural asymmetry when employing antithesis and juxtaposition to maintain authenticity and impact.
- Neglecting Revision : Rushing through the revision process can result in missed opportunities to refine and improve your use of antithesis and juxtaposition. Take the time to review your writing carefully and make necessary adjustments for clarity and effectiveness.
By being mindful of these common mistakes, you can use antithesis and juxtaposition effectively to enhance your writing and captivate your audience.
You will like: Oxymoron vs Juxtaposition
Tips for Avoiding These Mistakes
To avoid common mistakes when using antithesis and juxtaposition, consider the following tips:
- Understand Their Purpose : Before incorporating antithesis or juxtaposition, ensure you understand their purpose in your writing. Use them to emphasize contrasts, deepen meaning, or evoke emotions effectively.
- Use Sparingly : Reserve antithesis and juxtaposition for moments where they can make the most impact. Overusing them can dilute their effectiveness and make your writing feel contrived.
- Focus on Clarity : Ensure that the contrast or comparison is clear and easily understandable to your readers. If the meaning is ambiguous, revise your sentence to provide clarity.
- Choose Strong Contrasts : Opt for contrasting elements that are significant and meaningful to your message or theme. Stronger contrasts result in more compelling and thought-provoking writing.
- Stay Relevant to Context : Ensure that the use of antithesis and juxtaposition aligns with the broader context of your writing, including theme, tone, and purpose. Make sure they serve to enhance rather than distract from your overall message.
- Seek Natural Pairings : Look for natural pairings of contrasting elements that fit organically within your writing. Avoid forcing contrasts that feel forced or out of place.
- Revise and Refine : Take the time to revise your writing and refine your use of antithesis and juxtaposition. Review your sentences for clarity, effectiveness, and relevance, and make adjustments as needed.
- Seek Feedback : Consider seeking feedback from peers or mentors to evaluate your use of antithesis and juxtaposition. Fresh perspectives can help identify areas for improvement and enhance the impact of your writing.
By following these tips, you can effectively utilize antithesis and juxtaposition to elevate your writing and engage your readers more effectively.
Where to Use Antithesis and Juxtaposition
Antithesis and juxtaposition can be used in various forms of writing to enhance clarity, emphasis, and engagement. Here are some contexts where you can effectively utilize these techniques:
- Literary Works : Antithesis and juxtaposition are commonly found in literature, including novels, short stories, and poetry. They can be used to create vivid imagery, convey themes, and develop characters.
- Speeches and Rhetorical Writing : In speeches, debates, or persuasive essays, antithesis and juxtaposition can help emphasize key points, engage the audience, and strengthen arguments.
- Advertising and Marketing : Antithesis and juxtaposition are frequently used in advertising to contrast products, highlight benefits, and create memorable slogans or taglines.
- Visual Arts and Design : In visual arts, such as paintings, photographs, and graphic design, juxtaposition can be used to create striking contrasts and convey complex messages or emotions.
- Film and Media : Antithesis and juxtaposition are prevalent in film, television, and other media forms. They can be used to create dramatic tension, contrast characters or settings, and convey thematic contrasts.
- Academic Writing : In academic essays, antithesis and juxtaposition can help illustrate contrasts, compare theories, and analyze opposing viewpoints.
- Creative Writing : Whether it’s fiction, non-fiction, or personal narratives, antithesis and juxtaposition can add depth, complexity, and interest to creative writing pieces.
- Social Commentary and Journalism : Antithesis and juxtaposition can be employed in journalistic articles or opinion pieces to highlight societal contrasts, critique issues, and provoke thought.
You will like: Paradox vs Paradigm
Where Not to Use Antithesis and Juxtaposition
While antithesis and juxtaposition can be powerful literary devices, there are certain contexts where their use may not be appropriate or effective:
- Technical Writing : In technical or scientific writing where clarity and precision are paramount, the use of antithesis and juxtaposition may introduce unnecessary complexity or ambiguity.
- Formal Reports : In formal reports or business documents where a straightforward presentation of information is required, the use of stylistic devices like antithesis and juxtaposition may detract from the professionalism and clarity of the content.
- Casual Communication : In casual communication such as emails, text messages, or informal memos, the use of antithesis and juxtaposition may come across as overly formal or pretentious.
- Sensitive Topics : When discussing sensitive or serious topics such as tragedy, trauma, or grief, the use of antithesis and juxtaposition may appear insensitive or inappropriate.
- Historical or Factual Accounts : In historical or factual accounts where accuracy and objectivity are essential, the use of stylistic devices like antithesis and juxtaposition may be seen as editorializing or biasing the narrative.
- Technical Descriptions : In technical descriptions or instructions where clarity and precision are crucial, the use of antithesis and juxtaposition may confuse or distract readers from understanding essential information.
- Legal Writing : In legal documents or contracts where precision and clarity of language are critical, the use of stylistic devices like antithesis and juxtaposition may introduce ambiguity or interpretation issues.
- Medical or Scientific Papers : In medical or scientific papers where conveying complex information accurately is paramount, the use of antithesis and juxtaposition may detract from the clarity and precision required in conveying technical concepts.
A Final look at Antithesis vs Juxtaposition
In wrapping up, let’s take one last look at antithesis vs juxtaposition. These are both handy tools for writers. Antithesis makes things stand out by putting opposites close together, while juxtaposition shows differences by putting them side by side. Learning when to use them can really make your writing pop, adding depth and interest. So, remember, mastering these techniques can help make your writing more engaging and memorable.
Dictionary.com (ANTITHESIS Definition & Usage Examples) , Wikipedia (Antithesis) , Merriam-Webster (Juxtaposition Definition & Meaning) , Grammarly (What is Juxtaposition? Definition and Examples) and Wikipedia (juxtaposition – Wiktionary, the free dictionary) .

Related Posts

Metonymy vs Synecdoche: What’s the Difference?

Motif vs Theme: Clarifying the Confusion

Metaphor vs Idiom: What’s the Difference?

Metaphor vs Analogy: What’s the Difference?

Analogy vs Simile: Don’t Be Confused by These Comparisons
Repetition vs Parallelism: What’s the Difference?
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
What are you looking for?
Quick links.
Click here to find all our contact information
What is antithesis? A guide with examples
Find out how to use antithesis to improve your writing and see examples of antithesis being used in literature, poetry and advertising.

Introduction
This blog post is part of the Semantix copywriters’ toolkit, which is a great resource for writing professionals and all those looking to improve their writing, including language and marketing students. Firstly, we’ll discuss the definition of antithesis, including how it differs from similar rhetorical devices . Then, we’ll look at how other writers have used antithesis to set contrast and add impact to their work, including some famous examples of antithesis in literature, poetry and marketing.
What is antithesis?
The word antithesis is sometimes used to mean ‘opposite’. For example, “She is slim and sporty – the very antithesis of her brother”. However, ‘antithesis’ (or ‘antitheses’ if plural) is also the name given to a particular rhetorical or literary device. In this blog post, we’ll be looking at ‘antithesis’ in its role as the rhetorical and literary device.
The word ‘antithesis’ comes from the Greek for ‘setting opposite’. It means to express a concept by creating contrast. This can be done in different ways according to different definitions: either using only the content of the expression, or the content and the grammatical structure. Using the content can be as simple as using words with opposite meanings in close proximity to each other, or more complex by describing concepts that contrast with one another. This draws the reader’s attention to the differences between the two things.
Antithesis often presents opposing ideas and presents those ideas in a parallel grammatical structure. This is unlike general parallelism, which presents a balance of elements in a structure (sentence, clause or other) without necessarily involving the content. Antithesis is usually created in two parts, but can also be formed by three or more opposing clauses.
Writers can use antithesis to communicate a concept that is best expressed through opposites. It’s a simple yet effective way to really drive a point home. As with other literary devices , the rules aren’t set in stone, it’s more about using the device in ways that create impact and bring the words to life.
Examples of antithesis in literature
What makes a good piece of writing truly great? You might argue that the key ingredients include memorability, impact and the beauty of a rhythmical grammatical structure – deliverables that can be served skillfully with antitheses.
When you put two antithetical concepts together in a short phrase, you get drama. And drama is what keeps the reader turning the pages.
In addition, the parallel structure often used in antithesis makes the words stand out from the other text on a page. Working like a mental stop sign, it compels the reader to notice the contrasting ideas and consider the meaning of that contrast.
Using antithesis, writers can present contradictions by balancing opposing words and statements. This builds contrasting images in a reader’s mind and creates a powerful impression of either a character or circumstance.
A good portion of the best-known writers in history have been masters of antithesis. For example, antithesis plays a big part in the language used by William Shakespeare. In fact, nearly every character he created uses it. For example, in Mac beth the witches chant, “Fair is foul, and foul is fair” – a simple but dramatic antithesis. One of the best-known Shakespearean quotes of all time is an antithesis from the play Hamlet , when the prince says, “To be, or not to be...”. In just six words Shakespeare creates a perfect contrast between existing and not existing, inviting the audience to ponder the meaning of life itself.
Another famous use of antithesis is the expression, “To err is human; to forgive, divine”, which was written in 1711 by English poet Alexander Pope in ‘ An Essay on Criticism, Part II ’. After the original creation of the statement, further iterations have added the word ‘is’ so, “To err is human; to forgive is divine”, which, arguably, improves the rhythm by creating an equal number of words in each part of the sentence.
And it’s not just the writers of old who wield the sword of antithesis so well: their modern counterparts are equally aware of its power. For example, the Green Lantern comic writers use antithesis at the start of Green Lantern’s oath in order to emphasise his mission to defeat evil at all costs:
In brightest day , in blackest night , No evil shall escape my sight. Let those who worship evil’s might Beware my power – Green Lantern’s light!
Antithesis in poetry.
Poetry is perhaps the writing genre where we find the most graceful use of words. That’s why there are lots of antitheses used in poetry throughout history.
Take a look at the two-part structures and conceptual contrasts from some of the world’s best-known poems:
"Better to reign in Hell , then serve in Heav’n" – Paradise Lost , John Milton, 1667
“much madness is divinest sense ” – 620, emily dickinson, “some say the world will end in fire / some say in ice ” – fire and ice, robert frost, 1920.
Occasionally, a writer might even make use of a triple antithesis:
“Herein lives wisdom, beauty , and increase ; / Without this, folly, age , and cold decay ” – Sonnet 11, William Shakespeare, 1609
Antithesis in speeches.
Of course, what works on paper often works in its spoken form too. Some of the best speeches of all time can thank, at least in part, antithesis for their success.
“That’s one small step for a man – one giant leap for mankind” – Neil Armstrong, 1969
“we must learn to live together as brothers or perish together as fools ” – martin luther king jr, 1964, “on this day, we gather because we have chosen hope over fear, unity of purpose over conflict and discord ” – barack obama, 2009, antithesis in advertising.
Marketers love to make us remember how truly wonderful their services or products are. Antithesis provides marketers with a powerful tool: contrast to underline a unique selling proposition (USP) and a memorable rhythm. That’s why you’ll find the path to marketing gold is littered with antitheses: the antithesis is the life-blood of the tagline or slogan.
Take a look at how each of these taglines uses a parallel structure and creates opposition:
“ Small business. Big future” – Santander
“ heavy on features. light on price” – apple, “ tough on stains. gentle on skin” – persil, “ less calories; more taste” – so good, “inspired by yesterday , built for tomorrow ” – nokia, “ all of the taste. none of the sugars” – alpro, “ smart listens to the head. stupid listens to the heart” – diesel, antithesis, chiasmus and parallelism – what are the differences.
Parallelism, sometimes called parallel structure or parallel construction, is the repetition of grammatical structures in a piece of writing in order to create a balanced, harmonious effect.
Parallelism requires only the repeated grammatical structure, while antithesis uses the content – you can’t set up opposing concepts by only using the structure!
Look at this example, “They have plundered our seas, ravaged our coasts, burnt our towns – all while caring for their own oceans and cities.” The beginning of this statement repeats the same structure while changing the verbs and nouns. It doesn’t create a contrast between each clause or suggest any form of opposition. That’s the key difference between other forms of parallelism and antithesis: parallelism doesn’t need to present opposites, but antithesis is all about the opposites.
If a similar phrase was written using antitheses, it might read something like this. “They have plundered our seas; but have nurtured their seas. They ravaged our coasts; they cared for their own. They burnt our towns while they built their cities.” In the ‘antithesis version’, each clause is juxtaposed with another concept to create impact. You can hear how much more powerful the second phrase is if you read both versions out loud.
While antithesis is parallelism, not all parallelism is antithesis! For example, chiasmus is also a form of parallelism. In fact, it’s sometimes described as an inverted parallelism and happens when word order or grammatical structure is reversed in two phrases. For example, the phrase, “Do I love you because you are beautiful? Or are you beautiful because I love you?” qualifies as a parallelism and a chiasmus but there’s no opposition so it’s not an antithesis.
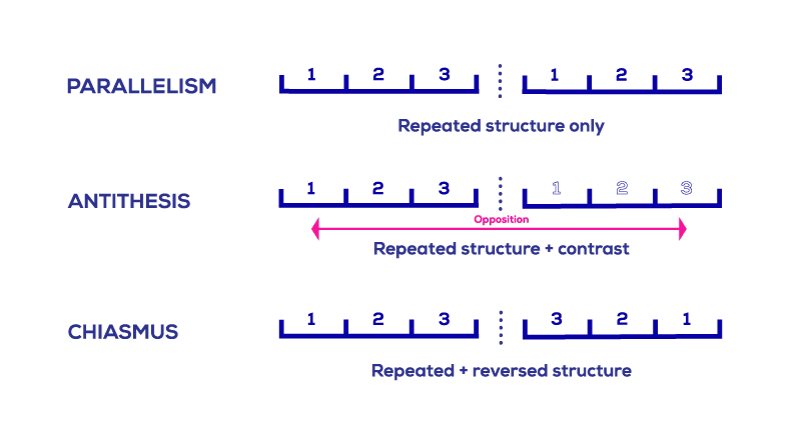
Semantix’s copywriting toolkit
Our copywriting toolkit is a valuable resource for anyone aiming to improve their writing skills. It contains definitions and examples of rhetorical devices in action, with guidelines on how and why they are used.
Using rhetorical devices, such as antitheses, is a time-proven method of taking your writing to another level and making sure that your words are impactful, memorable and effective. Whether you’re writing for pleasure or writing for business, they create drama and keep your readers or listeners engaged.
Semantix’s copywriting services
As the leading language solution provider in the Nordics, language is our passion. Every day, we help our clients reach new target audiences and enter new global marketplaces. We believe that language should be used as an opportunity to boost business and never be seen as a barrier.
Our copywriting services are available in more than 200 languages, and we only work with native-speaking translators . By matching you with a multilingual copywriter with experience in your specific industry, we’ll help you make every word work hard for your business in every language.
Want to find out more about our multilingual copywriting services?
Further reading.
- A Handlist Of Rhetorical Terms – Richard Lanham, University of California Press, 2013
- Simplified Glossary Of Literary Terms/Devices: An Easy-To-Use Source Of Definitions, Examples And Exercises For Students And Teachers – Victor Igiri, 2022
- The Oxford Dictionary Of Literary Terms (Oxford Quick Reference) 4th Edition – Chris Baldick, OUP Oxford, 2015
- The Elements Of Eloquence – Mark Forsyth, Icon Books, 2013
- The Elements Of Rhetoric – Ryan N S Topping, Angelico Press, 2016
- The Penguin Dictionary Of Literary Terms And Literary Theory – J A Cuddon, Penguin, 2014
- The Rhetorical Device: Literary Resources For The Writer Vol. 1 of 2 – Paul F Kisak, CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform, 2016
- Writing With Clarity And Style: A Guide To Rhetorical Devices For Contemporary Writers – Robert A Harris, Routledge, 2017
- The Use Of Rhetorical Devices In Selected Speeches by Clinton & Trump: Discourse From The Electoral Campaign 2016 – Larissa Wolf, AV Akademikerverlag, 2018
- American rhetoric (online) Antithesis blog post
- Studiobinder (online) ‘What is antithesis’ blog post
- The Oxford Dictionary O f Literary Terms (Oxford Quick Reference) 4th Edition – Chris Baldick, OUP Oxford, 2015
- Voltaire, The Project Gutenberg EBook Of A Philosophical Dictionary, Volume 4 (of 10).
- Toastmasters (online) ‘The Crafting of Eloquence’ blog post .
Related content

A guide to the literary device anaphora – for professional wordsmiths

Literary devices list: examples of literary devices and how to use them
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Definition of antithesis
Did you know.
Writers and speechmakers use the traditional pattern known as antithesis for its resounding effect; John Kennedy's famous "ask not what your country can do for you—ask what you can do for your country" is an example. But antithesis normally means simply "opposite". Thus, war is the antithesis of peace, wealth is the antithesis of poverty, and love is the antithesis of hate. Holding two antithetical ideas in one's head at the same time—for example, that you're the sole master of your fate but also the helpless victim of your terrible upbringing—is so common as to be almost normal.
Examples of antithesis in a Sentence
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'antithesis.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
Late Latin, from Greek, literally, opposition, from antitithenai to oppose, from anti- + tithenai to set — more at do
1529, in the meaning defined at sense 1b(1)
Dictionary Entries Near antithesis
anti-theoretical
Cite this Entry
“Antithesis.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/antithesis. Accessed 30 Aug. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of antithesis, more from merriam-webster on antithesis.
Nglish: Translation of antithesis for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of antithesis for Arabic Speakers
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about antithesis
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day, mise-en-scène.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
Plural and possessive names: a guide, 31 useful rhetorical devices, more commonly misspelled words, why does english have so many silent letters, your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, popular in wordplay, 8 words for lesser-known musical instruments, it's a scorcher words for the summer heat, 7 shakespearean insults to make life more interesting, birds say the darndest things, 10 words from taylor swift songs (merriam's version), games & quizzes.

- English Grammar
- Figures Of Speech
Antithesis: Meaning, Definition and Examples
Figures of speech , otherwise known as rhetorical devices, are used in the English language to beautify and make your language look and sound a lot more effective rather than a literal presentation of information. Each figure of speech has its function and is meant to perform its roles giving the context a unique effect. In this article, you will learn about one such figure of speech called antithesis. Read through the article to learn more about what antithesis is, its definition and how it differs from an oxymoron. You can also check out the examples and analyse how it is written for an in-depth understanding of the same.
Table of Contents
What is antithesis – meaning and definition, what differentiates an antithesis from an oxymoron, some common examples of antithesis, frequently asked questions on antithesis.
An antithesis is a figure of speech that states strongly contrasting ideas placed in juxtaposition. They contain compound sentences with the two independent clauses separated by a comma or a semicolon , in most cases. However, there are also instances where the antithesis is a compound sentence with a conjunction . An antithesis is mainly used to portray the stark difference between the two opposing ideas.
Antithesis, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a contrast between two things”, and according to the Cambridge Dictionary, “a difference or opposition between two things”. The Merriam-Webster Dictionary gives a more explanatory definition. According to it, antithesis is “the rhetorical contrast of ideas by means of parallel arrangements of words, clauses, or sentences”.
Knowing the difference between an antithesis and an oxymoron will help you comprehend and use both the rhetorical devices effectively. Take a look at the table given below to learn more.
|
|
|
| in juxtaposition. | to produce an effect. |
Here are some of the most common examples of antithesis for your reference.
- Hope for the best; prepare for the worst.
- Keep your mouth closed and your eyes open.
- “It was the best of times, it was the worst of times. It was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness.” – Charles Dickens
- “That’s one small step for a man, one giant leap for mankind.” – Neil Armstrong
- “Better to reign in Hell, than to serve in Heaven.” – John Milton
- Speech is silver, but silence is gold.
- “Give every man thy ear, but few thy voice.” – William Shakespeare
- Keep your friends close; keep your enemies closer.
- “To err is human; to forgive divine.” – Alexander Pope
- Money is the root of all evil: poverty is the fruit of all goodness.
What is antithesis?
An antithesis is a figure of speech that states strongly contrasting ideas placed in juxtaposition. They contain compound sentences with the two independent clauses separated by a comma or a semicolon, in most cases. However, there are also instances where the antithesis is a compound sentence with a conjunction.
What is the definition of antithesis?
What is the difference between antithesis and oxymoron.
The main difference between an antithesis and an oxymoron is that antithesis refers to the use of two contrasting ideas or thoughts conveyed in two independent clauses placed in juxtaposition, separated by a comma, a semicolon or a conjunction; whereas, the term ‘oxymoron’ refers to the use of two opposite words within a phrase to create an effect.
Give some examples of antithesis.
Here are a few examples of antithesis for your reference.
- “Love is an ideal thing, marriage a real thing.” – Goethe
- “Folks who have no vices have very few virtues.” – Abraham Lincoln
- “Man proposes, God disposes.”
- Beggars can’t be choosers.
- Be slow in choosing, but slower in changing.
| ENGLISH Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
How to Use Antithesis in Your Writing (With Examples)

Antithesis is a rhetorical device that's often misunderstood, even by writing professionals. It may be tempting to avoid using it in your writing, but there are many reasons why you should give it another look, including the following 10 reasons to use antithesis figures of speech in your writing.
Antithesis: Why You Should Use It In Your Writing
Antithesis creates a clear contrast.
An antithesis figure of speech creates a clear contrast between two opposite ideas. The important thing to keep in mind is that both ideas need to be logically connected and make sense together.
One of the most common examples of an antithesis is the juxtaposition between life and death, where one would represent the world as we know it, while the other represents what follows it. Another example is that of light and darkness; they are both contrasting concepts, but they still connect in some way because they are opposites.
Antithesis highlights contradictions
Antithesis is the use of words that are opposite or contrasting in meaning. For example, to be or not to be. Antithesis is used in writing to create a dramatic effect.
Contrary to what you might think, an antithetical statement can enhance a passage instead of detracting from it. It helps to show two sides of an argument and bring balance to your writing.
Effective use of antithesis figures of speech will also bring out the nuances in your subject matter and make it easier for readers to understand your point. The classic example of this technique is found in Hamlet’s famous line to be or not to be; this juxtaposition highlights how we all have a choice about life and death.
Antithesis adds rhythm to your writing
When you're writing, it's easy to fall into a rhythm of saying the same thing over and over again. But by adding antithesis in your writing, you can add rhythm that'll make your text more interesting. Antithesis is when you say the opposite of what you just said, or contrast one idea with another.
An example of an antithesis figure of speech would be I'm not hungrily followed by I'm starving. The two sentences are contrasting ideas which will likely keep your reader engaged because they don't know what to expect next.
Here are some other antithesis figure of speech examples in common phrases: all work and no play makes Jack a dull boy, the exception proves the rule, don't shoot the messenger. The use of antithesis has several benefits to your writing including keeping readers interested and reinforcing the meaning behind certain phrases. Adding this type of contrast in your writing can be very beneficial for making a point clear.
Antithesis makes your writing more memorable
It has been proven time and time again that people are more likely to remember something if it's in a form that contrasts with what they've already heard. You can use antithesis in your writing by presenting two opposing ideas or concepts and letting the reader decide which one they believe is right.
Consider these two sentences of antithesis figure of speech examples : We should have left hours ago and It's too late to leave now. The first sentence tells readers that they should have left long ago, while the second sentence tells them there is no point in leaving since it's too late. Antithesis can be used for all sorts of things, from metaphors to titles.
Antithesis can help you make a persuasive argument
An antithesis is a sentence, phrase, or word that contrasts with the previous one. For example, He was strong and brave versus He was weak. Antitheses are a great way to add power to your argument by making it more persuasive.
One common use of an antithesis is in the famous quote from John F Kennedy's inaugural address: Ask not what your country can do for you; ask what you can do for your country. The first part of this statement is a request for help, while the second part has a much more powerful tone of asking people to contribute their talents.
When we hear these words, we know that JFK wants us to get up off our couches and participate in life - whether as a citizen or volunteers. What better way to make an impact than through your writing?
A good rule of thumb is never to have two statements the same, which means finding some way of contrasting them (e.g., no quotes should be used twice). However, don't worry if this seems like too much work - just reading over what you've written will probably be enough to come up with some opposites.
Antithesis can be used to create a dramatic effect
An antithesis is a sentence, phrase, or clause that contrasts with another. One of the most common types of antitheses is those that compare two different things.
For antithesis figure of speech examples , some people who are too proud to say they're sorry could be compared to some people who are humble enough to say they're sorry. Antitheses can also be used as a way to show contrast like he was quick and agile as opposed to he was slow and clumsy. By using an antithesis in your writing you can create a dramatic effect, show contrast, or even make an argument.
Antithesis can help you clarify your ideas
When you use antithesis, you are creating an inherent contradiction that adds a certain level of complexity to your writing. This can be done by placing two words, phrases, or clauses next to one another that are opposites.
One antithesis figure of speech example of this is the phrase out with the old and in with the new. Antitheses can also be created by contrasting ideas, colors, nouns, pronouns, or verbs. The effect can help you clarify your thoughts and make your writing more interesting for readers. Examples include Jane walking down the street and Joe running down the street; blue is cold while red is warm; we want them to do it while they don't want us to tell them what to do.
Take these five sentences, I'm not angry anymore, said John after drinking some tea. I'm very calm, he added when he noticed her worried expression. That's good, she responded as she reached over and patted his hand. These sentences would read better if they were paired with their antithesis: I'm not angry anymore, said John after drinking some tea. I'm very mad! he added when he noticed her worried expression. That's bad, she responded as she reached over and slapped his hand.
Antithesis can make your writing more concise
An antithesis is a figure of speech that is used to create balance or contrast between two opposing ideas. The two opposite ideas are set next to each other to show their differences and similarities.
Antitheses can make your writing more concise by adding a second idea that clarifies the original one. They can also be used to build up the suspense because they make the reader want to know what the contrasting idea is.
Antitheses are most often used in dialogue and prose, but they can be used in poetry as well. One thing to keep in mind when using an antithesis is not to use it too often. As with any technique, overusing it will take away from its power and effectiveness.
A good antithesis figure of speech example of an effective use of an antithesis comes from Anne Frank's diary: How on earth have people come so far, yet learned so little?
Antithesis can add emphasis
Antithesis is a rhetorical technique in which two words, phrases, clauses, or sentences contrast in meaning. This is done to add emphasis to the point that is being made. For example, The world is round can be contrasted with The world is flat.
When using an antithesis in your writing you can bring out the point you're trying to make and give it more weight by contrasting it with another idea. Using antithesis can help add emphasis because when you use one word or phrase and then it's the opposite, this sets up a clear relationship between these two concepts.
Using antithesis can make your writing more interesting
One of the best ways to make your writing more interesting is to use antithesis. Antitheses are opposites that are put together in a sentence. They can be used as a rhetorical device or for emphasis. There are many types of antitheses, but we will focus on the most common one, which is called verbal antithesis.
Verbal antitheses can be defined as words and phrases placed in pairs to contrast their meanings and create an effect of balance and harmony between them. A famous example of this is from Shakespeare's Romeo and Juliet where he has these lines: What light through yonder window breaks?
Antithesis in Your Writing: Ways to Make Your Words Work Harder for You
Antithesis is the best tool you can use to make your writing work harder and get noticed. What exactly is antithesis? Here’s an example: Many people are afraid of heights, but I would love to stand on top of Mount Everest just so I could have bragging rights. In the above sentence, it’s clear that mountain top and bragging rights are opposites, so both are used as examples of antithesis in writing (the first one uses spatial opposites, and the second one uses verbal opposites). But what about this sentence?
1) Start with a strong thesis
Since you are reading this sentence, I'm going to assume that you have a basic understanding of what an antithesis is. Now let's break down the definition and explore some ways that we can use it as a rhetorical device.
Antitheses are used when two opposite ideas or statements are presented together, typically to make a point or strengthen an argument. When we use antithesis, the two contrasting parts of our sentence are balanced against each other, which is why it is often referred to as the figure of balance.
The word antithesis comes from the Greek language meaning opposite and has been used by many well-known writers throughout history including Shakespeare and Aristotle.
2) Introduce your topic
Antithesis is the juxtaposition of two contrasting or opposing words, phrases, clauses, or sentences within a sentence or phrase. Some examples of antithetical pairs include peace and war, strong and weak, and life and death. The use of this rhetorical device emphasizes one side of the pair while diminishing the other.
Antithesis is often used as a literary device in poetry, prose, and other forms of writing. It can also be used to emphasize an idea, which can lead to varying interpretations of the meaning. For example, consider these two sentences:
- No matter how hard you work, you'll never be good enough.
- However hard you work, you will never be good enough!
3) Introduce your antithesis
An antithesis is a figure of speech that juxtaposes two ideas or concepts. When it's done well, it can make your writing more powerful by adding an element of contrast, irony, or surprise. This post will provide you with examples of what an antithesis looks like and how you can implement it into your writing. Let's get started!
First, let's look at the following sentence: I love working at this job. It sounds great on its face. However, consider the following sentence where the same idea is given as an antithesis: I hate working at this job. Now it's a little less pleasant and could use some context as to why this person feels so strongly about their current job.
What if I told you that they had been harassed? What if they work long hours for very low pay? That would give you additional information about why someone might hate their current job but still want to do it out of necessity.
4) Develop your ideas
The word antithesis comes from the Greek words anti, meaning against or opposite of, and thesis, meaning position, proposition, or opinion.
Antithesis means a juxtaposition of two opposing thoughts. It's a rhetorical device that uses contrast to create emphasis. Antithesis is like a yin-yang symbol, with each side balancing out the other side.
Antithesis can be used as either a synonym or antonym. For example, if you want to emphasize one quality over another, you might use antithesis by pairing it with its opposite; such as dark and light. This type of antithetical contrast is called chiastic antithesis.
5) Use concrete examples
- Create a stark contrast
- Create emphasis
- Clarify thoughts
- Show the duality of a situation
- Increase dramatic tension
- Emphasize an idea or emotion by juxtaposing it with its opposite
6) Be clear and concise
An antithesis is a contrasting idea that creates a balance within a sentence. It can be used effectively when there are two opposing ideas, but the contrasting idea is not simply the opposite of the original idea. Antitheses can also be used as one of many other rhetorical devices, such as anaphora or personification. Here are some examples of antithesis at work:
The father was generous with his time and money. The father was stingy with his time and money. She loved her job. She hated her job. They were sitting on their hands. They were dancing their fingers off. Here's what I have found, he said, shoving all of his papers in front of me. Take your pick! There's something for every type of student here!
My hand shoots out instinctively, grabbing my assignment from him. He offers no resistance, though it must be clear from my expression that I don't want this paper. There is nothing on it but meaningless scribbles. No instructions, no questions, and nothing at all to help me understand what it is supposed to do for me.
I glance up through narrowed eyes and see him watching me carefully—as if waiting for something—but I am too angry now to figure out what it might be. So I drop the assignment back onto the table and stalk away without another word.
7) Use simple language
What is Antithesis? The definition of Antithesis is the direct opposite or contrast. What does this mean? This means that you are using two different ideas, words, phrases, etc. together to create a more powerful meaning.
How do you use Antithesis? Here are some examples of Antithesis that you can use in your writing. In these sentences, we have put an example sentence with antithesis first and then followed it with another sentence without antithesis. He was alone but not lonely. He was lonely but not alone. He felt hopeless yet confident. He felt confident yet hopeless.
8 )Avoid clichés
A cliché is a phrase that is so overused and tired that it has lost its meaning. Here are some examples of clichés and how you can avoid them: Just do it. Instead say, Don't just sit around waiting. - You're never too old to learn. Instead say, Age is just a number. - He's a diamond in the rough. Say, I see potential here. Or He has a lot of untapped talent. Think about using contrast: Contrast means comparing two things or ideas side-by-side to emphasize their differences. If someone is poor, for example, then he might be very rich somewhere else. If he loves his job one day but hates it the next day, the contrast will highlight the changes in his emotions. Example sentences:
- Poverty exists in every corner of our country.
- It's hard when you're rich one day but poor another day.
9) Edit and proofread your work
There are many ways you can use antithesis to spice up your writing. The most common is contrasting two different words or phrases, but there are also plenty of other ways that you can use this literary device. Below, you'll find a list of a few examples and some tips on how to use them.
Contrasting two words or phrases using opposites, such as up-down or black-white. This is probably the most common way people use antithetical language and it's easy to see why; the contrast makes readers pause and thinks about what was said before continuing with the sentence. A quick example would be The green trees swaying in the wind.
One could quickly assume that this is because they're blowing in the wind, but if we add a little more information by saying The green trees swayed gently back and forth, then we know that they're not just swaying due to strong winds.
A good rule of thumb when choosing which words or phrases to use when doing this type of comparison is to pick ones that have opposite meanings from each other. If you want to say something like I love cake while still contrasting two things, then say I love cake more than I love bread. It doesn't always need to be an opposing word though;
10) Follow the rules of grammar
An antithesis is a rhetorical device that presents two contrasting ideas, usually through the use of parallelism. It has been used extensively throughout literary history and can be found in many different forms of writing. Antitheses are typically introduced with a coordinating conjunction such as but, yet, or however. They also often contain one or more correlating conjunctions such as although or nevertheless.
In this sentence, the antithesis is introduced with the conjunctions but and yet: Yet we should not forget his contributions.
In this sentence, the antithesis is introduced with the conjunctions however and nevertheless: However difficult it may seem, you will have to carry on.
Antithesis means the placing of contrasting ideas together, especially as a rhetorical device. If you're not quite sure what it means or how to use it, don't worry! That's what this article is for! By the time you're finished reading, you'll know all about antithesis in your writing and have even learned some cool ways to incorporate it into your style.
SoME develop and delivers impactful transformative Communication programs for the 21st-century post-pandemic workplace. We strongly believe effective, assertive, and empathetic Communication skills will enable our learners to present themselves confidently, manage conflicts betters, collaborate capably, and become tomorrow's competent professionals and leaders.
We offer a range of programs that include: Inbound Sales Training; Email Marketing for Beginners; Persuasive Communication Techniques for Managers; Presentation Skills for IT Professionals; Social Media Strategies for Small Businesses; Public Speaking for Introverts etc.
Our mission is simple—we want to make a difference in people's lives by helping them develop communication skills that will help them be more successful both personally and professionally.
How do you use antithesis in writing?
Incorporating antithesis into your writing will make it more powerful. Antithesis is the act of juxtaposing two opposite or contrasting words, phrases, clauses, or sentences within a sentence. This technique creates emphasis on the meaning and can be used to show irony or emphasize a point.
What are antithesis and its examples?
When you're writing, it's important to use antithesis or the act of putting two opposing ideas together.
This can be done through contrast in words, phrases, clauses, and sentences. It can also be done through an oppositional sentence structure. Here are some examples of antithesis that make your writing more powerful and engaging!
What is an antithesis in writing?
An antithesis is a sentence that contrasts an idea with its opposite. It's usually used as the second half of a sentence. When you use antitheses, you can make your words work harder and make your writing more interesting. Here are some examples of how you might use an antithesis in your writing:
- I've never been more lost than when I found myself on the road less traveled.
- A man who was once very wise now lives as if he knows nothing at all.
Recent Blogs

What is Social Learning Theory? How to Adopt It in The Workplace
Explore the transformative power of social learning theory in the OB. If you're curious about what social learning theory is and how it can revolutionize your workplace,...

Why Are Employees Your Greatest Asset and How to Mentor Them
In the dynamic landscape of modern businesses, employees are the most valuable asset of any organisation. Their skills, knowledge, creativity, and dedication fuel an organisation's...

Dealing with difficult employees: An employer's guide
In any workplace, you're likely to encounter a variety of personalities and work styles. While most employees are cooperative and contribute positively to the team, there may be in...

How to stop being self-conscious: Strategies to feel more confident
In a world where self-confidence reigns supreme, it's all too easy to feel self-conscious. But what does it really mean to be self-conscious?And why does it have such a profound im...

How to prepare your team to handle negotiations?
In the dynamic business world, the ability to negotiate effectively and deliver persuasive pitches can be the key differentiator between triumph and failure. Whether you're seeking...

Effective Communication skills can improve your self-confidence and boost career growth
In today's fast-paced and competitive professional world, self-confidence is a valuable asset that can significantly impact your career growth and success. Whether you're seeking a...

Difference between KRA and KPI
In the realm of performance management and goal setting, the terms KRA (Key Result Area) and KPI (Key Performance Indicator) are frequently used, but they serve distinct purposes i...

What is the difference between a boss and a leader?
In the world of management and leadership, the terms "boss" and "leader" are often used interchangeably. However, they represent distinct approaches to managing and inspiring a tea...

How to interview for a job when you have no work experience?
Landing your first job can be both exciting and nerve-wracking, especially when you lack work experience. However, with the right approach and preparation, you can ace your job int...

9 steps for improving collaboration between teams
In today's rapidly evolving workplace, effective team collaboration is more critical than ever. Whether you're in a traditional office, a remote team, or a hybrid work environment,...

How being intentional can advance your career?
In a world filled with constant distractions and fast-paced living, the concept of being intentional stands out as a beacon of purpose and direction. But what does it mean to...

How to improve your problem solving skills?
Problem solving is a critical skill that permeates various aspects of life, from personal challenges to professional endeavors. The ability to tackle issues, make decisions, and fi...

Complete Guide to Debating: Improve your Debating Skills
In the world of communication and persuasion, mastering the art of debate is a skill that can truly set you apart. Whether you're a student, a professional, or simply someone who w...

Experimentation brings innovation: An experimental workplace
Experimentation is the lifeblood of innovation, breathing new life into stagnant routines and sparking transformative ideas. Organisations that embrace a culture of experimentation...

How to Build a Healthy Workplace Environment?
In today's highly competitive work landscape, the importance of cultivating a healthy workplace environment cannot be overstated. A positive work environment not only contributes t...

How Would You Define Success?
Success, a word that carries different meanings for different individuals, is a universal aspiration.The concept of what is success in life has captivated minds for centuries, fuel...

Why is Networking Important
The importance of networking has never been more evident. Whether you're a seasoned professional or just starting out, building and nurturing a strong professional network can be t...

Guide to Choosing a Successful Speech Topic
Effective communication skills have become more crucial in today's rapidly changing world. Whether you're a student, a professional, or someone simply looking to enhance your publi...

The Importance of Storytelling in Business, with Examples
In the dynamic world of business, where information is abundant, and attention spans are fleeting, storytelling has emerged as a powerful tool that captivates audiences and leaves...

10 Best Practices for Giving a Remote Presentation
After COVID, with more companies embracing the WFH hybrid model of working, virtual presentations have become a fundamental part of professional communication. Whether you're an ex...
Your success. Powered by the Six Cs.
Knowledge centre.
Copyright © School Of Meaningful Experiences private limited, Privacy Policy, Cookie Policy and Terms of Use | Sitemap
Chat with us now
Your account has been created.
Join our team
Interact with our admission team, download brochure, no result found.
OTP has been sent, Please check your E-mail
Resend OTP in:
Verify Your Details

- Scholarly Community Encyclopedia
- Log in/Sign up

| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | handwiki | -- | 1044 | 2022-10-31 01:38:44 |
Video Upload Options
- MDPI and ACS Style
- Chicago Style
In philosophy, the triad of thesis, antithesis, synthesis (German: These, Antithese, Synthese; originally: Thesis, Antithesis, Synthesis) is a progression of three ideas or propositions. The first idea, the thesis, is a formal statement illustrating a point; it is followed by the second idea, the antithesis, that contradicts or negates the first; and lastly, the third idea, the synthesis, resolves the conflict between the thesis and antithesis. It is often used to explain the dialectical method of German philosopher Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel, but Hegel never used the terms himself; instead his triad was concrete, abstract, absolute. The thesis, antithesis, synthesis triad actually originated with Johann Fichte.
1. History of the Idea
Thomas McFarland (2002), in his Prolegomena to Coleridge's Opus Maximum , [ 1 ] identifies Immanuel Kant's Critique of Pure Reason (1781) as the genesis of the thesis/antithesis dyad. Kant concretises his ideas into:
- Thesis: "The world has a beginning in time, and is limited with regard to space."
- Antithesis: "The world has no beginning and no limits in space, but is infinite, in respect to both time and space."
Inasmuch as conjectures like these can be said to be resolvable, Fichte's Grundlage der gesamten Wissenschaftslehre ( Foundations of the Science of Knowledge , 1794) resolved Kant's dyad by synthesis, posing the question thus: [ 1 ]
- No synthesis is possible without a preceding antithesis. As little as antithesis without synthesis, or synthesis without antithesis, is possible; just as little possible are both without thesis.
Fichte employed the triadic idea "thesis–antithesis–synthesis" as a formula for the explanation of change. [ 2 ] Fichte was the first to use the trilogy of words together, [ 3 ] in his Grundriss des Eigentümlichen der Wissenschaftslehre, in Rücksicht auf das theoretische Vermögen (1795, Outline of the Distinctive Character of the Wissenschaftslehre with respect to the Theoretical Faculty ): "Die jetzt aufgezeigte Handlung ist thetisch, antithetisch und synthetisch zugleich." ["The action here described is simultaneously thetic, antithetic, and synthetic." [ 4 ] ]
Still according to McFarland, Schelling then, in his Vom Ich als Prinzip der Philosophie (1795), arranged the terms schematically in pyramidal form.
According to Walter Kaufmann (1966), although the triad is often thought to form part of an analysis of historical and philosophical progress called the Hegelian dialectic, the assumption is erroneous: [ 5 ]
Whoever looks for the stereotype of the allegedly Hegelian dialectic in Hegel's Phenomenology will not find it. What one does find on looking at the table of contents is a very decided preference for triadic arrangements. ... But these many triads are not presented or deduced by Hegel as so many theses, antitheses, and syntheses. It is not by means of any dialectic of that sort that his thought moves up the ladder to absolute knowledge.
Gustav E. Mueller (1958) concurs that Hegel was not a proponent of thesis, antithesis, and synthesis, and clarifies what the concept of dialectic might have meant in Hegel's thought. [ 6 ]
"Dialectic" does not for Hegel mean "thesis, antithesis, and synthesis." Dialectic means that any "ism" – which has a polar opposite, or is a special viewpoint leaving "the rest" to itself – must be criticized by the logic of philosophical thought, whose problem is reality as such, the "World-itself".
According to Mueller, the attribution of this tripartite dialectic to Hegel is the result of "inept reading" and simplistic translations which do not take into account the genesis of Hegel's terms:
Hegel's greatness is as indisputable as his obscurity. The matter is due to his peculiar terminology and style; they are undoubtedly involved and complicated, and seem excessively abstract. These linguistic troubles, in turn, have given rise to legends which are like perverse and magic spectacles – once you wear them, the text simply vanishes. Theodor Haering's monumental and standard work has for the first time cleared up the linguistic problem. By carefully analyzing every sentence from his early writings, which were published only in this century, he has shown how Hegel's terminology evolved – though it was complete when he began to publish. Hegel's contemporaries were immediately baffled, because what was clear to him was not clear to his readers, who were not initiated into the genesis of his terms. An example of how a legend can grow on inept reading is this: Translate "Begriff" by "concept," "Vernunft" by "reason" and "Wissenschaft" by "science" – and they are all good dictionary translations – and you have transformed the great critic of rationalism and irrationalism into a ridiculous champion of an absurd pan-logistic rationalism and scientism. The most vexing and devastating Hegel legend is that everything is thought in "thesis, antithesis, and synthesis." [ 7 ]
Karl Marx (1818–1883) and Friedrich Engels (1820–1895) adopted and extended the triad, especially in Marx's The Poverty of Philosophy (1847). Here, in Chapter 2, Marx is obsessed by the word "thesis"; [ 8 ] it forms an important part of the basis for the Marxist theory of history. [ 9 ]
2. Writing Pedagogy
In modern times, the dialectic of thesis, antithesis, and synthesis has been implemented across the world as a strategy for organizing expositional writing. For example, this technique is taught as a basic organizing principle in French schools: [ 10 ]
The French learn to value and practice eloquence from a young age. Almost from day one, students are taught to produce plans for their compositions, and are graded on them. The structures change with fashions. Youngsters were once taught to express a progression of ideas. Now they follow a dialectic model of thesis-antithesis-synthesis. If you listen carefully to the French arguing about any topic they all follow this model closely: they present an idea, explain possible objections to it, and then sum up their conclusions. ... This analytical mode of reasoning is integrated into the entire school corpus.
Thesis, Antithesis, and Synthesis has also been used as a basic scheme to organize writing in the English language. For example, the website WikiPreMed.com advocates the use of this scheme in writing timed essays for the MCAT standardized test: [ 11 ]
For the purposes of writing MCAT essays, the dialectic describes the progression of ideas in a critical thought process that is the force driving your argument. A good dialectical progression propels your arguments in a way that is satisfying to the reader. The thesis is an intellectual proposition. The antithesis is a critical perspective on the thesis. The synthesis solves the conflict between the thesis and antithesis by reconciling their common truths, and forming a new proposition.
- Samuel Taylor Coleridge: Opus Maximum. Princeton University Press, 2002, p. 89.
- Harry Ritter, Dictionary of Concepts in History. Greenwood Publishing Group (1986), p.114
- Williams, Robert R. (1992). Recognition: Fichte and Hegel on the Other. SUNY Press. p. 46, note 37.
- Fichte, Johann Gottlieb; Breazeale, Daniel (1993). Fichte: Early Philosophical Writings. Cornell University Press. p. 249.
- Walter Kaufmann (1966). "§ 37". Hegel: A Reinterpretation. Anchor Books. ISBN 978-0-268-01068-3. OCLC 3168016. https://archive.org/details/hegelreinterpret00kauf.
- Mueller, Gustav (1958). "The Hegel Legend of "Thesis-Antithesis-Synthesis"". Journal of the History of Ideas 19 (4): 411–414. doi:10.2307/2708045. https://dx.doi.org/10.2307%2F2708045
- Mueller 1958, p. 411.
- marxists.org: Chapter 2 of "The Poverty of Philosophy", by Karl Marx https://www.marxists.org/archive/marx/works/1847/poverty-philosophy/ch02.htm
- Shrimp, Kaleb (2009). "The Validity of Karl Marx's Theory of Historical Materialism". Major Themes in Economics 11 (1): 35–56. https://scholarworks.uni.edu/mtie/vol11/iss1/5/. Retrieved 13 September 2018.
- Nadeau, Jean-Benoit; Barlow, Julie (2003). Sixty Million Frenchmen Can't Be Wrong: Why We Love France But Not The French. Sourcebooks, Inc.. p. 62. https://archive.org/details/sixtymillionfren00nade_041.
- "The MCAT writing assignment.". Wisebridge Learning Systems, LLC. http://www.wikipremed.com/mcat_essay.php. Retrieved 1 November 2015.

- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Advisory Board

Learning Materials
- Business Studies
- Combined Science
- Computer Science
- Engineering
- English Literature
- Environmental Science
- Human Geography
- Macroeconomics
- Microeconomics
When Neil Armstrong walked on the moon he said, 'that's one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind' – this is a famous example of antithesis. Antithesis is a literary device used to show the difference or contrast between two objects. Synonyms for antithesis are 'opposite' or 'contrast.' Antithesis can be found in everyday use of figures of speech.
Create learning materials about Antithesis with our free learning app!
- Instand access to millions of learning materials
- Flashcards, notes, mock-exams and more
- Everything you need to ace your exams
Millions of flashcards designed to help you ace your studies
- Cell Biology
What effect can antithesis have in novels?
How can antithesis be used in persuasive writing?
Which phrase is an example of antithesis?
Can antithesis be used to juxtapose two different ideas?
Which is an example of parallelism and antithesis being used at the same time?
True or False: Antithesis is used in everyday figures of speech.
Can antithesis only be used in literary works?
What is a figure of speech?
What is antithesis?
Which word is a synonym for antithesis?
Why is antithesis used in plays?
Review generated flashcards
to start learning or create your own AI flashcards
Start learning or create your own AI flashcards
- American Drama
- American Literary Movements
- American Literature
- American Poetry
- American Regionalism Literature
- American Short Fiction
- Literary Criticism and Theory
- Literary Devices
- Academic and Campus Novel
- Adventure Fiction
- African Literature
- Amatory Fiction
- Antistrophe
- Autobiography
- Biblical Narrative
- Bildungsroman
- Blank Verse
- Children's Fiction
- Chivalric Romance
- Christian Drama
- Cliffhanger
- Closet drama
- Comedy in Drama
- Contemporary Fantasy
- Creative Non-Fiction
- Crime Fiction
- Cyberpunk Literature
- Detective Fiction
- Didactic Poetry
- Domestic Drama
- Dramatic Devices
- Dramatic Monologue
- Dramatic Structure
- Dramatic Terms
- Dramatis Personae
- Dystopian Fiction
- Elegiac Couplet
- English Renaissance Theatre
- Epic Poetry
- Epistolary Fiction
- Experimental Fiction
- Fantasy Fiction
- Feminist Literature
- Fictional Devices
- First World War Fiction
- Flash Fiction
- Foreshadowing
- Framed Narrative
- Free Indirect Discourse
- Genre Fiction
- Ghost Stories
- Gothic Novel
- Hard Low Fantasy
- Heroic Couplet
- Heroic Drama
- Historical Fantasy Fiction
- Historical Fiction
- Historical Romance Fiction
- Historiographic Metafiction
- Horatian Ode
- Horatian Satire
- Horror Novel
- Hyperrealism
- Iambic Pentameter
- Indian Literature
- Interleaving
- Internal Rhyme
- Intertextuality
- Irish Literature
- Limerick Poem
- Linear Narrative
- Literary Antecedent
- Literary Archetypes
- Literary Fiction
- Literary Form
- Literary Realism
- Literary Terms
- Literature Review
- Liturgical Dramas
- Lyric Poetry
- Magical Realism
- Malapropism
- Medieval Drama
- Metafiction
- Metrical Foot
- Miracle Plays
- Morality Plays
- Mystery Novels
- Mystery Play
- Narrative Discourse
- Narrative Form
- Narrative Literature
- Narrative Nonfiction
- Narrative Poetry
- Neo-Realism
- Non Fiction Genres
- Non-Fiction
- Non-linear Narrative
- Northern Irish Literature
- One-Act Play
- Oral Narratives
- Organic Poetry
- Pastoral Fiction
- Pastoral Poetry
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Petrarchan Sonnet
- Picaresque Novel
- Poetic Devices
- Poetic Form
- Poetic Genre
- Poetic Terms
- Political Satire
- Postcolonial Literature
- Prose Poetry
- Psychological Fiction
- Queer Literature
- Regency Romance
- Regional Fiction
- Religious Fiction
- Research Article
- Restoration Comedy
- Rhyme Scheme
- Roman a clef
- Romance Fiction
- Satirical Poetry
- Sceptical Literature
- Science Fiction
- Scottish Literature
- Second World War Fiction
- Sentimental Comedy
- Sentimental Novel
- Shakespearean Sonnet
- Short Fiction
- Social Realism Literature
- Speculative Fiction
- Spenserian Sonnet
- Stream of Consciousness
- Supernatural Fiction
- The Early Novel
- Theatre of the Absurd
- Theatrical Realism
- Tragedy in Drama
- Tragicomedy
- Translations and English Literature
- Urban Fiction
- Utopian Fiction
- Verse Fable
- Volta Poetry
- Welsh Literature
- Western Novels
- Women's fiction
- Literary Elements
- Literary Movements
- Literary Studies
- Non-Fiction Authors
Antithesis: meaning and synonyms
Antithesis is a commonly used literary device that can be found in novels, poems, plays and in our day to day speech.
Antithesis – A literary device that states that two objects are different from each other
This is a type of literary device that can be used to highlight the differences between two objects in a positive or negative way. There are many synonyms for antithesis, including, opposite or contrast. Antithesis can be used in two ways.
1. To juxtapose two different ideas
This type of antithesis is commonly used alongside parallelism.
Parallelism – Phrases placed in succession to each other that use the same grammatical structure.
Writers are able to use the two devices together to pair opposite objects together in their sentences. When antithesis and parallelism are used at the same time, this creates rhythm. An example of antithesis being used alongside parallelism is seen in the song 'Hello Goodbye' (1967) by The Beatles:
You say yes, I say no
The phrase 'You say yes' is mirrored in the second half of the sentence, 'I say no'. There are also two forms of antithesis in this sentence, 'you' is the antithesis of 'I' and 'yes' is the antithesis of 'no'. By using antithesis, the singer is showing how different he is to the other person.
2. To describe one thing as the opposite of another
Another way to use antithesis is as a way to describe one thing as the opposite of the other. When antithesis is used this way it is meant to create a contrast between two objects. Sometimes, this will be done by using the word 'antithesis' itself in the sentence, this can be seen below,
He is the antithesis of a good friend.
Here, the word 'antithesis' is used to imply that the person is the opposite of a good friend.
Antithesis: examples
Examples of antithesis can be found across media, including literature – from poems and songs to novels and our everyday speech.
Figures of speech
Figures of speech are phrases that are used in a non-literal sense for effect and we use them in our everyday speech.
A figure of speech – A word or phrase that is used in a non-literal sense for rhetorical effect.
Antithesis is used frequently in figures of speech to provide a reason for something. Below are two examples of figures of speech that use antithesis.
Easy come, easy go
We know that these figures of speech use antithesis as they use objects that are the opposite of each other. In the first example, 'come' is the opposite of 'go' as the former is to enter into something, while the latter is to leave. From this, we know that the figure of speech is being used to mean that if something comes easily, it will also leave easily.
One man’s junk is another man’s treasure.
The second example is similar to the first one, as we can infer what the figure of speech means. The word 'junk' (or rubbish) is the opposite of 'treasure'. This means that the figure of speech is saying that what is rubbish to one man, will be treasured by another.
Some of the most famous phrases that use antithesis come from plays. This is frequently noted in the plays of William Shakespeare , who used antithesis as a dramatic device when writing his works. Antithesis can be used in plays to show the differences between characters and their motivations, as well as to show a character's inner strife. One of the most well-known examples of this is seen in Shakespeare's play Hamlet (1603)
To be, or not to be, that is the question.
Here, Shakespeare uses antithesis to show that Hamlet is asking himself an important question; 'to live, or to die?'. The presence of antithesis may be harder to see here than in modern writing. However, the use of the word 'not' shows that the device is being used. Shakespeare contrasts the phrase 'to be' with 'not to be', showing that the character is questioning his own mortality. Antithesis is used at a crucial point in this play to relay to the audience Hamlet 's internal conflict .
Antithesis can also be frequently found in poetry. Antithesis is commonly seen alongside parallelism when it is used in poetry. It is effective when used in poetry as an antithesis can be used to reinforce rhythm in the poem. It can also contribute to the overall lyrical quality of the poem. An example of antithesis in poetry can be found in 'Fire and Ice' (1920) by Robert Frost .
'Fire' is hot and is, therefore, the antithesis of 'ice' which is cold. However, there is a second antithesis that is also present in the poem. The poem centres around ways the world may end, and so, 'fire' and 'ice' also are used as symbols for different causes of the earth's destruction. 'Fire' is a metaphor for greed, while 'ice' is a metaphor for hate or bigotry. Therefore, Frost uses antithesis for both the elements and what they represent.
Antithesis is also used commonly in novels. Here, an antithesis can be used to set up conflicts between characters, themes or settings in the novel . Antithesis can also be used to draw the reader's attention to a certain word or phrase. This will make it more memorable, especially if it is a theme that will be used throughout the novel. One of the most well-known examples of antithesis in literature is seen in Charles Dickens ' A Tale of Two Cities (1859).
It was the best of times, it was the worst of times
This is an example of parallelism and antithesis being used at the same time as the sentence mirrors itself. If the sentence is divided in two at the comma, it can be seen that the two halves are the same, except for the words 'best' and 'worst'. From this, the reader can gather that in the city, some people had a good time, while others did not. This sets up a conflict that is at the heart of the novel .
Antithesis: the use of and effect
When used correctly antithesis can be an extremely effective device. Antithesis can be used to show how vastly different two things are, as it places the objects side by side for comparison. This is particularly effective in persuasive writing such as a speech or argument. In persuasive writing, antithesis is also a useful device as it can highlight why what you are arguing for is better than what you are arguing against.
Antithesis is also effective when used in poems and novels. If anthesis is used as a literary device it can help create a rhythm throughout the poem. This is especially effective when used alongside parallelism. Antithesis can be used to create a lyrical effect on the writing, making it sound more musical. This is effective as it helps make writing more memorable.
Antithesis - Key takeaways
- Antithesis is a literary device that states that two objects are different from each other.
- It can be used alongside parallelism.
- It can be used to contrast two objects or show that one is the opposite of another.
- Antithesis can be found in persuasive writing, poems, figures of speech and plays.
- Antithesis can be used to create rhythm or to make an argument.
Flashcards in Antithesis 14
Antithesis can be used to make a phrase more memorable, as well as establish conflict in the novel.
Antithesis can be used to show how vastly different two things are, as it places the objects side by side for comparison.
'Easy come, easy go'
Yes! Antithesis can be used to juxtapose two different ideas.
'To be, or not to be'
True! Antithesis is used in everyday figures of speech.

Learn with 14 Antithesis flashcards in the free StudySmarter app
We have 14,000 flashcards about Dynamic Landscapes.
Already have an account? Log in
Frequently Asked Questions about Antithesis
Antithesis is a literary device that states that two objects are different from each other
What are examples of antithesis?
Examples of antithesis include, the figure of speech 'easy come, easy go' and 'It was the best of times, it was the worst of times' from A Tale of Two Cities (1859) by Charles Dickens.
How do you use antithesis in a sentence?
To use antithesis in a sentence, first pick two objects that are the opposite of each other, for example 'best' and 'worst'. Next work out what you want to say, for example, that you should be optimistic, but still prepare for bad things to happen. Try and shorten your idea using your opposite words, 'hope for the best, prepare for the worst'.
Is antithesis the same as opposite?
Yes, antithesis and opposite are effectively the same thing and can be used as synonyms of each other. However, antithesis will sometimes also be used in conjunction with parallelism also.
What are the uses of antithesis?
Antithesis is useful in writing as it can be used in arguments to show why one idea is better than another. It is also effective in literary works as it can be used to create rhythm, establish conflicts and make an idea more memorable.
Test your knowledge with multiple choice flashcards

Join the StudySmarter App and learn efficiently with millions of flashcards and more!
Keep learning, you are doing great.
Discover learning materials with the free StudySmarter app

About StudySmarter
StudySmarter is a globally recognized educational technology company, offering a holistic learning platform designed for students of all ages and educational levels. Our platform provides learning support for a wide range of subjects, including STEM, Social Sciences, and Languages and also helps students to successfully master various tests and exams worldwide, such as GCSE, A Level, SAT, ACT, Abitur, and more. We offer an extensive library of learning materials, including interactive flashcards, comprehensive textbook solutions, and detailed explanations. The cutting-edge technology and tools we provide help students create their own learning materials. StudySmarter’s content is not only expert-verified but also regularly updated to ensure accuracy and relevance.

StudySmarter Editorial Team
Team English Literature Teachers
- 8 minutes reading time
- Checked by StudySmarter Editorial Team
Study anywhere. Anytime.Across all devices.
Create a free account to save this explanation..
Save explanations to your personalised space and access them anytime, anywhere!
By signing up, you agree to the Terms and Conditions and the Privacy Policy of StudySmarter.
Sign up to highlight and take notes. It’s 100% free.
Join over 22 million students in learning with our StudySmarter App
The first learning app that truly has everything you need to ace your exams in one place
- Flashcards & Quizzes
- AI Study Assistant
- Study Planner
- Smart Note-Taking

Newest Articles
- Exploring the Role of Research Design and Methodology
- Writing Essays and Articles on Philosophy
- Intuitionism, Skepticism, and Agnosticism: A Comprehensive Overview
- Exploring Idealism: The History and Concepts of a Modern Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Theory of Forms
- Epistemology
- Materialism
- Moral relativism
- Utilitarianism
- Virtue ethics
- Normative ethics
- Applied ethics
- Moral Psychology
- Philosophy of art
- Philosophy of language
- Philosophy of beauty
- Nature of Art
- Philosophy of Film
- Philosophy of Music
- Deductive reasoning
- Inductive reasoning
- Justification
- Perception and Knowledge
- Beliefs and Truth
- Modern philosophy
- Romanticism
- Analytic philosophy
- Enlightenment philosophy
- Existentialism
- Enlightenment
- Ancient philosophy
- Classical Greek philosophy
- Renaissance philosophy
- Medieval philosophy
- Pre-Socratic philosophy
- Hellenistic philosophy
- Presocratic philosophy
- Rationalism
- Scholasticism
- Jewish philosophy
- Early Islamic philosophy
- Reasoning and Argumentation
- Seeking Justice After a Tractor-Trailer Accident: Why You Need an Experienced Lawyer
- Critical Thinking
- Fallacies and logical errors
- Skepticism and doubt
- Creative Thinking
- Lateral thinking
- Thought experiments
- Argumentation and Logic
- Syllogisms and Deductive Reasoning
- Fallacies and Rebuttals
- Inductive Reasoning and Analogy
- Reasoning and Problem-Solving
- Critical Thinking and Decision Making
- Creative Thinking and Problem Solving
- Analytical Thinking and Reasoning
- Philosophical Writing and Analysis
- Argumentative Writing and Analysis
- Interpreting Philosophical Texts
- Philosophical Research Methods
- Qualitative Research Methods in Philosophy
- Quantitative Research Methods in Philosophy
- Research Design and Methodology
- Ethics and Morality
- Aesthetics and Beauty
- Metaphysical terms
- Ontological argument
- Ethical terms
- Aesthetic terms
- Metaphysical theories
- Kant's Categorical Imperative
- Aristotle's Four Causes
- Plato's Theory of Forms
- Hegel's Dialectic
- Ethical theories
- Aesthetic theories
- John Dewey's aesthetic theory
- Immanuel Kant's aesthetic theory
- Modern philosophical texts
- Foucault's The Order of Things
- Descartes' Meditations
- Nietzsche's Beyond Good and Evil
- Wittgenstein's Tractatus Logico-Philosophicus
- Ancient philosophical texts
- Kant's Critique of Pure Reason
- Hegel's Phenomenology of Spirit
- Aristotle's Nicomachean Ethics
- Plato's Republic
- Ancient philosophers
- Modern philosophers
- Modern philosophical schools
- German Idealism
- British Empiricism
- Ancient philosophical schools
- The Skeptic school
- The Cynic school
- The Stoic school
- The Epicurean school
- The Socratic school
- Philosophy of Language
- Semantics and Pragmatics of Language Usage
- Analytic-Synthetic Distinction
- Meaning of Words and Phrases
- Philosophy of Science
- Scientific Realism and Rationalism
- Induction and the Hypothetico-Deductive Model
- Theory-Ladenness and Underdetermination
- Philosophy of Mind
- Mind-Body Dualism and Emergentism
- Materialism and Physicalism
- Identity Theory and Personal Identity
- Philosophy of Religion
- Religious Pluralism and Exclusivism
- The Problem of Evil and Suffering
- Religious Experience and Faith
- Metaphysical Theories
- Idealism and Realism
- Determinism, Fatalism, and Libertarianism
- Phenomenalism and Nominalism
- Epistemological Theories
- Intuitionism, Skepticism, and Agnosticism
- Rationalism and Empiricism
- Foundationalism and Coherentism
- Aesthetic Theories
- Formalist Aesthetics, Emotional Aesthetics, Experiential Aesthetics
- Relational Aesthetics, Sociological Aesthetics, Historical Aesthetics
- Naturalistic Aesthetics, Immanent Aesthetics, Transcendental Aesthetics
- Ethical Theories
- Virtue Ethics, Utilitarianism, Deontology
- Subjectivism, Egoism, Hedonism
- Social Contract Theory, Natural Law Theory, Care Ethics
- Metaphysical Terms
- Cause, Necessity, Possibility, Impossibility
- Identity, Persistence, Time, Space
- Substance, Attribute, Essence, Accident
- Logic and Argumentation Terms
- Analogy, Syllogism, Deduction, Induction
- Inference, Validity, Soundness, Refutation
- Premise, Conclusion, Entailment, Contradiction
- Epistemological Terms
- Perception and Knowledge Claims
- Infallibility, Verifiability, Coherence Theory of Truth
- Justification, Beliefs and Truths
- Ethical Terms
- Modern Texts
- A Vindication of the Rights of Woman by Mary Wollstonecraft
- Thus Spoke Zarathustra by Friedrich Nietzsche
- The Critique of Pure Reason by Immanuel Kant
- Medieval Texts
- The Guide for the Perplexed by Moses Maimonides
- The Summa Theologiae by Thomas Aquinas
- The Incoherence of the Incoherence by Averroes
- Ancient Texts
- The Nicomachean Ethics by Aristotle
- The Art of Rhetoric by Cicero
- The Republic by Plato
- Hegel's Dialectic: A Comprehensive Overview
- Philosophical theories
Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel's dialectic is one of the most influential philosophical theories of the modern era. It has been studied and debated for centuries, and its influence can be seen in many aspects of modern thought. Hegel's dialectic has been used to explain a wide range of topics from politics to art, from science to religion. In this comprehensive overview, we will explore the major tenets of Hegel's dialectic and its implications for our understanding of the world. Hegel's dialectic is based on the premise that all things have an inherent contradiction between their opposites.
It follows that any idea or concept can be understood through a synthesis of the two opposing forces. This synthesis creates a new and higher understanding, which then leads to further progress and development. Hegel's dialectic has been used in many different fields, from philosophy to economics, and it provides an important framework for understanding how our world works. In this article, we will explore the historical origins and development of Hegel's dialectic. We will also examine its application in various fields, from politics to art, from science to religion.
Finally, we will consider the implications of Hegel's dialectic for our understanding of the world today. Hegel's dialectic is a philosophical theory developed by German philosopher Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel in the early 19th century. It is based on the concept of thesis, antithesis and synthesis , which are steps in the process of progress. The thesis is an idea or statement that is the starting point of an argument. The antithesis is a statement that contradicts or negates the thesis.
The synthesis is a combination of the two opposing ideas, which produces a new idea or statement. This process can be repeated multiple times, leading to an evolution of ideas. Hegel's dialectic has been used in many fields, such as politics and economics . It has been used to explain how ideas progress through debate and discussion.
In politics, it has been used to explain how different points of view can lead to compromise or resolution. In economics, it has been used to explain how different economic theories can lead to new solutions and strategies. Hegel's dialectic can also be applied to everyday life. For example, it can be used to resolve conflicts between people or groups.
Thesis, Antithesis and Synthesis
Thesis and antithesis are two conflicting ideas, while synthesis is the result of their interaction. The dialectic process is a way of understanding how the world works, as it helps to explain the constant flux of ideas and events. It also helps to explain how change and progress are possible. Thesis and antithesis can be thought of as two sides of a coin. One side represents an idea or opinion, while the other side represents its opposite.
When the two sides come together, they create a synthesis that incorporates both sides. This synthesis can then be used to create new ideas or opinions. The dialectic process can be applied in various contexts, such as politics and economics. In politics, it can be used to explain how different factions come together to create policies that are beneficial to all parties. In economics, it can be used to explain how supply and demand interact to create a stable market. Hegel's dialectic can also be used in everyday life.
Applications of Hegel's Dialectic
For example, in the political sphere, it can be used to explore how different ideologies can be reconciled or how compromises can be reached. In economics, Hegel's dialectic has been used to explain the process of economic growth and development. It can be seen as a way of understanding how different economic systems interact with each other and how different economic actors are affected by changes in the marketplace. For example, it can help to explain how different economic policies can lead to different outcomes. Hegel's dialectic has also been applied to other social sciences, such as sociology and anthropology. In particular, it has been used to explore how different social systems interact with each other and how different social groups are affected by changes in their environment.
Using Hegel's Dialectic in Everyday Life
This process can be used to explain how various aspects of life, such as career or relationships, evolve over time. Thesis represents an idea or concept, while antithesis represents the opposite of that idea or concept. Synthesis is the resolution between the two opposing forces. This process is repeated until a conclusion is reached.
For example, in a career conflict between two people, one might present an idea while the other presents the opposite idea. Through discussion and negotiation, the two parties can come to a synthesis that meets both their needs. Hegel's dialectic can also be used to resolve conflicts between groups of people. It involves each party presenting their ideas and opinions, then engaging in dialogue to reach a compromise or agreement.
This process can be applied to any area of life, from politics and economics to relationships and personal growth. It helps to create understanding and respect between different perspectives, allowing everyone to come together in a meaningful way. By understanding and applying Hegel's dialectic in everyday life, we can better navigate our relationships and interactions with others. Through dialogue, negotiation, and compromise we can work towards resolutions that benefit all parties involved.
In economics, it has been used to explain how market forces interact with each other and how different economic theories can be used to explain the same phenomenon. The dialectic has also been used in other fields such as philosophy, science, and psychology. In philosophy, it has been used to explain the relationship between theory and practice and how theories evolve over time. In science, it has been used to explain the relationship between empirical evidence and logical reasoning.
This theory can be applied to any area of life, from career to relationships. The core of Hegel's dialectic involves the concept of thesis, antithesis, and synthesis, which is a way of understanding how ideas evolve over time. In this way, the dialectic helps to identify contradictions in a situation and find a resolution through synthesis. In terms of its application to everyday life, the dialectic can be used to find common ground between two opposing sides. For example, if two people are in disagreement, the dialectic can help them identify the underlying issues and then work to resolve them.
Additionally, it can help individuals and groups identify areas where they have common interests, which can lead to more productive conversations and outcomes. The dialectic is also useful in understanding how different perspectives can lead to different solutions. By recognizing different points of view, individuals and groups can gain insight into why certain solutions may not work for everyone involved. This can help to create a more productive environment for collaboration. Finally, the dialectic can be used as a tool for self-reflection. By understanding how different ideas evolve over time and how different perspectives interact, individuals can gain insight into their own views and values.
For example, it can be used to explain the development of a new policy proposal or a new form of government. In economics, Hegel's dialectic can be used to explain the dynamics of supply and demand, or the emergence of a new economic system. In addition, Hegel's dialectic has been applied in other areas, such as education and religion. In education, this theory can be used to explain the process of learning and understanding new concepts. In religion, it can be used to explain the evolution of religious beliefs and practices over time.
This is followed by a synthesis of the two, which creates a new, higher form of understanding. This new understanding then forms the basis for further analysis, which can lead to further synthesis and resolution. Hegel's dialectic can be applied to any area of life, such as career or relationships. For example, if two people have different approaches to a problem, they can use the dialectic to work together to find a solution that works for both of them.
This could involve identifying their respective points of view and then looking for common ground where they can agree. As the synthesis forms, it can provide a basis for further discussion, which may eventually lead to a resolution. The same process can be used to resolve conflicts between groups, such as political parties or countries. By recognizing each side's point of view and then looking for common ground, it is possible to find ways to bridge the divide between them.
This can help create an atmosphere of mutual understanding and respect, which can lead to constructive dialogue and positive outcomes. Hegel's dialectic is a valuable tool for helping people and groups come to agreement and harmony despite their differences. By recognizing both sides' points of view and then looking for common ground, it is possible to create a synthesis that can provide a basis for further discussion and resolution. Hegel's dialectic is a powerful philosophical tool that helps to explain how ideas evolve over time. Through the concept of thesis, antithesis and synthesis, it provides a framework for understanding how opposing forces interact and ultimately create new ideas and solutions.
This theory has been applied to many areas, such as politics and economics, and can be used in everyday life. The article has provided a comprehensive overview of Hegel's dialectic and its various applications.
Top Articles

- Understanding Existentialism: A Brief Introduction

- Foundationalism and Coherentism: An Overview

- Lateral Thinking: An Overview
- Exploring Nietzsche's Beyond Good and Evil
- Understanding Utilitarianism: A Guide
- Exploring Plato's Theory of Forms
- Exploring the Philosophy of Immanuel Kant
- Exploring the Analytic-Synthetic Distinction in Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Art: Exploring Aesthetics and Beauty
- Exploring Expression: A Philosophical and Aesthetic Overview
- The Critique of Pure Reason by Immanuel Kant: A Comprehensive Overview
- Exploring the Philosophy of Beauty
- Induction and the Hypothetico-Deductive Model: A Comprehensive Overview
- Exploring the Life and Works of David Hume
- Philosophy of Film: Exploring Aesthetics and Types of Philosophy
- Understanding Inference, Validity, Soundness, and Refutation
- Materialism and Physicalism: Exploring the Philosophical Concepts
- Analytic Philosophy: A Comprehensive Overview
- Exploring Syllogisms and Deductive Reasoning
- Exploring Social Contract Theory, Natural Law Theory, and Care Ethics
- Analytic Philosophy: A Primer
- Exploring the Phenomenon: A Philosophical and Metaphysical Investigation
- Exploring the Theory of Forms: A Comprehensive Overview
- Exploring Aesthetic Theories: Formalism, Emotionalism and Experientialism
- The Stoic School: An Overview
- Exploring Cosmology: What We Know and What We Don't
- Virtue Ethics: What it is and How it Works
- Exploring Plato's Republic
- Understanding Virtue Ethics, Utilitarianism and Deontology
- Early Islamic Philosophy
- Idealism and Realism: A Philosophical Comparison
- A Comprehensive Overview of Kant's Categorical Imperative
- Exploring the History and Impact of Empiricism
- Exploring 'The Summa Theologiae' by Thomas Aquinas
- A Comprehensive Overview of Foucault's The Order of Things
- Aristotle: A Comprehensive Overview
- Understanding Inductive Reasoning
- Exploring Subjectivism, Egoism and Hedonism
- Exploring Skepticism and Doubt: A Philosophical and Critical Thinking Perspective
- Exploring Hellenistic Philosophy: An Introduction
- Exploring Rationalism and Empiricism
- Understanding Inductive Reasoning and Analogy
- Altruism: Exploring the Power of Selflessness
- Exploring Kant's Critique of Pure Reason
- An Introduction to Scholasticism and its Role in Medieval Philosophy
Exploring the Rationalism of Renaissance Philosophy
- Exploring Theology: A Comprehensive Overview
Understanding Fallacies and Rebuttals
- Exploring the Concept of Beauty
- Exploring Inference: A Philosophical Thinking Primer
- Exploring Theory-Ladenness and Underdetermination
- Understanding Utilitarianism
- Exploring Religious Pluralism and Exclusivism
- Exploring Hegel's Phenomenology of Spirit
- Exploring Moral Psychology: A Closer Look
- The Art of Rhetoric by Cicero: A Comprehensive Overview
- Exploring Pre-Socratic Philosophy: An Overview
- Understanding Fallacies and Logical Errors
- Exploring Virtue: A Philosophical and Ethical Perspective
- Deontology: An Introduction to an Ethical Theory
- Substance, Attribute, Essence, and Accident: A Philosophical and Metaphysical Overview
- Perception and Knowledge: An Overview
- Justification: A Comprehensive Overview
- Classical Greek Philosophy: A Comprehensive Overview
- Exploring Virtue Ethics: The Philosophical Theory
- Medieval Philosophy: An Overview
- Exploring Noumenon: A Philosophical and Metaphysical Overview
- A Comprehensive Overview of Presocratic Philosophy
- The Problem of Evil and Suffering: A Philosophical Exploration
- Epistemology: Understanding the Nature of Knowledge
- An Overview of Friedrich Nietzsche's Thus Spoke Zarathustra
- Exploring the Concept of Idealism
- Understanding Deontology: Ethics and Principles
- Exploring Identity, Persistence, Time, and Space
- Exploring the Skeptic School of Ancient Philosophy
- Exploring Aristotle's Four Causes
- The Cynic School: An In-depth Look
- Exploring Infallibility, Verifiability, and the Coherence Theory of Truth
- Exploring Egoism: What It Is and What It Means
- Understanding the Meaning of Words and Phrases
- Exploring the Socratic School: An Overview
- Explore The Epicurean School of Ancient Philosophy
- Exploring Jewish Philosophy
- Philosophy of Music: Exploring the Aesthetics of Sound
- Understanding Utilitarianism: An Overview
- Comparing Analogy, Syllogism, Deduction and Induction
Exploring Ontology: A Comprehensive Overview
- Exploring the Life and Work of Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel
- Exploring Deductive Reasoning
New Articles

Which cookies do you want to accept?
- Anatomy & Physiology
- Astrophysics
- Earth Science
- Environmental Science
- Organic Chemistry
- Precalculus
- Trigonometry
- English Grammar
- U.S. History
- World History
... and beyond
- Socratic Meta
- Featured Answers

What is Hegel's concept of thesis, antithesis and synthesis, in simple terms?


COMMENTS
Definition of Antithesis. Antithesis is a literary device that refers to the juxtaposition of two opposing elements through the parallel grammatical structure. The word antithesis, meaning absolute opposite, is derived from Greek for "setting opposite," indicating when something or someone is in direct contrast or the obverse of another thing or person.
Antithesis is a figure of speech that juxtaposes two contrasting or opposing ideas, usually within parallel grammatical structures. For instance, Neil Armstrong used antithesis when he stepped onto the surface of the moon in 1969 and said, "That's one small step for a man, one giant leap for mankind." This is an example of antithesis because ...
Antithesis (pl.: antitheses; Greek for "setting opposite", from ἀντι-"against" and θέσις "placing") is used in writing or speech either as a proposition that contrasts with or reverses some previously mentioned proposition, or when two opposites are introduced together for contrasting effect. [1] [2]Antithesis can be defined as "a figure of speech involving a seeming contradiction of ...
Antithesis performs a very similar function, but does so in a more complicated way by using full sentences (rather than single words or images) to express the two halves of the juxtaposition. Here is an antithesis built around some of the common expressions from above "Sheep go to Heaven; goats go to Hell."
Antithesis (pronounced an-TITH-uh-sis) deals in opposites. The Merriam-Webster definition of antithesis is "the direct opposite," and in Greek the meaning is "setting opposite.". As a tool for writing, antithesis creates a juxtaposition of qualities using a parallel grammatical structure. In other words, it's setting opposites next to ...
Antithesis is a literary device that involves the use of contrasting ideas, words, or phrases in a parallel structure. Here are some examples of antithesis in literature, speeches, and advertising. Antithesis in Literature. Antithesis is commonly used in literature to highlight the contrast between two opposing ideas or themes.
Antithesis Definition Antithesis, which literally means "opposite," is a rhetorical device wherein opposite thoughts are prepare in a sentence to obtain a contrasting effect. ... makes use of phrases to convey ideas in exceptional methods from the commonplace words and expressions of daily life. Thus, it conveys meaning greater vividly than ...
Definition of Antithesis. Antithesis is used in everyday speech, novels, poems, short stories, plays, and more.The rhetorical device can be used in very different ways in order to achieve varied outcomes.. Parallelism is an important part of antithesis. The structure of the words around the contrasting ideas is usually identical, at least in part. This allows the juxtaposed words to be as ...
Antithesis (ann-TIH-thuh-suhs), put simply, means the absolute opposite of something. As a literary term, it refers to the juxtaposition of two opposing entities in parallel structure. Antithesis is an effective literary device because humans tend to define through contrast. Therefore, antithesis can help readers understand something by defining its opposite.
Antithesis is the use of contrasting concepts, words, or sentences within parallel grammatical structures. This combination of a balanced structure with opposite ideas serves to highlight the contrast between them. For example, the following famous Muhammad Ali quote is an example of antithesis: "Float like a butterfly, sting like a bee.".
The English language is full of literary devices that can enliven your writing. One tool used often in literature and politics is called antithesis.
An antithesis is just that—an "anti" "thesis.". An antithesis is used in writing to express ideas that seem contradictory. An antithesis uses parallel structure of two ideas to communicate this contradiction. Example of Antithesis: "Float like a butterfly, sting like a bee." -Muhammad Ali. This example of antithesis is a famous ...
An antithesis is defined as something which is the explicit opposite of something else. A common example of antithesis in everyday life are the concepts of speaking versus listening. One is the ...
Antithesis. Antithesis is a literary device that pairs contrasting ideas together in a sentence to highlight their differences. This technique emphasizes the distinction between the ideas, making their unique characteristics more noticeable and impactful. By using antithesis, writers can draw attention to specific traits and enhance the clarity ...
Antithesis and juxtaposition, while both serving to highlight contrasts, diverge in their methods and intents. Antithesis, exemplified by phrases like "to be or not to be" or "love is an ideal thing, marriage a real thing," places opposing concepts or words in close proximity to underscore their differences and provoke thought.
The word antithesis is sometimes used to mean 'opposite'. For example, "She is slim and sporty - the very antithesis of her brother". However, 'antithesis' (or 'antitheses' if plural) is also the name given to a particular rhetorical or literary device. In this blog post, we'll be looking at 'antithesis' in its role as ...
antithesis: [noun] the direct opposite. the rhetorical contrast of ideas by means of parallel arrangements of words, clauses, or sentences (as in "action, not words" or "they promised freedom and provided slavery"). opposition, contrast. the second of two opposing words, clauses, or sentences that are being rhetorically contrasted.
Antithesis is a figure of speech that places two completely contrasting ideas or clauses in juxtaposition. An oxymoron is a figure of speech that contains two opposing or contrasting words placed adjacent to each other within a phrase to produce an effect. For example: "Art is long, and Time is fleeting.". For example:
Antithesis is the use of words that are opposite or contrasting in meaning. For example, to be or not to be. Antithesis is used in writing to create a dramatic effect. Contrary to what you might think, an antithetical statement can enhance a passage instead of detracting from it. It helps to show two sides of an argument and bring balance to ...
0. 0. In philosophy, the triad of thesis, antithesis, synthesis (German: These, Antithese, Synthese; originally: Thesis, Antithesis, Synthesis) is a progression of three ideas or propositions. The first idea, the thesis, is a formal statement illustrating a point; it is followed by the second idea, the antithesis, that contradicts or negates ...
Antithesis is a literary device that states that two objects are different from each other. It can be used alongside parallelism. It can be used to contrast two objects or show that one is the opposite of another. Antithesis can be found in persuasive writing, poems, figures of speech and plays.
Thesis, Antithesis and Synthesis Hegel's dialectic is based on the principle of thesis, antithesis and synthesis. Thesis and antithesis are two conflicting ideas, while synthesis is the result of their interaction. The dialectic process is a way of understanding how the world works, as it helps to explain the constant flux of ideas and events.
Antithesis refers to the refutation of the idea. Synthesis is the moulding of the idea and its refutations into a new idea. For instance, I can crudely write an example like this: Thesis - There is a God. Antithesis - There is a lot of bad in the world. Synthesis - There is a God but His ways are mysterious. See below: A couple of things to ...