Home Blog Design Understanding Data Presentations (Guide + Examples)

Understanding Data Presentations (Guide + Examples)

In this age of overwhelming information, the skill to effectively convey data has become extremely valuable. Initiating a discussion on data presentation types involves thoughtful consideration of the nature of your data and the message you aim to convey. Different types of visualizations serve distinct purposes. Whether you’re dealing with how to develop a report or simply trying to communicate complex information, how you present data influences how well your audience understands and engages with it. This extensive guide leads you through the different ways of data presentation.
Table of Contents
What is a Data Presentation?
What should a data presentation include, line graphs, treemap chart, scatter plot, how to choose a data presentation type, recommended data presentation templates, common mistakes done in data presentation.
A data presentation is a slide deck that aims to disclose quantitative information to an audience through the use of visual formats and narrative techniques derived from data analysis, making complex data understandable and actionable. This process requires a series of tools, such as charts, graphs, tables, infographics, dashboards, and so on, supported by concise textual explanations to improve understanding and boost retention rate.
Data presentations require us to cull data in a format that allows the presenter to highlight trends, patterns, and insights so that the audience can act upon the shared information. In a few words, the goal of data presentations is to enable viewers to grasp complicated concepts or trends quickly, facilitating informed decision-making or deeper analysis.
Data presentations go beyond the mere usage of graphical elements. Seasoned presenters encompass visuals with the art of data storytelling , so the speech skillfully connects the points through a narrative that resonates with the audience. Depending on the purpose – inspire, persuade, inform, support decision-making processes, etc. – is the data presentation format that is better suited to help us in this journey.
To nail your upcoming data presentation, ensure to count with the following elements:
- Clear Objectives: Understand the intent of your presentation before selecting the graphical layout and metaphors to make content easier to grasp.
- Engaging introduction: Use a powerful hook from the get-go. For instance, you can ask a big question or present a problem that your data will answer. Take a look at our guide on how to start a presentation for tips & insights.
- Structured Narrative: Your data presentation must tell a coherent story. This means a beginning where you present the context, a middle section in which you present the data, and an ending that uses a call-to-action. Check our guide on presentation structure for further information.
- Visual Elements: These are the charts, graphs, and other elements of visual communication we ought to use to present data. This article will cover one by one the different types of data representation methods we can use, and provide further guidance on choosing between them.
- Insights and Analysis: This is not just showcasing a graph and letting people get an idea about it. A proper data presentation includes the interpretation of that data, the reason why it’s included, and why it matters to your research.
- Conclusion & CTA: Ending your presentation with a call to action is necessary. Whether you intend to wow your audience into acquiring your services, inspire them to change the world, or whatever the purpose of your presentation, there must be a stage in which you convey all that you shared and show the path to staying in touch. Plan ahead whether you want to use a thank-you slide, a video presentation, or which method is apt and tailored to the kind of presentation you deliver.
- Q&A Session: After your speech is concluded, allocate 3-5 minutes for the audience to raise any questions about the information you disclosed. This is an extra chance to establish your authority on the topic. Check our guide on questions and answer sessions in presentations here.
Bar charts are a graphical representation of data using rectangular bars to show quantities or frequencies in an established category. They make it easy for readers to spot patterns or trends. Bar charts can be horizontal or vertical, although the vertical format is commonly known as a column chart. They display categorical, discrete, or continuous variables grouped in class intervals [1] . They include an axis and a set of labeled bars horizontally or vertically. These bars represent the frequencies of variable values or the values themselves. Numbers on the y-axis of a vertical bar chart or the x-axis of a horizontal bar chart are called the scale.

Real-Life Application of Bar Charts
Let’s say a sales manager is presenting sales to their audience. Using a bar chart, he follows these steps.
Step 1: Selecting Data
The first step is to identify the specific data you will present to your audience.
The sales manager has highlighted these products for the presentation.
- Product A: Men’s Shoes
- Product B: Women’s Apparel
- Product C: Electronics
- Product D: Home Decor
Step 2: Choosing Orientation
Opt for a vertical layout for simplicity. Vertical bar charts help compare different categories in case there are not too many categories [1] . They can also help show different trends. A vertical bar chart is used where each bar represents one of the four chosen products. After plotting the data, it is seen that the height of each bar directly represents the sales performance of the respective product.
It is visible that the tallest bar (Electronics – Product C) is showing the highest sales. However, the shorter bars (Women’s Apparel – Product B and Home Decor – Product D) need attention. It indicates areas that require further analysis or strategies for improvement.
Step 3: Colorful Insights
Different colors are used to differentiate each product. It is essential to show a color-coded chart where the audience can distinguish between products.
- Men’s Shoes (Product A): Yellow
- Women’s Apparel (Product B): Orange
- Electronics (Product C): Violet
- Home Decor (Product D): Blue

Bar charts are straightforward and easily understandable for presenting data. They are versatile when comparing products or any categorical data [2] . Bar charts adapt seamlessly to retail scenarios. Despite that, bar charts have a few shortcomings. They cannot illustrate data trends over time. Besides, overloading the chart with numerous products can lead to visual clutter, diminishing its effectiveness.
For more information, check our collection of bar chart templates for PowerPoint .
Line graphs help illustrate data trends, progressions, or fluctuations by connecting a series of data points called ‘markers’ with straight line segments. This provides a straightforward representation of how values change [5] . Their versatility makes them invaluable for scenarios requiring a visual understanding of continuous data. In addition, line graphs are also useful for comparing multiple datasets over the same timeline. Using multiple line graphs allows us to compare more than one data set. They simplify complex information so the audience can quickly grasp the ups and downs of values. From tracking stock prices to analyzing experimental results, you can use line graphs to show how data changes over a continuous timeline. They show trends with simplicity and clarity.
Real-life Application of Line Graphs
To understand line graphs thoroughly, we will use a real case. Imagine you’re a financial analyst presenting a tech company’s monthly sales for a licensed product over the past year. Investors want insights into sales behavior by month, how market trends may have influenced sales performance and reception to the new pricing strategy. To present data via a line graph, you will complete these steps.
First, you need to gather the data. In this case, your data will be the sales numbers. For example:
- January: $45,000
- February: $55,000
- March: $45,000
- April: $60,000
- May: $ 70,000
- June: $65,000
- July: $62,000
- August: $68,000
- September: $81,000
- October: $76,000
- November: $87,000
- December: $91,000
After choosing the data, the next step is to select the orientation. Like bar charts, you can use vertical or horizontal line graphs. However, we want to keep this simple, so we will keep the timeline (x-axis) horizontal while the sales numbers (y-axis) vertical.
Step 3: Connecting Trends
After adding the data to your preferred software, you will plot a line graph. In the graph, each month’s sales are represented by data points connected by a line.

Step 4: Adding Clarity with Color
If there are multiple lines, you can also add colors to highlight each one, making it easier to follow.
Line graphs excel at visually presenting trends over time. These presentation aids identify patterns, like upward or downward trends. However, too many data points can clutter the graph, making it harder to interpret. Line graphs work best with continuous data but are not suitable for categories.
For more information, check our collection of line chart templates for PowerPoint and our article about how to make a presentation graph .
A data dashboard is a visual tool for analyzing information. Different graphs, charts, and tables are consolidated in a layout to showcase the information required to achieve one or more objectives. Dashboards help quickly see Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). You don’t make new visuals in the dashboard; instead, you use it to display visuals you’ve already made in worksheets [3] .
Keeping the number of visuals on a dashboard to three or four is recommended. Adding too many can make it hard to see the main points [4]. Dashboards can be used for business analytics to analyze sales, revenue, and marketing metrics at a time. They are also used in the manufacturing industry, as they allow users to grasp the entire production scenario at the moment while tracking the core KPIs for each line.
Real-Life Application of a Dashboard
Consider a project manager presenting a software development project’s progress to a tech company’s leadership team. He follows the following steps.
Step 1: Defining Key Metrics
To effectively communicate the project’s status, identify key metrics such as completion status, budget, and bug resolution rates. Then, choose measurable metrics aligned with project objectives.
Step 2: Choosing Visualization Widgets
After finalizing the data, presentation aids that align with each metric are selected. For this project, the project manager chooses a progress bar for the completion status and uses bar charts for budget allocation. Likewise, he implements line charts for bug resolution rates.

Step 3: Dashboard Layout
Key metrics are prominently placed in the dashboard for easy visibility, and the manager ensures that it appears clean and organized.
Dashboards provide a comprehensive view of key project metrics. Users can interact with data, customize views, and drill down for detailed analysis. However, creating an effective dashboard requires careful planning to avoid clutter. Besides, dashboards rely on the availability and accuracy of underlying data sources.
For more information, check our article on how to design a dashboard presentation , and discover our collection of dashboard PowerPoint templates .
Treemap charts represent hierarchical data structured in a series of nested rectangles [6] . As each branch of the ‘tree’ is given a rectangle, smaller tiles can be seen representing sub-branches, meaning elements on a lower hierarchical level than the parent rectangle. Each one of those rectangular nodes is built by representing an area proportional to the specified data dimension.
Treemaps are useful for visualizing large datasets in compact space. It is easy to identify patterns, such as which categories are dominant. Common applications of the treemap chart are seen in the IT industry, such as resource allocation, disk space management, website analytics, etc. Also, they can be used in multiple industries like healthcare data analysis, market share across different product categories, or even in finance to visualize portfolios.
Real-Life Application of a Treemap Chart
Let’s consider a financial scenario where a financial team wants to represent the budget allocation of a company. There is a hierarchy in the process, so it is helpful to use a treemap chart. In the chart, the top-level rectangle could represent the total budget, and it would be subdivided into smaller rectangles, each denoting a specific department. Further subdivisions within these smaller rectangles might represent individual projects or cost categories.
Step 1: Define Your Data Hierarchy
While presenting data on the budget allocation, start by outlining the hierarchical structure. The sequence will be like the overall budget at the top, followed by departments, projects within each department, and finally, individual cost categories for each project.
- Top-level rectangle: Total Budget
- Second-level rectangles: Departments (Engineering, Marketing, Sales)
- Third-level rectangles: Projects within each department
- Fourth-level rectangles: Cost categories for each project (Personnel, Marketing Expenses, Equipment)
Step 2: Choose a Suitable Tool
It’s time to select a data visualization tool supporting Treemaps. Popular choices include Tableau, Microsoft Power BI, PowerPoint, or even coding with libraries like D3.js. It is vital to ensure that the chosen tool provides customization options for colors, labels, and hierarchical structures.
Here, the team uses PowerPoint for this guide because of its user-friendly interface and robust Treemap capabilities.
Step 3: Make a Treemap Chart with PowerPoint
After opening the PowerPoint presentation, they chose “SmartArt” to form the chart. The SmartArt Graphic window has a “Hierarchy” category on the left. Here, you will see multiple options. You can choose any layout that resembles a Treemap. The “Table Hierarchy” or “Organization Chart” options can be adapted. The team selects the Table Hierarchy as it looks close to a Treemap.
Step 5: Input Your Data
After that, a new window will open with a basic structure. They add the data one by one by clicking on the text boxes. They start with the top-level rectangle, representing the total budget.

Step 6: Customize the Treemap
By clicking on each shape, they customize its color, size, and label. At the same time, they can adjust the font size, style, and color of labels by using the options in the “Format” tab in PowerPoint. Using different colors for each level enhances the visual difference.
Treemaps excel at illustrating hierarchical structures. These charts make it easy to understand relationships and dependencies. They efficiently use space, compactly displaying a large amount of data, reducing the need for excessive scrolling or navigation. Additionally, using colors enhances the understanding of data by representing different variables or categories.
In some cases, treemaps might become complex, especially with deep hierarchies. It becomes challenging for some users to interpret the chart. At the same time, displaying detailed information within each rectangle might be constrained by space. It potentially limits the amount of data that can be shown clearly. Without proper labeling and color coding, there’s a risk of misinterpretation.
A heatmap is a data visualization tool that uses color coding to represent values across a two-dimensional surface. In these, colors replace numbers to indicate the magnitude of each cell. This color-shaded matrix display is valuable for summarizing and understanding data sets with a glance [7] . The intensity of the color corresponds to the value it represents, making it easy to identify patterns, trends, and variations in the data.
As a tool, heatmaps help businesses analyze website interactions, revealing user behavior patterns and preferences to enhance overall user experience. In addition, companies use heatmaps to assess content engagement, identifying popular sections and areas of improvement for more effective communication. They excel at highlighting patterns and trends in large datasets, making it easy to identify areas of interest.
We can implement heatmaps to express multiple data types, such as numerical values, percentages, or even categorical data. Heatmaps help us easily spot areas with lots of activity, making them helpful in figuring out clusters [8] . When making these maps, it is important to pick colors carefully. The colors need to show the differences between groups or levels of something. And it is good to use colors that people with colorblindness can easily see.
Check our detailed guide on how to create a heatmap here. Also discover our collection of heatmap PowerPoint templates .
Pie charts are circular statistical graphics divided into slices to illustrate numerical proportions. Each slice represents a proportionate part of the whole, making it easy to visualize the contribution of each component to the total.
The size of the pie charts is influenced by the value of data points within each pie. The total of all data points in a pie determines its size. The pie with the highest data points appears as the largest, whereas the others are proportionally smaller. However, you can present all pies of the same size if proportional representation is not required [9] . Sometimes, pie charts are difficult to read, or additional information is required. A variation of this tool can be used instead, known as the donut chart , which has the same structure but a blank center, creating a ring shape. Presenters can add extra information, and the ring shape helps to declutter the graph.
Pie charts are used in business to show percentage distribution, compare relative sizes of categories, or present straightforward data sets where visualizing ratios is essential.
Real-Life Application of Pie Charts
Consider a scenario where you want to represent the distribution of the data. Each slice of the pie chart would represent a different category, and the size of each slice would indicate the percentage of the total portion allocated to that category.
Step 1: Define Your Data Structure
Imagine you are presenting the distribution of a project budget among different expense categories.
- Column A: Expense Categories (Personnel, Equipment, Marketing, Miscellaneous)
- Column B: Budget Amounts ($40,000, $30,000, $20,000, $10,000) Column B represents the values of your categories in Column A.
Step 2: Insert a Pie Chart
Using any of the accessible tools, you can create a pie chart. The most convenient tools for forming a pie chart in a presentation are presentation tools such as PowerPoint or Google Slides. You will notice that the pie chart assigns each expense category a percentage of the total budget by dividing it by the total budget.
For instance:
- Personnel: $40,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 40%
- Equipment: $30,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 30%
- Marketing: $20,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 20%
- Miscellaneous: $10,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 10%
You can make a chart out of this or just pull out the pie chart from the data.

3D pie charts and 3D donut charts are quite popular among the audience. They stand out as visual elements in any presentation slide, so let’s take a look at how our pie chart example would look in 3D pie chart format.

Step 03: Results Interpretation
The pie chart visually illustrates the distribution of the project budget among different expense categories. Personnel constitutes the largest portion at 40%, followed by equipment at 30%, marketing at 20%, and miscellaneous at 10%. This breakdown provides a clear overview of where the project funds are allocated, which helps in informed decision-making and resource management. It is evident that personnel are a significant investment, emphasizing their importance in the overall project budget.
Pie charts provide a straightforward way to represent proportions and percentages. They are easy to understand, even for individuals with limited data analysis experience. These charts work well for small datasets with a limited number of categories.
However, a pie chart can become cluttered and less effective in situations with many categories. Accurate interpretation may be challenging, especially when dealing with slight differences in slice sizes. In addition, these charts are static and do not effectively convey trends over time.
For more information, check our collection of pie chart templates for PowerPoint .
Histograms present the distribution of numerical variables. Unlike a bar chart that records each unique response separately, histograms organize numeric responses into bins and show the frequency of reactions within each bin [10] . The x-axis of a histogram shows the range of values for a numeric variable. At the same time, the y-axis indicates the relative frequencies (percentage of the total counts) for that range of values.
Whenever you want to understand the distribution of your data, check which values are more common, or identify outliers, histograms are your go-to. Think of them as a spotlight on the story your data is telling. A histogram can provide a quick and insightful overview if you’re curious about exam scores, sales figures, or any numerical data distribution.
Real-Life Application of a Histogram
In the histogram data analysis presentation example, imagine an instructor analyzing a class’s grades to identify the most common score range. A histogram could effectively display the distribution. It will show whether most students scored in the average range or if there are significant outliers.
Step 1: Gather Data
He begins by gathering the data. The scores of each student in class are gathered to analyze exam scores.
| Names | Score |
|---|---|
| Alice | 78 |
| Bob | 85 |
| Clara | 92 |
| David | 65 |
| Emma | 72 |
| Frank | 88 |
| Grace | 76 |
| Henry | 95 |
| Isabel | 81 |
| Jack | 70 |
| Kate | 60 |
| Liam | 89 |
| Mia | 75 |
| Noah | 84 |
| Olivia | 92 |
After arranging the scores in ascending order, bin ranges are set.
Step 2: Define Bins
Bins are like categories that group similar values. Think of them as buckets that organize your data. The presenter decides how wide each bin should be based on the range of the values. For instance, the instructor sets the bin ranges based on score intervals: 60-69, 70-79, 80-89, and 90-100.
Step 3: Count Frequency
Now, he counts how many data points fall into each bin. This step is crucial because it tells you how often specific ranges of values occur. The result is the frequency distribution, showing the occurrences of each group.
Here, the instructor counts the number of students in each category.
- 60-69: 1 student (Kate)
- 70-79: 4 students (David, Emma, Grace, Jack)
- 80-89: 7 students (Alice, Bob, Frank, Isabel, Liam, Mia, Noah)
- 90-100: 3 students (Clara, Henry, Olivia)
Step 4: Create the Histogram
It’s time to turn the data into a visual representation. Draw a bar for each bin on a graph. The width of the bar should correspond to the range of the bin, and the height should correspond to the frequency. To make your histogram understandable, label the X and Y axes.
In this case, the X-axis should represent the bins (e.g., test score ranges), and the Y-axis represents the frequency.

The histogram of the class grades reveals insightful patterns in the distribution. Most students, with seven students, fall within the 80-89 score range. The histogram provides a clear visualization of the class’s performance. It showcases a concentration of grades in the upper-middle range with few outliers at both ends. This analysis helps in understanding the overall academic standing of the class. It also identifies the areas for potential improvement or recognition.
Thus, histograms provide a clear visual representation of data distribution. They are easy to interpret, even for those without a statistical background. They apply to various types of data, including continuous and discrete variables. One weak point is that histograms do not capture detailed patterns in students’ data, with seven compared to other visualization methods.
A scatter plot is a graphical representation of the relationship between two variables. It consists of individual data points on a two-dimensional plane. This plane plots one variable on the x-axis and the other on the y-axis. Each point represents a unique observation. It visualizes patterns, trends, or correlations between the two variables.
Scatter plots are also effective in revealing the strength and direction of relationships. They identify outliers and assess the overall distribution of data points. The points’ dispersion and clustering reflect the relationship’s nature, whether it is positive, negative, or lacks a discernible pattern. In business, scatter plots assess relationships between variables such as marketing cost and sales revenue. They help present data correlations and decision-making.
Real-Life Application of Scatter Plot
A group of scientists is conducting a study on the relationship between daily hours of screen time and sleep quality. After reviewing the data, they managed to create this table to help them build a scatter plot graph:
| Participant ID | Daily Hours of Screen Time | Sleep Quality Rating |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 9 | 3 |
| 2 | 2 | 8 |
| 3 | 1 | 9 |
| 4 | 0 | 10 |
| 5 | 1 | 9 |
| 6 | 3 | 7 |
| 7 | 4 | 7 |
| 8 | 5 | 6 |
| 9 | 5 | 6 |
| 10 | 7 | 3 |
| 11 | 10 | 1 |
| 12 | 6 | 5 |
| 13 | 7 | 3 |
| 14 | 8 | 2 |
| 15 | 9 | 2 |
| 16 | 4 | 7 |
| 17 | 5 | 6 |
| 18 | 4 | 7 |
| 19 | 9 | 2 |
| 20 | 6 | 4 |
| 21 | 3 | 7 |
| 22 | 10 | 1 |
| 23 | 2 | 8 |
| 24 | 5 | 6 |
| 25 | 3 | 7 |
| 26 | 1 | 9 |
| 27 | 8 | 2 |
| 28 | 4 | 6 |
| 29 | 7 | 3 |
| 30 | 2 | 8 |
| 31 | 7 | 4 |
| 32 | 9 | 2 |
| 33 | 10 | 1 |
| 34 | 10 | 1 |
| 35 | 10 | 1 |
In the provided example, the x-axis represents Daily Hours of Screen Time, and the y-axis represents the Sleep Quality Rating.

The scientists observe a negative correlation between the amount of screen time and the quality of sleep. This is consistent with their hypothesis that blue light, especially before bedtime, has a significant impact on sleep quality and metabolic processes.
There are a few things to remember when using a scatter plot. Even when a scatter diagram indicates a relationship, it doesn’t mean one variable affects the other. A third factor can influence both variables. The more the plot resembles a straight line, the stronger the relationship is perceived [11] . If it suggests no ties, the observed pattern might be due to random fluctuations in data. When the scatter diagram depicts no correlation, whether the data might be stratified is worth considering.
Choosing the appropriate data presentation type is crucial when making a presentation . Understanding the nature of your data and the message you intend to convey will guide this selection process. For instance, when showcasing quantitative relationships, scatter plots become instrumental in revealing correlations between variables. If the focus is on emphasizing parts of a whole, pie charts offer a concise display of proportions. Histograms, on the other hand, prove valuable for illustrating distributions and frequency patterns.
Bar charts provide a clear visual comparison of different categories. Likewise, line charts excel in showcasing trends over time, while tables are ideal for detailed data examination. Starting a presentation on data presentation types involves evaluating the specific information you want to communicate and selecting the format that aligns with your message. This ensures clarity and resonance with your audience from the beginning of your presentation.
1. Fact Sheet Dashboard for Data Presentation

Convey all the data you need to present in this one-pager format, an ideal solution tailored for users looking for presentation aids. Global maps, donut chats, column graphs, and text neatly arranged in a clean layout presented in light and dark themes.
Use This Template
2. 3D Column Chart Infographic PPT Template

Represent column charts in a highly visual 3D format with this PPT template. A creative way to present data, this template is entirely editable, and we can craft either a one-page infographic or a series of slides explaining what we intend to disclose point by point.
3. Data Circles Infographic PowerPoint Template

An alternative to the pie chart and donut chart diagrams, this template features a series of curved shapes with bubble callouts as ways of presenting data. Expand the information for each arch in the text placeholder areas.
4. Colorful Metrics Dashboard for Data Presentation

This versatile dashboard template helps us in the presentation of the data by offering several graphs and methods to convert numbers into graphics. Implement it for e-commerce projects, financial projections, project development, and more.
5. Animated Data Presentation Tools for PowerPoint & Google Slides

A slide deck filled with most of the tools mentioned in this article, from bar charts, column charts, treemap graphs, pie charts, histogram, etc. Animated effects make each slide look dynamic when sharing data with stakeholders.
6. Statistics Waffle Charts PPT Template for Data Presentations

This PPT template helps us how to present data beyond the typical pie chart representation. It is widely used for demographics, so it’s a great fit for marketing teams, data science professionals, HR personnel, and more.
7. Data Presentation Dashboard Template for Google Slides

A compendium of tools in dashboard format featuring line graphs, bar charts, column charts, and neatly arranged placeholder text areas.
8. Weather Dashboard for Data Presentation

Share weather data for agricultural presentation topics, environmental studies, or any kind of presentation that requires a highly visual layout for weather forecasting on a single day. Two color themes are available.
9. Social Media Marketing Dashboard Data Presentation Template

Intended for marketing professionals, this dashboard template for data presentation is a tool for presenting data analytics from social media channels. Two slide layouts featuring line graphs and column charts.
10. Project Management Summary Dashboard Template

A tool crafted for project managers to deliver highly visual reports on a project’s completion, the profits it delivered for the company, and expenses/time required to execute it. 4 different color layouts are available.
11. Profit & Loss Dashboard for PowerPoint and Google Slides

A must-have for finance professionals. This typical profit & loss dashboard includes progress bars, donut charts, column charts, line graphs, and everything that’s required to deliver a comprehensive report about a company’s financial situation.
Overwhelming visuals
One of the mistakes related to using data-presenting methods is including too much data or using overly complex visualizations. They can confuse the audience and dilute the key message.
Inappropriate chart types
Choosing the wrong type of chart for the data at hand can lead to misinterpretation. For example, using a pie chart for data that doesn’t represent parts of a whole is not right.
Lack of context
Failing to provide context or sufficient labeling can make it challenging for the audience to understand the significance of the presented data.
Inconsistency in design
Using inconsistent design elements and color schemes across different visualizations can create confusion and visual disarray.
Failure to provide details
Simply presenting raw data without offering clear insights or takeaways can leave the audience without a meaningful conclusion.
Lack of focus
Not having a clear focus on the key message or main takeaway can result in a presentation that lacks a central theme.
Visual accessibility issues
Overlooking the visual accessibility of charts and graphs can exclude certain audience members who may have difficulty interpreting visual information.
In order to avoid these mistakes in data presentation, presenters can benefit from using presentation templates . These templates provide a structured framework. They ensure consistency, clarity, and an aesthetically pleasing design, enhancing data communication’s overall impact.
Understanding and choosing data presentation types are pivotal in effective communication. Each method serves a unique purpose, so selecting the appropriate one depends on the nature of the data and the message to be conveyed. The diverse array of presentation types offers versatility in visually representing information, from bar charts showing values to pie charts illustrating proportions.
Using the proper method enhances clarity, engages the audience, and ensures that data sets are not just presented but comprehensively understood. By appreciating the strengths and limitations of different presentation types, communicators can tailor their approach to convey information accurately, developing a deeper connection between data and audience understanding.
[1] Government of Canada, S.C. (2021) 5 Data Visualization 5.2 Bar Chart , 5.2 Bar chart . https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/edu/power-pouvoir/ch9/bargraph-diagrammeabarres/5214818-eng.htm
[2] Kosslyn, S.M., 1989. Understanding charts and graphs. Applied cognitive psychology, 3(3), pp.185-225. https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/pdfs/ADA183409.pdf
[3] Creating a Dashboard . https://it.tufts.edu/book/export/html/1870
[4] https://www.goldenwestcollege.edu/research/data-and-more/data-dashboards/index.html
[5] https://www.mit.edu/course/21/21.guide/grf-line.htm
[6] Jadeja, M. and Shah, K., 2015, January. Tree-Map: A Visualization Tool for Large Data. In GSB@ SIGIR (pp. 9-13). https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-1393/gsb15proceedings.pdf#page=15
[7] Heat Maps and Quilt Plots. https://www.publichealth.columbia.edu/research/population-health-methods/heat-maps-and-quilt-plots
[8] EIU QGIS WORKSHOP. https://www.eiu.edu/qgisworkshop/heatmaps.php
[9] About Pie Charts. https://www.mit.edu/~mbarker/formula1/f1help/11-ch-c8.htm
[10] Histograms. https://sites.utexas.edu/sos/guided/descriptive/numericaldd/descriptiven2/histogram/ [11] https://asq.org/quality-resources/scatter-diagram
Like this article? Please share
Data Analysis, Data Science, Data Visualization Filed under Design
Related Articles

Filed under Google Slides Tutorials • June 3rd, 2024
How To Make a Graph on Google Slides
Creating quality graphics is an essential aspect of designing data presentations. Learn how to make a graph in Google Slides with this guide.

Filed under Design • March 27th, 2024
How to Make a Presentation Graph
Detailed step-by-step instructions to master the art of how to make a presentation graph in PowerPoint and Google Slides. Check it out!

Filed under Presentation Ideas • February 12th, 2024
Turning Your Data into Eye-opening Stories
What is Data Storytelling is a question that people are constantly asking now. If you seek to understand how to create a data storytelling ppt that will complete the information for your audience, you should read this blog post.
Leave a Reply
Data presentation: A comprehensive guide
Learn how to create data presentation effectively and communicate your insights in a way that is clear, concise, and engaging.
Raja Bothra
Building presentations

Hey there, fellow data enthusiast!
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on data presentation.
Whether you're an experienced presenter or just starting, this guide will help you present your data like a pro. We'll dive deep into what data presentation is, why it's crucial, and how to master it. So, let's embark on this data-driven journey together.
What is data presentation?
Data presentation is the art of transforming raw data into a visual format that's easy to understand and interpret. It's like turning numbers and statistics into a captivating story that your audience can quickly grasp. When done right, data presentation can be a game-changer, enabling you to convey complex information effectively.
Why are data presentations important?
Imagine drowning in a sea of numbers and figures. That's how your audience might feel without proper data presentation. Here's why it's essential:
- Clarity : Data presentations make complex information clear and concise.
- Engagement : Visuals, such as charts and graphs, grab your audience's attention.
- Comprehension : Visual data is easier to understand than long, numerical reports.
- Decision-making : Well-presented data aids informed decision-making.
- Impact : It leaves a lasting impression on your audience.
Types of data presentation:
Now, let's delve into the diverse array of data presentation methods, each with its own unique strengths and applications. We have three primary types of data presentation, and within these categories, numerous specific visualization techniques can be employed to effectively convey your data.
1. Textual presentation
Textual presentation harnesses the power of words and sentences to elucidate and contextualize your data. This method is commonly used to provide a narrative framework for the data, offering explanations, insights, and the broader implications of your findings. It serves as a foundation for a deeper understanding of the data's significance.
2. Tabular presentation
Tabular presentation employs tables to arrange and structure your data systematically. These tables are invaluable for comparing various data groups or illustrating how data evolves over time. They present information in a neat and organized format, facilitating straightforward comparisons and reference points.
3. Graphical presentation
Graphical presentation harnesses the visual impact of charts and graphs to breathe life into your data. Charts and graphs are powerful tools for spotlighting trends, patterns, and relationships hidden within the data. Let's explore some common graphical presentation methods:
- Bar charts: They are ideal for comparing different categories of data. In this method, each category is represented by a distinct bar, and the height of the bar corresponds to the value it represents. Bar charts provide a clear and intuitive way to discern differences between categories.
- Pie charts: It excel at illustrating the relative proportions of different data categories. Each category is depicted as a slice of the pie, with the size of each slice corresponding to the percentage of the total value it represents. Pie charts are particularly effective for showcasing the distribution of data.
- Line graphs: They are the go-to choice when showcasing how data evolves over time. Each point on the line represents a specific value at a particular time period. This method enables viewers to track trends and fluctuations effortlessly, making it perfect for visualizing data with temporal dimensions.
- Scatter plots: They are the tool of choice when exploring the relationship between two variables. In this method, each point on the plot represents a pair of values for the two variables in question. Scatter plots help identify correlations, outliers, and patterns within data pairs.
The selection of the most suitable data presentation method hinges on the specific dataset and the presentation's objectives. For instance, when comparing sales figures of different products, a bar chart shines in its simplicity and clarity. On the other hand, if your aim is to display how a product's sales have changed over time, a line graph provides the ideal visual narrative.
Additionally, it's crucial to factor in your audience's level of familiarity with data presentations. For a technical audience, more intricate visualization methods may be appropriate. However, when presenting to a general audience, opting for straightforward and easily understandable visuals is often the wisest choice.
In the world of data presentation, choosing the right method is akin to selecting the perfect brush for a masterpiece. Each tool has its place, and understanding when and how to use them is key to crafting compelling and insightful presentations. So, consider your data carefully, align your purpose, and paint a vivid picture that resonates with your audience.
What to include in data presentation?
When creating your data presentation, remember these key components:
- Data points : Clearly state the data points you're presenting.
- Comparison : Highlight comparisons and trends in your data.
- Graphical methods : Choose the right chart or graph for your data.
- Infographics : Use visuals like infographics to make information more digestible.
- Numerical values : Include numerical values to support your visuals.
- Qualitative information : Explain the significance of the data.
- Source citation : Always cite your data sources.
How to structure an effective data presentation?
Creating a well-structured data presentation is not just important; it's the backbone of a successful presentation. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you craft a compelling and organized presentation that captivates your audience:
1. Know your audience
Understanding your audience is paramount. Consider their needs, interests, and existing knowledge about your topic. Tailor your presentation to their level of understanding, ensuring that it resonates with them on a personal level. Relevance is the key.
2. Have a clear message
Every effective data presentation should convey a clear and concise message. Determine what you want your audience to learn or take away from your presentation, and make sure your message is the guiding light throughout your presentation. Ensure that all your data points align with and support this central message.
3. Tell a compelling story
Human beings are naturally wired to remember stories. Incorporate storytelling techniques into your presentation to make your data more relatable and memorable. Your data can be the backbone of a captivating narrative, whether it's about a trend, a problem, or a solution. Take your audience on a journey through your data.
4. Leverage visuals
Visuals are a powerful tool in data presentation. They make complex information accessible and engaging. Utilize charts, graphs, and images to illustrate your points and enhance the visual appeal of your presentation. Visuals should not just be an accessory; they should be an integral part of your storytelling.
5. Be clear and concise
Avoid jargon or technical language that your audience may not comprehend. Use plain language and explain your data points clearly. Remember, clarity is king. Each piece of information should be easy for your audience to digest.
6. Practice your delivery
Practice makes perfect. Rehearse your presentation multiple times before the actual delivery. This will help you deliver it smoothly and confidently, reducing the chances of stumbling over your words or losing track of your message.
A basic structure for an effective data presentation
Armed with a comprehensive comprehension of how to construct a compelling data presentation, you can now utilize this fundamental template for guidance:
In the introduction, initiate your presentation by introducing both yourself and the topic at hand. Clearly articulate your main message or the fundamental concept you intend to communicate.
Moving on to the body of your presentation, organize your data in a coherent and easily understandable sequence. Employ visuals generously to elucidate your points and weave a narrative that enhances the overall story. Ensure that the arrangement of your data aligns with and reinforces your central message.
As you approach the conclusion, succinctly recapitulate your key points and emphasize your core message once more. Conclude by leaving your audience with a distinct and memorable takeaway, ensuring that your presentation has a lasting impact.
Additional tips for enhancing your data presentation
To take your data presentation to the next level, consider these additional tips:
- Consistent design : Maintain a uniform design throughout your presentation. This not only enhances visual appeal but also aids in seamless comprehension.
- High-quality visuals : Ensure that your visuals are of high quality, easy to read, and directly relevant to your topic.
- Concise text : Avoid overwhelming your slides with excessive text. Focus on the most critical points, using visuals to support and elaborate.
- Anticipate questions : Think ahead about the questions your audience might pose. Be prepared with well-thought-out answers to foster productive discussions.
By following these guidelines, you can structure an effective data presentation that not only informs but also engages and inspires your audience. Remember, a well-structured presentation is the bridge that connects your data to your audience's understanding and appreciation.
Do’s and don'ts on a data presentation
- Use visuals : Incorporate charts and graphs to enhance understanding.
- Keep it simple : Avoid clutter and complexity.
- Highlight key points : Emphasize crucial data.
- Engage the audience : Encourage questions and discussions.
- Practice : Rehearse your presentation.
Don'ts:
- Overload with data : Less is often more; don't overwhelm your audience.
- Fit Unrelated data : Stay on topic; don't include irrelevant information.
- Neglect the audience : Ensure your presentation suits your audience's level of expertise.
- Read word-for-word : Avoid reading directly from slides.
- Lose focus : Stick to your presentation's purpose.
Summarizing key takeaways
- Definition : Data presentation is the art of visualizing complex data for better understanding.
- Importance : Data presentations enhance clarity, engage the audience, aid decision-making, and leave a lasting impact.
- Types : Textual, Tabular, and Graphical presentations offer various ways to present data.
- Choosing methods : Select the right method based on data, audience, and purpose.
- Components : Include data points, comparisons, visuals, infographics, numerical values, and source citations.
- Structure : Know your audience, have a clear message, tell a compelling story, use visuals, be concise, and practice.
- Do's and don'ts : Do use visuals, keep it simple, highlight key points, engage the audience, and practice. Don't overload with data, include unrelated information, neglect the audience's expertise, read word-for-word, or lose focus.
FAQ's on a data presentation
1. what is data presentation, and why is it important in 2024.
Data presentation is the process of visually representing data sets to convey information effectively to an audience. In an era where the amount of data generated is vast, visually presenting data using methods such as diagrams, graphs, and charts has become crucial. By simplifying complex data sets, presentation of the data may helps your audience quickly grasp much information without drowning in a sea of chart's, analytics, facts and figures.
2. What are some common methods of data presentation?
There are various methods of data presentation, including graphs and charts, histograms, and cumulative frequency polygons. Each method has its strengths and is often used depending on the type of data you're using and the message you want to convey. For instance, if you want to show data over time, try using a line graph. If you're presenting geographical data, consider to use a heat map.
3. How can I ensure that my data presentation is clear and readable?
To ensure that your data presentation is clear and readable, pay attention to the design and labeling of your charts. Don't forget to label the axes appropriately, as they are critical for understanding the values they represent. Don't fit all the information in one slide or in a single paragraph. Presentation software like Prezent and PowerPoint can help you simplify your vertical axis, charts and tables, making them much easier to understand.
4. What are some common mistakes presenters make when presenting data?
One common mistake is trying to fit too much data into a single chart, which can distort the information and confuse the audience. Another mistake is not considering the needs of the audience. Remember that your audience won't have the same level of familiarity with the data as you do, so it's essential to present the data effectively and respond to questions during a Q&A session.
5. How can I use data visualization to present important data effectively on platforms like LinkedIn?
When presenting data on platforms like LinkedIn, consider using eye-catching visuals like bar graphs or charts. Use concise captions and e.g., examples to highlight the single most important information in your data report. Visuals, such as graphs and tables, can help you stand out in the sea of textual content, making your data presentation more engaging and shareable among your LinkedIn connections.
Create your data presentation with prezent
Prezent can be a valuable tool for creating data presentations. Here's how Prezent can help you in this regard:
- Time savings : Prezent saves up to 70% of presentation creation time, allowing you to focus on data analysis and insights.
- On-brand consistency : Ensure 100% brand alignment with Prezent's brand-approved designs for professional-looking data presentations.
- Effortless collaboration : Real-time sharing and collaboration features make it easy for teams to work together on data presentations.
- Data storytelling : Choose from 50+ storylines to effectively communicate data insights and engage your audience.
- Personalization : Create tailored data presentations that resonate with your audience's preferences, enhancing the impact of your data.
In summary, Prezent streamlines the process of creating data presentations by offering time-saving features, ensuring brand consistency, promoting collaboration, and providing tools for effective data storytelling. Whether you need to present data to clients, stakeholders, or within your organization, Prezent can significantly enhance your presentation-making process.
So, go ahead, present your data with confidence, and watch your audience be wowed by your expertise.
Thank you for joining us on this data-driven journey. Stay tuned for more insights, and remember, data presentation is your ticket to making numbers come alive! Sign up for our free trial or book a demo !
More zenpedia articles

How to craft an effective pitch deck presentation?

How remote teams can achieve their communication goals with effective strategies

100 interesting persuasive speech topics to amaze your audience
Get the latest from Prezent community
Join thousands of subscribers who receive our best practices on communication, storytelling, presentation design, and more. New tips weekly. (No spam, we promise!)
Call Us Today! +91 99907 48956 | [email protected]

It is the simplest form of data Presentation often used in schools or universities to provide a clearer picture to students, who are better able to capture the concepts effectively through a pictorial Presentation of simple data.
2. Column chart

It is a simplified version of the pictorial Presentation which involves the management of a larger amount of data being shared during the presentations and providing suitable clarity to the insights of the data.
3. Pie Charts

Pie charts provide a very descriptive & a 2D depiction of the data pertaining to comparisons or resemblance of data in two separate fields.
4. Bar charts

A bar chart that shows the accumulation of data with cuboid bars with different dimensions & lengths which are directly proportionate to the values they represent. The bars can be placed either vertically or horizontally depending on the data being represented.
5. Histograms
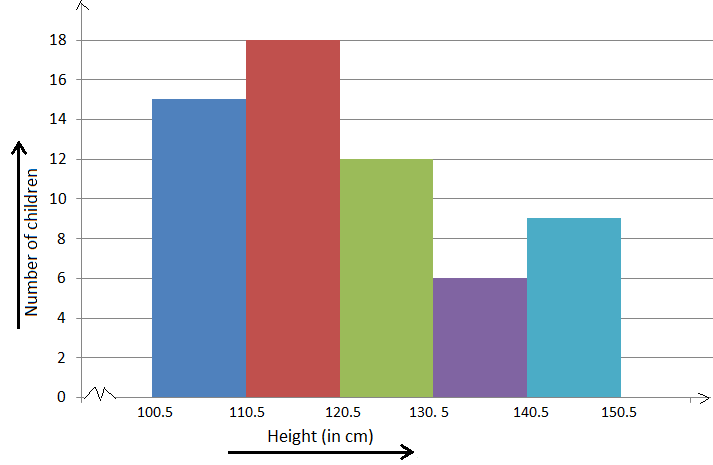
It is a perfect Presentation of the spread of numerical data. The main differentiation that separates data graphs and histograms are the gaps in the data graphs.
6. Box plots

Box plot or Box-plot is a way of representing groups of numerical data through quartiles. Data Presentation is easier with this style of graph dealing with the extraction of data to the minutes of difference.

Map Data graphs help you with data Presentation over an area to display the areas of concern. Map graphs are useful to make an exact depiction of data over a vast case scenario.
All these visual presentations share a common goal of creating meaningful insights and a platform to understand and manage the data in relation to the growth and expansion of one’s in-depth understanding of data & details to plan or execute future decisions or actions.
Importance of Data Presentation
Data Presentation could be both can be a deal maker or deal breaker based on the delivery of the content in the context of visual depiction.
Data Presentation tools are powerful communication tools that can simplify the data by making it easily understandable & readable at the same time while attracting & keeping the interest of its readers and effectively showcase large amounts of complex data in a simplified manner.
If the user can create an insightful presentation of the data in hand with the same sets of facts and figures, then the results promise to be impressive.
There have been situations where the user has had a great amount of data and vision for expansion but the presentation drowned his/her vision.
To impress the higher management and top brass of a firm, effective presentation of data is needed.
Data Presentation helps the clients or the audience to not spend time grasping the concept and the future alternatives of the business and to convince them to invest in the company & turn it profitable both for the investors & the company.
Although data presentation has a lot to offer, the following are some of the major reason behind the essence of an effective presentation:-
- Many consumers or higher authorities are interested in the interpretation of data, not the raw data itself. Therefore, after the analysis of the data, users should represent the data with a visual aspect for better understanding and knowledge.
- The user should not overwhelm the audience with a number of slides of the presentation and inject an ample amount of texts as pictures that will speak for themselves.
- Data presentation often happens in a nutshell with each department showcasing their achievements towards company growth through a graph or a histogram.
- Providing a brief description would help the user to attain attention in a small amount of time while informing the audience about the context of the presentation
- The inclusion of pictures, charts, graphs and tables in the presentation help for better understanding the potential outcomes.
- An effective presentation would allow the organization to determine the difference with the fellow organization and acknowledge its flaws. Comparison of data would assist them in decision making.
Recommended Courses

Data Visualization
Using powerbi &tableau.

Tableau for Data Analysis

MySQL Certification Program

The PowerBI Masterclass
Need help call our support team 7:00 am to 10:00 pm (ist) at (+91 999-074-8956 | 9650-308-956), keep in touch, email: [email protected].
WhatsApp us
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Present Your Data Like a Pro
- Joel Schwartzberg

Demystify the numbers. Your audience will thank you.
While a good presentation has data, data alone doesn’t guarantee a good presentation. It’s all about how that data is presented. The quickest way to confuse your audience is by sharing too many details at once. The only data points you should share are those that significantly support your point — and ideally, one point per chart. To avoid the debacle of sheepishly translating hard-to-see numbers and labels, rehearse your presentation with colleagues sitting as far away as the actual audience would. While you’ve been working with the same chart for weeks or months, your audience will be exposed to it for mere seconds. Give them the best chance of comprehending your data by using simple, clear, and complete language to identify X and Y axes, pie pieces, bars, and other diagrammatic elements. Try to avoid abbreviations that aren’t obvious, and don’t assume labeled components on one slide will be remembered on subsequent slides. Every valuable chart or pie graph has an “Aha!” zone — a number or range of data that reveals something crucial to your point. Make sure you visually highlight the “Aha!” zone, reinforcing the moment by explaining it to your audience.
With so many ways to spin and distort information these days, a presentation needs to do more than simply share great ideas — it needs to support those ideas with credible data. That’s true whether you’re an executive pitching new business clients, a vendor selling her services, or a CEO making a case for change.
- JS Joel Schwartzberg oversees executive communications for a major national nonprofit, is a professional presentation coach, and is the author of Get to the Point! Sharpen Your Message and Make Your Words Matter and The Language of Leadership: How to Engage and Inspire Your Team . You can find him on LinkedIn and X. TheJoelTruth
Partner Center
What is Data Visualization? Definition, Examples, Best Practices
This guide provides an introduction to data visualization, including real-world examples, best practices and editable templates.
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share through Email
- Print this page
- Bookmark this page
Resource Details
June 5, 2020
Data visualization is the visual presentation of data or information. The goal of data visualization is to communicate data or information clearly and effectively to readers. Typically, data is visualized in the form of a chart, infographic, diagram, or map.
The field of data visualization combines both art and data science. While data visualization can be creative and pleasing to look at, it should also be functional in its visual communication of the data.
This resource explains the fundamentals of data visualization, including examples of different types of data visualizations and when and how to use them to illustrate findings and insights.
Do you have feedback on this resource?
Thank you for your feedback as we strive to curate and publish resources to help social impact organizations succeed with data.
Send us a note
Explore More
Related Guides & Resources
Getting started with data visualization.
Visualizing data is one of the most effective ways of communicating data. This can take many forms from live digital data dashboards to static charts shared in social media channels.
Communicating Results: Design your Visualization
Let’s get visual: nonprofit data visualization.
What Is Data Visualization: Brief Theory, Useful Tips and Awesome Examples
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
By Al Boicheva
in Insights , Inspiration
3 years ago
Viewed 11,812 times
Spread the word about this article:
Updated: June 23, 2022
To create data visualization in order to present your data is no longer just a nice to have skill. Now, the skill to effectively sort and communicate your data through charts is a must-have for any business in any field that deals with data. Data visualization helps businesses quickly make sense of complex data and start making decisions based on that data. This is why today we’ll talk about what is data visualization. We’ll discuss how and why does it work, what type of charts to choose in what cases, how to create effective charts, and, of course, end with beautiful examples.
So let’s jump right in. As usual, don’t hesitate to fast-travel to a particular section of your interest.
Article overview: 1. What Does Data Visualization Mean? 2. How Does it Work? 3. When to Use it? 4. Why Use it? 5. Types of Data Visualization 6. Data Visualization VS Infographics: 5 Main Differences 7. How to Create Effective Data Visualization?: 5 Useful Tips 8. Examples of Data Visualization
1. What is Data Visualization?
Data Visualization is a graphic representation of data that aims to communicate numerous heavy data in an efficient way that is easier to grasp and understand . In a way, data visualization is the mapping between the original data and graphic elements that determine how the attributes of these elements vary. The visualization is usually made by the use of charts, lines, or points, bars, and maps.
- Data Viz is a branch of Descriptive statistics but it requires both design, computer, and statistical skills.
- Aesthetics and functionality go hand in hand to communicate complex statistics in an intuitive way.
- Data Viz tools and technologies are essential for making data-driven decisions.
- It’s a fine balance between form and functionality.
- Every STEM field benefits from understanding data.
2. How Does it Work?
If we can see it, our brains can internalize and reflect on it. This is why it’s much easier and more effective to make sense of a chart and see trends than to read a massive document that would take a lot of time and focus to rationalize. We wouldn’t want to repeat the cliche that humans are visual creatures, but it’s a fact that visualization is much more effective and comprehensive.
In a way, we can say that data Viz is a form of storytelling with the purpose to help us make decisions based on data. Such data might include:
- Tracking sales
- Identifying trends
- Identifying changes
- Monitoring goals
- Monitoring results
- Combining data
3. When to Use it?
Data visualization is useful for companies that deal with lots of data on a daily basis. It’s essential to have your data and trends instantly visible. Better than scrolling through colossal spreadsheets. When the trends stand out instantly this also helps your clients or viewers to understand them instead of getting lost in the clutter of numbers.
With that being said, Data Viz is suitable for:
- Annual reports
- Presentations
- Social media micronarratives
- Informational brochures
- Trend-trafficking
- Candlestick chart for financial analysis
- Determining routes
Common cases when data visualization sees use are in sales, marketing, healthcare, science, finances, politics, and logistics.
4. Why Use it?
Short answer: decision making. Data Visualization comes with the undeniable benefits of quickly recognizing patterns and interpret data. More specifically, it is an invaluable tool to determine the following cases.
- Identifying correlations between the relationship of variables.
- Getting market insights about audience behavior.
- Determining value vs risk metrics.
- Monitoring trends over time.
- Examining rates and potential through frequency.
- Ability to react to changes.
5. Types of Data Visualization
As you probably already guessed, Data Viz is much more than simple pie charts and graphs styled in a visually appealing way. The methods that this branch uses to visualize statistics include a series of effective types.
Map visualization is a great method to analyze and display geographically related information and present it accurately via maps. This intuitive way aims to distribute data by region. Since maps can be 2D or 3D, static or dynamic, there are numerous combinations one can use in order to create a Data Viz map.
COVID-19 Spending Data Visualization POGO by George Railean
The most common ones, however, are:
- Regional Maps: Classic maps that display countries, cities, or districts. They often represent data in different colors for different characteristics in each region.
- Line Maps: They usually contain space and time and are ideal for routing, especially for driving or taxi routes in the area due to their analysis of specific scenes.
- Point Maps: These maps distribute data of geographic information. They are ideal for businesses to pinpoint the exact locations of their buildings in a region.
- Heat Maps: They indicate the weight of a geographical area based on a specific property. For example, a heat map may distribute the saturation of infected people by area.
Charts present data in the form of graphs, diagrams, and tables. They are often confused with graphs since graphs are indeed a subcategory of charts. However, there is a small difference: graphs show the mathematical relationship between groups of data and is only one of the chart methods to represent data.
Infographic Data Visualization by Madeline VanRemmen
With that out of the way, let’s talk about the most basic types of charts in data visualization.
They use a series of bars that illustrate data development. They are ideal for lighter data and follow trends of no more than three variables or else, the bars become cluttered and hard to comprehend. Ideal for year-on-year comparisons and monthly breakdowns.
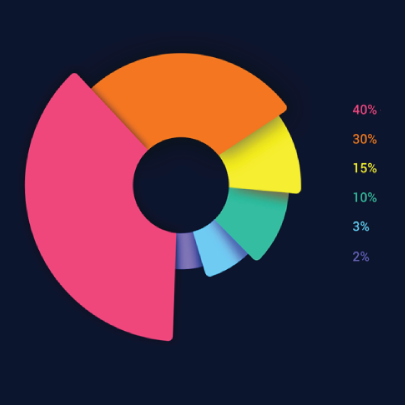
These familiar circular graphs divide data into portions. The bigger the slice, the bigger the portion. They are ideal for depicting sections of a whole and their sum must always be 100%. Avoid pie charts when you need to show data development over time or lack a value for any of the portions. Doughnut charts have the same use as pie charts.
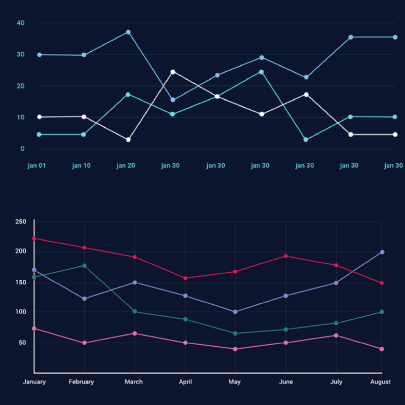
They use a line or more than one lines that show development over time. It allows tracking multiple variables at the same time. A great example is tracking product sales by a brand over the years. Area charts have the same use as line charts.
Scatter Plot
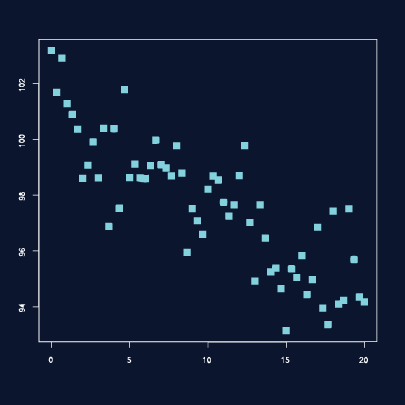
These charts allow you to see patterns through data visualization. They have an x-axis and a y-axis for two different values. For example, if your x-axis contains information about car prices while the y-axis is about salaries, the positive or negative relationship will tell you about what a person’s car tells about their salary.
Unlike the charts we just discussed, tables show data in almost a raw format. They are ideal when your data is hard to present visually and aim to show specific numerical data that one is supposed to read rather than visualize.
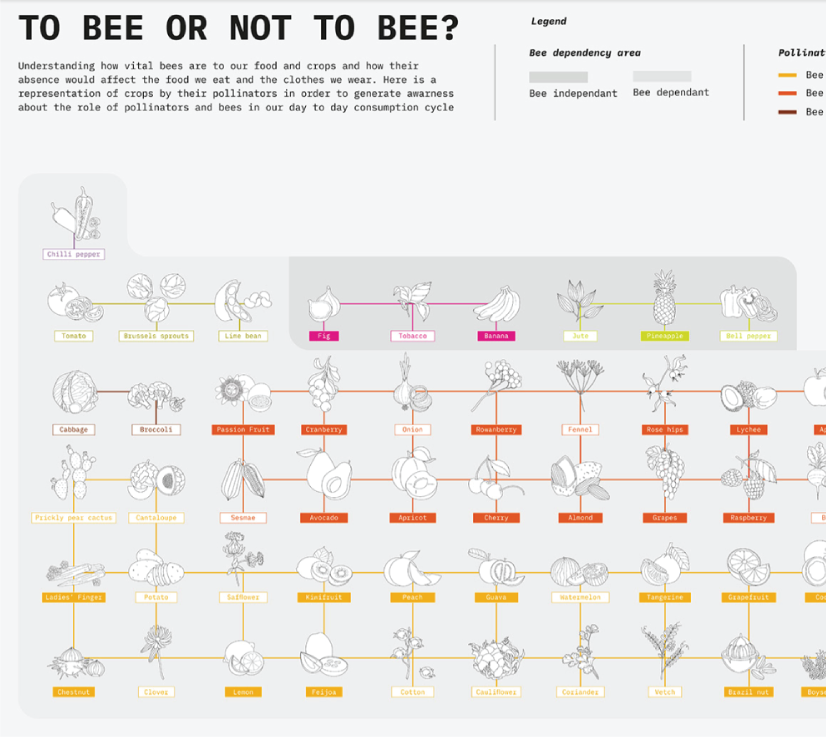
Data Visualisation | To bee or not to bee by Aishwarya Anand Singh
For example, charts are perfect to display data about a particular illness over a time period in a particular area, but a table comes to better use when you also need to understand specifics such as causes, outcomes, relapses, a period of treatment, and so on.
6. Data Visualization VS Infographics
5 main differences.
They are not that different as both visually represent data. It is often you search for infographics and find images titled Data Visualization and the other way around. In many cases, however, these titles aren’t misleading. Why is that?
- Data visualization is made of just one element. It could be a map, a chart, or a table. Infographics , on the other hand, often include multiple Data Viz elements.
- Unlike data visualizations that can be simple or extremely complex and heavy, infographics are simple and target wider audiences. The latter is usually comprehensible even to people outside of the field of research the infographic represents.
- Interestingly enough, data Viz doesn’t offer narratives and conclusions, it’s a tool and basis for reaching those. While infographics, in most cases offer a story and a narrative. For example, a data visualization map may have the title “Air pollution saturation by region”, while an infographic with the same data would go “Areas A and B are the most polluted in Country C”.
- Data visualizations can be made in Excel or use other tools that automatically generate the design unless they are set for presentation or publishing. The aesthetics of infographics , however, are of great importance and the designs must be appealing to wider audiences.
- In terms of interaction, data visualizations often offer interactive charts, especially in an online form. Infographics, on the other hand, rarely have interaction and are usually static images.
While on topic, you could also be interested to check out these 50 engaging infographic examples that make complex data look great.
7. Tips to Create Effective Data Visualization
The process is naturally similar to creating Infographics and it revolves around understanding your data and audience. To be more precise, these are the main steps and best practices when it comes to preparing an effective visualization of data for your viewers to instantly understand.
1. Do Your Homework
Preparation is half the work already done. Before you even start visualizing data, you have to be sure you understand that data to the last detail.
Knowing your audience is undeniable another important part of the homework, as different audiences process information differently. Who are the people you’re visualizing data for? How do they process visual data? Is it enough to hand them a single pie chart or you’ll need a more in-depth visual report?
The third part of preparing is to determine exactly what you want to communicate to the audience. What kind of information you’re visualizing and does it reflect your goal?
And last, think about how much data you’ll be working with and take it into account.
2. Choose the Right Type of Chart
In a previous section, we listed the basic chart types that find use in data visualization. To determine best which one suits your work, there are a few things to consider.
- How many variables will you have in a chart?
- How many items will you place for each of your variables?
- What will be the relation between the values (time period, comparison, distributions, etc.)
With that being said, a pie chart would be ideal if you need to present what portions of a whole takes each item. For example, you can use it to showcase what percent of the market share takes a particular product. Pie charts, however, are unsuitable for distributions, comparisons, and following trends through time periods. Bar graphs, scatter plots,s and line graphs are much more effective in those cases.
Another example is how to use time in your charts. It’s way more accurate to use a horizontal axis because time should run left to right. It’s way more visually intuitive.
3. Sort your Data
Start with removing every piece of data that does not add value and is basically excess for the chart. Sometimes, you have to work with a huge amount of data which will inevitably make your chart pretty complex and hard to read. Don’t hesitate to split your information into two or more charts. If that won’t work for you, you could use highlights or change the entire type of chart with something that would fit better.
Tip: When you use bar charts and columns for comparison, sort the information in an ascending or a descending way by value instead of alphabetical order.
4. Use Colors to Your Advantage
In every form of visualization, colors are your best friend and the most powerful tool. They create contrasts, accents, and emphasis and lead the eye intuitively. Even here, color theory is important.
When you design your chart, make sure you don’t use more than 5 or 6 colors. Anything more than that will make your graph overwhelming and hard to read for your viewers. However, color intensity is a different thing that you can use to your advantage. For example, when you compare the same concept in different periods of time, you could sort your data from the lightest shade of your chosen color to its darker one. It creates a strong visual progression, proper to your timeline.
Things to consider when you choose colors:
- Different colors for different categories.
- A consistent color palette for all charts in a series that you will later compare.
- It’s appropriate to use color blind-friendly palettes.
5. Get Inspired
Always put your inspiration to work when you want to be at the top of your game. Look through examples, infographics, and other people’s work and see what works best for each type of data you need to implement.
This Twitter account Data Visualization Society is a great way to start. In the meantime, we’ll also handpick some amazing examples that will get you in the mood to start creating the visuals for your data.
8. Examples for Data Visualization
As another art form, Data Viz is a fertile ground for some amazing well-designed graphs that prove that data is beautiful. Now let’s check out some.
Dark Souls III Experience Data
We start with Meng Hsiao Wei’s personal project presenting his experience with playing Dark Souls 3. It’s a perfect example that infographics and data visualization are tools for personal designs as well. The research is pretty massive yet very professionally sorted into different types of charts for the different concepts. All data visualizations are made with the same color palette and look great in infographics.
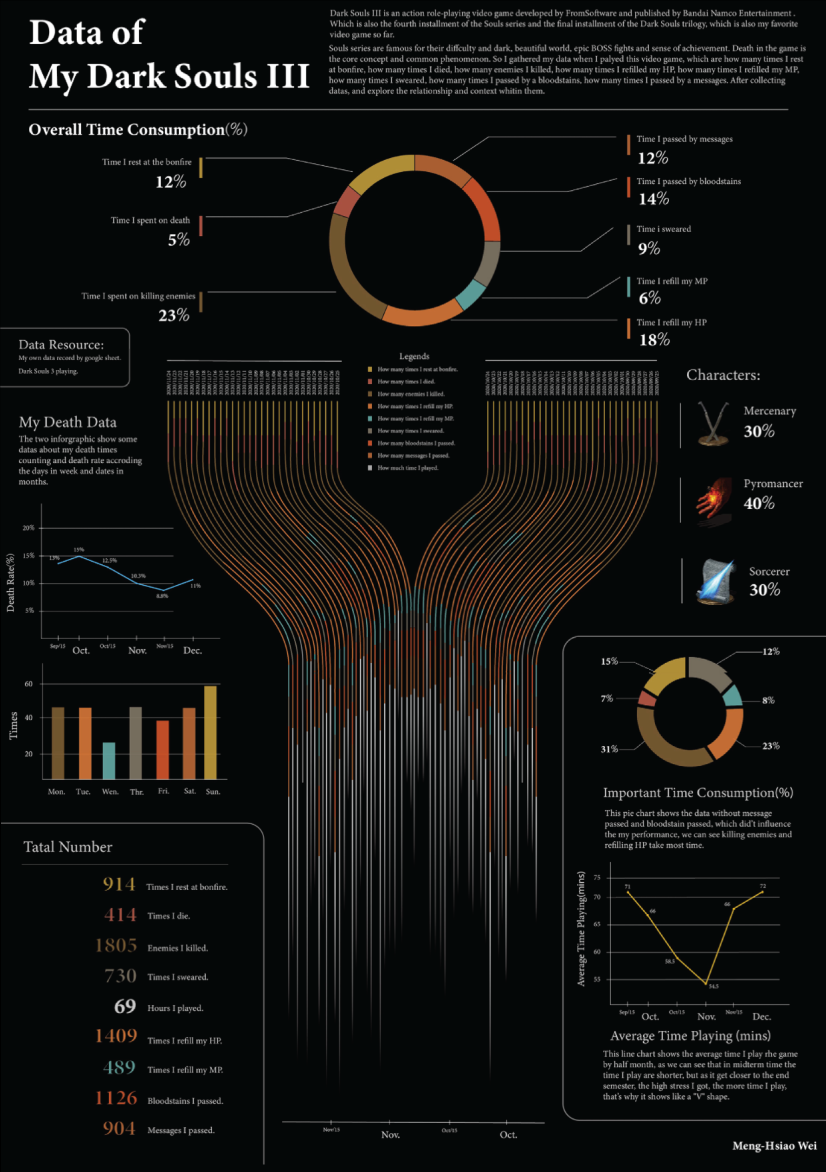
My dark souls 3 playing data by Meng Hsiao Wei
Greatest Movies of all Time
Katie Silver has compiled a list of the 100 greatest movies of all time based on critics and crowd reviews. The visualization shows key data points for every movie such as year of release, oscar nominations and wins, budget, gross, IMDB score, genre, filming location, setting of the film, and production studio. All movies are ordered by the release date.
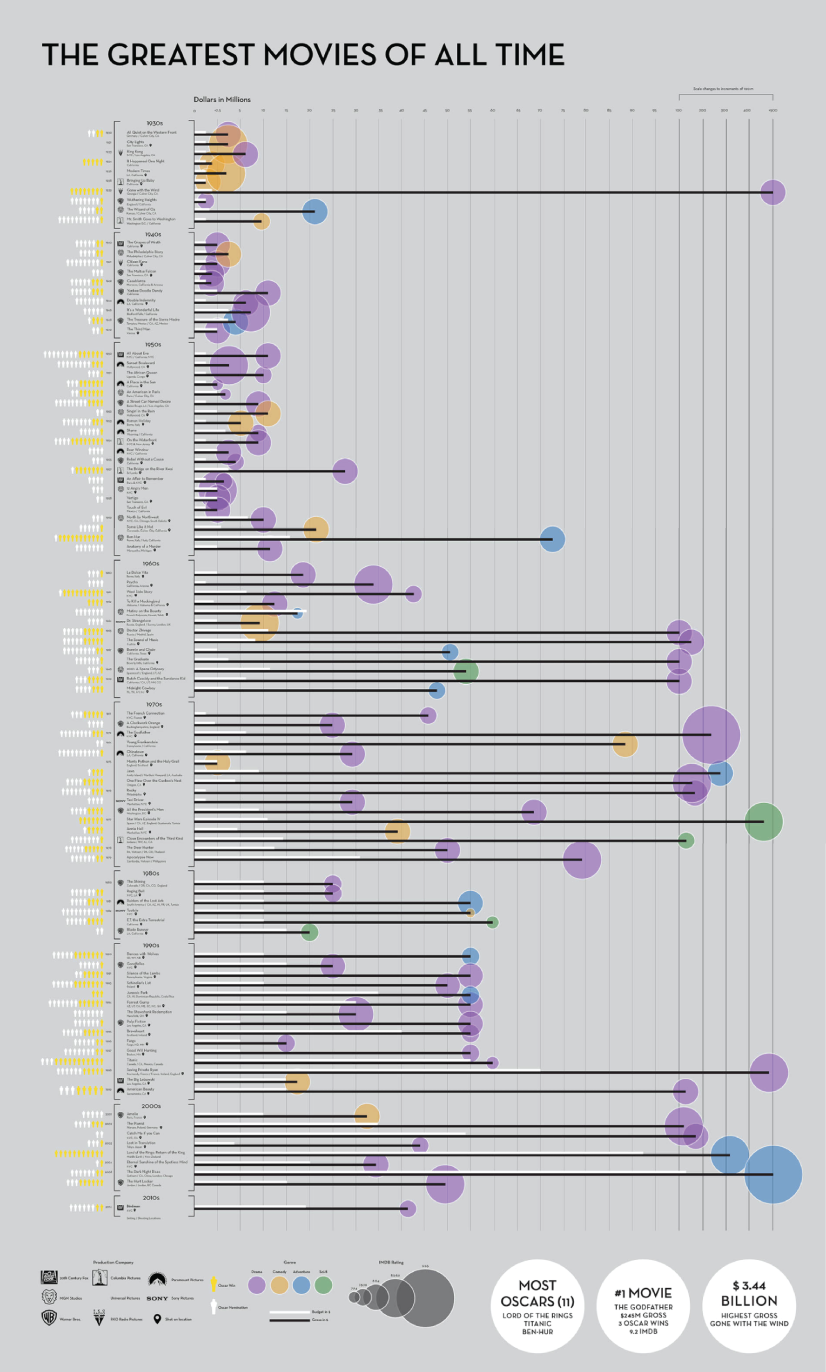
100 Greatest Movies Data Visualization by Katie Silver
The Most Violent Cities
Federica Fragapane shows data for the 50 most violent cities in the world in 2017. The items are arranged on a vertical axis based on population and ordered along the horizontal axis according to the homicide rate.
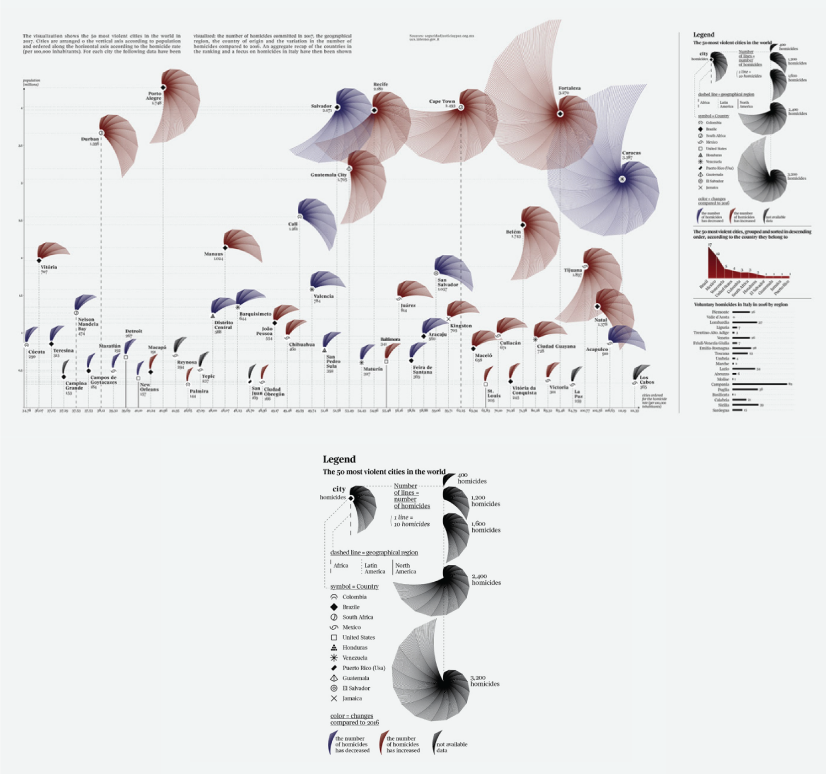
The Most Violent Cities by Federica Fragapane
Family Businesses as Data
These data visualizations and illustrations were made by Valerio Pellegrini for Perspectives Magazine. They show a pie chart with sector breakdown as well as a scatter plot for contribution for employment.
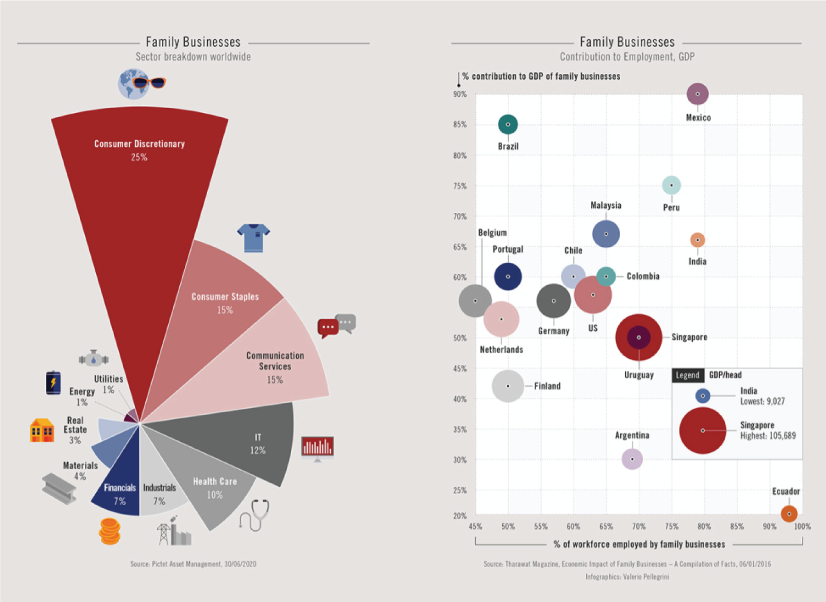
PERSPECTIVES MAGAZINE – Family Businesses by Valerio Pellegrini
Orbit Map of the Solar System
The map shows data on the orbits of more than 18000 asteroids in the solar system. Each asteroid is shown at its position on New Years’ Eve 1999, colored by type of asteroid.
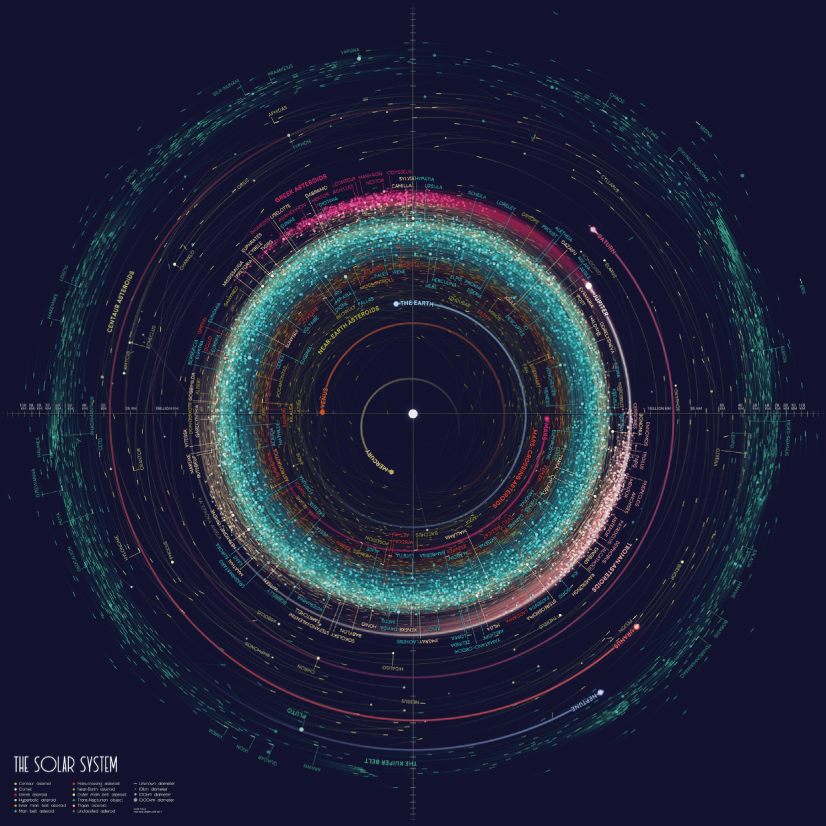
An Orbit Map of the Solar System by Eleanor Lutz
The Semantics Of Headlines
Katja Flükiger has a take on how headlines tell the story. The data visualization aims to communicate how much is the selling influencing the telling. The project was completed at Maryland Institute College of Art to visualize references to immigration and color-coding the value judgments implied by word choice and context.
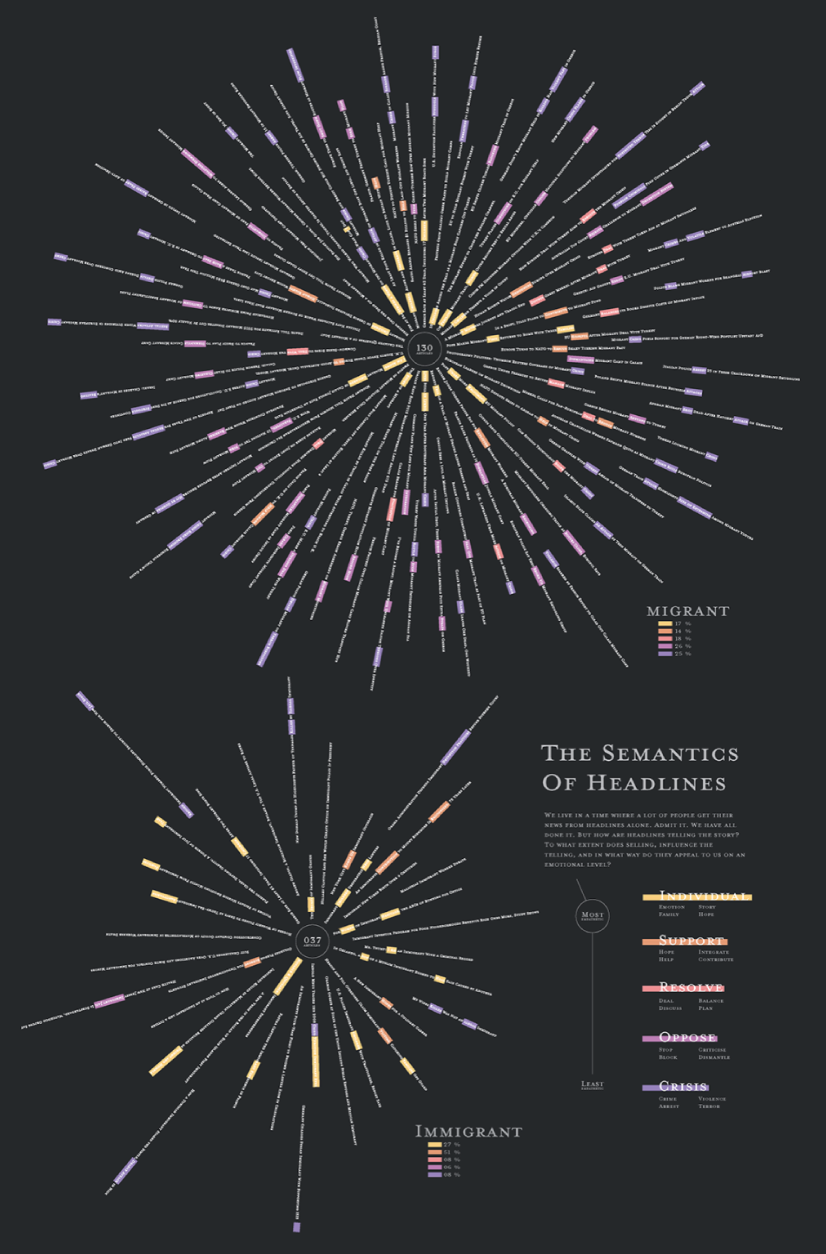
The Semantics of Headlines by Katja Flükiger
Moon and Earthquakes
This data visualization works on answering whether the moon is responsible for earthquakes. The chart features the time and intensity of earthquakes in response to the phase and orbit location of the moon.

Moon and Earthquakes by Aishwarya Anand Singh
Dawn of the Nanosats
The visualization shows the satellites launched from 2003 to 2015. The graph represents the type of institutions focused on projects as well as the nations that financed them. On the left, it is shown the number of launches per year and satellite applications.
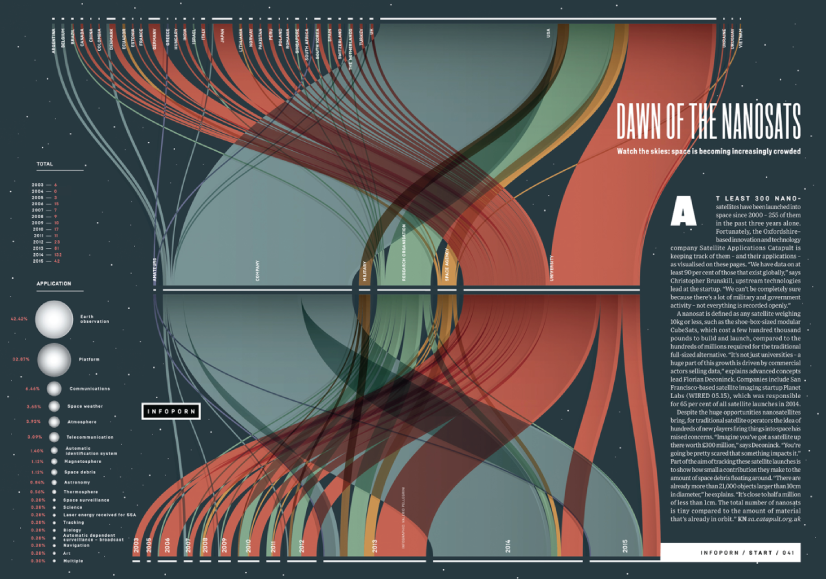
WIRED UK – Dawn of the by Nanosats by Valerio Pellegrini
Final Words
Data visualization is not only a form of science but also a form of art. Its purpose is to help businesses in any field quickly make sense of complex data and start making decisions based on that data. To make your graphs efficient and easy to read, it’s all about knowing your data and audience. This way you’ll be able to choose the right type of chart and use visual techniques to your advantage.
You may also be interested in some of these related articles:
- Infographics for Marketing: How to Grab and Hold the Attention
- 12 Animated Infographics That Will Engage Your Mind from Start to Finish
- 50 Engaging Infographic Examples That Make Complex Ideas Look Great
- Good Color Combinations That Go Beyond Trends: Inspirational Examples and Ideas

Add some character to your visuals
Cartoon Characters, Design Bundles, Illustrations, Backgrounds and more...
Like us on Facebook
Subscribe to our newsletter
Be the first to know what’s new in the world of graphic design and illustrations.
- [email protected]
Browse High Quality Vector Graphics
E.g.: businessman, lion, girl…
Related Articles
Animation trends 2022: experimental and open-minded, can you become a graphic designer without a design degree in 2022, top 7 infographic creator tools to try now (no design skills required), looking for stock illustrations – guide to all free and premium sources, cartoon yourself today with 10+ tools, tutorials & tips, check out our infographics bundle with 500+ infographic templates:, enjoyed this article.
Don’t forget to share!
- Comments (2)

Al Boicheva
Al is an illustrator at GraphicMama with out-of-the-box thinking and a passion for anything creative. In her free time, you will see her drooling over tattoo art, Manga, and horror movies.

Thousands of vector graphics for your projects.
Hey! You made it all the way to the bottom!
Here are some other articles we think you may like:

Inspiration
40+ great flat design examples with outline retro 70s vibes.
by Lyudmil Enchev

8 Key Presentation Ideas to Steal The Audience
by Al Boicheva

How to Create Flyer Design: Tutorials & Ideas for Non-Professionals
by Iveta Pavlova
Looking for Design Bundles or Cartoon Characters?
A source of high-quality vector graphics offering a huge variety of premade character designs, graphic design bundles, Adobe Character Animator puppets, and more.
A Guide to Effective Data Presentation
Key objectives of data presentation, charts and graphs for great visuals, storytelling with data, visuals, and text, audiences and data presentation, the main idea in data presentation, storyboarding and data presentation, additional resources, data presentation.
Tools for effective data presentation
Financial analysts are required to present their findings in a neat, clear, and straightforward manner. They spend most of their time working with spreadsheets in MS Excel, building financial models , and crunching numbers. These models and calculations can be pretty extensive and complex and may only be understood by the analyst who created them. Effective data presentation skills are critical for being a world-class financial analyst .

It is the analyst’s job to effectively communicate the output to the target audience, such as the management team or a company’s external investors. This requires focusing on the main points, facts, insights, and recommendations that will prompt the necessary action from the audience.
One challenge is making intricate and elaborate work easy to comprehend through great visuals and dashboards. For example, tables, graphs, and charts are tools that an analyst can use to their advantage to give deeper meaning to a company’s financial information. These tools organize relevant numbers that are rather dull and give life and story to them.
Here are some key objectives to think about when presenting financial analysis:
- Visual communication
- Audience and context
- Charts, graphs, and images
- Focus on important points
- Design principles
- Storytelling
- Persuasiveness
For a breakdown of these objectives, check out Excel Dashboards & Data Visualization course to help you become a world-class financial analyst.
Charts and graphs make any financial analysis readable, easy to follow, and provide great data presentation. They are often included in the financial model’s output, which is essential for the key decision-makers in a company.
The decision-makers comprise executives and managers who usually won’t have enough time to synthesize and interpret data on their own to make sound business decisions. Therefore, it is the job of the analyst to enhance the decision-making process and help guide the executives and managers to create value for the company.
When an analyst uses charts, it is necessary to be aware of what good charts and bad charts look like and how to avoid the latter when telling a story with data.
Examples of Good Charts
As for great visuals, you can quickly see what’s going on with the data presentation, saving you time for deciphering their actual meaning. More importantly, great visuals facilitate business decision-making because their goal is to provide persuasive, clear, and unambiguous numeric communication.
For reference, take a look at the example below that shows a dashboard, which includes a gauge chart for growth rates, a bar chart for the number of orders, an area chart for company revenues, and a line chart for EBITDA margins.
To learn the step-by-step process of creating these essential tools in MS Excel, watch our video course titled “ Excel Dashboard & Data Visualization .” Aside from what is given in the example below, our course will also teach how you can use other tables and charts to make your financial analysis stand out professionally.
Learn how to build the graph above in our Dashboards Course !
Example of Poorly Crafted Charts
A bad chart, as seen below, will give the reader a difficult time to find the main takeaway of a report or presentation, because it contains too many colors, labels, and legends, and thus, will often look too busy. It also doesn’t help much if a chart, such as a pie chart, is displayed in 3D, as it skews the size and perceived value of the underlying data. A bad chart will be hard to follow and understand.
Aside from understanding the meaning of the numbers, a financial analyst must learn to combine numbers and language to craft an effective story. Relying only on data for a presentation may leave your audience finding it difficult to read, interpret, and analyze your data. You must do the work for them, and a good story will be easier to follow. It will help you arrive at the main points faster, rather than just solely presenting your report or live presentation with numbers.
The data can be in the form of revenues, expenses, profits, and cash flow. Simply adding notes, comments, and opinions to each line item will add an extra layer of insight, angle, and a new perspective to the report.
Furthermore, by combining data, visuals, and text, your audience will get a clear understanding of the current situation, past events, and possible conclusions and recommendations that can be made for the future.
The simple diagram below shows the different categories of your audience.
This chart is taken from our course on how to present data .
Internal Audience
An internal audience can either be the executives of the company or any employee who works in that company. For executives, the purpose of communicating a data-filled presentation is to give an update about a certain business activity such as a project or an initiative.
Another important purpose is to facilitate decision-making on managing the company’s operations, growing its core business, acquiring new markets and customers, investing in R&D, and other considerations. Knowing the relevant data and information beforehand will guide the decision-makers in making the right choices that will best position the company toward more success.
External Audience
An external audience can either be the company’s existing clients, where there are projects in progress, or new clients that the company wants to build a relationship with and win new business from. The other external audience is the general public, such as the company’s external shareholders and prospective investors of the company.
When it comes to winning new business, the analyst’s presentation will be more promotional and sales-oriented, whereas a project update will contain more specific information for the client, usually with lots of industry jargon.
Audiences for Live and Emailed Presentation
A live presentation contains more visuals and storytelling to connect more with the audience. It must be more precise and should get to the point faster and avoid long-winded speech or text because of limited time.
In contrast, an emailed presentation is expected to be read, so it will include more text. Just like a document or a book, it will include more detailed information, because its context will not be explained with a voice-over as in a live presentation.
When it comes to details, acronyms, and jargon in the presentation, these things depend on whether your audience are experts or not.
Every great presentation requires a clear “main idea”. It is the core purpose of the presentation and should be addressed clearly. Its significance should be highlighted and should cause the targeted audience to take some action on the matter.
An example of a serious and profound idea is given below.

To communicate this big idea, we have to come up with appropriate and effective visual displays to show both the good and bad things surrounding the idea. It should put emphasis and attention on the most important part, which is the critical cash balance and capital investment situation for next year. This is an important component of data presentation.
The storyboarding below is how an analyst would build the presentation based on the big idea. Once the issue or the main idea has been introduced, it will be followed by a demonstration of the positive aspects of the company’s performance, as well as the negative aspects, which are more important and will likely require more attention.
Various ideas will then be suggested to solve the negative issues. However, before choosing the best option, a comparison of the different outcomes of the suggested ideas will be performed. Finally, a recommendation will be made that centers around the optimal choice to address the imminent problem highlighted in the big idea.
This storyboard is taken from our course on how to present data .
To get to the final point (recommendation), a great deal of analysis has been performed, which includes the charts and graphs discussed earlier, to make the whole presentation easy to follow, convincing, and compelling for your audience.
CFI offers the Business Intelligence & Data Analyst (BIDA)® certification program for those looking to take their careers to the next level. To keep learning and developing your knowledge base, please explore the additional relevant resources below:
- Investment Banking Pitch Books
- Excel Dashboards
- Financial Modeling Guide
- Startup Pitch Book
- See all business intelligence resources
- Share this article

Create a free account to unlock this Template
Access and download collection of free Templates to help power your productivity and performance.
Already have an account? Log in
Supercharge your skills with Premium Templates
Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates.
Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs.
Already have a Self-Study or Full-Immersion membership? Log in
Access Exclusive Templates
Gain unlimited access to more than 250 productivity Templates, CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs, hundreds of resources, expert reviews and support, the chance to work with real-world finance and research tools, and more.
Already have a Full-Immersion membership? Log in
- Data Science
Caltech Bootcamp / Blog / /
What is Data Visualization, and What is its Role in Data Science?
- Written by Karin Kelley
- Updated on July 29, 2024

How do you transform endless rows of data into a story that can drive decisions and inspire action? Data visualization is the answer. In our data-driven world, converting complex data sets into intuitive, visual formats is essential for uncovering insights and making informed decisions.
This blog answers the high-level question: “What is data visualization?” and discusses its importance, various categories, techniques, and practical applications. We’ll explore how visualizing data can turn raw numbers into powerful narratives that inform, engage, and persuade. Those looking to master this skill and advance their data science career should consider enrolling in a comprehensive data science bootcamp .
So, What is Data Visualization?
Data visualization is the graphical representation of information and data. Using visual elements like charts, graphs, and maps, data visualization tools provide an accessible way to see and understand trends, outliers, and patterns in data. This visual context helps users understand the data’s insights and make data-driven decisions more effectively. It’s a powerful tool for exploratory data analysis and conveying findings to others.
Data visualization involves transforming raw data into visual formats that reveal patterns, trends, and correlations. This transformation process can range from simple static charts to highly interactive and complex visualizations. The goal is to make the data more understandable, insightful, and actionable. Effective data visualization leverages visual perception principles to present data in a way that is both aesthetically pleasing and informative.
It is not just about creating pretty pictures but about creating meaningful representations that can tell a story or answer a question. This process involves understanding the audience, selecting the appropriate visualization techniques, and presenting the data in a way that aligns with the intended message. For instance, a bar chart might be used to compare sales figures across different regions, while a line chart could illustrate trends in stock prices over time.
Also Read: Technology at Work: Data Science in Finance
Why is Data Visualization Important?
Data visualization is essential because it transforms complex data into clear and actionable insights. Converting raw numbers into visual formats allows for quick comprehension and informed decision-making.
Here are some key reasons why data visualization is so crucial.
- Unlocking the narrative: Data visualization helps uncover the story hidden within data, allowing decision-makers to grasp complex concepts and identify new patterns.
- Effective communication: It plays a vital role in presenting data findings clearly and concisely, ensuring that the message is easily understood.
- Handling big data : Visualization tools enable data scientists and analysts to interpret large data sets quickly and efficiently, driving better business strategies and operations.
- Immediate understanding: Humans are inherently visual creatures, and our brains process visual information more effectively than text or numbers alone. Visual representations allow us to quickly identify trends, spot outliers, and understand relationships within the data.
- Essential for quick decision-making: This immediate comprehension is particularly valuable in fast-paced environments where quick decision-making is crucial.
- Broadening audience reach : Data visualization makes complex data accessible and understandable to a broader audience, including business executives, policymakers, and laypersons.
- Democratizing data: By making data more accessible, visualization empowers more people to engage with and make informed decisions based on data.
What is Data Visualization? Big Data Visualization Categories
Big data visualization involves handling vast and complex data sets, often requiring advanced tools and techniques. It can be categorized into three main types:
Interactive Visualization
This allows users to engage with the data dynamically. Interactive dashboards and reports enable users to manipulate data and uncover insights through various filters and controls. Tools like Tableau and Power BI are commonly used to create interactive visualizations that allow users to drill down into data, explore different perspectives, and gain deeper insights.
Real-time Visualization
This involves visualizing data as it is collected. It’s particularly useful for monitoring live data streams, such as social media feeds, sensor data, or financial market movements. Real-time visualization tools can provide up-to-the-minute insights, enabling quick responses to changing conditions. For example, financial traders use real-time visualization to monitor market movements and make timely investment decisions.
3D Visualization
3D visualization can provide additional depth and clarity for particularly complex data sets. It’s often used in medical imaging, geospatial analysis, and engineering. 3D visualizations can help to understand complex structures and relationships that might be difficult to interpret in two dimensions. For example, 3D visualizations of MRI or CT scans in medical imaging can help doctors diagnose and plan treatments more effectively.
Also Read: The Top Data Science Interview Questions for 2024
Top Data Visualization Techniques
Numerous techniques are available for data visualization, each serving different purposes and data types. Here are some of the top ones.
Bar Charts and Column Charts
These compare different categories or track changes over time. They are simple yet effective for presenting categorical data. Bar charts can be used to compare sales figures across various regions, while column charts can show the change in sales over different quarters.
Line Charts
Line charts connect individual data points to show continuous data, which is ideal for showing trends over time. They are often used to illustrate trends in stock prices, website traffic, or temperature changes over time. Line charts can help to identify patterns and predict future trends.
Pie Charts and Donut Charts
These charts show the proportions of a whole. While popular, they should be used carefully as they can sometimes be misleading. Pie charts are best used for showing simple proportions, such as the market share of different companies. Donut charts are similar but have a central hole, making them visually distinct.
These visualize data through color variations. They effectively show data density and variations across different categories or geographical areas. Heat maps are often used in fields like marketing to show customer activity across various regions or in scientific research to show gene expression levels.
Scatter Plots
These display values for typically two variables for a data set, showing how much one variable is affected by another. Scatter plots help identify correlations and relationships between variables. For example, a scatter plot might show the relationship between advertising spend and sales revenue.
Bubble Charts
Similar to scatter plots, but with an added data dimension represented by the bubble size. Bubble charts can show the relationship between three variables, with the size of the bubble representing the third variable. They are often used in business to show the performance of different products or regions.
Geospatial Maps
Geospatial maps visualize data related to geographical locations and are useful in fields like meteorology, urban planning, and logistics. They can show the distribution of phenomena across different regions, such as the spread of diseases, population density, or delivery routes.
Also Read: Big Data and Analytics: Unlocking the Future
What is Data Visualization? Use Cases and Applications
Data visualization is used across various industries and applications, enhancing the ability to understand and utilize data effectively:
Business Intelligence
Companies use data visualization for performance tracking, market analysis, and strategic planning. Tableau and Power BI are popular for creating interactive dashboards and reports. These tools enable businesses to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs), track sales performance, and analyze real-time market trends. For example, a retail company might use a dashboard to monitor daily sales figures, inventory levels, and customer feedback.
Visualization helps understand patient data, track disease outbreaks, and optimize healthcare operations. For example, heat maps can show the spread of diseases geographically, allowing public health officials to allocate resources effectively. In hospitals, data visualization can be used to monitor patient vitals, track the progress of treatments, and identify potential complications early.
In finance, visualization aids in tracking stock market trends, risk management, and portfolio analysis. Real-time visualization tools are crucial for making timely investment decisions. For example, traders use real-time charts to monitor stock prices, identify trends, and execute trades. Risk managers use visualizations to assess portfolios’ risk exposure and develop mitigation strategies.
Marketers use visualization to analyze consumer behavior, campaign performance, and market trends. Interactive dashboards can show the impact of marketing efforts in real time. For example, a marketing team might use a dashboard to track the performance of different campaigns, analyze customer engagement, and optimize marketing strategies based on data insights.
Data visualization improves teaching methods, tracks student performance, and research trends. Educational institutions use visual tools to analyze and present data on student outcomes. For example, schools use dashboards to monitor student attendance, track academic performance, and identify students who need additional support. Researchers use data visualization to analyze education trends and develop evidence-based policies.
Scientific Research
Scientists use data visualization to interpret complex data sets from experiments and simulations. 3D visualizations can provide in-depth insights into scientific phenomena. For example, climate scientists use visualizations to analyze data from climate models, track changes in temperature and precipitation patterns, and predict future climate scenarios. Biologists use visualizations to analyze gene expression data and understand diseases’ underlying mechanisms.

Government and Public Policy
Governments use data visualization to analyze population data, economic indicators, and public health information. This aids in policy-making and public communication. For example, governments use visualizations to track the spread of COVID-19, monitor economic performance, and allocate resources. Policymakers use data visualization to analyze different policies’ impact and communicate findings to the public.
Also Read: Five Outstanding Data Visualization Examples for Marketing
Building Data Science and Data Visualization Skills
Data visualization is more than just a way to present data; it’s a crucial tool for making sense of complex information and driving informed decision-making across various sectors. Aspiring data scientists and analysts should prioritize gaining data visualization expertise to unlock their data’s full potential. Enrolling in a comprehensive data science program can provide the necessary skills and knowledge to excel in this field.
As data continues to grow in volume and complexity, the importance of data visualization will only increase, making it a vital skill for the future. By harnessing the power of data visualization, individuals and organizations can turn data into actionable insights, drive better decisions, and achieve their goals. Whether you’re working in business, healthcare, finance, education, scientific research, or government, data visualization can help you understand and leverage the power of data.
You might also like to read:
Data Science Bootcamps vs. Traditional Degrees: Which Learning Path to Choose?
Data Scientist vs. Machine Learning Engineer
What is A/B Testing in Data Science?
What is Natural Language Generation in Data Science, and Why Does It Matter?
What is Exploratory Data Analysis? Types, Tools, Importance, etc.
Data Science Bootcamp
- Learning Format:
Online Bootcamp
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recommended Articles

What is Bayesian Statistics, and How Does it Differ from Classical Methods?
What is Bayesian statistics? Learn about this tool used in data science, its fundamentals, uses, and advantages.

What is Data Imputation, and How Can You Use it to Handle Missing Data?
This article defines data imputation and demonstrates its importance, techniques, and challenges.

What is Data Governance, How Does it Work, Who Performs it, and Why is it Essential?
What is data governance? This article explores its goals and components, how to implement it, best practices, and more.

Technology at Work: Data Science in Finance
In today’s data-driven world, industries leverage advanced data analytics and AI-powered tools to improve services and their bottom line. The financial services industry is at the forefront of this innovation. This blog discusses data science in finance, including how companies use it, the skills required to leverage it, and more.

The Top Data Science Interview Questions for 2024
This article covers popular basic and advanced data science interview questions and the difference between data analytics and data science.

Big Data and Analytics: Unlocking the Future
Unlock the potential and benefits of big data and analytics in your career. Explore essential roles and discover the advantages of data-driven decision-making.
Learning Format
Program Benefits
- 12+ tools covered, 25+ hands-on projects
- Masterclasses by distinguished Caltech CTME instructors
- Caltech CTME Circle Membership
- Industry-specific training from global experts
- Call us on : 1800-212-7688
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Graphic Design What is Data Visualization? (Definition, Examples, Best Practices)
What is Data Visualization? (Definition, Examples, Best Practices)
Written by: Midori Nediger Jun 05, 2020
Words don’t always paint the clearest picture. Raw data doesn’t always tell the most compelling story.
The human mind is very receptive to visual information. That’s why data visualization is a powerful tool for communication.
But if “data visualization” sounds tricky and technical don’t worry—it doesn’t have to be.
This guide will explain the fundamentals of data visualization in a way that anyone can understand. Included are a ton of examples of different types of data visualizations and when to use them for your reports, presentations, marketing, and more.
Table of Contents
- What is data visualization?
What is data visualization used for?
Types of data visualizations.
- How to present data visually (for businesses, marketers, nonprofits, and education)
- Data visualization examples
Data visualization is used everywhere.
Businesses use data visualization for reporting, forecasting, and marketing.
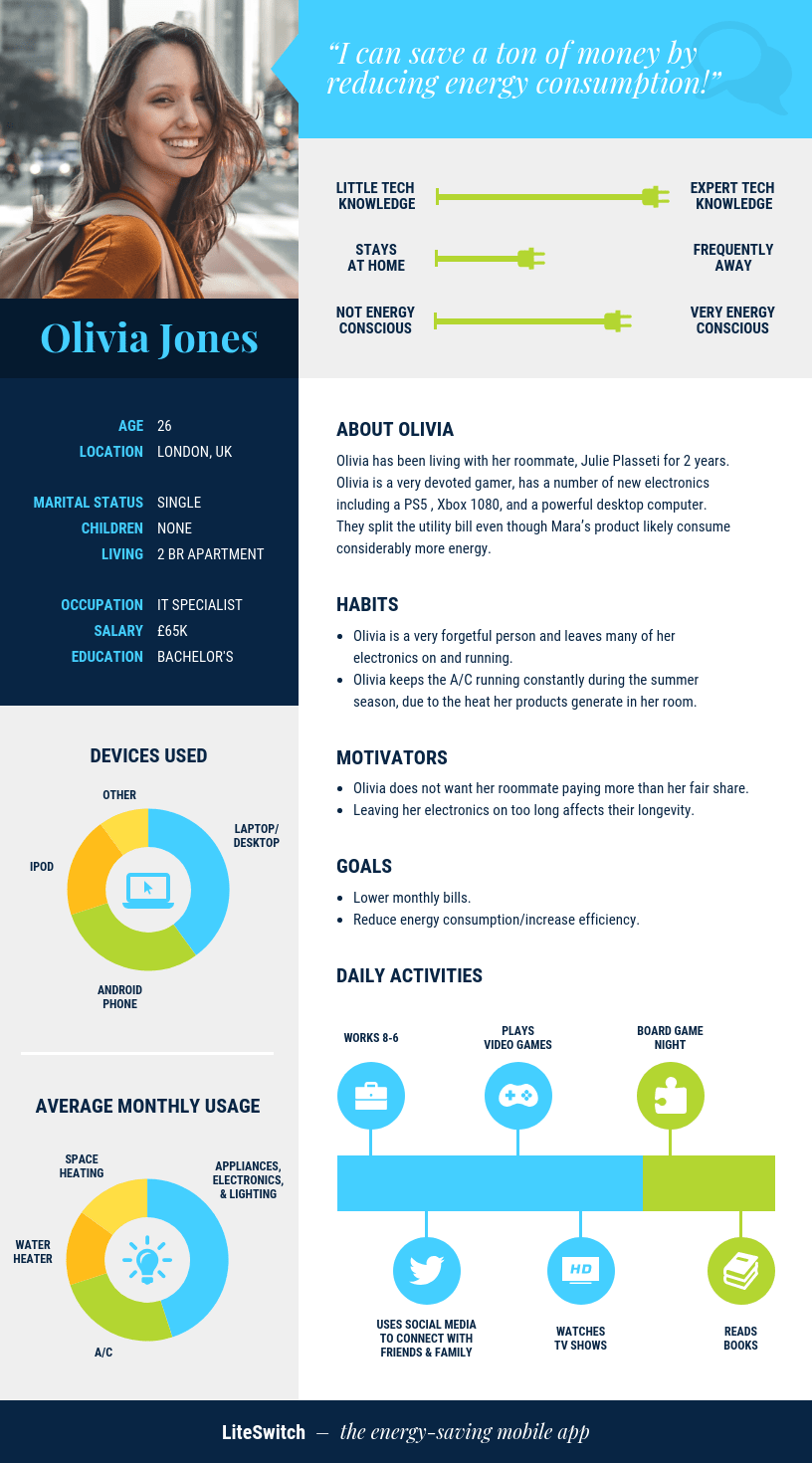
CREATE THIS REPORT TEMPLATE
Nonprofits use data visualizations to put stories and faces to numbers.

Source: Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation
Scholars and scientists use data visualization to illustrate concepts and reinforce their arguments.
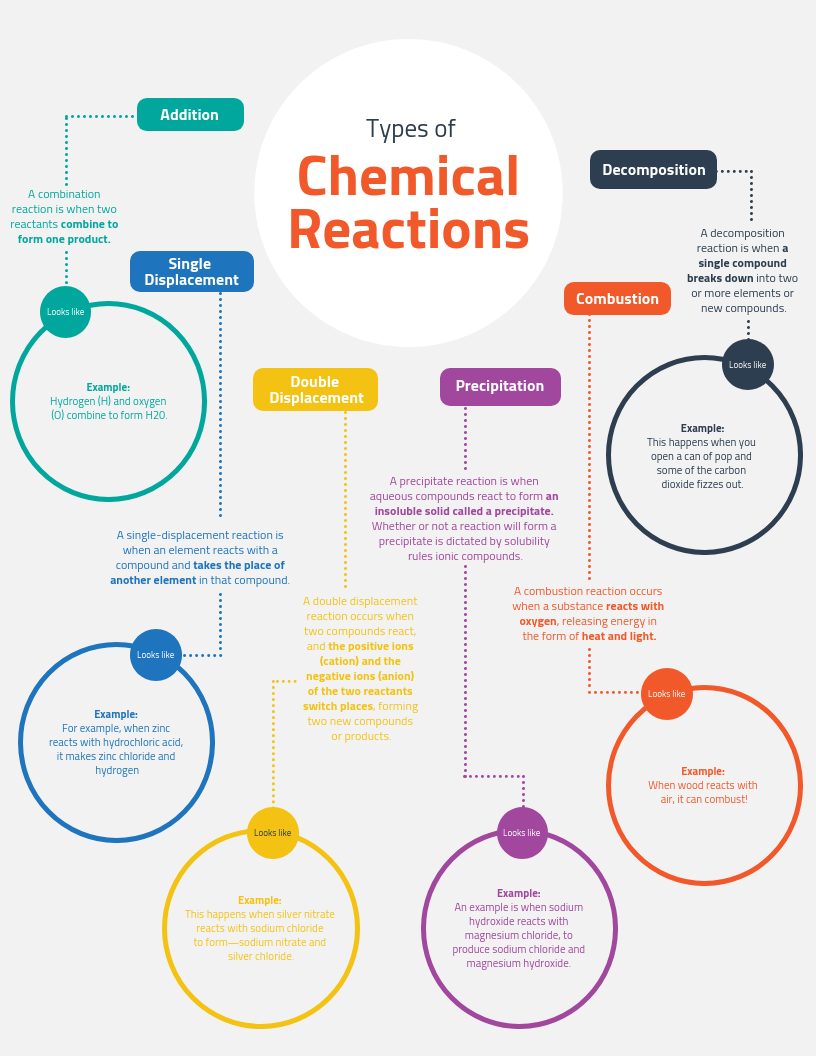
CREATE THIS MIND MAP TEMPLATE
Reporters use data visualization to show trends and contextualize stories.
While data visualizations can make your work more professional, they can also be a lot of fun.
What is data visualization? A simple definition of data visualization:
Data visualization is the visual presentation of data or information. The goal of data visualization is to communicate data or information clearly and effectively to readers. Typically, data is visualized in the form of a chart , infographic , diagram or map.
The field of data visualization combines both art and data science. While a data visualization can be creative and pleasing to look at, it should also be functional in its visual communication of the data.
Data, especially a lot of data, can be difficult to wrap your head around. Data visualization can help both you and your audience interpret and understand data.
Data visualizations often use elements of visual storytelling to communicate a message supported by the data.
There are many situations where you would want to present data visually.
Data visualization can be used for:
- Making data engaging and easily digestible
- Identifying trends and outliers within a set of data
- Telling a story found within the data
- Reinforcing an argument or opinion
- Highlighting the important parts of a set of data
Let’s look at some examples for each use case.
1. Make data digestible and easy to understand
Often, a large set of numbers can make us go cross-eyed. It can be difficult to find the significance behind rows of data.
Data visualization allows us to frame the data differently by using illustrations, charts, descriptive text, and engaging design. Visualization also allows us to group and organize data based on categories and themes, which can make it easier to break down into understandable chunks.
Related : How to Use Data Visualization in Your Infographics
For example, this infographic breaks down the concept of neuroplasticity in an approachable way:
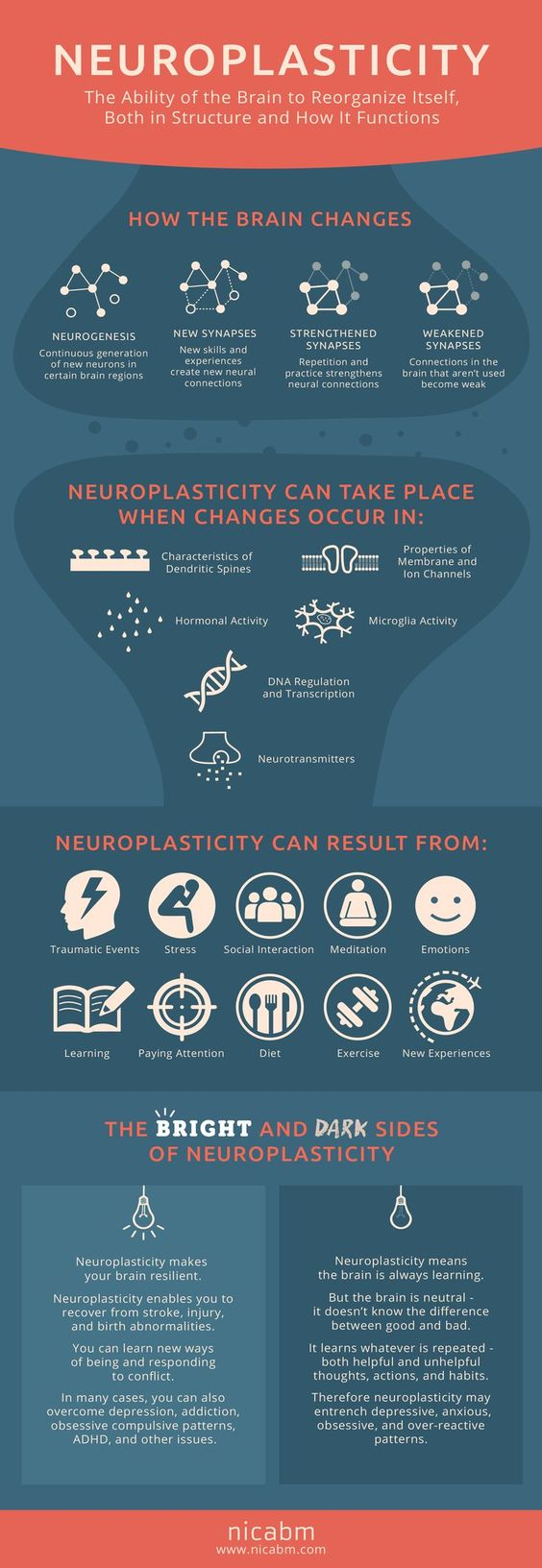
Source: NICABM
The same goes for complex, specialized concepts. It can often be difficult to break down the information in a way that non-specialists will understand. But an infographic that organizes the information, with visuals, can demystify concepts for novice readers.

CREATE THIS INFOGRAPHIC TEMPLATE
NEW! Introducing: Marketing Statistics Report 2022
It’s 2022 already. Marketers, are you still using data from pre-COVID times?
Don’t make decisions based on outdated data that no longer applies. It’s time you keep yourself informed of the latest marketing statistics and trends during the past two years, and learn how COVID-19 has affected marketing efforts in different industries — with this FREE marketing statistics report put together by Venngage and HubSpot .
The report uses data gathered from over 100,000 customers of HubSpot CRM. In addition to that, you’ll also know about the trends in using visuals in content marketing and the impacts of the pandemic on visual content, from 200+ marketers all over the world interviewed by Venngage.

GET YOUR FREE COPY
2. Identify trends and outliers
If you were to sift through raw data manually, it could take ages to notice patterns, trends or outlying data. But by using data visualization tools like charts, you can sort through a lot of data quickly.
Even better, charts enable you to pick up on trends a lot quicker than you would sifting through numbers.
For example, here’s a simple chart generated by Google Search Console that shows the change in Google searches for “toilet paper”. As you can see, in March 2020 there was a huge increase in searches for toilet paper:
Source: How to Use SEO Data to Fuel Your Content Marketing Strategy in 2020
This chart shows an outlier in the general trend for toilet paper-related Google searches. The reason for the outlier? The outbreak of COVID-19 in North America. With a simple data visualization, we’ve been able to highlight an outlier and hint at a story behind the data.
Uploading your data into charts, to create these kinds of visuals is easy. While working on your design in the editor, select a chart from the left panel. Open the chart and find the green IMPORT button under the DATA tab. Then upload the CSV file and your chart automatically visualizes the information.
3. Tell a story within the data
Numbers on their own don’t tend to evoke an emotional response. But data visualization can tell a story that gives significance to the data.
Designers use techniques like color theory , illustrations, design style and visual cues to appeal to the emotions of readers, put faces to numbers, and introduce a narrative to the data.
Related : How to Tell a Story With Data (A Guide for Beginners)
For example, here’s an infographic created by World Vision. In the infographics, numbers are visualized using illustrations of cups. While comparing numbers might impress readers, reinforcing those numbers with illustrations helps to make an even greater impact.

Source: World Vision
Meanwhile, this infographic uses data to draw attention to an often overlooked issue:
Read More: The Coronavirus Pandemic and the Refugee Crisis
4. Reinforce an argument or opinion
When it comes to convincing people your opinion is right, they often have to see it to believe it. An effective infographic or chart can make your argument more robust and reinforce your creativity.
For example, you can use a comparison infographic to compare sides of an argument, different theories, product/service options, pros and cons, and more. Especially if you’re blending data types.

5. Highlight an important point in a set of data
Sometimes we use data visualizations to make it easier for readers to explore the data and come to their own conclusions. But often, we use data visualizations to tell a story, make a particular argument, or encourage readers to come to a specific conclusion.
Designers use visual cues to direct the eye to different places on a page. Visual cues are shapes, symbols, and colors that point to a specific part of the data visualization, or that make a specific part stand out.
For example, in this data visualization, contrasting colors are used to emphasize the difference in the amount of waste sent to landfills versus recycled waste:
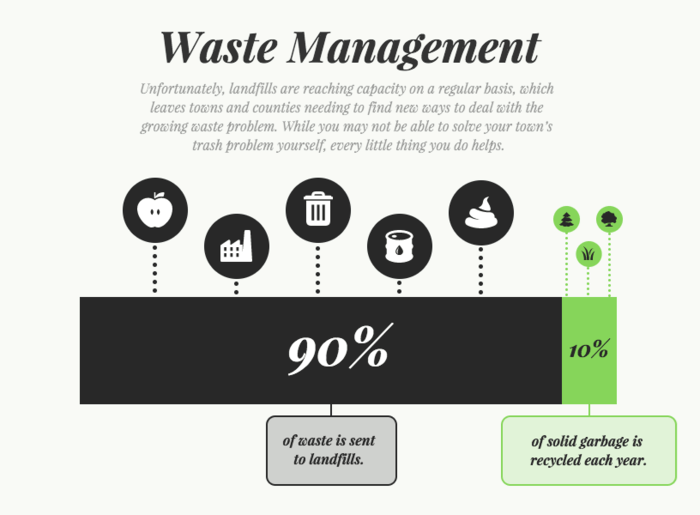
Here’s another example. This time, a red circle and an arrow are used to highlight points on the chart where the numbers show a drop:
Highlighting specific data points helps your data visualization tell a compelling story.
6. Make books, blog posts, reports and videos more engaging
At Venngage, we use data visualization to make our blog posts more engaging for readers. When we write a blog post or share a post on social media, we like to summarize key points from our content using infographics.
The added benefit of creating engaging visuals like infographics is that it has enabled our site to be featured in publications like The Wall Street Journal , Mashable , Business Insider , The Huffington Post and more.
That’s because data visualizations are different from a lot of other types of content people consume on a daily basis. They make your brain work. They combine concrete facts and numbers with impactful visual elements. They make complex concepts easier to grasp.
Here’s an example of an infographic we made that got a lot of media buzz:
Read the Blog Post: Every Betrayal Ever in Game of Thrones
We created this infographic because a bunch of people on our team are big Game of Thrones fans and we wanted to create a visual that would help other fans follow the show. Because we approached a topic that a lot of people cared about in an original way, the infographic got picked up by a bunch of media sites.
Whether you’re a website looking to promote your content, a journalist looking for an original angle, or a creative building your portfolio, data visualizations can be an effective way to get people’s attention.
Data visualizations can come in many different forms. People are always coming up with new and creative ways to present data visually.
Generally speaking, data visualizations usually fall under these main categories:
An infographic is a collection of imagery, charts, and minimal text that gives an easy-to-understand overview of a topic.
While infographics can take many forms, they can typically be categorized by these infographic types:
- Statistical infographics
- Informational infographics
- Timeline infographics
- Process infographics
- Geographic infographics
- Comparison infographics
- Hierarchical infographics
- List infographics
- Resume infographics
Read More: What is an Infographic? Examples, Templates & Design Tips
Charts
In the simplest terms, a chart is a graphical representation of data. Charts use visual symbols like line, bars, dots, slices, and icons to represent data points.
Some of the most common types of charts are:
- Bar graphs /charts
- Line charts
- Bubble charts
- Stacked bar charts
- Word clouds
- Pictographs
- Area charts
- Scatter plot charts
- Multi-series charts
The question that inevitably follows is: what type of chart should I use to visualize my data? Does it matter?
Short answer: yes, it matters. Choosing a type of chart that doesn’t work with your data can end up misrepresenting and skewing your data.
For example: if you’ve been in the data viz biz for a while, then you may have heard some of the controversy surrounding pie charts. A rookie mistake that people often make is using a pie chart when a bar chart would work better.
Pie charts display portions of a whole. A pie chart works when you want to compare proportions that are substantially different. Like this:
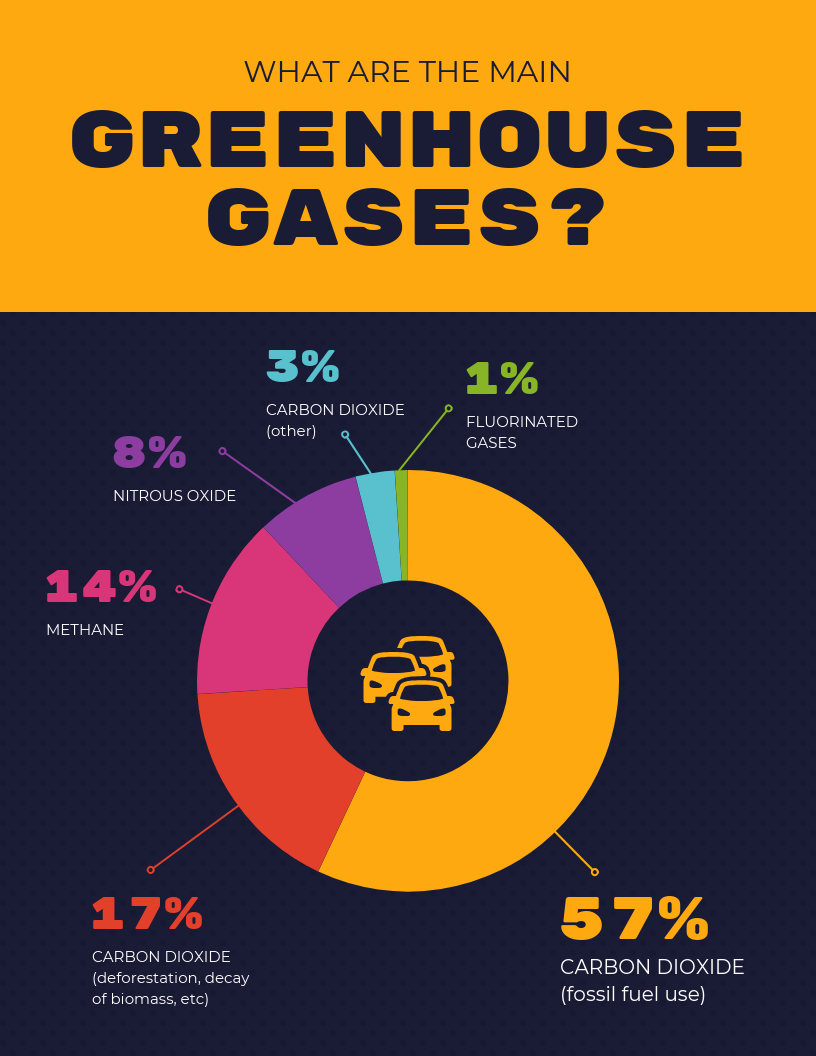
CREATE THIS CHART TEMPLATE
But when your proportions are similar, a pie chart can make it difficult to tell which slice is bigger than the other. That’s why, in most other cases, a bar chart is a safer bet.
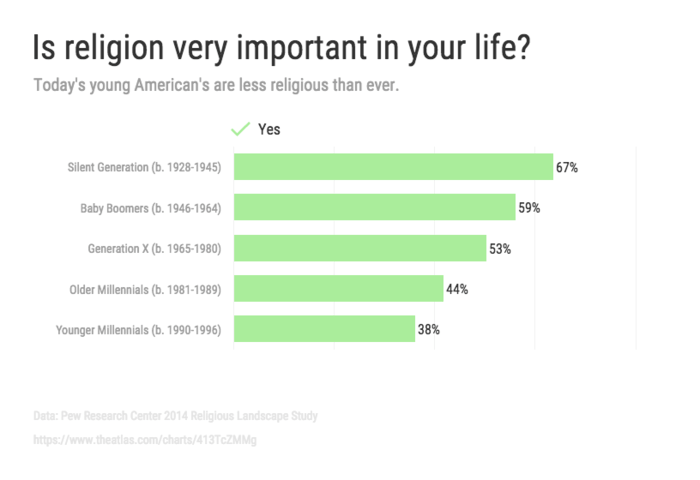
Here is a cheat sheet to help you pick the right type of chart for your data:

Want to make better charts? Make engaging charts with Venngage’s Chart Maker .
Related : How to Choose the Best Types of Charts For Your Data
Similar to a chart, a diagram is a visual representation of information. Diagrams can be both two-dimensional and three-dimensional.
Some of the most common types of diagrams are:
- Venn diagrams
- Tree diagrams
- SWOT analysis
- Fishbone diagrams
- Use case diagrams
Diagrams are used for mapping out processes, helping with decision making, identifying root causes, connecting ideas, and planning out projects.
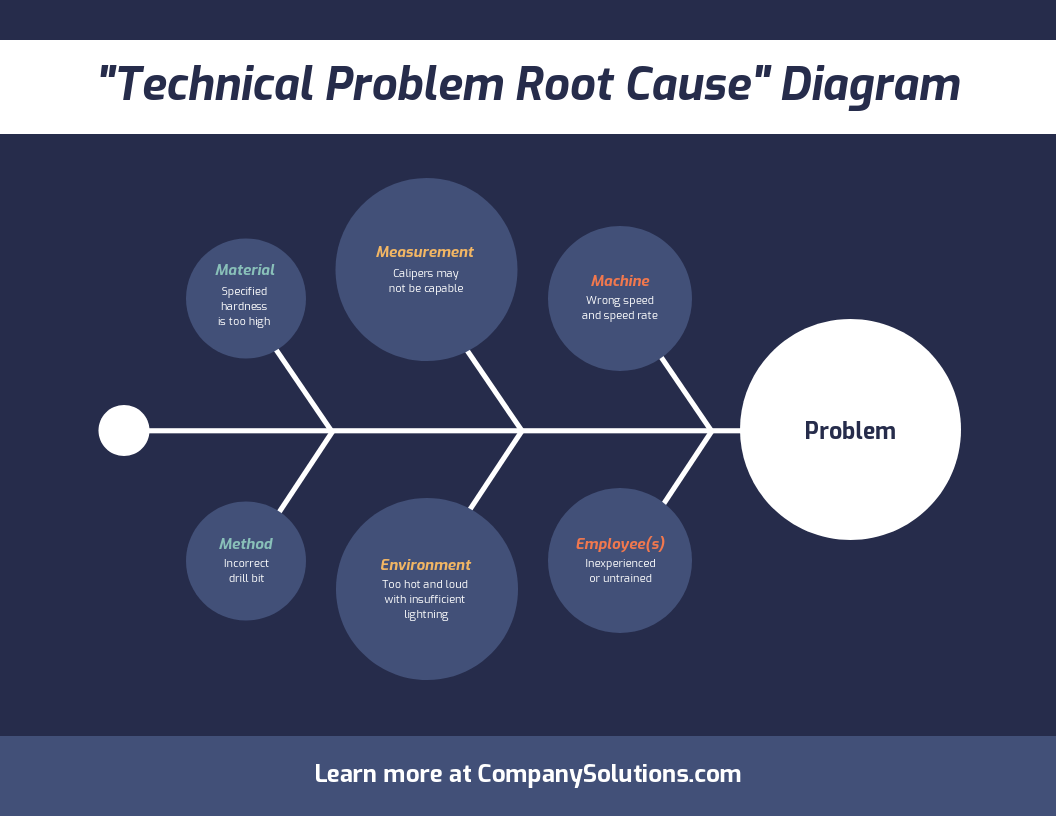
CREATE THIS DIAGRAM TEMPLATE
Want to make a diagram ? Create a Venn diagram and other visuals using our free Venn Diagram Maker .
A map is a visual representation of an area of land. Maps show physical features of land like regions, landscapes, cities, roads, and bodies of water.
Source: National Geographic
A common type of map you have probably come across in your travels is a choropleth map . Choropleth maps use different shades and colors to indicate average quantities.
For example, a population density map uses varying shades to show the difference in population numbers from region to region:
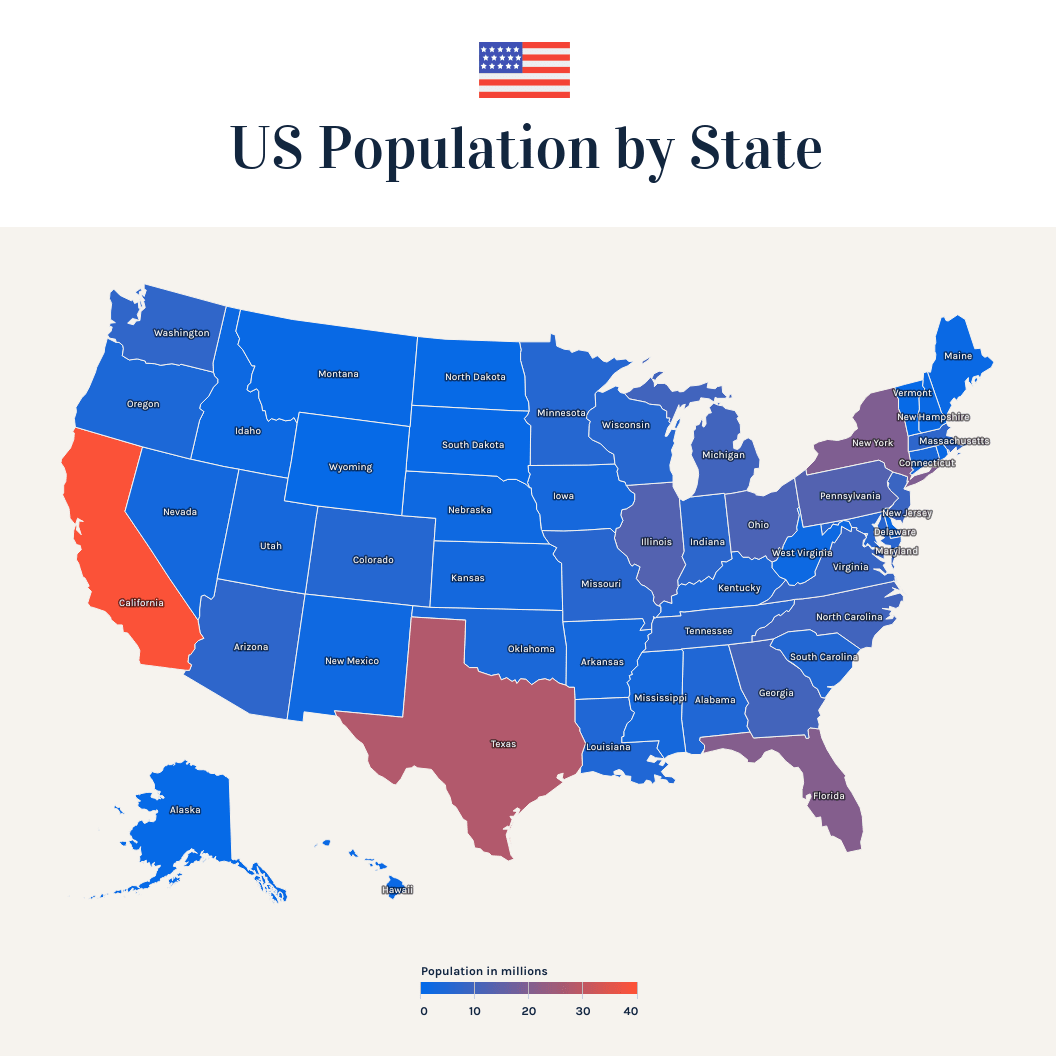
Create your own map for free with Venngage’s Map Maker .
How to present data visually (data visualization best practices)
While good data visualization will communicate data or information clearly and effectively, bad data visualization will do the opposite. Here are some practical tips for how businesses and organizations can use data visualization to communicate information more effectively.
Not a designer? No problem. Venngage’s Graph Maker will help you create better graphs in minutes.
1. Avoid distorting the data
This may be the most important point in this whole blog post. While data visualizations are an opportunity to show off your creative design chops, function should never be sacrificed for fashion.
The chart styles, colors, shapes, and sizing you use all play a role in how the data is interpreted. If you want to present your data accurately and ethically, then you need to take care to ensure that your data visualization does not present the data falsely.
There are a number of different ways data can be distorted in a chart. Some common ways data can be distorted are:
- Making the baselines something other than 0 to make numbers seem bigger or smaller than they are – this is called “truncating” a graph
- Compressing or expanding the scale of the Y-axis to make a line or bar seem bigger or smaller than it should be
- Cherry picking data so that only the data points you want to include are on a graph (i.e. only telling part of the story)
- Using the wrong type of chart, graph or diagram for your data
- Going against standard, expected data visualization conventions
Because people use data visualizations to reinforce their opinions, you should always read data visualizations with a critical eye. Often enough, writers may be using data visualization to skew the data in a way that supports their opinions, but that may not be entirely truthful.
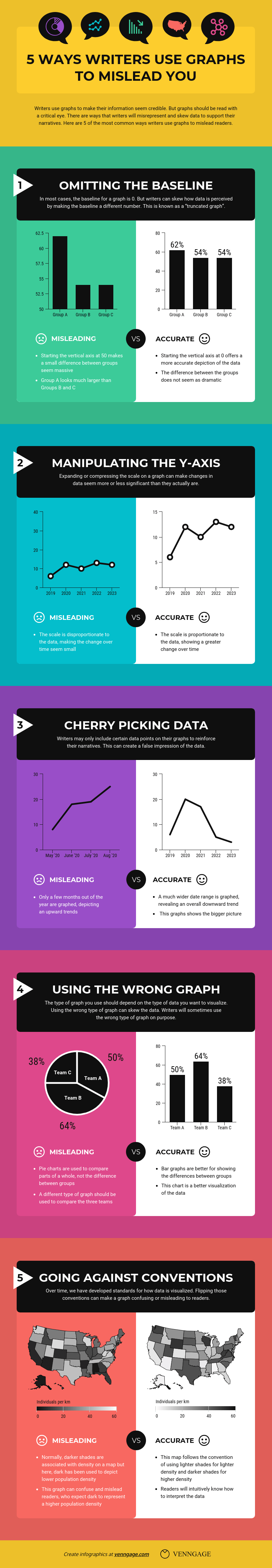
Read More: 5 Ways Writers Use Graphs To Mislead You
Want to create an engaging line graph? Use Venngage’s Line Graph Maker to create your own in minutes.
2. Avoid cluttering up your design with “chartjunk”
When it comes to best practices for data visualization, we should turn to one of the grandfather’s of data visualization: Edward Tufte. He coined the term “ chartjunk ”, which refers to the use of unnecessary or confusing design elements that skews or obscures the data in a chart.
Here’s an example of a data visualization that suffers from chartjunk:
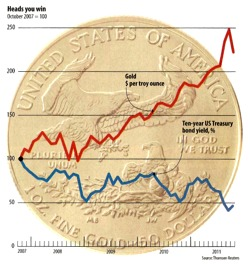
Source: ExcelUser
In this example, the image of the coin is distracting for readers trying to interpret the data. Note how the fonts are tiny – almost unreadable. Mistakes like this are common when a designers tries to put style before function.
Read More : The Worst Infographics of 2020 (With Lessons for 2021)
3. Tell a story with your data
Data visualizations like infographics give you the space to combine data and narrative structure in one page. Visuals like icons and bold fonts let you highlight important statistics and facts.
For example, you could customize this data visualization infographic template to show the benefit of using your product or service (and post it on social media):
USE THIS TEMPLATE
This data visualization relies heavily on text and icons to tell the story of its data:
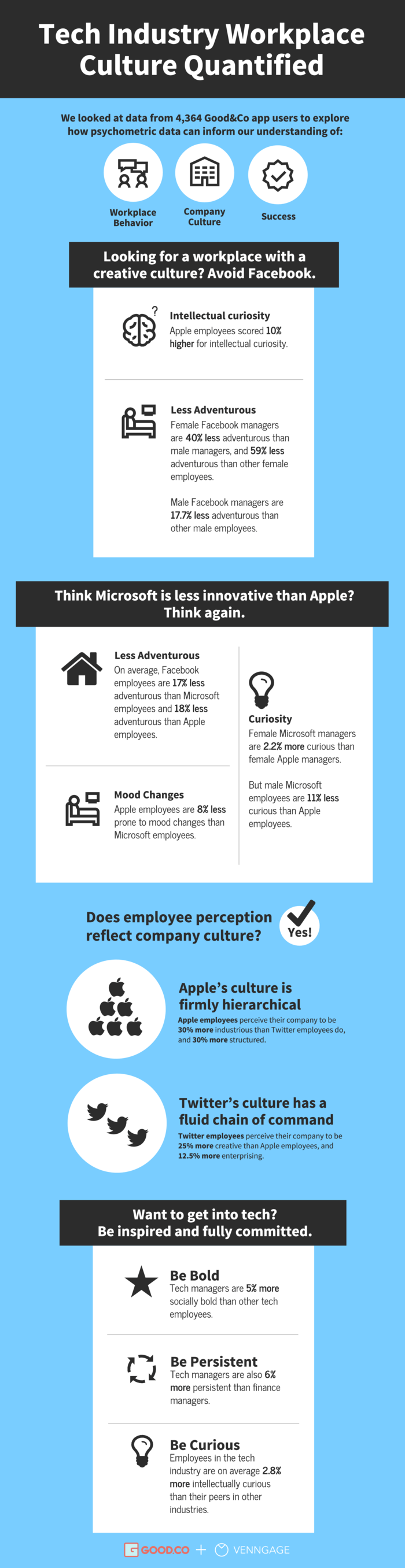
This type of infographic is perfect for those who aren’t as comfortable with charts and graphs. It’s also a great way to showcase original research, get social shares and build brand awareness.
4. Combine different types of data visualizations
While you may choose to keep your data visualization simple, combining multiple types of charts and diagrams can help tell a more rounded story.
Don’t be afraid to combine charts, pictograms and diagrams into one infographic. The result will be a data visualization infographic that is engaging and rich in visual data.

Design Tip: This data visualization infographic would be perfect for nonprofits to customize and include in an email newsletter to increase awareness (and donations).
Or take this data visualization that also combines multiple types of charts, pictograms, and images to engage readers. It could work well in a presentation or report on customer research, customer service scores, quarterly performance and much more:
Design Tip: This infographic could work well in a presentation or report on customer research, customer service scores, quarterly performance and much more.
Make your own bar graph in minutes with our free Bar Graph Maker .
5. Use icons to emphasize important points
Icons are perfect for attracting the eye when scanning a page. (Remember: use visual cues!)
If there are specific data points that you want readers to pay attention to, placing an icon beside it will make it more noticeable:
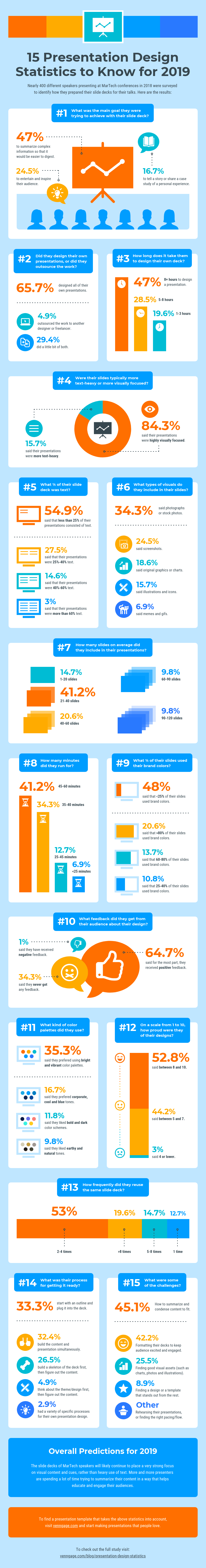
Design Tip: This infographic template would work well on social media to encourage shares and brand awareness.
You can also pair icons with headers to indicate the beginning of a new section.
Meanwhile, this infographic uses icons like bullet points to emphasize and illustrate important points.
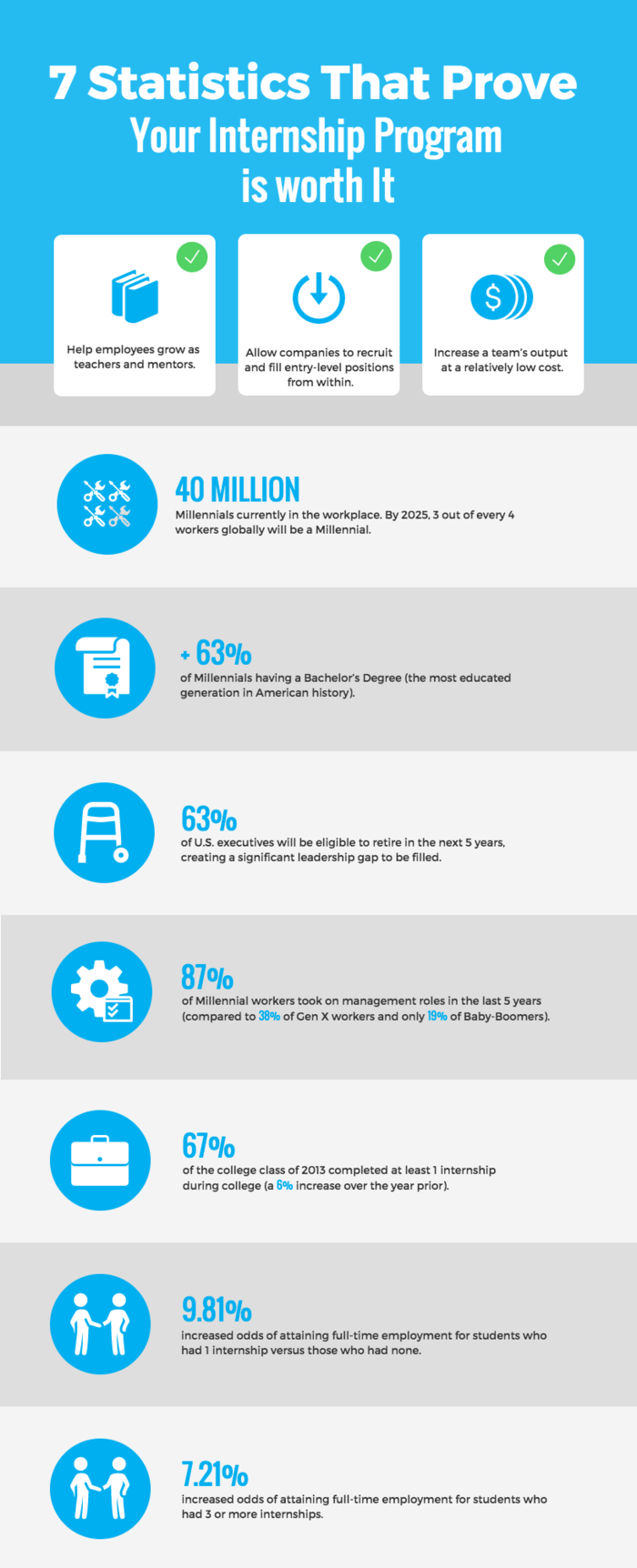
Design Tip: This infographic would make a great sales piece to promote your course or other service.
6. Use bold fonts to make text information engaging
A challenge people often face when setting out to visualize information is knowing how much text to include. After all, the point of data visualization is that it presents information visually, rather than a page of text.
Even if you have a lot of text information, you can still create present data visually. Use bold, interesting fonts to make your data exciting. Just make sure that, above all else, your text is still easy to read.
This data visualization uses different fonts for the headers and body text that are bold but clear. This helps integrate the text into the design and emphasizes particular points:

Design Tip: Nonprofits could use this data visualization infographic in a newsletter or on social media to build awareness, but any business could use it to explain the need for their product or service.
As a general rule of thumb, stick to no more than three different font types in one infographic.
This infographic uses one font for headers, another font for body text, and a third font for accent text.
Read More: How to Choose Fonts For Your Designs (With Examples)
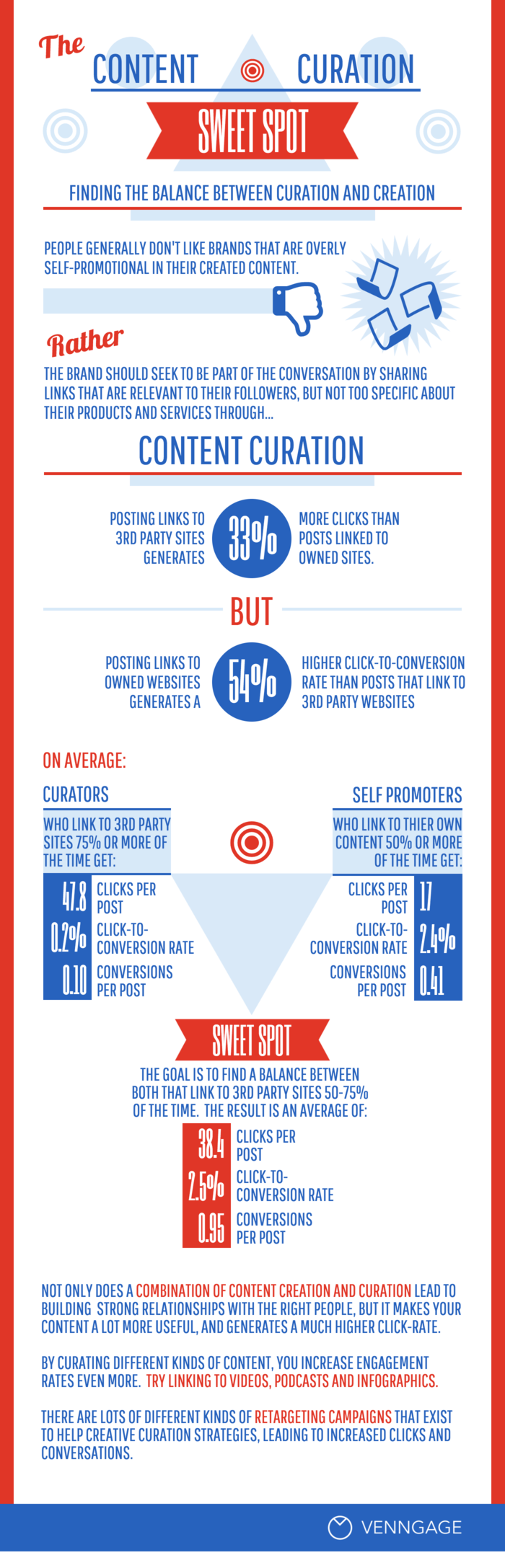
Design Tip: Venngage has a library of fonts to choose from. If you can’t find the icon you’re looking for , you can always request they be added. Our online editor has a chat box with 24/7 customer support.
7. Use colors strategically in your design
In design, colors are as functional as they are fashionable. You can use colors to emphasize points, categorize information, show movement or progression, and more.
For example, this chart uses color to categorize data:
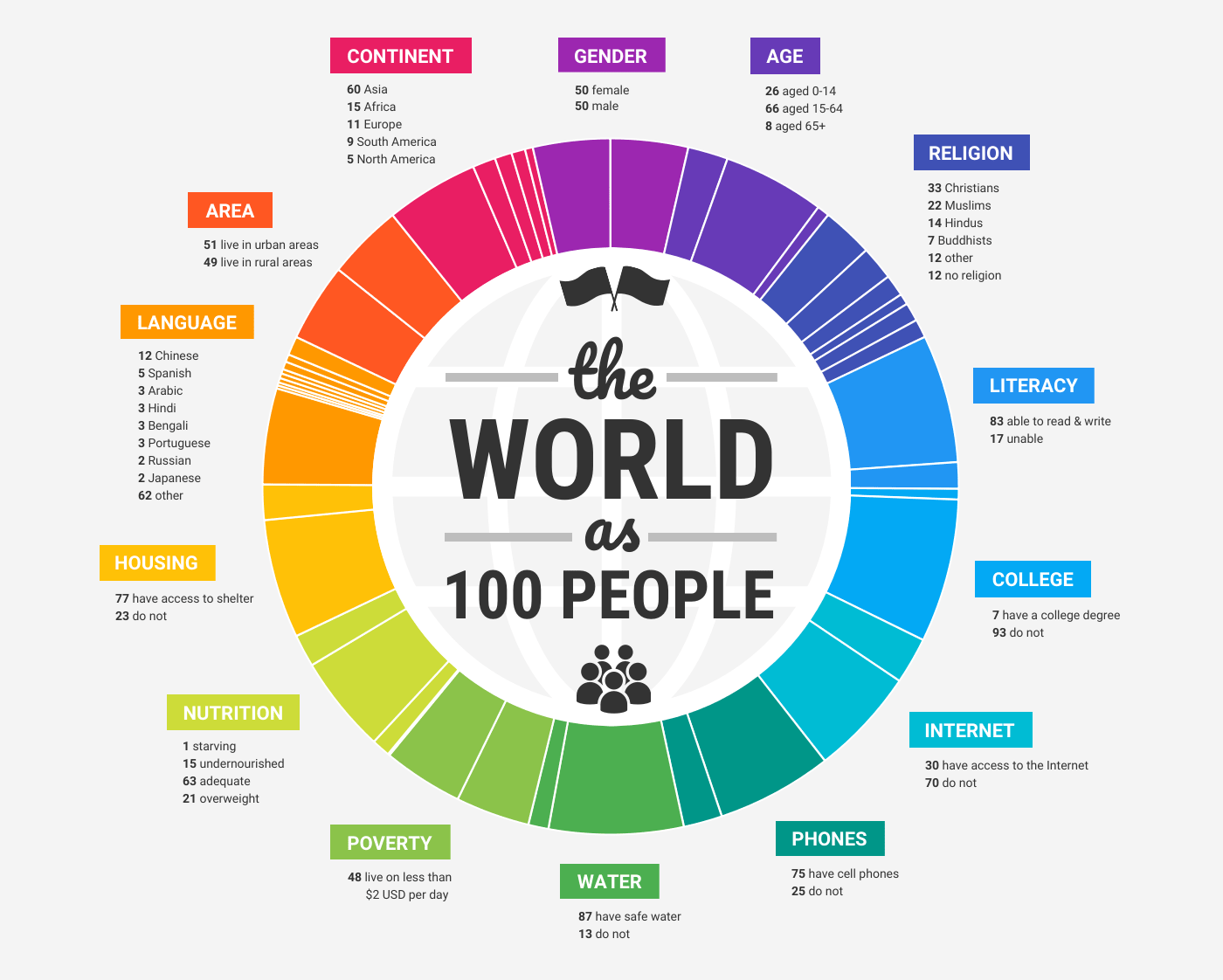
Design Tip : This pie chart can actually be customized in many ways. Human resources could provide a monthly update of people hired by department, nonprofits could show a breakdown of how they spent donations and real estate agents could show the average price of homes sold by neighbourhood.
You can also use light colored text and icons on dark backgrounds to make them stand out. Consider the mood that you want to convey with your infographic and pick colors that will reflect that mood. You can also use contrasting colors from your brand color palette.
This infographic template uses a bold combination of pinks and purples to give the data impact:
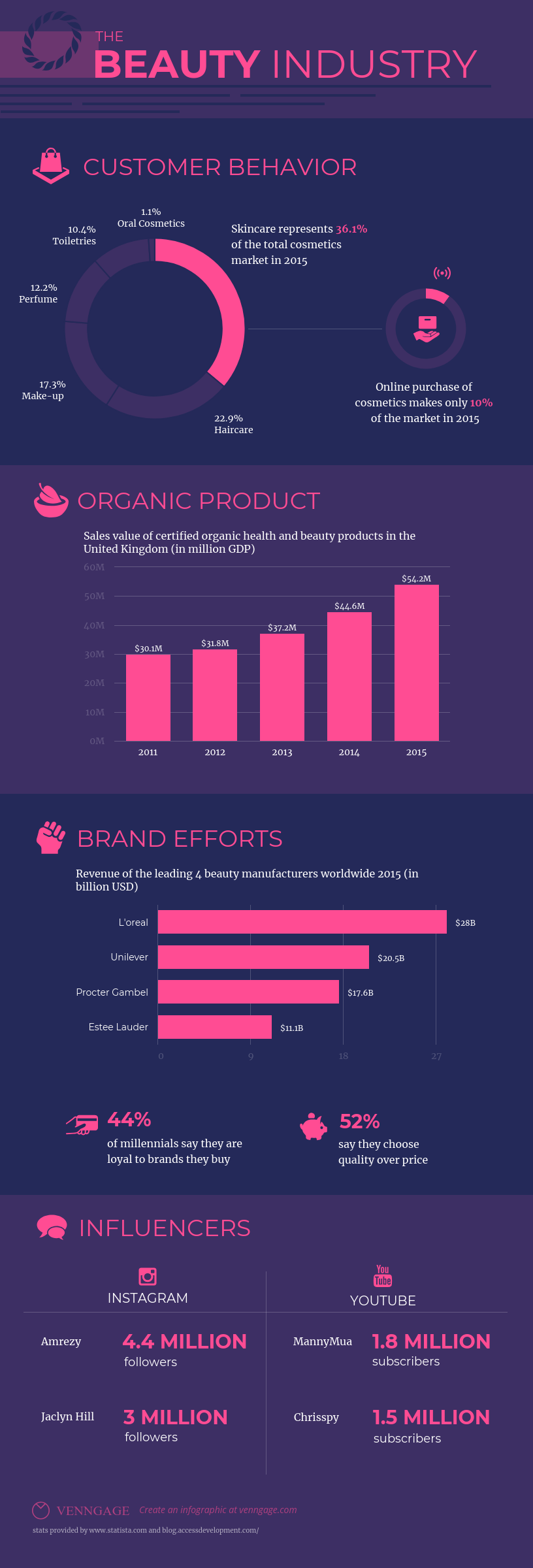
Read More: How to Pick Colors to Captivate Readers and Communicate Effectively
8. Show how parts make up a whole
It can be difficult to break a big topic down into smaller parts. Data visualization can make it a lot easier for people to conceptualize how parts make up a whole.
Using one focus visual, diagram or chart can convey parts of a whole more effectively than a text list can. Look at how this infographic neatly visualizes how marketers use blogging as part of their strategy:
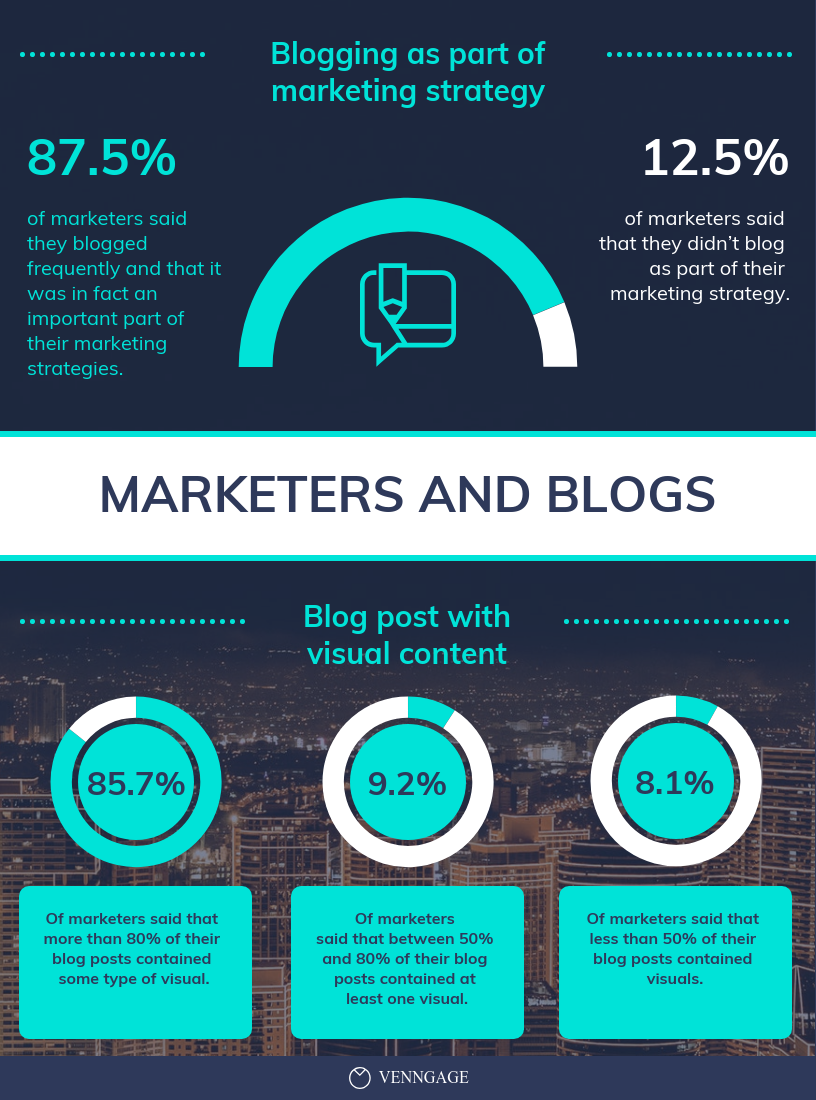
Design Tip: Human resources could use this graphic to show the results of a company survey. Or consultants could promote their services by showing their success rates.
Or look at how this infographic template uses one focus visual to illustrate the nutritional makeup of a banana:
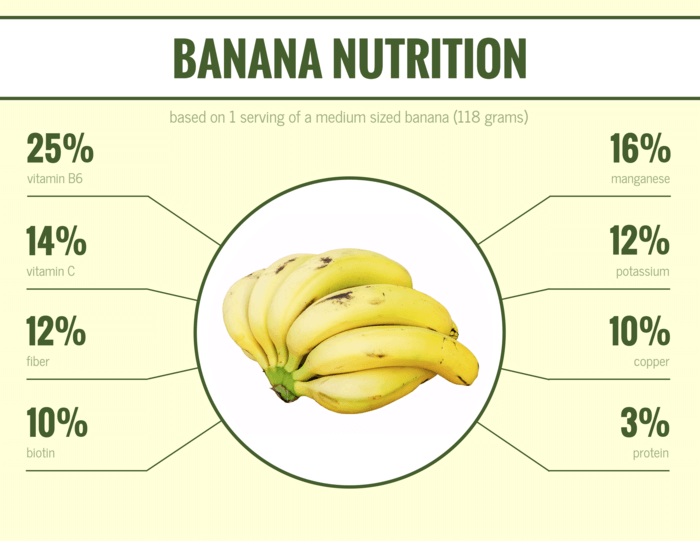
CREATE THIS FLYER TEMPLATE
9. Focus on one amazing statistic
If you are preparing a presentation, it’s best not to try and cram too many visuals into one slide. Instead, focus on one awe-inspiring statistic and make that the focus of your slide.
Use one focus visual to give the statistic even more impact. Smaller visuals like this are ideal for sharing on social media, like in this example:

Design Tip: You can easily swap out the icon above (of Ontario, Canada) using Venngage’s drag-and-drop online editor and its in-editor library of icons. Click on the template above to get started.
This template also focuses on one key statistic and offers some supporting information in the bar on the side:

10. Optimize your data visualization for mobile
Complex, information-packed infographics are great for spicing up reports, blog posts, handouts, and more. But they’re not always the best for mobile viewing.
To optimize your data visualization for mobile viewing, use one focus chart or icon and big, legible font. You can create a series of mobile-optimized infographics to share multiple data points in a super original and attention-grabbing way.
For example, this infographic uses concise text and one chart to cut to the core message behind the data:
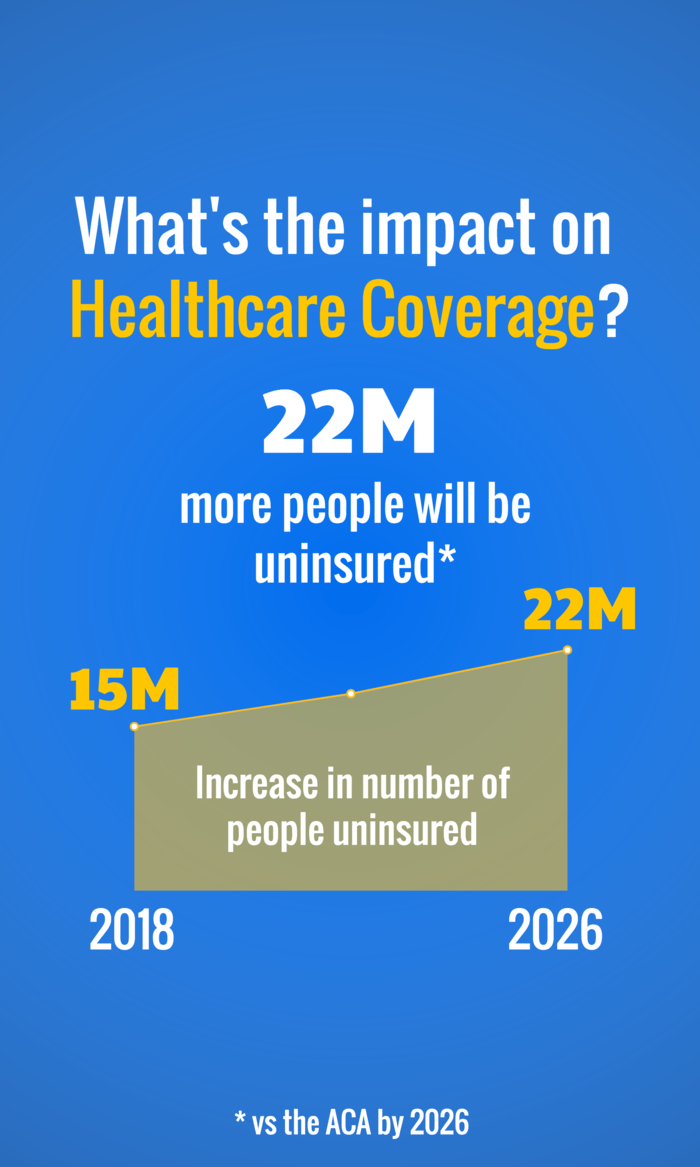
CREATE THIS SOCIAL MEDIA TEMPLATE
Some amazing data visualization examples
Here are some of the best data visualization examples I’ve come across in my years writing about data viz.
Evolution of Marketing Infographic
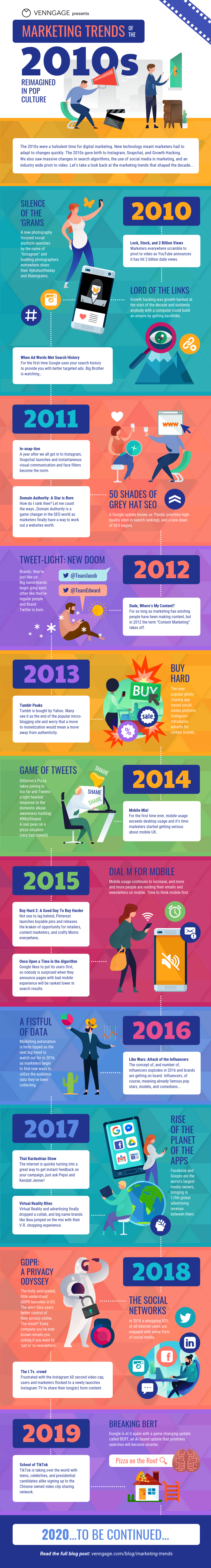
Graphic Design Trends Infographic

Stop Shark Finning Nonprofit Infographic

Source: Ripetungi
Coronavirus Impact on Environment Data Visualization

What Disney Characters Tell Us About Color Theory
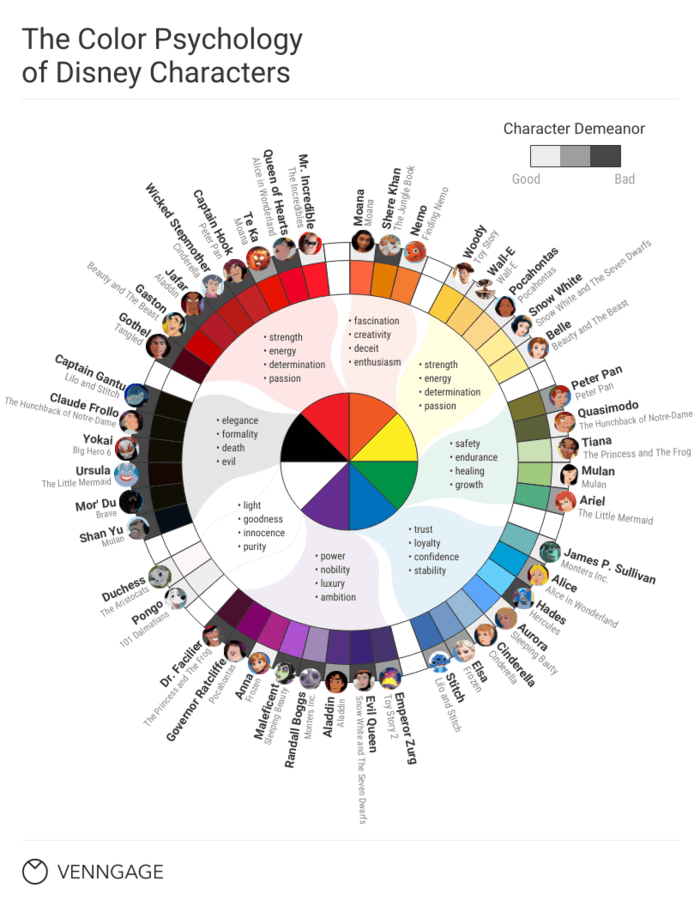
World’s Deadliest Animal Infographic
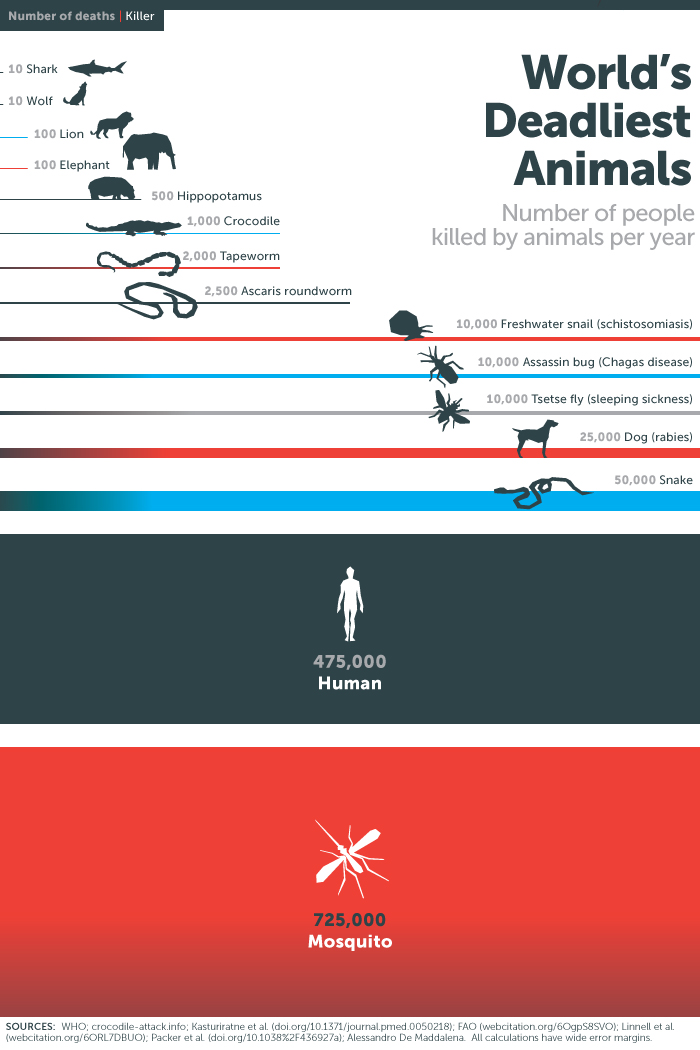
Source: Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation
The Secret Recipe For a Viral Creepypasta
Read More: Creepypasta Study: The Secret Recipe For a Viral Horror Story
The Hero’s Journey Infographic
Read More: What Your 6 Favorite Movies Have in Common
Emotional Self Care Guide Infographic

Source: Carley Schweet
Want to look at more amazing data visualization? Read More: 50+ Infographic Ideas, Examples & Templates for 2020 (For Marketers, Nonprofits, Schools, Healthcare Workers, and more)
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
- Artificial Intelligence
- Generative AI
- Business Operations
- Cloud Computing
- Data Center
- Data Management
- Emerging Technology
- Enterprise Applications
- IT Leadership
- Digital Transformation
- IT Strategy
- IT Management
- Diversity and Inclusion
- IT Operations
- Project Management
- Software Development
- Vendors and Providers
- Enterprise Buyer’s Guides
- United States
- Middle East
- España (Spain)
- Italia (Italy)
- Netherlands
- United Kingdom
- New Zealand
- Data Analytics & AI
- Newsletters
- Foundry Careers
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Copyright Notice
- Member Preferences
- About AdChoices
- Your California Privacy Rights
Our Network
- Computerworld
- Network World
What is data visualization? Presenting data for decision-making
Data visualization is the presentation of data in a graphical format to make it easier for decision makers to see and understand trends, outliers, and patterns in data..

Data visualization definition
Data visualization is the presentation of data in a graphical format such as a plot, graph, or map to make it easier for decision makers to see and understand trends, outliers, and patterns in data.
Maps and charts were among the earliest forms of data visualization. One of the most well-known early examples of data visualization was a flow map created by French civil engineer Charles Joseph Minard in 1869 to help understand what Napoleon’s troops suffered in the disastrous Russian campaign of 1812. The map used two dimensions to depict the number of troops, distance, temperature, latitude and longitude, direction of travel, and location relative to specific dates.
Today, data visualization encompasses all manners of presenting data visually, from dashboards to reports, statistical graphs, heat maps, plots, infographics, and more.
What is the business value of data visualization?
Data visualization helps people analyze data, especially large volumes of data, quickly and efficiently.
By providing easy-to-understand visual representations of data, it helps employees make more informed decisions based on that data. Presenting data in visual form can make it easier to comprehend, enable people to obtain insights more quickly. Visualizations can also make it easier to communicate those insights and to see how independent variables relate to one another. This can help you see trends, understand the frequency of events, and track connections between operations and performance, for example.
Key data visualization benefits include:
- Unlocking the value big data by enabling people to absorb vast amounts of data at a glance
- Increasing the speed of decision-making by providing access to real-time and on-demand information
- Identifying errors and inaccuracies in data quickly
What are the types of data visualization?
There are myriad ways of visualizing data, but data design agency The Datalabs Agency breaks data visualization into two basic categories:
- Exploration: Exploration visualizations help you understand what the data is telling you.
- Explanation: Explanation visualizations tell a story to an audience using data .
It is essential to understand which of those two ends a given visualization is intended to achieve. The Data Visualisation Catalogue , a project developed by freelance designer Severino Ribecca, is a library of different information visualization types.
Some of the most common specific types of visualizations include:
2D area: These are typically geospatial visualizations. For example, cartograms use distortions of maps to convey information such as population or travel time. Choropleths use shades or patterns on a map to represent a statistical variable, such as population density by state.
Temporal: These are one-dimensional linear visualizations that have a start and finish time. Examples include a time series, which presents data like website visits by day or month, and Gantt charts, which illustrate project schedules.
Multidimensional: These common visualizations present data with two or more dimensions. Examples include pie charts, histograms, and scatter plots.
Hierarchical: These visualizations show how groups relate to one another. Tree diagrams are an example of a hierarchical visualization that shows how larger groups encompass sets of smaller groups.
Network: Network visualizations show how data sets are related to one another in a network. An example is a node-link diagram, also known as a network graph , which uses nodes and link lines to show how things are interconnected.
What are some data visualization examples?
Tableau has collected what it considers to be 10 of the best data visualization examples . Number one on Tableau’s list is Minard’s map of Napoleon’s march to Moscow, mentioned above. Other prominent examples include:
- A dot map created by English physician John Snow in 1854 to understand the cholera outbreak in London that year. The map used bar graphs on city blocks to indicate cholera deaths at each household in a London neighborhood. The map showed that the worst-affected households were all drawing water from the same well, which eventually led to the insight that wells contaminated by sewage had caused the outbreak.
- An animated age and gender demographic breakdown pyramid created by Pew Research Center as part of its The Next America project , published in 2014. The project is filled with innovative data visualizations. This one shows how population demographics have shifted since the 1950s, with a pyramid of many young people at the bottom and very few older people at the top in the 1950s to a rectangular shape in 2060.
- A collection of four visualizations by Hanah Anderson and Matt Daniels of The Pudding that illustrate gender disparity in pop culture by breaking down the scripts of 2,000 movies and tallying spoken lines of dialogue for male and female characters. The visualizations include a breakdown of Disney movies, the overview of 2,000 scripts, a gradient bar with which users can search for specific movies, and a representation of age biases shown toward male and female roles.
Data visualization tools
Data visualization software encompasses many applications, tools, and scripts. They provide designers with the tools they need to create visual representations of large data sets. Some of the most popular include the following:
Domo: Domo is a cloud software company that specializes in business intelligence tools and data visualization. It focuses on business-user deployed dashboards and ease of use, making it a good choice for small businesses seeking to create custom apps.
Dundas BI: Dundas BI is a BI platform for visualizing data, building and sharing dashboards and reports, and embedding analytics.
Infogram: Infogram is a drag-and-drop visualization tool for creating visualizations for marketing reports, infographics, social media posts, dashboards, and more. Its ease-of-use makes it a good option for non-designers as well.
Klipfolio: Klipfolio is designed to enable users to access and combine data from hundreds of services without writing any code. It leverages pre-built, curated instant metrics and a powerful data modeler, making it a good tool for building custom dashboards.
Looker: Now part of Google Cloud, Looker has a plug-in marketplace with a directory of different types of visualizations and pre-made analytical blocks. It also features a drag-and-drop interface.
Microsoft Power BI: Microsoft Power BI is a business intelligence platform integrated with Microsoft Office. It has an easy-to-use interface for making dashboards and reports. It’s very similar to Excel so Excel skills transfer well. It also has a mobile app.
Qlik: Qlik’s Qlik Sense features an “associative” data engine for investigating data and AI-powered recommendations for visualizations. It is continuing to build out its open architecture and multicloud capabilities.
Sisense: Sisense is an end-to-end analytics platform best known for embedded analytics. Many customers use it in an OEM form.
Tableau: One of the most popular data visualization platforms on the market, Tableau is a platform that supports accessing, preparing, analyzing, and presenting data. It’s available in a variety of options, including a desktop app, server, and hosted online versions, and a free, public version. Tableau has a steep learning curve but is excellent for creating interactive charts.
Data visualization certifications
Data visualization skills are in high demand. Individuals with the right mix of experience and skills can demand high salaries. Certifications can help.
Some of the popular certifications include the following:
- Data Visualization Nanodegree (Udacity)
- Professional Certificate in IBM Data Science (IBM)
- Data Visualization with Python (DataCamp)
- Data Analysis and Visualization with Power BI (Udacity)
- Data Visualization with R (Dataquest)
- Visualize Data with Python (Codecademy)
- Professional Certificate in Data Analytics and Visualization with Excel and R (IBM)
- Data Visualization with Tableau Specialization (UCDavis)
- Data Visualization with R (DataCamp)
- Excel Skills for Data Analytics and Visualization Specialization (Macquarie University)
Data visualization jobs and salaries
Here are some of the most popular job titles related to data visualization and the average salary for each position, according to data from PayScale .
- Data analyst: $64K
- Data scientist: $98K
- Data visualization specialist: $76K
- Senior data analyst: $88K
- Senior data scientist: $112K
- BI analyst: $65K
- Analytics specialist: $71K
- Marketing data analyst: $61K
Related content
Tableau further democratizes analytics with ai-fueled features, the secret to successful citizen data science programs: good governance, tableau’s new slack capabilities democratize data, from our editors straight to your inbox, show me more, salesforce: latest news and insights.

Salesforce mulls consumption pricing for AI agents

Navigate AI market uncertainty by bringing AI to your data

CIO Leadership Live Australia with Nazih Battal, Chief Information and Technology Officer at Rashays

Mike Aiello, CTO at Secureworks, joins CIO Leadership Live from Foundry's CIO100 event NEW

CIO Leadership Live Australia with Andrew Dome, Chief Digital Information Officer at Uniting

Kubecost helps firms monitor, optimize their Kubernetes and cloud spend

Mike Aiello, CTO at Secureworks, joins CIO Leadership Live from Foundry's CIO100 event

Sponsored Links
- Everybody's ready for AI except your data. Unlock the power of AI with Informatica
- Everyone’s moving to the cloud. Are they realizing expected value?
- The future of identity is here. Unlock brand growth with Merkury
- The cloud shouldn’t be complicated. Unlock its potential with SAS.

Data visualization is the representation of data through use of common graphics, such as charts, plots, infographics and even animations. These visual displays of information communicate complex data relationships and data-driven insights in a way that is easy to understand.
Data visualization can be utilized for a variety of purposes, and it’s important to note that is not only reserved for use by data teams. Management also leverages it to convey organizational structure and hierarchy while data analysts and data scientists use it to discover and explain patterns and trends. Harvard Business Review (link resides outside ibm.com) categorizes data visualization into four key purposes: idea generation, idea illustration, visual discovery, and everyday dataviz. We’ll delve deeper into these below:
Idea generation
Data visualization is commonly used to spur idea generation across teams. They are frequently leveraged during brainstorming or Design Thinking sessions at the start of a project by supporting the collection of different perspectives and highlighting the common concerns of the collective. While these visualizations are usually unpolished and unrefined, they help set the foundation within the project to ensure that the team is aligned on the problem that they’re looking to address for key stakeholders.
Idea illustration
Data visualization for idea illustration assists in conveying an idea, such as a tactic or process. It is commonly used in learning settings, such as tutorials, certification courses, centers of excellence, but it can also be used to represent organization structures or processes, facilitating communication between the right individuals for specific tasks. Project managers frequently use Gantt charts and waterfall charts to illustrate workflows . Data modeling also uses abstraction to represent and better understand data flow within an enterprise’s information system, making it easier for developers, business analysts, data architects, and others to understand the relationships in a database or data warehouse.
Visual discovery
Visual discovery and every day data viz are more closely aligned with data teams. While visual discovery helps data analysts, data scientists, and other data professionals identify patterns and trends within a dataset, every day data viz supports the subsequent storytelling after a new insight has been found.
Data visualization
Data visualization is a critical step in the data science process, helping teams and individuals convey data more effectively to colleagues and decision makers. Teams that manage reporting systems typically leverage defined template views to monitor performance. However, data visualization isn’t limited to performance dashboards. For example, while text mining an analyst may use a word cloud to to capture key concepts, trends, and hidden relationships within this unstructured data. Alternatively, they may utilize a graph structure to illustrate relationships between entities in a knowledge graph. There are a number of ways to represent different types of data, and it’s important to remember that it is a skillset that should extend beyond your core analytics team.
Use this model selection framework to choose the most appropriate model while balancing your performance requirements with cost, risks and deployment needs.
Register for the ebook on generative AI
The earliest form of data visualization can be traced back the Egyptians in the pre-17th century, largely used to assist in navigation. As time progressed, people leveraged data visualizations for broader applications, such as in economic, social, health disciplines. Perhaps most notably, Edward Tufte published The Visual Display of Quantitative Information (link resides outside ibm.com), which illustrated that individuals could utilize data visualization to present data in a more effective manner. His book continues to stand the test of time, especially as companies turn to dashboards to report their performance metrics in real-time. Dashboards are effective data visualization tools for tracking and visualizing data from multiple data sources, providing visibility into the effects of specific behaviors by a team or an adjacent one on performance. Dashboards include common visualization techniques, such as:
- Tables: This consists of rows and columns used to compare variables. Tables can show a great deal of information in a structured way, but they can also overwhelm users that are simply looking for high-level trends.
- Pie charts and stacked bar charts: These graphs are divided into sections that represent parts of a whole. They provide a simple way to organize data and compare the size of each component to one other.
- Line charts and area charts: These visuals show change in one or more quantities by plotting a series of data points over time and are frequently used within predictive analytics. Line graphs utilize lines to demonstrate these changes while area charts connect data points with line segments, stacking variables on top of one another and using color to distinguish between variables.
- Histograms: This graph plots a distribution of numbers using a bar chart (with no spaces between the bars), representing the quantity of data that falls within a particular range. This visual makes it easy for an end user to identify outliers within a given dataset.
- Scatter plots: These visuals are beneficial in reveling the relationship between two variables, and they are commonly used within regression data analysis. However, these can sometimes be confused with bubble charts, which are used to visualize three variables via the x-axis, the y-axis, and the size of the bubble.
- Heat maps: These graphical representation displays are helpful in visualizing behavioral data by location. This can be a location on a map, or even a webpage.
- Tree maps, which display hierarchical data as a set of nested shapes, typically rectangles. Treemaps are great for comparing the proportions between categories via their area size.
Access to data visualization tools has never been easier. Open source libraries, such as D3.js, provide a way for analysts to present data in an interactive way, allowing them to engage a broader audience with new data. Some of the most popular open source visualization libraries include:
- D3.js: It is a front-end JavaScript library for producing dynamic, interactive data visualizations in web browsers. D3.js (link resides outside ibm.com) uses HTML, CSS, and SVG to create visual representations of data that can be viewed on any browser. It also provides features for interactions and animations.
- ECharts: A powerful charting and visualization library that offers an easy way to add intuitive, interactive, and highly customizable charts to products, research papers, presentations, etc. Echarts (link resides outside ibm.com) is based in JavaScript and ZRender, a lightweight canvas library.
- Vega: Vega (link resides outside ibm.com) defines itself as “visualization grammar,” providing support to customize visualizations across large datasets which are accessible from the web.
- deck.gl: It is part of Uber's open source visualization framework suite. deck.gl (link resides outside ibm.com) is a framework, which is used for exploratory data analysis on big data. It helps build high-performance GPU-powered visualization on the web.
With so many data visualization tools readily available, there has also been a rise in ineffective information visualization. Visual communication should be simple and deliberate to ensure that your data visualization helps your target audience arrive at your intended insight or conclusion. The following best practices can help ensure your data visualization is useful and clear:
Set the context: It’s important to provide general background information to ground the audience around why this particular data point is important. For example, if e-mail open rates were underperforming, we may want to illustrate how a company’s open rate compares to the overall industry, demonstrating that the company has a problem within this marketing channel. To drive an action, the audience needs to understand how current performance compares to something tangible, like a goal, benchmark, or other key performance indicators (KPIs).
Know your audience(s): Think about who your visualization is designed for and then make sure your data visualization fits their needs. What is that person trying to accomplish? What kind of questions do they care about? Does your visualization address their concerns? You’ll want the data that you provide to motivate people to act within their scope of their role. If you’re unsure if the visualization is clear, present it to one or two people within your target audience to get feedback, allowing you to make additional edits prior to a large presentation.
Choose an effective visual: Specific visuals are designed for specific types of datasets. For instance, scatter plots display the relationship between two variables well, while line graphs display time series data well. Ensure that the visual actually assists the audience in understanding your main takeaway. Misalignment of charts and data can result in the opposite, confusing your audience further versus providing clarity.
Keep it simple: Data visualization tools can make it easy to add all sorts of information to your visual. However, just because you can, it doesn’t mean that you should! In data visualization, you want to be very deliberate about the additional information that you add to focus user attention. For example, do you need data labels on every bar in your bar chart? Perhaps you only need one or two to help illustrate your point. Do you need a variety of colors to communicate your idea? Are you using colors that are accessible to a wide range of audiences (e.g. accounting for color blind audiences)? Design your data visualization for maximum impact by eliminating information that may distract your target audience.
An AI-infused integrated planning solution that helps you transcend the limits of manual planning.
Build, run and manage AI models. Prepare data and build models on any cloud using open source code or visual modeling. Predict and optimize your outcomes.
Unlock the value of enterprise data and build an insight-driven organization that delivers business advantage with IBM Consulting.
Your trusted Watson co-pilot for smarter analytics and confident decisions.
Use features within IBM Watson® Studio that help you visualize and gain insights into your data, then cleanse and transform your data to build high-quality predictive models.
Data Refinery makes it easy to explore, prepare, and deliver data that people across your organization can trust.
Learn how to use Apache Superset (a modern, enterprise-ready business intelligence web application) with Netezza database to uncover the story behind the data.
Predict outcomes with flexible AI-infused forecasting and analyze what-if scenarios in real-time. IBM Planning Analytics is an integrated business planning solution that turns raw data into actionable insights. Deploy as you need, on premises or on cloud.

- PRESENTATION SKILLS
Presenting Data
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Presentation Skills:
- A - Z List of Presentation Skills
- Top Tips for Effective Presentations
- General Presentation Skills
- What is a Presentation?
- Preparing for a Presentation
- Organising the Material
- Writing Your Presentation
- Deciding the Presentation Method
- Managing your Presentation Notes
- Working with Visual Aids
- Managing the Event
- Coping with Presentation Nerves
- Dealing with Questions
- How to Build Presentations Like a Consultant
- 7 Qualities of Good Speakers That Can Help You Be More Successful
- Self-Presentation in Presentations
- Specific Presentation Events
- Remote Meetings and Presentations
- Giving a Speech
- Presentations in Interviews
- Presenting to Large Groups and Conferences
- Giving Lectures and Seminars
- Managing a Press Conference
- Attending Public Consultation Meetings
- Managing a Public Consultation Meeting
- Crisis Communications
- Elsewhere on Skills You Need:
- Communication Skills
- Facilitation Skills
- Teams, Groups and Meetings
- Effective Speaking
- Question Types
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
When and how should you use data in a presentation?
The answer is that you should use figures and numbers whenever they give the best evidence to back up your argument, or to tell your story. But how to present that data is more difficult.
Many people are not interested in tables of numbers, and may struggle to understand graphs. How can you help walk them through the data?
This page is designed to help you to answer that question by setting out some simple rules for presenting data.
Remember that You Are Telling Your Audience a Story
All presentations are basically story-telling opportunities.
Human beings have been hard-wired, over millions of years of evolution, to enjoy and respond to stories. It’s best to work with it, not fight it, because if you tell your audience a story, they are likely to listen much more carefully, and also move towards a logical conclusion: the insight to which you are trying to lead them.
Once you understand this, the issue of using data falls into place: it is to provide evidence of how your story unfolds.
Use Data to Tell the Story
You are not presenting data as such, you are using data to help you to tell your story in a more meaningful way.
This means that whenever you are required to present data, you should be asking yourself:
‘ What is the story in this data? ’,
‘ How best can I tell this story to my audience? ’
A Picture Tells a Thousand Words
90% of the information sent to the brain is visual and over 90% of all human communication is visual. Processing text requires our brains to work much harder than when processing images. In fact, the brain can process pictorial information 60,000 times faster than written information.
There is considerable truth in the saying ‘a picture tells a thousand words’ . It may not be literally a thousand, but it is often much easier to use a picture than to describe numerical information in words.
The data itself may be vitally important, but without a visual presentation of that data, its impact (and therefore your message) may be lost.
There are many people in the world who do not find it easy to understand numbers.
There are also many people who will simply switch off if you show them figures in a table. But if you present data in a graph or pie chart, you make a pictorial representation of the data. It makes the numbers much easier to understand. Trends and proportions become more obvious.
Consider this set of data:
| Sales | |
| 1st Qtr | 7.5 |
| 2nd Qtr | 3.1 |
| 3rd Qtr | 1.5 |
| 4th Qtr | 1.1 |
Even for the highly numerate, the immediate point is only that there are lot more sales in the first quarter. You would have to do some adding up and dividing to work out the relationships between the four numbers. It also requires much more concentration to read and absorb the information in this format.
Now consider the same data in a pie chart:
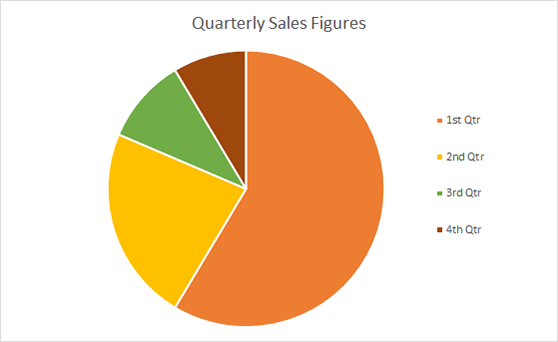
It is immediately and shiningly obvious, even for those who struggle with numbers, that more than half of all sales were in the first quarter, and that over 75% were in the first two quarters.
What’s more, nobody is going to be straining from the back of the room to read your figures. You really can see a lot more from a picture.
But, and this is important, make sure that the graph is a good one.
Check that your graph or chart is visually appealing, that all the labels are clear, and that you have used an appropriate type of graph or chart. Poor graph-making is always obvious and can lead to confusion. Your message will also have much more impact if you choose the right type of graph or chart.
For more about this, see our page on Graphs and Charts .
KISS: Keep It Simple, Stupid!
When you’re good at statistics, it’s very tempting to do some really whizzy analysis. And once you’ve done that, you really want to show everyone how clever you are, and how much work you’ve done.
But does it really help to make your point?
Then don’t present it.
In the (relatively rare) cases when you actually need some really whizzy analysis, you then need to ask yourself whether everyone will understand it. And, in these days of presentations being posted on the internet, will the casual reader of your slides understand it later?
Once again, if the answer is ‘probably not’, then don’t use it.
Leave It Out...
If you can’t summarise your analysis in one or two brief and clear sentences, then don’t include it.
It also follows that if you don’t need to include data to make your point, then it may be best not to do so. A slide that is likely to be misunderstood or produce confusion is worse than no slide at all. So cut out all unnecessary data and focus on what you really need to tell your story .
Remember KISS: Keep It Simple, Stupid.
Highlight the Main Features to Draw Out the Insights
We’re not suggesting that you should ‘ dumb down ’ your presentation, but there is no harm in highlighting the key features, as well as cutting out unnecessary data.
Suppose once again that you are using the sales figures from the last four quarters. You want to show the actual figures. Why not use a highlighting tool to emphasise that the first quarter is more than half?
With PowerPoint and other presentation software, you can make each circle appear separately, as you make your point and discuss the insights.
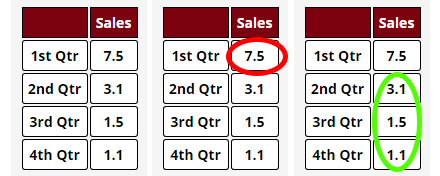
A little creative use of the technology can help you to highlight certain figures, and once again, make the story clearer.
Take-home message
Paradoxically, your presentation of any data should be designed to move the conversation away from the data and into the insight and action that should result from it.
In other words:
‘What happened there?’
‘What are we going to do about it?’
If you look at your presentation, data and all, and it’s not clear how you would get from the data to the insight and then the action, it’s probably a good idea to look at it again.
Remember, it’s the story that matters… and then what happens as a result.
Continue to: Writing Your Presentation Working with Visual Aids
See also: What is Your Story? How to Identify Your Story from Raw Data Crisis Communications Presenting to Large Groups Simple Statistical Analysis
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Creating Brand Value
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
17 Data Visualization Techniques All Professionals Should Know

- 17 Sep 2019
There’s a growing demand for business analytics and data expertise in the workforce. But you don’t need to be a professional analyst to benefit from data-related skills.
Becoming skilled at common data visualization techniques can help you reap the rewards of data-driven decision-making , including increased confidence and potential cost savings. Learning how to effectively visualize data could be the first step toward using data analytics and data science to your advantage to add value to your organization.
Several data visualization techniques can help you become more effective in your role. Here are 17 essential data visualization techniques all professionals should know, as well as tips to help you effectively present your data.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Data Visualization?
Data visualization is the process of creating graphical representations of information. This process helps the presenter communicate data in a way that’s easy for the viewer to interpret and draw conclusions.
There are many different techniques and tools you can leverage to visualize data, so you want to know which ones to use and when. Here are some of the most important data visualization techniques all professionals should know.
Data Visualization Techniques
The type of data visualization technique you leverage will vary based on the type of data you’re working with, in addition to the story you’re telling with your data .
Here are some important data visualization techniques to know:
- Gantt Chart
- Box and Whisker Plot
- Waterfall Chart
- Scatter Plot
- Pictogram Chart
- Highlight Table
- Bullet Graph
- Choropleth Map
- Network Diagram
- Correlation Matrices
1. Pie Chart

Pie charts are one of the most common and basic data visualization techniques, used across a wide range of applications. Pie charts are ideal for illustrating proportions, or part-to-whole comparisons.
Because pie charts are relatively simple and easy to read, they’re best suited for audiences who might be unfamiliar with the information or are only interested in the key takeaways. For viewers who require a more thorough explanation of the data, pie charts fall short in their ability to display complex information.
2. Bar Chart
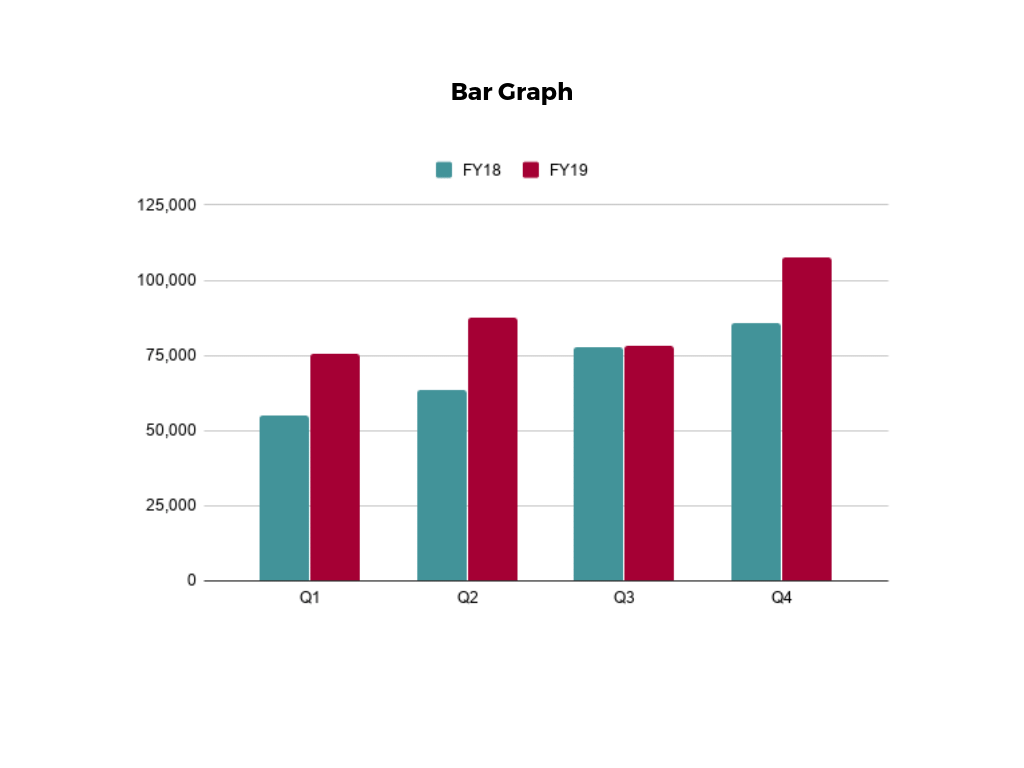
The classic bar chart , or bar graph, is another common and easy-to-use method of data visualization. In this type of visualization, one axis of the chart shows the categories being compared, and the other, a measured value. The length of the bar indicates how each group measures according to the value.
One drawback is that labeling and clarity can become problematic when there are too many categories included. Like pie charts, they can also be too simple for more complex data sets.
3. Histogram

Unlike bar charts, histograms illustrate the distribution of data over a continuous interval or defined period. These visualizations are helpful in identifying where values are concentrated, as well as where there are gaps or unusual values.
Histograms are especially useful for showing the frequency of a particular occurrence. For instance, if you’d like to show how many clicks your website received each day over the last week, you can use a histogram. From this visualization, you can quickly determine which days your website saw the greatest and fewest number of clicks.
4. Gantt Chart

Gantt charts are particularly common in project management, as they’re useful in illustrating a project timeline or progression of tasks. In this type of chart, tasks to be performed are listed on the vertical axis and time intervals on the horizontal axis. Horizontal bars in the body of the chart represent the duration of each activity.
Utilizing Gantt charts to display timelines can be incredibly helpful, and enable team members to keep track of every aspect of a project. Even if you’re not a project management professional, familiarizing yourself with Gantt charts can help you stay organized.
5. Heat Map
A heat map is a type of visualization used to show differences in data through variations in color. These charts use color to communicate values in a way that makes it easy for the viewer to quickly identify trends. Having a clear legend is necessary in order for a user to successfully read and interpret a heatmap.
There are many possible applications of heat maps. For example, if you want to analyze which time of day a retail store makes the most sales, you can use a heat map that shows the day of the week on the vertical axis and time of day on the horizontal axis. Then, by shading in the matrix with colors that correspond to the number of sales at each time of day, you can identify trends in the data that allow you to determine the exact times your store experiences the most sales.
6. A Box and Whisker Plot
A box and whisker plot , or box plot, provides a visual summary of data through its quartiles. First, a box is drawn from the first quartile to the third of the data set. A line within the box represents the median. “Whiskers,” or lines, are then drawn extending from the box to the minimum (lower extreme) and maximum (upper extreme). Outliers are represented by individual points that are in-line with the whiskers.
This type of chart is helpful in quickly identifying whether or not the data is symmetrical or skewed, as well as providing a visual summary of the data set that can be easily interpreted.
7. Waterfall Chart
A waterfall chart is a visual representation that illustrates how a value changes as it’s influenced by different factors, such as time. The main goal of this chart is to show the viewer how a value has grown or declined over a defined period. For example, waterfall charts are popular for showing spending or earnings over time.
8. Area Chart

An area chart , or area graph, is a variation on a basic line graph in which the area underneath the line is shaded to represent the total value of each data point. When several data series must be compared on the same graph, stacked area charts are used.
This method of data visualization is useful for showing changes in one or more quantities over time, as well as showing how each quantity combines to make up the whole. Stacked area charts are effective in showing part-to-whole comparisons.
9. Scatter Plot

Another technique commonly used to display data is a scatter plot . A scatter plot displays data for two variables as represented by points plotted against the horizontal and vertical axis. This type of data visualization is useful in illustrating the relationships that exist between variables and can be used to identify trends or correlations in data.
Scatter plots are most effective for fairly large data sets, since it’s often easier to identify trends when there are more data points present. Additionally, the closer the data points are grouped together, the stronger the correlation or trend tends to be.
10. Pictogram Chart
Pictogram charts , or pictograph charts, are particularly useful for presenting simple data in a more visual and engaging way. These charts use icons to visualize data, with each icon representing a different value or category. For example, data about time might be represented by icons of clocks or watches. Each icon can correspond to either a single unit or a set number of units (for example, each icon represents 100 units).
In addition to making the data more engaging, pictogram charts are helpful in situations where language or cultural differences might be a barrier to the audience’s understanding of the data.
11. Timeline

Timelines are the most effective way to visualize a sequence of events in chronological order. They’re typically linear, with key events outlined along the axis. Timelines are used to communicate time-related information and display historical data.
Timelines allow you to highlight the most important events that occurred, or need to occur in the future, and make it easy for the viewer to identify any patterns appearing within the selected time period. While timelines are often relatively simple linear visualizations, they can be made more visually appealing by adding images, colors, fonts, and decorative shapes.
12. Highlight Table

A highlight table is a more engaging alternative to traditional tables. By highlighting cells in the table with color, you can make it easier for viewers to quickly spot trends and patterns in the data. These visualizations are useful for comparing categorical data.
Depending on the data visualization tool you’re using, you may be able to add conditional formatting rules to the table that automatically color cells that meet specified conditions. For instance, when using a highlight table to visualize a company’s sales data, you may color cells red if the sales data is below the goal, or green if sales were above the goal. Unlike a heat map, the colors in a highlight table are discrete and represent a single meaning or value.
13. Bullet Graph

A bullet graph is a variation of a bar graph that can act as an alternative to dashboard gauges to represent performance data. The main use for a bullet graph is to inform the viewer of how a business is performing in comparison to benchmarks that are in place for key business metrics.
In a bullet graph, the darker horizontal bar in the middle of the chart represents the actual value, while the vertical line represents a comparative value, or target. If the horizontal bar passes the vertical line, the target for that metric has been surpassed. Additionally, the segmented colored sections behind the horizontal bar represent range scores, such as “poor,” “fair,” or “good.”
14. Choropleth Maps

A choropleth map uses color, shading, and other patterns to visualize numerical values across geographic regions. These visualizations use a progression of color (or shading) on a spectrum to distinguish high values from low.
Choropleth maps allow viewers to see how a variable changes from one region to the next. A potential downside to this type of visualization is that the exact numerical values aren’t easily accessible because the colors represent a range of values. Some data visualization tools, however, allow you to add interactivity to your map so the exact values are accessible.
15. Word Cloud

A word cloud , or tag cloud, is a visual representation of text data in which the size of the word is proportional to its frequency. The more often a specific word appears in a dataset, the larger it appears in the visualization. In addition to size, words often appear bolder or follow a specific color scheme depending on their frequency.
Word clouds are often used on websites and blogs to identify significant keywords and compare differences in textual data between two sources. They are also useful when analyzing qualitative datasets, such as the specific words consumers used to describe a product.
16. Network Diagram

Network diagrams are a type of data visualization that represent relationships between qualitative data points. These visualizations are composed of nodes and links, also called edges. Nodes are singular data points that are connected to other nodes through edges, which show the relationship between multiple nodes.
There are many use cases for network diagrams, including depicting social networks, highlighting the relationships between employees at an organization, or visualizing product sales across geographic regions.
17. Correlation Matrix

A correlation matrix is a table that shows correlation coefficients between variables. Each cell represents the relationship between two variables, and a color scale is used to communicate whether the variables are correlated and to what extent.
Correlation matrices are useful to summarize and find patterns in large data sets. In business, a correlation matrix might be used to analyze how different data points about a specific product might be related, such as price, advertising spend, launch date, etc.
Other Data Visualization Options
While the examples listed above are some of the most commonly used techniques, there are many other ways you can visualize data to become a more effective communicator. Some other data visualization options include:
- Bubble clouds
- Circle views
- Dendrograms
- Dot distribution maps
- Open-high-low-close charts
- Polar areas
- Radial trees
- Ring Charts
- Sankey diagram
- Span charts
- Streamgraphs
- Wedge stack graphs
- Violin plots

Tips For Creating Effective Visualizations
Creating effective data visualizations requires more than just knowing how to choose the best technique for your needs. There are several considerations you should take into account to maximize your effectiveness when it comes to presenting data.
Related : What to Keep in Mind When Creating Data Visualizations in Excel
One of the most important steps is to evaluate your audience. For example, if you’re presenting financial data to a team that works in an unrelated department, you’ll want to choose a fairly simple illustration. On the other hand, if you’re presenting financial data to a team of finance experts, it’s likely you can safely include more complex information.
Another helpful tip is to avoid unnecessary distractions. Although visual elements like animation can be a great way to add interest, they can also distract from the key points the illustration is trying to convey and hinder the viewer’s ability to quickly understand the information.
Finally, be mindful of the colors you utilize, as well as your overall design. While it’s important that your graphs or charts are visually appealing, there are more practical reasons you might choose one color palette over another. For instance, using low contrast colors can make it difficult for your audience to discern differences between data points. Using colors that are too bold, however, can make the illustration overwhelming or distracting for the viewer.
Related : Bad Data Visualization: 5 Examples of Misleading Data
Visuals to Interpret and Share Information
No matter your role or title within an organization, data visualization is a skill that’s important for all professionals. Being able to effectively present complex data through easy-to-understand visual representations is invaluable when it comes to communicating information with members both inside and outside your business.
There’s no shortage in how data visualization can be applied in the real world. Data is playing an increasingly important role in the marketplace today, and data literacy is the first step in understanding how analytics can be used in business.
Are you interested in improving your analytical skills? Learn more about Business Analytics , our eight-week online course that can help you use data to generate insights and tackle business decisions.
This post was updated on January 20, 2022. It was originally published on September 17, 2019.

About the Author
10 Methods of Data Presentation That Really Work in 2024
Leah Nguyen • 20 August, 2024 • 13 min read
Have you ever presented a data report to your boss/coworkers/teachers thinking it was super dope like you’re some cyber hacker living in the Matrix, but all they saw was a pile of static numbers that seemed pointless and didn't make sense to them?
Understanding digits is rigid . Making people from non-analytical backgrounds understand those digits is even more challenging.
How can you clear up those confusing numbers and make your presentation as clear as the day? Let's check out these best ways to present data. 💎
| How many type of charts are available to present data? | 7 |
| How many charts are there in statistics? | 4, including bar, line, histogram and pie. |
| How many types of charts are available in Excel? | 8 |
| Who invented charts? | William Playfair |
| When were the charts invented? | 18th Century |
More Tips with AhaSlides
- Marketing Presentation
- Survey Result Presentation
- Types of Presentation

Start in seconds.
Get any of the above examples as templates. Sign up for free and take what you want from the template library!
Data Presentation - What Is It?
The term ’data presentation’ relates to the way you present data in a way that makes even the most clueless person in the room understand.
Some say it’s witchcraft (you’re manipulating the numbers in some ways), but we’ll just say it’s the power of turning dry, hard numbers or digits into a visual showcase that is easy for people to digest.
Presenting data correctly can help your audience understand complicated processes, identify trends, and instantly pinpoint whatever is going on without exhausting their brains.
Good data presentation helps…
- Make informed decisions and arrive at positive outcomes . If you see the sales of your product steadily increase throughout the years, it’s best to keep milking it or start turning it into a bunch of spin-offs (shoutout to Star Wars👀).
- Reduce the time spent processing data . Humans can digest information graphically 60,000 times faster than in the form of text. Grant them the power of skimming through a decade of data in minutes with some extra spicy graphs and charts.
- Communicate the results clearly . Data does not lie. They’re based on factual evidence and therefore if anyone keeps whining that you might be wrong, slap them with some hard data to keep their mouths shut.
- Add to or expand the current research . You can see what areas need improvement, as well as what details often go unnoticed while surfing through those little lines, dots or icons that appear on the data board.
Methods of Data Presentation and Examples
Imagine you have a delicious pepperoni, extra-cheese pizza. You can decide to cut it into the classic 8 triangle slices, the party style 12 square slices, or get creative and abstract on those slices.
There are various ways to cut a pizza and you get the same variety with how you present your data. In this section, we will bring you the 10 ways to slice a pizza - we mean to present your data - that will make your company’s most important asset as clear as day. Let's dive into 10 ways to present data efficiently.
#1 - Tabular
Among various types of data presentation, tabular is the most fundamental method, with data presented in rows and columns. Excel or Google Sheets would qualify for the job. Nothing fancy.
This is an example of a tabular presentation of data on Google Sheets. Each row and column has an attribute (year, region, revenue, etc.), and you can do a custom format to see the change in revenue throughout the year.
When presenting data as text, all you do is write your findings down in paragraphs and bullet points, and that’s it. A piece of cake to you, a tough nut to crack for whoever has to go through all of the reading to get to the point.
- 65% of email users worldwide access their email via a mobile device.
- Emails that are optimised for mobile generate 15% higher click-through rates.
- 56% of brands using emojis in their email subject lines had a higher open rate.
(Source: CustomerThermometer )
All the above quotes present statistical information in textual form. Since not many people like going through a wall of texts, you’ll have to figure out another route when deciding to use this method, such as breaking the data down into short, clear statements, or even as catchy puns if you’ve got the time to think of them.
#3 - Pie chart
A pie chart (or a ‘donut chart’ if you stick a hole in the middle of it) is a circle divided into slices that show the relative sizes of data within a whole. If you’re using it to show percentages, make sure all the slices add up to 100%.
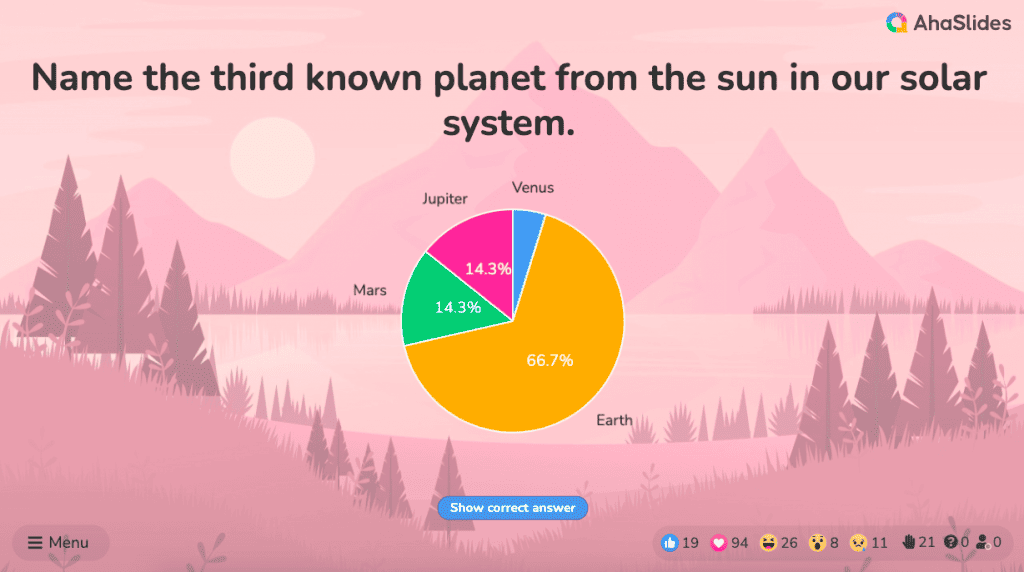
The pie chart is a familiar face at every party and is usually recognised by most people. However, one setback of using this method is our eyes sometimes can’t identify the differences in slices of a circle, and it’s nearly impossible to compare similar slices from two different pie charts, making them the villains in the eyes of data analysts.
#4 - Bar chart
The bar chart is a chart that presents a bunch of items from the same category, usually in the form of rectangular bars that are placed at an equal distance from each other. Their heights or lengths depict the values they represent.
They can be as simple as this:
Or more complex and detailed like this example of data presentation. Contributing to an effective statistic presentation, this one is a grouped bar chart that not only allows you to compare categories but also the groups within them as well.
#5 - Histogram
Similar in appearance to the bar chart but the rectangular bars in histograms don’t often have the gap like their counterparts.
Instead of measuring categories like weather preferences or favourite films as a bar chart does, a histogram only measures things that can be put into numbers.
Teachers can use presentation graphs like a histogram to see which score group most of the students fall into, like in this example above.
#6 - Line graph
Recordings to ways of displaying data, we shouldn't overlook the effectiveness of line graphs. Line graphs are represented by a group of data points joined together by a straight line. There can be one or more lines to compare how several related things change over time.
On a line chart’s horizontal axis, you usually have text labels, dates or years, while the vertical axis usually represents the quantity (e.g.: budget, temperature or percentage).
#7 - Pictogram graph
A pictogram graph uses pictures or icons relating to the main topic to visualise a small dataset. The fun combination of colours and illustrations makes it a frequent use at schools.
Pictograms are a breath of fresh air if you want to stay away from the monotonous line chart or bar chart for a while. However, they can present a very limited amount of data and sometimes they are only there for displays and do not represent real statistics.
#8 - Radar chart
If presenting five or more variables in the form of a bar chart is too stuffy then you should try using a radar chart, which is one of the most creative ways to present data.
Radar charts show data in terms of how they compare to each other starting from the same point. Some also call them ‘spider charts’ because each aspect combined looks like a spider web.
Radar charts can be a great use for parents who’d like to compare their child’s grades with their peers to lower their self-esteem. You can see that each angular represents a subject with a score value ranging from 0 to 100. Each student’s score across 5 subjects is highlighted in a different colour.
If you think that this method of data presentation somehow feels familiar, then you’ve probably encountered one while playing Pokémon .
#9 - Heat map
A heat map represents data density in colours. The bigger the number, the more colour intensity that data will be represented.
Most US citizens would be familiar with this data presentation method in geography. For elections, many news outlets assign a specific colour code to a state, with blue representing one candidate and red representing the other. The shade of either blue or red in each state shows the strength of the overall vote in that state.
Another great thing you can use a heat map for is to map what visitors to your site click on. The more a particular section is clicked the ‘hotter’ the colour will turn, from blue to bright yellow to red.
#10 - Scatter plot
If you present your data in dots instead of chunky bars, you’ll have a scatter plot.
A scatter plot is a grid with several inputs showing the relationship between two variables. It’s good at collecting seemingly random data and revealing some telling trends.
For example, in this graph, each dot shows the average daily temperature versus the number of beach visitors across several days. You can see that the dots get higher as the temperature increases, so it’s likely that hotter weather leads to more visitors.
5 Data Presentation Mistakes to Avoid
#1 - assume your audience understands what the numbers represent.
You may know all the behind-the-scenes of your data since you’ve worked with them for weeks, but your audience doesn’t.
Showing without telling only invites more and more questions from your audience, as they have to constantly make sense of your data, wasting the time of both sides as a result.
While showing your data presentations, you should tell them what the data are about before hitting them with waves of numbers first. You can use interactive activities such as polls , word clouds , online quizzes and Q&A sections , combined with icebreaker games , to assess their understanding of the data and address any confusion beforehand.
#2 - Use the wrong type of chart
Charts such as pie charts must have a total of 100% so if your numbers accumulate to 193% like this example below, you’re definitely doing it wrong.
Before making a chart, ask yourself: what do I want to accomplish with my data? Do you want to see the relationship between the data sets, show the up and down trends of your data, or see how segments of one thing make up a whole?
Remember, clarity always comes first. Some data visualisations may look cool, but if they don’t fit your data, steer clear of them.
#3 - Make it 3D
3D is a fascinating graphical presentation example. The third dimension is cool, but full of risks.
Can you see what’s behind those red bars? Because we can’t either. You may think that 3D charts add more depth to the design, but they can create false perceptions as our eyes see 3D objects closer and bigger than they appear, not to mention they cannot be seen from multiple angles.
#4 - Use different types of charts to compare contents in the same category
This is like comparing a fish to a monkey. Your audience won’t be able to identify the differences and make an appropriate correlation between the two data sets.
Next time, stick to one type of data presentation only. Avoid the temptation of trying various data visualisation methods in one go and make your data as accessible as possible.
#5 - Bombard the audience with too much information
The goal of data presentation is to make complex topics much easier to understand, and if you’re bringing too much information to the table, you’re missing the point.
The more information you give, the more time it will take for your audience to process it all. If you want to make your data understandable and give your audience a chance to remember it, keep the information within it to an absolute minimum. You should end your session with open-ended questions to see what your participants really think.
What are the Best Methods of Data Presentation?
Finally, which is the best way to present data?
The answer is…
There is none! Each type of presentation has its own strengths and weaknesses and the one you choose greatly depends on what you’re trying to do.
For example:
- Go for a scatter plot if you’re exploring the relationship between different data values, like seeing whether the sales of ice cream go up because of the temperature or because people are just getting more hungry and greedy each day?
- Go for a line graph if you want to mark a trend over time.
- Go for a heat map if you like some fancy visualisation of the changes in a geographical location, or to see your visitors' behaviour on your website.
- Go for a pie chart (especially in 3D) if you want to be shunned by others because it was never a good idea👇
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a chart presentation.
A chart presentation is a way of presenting data or information using visual aids such as charts, graphs, and diagrams. The purpose of a chart presentation is to make complex information more accessible and understandable for the audience.
When can I use charts for the presentation?
Charts can be used to compare data, show trends over time, highlight patterns, and simplify complex information.
Why should you use charts for presentation?
You should use charts to ensure your contents and visuals look clean, as they are the visual representative, provide clarity, simplicity, comparison, contrast and super time-saving!
What are the 4 graphical methods of presenting data?
Histogram, Smoothed frequency graph, Pie diagram or Pie chart, Cumulative or ogive frequency graph, and Frequency Polygon.
Leah Nguyen
Words that convert, stories that stick. I turn complex ideas into engaging narratives - helping audiences learn, remember, and take action.
Tips to Engage with Polls & Trivia
More from AhaSlides

- List of Commerce Articles
- Diagrammatic Presentation Of Data
Diagrammatic Presentation of Data
The diagrammatic presentation of data gives an immediate understanding of the real situation to be defined by the data in comparison to the tabular presentation of data or textual representations. It translates the highly complex ideas included in numbers into a more concrete and quickly understandable form pretty effectively. Diagrams may be less certain but are much more efficient than tables in displaying the data. There are many kinds of diagrams in general use. Amongst them the significant ones are the following:
(i) Geometric diagram
(ii) Frequency diagram
(iii) Arithmetic line graph
Also check: Meaning and Objective of Tabulation
Basics of Diagrammatic Presentation
Concept of Diagrammatic Presentation
- It is a technique of presenting numeric data through pictograms, cartograms, bar diagrams, and pie diagrams. It is the most attractive and appealing way to represent statistical data. Diagrams help in visual comparison and they have a bird’s eye view.
- Under pictograms, we use pictures to present data. For example, if we have to show the production of cars, we can draw cars. Suppose the production of cars is 40,000, we can show it by a picture having four cars, where 1 car represents 10,000 units.
- Under cartograms, we make use of maps to show the geographical allocation of certain things.
- Bar diagrams are rectangular and placed on the same base. Their heights represent the magnitude/value of the variable. The width of all the bars and the gaps between the two bars are kept the same.
- Pie diagram is a circle that is subdivided or partitioned to show the proportion of various components of the data.
- Out of the given diagrams, only one-dimensional bar diagrams and pie diagrams are there in our scope.
General Guidelines
Title: Every diagram must be given a suitable title which should be small and self-explanatory.
Size: The size of the diagram should be appropriate, i.e., neither too small nor too big.
Paper used: Diagrams are generally prepared on blank paper.
Scale: Under one-dimensional diagrams, especially bar diagrams, the y-axis is more important from the point of view of the decision of scale because we represent magnitude along this axis.
Index: When two or more variables are presented and different types of line/shading patterns are used to distinguish, an index must be given to show their details.
Selection of proper type of diagram: It is very important to select the correct type of diagram to represent data effectively.
Advantages of Diagrammatic Presentation
(1) Diagrams are attractive and impressive: The data presented in the form of diagrams can attract the attention of even a common man.
(2) Easy to remember: (a) Diagrams have a great memorising effect. (b) The picture created in mind by the diagrams last much longer than those created by figures presented through the tabular forms.
(3) Diagrams save time : (a) They present complex mass data in a simplified manner. (b) The data presented in the form of diagrams can be understood by the user very quickly.
(4) Diagrams simplify data: Diagrams are used to represent a huge mass of complex data in a simplified and intelligible form which is easy to understand.
(5) Diagrams are useful in making comparison: It becomes easier to compare two sets of data visually by presenting them through diagrams.
(6) More informative : Diagrams not only depict the characteristics of data but also bring out other hidden facts and relations which are not possible from the classified and tabulated data.
Types of One-Dimensional Diagram
One-dimensional diagram is a diagram in which only the length of the diagram is considered. It can be drawn in the form of a line or various types of bars.
The following are the types of one-dimensional diagram.
(1) Simple bar diagram
Simple bar diagram consists of a group of rectangular bars of equal width for each class or category of data.
(2) Multiple bar diagram
This diagram is used when we have to make a comparison between two or more variables like income and expenditure, import and export for different years, marks obtained in different subjects in different classes, etc.
(3) Subdivided bar diagram
This diagram is constructed by subdividing the bars in the ratio of various components.
(4) Percentage bar diagram
The subdivided bar diagram presented on a percentage basis is known as the percentage bar diagram.
(5) Broken-scale bar diagram
This diagram is used when the value of one observation is very high as compared to the other.
To gain space for the smaller bars of the series, the larger bars may be broken.
The value of each bar is written at the top of the bar.
(6) Deviation bar diagram
Deviation bars are used to represent net changes in the data like net profit, net loss, net exports, net imports, etc.
Meaning of Pie Diagram
A pie diagram is a circle that is divided into sections. The size of each section indicates the magnitude of each component as a part of the whole.
Steps involved in constructing pie diagram
- Convert the given values into percentage form and multiply it with 3.6’ to get the amount of angle for each item.
- Draw a circle and start the diagram at the 12 O‘clock position.
- Take the highest angle first with the protector (D) and mark the lower angles successively.
- Shade different angles differently to show distinction in each item.
Solved Questions
Q.1. Why is a diagrammatic presentation better than tabulation of data?
It makes the data more attractive as compared to tabulation and helps in visual comparison.
Q.2. Why do media persons prefer diagrammatic presentation of data?
Because it has an eye-catching effect and a long-lasting impact upon its readers/viewers.
Q.3. What will be the degree of an angle in the pie diagram if a family spends 50% of its income in food?
(50 ÷ 100) X 360 (Or) 50 x 3.6 = 180’
Q.4. Which bar diagram is used to show two or more characteristics of the data?
Multiple bar diagram
Q.5. Mention the sum of all the angles formed at the centre of a circle.
Q.6. Name a bar diagram where the height of all the bars is the same.
Percentage bar diagram
Q.7. Which diagram can be used to depict various components of a variable?
Subdivided bar diagram
Q.8. What is a multiple bar diagram?
A multiple bar diagram is one that shows more than one characteristic of data.
Q.9. Which bar diagram is used to represent the net changes in data?
Deviation bar diagram
Q.10. What is the other name of the subdivided bar Diagram?
Component bar diagram
The above-mentioned concept is for CBSE Class 11 Statistics for Economics – Diagrammatic Presentation of Data. For solutions and study materials, visit our website or download the app for more information and the best learning experience.
| COMMERCE Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Byjus is a good learning app
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Presentation of Data

Data Presenting for Clearer Reference
Imagine the statistical data without a definite presentation, will be burdensome! Data presentation is one of the important aspects of Statistics. Presenting the data helps the users to study and explain the statistics thoroughly. We are going to discuss this presentation of data and know-how information is laid down methodically.
In this context, we are going to present the topic - Presentation of Data which is to be referred to by the students and the same is to be studied in regard to the types of presentations of data.
Presentation of Data and Information
Statistics is all about data. Presenting data effectively and efficiently is an art. You may have uncovered many truths that are complex and need long explanations while writing. This is where the importance of the presentation of data comes in. You have to present your findings in such a way that the readers can go through them quickly and understand each and every point that you wanted to showcase. As time progressed and new and complex research started happening, people realized the importance of the presentation of data to make sense of the findings.
Define Data Presentation
Data presentation is defined as the process of using various graphical formats to visually represent the relationship between two or more data sets so that an informed decision can be made based on them.
Types of Data Presentation
Broadly speaking, there are three methods of data presentation:
Diagrammatic
Textual Ways of Presenting Data
Out of the different methods of data presentation, this is the simplest one. You just write your findings in a coherent manner and your job is done. The demerit of this method is that one has to read the whole text to get a clear picture. Yes, the introduction, summary, and conclusion can help condense the information.
Tabular Ways of Data Presentation and Analysis
To avoid the complexities involved in the textual way of data presentation, people use tables and charts to present data. In this method, data is presented in rows and columns - just like you see in a cricket match showing who made how many runs. Each row and column have an attribute (name, year, sex, age, and other things like these). It is against these attributes that data is written within a cell.
Diagrammatic Presentation: Graphical Presentation of Data in Statistics
This kind of data presentation and analysis method says a lot with dramatically short amounts of time.
Diagrammatic Presentation has been divided into further categories:
Geometric Diagram
When a Diagrammatic presentation involves shapes like a bar or circle, we call that a Geometric Diagram. Examples of Geometric Diagram
Bar Diagram
Simple Bar Diagram
Simple Bar Diagram is composed of rectangular bars. All of these bars have the same width and are placed at an equal distance from each other. The bars are placed on the X-axis. The height or length of the bars is used as the means of measurement. So, on the Y-axis, you have the measurement relevant to the data.
Suppose, you want to present the run scored by each batsman in a game in the form of a bar chart. Mark the runs on the Y-axis - in ascending order from the bottom. So, the lowest scorer will be represented in the form of the smallest bar and the highest scorer in the form of the longest bar.
Multiple Bar Diagram
(Image will be uploaded soon)
In many states of India, electric bills have bar diagrams showing the consumption in the last 5 months. Along with these bars, they also have bars that show the consumption that happened in the same months of the previous year. This kind of Bar Diagram is called Multiple Bar Diagrams.
Component Bar Diagram
(image will be uploaded soon)
Sometimes, a bar is divided into two or more parts. For example, if there is a Bar Diagram, the bars of which show the percentage of male voters who voted and who didn’t and the female voters who voted and who didn’t. Instead of creating separate bars for who did and who did not, you can divide one bar into who did and who did not.
A pie chart is a chart where you divide a pie (a circle) into different parts based on the data. Each of the data is first transformed into a percentage and then that percentage figure is multiplied by 3.6 degrees. The result that you get is the angular degree of that corresponding data to be drawn in the pie chart. So, for example, you get 30 degrees as the result, on the pie chart you draw that angle from the center.
Frequency Diagram
Suppose you want to present data that shows how many students have 1 to 2 pens, how many have 3 to 5 pens, how many have 6 to 10 pens (grouped frequency) you do that with the help of a Frequency Diagram. A Frequency Diagram can be of many kinds:
Where the grouped frequency of pens (from the above example) is written on the X-axis and the numbers of students are marked on the Y-axis. The data is presented in the form of bars.
Frequency Polygon
When you join the midpoints of the upper side of the rectangles in a histogram, you get a Frequency Polygon
Frequency Curve
When you draw a freehand line that passes through the points of the Frequency Polygon, you get a Frequency Curve.
Ogive
Suppose 2 students got 0-20 marks in maths, 5 students got 20-30 marks and 4 students got 30-50 marks in Maths. So how many students got less than 50 marks? Yes, 5+2=7. And how many students got more than 20 marks? 5+4=9. This type of more than and less than data are represented in the form of the ogive. The meeting point of the less than and more than line will give you the Median.
Arithmetic Line Graph
If you want to see the trend of Corona infection vs the number of recoveries from January 2020 to December 2020, you can do that in the form of an Arithmetic Line Graph. The months should be marked on the X-axis and the number of infections and recoveries are marked on the Y-axis. You can compare if the recovery is greater than the infection and if the recovery and infection are going at the same rate or not with the help of this Diagram.
Did You Know?
Sir Ronald Aylmer Fisher is known as the father of modern statistics.

FAQs on Presentation of Data
1. What are the 4 types of Tabular Presentation?
The tabular presentation method can be further divided into 4 categories:
Qualitative
Quantitative
Qualitative classification is done when the attributes in the table are some kind of ‘quality’ or feature. Suppose you want to make a table where you would show how many batsmen made half-centuries and how many batsmen made centuries in IPL 2020. Notice that the data would have only numbers - no age, sex, height is needed. This type of tabulation is called quantitative tabulation.
If you want to make a table that would inform which year’s world cup, which team won. The classifying variable, here, is year or time. This kind of classification is called Temporal classification.
If you want to list the top 5 coldest places in the world. The classifying variable here would be a place in each case. This kind of classification is called Spatial Classification.
2. Are bar charts and histograms the Same?
No, they are not the same. With a histogram, you measure the frequency of quantitative data. With bar charts, you compare categorical data.
3. What is the definition of Data Presentation?
When research work is completed, the data gathered from it can be quite large and complex. Organizing the data in a coherent, easy-to-understand, quick to read and graphical way is called data presentation.
More From Forbes
Data governance: transforming data into business strategy.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Cory McNeley is the Managing Director of UHY Consulting .
Data is a vital asset for modern organizations, providing insights that drive strategic decision making. And the amount of data created, consumed and stored is only increasing . Without proper management, the information gathered can become unwieldy and unusable, compromising analytics and insights and threatening operational efficiency and business performance.
Here's how businesses can maximize their data’s potential.
The Value Of Data
Data governance is essential for effective data management. It establishes a framework for structuring and organizing information—including how it’s defined, cataloged, stored and accessed—and the rules, policies and processes for handling it. This framework creates a unified reference point for quickly identifying what data is collected, where it comes from and how to access and use it.
Data governance defines the purpose, vision and goals underpinning a company’s data practices and builds trust in the quality and integrity of data to advance strategic objectives. Rather than viewing data governance merely as a set of security and compliance procedures, treating it as an enabler unlocks its power to transform data into business strategy by producing consistently high-quality, trusted information for qualified, fact-based decisions.
Today’s NYT Mini Crossword Clues And Answers For Saturday, August 31
Desperate to save pokrovsk, the ukrainian national guard has deployed one of its few offensive brigades, novak djokovic follows carlos alcaraz out of the u.s. open as stunning upsets continue, the dangers of bad data.
Executives often question the quality of their data when making data-driven decisions. Bad or poor quality is not just incorrect; it is irrelevant, disorganized, inaccessible, duplicative, inconsistent or contradictory. Bad data can stem from a lack of vision, strategy and controls around data management. In organizations that don’t prioritize governance, valuable information is often inaccessible and untrustworthy due to the absence of a unified source of truth. Disorganized and disparate sources across multiple systems and applications trap data in silos, hindering its quality and potential.
Bad data is a significant business liability. It can cause errors and inefficiencies, reducing productivity. Employees waste approximately two hours daily on non-value-added activities, primarily tracking down or validating information. Making important business decisions based on incorrect data or misleading insights can steer an organization down the wrong path, endangering its market share, reputation and consumer trust.
How To Create A Data Governance Plan
When developing your data governance plan, you'll need to define the scope, objectives, stakeholders and risks, as well as determine how the plan aligns with the overall strategic goals of the organization. Building out a robust plan may require months of pre-planning with involvement from a multitude of departments, including executive leadership, IT, legal and the data management teams. Depending on the complexity and structure of your organization, timelines will vary dramatically, but here are a few steps to help you get started.
Define your goal.
The primary purpose of collecting data is to gain intelligence—you want to learn something about the company or its environment to develop strategies and initiatives that improve the business. However, many executives I know admit to not using all their data effectively. Developing data as an asset with a defined purpose and future goals helps clarify the problems a company needs data to solve, such as increasing operational efficiency, reducing costs, driving innovation or enhancing customer experiences. This approach also changes the vision and philosophy around data practices by applying a “customer” lens to understand and meet user needs.
Investing in data as an asset plans for an unknown future by designing an extensible data governance model that can evolve with the business' needs. This allows organizations to scale data operations with a strategy and roadmap for growth and transformation. Purpose-driven data governance provides a centralized, structured approach to embedding data capabilities that maximize data quality and usefulness throughout its lifecycle. It also facilitates continuous improvement with a structure for refining and enhancing data quality and usefulness.
Prioritize high-quality data.
High-quality data is essential for making informed business decisions and developing reliable analytics. Good data is accurate, consistent, complete, timely and relevant. Feeding good data into business models helps organizations identify market trends, customer preferences and innovation opportunities, as well as predict outcomes, solve business challenges and drive performance and profitability.
Data governance builds a system for cultivating high-quality data from the point of creation. It enhances the quality and reliability of business insights derived from data by ensuring only the best, most useful information is presented for analysis through multidimensional collection, categorization and filtering. These factors turn data into business strategy by eradicating bad data and creating consistently high-quality, trusted information organizations can use to navigate complexities and opportunities, improve decision making and foster innovation with confidence and agility.
Educate your team.
For an organization to become truly data-driven, data management must be holistic and centralized, with everyone responsible for understanding and applying best practices. Before expending resources on data governance, companies should understand how data impacts the business, including the value of their existing data, how its volume is predicted to grow over time and how they plan to use it to advance business objectives.
Education is the key. It should be engrained into the foundation principles of the organization starting with the onboarding process. All new employees should understand the importance of data integrity from the day of hire. Continual reinforcement via presentations or town halls can be implemented to ensure the message is being delivered to existing employees. Seek to inform employees about the importance of quality data and the ramifications of poor quality data.
With a tailored strategy and a measured approach, organizations can design a scalable governance program that enables data to evolve in the right direction to deliver continuous value.
Forbes Business Council is the foremost growth and networking organization for business owners and leaders. Do I qualify?

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions

COMMENTS
This method of displaying data uses diagrams and images. It is the most visual type for presenting data and provides a quick glance at statistical data. There are four basic types of diagrams, including: Pictograms: This diagram uses images to represent data. For example, to show the number of books sold in the first release week, you may draw ...
A data presentation is a slide deck that aims to disclose quantitative information to an audience through the use of visual formats and narrative techniques derived from data analysis, making complex data understandable and actionable. ... Step 1: Define Your Data Hierarchy. While presenting data on the budget allocation, start by outlining the ...
Definition: Data presentation is the art of visualizing complex data for better understanding. Importance: Data presentations enhance clarity, engage the audience, aid decision-making, and leave a lasting impact. Types: Textual, Tabular, and Graphical presentations offer various ways to present data.
Data Analysis and Data Presentation have a practical implementation in every possible field. It can range from academic studies, commercial, industrial and marketing activities to professional practices. In its raw form, data can be extremely complicated to decipher and in order to extract meaningful insights from the data, data analysis is an important step towards breaking down data into ...
TheJoelTruth. While a good presentation has data, data alone doesn't guarantee a good presentation. It's all about how that data is presented. The quickest way to confuse your audience is by ...
Data presentations are usually more about the information they convey and less about the data themselves. When giving a presentation, it's good practice to emphasize the data and explain what it means to the audience. Ensure your presentation focuses on answering certain questions and impacting your audience.
Overview. Data visualization is the visual presentation of data or information. The goal of data visualization is to communicate data or information clearly and effectively to readers. Typically, data is visualized in the form of a chart, infographic, diagram, or map. The field of data visualization combines both art and data science.
In a way, data visualization is the mapping between the original data and graphic elements that determine how the attributes of these elements vary. The visualization is usually made by the use of charts, lines, or points, bars, and maps. Data Viz is a branch of Descriptive statistics but it requires both design, computer, and statistical skills.
Effective data presentation skills are critical for being a world-class financial analyst. It is the analyst's job to effectively communicate the output to the target audience, such as the management team or a company's external investors. This requires focusing on the main points, facts, insights, and recommendations that will prompt the ...
Data visualization is the representation of information and data using charts, graphs, maps, and other visual tools. These visualizations allow us to easily understand any patterns, trends, or outliers in a data set. Data visualization also presents data to the general public or specific audiences without technical knowledge in an accessible ...
Unlocking the narrative: Data visualization helps uncover the story hidden within data, allowing decision-makers to grasp complex concepts and identify new patterns. Effective communication: It plays a vital role in presenting data findings clearly and concisely, ensuring that the message is easily understood.
Data visualization is the graphical representation of information and data. By using v isual elements like charts, graphs, and maps, data visualization tools provide an accessible way to see and understand trends, outliers, and patterns in data. Additionally, it provides an excellent way for employees or business owners to present data to non ...
8. Tabular presentation. Presenting data in rows and columns, often used for precise data values and comparisons. Tabular data presentation is all about clarity and precision. Think of it as presenting numerical data in a structured grid, with rows and columns clearly displaying individual data points.
A simple definition of data visualization: Data visualization is the visual presentation of data or information. The goal of data visualization is to communicate data or information clearly and effectively to readers. Typically, data is visualized in the form of a chart, infographic, diagram or map. The field of data visualization combines both ...
Data visualization definition. Data visualization is the presentation of data in a graphical format such as a plot, graph, or map to make it easier for decision makers to see and understand trends ...
Data visualization. Data visualization is a critical step in the data science process, helping teams and individuals convey data more effectively to colleagues and decision makers. Teams that manage reporting systems typically leverage defined template views to monitor performance. However, data visualization isn't limited to performance ...
Data sets can be presented either by listing all the elements or by giving a table of values and frequencies. This page titled 1.3: Presentation of Data is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Anonymous via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform. In ...
When and how should you use data in a presentation? The answer is that you should use figures and numbers whenever they give the best evidence to back up your argument, or to tell your story. But how to present that data is more difficult. Many people are not interested in tables of numbers, and may struggle to understand graphs.
Here are some important data visualization techniques to know: 1. Pie Chart. Pie charts are one of the most common and basic data visualization techniques, used across a wide range of applications. Pie charts are ideal for illustrating proportions, or part-to-whole comparisons.
Among various types of data presentation, tabular is the most fundamental method, with data presented in rows and columns. Excel or Google Sheets would qualify for the job. Nothing fancy. This is an example of a tabular presentation of data on Google Sheets.
How to create data presentations. If you're ready to create your data presentation, here are some steps you can take: 1. Collect your data. The first step to creating a data presentation is to collect the data you want to use in your share. You might have some guidance about what audience members are looking for in your talk.
Presentation of data is an important process in statistics, which helps to easily understand the main features of data at a glance. Visit BYJU'S to learn how to present the data in a meaningful way with examples.
Concept of Diagrammatic Presentation. It is a technique of presenting numeric data through pictograms, cartograms, bar diagrams, and pie diagrams. It is the most attractive and appealing way to represent statistical data. Diagrams help in visual comparison and they have a bird's eye view.
Define Data Presentation. Data presentation is defined as the process of using various graphical formats to visually represent the relationship between two or more data sets so that an informed decision can be made based on them. Types of Data Presentation. Broadly speaking, there are three methods of data presentation:
Data is a vital asset for modern organizations, providing insights that drive strategic decision making. And the amount of data created, consumed and stored is only increasing.Without proper ...