- University College
- Careers and Leadership
- Student Life
- Arts and Culture
- Howling Success
- Pack Essentials
- Alumni and Friends
- Give Now

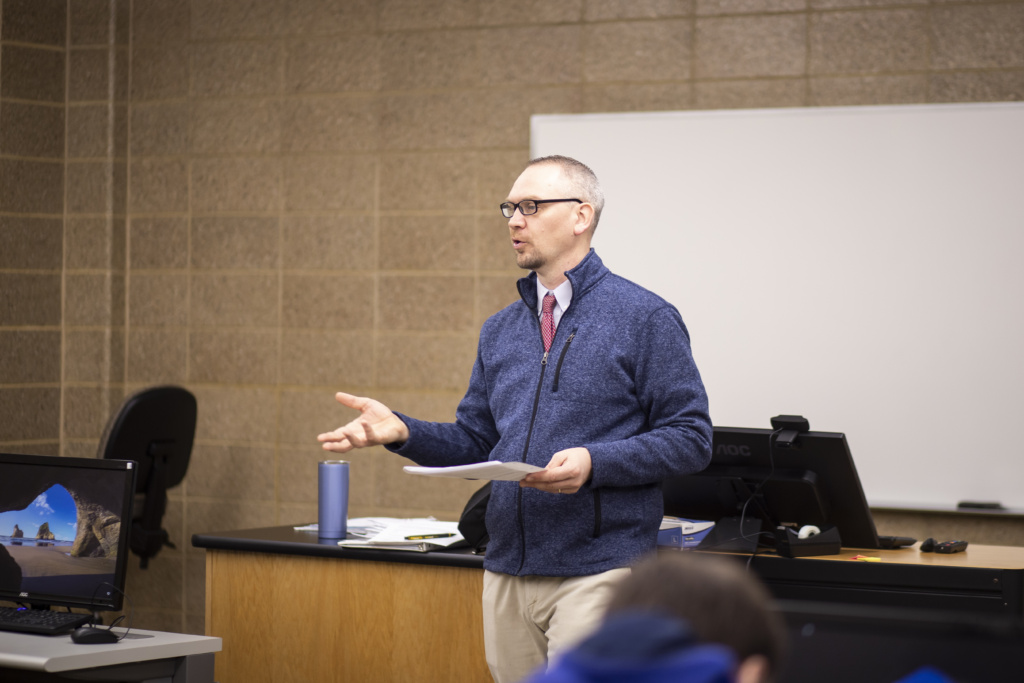
Applying Critical and Creative Thinking Skills in College and Everyday Life
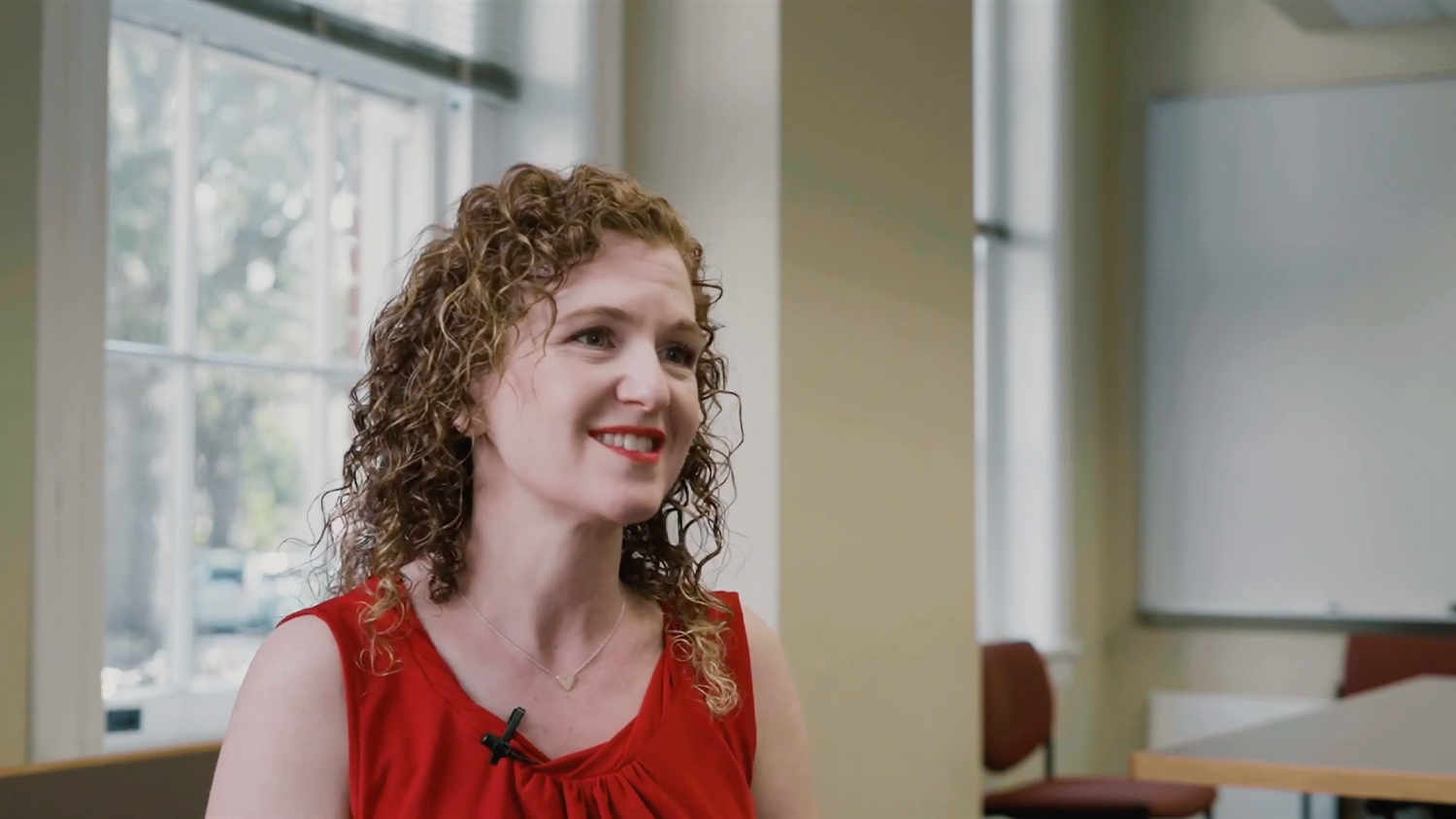
Sue Carson, former director of TH!NK and professor of plant and microbial biology, discusses the importance of critical and creative thinking skills in college and everyday life.

By Alison Krowiak, DASA Assessment
This article is part of a series on NC State’s Pack Proficiencies, which include the five skills NC State faculty think all NC State undergraduates should develop before they graduate: written communication, oral communication, quantitative literacy, critical thinking, and creative thinking.
At NC State, critical and creative thinking are a key part of how we Think and Do the Extraordinary. Critical thinking is the active, persistent and careful consideration of a belief or form of knowledge. Every time students use evidence to form judgements, analyze the ideas or conditions that support conclusions, and evaluate their own thinking, they engage their critical thinking skills.
Creative thinking is just as important and involves the generation of new ideas within or across disciplines. It can draw upon or break the rules in an effort to bring together existing ideas into a new configuration. The ability to think of creative solutions is utilized in every major program at NC State and in every field our students enter upon graduation.
Like all the Pack Proficiencies, these essential skills are taught in General Education classes and reinforced throughout each major program. Sue Carson, professor of plant and microbial biology and former director of the TH!NK program, describes the value for every NC State student in developing their critical and creative thinking competencies. Interview excerpts are edited for brevity and clarity.
How are critical and creative thinking competencies defined?
When I think about critical and creative thinking, I think of them as very intertwined. It often starts with raising a new question or formulating a new problem, gathering and assessing information, coming up with multiple alternative ideas for how to approach the question or how to approach the problem. It involves considering alternatives of the problem, reaching conclusions and effectively communicating about them. Other important aspects of critical and creative thinking include intellectual risk-taking and self-reflection along each stage of the process.
Why should NC States develop proficiencies in critical and creative thinking?
In all of our disciplines, and in all of our careers, to be a leader you need to be a creative thinker. You have to be able to identify problems and questions, and be able to figure out solutions. Even in our everyday lives, critical and creative thinking is so important. Questions like, “Who are you going to vote for in the next election? What daycare are you going to choose for your children? What phone are you going to buy?” all require those skills.
How can students develop their critical and creative thinking skills?
I think that most people understand that critical thinking is a skill that can be developed through practice and feedback. But there’s a misconception that creativity is something that’s innate, and that’s just not true. Creativity is a cognitive process that you can develop through practice and feedback. Creativity is also not confined to the arts. Fields in science, engineering, social sciences, and more need to be creative. We all need to be creative in our lives every day, and it is a skill that we can develop.
How can students develop their critical thinking skills inside and outside the classroom?
When students are selecting their classes, they can choose courses that are more geared toward project-based work. I think that is a good way for students to get feedback on their critical and creative thinking. There are a lot of opportunities outside the class as well. Engaging in undergraduate research is one way. Another way would be service learning projects that allow students to make decisions and have ownership of that project. If the student is able to have ownership and make decisions and identify the questions and problems, it can help develop critical and creative thinking. There is a whole range of opportunities that allow you to do that at NC State.
To learn more about the Pack Proficiencies and how they are assessed, visit go.ncsu.edu/PackProficiencies .
- Faculty and Staff
- Student Success
- college of sciences
- DASA Assessment
More From Academic and Student Affairs News

Welcome Back, NC State Faculty
Interim leaders named for university college, arts nc state .

UNC System Research Grant Transforms First-Year Engineering Course

- Schools & departments

Critical thinking
Advice and resources to help you develop your critical voice.
Developing critical thinking skills is essential to your success at University and beyond. We all need to be critical thinkers to help us navigate our way through an information-rich world.
Whatever your discipline, you will engage with a wide variety of sources of information and evidence. You will develop the skills to make judgements about this evidence to form your own views and to present your views clearly.
One of the most common types of feedback received by students is that their work is ‘too descriptive’. This usually means that they have just stated what others have said and have not reflected critically on the material. They have not evaluated the evidence and constructed an argument.
What is critical thinking?
Critical thinking is the art of making clear, reasoned judgements based on interpreting, understanding, applying and synthesising evidence gathered from observation, reading and experimentation. Burns, T., & Sinfield, S. (2016) Essential Study Skills: The Complete Guide to Success at University (4th ed.) London: SAGE, p94.
Being critical does not just mean finding fault. It means assessing evidence from a variety of sources and making reasoned conclusions. As a result of your analysis you may decide that a particular piece of evidence is not robust, or that you disagree with the conclusion, but you should be able to state why you have come to this view and incorporate this into a bigger picture of the literature.
Being critical goes beyond describing what you have heard in lectures or what you have read. It involves synthesising, analysing and evaluating what you have learned to develop your own argument or position.
Critical thinking is important in all subjects and disciplines – in science and engineering, as well as the arts and humanities. The types of evidence used to develop arguments may be very different but the processes and techniques are similar. Critical thinking is required for both undergraduate and postgraduate levels of study.
What, where, when, who, why, how?
Purposeful reading can help with critical thinking because it encourages you to read actively rather than passively. When you read, ask yourself questions about what you are reading and make notes to record your views. Ask questions like:
- What is the main point of this paper/ article/ paragraph/ report/ blog?
- Who wrote it?
- Why was it written?
- When was it written?
- Has the context changed since it was written?
- Is the evidence presented robust?
- How did the authors come to their conclusions?
- Do you agree with the conclusions?
- What does this add to our knowledge?
- Why is it useful?
Our web page covering Reading at university includes a handout to help you develop your own critical reading form and a suggested reading notes record sheet. These resources will help you record your thoughts after you read, which will help you to construct your argument.
Reading at university
Developing an argument
Being a university student is about learning how to think, not what to think. Critical thinking shapes your own values and attitudes through a process of deliberating, debating and persuasion. Through developing your critical thinking you can move on from simply disagreeing to constructively assessing alternatives by building on doubts.
There are several key stages involved in developing your ideas and constructing an argument. You might like to use a form to help you think about the features of critical thinking and to break down the stages of developing your argument.
Features of critical thinking (pdf)
Features of critical thinking (Word rtf)
Our webpage on Academic writing includes a useful handout ‘Building an argument as you go’.
Academic writing
You should also consider the language you will use to introduce a range of viewpoints and to evaluate the various sources of evidence. This will help your reader to follow your argument. To get you started, the University of Manchester's Academic Phrasebank has a useful section on Being Critical.
Academic Phrasebank
Developing your critical thinking
Set yourself some tasks to help develop your critical thinking skills. Discuss material presented in lectures or from resource lists with your peers. Set up a critical reading group or use an online discussion forum. Think about a point you would like to make during discussions in tutorials and be prepared to back up your argument with evidence.
For more suggestions:
Developing your critical thinking - ideas (pdf)
Developing your critical thinking - ideas (Word rtf)
Published guides
For further advice and more detailed resources please see the Critical Thinking section of our list of published Study skills guides.
Study skills guides
This article was published on 2024-02-26
Critical thinking for college, career, and citizenship
Subscribe to the center for universal education bulletin, diane f. halpern dfh diane f. halpern diane f. halpern is the dean of social sciences, emerita at the minerva schools at kgi and a past president of the american psychological association and the society for teaching of psychology. diane has published hundreds of articles and many books including, thought and knowledge: an introduction to critical thinking (5th ed., 2014); sex differences in cognitive abilities (4th ed.), and women at the top: powerful leaders tell us how to combine work and family (co-authored with fanny cheung). her other recent books include psychological science (5th ed. with michael gazzaniga and todd heatherton) and the edited book, undergraduate education in psychology: a blueprint for the future of the discipline..
May 26, 2016
Editor’s note: In the “ Becoming Brilliant ” blog series, experts explore the six competencies that reflect how children learn and grow as laid out by Kathy Hirsh-Pasek and Roberta Golinkoff in their new book “ Becoming Brilliant .”
Education is about the future—students learn in schools and other places based on two underlying assumptions: (a) What they learn today will be recalled sometime in the future when the knowledge is needed, and (b) today’s learning will transfer across time, place, and space. Teachers are preparing students for higher levels of education, careers that may not even exist today, and the increasingly complex world of citizenship—voting intelligently, recognizing, and supporting good options for societal problems. With the amount of information increasing exponentially and new information often replacing what we formerly believed to be true, the twin abilities of learning well and thinking critically are essential skills for students at every level.
But what does it mean to think critically?
Critical thinking is using the skills or strategies that that are most likely to lead to a desired outcome. It is purposeful, reasoned, and goal-directed. It is the sort of thinking we should be engaging in when deciding what and whom to believe, which of two job offers to accept, or whether vaccinations really do cause autism. It is different from, but often relies upon, simple recall (e.g., what does five plus seven equal?), unsupported opinions (e.g., I like vanilla ice cream), and automated actions (e.g., stopping at a red light).
Critical thinking has two main components: understanding information at a deep, meaningful level, and overcoming fallacies and biases. For example, suppose you are learning about a new theory. You could learn to recite the definition of the theory with little meaning (e.g., photosynthesis is a process used by plants to synthesize foods from carbon dioxide and water using sunlight) or you could process it at a deeper level. There are many learning activities that facilitate deep level processing. For example, you could write out the theory in your own words, explain it to someone who is not familiar with it, and provide evidence for (and possibly against) the theory. What is it explaining? What theory is it replacing (if applicable)? What is its history? How could it be applied to an everyday problem? If you could answer these questions, the theory would become easier to recall, and you could use it to generate new theories or see flaws or strengths in other theories. Argument analysis is another example of deep processing. Critical thinkers learn to identify the conclusion, the evidence, and reasoning used to support the conclusion. They also look for assumptions, counterevidence, and limiting conditions (times when the conclusion may not apply).
Some educators prefer to consider critical thinking as “debiasing” or recognizing and resisting fallacies. Suppose someone asks you if children become brilliant because of their nature or nurture. This is an example of the “either-or” fallacy, and anyone who is trained to recognize it can avoid its pitfalls. Similarly, critical thinkers recognize when correlational data are being used to make causal claims. For example, an article in the Los Angeles Times told readers that if they want their children to get good grades they should make sure that their kids’ friends get good grades. But after reading the article, it was apparent that children with good grades had friends with good grades, and children with poor grades had friends with poor grades. But nowhere did it show that kids with poor grades would improve by friending kids with good grades. The data were correlational, which any critical thinker should recognize.
If you are thinking critically, and I hope you are, you may be wondering: Can we teach students to be better thinkers? The answer is a resounding “yes.” There is a large amount of research literature (reviewed in my book, “Thought and Knowledge: An Introduction to Critical Thinking”). In one project that I conducted with a doctoral student, who is now Dr. Lisa Marin, we went into very low-performing high schools in California. There were several studies, some that involved parents and some in which classes were assigned at random with different critical thinking instruction. We found that when critical thinking skills were deliberately taught (not as an ancillary to other content), students improved in their abilities to think critically. There are many studies showing substantial gains in critical thinking in college students, the military, and other populations as well. Critical thinking can be taught at any grade, as long as it is taught in a way that is developmentally appropriate.
Finally, critical thinking has a self-reflective component. Good thinkers consider the steps of problem solving, how they are mentally approaching a problem, and the quality of their conclusion or solution.
Those who care about the future for today’s children understand that the jobs of the future will require the ability to think critically. So let’s be sure that our students are ready for college, careers, and citizenship by including deliberate instruction in critical thinking. It is probably the most difficult topic to teach and learn, but it is also the most important.
Global Education Higher Education
Global Economy and Development
Center for Universal Education
August 2, 2024
June 20, 2024
Elyse Painter, Emily Gustafsson-Wright
January 5, 2024

Online Students
For All Online Programs
International Students
On Campus, need or have Visa
Campus Students
For All Campus Programs
The Importance of Critical Thinking Skills, For Students and Ourselves

Critical thinking is a vital, yet often neglected, skill. In higher education, Chris Griffiths , author of “The Creative Thinking Handbook,” noted in a TLNT blog article that critical thinking is “the ability to think clearly and independently about a subject or problem ... (and the) consideration of multiple perspectives, the checking of biases, and a detailed understanding of relevant context.” Put more simply, it means objective analysis, but we often form judgments without that all-important objective evaluation.
Employers on the Southern New Hampshire University (SNHU) Social Sciences Advisory Board tell us that they need people with critical thinking skills, but applicants often lack this ability. Their desire for critical thinkers is reflected in current research showing that critical thinking is one skill that cannot be taken over by artificial intelligence (AI) and that higher education must take a proactive role in preparing students with this skill.
What Skills Do Critical Thinkers Have?
According to, Dr. Norman Herr , a professor of science education, critical thinking skills can be boiled down to the following key elements:
- Identification of premises and conclusions — Break arguments down into logical statements
- Clarification of arguments — Identify ambiguity in these stated assertions
- Establishment of facts — Search for contradictions to determine if an argument or theory is complete and reasonable
- Evaluation of logic — Use inductive or deductive reasoning to decide if conclusions drawn are adequately supported
- Final evaluation — Weigh the arguments against the evidence presented
When translated to the professional world, the National Association of Colleges and Employers (NACE) identifies critical thinking as a top skill ( NACE PDF Source ). NACE said that students should be ready to demonstrate it by inclusive reasoning and judgement to make decisions and solve problems; analyzing and communicating information from multiple sources with awareness of biases that could impact outcomes; and communicating that information accurately to diverse groups of stakeholders.
As educators, we must teach our students those critical thinking skills and practice them ourselves to objectively analyze an onslaught of information. Ideas, especially plausible-sounding philosophies, should be challenged and put through rigorous credibility tests.
Red Flags for Unreliable Information
The School Library Journal lists four types of information that should raise red flags when we’re watching the news, reading social media, or at any point in our everyday lives when we’re confronted with something purported to be “fact:”
- Fake news , which refers to purported news that is demonstrably untrue.
- Misinformation , which is spread by those who don’t realize that it’s false or only partially true .
- Disinformation , which is deliberately spread by people who know that it’s not accurate and who want to spread a false message.
- Propaganda , which is information that is spread with a specific agenda. It may or may not be false, but it’s intended to get an emotional reaction.
These information types may overlap, especially with the extinction of local news sources. As of 2023, there were only 1,213 daily local newspapers left in the U.S., and they continue to disappear at a rate of two each week, according to a report from The State of Local News Project. The report also notes that there are over 200 counties with no local print, broadcast, or digital news outlets and over 1,500 with only one. This lack of access to local news is overwhelmingly found in high poverty areas, often with predominantly Black, Hispanic or Native-American populations.
This provides opportunities for biased websites to fill the gap; misinformation tracker NewsGuard said that there are almost 1,300 websites positioning themselves as local news while pushing political agendas.

Updated Tools to Support Critical Thinking
SNHU and other colleges and universities across the U.S. must use updated tools to help their students think critically about the information they consume. Currently, many institutions of higher learning fail to teach students how to identify misinformation sources.
AI acts as a cautionary example of the way in which the landscape can transform quickly and dramatically. Generative AI has the ability to converse on any topic and write in the style of anything from an essay to a news article with an air of authority. Griffiths noted that, while it mimics something written via independent thought, it’s regurgitating a mishmash of existing ideas drawn from its training data. It incorporates any biases in that data and even “hallucinates,” providing output as factual when it’s partially or entirely untrue.
Bad actors can leverage AI technology to create written, graphic and audio content that masquerades as real news. One relatively harmless example is the AI-generated photos that supposedly show Katy Perry attending the 2024 Met Gala. Although she was not there, the ruse was so convincing that it even fooled her mother. While the Perry pictures did not cause widespread harm, they show how easily bad actors can convince others of a deepfake’s authenticity. Videos can also be created or manipulated easily to create fake news stories like a supposed Tucker Carlson interview with a Pfizer official about a new FDA-approved diabetes cure. The “story” was actually an ad for an unproven dietary supplement.
As educators in institutions of higher education, we must afford learners as many opportunities as possible to hone their critical thinking skills when interacting with instructors and fellow students.
Greg Lukianoff and Johnathan Haidt, authors of "The Coddling of the American Mind," contend that “one of the most brilliant features of universities is that, when they are working properly, they are communities of scholars who cancel out one another’s confirmation biases .”
Without exploring opposing viewpoints, students may fall prey to confirmation bias, further cementing ideas that they already believe to be true. Being inclusive when it comes to viewpoint diversity is indispensable for avoiding these echo chambers that circumvent having one’s ideas challenged.
How to Think Critically
As we teach our students the importance of critical thinking, how do we equip them to sift through the onslaught of information they encounter every day, both personally and in their educational pursuits? And how do we do the same for ourselves?
Here are four critical thinking examples that anyone can apply when evaluating information:
Consider Vested Interest
Consider whether the person who wrote or is sharing the information has any vested interest in doing so. For example, a writer may have a degree and professional experience that gives them expertise to write an article on specific communication techniques.
Be aware that the writer’s credibility can be affected by outside interests. These include being paid to write a book with a certain viewpoint, giving paid seminars, affiliation with certain organizations or anything else that creates a financial or personal interest in promoting a specific perspective.
Examine Biases
Consider the venue in which the person is sharing the information. Newscasts and newspapers once were slanted more toward neutrality, although there was never an era when bias was completely absent. The 19th century even had its own version of clickbait in the form of yellow journalism .
Today, it’s getting more difficult for those with critical thinking skills to find unbiased sources. Use websites like AllSides , which rates major sites on their leanings.
Read Beyond Clickbait Headlines
Websites create headlines to generate traffic and ad revenue, not to support critical thinking or give accurate information. Too many people go by what the headline says without reading more deeply, even though media misrepresentation of studies is rampant.
Often, the information contained within the article is not accurately represented in the headline. Sometimes there’s even a direct contradiction, or the publication is focusing on one single study that may mean nothing because other studies have contradictory results.
Fact-Check Information
Use Snopes , Fact Check , and other fact-checking websites that examines viral memes and news stories for truthfulness. Ironically, Snopes itself has been the victim of misinformation campaigns designed to discredit its efforts to promote the importance of critical thinking.
Why is Critical Thinking so Important?
Misinformation, if not addressed, easily turns into disinformation when it’s readily shared by students, individuals and groups that may know it’s wrong. They may continue to intentionally spread it to cast doubt or stir divisiveness. Students listen to their peers, and the more critical thinking is addressed in a course, the more we prepare students not to fall into the misinformation trap.
Courtney Brown and Sherrish Holland , of the Center for the Professional Education of Teachers, argue that for educators, the challenge is now far more about how they need to inform their students to interpret and assess the information they come across and not simply how to gain access to it. The term “fake news” is used to discredit anyone trying to clarify fact from fiction. Fake news is a cover for some people when they are being deliberately deceptive.
As educators become clearer about the distinction, it can be better communicated to students.
Teaching Students to Think Critically
Anyone in a teaching position should point their students toward reliable references. For example, at SNHU, instructors can send students to databases in the Shapiro Library . For other materials, they should teach them to evaluate their integrity based on the four elements of critical thinking.
Is the premise legitimate or is it clickbait? Are the arguments in the article supported by evidence? Do the facts paint a reasonable picture, or are there contradictions? Is the article based on logic, or is it designed to draw in readers by misrepresenting its content? Is it hosted on a biased site, and do its authors have connections that could cause bias? Does it pass a fact check as a final evaluation?
Instructors can also incorporate these elements into announcements, discussion posts and feedback. For example, they can post two articles with differing viewpoints on the week’s material. For each, they can break down the publication’s possible slant, the way in which any research-based material is presented, and the author’s credentials. This demonstrates the different ways in which similar material can be presented, depending on the source and authors’ affiliations and biases.
Anyone Can Promote Critical Thinking
Even if you don’t teach, use those points in conversations to help others hone their critical thinking skills. If someone shares misinformation with you, don’t be combative. Instead, use probing statements and questions designed to spark their critical thinking.
Here are some examples:
- “That’s very interesting. Do you think the person they’re quoting might be letting his business interests color what he’s saying?”
- “I know that sometimes the media oversimplifies research. I wonder who funded that study and if that’s influencing what they’re saying.”
Of course, you need to adapt to the situation and to make what you say sound organic and conversational, but the core idea remains the same. Inspire the other person to use critical thinking skills. Give them reasons to look more deeply into the topic instead of blindly accepting information.
American cultural anthropologist Margaret Mead said, “Children must be taught how to think, not what to think.” Her sentiment is true for learners of any age, which makes it crucial for educators to maintain sharp critical thinking skills and pass them along to students to support them in their careers and in everyday life.
A degree can change your life. Choose your program from 200+ SNHU degrees that can take you where you want to go.

Dr. Nickolas Dominello is the senior associate dean on the social sciences team at Southern New Hampshire University. He joined SNHU in 2014, served as a lead psychology faculty member, was promoted to associate dean in 2018 and then to senior associate dean in 2023. Dominello completed his doctoral training at Capella University in 2013, becoming a PhD in Psychology. He also has a Master of Arts in Education at the secondary level, and he has over 20 years of experience working as an educator.

Dr. Barbara Lesniak is the executive director of Social Sciences at Southern New Hampshire University. She started at SNHU as an adjunct in 2012, and her previous roles included associate dean of psychology and senior dean. Her experience outside of academia includes 15 years designing and delivering classroom and web-based courses in the corporate world and providing face-to-face and online counseling services. She specialized in helping online clients in acute crisis situations. Lesniak has a PsyD in Psychology and, as a lifelong learner, she earned an MFA and MS in Marketing at SNHU and is currently working on an MS in Organizational Leadership.

Dr. Tom MacCarty is an associate dean on the social sciences team and oversees the MS in Psychology program at Southern New Hampshire University. He received his PhD in Industrial/Organizational Psychology from Northcentral University. He also holds a Certificate of Advanced Graduate Studies in School Psychology and a Master of Arts Degree in Counseling Psychology from Norwich University. MacCarty can be found on LinkedIn .
Explore more content like this article

What is the Difference Between Bachelor’s and Master’s Degrees?

Academic Referencing: How to Cite a Research Paper

What is Considered Plagiarism And How to Avoid It
About southern new hampshire university.

SNHU is a nonprofit, accredited university with a mission to make high-quality education more accessible and affordable for everyone.
Founded in 1932, and online since 1995, we’ve helped countless students reach their goals with flexible, career-focused programs . Our 300-acre campus in Manchester, NH is home to over 3,000 students, and we serve over 135,000 students online. Visit our about SNHU page to learn more about our mission, accreditations, leadership team, national recognitions and awards.

Improving Critical Thinking Skills in College Students
by Matthew Mahavongtrakul | Mar 6, 2020 | 390X
Erica M. Leung, Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
“People grow best where they continuously experience an ingenious blend of support and challenge.” -Robert Kegan 1
Cognitive Development of College Students
Most students enter college with the notion that there are right and wrong answers and the road to knowledge is straightforward. 2 Students undergo significant cognitive growth during college, shifting their view of knowledge from objective duality to subjective multiplicity (i.e. there are various opinions, which are all valid). 2 By the time of their graduation, few students reach the cognitive stage of relativism (i.e. not all opinions are equally valid, so facts and context matter), which relies heavily on critical thinking skills to make judgments. 2
This may come as a surprise as instructors tend to expect students to have the same cognitive abilities and critical thinking skills as they do. Instead, college students are just learning how to reframe knowledge. With this in mind, instructors need to meet students where they are in their cognitive development and guide them through the process. A short epistemological belief survey may help in determining students’ stage of cognitive development.
Techniques for Developing Critical Thinking Skills
What is critical thinking? Can it be taught in the classroom? How is it measured? How can instructors help students navigate the road to independent critical thinking? Here are a few promising approaches to facilitate and encourage critical thinking:
- Collaborative learning wherein students learn from each other and work together using activities like discussion boards, case studies, role playing, peer teaching, and group projects. This technique exposes students to different interpretations of information and the diversity of fellow students’ experiences and knowledge. Collaborative learning allows students to discuss information, clarify ideas, and evaluate the validity of others’ ideas in a safe and positive environment. 3-5
- Higher-level thinking questions that prompt students to answer questions like whether they “agree or disagree” and “why”. Well-written questions will challenge students to interpret, analyze, and recognize assumptions before reaching a conclusion. 6 Examples of different levels of questions according to Bloom’s Taxonomy can be viewed here .
- Reflective written assignments that ask students to apply their experiences to different concepts, allowing students to play a more active role in their learning and self-growth. These reflections can encourage students to identify the relevance of the information to their own lives, question the information’s validity, and seek better sources. 6-8 A framework for reflective writing that can help guide students through the process can be found here .
- Open-book assessments that allow students to use notes, textbooks, and/or other resources. These foster intellectual engagement with the material instead of rote memorization, cramming, and anxiety before the exam. Since students are afforded more resources, instructors have an opportunity to ask higher level questions. Overall, these types of assessments simulate a more real-world environment, which promotes problem solving over recall. 9
Although there is debate on its definition, critical thinking is an important outcome of higher education and is highly valued by employers. It is therefore up to the instructor to incorporate ways to improve critical thinking in their students to prepare them for their futures.
- Kegan, R. In over our heads: The mental demands of modern life. (Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA, 1994).
- Black, S. & Allen, J. D. Part 3: College Student Development. TRL 58 , 214-228 (2017).
- Loes, C. N. & Pascarella, E. T. Collaborative Learning and Critical Thinking: Testing the Link. J. High. Educ. 88 , 726-753 (2017).
- Gokhale, A. A. Collaborative Learning Enhances Critical Thinking. J. Technol. Educ. 7 , 22-30 (1995).
- Szabo, Z. & Schwartz, J. Learning methods for teacher education: the use of online discussions to improve critical thinking. Technol. Pedagog. Educ. 20 , 79-94 (2011).
- Walker, S. E. Active Learning Strategies to Promote Critical Thinking. J. Athl. Train. 38 , 263-267 (2003).
- Mintzberg, H. & Gosling, J. Educating Managers Beyond Borders. Acad. Manag. Learn. Educ. 1 , 64-76 (2002).
- Naber, J. & Wyatt, T. H. The effect of reflective writing interventions on the critical thinking skills and dispositions of baccalaureate nursing students. Educ. Today 34 , 67-72 (2014).
- Johans, B., Dinkens, A., & Moore, J. A systematic review comparing open-book and closed-book examinations: Evaluating effects on development of critical thinking skills. Nurse Educ. Pract. 27 , 89-94 (2017).
Matthew Mahavongtrakul edited this post on March 6th, 2020.
Recent Posts
- Inclusive Teaching and Beyond: The Need for Institutional Change
- Abundant Learning: How Online Courses Build Equity and Access
- Pedagogies of Possibility in a Post-Pandemic Classroom
- Critical University Studies: Rethinking Academia from Within
- Learning Assistants as Peer Educators in Large Online Courses
- Invest for Eternity
- Giving Clubs
- Annual Fund
- The Heritage Project
- Global Encounters
- Leadership Breakfasts
- MBU Golf Classic
- Pastors Masters
- MARANATHA PLUS

Read MBU’s latest coronavirus news and updates. Learn More
Maranatha baptist university.

How Higher Education Fosters Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Skills
“Education is not the learning of facts, but the training of the mind to think.” –Albert Einstein
Critical thinking and problem-solving are the most essential skills that any college student can develop. If students are unable to think through an issue critically, they will be ill-equipped to distinguish between truth and deception. Valid conclusions can only come from the pursuit of truth. In comparison, problem-solving skills give an individual the tools to do something with the information they have gained. This combined skillset is invaluable in the professional world and everyday life.
If these skills are so important, what is the best way to foster and develop them? Education is a start. Whether it’s higher education through attending a university or self-education through personal study, the only way to develop these skills is through active participation in learning. Almost all colleges and universities cite critical thinking as one of their core objectives. So, what are the best ways for higher education to help students grow and develop these skills?
From the idea that teaching critical thinking is impossible to new approaches in teaching styles, the last two decades have produced varying theories on critical thinking. One fact that is certain, however, is that problem-solving is a natural outgrowth of critical thinking. Although there is no argument over whether critical thinking is important, there are multiple perspectives on the best ways to develop this skill. Most research, however, seems to support a hands-on, interactive approach.
Andreucci-Annunziata et al. (2023) suggests that “pedagogical approaches to critical thinking have been synthesized into four types: general method; infusion; immersion and mixed method.” The general method is teaching critical thinking as its own subject, infusion is teaching critical thinking in relation to a specific subject matter, immersion is teaching a subject in a way that encourages critical thinking, and “the mixed method consists of a combination of the general method and the infusion or immersion method.” These methods are combined with instructional strategies such as writing exercises, in-class discussion, brainstorming, using online discussion forums, etc. With so many methods and strategies available what is the best approach for educators? Two strategies seem to be gaining momentum: Decision-Based Learning and Discussion-Based Learning.
Decision-Based Learning
Decision-Based Learning (DBL), a problem-solving strategy, is a new possibility. According to one study DBL teaches students how to look at the components of a problem and come to a rational decision. Evidence shows that there is a correlation between the development of problem-solving and critical thinking skills (Plummer et al. 2022). This style encourages students to look at all sides of an issue and come to a valid conclusion.
Discussion-Based Learning
On the other hand, Discussion-Based Learning also shows promise. Various universities across the U.S. and Canada cite Discussion-Based Learning, or a form of it, as one of their primary teaching methods. Examples include the University of Calgary, Brown University, and Columbia University. The fact that discussion plays a major role in developing critical thinking and problem-solving skills is indisputable. Studies of different methods continue to support Discussion-Based Learning as one of the primary ways for students to develop both skills. In-class discussion and thought-provoking questions continue to promote the development of critical thinking within the classroom.
Are Educators Doing a Good Job?
Some researchers and professionals argue that colleges are failing to teach their students the art of critical thinking. One researcher suggests that colleges and universities fail to understand that there is a difference between “teaching students what to think (highly educated) and teaching them how to think (better educated)” (Flores, Kevin L., et al.). A student can fill their mind with countless pieces of information without developing the skills needed to interpret and apply that information.
To combat this tendency, educators must challenge students to think through issues themselves. When students are given the tools needed to think critically, a new world of knowledge is opened to them. Regardless of varying strategies, education needs a firm foundation to stand on. At Maranatha, that foundation is the Bible.
What Makes Maranatha Different?
Education firmly grounded in biblical truth does not leave room for conclusions drawn from emotion. Instead, biblically grounded education creates an environment that fosters critical thinking and a pursuit of the truth. At Maranatha, professors understand the value of preparing students to be critical thinkers. In a world that seeks to reject a biblical worldview through science and philosophy, it is more important than ever for students to graduate grounded in biblical principles.
Mr. Nathan Huffstutler, Associate Professor in the Department of Humanities, explains, “A biblical worldview emphasizes truth. God is a God of truth. If you believe that God is a God of truth, that will make you more passionate in your search for truth. When we deal with current events or with history, it’s not just opinions that we’re trying to find. That doesn’t mean that some questions don’t have nuance or gray areas. There are some issues that are very complex, but a biblical worldview aids in the pursuit of truth even in difficult subjects.”
Without the ability to analyze ideas through a biblical lens, students will be tossed about by every new theory, unable to distinguish between the truth and lies disguised as truth. Only when students understand how to think will they be able to properly analyze ideas and come to their own conclusions.
Mr. Huffstutler further explains how he implements the instruction of critical thinking into the classroom, “I personally use discussion questions. I’ll give a question and then require students to back up their answers with evidence. They must demonstrate in their answers that it is not just their opinion. I strive to show my students how to back up their statements based on facts and support from the text. That’s what critical thinking is.”
Discussion is the first step in the process of developing critical thinking. In-class discussion has the power to sharpen minds as students are forced to think through their reasoning and evidence. Current and past students are reaping the benefits of an education that emphasizes the development of this invaluable skill.
Hannah Mayes (’20 Communication Arts—Theatre), a teacher at Maranatha Baptist Academy and Adjunct Professor at the University, shares her experience, “The focus Maranatha professors have on teaching students how to think is particularly evident when teachers would continuously ask us, ‘Why?’ Professors encouraged us to evaluate our answers in light of a biblical worldview, but not merely so we could provide a ‘right’ answer. Many instructors encouraged me to look further beyond the simple answer, use credible sources to support my answer, and apply what I had learned to my everyday life. These interactions seemed challenging at the time, but I find myself encouraging my own students to keep asking why and how — not just what.”
Keeping the focus on teaching students how to think is essential in the development of critical thinking. When academics are taught with a biblical worldview, students are encouraged to find the truth and evidence to back up their claims. Without these skills, students will be incapable of succeeding in a professional environment.
So, does higher education foster critical thinking and problem-solving? Yes. But only when students and professors work together to find the truth, based on facts, can critical thinking flourish.
Andreucci-Annunziata, P., Riedemann, A., Cortes, S., Mellado, A., Del Rio, M. T., & Vega-Munoz, A. (2023). Conceptualizations and instructional strategies on critical thinking in higher education: A systematic review of systematic reviews. Frontiers in Education, 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2023.1141686
Flores, K. L., Matkin, G. S., Burbach, M. E., Quinn, C., & Harding, H. E. (2012). Deficient Critical Thinking Skills among College Graduates: Implications for leadership. Educational Philosophy and Theory, 44 (2), 212-230. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-5812.2010.00672.x
Plummer, K. J., Kebritchi, M., Leary, H. M., & Halverson, D.M. (2022). Enhancing Critical Thinking Skills through Decision-Based Learning. Innovative Higher Education, 47 (4), 711-734. https://doi.org/101007/s10755-022-09595-9

Similar Blog Post 1
Student pov: 5 things about college that no one tells you.
Similar Blog Post 2
The benefits of participating in fine arts.

Similar Blog Post 3
Student pov: developing effective time management as a college student.
Classroom Q&A
With larry ferlazzo.
In this EdWeek blog, an experiment in knowledge-gathering, Ferlazzo will address readers’ questions on classroom management, ELL instruction, lesson planning, and other issues facing teachers. Send your questions to [email protected]. Read more from this blog.
Eight Instructional Strategies for Promoting Critical Thinking

- Share article
(This is the first post in a three-part series.)
The new question-of-the-week is:
What is critical thinking and how can we integrate it into the classroom?
This three-part series will explore what critical thinking is, if it can be specifically taught and, if so, how can teachers do so in their classrooms.
Today’s guests are Dara Laws Savage, Patrick Brown, Meg Riordan, Ph.D., and Dr. PJ Caposey. Dara, Patrick, and Meg were also guests on my 10-minute BAM! Radio Show . You can also find a list of, and links to, previous shows here.
You might also be interested in The Best Resources On Teaching & Learning Critical Thinking In The Classroom .
Current Events
Dara Laws Savage is an English teacher at the Early College High School at Delaware State University, where she serves as a teacher and instructional coach and lead mentor. Dara has been teaching for 25 years (career preparation, English, photography, yearbook, newspaper, and graphic design) and has presented nationally on project-based learning and technology integration:
There is so much going on right now and there is an overload of information for us to process. Did you ever stop to think how our students are processing current events? They see news feeds, hear news reports, and scan photos and posts, but are they truly thinking about what they are hearing and seeing?
I tell my students that my job is not to give them answers but to teach them how to think about what they read and hear. So what is critical thinking and how can we integrate it into the classroom? There are just as many definitions of critical thinking as there are people trying to define it. However, the Critical Think Consortium focuses on the tools to create a thinking-based classroom rather than a definition: “Shape the climate to support thinking, create opportunities for thinking, build capacity to think, provide guidance to inform thinking.” Using these four criteria and pairing them with current events, teachers easily create learning spaces that thrive on thinking and keep students engaged.
One successful technique I use is the FIRE Write. Students are given a quote, a paragraph, an excerpt, or a photo from the headlines. Students are asked to F ocus and respond to the selection for three minutes. Next, students are asked to I dentify a phrase or section of the photo and write for two minutes. Third, students are asked to R eframe their response around a specific word, phrase, or section within their previous selection. Finally, students E xchange their thoughts with a classmate. Within the exchange, students also talk about how the selection connects to what we are covering in class.
There was a controversial Pepsi ad in 2017 involving Kylie Jenner and a protest with a police presence. The imagery in the photo was strikingly similar to a photo that went viral with a young lady standing opposite a police line. Using that image from a current event engaged my students and gave them the opportunity to critically think about events of the time.
Here are the two photos and a student response:
F - Focus on both photos and respond for three minutes
In the first picture, you see a strong and courageous black female, bravely standing in front of two officers in protest. She is risking her life to do so. Iesha Evans is simply proving to the world she does NOT mean less because she is black … and yet officers are there to stop her. She did not step down. In the picture below, you see Kendall Jenner handing a police officer a Pepsi. Maybe this wouldn’t be a big deal, except this was Pepsi’s weak, pathetic, and outrageous excuse of a commercial that belittles the whole movement of people fighting for their lives.
I - Identify a word or phrase, underline it, then write about it for two minutes
A white, privileged female in place of a fighting black woman was asking for trouble. A struggle we are continuously fighting every day, and they make a mockery of it. “I know what will work! Here Mr. Police Officer! Drink some Pepsi!” As if. Pepsi made a fool of themselves, and now their already dwindling fan base continues to ever shrink smaller.
R - Reframe your thoughts by choosing a different word, then write about that for one minute
You don’t know privilege until it’s gone. You don’t know privilege while it’s there—but you can and will be made accountable and aware. Don’t use it for evil. You are not stupid. Use it to do something. Kendall could’ve NOT done the commercial. Kendall could’ve released another commercial standing behind a black woman. Anything!
Exchange - Remember to discuss how this connects to our school song project and our previous discussions?
This connects two ways - 1) We want to convey a strong message. Be powerful. Show who we are. And Pepsi definitely tried. … Which leads to the second connection. 2) Not mess up and offend anyone, as had the one alma mater had been linked to black minstrels. We want to be amazing, but we have to be smart and careful and make sure we include everyone who goes to our school and everyone who may go to our school.
As a final step, students read and annotate the full article and compare it to their initial response.
Using current events and critical-thinking strategies like FIRE writing helps create a learning space where thinking is the goal rather than a score on a multiple-choice assessment. Critical-thinking skills can cross over to any of students’ other courses and into life outside the classroom. After all, we as teachers want to help the whole student be successful, and critical thinking is an important part of navigating life after they leave our classrooms.

‘Before-Explore-Explain’
Patrick Brown is the executive director of STEM and CTE for the Fort Zumwalt school district in Missouri and an experienced educator and author :
Planning for critical thinking focuses on teaching the most crucial science concepts, practices, and logical-thinking skills as well as the best use of instructional time. One way to ensure that lessons maintain a focus on critical thinking is to focus on the instructional sequence used to teach.
Explore-before-explain teaching is all about promoting critical thinking for learners to better prepare students for the reality of their world. What having an explore-before-explain mindset means is that in our planning, we prioritize giving students firsthand experiences with data, allow students to construct evidence-based claims that focus on conceptual understanding, and challenge students to discuss and think about the why behind phenomena.
Just think of the critical thinking that has to occur for students to construct a scientific claim. 1) They need the opportunity to collect data, analyze it, and determine how to make sense of what the data may mean. 2) With data in hand, students can begin thinking about the validity and reliability of their experience and information collected. 3) They can consider what differences, if any, they might have if they completed the investigation again. 4) They can scrutinize outlying data points for they may be an artifact of a true difference that merits further exploration of a misstep in the procedure, measuring device, or measurement. All of these intellectual activities help them form more robust understanding and are evidence of their critical thinking.
In explore-before-explain teaching, all of these hard critical-thinking tasks come before teacher explanations of content. Whether we use discovery experiences, problem-based learning, and or inquiry-based activities, strategies that are geared toward helping students construct understanding promote critical thinking because students learn content by doing the practices valued in the field to generate knowledge.

An Issue of Equity
Meg Riordan, Ph.D., is the chief learning officer at The Possible Project, an out-of-school program that collaborates with youth to build entrepreneurial skills and mindsets and provides pathways to careers and long-term economic prosperity. She has been in the field of education for over 25 years as a middle and high school teacher, school coach, college professor, regional director of N.Y.C. Outward Bound Schools, and director of external research with EL Education:
Although critical thinking often defies straightforward definition, most in the education field agree it consists of several components: reasoning, problem-solving, and decisionmaking, plus analysis and evaluation of information, such that multiple sides of an issue can be explored. It also includes dispositions and “the willingness to apply critical-thinking principles, rather than fall back on existing unexamined beliefs, or simply believe what you’re told by authority figures.”
Despite variation in definitions, critical thinking is nonetheless promoted as an essential outcome of students’ learning—we want to see students and adults demonstrate it across all fields, professions, and in their personal lives. Yet there is simultaneously a rationing of opportunities in schools for students of color, students from under-resourced communities, and other historically marginalized groups to deeply learn and practice critical thinking.
For example, many of our most underserved students often spend class time filling out worksheets, promoting high compliance but low engagement, inquiry, critical thinking, or creation of new ideas. At a time in our world when college and careers are critical for participation in society and the global, knowledge-based economy, far too many students struggle within classrooms and schools that reinforce low-expectations and inequity.
If educators aim to prepare all students for an ever-evolving marketplace and develop skills that will be valued no matter what tomorrow’s jobs are, then we must move critical thinking to the forefront of classroom experiences. And educators must design learning to cultivate it.
So, what does that really look like?
Unpack and define critical thinking
To understand critical thinking, educators need to first unpack and define its components. What exactly are we looking for when we speak about reasoning or exploring multiple perspectives on an issue? How does problem-solving show up in English, math, science, art, or other disciplines—and how is it assessed? At Two Rivers, an EL Education school, the faculty identified five constructs of critical thinking, defined each, and created rubrics to generate a shared picture of quality for teachers and students. The rubrics were then adapted across grade levels to indicate students’ learning progressions.
At Avenues World School, critical thinking is one of the Avenues World Elements and is an enduring outcome embedded in students’ early experiences through 12th grade. For instance, a kindergarten student may be expected to “identify cause and effect in familiar contexts,” while an 8th grader should demonstrate the ability to “seek out sufficient evidence before accepting a claim as true,” “identify bias in claims and evidence,” and “reconsider strongly held points of view in light of new evidence.”
When faculty and students embrace a common vision of what critical thinking looks and sounds like and how it is assessed, educators can then explicitly design learning experiences that call for students to employ critical-thinking skills. This kind of work must occur across all schools and programs, especially those serving large numbers of students of color. As Linda Darling-Hammond asserts , “Schools that serve large numbers of students of color are least likely to offer the kind of curriculum needed to ... help students attain the [critical-thinking] skills needed in a knowledge work economy. ”
So, what can it look like to create those kinds of learning experiences?
Designing experiences for critical thinking
After defining a shared understanding of “what” critical thinking is and “how” it shows up across multiple disciplines and grade levels, it is essential to create learning experiences that impel students to cultivate, practice, and apply these skills. There are several levers that offer pathways for teachers to promote critical thinking in lessons:
1.Choose Compelling Topics: Keep it relevant
A key Common Core State Standard asks for students to “write arguments to support claims in an analysis of substantive topics or texts using valid reasoning and relevant and sufficient evidence.” That might not sound exciting or culturally relevant. But a learning experience designed for a 12th grade humanities class engaged learners in a compelling topic— policing in America —to analyze and evaluate multiple texts (including primary sources) and share the reasoning for their perspectives through discussion and writing. Students grappled with ideas and their beliefs and employed deep critical-thinking skills to develop arguments for their claims. Embedding critical-thinking skills in curriculum that students care about and connect with can ignite powerful learning experiences.
2. Make Local Connections: Keep it real
At The Possible Project , an out-of-school-time program designed to promote entrepreneurial skills and mindsets, students in a recent summer online program (modified from in-person due to COVID-19) explored the impact of COVID-19 on their communities and local BIPOC-owned businesses. They learned interviewing skills through a partnership with Everyday Boston , conducted virtual interviews with entrepreneurs, evaluated information from their interviews and local data, and examined their previously held beliefs. They created blog posts and videos to reflect on their learning and consider how their mindsets had changed as a result of the experience. In this way, we can design powerful community-based learning and invite students into productive struggle with multiple perspectives.
3. Create Authentic Projects: Keep it rigorous
At Big Picture Learning schools, students engage in internship-based learning experiences as a central part of their schooling. Their school-based adviser and internship-based mentor support them in developing real-world projects that promote deeper learning and critical-thinking skills. Such authentic experiences teach “young people to be thinkers, to be curious, to get from curiosity to creation … and it helps students design a learning experience that answers their questions, [providing an] opportunity to communicate it to a larger audience—a major indicator of postsecondary success.” Even in a remote environment, we can design projects that ask more of students than rote memorization and that spark critical thinking.
Our call to action is this: As educators, we need to make opportunities for critical thinking available not only to the affluent or those fortunate enough to be placed in advanced courses. The tools are available, let’s use them. Let’s interrogate our current curriculum and design learning experiences that engage all students in real, relevant, and rigorous experiences that require critical thinking and prepare them for promising postsecondary pathways.

Critical Thinking & Student Engagement
Dr. PJ Caposey is an award-winning educator, keynote speaker, consultant, and author of seven books who currently serves as the superintendent of schools for the award-winning Meridian CUSD 223 in northwest Illinois. You can find PJ on most social-media platforms as MCUSDSupe:
When I start my keynote on student engagement, I invite two people up on stage and give them each five paper balls to shoot at a garbage can also conveniently placed on stage. Contestant One shoots their shot, and the audience gives approval. Four out of 5 is a heckuva score. Then just before Contestant Two shoots, I blindfold them and start moving the garbage can back and forth. I usually try to ensure that they can at least make one of their shots. Nobody is successful in this unfair environment.
I thank them and send them back to their seats and then explain that this little activity was akin to student engagement. While we all know we want student engagement, we are shooting at different targets. More importantly, for teachers, it is near impossible for them to hit a target that is moving and that they cannot see.
Within the world of education and particularly as educational leaders, we have failed to simplify what student engagement looks like, and it is impossible to define or articulate what student engagement looks like if we cannot clearly articulate what critical thinking is and looks like in a classroom. Because, simply, without critical thought, there is no engagement.
The good news here is that critical thought has been defined and placed into taxonomies for decades already. This is not something new and not something that needs to be redefined. I am a Bloom’s person, but there is nothing wrong with DOK or some of the other taxonomies, either. To be precise, I am a huge fan of Daggett’s Rigor and Relevance Framework. I have used that as a core element of my practice for years, and it has shaped who I am as an instructional leader.
So, in order to explain critical thought, a teacher or a leader must familiarize themselves with these tried and true taxonomies. Easy, right? Yes, sort of. The issue is not understanding what critical thought is; it is the ability to integrate it into the classrooms. In order to do so, there are a four key steps every educator must take.
- Integrating critical thought/rigor into a lesson does not happen by chance, it happens by design. Planning for critical thought and engagement is much different from planning for a traditional lesson. In order to plan for kids to think critically, you have to provide a base of knowledge and excellent prompts to allow them to explore their own thinking in order to analyze, evaluate, or synthesize information.
- SIDE NOTE – Bloom’s verbs are a great way to start when writing objectives, but true planning will take you deeper than this.
QUESTIONING
- If the questions and prompts given in a classroom have correct answers or if the teacher ends up answering their own questions, the lesson will lack critical thought and rigor.
- Script five questions forcing higher-order thought prior to every lesson. Experienced teachers may not feel they need this, but it helps to create an effective habit.
- If lessons are rigorous and assessments are not, students will do well on their assessments, and that may not be an accurate representation of the knowledge and skills they have mastered. If lessons are easy and assessments are rigorous, the exact opposite will happen. When deciding to increase critical thought, it must happen in all three phases of the game: planning, instruction, and assessment.
TALK TIME / CONTROL
- To increase rigor, the teacher must DO LESS. This feels counterintuitive but is accurate. Rigorous lessons involving tons of critical thought must allow for students to work on their own, collaborate with peers, and connect their ideas. This cannot happen in a silent room except for the teacher talking. In order to increase rigor, decrease talk time and become comfortable with less control. Asking questions and giving prompts that lead to no true correct answer also means less control. This is a tough ask for some teachers. Explained differently, if you assign one assignment and get 30 very similar products, you have most likely assigned a low-rigor recipe. If you assign one assignment and get multiple varied products, then the students have had a chance to think deeply, and you have successfully integrated critical thought into your classroom.

Thanks to Dara, Patrick, Meg, and PJ for their contributions!
Please feel free to leave a comment with your reactions to the topic or directly to anything that has been said in this post.
Consider contributing a question to be answered in a future post. You can send one to me at [email protected] . When you send it in, let me know if I can use your real name if it’s selected or if you’d prefer remaining anonymous and have a pseudonym in mind.
You can also contact me on Twitter at @Larryferlazzo .
Education Week has published a collection of posts from this blog, along with new material, in an e-book form. It’s titled Classroom Management Q&As: Expert Strategies for Teaching .
Just a reminder; you can subscribe and receive updates from this blog via email (The RSS feed for this blog, and for all Ed Week articles, has been changed by the new redesign—new ones won’t be available until February). And if you missed any of the highlights from the first nine years of this blog, you can see a categorized list below.
- This Year’s Most Popular Q&A Posts
- Race & Racism in Schools
- School Closures & the Coronavirus Crisis
- Classroom-Management Advice
- Best Ways to Begin the School Year
- Best Ways to End the School Year
- Student Motivation & Social-Emotional Learning
- Implementing the Common Core
- Facing Gender Challenges in Education
- Teaching Social Studies
- Cooperative & Collaborative Learning
- Using Tech in the Classroom
- Student Voices
- Parent Engagement in Schools
- Teaching English-Language Learners
- Reading Instruction
- Writing Instruction
- Education Policy Issues
- Differentiating Instruction
- Math Instruction
- Science Instruction
- Advice for New Teachers
- Author Interviews
- Entering the Teaching Profession
- The Inclusive Classroom
- Learning & the Brain
- Administrator Leadership
- Teacher Leadership
- Relationships in Schools
- Professional Development
- Instructional Strategies
- Best of Classroom Q&A
- Professional Collaboration
- Classroom Organization
- Mistakes in Education
- Project-Based Learning
I am also creating a Twitter list including all contributors to this column .
The opinions expressed in Classroom Q&A With Larry Ferlazzo are strictly those of the author(s) and do not reflect the opinions or endorsement of Editorial Projects in Education, or any of its publications.
Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In

The Importance of Critical Thinking Skills for Students
Link Copied
Share on Facebook
Share on Twitter
Share on LinkedIn
.jpg)
Brains at Work!
If you’re moving toward the end of your high school career, you’ve likely heard a lot about college life and how different it is from high school. Classes are more intense, professors are stricter, and the curriculum is more complicated. All in all, it’s very different compared to high school.
Different doesn’t have to mean scary, though. If you’re nervous about beginning college and you’re worried about how you’ll learn in a place so different from high school, there are steps you can take to help you thrive in your college career.
If you’re wondering how to get accepted into college and how to succeed as a freshman in such a new environment, the answer is simple: harness the power of critical thinking skills for students.
What is critical thinking?
Critical thinking entails using reasoning and the questioning of assumptions to address problems, assess information, identify biases, and more. It's a skillset crucial for students navigating their academic journey and beyond, including how to get accepted into college . At its crux, critical thinking for students has everything to do with self-discipline and making active decisions to 'think outside the box,' allowing individuals to think beyond a concept alone in order to understand it better.
Critical thinking skills for students is a concept highly encouraged in any and every educational setting, and with good reason. Possessing strong critical thinking skills will make you a better student and, frankly, help you gain valuable life skills. Not only will you be more efficient in gathering knowledge and processing information, but you will also enhance your ability to analyse and comprehend it.
Importance of critical thinking for students
Developing critical thinking skills for students is essential for success at all academic levels, particularly in college. It introduces reflection and perspective while encouraging you to question what you’re learning! Even if you’ve seen solid facts. Asking questions, considering other perspectives, and self-reflection cultivate resilient students with endless potential for learning, retention, and personal growth.A well-developed set of critical thinking skills for students will help them excel in many areas. Here are some critical thinking examples for students:
1. Decision-making
If you’re thinking critically, you’re not making impulse decisions or snap judgments; you’re taking the time to weigh the pros and cons. You’re making informed decisions. Critical thinking skills for students can make all the difference.
2. Problem-solving
Students with critical thinking skills are more effective in problem-solving. This reflective thinking process helps you use your own experiences to ideate innovations, solutions, and decisions.
3. Communication
Strong communication skills are a vital aspect of critical thinking for students, helping with their overall critical thinking abilities. How can you learn without asking questions? Critical thinking for students is what helps them produce the questions they may not have ever thought to ask. As a critical thinker, you’ll get better at expressing your ideas concisely and logically, facilitating thoughtful discussion, and learning from your teachers and peers.
4. Analytical skills
Developing analytical skills is a key component of strong critical thinking skills for students. It goes beyond study tips on reviewing data or learning a concept. It’s about the “Who? What? Where? Why? When? How?” When you’re thinking critically, these questions will come naturally, and you’ll be an expert learner because of it.
How can students develop critical thinking skills
Although critical thinking skills for students is an important and necessary process, it isn’t necessarily difficult to develop these observational skills. All it takes is a conscious effort and a little bit of practice. Here are a few tips to get you started:
1. Never stop asking questions
This is the best way to learn critical thinking skills for students. As stated earlier, ask questions—even if you’re presented with facts to begin with. When you’re examining a problem or learning a concept, ask as many questions as you can. Not only will you be better acquainted with what you’re learning, but it’ll soon become second nature to follow this process in every class you take and help you improve your GPA .
2. Practice active listening
As important as asking questions is, it is equally vital to be a good listener to your peers. It is astounding how much we can learn from each other in a collaborative environment! Diverse perspectives are key to fostering critical thinking skills for students. Keep an open mind and view every discussion as an opportunity to learn.
3. Dive into your creativity
Although a college environment is vastly different from high school classrooms, one thing remains constant through all levels of education: the importance of creativity. Creativity is a guiding factor through all facets of critical thinking skills for students. It fosters collaborative discussion, innovative solutions, and thoughtful analyses.
4. Engage in debates and discussions
Participating in debates and discussions helps you articulate your thoughts clearly and consider opposing viewpoints. It challenges the critical thinking skills of students about the evidence presented, decoding arguments, and constructing logical reasoning. Look for debates and discussion opportunities in class, online forums, or extracurricular activities.
5. Look out for diverse sources of information
In today's digital age, information is easily available from a variety of sources. Make it a habit to explore different opinions, perspectives, and sources of information. This not only broadens one's understanding of a subject but also helps in distinguishing between reliable and biased sources, honing the critical thinking skills of students.
Unlock the power of critical thinking skills while enjoying a seamless student living experience!
Book through amber today!
6. Practice problem-solving
Try engaging in challenging problems, riddles or puzzles that require critical thinking skills for students to solve. Whether it's solving mathematical equations, tackling complex scenarios in literature, or analysing data in science experiments, regular practice of problem-solving tasks sharpens your analytical skills. It enhances your ability to think critically under pressure.
Nurturing critical thinking skills helps students with the tools to navigate the complexities of academia and beyond. By learning active listening, curiosity, creativity, and problem-solving, students can create a sturdy foundation for lifelong learning. By building upon all these skills, you’ll be an expert critical thinker in no time—and you’ll be ready to conquer all that college has to offer!
Frequently Asked Questions
What questions should i ask to be a better critical thinker, how can i sharpen critical thinking skills for students, how do i avoid bias, can i use my critical thinking skills outside of school, will critical thinking skills help students in their future careers.
Your ideal student home & a flight ticket awaits
Follow us on :

Related Posts

13 Mind-Blowing Benefits of Public Transportation

18 Best AI Tools For Students In 2024

What Is Greek Life? A Complete Guide to Sororities & Fraternities

amber © 2024. All rights reserved.
4.8/5 on Trustpilot
Rated as "Excellent" • 4800+ Reviews by students
Rated as "Excellent" • 4800+ Reviews by Students
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Fostering creativity and critical thinking in college: a cross-cultural investigation.

- 1 Department of Psychology, Pace University, New York, NY, United States
- 2 Developmental and Educational Research Center for Children's Creativity, Faculty of Education, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, China
Enhancing creativity and critical thinking have garnered the attention of educators and researchers for decades. They have been highlighted as essential skills for the 21st century. A total of 103 United States students (53 female, 24 male, two non-binary, and 24 non-reporting) and 166 Chinese students (128 female, 30 male, one non-binary, and seven non-reporting) completed an online survey. The survey includes the STEAM-related creative problem solving, Sternberg scientific reasoning tasks, psychological critical thinking (PCT) exam, California critical thinking (CCT) skills test, and college experience survey, as well as a demographic questionnaire. A confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) yields a two-factor model for all creativity and critical thinking measurements. Yet, the two latent factors are strongly associated with each other ( r =0.84). Moreover, Chinese students outperform American students in measures of critical thinking, whereas Americans outperform Chinese students in measures of creativity. Lastly, the results also demonstrate that having some college research experience (such as taking research method courses) could positively influence both United States and Chinese students’ creativity and critical thinking skills. Implications are discussed.

Introduction
Creativity and critical thinking have been recognized as essential skills in the 21st century ( National Education Association, 2012 ). Many researchers and educators have focused on these two skills, including acquisition, enhancement, and performance. In addition, numerous studies have been devoted to understanding the conceptual complexities involved in creativity and critical thinking. Although similar to each other, creativity and critical thinking are distinctive by definition, each with a different emphasis.
The concept of creativity has evolved over the years. It was almost exclusively conceptualized as divergent thinking when Guilford (1956 , 1986) proposed divergent thinking as a part of intelligence. Earlier measures of creativity took the approach of divergent thinking, measuring creative potential ( Wallach and Kogan, 1965 ; Torrance, 1966 , 1988 ; Runco and Albert, 1986 ; Kim, 2005 ). In 1990s, many creativity scholars challenged the validity of tests of divergent thinking, and suggested that divergent thinking only captures the trivial sense of creativity, and proposed to use the product-oriented method to measure creativity ( Csikszentmihalyi, 1988 ; Amabile, 1996 ; Sternberg and Lubart, 1999 ). A system model of creativity, which recognizes the important roles individual, field, and domain have played, was used as a framework to conceptualize creativity. A widely accepted definition for creativity is a person’s ability to generate an idea or product that is deemed as both novel and appropriate by experts in a field of human activities ( Scott and Bruce, 1994 ; Amabile, 1996 ; Csikszentmihalyi, 1999 ; Sternberg and Lubart, 1999 ; Hunter et al., 2007 ). Corazza and Lubart (2021) recently proposed a dynamic definition of creativity, in which creativity is defined as a context-embedded phenomenon that is tightly related to the cultural and social environment. Based on this new definition, measures of creativity should be context-specific and culturally relevant, especially when it is examined cross-culturally.
Similarly, the conceptualization of critical thinking has also evolved over the years. Earlier definitions emphasized the broad multidimensional aspects of critical thinking, including at least three aspects: attitude, knowledge, and skills ( Glaser, 1941 ). The definition has been evolved to include specific components for each aspect ( Watson and Glaser, 1980 ). For example, critical thinking is recognized as the ability to use cognitive skills or strategies to increase the probability of a desirable outcome ( Halpern, 1999 ). More specifically, cognitive skills such as evaluation, problem-solving, reflective thinking, logical reasoning, and probability thinking are recognized as parts of critical thinking skills in research and assessments ( Ennis, 1987 , Scriven and Paul, 1987 , Halpern, 1999 ). Moving into the 21st century, metacognition and self-regulatory skills have also become essential components for critical thinking in addition to the cognitive skills recognized by earlier scholars ( Korn, 2014 , Paul and Elder, 2019 ).
Similar to the concept of creativity, critical thinking is also viewed as multidimensional and domain specific ( Bensley and Murtagh, 2012 ). For example, critical thinking in psychology, also referred to as psychological critical thinking (PCT), is defined as one’s ability to evaluate claims in a way that explicitly incorporates basic principles of psychological science ( Lawson, 1999 ). As one of the important hub sciences, psychology is often regarded as a foundational course for scientific training in American higher education ( Boyack et al., 2005 ). In psychological discourse, critical thinking is often defined in tandem with scientific thinking, which places significance on hypothesis-testing and problem-solving in order to reduce bias and erroneous beliefs ( Halpern, 1984 ; American Psychological Association, 2016 ; Lamont, 2020 ; Sternberg and Halpern, 2020 ). Based on this definition, measures of critical thinking should assess cognitive skills (i.e., evaluation, logical reasoning) and ability to utilize scientific methods for problem-solving.
In addition to the evolution of the definitions of critical thinking and creativity, research into these two concepts has led to the development of various measurements. For both concepts, there have been numerous measurements that have been studied, utilized, and improved.
The complexities associated with creativity (i.e., context-relevant and domain-specificity) pose a major issue for its measurement. Many different types of creativity measures have been developed in the past. Measures using a divergent thinking approach, such as the Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking ( Torrance, 1974 ) and Alternate Uses Test ( Guilford et al., 1960 ), a product-oriented approach, a third person nomination approach, as well as a self-report approach measuring personality ( Gough, 1979 ), creative behavior ( Hocevar and Michael, 1979 ; Rodriguez-Boerwinkle et al., 2021 ), and creative achievement ( Carson et al., 2005 ; Diedrich et al., 2018 ).
Both the divergent thinking and the product-oriented approaches have been widely used in the creativity literature to objectively measure creativity. The tasks of both approaches are generally heuristic, meaning that no correct answer is expected and the process does not need to be rational. When scoring divergent thinking, the number of responses (i.e., fluency) and the rareness of the response (i.e., originality) were used to represent creativity. When scoring products using the product-orientated approach, a group of experts provides their subjective ratings on various dimensions such as originality, appropriateness, and aesthetically appealing to these products using their subjective criteria. When there is a consensus among the experts, average ratings of these expert scores are used to represent the creativity of the products. This approach is also named as Consensual Assessment Technique (CAT; Amabile, 1982 , 1996 ). Some scholars viewed the CAT approach as focusing on the convergent aspect of creativity ( Lubart et al., 2013 ). Recognizing the importance of divergent and convergent thinking in conceptualizing creativity, Lubart et al. (2013) have suggested including divergent thinking and product-oriented approach (i.e., CAT) to objective measures of creativity ( Barbot et al., 2011 ).
Similar to measures of creativity, measurements of critical thinking are also multilevel and multi-approach. In an article reviewing the construction of critical thinking in psychological studies, Lamont (2020) argues that critical thinking became a scientific object when psychologists attempted to measure it. Different from measures of creativity, where the tasks are heuristic in nature, measures of critical thinking require participants to engage in logical thinking. Therefore, the nature of critical thinking tasks is more algorithmic.
The interest in the study of critical thinking is evident in the increased efforts in the past decades to measure such a complex, multidimensional skill. Watson-Glaser Tests for Critical Thinking ( Watson and Glaser, 1938 ) is widely recognized as the first official measure of critical thinking. Since then, numerous measurements of critical thinking have been developed to evaluate both overall and domain-specific critical thinking, such as the PCT Exam ( Lawson, 1999 ; See Mueller et al., 2020 for list of assessments). A few of the most commonly used contemporary measures of critical thinking include the Watson-Glaser Test for Critical Thinking Appraisals ( Watson and Glaser, 1980 ), Cornell Critical Thinking Test ( Ennis et al., 1985 ), and California Critical Thinking (CCT) Skills Test ( Facione and Facione, 1994 ). As the best established and widely used standardized critical thinking measures, these tests have been validated in various studies and have been used as a criterion for meta-analyses ( Niu et al., 2013 ; Ross et al., 2013 ).
There have also been concerns regarding the usage of these standardized measures of critical thinking on its own due to its emphasis on measuring general cognitive abilities of participants, while negating the domain-specific aspect of critical thinking ( Lamont, 2020 ). The issues associated with standardized measures are not unique to standardized critical thinking measures, as same types of criticisms have been raised for standardized college admissions measures such as the Graduate Record Exam (GRE). To develop an assessment that encompasses a broader range of student abilities that is more aligned to scientific disciplines, Sternberg and Sternberg (2017) developed a scientific inquiry and reasoning measure. This measure is aimed to assess participants’ ability to utilize scientific methods and to think scientifically in order to investigate a topic or solve a problem ( Sternberg and Sternberg, 2017 ). The strength of this measure is that it assesses students’ abilities (i.e., ability to think critically) that are domain-specific and relevant to the sciences. Considering the multidimensional aspect of critical thinking, a combination of a standardized critical thinking measure, an assessment measuring cognitive abilities involved in critical thinking; and a measure that assesses domain-specific critical thinking, would provide a comprehensive evaluation of critical thinking.
The Relationship Between Creativity and Critical Thinking
Most of the studies thus far referenced have investigated creativity and critical thinking separately; however, the discussion on the relationship between creativity and critical thinking spans decades of research ( Barron and Harrington, 1981 ; Glassner and Schwartz, 2007 ; Wechsler et al., 2018 ; Akpur, 2020 ). Some earlier studies on the relationship between divergent thinking and critical thinking have observed a moderate correlation ( r =0.23, p <0.05) between the two ( Gibson et al., 1968 ). Using measures of creative personality, Gadzella and Penland (1995) also found a moderate correlation ( r =0.36, p <0.05) between creative personality and critical thinking.
Recent studies have further supported the positive correlation between critical thinking and creativity. For example, using the creative thinking disposition scale to measure creativity, Akpur (2020) found a moderate correlation between the two among college students ( r =0.27, p <0.05). Similarly, using the critical thinking disposition scale to measure critical thinking and scientific creativity scale and creative self-efficacy scale to measure creativity, Qiang et al. (2020) studied the relationship between critical thinking and creativity to a large sample of high school students ( n =1,153). They found that the relationship between the two varied depending on the type of measurement of creativity. More specifically, the correlation between critical thinking disposition and creative self-efficacy was r =0.045 ( p <0.001), whereas the correlation between critical thinking disposition and scientific creativity was r =0.15 ( p <0.01).
Recognizing the moderate relationship between the two, researchers have also aimed to study the independence of creativity and critical thinking. Some studies have found evidence that these constructs are relatively autonomous. The results of Wechsler et al. (2018) study, which aimed to investigate whether creativity and critical thinking are independent or complementary processes, found a relative autonomy of creativity and critical thinking and found that the variables were only moderately correlated. The researchers in this study suggest that a model that differentiated the two latent variables associated with creativity and critical thinking dimensions was the most appropriate method of analysis ( Wechsler et al., 2018 ). Evidence to suggest that creativity and critical thinking are fairly independent processes was also found in study of Ling and Loh (2020) . The results of their research, which examined the relationship of creativity and critical thinking to pattern recognition, revealed that creativity is a weak predictor of pattern recognition. In contrast, critical thinking is a good predictor ( Ling and Loh, 2020 ).
It is worth noting that a possible explanation for the inconsistencies in these studies’ results is the variance in the definition and the measures used to evaluate creativity and critical thinking. Based on the current literature on the relationship between creativity and critical thinking, we believe that more investigation was needed to further clarify the relationship between creativity and critical thinking which became a catalyst for the current study.
Cross-Cultural Differences in Creativity and Critical Thinking Performance
Results from various cross-cultural studies suggest that there are differences in creativity and critical thinking skills among cultures. A common belief is that individuals from Western cultures are believed to be more critical and creative compared to non-Westerners, whereas individuals from non-Western cultures are believed to be better at critical thinking related tasks compared to Westerners ( Ng, 2001 ; Wong and Niu, 2013 ; Lee et al., 2015 ). For example, Wong and Niu (2013) found a persistent cultural stereotype regarding creativity and critical thinking skills that exist cross-culturally. In their study, both Chinese and Americans believed that Chinese perform better in deductive reasoning (a skill comparable to critical thinking) and that Americans perform better on creativity. This stereotype belief was found to be incredibly persistent as participants did not change their opinions even when presented with data that contradicted their beliefs.
Interestingly, research does suggest that such a stereotype might be based on scientific evidence ( Niu et al., 2007 ; Wong and Niu, 2013 ). In the same study, it was revealed that Chinese did in fact perform better than Americans in deductive reasoning, and Americans performed better in creativity tests ( Wong and Niu, 2013 ). Similarly, Lee et al. (2015) found that compared to American students, Korean students believed that they are more prone to use receptive learning abilities (remembering and reproducing what is taught) instead of critical and creative learning abilities.
Cultural Influence on Critical Thinking
Other studies investigating the cultural influence on critical thinking have had more nuanced findings. Manalo et al. (2013) study of university students from New Zealand and Japan found that culture-related factors (self-construal, regulatory mode, and self-efficacy) do influence students’ critical thinking use. Still, the differences in those factors do not necessarily equate to differences in critical thinking. Their results found that students from Western and Asian cultural environments did not have significant differences in their reported use of critical thinking. The researchers in this study suggest that perhaps the skills and values nurtured in the educational environment have a more significant influence on students’ use of critical thinking ( Manalo et al., 2013 ).
Another study found that New Zealand European students performed better on objective measures of critical thinking than Chinese students. Still, such differences could be explained by the student’s English proficiency and not dialectical thinking style. It was also revealed in this study that Chinese students tended to rely more on dialectical thinking to solve critical thinking problems compared to the New Zealand European students ( Lun et al., 2010 ). Other research on the cultural differences in thinking styles revealed that Westerners are more likely to use formal logical rules in reasoning. In contrast, Asians are more likely to use intuitive experience-based sense when solving critical thinking problems ( Nisbett et al., 2001 ).
These studies suggest that culture can be used as a broad taxonomy to explain differences in critical thinking use. Still, one must consider the educational environment and thinking styles when studying the nature of the observed discrepancies. For instance, cultural differences in thinking style, in particular, might explain why Westerners perform better on some critical thinking measures, whereas Easterners perform better on others.
Cultural Influence on Creative Performance
Historically, creativity studies have suggested that individuals from non-Western cultures are not as creative as Westerners ( Torrance, 1974 ; Jellen and Urban, 1989 ; Niu and Sternberg, 2001 ; Tang et al., 2015 ). For example, in one study, Americans generated more aesthetically pleasing artworks (as judged by both American and Chinese judges) than Chinese ( Niu and Sternberg, 2001 ). However, recent creativity research has suggested that cross-cultural differences are primarily attributable to the definition of creativity rather than the level of creativity between cultures. As aforementioned, creativity is defined as an idea or product that is both novel and appropriate. Many cross-cultural studies have found that Westerners have a preference and perform better in the novelty aspect, and Easterners have a preference and perform better in the appropriateness aspect. In cross-cultural studies, Rockstuhl and Ng (2008) found that Israelis tend to generate more original ideas than their Singaporean counterparts. In contrast, Singaporeans tend to produce more appropriate ideas. Bechtoldt et al. (2012) found in their study that Koreans generated more useful ideas, whereas Dutch students developed more original ideas. Liou and Lan (2018) found Taiwanese tend to create and select more useful ideas, whereas Americans tend to generate and choose more novel ideas. The differences in creativity preference and performance found in these studies suggest that cultural influence is a prominent factor in creativity.
In summary, cross-cultural studies have supported the notion that culture influences both creativity and critical thinking. This cultural influence seems relatively unambiguous in creativity as it has been found in multiple studies that cultural background can explain differences in performance and preference to the dual features of creativity. Critical thinking has also been influenced by culture, albeit in an opaquer nature in comparison to creativity. Critical thinking is ubiquitous in all cultures, but the conception of critical thinking and the methods used to think critically (i.e., thinking styles) are influenced by cultural factors.
Influence of College Experience on Creativity and Critical Thinking
Given its significance as a core academic ability, the hypothesis of many colleges and universities emphasize that students will gain critical thinking skills as the result of their education. Fortunately, studies have shown that these efforts have had some promising outcomes. Around 92% of students in multi-institution research reported gains in critical thinking. Only 8.9% of students believed that their critical thinking had not changed or had grown weaker ( Tsui, 1998 ). A more recent meta-analysis by Huber and Kuncel (2016) found that students make substantial gains in critical thinking during college. In addition, the efforts to enhance necessary thinking skills have led to the development of various skill-specific courses. Mill et al. (1994) found that among three groups of undergraduate students, a group that received tutorial sessions and took research methodology and statistics performed significantly better on scientific reasoning and critical thinking abilities tests than control groups. Penningroth et al. (2007) found that students who took a class in which they were required to engage in active learning and critical evaluation of claims by applying scientific concepts, had greater improvement in psychological critical thinking than students in the comparison groups. There have also been studies in which students’ scientific inquiry and critical thinking skills have improved by taking a course designed with specific science thinking and reasoning modules ( Stevens and Witkow, 2014 ; Stevens et al., 2016 ).
Using a Survey of Undergraduate Research Experience (SURE), Lopatto (2004 , 2008) found that research experience can help students gain various learning skills such as ability to integrate theory and practice, ability to analyze data, skill in the interpretation of results, and understanding how scientists work on problem. All of these learning skills correspond to at least one of the dimensions mentioned earlier in the definition of critical thinking (i.e., evaluation, analytical thinking, and problem solving through). Thus, results of SURE provide evidence that critical thinking can be enhanced through research experience ( Lopatto, 2004 , 2008 ).
In comparison to critical thinking, only a few studies have examined the interaction between creativity and college experience. Previous research on STEM provides some evidence to suggest that STEM education can promote the learner’s creativity ( Land, 2013 , Guo and Woulfin, 2016 , Kuo et al., 2018 ). Notably, study of Kuo et al. (2018) suggest that project-based learning in STEM has the merits of improving one’s creativity. They found that the STEM Interdisciplinary Project-Based Learning (IPBL) course is a practical approach to improve college student’s creativity ( Kuo et al., 2018 ). College research experience in particular, has been reported as important or very important by faculty and students for learning how to approach problems creatively ( Zydney et al., 2002 ).
Although specific college courses aimed to enhance creativity have been scarce, some training programs have been developed specifically to improve creativity. Scott et al. (2004) conducted a quantitative review of various creativity training and found that divergent thinking, creative problem solving, and creativity performance can be enhanced through skill-specific training programs. Embodied creativity training programs, consisting of creativity fitness exercises and intensive workshops, have also been effective in enhancing participants’ creative production and improving their creative self-efficacy ( Byrge and Tang, 2015 ).
Both critical thinking and creativity were also found to be important in students’ learning. Using a longitudinal design for one semester to 52 graduate students in biology, Siburian et al. (2019) studied how critical thinking and creative thinking contribute to improving cognitive learning skills. They found that both critical and creative thinking significantly contributes to enhancing cognitive learning skills ( R 2 =0.728). They each contribute separately to the development of cognitive learning skills ( b was 0.123 between critical thinking and cognitive learning and 0.765 between creative thinking and cognitive learning). The results from research on creativity and critical thinking indicate that training and experiences of students in college can enhance both of these skills.
Current Study
Previous literature on creativity and critical thinking suggests that there is a positive correlation between these two skills. Moreover, cultural background influences creativity and critical thinking conception and performance. However, our literature review suggests that there are only a few studies that have investigated creativity and critical thinking simultaneously to examine whether cultural background is a significant influence in performance. In addition, most of the past research on creativity and critical thinking have relied on dispositions or self-reports to measure the two skills and the investigation on the actual performance have been scarce. Lastly, past studies suggest that the acquisition and enhancement of these skills are influenced by various factors. Notably, college experience and skill-specific training have been found to improve both creativity and critical thinking. However, it is not yet clear how college experience aids in fostering creativity and critical thinking and which elements of college education are beneficial for enhancing these two skills. The cultural influence on creativity and critical thinking performance also needs further investigation.
The current study aimed to answer two questions related to this line of thought. How does culture influence creativity and critical thinking performance? How does college experience affect creativity and critical thinking? Based on past findings, we developed three hypotheses. First, we hypothesized that there is a positive association between critical thinking and creativity. Second, we suggest that college students from different countries have different levels of creativity and critical thinking. More specifically, we predicted that United States students would perform better than Chinese students on both creativity and critical thinking. Last, we hypothesized that having college research experience (through courses or research labs) will enhance creativity and critical thinking.
Materials and Methods
Participants.
The study was examined by the Internal Review Board by the host university in the United States and obtained an agreement from a partner university in China to meet the ethical standard of both countries.
Participants include 103 university students from the United States and 166 university students from Mainland China. Among all participants, 181 were female (67.3%), 54 were male (20.1%), non-binary or gender fluid ( n =3, 1.1%), and some did not report their gender ( n =31, 11.5%). The majority of participants majored in social sciences ( n =197, 73.2%). Other disciplines include business and management ( n =38, 14.1%), engineering and IT ( n =20, 7.4%), and sciences ( n =14, 5.2%). A Chi-square analysis was performed to see if the background in major was different between the American and Chinese samples. The results showed that the two samples are comparable in college majors, X 2 (3, 265) =5.50, p =0.138.
The American participants were recruited through campus recruitment flyers and a commercial website called Prolific (online survey distribution website). Ethnicities of the American participants were White ( n =44, 42.7%), Asian ( n =13, 12.6%), Black or African American ( n =11, 10.7%), Hispanic or Latinos ( n =5, 4.9%), and some did not report their ethnicity ( n =30, 29.1%). The Chinese participants were recruited through online recruitment flyers. All Chinese students were of Han ethnicity.
After reviewing and signing an online consent form, both samples completed a Qualtrics survey containing creativity and critical thinking measures.
Measurements
Steam related creative problem solving.
This is a self-designed measurement, examining participant’s divergent and convergent creative thinking in solving STEAM-related real-life problems. It includes three vignettes, each depicting an issue that needs to be resolved. Participants were given a choice to pick two vignettes to which they would like to provide possible solutions for. Participants were asked to provide their answers in two parts. In the first part, participants were asked to provide as many solutions as they can think of for the problem depicted (divergent). In the second part, participants were asked to choose one of the solutions they gave in the first part that they believe is the most creative and elaborate on how they would carry out the solution (convergent).
The responses for the first part of the problem (i.e., divergent) were scored based on fluency (number of solutions given). Each participant received a score on fluency by averaging the number of solutions given across three tasks. In order to score the originality of the second part of the solution (i.e., convergent), we invited four graduate students who studied creativity for at least 1year as expert judges to independently rate the originality of all solutions. The Cronbach’s Alpha of the expert ratings was acceptable for all three vignette solutions (0.809, 0.906, and 0.703). We then averaged the originality scores provided by the four experts to represent the originality of each solution. We then averaged the top three solutions as rated by the experts to represent the student’s performance on originality. In the end, each student received two scores on this task: fluency and originality.
Psychological Critical Thinking Exam
We adopted an updated PCT Exam developed by Lawson et al. (2015) , which made improvements to the original measure ( Lawson, 1999 ). We used PCT to measure the participants’ domain-specific critical thinking: critical thinking involved in the sciences. The initial assessment aimed to examine the critical thinking of psychology majors; however, the updated measure was developed so that it can be used to examine students’ critical thinking in a variety of majors. The split-half reliability of the revised measurement was 0.88, and test-retest reliability was 0.90 ( Lawson et al., 2015 ). Participants were asked to identify issues with a problematic claim made in two short vignettes. For example, one of the questions states:
Over the past few years, Jody has had several dreams that apparently predicted actual events. For example, in one dream, she saw a car accident and later that week she saw a van run into the side of a pickup truck. In another dream, she saw dark black clouds and lightning and 2days later a loud thunderstorm hit her neighborhood. She believes these events are evidence that she has a psychic ability to predict the future through her dreams. Could the event have occurred by chance? State whether or not there is a problem with the person’s conclusions and explain the problem (if there is one).
Responses were scored based on the rubric provided in the original measurement ( Lawson et al., 2015 ). If no problem was identified the participants would receive zero points. If a problem was recognized but misidentified, the participants would receive one point. If the main problem was identified and other less relevant problems were identified, the participants received two points. If participants identified only the main problem, they received three points. Following the rubric, four graduate students independently rated the students’ critical thinking task. The Cronbach’s Alpha of the expert ratings was acceptable for both vignettes (0.773 and 0.712). The average of the four scores given by the experts was used as the final score for the participants.
California Critical Thinking Skills Test
This objective measure of critical thinking was developed by Facione and Facione (1994) . We used CCT to measure a few of the multidimensions of critical thinking such as evaluation, logical reasoning, and probability thinking. Five sample items provided from Insight Assessment were used instead of the standard 40-min long CCT. Participants were presented with everyday scenarios with 4–6 answer choices. Participants were asked to make an accurate and complete interpretation of the question in order to correctly answer the question by choosing the right answer choice (each correct answer was worth one point). This test is commonly used to measure critical thinking, and previous research has reported its reliability as r =0.86 ( Hariri and Bagherinejad, 2012 ).
Sternberg Scientific Inquiry and Reasoning
This measure was developed by Sternberg and Sternberg (2017) as an assessment of scientific reasoning. We used this assessment as a domain-specific assessment to measure participants’ scientific creativity (generating testable hypotheses) and scientific critical thinking involved in generating experiments. For this two-part measure, participants were asked to read two short vignettes. For one of the vignettes, participants were asked to generate as many hypotheses as possible to explain the events described in the vignette. For the other, create an experiment to test the hypothesis mentioned in the vignette.
After carefully reviewing the measurement, we notice that the nature of the tasks in the first part of this measure (hypothesis generation) relied on heuristics, requiring participants to engage in divergent thinking. The number of valid hypotheses provided (i.e., fluency) was used to represent the performance of this task. We, therefore, deem that this part measures creativity. In contrast, the second part of the measure, experiment generation, asked participants to use valid scientific methods to design an experiment following the procedure of critical thinking such as evaluation, problem-solving, and task evaluation. Its scoring also followed algorithms so that a correct answer could be achieved. For the above reasons, we believe hypotheses generation is a measurement of creativity and experiment generation is a measurement for critical thinking.
Based on the recommended scoring manual, one graduate student calculated the fluency score from the hypothesis generation measurement. Four experts read through all students’ responses to the experiment generation. They discussed a rubric on how to score these responses, using a four-point scale, with a “0” representing no response or wrong response, a “1” representing partially correct, a “2” representing correct response. An additional point (the three points) was added if the participant provided multiple design methods. Based on the above rubric, the four experts independently scored this part of the questionnaire. The Cronbach’s Alpha of the four expert ratings was 0.792. The average score of the four judges was used to represent their critical thinking scores on this task.
College Experience Survey
Participants were asked about their past research experience, either specifically in psychology or in general academia. Participants were asked to choose between three choices: no research experience, intermediate research experience (i.e., research work for class, research work for lab), and advanced research experience (i.e., professional research experience, published works).
Demographic and Background Questionnaire
Series of standard demographic questions were asked, including participants’ age, gender, and ethnicity.
We performed a Pearson correlation to examine the relationship between creativity and critical thinking (the two-c), which include performances on three measures on creativity ( creativity originality , creativity fluency , and hypothesis generation ) and three measures on critical thinking ( experiment generation , CCT , and PCT ).
Most of the dependent variables had a significantly positive correlation. The only insignificant correlation was found between Sternberg hypothesis generation and CCT, r (247) =0.024, p =0.708 (see Table 1 ).
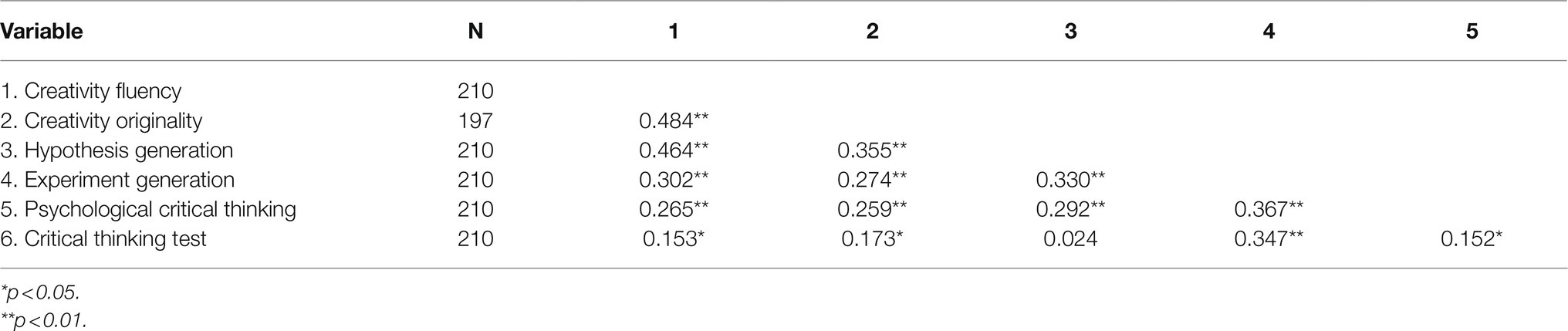
Table 1 . Correlation coefficients for study variables.
Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) was conducted by applying SEM through AMOS 21 software program and the maximum likelihood method. One-factor and two-factor models have been analyzed, respectively (see Figure 1 ).
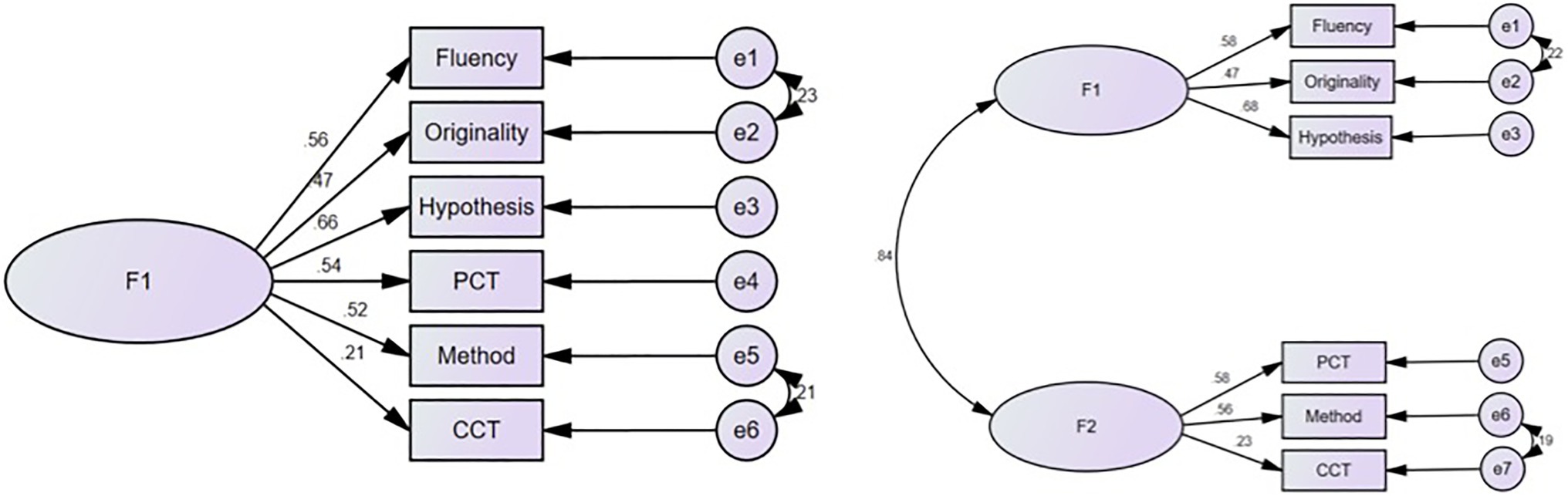
Figure 1 . The comparison of the two confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) models: one-factor vs. two-factor.
As it is demonstrated in Table 2 , the value ranges of the most addressed fit indices used in the analysis of SEM are presented. Comparing two models, χ 2 /df of the two-factor model is in a good fit, while the index of the one-factor model is in acceptable fit. The comparison of the two models suggest that the two-factor model is a better model than the one-factor model.
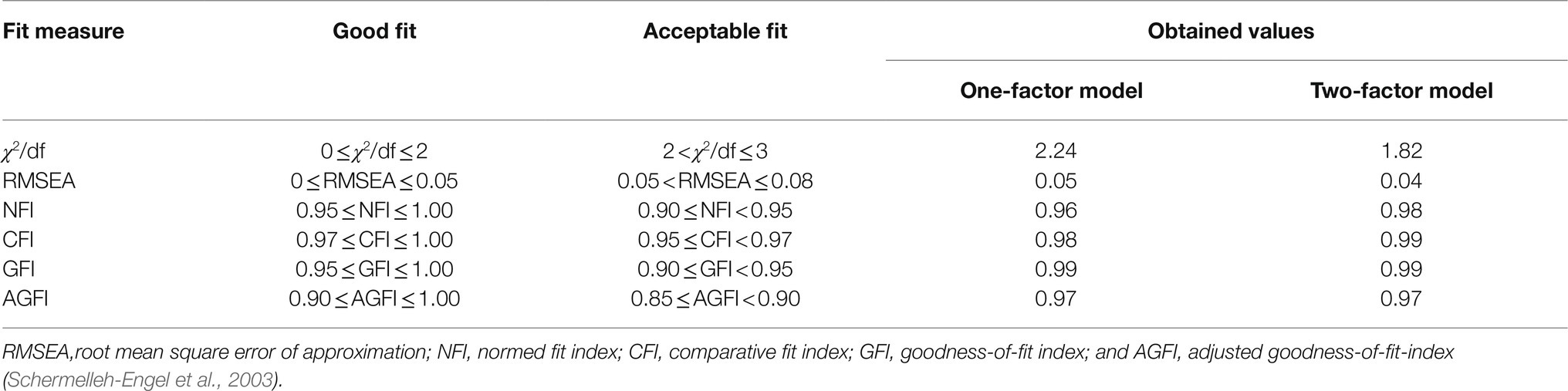
Table 2 . Recommended values for evaluation and the obtained values.
Cross-Cultural Differences in Critical Thinking and Creativity
We conducted a 2 (Country: the United States vs. China)×2 (Two-C: Creativity and Critical Thinking) ANOVA to investigate the cultural differences in critical thinking and creativity. We averaged scores of three critical thinking measurement ( experiment generation , PCT , and CCT ) to represent critical thinking and averaged three creativity scores ( creativity originality , creativity fluency , and hypothesis generation ).
This analysis revealed a significant main effect for the type of thinking (i.e., creative vs. critical thinking), F (1,247) =464.77, p <0.01, η p 2 =0.653. Moreover, there was a significant interaction between country (i.e., the United States vs. China) and type of thinking, F (1,247) =62.00, p <0.01, η p 2 =0.201. More specifically, Chinese students ( M =1.32, SD =0.59) outperformed American students ( M =1.02, SD =0.44) on critical thinking. In contrast, American students ( M =2.59, SD =1.07) outperformed Chinese students ( M =2.05, SD =0.83) on creativity.
Influence of Research Experience on Critical Thinking and Creativity
The last hypothesis states that having college research experience (through courses or research lab) would enhance students’ creativity and critical thinking from both countries. We performed a 2 (Two-C: Creativity and Critical Thinking)×2 (Country: the United States vs. China)×3 (Research Experience: Advanced vs. Some vs. No) ANOVA to test this hypothesis. This analysis revealed a significant main effect for research experience, F (2,239) =4.05, p =0.019, η p 2 =0.033. Moreover, there was a significant interaction between country (i.e., the United States vs. China) and research experience, F (2,239) =5.77, p =0.004, η p 2 =0.046. In addition, there was a three-way interaction among country, two-C, and research experience. More specifically, with an increase of research experience for American students, both critical thinking and creativity improved. In contrast, for Chinese students, the impact of research experience was not significant for creativity. However, some research experience positively impacted Chinese students’ critical thinking (see Figure 2 ).
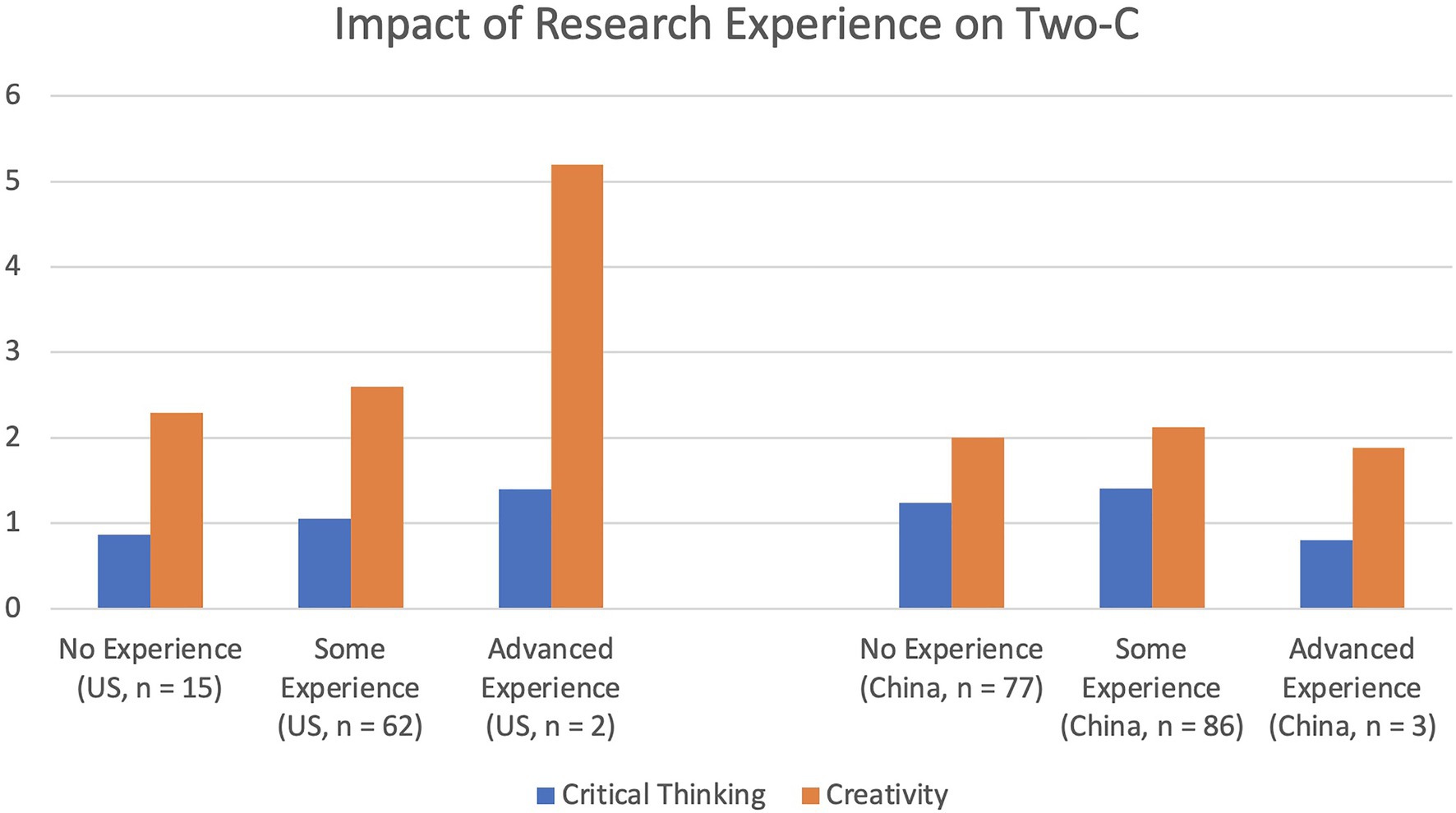
Figure 2 . Estimated marginal means of Two-C for the United States and Chinese samples.
The current study aimed to investigate the relationship between creativity and critical thinking, how culture influences creativity and critical thinking, and how college research experience affects creativity and critical thinking. Our results supported the first hypothesis regarding the positive correlation among all of the dependent variables. The mean correlation between the measures of creativity and critical thinking was 0.230. This result was in line with the findings from previous research ( Gibson et al., 1968 ; Gadzella and Penland, 1995 ; Siburian et al., 2019 ; Akpur, 2020 ; Qiang et al., 2020 ). Moreover, our confirmatory factor analysis yielded similar results as analysis of Wechsler et al. (2018) and Akpur (2020) and provides more evidence of the relative independence between creativity and critical thinking. We found that at the latent variable level, the two skills are highly correlated to each other ( r =0.84). In addition, we found that although the one-factor model was an acceptable fit, a two-factor model was a better fit for analysis. This result suggests that despite the correlation between creativity and critical thinking, the two skills should be studied as separate factors for an appropriate and comprehensive analysis.
The results of this study partially confirmed our second hypothesis and replicated the findings from past studies ( Niu et al., 2007 ; Lun et al., 2010 ; Wong and Niu, 2013 ; Tang et al., 2015 ). As predicted, there was a significant main effect for culture in students’ performance for all six measures in the two-C analysis model. United States students performed better than Chinese students in all three creativity measures, and Chinese students performed better than United States students in all critical thinking measures. Given the diversity in the type of measures used in this study, the results suggest that United States and Chinese students’ performance aligns with the stereotype belief found in study of Wong and Niu (2013) . The findings from the current study suggest that the stereotype belief observed in both United States and Chinese students (United States students generally perform better on creativity tasks, while Chinese students perform typically better on critical thinking tasks) is not entirely unfounded. Furthermore, the clear discrepancy in performance between United States and Chinese students provides more evidence to suggest that creativity and critical thinking are relatively autonomous skills. Although, a high correlation between these two skills was found in our study, the fact that students from two different cultures have two different development trajectories in critical thinking and creativity suggests that these two skills are relatively autonomous.
Lastly, the results also confirmed our third hypothesis, that is, college research experience did have a positive influence on students’ creativity and critical thinking. Compared to students with no research experience, students with some research experience performed significantly better in all measures of creativity and critical thinking. This finding is consistent with the previous literature ( Mill et al., 1994 ; Penningroth et al., 2007 ; Stevens and Witkow, 2014 ; Stevens et al., 2016 ; Kuo et al., 2018 ). The result of our study suggests that college research experience is significant to enhance both creativity and critical thinking. As research experience becomes a more essential component of college education, our results suggest that it not only can add credential for applying to graduate school or help students learn skills specific to research, but also help students enhance both creativity and critical thinking. Furthermore, it is worth noting that this nature held true for both Chinese and American students. To our knowledge, this is a first investigation examining the role of research experience in both creativity and critical thinking cross-culturally.
In addition to the report of our findings, we would like to address some limitations of our study. First, we would like to note that this is a correlational and cross-sectional study. A positive correlation between research experience and the two dependent variables does not necessarily mean causation. Our results indeed indicate a positive correlation between research experience and the two-C variables; however, we are not sure of the nature of this relationship. It is plausible that students with higher creativity and critical thinking skills are more engaged in research as much as it is to argue in favor of a reversed directional relationship. Second, we would like to note the sample bias in our study. Majority of our participants were female, majoring in the social sciences and a relatively high number of participants chose not to report their gender. Third, we would like to note that our study did not measure all creativity and critical thinking dimensions, we discussed in the introduction. Instead, we focused on a few key dimensions of creativity and critical thinking. Our primary focus was on divergent thinking, convergent thinking, and scientific creativity as well as few key dimensions of critical thinking (evaluation, logical reasoning, and probability thinking), scientific critical thinking involved in problem solving and hypothesis testing. Moreover, our results do not show what specific components of research training are beneficial for the enhancement of creativity and critical thinking.
For future research, a longitudinal design involving a field experiment will help investigate how different research training components affect the development of creativity and critical thinking. In addition, a cross-cultural study can further examine how and why the students from different cultures differ from each other in the development of these two potentials. As such, it might shed some light on the role of culture in creativity and critical thinking.
Conclusion and Implication
The result of our study provides few insights to the study of creativity and critical thinking. First, creativity and critical thinking are a different construct yet highly correlated. Second, whereas Americans perform better on creativity measures, Chinese perform better on critical thinking measures. Third, for both American and Chinese students, college research experience is a significant influence on the enhancement of creativity and critical thinking. As research experience becomes more and more essential to college education, its role can not only add professional and postgraduate credentials, but also help students enhance both creativity and critical thinking.
Based on our results, we recommend that research training be prioritized in higher education. Moreover, each culture has strengths to develop one skill over the other, hence, each culture could invest more in developing skills that were found to be weaker in our study. Eastern cultures can encourage more creativity and Western cultures can encourage more critical thinking.
To conclude, we would like to highlight that, although recognized globally as essential skills, methods to foster creativity and critical thinking skills and understanding creativity and critical thinking as a construct requires further research. Interestingly, our study found that experience of research itself can help enhance creativity and critical thinking. Our study also aimed to expand the knowledge of creativity and critical thinking literature through an investigation of the relationship of the two variables and how cultural background influences the performance of these two skills. We hope that our findings can provide insights for researchers and educators to find constructive methods to foster students’ essential 21st century skills, creativity and critical thinking, to ultimately enhance their global competence and life success.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics Statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Institutional Review Board at Pace University. The participants provided their informed consent online prior to participating in the study.
Author Contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct, and intellectual contribution to the work, and approved it for publication.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
This work was supported by the International Joint Research Project of Faculty of Education, Beijing Normal University (ICER201904), and a scholarly research funding by Pace University.
Akpur, U. (2020). Critical, reflective, creative thinking and their reflections on academic achievement. Think. Skills Creat. 37:100683. doi: 10.1016/j.tsc.2020.100683
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Amabile, T. M. (1982). Social psychology of creativity: a consensual assessment technique. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 43, 997–1013. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.43.5.997
Amabile, T. M. (1996). Creativity in Context: Update to “The Social Psychology of Creativity. ” Boulder, CO: Westview Press.
Google Scholar
American Psychological Association (2016). Guidelines for the undergraduate psychology major: version 2.0. Am. Psychol. 71, 102–111. doi: 10.1037/a0037562
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Barbot, B., Besançon, M., and Lubart, T. (2011). Assessing creativity in the classroom. Open Educ. J. 4, 58–66. doi: 10.2174/1874920801104010058
Barron, F., and Harrington, D. M. (1981). Creativity, intelligence, and personality. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 32, 439–476. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ps.32.020181.002255
Bechtoldt, M., Choi, H., and Nijstad, A. B. (2012). Individuals in mind, mates by heart: individualistic self-construal and collective value orientation as predictors of group creativity. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 48, 838–844. doi: 10.1016/j.jesp.2012.02.014
Bensley, D. A., and Murtagh, M. P. (2012). Guidelines for a scientific approach to critical thinking assessment. Teach. Psychol. 39, 5–16. doi: 10.1177/0098628311430642
Boyack, K. W., Klavans, R., and Börner, K. (2005). Mapping the backbone of science. Scientometrics 64, 351–374. doi: 10.1007/s11192-005-0255-6
Byrge, C., and Tang, C. (2015). Embodied creativity training: effects on creative self-efficacy and creative production. Think. Skills Creat. 16, 51–61. doi: 10.1016/j.tsc.2015.01.002
Carson, S. H., Peterson, J. B., and Higgins, D. M. (2005). Reliability, validity, and factor structure of the creative achievement questionnaire. Creat. Res. J. 17, 37–50. doi: 10.1207/s15326934crj1701_4
Corazza, G. E., and Lubart, T. (2021). Intelligence and creativity: mapping constructs on the space-time continuum. J. Intell. 9:1. doi: 10.3390/jintelligence9010001
Csikszentmihalyi, M. (1988). “Society, culture, and person: A systems view of creativity” in The Nature of Creativity: Contemporary Psychological Perspectives. ed. Sternberg, R. J. (New York: Cambridge University Press), 325–339.
Csikszentmihalyi, M. (1999). “Implications of a systems perspective for the study of creativity” in Handbook of Creativity. ed. Sternberg, R. J. (New York, NY: Cambridge University Press), 313–335.
Diedrich, J., Jauk, E., Silvia, P. J., Gredlein, J. M., Neubauer, A. C., and Benedek, M. (2018). Assessment of real-life creativity: the inventory of creative activities and achievements (ICAA). Psychol. Aesthet. Creat. Arts 12, 304–316. doi: 10.1037/aca0000137
Ennis, R. H. (1987). “A taxonomy of critical thinking dispositions and abilities” in Teaching Thinking Skills: Theory and Practice. eds. Baron, J. B., and Sternberg, R. J. (New York, NY: W H Freeman/Times Books/Henry Holt & Co.), 9–26.
Ennis, R. H., Millman, J., and Tomko, T. N. (1985). Cornell Critical Thinking Test Level x and Level z Manual. 3rd Edn . Pacific Grove, CA: Midwest Publications.
Facione, P. A., and Facione, N. (1994). The California Critical Thinking Skills Test: Test Manual. Millbrae, CA: California Academic Press.
Gadzella, B. M., and Penland, E. (1995). Is creativity related to scores on critical thinking? Psychol. Rep. 77, 817–818. doi: 10.2466/pr0.1995.77.3.817
Gibson, J. W., Kibler, R. J., and Barker, L. L. (1968). Some relationships between selected creativity and critical thinking measures. Psychol. Rep. 23, 707–714. doi: 10.2466/pr0.1968.23.3.707
Glaser, E. M. (1941). An Experiment in the Development of Critical Thinking. New York, NY: Teachers College, Columbia University.
Glassner, A., and Schwartz, B. (2007). What stands and develops between creative and critical thinking? Argumentation? Think. Skills Creat. 2, 10–18. doi: 10.1016/j.tsc.2006.10.001
Gough, H. G. (1979). A creative personality scale for the adjective check list. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 37, 1398–1405. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.37.8.1398
Guilford, J. P. (1956). The structure of intellect. Psychol. Bull. 53, 267–293. doi: 10.1037/h0040755
Guilford, J. P. (1986). Creative Talents: Their Nature, Uses and Development. Buffalo, NY: Bearly Ltd.
Guilford, J. P., Christensen, P. R., Merrifield, P. R., and Wilson, R. C. (1960). Alternate Uses Manual. Menlo Park, CA: Mind Garden, Inc.
Guo, J., and Woulfin, S. (2016). Twenty-first century creativity: an investigation of how the partnership for 21st century instructional framework reflects the principles of creativity. Roeper Rev. 38, 153–161. doi: 10.1080/02783193.2016.1183741
Halpern, D. F. (1984). Thought and Knowledge: An Introduction to Critical Thinking. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Halpern, D. F. (1999). Teaching for critical thinking: helping college students develop the skills and dispositions of a critical thinker. New Dir. Teach. Learn. 1999, 69–74. doi: 10.1002/tl.8005
Hariri, N., and Bagherinejad, Z. (2012). Evaluation of critical thinking skills in students of health faculty, Mazandaran university of medical sciences. J. Mazand. Univ. Med. Sci. 21, 166–173.
Hocevar, D., and Michael, W. B. (1979). The effects of scoring formulas on the discriminant validity of tests of divergent thinking. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 39, 917–921. doi: 10.1177/001316447903900427
Huber, C. R., and Kuncel, N. R. (2016). Does college teach critical thinking? A meta-analysis. Rev. Educ. Res. 86, 431–468. doi: 10.3102/0034654315605917
Hunter, S. T., Bedell, K. E., and Mumford, M. D. (2007). Climate for creativity: a quantitative review. Creat. Res. J. 19, 69–90. doi: 10.1080/10400410709336883
Jellen, H. U., and Urban, K. (1989). Assessing creative potential worldwide: the first cross-cultural application of the test for creative thinking–drawing production (TCT–DP). Gifted Educ. 6, 78–86. doi: 10.1177/026142948900600204
Kim, K. H. (2005). Can only intelligent people be creative? A meta-analysis. J. Sec. Gifted Educ. 16, 57–66. doi: 10.4219/jsge-2005-473
Korn, M. (2014). Bosses Seek ‘Critical Thinking,’ but What Is That? Wall Street Journal. Available at: https://online.wsj.com/articles/bosses-seek-critical-thinking-but-what-is-that-1413923730 (Accessed October 18, 2021).
Kuo, H.-C., Tseng, Y.-C., and Yang, Y.-T. C. (2018). Promoting college student's learning motivation and creativity through a STEM interdisciplinary PBL human-computer interaction system design and development course. Think. Skills Creat. 31, 1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.tsc.2018.09.001
Lamont, P. (2020). The construction of "critical thinking": between how we think and what we believe. Hist. Psychol. 23, 232–251. doi: 10.1037/hop0000145
Land, M. H. (2013). Full STEAM ahead: the benefits of integrating the arts into STEM. Compl. Adapt. Syst. 20, 547–552. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2013.09.317
Lawson, T. J. (1999). Assessing psychological critical thinking as a learning outcome for psychology majors. Teach. Psychol. 26, 207–209. doi: 10.1207/S15328023TOP260311
Lawson, T. J., Jordan-Fleming, M. K., and Bodle, J. H. (2015). Measuring psychological critical thinking. Teach. Psychol. 42, 248–253. doi: 10.1177/0098628315587624
Lee, H.-J., Lee, J., Makara, K. A., Fishman, B. J., and Hong, Y. I. (2015). Does higher education foster critical and creative learners? An exploration of two universities in South Korea and the USA. High. Educ. Res. Dev. 34, 131–146. doi: 10.1080/07294360.2014.892477
Ling, M. K. D., and Loh, S. C. (2020). Relationship of creativity and critical thinking to pattern recognition among Singapore private school students. J. Educ. Res. 113, 59–76. doi: 10.1080/00220671.2020.1716203
Liou, S., and Lan, X. (2018). Situational salience of norms moderates cultural differences in the originality and usefulness of creative ideas generated or selected by teams. J. Cross-Cult. Psychol. 49, 290–302. doi: 10.1177/0022022116640897
Lopatto, D. (2004). Survey of undergraduate research experiences (SURE): first findings. Cell Biol. Educ. 3, 270–277. doi: 10.1187/cbe.04-07-0045
Lopatto, D. (2008). “Exploring the benefits of undergraduate research experiences: The SURE survey” in Creating Effective Undergraduate Research Programs in Science eds. R. Taraban and R. L. Blanton (New York: Teachers College Press), 112–132.
Lubart, T., Zenasni, F., and Barbot, B. (2013). Creative potential and its measurement. Int. J. Talent Dev. Creat. 1, 41–50.
Lun, V. M.-C., Fischer, R., and Ward, C. (2010). Exploring cultural differences in critical thinking: is it about my thinking style or the language I speak? Learn. Individ. Differ. 20, 604–616. doi: 10.1016/j.lindif.2010.07.001
Manalo, E., Kusumi, T., Koyasu, M., Michita, Y., and Tanaka, Y. (2013). To what extent do culture-related factors influence university students' critical thinking use? Think. Skills Creat. 10, 121–132. doi: 10.1016/j.tsc.2013.08.003
Mill, D., Gray, T., and Mandel, D. R. (1994). Influence of research methods and statistics courses on everyday reasoning, critical abilities, and belief in unsubstantiated phenomena. Can. J. Behav. Sci. 26, 246–258. doi: 10.1037/0008-400X.26.2.246
Mueller, J. F., Taylor, H. K., Brakke, K., Drysdale, M., Kelly, K., Levine, G. M., et al. (2020). Assessment of scientific inquiry and critical thinking: measuring APA goal 2 student learning outcomes. Teach. Psychol. 47, 274–284. doi: 10.1177/0098628320945114
National Education Association (2012). Preparing 21st Century Students for a Global Society: An educator's Guide to the "Four Cs". Alexandria, VA: National Education Association.
Ng, A.K. (2001). Why Asians Are less Creative than Westerners. Singapore: Prentice Hall.
Nisbett, R. E., Peng, K., Choi, I., and Norenzayan, A. (2001). Culture and systems of thought: holistic versus analytic cognition. Psychol. Rev. 108, 291–310. doi: 10.1037/0033-295X.108.2.291
Niu, L., Behar-Horenstein, L. S., and Garvan, C. W. (2013). Do instructional interventions influence college students' critical thinking skills? A meta-analysis. Educ. Res. Rev. 9, 114–128. doi: 10.1016/j.edurev.2012.12.002
Niu, W., and Sternberg, R. J. (2001). Cultural influences on artistic creativity and its evaluation. Int. J. Psychol. 36, 225–241. doi: 10.1080/00207590143000036
Niu, W., Zhang, J. X., and Yang, Y. (2007). Deductive reasoning and creativity: a cross-cultural study. Psychol. Rep. 100, 509–519. doi: 10.2466/pr0.100.2.509-519
Paul, R., and Elder, L. (2019). The Miniature Guide to Critical Thinking Concepts and Tools. 8th Edn . Lanham, MD: Foundation for Critical Thinking.
Penningroth, S. L., Despain, L. H., and Gray, M. J. (2007). A course designed to improve psychological critical thinking. Teach. Psychol. 34, 153–157. doi: 10.1080/00986280701498509
Qiang, R., Han, Q., Guo, Y., Bai, J., and Karwowski, M. (2020). Critical thinking disposition and scientific creativity: the mediating role of creative self-efficacy. J. Creat. Behav. 54, 90–99. doi: 10.1002/jocb.347
Rockstuhl, T., and Ng, K.-Y. (2008). The effects of cultural intelligence on interpersonal trust in multicultural teams. In Handbook of Cultural Intelligence: Theory, Measurement, and Applications. (eds.) Ang, S., and Dyne, L.Van. Armonk, NY: M.E. Sharpe. 206–220.
Rodriguez-Boerwinkle, R., Silvia, P., Kaufman, J. C., Reiter-Palmon, R., and Puryear, J. S. (2021). Taking inventory of the creative behavior inventory: an item response theory analysis of the CBI. [Preprint]. doi: 10.31234/osf.io/b7cfd
Ross, D., Loeffler, K., Schipper, S., Vandermeer, B., and Allan, G. M. (2013). Do scores on three commonly used measures of critical thinking correlate with academic success of health professions trainees? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acad. Med. 88, 724–734. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0b013e31828b0823
Runco, M. A., and Albert, R. S. (1986). The threshold theory regarding creativity and intelligence: an empirical test with gifted and nongifted children. Creat. Child Adult Q. 11, 212–218.
Schermelleh-Engel, K., Moosbrugger, H., and Müller, H. (2003). Evaluating the fit of structural equation models: Tests of significance and descriptive goodness-of-fit measures. Methods of Psychological Research 8, 23–74.
Scott, S. G., and Bruce, R. A. (1994). Determinants of innovative behavior: a path model of individual innovation in the workplace. Acad. Manag. J. 37, 580–607.
Scott, G., Leritz, L. E., and Mumford, M. D. (2004). The effectiveness of creativity training: a quantitative review. Creat. Res. J. 16, 361–388. doi: 10.1080/10400410409534549
Scriven, M., and Paul, R. (1987). Defining Critical Thinking. In 8th Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking and Education Reform ; August 2–5, 1987.
Siburian, J., Corebima, A. D., Ibrohim,, and Saptasari, M. (2019). The correlation between critical and creative thinking skills on cognitive learning results. Eurasian J. Educ. Res. 19, 99–114. doi: 10.14689/EJER.2019.81.6
Sternberg, R. J., and Halpern, D. F. (eds.) (2020). Critical Thinking in Psychology. 2nd Edn . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Sternberg, R. J., and Lubart, T. I. (1999). “The concept of creativity: prospects and paradigms” in Handbook of Creativity. ed. Sternberg, R. J. (New York, NY: Cambridge University Press), 3–15.
Sternberg, R. J., and Sternberg, K. (2017). Measuring scientific reasoning for graduate admissions in psychology and related disciplines. J. Intell. 5, 29. doi: 10.3390/jintelligence5030029
Stevens, C., and Witkow, M. R. (2014). Training scientific thinking skills: evidence from an MCAT 2015 aligned classroom module. Teach. Psychol. 41, 115–121. doi: 10.1177/0098628314530341
Stevens, C., Witkow, M. R., and Smelt, B. (2016). Strengthening scientific reasoning skills in introductory psychology: evidence from community college and liberal arts classrooms. Scholarsh. Teach. Learn. Psychol. 2, 245–260. doi: 10.1037/stl0000070
Tang, M., Werner, C., Cao, G., Tumasjan, A., Shen, J., Shi, J., et al. (2015). Creative expression and its evaluation on work-related verbal tasks: a comparison of Chinese and German samples. J. Creat. Behav. 52, 91–103. doi: 10.1002/jocb.134
Torrance, E. P. (1966). The Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking-Norms-Technical Manual Research Edition-Verbal Tests, Forms A and B Figural Tests, Forms A and B. Princeton, NJ: Personnel Press.
Torrance, E. P. (1974). Torrance Tests of Creativity Thinking: Norms–Technical Manual. Lexington, MA: Ginn.
Torrance, E. P. (1988). “The nature of creativity as manifest in its testing” in The Nature of Creativity. ed. Sternberg, R. J. (New York: Cambridge University Press), 43–73.
Tsui, L. (1998). Fostering Critical Thinking in College Students: A Mixed-Methods Study of Influences Inside and Outside of the Classroom (Doctoral dissertation). Available from ProQuest Dissertations and Theses database. (UMI No. 9917229)
Wallach, M. A., and Kogan, N. (1965). Modes of Thinking in Young Children: A Study of the Creativity-Intelligence Distinction. New York: Holt, Rinehart & Winston.
Watson, G. B., and Glaser, E. M. (1938). The Watson-Glaser Tests of Critical Thinking. New York, NY: Institute for Propaganda Analysis.
Watson, G. B., and Glaser, E. M. (1980). WGCTA Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal Manual: Forms A and B. San Antonio: The Psychological Corporation.
Wechsler, S. M., Saiz, C., Rivas, S. F., Vendramini, C. M. M., Almeida, L. S., Mundim, M. C., et al. (2018). Creative and critical thinking: independent or overlapping components? Think. Skills Creat. 27, 114–122. doi: 10.1016/j.tsc.2017.12.003
Wong, R., and Niu, W. (2013). Cultural difference in stereotype perceptions and performances in nonverbal deductive reasoning and creativity. J. Creat. Behav. 47, 41–59. doi: 10.1002/jocb.22
Zydney, A. L., Bennett, J. S., Shahid, A., and Bauer, K. W. (2002). Faculty perspectives regarding the undergraduate research experience in science and engineering. J. Eng. Educ. 91, 291–297. doi: 10.1002/j.2168-9830.2002.tb00706.x
Keywords: creativity, critical thinking, cross-cultural differences, college, research experience
Citation: Park JH, Niu W, Cheng L and Allen H (2021) Fostering Creativity and Critical Thinking in College: A Cross-Cultural Investigation. Front. Psychol . 12:760351. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.760351
Received: 18 August 2021; Accepted: 11 October 2021; Published: 11 November 2021.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2021 Park, Niu, Cheng and Allen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Li Cheng, [email protected]
† These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Chapter 8: Thinking, Communicating & Problem-Solving
Critical thinking & problem-solving, assess your critical thinking strategies.
- Visit the Quia Critical Thinking Quiz page and click on Start Now (you don’t need to enter your name).
- Select the best answer for each question, and then click on Submit Answers. A score of 70 percent or better on this quiz is considered passing.
- Based on the content of the questions, do you feel you use good critical thinking strategies in college? In what ways could you improve as a critical thinker?

The essence of the independent mind lies not in what it thinks, but in how it thinks. —Christopher Hitchens, author and journalist
Critical Thinking
As a college student, you are tasked with engaging and expanding your thinking skills. One of the most important of these skills is critical thinking. Critical thinking is important because it relates to nearly all tasks, situations, topics, careers, environments, challenges, and opportunities. It’s a discipline-general thinking skill, not a thinking skill that’s reserved for a one subject alone or restricted to a particular content area. Of all your thinking skills, critical thinking may have the greatest value.
What Is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking is clear, reasonable, reflective thinking focused on deciding what to believe or do. It means asking probing questions like, “How do we know?” or “Is this true in every case or just in this instance?” It involves being skeptical and challenging assumptions, rather than simply memorizing facts or blindly accepting what you hear or read. Critical thinking skills will help you in any profession or any circumstance of life, from science to art to business to teaching.
Critical thinkers are curious and reflective people. They explore and probe new areas and seek knowledge, clarification, and solutions. They ask pertinent questions, evaluate statements and arguments, and distinguish between facts and opinion. They are also willing to examine their own beliefs, possessing a manner of humility that allows them to admit lack of knowledge or understanding when needed. Critical thinkers are open to changing their mind. Perhaps most of all, they actively enjoy learning and view seeking new knowledge as a lifelong pursuit.
Thinking critically will help you develop more balanced arguments, express yourself clearly, read more critically, and glean important information efficiently. With critical thinking, you become a clearer thinker and problem solver.
| What Critical Thinking Is | What Critical Thinking Is Not |
|---|---|
| Skepticism | Memorizing |
| Examining assumptions | Group thinking |
| Challenging reasoning | Blind acceptance of authority |
| Uncovering biases | Believing stereotypes |
The following video, from Lawrence Bland, presents the major concepts and benefits of critical thinking.
The Role of Logic in Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is fundamentally a process of questioning information and data. You may question the information you read in a textbook, or you may question what a politician or a professor or a classmate says. You can also question a commonly-held belief or a new idea. With critical thinking, anything and everything is subject to question and examination for the purpose of logically constructing reasoned perspectives.
The word logic comes from the Ancient Greek logike , referring to the science or art of reasoning. Using logic, a person evaluates arguments and reasoning and strives to distinguish between good and bad reasoning or between truth and falsehood. Using logic, you can evaluate ideas or claims people make, make good decisions, and form sound beliefs about the world. [1] . Logical thinkers provide reasonable and appropriate evidence to support their claims, acknowledge the strengths of the opposing side’s position, actively investigate a variety of possible outcomes or new solutions, and use measured and objective language to present their positions.
Clarify Thinking
When you use critical thinking to evaluate information, you need to clarify your thinking to yourself and likely to others. Doing this well is mainly a process of asking and answering logical, probing questions. Design your questions to fit your needs, but be sure to cover adequate ground.
- What is the purpose?
- What question are we trying to answer?
- What point of view is being expressed?
- What assumptions are we or others making?
- What are the facts and data we know, and how do we know them?
- What are the concepts we’re working with?
- What are the conclusions, and do they make sense?
- What are the implications?
Avoid Fallacies
You’ll also want to make sure you can avoid and spot logical fallacies. Fallacies are faults in thinking or illogical approaches used to persuade the other side. Statements such as, everyone else is doing it ca n be very persuasive even though they demonstrate faulty logic, in this case, the bandwagon appeal. These fallacies can undermine your authority and weaken your position. Students shouldn’t park in the faculty lot because that lot is for faculty is another example of a logical fallacy, this time circular reasoning.
Consult the two websites below to identify and avoid some of the many kinds of logical fallacies:
- Fallacies Files—Home
- Logical Fallacies Jeopardy
Applying critical thinking
The following questions may apply to formulating a logical, reasoned perspective in the scenario below or any other situation:
- What is happening? Gather the basic information and begin to think of questions.
- Why is it important? Ask yourself why it’s significant and whether or not you agree.
- What don’t I see? Is there anything important missing?
- How do I know? Ask yourself where the information came from and how it was constructed.
- Who is saying it? What’s the position of the speaker and what is influencing them?
- What else? What if? What other ideas exist and are there other possibilities?
A man has a Ph.D. in political science, and he works as a professor at a local college. His wife works at the college, too. They have three young children in the local school system, and their family is well known in the community. The man is now running for political office.
Are his credentials and experience sufficient for entering public office? Will he be effective in political office? Some voters might believe that his personal life and current job, on the surface, suggest he will do well in the position, and they will vote for him. In truth, the characteristics described don’t guarantee that the man will do a good job. The information is somewhat irrelevant.
What else might you want to know? How about whether the man had already held a political office and done a good job? In this case, we want to ask, How much information is adequate in order to make a decision based on logic instead of assumptions?
Problem-Solving with Critical Thinking
For most people, a typical day is filled with critical thinking and problem-solving challenges. In fact, critical thinking and problem-solving go hand-in-hand. They both refer to using knowledge, facts, and data to solve problems effectively, but with problem-solving, you are specifically identifying, selecting, and defending your solution.
Applying the strategies described in the action checklist below can help you utilize critical thinking skills to solve problems.
| STRATEGIES | ACTION CHECKLIST | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Define the problem | |
| 2 | Identify available solutions | |
| 3 | Select your solution |
Problem-solving can be an efficient and rewarding process, especially if you are organized and mindful of critical steps and strategies. Remember, too, to assume the attributes of a good critical thinker. If you are curious, reflective, knowledge-seeking, open to change, probing, organized, and ethical, your challenge or problem will be less of a hurdle, and you’ll be in a good position to find intelligent solutions.
Developing Yourself As a Critical Thinker and Problem-Solver
Critical thinking is a fundamental skill for college students, but it should also be a lifelong pursuit that we continually refine. Below are additional strategies to develop yourself as a critical thinker in college and in everyday life:
- Reflect and practice : Always reflect on what you’ve learned. Is it true all the time? How did you arrive at your conclusions?
- Use wasted time : It’s certainly important to make time for relaxing, but if you find you are indulging in too much of a good thing, think about using your time more constructively. Determine when you do your best thinking and try to learn something new during that part of the day.
- Redefine the way you see things : It can be very uninteresting to always think the same way. Challenge yourself to see familiar things in new ways. Put yourself in someone else’s shoes and consider a certain situation from a different angle or perspective. If you’re trying to solve a problem, list all your concerns, such as what you need in order to solve it, who can help, and what some possible barriers might be. It’s often possible to reframe a problem as an opportunity. Try to find a solution where there seems to be none.
- Analyze the influences on your thinking and in your life : Why do you think or feel the way you do? Analyze your influences. Think about who in your life influences you. Do you feel or react a certain way because of social convention or because you believe it is what is expected of you? Try to break out of any molds that may be constricting you.
- Express yourself : Critical thinking also involves being able to express yourself clearly. Most important in expressing yourself clearly is stating one point at a time. You might be inclined to argue every thought, but you might have greater impact if you focus only on your main arguments. This will help others to follow your thinking clearly. For more abstract ideas, assume that your audience may not understand. Provide examples, analogies, or metaphors where you can.
- Enhance your wellness : It’s easier to think critically when you take care of your mental and physical health. Try taking 10-minute activity breaks to reach 30 to 60 minutes of physical activity each day . Try taking a break between classes and walk to the coffee shop that’s farthest away. Scheduling physical activity into your day can help lower stress and increase mental alertness.
- Do your most difficult work when you have the most energy: Think about the time of day you are most effective and have the most energy. Plan to do your most difficult thinking during these times.
Reflect on Critical Thinking
- Think about someone whom you consider to be a critical thinker (friend, professor, historical figure, etc). What qualities does he/she have?
- Review some of the critical thinking strategies discussed on this page. Choose one strategy that makes sense to you. How can you apply this critical thinking technique to your academic work?
- Habits of mind are attitudes and beliefs that influence how you approach the world (inquiring attitude, open mind, respect for truth, etc.). What is one habit of mind you would like to actively develop over the next year? How will you develop a daily practice to cultivate this habit?
Cultivate Critical Habits of Mind
Earlier in this text we discussed, “habits of mind,” the personal commitments, values, and standards people have about the principle of good thinking. Consider your intellectual commitments, values, and standards. Do you approach problems with an open mind, a respect for truth, and an inquiring attitude? Some good habits to have when thinking critically are being receptive to having your opinions changed, having respect for others, being independent and not accepting something is true until you’ve had the time to examine the available evidence. Other important habits of mind include being fair-minded, having respect for a reason, having an inquiring mind, not making assumptions, and always, especially, questioning your own conclusions. In their quest towards developing an intellectual work ethic, critical thinkers constantly try to work these qualities into their daily lives.
problem-solving with critical thinking
Below are some examples of using critical thinking to problem-solve. Can you think of additional action steps to apply to the following situations? You may want to look back to Chapter 2 “Defining Goals” to utilize the five step problem solving strategy described there.
- Your roommate was upset and said some unkind words to you, which has put a crimp in the relationship. You try to see through the angry behaviors to determine how you might best support your roommate and help bring the relationship back to a comfortable spot.
- Your campus club has been languishing on account of lack of participation and funds. The new club president, though, is a marketing major and has identified some strategies to interest students in joining and supporting the club. Implementation is forthcoming.
- Your final art class project challenges you to conceptualize form in new ways. On the last day of class when students present their projects, you describe the techniques you used to fulfill the assignment. You explain why and how you selected that approach.
- Your math teacher sees that the class is not quite grasping a concept. She uses clever questioning to dispel anxiety and guide you to new understanding of the concept.
- You have a job interview for a position that you feel you are only partially qualified for, although you really want the job and you are excited about the prospects. You analyze how you will explain your skills and experiences in a way to show that you are a good match for the prospective employer.
- You are doing well in college, and most of your college and living expenses are covered. But there are some gaps between what you want and what you feel you can afford. You analyze your income, savings, and budget to better calculate what you will need to stay in college and maintain your desired level of spending.
- "logike." Wordnik. n.d. Web. 16 Feb 2016. ↵
- "Student Success-Thinking Critically In Class and Online." Critical Thinking Gateway . St Petersburg College, n.d. Web. 16 Feb 2016. ↵
- Critical Thinking Skills. Authored by : Linda Bruce. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Critical Thinking. Provided by : Critical and Creative Thinking Program. Located at : http://cct.wikispaces.umb.edu/Critical+Thinking . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Thinking Critically. Authored by : UBC Learning Commons. Provided by : The University of British Columbia, Vancouver Campus. Located at : http://www.oercommons.org/courses/learning-toolkit-critical-thinking/view . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Critical Thinking 101: Spectrum of Authority. Authored by : UBC Leap. Located at : https://youtu.be/9G5xooMN2_c . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of students putting post-its on wall. Authored by : Hector Alejandro. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/7b2Ax2 . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Foundations of Academic Success. Authored by : Thomas C. Priester, editor. Provided by : Open SUNY Textbooks. Located at : http://textbooks.opensuny.org/foundations-of-academic-success/ . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Image of three students. Authored by : PopTech. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/8tXtQp . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Critical Thinking.wmv. Authored by : Lawrence Bland. Located at : https://youtu.be/WiSklIGUblo . License : All Rights Reserved . License Terms : Standard YouTube License

Privacy Policy
Translate this page from English...
*Machine translated pages not guaranteed for accuracy. Click Here for our professional translations.
College and University Students

Why Critical Thinking?

"As grads look to the future, they're all thinking one thing: Hire us...In general, students in fields that require critical thinking skills, problem-solving, and face-to-face contact will fare best in this new economy, no matter where they look for jobs", said Jim Kurre, associate professor of economics at Penn State Behrend and director of the Economic Research Institute of Erie. Erie Times News, PA - May 20, 2008 "Employers report that such applied skills as critical thinking, teamwork, and effective communication are essential to the preparation for today’s workplace"... Tom Pauken East Texas Review, TX - Jun 11, 2008
Studying the following articles and pages will help you build a stronger understanding of the core concepts in critical thinking
- Becoming a Critic Of Your Thinking
- Glossary of Critical Thinking Terms
- Universal Intellectual Standards
- Valuable Intellectual Traits
- Distinguishing Between Inferences and Assumptions
- Thinking With Concepts

In addition to the basic review of the definition and concept of critical thinking , the following pages and articles are recommended reading for the college, university or pre-collegiate student.
College Info Geek
7 Ways to Improve Your Critical Thinking Skills
C.I.G. is supported in part by its readers. If you buy through our links, we may earn an affiliate commission. Read more here.

When I was in 7th grade, my U.S. history teacher gave my class the following advice:
Your teachers in high school won’t expect you to remember every little fact about U.S. history. They can fill in the details you’ve forgotten. What they will expect, though, is for you to be able to think ; to know how to make connections between ideas and evaluate information critically.
I didn’t realize it at the time, but my teacher was giving a concise summary of critical thinking. My high school teachers gave similar speeches when describing what would be expected of us in college: it’s not about the facts you know, but rather about your ability to evaluate them.
And now that I’m in college, my professors often mention that the ability to think through and solve difficult problems matters more in the “real world” than specific content.
Despite hearing so much about critical thinking all these years, I realized that I still couldn’t give a concrete definition of it, and I certainly couldn’t explain how to do it. It seemed like something that my teachers just expected us to pick up in the course of our studies. While I venture that a lot of us did learn it, I prefer to approach learning deliberately, and so I decided to investigate critical thinking for myself.
What is it, how do we do it, why is it important, and how can we get better at it? This post is my attempt to answer those questions.
In addition to answering these questions, I’ll also offer seven ways that you can start thinking more critically today, both in and outside of class.
What Is Critical Thinking?
“Critical thinking is the intellectually disciplined process of actively and skillfully conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and/or evaluating information gathered from, or generated by, observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, or communication, as a guide to belief and action.” – The Foundation for Critical Thinking
The above definition from the Foundation for Critical Thinking website is pretty wordy, but critical thinking, in essence, is not that complex.
Critical thinking is just deliberately and systematically processing information so that you can make better decisions and generally understand things better. The above definition includes so many words because critical thinking requires you to apply diverse intellectual tools to diverse information.
Ways to critically think about information include:
- Conceptualizing
- Synthesizing
That information can come from sources such as:
- Observation
- Communication
And all this is meant to guide:
You can also define it this way:
Critical thinking is the opposite of regular, everyday thinking.
Moment to moment, most thinking happens automatically. When you think critically, you deliberately employ any of the above intellectual tools to reach more accurate conclusions than your brain automatically would (more on this in a bit).
This is what critical thinking is. But so what?
Why Does Critical Thinking Matter?

Most of our everyday thinking is uncritical.
If you think about it, this makes sense. If we had to think deliberately about every single action (such as breathing, for instance), we wouldn’t have any cognitive energy left for the important stuff like D&D. It’s good that much of our thinking is automatic.
We can run into problems, though, when we let our automatic mental processes govern important decisions. Without critical thinking, it’s easy for people to manipulate us and for all sorts of catastrophes to result. Anywhere that some form of fundamentalism led to tragedy (the Holocaust is a textbook example), critical thinking was sorely lacking.
Even day to day, it’s easy to get caught in pointless arguments or say stupid things just because you failed to stop and think deliberately.
But you’re reading College Info Geek, so I’m sure you’re interested to know why critical thinking matters in college.
Here’s why:
According to Andrew Roberts, author of The Thinking Student’s Guide to College , c ritical thinking matters in college because students often adopt the wrong attitude to thinking about difficult questions. These attitudes include:
Ignorant Certainty
Ignorant certainty is the belief that there are definite, correct answers to all questions–all you have to do is find the right source (102). It’s understandable that a lot of students come into college thinking this way–it’s enough to get you through most of your high school coursework.
In college and in life, however, the answers to most meaningful questions are rarely straightforward. To get anywhere in college classes (especially upper-level ones), you have to think critically about the material.
Naive Relativism
Naive relativism is the belief that there is no truth and all arguments are equal (102-103). According to Roberts, this is often a view that students adopt once they learn the error of ignorant certainty.
While it’s certainly a more “critical” approach than ignorant certainty, naive relativism is still inadequate since it misses the whole point of critical thinking: arriving at a more complete, “less wrong” answer.
Part of thinking critically is evaluating the validity of arguments (yours and others’). Therefore, to think critically you must accept that some arguments are better (and that some are just plain awful).
Critical thinking also matters in college because:
- It allows you to form your own opinions and engage with material beyond a superficial level. This is essential to crafting a great essay and having an intelligent discussion with your professors or classmates. Regurgitating what the textbook says won’t get you far.
- It allows you to craft worthy arguments and back them up. If you plan to go on to graduate school or pursue a PhD., original, critical thought is crucial
- It helps you evaluate your own work. This leads to better grades (who doesn’t want those?) and better habits of mind.
Doing college level work without critical is a lot like walking blindfolded: you’ll get somewhere , but it’s unlikely to be the place you desire.

The value of critical thinking doesn’t stop with college, however. Once you get out into the real world, critical thinking matters even more. This is because:
- It allows you to continue to develop intellectually after you graduate. Progress shouldn’t stop after graduation –you should keep learning as much as you can. When you encounter new information, knowing how to think critically will help you evaluate and use it.
- It helps you make hard decisions. I’ve written before about how defining your values helps you make better decisions. Equally important in the decision-making process is the ability to think critically. Critical thinking allows you compare the pros and cons of your available options, showing that you have more options than you might imagine .
- People can and will manipulate you . At least, they will if you take everything at face value and allow others to think for you. Just look at ads for the latest fad diet or “miracle” drug–these rely on ignorance and false hope to get people to buy something that is at best useless and at worst harmful. When you evaluate information critically (especially information meant to sell something), you can avoid falling prey to unethical companies and people.
- It makes you more employable (and better paid). The best employees not only know how to solve existing problems–they also know how to come up with solutions to problems no one ever imagined. To get a great job after graduating , you need to be one of those employees, and critical thinking is the key ingredient to solving difficult, novel problems.
Take my free productivity masterclass
With a proper productivity system, nothing ever slips through the cracks. In just one hour, you'll learn how to set up your to-do list, calendar, note-taking system, file management, and more — the smart way.
7 Ways to Think More Critically

Now we come to the part that I’m sure you’ve all been waiting for: how the heck do we get better at critical thinking? Below, you’ll find seven ways to get started.
1. Ask Basic Questions
“The world is complicated. But does every problem require a complicated solution?” – Stephen J. Dubner
Sometimes an explanation becomes so complex that the original question get lost. To avoid this, continually go back to the basic questions you asked when you set out to solve the problem.
Here are a few key basic question you can ask when approaching any problem:
- What do you already know?
- How do you know that?
- What are you trying to prove, disprove, demonstrated, critique, etc.?
- What are you overlooking?
Some of the most breathtaking solutions to problems are astounding not because of their complexity, but because of their elegant simplicity. Seek the simple solution first.
2. Question Basic Assumptions
“When you assume, you make an ass out of you and me.”
The above saying holds true when you’re thinking through a problem. it’s quite easy to make an ass of yourself simply by failing to question your basic assumptions.
Some of the greatest innovators in human history were those who simply looked up for a moment and wondered if one of everyone’s general assumptions was wrong. From Newton to Einstein to Yitang Zhang , questioning assumptions is where innovation happens.
You don’t even have to be an aspiring Einstein to benefit from questioning your assumptions. That trip you’ve wanted to take? That hobby you’ve wanted to try? That internship you’ve wanted to get? That attractive person in your World Civilizations class you’ve wanted to talk to?
All these things can be a reality if you just question your assumptions and critically evaluate your beliefs about what’s prudent, appropriate, or possible.
If you’re looking for some help with this process, then check out Oblique Strategies . It’s a tool that musician Brian Eno and artist Peter Schmidt created to aid creative problem solving . Some of the “cards” are specific to music, but most work for any time you’re stuck on a problem.
3. Be Aware of Your Mental Processes
Human thought is amazing, but the speed and automation with which it happens can be a disadvantage when we’re trying to think critically. Our brains naturally use heuristics (mental shortcuts) to explain what’s happening around us.
This was beneficial to humans when we were hunting large game and fighting off wild animals, but it can be disastrous when we’re trying to decide who to vote for.
A critical thinker is aware of their cognitive biases and personal prejudices and how they influence seemingly “objective” decisions and solutions.
All of us have biases in our thinking. Becoming aware of them is what makes critical thinking possible.
4. Try Reversing Things
A great way to get “unstuck” on a hard problem is to try reversing things. It may seem obvious that X causes Y, but what if Y caused X?
The “chicken and egg problem” a classic example of this. At first, it seems obvious that the chicken had to come first. The chicken lays the egg, after all. But then you quickly realize that the chicken had to come from somewhere, and since chickens come from eggs, the egg must have come first. Or did it?
Even if it turns out that the reverse isn’t true, considering it can set you on the path to finding a solution.
5. Evaluate the Existing Evidence
“If I have seen further it is by standing on the shoulders of giants.” – Isaac Newton
When you’re trying to solve a problem, it’s always helpful to look at other work that has been done in the same area. There’s no reason to start solving a problem from scratch when someone has already laid the groundwork.
It’s important, however, to evaluate this information critically, or else you can easily reach the wrong conclusion. Ask the following questions of any evidence you encounter:
- Who gathered this evidence?
- How did they gather it?
Take, for example, a study showing the health benefits of a sugary cereal. On paper, the study sounds pretty convincing. That is, until you learn that a sugary cereal company funded it.
You can’t automatically assume that this invalidates the study’s results, but you should certainly question them when a conflict of interests is so apparent.
6. Remember to Think for Yourself
Don’t get so bogged down in research and reading that you forget to think for yourself –sometimes this can be your most powerful tool.
Writing about Einstein’s paper “On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies” (the paper that contained the famous equation E=mc 2 ), C.P. Snow observed that “it was as if Einstein ‘had reached the conclusions by pure thought, unaided, without listening to the opinions of others. To a surprisingly large extent, that is precisely what he had done'”(121).
Don’t be overconfident, but recognize that thinking for yourself is essential to answering tough questions. I find this to be true when writing essays–it’s so easy to get lost in other people’s work that I forget to have my own thoughts. Don’t make this mistake.
For more on the importance of thinking for yourself, check out our article on mental laziness .
7. Understand That No One Thinks Critically 100% of the Time
“Critical thinking of any kind is never universal in any individual; everyone is subject to episodes of undisciplined or irrational thought.” – Michael Scriven and Richard Paul
You can’t think critically all the time, and that’s okay. Critical thinking is a tool that you should deploy when you need to make important decisions or solve difficult problems, but you don’t need to think critically about everything.
And even in important matters, you will experience lapses in your reasoning. What matters is that you recognize these lapses and try to avoid them in the future.
Even Isaac Newton, genius that he was, believed that alchemy was a legitimate pursuit .
As I hope you now see, learning to think critically will benefit you both in the classroom and beyond. I hope this post has given you some ideas about how you can think more critically in your own life. Remember: learning to think critically is a lifelong journey, and there’s always more to learn.
For a look at critical thinking principles in action, check out our guide to strategic thinking .
- http://www.criticalthinking.org/pages/defining-critical-thinking/766
- http://calnewport.com/blog/2015/11/25/the-feynman-notebook-method/
- The Thinking Student’s Guide to College by Andrew Roberts (the source of several of the seven ways to think more critically)
- What the Best College Teachers Do by Ken Bain (the source of several of the seven ways to think more critically)
- A Short History of Nearly Everything by Bill Bryson (the source for the C.P. Snow quote about Einstein and the information about Isaac Newton).
Image Credits: skyline , waterfall , vaulted ceiling , snowy road , thinker
We use cookies on our website to support technical features that enhance your user experience, and to help us improve our website. By continuing to use this website, you accept our privacy policy .
- Student Login
- Call Us: 888-549-6755
- 888-559-6763
- Search site Search our site Search Now Close
- Request Info
Skip to Content (Press Enter)
6 Critical Thinking Skills You Need to Master Now
By Will Erstad on 01/22/2018

No matter what walk of life you come from, what industry you’re interested in pursuing or how much experience you’ve already garnered, we’ve all seen firsthand the importance of critical thinking skills. In fact, lacking such skills can truly make or break a person’s career, as the consequences of one’s inability to process and analyze information effectively can be massive.
“The ability to think critically is more important now than it has ever been,” urges Kris Potrafka , founder and CEO of Music Firsthand. “Everything is at risk if we don’t all learn to think more critically.” If people cannot think critically, he explains, they not only lessen their prospects of climbing the ladder in their respective industries, but they also become easily susceptible to things like fraud and manipulation.
With that in mind, you’re likely wondering what you can do to make sure you’re not one of those people. Developing your critical thinking skills is something that takes concentrated work. It can be best to begin by exploring the definition of critical thinking and the skills it includes—once you do, you can then venture toward the crucial question at hand: How can I improve?
This is no easy task, which is why we aimed to help break down the basic elements of critical thinking and offer suggestions on how you can hone your skills and become a better critical thinker.
What is critical thinking?
Even if you want to be a better critical thinker, it’s hard to improve upon something you can’t define. Critical thinking is the analysis of an issue or situation and the facts, data or evidence related to it. Ideally, critical thinking is to be done objectively—meaning without influence from personal feelings, opinions or biases—and it focuses solely on factual information.
Critical thinking is a skill that allows you to make logical and informed decisions to the best of your ability. For example, a child who has not yet developed such skills might believe the Tooth Fairy left money under their pillow based on stories their parents told them. A critical thinker, however, can quickly conclude that the existence of such a thing is probably unlikely—even if there are a few bucks under their pillow.
6 Crucial critical thinking skills (and how you can improve them)
While there’s no universal standard for what skills are included in the critical thinking process, we’ve boiled it down to the following six. Focusing on these can put you on the path to becoming an exceptional critical thinker.
1. Identification
The first step in the critical thinking process is to identify the situation or problem as well as the factors that may influence it. Once you have a clear picture of the situation and the people, groups or factors that may be influenced, you can then begin to dive deeper into an issue and its potential solutions.
How to improve: When facing any new situation, question or scenario, stop to take a mental inventory of the state of affairs and ask the following questions:
- Who is doing what?
- What seems to be the reason for this happening?
- What are the end results, and how could they change?
2. Research
When comparing arguments about an issue, independent research ability is key. Arguments are meant to be persuasive—that means the facts and figures presented in their favor might be lacking in context or come from questionable sources. The best way to combat this is independent verification; find the source of the information and evaluate.
How to improve: It can be helpful to develop an eye for unsourced claims. Does the person posing the argument offer where they got this information from? If you ask or try to find it yourself and there’s no clear answer, that should be considered a red flag. It’s also important to know that not all sources are equally valid—take the time to learn the difference between popular and scholarly articles .
3. Identifying biases
This skill can be exceedingly difficult, as even the smartest among us can fail to recognize biases. Strong critical thinkers do their best to evaluate information objectively. Think of yourself as a judge in that you want to evaluate the claims of both sides of an argument, but you’ll also need to keep in mind the biases each side may possess.
It is equally important—and arguably more difficult—to learn how to set aside your own personal biases that may cloud your judgment. “Have the courage to debate and argue with your own thoughts and assumptions,” Potrafka encourages. “This is essential for learning to see things from different viewpoints.”
How to improve: “Challenge yourself to identify the evidence that forms your beliefs, and assess whether or not your sources are credible,” offers Ruth Wilson, director of development at Brightmont Academy .
First and foremost, you must be aware that bias exists. When evaluating information or an argument, ask yourself the following:
- Who does this benefit?
- Does the source of this information appear to have an agenda?
- Is the source overlooking, ignoring or leaving out information that doesn’t support its beliefs or claims?
- Is this source using unnecessary language to sway an audience’s perception of a fact?
4. Inference
The ability to infer and draw conclusions based on the information presented to you is another important skill for mastering critical thinking. Information doesn’t always come with a summary that spells out what it means. You’ll often need to assess the information given and draw conclusions based upon raw data.
The ability to infer allows you to extrapolate and discover potential outcomes when assessing a scenario. It is also important to note that not all inferences will be correct. For example, if you read that someone weighs 260 pounds, you might infer they are overweight or unhealthy. Other data points like height and body composition, however, may alter that conclusion.
How to improve: An inference is an educated guess, and your ability to infer correctly can be polished by making a conscious effort to gather as much information as possible before jumping to conclusions. When faced with a new scenario or situation to evaluate, first try skimming for clues—things like headlines, images and prominently featured statistics—and then make a point to ask yourself what you think is going on.
5. Determining relevance
One of the most challenging parts of thinking critically during a challenging scenario is figuring out what information is the most important for your consideration. In many scenarios, you’ll be presented with information that may seem important, but it may pan out to be only a minor data point to consider.
How to improve: The best way to get better at determining relevance is by establishing a clear direction in what you’re trying to figure out. Are you tasked with finding a solution? Should you be identifying a trend? If you figure out your end goal, you can use this to inform your judgment of what is relevant.
Even with a clear objective, however, it can still be difficult to determine what information is truly relevant. One strategy for combating this is to make a physical list of data points ranked in order of relevance. When you parse it out this way, you’ll likely end up with a list that includes a couple of obviously relevant pieces of information at the top of your list, in addition to some points at the bottom that you can likely disregard. From there, you can narrow your focus on the less clear-cut topics that reside in the middle of your list for further evaluation.
6. Curiosity
It’s incredibly easy to sit back and take everything presented to you at face value, but that can also be also a recipe for disaster when faced with a scenario that requires critical thinking. It’s true that we’re all naturally curious—just ask any parent who has faced an onslaught of “Why?” questions from their child. As we get older, it can be easier to get in the habit of keeping that impulse to ask questions at bay. But that’s not a winning approach for critical thinking.
How to improve: While it might seem like a curious mind is just something you’re born with, you can still train yourself to foster that curiosity productively. All it takes is a conscious effort to ask open-ended questions about the things you see in your everyday life, and you can then invest the time to follow up on these questions.
“Being able to ask open-ended questions is an important skill to develop—and bonus points for being able to probe,” Potrafka says.
Become a better critical thinker
Thinking critically is vital for anyone looking to have a successful college career and a fruitful professional life upon graduation. Your ability to objectively analyze and evaluate complex subjects and situations will always be useful. Unlock your potential by practicing and refining the six critical thinking skills above.
Most professionals credit their time in college as having been crucial in the development of their critical thinking abilities. If you’re looking to improve your skills in a way that can impact your life and career moving forward, higher education is a fantastic venue through which to achieve that. For some of the surefire signs you’re ready to take the next step in your education, visit our article, “ 6 Signs You’re Ready to Be a College Student .”
RELATED ARTICLES:
- How To Build Your Management Skills
- 6 Common Concerns of Adult Learners (And Why They Shouldn’t Worry)
- I Hate My Job … What Should I Do?
EDITOR’S NOTE: This article was originally published in December 2012. It has since been updated.
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Pinterest
- Share on LinkedIn
Request More Information
Talk with an admissions advisor today.
Fill out the form to receive information about:
- Program Details and Applying for Classes
- Financial Aid (for those who qualify)
- Customized Support Services
- Detailed Program Plans
There are some errors in the form. Please correct the errors and submit again.
Please enter your first name.
Please enter your last name.
There is an error in email. Make sure your answer has:
- An "@" symbol
- A suffix such as ".com", ".edu", etc.
There is an error in phone number. Make sure your answer has:
- 10 digits with no dashes or spaces
- No country code (e.g. "1" for USA)
There is an error in ZIP code. Make sure your answer has only 5 digits.
We offer tuition savings for many employers—see if yours is one of them.
Please enter Corporate Employer.
Can’t find your employer? Select "Other Employer Not In List" or "Not Employed".
Please choose a School of study.
Please choose a program.
Please choose a degree.
The program you have selected is not available in your ZIP code. Please select another program or contact an Admissions Advisor (877.530.9600) for help.
The program you have selected requires a nursing license. Please select another program or contact an Admissions Advisor (877.530.9600) for help.
Rasmussen University is not enrolling students in your state at this time.
By selecting "Submit," I authorize Rasmussen University to contact me by email, phone or text message at the number provided. There is no obligation to enroll. This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
About the author
Will Erstad
Will is a Sr. Content Specialist at Collegis Education. He researches and writes student-focused articles on a variety of topics for Rasmussen University. He is passionate about learning and enjoys writing engaging content to help current and future students on their path to a rewarding education.

Posted in Career Search
- college student tips
- career advice
Related Content

Jordan Jantz | 11.14.2022

Kalie Debelak | 10.17.2022

Patrick Flavin | 10.10.2022

Jordan Jantz | 09.05.2022
This piece of ad content was created by Rasmussen University to support its educational programs. Rasmussen University may not prepare students for all positions featured within this content. Please visit www.rasmussen.edu/degrees for a list of programs offered. External links provided on rasmussen.edu are for reference only. Rasmussen University does not guarantee, approve, control, or specifically endorse the information or products available on websites linked to, and is not endorsed by website owners, authors and/or organizations referenced. Rasmussen University is accredited by the Higher Learning Commission, an institutional accreditation agency recognized by the U.S. Department of Education.

Teaching critical thinking in digital spaces
Vol. 55 No. 6 Print version: page 10
- Misinformation and Disinformation
- Social Media and Internet

- There’s a movement afoot to equip K–12 students with the skills they need to identify misinformation on social media.
- Psychologists are a key part of the effort to help youth build digital literacy skills and create science-backed digital literacy tools for educators.
- Efforts to improve digital literacy among youth will help protect the next generation from the spread of false information online and guide youth on how to use social media safely.
At least 21 state legislatures have taken steps to reform K–12 media and information literacy education, with California, Delaware, Illinois, and New Jersey passing comprehensive reforms ( U.S. Media Literacy Policy Report, Media Literacy Now , 2024 ). The largely bipartisan efforts are a response to challenges that most school curriculums do not yet address or teach—skills like sorting out what is true or false online, identifying when content is produced by artificial intelligence (AI), and how to use social media safely.
“We’ve all seen how the spread of online misinformation and disinformation is growing and that it has real-world consequences,” said Assemblymember Marc Berman, JD, an attorney who represents California’s 23rd District and spearheaded the state’s digital literacy education law. “I can’t force adults to go back to school and take media literacy, but at a minimum, we can make sure that our young people are getting the skills they need for today’s world.”
People of all ages are susceptible to misinformation, but youth—who spend an average of 4 to 6 hours per day online— say they need help . In one survey of young adults in Canada, 84% were unsure they could distinguish fact from fiction on social media ( Youth Science Survey , Canada Foundation for Innovation, 2021 ). In a study led by educational psychologist Sam Wineburg, PhD, 82% of middle school students could not tell the difference between an online news story and an advertisement ( Evaluating Information: The Cornerstone of Civic Online Reasoning , Stanford Digital Repository, 2016 ).
“It’s those kinds of findings that have gotten the attention of legislators,” said Wineburg, who is an emeritus professor at Stanford University and cofounder of the Digital Inquiry Group (DIG), a nonprofit that creates free research-backed digital literacy tools for educators.
“Increasingly, as young people’s apps of choice are TikTok and YouTube, the adults have woken up to the fact that quality information is to civic understanding what clean air and water are to civic health,” Wineburg said.
The most comprehensive programs, which are now being developed and tested for K–12 audiences, also aim to teach students how to locate and assess the source of online information and to think critically about how generative AI produces content. They also teach students about digital citizenship, which involves engaging respectfully with others online.
Psychologists are a key part of those efforts. In its 2023 Health Advisory on Social Media Use in Adolescence , APA recommended psychologically informed media literacy training for youth, guidance echoed by U.S. Surgeon General Vivek H. Murthy. What is needed now is ongoing research on what works, as well as strong collaboration with journalists, educators, and policymakers to swiftly put research insights into practice.
This year, APA also released an updated scientific roundup focused on the risks of social media content, features, and functions . The report also provides concrete recommendations for minimizing psychological harm, including tips for monitoring use.
“To me, this is really one of the most important things we can be doing right now as psychologists, given how misinformation has made science political in ways that are really frightening,” said Susan Nolan, PhD, a professor of psychology at Seton Hall University in New Jersey who studies and advocates for scientific literacy.
Media literacy reform
While social media platforms typically require users to be 13 or older, most adolescents create accounts before then, at a time when their brains are particularly vulnerable to social influence ( The Common Sense Census: Plugged-In Parents of Tweens and Teens, Common Sense Media , 2016 ). In addition to the interpersonal risks of getting online, surveys show that adolescents are more likely to believe conspiracy theories than adults—particularly those adolescents who spend a lot of time on social media (“ Belief in Conspiracy Theories Higher Among Teenagers Than Adults, as Majority of Americans Support Social Media Reform, New Polling Finds ,” Center for Countering Digital Hate, Aug. 16, 2023).
“Media literacy is literacy in the 21st century, and we don’t start teaching literacy in high school,” said Erin McNeill, founder and CEO of Media Literacy Now , an organization dedicated to K–12 media literacy reform. “It’s an essential life skill that has to be built on a foundation, not rolled out at the last minute.”
Psychological research has played an important role in demonstrating the need for starting media literacy training early and in passing corresponding educational reforms at the state level. In a 2021 study by Wineburg and his colleagues, 3,446 census-matched high school students were tasked with investigating a website, CO2 Science , and evaluating whether it provided reliable information about human-induced climate change. Only 4% of students discovered that the site’s chief sponsor was ExxonMobil ( Educational Researcher, Vol. 50, No. 8, 2021 ).
More than half of the students in the study also believed that a Facebook video that appeared to show ballot stuffing, shot in Russia and posted anonymously, was “strong evidence” of U.S. voter fraud.
“We leaned on these studies when justifying the legislation because they show how the internet and social media make it a lot easier to select only the information that supports our preexisting beliefs, rather than providing a more balanced view,” said Berman, who also pointed to APA’s 2023 Health Advisory on Social Media Use in Adolescence to support the need for policy reform.
Drawing on psychological research, APA’s latest guidance recommends a series of digital literacy competencies that can provide a starting point for policymakers. Those include understanding the tactics used to spread mis- and disinformation, limiting overgeneralizations that lead people to incorrectly interpret others’ beliefs, and helping young people learn to nourish healthy online relationships.
“Developmentally, adolescents are especially vulnerable to the features of social media that are designed to keep users online, such as likes, push notifications, autoplay, and algorithms that deliver extreme content,” said Sophia Choukas-Bradley, PhD, an associate professor of psychology at the University of Pittsburgh who contributed to both APA reports. “As psychologists, we need to provide teens with digital literacy and skills to combat these design features while simultaneously pushing for policies that require tech companies to change the platforms themselves.”
With legislation now in place, New Jersey’s Department of Education is crafting its detailed information literacy standards, drawing on APA’s Resolution on Combating Misinformation and Promoting Psychological Science Literacy (PDF, 53KB) in the process. The curriculum will include training on such topics as the scientific method, the difference between primary and secondary sources, how to differentiate fact from opinion, and the ethical production of information (including data ethics).
“When you look at what is in the curriculum, really all of it ultimately ties to psychology,” Nolan said about the New Jersey law.
Progress at the state level is meaningful, but mandates do not necessarily equal action. It can take years for state educational boards to develop and implement curriculum reforms, especially if research has not clearly shown what works.
“It’s one thing to pass a law, but it’s quite another to develop and fund evidence-based professional development programs for teachers, many of whom do not feel up to this task” without further training, Wineburg said.

Equipping and empowering youth
Policymakers, educators, librarians, and even journalists are putting their heads together to decide what and how to teach media literacy to kids and teens. But those on the front lines also stress the importance of sound science that can guide the development of interventions from the get-go.
“What happens often in K–12 education is we get separated from the research,” said Kathryn Procope, EdD, executive director at Howard University Middle School of Mathmatics and Science in Washington, D.C. “Getting connected with what the research says can help educators sit down collectively and decide what we’re going to do” when new challenges arise.
DIG offers one solution: its Civic Online Reasoning program, a free curriculum that teaches lateral reading—a fact-checking method where readers evaluate source credibility, such as by searching for background in a separate browser tab. The program also teaches skills such as click restraint, the strategy of looking past the first results suggested by search engines to results from more credible sources.
“Behind lateral reading is the idea that we need to think about online information in a fundamentally different way,” Wineburg said. “Rather than immediately looking at the claim, we want people asking: Who is the person or the organization behind this claim?”
Studies of lateral reading interventions show that they can change the way young people interact with information online. Students who completed six 50-minute lessons in a field study across six Lincoln, Nebraska, high schools were significantly more accurate in assessing source credibility than their peers who did not get the intervention ( Journal of Educational Psychology , Vol. 114, No. 5, 2022 ). In Canada, 2,278 middle and high school students completed the CRTL-F lateral reading program. Beforehand, only 6% could identify the agenda of an advocacy group, but that number rose to 31% after the intervention and to 49% 6 weeks later ( Brodsky, J. E., et al., AERA Open , Vol. 9, 2023; The Digital Media Literacy Gap , CIVIX Canada, 2021 ).
Research conducted in Germany and Italy also found that lateral reading helped news consumers identify false information online, and that pop-up reminders and monetary incentives can increase the practice of lateral reading and click restraint ( Fendt, M., et al., Computers in Human Behavior , Vol. 146, 2023 ; Panizza, F., et al., Scientific Reports , Vol. 12, 2022 ).
Choukas-Bradley is working with the Center for Digital Thriving at Harvard Graduate School of Education and Common Sense Media to develop and evaluate resources that educate adolescents about the social media features designed to keep them online, as well as to teach cognitive and behavioral techniques that promote healthier social media use.
“We listen closely to students and then trace the connections to key evidence-based practices,” said Emily Weinstein, EdD, cofounder of the Center for Digital Thriving, which offers resources codesigned by educators, students, and clinical psychologists.
For example, teens share common thinking traps that are amplified by tech, such as “everyone on social media is happier than me,” or “my friend must be mad if they haven’t responded to my Snap.” Both are examples of cognitive distortions, for which psychologists have a robust evidence base.
“There’s real power in the idea that ‘if you can name it, you can tame it,’ which is one reason we want every student to know about common thinking traps,” Weinstein said.
Educators and researchers are aware of the irony behind adults teaching digital natives how to use platforms with which they are already intimately familiar. For that reason, some are working with kids and teens to teach digital literacy in ways that are meaningful to them.
“Students are far ahead of educators when it comes to using new technologies, so the more that young people are involved in the design of the curriculum that will be used to teach media literacy in 2024 and beyond, the better,” said Chelsea Waite, a principal investigator at the Center on Reinventing Public Education at Arizona State University’s Mary Lou Fulton Teachers College who studies innovative practices at K–12 schools across the United States.
DIG has partnered with Microsoft to integrate information literacy quests that focus on exploring bias and persuasion—for example, when information is trustworthy enough to be shared with others—into the video game Minecraft. Mizuko Ito, PhD, a cultural anthropologist who has studied youth-centered learning for years and directs the Connected Learning Lab at the University of California, Irvine, coleads the Connected Learning Alliance , which fosters partnerships between researchers, developers, and youth to generate new technologies that prioritize connection and well-being rather than profit. One of the organization’s latest projects, Connected Camps , pairs 8- to 13-year-old gamers with college gamers to learn about digital citizenship and to become part of a prosocial online community.
“We know that it’s so much more effective to do online literacy learning and skills development within the context of something youth actually care about, like the gaming universe,” Ito said.
Other youth media organizations are leveraging content young people care about to equip and empower them to create positive online spaces. The This Teenage Life podcast, for example, is a school-based program that teaches kids to produce a podcast while thinking critically about how to engage with today’s digital ecosystem and be a good citizen online.
“As educators, we have to remember that young people nowadays are going to ask: Why am I learning this? It doesn’t have anything to do with what I care about,” Procope said. “That means that we have to do what we’re doing a lot differently.”
[ Related: New approaches to AI in the K-12 classroom ]
From the ground up
The online world has wrought so much change that many experts say education must fundamentally change, too.
“Right now, the approach is to treat information literacy as a patch to put on the whole of the curriculum,” Wineburg said. “But really the challenge, when students are leading digital lives, is to fundamentally rethink the entire curriculum we have.”
That’s a tall order, but a starting point is to interweave digital and media literacy lessons throughout multiple courses rather than treat the subject as a separate entity. For example, a high school biology lesson about vaccines will be more meaningful to students if it acknowledges and addresses the pseudoscientific information they see daily on TikTok, such as the supposed health benefits of castor oil, Wineburg said. Another idea: Students can learn about the strengths and weaknesses of ChatGPT in a history class by asking questions about a historical event where the facts are unclear, such as who fired the first shot in the Battle of Lexington, the first volley in the Revolutionary War.
“Whether it’s debunking pseudoscience on social media or understanding the nuances of AI in history class, every subject offers an opportunity to cultivate these skills,” said Nicole Barnes, PhD, senior director of APA’s Center for Psychology in Schools and Education (CPSE). “After all, we’re not just preparing students for exams but for life in a digital world. This is exactly what we are doing in the CPSE—providing pre-K–12 educators with teaching and learning resources that are grounded in psychological science.”
Several states are aiming for such integration by giving librarians a central role in administering media literacy training throughout schools. The International Society for Technology in Education (ISTE) also recommends a comprehensive approach to K–12 training on technology and online media.
“The people leading these efforts—from national organizations to state legislators—are starting to see this as something that needs to be integrated throughout the entire curriculum,” McNeill said.
The top priority now is to provide states, districts, and schools with packaged materials that have been vetted by peer-reviewed research, Wineburg said. Educators should be wary of for-profit tools that have not been proven effective based on field studies in real classrooms. Still, McNeill said the current wave of digital literacy legislation is progress to be proud of.
“While we still have a lot to learn, we also know that there are risks for youth online,” McNeill said. “We have enough evidence now that there’s plenty of reason to take action.”
Get the facts
A new book for teens on spotting false information.

Further reading
What fact-checkers know about media literacy—and students should, too Terada, Y., Edutopia , May 26, 2022
Teaching lateral reading: Interventions to help people read like fact checkers McGrew, S., Current Opinion in Psychology , 2024
Building media literacy into school curriculums worldwide Leedom, M., News Decoder , Feb. 29, 2024
Teaching digital well-being: Evidence-based resources to help youth thrive Weinstein, E., et al., Center for Digital Thriving, 2023
Fighting fake news in the classroom Pappas, S., Monitor on Psychology , January/February 2022
How to use ChatGPT as a learning tool Abramson, A., Monitor on Psychology , June 2023
Recommended Reading
Six things psychologists are talking about.
The APA Monitor on Psychology ® sister e-newsletter offers fresh articles on psychology trends, new research, and more.
Welcome! Thank you for subscribing.
Speaking of Psychology
Subscribe to APA’s audio podcast series highlighting some of the most important and relevant psychological research being conducted today.
Subscribe to Speaking of Psychology and download via:

Contact APA
Related and recent.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Which is unfortunate, he says, since developing critical-thinking skills is vital not only to students' readiness for college and career, but to their civic readiness, as well. "It's important to recognize that critical thinking is not just something that takes place in the classroom or in the workplace, it's something that takes place — and ...
According to the University of the People in California, having critical thinking skills is important because they are [1]: Universal. Crucial for the economy. Essential for improving language and presentation skills. Very helpful in promoting creativity. Important for self-reflection.
Every time students use evidence to form judgements, analyze the ideas or conditions that support conclusions, and evaluate their own thinking, they engage their critical thinking skills. Creative thinking is just as important and involves the generation of new ideas within or across disciplines.
As a college student, you are tasked with engaging and expanding your thinking skills. One of the most important of these skills is critical thinking. Critical thinking is important because it relates to nearly all tasks, situations, topics, careers, environments, challenges, and opportunities. It's a "domain-general" thinking skill—not ...
The CAAP Critical Thinking measures students' skills in analyzing elements of an argument, evaluating an argument, and extending arguments (CAAP Program Management, 2012) ... 2010) are great examples of how a common framework can be created to align expectations about college students' critical thinking skills. While one should pay attention to ...
Critical thinking is a kind of thinking in which you question, analyse, interpret , evaluate and make a judgement about what you read, hear, say, or write. The term critical comes from the Greek word kritikos meaning "able to judge or discern". Good critical thinking is about making reliable judgements based on reliable information.
Critical thinking is the art of making clear, reasoned judgements based on interpreting, understanding, applying and synthesising evidence gathered from observation, reading and experimentation. Burns, T., & Sinfield, S. (2016) Essential Study Skills: The Complete Guide to Success at University (4th ed.) London: SAGE, p94.
Critical thinking is using the skills or strategies that that are most likely to lead to a desired outcome. It is purposeful, reasoned, and goal-directed. It is the sort of thinking we should be ...
Here are six ways high school students can develop critical-thinking skills before college: Build your domain-specific skillset. Conduct experiments. Question your presumptions. Read books written ...
The Importance of Critical Thinking Skills, For Students and Ourselves. Critical thinking is a vital, yet often neglected, skill. In higher education, Chris Griffiths, author of "The Creative Thinking Handbook," noted in a TLNT blog article that critical thinking is "the ability to think clearly and independently about a subject or ...
Even without explicit attempts to foster critical thinking, there is certainly a widespread perception that college breeds critical thinkers. Tsui (1998) reported that 92% of students in a large multi-institution study believed they had made some gains in critical thinking, and 39.3% thought their critical thinking had grown much stronger. Only 8.9% believed it had not changed or had grown weaker.
This may come as a surprise as instructors tend to expect students to have the same cognitive abilities and critical thinking skills as they do. Instead, college students are just learning how to reframe knowledge. With this in mind, instructors need to meet students where they are in their cognitive development and guide them through the process.
According to one study DBL teaches students how to look at the components of a problem and come to a rational decision. Evidence shows that there is a correlation between the development of problem-solving and critical thinking skills (Plummer et al. 2022). This style encourages students to look at all sides of an issue and come to a valid ...
Students grappled with ideas and their beliefs and employed deep critical-thinking skills to develop arguments for their claims. Embedding critical-thinking skills in curriculum that students care ...
Importance of critical thinking for students 1. Decision-making 2. Problem-solving 3. Communication 4. Analytical skills How can students develop critical thinking skills 1. Never stop asking questions 2. Practice active listening 3. Dive into your creativity 4. Engage in debates and discussions 5.
Following the rubric, four graduate students independently rated the students' critical thinking task. The Cronbach's Alpha of the expert ratings was acceptable for both vignettes (0.773 and 0.712). The average of the four scores given by the experts was used as the final score for the participants. California Critical Thinking Skills Test
Critical Thinking. As a college student, you are tasked with engaging and expanding your thinking skills. One of the most important of these skills is critical thinking. Critical thinking is important because it relates to nearly all tasks, situations, topics, careers, environments, challenges, and opportunities.
Studies Reveal That Critical Thinking Is Rare in the College Classroom Research demonstrates that, contrary to popular faculty belief, critical thinking is not fostered in the typical college classroom. ... only 8% were able to provide a clear conception of the critical thinking skills they thought were most important for their students to ...
In the articles below, as well as the bundle and thinker's guide set we recommend for college and university students, we introduce you to the tools of mind you need to reason well through the problems and issues you face, whether in the classroom, in your personal life, or in your professional life. If you take these ideas seriously, you could ...
The above definition includes so many words because critical thinking requires you to apply diverse intellectual tools to diverse information. Ways to critically think about information include: Conceptualizing. Analyzing. Synthesizing. Evaluating. That information can come from sources such as:
Twenty-seven studies are reviewed that investigate the effect of instructional methods, courses, programs, and general college experiences on changes in college students'. critical thinking. Only two studies used true experimental designs; most were nonequiva-. lent pretest-posttest control group designs.
Here, we argue that student voice in critical thinking research has not received enough attention and that student perspectives can contribute to its theories of teaching and learning. The research was conducted by three undergraduate authors and examine what fellow students had to say about developing critical thinking. An empirical model ...
Critical thinking is a skill that allows you to make logical and informed decisions to the best of your ability. For example, a child who has not yet developed such skills might believe the Tooth Fairy left money under their pillow based on stories their parents told them. A critical thinker, however, can quickly conclude that the existence of ...
At least 21 state legislatures have taken steps to reform K-12 media and information literacy education, with California, Delaware, Illinois, and New Jersey passing comprehensive reforms (U.S. Media Literacy Policy Report, Media Literacy Now, 2024).The largely bipartisan efforts are a response to challenges that most school curriculums do not yet address or teach—skills like sorting out ...
Mathematics in the Modern World is a college course that aims to develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills through fundamental mathematical concepts, emphasizing their real-world ...