Are you seeking one-on-one college counseling and/or essay support? Limited spots are now available. Click here to learn more.

How to Write the AP Lit Prose Essay with Examples
March 30, 2024
AP Lit Prose Essay Examples – The College Board’s Advanced Placement Literature and Composition Course is one of the most enriching experiences that high school students can have. It exposes you to literature that most people don’t encounter until college , and it helps you develop analytical and critical thinking skills that will enhance the quality of your life, both inside and outside of school. The AP Lit Exam reflects the rigor of the course. The exam uses consistent question types, weighting, and scoring parameters each year . This means that, as you prepare for the exam, you can look at previous questions, responses, score criteria, and scorer commentary to help you practice until your essays are perfect.
What is the AP Lit Free Response testing?
In AP Literature, you read books, short stories, and poetry, and you learn how to commit the complex act of literary analysis . But what does that mean? Well, “to analyze” literally means breaking a larger idea into smaller and smaller pieces until the pieces are small enough that they can help us to understand the larger idea. When we’re performing literary analysis, we’re breaking down a piece of literature into smaller and smaller pieces until we can use those pieces to better understand the piece of literature itself.
So, for example, let’s say you’re presented with a passage from a short story to analyze. The AP Lit Exam will ask you to write an essay with an essay with a clear, defensible thesis statement that makes an argument about the story, based on some literary elements in the short story. After reading the passage, you might talk about how foreshadowing, allusion, and dialogue work together to demonstrate something essential in the text. Then, you’ll use examples of each of those three literary elements (that you pull directly from the passage) to build your argument. You’ll finish the essay with a conclusion that uses clear reasoning to tell your reader why your argument makes sense.
AP Lit Prose Essay Examples (Continued)
But what’s the point of all of this? Why do they ask you to write these essays?
Well, the essay is, once again, testing your ability to conduct literary analysis. However, the thing that you’re also doing behind that literary analysis is a complex process of both inductive and deductive reasoning. Inductive reasoning takes a series of points of evidence and draws a larger conclusion. Deductive reasoning departs from the point of a broader premise and draws a singular conclusion. In an analytical essay like this one, you’re using small pieces of evidence to draw a larger conclusion (your thesis statement) and then you’re taking your thesis statement as a larger premise from which you derive your ultimate conclusion.
So, the exam scorers are looking at your ability to craft a strong thesis statement (a singular sentence that makes an argument), use evidence and reasoning to support that argument, and then to write the essay well. This is something they call “sophistication,” but they’re looking for well-organized thoughts carried through clear, complete sentences.
This entire process is something you can and will use throughout your life. Law, engineering, medicine—whatever pursuit, you name it—utilizes these forms of reasoning to run experiments, build cases, and persuade audiences. The process of this kind of clear, analytical thinking can be honed, developed, and made easier through repetition.
Practice Makes Perfect
Because the AP Literature Exam maintains continuity across the years, you can pull old exam copies, read the passages, and write responses. A good AP Lit teacher is going to have you do this time and time again in class until you have the formula down. But, it’s also something you can do on your own, if you’re interested in further developing your skills.
AP Lit Prose Essay Examples
Let’s take a look at some examples of questions, answers and scorer responses that will help you to get a better idea of how to craft your own AP Literature exam essays.
In the exam in 2023, students were asked to read a poem by Alice Cary titled “Autumn,” which was published in 1874. In it, the speaker contemplates the start of autumn. Then, students are asked to craft a well-written essay which uses literary techniques to convey the speaker’s complex response to the changing seasons.
The following is an essay that received a perfect 6 on the exam. There are grammar and usage errors throughout the essay, which is important to note: even though the writer makes some mistakes, the structure and form of their argument was strong enough to merit a 6. This is what your scorers will be looking for when they read your essay.
Example Essay
Romantic and hyperbolic imagery is used to illustrate the speaker’s unenthusiastic opinion of the coming of autumn, which conveys Cary’s idea that change is difficult to accept but necessary for growth.
Romantic imagery is utilized to demonstrate the speaker’s warm regard for the season of summer and emphasize her regretfulness for autumn’s coming, conveying the uncomfortable change away from idyllic familiarity. Summer, is portrayed in the image of a woman who “from her golden collar slips/and strays through stubble fields/and moans aloud.” Associated with sensuality and wealth, the speaker implies the interconnection between a season and bounty, comfort, and pleasure. Yet, this romantic view is dismantled by autumn, causing Summer to “slip” and “stray through stubble fields.” Thus, the coming of real change dethrones a constructed, romantic personification of summer, conveying the speaker’s reluctance for her ideal season to be dethroned by something much less decorated and adored.
Summer, “she lies on pillows of the yellow leaves,/ And tries the old tunes for over an hour”, is contrasted with bright imagery of fallen leaves/ The juxtaposition between Summer’s character and the setting provides insight into the positivity of change—the yellow leaves—by its contrast with the failures of attempting to sustain old habits or practices, “old tunes”. “She lies on pillows” creates a sympathetic, passive image of summer in reaction to the coming of Autumn, contrasting her failures to sustain “old tunes.” According to this, it is understood that the speaker recognizes the foolishness of attempting to prevent what is to come, but her wishfulness to counter the natural progression of time.
Hyperbolic imagery displays the discrepancies between unrealistic, exaggerated perceptions of change and the reality of progress, continuing the perpetuation of Cary’s idea that change must be embraced rather than rejected. “Shorter and shorter now the twilight clips/The days, as though the sunset gates they crowd”, syntax and diction are used to literally separate different aspects of the progression of time. In an ironic parallel to the literal language, the action of twilight’s “clip” and the subject, “the days,” are cut off from each other into two different lines, emphasizing a sense of jarring and discomfort. Sunset, and Twilight are named, made into distinct entities from the day, dramatizing the shortening of night-time into fall. The dramatic, sudden implications for the change bring to mind the switch between summer and winter, rather than a transitional season like fall—emphasizing the Speaker’s perspective rather than a factual narration of the experience.
She says “the proud meadow-pink hangs down her head/Against the earth’s chilly bosom, witched with frost”. Implying pride and defeat, and the word “witched,” the speaker brings a sense of conflict, morality, and even good versus evil into the transition between seasons. Rather than a smooth, welcome change, the speaker is practically against the coming of fall. The hyperbole present in the poem serves to illustrate the Speaker’s perspective and ideas on the coming of fall, which are characterized by reluctance and hostility to change from comfort.
The topic of this poem, Fall–a season characterized by change and the deconstruction of the spring and summer landscape—is juxtaposed with the final line which evokes the season of Spring. From this, it is clear that the speaker appreciates beautiful and blossoming change. However, they resent that which destroys familiar paradigms and norms. Fall, seen as the death of summer, is characterized as a regression, though the turning of seasons is a product of the literal passage of time. Utilizing romantic imagery and hyperbole to shape the Speaker’s perspective, Cary emphasizes the need to embrace change though it is difficult, because growth is not possible without hardship or discomfort.
Scoring Criteria: Why did this essay do so well?
When it comes to scoring well, there are some rather formulaic things that the judges are searching for. You might think that it’s important to “stand out” or “be creative” in your writing. However, aside from concerns about “sophistication,” which essentially means you know how to organize thoughts into sentences and you can use language that isn’t entirely elementary, you should really focus on sticking to a form. This will show the scorers that you know how to follow that inductive/deductive reasoning process that we mentioned earlier, and it will help to present your ideas in the most clear, coherent way possible to someone who is reading and scoring hundreds of essays.
So, how did this essay succeed? And how can you do the same thing?
First: The Thesis
On the exam, you can either get one point or zero points for your thesis statement. The scorers said, “The essay responds to the prompt with a defensible thesis located in the introductory paragraph,” which you can read as the first sentence in the essay. This is important to note: you don’t need a flowery hook to seduce your reader; you can just start this brief essay with some strong, simple, declarative sentences—or go right into your thesis.
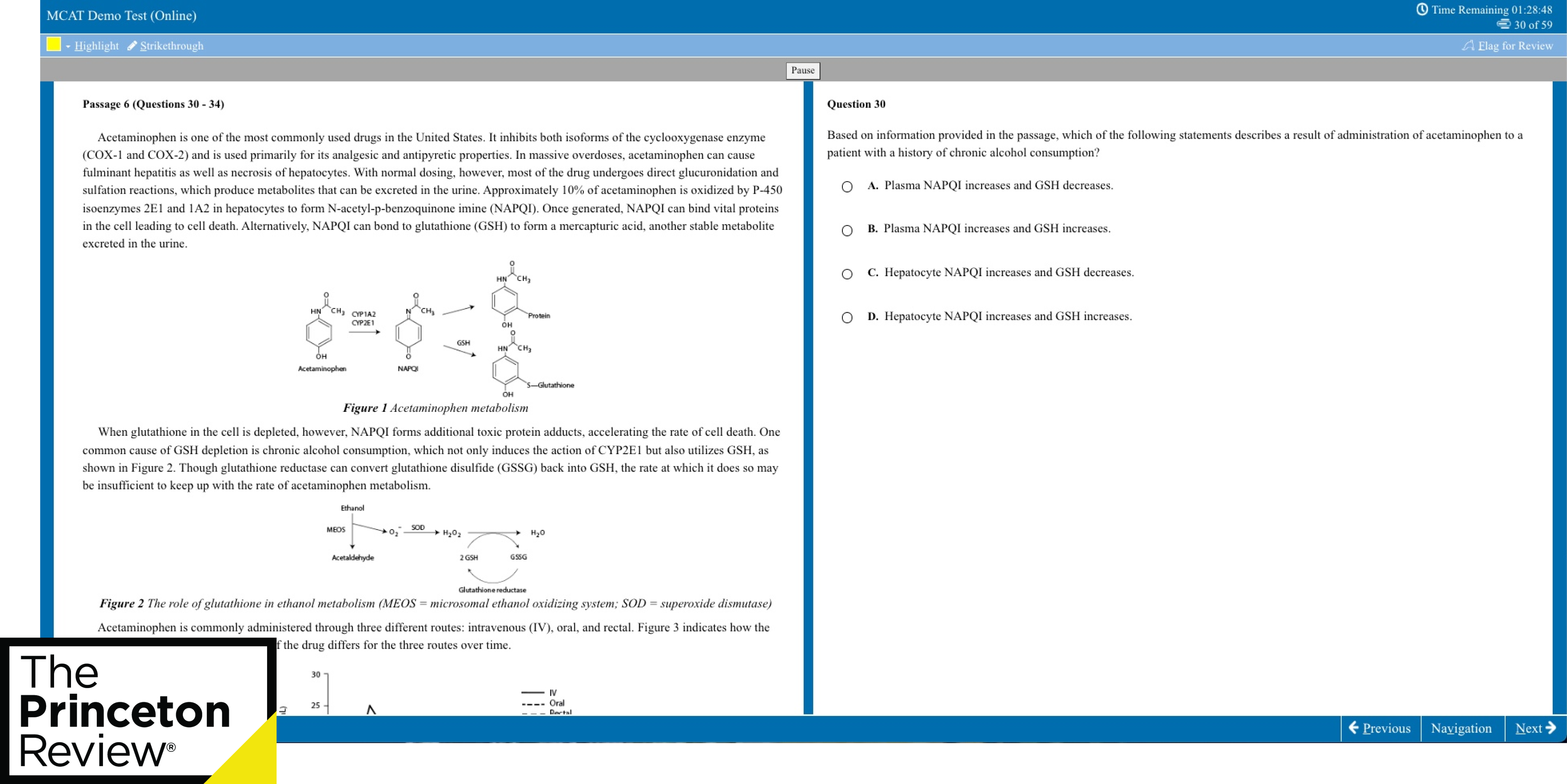
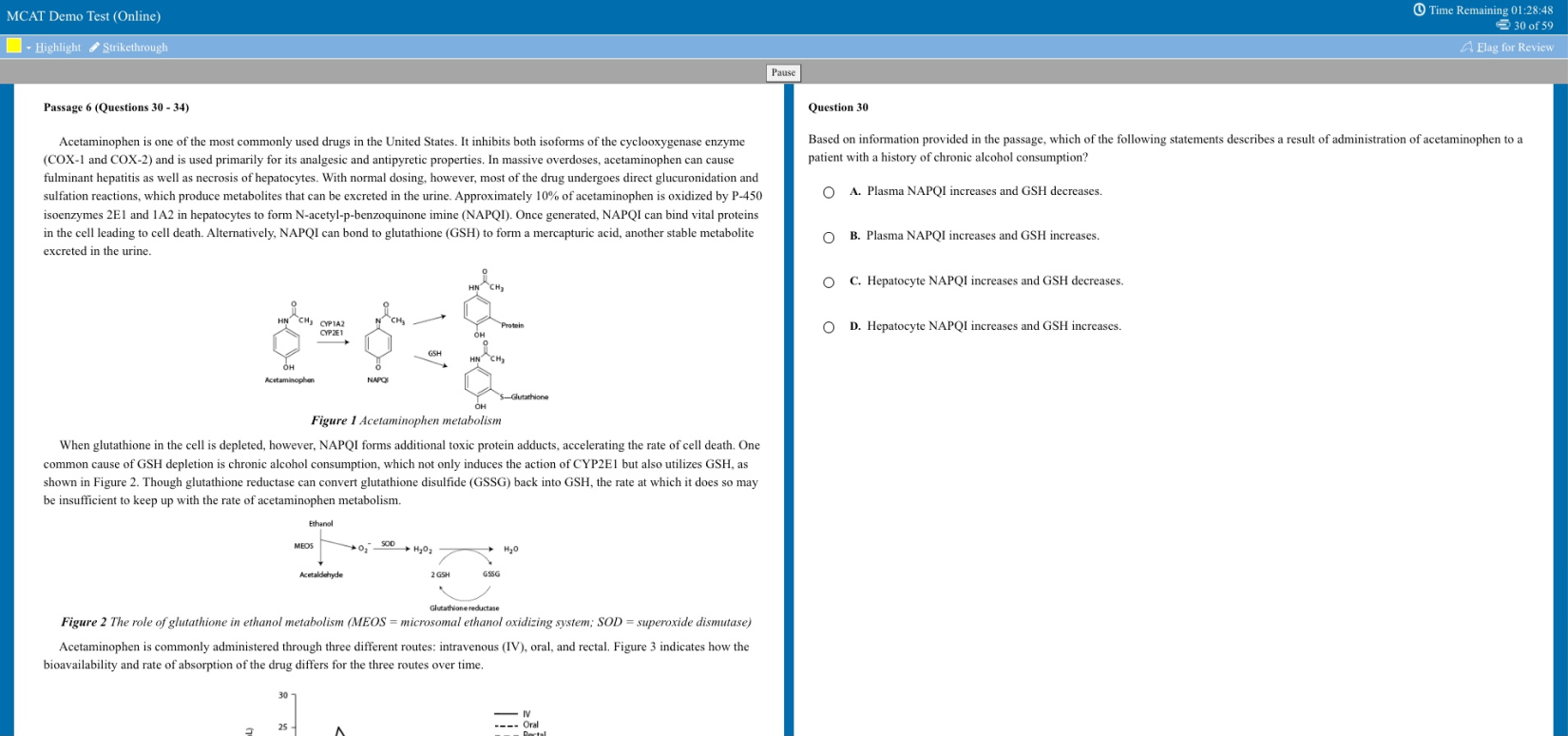
What makes a good thesis? A good thesis statement does the following things:
- Makes a claim that will be supported by evidence
- Is specific and precise in its use of language
- Argues for an original thought that goes beyond a simple restating of the facts
If you’re sitting here scratching your head wondering how you come up with a thesis statement off the top of your head, let me give you one piece of advice: don’t.
The AP Lit scoring criteria gives you only one point for the thesis for a reason: they’re just looking for the presence of a defensible claim that can be proven by evidence in the rest of the essay.
Second: Write your essay from the inside out
While the thesis is given one point, the form and content of the essay can receive anywhere from zero to four points. This is where you should place the bulk of your focus.
My best advice goes like this:
- Choose your evidence first
- Develop your commentary about the evidence
- Then draft your thesis statement based on the evidence that you find and the commentary you can create.
It will seem a little counterintuitive: like you’re writing your essay from the inside out. But this is a fundamental skill that will help you in college and beyond. Don’t come up with an argument out of thin air and then try to find evidence to support your claim. Look for the evidence that exists and then ask yourself what it all means. This will also keep you from feeling stuck or blocked at the beginning of the essay. If you prepare for the exam by reviewing the literary devices that you learned in the course and practice locating them in a text, you can quickly and efficiently read a literary passage and choose two or three literary devices that you can analyze.
Third: Use scratch paper to quickly outline your evidence and commentary
Once you’ve located two or three literary devices at work in the given passage, use scratch paper to draw up a quick outline. Give each literary device a major bullet point. Then, briefly point to the quotes/evidence you’ll use in the essay. Finally, start to think about what the literary device and evidence are doing together. Try to answer the question: what meaning does this bring to the passage?
A sample outline for one paragraph of the above essay might look like this:
Romantic imagery
Portrayal of summer
- Woman who “from her golden collar… moans aloud”
- Summer as bounty
Contrast with Autumn
- Autumn dismantles Summer
- “Stray through stubble fields”
- Autumn is change; it has the power to dethrone the romance of Summer/make summer a bit meaningless
Recognition of change in a positive light
- Summer “lies on pillows / yellow leaves / tries old tunes”
- Bright imagery/fallen leaves
- Attempt to maintain old practices fails: “old tunes”
- But! There is sympathy: “lies on pillows”
Speaker recognizes: she can’t prevent what is to come; wishes to embrace natural passage of time
By the time the writer gets to the end of the outline for their paragraph, they can easily start to draw conclusions about the paragraph based on the evidence they have pulled out. You can see how that thinking might develop over the course of the outline.
Then, the speaker would take the conclusions they’ve drawn and write a “mini claim” that will start each paragraph. The final bullet point of this outline isn’t the same as the mini claim that comes at the top of the second paragraph of the essay, however, it is the conclusion of the paragraph. You would do well to use the concluding thoughts from your outline as the mini claim to start your body paragraph. This will make your paragraphs clear, concise, and help you to construct a coherent argument.
Repeat this process for the other one or two literary devices that you’ve chosen to analyze, and then: take a step back.
Fourth: Draft your thesis
Once you quickly sketch out your outline, take a moment to “stand back” and see what you’ve drafted. You’ll be able to see that, among your two or three literary devices, you can draw some commonality. You might be able to say, as the writer did here, that romantic and hyperbolic imagery “illustrate the speaker’s unenthusiastic opinion of the coming of autumn,” ultimately illuminating the poet’s idea “that change is difficult to accept but necessary for growth.”
This is an original argument built on the evidence accumulated by the student. It directly answers the prompt by discussing literary techniques that “convey the speaker’s complex response to the changing seasons.” Remember to go back to the prompt and see what direction they want you to head with your thesis, and craft an argument that directly speaks to that prompt.
Then, move ahead to finish your body paragraphs and conclusion.
Fifth: Give each literary device its own body paragraph
In this essay, the writer examines the use of two literary devices that are supported by multiple pieces of evidence. The first is “romantic imagery” and the second is “hyperbolic imagery.” The writer dedicates one paragraph to each idea. You should do this, too.
This is why it’s important to choose just two or three literary devices. You really don’t have time to dig into more. Plus, more ideas will simply cloud the essay and confuse your reader.
Using your outline, start each body paragraph with a “mini claim” that makes an argument about what it is you’ll be saying in your paragraph. Lay out your pieces of evidence, then provide commentary for why your evidence proves your point about that literary device.
Move onto the next literary device, rinse, and repeat.
Sixth: Commentary and Conclusion
Finally, you’ll want to end this brief essay with a concluding paragraph that restates your thesis, briefly touches on your most important points from each body paragraph, and includes a development of the argument that you laid out in the essay.
In this particular example essay, the writer concludes by saying, “Utilizing romantic imagery and hyperbole to shape the Speaker’s perspective, Cary emphasizes the need to embrace change though it is difficult, because growth is not possible without hardship or discomfort.” This is a direct restatement of the thesis. At this point, you’ll have reached the end of your essay. Great work!
Seventh: Sophistication
A final note on scoring criteria: there is one point awarded to what the scoring criteria calls “sophistication.” This is evidenced by the sophistication of thought and providing a nuanced literary analysis, which we’ve already covered in the steps above.
There are some things to avoid, however:
- Sweeping generalizations, such as, “From the beginning of human history, people have always searched for love,” or “Everyone goes through periods of darkness in their lives, much like the writer of this poem.”
- Only hinting at possible interpretations instead of developing your argument
- Oversimplifying your interpretation
- Or, by contrast, using overly flowery or complex language that does not meet your level of preparation or the context of the essay.
Remember to develop your argument with nuance and complexity and to write in a style that is academic but appropriate for the task at hand.
If you want more practice or to check out other exams from the past, go to the College Board’s website .
Brittany Borghi
After earning a BA in Journalism and an MFA in Nonfiction Writing from the University of Iowa, Brittany spent five years as a full-time lecturer in the Rhetoric Department at the University of Iowa. Additionally, she’s held previous roles as a researcher, full-time daily journalist, and book editor. Brittany’s work has been featured in The Iowa Review, The Hopkins Review, and the Pittsburgh City Paper, among others, and she was also a 2021 Pushcart Prize nominee.
- 2-Year Colleges
- ADHD/LD/Autism/Executive Functioning
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Essay
- College Search/Knowledge
- College Success
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Data Visualizations
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High School Success
- High Schools
- Homeschool Resources
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Outdoor Adventure
- Private High School Spotlight
- Research Programs
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Teacher Tools
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight
“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.

Expert's Guide to the AP Literature Exam

AP English Literature: Exam Format and Question Types
The AP English Literature and Composition exam is designed to test students' understanding and analysis of literary works. It consists of two main sections: multiple-choice and free-response. Understanding the exam format and question types is crucial for success.
1. Multiple-Choice Section:
- Format: 55 questions with four or five answer choices.
- Time: 60 minutes.
- Content: Passage-based questions that assess comprehension, interpretation, and analysis of literary texts.
- Question Types: These include identifying literary devices, analyzing the author's tone, understanding the meaning of words in context, and interpreting the overall purpose and structure of a passage.
2. Free-Response Section:
- Format: Three essay prompts.
- Time: 120 minutes.
- Question Types:
a. Poetry Analysis Essay: Students analyze a poem and discuss its poetic techniques, theme, and meaning.
b. Prose Analysis Essay: Students analyze a prose passage, focusing on its style, tone, and literary devices.
c. Open-Ended Essay: Students choose a novel or play and respond to a prompt by developing a thesis and supporting it with evidence and analysis.
Key Tips for Success:
1. Read and annotate the texts carefully to understand the nuances and literary devices used.
2. Practice close reading to develop a deep understanding of the passages.
3. Review literary terms and techniques commonly used in literature.
4. Develop strong essay writing skills by structuring your responses with clear introductions, well-supported arguments, and insightful analysis.
5. Manage your time effectively during the exam to allocate enough time for each question.
6. Practice with past exams and sample questions to become familiar with the exam format and timing.
By understanding the exam format and question types, and employing effective strategies, students can confidently approach the AP English Literature exam and demonstrate their analytical skills and understanding of literary works.
How Is the AP Literature Test Graded?
The AP Literature and Composition exam is graded on a scale of 1 to 5, with 5 being the highest score. The scoring process involves multiple steps to ensure fairness and consistency in evaluating students' performance. Here's an overview of how the AP Literature test is graded:
- Raw Score: The number of correct answers is counted, and there is no penalty for incorrect responses.
- Conversion to Scaled Score: The raw score is converted to a scaled score ranging from 1 to 45. This score is then weighted and combined with the free-response section score to determine the overall exam score.
- Essay Scores: Each essay is scored on a 0 to 6 scale by trained AP readers. These readers are experienced English teachers and college professors who follow a detailed rubric provided by the College Board.
- Scoring Rubric: The rubric assesses students' ability to understand the prompt, analyze the text, develop a thesis, provide supporting evidence, and demonstrate strong writing skills.
- Holistic Approach: AP readers consider the overall quality of the essay, including its coherence, organization, use of evidence, and insightfulness.
- Final Scores: The scores from the three essays are added together to give a total essay score ranging from 0 to 18.
3. Composite Score:
- Weighting: The multiple-choice section and the essay section are weighted to calculate the final composite score.
- Composite Score Calculation: The multiple-choice score is converted to a scaled score on a 1 to 45 scale. This score is combined with the essay score on a 0 to 18 scale, with the essay score weighted more heavily.
- Conversion to AP Grade: The composite score is converted to the final AP grade on a scale of 1 to 5.
The exact cutoffs for each AP grade may vary from year to year, depending on the performance of students across the country. Generally, a score of 3 is considered a passing grade, while scores of 4 and 5 indicate higher levels of mastery and may result in college credit or advanced placement.
It's important to note that the grading process for the AP Literature exam is rigorous and aims to maintain consistency and fairness. The College Board takes several measures to ensure accurate and reliable scoring, including extensive training for AP readers and a robust quality assurance process.
Understanding how the AP Literature test is graded can help students prepare effectively and focus on developing the necessary skills to excel in both the multiple-choice and free-response sections.
Skill-Building for Success on the AP Literature Exam
To achieve success on the AP Literature exam, it is crucial to develop and refine certain skills that will enhance your ability to analyze and interpret literary texts effectively. Here are some key skill-building strategies to help you prepare for the AP Literature exam:
1. Close Reading: Practice close reading of literary texts to develop a deep understanding of the author's purpose, themes, and literary techniques. Pay attention to details, symbolism, imagery, and figurative language. Take notes and annotate the text to capture your observations and interpretations.
2. Literary Analysis: Enhance your ability to analyze and interpret literary works. Focus on identifying and discussing literary elements such as plot, character development, setting, point of view, symbolism, and themes. Practice analyzing how these elements contribute to the overall meaning and impact of the text.
3. Essay Writing: Master the art of writing strong, well-structured essays. Familiarize yourself with the three essay prompts in the free-response section: the poetry analysis essay, the prose analysis essay, and the open-ended essay. Practice developing clear and concise thesis statements, providing textual evidence to support your arguments, and organizing your essay effectively.
4. Time Management: Develop effective time management skills to ensure you can complete all sections of the exam within the allocated time. Practice timed essay writing to improve your ability to plan, write, and revise your essays under time constraints. Use practice exams to simulate the actual testing conditions and become comfortable with the time limits.
5. Vocabulary Expansion: Build a strong vocabulary to enhance your comprehension and analysis of complex texts. Read widely, including classic literature and contemporary works, to expose yourself to various writing styles, themes, and vocabulary. Learn new words, their meanings, and how to use them appropriately in your writing.
6. Exam Strategies: Familiarize yourself with the exam format, question types, and scoring rubrics. Review sample questions and essay prompts from past exams to understand the expectations and requirements. Practice answering multiple-choice questions strategically by eliminating incorrect options and making educated guesses when necessary.
7. Practice and Review: Regularly practice with sample questions, timed exams, and essay prompts. Seek feedback from teachers or peers on your essays to identify areas for improvement. Review your mistakes and focus on strengthening your weak areas. Use study guides, review books, and online resources to reinforce your understanding of key literary concepts.
8. Reading Widely: Read a diverse range of literature, including novels, plays, poetry, and non-fiction. Engage with different genres, time periods, and cultural perspectives. This will expand your literary knowledge, expose you to various writing styles, and help you make connections across texts.
Remember, consistent practice and focused skill-building are essential for success on the AP Literature exam. Develop a study plan that incorporates these strategies, and dedicate regular time to practice, review, and refine your skills. With preparation and a solid foundation in literary analysis, you can approach the exam with confidence and achieve a strong performance.
AP Literature: 6 Critical Test-Day Tips
Preparing for the AP Literature exam is essential, but it's equally important to have effective strategies for test day. Here are six critical tips to help you perform your best on the AP Literature exam:
1. Read the Instructions Carefully: Before diving into the exam, take a moment to read and understand the instructions for each section. Pay attention to any specific guidelines or requirements, such as the number of questions to answer or the time allotted for each section. Familiarize yourself with the scoring rubrics to know how your responses will be evaluated.
2. Pace Yourself: Time management is crucial during the exam. Allocate your time wisely to ensure you have enough time to answer all the questions. Plan your approach for each section and stick to your allocated time. For example, in the multiple-choice section, aim to answer each question within one minute to allow time for review.
3. Analyze Prompts and Questions: Take the time to carefully analyze the prompts and questions before answering. Understand what each question is asking for and how it relates to the given texts. Highlight keywords and key phrases to ensure you stay focused on addressing the specific requirements of each question. Pay attention to directive words like "analyze," "compare," or "evaluate" to guide your response.
4. Organize Your Essay: In the essay sections, it's crucial to have a clear and well-organized structure. Start with a concise and strong thesis statement that directly addresses the prompt. Use topic sentences to introduce each paragraph and ensure a logical flow of ideas. Support your arguments with evidence from the texts, and provide insightful analysis to demonstrate your understanding.
5. Engage with Texts: Show a deep engagement with the literary texts in your responses. Use specific examples and quotations from the texts to support your analysis. Referencing key scenes, dialogues, or literary devices demonstrates a thorough understanding of the texts and enhances the strength of your arguments. Avoid vague or general statements and focus on precise textual evidence.
6. Review and Revise: Before submitting your responses, take a few minutes to review and revise your work. Check for any grammatical or spelling errors and ensure your writing is clear and concise. Verify that you have addressed all parts of the question and that your arguments are well-supported. If time allows, read your essays aloud to catch any awkward phrasing or unclear ideas.
Remember, practice is key to success on the AP Literature exam. Familiarize yourself with the exam format, practice with sample questions and essays, and seek feedback on your writing. Develop a study schedule that allows you to build your skills and knowledge over time. By following these critical test-day tips and remaining calm and focused, you can approach the AP Literature exam with confidence and maximize your chances of achieving a high score.
In conclusion, the AP Literature exam requires a combination of critical reading skills, strong analytical thinking, and effective writing abilities. By understanding the exam format and question types, knowing how the test is graded, and building essential skills, you can set yourself up for success. Additionally, following critical test-day tips, such as managing your time, carefully analyzing prompts, organizing your essays, engaging with the texts, and reviewing your work, will help you perform your best on the exam. With diligent preparation and practice, you can approach the AP Literature exam with confidence and increase your likelihood of achieving a favorable score.
You Might Also Like

The Perfect College Essay Structure
The Fundamentals of writing an Essay which includes the process of brainstorming, drafting, and finalizing.

Know All the Different Types of Scholarships Available
Want to get college scholarship for your study? Know about scholarship programs & check the availability of different types of scholarships - Read our blog

Scholarship Application Process
Filling out college scholarship applications is indeed a time-consuming task that needs much effort and patience. This guide will help you through the entire scholarship application process

Free Resources

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
Every AP Literature Practice Test Available: Free and Official
Advanced Placement (AP)

When you're studying for your AP Literature Exam, you're going to want to use practice tests and questions to hone your skills. But where can you find AP literature practice tests? And are all practice exams equally useful for you?
The real exam has 55 multiple-choice questions and three free-response questions, but there are practice tests with every conceivable number and combination of question types.
In this article, you'll learn where to find every official College Board AP English Literature and Composition practice exam, free unofficial tests, and paid practice test resources. You'll also find out which tests are high-quality and how you can best use different practice exams to fulfill your studying needs.
Official Free AP Literature Practice Tests
The gold standard of AP English Literature practice tests and AP English Literature practice exam questions are College Board released materials . That's because the College Board administers the AP exams, so their practice questions are most like the actual AP questions you'll see on the test.
There are three different kinds of resources offered by the College Board: complete released exams from past years, released free-response questions from past years, and sample questions from the "AP Course And Exam Description."
Official Released College Board Exams
There are three official released College Board Exams. However, only the most recent one (from 2012) is complete. The 1999 and 1987 exams have the standard 55 multiple-choice questions, but both are missing parts of the three question free-response section. You can still use them as complete exams if you supplement them with released free-response questions from past years which we recommend since official multiple-choice problems are hard to come by.
2012 AP English Literature and Composition Exam
This is the best AP Lit practice test available. It's the most recent exam released by the College Board, and it follows the format of the current test with 55 multiple-choice questions and three free-response questions. Definitely make use of this test!
1999 AP English Literature and Composition Exam
This test excludes the poetry and prose analysis questions of the free-response section and only has the student choice question. So, to take it as a complete exam, you'd need to supplement it with questions 1 and 2 from the released free-response questions below . You can actually get question 2 for the 1999 test from the official free-response questions bank, but the excerpt for question 1 can't be reprinted, so you'll need to supplement with another poetry analysis question.
1987 AP English Literature and Composition Exam For reasons that are not totally clear, this exam excludes the third essay question, the poetry analysis. If you want to take this as "complete" exam practice, use a free-response poetry analysis prompt from the bank of free response questions linked below.

Or supplement with this tree-poem.
Official Free-Response Questions
There may not be very many complete released exams, but there are tons of free-response questions available from previous administrations of the test. These are great practice, not just for writing complete essays, but for practicing writing thesis statements, outlines, and so on.
What's also great about these is that most of them come with sample response and scoring guidelines, so you'll be able to see exactly what makes a high-quality AP essay by College Board standards. Be aware, though, that some of the prose and poetry excerpts can't be reprinted due to copyright concerns.
Below is the link to all the free-response questions available. The questions go all the way back to 1999, and since there haven't been many changes to the free-response part of the exam, all of these questions can be useful during your studying.
AP English Lit Free Response Questions 1999-2021
Sample Questions From the Course and Exam Description
The 2019 AP English Literature Course and Exam Description has practice multiple-choice questions and free-response questions.They don't add up to a complete test--there are only 19 multiple-choice questions instead of 55–but there are three free response questions (enough for a full test). Even though there aren’t many multiple-choice questions, they are great for simple practice.
If you're looking for more questions like these, you can revisit the old exam description booklets as well . (Just keep in mind that some of the other information in the booklet may be out of date!)
Your Teacher
Your AP teacher may have access to copies of old AP exams that you can use for practice. They probably can't let you take them out of the classroom, but they may be allowed to loan them to you in a supervised setting. This is because teachers can purchase resources directly from the College Board that students can't. Asking your teacher may not bear fruit, but it's worth a try.

Why are you asking me for AP Lit practice tests? I'm your Econ teacher!
Free Unofficial AP Literature Practice Tests
In addition to the free College Board resources, there are also several places online where you can get free, unofficial practice tests. Be aware that, because these resources aren't College-Board created or approved, they are of variable quality. For each of these resources we'll describe what's offered and how it compares to official College Board tests.
Varsity Tutors AP Literature Practice Tests
This site has multiple-choice practice quizzes divided by concept--things like "interpreting the passage," "claims and argument," and "interpreting excerpts." The questions aren't worded exactly the same way as AP test questions, but they are still okay for testing your passage-interpretation skills. Basically, the questions test for similar skills, but don't necessarily mimic AP test questions in style.
Also, the site provides the date, title, and author of each work, which is not something you'll receive on the AP exam. You can make a free account at the site to track your scores, but it's not necessary to be able to take the tests.

Kittens not included with free practice tests, unfortunately.
Albert AP English Literature Quizzes
Albert offers multiple-choice quizzes divided into prose, poetry, and drama categories. You are given the title, date, and author of the work--which you will not receive on the real AP exam. Like the Varsity Tutors quizzes, Albert offers questions that test similar skills as the AP exam, but the questions are worded differently.
High School Test Prep Tests
This site offers three short multiple-choice practice tests. You're given the title and author of the work. The questions for these tests are fairly surface-level, so I would only use these if you are working on your reading comprehension skills.
CrackAP English Literature Quizzes
CrackAP has over 40 short AP Lit quizzes. Each quiz gives a passage then has 15 multiple-choice questions on it. The questions are somewhat easier than you'll find on the real AP exam, but if you need some quick practice, this can do the trick. This resource also has examples of past free response questions, which can be useful study tools, too!
Practice Quiz AP English Literature
This site offers a 20-question multiple-choice quiz on two passages--one poetry, and one prose. The passages are extremely basic, however, so I would only use this resource if you are working on your reading comprehension skills.

The queens of AP Lit practice give you their blessing.
Paid Unofficial Practice Tests
There are also several paid resources that offer unofficial practice questions.
This is a subscription service with questions for tons of different tests—SAT, ACT, and AP exams.They also have videos and other review resources. We can't really speak to the quality of the questions because the entire service is behind a paywall of about $25 a month.
The Princeton Review AP Literature Study Guide 2021
Published study guides are an excellent way to practice for the AP Literature exam. These books are put together by experts who have inside knowledge of the test, and The Princeton Review is one of the best out there.
This study guide has three practice tests, along with other types of sample questions and expert explanations to help you improve your analytical skills.
Barron's AP English Literature and Composition, 7th Edition
Like The Princeton Review study guide, the Barron's AP Literature study guide is another great resource for students looking for extra exam prep. This guide has four practice tests and sample essay questions , along with an expert walk-through of the AP Literature exam itself.
If you're looking for a guide that gives you practice and provides tips for mastering the exam, this would be a good pick!
This subscription service offers access to tons of test prep, including the SAT, ACT and lots of AP courses. Their AP Literature resources include two full-length practice tests, three sets of flashcards to help you study, and several instructional videos.
Prices for subscriptions start at $39 dollars per month, and some plans include live tutoring and writing instruction . If you choose to subscribe, you get access to all of their course and test-prep materials, so if you’re taking several AP classes, this could be a good source.

I definitely advise paying for all of these resources with whatever loose foreign change you have lying around.
How to Use AP Literature Practice Tests
How to use a given practice test depends somewhat on the resource itself. We'll offer some recommendations here on how to best use different resources.
Complete Official Released Tests
The best way to use a complete official practice test is to do a practice-run for the exam . So find a quiet room, bring a timer or watch so you can time sections, and get to work! This will help you get familiar with the exam experience so you'll feel more comfortable on exam day!
Since there are two complete AP Lit practice tests, it makes sense to take one early on in your studying time, and one later. You can get a parent, tutor or teacher to grade the exams. The early test will help you figure out what you need to work on, and the later test will show you how you've improved! Since the AP English Literature test is more skills-heavy than content-heavy, you shouldn't feel totally lost taking a practice test even in the middle of the school year.
Official Released Free-Response and Sample Questions
Official resources that aren't complete tests are best for practicing individual sections of the test. The sample multiple-choice questions in the "Course and Exam Description" make for great AP English Literature multiple-choice practice--they'll help you get familiar with the style of the questions and practice close-reading.
The wealth of released free-response questions are great resources for building your timed essay-writing skills. You can practice complete essays or develop essay outlines.
Unofficial Practice Tests and Resources
Since unofficial practice tests aren't going to be quite as similar to the real AP exam as official College Board materials, they won't be quite as useful for preparing for the format of the exam or its questions. However, they can be very valuable close-reading practice. And since that's a critical skill for the exam, it's still worth it to use unofficial resources.

Be very quiet. She's close-reading.
Key Takeaways
Practice tests and questions are a hugely important resource as you prep for the AP Lit exam. The gold standard of practice resources are those that come from the College Board, but there are many other places where you can get practice questions that will help you hone your close-reading skills for the exam. Most of the resources listed in this article are free, but a few are paid.
Remember: official College Board practice tests are best for simulating the exam experience. Actual College Board questions are good for focused preparation for individual sections of the exam--especially the essays. Unofficial resources are best used for further honing your close-reading skills after you’ve practiced with the official materials.
Now that you know where to find these resources, you're ready to start studying for your AP Literature exam!

What's Next?
Wondering what you should be reading for AP Lit? Check out our list of 127 great books to help you prepare for the AP Literature exam.
Need more study guidance for your APs? See my five-step AP prep plan. Or see our guide on when to start studying for your APs.
If you're looking for practice tests for other AP exams, see our assembled practice tests for AP US History , AP Chemistry , AP Biology , AP World History , and AP Psychology .

These recommendations are based solely on our knowledge and experience. If you purchase an item through one of our links, PrepScholar may receive a commission.
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Ellen has extensive education mentorship experience and is deeply committed to helping students succeed in all areas of life. She received a BA from Harvard in Folklore and Mythology and is currently pursuing graduate studies at Columbia University.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
Ultimate Guide to the AP English Literature and Composition Exam
Do you know how to improve your profile for college applications.
See how your profile ranks among thousands of other students using CollegeVine. Calculate your chances at your dream schools and learn what areas you need to improve right now — it only takes 3 minutes and it's 100% free.
The English Literature and Composition exam is one of the most popular AP exams among self-studiers and enrolled students alike. In 2019, a total of 380,136 students took the AP Literature exam, making it the third most favored AP exam, trailing only English Language and U.S. History in popularity. If you are interested in taking the AP Literature exam—and are taking a class or self-studying—read on for a breakdown of the test and CollegeVine’s advice for how to best prepare for it.
When is the AP Literature Exam?
2020’s AP English Literature and Composition exam day is Wednesday, May 6, 2020 at 8 AM. Check out our blog 2020 AP Exam Schedule: Everything You Need to Know to learn more about this year’s AP exam dates and times.
What Does the AP Literature Exam Cover?
The AP Literature course engages students in careful reading and critical analysis of fictional literature, leading to a deeper understanding of the ways in which writers provide both meaning and pleasure to their readers—considering structure, style, theme, and smaller-scale elements such as figurative language, imagery, symbolism, and tone.
Although there is no required reading list, the College Board formerly provided a list of prospective authors in its past AP Literature course description. Regardless of which specific titles are read in preparation for the exam, students should be familiar with works from both British and American authors written from the 16th century to the present. Ten of the commonly studied works in AP Literature courses are:
- Great Expectations , Charles Dickens
- Invisible Man , Ralph Ellison
- Beloved , Toni Morrison
- King Lear , William Shakespeare
- Heart of Darkness , Joseph Conrad
- The Portrait of a Lady , Henry James
- Wuthering Heights , Emily Bronte
- Their Eyes Were Watching God , Zora Neale Hurston
- To Kill a Mockingbird , Harper Lee
- A Portrait of the Artist as a Young Man , James Joyce
How Long is the AP Literature Exam? What is the Format?
The AP Literature exam is one of the longer AP exams, clocking in at 3 hours. It is comprised of two sections.
Section 1: Multiple Choice
1 hour | 45 Questions | 45% of Score
The first section of the AP Literature exam is one hour long and consists of 45 multiple-choice questions—23-25 Reading questions and 20-22 Writing questions. The multiple-choice questions are grouped in five sets of questions, with each set linked to a passage of prose fiction or poetry that contains between 8 and 13 questions. Students receive two sets of questions about both prose fiction and poetry, with the fifth set varying between prose fiction and poetry. The function of the multiple choice section is to assess a student’s ability to:
1. Understand and interpret word choice, comparisons, and figurative language
This is one of the most common questions types on the AP Lit exam. Students are frequently asked to infer the meaning of certain words and phrases, and how they impact the rest of the passage. You will also be asked to identify and interpret figurative language.

Source: The College Board
2. Understand the theme of the poem or passage
You should be able to summarize and articulate what the excerpt is about and what sort of message it conveys.

3. Paraphrase or reformulate selected lines from the passage
Students are tested on their reading comprehension by being asked to select the reformulated response that most closely aligns with the original excerpt.

4. Explain the function of…
- The narrator or speaker: Know how a narrator’s or speaker’s perspective controls the details and emphases that affect how readers experience and interpret a text.

- Characters : Grasp how characters allow the reader to explore values, beliefs, assumptions, biases, and cultural norms.

- The plot and structure : Understand what the author conveys by the arrangement of the sections of text, their relationship to each other, and sequence, along with how the reader’s interpretation of the text is affected by these choices.
- Symbols and motifs : Describe the purpose of symbols and motifs and how they contribute to the meaning of the passage.

5. Identify parts of speech, verse forms, and meters
You’ll occasionally need more technical knowledge of parts of speech (adjective, adverb, etc.) and verse forms (blank verse, free verse, sonnet, etc.). You should also have a basic knowledge of poetic meter (iambic pentameter, trochaic tetrameter, etc).

Section 2: Free Response
2 hours 15 minutes | 3 questions | 55% of Score
The second section of the AP Literature exam is two hours (plus a 15-minute reading period) and contains three free response questions. These prompts test three core abilities:
- A literary analysis of a poem
- A literary analysis of a piece of prose fiction (this may include drama)
- An analysis that examines a specific concept, issue, or element in a meritorious literary work selected by the student.
The free response essays are graded by college and AP Lit teachers following a standardized rubric.
Below are 3 example free response questions from 2019’s AP Literature Exam:
1. “Carefully read P. K. Page’s 1943 poem “The Landlady.” Then, in a well-organized essay, analyze the speaker’s complex portrayal of the landlady. You may wish to consider such elements as imagery, selection of detail, and tone.”
2. “Carefully read the following excerpt from William Dean Howells’ novel The Rise of Silas Lapham (1885). Then, in a well-constructed essay, analyze how the author portrays the complex experience of two sisters, Penelope and Irene, within their family and society. You may wish to consider such literary elements as style, tone, and selection of detail.”

AP Literature Exam Score Distribution, Average Score, and Passing Rate
| AP Literature and Composition | 6.2% | 15.7% | 27.8% | 34.3% | 16.0% |
The AP Literature exam is extremely challenging, with less than half (49.7%) of students achieving a passing score of 3 or higher. The average student score is 2.62—only Physics (2.51) and Human Geography (2.55) have lower average scores. If you’re curious about other score distributions, see our post Easiest and Hardest AP Exams .
Best Ways to Study for the AP Literature Exam
One of the first steps you should take when preparing for the AP Literature exam is to look at its full course description . This will help guide your studying and understanding of the knowledge required for the AP Literature exam. Below are a few more steps you can take to ace the AP Literature exam.
Step 1: Assess Your Skills
Practice Questions and Tests: Take a practice test to assess your initial knowledge. The College Board’s AP English Literature Course and Exam Description offers some sample multiple-choice questions, and the College Board also provides six sample AP Lit free-response questions with scoring commentaries . Older versions of the AP English Literature exam are also available; you can find a copy of the 2012 AP Lit exam and the 1999 AP Lit exam . Search around the web and you’ll likely turn up even more practice exams with answers keys —some will even have explanations of the questions. You’ll also find practice tests in many of the official study guides, and some even include a diagnostic test to act as your initial assessment.
Identify Areas in Need of Improvement: Once you have taken some kind of formative assessment, score it to identify your areas of strength and areas in need of improvement. It can be helpful to have a friend (or even better, a teacher) score your free-response essays, since they are more subjective than the multiple-choice section. With an accurate formative assessment, you’ll have a better idea of where to focus your studying efforts.
Step 2: Know Your Material
In the case of the AP Literature exam, this means focusing on your reading and writing skills.
Become an Active Reader: When reading, take care to go slowly and reread important or complex sections. Pause often to consider meaning, context, and intent. Become an active reader, underlining and taking notes as you go. Remember that the importance of the text comes not only from the author, but also from how the text affects you, the reader. Pay attention to how you feel and why you feel that way. Visit the College Board’s Reading Study Skills for more information.
Write Frequently: Prepare for the writing section of your exam by writing frequently. According to the College Board, the goal is to become a “practiced, logical, clear, and honest” writer through the writing process. This means that you will plan, draft, review, redraft, edit, and polish your writing again and again. To be a successful writer on your exam, you will need to organize your ideas ahead of time, use your text wisely to support a clearly stated thesis, and provide a logical argument. Finally, you should pay close attention to your use of grammar, vocabulary, and sentence structure. Visit the College Board’s Writing Study Skills for more information.
Get Expert Advice: For more specific guidance about test preparation, consider using a formal study guide. One good choice is Barron’s AP English Literature and Composition, 6th Edition . This study guide contains a review of test topics covering details test takers need to know about poetry, fiction, and drama, and includes five full-length practice tests. Some users do criticize it for providing few examples of scored student essays, but plenty of those are available on the College Board scoring examples page .
The Princeton Review’s Cracking the AP English Language & Composition Exam, 2020 Edition: Proven Techniques to Help You Score a 5 is another solid choice containing a summary of test strategies and a focused review of course content.
Alternatively, there are many online study resources available. Some AP teachers have even published their own study guides or review sheets online. You can find one such guide here .
Consider using an app to study: A convenient way to study is to use one of the recently-developed apps for AP exams. These can be free or cost a small fee, and they provide an easy way to quiz yourself on-the-go. Make sure you read reviews before choosing one—their quality varies widely. One that does receive good reviews is the McGraw Hill 5 which also saves you some money by covering 14 different AP subjects.
Step 3: Practice Multiple-Choice Questions
Once you have your theory down, test it out by practicing multiple-choice questions. You can find these in most study guides or through online searches. There are some available in the College Board’s course description.
Try to keep track of which concept areas are still tripping you up, and go back over this theory again. Keep in mind that the key to answering questions correctly is understanding the passage, so practice active reading skills as you’re tackling the multiple-choice questions. This includes underlining, mouthing words, and circling key points. Remember, the answer will always be found in the text, and often the question will tell you exactly where in the text to look for it.
Step 4: Practice Free-Response Essays
Focus on Writing Skills: Use a rich vocabulary, varied sentence structure, and logical progression of ideas. Make sure that your words flow easily from one to the next. According to the College Board’s scoring criteria , writing that suffers from grammatical and/or mechanical errors that interfere with communication cannot earn a the maximum score of a 6, no matter how strong your thesis, compelling your argument, or convincing your evidence is.
Cultivate Cohesive Writing: You should also strive to write a thoughtful and persuasive analysis of the literature. Begin by writing a quick outline to structure your piece. Make sure that your introduction leads to a clearly stated thesis and use supporting paragraphs to build this argument. Use quotes judiciously in your answers and focus on writing with sophistication and clarity.
Practice, Practice, Practice: The best way to prepare for these free-response questions is through repeated exercises analyzing short prose passages and poems, and through practicing with open analytical questions.
Understand Scoring: As you prepare for the writing portion of your exam, be sure to review how your free responses will be scored. Each free-response essay is graded on a scale from 0 to 6 with points awarded for three elements: Thesis (0-1 point), Evidence and Commentary (0-4 points), and Sophistication (0-1 point). A comprehensive explanation of the College Board’s scoring rubric is found on their website.
Study the free-response questions and scored student responses with written explanations provided by the College Board . The most effective way to use these is to read and respond to the prompts first, then review the student samples and scoring explanations. Use this feedback to practice another prompt and repeat the cycle until you are confident that your responses are as strong as the top scorers’.
Step 5: Take Another Practice Test
As you did at the beginning of your studying, take a practice test to see which areas you’ve improved in and which still require practice.
If you have time, repeat each of the steps above to incrementally increase your score.
Step 6: Exam Day Specifics
If you’re taking the AP course associated with this exam, your teacher will walk you through how to register. If you’re self-studying, check out CollegeVine’s How to Self-Register for AP Exams .
For information about what to bring to the exam, see CollegeVine’s What Should I Bring to My AP Exam (And What Should I Definitely Leave at Home)?
CollegeVine can’t predict how you’ll score on your AP Literature exam, but we can help take the guesswork out of college admissions. Our free chancing engine uses a data-driven algorithm taking into consideration criteria such as GPA, standardized test scores, and extracurricular activities to tell you your odds of acceptance at over 500 colleges and universities.
Check out these other Collegevine articles for more information about AP exams.
- 2020 AP Exam Schedule
- How Long is Each AP Exam?
Want access to expert college guidance — for free? When you create your free CollegeVine account, you will find out your real admissions chances, build a best-fit school list, learn how to improve your profile, and get your questions answered by experts and peers—all for free. Sign up for your CollegeVine account today to get a boost on your college journey.
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

This site uses various technologies, as described in our Privacy Policy, for personalization, measuring website use/performance, and targeted advertising, which may include storing and sharing information about your site visit with third parties. By continuing to use this website you consent to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use .
We are experiencing sporadically slow performance in our online tools, which you may notice when working in your dashboard. Our team is fully engaged and actively working to improve your online experience. If you are experiencing a connectivity issue, we recommend you try again in 10-15 minutes. We will update this space when the issue is resolved.
Enter your email to unlock an extra $25 off an SAT or ACT program!
By submitting my email address. i certify that i am 13 years of age or older, agree to recieve marketing email messages from the princeton review, and agree to terms of use., guide to the ap english literature and composition exam.

Do you know how to conduct a close reading of prose and poetry? Can you write effectively under time constraints? The AP ® English Literature and Composition exam tests topics and skills discussed in your AP English Literature course. If you score high enough, your AP English score could earn you college credit!
Check out our AP English Literature Guide for what you need to know about the exam:
- Exam Overview
- Structure & Question Types
- How to Prepare
What’s on the AP English Literature & Composition Exam?
The College Board lists 6 Skill Categories that should be covered in your AP English Literature and Composition course, or as you prepare for the test:
- Character—Characters in literature show a wide range of values, beliefs, assumptions, biases, and cultural norms, and provide an opportunity to study and explore what the characters represent.
- Setting—A setting and the details associated with it represent a time and place, but also convey values associated with the setting.
- Structure—Structure refers to the arrangements of sections and parts of a text, the relationship of the parts to each other, and the sequence in which the text reveals information. These are all choices made by a writer that allow you to interpret a text.
- Narration—Any narrator’s or speaker’s perspective controls the details and emphases that readers encounter; therefore, narration affects how readers experience and interpret a text.
- Figurative language—Comparisons, representations, and associations shift meaning from the literal to the figurative. Figurative language can include word choice, imagery, and symbols. Simile, metaphor, personification, and allusions are all examples of figurative language.
- Literary argumentation—How do you write about literature yourself? You develop your interpretation (using the first five of the Big Six!) and then communicate it. You need to develop a thesis—a defensible claim—and support it with textual evidence.
The multiple-choice section of the AP English Literature and Composition exam will be testing your knowledge of the Big Six. Each one is weighted a certain amount in the multiple-choice questions.
AP English Literature & Composition Book List
There is no required reading or book list for the AP English Literature exam, but the College Board provides a list of authors and poets with whom you should be familiar and whose work is of the caliber and density that you are expected to understand. These lists include:
- Poetry: W.H. Auden, Elizabeth Bishop, William Blake, Anne Bradstreet, Edward Kamau Brathwaite, Gwendolyn Brooks, Robert Browning, George Gordon/Lord Byron, Lorna Dee Cervantes, Geoffrey Chaucer, Lucille Clifton, Samuel Taylor Coleridge, Billy Collins, H.D. (Hilda Doolittle), Emily Dickinson, John Donne, Rita Dove, Paul Laurence Dunbar, T.S. Eliot, Robert Frost, Joy Harjo, Seamus Heaney, George Herbert, Garrett Hongo, Gerard Manley Hopkins, Langston Hughes, Ben Jonson, John Keats, Philip Larkin, Robert Lowell, Andrew Marvell, John Milton, Marianne Moore, Sylvia Plath, Edgar Allan Poe, Alexander Pope, Adrienne Rich, Anne Sexton, William Shakespeare, Percy Bysshe Shelley, Leslie Marmon Silko, Cathy Song, Wallace Stevens, Alfred, Lord Tennyson, Derek Walcott, Walt Whitman, Richard Wilbur, William Carlos Williams, William Wordsworth, William Butler Yeats
- Drama: Aeschylus, Edward Albee, Amiri Baraka, Samuel Beckett, Anton Chekhov, Caryl Churchill, William Congreve, Athol Fugard, Lorraine Hansberry, Lillian Hellman, David Henry Hwang, Henrik Ibsen, Ben Jonson, David Mamet, Arthur Miller, Molière, Marsha Norman, Sean O’Casey, Eugene O’Neill, Suzan-Lori Parks, Harold Pinter, Luigi Pirandello, William Shakespeare, George Bernard Shaw, Sam Shepard, Sophocles, Tom Stoppard, Luis Valdez, Oscar Wilde, Tennessee Williams, August Wilson
- Fiction (Novel and Short Story): Chinua Achebe, Sherman Alexie, Isabel Allende, Rudolfo Anaya, Margaret Atwood, Jane Austen, James Baldwin, Saul Bellow, Charlotte Bronte, Emily Bronte, Raymond Carver, Willa Cather, John Cheever, Kate Chopin, Sandra Cisneros, Joseph Conrad, Edwidge Danticat, Daniel Defoe, Anita Desai, Charles Dickens, Fyodor Dostoevsky, George Eliot, Ralph Ellison, Louise Erdrich, William Faulkner, Henry Fielding, F. Scott Fitzgerald, E.M. Forster, Thomas Hardy, Nathaniel Hawthorne, Ernest Hemingway, Zora Neale Hurston, Kazuo Ishiguro, Henry James, Ha Jin, Edward P. Jones, James Joyce, Maxine Hong Kingston, Joy Kogawa, Jhumpa Lahiri, Margaret Laurence, D.H. Lawrence, Chang-rae Lee, Bernard Malamud, Gabriel García Márquez, Cormac McCarthy, Ian McEwan, Herman Melville, Toni Morrison, Bharati Mukherjee, Vladimir Nabokov, Flannery O’Connor, Orhan Pamuk, Katherine Anne Porter, Marilynne Robinson, Jonathan Swift, Mark Twain, John Updike, Alice Walker, Evelyn Waugh, Eudora Welty, Edith Wharton, John Edgar Wideman, Virginia Woolf, Richard Wright
- Expository Prose: Joseph Addison, Gloria Anzaldua, Matthew Arnold, James Baldwin, James Boswell, Joan Didion, Frederick Douglass, W.E.B. Du Bois, Ralph Waldo Emerson, William Hazlitt, bell hooks, Samuel Johnson, Charles Lamb, Thomas Macaulay, Mary McCarthy, John Stuart Mill, George Orwell, Michael Pollan, Richard Rodriguez, Edward Said, Lewis Thomas, Henry David Thoreau, E.B. White, Virginia Woolf
Read More: Review for the exam with our AP English Literature Cram Courses
AP English Literature Structure & Question Types
The AP English Literature & Composition exam takes 3 hours to complete and consists of two sections: a multiple-choice section and a free response section.
|
|
|
| |
| Section 1 | 60 minutes | 55 multiple-choice questions | 45% |
| Section 2 | 120 minutes | 3 free response questions | 55% |
Multiple-Choice
AP English Literature multiple-choice questions are grouped in sets. You will be given 5 passages or poems to read, with 8-13 multiple-choice questions to assess your reading comprehension. Each multiple-choice question has 5 answer choices (A through E). That’s a lot of reading then recalling, understanding, and interpreting. Use your time effectively and wisely!
Free Response
- Respond to the prompt with a thesis that presents an interpretation and may establish a line of reasoning.
- Select and use evidence to develop and support your line of reasoning.
- Explain the relationship between the evidence and your thesis.
- Use appropriate grammar and punctuation in communicating your argument.
How to Interpret AP English Literature Scores
AP scores are reported from 1 to 5. Colleges are generally looking for a 4 or 5 on the AP English Literature exam, but some may grant credit for a 3. (Here's a quick overview of AP credit policy .) Each test is curved so scores vary from year to year. Here’s how AP English Lit students scored on the May 2022 test:
|
|
|
|
| 5 | Extremely qualified | 16.9% |
| 4 | Well qualified | 27.3% |
| 3 | Qualified | 33.7% |
| 2 | Possibly qualified | 14.1% |
| 1 | No recommendation | 7.9% |
Source: College Board
How can I prepare?
AP classes are great, but for many students they’re not enough! For a thorough review of AP English Literature content and strategy, pick the AP prep option that works best for your goals and learning style.
- AP Exams

Explore Colleges For You
Connect with our featured colleges to find schools that both match your interests and are looking for students like you.

Career Quiz
Take our short quiz to learn which is the right career for you.

Get Started on Athletic Scholarships & Recruiting!
Join athletes who were discovered, recruited & often received scholarships after connecting with NCSA's 42,000 strong network of coaches.

Best 389 Colleges
165,000 students rate everything from their professors to their campus social scene.
SAT Prep Courses
1400+ course, act prep courses, free sat practice test & events, 1-800-2review, free digital sat prep try our self-paced plus program - for free, get a 14 day trial.
Free MCAT Practice Test
I already know my score.
MCAT Self-Paced 14-Day Free Trial
Enrollment Advisor
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 1
1-877-LEARN-30
Mon-Fri 9AM-10PM ET
Sat-Sun 9AM-8PM ET
Student Support
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 2
Mon-Fri 9AM-9PM ET
Sat-Sun 8:30AM-5PM ET
Partnerships
- Teach or Tutor for Us
College Readiness
International
Advertising
Affiliate/Other
- Enrollment Terms & Conditions
- Accessibility
- Cigna Medical Transparency in Coverage
Register Book
Local Offices: Mon-Fri 9AM-6PM
- SAT Subject Tests
Academic Subjects
- Social Studies
Find the Right College
- College Rankings
- College Advice
- Applying to College
- Financial Aid
School & District Partnerships
- Professional Development
- Advice Articles
- Private Tutoring
- Mobile Apps
- International Offices
- Work for Us
- Affiliate Program
- Partner with Us
- Advertise with Us
- International Partnerships
- Our Guarantees
- Accessibility – Canada
Privacy Policy | CA Privacy Notice | Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information | Your Opt-Out Rights | Terms of Use | Site Map
©2024 TPR Education IP Holdings, LLC. All Rights Reserved. The Princeton Review is not affiliated with Princeton University
TPR Education, LLC (doing business as “The Princeton Review”) is controlled by Primavera Holdings Limited, a firm owned by Chinese nationals with a principal place of business in Hong Kong, China.
AP English Literature and Composition Practice Tests
The AP English Literature and Composition Exam is 3 hours long and broken up into two sections.
Section I (One hour)
45 percent of total score 55 multiple-choice questions based on 2 or 3 poems and 2 or 3 passages of fiction
Section II (Two hours)
55 percent of total score 3 essays
Essay 1: An analysis of a poem
Essay 2: An analysis of a prose passage from a work of fiction, a letter, or a speech in a play
Essay 3: An analytical essay on a novel or play of your choice
AP English Literature and Composition Glossary
If you are a mobile user, click here: Do AP English Literature and Composition Practice Questions .
AP English Literature and Composition Multiple-Choice Practice Tests
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 1
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 2
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 3
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 4
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 5
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 6
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 7
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 8
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 9
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 10
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 11
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 12
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 13
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 14
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 15
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 16
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 17
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 18
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 19
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 20
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 21
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 22
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 23
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 24
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 25
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 26
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 27
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 28
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 29
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 30
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 31
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 32
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 33
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 34
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 35
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 36
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 37
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 38
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 39
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 40
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 41
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 42
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 43
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 1: the 2001 novel White Teeth
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 2: the 2002 poem "Litany"
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 3: Almost Livin' Almost Dyin'
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 4: Poem The Good Life
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 5: Beginnings
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 6: a novel
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 7: Planetarium
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 8: Quicksand
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 9: the poem Paterson
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 10: Jonathan Swift’s essay
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 11: Poem The Mower's Song
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 12: An Occurrence at Owl Creek Bridge
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 13: Poem Cozy Apologia
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 14: a short story
- AP English Literature and Composition Practice Test 15: a novel
AP English Literature and Composition Free-Response Practice Tests
- AP English Literature and Composition Free-Response Practice Test 1
- AP English Literature and Composition Free-Response Practice Test 2
- AP English Literature and Composition Free-Response Practice Test 3
- AP English Literature and Composition Free-Response Practice Test 4
- AP English Literature and Composition Free-Response Practice Test 5
AP English Literature and Composition Downloads
- AP English Literature Practice Test 1 pdf download
- AP English Literature Practice Test 2 pdf download
- AP English Literature Practice Test 3 pdf download
- More AP English Literature and Composition Downloads
AP English Literature and Composition Writing Study Skills
Writing is central to the AP English courses and exams. Both courses have two goals: to provide you with opportunities to become skilled, mature, critical readers, and to help you to develop into practiced, logical, clear, and honest writers. In AP English, writing is taught as “process”—that is, thinking, planning, drafting the text, then reviewing, discussing, redrafting, editing, polishing, and finishing it. It’s also important that AP students learn to write “on call” or “on demand.” Learning to write critical or expository essays on call takes time and practice.
Here are some key guidelines to remember in learning to write a critical essay:
- Take time to organize your ideas.
- Make pertinent use of the text given to you to analyze.
- Quote judiciously from it to support your observations.
- Be logical in your exposition of ideas.
If you acquire these skills—organizing ideas, marshalling evidence, being logical in analysis, and using the text judiciously—you should have little trouble writing your essays on the AP Exam. Practice in other kinds of writing—narrative, argument, exposition, and personal writing—all have their place alongside practice in writing on demand.
As you study and practice writing, consider the following points.
Reading directly influences writing skills and habits.
Reading and writing are intertwined. When you read what published authors have written you are immersed not just in their ideas, but in the pulsing of their sentences and the aptness of their diction. The more you read, the more that the rhythm of the English language will be available to influence your writing. Reading is not a substitute for writing, but it does help lay the foundation that makes good writing possible.
Writing is fun.
When you have penned what you think is a great sentence or a clean, logical paragraph, read it over to yourself out loud. Enjoy it. Delight in the ideas, savor the diction, and let the phrases and clauses roll around in your mind. Claim it as part of your self. You may discover you have a voice worthy of respect.
A tip from E. M. Forster
He is reputed to have said that he never knew clearly what it was he thought until he spoke it; and once he had said it, he never knew clearly what it was that he said until he had written it down. Then, Forster noted, he could play with it and give it final form. Be like Forster: think, speak, write, analyze your writing, then give it final shape.
Grammar, mechanics, and rhetoric
Think of them as elements that you can order to clean up your ideas, to sharpen your statements, to make your words and sentences glisten and stick.
Writers and critical readers have a “technical vocabulary” they use when talking about the language of drama, poetry, and fiction. Compile a list of such words. Notice writing that uses such vocabulary. Here are some of the words you should already know: syntax, tone, rhetoric, attitude, antecedent, denouement, exposition, climax, atmosphere, voice, speaker, stock character, thesis, ideology, persuasion, paradox, allusion, ambivalence, syllogism, and aphorism.
Your teachers may specify an audience that you are supposed to keep in mind when writing a paper. Most of us in daily life are not writing for a particular person or audience, but rather for someone called “the general reader.” The general reader is someone, anyone, who possesses an average intelligence and has a fairly sound general education. This general reader is interested in the events of the day and in the world as a whole. He or she has a good measure of sympathy for humankind, appreciates the happy as well as the unhappy accidents of life. This reader also is blessed with a good sense of humor and the ability to listen to others; to writers like you, in fact. Keep the general reader in mind when you write.
Pay close attention to the task verbs used in the free-response questions. Each one directs you to complete a specific type of response. Here are the task verbs you’ll see on the exam:
- Analyze: Examine methodically and in detail the structure of the topic of the question for purposes of interpretation and explanation.
- Choose: Select a literary work among provided choices.
- Read: Look at or view printed directions and provided passages.
All Subjects
📚 AP English Literature
Unit 1 – intro to short fiction.
Unit 1 Overview: Introduction to Short Fiction
Interpreting the role of character in fiction
Identifying and interpreting setting
Understanding how a story’s structure affects interpretations
Understanding and interpreting a narrator’s perspective
Reading texts literally and figuratively
The basics of literary analysis
Unit 2 – Intro to Poetry
Unit 2 Overview: Introduction to Poetry
Identifying characters in poetry
Understanding & interpreting meaning in poetic structure
Analyzing word choice to find meaning
Identifying techniques in poetry to analyze literary works
Unit 3 – Intro to Longer Fiction & Drama
Unit 3 Overview: Introduction to Longer Fiction and Drama
Interpreting character description and perspective
Character evolution throughout a narrative
Conflict and plot development
Interpreting symbolism
Identifying evidence and supporting literary arguments
Unit 4 – Character, Conflict, & Storytelling in Short Fiction
Unit 4 Overview: Character, Conflict, and Storytelling
Protagonists, antagonists, character relationships, and conflict
Character interactions with setting and its significance
Archetypes in literature
Types of narration like stream of consciousness
Narrative distance, tone, and perspective
Unit 5 – Structure & Figurative Language in Poetry
Unit 5 Overview: Structure and Figurative Language
Traits of closed and open structures in poetry
Use of techniques like imagery and hyperbole
Types of comparisons in poetry including personification and allusion
Identifying and interpreting extended metaphors

Unit 6 – Literary Techniques in Longer Works
Unit 6 Overview: Literary Techniques in Longer Works
Interpreting foil characters
Understanding and interpreting character complexity
Understanding nonlinear narrative structures like flashbacks and foreshadowing
The effect of narrative tone and bias on reading
Characters as symbols, metaphors, and archetypes
Developing literary arguments within a broader context of works
Unit 7 – Societal & Historical Context in Short Fiction
Unit 7 Overview: Societal and Historical Context
Sudden and more gradual change in characters
Epiphany as a driver of plot
Relationships between characters and groups
Character interactions with changing and contrasting settings
The significance of the pacing of a narrative
Setting as a symbol
Interpreting texts in their historical and societal contexts
Unit 8 – Advanced Techniques in Poetry
Unit 8 Overview: Advanced Techniques in Poetry
Looking at Punctuation and Structural Patterns
Interpreting juxtaposition, paradox, and irony
How ambiguity can allow for various interpretations
Identifying symbols, conceits, and allusions
Learning proper attribution and citation in literary analysis
Unit 9 – Nuanced Analysis in Longer Works
Unit 9 Overview: Nuanced Analysis
Looking at a character’s response to the resolution of a narrative
Suspense, resolution, and plot development
Narrative inconsistencies and contrasting perspectives
Study Tools
2024 AP English Literature Exam Guide
Frequently Asked Questions
Most Frequently Cited on the AP English Literature Exam
What Is Poetry and How Can It Be Analyzed?
AP Lit Reading List
What is Classic Literature?
How Can I Be Prepared for the AP English Literature FRQs?
Best AP English Literature Quizlet Decks by Unit
How Can I Get a 5 in AP AP English Literature?
What Are the Best AP English Literature Textbooks and Prep Books?
Is AP English Literature Hard? Is AP English Literature Worth Taking?
What Types of Multiple-Choice Questions will Appear on the AP English Literature Exam?
What Are the Best Quizlet Decks for AP English Literature?
How Do I Self-Study AP English Literature?
What Memes Are Perfect for AP English Literature?
How Can I Utilize My Time Wisely on the FRQ Section of the AP Lit Exam?
Exam Skills
Score Higher on AP Literature 2024: MCQ Tips from Students
Score Higher on AP Literature 2024: Tips for FRQ 1 (Poetry Analysis)
Score Higher on AP Literature 2024: Tips for FRQ 2 (Prose Fiction Analysis)
Score Higher on AP Literature 2024: Tips for FRQ 3 (Literary Argument)
AP Lit Prose Analysis Practice Essays & Feedback
Short Fiction Overview
English Literature Multiple Choice
AP English Literature Multiple Choice Help (MCQ)
AP Lit: Poetry Overview
AP Lit Prose Analysis Practice Prompt Answers & Feedback: Fahrenheit 451 (Diction)
FRQ 2: Prose Analysis
AP Lit Prose Analysis: Practice Prompt Samples & Feedback
Culturally Relevant Pedagogy and AP Lit
Culturally Relevant Pedagogy and AP Lit - Slides
Literary Device Review
Literary Device Review - Slides
Creating a Short Fiction "Boot Camp"
Creating a Short Fiction "Boot Camp" - Slides
Breaking Down an Exam Prompt - Slides
Breaking Down an Exam Prompt
AP Literature - Theme Statements and Thesis Statements
Defending a Claim - Slides
Defending a Claim
AP Lit - Annotating for Understanding - Slides
AP Lit - Annotating for Understanding
Complexity of Poetry - Slides
Complexity of Poetry
How to Read a Poem
How Form Creates Meaning
How Form Creates Meaning - Slides
Student Open Poetry Study
Characters and Relationships
Characters and Relationships - Slides
Finding Theme Through Characterization
Annotating for Analysis, Part 2
Annotating for Analysis, Part 2 - Slides
Multiple Choice Intro
Multiple Choice Intro - Slides
Prose MC Strategies and Practice
Prose Analysis Prompt Deconstruction and Strategies
Prose Analysis Prompt Deconstruction and Strategies - Slides
Prose Analysis (Q2) Thesis and Introduction
Prose Analysis (Q2) Thesis and Introduction - Slides
Prose Analysis (Q2) Evidence and Commentary
Prose Analysis (Q2) Evidence and Commentary - Slides
Figurative Language and Function - Slides
Figurative Language and Function
Q1 Thesis and Introduction
Poetry Analysis (Q1) Thesis and Introduction
Poetry Analysis (Q1) Evidence and Commentary
Poetry Analysis (Q1) Evidence and Commentary - Slides
Commentary and Sophistication FAQs
Commentary and Sophistication - Slides
Prose Analysis: Setting and Characterization
Literary Argument (Q3): Setting, Characterization and Theme - Slides
AP Lit: Writing a Thesis and FRQ 3 Practice
AP Cram Sessions 2021
Download AP Literature Cheat Sheet PDF Cram Chart
🌶️ AP Lit Cram Review: Long Fiction I
AP English Literature Cram Unit 1: Short Fiction I
🌶️ AP Lit Cram Review: Unit 2: Poetry I
AP English Literature Cram Unit 2: Poetry I
AP English Literature Cram Unit 3: Longer Fiction or Drama I
🌶️ AP Lit Cram Review: Unit 3: Longer Fiction or Drama I
🌶️ AP Lit Cram Review: Unit 4: Short Fiction II
AP English Literature Cram Unit 4: Short Fiction II
🌶️ AP Lit Cram Review: Unit 5: Poetry II
AP English Literature Cram Unit 5: Poetry II
AP English Literature Cram Unit 6: Longer Fiction or Drama II
🌶️ AP Lit Cram Review: Unit 6: Longer Fiction or Drama II
🌶️ AP Lit Cram Review: Unit 7: Short Fiction III
AP English Literature Cram Unit 7: Short Fiction III
🌶️ AP Lit Cram Review: Unit 8: Poetry III
AP English Literature Cram Unit 8: Poetry III
🌶️ AP Lit Cram Review: Unit 9: Longer Fiction or Drama III
AP English Literature Cram Unit 9: Longer Fiction or Drama III
🌶️ AP Lit Cram Review: Free Response Tips and Tricks
AP English Literature Free Response Tips and Tricks
AP English Literature Cram Free Response Tips and Tricks
🌶️ AP English Literature Finale May 4, 2021
AP English Literature Finale
🌶️ AP English Literature Finale Watch Party Admin 2
🌶️ AP English Literature Finale Watch Party Admin 3
Live Cram Sessions 2020
Function of Structure - Slides
Prose Analysis: Foundation of Function
Explaining Figurative Language - Slides
Prose Analysis: Figuratively Speaking
Prose-based Argument: What + Where = Why
Lit Cram 3 - Slides
Prose Analysis: Characters & Relationships
Diction and Syntax - Slides
Prose Analysis: "It's Not What You Say"
Prose Analysis: Complexity and Conflict
Lit Cram 6: Complexity and Conflict - Slides
Final Review: Tips and Tricks - Slides
Final Review: Tips and Tricks
Lit Cram 7: Symbolism - Slides
Prose Analysis: Setting & Symbols
Prose Prompt Process and Practice
Prose Practice - Slides
Real Time Prose Analysis
Presentation Slides
🎉NMSI AP Reader Chat: English Literature
Q&A Student Study Session
📚 AP Lit 5-hour Cram Finale
📚 AP Lit 1-hour Cram Finale
AP Exam Format and Strategies

Stay Connected
© 2024 fiveable inc. all rights reserved., ap® and sat® are trademarks registered by the college board, which is not affiliated with, and does not endorse this website..

AP® English Literature
The ultimate list of ap® english literature tips.
- The Albert Team
- Last Updated On: March 1, 2022

Managing to score a 5 on the AP® English Literature and Composition exam is no easy task. In 2020, for example, only 12.5% of students earned a 5 on the test. But don’t let that statistic scare you! While such a number may make you want to throw in the towel, it is possible to ace this exam through hard work, preparation, and determination. In this post, we’ll break down tons of AP® English Literature tips for you to tackle your exam.
The AP® English Literature and Composition exam is designed to test your ability to think critically and analyze literary excerpts. The test is three hours long and consists of a multiple-choice portion (worth 45% of your grade) and a free response portion (worth 55% of your grade).
The best way to score a 5 on the AP® English Literature exam is to practice, practice, practice. And we’re here to help. Below, we’ve compiled an ultimate list of AP® English Literature practice tests, study guides, AP® Lit prose essay examples, test-taking strategies, and more. Think of this page as the ultimate AP® English Literature review.
If you’re looking for online solutions, use Albert . If you’re looking for old school review books, read this for the best AP® English Literature review books .
What We Review
Overall How To Study for AP® English Literature: 9 Tips for 4s and 5s
1. complete any and all summer work assigned.
AP® English Literature, as its title indicates, requires a lot of reading. Chances are, your teacher will provide you with a reading list and expect the required titles to be read when you walk into your first day of class. In some cases, you may even be assigned a report or project to be completed before you begin the class.
These summer assignments serve as crucial moments in the long and difficult process of developing yourself into a budding literary critic. If you take it seriously and complete a proficient assignment, it will show your teacher that you are in the course to learn. This attitude will make the school year a lot more bearable for both you and your instructor.
2. Read Thomas Foster’s How To Read Literature Like a Professor
Foster’s book offers an accessible and entertaining gateway into the complex and often confusing world of literary criticism. Chapters include explanations and reviews of subjects like symbolism, theme, irony, context, and more.
It is an excellent way to begin getting yourself to think deeply about literature, and it offers clear examples of close- and critical reading. It also discusses a wide variety of classic literary works which will help familiarize you with what academics call the “canon.” (More on this in the next tip.) It’s very readable too. Buy it, read it, mark it up, and keep it by your side throughout the class.
3. Become familiar with the Western Canon
Often referred to simply as “The Canon,” the Western Canon is the body of high-culture literature, music, philosophy, and works of art that is highly valued in the West, i.e. the poems, prose passages, and drama selections that you will mostly see on the AP® Lit exam.
Cultivating a basic understanding of these texts and their authors will not only familiarize you with the history and development of the English tradition but also strengthen your understanding of the “conversation of literature,” the innumerable and complex ways that authors and their works speak to each other and interact. We recommend reading at least the first chapter of Harold Bloom’s book on the subject to get a basic understanding.
We also insist that you familiarize yourself with the various problems that the upholding of such a canon produces. During the 80’s and 90’s, a canon war of sorts took place among English departments, with progressives aiming to dismantle the canon on the grounds that it neglects many African-American, female, queer, and impoverished writers in favor of spotlighting “dead white males.” Understanding this friction will deeply enrich your understanding of literature and increase your chances of scoring a 5 on the exam.
4. Learn how to analyze text

Analyzing literary text comprises an incredibly large portion of the AP® English Literature course and exam. It’s important that you learn how to examine the text both as a whole and as a part. Analyze the setting, characters, and plot of the piece. However, it’s also imperative that you understand how to look deeper within the details. Deconstruct the text and examine its theme, look for literary devices, and motives. Do not merely summarize. Foster’s book from tip #2 is a great place to start developing your critical reading skills.
5. Develop a daily reading habit
This is literature! Therefore, you should become accustomed to reading…a lot! However, this does not necessarily mean that you have to aim to read an outrageous number of books or anything. You just need to at least make an attempt to read every day.
Get a subscription to a major publication like The New Yorker or The New York Times , or you can check out our comprehensive AP® English Literature Reading List for a list of essential works. As you read, try to dissect the depth of the text. After a few days of this, you’ll be surprised at how easy analysis can come to you once you train your mind to question everything.
6. Ask questions to seek clarity
Your teacher is there to help; it’s their job. If there’s anything you don’t understand, be sure to ask your instructor even if you feel embarrassed or shy. Understanding a concept you previously had trouble with is sure to be a huge weight off of your shoulders. Asking questions and literature go hand-in-hand. Some go-to’s include:
- “How did the author create that tone?”
- “How do you properly weave evidence into your argument?
- “What is the meaning of this word?”
7. Form a study group and meet either weekly or bi-weekly
Studying with other people provides opportunities to approach subject matter from different angles, and analyzing literature is all about understanding and engaging with various perspectives.
Everyone brings their own experience to the text, and what better way to learn about new perspectives than through a study group? Meet weekly or bi-weekly at a coffee shop or friend’s house, and maintain a focused but casual tone. Also, create a checklist of what to review with your group prior to meeting to provide structure to the meeting.
8 . Make flashcards of literary devices, terms, concepts, works, and more
The AP® English Literature exam consists of tons of questions involving literary devices, authorial intention, works and authors, and more, so it is imperative that you develop a strong understanding of the literary lexicon.
The easiest way to strengthen your vocabulary is to make yourself some flashcards with the most common literary devices, authors, works, and rhetorical techniques, and carve out at least 30 minutes per day to review. If you’d prefer to use an online resource, make some flashcards over at Quizlet !
9. Experiment with different study styles
Everyone has different preferences when it comes to studying. Maybe you’re a visual learner. Perhaps you like to listen to the material to really understand it. The best way to find out what form of studying helps you best is to experiment. Use flashcards one day, read and summarize material the next, take a practice exam after that, and then try a study group. Variety is key!
Now that you have a grasp on how to get through the actual coursework of your AP® English Literature and Composition class, it’s time to learn how to study for the exam at the end of the year.
First, we’ll take a look at some tips that are sure to help you ace the first portion of the AP® Literature exam: the multiple-choice section. This portion is worth 45% of your total score and it consists of several passages to read and 55 questions to answer, which you have exactly one hour to complete.
Let’s get started.
Return to the Table of Contents
AP® English Literature Multiple-Choice Review: 11 Tips

1. Choose a multiple-choice strategy: read the passages first or read the questions first
Most people are familiar with the classic shortcut when it comes to taking multiple choice tests—read the questions first, then scan the passages to look for the answers. This method of approaching the AP® English Literature exam can work. It can give you a more focused, determined approach on what to look for when reading the passage. But it can also be distracting to some.
On the other hand, you can read the passages first and then answer the questions. This is the more straightforward, perhaps more traditional way of approaching the multiple-choice section, and it works best for people who like to do things in logical, sequential ways. Work through a few practice exams, and then decide which works best for you and stick with it.
2. Look deep within the text for implications and subtleties
Analyze the passages within the exam very carefully. There will undoubtedly be questions covering the tone of the passage, or the author’s purpose for writing it. Was it to inform or persuade the audience? To create a specific mood or tone? Perhaps the author used some literary devices like allusions or irony. Closely read the passages and you will have no problem identifying the answers to questions that are specific to the literature side of AP® English. Avoid interpreting the text at face-value.
3. Carefully read the questions and mark them up
If you don’t understand what the question is asking, you can’t possibly expect to know the answer. Take a deep breath and calmly read the questions, dissecting them completely by marking them up with underlines, circles, and more. If you’d like you could create your own system, where underlining represents, say, imagery, and circles represent irony, etc.
Sometimes, the writers of the test will throw in certain words or phrases that lead the question in a different direction. For example, the words “ EXCEPT ” and “ NOT ” are often used at the end of questions, and this can confuse you. Underline these keywords to force yourself to pay attention to them.
4. Eliminate answer choices that are obviously incorrect
Ever since you were young, you’ve likely heard the helpful suggestion of deducing answers. If you’re familiar with the subject matter of the question, it should be easy to rule out at least one of the choices that you have determined not to be correct.
Physically mark out the answers you believe are wrong by crossing or exxing them out. It will help you to visually see which answers couldn’t possibly be correct, and it will make the multiple-choice questions much more manageable.
5. Reread parts of the passage that are pertinent to the AP® English Literature questions
If a certain question throws you slightly off, return to the passage to clear up your confusion. Most of the time, the answer can be found either directly inside the text or just outside of it through implication and metaphor.
You may even want to put a star, dash, or some other marking beside portions of the text that contain answers or key phrases or moments. That way, if you have extra time at the end of the test, you can go back and check your answers quickly.
6. Pay attention to time

This is a timed exam. You have 60 minutes to complete 55 questions. This allows for an average of less than a minute per question when you account for time spent reading passages. You have absolutely no time to sit at your desk staring blankly at questions you don’t quite understand.
Luckily, there is no penalty for answers marked wrong—or answers not marked at all—on the AP® English Literature exam. This means you should definitely skip the questions you’re unsure of. Mark them in some sort of way so that it is noticeable that you haven’t answered them yet. Then, if you have some time at the end of the test, you can go back and see if you can come up with the answer. Alternatively, if you can’t seem to find an answer: guess!
7. Formulate summaries of the passages in the margins
If you are a fast worker, this tip may prove extremely helpful for you. A few of the multiple-choice questions may test your overall comprehension of the passages you read. In the margins of the page beside the passage, jot down a few bullet points outlining the plot progression as you read. This way you can refer back to your notes when answering questions rather than searching the entire text. Think of this strategy as you are creating a treasure map of the passage, drawing up a guide which will lead you to the hidden treasure.
8. Be wary of “All of the above” and “None of the above.”
There will be a few times where “all of the above” and “none of the above” appear as answer choices on the AP® English Language exam. These can be tricky. Remember that “all of the above” means that every single provided answer choice is correct, so if you are somewhat unsure of a single answer then be weary of “all of the above.” The same goes for “none of the above.” Be confident that all choices are either correct or incorrect.
9. Create a daily study routine and stick to it
You will not be able to score a 5 if you decide to cram the night or even week before the exam. Therefore, you must develop a daily study schedule as soon as the year begins. One way to do this is to set an alarm on your phone to remind you to study. Moreover, take the flashcards you’ve made with you wherever you go. Keep them in your wallet, in your purse, or even in your car. Whenever you have a moment of free time, instead of scrolling through Twitter or Facebook on your phone, run through a review of your terms. Ultimately, create your own AP® English Literature study guide. It’ll stick better in your memory and help your AP® Literature exam score in the long run.
10. Work through multiple practice exams
The most helpful and effective way to prepare for the multiple-choice portion of the AP® English Literature exam is by testing yourself. Prepare early in the semester for the test by taking practice exams. We offer tons of practice assessments with our AP® English Literature course and so does College Board , but if you’re more of a pen and paper person, you can use the recommended AP® Lit books here .
Shoot for one practice exam per month, and be sure to time yourself when working through the practice exams. This will help familiarize you with the ins and outs of the exam itself while simultaneously strengthening your test-taking skills. We can’t stress this tip enough.
11. Don’t let your stress and anxiety overwhelm you
Sure, the AP® English Literature exam is a difficult and important test. And yes, it affects the amount of college credit you receive coming out of high school. But at the end of the day, it’s just a test. Anxiety and stress can severely affect your ability to function and think correctly. Take a deep breath periodically throughout the test. It’ll help calm your body and soothe your mind so you can concentrate better.
Now that you have some tips on how to tackle the multiple-choice portion of the AP® English Literature exam, it’s time to focus on the most challenging part: the free response portion. In this portion, you have two hours to complete three essays. This section tests your ability to analyze passages and dissect them to form logical interpretations to be illustrated in your essays.
Here are some tips for nailing the free response portion of the AP® English Literature and Composition exam:
AP® English Literature Free-Response Review: 13 Tips

1. Critically read and mark-up the question
The first step towards writing an awesome essay on the AP® Literature exam is reading (and understanding) the question. What are the authors of the test asking for specifically? As you read the question, underline, highlight, or circle key words and phrases. Think critically about what the question is asking of you. The scorers of the free response portion want essays that are clear and to the point. Simply restating the prompt will result in a huge deduction of points. Regurgitating the question will show the reader that you may not be confident in your ability to dissect passages. Avoid this by spending time with the question and marking the AP® English Literature prompts up.

Here, the key words and phrases to underline are “analyze” and “portrayal” as they point you toward what you are to do and where you are to focus. Additionally, the prompt includes further areas to highlight including, “imagery, selection of detail, and tone.”
2. Develop a strong, well-developed AP® English Literature thesis statement
A well-written thesis is the basis of all successful essays. As mentioned previously, do NOT restate the question. In fact, one of the biggest mistakes students made in the 2019 exam involved moving from commentary (point by point observations) to more cohesive claims. In other words, students had difficulty strengthening their observations into arguments. Many times, this error stems from having a weak thesis statement. Think of your thesis as your essay’s central claim, its expression of its argument. Crafting a perfect thesis statement is indeed difficult, so if you find yourself totally lost, check out AP’s very own video lecture on the subject .
Here are examples of good and bad thesis statements over an essay concerning free speech:
- Bad Thesis: “This paper will consider the advantages and disadvantages of certain restrictions on free speech.”
- Good Thesis: “Even though there may be considerable advantages to restricting hate speech, the possibility of chilling open dialogue on crucial racial issues is too great and too high a price to pay.”
3. Structure the essay with a cohesive mode of organization
Organization is key to writing a great essay. If your analysis moves all over the place in a discursive manner, the reader will get angry, and you don’t want to make the reader angry. You should be greatly familiar with the basic five paragraph essay outline before taking the exam. While this outline isn’t necessarily set in stone (it can be adjusted, expanded, shortened, etc.), it does serve as a tried and true method of organization.
After you dissect the question, prepare an outline within the first few minutes of writing your essay. Perhaps even use a diagram, if you’re a visual learner. A clear and precise outline can help prevent rambling when answering the question in your essay.
4. Use high-level, academic vocabulary
Since this is an exam for an Advanced Placement English course, it is imperative that you use a vocabulary that reflects a higher level of education. Avoid slang, colloquialism, and vague language like, “sort of,” “kind of,” and “very.” These lower the professional and academic tone of your essay, and they will obfuscate your writing with ambiguity.
On the other hand, don’t go overboard with smarty-pants language that you don’t have control of. This will render your essay pretentious and unclear. To strengthen your academic vocabulary, you should make flashcards on Quizlet and develop a daily study habit. Check out our 15 Must Know Rhetorical Terms for AP® English Literature page , too.
5. Mark-up the passage and refer back to it
On the first two essays, you will be asked to read a passage and analyze it according to the instructions given in the question. Use the passage to your advantage. As you read mark it up by circling, highlighting, or underlining key words or phrases. One common misconception that occurred in the 2019 exam was students relying on plot summary instead of focusing more specifically on details or elements and explaining how these illustrate their points. To avoid this, frequently refer back to specific parts of the text.
6. Develop familiarity with many literary works to ace the third FRQ
The third free response question on the AP® Literature exam is more open-ended than the first two. AP® describes the FRQ as this: “An analysis that examines a specific concept, issue, or element in a work of literary merit selected by the student.” Essentially, you will respond to an open-ended prompt by selecting your own work of literary merit to analyze. Therefore, you must become familiar with a wide variety of texts that could help you answer the question. It’s important that you keep this particular essay question in mind as you work throughout the semester. Check out our Ultimate AP® English Literature Reading List!
7. Practice frequently using previous exams and consulting rubrics
As they say, practice really does make perfect. A good option for practicing free response questions involves searching the Internet for old exam rubrics. These show you exactly what the scorers are looking for in an essay. The AP® Literature section of AP® Central has several practice exams for your use. Take advantage of this and practice writing essays using different prompts from previous exams. We also offer practice exams filled with free response prompts that can help you develop your writing skills.
8. Use a good writing utensil

Nothing is worse than getting halfway through an essay and having your pen run out of ink, or your pencil getting smudged. Often, readers prefer the look and clarity of black ink to colored ink or the graphite of pencil. Take that into mind when going into the free response portion of the exam, and have a handful of backup writing utensils at hand when you take the test. The Ticonderoga pencil is a tried and tested stalwart, and we recommend it.
9. Pace yourself throughout the test
Before the free response portion begins, work out how much time you need to spend on each question. It may even be helpful to bring a watch to time yourself on each essay. Remember: there are three essay questions total: one literary analysis of a poem, one of a passage of prose fiction, and one analysis of a specific concept, issue, or element in a work of literary merit. You have a total of two hours, so we recommend that you spend 40 minutes per question. However, you also need to be sure that you are not rushing through the questions and leaving vital information out of your essays. Time yourself when you take practice exams, and go from there.
10. Write legibly
When facing the pressure of taking difficult tests, you might find yourself rushing through the essay questions because of time constraints. This often leads to messy handwriting that will give your scorer a headache. The clarity of your writing is necessary for a good score on your essay. If the reader cannot decipher your chicken scratch, how can they possibly score it? In order to perfect this skill before the exam, practice writing legibly under pressure during practice exams and other essays.
11. Don’t leave any question blank
Although this may be acceptable for the multiple-choice portion of the exam, it is absolutely inexcusable for your essays. You only get three chances to prove your competency in the free response portion, and the section at large counts for 55% of your overall score. Some might say that the FRQ section is the most important portion of the exam because of its weight. Write, write, and write even if you are totally stumped by the prompt. Take advantage of this opportunity to show the readers how much you’ve learned from taking this AP® course.
12. Understand what the AP® readers are looking for
As we said earlier, rubrics are a great resource to use when preparing for the AP® English Literature exam. They reflect exactly how your essay will be scored. It’s vital to understand exactly what the readers are looking for in a good essay. This includes:
a) Thesis: This requirement emphasizes the importance of crafting an effective thesis statement. Students must respond to the prompt with a thesis that presents a defensible interpretation of the poem.
b) Evidence and commentary: This section assesses your ability to cite and analyze textual evidence. It stresses that you provide specific evidence to support all claims in a line of reasoning, and consistently explain how the evidence supports that line of reasoning. Additionally, you must explain how multiple literary elements or techniques in the poem contribute to its meaning.
c) Sophistication: This component of the rubric is tough because sophistication is not something you can simply check off. Ultimately, the scorer wants your essay to demonstrate sophistication of thought and/or develops a complex literary argument.
13. Listen to your teacher
This is perhaps the most important of all the AP® Lit free response tips. Over the course of the semester, your teacher will provide you with ample advice for the exam. Pay close attention to your teacher’s guidance, and frequently meet with them to discuss your progress.
Seriously, meet with your teachers and continue asking how you can improve, what you’re doing well, what you’re not doing so well, etc. If the information your teacher gives you wasn’t relevant, they wouldn’t waste their time giving it to you. Your instructor knows the exam; it’s only logical to follow their advice.
In the event that you have a bad teacher, consult online resources like us, and perhaps begin formulating relationships with other teachers who are known to be excellent. Moreover, meet with students who excel in the course, and try to form study groups with them.
The AP® English Literature and Composition exam is all about analysis of different literary works. Hopefully, these tips will help you tackle this massive exam with ease.
Study Tips from AP® English Literature Teachers
We asked a number of AP® English Literature teachers to share their favorite AP® Lit tips and have compiled them here for you to review.
AP® English Literature Multiple Choice Tips:
1. Debate the questions
Get students to debate the answers to AP® multiple choice questions without your help. After they “quiz” on a passage and the questions for it, ask them how they think they did. The answer is always mixed, so give them an option: Keep the score they currently have OR discuss the answers in a large group without teacher’s help and take that community grade.
They always pick the latter. Participating in the discussion helps students practice justifying their answers (tell them you will keep track to make sure that everyone participates at least ___ time(s).) As you observe their process, you will gain all kinds of insight into students’ thinking process, they will learn from the ways their classmates explain their choices, and their scores are almost always 100! Thanks for the tip from Wendy R. from Weslaco East High School.
2. Brush up on your vocabulary
If you don’t understand the vocabulary used in the questions and/or answers, you will not be able to find the correct answer. There are many words with multiple meanings/nuances of meaning that will bring you to the wrong conclusion. Pay attention to the wording of the questions and answers! Thanks for the tip from Susan R. from Palm Beach Gardens High.
3. Consider Audience, Occasion & Purpose
Whether you’re speaking, reading or writing, you’re thinking: Audience, Occasion & Purpose. Who is the audience? What is the occasion? And what is the purpose of the author’s writing? Breaking down writing and literature into these three components can make the exam much easier and more digestible. Thanks for the tip from Mike L. at Tilton School.
AP® English Literature Free Response Tips:
1. Always remember to consider the author’s purpose
Retelling what happened in the story is not an analysis. You must understand and relay why the author wrote it the way he/she did and what he/she is trying to tell readers! That’s crucial! Thanks for the tip from Kim F. from Tavares High.
2. Strive for originality
Think about the fact that the AP® readers have been looking at essays on the same topics for three days. What will you do to be original and stand out that will surprise the reader at 4:30 pm on day three? Brainstorm what everyone else will say before writing. Then, don’t write on those topics. Originality will hook your reader. Thanks for the tip from Mike G. from MPS.
3. Don’t just summarize the author’s devices or techniques
Focused writing on two or three aspects of the text (characterization, use of devices, etc) accompanied with analysis will generate a higher score than lightly touching on five to ten aspects. As a reader, we are happy that you can identify techniques, but what we are looking for is analysis. And, we also know that analysis is tough to achieve. Think deep about the text. What was the author trying to say about the human condition with this scene, with that image? Thanks for the tip from Matt U. at Liberty High.
4. Always answer the question: “So what?”
Yes, the writer used an extended metaphor, so what? Why did they choose that metaphor? How does that choice reflect the author’s intent? What effect does it create within the text and within the reader? Provide the reader with the “so what” to help drive your analysis deeper. Thanks for the second tip from Matt U. at Liberty High.
5. Students who read widely and regularly are far more prepared to write and communicate clearly with a deeper understanding than students who do not read
Reading expands knowledge, vocabulary usage, and comprehension, and it enables students to make connections within and between content areas which have real-world applications. Reading widely across genres will broaden your perspective, too. Thanks for the tip from Elizabeth B. from Harrison High.
6. Use something you’ve read in AP® Lit for the third question
While you may be tempted to analyze a novel you’ve read on your own for the third FRQ, you should stick to what you’ve read in class. You will have spent more time and analytical energy on those books and plays than you did on your own.. Prepare for Question 3 before the exam by reviewing everything you’ve read in AP® English Literature. Thanks for the tip from Erin M. at Mercy County Senior High.
7. Turn your words into pictures and your pictures into words
Meaning: If you have an idea, anchor it to something concrete. If you have something concrete, associate it with an idea. Be able to move back and forth between the abstract and the literal. Most if not all deep literature involves this sort of mental navigation, so it’s best that you become familiar with it. Thanks for the tip from Jeff T. at Lynden Christian High School.
8. Never be unacceptably brief
Even if the selection is difficult or slim, there’ll be something in it that all students can latch onto and dissect. Sometimes, even the smallest moments in literature are actually the biggest through moments of metaphor, symbolism, and more. So if you find yourself writing 1-2 sentence paragraphs, return to the smaller moments and think BIG!Thanks for the third tip from Bill O. from El Molino High.
9. Do not merely skim to point out literary devices
Zoom deep into the text to identify the device, explain in detail how the device is functioning and then zoom out to explain how it works to support the passage as a whole and how it connects to the universal human condition. Focus on two primary ideas (literary devices, elements of composition, etc…) for each essay in order to go deeper in analysis of each. This means the difference between writing a college level paper and writing a high school level paper. Thanks for the tip from Jodi G. from Saugus High. Thanks for the tip from Erin M. at Mercy County Senior High.
10. Deconstruct the prompt
Make sure you understand exactly what the prompt is asking you to do. Then use it as a focus for your annotation of the text on Q1 and Q2 and as a launching point for your notes and thesis for Q3. Spend a lot of time marking up and breaking down the prompt before you attempt the essays. Look for key words, phrases, action verbs, etc. Thanks for the tip from Erin M. at Mercy County Senior High.
11. Find a good literary timeline to conceptualize what you read in terms of the art movement and historical time period
Since the AP® Literature Exam is a test over, well, literature, knowing the historical progression of literature is vital. This is where a literary timeline comes in handy. Check out this one on Pinterest for a general idea. These can provide insight into the texts as well as help you remember what you have read. Thanks for the tip from Paul H. at Walled Lake Central High.
Wrapping Things Up: The Ultimate List of AP® English Literature Tips
Scoring a 5 on the AP® English Literature exam is a difficult feat to accomplish. However, with proper preparation, some hard work, and consistent practice, you can ace the exam. Remember that the AP® English Literature and Composition exam is designed to test your ability to read critically and deeply analyze literature. The test is three hours long and consists of a multiple-choice portion (worth 45% of your grade) and a free response portion (worth 55% of your grade).
To adequately prepare, you must develop an effective study routine. Make flashcards of common literary concepts and terms using Quizlet. Take practice exams either through Albert , and be sure to time yourself each time you take one of the tests. Finally, cultivate a daily reading schedule which incorporates literature (fiction or poetry, preferably for this exam). This will familiarize you with the wide and complex world of literature and sharpen your literary skills. We also offer tons of practice on various novels and essential works that can be super helpful, too.
After taking a few practice exams, identify which section of the test you are better or worse at. Do you ace the multiple choice but flunk the free-response questions? Whichever it is, be sure to practice and develop your weaker skills. Focusing on the components of the test that you consistently ace—though it may be tempting—will make your score lopsided. Again, we must reiterate: practice, practice, practice.
Interested in a school license?
4 thoughts on “the ultimate list of ap® english literature tips”.
Ahhh….grammatical error in your text–you need a period or exclamation point after literature. (See below)
5. Read: This is a literature Therefore, you should be getting a good amount of
Thank you for catching that. We have fixed it!
These tips will be very helpful for me during this year of AP® Lit. I found tip 23 most important because I always take to much time on things like the intro that I don’t realize I’m wasting much of my time.
Thanks for sharing what you found most helpful, Antonio!
Comments are closed.
Popular Posts

AP® Score Calculators
Simulate how different MCQ and FRQ scores translate into AP® scores

AP® Review Guides
The ultimate review guides for AP® subjects to help you plan and structure your prep.

Core Subject Review Guides
Review the most important topics in Physics and Algebra 1 .

SAT® Score Calculator
See how scores on each section impacts your overall SAT® score

ACT® Score Calculator
See how scores on each section impacts your overall ACT® score

Grammar Review Hub
Comprehensive review of grammar skills

AP® Posters
Download updated posters summarizing the main topics and structure for each AP® exam.
AP English Literature & Composition
Ap english literature.
Use the menu above to get started with the best AP English Literature practice exams, free response questions, vocabulary quizzes, and study guides. There are some amazing free online resources available for your test prep and review.
AP English Literature & Composition Exam
The AP English Literature and Composition course focuses on both the reading of literature and writing about it. The reading assignments cover a variety of genres and time periods and students should engage in the critical analysis of each text. The writing focuses on the experience, evaluation, and interpretation of the literature.
The AP English Literature Exam format is:
Multiple-Choice Section -60 minutes -45% of final grade -55 multiple choice questions
Free-Response Section -120 minutes -55% of final grade -3 essay questions:
- Literary analysis of a given poem
- Literary analysis of a given passage of prose fiction
- Literary analysis that examines a specific concept, issue, or element in a literary work that you select
When is the AP English Literature Exam?
The AP English Literature and Composition Exam date for the 2022–2023 school year is Wednesday, May 3, 2023 at 8 a.m . The test is only offered once per year.
AP English Literature | Practice Exams | Free Response | Vocab | Study Guides
Guide to the AP® English Literature and Composition Exam
Why take ap ® english literature.
AP ® English Literature and Composition is a fantastic way to improve your skills in writing and analysis—not to mention give you college credit before you even set foot on campus.
It seems like a no-brainer, but you might still be wondering if taking the course is really worth it.
In most cases, taking an AP ® class is absolutely worth the effort. The skills you develop in an AP ® English Literature and Composition class are ones that you’ll carry with you throughout your entire educational (and professional) career. Think of all the literary references you’ll be able to make before you even get to college!
Throughout the AP ® English Literature and Composition course, students will be exposed to a wide variety of literary works; novels, plays, poems, prose, and short stories. This broad literary exposure is a great opportunity for you to develop an appreciation of the ways that literature reflects and comments on a range of experiences, institutions, and social structures. Most of the works you study will be selected at the discretion of your AP ® English Literature teacher. Throughout the course, you may study an entire play, work of fiction, or series of poetry, or you may focus on one or two excerpts from any given literary work. The compositions you study will all be written in, or translated into English, giving you the chance to experience an even greater range of literary works, authors, and styles from all over the world.
How to sign up for AP ® English Literature
To register for the AP ® Lit exam, you need to contact your school’s AP ® coordinator, who can help facilitate your courses and exams.
Bear in mind you’ll likely need to complete requirements to be eligible to enroll in an AP ® course. In order to register for the AP ® English Literature Exam, you have to join your class section online, on College Board’s My AP ® portal. Some schools will automatically register you for the exam if you’re enrolled in an AP ® English Literature class, but others won’t, and you will have to register online through the portal. If you are unsure whether or not you are registered for the AP ® English Literature Exam, check with your AP ® Coordinator.
There is also a deadline for exam registration, so make sure you register through your AP ® Coordinator by then to avoid paying any late fees. The deadline to register for exams is in the fall, but specific deadlines may vary by school—be sure to check with your teacher or AP ® Coordinator.
How much does the AP ® Exam cost?
Each AP ® Exam costs a total of $96—if you’re in the mainland United States and its territories and commonwealths, Canada, or a U.S. Department of Defense Dependents School.
If you’re outside of those areas, the AP ® Exam will cost $126 per exam.
The College Board has a financial aid program that offers a $34 fee reduction in the exam. Read more about exam fees here .
You cannot use the My AP ® portal to pay fees—they will be collected by your AP ® Coordinator.
When you take into account the cost of a college course versus the cost of the exam, though, you’ll see that the AP ® Exam is actually a bargain. With a passing score, you may be able to earn college credit and save hundreds or even thousands of dollars.
When can I take the AP ® English Literature Exam?
The AP ® English Literature and Composition date in 2022 is Wednesday, May 4th. You can find more information about dates and late-testing schedules for the 2022 AP ® English Literature Exam in our 2022 AP ® Exam Dates article.
What’s on the AP ® English Literature Exam and course?
A lot of colleges all over the U.S. require you to fulfill a writing course before you’re allowed to graduate. Students typically take this “expository writing” or “writing and composition” course during their freshman year of college. Taking the AP ® English Literature Exam could give you the opportunity to fulfill this requirement without taking a college writing course.
The AP ® English Literature course is comprehensive when it comes to English Literature, covering certain skill categories including your ability to:
- Explain the function of character
- Explain the function of setting
- Explain the function of plot and structure
- Explain the function of the narrator or speaker
- Explain the function of word choice, imagery, and symbols
- Explain the function of comparison
- Develop textually substantiated arguments about interpretations of part or all of a text
When it comes time to take the exam, you’ll have 3 hours and 15 minutes to complete it. There are two sections on the exam. The first consists of excerpts from non-fiction texts with multiple-choice questions. The second is a free-response section made up of three prompts you must answer in essay form.
Section I is a 55-question multiple-choice section which counts for 45% of your exam score. The multiple-choice section includes five sets of 8 to 13 questions per set, with each set of questions constructed around a preceding passage of prose fiction or poetry of varying difficulty. You should expect at least two prose fiction passages and at least two poetry passages in this section.
Section II of the AP ® English Literature Exam is the free-response section, and counts for 55% of your overall exam score. In this section, you will have two hours to answer three prompts as handwritten essays. Each of the free-response questions will address the following topics, always in the same order:
Question 1: Poetry Analysis
You will be presented with a passage of poetry of approximately 100 to 300 words, and given a prompt in connection with that passage. You are expected to demonstrate a well-written analysis of the passage by responding to the prompt with a thesis that presents your own interpretation, using appropriate evidence to develop and support your line of reasoning.
Question 2: Prose Fiction Analysis
You will be presented with a passage of prose fiction of approximately 500 to 700 words, and given a prompt in connection with that passage. You are expected to demonstrate a well-written analysis of the passage by responding to the prompt with a thesis that presents your own interpretation, using appropriate evidence to develop and support your line of reasoning.
Have a look at this YouTube playlist for an in-depth walkthrough of the Prose Fiction Analysis essay .
Question 3: Literary Argument
This is also called the thematic analysis. In this essay, you will write about a specific theme in reference to a work that you get to choose. We’ll say that again: the theme itself is given to you in the exam, but you can choose which work of fiction you want to write your essay about. For example, the exam might require you to discuss the topic of “unrequited love” and then suggest a list of different books and plays (around 40 different works) for you to analyze that theme. You can still choose a work from beyond that list, so you have a lot of control over this section.
What is the Test Format for the AP ® English Literature Exam?
Here’s what the structure of the exam looks like broken down by section and question type, along with how much each section impacts the ultimate score:
- 55 questions that cover excerpts from short fiction, poetry, and longer fiction or drama
- 45% of final exam score
- Three questions with prompts covering synthesis, rhetorical analysis, and argument
- Two hours and 15 minutes including a 15-minute reading time
- 55% of final exam score
How is the AP ® English Literature Exam Scored?
Each AP ® Exam is scored on a scale of one to five. The higher your score, the better it is for you.
Check out the table below for a breakdown of what each score means.
| AP Score | What it means |
| 5 | Best. The highest score you can get on your AP English Language Exam. This score typically guarantees college credit or placement out of a required course at colleges that accept AP Exams. |
| 4 | Excellent. While not the highest, this is still an incredibly good score. You’ll usually get college credit with it. |
| 3 | Very good. This is often called a “passing” score and is the usual threshold for colleges to give you credit, though not at the most competitive colleges. |
| 2 | Okay. Even though this is not a “passing” score, it can still reflect some significant improvement over the course of a year. |
| 1 | Not the best. We all have to start from somewhere! |
When it comes to AP ® English Literature and Composition, you’ll want to aim for a score of three or higher. Many colleges will give you college credit or placement out of a required course if you score within that range.
College credit for AP ® Exams varies from school to school though. So, if you want to know the score that a specific school will accept in exchange for credit, you’ll need to check with the school’s registrar’s office to find out information about AP ® credit for English Literature and Composition. Often, you can find this information on the school’s website. You can also check out the College Board’s search tool for AP ® credit policies.
NOTE: Colleges sometimes change their requirements for awarding college credit or offering placement out of required courses. Always check in with the college to make sure you have the most relevant and recent information.
The multiple-choice section is scored via computer. When the computer analyzes your answers, it does not deduct points if your answer is incorrect or unanswered. You read that right. You only stand to gain points when you answer questions. It is always in your best interest to answer every question and leave nothing blank.
The free-response section is a bit more complicated. Rather than using a computer, the free-response section is scored by actual humans. This occurs during an event called the AP ® Reading, an annual convention in June during which thousands of college professors and AP ® teachers nationwide convene to help judge and score AP ® essays.
The free-response essays are each scored on a scale of 0–6, with 6 being the best score you can get and 0 being the worst.
Combined, the raw points you get from both sections give you your composite score. It’s your composite score that determines your scaled score of 1–5.
Bottom line: Graders are looking for essays that showcase a strong command of literary texts, the ability to craft compelling and well-sourced arguments, and the ability to analyze text for its rhetorical structure.
What’s the Difference Between AP ® English Literature and AP ® English Language?
Ok, so there’s an AP ® English Literature and Composition Exam and an AP ® English Language and Composition Exam. What’s the difference between the two, and how do you know which one to take?
While the two share a lot of similarities, there are some crucial differences between the two courses. Knowing which one you want to take will determine the knowledge you’ll gain before going to college. In turn, this can help you decide:
- Whether you prefer fiction or nonfiction writing
- Which classes you take in college
- Your skills as a reader and writer
Here is a brief overview of both courses:
The AP ® English Literature and Composition course teaches the basics of college-level literary analysis and close reading. You will dive deep into texts and be challenged to think about literature deeply and critically. In the course, you will learn topics such as:
- Close reading
- Textual analysis
- Literary devices
- Language and vocabulary
- Stylistic maturity in writing
- Written organizational skills
In the AP ® English Language and Composition course, you will learn the rhetorical and writing skills necessary to interpret ALL kinds of texts.
The AP ® English Language exam course is comprehensive when it comes to rhetoric and writing, covering topics such as:
- Rhetorical analysis of prose
- Reading comprehension
- Written argumentation
- MLA, APA, and Chicago-style citation
- Reputable sourcing
- Synthesis of information from multiple texts
The AP ® English Literature course will give you an understanding and appreciation for reading and analyzing literature. This skill is important in order to understand the context of the world around you. The course will give you the tools to approach topics thoughtfully and deeply.
For a more in-depth look at the differences between the AP ® Lit and AP ® Lang courses, check out this article: AP ® English Literature vs AP ® English Language.
What Can I Bring to My AP ® English Literature Exam?
Below is a list of all the things you can bring with you into the exam room. Note: It’s possible that not all of the items will apply to you (e.g., the Student Accommodations Letter).
- Two No. 2 pencils with erasers. These will be used on the multiple-choice portion of the exam.
- Two black or dark blue ink pens. These will be used for the free-response questions. Be sure to bring black or dark blue ink pens only. Leave your turquoise gel pens at home.
- A watch. This is a simple analog or digital watch with no internet access or alarms. Don’t even try to bring your smartwatch in the room.
- The AP ® Student Pack. This is given to you just before you take your exam and contains a label that you need to place on your exam. Follow the labeling instructions carefully.
- Government- or school-issued ID. If you don’t attend the school where you’re taking the AP ® English Literature Exam, you must also bring a government- or school-issued ID.
- College Board SSD Student Accommodation Letter. If you require accommodations beyond the regular exam, you’ll receive a letter that verifies this (e.g. you need extra time or a large-type exam).
- Remember, you won’t have to bring all these things—but it’s in your best interest to be as prepared as you can for the exam.
Take a look at our Test Day Checklist to make sure you are 100% prepared to take your AP ® English Literature and Composition Exam when the time comes!
How do I study for AP ® English Literature?
#1: Read, read, read!
But try to read with PURPOSE! The more time you spend devouring all kinds of literature and reflecting on what you’re reading, the better! This is a great way to prepare for the Poetry and Prose Fiction Analysis Essays in the free-response section of your AP ® Lit exam. Both of these questions will require you to make astute analyses of whatever texts you are given.
Don’t let yourself get caught off guard with a passage you are unfamiliar with; make sure your literary intake is broad enough that you feel just as comfortable analyzing a sonnet as a play. To answer the questions well, you should be able to read and annotate the given passages speedily. Where you can, try to practice annotating whatever you’re reading in the lead up to the AP ® English Literature Exam. This will be immensely helpful for formulating your answers!
#2: Take practice tests
Take some advice from the Boy Scouts and ‘Be Prepared’! You don’t want to take your first AP ® English Literature Exam on test day. To that end, take as many practice tests as you can before the big day. Take note of the areas you performed the weakest in and dedicate extra study time to those areas. Only by practicing over and over again can you expect to be better at any skill—including test-taking. If you don’t have much experience taking practice tests, check out John Moscatiello’s Step-by-Step Guide to taking a practice test like a pro .
#3: Write as much as you can
A lot of students tend to worry most about the free-response sections. With enough practice, these will get easier and easier to answer! For more tips, Marco Learning’s AP ® Literature teacher, Heather Garcia, has some excellent advice on How to Crush It on the AP ® English Literature Exam Essays .
#4: Find resources that work
When it comes to studying for your exam, there is no “one size fits all”. Just because your older brother studied best by comparing and contrasting Shakespearean sonnets, doesn’t mean that’s right for you. (It probably isn’t too effective for most people, to be honest!) We encourage you to take some time to figure out what study methods you are most comfortable with; it could be a mixture of everything!
We know it can be overwhelming starting from scratch. If you feel stuck, we suggest downloading our free AP ® English Literature study guide as a jumping-off point and going from there.
If you’re looking for live video reviews before the AP ® Exams, Marco Learning hosts live AP ® review sessions on our YouTube channel .

Please read Marco Learning’s Terms and Conditions, click to agree, and submit to continue to your content.
Please read Marco Learning’s Terms and Conditions, click to agree, and submit at the bottom of the window.
MARCO LEARNING TERMS OF USE
Last Modified: 1/24/2023
Acceptance of the Terms of Use
These terms of use are entered into by and between You and Marco Learning LLC (“ Company “, “ we “, or “ us “). The following terms and conditions (these “ Terms of Use “), govern your access to and use of Marco Learning , including any content, functionality, and services offered on or through Marco Learning (the “ Website “), whether as a guest or a registered user.
Please read the Terms of Use carefully before you start to use the Website. By using the Website or by clicking to accept or agree to the Terms of Use when this option is made available to you, you accept and agree to be bound and abide by these Terms of Use. You may not order or obtain products or services from this website if you (i) do not agree to these Terms of Use, or (ii) are prohibited from accessing or using this Website or any of this Website’s contents, goods or services by applicable law . If you do not want to agree to these Terms of Use, you must not access or use the Website.
This Website is offered and available to users who are 13 years of age or older, and reside in the United States or any of its territories or possessions. Any user under the age of 18 must (a) review the Terms of Use with a parent or legal guardian to ensure the parent or legal guardian acknowledges and agrees to these Terms of Use, and (b) not access the Website if his or her parent or legal guardian does not agree to these Terms of Use. By using this Website, you represent and warrant that you meet all of the foregoing eligibility requirements. If you do not meet all of these requirements, you must not access or use the Website.
Changes to the Terms of Use
We may revise and update these Terms of Use from time to time in our sole discretion. All changes are effective immediately when we post them, and apply to all access to and use of the Website thereafter.
These Terms of Use are an integral part of the Website Terms of Use that apply generally to the use of our Website. Your continued use of the Website following the posting of revised Terms of Use means that you accept and agree to the changes. You are expected to check this page each time you access this Website so you are aware of any changes, as they are binding on you.
Accessing the Website and Account Security
We reserve the right to withdraw or amend this Website, and any service or material we provide on the Website, in our sole discretion without notice. We will not be liable if for any reason all or any part of the Website is unavailable at any time or for any period. From time to time, we may restrict access to some parts of the Website, or the entire Website, to users, including registered users.
You are responsible for (i) making all arrangements necessary for you to have access to the Website, and (ii) ensuring that all persons who access the Website through your internet connection are aware of these Terms of Use and comply with them.
To access the Website or some of the resources it offers, you may be asked to provide certain registration details or other information. It is a condition of your use of the Website that all the information you provide on the Website is correct, current, and complete. You agree that all information you provide to register with this Website or otherwise, including but not limited to through the use of any interactive features on the Website, is governed by our Marco Learning Privacy Policy , and you consent to all actions we take with respect to your information consistent with our Privacy Policy.
If you choose, or are provided with, a user name, password, or any other piece of information as part of our security procedures, you must treat such information as confidential, and you must not disclose it to any other person or entity. You also acknowledge that your account is personal to you and agree not to provide any other person with access to this Website or portions of it using your user name, password, or other security information. You agree to notify us immediately of any unauthorized access to or use of your user name or password or any other breach of security. You also agree to ensure that you exit from your account at the end of each session. You should use particular caution when accessing your account from a public or shared computer so that others are not able to view or record your password or other personal information.
We have the right to disable any user name, password, or other identifier, whether chosen by you or provided by us, at any time in our sole discretion for any or no reason, including if, in our opinion, you have violated any provision of these Terms of Use.
Intellectual Property Rights
The Website and its entire contents, features, and functionality (including but not limited to all information, software, text, displays, images, graphics, video, other visuals, and audio, and the design, selection, and arrangement thereof) are owned by the Company, its licensors, or other providers of such material and are protected by United States and international copyright, trademark, patent, trade secret, and other intellectual property or proprietary rights laws. Your use of the Website does not grant to you ownership of any content, software, code, date or materials you may access on the Website.
These Terms of Use permit you to use the Website for your personal, non-commercial use only. You must not reproduce, distribute, modify, create derivative works of, publicly display, publicly perform, republish, download, store, or transmit any of the material on our Website, except as follows:
- Your computer may temporarily store copies of such materials in RAM incidental to your accessing and viewing those materials.
- You may store files that are automatically cached by your Web browser for display enhancement purposes.
- You may print or download one copy of a reasonable number of pages of the Website for your own personal, non-commercial use and not for further reproduction, publication, or distribution.
- If we provide desktop, mobile, or other applications for download, you may download a single copy to your computer or mobile device solely for your own personal, non-commercial use, provided you agree to be bound by our end user license agreement for such applications.
- If we provide social media features with certain content, you may take such actions as are enabled by such features.
You must not:
- Modify copies of any materials from this site.
- Use any illustrations, photographs, video or audio sequences, or any graphics separately from the accompanying text.
- Delete or alter any copyright, trademark, or other proprietary rights notices from copies of materials from this site.
You must not access or use for any commercial purposes any part of the Website or any services or materials available through the Website.
If you wish to make any use of material on the Website other than that set out in this section, please contact us
If you print, copy, modify, download, or otherwise use or provide any other person with access to any part of the Website in breach of the Terms of Use, your right to use the Website will stop immediately and you must, at our option, return or destroy any copies of the materials you have made. No right, title, or interest in or to the Website or any content on the Website is transferred to you, and all rights not expressly granted are reserved by the Company. Any use of the Website not expressly permitted by these Terms of Use is a breach of these Terms of Use and may violate copyright, trademark, and other laws.
Trademarks, logos, service marks, trade names, and all related names, logos, product and service names, designs, and slogans are trademarks of the Company or its affiliates or licensors (collectively, the “ Trademarks ”). You must not use such Trademarks without the prior written permission of the Company. All other names, logos, product and service names, designs, and slogans on this Website are the trademarks of their respective owners.
Prohibited Uses
You may use the Website only for lawful purposes and in accordance with these Terms of Use. You agree not to use the Website:
- In any way that violates any applicable federal, state, local, or international law or regulation (including, without limitation, any laws regarding the export of data or software to and from the US or other countries).
- For the purpose of exploiting, harming, or attempting to exploit or harm minors in any way by exposing them to inappropriate content, asking for personally identifiable information, or otherwise.
- To send, knowingly receive, upload, download, use, or re-use any material that does not comply with the Content Standards set out in these Terms of Use.
- To transmit, or procure the sending of, any advertising or promotional material, including any “junk mail”, “chain letter”, “spam”, or any other similar solicitation.
- To impersonate or attempt to impersonate the Company, a Company employee, another user, or any other person or entity (including, without limitation, by using email addresses or screen names associated with any of the foregoing).
- To engage in any other conduct that restricts or inhibits anyone’s use or enjoyment of the Website, or which, as determined by us, may harm the Company or users of the Website or expose them to liability.
Additionally, you agree not to:
- Use the Website in any manner that could disable, overburden, damage, or impair the site or interfere with any other party’s use of the Website, including their ability to engage in real time activities through the Website.
- Use any robot, spider, or other automatic device, process, or means to access the Website for any purpose, including monitoring or copying any of the material on the Website.
- Use any manual process to monitor or copy any of the material on the Website or for any other unauthorized purpose without our prior written consent.
- Use any device, software, or routine that interferes with the proper working of the Website.
- Introduce any viruses, Trojan horses, worms, logic bombs, or other material that is malicious or technologically harmful.
- Attempt to gain unauthorized access to, interfere with, damage, or disrupt any parts of the Website, the server on which the Website is stored, or any server, computer, or database connected to the Website.
- Attack the Website via a denial-of-service attack or a distributed denial-of-service attack.
- Otherwise attempt to interfere with the proper working of the Website.
If you use, or assist another person in using the Website in any unauthorized way, you agree that you will pay us an additional $50 per hour for any time we spend to investigate and correct such use, plus any third party costs of investigation we incur (with a minimum $300 charge). You agree that we may charge any credit card number provided for your account for such amounts. You further agree that you will not dispute such a charge and that we retain the right to collect any additional actual costs.
User Contributions
The Website may contain message boards, chat rooms, personal web pages or profiles, forums, bulletin boards, and other interactive features (collectively, “ Interactive Services “) that allow users to post, submit, publish, display, or transmit to other users or other persons (hereinafter, “ post “) content or materials (collectively, “ User Contributions “) on or through the Website.
All User Contributions must comply with the Content Standards set out in these Terms of Use.
Any User Contribution you post to the site will be considered non-confidential and non-proprietary. By providing any User Contribution on the Website, you grant us and our affiliates and service providers, and each of their and our respective licensees, successors, and assigns the right to use, reproduce, modify, perform, display, distribute, and otherwise disclose to third parties any such material for any purpose.
You represent and warrant that:
- You own or control all rights in and to the User Contributions and have the right to grant the license granted above to us and our affiliates and service providers, and each of their and our respective licensees, successors, and assigns.
- All of your User Contributions do and will comply with these Terms of Use.
You understand and acknowledge that you are responsible for any User Contributions you submit or contribute, and you, not the Company, have full responsibility for such content, including its legality, reliability, accuracy, and appropriateness.
For any academic source materials such as textbooks and workbooks which you submit to us in connection with our online tutoring services, you represent and warrant that you are entitled to upload such materials under the “fair use” doctrine of copyright law. In addition, if you request that our system display a representation of a page or problem from a textbook or workbook, you represent and warrant that you are in proper legal possession of such textbook or workbook and that your instruction to our system to display a page or problem from your textbook or workbook is made for the sole purpose of facilitating your tutoring session, as “fair use” under copyright law.
You agree that we may record all or any part of any live online classes and tutoring sessions (including voice chat communications) for quality control and other purposes. You agree that we own all transcripts and recordings of such sessions and that these Terms of Use will be deemed an irrevocable assignment of rights in all such transcripts and recordings to us.
We are not responsible or liable to any third party for the content or accuracy of any User Contributions posted by you or any other user of the Website.
Monitoring and Enforcement: Termination
We have the right to:
- Remove or refuse to post any User Contributions for any or no reason in our sole discretion.
- Take any action with respect to any User Contribution that we deem necessary or appropriate in our sole discretion, including if we believe that such User Contribution violates the Terms of Use, including the Content Standards, infringes any intellectual property right or other right of any person or entity, threatens the personal safety of users of the Website or the public, or could create liability for the Company.
- Disclose your identity or other information about you to any third party who claims that material posted by you violates their rights, including their intellectual property rights or their right to privacy.
- Take appropriate legal action, including without limitation, referral to law enforcement, for any illegal or unauthorized use of the Website.
- Terminate or suspend your access to all or part of the Website for any or no reason, including without limitation, any violation of these Terms of Use.
Without limiting the foregoing, we have the right to cooperate fully with any law enforcement authorities or court order requesting or directing us to disclose the identity or other information of anyone posting any materials on or through the Website. YOU WAIVE AND HOLD HARMLESS THE COMPANY AND ITS AFFILIATES, LICENSEES, AND SERVICE PROVIDERS FROM ANY CLAIMS RESULTING FROM ANY ACTION TAKEN BY ANY OF THE FOREGOING PARTIES DURING, OR TAKEN AS A CONSEQUENCE OF, INVESTIGATIONS BY EITHER SUCH PARTIES OR LAW ENFORCEMENT AUTHORITIES.
However, we do not undertake to review material before it is posted on the Website, and cannot ensure prompt removal of objectionable material after it has been posted. Accordingly, we assume no liability for any action or inaction regarding transmissions, communications, or content provided by any user or third party. We have no liability or responsibility to anyone for performance or nonperformance of the activities described in this section.
Content Standards
These content standards apply to any and all User Contributions and use of Interactive Services. User Contributions must in their entirety comply with all applicable federal, state, local, and international laws and regulations. Without limiting the foregoing, User Contributions must not:
- Contain any material that is defamatory, obscene, indecent, abusive, offensive, harassing, violent, hateful, inflammatory, or otherwise objectionable.
- Promote sexually explicit or pornographic material, violence, or discrimination based on race, sex, religion, nationality, disability, sexual orientation, or age.
- Infringe any patent, trademark, trade secret, copyright, or other intellectual property or other rights of any other person.
- Violate the legal rights (including the rights of publicity and privacy) of others or contain any material that could give rise to any civil or criminal liability under applicable laws or regulations or that otherwise may be in conflict with these Terms of Use and our Privacy Policy .
- Be likely to deceive any person.
- Promote any illegal activity, or advocate, promote, or assist any unlawful act.
- Cause annoyance, inconvenience, or needless anxiety or be likely to upset, embarrass, alarm, or annoy any other person.
- Impersonate any person, or misrepresent your identity or affiliation with any person or organization.
- Involve commercial activities or sales, such as contests, sweepstakes, and other sales promotions, barter, or advertising.
- Give the impression that they emanate from or are endorsed by us or any other person or entity, if this is not the case.
(collectively, the “ Content Standards ”)
Copyright Infringement
If you believe that any User Contributions violate your copyright, please contact us and provide the following information:
- An electronic or physical signature of the person authorized to act on behalf of the owner of the copyright interest;
- A description of the copyrighted work that you claim has been infringed;
- A description of where the material you claim is infringing is located on the website (and such description must reasonably sufficient to enable us to find the alleged infringing material);
- Your address, telephone number and email address;
- A written statement by you that you have a good faith belief that the disputed use is not authorized by the copyright owner, its agent, or the law; and
- A statement by you, made under the penalty of perjury, that the above information in your notice is accurate and that you are the copyright owner or authorized to act on the copyright owner’s behalf.
We may terminate the accounts of any infringers.
Reliance on Information Posted
From time to time, we may make third party opinions, advice, statements, offers, or other third party information or content available on the Website or from tutors under tutoring services (collectively, “Third Party Content”). All Third Party Content is the responsibility of the respective authors thereof and should not necessarily be relied upon. Such third party authors are solely responsible for such content. WE DO NOT (I) GUARANTEE THE ACCURACY, COMPLETENESS OR USEFULNESS OF ANY THIRD PARTY CONTENT ON THE SITE OR ANY VERIFICATION SERVICES DONE ON OUR TUTORS OR INSTRUCTORS, OR (II) ADOPT, ENDORSE OR ACCEPT RESPONSIBILITY FOR THE ACCURACY OR RELIABILITY OF ANY OPINION, ADVICE, OR STATEMENT MADE BY ANY TUTOR OR INSTRUCTOR OR ANY PARTY THAT APPEARS ON THE WEBSITE. UNDER NO CIRCUMSTANCES WILL WE BE RESPONSBILE OR LIABLE FOR ANY LOSS OR DAMAGE RESULTING FROM YOUR RELIANCE ON INFORMATION OR OTHER CONENT POSTED ON OR AVAILBLE FROM THE WEBSITE.
Changes to the Website
We may update the content on this Website from time to time, but its content is not necessarily complete or up-to-date. Any of the material on the Website may be out of date at any given time, and we are under no obligation to update such material.
Information About You and Your Visits to the Website
All information we collect on this Website is subject to our Privacy Policy . By using the Website, you consent to all actions taken by us with respect to your information in compliance with the Privacy Policy.
Online Purchases and Other Terms and Conditions
All purchases through our site or other transactions for the sale of services and information formed through the Website or resulting from visits made by you are governed by our Terms of Sale, which are hereby incorporated into these Terms of Use.
Additional terms and conditions may also apply to specific portions, services, or features of the Website. All such additional terms and conditions are hereby incorporated by this reference into these Terms of Use.
Linking to the Website and Social Media Features
You may link to our homepage, provided you do so in a way that is fair and legal and does not damage our reputation or take advantage of it, but you must not establish a link in such a way as to suggest any form of association, approval, or endorsement on our part without our express written consent.
This Website may provide certain social media features that enable you to:
- Link from your own or certain third-party websites to certain content on this Website.
- Send emails or other communications with certain content, or links to certain content, on this Website.
- Cause limited portions of content on this Website to be displayed or appear to be displayed on your own or certain third-party websites.
You may use these features solely as they are provided by us, and solely with respect to the content they are displayed with and otherwise in accordance with any additional terms and conditions we provide with respect to such features. Subject to the foregoing, you must not:
- Establish a link from any website that is not owned by you.
- Cause the Website or portions of it to be displayed on, or appear to be displayed by, any other site, for example, framing, deep linking, or in-line linking.
- Link to any part of the Website other than the homepage.
- Otherwise take any action with respect to the materials on this Website that is inconsistent with any other provision of these Terms of Use.
The website from which you are linking, or on which you make certain content accessible, must comply in all respects with the Content Standards set out in these Terms of Use.
You agree to cooperate with us in causing any unauthorized framing or linking immediately to stop. We reserve the right to withdraw linking permission without notice.
We may disable all or any social media features and any links at any time without notice in our discretion.
Links from the Website
If the Website contains links to other sites and resources provided by third parties (“ Linked Sites ”), these links are provided for your convenience only. This includes links contained in advertisements, including banner advertisements and sponsored links. You acknowledge and agree that we have no control over the contents, products, services, advertising or other materials which may be provided by or through those Linked sites or resources, and accept no responsibility for them or for any loss or damage that may arise from your use of them. If you decide to access any of the third-party websites linked to this Website, you do so entirely at your own risk and subject to the terms and conditions of use for such websites.
You agree that if you include a link from any other website to the Website, such link will open in a new browser window and will link to the full version of an HTML formatted page of this Website. You are not permitted to link directly to any image hosted on the Website or our products or services, such as using an “in-line” linking method to cause the image hosted by us to be displayed on another website. You agree not to download or use images hosted on this Website or another website, for any purpose, including, without limitation, posting such images on another website. You agree not to link from any other website to this Website in any manner such that the Website, or any page of the Website, is “framed,” surrounded or obfuscated by any third party content, materials or branding. We reserve all of our rights under the law to insist that any link to the Website be discontinued, and to revoke your right to link to the Website from any other website at any time upon written notice to you.
Geographic Restrictions
The owner of the Website is based in the state of New Jersey in the United States. We provide this Website for use only by persons located in the United States. We make no claims that the Website or any of its content is accessible or appropriate outside of the United States. Access to the Website may not be legal by certain persons or in certain countries. If you access the Website from outside the United States, you do so on your own initiative and are responsible for compliance with local laws.
Disclaimer of Warranties
You understand that we cannot and do not guarantee or warrant that files available for downloading from the internet or the Website will be free of viruses or other destructive code. You are responsible for implementing sufficient procedures and checkpoints to satisfy your particular requirements for anti-virus protection and accuracy of data input and output, and for maintaining a means external to our site for any reconstruction of any lost data. TO THE FULLEST EXTENT PROVIDED BY LAW, WE WILL NOT BE LIABLE FOR ANY LOSS OR DAMAGE CAUSED BY A DISTRIBUTED DENIAL-OF-SERVICE ATTACK, VIRUSES, OR OTHER TECHNOLOGICALLY HARMFUL MATERIAL THAT MAY INFECT YOUR COMPUTER EQUIPMENT, COMPUTER PROGRAMS, DATA, OR OTHER PROPRIETARY MATERIAL DUE TO YOUR USE OF THE WEBSITE OR ANY SERVICES OR ITEMS OBTAINED THROUGH THE WEBSITE OR TO YOUR DOWNLOADING OF ANY MATERIAL POSTED ON IT, OR ON ANY WEBSITE LINKED TO IT.
YOUR USE OF THE WEBSITE, ITS CONTENT, AND ANY SERVICES OR ITEMS OBTAINED THROUGH THE WEBSITE IS AT YOUR OWN RISK. THE WEBSITE, ITS CONTENT, AND ANY SERVICES OR ITEMS OBTAINED THROUGH THE WEBSITE ARE PROVIDED ON AN “AS IS” AND “AS AVAILABLE” BASIS, WITHOUT ANY WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. NEITHER THE COMPANY NOR ANY PERSON ASSOCIATED WITH THE COMPANY MAKES ANY WARRANTY OR REPRESENTATION WITH RESPECT TO THE COMPLETENESS, SECURITY, RELIABILITY, QUALITY, ACCURACY, OR AVAILABILITY OF THE WEBSITE. WITHOUT LIMITING THE FOREGOING, NEITHER THE COMPANY NOR ANYONE ASSOCIATED WITH THE COMPANY REPRESENTS OR WARRANTS THAT THE WEBSITE, ITS CONTENT, OR ANY SERVICES OR ITEMS OBTAINED THROUGH THE WEBSITE WILL BE ACCURATE, RELIABLE, ERROR-FREE, OR UNINTERRUPTED, THAT DEFECTS WILL BE CORRECTED, THAT OUR SITE OR THE SERVER THAT MAKES IT AVAILABLE ARE FREE OF VIRUSES OR OTHER HARMFUL COMPONENTS, OR THAT THE WEBSITE OR ANY SERVICES OR ITEMS OBTAINED THROUGH THE WEBSITE WILL OTHERWISE MEET YOUR NEEDS OR EXPECTATIONS.
TO THE FULLEST EXTENT PROVIDED BY LAW, THE COMPANY HEREBY DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, WHETHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, STATUTORY, OR OTHERWISE, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ANY WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, NON-INFRINGEMENT, AND FITNESS FOR PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
THE FOREGOING DOES NOT AFFECT ANY WARRANTIES THAT CANNOT BE EXCLUDED OR LIMITED UNDER APPLICABLE LAW.
Limitation on Liability
TO THE FULLEST EXTENT PROVIDED BY LAW, IN NO EVENT WILL THE COMPANY, ITS AFFILIATES, OR THEIR LICENSORS, SERVICE PROVIDERS, EMPLOYEES, AGENTS, OFFICERS, OR DIRECTORS BE LIABLE FOR DAMAGES OF ANY KIND, UNDER ANY LEGAL THEORY, ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH YOUR USE, OR INABILITY TO USE, THE WEBSITE, ANY WEBSITES LINKED TO IT, ANY CONTENT ON THE WEBSITE OR SUCH OTHER WEBSITES, INCLUDING ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR PUNITIVE DAMAGES, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PERSONAL INJURY, PAIN AND SUFFERING, EMOTIONAL DISTRESS, LOSS OF REVENUE, LOSS OF PROFITS, LOSS OF BUSINESS OR ANTICIPATED SAVINGS, LOSS OF USE, LOSS OF GOODWILL, LOSS OF DATA, AND WHETHER CAUSED BY TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE), BREACH OF CONTRACT, OR OTHERWISE, EVEN IF FORESEEABLE.
THE FOREGOING DOES NOT AFFECT ANY LIABILITY THAT CANNOT BE EXCLUDED OR LIMITED UNDER APPLICABLE LAW.
Indemnification
You agree to defend, indemnify, and hold harmless the Company, its affiliates, licensors, and service providers, and its and their respective officers, directors, employees, contractors, agents, licensors, suppliers, successors, and assigns from and against any claims, liabilities, damages, judgments, awards, losses, costs, expenses, or fees (including reasonable attorneys’ fees) arising out of or relating to your violation of these Terms of Use or your use of the Website, including, but not limited to, your User Contributions, any use of the Website’s content, services, and products other than as expressly authorized in these Terms of Use or your use of any information obtained from the Website.
Governing Law and Jurisdiction
All matters relating to the Website and these Terms of Use and any dispute or claim arising therefrom or related thereto (in each case, including non-contractual disputes or claims), shall be governed by and construed in accordance with the internal laws of the State of New Jersey without giving effect to any choice or conflict of law provision or rule (whether of the State of New Jersey or any other jurisdiction).
Any legal suit, action, or proceeding arising out of, or related to, these Terms of Use or the Website shall be instituted exclusively in the federal courts of the United States or the courts of the State of New Jersey in each case located in the County of Monmouth although we retain the right to bring any suit, action, or proceeding against you for breach of these Terms of Use in your country of residence or any other relevant country. You waive any and all objections to the exercise of jurisdiction over you by such courts and to venue in such courts. You may not under any circumstances commence or maintain against us any class action, class arbitration, or other representative action or proceeding.
Arbitration
By using this Website, you agree, at Company’s sole discretion, that it may require you to submit any disputes arising from the use of these Terms of Use or the Website, including disputes arising from or concerning their interpretation, violation, invalidity, non-performance, or termination, to final and binding arbitration under the Rules of Arbitration of the American Arbitration Association applying New Jersey law. In doing so, YOU GIVE UP YOUR RIGHT TO GO TO COURT to assert or defend any claims between you and us. YOU ALSO GIVE UP YOUR RIGHT TO PARTICIPATE IN A CLASS ACTION OR OTHER CLASS PROCEEDING. Your rights may be determined by a NEUTRAL ARBITRATOR, NOT A JUDGE OR JURY. You are entitled to a fair hearing before the arbitrator. The arbitrator can grant any relief that a court can, but you should note that arbitration proceedings are usually simpler and more streamlined than trials and other judicial proceedings. Decisions by the arbitrator are enforceable in court and may be overturned by a court only for very limited reasons.
Any proceeding to enforce this arbitration provision, including any proceeding to confirm, modify, or vacate an arbitration award, may be commenced in any court of competent jurisdiction. In the event that this arbitration provision is for any reason held to be unenforceable, any litigation against Company must be commenced only in the federal or state courts located in Monmouth County, New Jersey. You hereby irrevocably consent to the jurisdiction of those courts for such purposes.
Limitation on Time to File Claims
ANY CAUSE OF ACTION OR CLAIM YOU MAY HAVE ARISING OUT OF OR RELATING TO THESE TERMS OF USE OR THE WEBSITE MUST BE COMMENCED WITHIN ONE (1) YEAR AFTER THE CAUSE OF ACTION ACCRUES, OTHERWISE, SUCH CAUSE OF ACTION OR CLAIM IS PERMANENTLY BARRED.
Waiver and Severability
No waiver by the Company of any term or condition set out in these Terms of Use shall be deemed a further or continuing waiver of such term or condition or a waiver of any other term or condition, and any failure of the Company to assert a right or provision under these Terms of Use shall not constitute a waiver of such right or provision.
If any provision of these Terms of Use is held by a court or other tribunal of competent jurisdiction to be invalid, illegal, or unenforceable for any reason, such provision shall be eliminated or limited to the minimum extent such that the remaining provisions of the Terms of Use will continue in full force and effect.
Entire Agreement
The Terms of Use, our Privacy Policy, and Terms of Sale constitute the sole and entire agreement between you and Marco Learning LLC regarding the Website and supersede all prior and contemporaneous understandings, agreements, representations, and warranties, both written and oral, regarding the Website.
Communications and Miscellaneous
If you provide us your email address, you agree and consent to receive email messages from us. These emails may be transaction or relationship communications relating to the products or services we offer, such as administrative notices and service announcements or changes, or emails containing commercial offers, promotions or special offers from us.
Your Comments and Concerns
This website is operated by Marco Learning LLC, a New Jersey limited liability company with an address of 113 Monmouth Road, Suite 1, Wrightstown, New Jersey 08562.
Please contact us for all other feedback, comments, requests for technical support, and other communications relating to the Website.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Download free-response questions from this year's exam and past exams along with scoring guidelines, sample responses from exam takers, and scoring distributions. If you are using assistive technology and need help accessing these PDFs in another format, contact Services for Students with Disabilities at 212-713-8333 or by email at ssd@info ...
The AP English Literature and Composition Exam has consistent question types, weighting, and scoring guidelines every year, so you and your students know what to expect on exam day. There will also be a consistent range of difficulty in the reading passages across all versions of the exam from year to year. The free-response questions will be ...
The AP Literature Exam is a three-hour exam that contains two sections in this order: An hour-long, 55-question multiple-choice section. A two-hour, three-question free-response section. The exam tests your ability to analyze works and excerpts of literature and cogently communicate that analysis in essay form.
The AP Lit Exam will ask you to write an essay with an essay with a clear, defensible thesis statement that makes an argument about the story, based on some literary elements in the short story. After reading the passage, you might talk about how foreshadowing, allusion, and dialogue work together to demonstrate something essential in the text. ...
The AP Lit prose essay is the second of the three essays included in the free-response section of the AP Lit exam, lasting around 40 minutes in total. A prose passage of approximately 500 to 700 words and a prompt will be given to guide your analytical essay. Worth about 18% of your total grade, the essay will be graded out of six points ...
Starting in the 2024-25 school year, AP English Literature and Composition multiple-choice questions (MCQs) will have four answer choices instead of five. This change will take effect with the 2025 exam. All resources have been updated to reflect this change. Exam Duration.
Course Skills. The AP English Literature and Composition framework included in the course and exam description outlines distinct skills that students should practice throughout the year—skills that will help them learn to read texts critically. Skill Categories. Exam Weighting (Multiple- Choice Section) Explain the function of character. 16% ...
Consider the new analytic rubric a How-To Guide, designed to earn you a 6 on each essay. And, unlike the AP® Lang exam, all three AP® Lit essays are graded essentially through the same rubric. Below, we'll spend some time breaking down the elements of the new rubric. First, let's take a look at the Thesis row. Row A: Thesis (0-1 Points)
Starting in the 2024-25 school year, AP English Literature and Composition multiple-choice questions (MCQs) will have four answer choices instead of five. This change will take effect with the 2025 exam. All resources have been updated to reflect this change.
3. Review literary terms and techniques commonly used in literature. 4. Develop strong essay writing skills by structuring your responses with clear introductions, well-supported arguments, and insightful analysis. 5. Manage your time effectively during the exam to allocate enough time for each question. 6.
This is the best AP Lit practice test available. It's the most recent exam released by the College Board, and it follows the format of the current test with 55 multiple-choice questions and three free-response questions. Definitely make use of this test! 1999 AP English Literature and Composition Exam. This test excludes the poetry and prose ...
The first section of the AP Literature exam is one hour long and consists of 45 multiple-choice questions—23-25 Reading questions and 20-22 Writing questions. The multiple-choice questions are grouped in five sets of questions, with each set linked to a passage of prose fiction or poetry that contains between 8 and 13 questions.
The AP English Literature & Composition exam takes 3 hours to complete and consists of two sections: a multiple-choice section and a free response section. Timing. Number of questions. % of Exam Score. Section 1. 60 minutes. 55 multiple-choice questions. 45%. Section 2.
The AP English Literature and Composition Exam is 3 hours long and broken up into two sections. Section I (One hour) 45 percent of total score 55 multiple-choice questions based on 2 or 3 poems and 2 or 3 passages of fiction. Section II (Two hours) 55 percent of total score 3 essays. Essay 1: An analysis of a poem.
Then, in a well-written essay, analyze how the character's reinvention contributes to an interpretation of the work as a whole. Do not merely summarize the plot. ... Free-Response Questions from the 2023 AP English Literature and Composition Exam Keywords: English Literature and Composition; Free-Response Questions; 2023; exam resources; exam ...
In AP English, writing is taught as "process"—that is, thinking, planning, drafting the text, then reviewing, discussing, redrafting, editing, polishing, and finishing it. It's also important that AP students learn to write "on call" or "on demand.". Learning to write critical or expository essays on call takes time and practice.
2024 AP English Literature exam study guides, practice quizzes, live reviews, community support | Fiveable ... AP Lit: Writing a Thesis and FRQ 3 Practice. AP Cram Sessions 2021. View all. Download AP Literature Cheat Sheet PDF Cram Chart. 1 min read. 🌶️ AP Lit Cram Review: Long Fiction I.
The best way to score a 5 on the AP® English Literature exam is to practice, practice, practice. And we're here to help. Below, we've compiled an ultimate list of AP® English Literature practice tests, study guides, AP® Lit prose essay examples, test-taking strategies, and more. Think of this page as the ultimate AP® English Literature ...
The writing focuses on the experience, evaluation, and interpretation of the literature. The AP English Literature Exam format is: Multiple-Choice Section. -60 minutes. -45% of final grade. -55 multiple choice questions. Free-Response Section. -120 minutes. -55% of final grade.
shaving. Read the poem carefully. Then, in a well-written essay, analyze how Blanco uses literary elements and techniques to develop the speaker's complex associations with the ritual of shaving. In a timed-writing situation and with an unfamiliar text, students were expected to complete three tasks successfully. They were expected to:
In the AP ® English Language and Composition course, you will learn the rhetorical and writing skills necessary to interpret ALL kinds of texts. The AP ® English Language exam course is comprehensive when it comes to rhetoric and writing, covering topics such as: Rhetorical analysis of prose. Reading comprehension.
Then, in a well-written essay, analyze how the author uses literary elements and techniques to develop a complex characterization of the community. ... AP® English Literature and Composition 2022 Scoring Guidelines. Reporting Category Scoring Criteria . Row C Sophistication (0-1 points)
AP® English Literature and Composition 2022 Scoring Guidelines. Question 3: Literary Argument 6 points . Many works of literature feature characters who accept or reject a hierarchical structure. This hierarchy may be social, economic, political, or familial, or it may apply to some other kind of structure.