Creative Thinking vs. Critical Thinking
What's the difference.
Creative thinking and critical thinking are two distinct but equally important cognitive processes. Creative thinking involves generating new ideas, concepts, and solutions by exploring various possibilities and thinking outside the box. It encourages imagination, originality, and innovation. On the other hand, critical thinking involves analyzing, evaluating, and questioning ideas, arguments, and information to make informed decisions and judgments. It emphasizes logical reasoning, evidence-based thinking, and the ability to identify biases and fallacies. While creative thinking focuses on generating ideas, critical thinking focuses on evaluating and refining those ideas. Both thinking processes are essential for problem-solving, decision-making, and personal growth.

Further Detail
Introduction.
Creative thinking and critical thinking are two distinct cognitive processes that play crucial roles in problem-solving, decision-making, and innovation. While they share some similarities, they also have distinct attributes that set them apart. In this article, we will explore the characteristics of creative thinking and critical thinking, highlighting their differences and showcasing how they complement each other in various contexts.
Creative Thinking
Creative thinking is a cognitive process that involves generating new ideas, concepts, or solutions by exploring possibilities, making connections, and thinking outside the box. It is characterized by originality, flexibility, and fluency of thought. Creative thinkers often challenge conventional wisdom, embrace ambiguity, and are open to taking risks. They are adept at finding alternative perspectives and exploring multiple solutions to problems.
One of the key attributes of creative thinking is the ability to think divergently. This means being able to generate a wide range of ideas or possibilities, often through brainstorming or free association. Creative thinkers are not limited by constraints and are willing to explore unconventional or unorthodox approaches to problem-solving.
Another important aspect of creative thinking is the ability to make connections between seemingly unrelated concepts or ideas. This skill, known as associative thinking, allows creative thinkers to draw upon a diverse range of knowledge and experiences to generate innovative solutions. They can see patterns, analogies, and relationships that others may overlook.
Furthermore, creative thinking involves the willingness to take risks and embrace failure as a learning opportunity. Creative thinkers understand that not all ideas will be successful, but they are not deterred by setbacks. They view failures as stepping stones towards finding the right solution and are persistent in their pursuit of innovative ideas.
In summary, creative thinking is characterized by divergent thinking, associative thinking, risk-taking, and persistence. It encourages the exploration of new ideas and unconventional approaches to problem-solving.
Critical Thinking
Critical thinking, on the other hand, is a cognitive process that involves analyzing, evaluating, and interpreting information to form reasoned judgments or decisions. It is characterized by logical, systematic, and objective thinking. Critical thinkers are skilled at identifying biases, assumptions, and fallacies in arguments, and they strive to make well-informed and rational decisions based on evidence.
One of the key attributes of critical thinking is the ability to think analytically. Critical thinkers break down complex problems or situations into smaller components, examine the relationships between them, and evaluate the evidence or information available. They are adept at identifying logical inconsistencies or flaws in reasoning, which helps them make sound judgments.
Another important aspect of critical thinking is the ability to evaluate information objectively. Critical thinkers are skeptical and question the validity and reliability of sources. They seek evidence, consider alternative viewpoints, and weigh the strengths and weaknesses of different arguments before forming their own opinions. This attribute is particularly valuable in today's information-rich society, where misinformation and biased narratives are prevalent.
Furthermore, critical thinking involves the ability to think systematically. Critical thinkers follow a logical and structured approach to problem-solving, ensuring that all relevant factors are considered. They are skilled at identifying assumptions, clarifying concepts, and drawing logical conclusions based on the available evidence. This systematic approach helps minimize errors and biases in decision-making.
In summary, critical thinking is characterized by analytical thinking, objective evaluation, skepticism, and systematic reasoning. It emphasizes the importance of evidence-based decision-making and helps individuals navigate complex and information-rich environments.
Complementary Attributes
While creative thinking and critical thinking have distinct attributes, they are not mutually exclusive. In fact, they often complement each other and can be seen as two sides of the same coin.
Creative thinking can benefit from critical thinking by providing a framework for evaluating and refining ideas. Critical thinking helps creative thinkers assess the feasibility, viability, and desirability of their innovative ideas. It allows them to identify potential flaws, consider alternative perspectives, and make informed decisions about which ideas to pursue further.
On the other hand, critical thinking can benefit from creative thinking by expanding the range of possibilities and solutions. Creative thinking encourages critical thinkers to explore unconventional approaches, challenge assumptions, and consider alternative viewpoints. It helps them break free from rigid thinking patterns and discover innovative solutions to complex problems.
Moreover, both creative thinking and critical thinking require open-mindedness and a willingness to embrace ambiguity. They both involve a certain level of discomfort and uncertainty, as individuals venture into uncharted territories of thought. By combining creative and critical thinking, individuals can develop a well-rounded cognitive toolkit that enables them to tackle a wide range of challenges.
Creative thinking and critical thinking are two distinct cognitive processes that bring unique attributes to problem-solving, decision-making, and innovation. Creative thinking emphasizes divergent thinking, associative thinking, risk-taking, and persistence, while critical thinking emphasizes analytical thinking, objective evaluation, skepticism, and systematic reasoning.
While they have their differences, creative thinking and critical thinking are not mutually exclusive. They complement each other and can be seen as two sides of the same coin. Creative thinking benefits from critical thinking by providing a framework for evaluation and refinement, while critical thinking benefits from creative thinking by expanding the range of possibilities and solutions.
By cultivating both creative and critical thinking skills, individuals can enhance their ability to navigate complex problems, make well-informed decisions, and drive innovation in various domains. These cognitive processes are not only valuable in academic and professional settings but also in everyday life, where the ability to think creatively and critically can lead to personal growth and success.
Comparisons may contain inaccurate information about people, places, or facts. Please report any issues.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Part Two: You are the President and CEO of You
Thinking Critically and Creatively
Dr. andrew robert baker.
Critical and creative thinking skills are perhaps the most fundamental skills involved in making judgments and solving problems. They are some of the most important skills I have ever developed. I use them everyday and continue to work to improve them both.
The ability to think critically about a matter—to analyze a question, situation, or problem down to its most basic parts—is what helps us evaluate the accuracy and truthfulness of statements, claims, and information we read and hear. It is the sharp knife that, when honed, separates fact from fiction, honesty from lies, and the accurate from the misleading. We all use this skill to one degree or another almost every day. For example, we use critical thinking every day as we consider the latest consumer products and why one particular product is the best among its peers. Is it a quality product because a celebrity endorses it? Because a lot of other people may have used it? Because it is made by one company versus another? Or perhaps because it is made in one country or another? These are questions representative of critical thinking.
The academic setting demands more of us in terms of critical thinking than everyday life. It demands that we evaluate information and analyze a myriad of issues. It is the environment where our critical thinking skills can be the difference between success and failure. In this environment we must consider information in an analytical, critical manner. We must ask questions—What is the source of this information? Is this source an expert one and what makes it so? Are there multiple perspectives to consider on an issue? Do multiple sources agree or disagree on an issue? Does quality research substantiate information or opinion? Do I have any personal biases that may affect my consideration of this information? It is only through purposeful, frequent, intentional questioning such as this that we can sharpen our critical thinking skills and improve as students, learners, and researchers. Developing my critical thinking skills over a twenty year period as a student in higher education enabled me to complete a quantitative dissertation, including analyzing research and completing statistical analysis, and earning my Ph.D. in 2014.
While critical thinking analyzes information and roots out the true nature and facets of problems, it is creative thinking that drives progress forward when it comes to solving these problems. Exceptional creative thinkers are people that invent new solutions to existing problems that do not rely on past or current solutions. They are the ones who invent solution C when everyone else is still arguing between A and B. Creative thinking skills involve using strategies to clear the mind so that our thoughts and ideas can transcend the current limitations of a problem and allow us to see beyond barriers that prevent new solutions from being found.
Brainstorming is the simplest example of intentional creative thinking that most people have tried at least once. With the quick generation of many ideas at once we can block-out our brain’s natural tendency to limit our solution-generating abilities so we can access and combine many possible solutions/thoughts and invent new ones. It is sort of like sprinting through a race’s finish line only to find there is new track on the other side and we can keep going, if we choose. As with critical thinking, higher education both demands creative thinking from us and is the perfect place to practice and develop the skill. Everything from word problems in a math class, to opinion or persuasive speeches and papers, call upon our creative thinking skills to generate new solutions and perspectives in response to our professor’s demands. Creative thinking skills ask questions such as—What if? Why not? What else is out there? Can I combine perspectives/solutions? What is something no one else has brought-up? What is being forgotten/ignored? What about ______? It is the opening of doors and options that follows problem-identification.
Consider an assignment that required you to compare two different authors on the topic of education and select and defend one as better. Now add to this scenario that your professor clearly prefers one author over the other. While critical thinking can get you as far as identifying the similarities and differences between these authors and evaluating their merits, it is creative thinking that you must use if you wish to challenge your professor’s opinion and invent new perspectives on the authors that have not previously been considered.
So, what can we do to develop our critical and creative thinking skills? Although many students may dislike it, group work is an excellent way to develop our thinking skills. Many times I have heard from students their disdain for working in groups based on scheduling, varied levels of commitment to the group or project, and personality conflicts too, of course. True—it’s not always easy, but that is why it is so effective. When we work collaboratively on a project or problem we bring many brains to bear on a subject. These different brains will naturally develop varied ways of solving or explaining problems and examining information. To the observant individual we see that this places us in a constant state of back and forth critical/creative thinking modes.
For example, in group work we are simultaneously analyzing information and generating solutions on our own, while challenging other’s analyses/ideas and responding to challenges to our own analyses/ideas. This is part of why students tend to avoid group work—it challenges us as thinkers and forces us to analyze others while defending ourselves, which is not something we are used to or comfortable with as most of our educational experiences involve solo work. Your professors know this—that’s why we assign it—to help you grow as students, learners, and thinkers!
Foundations of Academic Success: Words of Wisdom Copyright © 2015 by Thomas Priester is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

- How It Works
Link copied to clipboard
A Discrete Geometry Drawing Challenge

Kids Learn “New Math” for Good Reasons
Look out big ideas are hiding in your arithmetic, how can you prove something true by proving something else can't be true, the value of mathematical simplicity, making math relevant, pictures help us remember math, puzzling with your kids, seven questions (and one strategy) to build critical thinking skills, dissections in science, math, and reasoning, why learn math you might never actually use, how do you grow a critical thinker, trouble with an sat-style math question plug in numbers, yes, you'll enjoy this puzzling mathematical paradox, math should be complex, not complicated, help your kids become stronger problem solvers with one question, how to teach your child persistence, sometimes a jigsaw puzzle is more than just a puzzle, napoleon... the mathematician, sat-style geometry trick: make the “best” picture, 5 tips for helping your child with math homework, sports build your kids' mathematics skills, where is the math in bubbles, what would you decide a probability puzzle, algebra is useful... right, help your child work through frustration in math, all games build math and critical thinking skills, teach kids how to respond to mistakes, there is awesome math in your kitchen, experiment, and grow a little problem-solving in your garden, help your child build a problem-solving strategy toolbox, 6 strategies for building a positive math mindset, the math of dice and fair games, the importance of out-of-the-box thinking, the benefits of taking a break in problem solving, 5 tips to help kids get unstuck in math, what is graph theory, and why does it matter so much, talking about mental math with kids is meaningful, teach kids to make mistakes, why should kids learn to generalize in math, being good at math does not depend on how "smart" we are, 5 reasons your family should play more games, homer simpson and... the pythagorean theorem, help your kids learn to jump in and experiment, one easy way to do more math with your kids, what happens when you can't build something to help solve a problem, not sure how to start a problem choose a path… and then maybe another path, what’s the difference between critical thinking skills and problem-solving skills, are you smarter than the smart-bots, word problems don't have to be scary, help your child learn more by saying less, help your kids to flex their focus, the power of geometry vocabulary, getting the pythagorean theorem (really) right, confident parents build confident problem solvers, using math models: can you see all the sets, playing cards: the most amazing learning tool, help your child to become a better problem solver, why is understanding patterns so important, did you know there's math hiding in your spreadsheet, if you like magic squares, this puzzle is for you, we have to teach our kids how to struggle, wondering why, with your child, is worthwhile, your favorite mathematician should be euler, the number line contains all your favorite books, the importance of frames of reference in learning, geometry is not boring, kids can learn so much through tangram paradoxes, it's not magic, it's number sense, division is not boring, teaching through mystery, the joy of discovering mathematics… for yourself, the power of notation in math, building your child's problem solving tools: drawing, the value of labeling things in math, how can a problem that feels incomplete be finished, we are all natural (math) problem solvers, how well do you really know pi, how exstemsions is different, a single picture can explain the pythagorean theorem.
Critical thinking vs. problem solving: the definitions
I was recently chatting with a colleague about the kinds of skills kids need to develop to be successful on the job, and in life. I started running down a list, and she said something along the lines of, “Well, critical thinking and problem solving… they’re the same thing right?” That’s a really interesting question! For my colleague, “critical thinking” and “problem solving” are just phrases that are out there, somehow related to learning. And just like with anything else in life, when you haven’t had a reason to investigate them deeply, they might just be ideas that seem to mean something vaguely similar… but what do these ideas really mean?
First, let’s start with some basic definitions. Critical thinking, according to dictionary.com, is “disciplined thinking that is clear, rational, open-minded and informed by evidence.” Well, that certainly sounds like something I want my kids to be proficient in! According to Merriam-Webster, problem solving is “the process or act of finding a solution to a problem”, and there’s another no-brainer, definitely something I want to instill in my children. Can we move from these definitions to a real understanding of the differences between these two skill sets?
Looking deeper: what skills are involved in critical thinking?
We’ve looked up definitions for critical thinking and problem solving, but these definitions don’t tell us anything about the skills that are involved in each. For instance, what exactly do my kids need to be able to do in order to think critically? Critical thinking skills are habits of mind that help us be more thoughtful, rational, creative, and curious. Critical thinking can involve collecting information, organizing what we collect, analyzing and evaluating the information we have, making connections between different ideas, understanding what’s relevant and what isn’t, and so much more. All of this gives us a basis on which an informed decision can be made.
But when do we make decisions? When we’re confronted with a task, challenge, or problem . Indeed, we apply critical thinking when we are faced with a problem that demands we apply some of those skills. Critical thinking skills are general plans of attack, applicable to a wide array of problems!

Looking deeper: what skills are involved in problem solving?
So now we’ve discovered something interesting: critical thinking skills are problem solving skills! And if you think about it, any critical thinking skill could conceivably be applied to finding the solution to some kind of problem. (In fact, it's hard to define critical thinking skills and not make them about problem solving in some way!) So, every critical thinking skill is a problem-solving skill.
Does that mean that every problem-solving skill is also a critical thinking skill? Actually, no. For starters, there are lots of skills that help us solve problems, but are not thinking skills! For example, brute strength is a body skill that is also a problem-solving skill. (But probably much of the time, you need to figure out how to use that strength, say, so you don't unnecessarily break your best friend’s TV when helping her move to a new home; critical thinking skills to the rescue!)
There are also problem-solving skills that are thinking skills, but just not critical thinking skills. For example, people with “emotional intelligence” can soothe tempers, read other people, and help move ideas forward in contexts that have nothing to do with problem solving. Skills of persuasion and oration are thinking skills, but they don't necessarily have to be critical thinking skills.
There are even problem-solving skills that are the complete opposite of critical thinking, like following directions, and mechanical and rote thinking. For example, learning the steps for solving a linear equation allows you to solve linear equations like a machine, no critical thinking required. However, rote thinking without critical thinking can be dangerous; you don't necessarily want to follow rules without checking that those rules make sense!
Critical thinking and problem solving: sometimes different, sometimes the same
We know that critical thinking skills are fundamental to problem-solving. And we know that there are other skills that help us solve problems, skills that aren’t critical thinking skills. Problem solving involves a wide array of techniques and attacks, some of which fall under critical thinking, and some which don’t. Aspects of critical thinking and problem solving can be different, or the same, but both sets of skills are incredibly important for all kids to have. There isn’t a skill we’ve talked about here where I think “Well, my kiddo could probably live without being able to do that….” Critical thinking is the foundation that allows us to tackle challenges of all kinds, supplemented by other problem-solving skills as needed. We want our kids to have all of these skills at their fingertips, so they can solve problems effectively, using strong evidence, logical thinking, and clear reasoning. All are vital ingredients to a successful and happy grown-up life!
Find this post useful? Follow the blog using the link at the top of the page to get notified when new posts appear!
Looking for tasks that require BOTH critical thinking, and problem solving? Check out our Teachers Pay Teachers store !
Want awesome tips and a mini-challenge, all designed to help you build vital problem-solving and critical thinking skills in your child? Click here to sign up for our monthly newsletter!

Work Life is Atlassian’s flagship publication dedicated to unleashing the potential of every team through real-life advice, inspiring stories, and thoughtful perspectives from leaders around the world.

Contributing Writer
Work Futurist

Senior Quantitative Researcher, People Insights
Principal Writer

How to build critical thinking skills for better decision-making
It’s simple in theory, but tougher in practice – here are five tips to get you started.
Get stories like this in your inbox
Have you heard the riddle about two coins that equal thirty cents, but one of them is not a nickel? What about the one where a surgeon says they can’t operate on their own son?
Those brain teasers tap into your critical thinking skills. But your ability to think critically isn’t just helpful for solving those random puzzles – it plays a big role in your career.
An impressive 81% of employers say critical thinking carries a lot of weight when they’re evaluating job candidates. It ranks as the top competency companies consider when hiring recent graduates (even ahead of communication ). Plus, once you’re hired, several studies show that critical thinking skills are highly correlated with better job performance.
So what exactly are critical thinking skills? And even more importantly, how do you build and improve them?
What is critical thinking?
Critical thinking is the ability to evaluate facts and information, remain objective, and make a sound decision about how to move forward.
Does that sound like how you approach every decision or problem? Not so fast. Critical thinking seems simple in theory but is much tougher in practice, which helps explain why 65% of employers say their organization has a need for more critical thinking.
In reality, critical thinking doesn’t come naturally to a lot of us. In order to do it well, you need to:
- Remain open-minded and inquisitive, rather than relying on assumptions or jumping to conclusions
- Ask questions and dig deep, rather than accepting information at face value
- Keep your own biases and perceptions in check to stay as objective as possible
- Rely on your emotional intelligence to fill in the blanks and gain a more well-rounded understanding of a situation
So, critical thinking isn’t just being intelligent or analytical. In many ways, it requires you to step outside of yourself, let go of your own preconceived notions, and approach a problem or situation with curiosity and fairness.
It’s a challenge, but it’s well worth it. Critical thinking skills will help you connect ideas, make reasonable decisions, and solve complex problems.
7 critical thinking skills to help you dig deeper
Critical thinking is often labeled as a skill itself (you’ll see it bulleted as a desired trait in a variety of job descriptions). But it’s better to think of critical thinking less as a distinct skill and more as a collection or category of skills.
To think critically, you’ll need to tap into a bunch of your other soft skills. Here are seven of the most important.
Open-mindedness
It’s important to kick off the critical thinking process with the idea that anything is possible. The more you’re able to set aside your own suspicions, beliefs, and agenda, the better prepared you are to approach the situation with the level of inquisitiveness you need.
That means not closing yourself off to any possibilities and allowing yourself the space to pull on every thread – yes, even the ones that seem totally implausible.
As Christopher Dwyer, Ph.D. writes in a piece for Psychology Today , “Even if an idea appears foolish, sometimes its consideration can lead to an intelligent, critically considered conclusion.” He goes on to compare the critical thinking process to brainstorming . Sometimes the “bad” ideas are what lay the foundation for the good ones.
Open-mindedness is challenging because it requires more effort and mental bandwidth than sticking with your own perceptions. Approaching problems or situations with true impartiality often means:
- Practicing self-regulation : Giving yourself a pause between when you feel something and when you actually react or take action.
- Challenging your own biases: Acknowledging your biases and seeking feedback are two powerful ways to get a broader understanding.
Critical thinking example
In a team meeting, your boss mentioned that your company newsletter signups have been decreasing and she wants to figure out why.
At first, you feel offended and defensive – it feels like she’s blaming you for the dip in subscribers. You recognize and rationalize that emotion before thinking about potential causes. You have a hunch about what’s happening, but you will explore all possibilities and contributions from your team members.
Observation
Observation is, of course, your ability to notice and process the details all around you (even the subtle or seemingly inconsequential ones). Critical thinking demands that you’re flexible and willing to go beyond surface-level information, and solid observation skills help you do that.
Your observations help you pick up on clues from a variety of sources and experiences, all of which help you draw a final conclusion. After all, sometimes it’s the most minuscule realization that leads you to the strongest conclusion.
Over the next week or so, you keep a close eye on your company’s website and newsletter analytics to see if numbers are in fact declining or if your boss’s concerns were just a fluke.
Critical thinking hinges on objectivity. And, to be objective, you need to base your judgments on the facts – which you collect through research. You’ll lean on your research skills to gather as much information as possible that’s relevant to your problem or situation.
Keep in mind that this isn’t just about the quantity of information – quality matters too. You want to find data and details from a variety of trusted sources to drill past the surface and build a deeper understanding of what’s happening.
You dig into your email and website analytics to identify trends in bounce rates, time on page, conversions, and more. You also review recent newsletters and email promotions to understand what customers have received, look through current customer feedback, and connect with your customer support team to learn what they’re hearing in their conversations with customers.
The critical thinking process is sort of like a treasure hunt – you’ll find some nuggets that are fundamental for your final conclusion and some that might be interesting but aren’t pertinent to the problem at hand.
That’s why you need analytical skills. They’re what help you separate the wheat from the chaff, prioritize information, identify trends or themes, and draw conclusions based on the most relevant and influential facts.
It’s easy to confuse analytical thinking with critical thinking itself, and it’s true there is a lot of overlap between the two. But analytical thinking is just a piece of critical thinking. It focuses strictly on the facts and data, while critical thinking incorporates other factors like emotions, opinions, and experiences.
As you analyze your research, you notice that one specific webpage has contributed to a significant decline in newsletter signups. While all of the other sources have stayed fairly steady with regard to conversions, that one has sharply decreased.
You decide to move on from your other hypotheses about newsletter quality and dig deeper into the analytics.
One of the traps of critical thinking is that it’s easy to feel like you’re never done. There’s always more information you could collect and more rabbit holes you could fall down.
But at some point, you need to accept that you’ve done your due diligence and make a decision about how to move forward. That’s where inference comes in. It’s your ability to look at the evidence and facts available to you and draw an informed conclusion based on those.
When you’re so focused on staying objective and pursuing all possibilities, inference can feel like the antithesis of critical thinking. But ultimately, it’s your inference skills that allow you to move out of the thinking process and onto the action steps.
You dig deeper into the analytics for the page that hasn’t been converting and notice that the sharp drop-off happened around the same time you switched email providers.
After looking more into the backend, you realize that the signup form on that page isn’t correctly connected to your newsletter platform. It seems like anybody who has signed up on that page hasn’t been fed to your email list.
Communication

3 ways to improve your communication skills at work
If and when you identify a solution or answer, you can’t keep it close to the vest. You’ll need to use your communication skills to share your findings with the relevant stakeholders – like your boss, team members, or anybody who needs to be involved in the next steps.
Your analysis skills will come in handy here too, as they’ll help you determine what information other people need to know so you can avoid bogging them down with unnecessary details.
In your next team meeting, you pull up the analytics and show your team the sharp drop-off as well as the missing connection between that page and your email platform. You ask the web team to reinstall and double-check that connection and you also ask a member of the marketing team to draft an apology email to the subscribers who were missed.
Problem-solving
Critical thinking and problem-solving are two more terms that are frequently confused. After all, when you think critically, you’re often doing so with the objective of solving a problem.
The best way to understand how problem-solving and critical thinking differ is to think of problem-solving as much more narrow. You’re focused on finding a solution.
In contrast, you can use critical thinking for a variety of use cases beyond solving a problem – like answering questions or identifying opportunities for improvement. Even so, within the critical thinking process, you’ll flex your problem-solving skills when it comes time to take action.
Once the fix is implemented, you monitor the analytics to see if subscribers continue to increase. If not (or if they increase at a slower rate than you anticipated), you’ll roll out some other tests like changing the CTA language or the placement of the subscribe form on the page.
5 ways to improve your critical thinking skills

Beyond the buzzwords: Why interpersonal skills matter at work
Think critically about critical thinking and you’ll quickly realize that it’s not as instinctive as you’d like it to be. Fortunately, your critical thinking skills are learned competencies and not inherent gifts – and that means you can improve them. Here’s how:
- Practice active listening: Active listening helps you process and understand what other people share. That’s crucial as you aim to be open-minded and inquisitive.
- Ask open-ended questions: If your critical thinking process involves collecting feedback and opinions from others, ask open-ended questions (meaning, questions that can’t be answered with “yes” or “no”). Doing so will give you more valuable information and also prevent your own biases from influencing people’s input.
- Scrutinize your sources: Figuring out what to trust and prioritize is crucial for critical thinking. Boosting your media literacy and asking more questions will help you be more discerning about what to factor in. It’s hard to strike a balance between skepticism and open-mindedness, but approaching information with questions (rather than unquestioning trust) will help you draw better conclusions.
- Play a game: Remember those riddles we mentioned at the beginning? As trivial as they might seem, games and exercises like those can help you boost your critical thinking skills. There are plenty of critical thinking exercises you can do individually or as a team .
- Give yourself time: Research shows that rushed decisions are often regrettable ones. That’s likely because critical thinking takes time – you can’t do it under the wire. So, for big decisions or hairy problems, give yourself enough time and breathing room to work through the process. It’s hard enough to think critically without a countdown ticking in your brain.
Critical thinking really is critical
The ability to think critically is important, but it doesn’t come naturally to most of us. It’s just easier to stick with biases, assumptions, and surface-level information.
But that route often leads you to rash judgments, shaky conclusions, and disappointing decisions. So here’s a conclusion we can draw without any more noodling: Even if it is more demanding on your mental resources, critical thinking is well worth the effort.
Advice, stories, and expertise about work life today.
Sage Advice®
Creative vs. critical thinking.
At Sage Collective, we champion our inspired model of 9 Ways of Vibrant living , and encourage everyone to discover new methods to help better their wellbeing. Today, we’re taking you back to Psych 101 to talk about the key differences between critical and creative thinking, why they’re both important, and ways you can practice both in your life to help you live more vibrantly:
What Are Creative and Critical Thinking?
Understanding the difference between critical and creative thinking can be broken down simply this way: creative thinking is approaching problems or situations in new ways and with a new perspective, whereas critical thinking is using logic to analyze a situation in order to make an informed decision. Essentially, creative thinking is more subjective (influenced by feelings) whereas critical thinking is more objective (influenced by logic). Both are important when decision-making, so let’s explore some of the reasons why.
Why Are They Important?
As we’ve discussed in previous blogs , creativity – particularly for adults – can lead to a happier, healthier lifestyle. The same rings true for thinking creatively! Brainstorming new solutions and exploring new ideas are imperative for older adults because it helps provide a sense of self that is innovative and capable. The goal with creative thinking is to have an open mind and to approach situations with diverse perspectives. As for critical thinking, it’s equally important to approach situations constructively and logically, but it is the synergy of both thinking patterns working together that makes us great problem solvers.
How to Improve Creative and Critical Thinking Skills:
To improve critical thinking skills, when you’re problem-solving, make a list of facts and then cause and effects. This will help you logically analyze outcomes, and come to a decision that way. To think more creatively, try asking yourself: what other considerations are there in this situation? What perspective could I be missing? An easy way to practice this is by brainstorming with another person– hearing a different perspective may inspire you to think of others as well, and is great practice for when you’re alone.

- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Creating Brand Value
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
What Is Creative Problem-Solving & Why Is It Important?

- 01 Feb 2022
One of the biggest hindrances to innovation is complacency—it can be more comfortable to do what you know than venture into the unknown. Business leaders can overcome this barrier by mobilizing creative team members and providing space to innovate.
There are several tools you can use to encourage creativity in the workplace. Creative problem-solving is one of them, which facilitates the development of innovative solutions to difficult problems.
Here’s an overview of creative problem-solving and why it’s important in business.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Creative Problem-Solving?
Research is necessary when solving a problem. But there are situations where a problem’s specific cause is difficult to pinpoint. This can occur when there’s not enough time to narrow down the problem’s source or there are differing opinions about its root cause.
In such cases, you can use creative problem-solving , which allows you to explore potential solutions regardless of whether a problem has been defined.
Creative problem-solving is less structured than other innovation processes and encourages exploring open-ended solutions. It also focuses on developing new perspectives and fostering creativity in the workplace . Its benefits include:
- Finding creative solutions to complex problems : User research can insufficiently illustrate a situation’s complexity. While other innovation processes rely on this information, creative problem-solving can yield solutions without it.
- Adapting to change : Business is constantly changing, and business leaders need to adapt. Creative problem-solving helps overcome unforeseen challenges and find solutions to unconventional problems.
- Fueling innovation and growth : In addition to solutions, creative problem-solving can spark innovative ideas that drive company growth. These ideas can lead to new product lines, services, or a modified operations structure that improves efficiency.

Creative problem-solving is traditionally based on the following key principles :
1. Balance Divergent and Convergent Thinking
Creative problem-solving uses two primary tools to find solutions: divergence and convergence. Divergence generates ideas in response to a problem, while convergence narrows them down to a shortlist. It balances these two practices and turns ideas into concrete solutions.
2. Reframe Problems as Questions
By framing problems as questions, you shift from focusing on obstacles to solutions. This provides the freedom to brainstorm potential ideas.
3. Defer Judgment of Ideas
When brainstorming, it can be natural to reject or accept ideas right away. Yet, immediate judgments interfere with the idea generation process. Even ideas that seem implausible can turn into outstanding innovations upon further exploration and development.
4. Focus on "Yes, And" Instead of "No, But"
Using negative words like "no" discourages creative thinking. Instead, use positive language to build and maintain an environment that fosters the development of creative and innovative ideas.
Creative Problem-Solving and Design Thinking
Whereas creative problem-solving facilitates developing innovative ideas through a less structured workflow, design thinking takes a far more organized approach.
Design thinking is a human-centered, solutions-based process that fosters the ideation and development of solutions. In the online course Design Thinking and Innovation , Harvard Business School Dean Srikant Datar leverages a four-phase framework to explain design thinking.
The four stages are:

- Clarify: The clarification stage allows you to empathize with the user and identify problems. Observations and insights are informed by thorough research. Findings are then reframed as problem statements or questions.
- Ideate: Ideation is the process of coming up with innovative ideas. The divergence of ideas involved with creative problem-solving is a major focus.
- Develop: In the development stage, ideas evolve into experiments and tests. Ideas converge and are explored through prototyping and open critique.
- Implement: Implementation involves continuing to test and experiment to refine the solution and encourage its adoption.
Creative problem-solving primarily operates in the ideate phase of design thinking but can be applied to others. This is because design thinking is an iterative process that moves between the stages as ideas are generated and pursued. This is normal and encouraged, as innovation requires exploring multiple ideas.
Creative Problem-Solving Tools
While there are many useful tools in the creative problem-solving process, here are three you should know:
Creating a Problem Story
One way to innovate is by creating a story about a problem to understand how it affects users and what solutions best fit their needs. Here are the steps you need to take to use this tool properly.
1. Identify a UDP
Create a problem story to identify the undesired phenomena (UDP). For example, consider a company that produces printers that overheat. In this case, the UDP is "our printers overheat."
2. Move Forward in Time
To move forward in time, ask: “Why is this a problem?” For example, minor damage could be one result of the machines overheating. In more extreme cases, printers may catch fire. Don't be afraid to create multiple problem stories if you think of more than one UDP.
3. Move Backward in Time
To move backward in time, ask: “What caused this UDP?” If you can't identify the root problem, think about what typically causes the UDP to occur. For the overheating printers, overuse could be a cause.
Following the three-step framework above helps illustrate a clear problem story:
- The printer is overused.
- The printer overheats.
- The printer breaks down.
You can extend the problem story in either direction if you think of additional cause-and-effect relationships.
4. Break the Chains
By this point, you’ll have multiple UDP storylines. Take two that are similar and focus on breaking the chains connecting them. This can be accomplished through inversion or neutralization.
- Inversion: Inversion changes the relationship between two UDPs so the cause is the same but the effect is the opposite. For example, if the UDP is "the more X happens, the more likely Y is to happen," inversion changes the equation to "the more X happens, the less likely Y is to happen." Using the printer example, inversion would consider: "What if the more a printer is used, the less likely it’s going to overheat?" Innovation requires an open mind. Just because a solution initially seems unlikely doesn't mean it can't be pursued further or spark additional ideas.
- Neutralization: Neutralization completely eliminates the cause-and-effect relationship between X and Y. This changes the above equation to "the more or less X happens has no effect on Y." In the case of the printers, neutralization would rephrase the relationship to "the more or less a printer is used has no effect on whether it overheats."
Even if creating a problem story doesn't provide a solution, it can offer useful context to users’ problems and additional ideas to be explored. Given that divergence is one of the fundamental practices of creative problem-solving, it’s a good idea to incorporate it into each tool you use.
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a tool that can be highly effective when guided by the iterative qualities of the design thinking process. It involves openly discussing and debating ideas and topics in a group setting. This facilitates idea generation and exploration as different team members consider the same concept from multiple perspectives.
Hosting brainstorming sessions can result in problems, such as groupthink or social loafing. To combat this, leverage a three-step brainstorming method involving divergence and convergence :
- Have each group member come up with as many ideas as possible and write them down to ensure the brainstorming session is productive.
- Continue the divergence of ideas by collectively sharing and exploring each idea as a group. The goal is to create a setting where new ideas are inspired by open discussion.
- Begin the convergence of ideas by narrowing them down to a few explorable options. There’s no "right number of ideas." Don't be afraid to consider exploring all of them, as long as you have the resources to do so.
Alternate Worlds
The alternate worlds tool is an empathetic approach to creative problem-solving. It encourages you to consider how someone in another world would approach your situation.
For example, if you’re concerned that the printers you produce overheat and catch fire, consider how a different industry would approach the problem. How would an automotive expert solve it? How would a firefighter?
Be creative as you consider and research alternate worlds. The purpose is not to nail down a solution right away but to continue the ideation process through diverging and exploring ideas.

Continue Developing Your Skills
Whether you’re an entrepreneur, marketer, or business leader, learning the ropes of design thinking can be an effective way to build your skills and foster creativity and innovation in any setting.
If you're ready to develop your design thinking and creative problem-solving skills, explore Design Thinking and Innovation , one of our online entrepreneurship and innovation courses. If you aren't sure which course is the right fit, download our free course flowchart to determine which best aligns with your goals.

About the Author
Critical Thinking vs Problem Solving: Which is the Key to Success?
Annie Walls
In today's fast-paced and complex world, success often hinges on our ability to think critically and solve problems effectively. Both critical thinking and problem solving are valuable skills that can help us navigate challenges and make informed decisions. However, understanding the differences between the two and knowing when to utilize each approach is key. In this article, we will explore the definitions, importance, and characteristics of critical thinking and problem solving. We will also discuss strategies for developing critical thinking skills and problem-solving techniques. By the end, you will have a clear understanding of the distinctions between critical thinking and problem solving and how to leverage them for success.
Key Takeaways
- Critical thinking and problem solving are both essential skills for success.
- Critical thinking involves analyzing, evaluating, and interpreting information to form well-reasoned judgments.
- Problem solving is the process of identifying and resolving a problem using logical and creative thinking.
- Critical thinking is more focused on understanding and evaluating information, while problem solving is more focused on finding solutions.
- Knowing when to apply critical thinking and problem solving can lead to better decision-making and problem-solving outcomes.
Understanding Critical Thinking
Definition of critical thinking.
Critical thinking is the ability to analyze and evaluate information objectively and independently. It involves questioning assumptions, considering multiple perspectives, and using logic and reasoning to make informed decisions. Critical thinking is an essential skill in today's complex and rapidly changing world, as it allows individuals to navigate through challenges, solve problems, and make sound judgments. It is not simply accepting information at face value, but rather actively engaging with it to determine its validity and reliability.
Importance of Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is an essential skill in today's rapidly changing world. With exponential technologies like artificial intelligence and robotics creating new disruptive business models almost overnight, the ability to think critically allows individuals and teams to navigate through uncertainty and find innovative solutions. In fact, a survey conducted by IBM found that 60% of Global CEOs consider 'creativity' as the most important leadership quality in business today. Additionally, the World Economic Forum predicts that 'creativity' will be one of the top skills required in the future job market.
Characteristics of a Critical Thinker
A critical thinker possesses several key characteristics that set them apart from others. One important characteristic is the ability to analyze information thoroughly. Critical thinkers are skilled at breaking down complex problems or situations into smaller, more manageable parts. They are able to examine each part individually and understand how they relate to the whole.
Another characteristic of a critical thinker is curiosity . Critical thinkers have a natural curiosity and a desire to learn. They are constantly asking questions and seeking out new information. This curiosity drives them to explore different perspectives and consider alternative solutions.
In addition, critical thinkers are open-minded . They are willing to consider different viewpoints and are not afraid to challenge their own beliefs. They understand that there may be multiple valid perspectives on a given issue and are willing to listen and learn from others.
Lastly, critical thinkers are reflective . They take the time to reflect on their own thinking processes and evaluate their own biases and assumptions. They are aware of the limitations of their own knowledge and actively seek to improve their thinking skills.
Developing Critical Thinking Skills
Critical thinking strategies.
Critical thinking strategies are essential for developing strong problem-solving skills. These strategies involve analyzing information, evaluating arguments, and making logical decisions. One important strategy is questioning assumptions . By challenging assumptions, critical thinkers can uncover hidden biases and explore alternative perspectives. Another strategy is seeking evidence . Critical thinkers rely on evidence to support their claims and make informed judgments. They also use creative thinking techniques to generate innovative solutions. By combining these strategies, individuals can enhance their critical thinking abilities and approach problems with a more analytical mindset.
Critical Thinking Exercises
Critical thinking exercises are a valuable tool for developing and honing your critical thinking skills. These exercises provide opportunities to practice analyzing information, evaluating arguments, and making logical connections. They help you become more aware of your own thought processes and biases, and they challenge you to think critically about complex issues.
One effective critical thinking exercise is the Socratic Method, which involves asking probing questions to stimulate critical thinking and encourage deeper analysis. This method helps you examine assumptions, consider alternative perspectives, and evaluate the validity of arguments.
Another useful exercise is the Red Team Exercise, where you take on the role of a critical thinker and analyze a problem or decision from a different perspective. This exercise helps you identify potential flaws or weaknesses in your own thinking and develop more robust solutions.
Remember, the key to improving your critical thinking skills is consistent practice and a willingness to challenge your own beliefs and assumptions.
Critical Thinking in Education
Critical thinking plays a crucial role in education. It helps students develop analytical and problem-solving skills, enabling them to think critically about the information they encounter. By teaching students how to think critically, educators empower them to evaluate and analyze different perspectives, make informed decisions, and solve complex problems. Critical thinking in education goes beyond memorization and regurgitation of facts; it encourages students to question assumptions, challenge conventional wisdom, and explore alternative solutions. This approach fosters creativity, innovation, and a deeper understanding of the subject matter.

Problem Solving Techniques
Definition of problem solving.
Problem solving is the process of finding solutions to difficult or complex issues. It involves identifying the problem, analyzing it, and coming up with effective strategies to overcome it. Creativity and critical thinking are important skills in problem solving, as they allow individuals to think outside the box and come up with innovative solutions. Problem solving can be applied to various aspects of life, including personal, professional, and academic settings.
Importance of Problem Solving
Problem solving is a crucial skill that is highly valued in various industries, from retail and healthcare to engineering, construction, and logistics. As automation continues to advance, many roles that do not require creativity are at risk. According to the World Economic Forum, creativity will be the third most important job skill by 2020. However, only 39% of people in today's workforce consider themselves to be creative. This highlights the need for individuals and organizations to develop problem-solving skills.
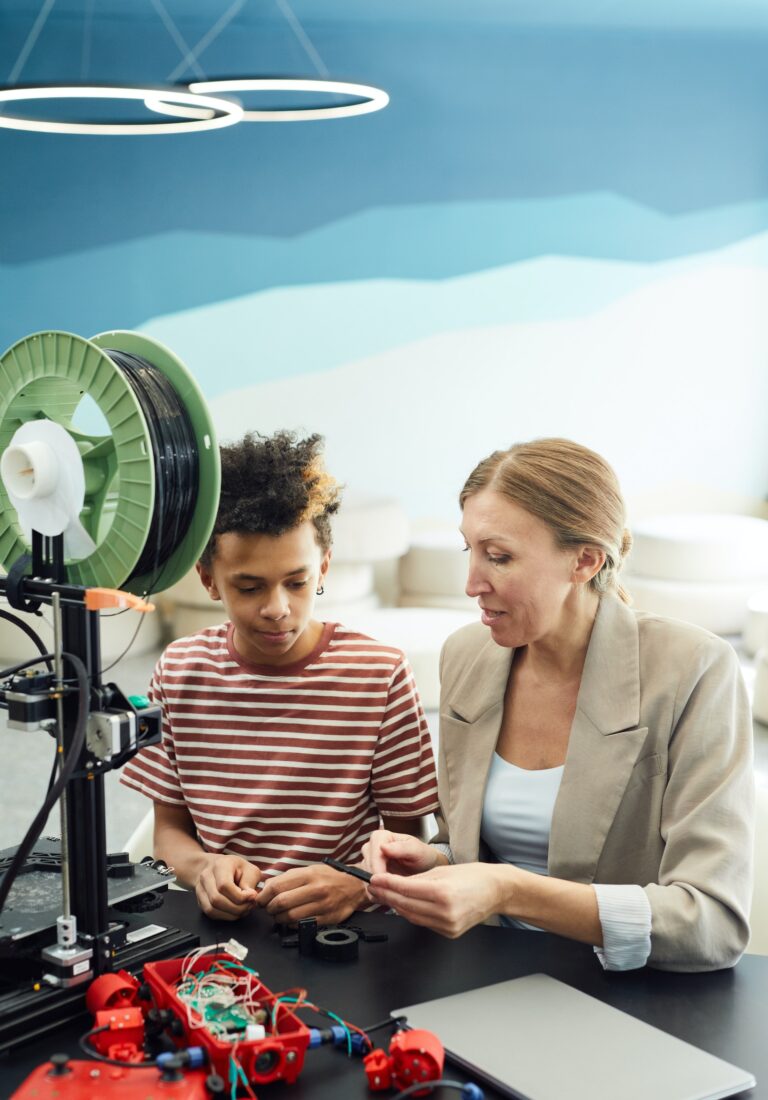
To succeed in a rapidly changing world, it is essential to foster a culture of creativity and innovation. Keynote speaker James Taylor, an internationally recognized leader in business and creativity, emphasizes the importance of unlocking the creative potential in people and teams. By developing problem-solving skills, individuals can adapt to technological change and find unique solutions to complex challenges.
In order to cultivate problem-solving abilities, organizations can implement strategies such as brainstorming sessions, design thinking workshops, and cross-functional collaboration. These approaches encourage diverse perspectives and enable individuals to think critically and creatively. Additionally, problem-solving exercises and case studies can provide practical opportunities for individuals to apply their problem-solving skills in real-world scenarios.
As James Taylor suggests, the future of leadership lies in the ability to foster creative collaboration between humans and machines. By embracing problem-solving techniques, individuals can harness the power of technology while leveraging their own critical thinking skills. This combination allows for innovative problem-solving approaches that can drive success in a rapidly evolving landscape.
Steps in Problem Solving
Problem solving is a systematic process that involves identifying, analyzing, and finding solutions to problems. It is an essential skill in both personal and professional settings. Here are the steps involved in problem solving:
- Identify the problem: The first step in problem solving is to clearly define and understand the problem at hand. This involves gathering information, identifying any underlying issues, and determining the root cause of the problem.
- Analyze the problem: Once the problem is identified, it is important to analyze it thoroughly. This includes examining the different aspects of the problem, considering various perspectives, and identifying any patterns or trends.
- Generate possible solutions: After analyzing the problem, it is time to brainstorm and generate possible solutions. This involves thinking creatively, considering different alternatives, and evaluating the potential outcomes of each solution.
- Evaluate and select a solution: Once a list of possible solutions is generated, it is important to evaluate each solution based on its feasibility, effectiveness, and potential impact. The best solution should be selected based on these criteria.
- Implement the solution: After selecting a solution, it is time to implement it. This involves putting the chosen solution into action and monitoring its progress.
- Evaluate the results: The final step in problem solving is to evaluate the results of the implemented solution. This includes assessing whether the problem has been solved, identifying any unforeseen consequences, and making any necessary adjustments.
Problem solving is a critical skill that can be developed and improved with practice. By following these steps, individuals can become more effective problem solvers and achieve success in various aspects of their lives.
Critical Thinking vs Problem Solving
Differences between critical thinking and problem solving.
Critical thinking and problem solving are two distinct but interconnected cognitive processes. While critical thinking involves analyzing and evaluating information to make informed decisions, problem solving focuses on finding solutions to specific challenges or issues. Critical thinking emphasizes the ability to think critically and objectively, considering multiple perspectives and evidence before drawing conclusions. On the other hand, problem solving is more action-oriented, involving identifying problems, generating alternatives, and implementing effective solutions.
In terms of approach, critical thinking is more focused on understanding and evaluating complex situations, while problem solving is about finding practical solutions to specific problems. Critical thinking often involves asking probing questions, challenging assumptions, and considering different viewpoints, while problem solving requires creativity, resourcefulness, and the ability to think outside the box.
Here is a comparison between critical thinking and problem solving:
It is important to note that critical thinking and problem solving are not mutually exclusive. In fact, they complement each other and are both essential for success in various aspects of life, including education, work, and personal relationships.
When to Use Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is a valuable skill that can be applied in various situations. Here are some scenarios where critical thinking can be particularly useful:
- Making important decisions: Critical thinking allows you to analyze information, evaluate options, and make informed decisions.
- Problem-solving: Critical thinking helps you identify and solve complex problems by breaking them down into manageable parts.
- Evaluating arguments: Critical thinking enables you to assess the validity and strength of arguments, helping you make more informed judgments.
In these situations, critical thinking can help you navigate challenges, make better choices, and achieve success.
When to Use Problem Solving
Problem solving is a valuable skill that can be applied in various situations. It is particularly useful when faced with complex challenges that require logical thinking and analytical skills. Identifying the root cause of a problem and developing effective solutions are key aspects of problem solving. Whether it's in the workplace, personal life, or academic setting, problem solving can help individuals overcome obstacles and achieve their goals.
Critical thinking and problem solving are two essential skills that are often used interchangeably, but they are actually distinct processes. Critical thinking involves analyzing and evaluating information to make informed decisions and solve complex problems. It requires the ability to think logically, consider multiple perspectives, and question assumptions. On the other hand, problem solving is the process of finding solutions to specific challenges or obstacles. It involves identifying the problem, brainstorming possible solutions, and implementing the best course of action. Both critical thinking and problem solving are crucial in today's fast-paced and ever-changing world. To enhance your critical thinking and problem-solving skills, visit Keynote Speaker James Taylor's website. James Taylor is an inspiring keynote speaker and internationally recognized leader in business creativity and innovation. Explore his website to gain valuable insights and strategies that will help you navigate challenges and make better decisions. Don't miss out on this opportunity to unlock your full potential!
In conclusion, both critical thinking and problem solving are essential skills for success in the real world. While critical thinking allows individuals to analyze and evaluate information, problem solving enables them to find effective solutions to complex problems. However , it is important to note that these skills are not mutually exclusive and often go hand in hand. By developing both critical thinking and problem solving abilities , individuals can enhance their decision-making skills and become more adaptable in today's rapidly changing world. Therefore, it is crucial for individuals to cultivate these skills through education, practice, and continuous learning.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between critical thinking and problem solving.
Critical thinking involves analyzing and evaluating information to make informed decisions, while problem solving is the process of finding solutions to specific issues or challenges.
Which is more important, critical thinking or problem solving?
Both critical thinking and problem solving are important skills for success. They complement each other and are often used together to solve complex problems.
How can I develop my critical thinking skills?
You can develop your critical thinking skills by practicing active listening, asking questions, evaluating evidence, and considering different perspectives.
What are some critical thinking strategies?
Some critical thinking strategies include analyzing arguments, identifying biases, evaluating sources, and considering alternative solutions.
What are the steps in problem solving?
The steps in problem solving typically include identifying the problem, gathering information, generating possible solutions, evaluating options, implementing a solution, and reflecting on the results.
When should I use critical thinking?
Critical thinking is useful in situations that require careful analysis, evaluation, and decision-making. It can be applied in various areas such as problem solving, decision making, and evaluating information.

Popular Posts
Robert hannigan – the power of neurodiversity in innovation, cybersecurity, gchq and counter-intelligence #342.
Explore key insights on intelligence and decision-making from Professor Sir David Omand’s book, focusing on critical thinking and creativity.
Sam Dixon of Womble Bond Dickinson, The Evolving Role of Lawyers in the AI Era #341
John craske of cms, collaboration between humans and machines in the legal industry #340, jd meier of microsoft, productivity strategies for success #339, sir david omand, author of how spies think – 10 lessons in critical thinking #338, meilleur conférencier principal en teambuilding.
Les conférences virtuelles et les sommets peuvent être des moyens très efficaces pour inspirer, informer
James is a top motivational keynote speaker who is booked as a creativity and innovation keynote speaker, AI speaker , sustainability speaker and leadership speaker . Recent destinations include: Dubai , Abu Dhabi , Orlando , Las Vegas , keynote speaker London , Barcelona , Bangkok , Miami , Berlin , Riyadh , New York , Zurich , motivational speaker Paris , Singapore and San Francisco
Latest News
- 415.800.3059
- [email protected]
- Media Interviews
- Meeting Planners
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
FIND ME ON SOCIAL
© 2024 James Taylor DBA P3 Music Ltd.

- Search Search Search …
- Search Search …
Are Problem Solving and Critical Thinking the Same? Debunking the Common Misconception

Problem solving and critical thinking are often considered synonymous, but they are two separate skills with distinct strategies, purposes, and applications. Understanding the differences between these two concepts is crucial for effectively overcoming challenges and making better decisions in both personal and professional environments.

Critical thinking refers to the process of objectively analyzing and evaluating information, arguments, beliefs, and opinions to form judgments, while problem solving is a solution-oriented process that requires identifying, analyzing, and implementing appropriate strategies to address issues and achieve desired outcomes. Although there is some overlap between these two skills, critical thinking is broader and essential for identifying the root causes of problems, whereas problem solving is more focused on finding solutions to the specific problems identified.
Key Takeaways
- Critical thinking and problem solving are distinct skills with different purposes and strategies.
- Critical thinking is an objective analysis and evaluation process, while problem solving focuses on finding solutions.
- Both skills are essential for overcoming challenges and making better decisions in personal and professional situations.
Understanding Critical Thinking
Characteristics of Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is a vital skill that involves the process of carefully and systematically analyzing, evaluating, and reflecting on information to make informed decisions, reasoned judgments, or solve problems. Key characteristics of critical thinking include logic, analysis, evaluation, synthesis, and assessment of evidence and arguments. To be an effective critical thinker, one should be open-minded, questioning, and willing to consider alternative viewpoints, drawing conclusions based on reason and evidence.
Techniques in Critical Thinking
Various techniques can be applied to enhance critical thinking skills , such as:
- Socratic questioning : Delving deeper into a topic by asking open-ended and probing questions.
- Argument analysis : Breaking down arguments into their core components to assess their logic and validity.
- Reflection : Taking time to consider and analyze your own thought processes, beliefs, and assumptions.
- Inference : Drawing conclusions based on the available evidence while avoiding biases and assumptions.
- Evaluation : Assessing the quality and relevance of evidence, arguments, and sources of information.
These techniques, along with a commitment to continuous improvement and feedback, can help individuals develop strong critical thinking skills .
The Process of Critical Thinking
The process of critical thinking typically involves a series of steps:
- Defining the problem or issue : Clearly identifying the problem or question to be addressed.
- Gathering information : Obtaining relevant data, evidence, and sources to support analysis and decision-making.
- Evaluating the information : Assessing the credibility, quality, and relevance of the collected information.
- Analyzing the information : Breaking down complex issues into smaller components and understanding their relationships.
- Synthesizing the information : Combining the analyzed components to form a coherent understanding or solution.
- Generating possible solutions : Brainstorming and considering multiple alternative solutions or viewpoints.
- Assessing potential solutions : Evaluating the pros and cons of each possible solution, weighing the evidence, and considering the implications.
- Making a decision or drawing a conclusion : Based on the reasoned analysis, selecting the most appropriate solution, or forming a well-supported conclusion.
By engaging in this process, individuals can develop a deep understanding of the issue at hand and arrive at informed decisions or judgments. Teaching critical thinking should involve guiding learners through these steps and encouraging them to think clearly and effectively.
Understanding Problem Solving
Stages of problem solving.
Problem solving is an essential skill that helps individuals tackle complex challenges in various aspects of life. It is an iterative process that typically consists of several stages. First, it involves identifying the problem and understanding its constraints. Next, one must gather necessary information and explore possible solutions. Finally, a person must evaluate the effectiveness of the potential solutions, select the best one, and implement it.
Developing strong problem-solving skills entails constant learning, asking questions, and seeking ways to expand one’s knowledge. By consistently practicing these skills, individuals become better equipped to handle tasks, challenges, and decisions creatively.
Techniques in Problem Solving
Various techniques aid in effective problem-solving, and these methods can be tailored according to the specific challenge faced. Some strategies include:
- Brainstorming: Generating a wide range of ideas without being critical of them in the initial stage.
- Decision making: Choosing the best solution after considering the pros and cons of multiple options.
- Creativity: Thinking outside the box and exploring unconventional approaches to resolving issues.
By understanding and applying these techniques, individuals can continually refine their problem-solving abilities and make informed choices. Furthermore, these skills contribute significantly to the identification of trends and important aspects of the challenge at hand.
The Process of Problem Solving
The process of problem solving starts by recognizing a challenge and defining it clearly. Once the issue is identified, individuals can create a plan of action by breaking down the problem into smaller, more manageable parts. This step helps in gathering relevant information and determining the necessary resources.
During the process, it’s crucial to remain open-minded and unbiased to ensure the effectiveness of the solution. This involves asking open-ended questions and leveraging the habits of mind, such as curiosity, persistence, and flexibility. Additionally, seeking feedback from others and being willing to revise the plan contributes to a more comprehensive approach to problem-solving.
The application of problem-solving skills is evident in many sectors, including the development of innovative products and solutions. By cultivating these abilities, individuals become more adept at adapting to various challenges and ultimately find success in their respective fields.
Comparing Critical Thinking and Problem Solving
Similarities between critical thinking and problem solving.
Both critical thinking and problem solving involve using a range of cognitive abilities to approach and address challenges. They are essential skills for navigating a world filled with complex tasks, arguments, and conflicts. These processes both require analysis, evaluation, reflection, and the application of experience.
Working through obstacles, individuals utilizing critical thinking and problem-solving skills often gather and interpret data, weigh evidence, and assess the potential consequences of various actions. This enables them to make well-informed decisions, beneficial to themselves and others.
Differences between Critical Thinking and Problem Solving
While there are similarities, critical thinking and problem-solving differ in key aspects. Critical thinking is a broader, intentional mode of thinking that involves reflection, evaluation, interpretation, and inference. It examines assumptions, biases, and potential alternative explanations, fostering the ability to tolerate ambiguity. At its core, critical thinking is about questioning and examining various perspectives as a way to recognize and challenge underlying assumptions.
Conversely, problem solving is more focused and solution-oriented. It requires a targeted analysis of a specific situation, considering relevant factors to devise a plan of action to overcome obstacles. Problem-solving skills come into play when individuals must navigate concrete challenges, often using practical, efficient strategies to develop realistic solutions.
In summary, while critical thinking encompasses a wider scope and focuses on questioning underlying assumptions, problem solving is more targeted and concentrates on finding solutions to specific situations. Both skills, however, are integral to navigating the complexities of life and work.
Critical Thinking, Problem Solving, and Career Relevance
Critical thinking and problem solving are two essential skills that individuals need to excel in their careers. Although these skills may seem similar, there are distinct differences between them. Developing both expertise in critical thinking and problem-solving competencies is vital for taking initiative and making well-informed decisions in various professional settings.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to analyze information, consider multiple perspectives, and evaluate the validity of an argument or idea. This skill helps individuals examine issues thoroughly, assess the credibility of sources, and arrive at well-reasoned conclusions. In contrast, problem solving is a more focused process that involves identifying obstacles and strategically mapping out solutions to address a specific issue at hand.
In the workplace, these skills are indispensable for anyone seeking to perform their duties efficiently and effectively. Critical thinking and problem solving are essential for professionals to adapt to changes, resolve conflicts, and make sound decisions. Moreover, having a strong grasp of both skills can lead to a successful career that involves analyzing complex situations and developing strategies to tackle challenges.
Some of the key career areas that demand high levels of critical thinking and problem-solving skills include management, engineering, finance, programming, and research. When individuals can think critically and solve problems, they demonstrate an ability to take control of their work and utilize their expertise to achieve better outcomes.
Professionals who excel in these competencies often display a higher level of initiative in their career. They can swiftly identify issues, analyze different options, and devise strategies to overcome challenges. This kind of proactive approach can lead to career growth and make their job role more satisfying.
In summary, critical thinking and problem solving are two distinct skills that are crucial for professional success. Developing these competencies can help individuals excel in various careers, demonstrate initiative, and achieve growth within their field.
You may also like

Strategic Thinking for New Managers: Mastering Essential Skills
Strategic thinking is a crucial skill for new managers to develop in order to drive organizational success. It involves analyzing various inputs, […]

Masterclass vs Skillshare: An In-Depth Comparison for Lifelong Learners
In the burgeoning market of online learning, MasterClass and SkillShare have emerged as two leading platforms, each offering a distinct approach to […]

Metacognition & Critical Thinking: Differences and Similarities
Two terms we usually confuse with each other are Critical Thinking and Metacognition. Even though they both describe the skill of being […]

SWOT Analysis for Personal and Professional Growth: Elevate Your Potential
Navigating personal and professional growth can be challenging without the right tools. A SWOT Analysis is a strategic method that offers clarity. […]
- Career Advice
- Job Search & Interview
- Productivity
- Public Speaking and Presentation
- Social & Interpersonal Skills
- Professional Development
- Remote Work
Eggcellent Work
Critical thinking vs problem solving: what’s the difference.
In our blog “Importance of Problem Solving Skills in Leadership ,” we highlighted problem solving skills as a distinct skill set. We outlined a 7-step approach in how the best leaders solve problems.
Critical thinking vs. problem solving
But are critical thinking and problem solving the same? Also, if there are differences, what are they? Although many educators and business leaders lump critical thinking and problem solving together, there are differences:
Problem solving uses many of the same skills required for critical thinking; e.g., observation, analysis, evaluation, interpretation, and reflection. Critical thinking is an important ingredient of problem solving.
Critical thinking vs. problem solving: Not all problems require critical thinking skills
Not every problem-solving skill is a critical thinking skill. That is because not every problem requires thinking. A problem like opening a stubborn pickle jar could simply require brute strength. On the other hand, it becomes a thinking skill when you remember to tap the edge of the pickle jar lid to loosen the seal.
Also, some problem-solving skills are the exact opposite of critical thinking. When you follow directions or use muscle memory or rote (memorization) thinking, there is no critical thinking required. Likewise, skills of persuasion or public oratory are thinking skills, but aren’t necessarily critical thinking skills.
Critical thinking vs. problem solving: The role of emotional intelligence
In our blog “ What is the role of communication in critical thinking ?” we highlighted one author’s argument that critical thinking and problem solving is not always a purely rational process. While critical thinkers are in great demand in the hiring marketplace, employees who are emotionally intelligent bring even greater value to an organization.
Writing for Business News Daily , editor Chad Brooks describes emotional intelligence as “the ability to understand your emotions and recognize the emotions and motivations of those around you.”
So, when looking for star performers, research shows “that emotional intelligence counts for twice as much as IQ and technical skills combined in determining who will be a star performer.”
Further, in today’s collaborative workplace environment, “hiring employees who can understand and control their emotions – while also identifying what makes those around them tick—is of the utmost importance.”
Finally, one expert notes that dealing with emotions is an important part of critical thinking. Emotions can be at the root of a problem. They are frequently symptomatic of problems below the surface. Problem solving when dealing with emotions requires openness to authentic emotional expressions. It requires the understanding that when someone is in pain, it is a problem that is real.
The Ultimate Guide To Critical Thinking
- Is Critical Thinking A Soft Skill Or Hard Skill?
- How To Improve Critical Thinking Skills At Work And Make Better Decisions
- 5 Creative and Critical Thinking Examples In Workplace
- 25 In-Demand Jobs That Require Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Skills
- Brainstorming: Techniques Used To Boost Critical Thinking and Creativity
Critical thinking and problem solving: A deeper dive
A recap of the distinct differences between critical thinking and problem solving.
Critical thinking, according to an article on Drexel University’s Graduate College webpage “utilizes analysis, reflection, evaluation, interpretation, and inference to synthesize information that is obtained through reading, observing, communicating, or experience.”
The goal of critical thinking is to evaluate the credibility of both the information and its source. It questions the central issue and how the information will inform intelligent decisions. Finally, it asks the question, “Where does this information lead me?”
Problem solving , as previously mentioned, uses many of those skills, but “it takes the process a step further to identify obstacles and then to strategically map out a set of solutions to solve the problem. That extra step in problem solving is identifying obstacles as well as mapping out a strategic set of solutions to resolve the problem.
How to develop critical thinking skills to become a better problem solver
1. develop your analytical skills..
Pay attention and be more observant. Ask the questions “who, what, where, and why” and learn as much as possible about the topic or problem. Map everything out to imprint or gain a visual understanding and focus on the differences between fact, opinion, and your own bias.
2. Learn the skill of evaluating
As a subset of analysis, you can become skilled in evaluation by:
- comparing similar and related topics, programs, and issues. How are they different, and where are the similarities?
- looking for trends that support (or refute) what you intuitively feel is the solution
- recognizing barriers or conflicts to successful problem resolution
- asking questions and gathering information—assuming nothing, ever.
3. Interpretation with the help of a mentor or someone more experienced
Interpreting a problem accurately employs both analytical and evaluating skills. With practice, you can develop this skill, but to hone your interpretation skills, it is advisable to seek the help of an experienced mentor.
You’ll need to do the following:
- know how your own biases or opinions can be a roadblock to the best decision making
- recognize that cultural differences can be a barrier to communication
- look at the problem from the point of view of others
- learn as much as you can about the problem, topic, or experience
- synthesize everything you have learned in order to make the connections and put the elements of a problem together to form its solution
4. Acquire the skill and habit of reflection.
Being reflective is applicable to almost every aspect of your personal and professional life. To open your mind to reflection, think back to your educational experience. Your instructor may have asked you to keep a reflective journal of your learning-related experiences. A reflective journal requires expressive writing, which, in turn, relieves stress.
Perhaps you have just had a disagreement with a coworker, who became abusive and personal. Not everyone can come up with those instant snappy comebacks on the spot, and it is usually best to disengage before the situation gets worse.
Here’s where reflective journaling helps. When you’re in a calmer state of mind, you can journal the incident to:
- gain deeper insights into your thought processes and actions—How do you feel about not defending yourself from the colleague’s accusations or personal abuse? What was the perfect response that eluded you in the stress of the moment?
- build a different approach to problems—It could be that your co-worker perceives you as unapproachable or unreceptive to suggestions and criticism. Maybe it’s time to have a frank discussion to help you see yourself through the eyes of the coworker.
- get closer to making significant changes in your life—Your journal entries may have displayed a pattern of your behavior on the job, which elicits consistent negative reactions from more than one co-worker.
Your takeaways:
- When evaluating critical thinking vs. problem solving, the elements of both appear to blend into a distinction without a difference.
- Good problem solvers employ the steps of critical thinking, but not all problem solving involves critical thinking.
- Emotional intelligence is an attribute that is a hybrid skill of problem solving and critical thinking.
- You can hone your critical thinking skills to become a better problem solver through application of analysis, evaluation, interpretation, and reflection.
10 Best Books On Critical Thinking And Problem Solving
- 12 Common Barriers To Critical Thinking (And How To Overcome Them)
- How To Promote Critical Thinking In The Workplace
Is Critical Thinking Overrated? Disadvantages Of Critical Thinking
11 principles of critical thinking .
Jenny Palmer
Founder of Eggcellentwork.com. With over 20 years of experience in HR and various roles in corporate world, Jenny shares tips and advice to help professionals advance in their careers. Her blog is a go-to resource for anyone looking to improve their skills, land their dream job, or make a career change.
Further Reading...

No Comments
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
What Is The Role Of Communication In Critical Thinking?

The Peak Performance Center
The pursuit of performance excellence, thinking skills.
Thinking skills are the mental activities you use to process information, make connections, make decisions, and create new ideas. You use your thinking skills when you try to make sense of experiences, solve problems, make decisions, ask questions, make plans, or organize information.
Everybody has thinking skills, but not everyone uses them effectively. Effective thinking skills are developed over a period of time. Good thinkers see possibilities where others see only obstacles or roadblocks. Good thinkers are able to make connection between various factors and be able to tie them together. They are also able to develop new and unique solutions to problems.
Thinking refers to the process of creating a logical series of connective facets between items of information. Often times, thinking just happens automatically. However, there are times when you consciously think. It may be about how to solve a problem or making a decision. Thinking enables you to connect and integrate new experiences into your existing understanding and perception of how things are.
The simplest thinking skills are learning facts and recall, while higher order skills include analysis, synthesis, problem solving, and evaluation .
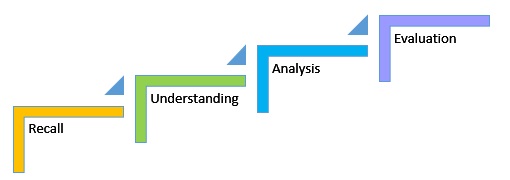
Core Thinking Skills
Thinking skills are cognitive operations or processes that are the building blocks of thinking. There are several core thinking skills including focusing, organizing, analyzing, evaluating and generating.
Focusing – attending to selected pieces of information while ignoring other stimuli.
Remembering – storing and then retrieving information.
Gathering – bringing to the conscious mind the relative information needed for cognitive processing.
Organizing – arranging information so it can be used more effectively.
Analyzing – breaking down information by examining parts and relationships so that its organizational structure may be understood.
Connecting – making connections between related items or pieces of information.
Integrating – connecting and combining information to better understand the relationship between the information.
Compiling – putting parts together to form a whole or building a structure or pattern from diverse elements.
Evaluating – assessing the reasonableness and quality of ideas or materials on order to present and defend opinions.
Generating – producing new information, ideas, products, or ways of viewing things.
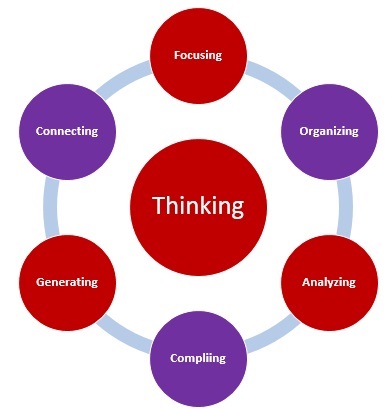
Classifications and Types of Thinking
Convergent or Analytical Thinking: Bringing facts and data together from various sourc es and then applying logic and knowledge to solve problems or to make informed decisions.
Divergent thinking: Breaking a topic apart to explore its various components and then generating new ideas and solutions.
Critical Thinking: Analysis and evaluation of information, beliefs, or knowledge.
Creative Thinking: Generation of new ideas breaking from established thoughts, theories, rules, and procedures.
Metacognition
Thinking about thinking is called Metacognition. It is a higher order thinking that enables understanding, analysis, and control of your cognitive processes. It can involve planning, monitoring, assessing, and evaluating your use of your cognitive skills.
In the simplest form, convergent thinking or deductive reasoning looks inward to find a solution, while divergent or creative thinking looks outward for a solution.
Both thinking skills are essential for school and life. Both require critical thinking skills to be effective. Both are used for solving problems, doing projects and achieving objectives. However, much of the thinking in formal education focuses on the convergent analytical thinking skills such as following or making a logical argument, eliminating the incorrect paths and then figuring out the single correct answer.
Standardized tests such as IQ tests only measure convergent thinking. Pattern recognition, logic thought flow, and the ability to solve problems with a single answer can all be tested and graded. Although it is an extremely valuable skill, there are no accurate tests able to measure divergent or creative thinking skills.
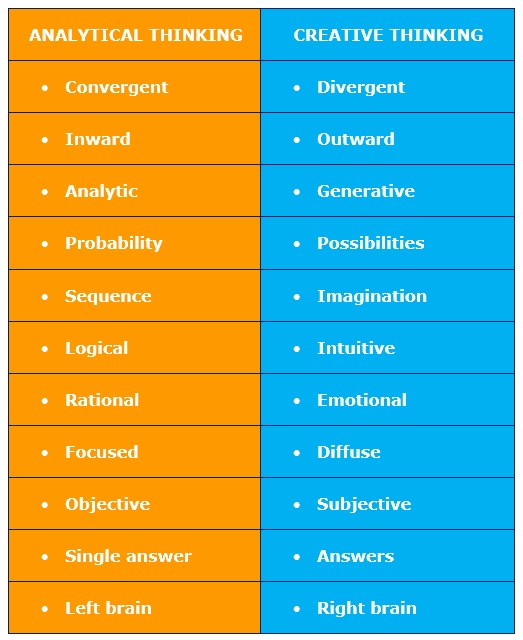
Types of thinking
Critical thinking
Blooms Taxonomy
Bloom’s Taxonomy Revised
Mind Mapping
Chunking Information
Brainstorming
Critical Thinking skills
Divergent and Convergent thinking skills are both “critical thinking” skills.
Critical thinking refers to the process of actively analyzing, synthesizing, and/or evaluating and reflecting on information gathered from observation, experience, or communication and is focused on deciding what to believe or do. Critical thinking is considered a higher order thinking skills, such as analysis, synthesis, and problem solving, inference, and evaluation.
The concept of higher order thinking skills became well known with the publication of Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives. Bloom’s Taxonomy was primarily created for academic education; however, it is relevant to all types of learning.
Often times when people are problem solving or decision making, he or she flips back and forth between convergent and divergent thinking. When first looking at a problem, people often analyze the facts and circumstances to determine the root cause. After which, they explore new and innovative options through divergent thinking, then switch back to convergent thinking to limit those down to one practical option.
Author: James Kelly, September 2011

Copyright © 2024 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Critical thinking vs. problem-solving Critical thinking and problem-solving can both help you resolve challenges, but the two practices have distinct purposes and strategies. Here are some differences between the two skills: Critical thinking This is a mode of thinking, compared to problem-solving, which is a set of solution-oriented strategies.
It emphasizes logical reasoning, evidence-based thinking, and the ability to identify biases and fallacies. While creative thinking focuses on generating ideas, critical thinking focuses on evaluating and refining those ideas. Both thinking processes are essential for problem-solving, decision-making, and personal growth.
While critical thinking involves the systematic evaluation of information and arguments, creative thinking is focused on generating novel and innovative ideas and solutions. Balancing these thinking styles results in enhanced productivity, better communication, and more creative and effective problem-solving.
Creative thinking involves generating new ideas and exploring unconventional solutions. Critical thinking focuses on analyzing, evaluating, and making logical judgments. The synergy of creative and critical thinking enhances problem-solving skills. Combining creative and critical thinking promotes innovation and growth.
Critical Thinking vs. Creative Thinking . Creative thinking is a way of looking at problems or situations from a fresh perspective to conceive of something new or original. Critical thinking is the logical, sequential disciplined process of rationalizing, analyzing, evaluating, and interpreting information to make informed judgments and/or ...
Critical and creative thinking skills are perhaps the most fundamental skills involved in making judgments and solving problems. They are some of the most important skills I have ever developed. I use them everyday and continue to work to improve them both. The ability to think critically about a matter—to analyze a question, situation, or ...
The first step to enhancing your critical thinking and problem solving skills is to think about them, become aware of them, then you can actively practice to improve them. Critical thinking and problem-solving are two important "soft" or essential skills hiring managers are looking for. According to a Linkedin survey, 57% of business ...
Critical thinking skills are habits of mind that help us be more thoughtful, rational, creative, and curious. Critical thinking can involve collecting information, organizing what we collect, analyzing and evaluating the information we have, making connections between different ideas, understanding what's relevant and what isn't, and so ...
Problem-solving. Critical thinking and problem-solving are two more terms that are frequently confused. After all, when you think critically, you're often doing so with the objective of solving a problem. The best way to understand how problem-solving and critical thinking differ is to think of problem-solving as much more narrow.
Understanding the difference between critical and creative thinking can be broken down simply this way: creative thinking is approaching problems or situations in new ways and with a new perspective, whereas critical thinking is using logic to analyze a situation in order to make an informed decision. Essentially, creative thinking is more ...
Creative problem-solving primarily operates in the ideate phase of design thinking but can be applied to others. This is because design thinking is an iterative process that moves between the stages as ideas are generated and pursued. This is normal and encouraged, as innovation requires exploring multiple ideas.
We will also discuss strategies for developing critical thinking skills and problem-solving techniques. By the end, you will have a clear understanding of the distinctions between critical thinking and problem solving and how to leverage them for success. Key Takeaways. Critical thinking and problem solving are both essential skills for success.
Critical thinking involves asking questions, defining a problem, examining evidence, analyzing assumptions and biases, avoiding emotional reasoning, avoiding oversimplification, considering other interpretations, and tolerating ambiguity. Dealing with ambiguity is also seen by Strohm & Baukus (1995) as an essential part of critical thinking ...
Critical Thinking: Problem Solving: Evaluation: Before accepting or rejecting a solution, it is necessary to evaluate if the source is valid and if the information is relevant and of high quality. Research to Collect Information: Collecting relevant, correct, and valid information is vital for solving an issue. Interpretation: It is the skill of interpreting, i.e., understanding the purpose ...
Debunking the Common Misconception. Problem solving and critical thinking are often considered synonymous, but they are two separate skills with distinct strategies, purposes, and applications. Understanding the differences between these two concepts is crucial for effectively overcoming challenges and making better decisions in both personal ...
Although many educators and business leaders lump critical thinking and problem solving together, there are differences: Problem solving uses many of the same skills required for critical thinking; e.g., observation, analysis, evaluation, interpretation, and reflection. Critical thinking is an important ingredient of problem solving.
There are several core thinking skills including focusing, organizing, analyzing, evaluating and generating. Focusing - attending to selected pieces of information while ignoring other stimuli. Remembering - storing and then retrieving information. Gathering - bringing to the conscious mind the relative information needed for cognitive ...