Python Tutorial
File handling, python modules, python numpy, python pandas, python matplotlib, python scipy, machine learning, python mysql, python mongodb, python reference, module reference, python how to, python examples, python assignment operators.
Assignment operators are used to assign values to variables:
| Operator | Example | Same As | Try it |
|---|---|---|---|
| = | x = 5 | x = 5 | |
| += | x += 3 | x = x + 3 | |
| -= | x -= 3 | x = x - 3 | |
| *= | x *= 3 | x = x * 3 | |
| /= | x /= 3 | x = x / 3 | |
| %= | x %= 3 | x = x % 3 | |
| //= | x //= 3 | x = x // 3 | |
| **= | x **= 3 | x = x ** 3 | |
| &= | x &= 3 | x = x & 3 | |
| |= | x |= 3 | x = x | 3 | |
| ^= | x ^= 3 | x = x ^ 3 | |
| >>= | x >>= 3 | x = x >> 3 | |
| <<= | x <<= 3 | x = x << 3 |

Related Pages

COLOR PICKER

Contact Sales
If you want to use W3Schools services as an educational institution, team or enterprise, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Report Error
If you want to report an error, or if you want to make a suggestion, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Top Tutorials
Top references, top examples, get certified.
- Python »
- 3.12.5 Documentation »
- The Python Language Reference »
- 6. Expressions
- Theme Auto Light Dark |
6. Expressions ¶
This chapter explains the meaning of the elements of expressions in Python.
Syntax Notes: In this and the following chapters, extended BNF notation will be used to describe syntax, not lexical analysis. When (one alternative of) a syntax rule has the form
and no semantics are given, the semantics of this form of name are the same as for othername .
6.1. Arithmetic conversions ¶
When a description of an arithmetic operator below uses the phrase “the numeric arguments are converted to a common type”, this means that the operator implementation for built-in types works as follows:
If either argument is a complex number, the other is converted to complex;
otherwise, if either argument is a floating-point number, the other is converted to floating point;
otherwise, both must be integers and no conversion is necessary.
Some additional rules apply for certain operators (e.g., a string as a left argument to the ‘%’ operator). Extensions must define their own conversion behavior.
6.2. Atoms ¶
Atoms are the most basic elements of expressions. The simplest atoms are identifiers or literals. Forms enclosed in parentheses, brackets or braces are also categorized syntactically as atoms. The syntax for atoms is:
6.2.1. Identifiers (Names) ¶
An identifier occurring as an atom is a name. See section Identifiers and keywords for lexical definition and section Naming and binding for documentation of naming and binding.
When the name is bound to an object, evaluation of the atom yields that object. When a name is not bound, an attempt to evaluate it raises a NameError exception.
6.2.1.1. Private name mangling ¶
When an identifier that textually occurs in a class definition begins with two or more underscore characters and does not end in two or more underscores, it is considered a private name of that class.
The class specifications .
More precisely, private names are transformed to a longer form before code is generated for them. If the transformed name is longer than 255 characters, implementation-defined truncation may happen.
The transformation is independent of the syntactical context in which the identifier is used but only the following private identifiers are mangled:
Any name used as the name of a variable that is assigned or read or any name of an attribute being accessed.
The __name__ attribute of nested functions, classes, and type aliases is however not mangled.
The name of imported modules, e.g., __spam in import __spam . If the module is part of a package (i.e., its name contains a dot), the name is not mangled, e.g., the __foo in import __foo.bar is not mangled.
The name of an imported member, e.g., __f in from spam import __f .
The transformation rule is defined as follows:
The class name, with leading underscores removed and a single leading underscore inserted, is inserted in front of the identifier, e.g., the identifier __spam occurring in a class named Foo , _Foo or __Foo is transformed to _Foo__spam .
If the class name consists only of underscores, the transformation is the identity, e.g., the identifier __spam occurring in a class named _ or __ is left as is.
6.2.2. Literals ¶
Python supports string and bytes literals and various numeric literals:
Evaluation of a literal yields an object of the given type (string, bytes, integer, floating-point number, complex number) with the given value. The value may be approximated in the case of floating-point and imaginary (complex) literals. See section Literals for details.
All literals correspond to immutable data types, and hence the object’s identity is less important than its value. Multiple evaluations of literals with the same value (either the same occurrence in the program text or a different occurrence) may obtain the same object or a different object with the same value.
6.2.3. Parenthesized forms ¶
A parenthesized form is an optional expression list enclosed in parentheses:
A parenthesized expression list yields whatever that expression list yields: if the list contains at least one comma, it yields a tuple; otherwise, it yields the single expression that makes up the expression list.
An empty pair of parentheses yields an empty tuple object. Since tuples are immutable, the same rules as for literals apply (i.e., two occurrences of the empty tuple may or may not yield the same object).
Note that tuples are not formed by the parentheses, but rather by use of the comma. The exception is the empty tuple, for which parentheses are required — allowing unparenthesized “nothing” in expressions would cause ambiguities and allow common typos to pass uncaught.
6.2.4. Displays for lists, sets and dictionaries ¶
For constructing a list, a set or a dictionary Python provides special syntax called “displays”, each of them in two flavors:
either the container contents are listed explicitly, or
they are computed via a set of looping and filtering instructions, called a comprehension .
Common syntax elements for comprehensions are:
The comprehension consists of a single expression followed by at least one for clause and zero or more for or if clauses. In this case, the elements of the new container are those that would be produced by considering each of the for or if clauses a block, nesting from left to right, and evaluating the expression to produce an element each time the innermost block is reached.
However, aside from the iterable expression in the leftmost for clause, the comprehension is executed in a separate implicitly nested scope. This ensures that names assigned to in the target list don’t “leak” into the enclosing scope.
The iterable expression in the leftmost for clause is evaluated directly in the enclosing scope and then passed as an argument to the implicitly nested scope. Subsequent for clauses and any filter condition in the leftmost for clause cannot be evaluated in the enclosing scope as they may depend on the values obtained from the leftmost iterable. For example: [x*y for x in range(10) for y in range(x, x+10)] .
To ensure the comprehension always results in a container of the appropriate type, yield and yield from expressions are prohibited in the implicitly nested scope.
Since Python 3.6, in an async def function, an async for clause may be used to iterate over a asynchronous iterator . A comprehension in an async def function may consist of either a for or async for clause following the leading expression, may contain additional for or async for clauses, and may also use await expressions.
If a comprehension contains async for clauses, or if it contains await expressions or other asynchronous comprehensions anywhere except the iterable expression in the leftmost for clause, it is called an asynchronous comprehension . An asynchronous comprehension may suspend the execution of the coroutine function in which it appears. See also PEP 530 .
Added in version 3.6: Asynchronous comprehensions were introduced.
Changed in version 3.8: yield and yield from prohibited in the implicitly nested scope.
Changed in version 3.11: Asynchronous comprehensions are now allowed inside comprehensions in asynchronous functions. Outer comprehensions implicitly become asynchronous.
6.2.5. List displays ¶
A list display is a possibly empty series of expressions enclosed in square brackets:
A list display yields a new list object, the contents being specified by either a list of expressions or a comprehension. When a comma-separated list of expressions is supplied, its elements are evaluated from left to right and placed into the list object in that order. When a comprehension is supplied, the list is constructed from the elements resulting from the comprehension.
6.2.6. Set displays ¶
A set display is denoted by curly braces and distinguishable from dictionary displays by the lack of colons separating keys and values:
A set display yields a new mutable set object, the contents being specified by either a sequence of expressions or a comprehension. When a comma-separated list of expressions is supplied, its elements are evaluated from left to right and added to the set object. When a comprehension is supplied, the set is constructed from the elements resulting from the comprehension.
An empty set cannot be constructed with {} ; this literal constructs an empty dictionary.
6.2.7. Dictionary displays ¶
A dictionary display is a possibly empty series of dict items (key/value pairs) enclosed in curly braces:
A dictionary display yields a new dictionary object.
If a comma-separated sequence of dict items is given, they are evaluated from left to right to define the entries of the dictionary: each key object is used as a key into the dictionary to store the corresponding value. This means that you can specify the same key multiple times in the dict item list, and the final dictionary’s value for that key will be the last one given.
A double asterisk ** denotes dictionary unpacking . Its operand must be a mapping . Each mapping item is added to the new dictionary. Later values replace values already set by earlier dict items and earlier dictionary unpackings.
Added in version 3.5: Unpacking into dictionary displays, originally proposed by PEP 448 .
A dict comprehension, in contrast to list and set comprehensions, needs two expressions separated with a colon followed by the usual “for” and “if” clauses. When the comprehension is run, the resulting key and value elements are inserted in the new dictionary in the order they are produced.
Restrictions on the types of the key values are listed earlier in section The standard type hierarchy . (To summarize, the key type should be hashable , which excludes all mutable objects.) Clashes between duplicate keys are not detected; the last value (textually rightmost in the display) stored for a given key value prevails.
Changed in version 3.8: Prior to Python 3.8, in dict comprehensions, the evaluation order of key and value was not well-defined. In CPython, the value was evaluated before the key. Starting with 3.8, the key is evaluated before the value, as proposed by PEP 572 .
6.2.8. Generator expressions ¶
A generator expression is a compact generator notation in parentheses:
A generator expression yields a new generator object. Its syntax is the same as for comprehensions, except that it is enclosed in parentheses instead of brackets or curly braces.
Variables used in the generator expression are evaluated lazily when the __next__() method is called for the generator object (in the same fashion as normal generators). However, the iterable expression in the leftmost for clause is immediately evaluated, so that an error produced by it will be emitted at the point where the generator expression is defined, rather than at the point where the first value is retrieved. Subsequent for clauses and any filter condition in the leftmost for clause cannot be evaluated in the enclosing scope as they may depend on the values obtained from the leftmost iterable. For example: (x*y for x in range(10) for y in range(x, x+10)) .
The parentheses can be omitted on calls with only one argument. See section Calls for details.
To avoid interfering with the expected operation of the generator expression itself, yield and yield from expressions are prohibited in the implicitly defined generator.
If a generator expression contains either async for clauses or await expressions it is called an asynchronous generator expression . An asynchronous generator expression returns a new asynchronous generator object, which is an asynchronous iterator (see Asynchronous Iterators ).
Added in version 3.6: Asynchronous generator expressions were introduced.
Changed in version 3.7: Prior to Python 3.7, asynchronous generator expressions could only appear in async def coroutines. Starting with 3.7, any function can use asynchronous generator expressions.
6.2.9. Yield expressions ¶
The yield expression is used when defining a generator function or an asynchronous generator function and thus can only be used in the body of a function definition. Using a yield expression in a function’s body causes that function to be a generator function, and using it in an async def function’s body causes that coroutine function to be an asynchronous generator function. For example:
Due to their side effects on the containing scope, yield expressions are not permitted as part of the implicitly defined scopes used to implement comprehensions and generator expressions.
Changed in version 3.8: Yield expressions prohibited in the implicitly nested scopes used to implement comprehensions and generator expressions.
Generator functions are described below, while asynchronous generator functions are described separately in section Asynchronous generator functions .
When a generator function is called, it returns an iterator known as a generator. That generator then controls the execution of the generator function. The execution starts when one of the generator’s methods is called. At that time, the execution proceeds to the first yield expression, where it is suspended again, returning the value of expression_list to the generator’s caller, or None if expression_list is omitted. By suspended, we mean that all local state is retained, including the current bindings of local variables, the instruction pointer, the internal evaluation stack, and the state of any exception handling. When the execution is resumed by calling one of the generator’s methods, the function can proceed exactly as if the yield expression were just another external call. The value of the yield expression after resuming depends on the method which resumed the execution. If __next__() is used (typically via either a for or the next() builtin) then the result is None . Otherwise, if send() is used, then the result will be the value passed in to that method.
All of this makes generator functions quite similar to coroutines; they yield multiple times, they have more than one entry point and their execution can be suspended. The only difference is that a generator function cannot control where the execution should continue after it yields; the control is always transferred to the generator’s caller.
Yield expressions are allowed anywhere in a try construct. If the generator is not resumed before it is finalized (by reaching a zero reference count or by being garbage collected), the generator-iterator’s close() method will be called, allowing any pending finally clauses to execute.
When yield from <expr> is used, the supplied expression must be an iterable. The values produced by iterating that iterable are passed directly to the caller of the current generator’s methods. Any values passed in with send() and any exceptions passed in with throw() are passed to the underlying iterator if it has the appropriate methods. If this is not the case, then send() will raise AttributeError or TypeError , while throw() will just raise the passed in exception immediately.
When the underlying iterator is complete, the value attribute of the raised StopIteration instance becomes the value of the yield expression. It can be either set explicitly when raising StopIteration , or automatically when the subiterator is a generator (by returning a value from the subgenerator).
Changed in version 3.3: Added yield from <expr> to delegate control flow to a subiterator.
The parentheses may be omitted when the yield expression is the sole expression on the right hand side of an assignment statement.
The proposal for adding generators and the yield statement to Python.
The proposal to enhance the API and syntax of generators, making them usable as simple coroutines.
The proposal to introduce the yield_from syntax, making delegation to subgenerators easy.
The proposal that expanded on PEP 492 by adding generator capabilities to coroutine functions.
6.2.9.1. Generator-iterator methods ¶
This subsection describes the methods of a generator iterator. They can be used to control the execution of a generator function.
Note that calling any of the generator methods below when the generator is already executing raises a ValueError exception.
Starts the execution of a generator function or resumes it at the last executed yield expression. When a generator function is resumed with a __next__() method, the current yield expression always evaluates to None . The execution then continues to the next yield expression, where the generator is suspended again, and the value of the expression_list is returned to __next__() ’s caller. If the generator exits without yielding another value, a StopIteration exception is raised.
This method is normally called implicitly, e.g. by a for loop, or by the built-in next() function.
Resumes the execution and “sends” a value into the generator function. The value argument becomes the result of the current yield expression. The send() method returns the next value yielded by the generator, or raises StopIteration if the generator exits without yielding another value. When send() is called to start the generator, it must be called with None as the argument, because there is no yield expression that could receive the value.
Raises an exception at the point where the generator was paused, and returns the next value yielded by the generator function. If the generator exits without yielding another value, a StopIteration exception is raised. If the generator function does not catch the passed-in exception, or raises a different exception, then that exception propagates to the caller.
In typical use, this is called with a single exception instance similar to the way the raise keyword is used.
For backwards compatibility, however, the second signature is supported, following a convention from older versions of Python. The type argument should be an exception class, and value should be an exception instance. If the value is not provided, the type constructor is called to get an instance. If traceback is provided, it is set on the exception, otherwise any existing __traceback__ attribute stored in value may be cleared.
Changed in version 3.12: The second signature (type[, value[, traceback]]) is deprecated and may be removed in a future version of Python.
Raises a GeneratorExit at the point where the generator function was paused. If the generator function then exits gracefully, is already closed, or raises GeneratorExit (by not catching the exception), close returns to its caller. If the generator yields a value, a RuntimeError is raised. If the generator raises any other exception, it is propagated to the caller. close() does nothing if the generator has already exited due to an exception or normal exit.
6.2.9.2. Examples ¶
Here is a simple example that demonstrates the behavior of generators and generator functions:
For examples using yield from , see PEP 380: Syntax for Delegating to a Subgenerator in “What’s New in Python.”
6.2.9.3. Asynchronous generator functions ¶
The presence of a yield expression in a function or method defined using async def further defines the function as an asynchronous generator function.
When an asynchronous generator function is called, it returns an asynchronous iterator known as an asynchronous generator object. That object then controls the execution of the generator function. An asynchronous generator object is typically used in an async for statement in a coroutine function analogously to how a generator object would be used in a for statement.
Calling one of the asynchronous generator’s methods returns an awaitable object, and the execution starts when this object is awaited on. At that time, the execution proceeds to the first yield expression, where it is suspended again, returning the value of expression_list to the awaiting coroutine. As with a generator, suspension means that all local state is retained, including the current bindings of local variables, the instruction pointer, the internal evaluation stack, and the state of any exception handling. When the execution is resumed by awaiting on the next object returned by the asynchronous generator’s methods, the function can proceed exactly as if the yield expression were just another external call. The value of the yield expression after resuming depends on the method which resumed the execution. If __anext__() is used then the result is None . Otherwise, if asend() is used, then the result will be the value passed in to that method.
If an asynchronous generator happens to exit early by break , the caller task being cancelled, or other exceptions, the generator’s async cleanup code will run and possibly raise exceptions or access context variables in an unexpected context–perhaps after the lifetime of tasks it depends, or during the event loop shutdown when the async-generator garbage collection hook is called. To prevent this, the caller must explicitly close the async generator by calling aclose() method to finalize the generator and ultimately detach it from the event loop.
In an asynchronous generator function, yield expressions are allowed anywhere in a try construct. However, if an asynchronous generator is not resumed before it is finalized (by reaching a zero reference count or by being garbage collected), then a yield expression within a try construct could result in a failure to execute pending finally clauses. In this case, it is the responsibility of the event loop or scheduler running the asynchronous generator to call the asynchronous generator-iterator’s aclose() method and run the resulting coroutine object, thus allowing any pending finally clauses to execute.
To take care of finalization upon event loop termination, an event loop should define a finalizer function which takes an asynchronous generator-iterator and presumably calls aclose() and executes the coroutine. This finalizer may be registered by calling sys.set_asyncgen_hooks() . When first iterated over, an asynchronous generator-iterator will store the registered finalizer to be called upon finalization. For a reference example of a finalizer method see the implementation of asyncio.Loop.shutdown_asyncgens in Lib/asyncio/base_events.py .
The expression yield from <expr> is a syntax error when used in an asynchronous generator function.
6.2.9.4. Asynchronous generator-iterator methods ¶
This subsection describes the methods of an asynchronous generator iterator, which are used to control the execution of a generator function.
Returns an awaitable which when run starts to execute the asynchronous generator or resumes it at the last executed yield expression. When an asynchronous generator function is resumed with an __anext__() method, the current yield expression always evaluates to None in the returned awaitable, which when run will continue to the next yield expression. The value of the expression_list of the yield expression is the value of the StopIteration exception raised by the completing coroutine. If the asynchronous generator exits without yielding another value, the awaitable instead raises a StopAsyncIteration exception, signalling that the asynchronous iteration has completed.
This method is normally called implicitly by a async for loop.
Returns an awaitable which when run resumes the execution of the asynchronous generator. As with the send() method for a generator, this “sends” a value into the asynchronous generator function, and the value argument becomes the result of the current yield expression. The awaitable returned by the asend() method will return the next value yielded by the generator as the value of the raised StopIteration , or raises StopAsyncIteration if the asynchronous generator exits without yielding another value. When asend() is called to start the asynchronous generator, it must be called with None as the argument, because there is no yield expression that could receive the value.
Returns an awaitable that raises an exception of type type at the point where the asynchronous generator was paused, and returns the next value yielded by the generator function as the value of the raised StopIteration exception. If the asynchronous generator exits without yielding another value, a StopAsyncIteration exception is raised by the awaitable. If the generator function does not catch the passed-in exception, or raises a different exception, then when the awaitable is run that exception propagates to the caller of the awaitable.
Returns an awaitable that when run will throw a GeneratorExit into the asynchronous generator function at the point where it was paused. If the asynchronous generator function then exits gracefully, is already closed, or raises GeneratorExit (by not catching the exception), then the returned awaitable will raise a StopIteration exception. Any further awaitables returned by subsequent calls to the asynchronous generator will raise a StopAsyncIteration exception. If the asynchronous generator yields a value, a RuntimeError is raised by the awaitable. If the asynchronous generator raises any other exception, it is propagated to the caller of the awaitable. If the asynchronous generator has already exited due to an exception or normal exit, then further calls to aclose() will return an awaitable that does nothing.
6.3. Primaries ¶
Primaries represent the most tightly bound operations of the language. Their syntax is:
6.3.1. Attribute references ¶
An attribute reference is a primary followed by a period and a name:
The primary must evaluate to an object of a type that supports attribute references, which most objects do. This object is then asked to produce the attribute whose name is the identifier. The type and value produced is determined by the object. Multiple evaluations of the same attribute reference may yield different objects.
This production can be customized by overriding the __getattribute__() method or the __getattr__() method. The __getattribute__() method is called first and either returns a value or raises AttributeError if the attribute is not available.
If an AttributeError is raised and the object has a __getattr__() method, that method is called as a fallback.
6.3.2. Subscriptions ¶
The subscription of an instance of a container class will generally select an element from the container. The subscription of a generic class will generally return a GenericAlias object.
When an object is subscripted, the interpreter will evaluate the primary and the expression list.
The primary must evaluate to an object that supports subscription. An object may support subscription through defining one or both of __getitem__() and __class_getitem__() . When the primary is subscripted, the evaluated result of the expression list will be passed to one of these methods. For more details on when __class_getitem__ is called instead of __getitem__ , see __class_getitem__ versus __getitem__ .
If the expression list contains at least one comma, it will evaluate to a tuple containing the items of the expression list. Otherwise, the expression list will evaluate to the value of the list’s sole member.
For built-in objects, there are two types of objects that support subscription via __getitem__() :
Mappings. If the primary is a mapping , the expression list must evaluate to an object whose value is one of the keys of the mapping, and the subscription selects the value in the mapping that corresponds to that key. An example of a builtin mapping class is the dict class.
Sequences. If the primary is a sequence , the expression list must evaluate to an int or a slice (as discussed in the following section). Examples of builtin sequence classes include the str , list and tuple classes.
The formal syntax makes no special provision for negative indices in sequences . However, built-in sequences all provide a __getitem__() method that interprets negative indices by adding the length of the sequence to the index so that, for example, x[-1] selects the last item of x . The resulting value must be a nonnegative integer less than the number of items in the sequence, and the subscription selects the item whose index is that value (counting from zero). Since the support for negative indices and slicing occurs in the object’s __getitem__() method, subclasses overriding this method will need to explicitly add that support.
A string is a special kind of sequence whose items are characters . A character is not a separate data type but a string of exactly one character.
6.3.3. Slicings ¶
A slicing selects a range of items in a sequence object (e.g., a string, tuple or list). Slicings may be used as expressions or as targets in assignment or del statements. The syntax for a slicing:
There is ambiguity in the formal syntax here: anything that looks like an expression list also looks like a slice list, so any subscription can be interpreted as a slicing. Rather than further complicating the syntax, this is disambiguated by defining that in this case the interpretation as a subscription takes priority over the interpretation as a slicing (this is the case if the slice list contains no proper slice).
The semantics for a slicing are as follows. The primary is indexed (using the same __getitem__() method as normal subscription) with a key that is constructed from the slice list, as follows. If the slice list contains at least one comma, the key is a tuple containing the conversion of the slice items; otherwise, the conversion of the lone slice item is the key. The conversion of a slice item that is an expression is that expression. The conversion of a proper slice is a slice object (see section The standard type hierarchy ) whose start , stop and step attributes are the values of the expressions given as lower bound, upper bound and stride, respectively, substituting None for missing expressions.
6.3.4. Calls ¶
A call calls a callable object (e.g., a function ) with a possibly empty series of arguments :
An optional trailing comma may be present after the positional and keyword arguments but does not affect the semantics.
The primary must evaluate to a callable object (user-defined functions, built-in functions, methods of built-in objects, class objects, methods of class instances, and all objects having a __call__() method are callable). All argument expressions are evaluated before the call is attempted. Please refer to section Function definitions for the syntax of formal parameter lists.
If keyword arguments are present, they are first converted to positional arguments, as follows. First, a list of unfilled slots is created for the formal parameters. If there are N positional arguments, they are placed in the first N slots. Next, for each keyword argument, the identifier is used to determine the corresponding slot (if the identifier is the same as the first formal parameter name, the first slot is used, and so on). If the slot is already filled, a TypeError exception is raised. Otherwise, the argument is placed in the slot, filling it (even if the expression is None , it fills the slot). When all arguments have been processed, the slots that are still unfilled are filled with the corresponding default value from the function definition. (Default values are calculated, once, when the function is defined; thus, a mutable object such as a list or dictionary used as default value will be shared by all calls that don’t specify an argument value for the corresponding slot; this should usually be avoided.) If there are any unfilled slots for which no default value is specified, a TypeError exception is raised. Otherwise, the list of filled slots is used as the argument list for the call.
CPython implementation detail: An implementation may provide built-in functions whose positional parameters do not have names, even if they are ‘named’ for the purpose of documentation, and which therefore cannot be supplied by keyword. In CPython, this is the case for functions implemented in C that use PyArg_ParseTuple() to parse their arguments.
If there are more positional arguments than there are formal parameter slots, a TypeError exception is raised, unless a formal parameter using the syntax *identifier is present; in this case, that formal parameter receives a tuple containing the excess positional arguments (or an empty tuple if there were no excess positional arguments).
If any keyword argument does not correspond to a formal parameter name, a TypeError exception is raised, unless a formal parameter using the syntax **identifier is present; in this case, that formal parameter receives a dictionary containing the excess keyword arguments (using the keywords as keys and the argument values as corresponding values), or a (new) empty dictionary if there were no excess keyword arguments.
If the syntax *expression appears in the function call, expression must evaluate to an iterable . Elements from these iterables are treated as if they were additional positional arguments. For the call f(x1, x2, *y, x3, x4) , if y evaluates to a sequence y1 , …, yM , this is equivalent to a call with M+4 positional arguments x1 , x2 , y1 , …, yM , x3 , x4 .
A consequence of this is that although the *expression syntax may appear after explicit keyword arguments, it is processed before the keyword arguments (and any **expression arguments – see below). So:
It is unusual for both keyword arguments and the *expression syntax to be used in the same call, so in practice this confusion does not often arise.
If the syntax **expression appears in the function call, expression must evaluate to a mapping , the contents of which are treated as additional keyword arguments. If a parameter matching a key has already been given a value (by an explicit keyword argument, or from another unpacking), a TypeError exception is raised.
When **expression is used, each key in this mapping must be a string. Each value from the mapping is assigned to the first formal parameter eligible for keyword assignment whose name is equal to the key. A key need not be a Python identifier (e.g. "max-temp °F" is acceptable, although it will not match any formal parameter that could be declared). If there is no match to a formal parameter the key-value pair is collected by the ** parameter, if there is one, or if there is not, a TypeError exception is raised.
Formal parameters using the syntax *identifier or **identifier cannot be used as positional argument slots or as keyword argument names.
Changed in version 3.5: Function calls accept any number of * and ** unpackings, positional arguments may follow iterable unpackings ( * ), and keyword arguments may follow dictionary unpackings ( ** ). Originally proposed by PEP 448 .
A call always returns some value, possibly None , unless it raises an exception. How this value is computed depends on the type of the callable object.
The code block for the function is executed, passing it the argument list. The first thing the code block will do is bind the formal parameters to the arguments; this is described in section Function definitions . When the code block executes a return statement, this specifies the return value of the function call.
The result is up to the interpreter; see Built-in Functions for the descriptions of built-in functions and methods.
A new instance of that class is returned.
The corresponding user-defined function is called, with an argument list that is one longer than the argument list of the call: the instance becomes the first argument.
The class must define a __call__() method; the effect is then the same as if that method was called.
6.4. Await expression ¶
Suspend the execution of coroutine on an awaitable object. Can only be used inside a coroutine function .
Added in version 3.5.
6.5. The power operator ¶
The power operator binds more tightly than unary operators on its left; it binds less tightly than unary operators on its right. The syntax is:
Thus, in an unparenthesized sequence of power and unary operators, the operators are evaluated from right to left (this does not constrain the evaluation order for the operands): -1**2 results in -1 .
The power operator has the same semantics as the built-in pow() function, when called with two arguments: it yields its left argument raised to the power of its right argument. The numeric arguments are first converted to a common type, and the result is of that type.
For int operands, the result has the same type as the operands unless the second argument is negative; in that case, all arguments are converted to float and a float result is delivered. For example, 10**2 returns 100 , but 10**-2 returns 0.01 .
Raising 0.0 to a negative power results in a ZeroDivisionError . Raising a negative number to a fractional power results in a complex number. (In earlier versions it raised a ValueError .)
This operation can be customized using the special __pow__() and __rpow__() methods.
6.6. Unary arithmetic and bitwise operations ¶
All unary arithmetic and bitwise operations have the same priority:
The unary - (minus) operator yields the negation of its numeric argument; the operation can be overridden with the __neg__() special method.
The unary + (plus) operator yields its numeric argument unchanged; the operation can be overridden with the __pos__() special method.
The unary ~ (invert) operator yields the bitwise inversion of its integer argument. The bitwise inversion of x is defined as -(x+1) . It only applies to integral numbers or to custom objects that override the __invert__() special method.
In all three cases, if the argument does not have the proper type, a TypeError exception is raised.
6.7. Binary arithmetic operations ¶
The binary arithmetic operations have the conventional priority levels. Note that some of these operations also apply to certain non-numeric types. Apart from the power operator, there are only two levels, one for multiplicative operators and one for additive operators:
The * (multiplication) operator yields the product of its arguments. The arguments must either both be numbers, or one argument must be an integer and the other must be a sequence. In the former case, the numbers are converted to a common type and then multiplied together. In the latter case, sequence repetition is performed; a negative repetition factor yields an empty sequence.
This operation can be customized using the special __mul__() and __rmul__() methods.
The @ (at) operator is intended to be used for matrix multiplication. No builtin Python types implement this operator.
This operation can be customized using the special __matmul__() and __rmatmul__() methods.
The / (division) and // (floor division) operators yield the quotient of their arguments. The numeric arguments are first converted to a common type. Division of integers yields a float, while floor division of integers results in an integer; the result is that of mathematical division with the ‘floor’ function applied to the result. Division by zero raises the ZeroDivisionError exception.
The division operation can be customized using the special __truediv__() and __rtruediv__() methods. The floor division operation can be customized using the special __floordiv__() and __rfloordiv__() methods.
The % (modulo) operator yields the remainder from the division of the first argument by the second. The numeric arguments are first converted to a common type. A zero right argument raises the ZeroDivisionError exception. The arguments may be floating-point numbers, e.g., 3.14%0.7 equals 0.34 (since 3.14 equals 4*0.7 + 0.34 .) The modulo operator always yields a result with the same sign as its second operand (or zero); the absolute value of the result is strictly smaller than the absolute value of the second operand [ 1 ] .
The floor division and modulo operators are connected by the following identity: x == (x//y)*y + (x%y) . Floor division and modulo are also connected with the built-in function divmod() : divmod(x, y) == (x//y, x%y) . [ 2 ] .
In addition to performing the modulo operation on numbers, the % operator is also overloaded by string objects to perform old-style string formatting (also known as interpolation). The syntax for string formatting is described in the Python Library Reference, section printf-style String Formatting .
The modulo operation can be customized using the special __mod__() and __rmod__() methods.
The floor division operator, the modulo operator, and the divmod() function are not defined for complex numbers. Instead, convert to a floating-point number using the abs() function if appropriate.
The + (addition) operator yields the sum of its arguments. The arguments must either both be numbers or both be sequences of the same type. In the former case, the numbers are converted to a common type and then added together. In the latter case, the sequences are concatenated.
This operation can be customized using the special __add__() and __radd__() methods.
The - (subtraction) operator yields the difference of its arguments. The numeric arguments are first converted to a common type.
This operation can be customized using the special __sub__() and __rsub__() methods.
6.8. Shifting operations ¶
The shifting operations have lower priority than the arithmetic operations:
These operators accept integers as arguments. They shift the first argument to the left or right by the number of bits given by the second argument.
The left shift operation can be customized using the special __lshift__() and __rlshift__() methods. The right shift operation can be customized using the special __rshift__() and __rrshift__() methods.
A right shift by n bits is defined as floor division by pow(2,n) . A left shift by n bits is defined as multiplication with pow(2,n) .
6.9. Binary bitwise operations ¶
Each of the three bitwise operations has a different priority level:
The & operator yields the bitwise AND of its arguments, which must be integers or one of them must be a custom object overriding __and__() or __rand__() special methods.
The ^ operator yields the bitwise XOR (exclusive OR) of its arguments, which must be integers or one of them must be a custom object overriding __xor__() or __rxor__() special methods.
The | operator yields the bitwise (inclusive) OR of its arguments, which must be integers or one of them must be a custom object overriding __or__() or __ror__() special methods.
6.10. Comparisons ¶
Unlike C, all comparison operations in Python have the same priority, which is lower than that of any arithmetic, shifting or bitwise operation. Also unlike C, expressions like a < b < c have the interpretation that is conventional in mathematics:
Comparisons yield boolean values: True or False . Custom rich comparison methods may return non-boolean values. In this case Python will call bool() on such value in boolean contexts.
Comparisons can be chained arbitrarily, e.g., x < y <= z is equivalent to x < y and y <= z , except that y is evaluated only once (but in both cases z is not evaluated at all when x < y is found to be false).
Formally, if a , b , c , …, y , z are expressions and op1 , op2 , …, opN are comparison operators, then a op1 b op2 c ... y opN z is equivalent to a op1 b and b op2 c and ... y opN z , except that each expression is evaluated at most once.
Note that a op1 b op2 c doesn’t imply any kind of comparison between a and c , so that, e.g., x < y > z is perfectly legal (though perhaps not pretty).
6.10.1. Value comparisons ¶
The operators < , > , == , >= , <= , and != compare the values of two objects. The objects do not need to have the same type.
Chapter Objects, values and types states that objects have a value (in addition to type and identity). The value of an object is a rather abstract notion in Python: For example, there is no canonical access method for an object’s value. Also, there is no requirement that the value of an object should be constructed in a particular way, e.g. comprised of all its data attributes. Comparison operators implement a particular notion of what the value of an object is. One can think of them as defining the value of an object indirectly, by means of their comparison implementation.
Because all types are (direct or indirect) subtypes of object , they inherit the default comparison behavior from object . Types can customize their comparison behavior by implementing rich comparison methods like __lt__() , described in Basic customization .
The default behavior for equality comparison ( == and != ) is based on the identity of the objects. Hence, equality comparison of instances with the same identity results in equality, and equality comparison of instances with different identities results in inequality. A motivation for this default behavior is the desire that all objects should be reflexive (i.e. x is y implies x == y ).
A default order comparison ( < , > , <= , and >= ) is not provided; an attempt raises TypeError . A motivation for this default behavior is the lack of a similar invariant as for equality.
The behavior of the default equality comparison, that instances with different identities are always unequal, may be in contrast to what types will need that have a sensible definition of object value and value-based equality. Such types will need to customize their comparison behavior, and in fact, a number of built-in types have done that.
The following list describes the comparison behavior of the most important built-in types.
Numbers of built-in numeric types ( Numeric Types — int, float, complex ) and of the standard library types fractions.Fraction and decimal.Decimal can be compared within and across their types, with the restriction that complex numbers do not support order comparison. Within the limits of the types involved, they compare mathematically (algorithmically) correct without loss of precision.
The not-a-number values float('NaN') and decimal.Decimal('NaN') are special. Any ordered comparison of a number to a not-a-number value is false. A counter-intuitive implication is that not-a-number values are not equal to themselves. For example, if x = float('NaN') , 3 < x , x < 3 and x == x are all false, while x != x is true. This behavior is compliant with IEEE 754.
None and NotImplemented are singletons. PEP 8 advises that comparisons for singletons should always be done with is or is not , never the equality operators.
Binary sequences (instances of bytes or bytearray ) can be compared within and across their types. They compare lexicographically using the numeric values of their elements.
Strings (instances of str ) compare lexicographically using the numerical Unicode code points (the result of the built-in function ord() ) of their characters. [ 3 ]
Strings and binary sequences cannot be directly compared.
Sequences (instances of tuple , list , or range ) can be compared only within each of their types, with the restriction that ranges do not support order comparison. Equality comparison across these types results in inequality, and ordering comparison across these types raises TypeError .
Sequences compare lexicographically using comparison of corresponding elements. The built-in containers typically assume identical objects are equal to themselves. That lets them bypass equality tests for identical objects to improve performance and to maintain their internal invariants.
Lexicographical comparison between built-in collections works as follows:
For two collections to compare equal, they must be of the same type, have the same length, and each pair of corresponding elements must compare equal (for example, [1,2] == (1,2) is false because the type is not the same).
Collections that support order comparison are ordered the same as their first unequal elements (for example, [1,2,x] <= [1,2,y] has the same value as x <= y ). If a corresponding element does not exist, the shorter collection is ordered first (for example, [1,2] < [1,2,3] is true).
Mappings (instances of dict ) compare equal if and only if they have equal (key, value) pairs. Equality comparison of the keys and values enforces reflexivity.
Order comparisons ( < , > , <= , and >= ) raise TypeError .
Sets (instances of set or frozenset ) can be compared within and across their types.
They define order comparison operators to mean subset and superset tests. Those relations do not define total orderings (for example, the two sets {1,2} and {2,3} are not equal, nor subsets of one another, nor supersets of one another). Accordingly, sets are not appropriate arguments for functions which depend on total ordering (for example, min() , max() , and sorted() produce undefined results given a list of sets as inputs).
Comparison of sets enforces reflexivity of its elements.
Most other built-in types have no comparison methods implemented, so they inherit the default comparison behavior.
User-defined classes that customize their comparison behavior should follow some consistency rules, if possible:
Equality comparison should be reflexive. In other words, identical objects should compare equal:
x is y implies x == y
Comparison should be symmetric. In other words, the following expressions should have the same result:
x == y and y == x x != y and y != x x < y and y > x x <= y and y >= x
Comparison should be transitive. The following (non-exhaustive) examples illustrate that:
x > y and y > z implies x > z x < y and y <= z implies x < z
Inverse comparison should result in the boolean negation. In other words, the following expressions should have the same result:
x == y and not x != y x < y and not x >= y (for total ordering) x > y and not x <= y (for total ordering)
The last two expressions apply to totally ordered collections (e.g. to sequences, but not to sets or mappings). See also the total_ordering() decorator.
The hash() result should be consistent with equality. Objects that are equal should either have the same hash value, or be marked as unhashable.
Python does not enforce these consistency rules. In fact, the not-a-number values are an example for not following these rules.
6.10.2. Membership test operations ¶
The operators in and not in test for membership. x in s evaluates to True if x is a member of s , and False otherwise. x not in s returns the negation of x in s . All built-in sequences and set types support this as well as dictionary, for which in tests whether the dictionary has a given key. For container types such as list, tuple, set, frozenset, dict, or collections.deque, the expression x in y is equivalent to any(x is e or x == e for e in y) .
For the string and bytes types, x in y is True if and only if x is a substring of y . An equivalent test is y.find(x) != -1 . Empty strings are always considered to be a substring of any other string, so "" in "abc" will return True .
For user-defined classes which define the __contains__() method, x in y returns True if y.__contains__(x) returns a true value, and False otherwise.
For user-defined classes which do not define __contains__() but do define __iter__() , x in y is True if some value z , for which the expression x is z or x == z is true, is produced while iterating over y . If an exception is raised during the iteration, it is as if in raised that exception.
Lastly, the old-style iteration protocol is tried: if a class defines __getitem__() , x in y is True if and only if there is a non-negative integer index i such that x is y[i] or x == y[i] , and no lower integer index raises the IndexError exception. (If any other exception is raised, it is as if in raised that exception).
The operator not in is defined to have the inverse truth value of in .
6.10.3. Identity comparisons ¶
The operators is and is not test for an object’s identity: x is y is true if and only if x and y are the same object. An Object’s identity is determined using the id() function. x is not y yields the inverse truth value. [ 4 ]
6.11. Boolean operations ¶
In the context of Boolean operations, and also when expressions are used by control flow statements, the following values are interpreted as false: False , None , numeric zero of all types, and empty strings and containers (including strings, tuples, lists, dictionaries, sets and frozensets). All other values are interpreted as true. User-defined objects can customize their truth value by providing a __bool__() method.
The operator not yields True if its argument is false, False otherwise.
The expression x and y first evaluates x ; if x is false, its value is returned; otherwise, y is evaluated and the resulting value is returned.
The expression x or y first evaluates x ; if x is true, its value is returned; otherwise, y is evaluated and the resulting value is returned.
Note that neither and nor or restrict the value and type they return to False and True , but rather return the last evaluated argument. This is sometimes useful, e.g., if s is a string that should be replaced by a default value if it is empty, the expression s or 'foo' yields the desired value. Because not has to create a new value, it returns a boolean value regardless of the type of its argument (for example, not 'foo' produces False rather than '' .)
6.12. Assignment expressions ¶
An assignment expression (sometimes also called a “named expression” or “walrus”) assigns an expression to an identifier , while also returning the value of the expression .
One common use case is when handling matched regular expressions:
Or, when processing a file stream in chunks:
Assignment expressions must be surrounded by parentheses when used as expression statements and when used as sub-expressions in slicing, conditional, lambda, keyword-argument, and comprehension-if expressions and in assert , with , and assignment statements. In all other places where they can be used, parentheses are not required, including in if and while statements.
Added in version 3.8: See PEP 572 for more details about assignment expressions.
6.13. Conditional expressions ¶
Conditional expressions (sometimes called a “ternary operator”) have the lowest priority of all Python operations.
The expression x if C else y first evaluates the condition, C rather than x . If C is true, x is evaluated and its value is returned; otherwise, y is evaluated and its value is returned.
See PEP 308 for more details about conditional expressions.
6.14. Lambdas ¶
Lambda expressions (sometimes called lambda forms) are used to create anonymous functions. The expression lambda parameters: expression yields a function object. The unnamed object behaves like a function object defined with:
See section Function definitions for the syntax of parameter lists. Note that functions created with lambda expressions cannot contain statements or annotations.
6.15. Expression lists ¶
Except when part of a list or set display, an expression list containing at least one comma yields a tuple. The length of the tuple is the number of expressions in the list. The expressions are evaluated from left to right.
An asterisk * denotes iterable unpacking . Its operand must be an iterable . The iterable is expanded into a sequence of items, which are included in the new tuple, list, or set, at the site of the unpacking.
Added in version 3.5: Iterable unpacking in expression lists, originally proposed by PEP 448 .
A trailing comma is required only to create a one-item tuple, such as 1, ; it is optional in all other cases. A single expression without a trailing comma doesn’t create a tuple, but rather yields the value of that expression. (To create an empty tuple, use an empty pair of parentheses: () .)
6.16. Evaluation order ¶
Python evaluates expressions from left to right. Notice that while evaluating an assignment, the right-hand side is evaluated before the left-hand side.
In the following lines, expressions will be evaluated in the arithmetic order of their suffixes:
6.17. Operator precedence ¶
The following table summarizes the operator precedence in Python, from highest precedence (most binding) to lowest precedence (least binding). Operators in the same box have the same precedence. Unless the syntax is explicitly given, operators are binary. Operators in the same box group left to right (except for exponentiation and conditional expressions, which group from right to left).
Note that comparisons, membership tests, and identity tests, all have the same precedence and have a left-to-right chaining feature as described in the Comparisons section.
Operator | Description |
|---|---|
, , value...}, | Binding or parenthesized expression, list display, dictionary display, set display |
, , , | Subscription, slicing, call, attribute reference |
x | Await expression |
| Exponentiation 5] |
, , | Positive, negative, bitwise NOT |
, , , , | Multiplication, matrix multiplication, division, floor division, remainder 6] |
, | Addition and subtraction |
, | Shifts |
| Bitwise AND |
| Bitwise XOR |
| Bitwise OR |
, in, , not, , , , , , | Comparisons, including membership tests and identity tests |
x | Boolean NOT |
| Boolean AND |
| Boolean OR |
– | Conditional expression |
| Lambda expression |
| Assignment expression |
Table of Contents
- 6.1. Arithmetic conversions
- 6.2.1.1. Private name mangling
- 6.2.2. Literals
- 6.2.3. Parenthesized forms
- 6.2.4. Displays for lists, sets and dictionaries
- 6.2.5. List displays
- 6.2.6. Set displays
- 6.2.7. Dictionary displays
- 6.2.8. Generator expressions
- 6.2.9.1. Generator-iterator methods
- 6.2.9.2. Examples
- 6.2.9.3. Asynchronous generator functions
- 6.2.9.4. Asynchronous generator-iterator methods
- 6.3.1. Attribute references
- 6.3.2. Subscriptions
- 6.3.3. Slicings
- 6.3.4. Calls
- 6.4. Await expression
- 6.5. The power operator
- 6.6. Unary arithmetic and bitwise operations
- 6.7. Binary arithmetic operations
- 6.8. Shifting operations
- 6.9. Binary bitwise operations
- 6.10.1. Value comparisons
- 6.10.2. Membership test operations
- 6.10.3. Identity comparisons
- 6.11. Boolean operations
- 6.12. Assignment expressions
- 6.13. Conditional expressions
- 6.14. Lambdas
- 6.15. Expression lists
- 6.16. Evaluation order
- 6.17. Operator precedence
Previous topic
5. The import system
7. Simple statements
- Report a Bug
- Show Source

- Python Basics
- Python - Home
- Python - Overview
- Python - History
- Python - Features
- Python vs C++
- Python - Hello World Program
- Python - Application Areas
- Python - Interpreter
- Python - Environment Setup
- Python - Virtual Environment
- Python - Basic Syntax
- Python - Variables
- Python - Data Types
- Python - Type Casting
- Python - Unicode System
- Python - Literals
- Python - Operators
- Python - Arithmetic Operators
- Python - Comparison Operators
Python - Assignment Operators
- Python - Logical Operators
- Python - Bitwise Operators
- Python - Membership Operators
- Python - Identity Operators
- Python - Operator Precedence
- Python - Comments
- Python - User Input
- Python - Numbers
- Python - Booleans
- Python Control Statements
- Python - Control Flow
- Python - Decision Making
- Python - If Statement
- Python - If else
- Python - Nested If
- Python - Match-Case Statement
- Python - Loops
- Python - for Loops
- Python - for-else Loops
- Python - While Loops
- Python - break Statement
- Python - continue Statement
- Python - pass Statement
- Python - Nested Loops
- Python Functions & Modules
- Python - Functions
- Python - Default Arguments
- Python - Keyword Arguments
- Python - Keyword-Only Arguments
- Python - Positional Arguments
- Python - Positional-Only Arguments
- Python - Arbitrary Arguments
- Python - Variables Scope
- Python - Function Annotations
- Python - Modules
- Python - Built in Functions
- Python Strings
- Python - Strings
- Python - Slicing Strings
- Python - Modify Strings
- Python - String Concatenation
- Python - String Formatting
- Python - Escape Characters
- Python - String Methods
- Python - String Exercises
- Python Lists
- Python - Lists
- Python - Access List Items
- Python - Change List Items
- Python - Add List Items
- Python - Remove List Items
- Python - Loop Lists
- Python - List Comprehension
- Python - Sort Lists
- Python - Copy Lists
- Python - Join Lists
- Python - List Methods
- Python - List Exercises
- Python Tuples
- Python - Tuples
- Python - Access Tuple Items
- Python - Update Tuples
- Python - Unpack Tuples
- Python - Loop Tuples
- Python - Join Tuples
- Python - Tuple Methods
- Python - Tuple Exercises
- Python Sets
- Python - Sets
- Python - Access Set Items
- Python - Add Set Items
- Python - Remove Set Items
- Python - Loop Sets
- Python - Join Sets
- Python - Copy Sets
- Python - Set Operators
- Python - Set Methods
- Python - Set Exercises
- Python Dictionaries
- Python - Dictionaries
- Python - Access Dictionary Items
- Python - Change Dictionary Items
- Python - Add Dictionary Items
- Python - Remove Dictionary Items
- Python - Dictionary View Objects
- Python - Loop Dictionaries
- Python - Copy Dictionaries
- Python - Nested Dictionaries
- Python - Dictionary Methods
- Python - Dictionary Exercises
- Python Arrays
- Python - Arrays
- Python - Access Array Items
- Python - Add Array Items
- Python - Remove Array Items
- Python - Loop Arrays
- Python - Copy Arrays
- Python - Reverse Arrays
- Python - Sort Arrays
- Python - Join Arrays
- Python - Array Methods
- Python - Array Exercises
- Python File Handling
- Python - File Handling
- Python - Write to File
- Python - Read Files
- Python - Renaming and Deleting Files
- Python - Directories
- Python - File Methods
- Python - OS File/Directory Methods
- Python - OS Path Methods
- Object Oriented Programming
- Python - OOPs Concepts
- Python - Classes & Objects
- Python - Class Attributes
- Python - Class Methods
- Python - Static Methods
- Python - Constructors
- Python - Access Modifiers
- Python - Inheritance
- Python - Polymorphism
- Python - Method Overriding
- Python - Method Overloading
- Python - Dynamic Binding
- Python - Dynamic Typing
- Python - Abstraction
- Python - Encapsulation
- Python - Interfaces
- Python - Packages
- Python - Inner Classes
- Python - Anonymous Class and Objects
- Python - Singleton Class
- Python - Wrapper Classes
- Python - Enums
- Python - Reflection
- Python Errors & Exceptions
- Python - Syntax Errors
- Python - Exceptions
- Python - try-except Block
- Python - try-finally Block
- Python - Raising Exceptions
- Python - Exception Chaining
- Python - Nested try Block
- Python - User-defined Exception
- Python - Logging
- Python - Assertions
- Python - Built-in Exceptions
- Python Multithreading
- Python - Multithreading
- Python - Thread Life Cycle
- Python - Creating a Thread
- Python - Starting a Thread
- Python - Joining Threads
- Python - Naming Thread
- Python - Thread Scheduling
- Python - Thread Pools
- Python - Main Thread
- Python - Thread Priority
- Python - Daemon Threads
- Python - Synchronizing Threads
- Python Synchronization
- Python - Inter-thread Communication
- Python - Thread Deadlock
- Python - Interrupting a Thread
- Python Networking
- Python - Networking
- Python - Socket Programming
- Python - URL Processing
- Python - Generics
- Python Libraries
- NumPy Tutorial
- Pandas Tutorial
- SciPy Tutorial
- Matplotlib Tutorial
- Django Tutorial
- OpenCV Tutorial
- Python Miscellenous
- Python - Date & Time
- Python - Maths
- Python - Iterators
- Python - Generators
- Python - Closures
- Python - Decorators
- Python - Recursion
- Python - Reg Expressions
- Python - PIP
- Python - Database Access
- Python - Weak References
- Python - Serialization
- Python - Templating
- Python - Output Formatting
- Python - Performance Measurement
- Python - Data Compression
- Python - CGI Programming
- Python - XML Processing
- Python - GUI Programming
- Python - Command-Line Arguments
- Python - Docstrings
- Python - JSON
- Python - Sending Email
- Python - Further Extensions
- Python - Tools/Utilities
- Python - GUIs
- Python Advanced Concepts
- Python - Abstract Base Classes
- Python - Custom Exceptions
- Python - Higher Order Functions
- Python - Object Internals
- Python - Memory Management
- Python - Metaclasses
- Python - Metaprogramming with Metaclasses
- Python - Mocking and Stubbing
- Python - Monkey Patching
- Python - Signal Handling
- Python - Type Hints
- Python - Automation Tutorial
- Python - Humanize Package
- Python - Context Managers
- Python - Coroutines
- Python - Descriptors
- Python - Diagnosing and Fixing Memory Leaks
- Python - Immutable Data Structures
- Python Useful Resources
- Python Compiler
- NumPy Compiler
- Matplotlib Compiler
- SciPy Compiler
- Python - Questions & Answers
- Python - Online Quiz
- Python - Programming Examples
- Python - Quick Guide
- Python - Useful Resources
- Python - Discussion
- Selected Reading
- UPSC IAS Exams Notes
- Developer's Best Practices
- Questions and Answers
- Effective Resume Writing
- HR Interview Questions
- Computer Glossary
Python Assignment Operator
The = (equal to) symbol is defined as assignment operator in Python. The value of Python expression on its right is assigned to a single variable on its left. The = symbol as in programming in general (and Python in particular) should not be confused with its usage in Mathematics, where it states that the expressions on the either side of the symbol are equal.
Example of Assignment Operator in Python
Consider following Python statements −
At the first instance, at least for somebody new to programming but who knows maths, the statement "a=a+b" looks strange. How could a be equal to "a+b"? However, it needs to be reemphasized that the = symbol is an assignment operator here and not used to show the equality of LHS and RHS.
Because it is an assignment, the expression on right evaluates to 15, the value is assigned to a.
In the statement "a+=b", the two operators "+" and "=" can be combined in a "+=" operator. It is called as add and assign operator. In a single statement, it performs addition of two operands "a" and "b", and result is assigned to operand on left, i.e., "a".
Augmented Assignment Operators in Python
In addition to the simple assignment operator, Python provides few more assignment operators for advanced use. They are called cumulative or augmented assignment operators. In this chapter, we shall learn to use augmented assignment operators defined in Python.
Python has the augmented assignment operators for all arithmetic and comparison operators.
Python augmented assignment operators combines addition and assignment in one statement. Since Python supports mixed arithmetic, the two operands may be of different types. However, the type of left operand changes to the operand of on right, if it is wider.
The += operator is an augmented operator. It is also called cumulative addition operator, as it adds "b" in "a" and assigns the result back to a variable.
The following are the augmented assignment operators in Python:
- Augmented Addition Operator
- Augmented Subtraction Operator
- Augmented Multiplication Operator
- Augmented Division Operator
- Augmented Modulus Operator
- Augmented Exponent Operator
- Augmented Floor division Operator
Augmented Addition Operator (+=)
Following examples will help in understanding how the "+=" operator works −
It will produce the following output −
Augmented Subtraction Operator (-=)
Use -= symbol to perform subtract and assign operations in a single statement. The "a-=b" statement performs "a=a-b" assignment. Operands may be of any number type. Python performs implicit type casting on the object which is narrower in size.
Augmented Multiplication Operator (*=)
The "*=" operator works on similar principle. "a*=b" performs multiply and assign operations, and is equivalent to "a=a*b". In case of augmented multiplication of two complex numbers, the rule of multiplication as discussed in the previous chapter is applicable.
Augmented Division Operator (/=)
The combination symbol "/=" acts as divide and assignment operator, hence "a/=b" is equivalent to "a=a/b". The division operation of int or float operands is float. Division of two complex numbers returns a complex number. Given below are examples of augmented division operator.
Augmented Modulus Operator (%=)
To perform modulus and assignment operation in a single statement, use the %= operator. Like the mod operator, its augmented version also is not supported for complex number.
Augmented Exponent Operator (**=)
The "**=" operator results in computation of "a" raised to "b", and assigning the value back to "a". Given below are some examples −

Augmented Floor division Operator (//=)
For performing floor division and assignment in a single statement, use the "//=" operator. "a//=b" is equivalent to "a=a//b". This operator cannot be used with complex numbers.
- Hands-on Python Tutorial »
- 1. Beginning With Python »
1.6. Variables and Assignment ¶
Each set-off line in this section should be tried in the Shell.
Nothing is displayed by the interpreter after this entry, so it is not clear anything happened. Something has happened. This is an assignment statement , with a variable , width , on the left. A variable is a name for a value. An assignment statement associates a variable name on the left of the equal sign with the value of an expression calculated from the right of the equal sign. Enter
Once a variable is assigned a value, the variable can be used in place of that value. The response to the expression width is the same as if its value had been entered.
The interpreter does not print a value after an assignment statement because the value of the expression on the right is not lost. It can be recovered if you like, by entering the variable name and we did above.
Try each of the following lines:
The equal sign is an unfortunate choice of symbol for assignment, since Python’s usage is not the mathematical usage of the equal sign. If the symbol ↤ had appeared on keyboards in the early 1990’s, it would probably have been used for assignment instead of =, emphasizing the asymmetry of assignment. In mathematics an equation is an assertion that both sides of the equal sign are already, in fact, equal . A Python assignment statement forces the variable on the left hand side to become associated with the value of the expression on the right side. The difference from the mathematical usage can be illustrated. Try:
so this is not equivalent in Python to width = 10 . The left hand side must be a variable, to which the assignment is made. Reversed, we get a syntax error . Try
This is, of course, nonsensical as mathematics, but it makes perfectly good sense as an assignment, with the right-hand side calculated first. Can you figure out the value that is now associated with width? Check by entering
In the assignment statement, the expression on the right is evaluated first . At that point width was associated with its original value 10, so width + 5 had the value of 10 + 5 which is 15. That value was then assigned to the variable on the left ( width again) to give it a new value. We will modify the value of variables in a similar way routinely.
Assignment and variables work equally well with strings. Try:
Try entering:
Note the different form of the error message. The earlier errors in these tutorials were syntax errors: errors in translation of the instruction. In this last case the syntax was legal, so the interpreter went on to execute the instruction. Only then did it find the error described. There are no quotes around fred , so the interpreter assumed fred was an identifier, but the name fred was not defined at the time the line was executed.
It is both easy to forget quotes where you need them for a literal string and to mistakenly put them around a variable name that should not have them!
Try in the Shell :
There fred , without the quotes, makes sense.
There are more subtleties to assignment and the idea of a variable being a “name for” a value, but we will worry about them later, in Issues with Mutable Objects . They do not come up if our variables are just numbers and strings.
Autocompletion: A handy short cut. Idle remembers all the variables you have defined at any moment. This is handy when editing. Without pressing Enter, type into the Shell just
Assuming you are following on the earlier variable entries to the Shell, you should see f autocompleted to be
This is particularly useful if you have long identifiers! You can press Alt-/ several times if more than one identifier starts with the initial sequence of characters you typed. If you press Alt-/ again you should see fred . Backspace and edit so you have fi , and then and press Alt-/ again. You should not see fred this time, since it does not start with fi .
1.6.1. Literals and Identifiers ¶
Expressions like 27 or 'hello' are called literals , coming from the fact that they literally mean exactly what they say. They are distinguished from variables, whose value is not directly determined by their name.
The sequence of characters used to form a variable name (and names for other Python entities later) is called an identifier . It identifies a Python variable or other entity.
There are some restrictions on the character sequence that make up an identifier:
The characters must all be letters, digits, or underscores _ , and must start with a letter. In particular, punctuation and blanks are not allowed.
There are some words that are reserved for special use in Python. You may not use these words as your own identifiers. They are easy to recognize in Idle, because they are automatically colored orange. For the curious, you may read the full list:
There are also identifiers that are automatically defined in Python, and that you could redefine, but you probably should not unless you really know what you are doing! When you start the editor, we will see how Idle uses color to help you know what identifies are predefined.
Python is case sensitive: The identifiers last , LAST , and LaSt are all different. Be sure to be consistent. Using the Alt-/ auto-completion shortcut in Idle helps ensure you are consistent.
What is legal is distinct from what is conventional or good practice or recommended. Meaningful names for variables are important for the humans who are looking at programs, understanding them, and revising them. That sometimes means you would like to use a name that is more than one word long, like price at opening , but blanks are illegal! One poor option is just leaving out the blanks, like priceatopening . Then it may be hard to figure out where words split. Two practical options are
- underscore separated: putting underscores (which are legal) in place of the blanks, like price_at_opening .
- using camel-case : omitting spaces and using all lowercase, except capitalizing all words after the first, like priceAtOpening
Use the choice that fits your taste (or the taste or convention of the people you are working with).
Table Of Contents
- 1.6.1. Literals and Identifiers
Previous topic
1.5. Strings, Part I
1.7. Print Function, Part I
- Show Source
Quick search
Enter search terms or a module, class or function name.
- Python Course
- Python Basics
- Interview Questions
- Python Quiz
- Popular Packages
- Python Projects
- Practice Python
- AI With Python
- Learn Python3
- Python Automation
- Python Web Dev
- DSA with Python
- Python OOPs
- Dictionaries
Assignment Operators in Python
The Python Operators are used to perform operations on values and variables. These are the special symbols that carry out arithmetic, logical, and bitwise computations. The value the operator operates on is known as the Operand. Here, we will cover Different Assignment operators in Python .
Operators |
| ||
|---|---|---|---|
| = | Assign the value of the right side of the expression to the left side operand | c = a + b |
| += | Add right side operand with left side operand and then assign the result to left operand | a += b |
| -= | Subtract right side operand from left side operand and then assign the result to left operand | a -= b |
| *= | Multiply right operand with left operand and then assign the result to the left operand | a *= b |
| /= | Divide left operand with right operand and then assign the result to the left operand | a /= b |
| %= | Divides the left operand with the right operand and then assign the remainder to the left operand | a %= b |
| //= | Divide left operand with right operand and then assign the value(floor) to left operand | a //= b |
| **= | Calculate exponent(raise power) value using operands and then assign the result to left operand | a **= b |
| &= | Performs Bitwise AND on operands and assign the result to left operand | a &= b |
| |= | Performs Bitwise OR on operands and assign the value to left operand | a |= b |
| ^= | Performs Bitwise XOR on operands and assign the value to left operand | a ^= b |
| >>= | Performs Bitwise right shift on operands and assign the result to left operand | a >>= b |
| <<= | Performs Bitwise left shift on operands and assign the result to left operand | a <<= b |
| := | Assign a value to a variable within an expression | a := exp |
Here are the Assignment Operators in Python with examples.
Assignment Operator
Assignment Operators are used to assign values to variables. This operator is used to assign the value of the right side of the expression to the left side operand.
Addition Assignment Operator
The Addition Assignment Operator is used to add the right-hand side operand with the left-hand side operand and then assigning the result to the left operand.
Example: In this code we have two variables ‘a’ and ‘b’ and assigned them with some integer value. Then we have used the addition assignment operator which will first perform the addition operation and then assign the result to the variable on the left-hand side.
S ubtraction Assignment Operator
The Subtraction Assignment Operator is used to subtract the right-hand side operand from the left-hand side operand and then assigning the result to the left-hand side operand.
Example: In this code we have two variables ‘a’ and ‘b’ and assigned them with some integer value. Then we have used the subtraction assignment operator which will first perform the subtraction operation and then assign the result to the variable on the left-hand side.
M ultiplication Assignment Operator
The Multiplication Assignment Operator is used to multiply the right-hand side operand with the left-hand side operand and then assigning the result to the left-hand side operand.
Example: In this code we have two variables ‘a’ and ‘b’ and assigned them with some integer value. Then we have used the multiplication assignment operator which will first perform the multiplication operation and then assign the result to the variable on the left-hand side.
D ivision Assignment Operator
The Division Assignment Operator is used to divide the left-hand side operand with the right-hand side operand and then assigning the result to the left operand.
Example: In this code we have two variables ‘a’ and ‘b’ and assigned them with some integer value. Then we have used the division assignment operator which will first perform the division operation and then assign the result to the variable on the left-hand side.
M odulus Assignment Operator
The Modulus Assignment Operator is used to take the modulus, that is, it first divides the operands and then takes the remainder and assigns it to the left operand.
Example: In this code we have two variables ‘a’ and ‘b’ and assigned them with some integer value. Then we have used the modulus assignment operator which will first perform the modulus operation and then assign the result to the variable on the left-hand side.
F loor Division Assignment Operator
The Floor Division Assignment Operator is used to divide the left operand with the right operand and then assigs the result(floor value) to the left operand.
Example: In this code we have two variables ‘a’ and ‘b’ and assigned them with some integer value. Then we have used the floor division assignment operator which will first perform the floor division operation and then assign the result to the variable on the left-hand side.
Exponentiation Assignment Operator
The Exponentiation Assignment Operator is used to calculate the exponent(raise power) value using operands and then assigning the result to the left operand.
Example: In this code we have two variables ‘a’ and ‘b’ and assigned them with some integer value. Then we have used the exponentiation assignment operator which will first perform exponent operation and then assign the result to the variable on the left-hand side.
Bitwise AND Assignment Operator
The Bitwise AND Assignment Operator is used to perform Bitwise AND operation on both operands and then assigning the result to the left operand.
Example: In this code we have two variables ‘a’ and ‘b’ and assigned them with some integer value. Then we have used the bitwise AND assignment operator which will first perform Bitwise AND operation and then assign the result to the variable on the left-hand side.
Bitwise OR Assignment Operator
The Bitwise OR Assignment Operator is used to perform Bitwise OR operation on the operands and then assigning result to the left operand.
Example: In this code we have two variables ‘a’ and ‘b’ and assigned them with some integer value. Then we have used the bitwise OR assignment operator which will first perform bitwise OR operation and then assign the result to the variable on the left-hand side.
Bitwise XOR Assignment Operator
The Bitwise XOR Assignment Operator is used to perform Bitwise XOR operation on the operands and then assigning result to the left operand.
Example: In this code we have two variables ‘a’ and ‘b’ and assigned them with some integer value. Then we have used the bitwise XOR assignment operator which will first perform bitwise XOR operation and then assign the result to the variable on the left-hand side.
Bitwise Right Shift Assignment Operator
The Bitwise Right Shift Assignment Operator is used to perform Bitwise Right Shift Operation on the operands and then assign result to the left operand.
Example: In this code we have two variables ‘a’ and ‘b’ and assigned them with some integer value. Then we have used the bitwise right shift assignment operator which will first perform bitwise right shift operation and then assign the result to the variable on the left-hand side.
Bitwise Left Shift Assignment Operator
The Bitwise Left Shift Assignment Operator is used to perform Bitwise Left Shift Opertator on the operands and then assign result to the left operand.
Example: In this code we have two variables ‘a’ and ‘b’ and assigned them with some integer value. Then we have used the bitwise left shift assignment operator which will first perform bitwise left shift operation and then assign the result to the variable on the left-hand side.
Walrus Operator
The Walrus Operator in Python is a new assignment operator which is introduced in Python version 3.8 and higher. This operator is used to assign a value to a variable within an expression.
Example: In this code, we have a Python list of integers. We have used Python Walrus assignment operator within the Python while loop . The operator will solve the expression on the right-hand side and assign the value to the left-hand side operand ‘x’ and then execute the remaining code.
Assignment Operators in Python – FAQs
What are assignment operators in python.
Assignment operators in Python are used to assign values to variables. These operators can also perform additional operations during the assignment. The basic assignment operator is = , which simply assigns the value of the right-hand operand to the left-hand operand. Other common assignment operators include += , -= , *= , /= , %= , and more, which perform an operation on the variable and then assign the result back to the variable.
What is the := Operator in Python?
The := operator, introduced in Python 3.8, is known as the “walrus operator”. It is an assignment expression, which means that it assigns values to variables as part of a larger expression. Its main benefit is that it allows you to assign values to variables within expressions, including within conditions of loops and if statements, thereby reducing the need for additional lines of code. Here’s an example: # Example of using the walrus operator in a while loop while (n := int(input("Enter a number (0 to stop): "))) != 0: print(f"You entered: {n}") This loop continues to prompt the user for input and immediately uses that input in both the condition check and the loop body.
What is the Assignment Operator in Structure?
In programming languages that use structures (like C or C++), the assignment operator = is used to copy values from one structure variable to another. Each member of the structure is copied from the source structure to the destination structure. Python, however, does not have a built-in concept of ‘structures’ as in C or C++; instead, similar functionality is achieved through classes or dictionaries.
What is the Assignment Operator in Python Dictionary?
In Python dictionaries, the assignment operator = is used to assign a new key-value pair to the dictionary or update the value of an existing key. Here’s how you might use it: my_dict = {} # Create an empty dictionary my_dict['key1'] = 'value1' # Assign a new key-value pair my_dict['key1'] = 'updated value' # Update the value of an existing key print(my_dict) # Output: {'key1': 'updated value'}
What is += and -= in Python?
The += and -= operators in Python are compound assignment operators. += adds the right-hand operand to the left-hand operand and assigns the result to the left-hand operand. Conversely, -= subtracts the right-hand operand from the left-hand operand and assigns the result to the left-hand operand. Here are examples of both: # Example of using += a = 5 a += 3 # Equivalent to a = a + 3 print(a) # Output: 8 # Example of using -= b = 10 b -= 4 # Equivalent to b = b - 4 print(b) # Output: 6 These operators make code more concise and are commonly used in loops and iterative data processing.

Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Python-Operators
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

Python Conditional Assignment
When you want to assign a value to a variable based on some condition, like if the condition is true then assign a value to the variable, else assign some other value to the variable, then you can use the conditional assignment operator.
In this tutorial, we will look at different ways to assign values to a variable based on some condition.
1. Using Ternary Operator
The ternary operator is very special operator in Python, it is used to assign a value to a variable based on some condition.
It goes like this:
Here, the value of variable will be value_if_true if the condition is true, else it will be value_if_false .
Let's see a code snippet to understand it better.
You can see we have conditionally assigned a value to variable c based on the condition a > b .
2. Using if-else statement
if-else statements are the core part of any programming language, they are used to execute a block of code based on some condition.
Using an if-else statement, we can assign a value to a variable based on the condition we provide.
Here is an example of replacing the above code snippet with the if-else statement.
3. Using Logical Short Circuit Evaluation
Logical short circuit evaluation is another way using which you can assign a value to a variable conditionally.
The format of logical short circuit evaluation is:
It looks similar to ternary operator, but it is not. Here the condition and value_if_true performs logical AND operation, if both are true then the value of variable will be value_if_true , or else it will be value_if_false .
Let's see an example:
But if we make condition True but value_if_true False (or 0 or None), then the value of variable will be value_if_false .
So, you can see that the value of c is 20 even though the condition a < b is True .
So, you should be careful while using logical short circuit evaluation.
While working with lists , we often need to check if a list is empty or not, and if it is empty then we need to assign some default value to it.
Let's see how we can do it using conditional assignment.
Here, we have assigned a default value to my_list if it is empty.
Assign a value to a variable conditionally based on the presence of an element in a list.
Now you know 3 different ways to assign a value to a variable conditionally. Any of these methods can be used to assign a value when there is a condition.
The cleanest and fastest way to conditional value assignment is the ternary operator .
if-else statement is recommended to use when you have to execute a block of code based on some condition.
Happy coding! 😊
Python Enhancement Proposals
- Python »
- PEP Index »
PEP 572 – Assignment Expressions
The importance of real code, exceptional cases, scope of the target, relative precedence of :=, change to evaluation order, differences between assignment expressions and assignment statements, specification changes during implementation, _pydecimal.py, datetime.py, sysconfig.py, simplifying list comprehensions, capturing condition values, changing the scope rules for comprehensions, alternative spellings, special-casing conditional statements, special-casing comprehensions, lowering operator precedence, allowing commas to the right, always requiring parentheses, why not just turn existing assignment into an expression, with assignment expressions, why bother with assignment statements, why not use a sublocal scope and prevent namespace pollution, style guide recommendations, acknowledgements, a numeric example, appendix b: rough code translations for comprehensions, appendix c: no changes to scope semantics.
This is a proposal for creating a way to assign to variables within an expression using the notation NAME := expr .
As part of this change, there is also an update to dictionary comprehension evaluation order to ensure key expressions are executed before value expressions (allowing the key to be bound to a name and then re-used as part of calculating the corresponding value).
During discussion of this PEP, the operator became informally known as “the walrus operator”. The construct’s formal name is “Assignment Expressions” (as per the PEP title), but they may also be referred to as “Named Expressions” (e.g. the CPython reference implementation uses that name internally).
Naming the result of an expression is an important part of programming, allowing a descriptive name to be used in place of a longer expression, and permitting reuse. Currently, this feature is available only in statement form, making it unavailable in list comprehensions and other expression contexts.
Additionally, naming sub-parts of a large expression can assist an interactive debugger, providing useful display hooks and partial results. Without a way to capture sub-expressions inline, this would require refactoring of the original code; with assignment expressions, this merely requires the insertion of a few name := markers. Removing the need to refactor reduces the likelihood that the code be inadvertently changed as part of debugging (a common cause of Heisenbugs), and is easier to dictate to another programmer.
During the development of this PEP many people (supporters and critics both) have had a tendency to focus on toy examples on the one hand, and on overly complex examples on the other.
The danger of toy examples is twofold: they are often too abstract to make anyone go “ooh, that’s compelling”, and they are easily refuted with “I would never write it that way anyway”.
The danger of overly complex examples is that they provide a convenient strawman for critics of the proposal to shoot down (“that’s obfuscated”).
Yet there is some use for both extremely simple and extremely complex examples: they are helpful to clarify the intended semantics. Therefore, there will be some of each below.
However, in order to be compelling , examples should be rooted in real code, i.e. code that was written without any thought of this PEP, as part of a useful application, however large or small. Tim Peters has been extremely helpful by going over his own personal code repository and picking examples of code he had written that (in his view) would have been clearer if rewritten with (sparing) use of assignment expressions. His conclusion: the current proposal would have allowed a modest but clear improvement in quite a few bits of code.
Another use of real code is to observe indirectly how much value programmers place on compactness. Guido van Rossum searched through a Dropbox code base and discovered some evidence that programmers value writing fewer lines over shorter lines.
Case in point: Guido found several examples where a programmer repeated a subexpression, slowing down the program, in order to save one line of code, e.g. instead of writing:
they would write:
Another example illustrates that programmers sometimes do more work to save an extra level of indentation:
This code tries to match pattern2 even if pattern1 has a match (in which case the match on pattern2 is never used). The more efficient rewrite would have been:
Syntax and semantics
In most contexts where arbitrary Python expressions can be used, a named expression can appear. This is of the form NAME := expr where expr is any valid Python expression other than an unparenthesized tuple, and NAME is an identifier.
The value of such a named expression is the same as the incorporated expression, with the additional side-effect that the target is assigned that value:
There are a few places where assignment expressions are not allowed, in order to avoid ambiguities or user confusion:
This rule is included to simplify the choice for the user between an assignment statement and an assignment expression – there is no syntactic position where both are valid.
Again, this rule is included to avoid two visually similar ways of saying the same thing.
This rule is included to disallow excessively confusing code, and because parsing keyword arguments is complex enough already.
This rule is included to discourage side effects in a position whose exact semantics are already confusing to many users (cf. the common style recommendation against mutable default values), and also to echo the similar prohibition in calls (the previous bullet).
The reasoning here is similar to the two previous cases; this ungrouped assortment of symbols and operators composed of : and = is hard to read correctly.
This allows lambda to always bind less tightly than := ; having a name binding at the top level inside a lambda function is unlikely to be of value, as there is no way to make use of it. In cases where the name will be used more than once, the expression is likely to need parenthesizing anyway, so this prohibition will rarely affect code.
This shows that what looks like an assignment operator in an f-string is not always an assignment operator. The f-string parser uses : to indicate formatting options. To preserve backwards compatibility, assignment operator usage inside of f-strings must be parenthesized. As noted above, this usage of the assignment operator is not recommended.
An assignment expression does not introduce a new scope. In most cases the scope in which the target will be bound is self-explanatory: it is the current scope. If this scope contains a nonlocal or global declaration for the target, the assignment expression honors that. A lambda (being an explicit, if anonymous, function definition) counts as a scope for this purpose.
There is one special case: an assignment expression occurring in a list, set or dict comprehension or in a generator expression (below collectively referred to as “comprehensions”) binds the target in the containing scope, honoring a nonlocal or global declaration for the target in that scope, if one exists. For the purpose of this rule the containing scope of a nested comprehension is the scope that contains the outermost comprehension. A lambda counts as a containing scope.
The motivation for this special case is twofold. First, it allows us to conveniently capture a “witness” for an any() expression, or a counterexample for all() , for example:
Second, it allows a compact way of updating mutable state from a comprehension, for example:
However, an assignment expression target name cannot be the same as a for -target name appearing in any comprehension containing the assignment expression. The latter names are local to the comprehension in which they appear, so it would be contradictory for a contained use of the same name to refer to the scope containing the outermost comprehension instead.
For example, [i := i+1 for i in range(5)] is invalid: the for i part establishes that i is local to the comprehension, but the i := part insists that i is not local to the comprehension. The same reason makes these examples invalid too:
While it’s technically possible to assign consistent semantics to these cases, it’s difficult to determine whether those semantics actually make sense in the absence of real use cases. Accordingly, the reference implementation [1] will ensure that such cases raise SyntaxError , rather than executing with implementation defined behaviour.
This restriction applies even if the assignment expression is never executed:
For the comprehension body (the part before the first “for” keyword) and the filter expression (the part after “if” and before any nested “for”), this restriction applies solely to target names that are also used as iteration variables in the comprehension. Lambda expressions appearing in these positions introduce a new explicit function scope, and hence may use assignment expressions with no additional restrictions.
Due to design constraints in the reference implementation (the symbol table analyser cannot easily detect when names are re-used between the leftmost comprehension iterable expression and the rest of the comprehension), named expressions are disallowed entirely as part of comprehension iterable expressions (the part after each “in”, and before any subsequent “if” or “for” keyword):
A further exception applies when an assignment expression occurs in a comprehension whose containing scope is a class scope. If the rules above were to result in the target being assigned in that class’s scope, the assignment expression is expressly invalid. This case also raises SyntaxError :
(The reason for the latter exception is the implicit function scope created for comprehensions – there is currently no runtime mechanism for a function to refer to a variable in the containing class scope, and we do not want to add such a mechanism. If this issue ever gets resolved this special case may be removed from the specification of assignment expressions. Note that the problem already exists for using a variable defined in the class scope from a comprehension.)
See Appendix B for some examples of how the rules for targets in comprehensions translate to equivalent code.
The := operator groups more tightly than a comma in all syntactic positions where it is legal, but less tightly than all other operators, including or , and , not , and conditional expressions ( A if C else B ). As follows from section “Exceptional cases” above, it is never allowed at the same level as = . In case a different grouping is desired, parentheses should be used.
The := operator may be used directly in a positional function call argument; however it is invalid directly in a keyword argument.
Some examples to clarify what’s technically valid or invalid:
Most of the “valid” examples above are not recommended, since human readers of Python source code who are quickly glancing at some code may miss the distinction. But simple cases are not objectionable:
This PEP recommends always putting spaces around := , similar to PEP 8 ’s recommendation for = when used for assignment, whereas the latter disallows spaces around = used for keyword arguments.)
In order to have precisely defined semantics, the proposal requires evaluation order to be well-defined. This is technically not a new requirement, as function calls may already have side effects. Python already has a rule that subexpressions are generally evaluated from left to right. However, assignment expressions make these side effects more visible, and we propose a single change to the current evaluation order:
- In a dict comprehension {X: Y for ...} , Y is currently evaluated before X . We propose to change this so that X is evaluated before Y . (In a dict display like {X: Y} this is already the case, and also in dict((X, Y) for ...) which should clearly be equivalent to the dict comprehension.)
Most importantly, since := is an expression, it can be used in contexts where statements are illegal, including lambda functions and comprehensions.
Conversely, assignment expressions don’t support the advanced features found in assignment statements:
- Multiple targets are not directly supported: x = y = z = 0 # Equivalent: (z := (y := (x := 0)))
- Single assignment targets other than a single NAME are not supported: # No equivalent a [ i ] = x self . rest = []
- Priority around commas is different: x = 1 , 2 # Sets x to (1, 2) ( x := 1 , 2 ) # Sets x to 1
- Iterable packing and unpacking (both regular or extended forms) are not supported: # Equivalent needs extra parentheses loc = x , y # Use (loc := (x, y)) info = name , phone , * rest # Use (info := (name, phone, *rest)) # No equivalent px , py , pz = position name , phone , email , * other_info = contact
- Inline type annotations are not supported: # Closest equivalent is "p: Optional[int]" as a separate declaration p : Optional [ int ] = None
- Augmented assignment is not supported: total += tax # Equivalent: (total := total + tax)
The following changes have been made based on implementation experience and additional review after the PEP was first accepted and before Python 3.8 was released:
- for consistency with other similar exceptions, and to avoid locking in an exception name that is not necessarily going to improve clarity for end users, the originally proposed TargetScopeError subclass of SyntaxError was dropped in favour of just raising SyntaxError directly. [3]
- due to a limitation in CPython’s symbol table analysis process, the reference implementation raises SyntaxError for all uses of named expressions inside comprehension iterable expressions, rather than only raising them when the named expression target conflicts with one of the iteration variables in the comprehension. This could be revisited given sufficiently compelling examples, but the extra complexity needed to implement the more selective restriction doesn’t seem worthwhile for purely hypothetical use cases.
Examples from the Python standard library
env_base is only used on these lines, putting its assignment on the if moves it as the “header” of the block.
- Current: env_base = os . environ . get ( "PYTHONUSERBASE" , None ) if env_base : return env_base
- Improved: if env_base := os . environ . get ( "PYTHONUSERBASE" , None ): return env_base
Avoid nested if and remove one indentation level.
- Current: if self . _is_special : ans = self . _check_nans ( context = context ) if ans : return ans
- Improved: if self . _is_special and ( ans := self . _check_nans ( context = context )): return ans
Code looks more regular and avoid multiple nested if. (See Appendix A for the origin of this example.)
- Current: reductor = dispatch_table . get ( cls ) if reductor : rv = reductor ( x ) else : reductor = getattr ( x , "__reduce_ex__" , None ) if reductor : rv = reductor ( 4 ) else : reductor = getattr ( x , "__reduce__" , None ) if reductor : rv = reductor () else : raise Error ( "un(deep)copyable object of type %s " % cls )
- Improved: if reductor := dispatch_table . get ( cls ): rv = reductor ( x ) elif reductor := getattr ( x , "__reduce_ex__" , None ): rv = reductor ( 4 ) elif reductor := getattr ( x , "__reduce__" , None ): rv = reductor () else : raise Error ( "un(deep)copyable object of type %s " % cls )
tz is only used for s += tz , moving its assignment inside the if helps to show its scope.
- Current: s = _format_time ( self . _hour , self . _minute , self . _second , self . _microsecond , timespec ) tz = self . _tzstr () if tz : s += tz return s
- Improved: s = _format_time ( self . _hour , self . _minute , self . _second , self . _microsecond , timespec ) if tz := self . _tzstr (): s += tz return s
Calling fp.readline() in the while condition and calling .match() on the if lines make the code more compact without making it harder to understand.
- Current: while True : line = fp . readline () if not line : break m = define_rx . match ( line ) if m : n , v = m . group ( 1 , 2 ) try : v = int ( v ) except ValueError : pass vars [ n ] = v else : m = undef_rx . match ( line ) if m : vars [ m . group ( 1 )] = 0
- Improved: while line := fp . readline (): if m := define_rx . match ( line ): n , v = m . group ( 1 , 2 ) try : v = int ( v ) except ValueError : pass vars [ n ] = v elif m := undef_rx . match ( line ): vars [ m . group ( 1 )] = 0
A list comprehension can map and filter efficiently by capturing the condition:
Similarly, a subexpression can be reused within the main expression, by giving it a name on first use:
Note that in both cases the variable y is bound in the containing scope (i.e. at the same level as results or stuff ).
Assignment expressions can be used to good effect in the header of an if or while statement:
Particularly with the while loop, this can remove the need to have an infinite loop, an assignment, and a condition. It also creates a smooth parallel between a loop which simply uses a function call as its condition, and one which uses that as its condition but also uses the actual value.
An example from the low-level UNIX world:
Rejected alternative proposals
Proposals broadly similar to this one have come up frequently on python-ideas. Below are a number of alternative syntaxes, some of them specific to comprehensions, which have been rejected in favour of the one given above.
A previous version of this PEP proposed subtle changes to the scope rules for comprehensions, to make them more usable in class scope and to unify the scope of the “outermost iterable” and the rest of the comprehension. However, this part of the proposal would have caused backwards incompatibilities, and has been withdrawn so the PEP can focus on assignment expressions.
Broadly the same semantics as the current proposal, but spelled differently.
Since EXPR as NAME already has meaning in import , except and with statements (with different semantics), this would create unnecessary confusion or require special-casing (e.g. to forbid assignment within the headers of these statements).
(Note that with EXPR as VAR does not simply assign the value of EXPR to VAR – it calls EXPR.__enter__() and assigns the result of that to VAR .)
Additional reasons to prefer := over this spelling include:
- In if f(x) as y the assignment target doesn’t jump out at you – it just reads like if f x blah blah and it is too similar visually to if f(x) and y .
- import foo as bar
- except Exc as var
- with ctxmgr() as var
To the contrary, the assignment expression does not belong to the if or while that starts the line, and we intentionally allow assignment expressions in other contexts as well.
- NAME = EXPR
- if NAME := EXPR
reinforces the visual recognition of assignment expressions.
This syntax is inspired by languages such as R and Haskell, and some programmable calculators. (Note that a left-facing arrow y <- f(x) is not possible in Python, as it would be interpreted as less-than and unary minus.) This syntax has a slight advantage over ‘as’ in that it does not conflict with with , except and import , but otherwise is equivalent. But it is entirely unrelated to Python’s other use of -> (function return type annotations), and compared to := (which dates back to Algol-58) it has a much weaker tradition.
This has the advantage that leaked usage can be readily detected, removing some forms of syntactic ambiguity. However, this would be the only place in Python where a variable’s scope is encoded into its name, making refactoring harder.
Execution order is inverted (the indented body is performed first, followed by the “header”). This requires a new keyword, unless an existing keyword is repurposed (most likely with: ). See PEP 3150 for prior discussion on this subject (with the proposed keyword being given: ).
This syntax has fewer conflicts than as does (conflicting only with the raise Exc from Exc notation), but is otherwise comparable to it. Instead of paralleling with expr as target: (which can be useful but can also be confusing), this has no parallels, but is evocative.
One of the most popular use-cases is if and while statements. Instead of a more general solution, this proposal enhances the syntax of these two statements to add a means of capturing the compared value:
This works beautifully if and ONLY if the desired condition is based on the truthiness of the captured value. It is thus effective for specific use-cases (regex matches, socket reads that return '' when done), and completely useless in more complicated cases (e.g. where the condition is f(x) < 0 and you want to capture the value of f(x) ). It also has no benefit to list comprehensions.
Advantages: No syntactic ambiguities. Disadvantages: Answers only a fraction of possible use-cases, even in if / while statements.
Another common use-case is comprehensions (list/set/dict, and genexps). As above, proposals have been made for comprehension-specific solutions.
This brings the subexpression to a location in between the ‘for’ loop and the expression. It introduces an additional language keyword, which creates conflicts. Of the three, where reads the most cleanly, but also has the greatest potential for conflict (e.g. SQLAlchemy and numpy have where methods, as does tkinter.dnd.Icon in the standard library).
As above, but reusing the with keyword. Doesn’t read too badly, and needs no additional language keyword. Is restricted to comprehensions, though, and cannot as easily be transformed into “longhand” for-loop syntax. Has the C problem that an equals sign in an expression can now create a name binding, rather than performing a comparison. Would raise the question of why “with NAME = EXPR:” cannot be used as a statement on its own.
As per option 2, but using as rather than an equals sign. Aligns syntactically with other uses of as for name binding, but a simple transformation to for-loop longhand would create drastically different semantics; the meaning of with inside a comprehension would be completely different from the meaning as a stand-alone statement, while retaining identical syntax.
Regardless of the spelling chosen, this introduces a stark difference between comprehensions and the equivalent unrolled long-hand form of the loop. It is no longer possible to unwrap the loop into statement form without reworking any name bindings. The only keyword that can be repurposed to this task is with , thus giving it sneakily different semantics in a comprehension than in a statement; alternatively, a new keyword is needed, with all the costs therein.
There are two logical precedences for the := operator. Either it should bind as loosely as possible, as does statement-assignment; or it should bind more tightly than comparison operators. Placing its precedence between the comparison and arithmetic operators (to be precise: just lower than bitwise OR) allows most uses inside while and if conditions to be spelled without parentheses, as it is most likely that you wish to capture the value of something, then perform a comparison on it:
Once find() returns -1, the loop terminates. If := binds as loosely as = does, this would capture the result of the comparison (generally either True or False ), which is less useful.
While this behaviour would be convenient in many situations, it is also harder to explain than “the := operator behaves just like the assignment statement”, and as such, the precedence for := has been made as close as possible to that of = (with the exception that it binds tighter than comma).
Some critics have claimed that the assignment expressions should allow unparenthesized tuples on the right, so that these two would be equivalent:
(With the current version of the proposal, the latter would be equivalent to ((point := x), y) .)
However, adopting this stance would logically lead to the conclusion that when used in a function call, assignment expressions also bind less tight than comma, so we’d have the following confusing equivalence:
The less confusing option is to make := bind more tightly than comma.
It’s been proposed to just always require parentheses around an assignment expression. This would resolve many ambiguities, and indeed parentheses will frequently be needed to extract the desired subexpression. But in the following cases the extra parentheses feel redundant:
Frequently Raised Objections
C and its derivatives define the = operator as an expression, rather than a statement as is Python’s way. This allows assignments in more contexts, including contexts where comparisons are more common. The syntactic similarity between if (x == y) and if (x = y) belies their drastically different semantics. Thus this proposal uses := to clarify the distinction.
The two forms have different flexibilities. The := operator can be used inside a larger expression; the = statement can be augmented to += and its friends, can be chained, and can assign to attributes and subscripts.
Previous revisions of this proposal involved sublocal scope (restricted to a single statement), preventing name leakage and namespace pollution. While a definite advantage in a number of situations, this increases complexity in many others, and the costs are not justified by the benefits. In the interests of language simplicity, the name bindings created here are exactly equivalent to any other name bindings, including that usage at class or module scope will create externally-visible names. This is no different from for loops or other constructs, and can be solved the same way: del the name once it is no longer needed, or prefix it with an underscore.
(The author wishes to thank Guido van Rossum and Christoph Groth for their suggestions to move the proposal in this direction. [2] )
As expression assignments can sometimes be used equivalently to statement assignments, the question of which should be preferred will arise. For the benefit of style guides such as PEP 8 , two recommendations are suggested.
- If either assignment statements or assignment expressions can be used, prefer statements; they are a clear declaration of intent.
- If using assignment expressions would lead to ambiguity about execution order, restructure it to use statements instead.
The authors wish to thank Alyssa Coghlan and Steven D’Aprano for their considerable contributions to this proposal, and members of the core-mentorship mailing list for assistance with implementation.
Appendix A: Tim Peters’s findings
Here’s a brief essay Tim Peters wrote on the topic.
I dislike “busy” lines of code, and also dislike putting conceptually unrelated logic on a single line. So, for example, instead of:
instead. So I suspected I’d find few places I’d want to use assignment expressions. I didn’t even consider them for lines already stretching halfway across the screen. In other cases, “unrelated” ruled:
is a vast improvement over the briefer:
The original two statements are doing entirely different conceptual things, and slamming them together is conceptually insane.
In other cases, combining related logic made it harder to understand, such as rewriting:
as the briefer:
The while test there is too subtle, crucially relying on strict left-to-right evaluation in a non-short-circuiting or method-chaining context. My brain isn’t wired that way.
But cases like that were rare. Name binding is very frequent, and “sparse is better than dense” does not mean “almost empty is better than sparse”. For example, I have many functions that return None or 0 to communicate “I have nothing useful to return in this case, but since that’s expected often I’m not going to annoy you with an exception”. This is essentially the same as regular expression search functions returning None when there is no match. So there was lots of code of the form:
I find that clearer, and certainly a bit less typing and pattern-matching reading, as:
It’s also nice to trade away a small amount of horizontal whitespace to get another _line_ of surrounding code on screen. I didn’t give much weight to this at first, but it was so very frequent it added up, and I soon enough became annoyed that I couldn’t actually run the briefer code. That surprised me!
There are other cases where assignment expressions really shine. Rather than pick another from my code, Kirill Balunov gave a lovely example from the standard library’s copy() function in copy.py :
The ever-increasing indentation is semantically misleading: the logic is conceptually flat, “the first test that succeeds wins”:
Using easy assignment expressions allows the visual structure of the code to emphasize the conceptual flatness of the logic; ever-increasing indentation obscured it.
A smaller example from my code delighted me, both allowing to put inherently related logic in a single line, and allowing to remove an annoying “artificial” indentation level:
That if is about as long as I want my lines to get, but remains easy to follow.
So, in all, in most lines binding a name, I wouldn’t use assignment expressions, but because that construct is so very frequent, that leaves many places I would. In most of the latter, I found a small win that adds up due to how often it occurs, and in the rest I found a moderate to major win. I’d certainly use it more often than ternary if , but significantly less often than augmented assignment.
I have another example that quite impressed me at the time.
Where all variables are positive integers, and a is at least as large as the n’th root of x, this algorithm returns the floor of the n’th root of x (and roughly doubling the number of accurate bits per iteration):
It’s not obvious why that works, but is no more obvious in the “loop and a half” form. It’s hard to prove correctness without building on the right insight (the “arithmetic mean - geometric mean inequality”), and knowing some non-trivial things about how nested floor functions behave. That is, the challenges are in the math, not really in the coding.
If you do know all that, then the assignment-expression form is easily read as “while the current guess is too large, get a smaller guess”, where the “too large?” test and the new guess share an expensive sub-expression.
To my eyes, the original form is harder to understand:
This appendix attempts to clarify (though not specify) the rules when a target occurs in a comprehension or in a generator expression. For a number of illustrative examples we show the original code, containing a comprehension, and the translation, where the comprehension has been replaced by an equivalent generator function plus some scaffolding.
Since [x for ...] is equivalent to list(x for ...) these examples all use list comprehensions without loss of generality. And since these examples are meant to clarify edge cases of the rules, they aren’t trying to look like real code.
Note: comprehensions are already implemented via synthesizing nested generator functions like those in this appendix. The new part is adding appropriate declarations to establish the intended scope of assignment expression targets (the same scope they resolve to as if the assignment were performed in the block containing the outermost comprehension). For type inference purposes, these illustrative expansions do not imply that assignment expression targets are always Optional (but they do indicate the target binding scope).
Let’s start with a reminder of what code is generated for a generator expression without assignment expression.
- Original code (EXPR usually references VAR): def f (): a = [ EXPR for VAR in ITERABLE ]
- Translation (let’s not worry about name conflicts): def f (): def genexpr ( iterator ): for VAR in iterator : yield EXPR a = list ( genexpr ( iter ( ITERABLE )))
Let’s add a simple assignment expression.
- Original code: def f (): a = [ TARGET := EXPR for VAR in ITERABLE ]
- Translation: def f (): if False : TARGET = None # Dead code to ensure TARGET is a local variable def genexpr ( iterator ): nonlocal TARGET for VAR in iterator : TARGET = EXPR yield TARGET a = list ( genexpr ( iter ( ITERABLE )))
Let’s add a global TARGET declaration in f() .
- Original code: def f (): global TARGET a = [ TARGET := EXPR for VAR in ITERABLE ]
- Translation: def f (): global TARGET def genexpr ( iterator ): global TARGET for VAR in iterator : TARGET = EXPR yield TARGET a = list ( genexpr ( iter ( ITERABLE )))
Or instead let’s add a nonlocal TARGET declaration in f() .
- Original code: def g (): TARGET = ... def f (): nonlocal TARGET a = [ TARGET := EXPR for VAR in ITERABLE ]
- Translation: def g (): TARGET = ... def f (): nonlocal TARGET def genexpr ( iterator ): nonlocal TARGET for VAR in iterator : TARGET = EXPR yield TARGET a = list ( genexpr ( iter ( ITERABLE )))
Finally, let’s nest two comprehensions.
- Original code: def f (): a = [[ TARGET := i for i in range ( 3 )] for j in range ( 2 )] # I.e., a = [[0, 1, 2], [0, 1, 2]] print ( TARGET ) # prints 2
- Translation: def f (): if False : TARGET = None def outer_genexpr ( outer_iterator ): nonlocal TARGET def inner_generator ( inner_iterator ): nonlocal TARGET for i in inner_iterator : TARGET = i yield i for j in outer_iterator : yield list ( inner_generator ( range ( 3 ))) a = list ( outer_genexpr ( range ( 2 ))) print ( TARGET )
Because it has been a point of confusion, note that nothing about Python’s scoping semantics is changed. Function-local scopes continue to be resolved at compile time, and to have indefinite temporal extent at run time (“full closures”). Example:
This document has been placed in the public domain.
Source: https://github.com/python/peps/blob/main/peps/pep-0572.rst
Last modified: 2023-10-11 12:05:51 GMT
- Docs »
- += Addition Assignment
- Edit on GitHub
+= Addition Assignment ¶
Description ¶.
Adds a value and the variable and assigns the result to that variable.
Return Value ¶
According to coercion rules.
Time Complexity ¶
Equivalent to A = A + B.
Conditional Statements in Python
Table of Contents
Introduction to the if Statement
Python: it’s all about the indentation, what do other languages do, which is better, the else and elif clauses, one-line if statements, conditional expressions (python’s ternary operator), the python pass statement.
Watch Now This tutorial has a related video course created by the Real Python team. Watch it together with the written tutorial to deepen your understanding: Conditional Statements in Python (if/elif/else)
From the previous tutorials in this series, you now have quite a bit of Python code under your belt. Everything you have seen so far has consisted of sequential execution , in which statements are always performed one after the next, in exactly the order specified.
But the world is often more complicated than that. Frequently, a program needs to skip over some statements, execute a series of statements repetitively, or choose between alternate sets of statements to execute.
That is where control structures come in. A control structure directs the order of execution of the statements in a program (referred to as the program’s control flow ).
Here’s what you’ll learn in this tutorial: You’ll encounter your first Python control structure, the if statement.
In the real world, we commonly must evaluate information around us and then choose one course of action or another based on what we observe:
If the weather is nice, then I’ll mow the lawn. (It’s implied that if the weather isn’t nice, then I won’t mow the lawn.)
In a Python program, the if statement is how you perform this sort of decision-making. It allows for conditional execution of a statement or group of statements based on the value of an expression.
The outline of this tutorial is as follows:
- First, you’ll get a quick overview of the if statement in its simplest form.
- Next, using the if statement as a model, you’ll see why control structures require some mechanism for grouping statements together into compound statements or blocks . You’ll learn how this is done in Python.
- Lastly, you’ll tie it all together and learn how to write complex decision-making code.
Ready? Here we go!
Take the Quiz: Test your knowledge with our interactive “Python Conditional Statements” quiz. You’ll receive a score upon completion to help you track your learning progress:
Interactive Quiz
Test your understanding of Python conditional statements
We’ll start by looking at the most basic type of if statement. In its simplest form, it looks like this:
In the form shown above:
- <expr> is an expression evaluated in a Boolean context, as discussed in the section on Logical Operators in the Operators and Expressions in Python tutorial.
- <statement> is a valid Python statement, which must be indented. (You will see why very soon.)
If <expr> is true (evaluates to a value that is “truthy”), then <statement> is executed. If <expr> is false, then <statement> is skipped over and not executed.
Note that the colon ( : ) following <expr> is required. Some programming languages require <expr> to be enclosed in parentheses, but Python does not.
Here are several examples of this type of if statement:
Note: If you are trying these examples interactively in a REPL session, you’ll find that, when you hit Enter after typing in the print('yes') statement, nothing happens.
Because this is a multiline statement, you need to hit Enter a second time to tell the interpreter that you’re finished with it. This extra newline is not necessary in code executed from a script file.
Grouping Statements: Indentation and Blocks
So far, so good.
But let’s say you want to evaluate a condition and then do more than one thing if it is true:
If the weather is nice, then I will: Mow the lawn Weed the garden Take the dog for a walk (If the weather isn’t nice, then I won’t do any of these things.)
In all the examples shown above, each if <expr>: has been followed by only a single <statement> . There needs to be some way to say “If <expr> is true, do all of the following things.”
The usual approach taken by most programming languages is to define a syntactic device that groups multiple statements into one compound statement or block . A block is regarded syntactically as a single entity. When it is the target of an if statement, and <expr> is true, then all the statements in the block are executed. If <expr> is false, then none of them are.
Virtually all programming languages provide the capability to define blocks, but they don’t all provide it in the same way. Let’s see how Python does it.
Python follows a convention known as the off-side rule , a term coined by British computer scientist Peter J. Landin. (The term is taken from the offside law in association football.) Languages that adhere to the off-side rule define blocks by indentation. Python is one of a relatively small set of off-side rule languages .
Recall from the previous tutorial on Python program structure that indentation has special significance in a Python program. Now you know why: indentation is used to define compound statements or blocks. In a Python program, contiguous statements that are indented to the same level are considered to be part of the same block.
Thus, a compound if statement in Python looks like this:
Here, all the statements at the matching indentation level (lines 2 to 5) are considered part of the same block. The entire block is executed if <expr> is true, or skipped over if <expr> is false. Either way, execution proceeds with <following_statement> (line 6) afterward.
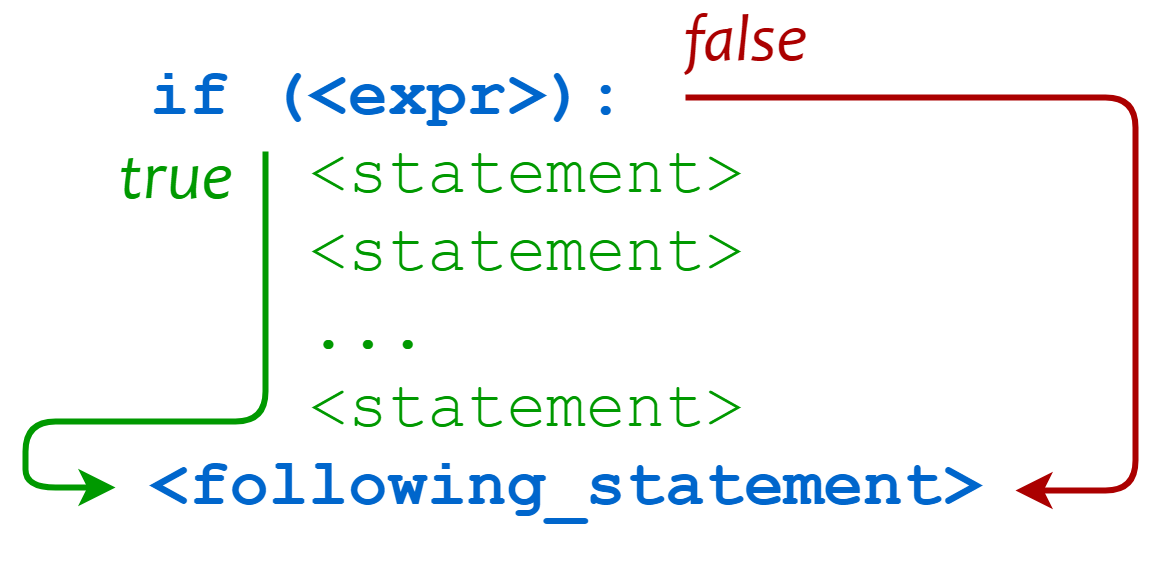
Notice that there is no token that denotes the end of the block. Rather, the end of the block is indicated by a line that is indented less than the lines of the block itself.
Note: In the Python documentation, a group of statements defined by indentation is often referred to as a suite . This tutorial series uses the terms block and suite interchangeably.
Consider this script file foo.py :
Running foo.py produces this output:
The four print() statements on lines 2 to 5 are indented to the same level as one another. They constitute the block that would be executed if the condition were true. But it is false, so all the statements in the block are skipped. After the end of the compound if statement has been reached (whether the statements in the block on lines 2 to 5 are executed or not), execution proceeds to the first statement having a lesser indentation level: the print() statement on line 6.
Blocks can be nested to arbitrary depth. Each indent defines a new block, and each outdent ends the preceding block. The resulting structure is straightforward, consistent, and intuitive.
Here is a more complicated script file called blocks.py :
The output generated when this script is run is shown below:
Note: In case you have been wondering, the off-side rule is the reason for the necessity of the extra newline when entering multiline statements in a REPL session. The interpreter otherwise has no way to know that the last statement of the block has been entered.
Perhaps you’re curious what the alternatives are. How are blocks defined in languages that don’t adhere to the off-side rule?
The tactic used by most programming languages is to designate special tokens that mark the start and end of a block. For example, in Perl blocks are defined with pairs of curly braces ( {} ) like this:
C/C++, Java , and a whole host of other languages use curly braces in this way.
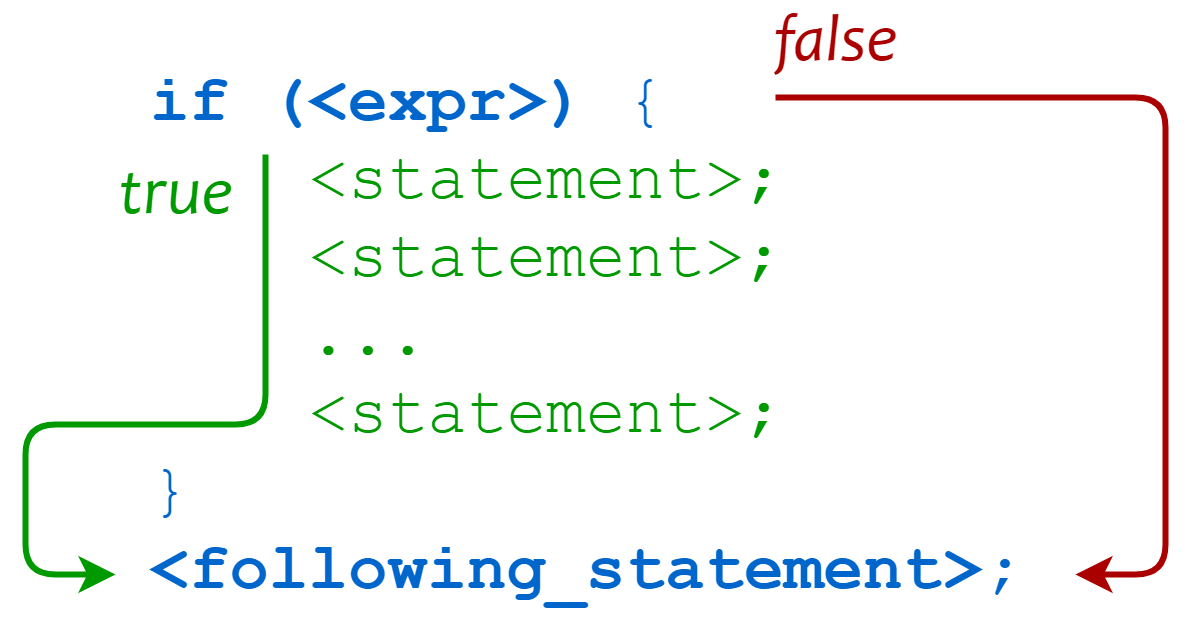
Other languages, such as Algol and Pascal, use keywords begin and end to enclose blocks.
Better is in the eye of the beholder. On the whole, programmers tend to feel rather strongly about how they do things. Debate about the merits of the off-side rule can run pretty hot.
On the plus side:
- Python’s use of indentation is clean, concise, and consistent.
- In programming languages that do not use the off-side rule, indentation of code is completely independent of block definition and code function. It’s possible to write code that is indented in a manner that does not actually match how the code executes, thus creating a mistaken impression when a person just glances at it. This sort of mistake is virtually impossible to make in Python.
- Use of indentation to define blocks forces you to maintain code formatting standards you probably should be using anyway.
On the negative side:
- Many programmers don’t like to be forced to do things a certain way. They tend to have strong opinions about what looks good and what doesn’t, and they don’t like to be shoehorned into a specific choice.
- Some editors insert a mix of space and tab characters to the left of indented lines, which makes it difficult for the Python interpreter to determine indentation levels. On the other hand, it is frequently possible to configure editors not to do this. It generally isn’t considered desirable to have a mix of tabs and spaces in source code anyhow, no matter the language.
Like it or not, if you’re programming in Python, you’re stuck with the off-side rule. All control structures in Python use it, as you will see in several future tutorials.
For what it’s worth, many programmers who have been used to languages with more traditional means of block definition have initially recoiled at Python’s way but have gotten comfortable with it and have even grown to prefer it.
Now you know how to use an if statement to conditionally execute a single statement or a block of several statements. It’s time to find out what else you can do.
Sometimes, you want to evaluate a condition and take one path if it is true but specify an alternative path if it is not. This is accomplished with an else clause:
If <expr> is true, the first suite is executed, and the second is skipped. If <expr> is false, the first suite is skipped and the second is executed. Either way, execution then resumes after the second suite. Both suites are defined by indentation, as described above.
In this example, x is less than 50 , so the first suite (lines 4 to 5) are executed, and the second suite (lines 7 to 8) are skipped:
Here, on the other hand, x is greater than 50 , so the first suite is passed over, and the second suite executed:
There is also syntax for branching execution based on several alternatives. For this, use one or more elif (short for else if ) clauses. Python evaluates each <expr> in turn and executes the suite corresponding to the first that is true. If none of the expressions are true, and an else clause is specified, then its suite is executed:
An arbitrary number of elif clauses can be specified. The else clause is optional. If it is present, there can be only one, and it must be specified last:
At most, one of the code blocks specified will be executed. If an else clause isn’t included, and all the conditions are false, then none of the blocks will be executed.
Note: Using a lengthy if / elif / else series can be a little inelegant, especially when the actions are simple statements like print() . In many cases, there may be a more Pythonic way to accomplish the same thing.
Here’s one possible alternative to the example above using the dict.get() method:
Recall from the tutorial on Python dictionaries that the dict.get() method searches a dictionary for the specified key and returns the associated value if it is found, or the given default value if it isn’t.
An if statement with elif clauses uses short-circuit evaluation, analogous to what you saw with the and and or operators. Once one of the expressions is found to be true and its block is executed, none of the remaining expressions are tested. This is demonstrated below:
The second expression contains a division by zero, and the third references an undefined variable var . Either would raise an error, but neither is evaluated because the first condition specified is true.
It is customary to write if <expr> on one line and <statement> indented on the following line like this:
But it is permissible to write an entire if statement on one line. The following is functionally equivalent to the example above:
There can even be more than one <statement> on the same line, separated by semicolons:
But what does this mean? There are two possible interpretations:
If <expr> is true, execute <statement_1> .
Then, execute <statement_2> ... <statement_n> unconditionally, irrespective of whether <expr> is true or not.
If <expr> is true, execute all of <statement_1> ... <statement_n> . Otherwise, don’t execute any of them.
Python takes the latter interpretation. The semicolon separating the <statements> has higher precedence than the colon following <expr> —in computer lingo, the semicolon is said to bind more tightly than the colon. Thus, the <statements> are treated as a suite, and either all of them are executed, or none of them are:
Multiple statements may be specified on the same line as an elif or else clause as well:
While all of this works, and the interpreter allows it, it is generally discouraged on the grounds that it leads to poor readability, particularly for complex if statements. PEP 8 specifically recommends against it.
As usual, it is somewhat a matter of taste. Most people would find the following more visually appealing and easier to understand at first glance than the example above:
If an if statement is simple enough, though, putting it all on one line may be reasonable. Something like this probably wouldn’t raise anyone’s hackles too much:
Python supports one additional decision-making entity called a conditional expression. (It is also referred to as a conditional operator or ternary operator in various places in the Python documentation.) Conditional expressions were proposed for addition to the language in PEP 308 and green-lighted by Guido in 2005.
In its simplest form, the syntax of the conditional expression is as follows:
This is different from the if statement forms listed above because it is not a control structure that directs the flow of program execution. It acts more like an operator that defines an expression. In the above example, <conditional_expr> is evaluated first. If it is true, the expression evaluates to <expr1> . If it is false, the expression evaluates to <expr2> .
Notice the non-obvious order: the middle expression is evaluated first, and based on that result, one of the expressions on the ends is returned. Here are some examples that will hopefully help clarify:
Note: Python’s conditional expression is similar to the <conditional_expr> ? <expr1> : <expr2> syntax used by many other languages—C, Perl and Java to name a few. In fact, the ?: operator is commonly called the ternary operator in those languages, which is probably the reason Python’s conditional expression is sometimes referred to as the Python ternary operator.
You can see in PEP 308 that the <conditional_expr> ? <expr1> : <expr2> syntax was considered for Python but ultimately rejected in favor of the syntax shown above.
A common use of the conditional expression is to select variable assignment. For example, suppose you want to find the larger of two numbers. Of course, there is a built-in function, max() , that does just this (and more) that you could use. But suppose you want to write your own code from scratch.
You could use a standard if statement with an else clause:
But a conditional expression is shorter and arguably more readable as well:
Remember that the conditional expression behaves like an expression syntactically. It can be used as part of a longer expression. The conditional expression has lower precedence than virtually all the other operators, so parentheses are needed to group it by itself.
In the following example, the + operator binds more tightly than the conditional expression, so 1 + x and y + 2 are evaluated first, followed by the conditional expression. The parentheses in the second case are unnecessary and do not change the result:
If you want the conditional expression to be evaluated first, you need to surround it with grouping parentheses. In the next example, (x if x > y else y) is evaluated first. The result is y , which is 40 , so z is assigned 1 + 40 + 2 = 43 :
If you are using a conditional expression as part of a larger expression, it probably is a good idea to use grouping parentheses for clarification even if they are not needed.
Conditional expressions also use short-circuit evaluation like compound logical expressions. Portions of a conditional expression are not evaluated if they don’t need to be.
In the expression <expr1> if <conditional_expr> else <expr2> :
- If <conditional_expr> is true, <expr1> is returned and <expr2> is not evaluated.
- If <conditional_expr> is false, <expr2> is returned and <expr1> is not evaluated.
As before, you can verify this by using terms that would raise an error:
In both cases, the 1/0 terms are not evaluated, so no exception is raised.
Conditional expressions can also be chained together, as a sort of alternative if / elif / else structure, as shown here:
It’s not clear that this has any significant advantage over the corresponding if / elif / else statement, but it is syntactically correct Python.
Occasionally, you may find that you want to write what is called a code stub: a placeholder for where you will eventually put a block of code that you haven’t implemented yet.
In languages where token delimiters are used to define blocks, like the curly braces in Perl and C, empty delimiters can be used to define a code stub. For example, the following is legitimate Perl or C code:
Here, the empty curly braces define an empty block. Perl or C will evaluate the expression x , and then even if it is true, quietly do nothing.
Because Python uses indentation instead of delimiters, it is not possible to specify an empty block. If you introduce an if statement with if <expr>: , something has to come after it, either on the same line or indented on the following line.
Consider this script foo.py :
If you try to run foo.py , you’ll get this:
The Python pass statement solves this problem. It doesn’t change program behavior at all. It is used as a placeholder to keep the interpreter happy in any situation where a statement is syntactically required, but you don’t really want to do anything:
Now foo.py runs without error:
With the completion of this tutorial, you are beginning to write Python code that goes beyond simple sequential execution:
- You were introduced to the concept of control structures . These are compound statements that alter program control flow —the order of execution of program statements.
- You learned how to group individual statements together into a block or suite .
- You encountered your first control structure, the if statement, which makes it possible to conditionally execute a statement or block based on evaluation of program data.
All of these concepts are crucial to developing more complex Python code.
The next two tutorials will present two new control structures: the while statement and the for statement. These structures facilitate iteration , execution of a statement or block of statements repeatedly.
🐍 Python Tricks 💌
Get a short & sweet Python Trick delivered to your inbox every couple of days. No spam ever. Unsubscribe any time. Curated by the Real Python team.

About John Sturtz

John is an avid Pythonista and a member of the Real Python tutorial team.
Each tutorial at Real Python is created by a team of developers so that it meets our high quality standards. The team members who worked on this tutorial are:

Master Real-World Python Skills With Unlimited Access to Real Python
Join us and get access to thousands of tutorials, hands-on video courses, and a community of expert Pythonistas:
Join us and get access to thousands of tutorials, hands-on video courses, and a community of expert Pythonistas:
What Do You Think?
What’s your #1 takeaway or favorite thing you learned? How are you going to put your newfound skills to use? Leave a comment below and let us know.
Commenting Tips: The most useful comments are those written with the goal of learning from or helping out other students. Get tips for asking good questions and get answers to common questions in our support portal . Looking for a real-time conversation? Visit the Real Python Community Chat or join the next “Office Hours” Live Q&A Session . Happy Pythoning!
Keep Learning
Related Topics: basics python
Recommended Video Course: Conditional Statements in Python (if/elif/else)
Keep reading Real Python by creating a free account or signing in:
Already have an account? Sign-In
- Stack Overflow for Teams Where developers & technologists share private knowledge with coworkers
- Advertising & Talent Reach devs & technologists worldwide about your product, service or employer brand
- OverflowAI GenAI features for Teams
- OverflowAPI Train & fine-tune LLMs
- Labs The future of collective knowledge sharing
- About the company Visit the blog
Collectives™ on Stack Overflow
Find centralized, trusted content and collaborate around the technologies you use most.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Get early access and see previews of new features.
Can we have assignment in a condition?
Is it possible to have assignment in a condition?
- 3 This is the first hit on google and the top answer is incorrect. Yes you can as of python.org/dev/peps/pep-0572 if a := somefunc(): #use a – Rqomey Commented Sep 7, 2021 at 14:09
10 Answers 10
Why not try it out?
Update: This is possible (with different syntax) in Python 3.8
- 46 this is intentionally forbidden as Guido, benevolent python dictator, finds them unnecessary and more confusing than useful. It's the same reason there's no post-increment or pre-increment operators (++). – Matt Boehm Commented Apr 8, 2010 at 22:53
- 6 he did allow the addition of augmented assigment in 2.0 because x = x + 1 requires additional lookup time while x += 1 was somewhat faster, but i'm sure he didn't even like doing that much. :-) – wescpy Commented Apr 8, 2010 at 23:56
- 1 hope, this will become possible soon. Python is just slow to evolve – Nik O'Lai Commented Aug 28, 2020 at 9:07
- 54 "why not try it out" - Because who knows what the syntax might be? Maybe OP tried that and it didn't work, but that doesn't mean the syntax isn't different, or that there's not a way to do it that's not intended – Levi H Commented Sep 22, 2020 at 17:09
- 12 Fun fact: := (the assignment expression) is also known as the "walrus operator" because if considered as a text based emoji it looks like a walrus. :) – jlsecrest Commented Nov 6, 2021 at 4:13
UPDATE - Original answer is near the bottom
Python 3.8 will bring in PEP572
Abstract This is a proposal for creating a way to assign to variables within an expression using the notation NAME := expr . A new exception, TargetScopeError is added, and there is one change to evaluation order.
https://lwn.net/Articles/757713/
The "PEP 572 mess" was the topic of a 2018 Python Language Summit session led by benevolent dictator for life (BDFL) Guido van Rossum. PEP 572 seeks to add assignment expressions (or "inline assignments") to the language, but it has seen a prolonged discussion over multiple huge threads on the python-dev mailing list—even after multiple rounds on python-ideas. Those threads were often contentious and were clearly voluminous to the point where many probably just tuned them out. At the summit, Van Rossum gave an overview of the feature proposal, which he seems inclined toward accepting, but he also wanted to discuss how to avoid this kind of thread explosion in the future.
https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0572/#examples-from-the-python-standard-library
Examples from the Python standard library site.py env_base is only used on these lines, putting its assignment on the if moves it as the "header" of the block. Current: env_base = os.environ.get("PYTHONUSERBASE", None) if env_base: return env_base Improved: if env_base := os.environ.get("PYTHONUSERBASE", None): return env_base _pydecimal.py Avoid nested if and remove one indentation level. Current: if self._is_special: ans = self._check_nans(context=context) if ans: return ans Improved: if self._is_special and (ans := self._check_nans(context=context)): return ans copy.py Code looks more regular and avoid multiple nested if. (See Appendix A for the origin of this example.) Current: reductor = dispatch_table.get(cls) if reductor: rv = reductor(x) else: reductor = getattr(x, "__reduce_ex__", None) if reductor: rv = reductor(4) else: reductor = getattr(x, "__reduce__", None) if reductor: rv = reductor() else: raise Error( "un(deep)copyable object of type %s" % cls) Improved: if reductor := dispatch_table.get(cls): rv = reductor(x) elif reductor := getattr(x, "__reduce_ex__", None): rv = reductor(4) elif reductor := getattr(x, "__reduce__", None): rv = reductor() else: raise Error("un(deep)copyable object of type %s" % cls) datetime.py tz is only used for s += tz, moving its assignment inside the if helps to show its scope. Current: s = _format_time(self._hour, self._minute, self._second, self._microsecond, timespec) tz = self._tzstr() if tz: s += tz return s Improved: s = _format_time(self._hour, self._minute, self._second, self._microsecond, timespec) if tz := self._tzstr(): s += tz return s sysconfig.py Calling fp.readline() in the while condition and calling .match() on the if lines make the code more compact without making it harder to understand. Current: while True: line = fp.readline() if not line: break m = define_rx.match(line) if m: n, v = m.group(1, 2) try: v = int(v) except ValueError: pass vars[n] = v else: m = undef_rx.match(line) if m: vars[m.group(1)] = 0 Improved: while line := fp.readline(): if m := define_rx.match(line): n, v = m.group(1, 2) try: v = int(v) except ValueError: pass vars[n] = v elif m := undef_rx.match(line): vars[m.group(1)] = 0 Simplifying list comprehensions A list comprehension can map and filter efficiently by capturing the condition: results = [(x, y, x/y) for x in input_data if (y := f(x)) > 0] Similarly, a subexpression can be reused within the main expression, by giving it a name on first use: stuff = [[y := f(x), x/y] for x in range(5)] Note that in both cases the variable y is bound in the containing scope (i.e. at the same level as results or stuff). Capturing condition values Assignment expressions can be used to good effect in the header of an if or while statement: # Loop-and-a-half while (command := input("> ")) != "quit": print("You entered:", command) # Capturing regular expression match objects # See, for instance, Lib/pydoc.py, which uses a multiline spelling # of this effect if match := re.search(pat, text): print("Found:", match.group(0)) # The same syntax chains nicely into 'elif' statements, unlike the # equivalent using assignment statements. elif match := re.search(otherpat, text): print("Alternate found:", match.group(0)) elif match := re.search(third, text): print("Fallback found:", match.group(0)) # Reading socket data until an empty string is returned while data := sock.recv(8192): print("Received data:", data) Particularly with the while loop, this can remove the need to have an infinite loop, an assignment, and a condition. It also creates a smooth parallel between a loop which simply uses a function call as its condition, and one which uses that as its condition but also uses the actual value. Fork An example from the low-level UNIX world: if pid := os.fork(): # Parent code else: # Child code
Original answer
http://docs.python.org/tutorial/datastructures.html
Note that in Python, unlike C, assignment cannot occur inside expressions. C programmers may grumble about this, but it avoids a common class of problems encountered in C programs: typing = in an expression when == was intended.
http://effbot.org/pyfaq/why-can-t-i-use-an-assignment-in-an-expression.htm
- 1 I like this answer because it actually points out why such a "feature" might have been deliberately left out of Python. When teaching beginner's programming, I have seen many make this mistake if (foo = 'bar') while intending to test the value of foo . – Jonathan Cross Commented Feb 19, 2019 at 23:25
- 3 @JonathanCross, This "feature" is actually going to be added in 3.8. It is unlikely to be used as sparingly as it should - but at least it is not a plain = – John La Rooy Commented Feb 19, 2019 at 23:52
- @JohnLaRooy: Looking at the examples, I think "unlikely to be used as sparingly as it should" was spot-on; Out of the ~10 examples, I find that only two actually improve the code. (Namely, as the sole expression either in a while condition, to avoid duplicating the line or having the loop condition in the body, or in an elif-chain to avoid nesting) – Aleksi Torhamo Commented Apr 10, 2020 at 11:07
- Doesn't work with ternary a if a := 1 == 1 else False → Invalid syntax :c So apparently still have to resort to the old awkward (lambda: (ret := foo(), ret if ret else None))()[-1] (i.e. as a way to avoid the repeated call to foo() in ternary) . – Hi-Angel Commented Nov 25, 2020 at 21:20
- 3 @Hi-Angel This actually works fine (Python 3.10.8). You just have to add parentheses according to what you actually want to express, i.e. either a if (a := 1) == 1 else False (yields 1 ) or a if (a := 1 == 1) else False (yields True ). – user686249 Commented Nov 29, 2022 at 15:54
Nope, the BDFL didn't like that feature.
From where I sit, Guido van Rossum, "Benevolent Dictator For Life”, has fought hard to keep Python as simple as it can be. We can quibble with some of the decisions he's made -- I'd have preferred he said 'No' more often. But the fact that there hasn't been a committee designing Python, but instead a trusted "advisory board", based largely on merit, filtering through one designer's sensibilities, has produced one hell of a nice language, IMHO.
- 20 Simple? This feature could simplified quite some of my code because it could have made it more compact and therefor more readable. Now I need two lines where I used to need one. I never got the point why Python rejected features other programming languages have for many years (and often for a very good reason). Especially this feature we're talking about here is very, very useful. – Regis May Commented Sep 10, 2017 at 8:09
- 7 Less code isn't always simpler or morde readable. Take a recursive function for example. It's loop-equivalent is often more readable. – F.M.F. Commented Apr 9, 2018 at 8:50
- 1 I don't like like the C version of it, but I really miss having something like rust's if let when I have an if elif chain, but need to store and use the value of the condition in each case. – Thayne Commented Jul 10, 2018 at 4:57
- 1 I have to say the code I am writing now (the reason I searched this issue) is MUCH uglier without this feature. Instead of using if followed by lots of else ifs, I need to keep indenting the next if under the last else. – MikeKulls Commented Oct 24, 2018 at 3:34
Yes, but only from Python 3.8 and onwards.
PEP 572 proposes Assignment Expressions and has already been accepted.
Quoting the Syntax and semantics part of the PEP:
In your specific case, you will be able to write
Not directly, per this old recipe of mine -- but as the recipe says it's easy to build the semantic equivalent, e.g. if you need to transliterate directly from a C-coded reference algorithm (before refactoring to more-idiomatic Python, of course;-). I.e.:
BTW, a very idiomatic Pythonic form for your specific case, if you know exactly what falsish value somefunc may return when it does return a falsish value (e.g. 0 ), is
so in this specific case the refactoring would be pretty easy;-).
If the return could be any kind of falsish value (0, None , '' , ...), one possibility is:
but you might prefer a simple custom generator:
- I would vote this up twice if I could. This is a great solution for those times when something like this is really needed. I adapted your solution to a regex Matcher class, which is instantiated once and then .check() is used in the if statement and .result() used inside its body to retrieve the match, if there was one. Thanks! :) – Teekin Commented Jul 26, 2018 at 15:23
Thanks to Python 3.8 new feature it will be possible to do such a thing from this version, although not using = but Ada-like assignment operator := . Example from the docs:
No. Assignment in Python is a statement, not an expression.
- And Guido wouldn't have it any other way. – Mark Ransom Commented Apr 8, 2010 at 22:51
- 1 @MarkRansom All hail Guido. Right .. sigh. – WestCoastProjects Commented Dec 11, 2017 at 4:49
- @javadba the guy has been right much more often than he's been wrong. I appreciate that having a single person in charge of the vision results in a much more coherent strategy than design by committee; I can compare and contrast with C++ which is my main bread and butter. – Mark Ransom Commented Dec 11, 2017 at 4:58
- I feel both ruby and scala ( v different languages) get it right significantly moreso than python: but in any case here is not the place.. – WestCoastProjects Commented Dec 11, 2017 at 6:11
- @MarkRansom "And Guido wouldn't have it any other way" - and yet, 10 years later we have Assignment Expressions ... – Tomerikoo Commented Apr 10, 2021 at 14:48
You can define a function to do the assigning for you:
One of the reasons why assignments are illegal in conditions is that it's easier to make a mistake and assign True or False:
In Python 3 True and False are keywords, so no risk anymore.
- 1 In [161]: l_empty==[] Out[161]: True In [162]: []==[] Out[162]: True I do not think that is the reason – volcano Commented Jan 2, 2014 at 13:23
- Pretty sure most people put == True on the right side anyway. – numbermaniac Commented Mar 11, 2019 at 7:27
The assignment operator - also known informally as the the walrus operator - was created at 28-Feb-2018 in PEP572 .
For the sake of completeness, I'll post the relevant parts so you can compare the differences between 3.7 and 3.8:
Your Answer
Reminder: Answers generated by artificial intelligence tools are not allowed on Stack Overflow. Learn more
Sign up or log in
Post as a guest.
Required, but never shown
By clicking “Post Your Answer”, you agree to our terms of service and acknowledge you have read our privacy policy .
Not the answer you're looking for? Browse other questions tagged python or ask your own question .
- The Overflow Blog
- Scaling systems to manage all the metadata ABOUT the data
- Navigating cities of code with Norris Numbers
- Featured on Meta
- We've made changes to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy - July 2024
- Bringing clarity to status tag usage on meta sites
- Feedback requested: How do you use tag hover descriptions for curating and do...
Hot Network Questions
- A short story where a space pilot has a device that sends the ship back in time just before losing a space battle. He is duplicated by accident
- What is the purpose of toroidal magnetic field in tokamak fusion device?
- If there is no free will, doesn't that provide a framework for an ethical model?
- A study on the speed of gravity
- Who became an oligarch after the collapse of the USSR
- Age is just a number!
- Trace operation as contraction - how can we contract only contravariant indices?
- Repeats: Simpler at the cost of more redundant?
- Why did evolution fail to protect humans against sun?
- Why does the definition of a braided monoidal category not mentions the braid equation?
- Is the Ted-Ed Leprechaun's Magic Bag Unique?
- What does it mean to have a truth value of a 'nothing' type instance?
- can a CPU once removed retain information that poses a security concern?
- Three 7-letter words, 21 unique letters, excludes either HM or QS
- Were there mistakes in converting Dijkstra's Algol-60 compiler to Pascal?
- Questions about best way to raise the handlebar on my bike
- Did the Space Shuttle weigh itself before deorbit?
- Dial “M” for murder
- Power line crossing data lines via the ground plane
- Does the Ghost achievement require no kills?
- What exactly is component based architecture and how do I get it to work?
- Testing Puzzles for Feedback: Enigmatic Puzzles 3
- I submitted a paper and later realised one reference was missing, although I had written the authors in the body text. What could happen?
- What is the meaning of "Exit, pursued by a bear"?

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Here, variable represents a generic Python variable, while expression represents any Python object that you can provide as a concrete value—also known as a literal—or an expression that evaluates to a value. To execute an assignment statement like the above, Python runs the following steps: Evaluate the right-hand expression to produce a concrete value or object.
For the future time traveler from Google, here is a new way (available from Python 3.8 onward): b = 1 if a := b: # this section is only reached if b is not 0 or false. # Also, a is set to b print(a, b) This is known as "the walrus operator". More info at the What's New In Python 3.8 page.
7.2.1. Augmented assignment statements ... The future statement is intended to ease migration to future versions of Python that introduce incompatible changes to the language. It allows use of the new features on a per-module basis before the release in which the feature becomes standard.
Multiple- target assignment: x = y = 75. print(x, y) In this form, Python assigns a reference to the same object (the object which is rightmost) to all the target on the left. OUTPUT. 75 75. 7. Augmented assignment : The augmented assignment is a shorthand assignment that combines an expression and an assignment.
The author selected the COVID-19 Relief Fund to receive a donation as part of the Write for DOnations program.. Introduction. Python 3.8, released in October 2019, adds assignment expressions to Python via the := syntax. The assignment expression syntax is also sometimes called "the walrus operator" because := vaguely resembles a walrus with tusks. ...
Variables and Assignment¶. When programming, it is useful to be able to store information in variables. A variable is a string of characters and numbers associated with a piece of information. The assignment operator, denoted by the "=" symbol, is the operator that is used to assign values to variables in Python.The line x=1 takes the known value, 1, and assigns that value to the variable ...
Each new version of Python adds new features to the language. For Python 3.8, the biggest change is the addition of assignment expressions.Specifically, the := operator gives you a new syntax for assigning variables in the middle of expressions. This operator is colloquially known as the walrus operator.. This tutorial is an in-depth introduction to the walrus operator.
Python Assignment Operators. Assignment operators are used to assign values to variables: Operator. Example. Same As. Try it. =. x = 5. x = 5.
Expressions — Python 3.12.5 documentation. 6. Expressions ¶. This chapter explains the meaning of the elements of expressions in Python. Syntax Notes: In this and the following chapters, extended BNF notation will be used to describe syntax, not lexical analysis. When (one alternative of) a syntax rule has the form.
Python Assignment Operator. The = (equal to) symbol is defined as assignment operator in Python. The value of Python expression on its right is assigned to a single variable on its left. The = symbol as in programming in general (and Python in particular) should not be confused with its usage in Mathematics, where it states that the expressions on the either side of the symbol are equal.
A variable is a name for a value. An assignment statement associates a variable name on the left of the equal sign with the value of an expression calculated from the right of the equal sign. Enter. width. Once a variable is assigned a value, the variable can be used in place of that value. The response to the expression width is the same as if ...
Assignment Operator. Assignment Operators are used to assign values to variables. This operator is used to assign the value of the right side of the expression to the left side operand. Python. # Assigning values using # Assignment Operator a = 3 b = 5 c = a + b # Output print(c) Output. 8.
Let's see a code snippet to understand it better. a = 10. b = 20 # assigning value to variable c based on condition. c = a if a > b else b. print(c) # output: 20. You can see we have conditionally assigned a value to variable c based on the condition a > b. 2. Using if-else statement.
Unparenthesized assignment expressions are prohibited for the value of a keyword argument in a call. Example: foo(x = y := f(x)) # INVALID foo(x=(y := f(x))) # Valid, though probably confusing. This rule is included to disallow excessively confusing code, and because parsing keyword arguments is complex enough already.
Description ¶. Adds a value and the variable and assigns the result to that variable.
In the form shown above: <expr> is an expression evaluated in a Boolean context, as discussed in the section on Logical Operators in the Operators and Expressions in Python tutorial. <statement> is a valid Python statement, which must be indented. (You will see why very soon.) If <expr> is true (evaluates to a value that is "truthy"), then <statement> is executed.
Solutions to the 'Applied Machine Learning In Python' Coursera course exercises - amirkeren/applied-machine-learning-in-python
All credit goes to @MarkDickinson, who answered this in a comment: Notice the + in (target_list "=")+, which means one or more copies.In foo = bar = 5, there are two (target_list "=") productions, and the expression_list part is just 5. All target_list productions (i.e. things that look like foo =) in an assignment statement get assigned, from left to right, to the expression_list on the right ...
PEP 572 seeks to add assignment expressions (or "inline assignments") to the language, but it has seen a prolonged discussion over multiple huge threads on the python-dev mailing list—even after multiple rounds on python-ideas. Those threads were often contentious and were clearly voluminous to the point where many probably just tuned them out.