APA Citation Style, 7th edition: Web Page with No Author
- General Style Guidelines
- One Author or Editor
- Two Authors or Editors
- Three to Five Authors or Editors
- Article or Chapter in an Edited Book
- Article in a Reference Book
- Edition other than the First
- Translation
- Government Publication
- Journal Article with 1 Author
- Journal Article with 2 Authors
- Journal Article with 3–20 Authors
- Journal Article 21 or more Authors
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Basic Web Page
- Web page from a University site
- Web Page with No Author
- Entry in a Reference Work
- Government Document
- Film and Television
- Youtube Video
- Audio Podcast
- Electronic Image
- Twitter/Instagram
- Lecture/PPT
- Conferences
- Secondary Sources
- Citation Support
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Formatting Your Paper

Document from a Web site with no Author
- When citing sources that you find on the Internet you only need to include a retrieval date if the information you viewed is likely to change over time. If you reference an article from a news source (e.g., CNN, NBC, Washington Post) or a site that may experience continuous updates, you would then need to include a retrieval date.
- New in 7th edition: You must include the site name in your citation, unless the site name is the same as the corporate author. For example, a citation of a CDC report would not include the site name.
Subject Guide

- << Previous: Web page from a University site
- Next: Blog post >>

- Last Updated: Jul 26, 2024 1:06 PM
- URL: https://guides.himmelfarb.gwu.edu/APA

- Himmelfarb Intranet
- Privacy Notice
- Terms of Use
- GW is committed to digital accessibility. If you experience a barrier that affects your ability to access content on this page, let us know via the Accessibility Feedback Form .
- Himmelfarb Health Sciences Library
- 2300 Eye St., NW, Washington, DC 20037
- Phone: (202) 994-2962
- [email protected]
- https://himmelfarb.gwu.edu
- UWF Libraries
APA Format & Citation Style, 7th edition
- Web Page with No Author
- General Style Guidelines
- One Author or Editor
- Two Authors or Editors
- Three or More Authors or Editors
- Article or Chapter in an Edited Book
- Article in a Reference Book
- Edition other than the First
- Translation
- Government Publication
- Journal Article with One Author
- Journal Article with 2 Authors
- Journal Article with 3 or More Authors
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Basic Web Page
- Web page from a University site
- Entry in a Reference Work
- Government Document
- Film and Television
- Youtube Video
- Audio Podcast
- Electronic Image
- Lecture/PPT
- Conferences
- Secondary Sources
- Formatting Your Paper
- APA Handouts & Guides This link opens in a new window
Document from a Web site with no Author
- When citing sources that you find on the Internet you only need to include a retrieval date if the information you viewed is likely to change over time. If you reference an article from a news source (e.g., CNN, NBC, Washington Post) or a site that may experience continuous updates, you would then need to include a retrieval date.
- New in 7th edition: You must include the site name in your citation, unless the site name is the same as the corporate author. For example, a citation of a CDC report would not include the site name.
- << Previous: Web page from a University site
- Next: Blog post >>
- Last Updated: May 17, 2024 11:13 AM
- URL: https://libguides.uwf.edu/apa7

APA 7 Citation & Style
- Why Cite Sources?
- How Citations Work in APA
- Database Sources (Journal Articles)
- Textbook or Book Source
- Website with an Author
- Website with No Author Listed
- In-Text Citations
- Writing Style
- Page Numbering
- Checklist (putting it all together)
- Need Help with APA?
APA Reference Entry for a Website with No Author Listed
In the video below, Keri from the Writing Center explains how to create an APA-style Reference entry for a website without an author listed.
- APA Reference: Website with NO Author Slides
Reference entries for a website without an author listed will include:
- Organizational Author.
- Title of page.
- Container or Site Name (if different than the organizational author, if it's the same--skip info here!)
Example website source (with elements color-coded):
National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal Skin Diseases. (2019). Scoliosis in children and teens. National Institute of Health. https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/scoliosis/
Example website source (final, as it would appear on a Reference page):
Example in-text citation for this source (color-coded):.
( National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal Skin Diseases, 2019 )
- Visit the page on in-text citations if you want more information about how those work!
- << Previous: Website with an Author
- Next: In-Text Citations >>
- Last Updated: May 15, 2024 9:28 AM
- URL: https://westerntc.libguides.com/APA7

Welcome to the Wayne G. Basler Library at Northeast State Community College

APA Citation Guide, 7th edition: Web Page with No Author
- General Guidelines
- One Author or Editor
- Two Authors or Editors
- Three to Five Authors or Editors
- Article or Chapter in an Edited Book
- Article in a Reference Book
- E-Books, not from a Database
- Edition other than the First
- Translation
- Government Publication
- Journal Article with One Author
- Journal Article with 2 Authors
- Journal Article with 3-20 Authors
- Journal Article 21 or more Authors
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Basic Web Page
- Web page from a University site
- Web Page with No Author
- Entry in a Reference Work
- Government Document
- Online Press Release
- Motion Picture
- Youtube Video
- Audio Podcast Episode
- Music Recording
- TikTok Video
- Electronic Image
- Lecture/PPT
- Classical Works
- Secondary Sources
- Avoiding Plagiarism
Document from a Web site with no Author (p. 264-265; 350-352)
- When citing sources that you find on the Internet you only need to include a retrieval date if the information you viewed is likely to change over time (p. 290). If you reference an article from a site that may experience continuous updates, you would then need to include a retrieval date.
- << Previous: Web page from a University site
- Next: Blog post >>
- Last Updated: Mar 6, 2024 6:15 PM
- URL: https://library.northeaststate.edu/APA
)
APA style citation when no author is listed
Published October 28, 2020. Updated November 14, 2021.
APA style uses a two-pronged system to ensure that each source used in a paper is credited: an in-text citation and a reference list entry.
A major component of these citations is the name of the author. However, there may be times when you cannot locate an author.
For help writing your essay, research paper , or other project, check out these writing tips .
Author element
There are five possible authors of a work:
- A single person or individual
- “Anonymous” cited as the author
- Two or more people or entities
- An organization, group, association, government agency, company, institution, etc.
- A combination of the above
No author vs. Organization author
Before you decide that your source has no author, take a moment to consider this:
Could the publisher of the source also be considered the author?
Often times, when no individual or individuals are cited as the author, you could assign the authorship of a work to the group that published it.
Examples of sources with no individual author but which have a group author:
- An entry on NASA’a website that is not credited to another author could be considered as penned by NASA.
- The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association was both published and authored by the American Psychological Association.
Further down on this page, we cover how to cite an organization as an author.
If you’ve determined that your work genuinely has no author, you can cite the source using the guidelines below.
APA style referencing for no author
If no author can be determined for a source, the title of the source is generally used in the author section of both in-text citations and reference list entries.
In-text citations
Before you create an in-text citation, look at how the source’s title would be formatted in the reference if there was an author.
- If the title would be italicized, then italicize the title in the in-text citation. This is often the format used for books, reference works, and reports.
- If the title would not be italicized in the reference, put the title in quotation marks in the in-text citation. This format is often used for websites, journal articles, newspaper articles, and magazine articles.
Using the format outlined above, write the source’s title, followed by a comma, and the year it was published. Enclose all of this in parenthesis.
If the source title is really long, a shortened version of the title is acceptable. Also, if you are citing a direct quotation and page numbers are available, include the page number(s) at the end of the citation but within the parentheses.
In-text citation template and examples:
( Source title , Year) or ( Source title , Year, p. #)
(“Source title,” Year) or (“Source title,” Year, p. #)
( Nothing but truth , 2020)
(“What I thought about Sam,” 1998, p. 11)
Move the source title into the beginning of the reference, the section where the author’s name would normally be. The font should be plain, italicized if applicable, in sentence case, and followed by a period.
Book reference template and example:
Book title . (Year). Publisher Name. DOI or URL if available
Nothing but truth . (2020). Weird Publishing.
Webpage reference template and example:
Webpage title. (Date). Site Name. URL
What I thought about Sam. (August 2,1998). Example Pages Site. https://www.madeupwebsite.net
APA style referencing for an author cited as “Anonymous”
If a source specifically says “Anonymous” is its author, use that in place of an author’s name.
(Anonymous, Year) or (Anonymous, Year, p. #)
(Anonymous, 2019)
(Anonymous, 2002, pp. 1-2)
Anonymous. (Year). Book title . Publisher Name. DOI or URL if available
Anonymous. (2016). Diary of an oxygen thief . Gallery Books.
APA style referencing for an organization as an author
In the case of an organization as an author, move the organization’s name into the author section of the citation or reference.
Within parentheses, include the organization name and a page number. Separate each information piece with a comma. If you are creating the citation for a direct quotation and page numbers are available, also include the page number(s).
In-text citation template and example:
(Organization Name, Year) or (Organization Name, Year, p. #)
(University of Hawaii, 2020)
If the organization has a really long name and you will be citing it more than once in a work, you may shorten it using the format below.
First in-text citation:
(Full Organization Name [Shortened Name], Year)
Subsequent in-text citations:
(Shortened Name, Year)
Example first in-text citation:
(National Aeronautics and Space Administration [NASA], 2018)
(NASA, 2018)
Place the organization in the author section. If the author and publisher are the same, just include it in the author section (leave out the publisher section). Let’s look at a few examples.
Book example:
American Psychological Association. (2020). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (7 th ed.). https://doi.org/10.1037/0000165-000
Website example:
XEAN News. (2017). The scourge of climate change and our lives 30 years from now. http://www.xeannewsoftheworld.co.uk/world-254387
APA Style Guides
APA Format: Annotated bibliography | Abstract | Block and direct quotes | Headings | Outline | Page Numbers | Sample paper | Title page
Citing Sources: In-text citations | Bibliography | Footnotes | Citing Multiple Authors | Citing Sources with No Authors | Using et al
APA Citation Generator: Article | Book | Image | Interview | Journal | Movie | PDF | Textbook | Website | YouTube
Published August 25, 2021.
To cite a book with no date in APA, use the core required elements: the name(s) of the author(s), the title of the book, and the publisher. Use “n.d.” in place of the publication year. The table below shows how to format the in-text citation and the reference-list entry for a book with no date in APA style.
In-Text Template and Citation
(Author Surname, n.d.)
(Tyler, n.d.)
Reference-List Template and Entry
Author Surname, F. M. (n.d.). Title of the book . Publisher.
Tyler, T. R. (n.d.). Why people obey the law . Yale University Press.
To cite a magazine article with no author in APA, use the core required elements: the date of publication, the title of the article, the magazine name, the volume and issue numbers (if applicable), the page number(s) (if applicable), and the DOI or URL (if applicable).
When there is no author name, move the title of the work to the author position. Enclose the magazine article’s name in double quotation marks (e.g., “Technical Considerations”).
The table below shows how to format the in-text citation and the reference-list entry for a magazine article with no author in APA style.
(“Magazine Article Title,” Publication Year)
(“Technical Considerations,” 2021)
Title of the magazine article. (Year, Month Day.) Magazine Name, Vol# (Issue #), page number(s) or DOI/URL
Why the adoption of SASE networks is accelerating. (2021, October 5). Fortune , (5)6, https://brand-studio.fortune.com/cloudflare/why-the-adoption-of-SASE-networks-is-accelerating/

What’s included with a Chegg Writing subscription
- Unlimited number of paper scans
- Plagiarism detection: Check against billions of sources
- Expert proofreading for papers on any subject
- Grammar scans for 200+ types of common errors
- Automatically create & save citations in 7,000+ styles
- Cancel subscription anytime, no obligation
Penn State University Libraries
Apa quick citation guide.
- In-text Citation
- Citing Generative AI
- Citing Web Pages and Social Media
- Citing Articles
- Citing Books
- Citing Business Reports
- Other Formats
- APA Style Quiz
Using In-text Citation
Include an in-text citation when you refer to, summarize, paraphrase, or quote from another source. For every in-text citation in your paper, there must be a corresponding entry in your reference list.
APA in-text citation style uses the author's last name and the year of publication, for example: (Field, 2005). For direct quotations, include the page number as well, for example: (Field, 2005, p. 14). For sources such as websites and e-books that have no page numbers , use a paragraph number, for example: (Field, 2005, para. 1). More information on direct quotation of sources without pagination is given on the APA Style and Grammar Guidelines web page.
Example paragraph with in-text citation
A few researchers in the linguistics field have developed training programs designed to improve native speakers' ability to understand accented speech (Derwing et al., 2002; Thomas, 2004). Their training techniques are based on the research described above indicating that comprehension improves with exposure to non-native speech. Derwing et al. (2002) conducted their training with students preparing to be social workers, but note that other professionals who work with non-native speakers could benefit from a similar program.
Derwing, T. M., Rossiter, M. J., & Munro, M. J. (2002). Teaching native speakers to listen to foreign-accented speech. Journal of Multilingual and Multicultural Development , 23 (4), 245-259.
Thomas, H. K. (2004). Training strategies for improving listeners' comprehension of foreign-accented speech (Doctoral dissertation). University of Colorado, Boulder.
Citing Web Pages In Text
Cite web pages in text as you would any other source, using the author and date if known. Keep in mind that the author may be an organization rather than a person. For sources with no author, use the title in place of an author.
For sources with no date use n.d. (for no date) in place of the year: (Smith, n.d.). For more information on citations for sources with no date or other missing information see the page on missing reference information on the APA Style and Grammar Guidelines web page.
Below are examples of using in-text citation with web pages.
Web page with author:
In-text citation
Heavy social media use can be linked to depression and other mental disorders in teens (Asmelash, 2019).
Reference entry
Asmelash, L. (2019, August 14). Social media use may harm teens' mental health by disrupting positive activities, study says . CNN. https://www.cnn.com/2019/08/13/health/social-media-mental-health-trnd/index.html
Web page with organizational author:
More than 300 million people worldwide are affected by depression (World Health Organization, 2018).
World Health Organization. (2018, March 22). Depression . https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/depression
Web page with no date:
Establishing regular routines, such as exercise, can help survivors of disasters recover from trauma (American Psychological Association [APA], n.d.).
American Psychological Association. (n.d.). Recovering emotionally from disaste r. http://www.apa.org/helpcenter/recovering-disasters.aspx
General Guidelines
In-text references should immediately follow the title, word, or phrase to which they are directly relevant, rather than appearing at the end of long clauses or sentences. In-text references should always precede punctuation marks. Below are examples of using in-text citation.
Author's name in parentheses:
One study found that the most important element in comprehending non-native speech is familiarity with the topic (Gass & Varonis, 1984).
Author's name part of narrative:
Gass and Varonis (1984) found that the most important element in comprehending non-native speech is familiarity with the topic.
Group as author: First citation: (American Psychological Association [APA], 2015) Subsequent citation: (APA, 2015)
Multiple works: (separate each work with semi-colons)
Research shows that listening to a particular accent improves comprehension of accented speech in general (Gass & Varonis, 1984; Krech Thomas, 2004).
Direct quote: (include page number and place quotation marks around the direct quote)
One study found that “the listener's familiarity with the topic of discourse greatly facilitates the interpretation of the entire message” (Gass & Varonis, 1984, p. 85).
Gass and Varonis (1984) found that “the listener’s familiarity with the topic of discourse greatly facilitates the interpretation of the entire message” (p. 85).
Note: For direct quotations of more than 40 words , display the quote as an indented block of text without quotation marks and include the authors’ names, year, and page number in parentheses at the end of the quote. For example:
This suggests that familiarity with nonnative speech in general, although it is clearly not as important a variable as topic familiarity, may indeed have some effect. That is, prior experience with nonnative speech, such as that gained by listening to the reading, facilitates comprehension. (Gass & Varonis, 1984, p. 77)
Works by Multiple Authors
APA style has specific rules for citing works by multiple authors. Use the following guidelines to determine how to correctly cite works by multiple authors in text. For more information on citing works by multiple authors see the APA Style and Grammar Guidelines page on in-text citation .
Note: When using multiple authors' names as part of your narrative, rather than in parentheses, always spell out the word and. For multiple authors' names within a parenthetic citation, use &.
One author: (Field, 2005)
Two authors: (Gass & Varonis, 1984)
Three or more authors: (Tremblay et al., 2010)
- << Previous: Overview
- Next: Citing Generative AI >>
- Last Updated: Jul 19, 2023 2:50 PM
- URL: https://guides.libraries.psu.edu/apaquickguide
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / APA Format / APA In-text Citations
APA In-Text Citations
Welcome to our guide on in-text citations! If you’re looking to learn the ins and outs of APA style in-text citations and how to do in-text citations APA, we’ve got you covered in this thorough guide.
The information below follows the 7th edition of the Publication manual of the American Psychological Association .
Here’s a run through of everything this page includes:
- APA Style overview
- In-text citations and why we use them
- Two types of APA in-text citations
- Corresponding entry in reference list
- In-text citations for direct quotes
Paraphrasing in APA
- In-text citations for sources with one author
- In-text citations for sources with multiple authors
- In-text citations for sources with no author or date
- Additional in-text citation examples
If you’re simply looking for a quick guide, check out our APA parenthetical citation guide, which serves as a lite-version of this page.
Let’s get started!
What is APA?
This is a term that you might hear your teacher, professor, or librarian throw around a lot. This abbreviation stands for
P sychological
A ssociation
This association is kind of a big deal. They do a lot of things related to psychology, but they’re also famous for creating one of the most popular citation styles, APA format . There are other big names on campus, such as MLA format , and Chicago, but this particular style is commonly used by individuals who are writing a science-related paper.
Even if your paper doesn’t necessarily fall into a “science” category, many educators ask their students to cite in this style since it’s so commonly used.
If you’re trying to find information about other commonly used styles, there are more styles on EasyBib.com.
What is an APA In-text Citation?
In plain and simple terms, APA in-text citations are found in the text of a project. Get it? In text. The purpose of an in-text citation in APA is to show the reader, while they’re reading your work, that a piece of information in your project was found elsewhere. They’re placed IN the wording or body of a project, not on the last page; the last page has full references. To learn more about those types of references, check out APA citation .
We’ve all heard about the word plagiarism , and you already know what it means. Simply put, including APA in-text citations are one way to prevent plagiarism.
Here’s what’s included in an APA 7th edition in-text citation:
- Last name(s) of the author(s) or Group name
- Year the source was published
- Page number (if available)
Depending on the number of authors and the source type, some in-text citations look different than others. Read on to learn how to structure an in-text citation for APA. In fact, if you’re looking for an easy route, EasyBib.com has an in-text citation APA generator, which does the work for you. Use our automatic generator to create your full references, and you’ll see an option on the final screen to format your APA in-text citations. An APA in-text citation generator and full reference generator all in one. What could beat that?
Why do we use in-text citations?
When you do a research project, you’re probably going to include facts from websites, databases, books, and other sources. When you add those facts into your project, you must show where those facts came from. It’s the responsible thing to do. It prevents plagiarism. You always give credit to the original author. It’s kind of like thanking them for their contribution to your paper.
Here’s the neat thing about in-text citations. Since they’re IN your project, readers get a quick idea as to where the information you included came from. In-text citations APA are not long and lengthy, like the full references on the APA reference page or APA bibliography . In-text citations are cute, little, and give us the perfect amount of information we need to understand where a fact came from. If you want to get the full information about the source, then you can flip to the back page of the paper, where the full reference is listed. The in-text citation APA style provides us with a tidbit of information. Just enough to glance at it and keep on going with reading the paper.
To recap, in-text citations are great because:
- They credit the original author of a work or information
- They let readers quickly see where the information is coming from
- Including helps make you an ethical writer
If you’re looking to learn more about footnotes in Chicago format , MLA in-text & parenthetical citations , or want to learn how to cite websites in MLA , EasyBib.com has the information you need to be a citing superstar.
Types of APA In-text Citations
Just like there are two days in the weekend, two types of peanut butter (creamy and nutty), and two types of foods we crave (salty and sweet), there are (you guessed it) two types of in-text citations.
The in-text citation APA option you include in your paper depends on how you craft your sentences.
Narrative In-Text APA Citations:
In-text citation APA format, in narrative form, is one that shows the author’s name in the sentence itself.
Narrative In-text APA Citation Example:
Tyson, Strauss, and Gott (2016) encourage the use of simplified terms when it comes to discussing and defining the universe. For example, a small white star is simply called a white dwarf. Keep it short and sweet because the universe is confusing enough (p. 22).
Parenthetical Citations:
This is a type of APA in-text citation where the author’s name(s) are in parentheses, usually at the end of the fact or quote.
Parenthetical Citation Example
Use simplified terms when discussing and defining the universe. For example, a small white star is simply called a white dwarf. Keep it short and sweet because the universe is confusing enough (Tyson, Strauss, & Gott, 2016, p. 22).
As you can see, the type of APA in-text citation you include, whether it’s a narrative one or one in parentheses, depends on how you decide to structure your sentences. It doesn’t matter if you use all narrative, all parentheses, or a mix of both.
What is important is that you’re a responsible researcher and you properly cite your sources!
Remember, most facts, quotes, stats, and copied and pasted information NEED an APA in-text citation next to it.
What’s the only type of information you don’t need to create an in-text citation APA for? Anything that’s common knowledge. For example, paper is made from trees. You and most people already knew that. That’s an example of common knowledge. It’s a piece of information that everyone already knows.
Now, before you simply include the author’s name(s), the date, and the page number in your project and think you’ve covered all your bases, you’re not quite done yet. In-text citations APA are only part of the puzzle.
The other piece of the puzzle is found on the last page of the project: the reference page. That’s where all of the full references are found in their entirety. In-text citations only include the author’s name, year published, and the page number.
The reference page, on the other hand, includes the title of each source, the publishers, the website addresses, and other information. Continue reading to learn why in-text citations and references on the reference page are the perfect match.
Before we continue, MLA works cited pages are very similar to the ones in this style. EasyBib.com has resources for many styles, to help you learn the ins and outs of referencing your work. We even have full pages on grammar topics too, to keep your paper in tip-top shape. Brush up on your noun , conjunction , and interjection skills with our easy-to-follow, comprehensive guides.
Corresponding entry in APA reference list
Would you ever put on one shoe and walk around without the other? Of course not. The same goes with in-text citations and full references. You must include both in your paper. Where there’s one there has to be the other.
Each and every in-text citation APA must have a matching full reference on the reference page (American Psychological Association, p. 262 ).
If you’re wondering why, it’s to allow the reader to get that sneak peek about the source while reading your paper (the APA in-text citation), and then learn all about it on the final page (the reference page). If the reader wants to get their hands on a copy of the sources you used, all of the information they need can be found on the reference page.
Remember those APA style in-text citation examples found above? Let’s take a peek at them again.
Here’s the one with the authors’ names in parentheses: Use simplified terms when discussing and defining the universe. For example, a small white star is simply called a white dwarf. Keep it short and sweet because the universe is confusing enough (deGrasse, Strauss, & Gott, 2016, p. 22).
Here’s the full reference, which would be found on the final page of the project:
Tyson, N. D., Strauss, M. A., and Gott, J. R. (2016). Welcome to the universe: An astrophysical tour. Princeton University Press.
Notice that in the above in-text citation APA example, the full title of the book, the place the book was published, and the publisher are displayed. If the reader wants to locate the book themselves, all of the information they need is found in the full reference.
One other important thing we’d like to point out is that the same information from the in-text citation APA (Tyson, Strauss, & Gott) matches the first part of the full reference. This is done to allow the reader to easily find the full reference on the final page.
Remember, always include both in-text citations AND full references in your projects.
In the body of projects, in-text citations APA serve an important purpose. They give the reader a snippet of understanding as to the origin of information. It’s just enough information to allow the reader to continue reading the paper in a natural and fluid manner, without having to trip over long, clunky references. If the reader wants to get a detailed understanding of a source, they can flip to the back page, the reference page, to scope out all of the nitty gritty details.
In the next two sections of this page, we’re going to switch gears and share how to properly format direct quotes and paraphrases.
If you’re looking for specific source types, check out APA citation website and APA book citation . These two resources will explain how to format those specific types of references. If you’re stuck and not sure how to start, check out Chapter 10 of the Publication manual for some sample citations.
Direct Quotes in APA
As Drake states in his lyrics, “We don’t like to do too much explaining,” so we’re going to keep this one short and to the point.
“Direct quotes” are a fancy term used for any text that has been copied and pasted into your paper. That Drake quote above is a direct quote.
Direct quotes are any words or sentences copied and pasted into your project, but they don’t necessarily have to be a person’s quote. Anytime you copy and paste text into your assignment, you must include an APA in-text citation next to it. This shows the reader that:
- The information came from another source
- You’re being a responsible researcher and clearly documenting the outside source.
Here are some guidelines to keep in mind when it comes to direct quotes:
- Direct quotes are a solid way to show evidence and prove your point, but use them sparingly. Your paper shouldn’t be riddled with copied and pasted text.
- Put quotation marks around the copied and pasted information. (The exception are APA block quotes , which are direct quotes longer than 40 words and are formatted differently.)
- Always include the page number for direct quotes, if one is available. When formatting APA page numbers for an in-text citation, include p. before the number. Use pp. for a page range.
To create a narrative APA in-text citation, include the author’s last name in the sentence like this:
- As Drake (2013) once said “We don’t like to do too much explaining.”
- In the above APA in-text citation example, the Drake quote was taken from the song, “Started From the Bottom,” in 2013. The title of the source would be included in the reference page.
Or, you include the author’s name in parentheses:
- “We don’t like to do too much explaining” (Drake, 2013).
If you are looking for more examples, go to page 272 of the American Psychological Association’s official Publication manual .
We said above that your entire paper shouldn’t have direct quotes everywhere. So, another way to include information from a source is by adding a paraphrase . Simply put, a paraphrase is restated information, but formed using your own words and writing style
APA paraphrases still need an in-text citation since the information was obtained elsewhere. Check out this quote from the song, “For Time,” by Drake:
“I like it when money makes a difference, but don’t make you different.”
To include it in your paper, without using the exact quote, make a paraphrase. Here’s one that would work:
Money has the ability to benefit things in your life, but it’s truly great when it doesn’t cause the person to act differently or change who they are (Drake, 2013).
The above APA in-text citation example is one with Drake’s name in parentheses. If you’d like to include the author’s name narratively, here’s an option:
In Drake’s (2013) lyrics, he shares that money has the ability to benefit things in your life. It’s truly great when it doesn’t cause the person to act differently or change who they are.
It is recommended to include page numbers for paraphrased material, but isn’t required.
Here’s more on paraphrases and direct quotes.
Organizing APA In-text Citations
Ready to learn how to structure your in-text citations? The next section dives deep into developing them and answers “How to do in-text citations APA.” Keep in mind that how each one is formed depends on the number of authors and other factors. All the examples below follow rules laid out in Chapter 8 of the Publication manual.
Even though the structure varies, most in-text citations APA are placed in this manner for narrative in-text citations:
Author’s Last Name (Year) “Quote or Paraphrase” (p. number).
For ones in parentheses, most are placed in this manner:
“Quote” or Paraphrase (Author’s Last Name, Year, p. number).
Notice that whether you choose to include a narrative in-text citation APA or one in parentheses, the author names and the year published are always together. They’re pretty much holding hands. Cute, huh?
Read on to learn the ins and outs of structuring various in-text citations.
Don’t forget, EasyBib.com has an in-text citation APA generator. Wondering what it’s all about? Here’s a quick explanation: We work for you so citing is easy for you. Yep, you read that correctly.
Our tools structure your in-text citations the way they’re supposed to be structured. Use our automatic generator to create your full references, and on the final screen you’ll see the option to create your in-text citations. An APA in-text citation generator that’s easy as pie!
Something else we do for you? We have a plagiarism checker that scans your paper for any instances of accidental copying. We also have tons of grammar pages to keep your page in check. Check out our adverb , preposition , and verb pages.
APA In-Text Citations for Sources with One Author
If your source has one author.
If your source has one author, lucky you! Your in-text citation is pretty simple to structure.
Narrative In-text APA Citation:
Author’s Last Name (Year published) are found in the sentence with a “direct quote” or paraphrase (p. number).
Parenthetical APA Citation:
“Direct quote” or Paraphrase (Author’s Last Name, Year published, p. number).
Citing multiple sources by the same author in the same year
You may have a bunch of case studies, articles, or books that you’re referencing, all by the same author. Let’s say you’re analyzing two works by Sigmund Freud, Jokes and Their Relation to the Unconscious and also Fragment of an Analysis of a Case of Hysteria , both of which were published in 1905. Placing (Freud, 1905) in the text would be confusing for the reader. How would the reader determine which source you’re referencing?
If this is the situation you’re in, there’s a pretty simple fix.
Place a lowercase a next to the year in the first source (Freud, 1905a). Place a lowercase b next to the second source (Freud, 1905b). Include those same lowercase letters in the full references on the reference page, like so:
Freud, S. (1905a). Fragment of an analysis of a case of hysteria . https://staferla.free.fr/Freud/Freud%20complete%20Works.pdf
Freud, S. (1905b). Jokes and their relation to the unconscious . https://staferla.free.fr/Freud/Freud%20complete%20Works.pdf
But there’s a catch. When you do this et al. can’t stand for only one author. After all it literally means “and others.” If you have two sources that are identical except for the last author, then you have to write out all the names every time. For example:
Gunderman, Slack, Rausch, and Smith (2017)
Gunderman, Slack, Rausch, and Johnston (2017)
These references are completely the same except for the very last name so you’d have to write all 4 names every time.
If your source has multiple works by the same author
What if you had 2 sources with the same author(s) and same publication year? Lucky for us the solution here is a lot simpler. Just a letter to the publication year!
Gunderman, Slack, and Rausch (2017)
Gunderman, Slack, and Rausch (2017a)
Gunderman, Slack, and Rausch (2017b)
Just remember to also follow this format in your works cited page even if there is an exact publication date available. See page 267 of your Publication Manual (American Psychological Association, 2020) for a further breakdown.
Need to create an APA in-text citation for a source without an author? How about an APA in-text citation for multiple authors? Continue reading to see the other ways to structure an APA style in-text citation.
APA In-Text Citations for Sources with Multiple Authors
Apa in-text citation for sources with two authors.
If your source has two authors, place them in the order they appear on the source. Do not place them in alphabetical order.
Use the word “and” in between the authors’ names.
1st Author’s Last Name and 2nd Author’s Last Name (Year published) are found somewhere in the sentence with a “direct quote” or paraphrase (p. number).
If you choose to include both authors’ names in parentheses, use an ampersand in between their names.
“Here is the direct quote” or Here is the paraphrase (1st Author’s Last Name & 2nd Author’s Last name, Year, p. number).
APA in-text citation for sources three or more authors
Only include the first author’s last name and then add ‘et al.’ Et al. is a fancy way of saying “and others” in Latin.
1st Author’s Last Name et al. (Year published) are found somewhere in the sentence with a “direct quote” or paraphrase (p. number).
“Here is the direct quote” or Paraphrase (1st Author’s Last Name et al., Year published, p. number).
If you have author of multiple works (with multiple authors)
Now here is where things can get a tad bit tricky. Sometimes authors with multiple works can cause some confusion in your citations. Generally when that happens you can tell the difference by the publication year, but when you can’t, that’s when you have to list as many authors as necessary to clear up the confusion.
Say you had the two sources below:
Gunderman, Slack, Rausch, and Maule (2017)
Gunderman, Byrnes, Oxner, Wigginton, and Draeger (2017)
Normally, they’d be written as:
Gunderman et al. (2017)
If you reduced both sources to Gunderman et al. (2017) you wouldn’t be able to tell which source you’re talking about. Instead cite it this way:
Gunderman, Slack, Rausch et al. (2017)
Gunderman, Byrnes, Oxner et al. (2017)
If you’re looking for more information on structuring journal articles, check out our APA journal page.
If you’re looking for a simple solution to referencing multiple authors, EasyBib.com creates in-text citations APA for you! Whether you need to create a reference for one or two authors, or an APA in-text citation for multiple authors, we’ve got you covered!
APA In-text citation no author or date
It’s common to come across sources without any authors. Movies, brochures, website pages often do not have a visible author’s name.
Citing a source with no author
If you find that the source you’re attempting to reference does not have an author, use the first few words from the reference list entry in the APA in-text citation with no author. Most often, it’s the title of the source.
Place the source name in quotation marks if the source is a:
- website page
Simply italicize the source name if the source is a:
- Or the full reference starts with italicized information
Remember, you do not have to use the entire title in your in-text citation APA no author. You can use only the first few words from the reference list.
“First few words of the webpage, article, or chapter Title” (Year) along with the “direct quote” or paraphrase (p. number). OR First few words of book, newspaper, report, or brochure (Year) along with the “direct quote” or paraphrase (p. number).
“Here is the direct quote” or paraphrase (“Web page, Article, or Chapter Title,” Year, p. number). OR “Here is the direct quote” or paraphrase ( Book, Newspaper, Report, or Brochure Title , Year, p. number).
Citing source with no date
No date? No problem! An APA in-text citation no date situation is easier to solve than you think. Only include the author’s name and the page number.
APA in-text citation no date example:
(Foster, p. 35).
Additional APA In-Text Citation Examples
Source by a group, organization, company, or government agency.
There are two types of groups: Ones that are abbreviated often and ones that are not abbreviated.
For example, think about these two citation style types: APA and Chicago. One is abbreviated (for the American Psychological Association) and the other is usually written as is (Chicago style).
Abbreviated groups
If the company is often abbreviated, in the first mention in text, display the full name and the abbreviation. In the second and any other subsequent mentions, only use the abbreviation.
1st mention:
Full Company’s Name (Abbreviation, Year) with the “direct quote” or paraphrase (p. number).
2nd mention:
Company Abbrev. (Year) “direct quote” or paraphrase (p. number).
“Direct quote” or paraphrase (Full Company’s Name [Abbreviation], Year, p. number).
“Direct quote” or paraphrase (Abbreviation, Year, p. number).

Non-abbreviated groups
Always include the full group, company, or organization’s name in each and every mention in text.
Full Name of Group (Year) with the “direct quote” or paraphrase (p. number).
“Direct quote” or paraphrase (Full Name of Group, Year, p. number).
Citing sources with different authors with the same last name
We’re not quite sure how the author of The Baby-Sitters Club (Ann M. Martin) could be used in a paper that’s also referencing the author of Game of Thrones (George R. R. Martin), but hey, it could happen! It’s a Martin party! It’s important to show the reader the difference between the two individuals to prevent any confusion. To differentiate between the two authors in the text, include their first initials.
Example of in-text citation APA:
“Here’s a quote” (A. Martin, Year, p. 6). G. Martin (Year) also states “this direct quote” (p. 45).
As always, keep the author names and the dates directly next to each other. They love being together and it’s a best practice.
Citing multiple sources in the same in-text citation
List sources alphabetically and separate with a semicolon.
Be sure to list authors alphabetically.
Johnson (2019), Smith and Adams (2015), and Washington (2017), examined…
“Direct quote” or Paraphrase (Author 1 Last Name, Year published, p. number if needed; Author 2 Last Name, Year published, p. number if needed)
Parenthetical Citation Examples:
(Johnson et al., 2019; Smith & Adams, 2015; Washington, 2017)
(Honda, 2006, p. 107; Sato, 1980)
If you want to emphasize a source because it is particularly important or relevant, add “see also” before the source’s citation. Think of “see also” as synonymous with “for more information see…”
(Johnson et al., 2019; see also Smith & Adams, 2015; Washington, 2017).
Citing a source within a source
Did you stumble upon the perfect quote that’s quoted in another source? It happens all of the time and it can be a little tricky to figure out how to quote a quote.
The American Psychological Association recommends locating the original quote, if possible. Instead of relying on secondary sources, take the time to locate the original source to make sure the quote is accurate. Finding and reading through the original source also provides you with further information on your research topic!
If finding the original source isn’t possible, due to out of print titles, web pages taken down, or other factors, then it’s okay to quote the secondary source. In your writing, use the phrase “as cited in Secondary Author’s Last name, Year.”
On the reference page, include the reference for the secondary source.
As cited in Shapiro’s (2019) article, Carranza stated, “Districts 3 and 15 are showing how we can have the important conversations and take bold action on this issue.”
Carranza stated, “Districts 3 and 15 are showing how we can have the important conversations and take bold action on this issue” (as cited in Shapiro, 2019).
On the reference page, Shapiro’s article would be referenced in its entirety.
Citing audiovisual material
APA in-text citations for YouTube videos , songs, podcasts, television shows, and other audiovisual materials look a bit different than other types of sources. They include an extra piece of information: a time stamp.
Bill Nye (2017) shares that the sun is over four-hundred septillion watts (13:15).
The sun is over four-hundred septillion watts (Bill Nye, 2017, 13:15).
If you’re still scratching your head, and feeling the urge to type “how to do in-text citations APA” into Google, click here for a website that we dig.
If you’re looking for a quick fix to developing your references, EasyBib.com has you covered! Our tools can help you create an APA in-text citation multiple authors, one author, no authors, plus more!
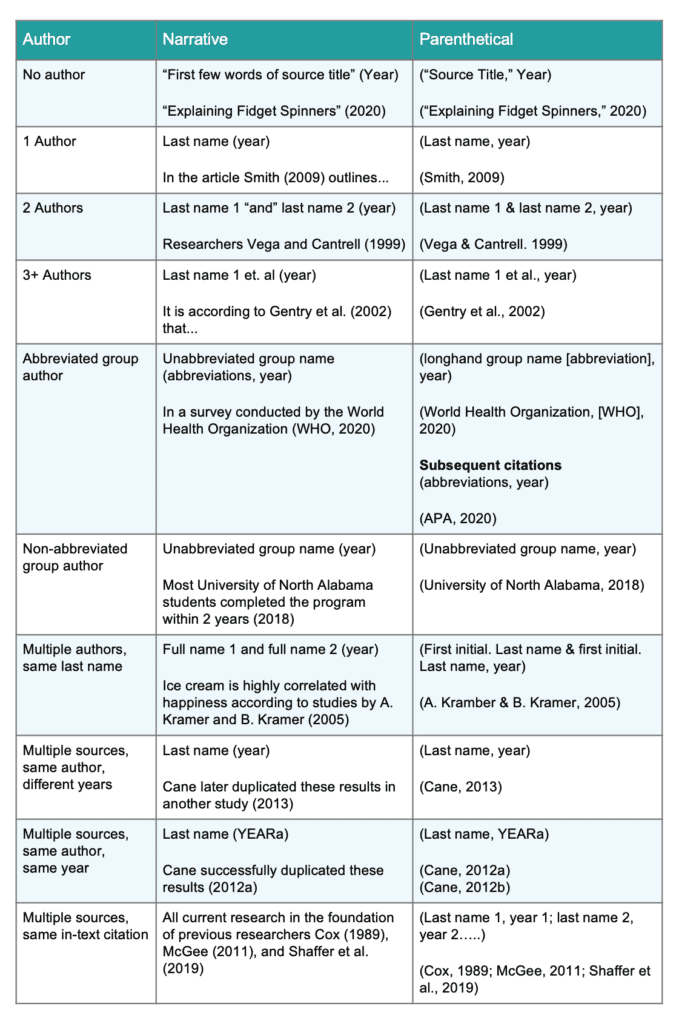
Overview of APA Parenthetical Citations for Websites
Here’s a quick overview of how to create an in-text citation for websites. Notice that since these are for online sources, the in-text citation has no page number.
| Author | Narrative | Parenthetical |
|---|---|---|
| No author | “First few words of source title” (Year) “Explaining Fidget Spinners” (2020) | (“Source Title,” Year) (“Explaining Fidget Spinners,” 2020) |
| 1 Author | Last name (year) In the article Smith (2009) outlines… | (Last name, year) (Smith, 2009) |
| 2 Authors | Last name 1 “and” last name 2 (year) Researchers Vega and Cantrell (1999) | (Last name 1 & last name 2, year) (Vega & Cantrell, 1999) |
| 3+ Authors | Last name 1 et. al (year) It is according to Gentry et al. (2002) that… | (Last name 1 et al., year) (Gentry et al., 2002) |
| Abbreviated group author | Unabbreviated group name (abbreviations, year) In a survey conducted by the World Health Organization (WHO, 2020) | (Longhand group name [abbreviation], year) (World Health Organization, [WHO], 2020) (abbreviations, year) |
| Non-abbreviated group author | Unabbreviated group name (year) Most University of North Alabama students completed the program within 2 years (2018) | (Unabbreviated group name, year) (University of North Alabama, 2018) |
| Multiple authors, same last name | Full name 1 and full name 2 (year) Ice cream is highly correlated with happiness according to studies by A. Kramer and B. Kramer (2005) | (First initial. Last name & first initial. Last name, year) (A. Kramer & B. Kramer, 2005) |
| Multiple sources, same author, different years | Last name (year) Cane later duplicated these results in another study (2013) | (Last name, year) (Cane, 2013) |
| Multiple sources, same author, same year | Last name (YEARa) Cane successfully duplicated these results (2012a) | (Last name, YEARa) (Cane, 2012a) |
| Multiple sources, same in-text citation | All current research in the foundation of previous researches Cox (1989), McGee (2011), and Shaffer et al. (2019) | (Last name 1, year 1; last name 2, year 2…..) (Cox, 1989; McGee 2011; Shaffer et al., 2019) |
Once again, if grammar isn’t your thing, and you’re looking for help related to specific parts of speech, check out our adjective , pronoun , and determiner pages, among many, many others!
Follow our EasyBib Twitter feed to find more citing tips, fun grammar facts, and the latest product updates.
American Psychological Association. (2020). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.) https:doi.org/10.1037/0000165-000
Published May 21, 2019. Updated October 25, 2020.
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Elise Barbeau . Michele Kirschenbaum is a school library media specialist and one of the in-house EasyBib librarians. Elise Barbeau is the Citation Specialist at Chegg. She has worked in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing.
APA Formatting Guide
APA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Multiple Authors
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Parenthetical Citations
- Reference Page
- Sample Paper
- APA 7 Updates
- View APA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all APA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
An in-text citation is a shortened version of the source being referred to in the paper. As the name implies, it appears in the text of the paper. A reference list entry, on the other hand, details the complete information of the source being cited and is listed at the end of the paper after the main text. An example of an in-text citation and the corresponding reference list entry for a journal article with one author is listed below for your understanding:
In-text citation template and example:
Only the author name and the publication year are used in in-text citations to direct the reader to the corresponding reference list entry.
Author Surname (Publication Year)
Elden (2003)
Parenthetical
(Author Surname, Publication Year)
(Elden, 2003)
Reference list entry template and example:
Complete information of the reference is used to guide the reader to locate the source for further reference. In the below template, “F” and “M” are first and middle initials, respectively. #–# denotes the page range.
Surname, F. M. (Publication Year). Title of the article: Subtitle. Journal Title, Volume (Issue), #–#. DOI
Elden, S. (2003). Plague, panopticon, police. Surveillance & Society, 1 (3), 240–253. https://doi:10.24908/ss.v1i3.3339
When you use APA style, all sources need to have in-text citations. In-text citations direct a reader to the reference entry to get more information on the source being cited in the text. If an in-text citation is not provided, your reader doesn’t know whether there is a source available in the reference list for the idea or topic being discussed in the text. Even if all the basic elements to cite a source are not available, try to provide an in-text citation with the information you do have. For example, if a source does not have an author, use a shortened version of the title in place of the author in your in-text citation. An example is given below for a parenthetical citation.
Author name available:
(Author Surname, Publication Year, p.# for direct quote)
Author name not available:
(“Title of the Work,” Publication Year, p.# for direct quote)
Therefore, in-text citations are essential to guide a reader to locate the corresponding sources in the reference list for the topics discussed in the text.
APA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Cite a Web Site in APA With No Author, Date, or Page Number
Last Updated: May 15, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Diane Stubbs and by wikiHow staff writer, Danielle Blinka, MA, MPA . Diane Stubbs is a Secondary English Teacher with over 22 years of experience teaching all high school grade levels and AP courses. She specializes in secondary education, classroom management, and educational technology. Diane earned a Bachelor of Arts in English from the University of Delaware and a Master of Education from Wesley College. There are 11 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 286,414 times.
Citing a website that doesn't list an author, date, or page number can be tricky. However, it's easier to do than you might think! You can cite a website using the title name, organization that published the page, or "anonymous," depending on the information available. For the date, you can include "n.d." for "no date." This allows you to create in-text citations and an entry on your References page.
Creating In-Text Citations

- "According to “Robotics for Beginners" (2018), titanium parts will create a sturdier robot."
- "Titanium parts are the best option for building a sturdy robot (“Robotics,” 2018)."

- "According to the American Cancer Society (2018), people undergoing chemotherapy benefit from having complimentary head wraps or wigs available."
- "People who are undergoing chemotherapy treatments have a better experience if complimentary head wraps and wigs are provided to them (American Cancer Society, 2018)."

- For an anonymous author, your citation will look like this: "(Anonymous, 2018)"

- A citation using a title for an author looks like this: "(“Robotics,” n.d.)"
- If you're using an organization name, your citation looks like this: "(National Robotics Society, n.d.)"
- For an anonymous author, your citation would look like this: "(Anonymous, n.d.)"

- For example, let's say you're citing the 4th paragraph of an article called, “Building a Healthy Relationship,” which has no author, page number, or date.
- "According to “Building a Healthy Relationship" (n.d., para. 4), communication is essential for a healthy partnership."
- "Partners must communicate if they want to have a healthy relationship (“Building,” n.d., para. 4)."

- You may have found valuable information on a web page titled “Reducing Congestion in Large Cities,” which has section headings titled “Improving Transit Networks,” “Increasing Highway Capacity,” “Collecting Tolls,” “HOV Lanes,” and “Metered Ramps.” However, there's no date or page number.
- Your citation might look like this: "(“Reducing,” n.d., “HOV”)"
Preparing Your References Page

- Let's say the name of the article you want to cite is “Ecuador: History and Culture.” The beginning of your entry would look like this: "Ecuador: History and culture."
- If the article includes an organization name or an anonymous author, you'll use that instead of the title.

- Your entry would now look like this: "Ecuador: History and culture. (n.d.)."

- This is what your entry should look like now: "Ecuador: History and culture. (n.d.). Select Latin America ."

- Here's how your final entry might look: "Ecuador: History and culture. (n.d.). Select Latin America . Retrieved from http://www.sla.com/ecuador.html/"

- If the website name is the same as the organization name, don't write it again after the page title. You can skip that part of the references entry and go straight to "Retrieved from."
- For example, let's say you're citing an article called “Relaxing with Deep Breathing,” which was published by the American Psychological Foundation. No date is provided.
- Here's what your entry would look like: "American Psychological Foundation. (n.d.). Relaxing with deep breathing. Retrieved from http://www.apf.com/Relaxing_and_deep_breathing/"

- You might be citing a web page titled “Being Mindful During a Dog Walk,” written by an anonymous author. It's posted on a website called Bark Bark Friends, but there isn't a date.
- Here how your entry would look: "Anonymous. (n.d.) Being Mindful During a Dog Walk. Bark Bark Friends . Retrieved from http://www.barkbarkfriends.com/mindful_dog_walks/"
Expert Q&A
- You don't have to include a retrieval or access date in your reference entry anymore. In prior editions of the APA style guide, you needed to include the date you accessed the website. [13] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- If you're in doubt about how to cite your source, talk to your instructor or your school's writing center. They can help you decide the best way to write your citation. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0

- Citing your sources can be frustrating, but don't give up! If you don't cite your source, you'll be plagiarizing the site where you got the information. This can cost you credit for the assignment and can result in other academic consequences. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/in_text_citations_author_authors.html
- ↑ https://aus.libguides.com/apa/apa-no-author-date
- ↑ https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/references/missing-information
- ↑ https://guides.libraries.psu.edu/apaquickguide/intext
- ↑ https://bowvalleycollege.libguides.com/c.php?g=714519&p=5093747
- ↑ https://columbiacollege-ca.libguides.com/apa/booksandebooks
- ↑ https://libguides.jcu.edu.au/apa/dates
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/reference_list_basic_rules.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/reference_list_electronic_sources.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.uagc.edu/format-your-reference-list
- ↑ https://libguides.ggc.edu/apastyle_7th/Authors/MissingorAnonymous
About This Article

Citing information from a website without an author, date, or page number isn’t as complicated as you might think. Try using the title in place of an author for an in-text citation. For example, for a page entitled “Robotics for Beginners,” you could write (“Robotics,” 2018). Alternatively, list the name of the organization that owns the website in your in-text citation, like “According to the American Cancer Society (2018).” If you don’t have a date, add “n.d.” instead. Replace page numbers by mentioning the paragraph your citation comes from. For instance, if it came from the fourth paragraph, add “para 4” to the end of an in-text citation. If you put all of this together, an in-text reference could look like, “According to Robotics for Beginners (n.d., para 4). For tips on how to write a citation for your reference page that doesn’t have an author, date, or page number, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Bonnie Huddle
Sep 30, 2017
Did this article help you?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
Frequently asked questions
How do i cite a source with no author in apa style.
When no individual author name is listed, but the source can clearly be attributed to a specific organization—e.g., a press release by a charity, a report by an agency, or a page from a company’s website—use the organization’s name as the author in the reference entry and APA in-text citations .
When no author at all can be determined—e.g. a collaboratively edited wiki or an online article published anonymously—use the title in place of the author. In the in-text citation, put the title in quotation marks if it appears in plain text in the reference list, and in italics if it appears in italics in the reference list. Shorten it if necessary.
Frequently asked questions: APA Style
APA footnotes use superscript numbers and should appear in numerical order. You can place footnotes at the bottom of the relevant pages, or on a separate footnotes page at the end:
- For footnotes at the bottom of the page, you can use your word processor to automatically insert footnotes .
- For footnotes at the end of the text in APA, place them on a separate page entitled “Footnotes,” after the r eference page . Indent the first line of each footnote, and double-space them.
For both approaches, place a space between the superscript number and the footnote text.
APA Style requires you to use APA in-text citations , not footnotes, to cite sources .
However, you can use APA footnotes sparingly for two purposes:
- Giving additional information
- Providing copyright attribution
Yes, APA language guidelines state that you should always use the serial comma (aka Oxford comma ) in your writing.
This means including a comma before the word “and” at the end of a list of three or more items: “spelling, grammar, and punctuation.” Doing this consistently tends to make your lists less ambiguous.
Yes, it’s perfectly valid to write sentences in the passive voice . The APA language guidelines do caution against overusing the passive voice, because it can obscure your meaning or be needlessly long-winded. For this reason, default to the active voice in most cases.
The passive voice is most useful when the point of the sentence is just to state what was done, not to emphasize who did it. For example, “The projector was mounted on the wall” is better than “James and I mounted the projector on the wall” if it’s not particularly important who mounted the projector.
Yes, APA language guidelines encourage you to use the first-person pronouns “I” or “we” when referring to yourself or a group including yourself in your writing.
In APA Style, you should not refer to yourself in the third person. For example, do not refer to yourself as “the researcher” or “the author” but simply as “I” or “me.” Referring to yourself in the third person is still common practice in some academic fields, but APA Style rejects this convention.
If you cite several sources by the same author or group of authors, you’ll distinguish between them in your APA in-text citations using the year of publication.
If you cite multiple sources by the same author(s) at the same point , you can just write the author name(s) once and separate the different years with commas, e.g., (Smith, 2020, 2021).
To distinguish between sources with the same author(s) and the same publication year, add a different lowercase letter after the year for each source, e.g., (Smith, 2020, 2021a, 2021b). Add the same letters to the corresponding reference entries .
According to the APA guidelines, you should report enough detail on inferential statistics so that your readers understand your analyses.
Report the following for each hypothesis test:
- the test statistic value
- the degrees of freedom
- the exact p value (unless it is less than 0.001)
- the magnitude and direction of the effect
You should also present confidence intervals and estimates of effect sizes where relevant.
The number of decimal places to report depends on what you’re reporting. Generally, you should aim to round numbers while retaining precision. It’s best to present fewer decimal digits to aid easy understanding.
Use one decimal place for:
- Standard deviations
- Descriptive statistics based on discrete data
Use two decimal places for:
- Correlation coefficients
- Proportions
- Inferential test statistics such as t values, F values, and chi-squares.
No, including a URL is optional in APA Style reference entries for legal sources (e.g. court cases , laws ). It can be useful to do so to aid the reader in retrieving the source, but it’s not required, since the other information included should be enough to locate it.
Generally, you should identify a law in an APA reference entry by its location in the United States Code (U.S.C.).
But if the law is either spread across various sections of the code or not featured in the code at all, include the public law number in addition to information on the source you accessed the law in, e.g.:
You should report methods using the past tense , even if you haven’t completed your study at the time of writing. That’s because the methods section is intended to describe completed actions or research.
In your APA methods section , you should report detailed information on the participants, materials, and procedures used.
- Describe all relevant participant or subject characteristics, the sampling procedures used and the sample size and power .
- Define all primary and secondary measures and discuss the quality of measurements.
- Specify the data collection methods, the research design and data analysis strategy, including any steps taken to transform the data and statistical analyses.
With APA legal citations, it’s recommended to cite all the reporters (publications reporting cases) in which a court case appears. To cite multiple reporters, just separate them with commas in your reference entry . This is called parallel citation .
Don’t repeat the name of the case, court, or year; just list the volume, reporter, and page number for each citation. For example:
In APA Style , when you’re citing a recent court case that has not yet been reported in print and thus doesn’t have a specific page number, include a series of three underscores (___) where the page number would usually appear:
In APA style, statistics can be presented in the main text or as tables or figures . To decide how to present numbers, you can follow APA guidelines:
- To present three or fewer numbers, try a sentence,
- To present between 4 and 20 numbers, try a table,
- To present more than 20 numbers, try a figure.
Since these are general guidelines, use your own judgment and feedback from others for effective presentation of numbers.
In an APA results section , you should generally report the following:
- Participant flow and recruitment period.
- Missing data and any adverse events.
- Descriptive statistics about your samples.
- Inferential statistics , including confidence intervals and effect sizes.
- Results of any subgroup or exploratory analyses, if applicable.
When citing a podcast episode in APA Style , the podcast’s host is listed as author , accompanied by a label identifying their role, e.g. Glass, I. (Host).
When citing a whole podcast series, if different episodes have different hosts, list the executive producer(s) instead. Again, include a label identifying their role, e.g. Lechtenberg, S. (Producer).
Like most style guides , APA recommends listing the book of the Bible you’re citing in your APA in-text citation , in combination with chapter and verse numbers. For example:
Books of the Bible may be abbreviated to save space; a list of standard abbreviations can be found here . Page numbers are not used in Bible citations.
Yes, in the 7th edition of APA Style , versions of the Bible are treated much like other books ; you should include the edition you used in your reference list .
Previously, in the 6th edition of the APA manual, it was recommended to just use APA 6 in-text citations to refer to the Bible, and omit it from the reference list.
To make it easy for the reader to find the YouTube video , list the person or organization who uploaded the video as the author in your reference entry and APA in-text citation .
If this isn’t the same person responsible for the content of the video, you might want to make this clear in the text. For example:
When you need to highlight a specific moment in a video or audio source, use a timestamp in your APA in-text citation . Just include the timestamp from the start of the part you’re citing. For example:
To include a direct quote in APA , follow these rules:
- Quotes under 40 words are placed in double quotation marks .
- Quotes of 40 words or more are formatted as block quote .
- The author, year, and page number are included in an APA in-text citation .
APA doesn’t require you to include a list of tables or a list of figures . However, it is advisable to do so if your text is long enough to feature a table of contents and it includes a lot of tables and/or figures .
A list of tables and list of figures appear (in that order) after your table of contents, and are presented in a similar way.
Copyright information can usually be found wherever the table or figure was published. For example, for a diagram in a journal article , look on the journal’s website or the database where you found the article. Images found on sites like Flickr are listed with clear copyright information.
If you find that permission is required to reproduce the material, be sure to contact the author or publisher and ask for it.
If you adapt or reproduce a table or figure from another source, you should include that source in your APA reference list . You should also include copyright information in the note for the table or figure, and include an APA in-text citation when you refer to it.
Tables and figures you created yourself, based on your own data, are not included in the reference list.
An APA in-text citation is placed before the final punctuation mark in a sentence.
- The company invested over 40,000 hours in optimizing its algorithm (Davis, 2011) .
- A recent poll suggests that EU membership “would be backed by 55 percent of Danish voters” in a referendum (Levring, 2018) .
In an APA in-text citation , you use the phrase “ as cited in ” if you want to cite a source indirectly (i.e., if you cannot find the original source).
Parenthetical citation: (Brown, 1829, as cited in Mahone, 2018) Narrative citation: Brown (1829, as cited in Mahone, 2018) states that…
On the reference page , you only include the secondary source (Mahone, 2018).
Popular word processors like Microsoft Word and Google Docs can order lists in alphabetical order, but they don’t follow the APA Style alphabetization guidelines .
If you use Scribbr’s APA Citation Generator to create citations, references are ordered automatically based on the APA guidelines, taking into account all the exceptions.
Order numerals as though they were spelled out:
- “20 tips to relax” is ordered on the “T” of “Twenty”.
- “100 cities you should visit” is ordered on the “O” of “One hundred”.
Read more about alphabetizing the APA reference page .
If the author of a work is unknown, order the reference by its title. Disregard the words “A”, “An”, and “The” at the beginning of the title.
- The privacy concerns around social media
- Teens, social media, and privacy
Yes, if relevant you can and should include APA in-text citations in your appendices . Use author-date citations as you do in the main text.
Any sources cited in your appendices should appear in your reference list . Do not create a separate reference list for your appendices.
When you include more than one appendix in an APA Style paper , they should be labeled “Appendix A,” “Appendix B,” and so on.
When you only include a single appendix, it is simply called “Appendix” and referred to as such in the main text.
Appendices in an APA Style paper appear right at the end, after the reference list and after your tables and figures if you’ve also included these at the end.
An appendix contains information that supplements the reader’s understanding of your research but is not essential to it. For example:
- Interview transcripts
- Questionnaires
- Detailed descriptions of equipment
Something is only worth including as an appendix if you refer to information from it at some point in the text (e.g. quoting from an interview transcript). If you don’t, it should probably be removed.
If you adapt or reproduce a table or figure from another source, you should include that source in your APA reference list . You should also acknowledge the original source in the note or caption for the table or figure.
APA doesn’t require you to include a list of tables or a list of figures . However, it is advisable to do so if your text is long enough to feature a table of contents and it includes a lot of tables and/or figures.
A list of tables and list of figures appear (in that order) after your table of contents , and are presented in a similar way.
In an APA Style paper , use a table or figure when it’s a clearer way to present important data than describing it in your main text. This is often the case when you need to communicate a large amount of information.
Before including a table or figure in your text, always reflect on whether it’s useful to your readers’ understanding:
- Could this information be quickly summarized in the text instead?
- Is it important to your arguments?
- Does the table or figure require too much explanation to be efficient?
If the data you need to present only contains a few relevant numbers, try summarizing it in the text (potentially including full data in an appendix ). If describing the data makes your text overly long and difficult to read, a table or figure may be the best option.
In an APA Style paper , the abstract is placed on a separate page after the title page (page 2).
An APA abstract is around 150–250 words long. However, always check your target journal’s guidelines and don’t exceed the specified word count.
In APA Style , all sources that are not retrievable for the reader are cited as personal communications . In other words, if your source is private or inaccessible to the audience of your paper , it’s a personal communication.
Common examples include conversations, emails, messages, letters, and unrecorded interviews or performances.
Interviews you conducted yourself are not included in your reference list , but instead cited in the text as personal communications .
Published or recorded interviews are included in the reference list. Cite them in the usual format of the source type (for example, a newspaper article , website or YouTube video ).
To cite a public post from social media , use the first 20 words of the post as a title, include the date it was posted and a URL, and mention the author’s username if they have one:
Dorsey, J. [@jack]. (2018, March 1). We’re committing Twitter to help increase the collective health, openness, and civility of public conversation, and to hold ourselves publicly [Tweet]. Twitter. https://twitter.com/jack/status/969234275420655616
To cite content from social media that is not publicly accessible (e.g. direct messages, posts from private groups or user profiles), cite it as a personal communication in the text, but do not include it in the reference list :
When contacted online, the minister stated that the project was proceeding “according to plan” (R. James, Twitter direct message, March 25, 2017).
When you quote or paraphrase a specific passage from a source, you need to indicate the location of the passage in your APA in-text citation . If there are no page numbers (e.g. when citing a website ) but the text is long, you can instead use section headings, paragraph numbers, or a combination of the two:
(Caulfield, 2019, Linking section, para. 1).
Section headings can be shortened if necessary. Kindle location numbers should not be used in ebook citations , as they are unreliable.
If you are referring to the source as a whole, it’s not necessary to include a page number or other marker.
APA Style usually does not require an access date. You never need to include one when citing journal articles , e-books , or other stable online sources.
However, if you are citing a website or online article that’s designed to change over time, it’s a good idea to include an access date. In this case, write it in the following format at the end of the reference: Retrieved October 19, 2020, from https://www.uva.nl/en/about-the-uva/about-the-university/about-the-university.html
The 7th edition APA Manual , published in October 2019, is the most current edition. However, the 6th edition, published in 2009, is still used by many universities and journals.
The APA Manual 7th edition can be purchased at Amazon as a hardcover, paperback or spiral-bound version. You can also buy an ebook version at RedShelf .
The American Psychological Association anticipates that most people will start using the 7th edition in the spring of 2020 or thereafter.
It’s best to ask your supervisor or check the website of the journal you want to publish in to see which APA guidelines you should follow.
If you’re citing from an edition other than the first (e.g. a 2nd edition or revised edition), the edition appears in the reference, abbreviated in parentheses after the book’s title (e.g. 2nd ed. or Rev. ed.).
In the 7th edition of the APA manual, no location information is required for publishers. The 6th edition previously required you to include the city and state where the publisher was located, but this is no longer the case.
In an APA reference list , journal article citations include only the year of publication, not the exact date, month, or season.
The inclusion of volume and issue numbers makes a more specific date unnecessary.
In an APA journal citation , if a DOI (digital object identifier) is available for an article, always include it.
If an article has no DOI, and you accessed it through a database or in print, just omit the DOI.
If an article has no DOI, and you accessed it through a website other than a database (for example, the journal’s own website), include a URL linking to the article.
You may include up to 20 authors in a reference list entry .
When an article has more than 20 authors, replace the names prior to the final listed author with an ellipsis, but do not omit the final author:
Davis, Y., Smith, J., Caulfield, F., Pullman, H., Carlisle, J., Donahue, S. D., James, F., O’Donnell, K., Singh, J., Johnson, L., Streefkerk, R., McCombes, S., Corrieri, L., Valck, X., Baldwin, F. M., Lorde, J., Wardell, K., Lao, W., Yang, P., . . . O’Brien, T. (2012).
Include the DOI at the very end of the APA reference entry . If you’re using the 6th edition APA guidelines, the DOI is preceded by the label “doi:”. In the 7th edition , the DOI is preceded by ‘https://doi.org/’.
- 6th edition: doi: 10.1177/0894439316660340
- 7th edition: https://doi.org/ 10.1177/0894439316660340
APA citation example (7th edition)
Hawi, N. S., & Samaha, M. (2016). The relations among social media addiction, self-esteem, and life satisfaction in university students. Social Science Computer Review , 35 (5), 576–586. https://doi.org/10.1177/0894439316660340
When citing a webpage or online article , the APA in-text citation consists of the author’s last name and year of publication. For example: (Worland & Williams, 2015). Note that the author can also be an organization. For example: (American Psychological Association, 2019).
If you’re quoting you should also include a locator. Since web pages don’t have page numbers, you can use one of the following options:
- Paragraph number: (Smith, 2018, para. 15).
- Heading or section name: ( CDC, 2020, Flu Season section)
- Abbreviated heading: ( CDC, 2020, “Key Facts” section)
Always include page numbers in the APA in-text citation when quoting a source . Don’t include page numbers when referring to a work as a whole – for example, an entire book or journal article.
If your source does not have page numbers, you can use an alternative locator such as a timestamp, chapter heading or paragraph number.
Instead of the author’s name, include the first few words of the work’s title in the in-text citation. Enclose the title in double quotation marks when citing an article, web page or book chapter. Italicize the title of periodicals, books, and reports.
No publication date
If the publication date is unknown , use “n.d.” (no date) instead. For example: (Johnson, n.d.).
The abbreviation “ et al. ” (meaning “and others”) is used to shorten APA in-text citations with three or more authors . Here’s how it works:
Only include the first author’s last name, followed by “et al.”, a comma and the year of publication, for example (Taylor et al., 2018).
APA Style papers should be written in a font that is legible and widely accessible. For example:
- Times New Roman (12pt.)
- Arial (11pt.)
- Calibri (11pt.)
- Georgia (11pt.)
The same font and font size is used throughout the document, including the running head , page numbers, headings , and the reference page . Text in footnotes and figure images may be smaller and use single line spacing.
The easiest way to set up APA format in Word is to download Scribbr’s free APA format template for student papers or professional papers.
Alternatively, you can watch Scribbr’s 5-minute step-by-step tutorial or check out our APA format guide with examples.
You need an APA in-text citation and reference entry . Each source type has its own format; for example, a webpage citation is different from a book citation .
Use Scribbr’s free APA Citation Generator to generate flawless citations in seconds or take a look at our APA citation examples .
APA format is widely used by professionals, researchers, and students in the social and behavioral sciences, including fields like education, psychology, and business.
Be sure to check the guidelines of your university or the journal you want to be published in to double-check which style you should be using.
Yes, page numbers are included on all pages, including the title page , table of contents , and reference page . Page numbers should be right-aligned in the page header.
To insert page numbers in Microsoft Word or Google Docs, click ‘Insert’ and then ‘Page number’.
Ask our team
Want to contact us directly? No problem. We are always here for you.
- Email [email protected]
- Start live chat
- Call +1 (510) 822-8066
- WhatsApp +31 20 261 6040

Our team helps students graduate by offering:
- A world-class citation generator
- Plagiarism Checker software powered by Turnitin
- Innovative Citation Checker software
- Professional proofreading services
- Over 300 helpful articles about academic writing, citing sources, plagiarism, and more
Scribbr specializes in editing study-related documents . We proofread:
- PhD dissertations
- Research proposals
- Personal statements
- Admission essays
- Motivation letters
- Reflection papers
- Journal articles
- Capstone projects
Scribbr’s Plagiarism Checker is powered by elements of Turnitin’s Similarity Checker , namely the plagiarism detection software and the Internet Archive and Premium Scholarly Publications content databases .
The add-on AI detector is powered by Scribbr’s proprietary software.
The Scribbr Citation Generator is developed using the open-source Citation Style Language (CSL) project and Frank Bennett’s citeproc-js . It’s the same technology used by dozens of other popular citation tools, including Mendeley and Zotero.
You can find all the citation styles and locales used in the Scribbr Citation Generator in our publicly accessible repository on Github .
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
In-Text Citations: Author/Authors

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Though the APA's author-date system for citations is fairly straightforward, author categories can vary significantly from the standard "one author, one source" configuration. There are also additional rules for citing authors of indirect sources, electronic sources, and sources without page numbers.
A Work by One Author
The APA manual recommends the use of the author-date citation structure for in-text citation references. This structure requires that any in-text citation (i.e., within the body of the text) be accompanied by a corresponding reference list entry. In the in-text citation provide the surname of the author but do not include suffixes such as "Jr.".
Citing Non-Standard Author Categories
A work by two authors.
Name both authors in the signal phrase or in parentheses each time you cite the work. Use the word "and" between the authors' names within the text and use the ampersand in parentheses.
A Work by Three or More Authors
List only the first author’s name followed by “et al.” in every citation, even the first, unless doing so would create ambiguity between different sources.
In et al. , et should not be followed by a period. Only "al" should be followed by a period.
If you’re citing multiple works with similar groups of authors, and the shortened “et al” citation form of each source would be the same, you’ll need to avoid ambiguity by writing out more names. If you cited works with these authors:
They would be cited in-text as follows to avoid ambiguity:
Since et al. is plural, it should always be a substitute for more than one name. In the case that et al. would stand in for just one author, write the author’s name instead.
Unknown Author
If the work does not have an author, cite the source by its title in the signal phrase or use the first word or two in the parentheses. Titles of books and reports are italicized; titles of articles, chapters, and web pages are in quotation marks. APA style calls for capitalizing important words in titles when they are written in the text (but not when they are written in reference lists).
Note : In the rare case that "Anonymous" is used for the author, treat it as the author's name (Anonymous, 2001). In the reference list, use the name Anonymous as the author.
Organization as an Author
If the author is an organization or a government agency, mention the organization in the signal phrase or in the parenthetical citation the first time you cite the source, just as you would an individual person.
If the organization has a well-known abbreviation, you may include the abbreviation in brackets the first time the source is cited and then use only the abbreviation in later citations. However, if you cite work from multiple organizations whose abbreviations are the same, do not use abbreviations (to avoid ambiguity).
Two or More Works in the Same Parentheses
When your parenthetical citation includes two or more works, order them the same way they appear in the reference list (viz., alphabetically), separated by a semi-colon.
If you cite multiple works by the same author in the same parenthetical citation, give the author’s name only once and follow with dates. No date citations go first, then years, then in-press citations.
Authors with the Same Last Name
To prevent confusion, use first initials with the last names.
Two or More Works by the Same Author in the Same Year
If you have two sources by the same author in the same year, use lower-case letters (a, b, c) with the year to order the entries in the reference list. Use the lower-case letters with the year in the in-text citation.
Introductions, Prefaces, Forewords, and Afterwords
When citing an Introduction, Preface, Foreword, or Afterword in-text, cite the appropriate author and year as usual.
Personal Communication
For interviews, letters, e-mails, and other person-to-person communication, cite the communicator's name, the fact that it was personal communication, and the date of the communication. Do not include personal communication in the reference list.
If using a footnote to reference personal communication, handle citations the same way.
Traditional Knowledge of Indigenous Peoples
When citing information you learned from a conversation with an Indigenous person who was not your research participant, use a variation of the personal communication citation above. Include the person’s full name, nation or Indigenous group, location, and any other relevant details before the “personal communication, date” part of the citation.
Citing Indirect Sources
Generally, writers should endeavor to read primary sources (original sources) and cite those rather than secondary sources (works that report on original sources). Sometimes, however, this is impossible. If you use a source that was cited in another source, name the original source in your signal phrase. List the secondary source in your reference list and include the secondary source in the parentheses. If you know the year of the original source, include it in the citation.
Electronic Sources
If possible, cite an electronic document the same as any other document by using the author-date style.
Unknown Author and Unknown Date
If no author or date is given, use the title in your signal phrase or the first word or two of the title in the parentheses and use the abbreviation "n.d." (for "no date").
Sources Without Page Numbers
When an electronic source lacks page numbers, you should try to include information that will help readers find the passage being cited. Use the heading or section name, an abbreviated heading or section name, a paragraph number (para. 1), or a combination of these.
Note: Never use the page numbers of webpages you print out; different computers print webpages with different pagination. Do not use Kindle location numbers; instead, use the page number (available in many Kindle books) or the method above.
Other Sources
The APA Publication Manual describes how to cite many different kinds of authors and content creators. However, you may occasionally encounter a source or author category that the manual does not describe, making the best way to proceed unclear.
In these cases, it's typically acceptable to apply the general principles of APA citation to the new kind of source in a way that's consistent and sensible. A good way to do this is to simply use the standard APA directions for a type of source that resembles the source you want to cite. For example, a sensible way to cite a virtual reality program would be to mimic the APA's guidelines for computer software.
You may also want to investigate whether a third-party organization has provided directions for how to cite this kind of source.

- WorldCat Discovery
- Course and Subject Guides
- Journal Finder
- New Books Feeds
- Course Reserves
- Room Reservations
- Faculty and Graduate Services
- Available Computers
- Events and Workshops
- Copyright and Fair Use
- Interlibrary Loan
- Request Forms
- Library Policies
- Borrowing & Access Policies
- Library Building
- American University of Sharjah
APA 6th Edition Citation Style
No author / no date.
- APA 6th Edition Guide
- Annual Report
- Article, Journal
- Article, Journal (with DOI)
- Article, Journal (without DOI)
- Book, Chapter in edited work
- Book, Electronic
- Dissertation / Thesis
- Dissertation / Thesis (Database)
- Email/Interviews
- Events, Live
- Newspaper Article
- Newspaper Article (Database)
- Newspaper Article (Website)
- Podcast, Audio
- Reference Work
- Reference Work (Database)
- Website Document
- Video, Online
Newspaper article (from the newspaper’s website) with no author
Proper Bibliographic Reference Format:
- Bibliographic references are double-spaced and indented half an inch after the first line.
- If there is no author, the article title comes first.
- For titles of newspapers, use italics and "headline" style capitalization.
- Use the URL of the homepage of the newspaper to avoid non-working URLs.
- It is no longer necessary to include the date of retrieval.
Barcelona to ban burqa in municipal buildings. (2010, June 14). Retrieved from http://gulfnews.com
In-Text Citations:
- Citations are placed in the context of discussion using the author’s last name and date of publication.
- When a work has no identified author, cite in text the first few words of the article title using double quotation marks, “headline- style” capitalization, and the year.
(“Barcelona to Ban Burqa,” 2010)
- Alternatively, you can integrate the citation into the sentence by means of narrative.
- There must be a total match between the reference list and the parenthetical citation, so the article title must stand in place of an author’s name in the essay.
“Barcelona to Ban Burqa” (2010) contends that the move is aimed at all dress that impedes identification.
Website with no author and no date
- If there is no date, use the abbreviation n.d.
United Arab Emirates architecture. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.uaeinteract.com/
- When a work has no identified author, cite in text the first few words of the article title using double quotation marks, “headline-style" capitalization, and the year.
(“United Arab Emirates Architecture,” n.d.)
“United Arab Emirates Architecture” (n.d.) describes building materials used in early settlements.
Journal or magazine article (from library database or online) with no author
- For titles of journals or magazines, use italics and "headline" style capitalization.
- Use the URL of the homepage of the journal or magazine to avoid non-working URLS
Famine relief: Just a simple matter of supplying food? (2002). Nutrition Noteworthy , 5(1). Retrieved from http://escholarship.org/uc/uclabiolchem_nutritionnoteworthy
- When a work has no identified author, cite in text the first few words of the article title using double quotation marks, “headline” style capitalization, and the year.
(“Famine Relief,” 2002)
“Famine Relief” (2002) examines the causes of poverty and famine in Africa.
Works With an Anonymous Author
When a work’s author is designated as “Anonymous,” cite in text the word Anonymous followed by a comma and the date:
(Anonymous, 2010)
In the reference list, an anonymous work is alphabetized by the word Anonymous
Anonymous. (2010). Food safety shake-up needed in the USA. The Lancet , 375(9732), 2122. Retrieved from http://www.thelancet.com
- << Previous: Video, Online
- Next: FAQ >>
- Last Updated: Oct 13, 2022 2:48 PM
- URL: https://aus.libguides.com/apa
© 2020 American University of Sharjah . All Rights Reserved.
Privacy Policy
Return to AUS
Official websites use .gov
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Births in the United States, 2023
NCHS Data Brief No. 507, August 2024
PDF Version (454 KB)
Joyce A. Martin, M.P.H., Brady E. Hamilton Ph.D., and Michelle J.K. Osterman, M.H.S.
- Key findings
The number of births and the general fertility rate declined from 2022 to 2023.
Birth rates declined for females ages 15–19 from 2022 to 2023., prenatal care beginning in the first trimester declined for the second year in a row in 2023., the preterm birth rate was unchanged from 2022 to 2023, but early-term births increased., data source and methods, about the authors, suggested citation.
Data from the National Vital Statistics System
- The number of births in the United States declined 2% from 2022 to 2023. The general fertility rate declined 3% in 2023 to 54.5 births per 1,000 females ages 15–44.
- Birth rates declined for females ages 15–19 (4%), 15–17 (2%), and 18–19 (5%), from 2022 to 2023.
- The percentage of mothers receiving prenatal care in the first trimester of pregnancy declined 1% from 2022 to 2023, while the percentage of mothers with no prenatal care increased 5%.
- The preterm birth rate was essentially unchanged at 10.41% in 2023, but the rate of early-term births rose 2% to 29.84%.
This report presents highlights from 2023 final birth data on key demographic and maternal and infant health indicators. The number of births, the general fertility rate (births per 1,000 females ages 15–44), teen birth rates, the distribution of births by trimester prenatal care began, and the distribution of births by gestational age (less than 37 weeks, 37–38 weeks, 39–40 weeks, and 41 or later weeks of gestation) are presented. For all indicators, results for 2023 are compared with those for 2022 and 2021.
Keywords : general fertility rate, prenatal care, gestational age, National Vital Statistics System.
- In 2023, 3,596,017 births were registered in the United States, down 2% from 2022 (3,667,758) and 2021 (3,664,292) ( Figure 1 , Table 1 ).
- The general fertility rate for the United States decreased 3% in 2023 to 54.5 births per 1,000 females ages 15–44 from 56.0 in 2022; the general fertility rate was also down 3% from 2021 (56.3).
Figure 1. Number of live births and general fertility rates: United States, 2021–2023
| Year | Births | Fertility rate |
|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 3,664,292 | 56.3 |
| 2022 | 3,667,758 | 56.0 |
| 2023 | 3,596,017 | 54.5 |
NOTES: General fertility rates are births per 1,000 women ages 15–44. Rates are based on population estimates as of July 1 for 2021, 2022, and 2023. SOURCE: National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System, natality data file.
- The birth rate for teenagers ages 15–19 declined 4% from 2022 to 2023, from 13.6 to 13.1 births per 1,000 females, and was down 6% from 2021 (13.9) ( Figure 2 , Table 2 ).
- From 2022 to 2023, the birth rate for teenagers ages 15–17 declined 2%, from 5.6 to 5.5; there was no change in the rate from 2021 to 2022.
- The rate for teenagers ages 18–19 declined 5% from 2022 to 2023, from 25.8 to 24.6 and has declined 8% since 2021 (26.6).
Figure 2. Birth rate for teenagers, by maternal age: United States, 2021–2023
| Maternal age | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 15–19 | 15–17 | 18–19 | |
| Percentage | ||||
| 2002 | 13.9 | 5.6 | 26.6 | |
| 2003 | 13.6 | 5.6 | 25.8 | |
| 2004 | 13.1 | 5.5 | 24.6 | |
NOTES: Age-specific birth rates are births per 1,000 females in specified age group. Rates are based on population estimates as of July 1 for each year 2021–2023. SOURCE: National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System, natality data file.
- Prenatal care beginning in the first trimester declined 1% in 2023 to 76.1%, from 77.0% in 2022. This follows a 2% decline from 2021 (78.3%) to 2022 ( Figure 3 , Table 3 ).
- Care beginning in the second trimester increased 4% in 2023, from 16.3% in 2022 to 16.9%. This follows a 6% increase from 2021 (15.4%).
- Care beginning in the third trimester increased 2% from 2022 (4.6%) to 2023 (4.7%) following a 10% increase from 2021 (4.2%) to 2022.
- The percentage of mothers receiving no prenatal care increased 5% in 2023 to 2.3% from 2.2% in 2022; the percentage of mothers with no prenatal care also rose 5% from 2021 (2.1%) to 2022.
Figure 3. Distribution of trimester prenatal care began: United States, 2021–2023
| Trimester | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | ||
| Percentage | ||||
| First trimester | 78.3 | 77.0 | 76.1 | |
| Second trimester | 15.4 | 16.3 | 16.9 | |
| Third trimester | 4.2 | 4.6 | 4.7 | |
| No care | 2.1 | 2.2 | 2.3 | |
SOURCE: National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System, natality data file.
- The percentage of infants born preterm was essentially unchanged from 2022 (10.38%) to 2023 (10.41%) but was down 1% from 2021 (10.49%) ( Figure 4 , Table 4 ).
- The percentage of infants born early term rose 2% from 2022 to 2023, from 29.31% to 29.84%, and was up 4% from 2021 (28.76%).
- In contrast, the percentage of full-term births declined 1%, from 2022 to 2023 (55.32% to 54.94%) and has declined 2% since 2021 (55.90%).
- The percentage of infants born late or post term was 4.82% in 2023, down 3% from 2022 (4.99%) and 1% from 2021 (4.85%).
Figure 4. Distribution of births by gestational age: United States, 2021–2023
| Gestational age | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Preterm | Early term | Full term | Late and post term |
| Percentage | ||||
| 2021 | 10.49 | 28.76 | 55.9 | 4.85 |
| 2022 | 10.38 | 29.31 | 55.32 | 4.99 |
| 2023 | 10.41 | 29.84 | 54.94 | 4.82 |
NOTES: Preterm is less than 37 weeks, early term is 37 to 38 weeks, full term is 39 to 40 weeks, and late and post-term is 41 weeks or more. Source: National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System, natality data file. SOURCE: National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System, natality data file.
U.S. birth certificate data for 2023 show continued declines in the number (2%) and rate (3%) of births from 2022 to 2023. Since the most recent high in 2007, the number of births has declined 17%, and the general fertility rate has declined 21% ( 1 ). The teen birth rate also continued to decline in 2023 and has declined two-thirds since 2007 ( 1 ). The percentage of women beginning care in the first trimester of pregnancy declined in 2023 and was down 3% from the most recent high in 2021; first trimester care had been on the rise from 2016 to 2021. At the same time, the percentage of women with late care or with no care rose from 2021 to 2023; late and no-care levels have risen steadily since 2016 ( 1 ). The preterm birth rate was essentially unchanged from 2022 to 2023, but early-term births rose 2%, and full-term and late- and post-term births declined 1% and 3%, respectively. Since the most recent low in 2014, preterm birth rates have risen 9% and early-term births by 21%, while full-term and late- and post-term births have declined ( 1 ).
General fertility rate : Number of births per 1,000 females ages 15–44.
Gestational age : Preterm is births delivered before 37 completed weeks of gestation, early term is 37–38 weeks, full term is 39–40 weeks, and late and post term is 41 or later weeks. Gestational age is based on the obstetric estimate of gestation in completed weeks.
Teenage birth rates : Births per 1,000 females in the specified age groups 15–19, 15–17, and 18–19.
Trimester prenatal care began : The timing of care based on the date a physician or other health care provider examined or counseled the pregnant woman for the pregnancy and the obstetric estimate of gestational age.
This report uses data from the natality data file from the National Vital Statistics System. The vital statistics natality file is based on information from birth certificates and includes information for all births occurring in the United States. This Data Brief accompanies the release of the 2023 natality public-use file ( 2 ). More detailed analyses of the topics presented in this report and other topics such as births by age of mother, tobacco use during pregnancy, pregnancy risk factors, prenatal care timing and utilization, receipt of WIC food, maternal body mass index, and breastfeeding are possible by using the annual natality files ( 2 ). Additional information from the 2023 final birth data file is available via the CDC WONDER platform and will be included in the final 2023 National Vital Statistics Births Report.
References to increases or decreases in rates or percentages indicate differences are statistically significant at the 0.05 level based on a two-tailed z test. References to decreases in the number of births indicate differences are statistically significant at the 0.05 level based on a two-tailed chi-squared test. Computations exclude records for which information is unknown.
Rates shown in this report are based on population estimates calculated from a base that incorporates the 2020 census, vintage 2020 estimates for April 1, 2020, and 2020 demographic analysis estimates. Rates are calculated based on population estimates as of July 1, 2022, (vintage 2022) and July 1, 2023 (vintage 2023) ( 1 , 3 ). The vintage 2023 population estimates include methodological changes made after the release of the vintage 2022 population estimates and projection ( 4 , 5 ). Changes in rates from 2022 to 2023 reflect changes in births and changes in population estimates.
Joyce A. Martin, Brady E. Hamilton, and Michelle J.K. Osterman are with the National Center for Health Statistics, Division of Vital Statistics.
- Osterman MJK, Hamilton BE, Martin JA, Driscoll AK, Valenzuela CP. Births: Final data for 2022. National Vital Statistics Reports; vol 73 no 1. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics. 2024. DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.15620/cdc:145588
- National Center for Health Statistics. Vital statistics online data portal .
- U.S. Census Bureau. Annual state resident population estimates for six race groups (five race alone groups and two or more races) by age, sex, and Hispanic origin: April 1, 2010, to July 1, 2023 . 2024.
- U.S. Census Bureau. Methodology for the United States population estimates: Vintage 2023 . Nation, states, counties, and Puerto Rico—April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2023. 2023.
- U.S. Census Bureau. Vintage 2023 release notes . 2024.
Martin JA, Hamilton BE, Osterman MJK. Births in the United States, 2023. NCHS Data Brief, no 507. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics. 2024. DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.15620/cdc/158789 .
Copyright information
All material appearing in this report is in the public domain and may be reproduced or copied without permission; citation as to source, however, is appreciated.
National Center for Health Statistics
Brian C. Moyer, Ph.D., Acting Director Amy M. Branum, Ph.D., Associate Director for Science
Division of Vital Statistics
Paul D. Sutton, Ph.D., Acting Director Andrés A. Berruti, Ph.D., M.A., Associate Director for Science
- Get E-mail Updates
- Data Visualization Gallery
- NHIS Early Release Program
- MMWR QuickStats
- Government Printing Office Bookstore

Newspaper Article References
This page contains reference examples for newspaper articles, including the following:
- Newspaper article
- Comment on an online newspaper article
1. Newspaper article
Carey, B. (2019, March 22). Can we get better at forgetting? The New York Times . https://www.nytimes.com/2019/03/22/health/memory-forgetting-psychology.html
Harlan, C. (2013, April 2). North Korea vows to restart shuttered nuclear reactor that can make bomb-grade plutonium. The Washington Post , A1, A4.
Stobbe, M. (2020, January 8). Cancer death rate in U.S. sees largest one-year drop ever. Chicago Tribune .
- Parenthetical citations : (Carey, 2019; Harlan, 2013; Stobbe, 2020)
- Narrative citations : Carey (2019), Harlan (2013), and Stobbe (2020)
- In the source element of the reference, provide at minimum the title of the newspaper in italic title case.
- If the newspaper article is from an online newspaper that has a URL that will resolve for readers (as in the Carey example), include the URL of the article at the end of the reference. If volume, issue, and/or page numbers for the article are missing, omit these elements from the reference.
- If you used a print version of the newspaper article (as in the Harlan example), provide the page or pages of the article after the newspaper title. Do not include the abbreviations “p.” or “pp.” before the page(s).
- If the newspaper article is from an academic research database, provide the title of the newspaper and any volume, issue, and/or page numbers that are available for the article. Do not include database information in the reference. If the article does not have volume, issue, or page numbers available, the reference in this case ends with the title of the newspaper (as in the Stobbe example).
- If the article is from a news website (e.g., CNN, HuffPost)—one that does not have an associated daily or weekly newspaper—use the format for a webpage on a news website instead.
2. Comment on an online newspaper article
sidneyf. (2020, October 7). Oh, I don’t know; perhaps the common-sense conclusion that packing people together — for hours — like sardines — may be an [Comment on the article “When will it be safe to travel again?”]. The Washington Post . https://wapo.st/3757UlS
- Parenthetical citation : sidneyf (2020)
- Narrative citation : sidneyf (2020)
- Credit the person who left the comment as the author using the format that appears with the comment (i.e., a real name or a username). The example shows a username.
- Provide the comment title or up to the first 20 words of the comment; then write “Comment on the article” and the title of the article on which the comment appeared (in quotation marks and sentence case, enclosed within square brackets).
- Link to the comment itself if possible. Either the full URL or a short URL is acceptable. The example shows a URL that the writer has shortened with the bitly URL shortening service.
- If the comment belongs to an article from a news website (e.g., CNN, HuffPost)—one that does not have an associated daily or weekly newspaper—use the format for a comment on a webpage on a news website.
Newspaper article references are covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Section 10.1 and the Concise Guide Section 10.1

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Cite in text the first few words of the reference list entry (usually the title) and the year. Use double quotation marks around the title or abbreviated title.: ("All 33 Chile Miners," 2010). Note: Use the full title of the web page if it is short for the parenthetical citation. Articles found on the web, like the example above, are not ...
Web Page with No Author; Search this Guide Search. APA Citation Style, 7th edition: Web Page with No Author. A guide to help users create citations using APA (American Psychological Association) style, 7th edition. ... In-Text Citation (Quotation): (Title of specific document, Year, page or paragraph number [if available]) ...
Revised on January 17, 2024. Webpage citations in APA Style consist of five components: author, publication date, title, website name, and URL. Unfortunately, some of these components are sometimes missing. For instance, there may be no author or publication date. This article explains how to handle different kinds and combinations of missing ...
Citing in-text when there are no authors. APA 7th ed. uses the author-date citation system for citing references in-text. In parenthetical citations, this structure includes the author's last name and the publication year (with a comma separating them) in parentheses. In narrative citations, the author's last name is incorporated into the ...
When creating an in-text citation in APA without an author, you use the title. For the in-text citation, use only the first few words if it's a long title. Use the full title if it's a shorter title. In-Text Citation Example for APA No Author. ( Concert Raises Thousands, 2019) ("Language Learning," 2019)
New in 7th edition: You must include the site name in your citation, unless the site name is the same as the corporate author. For example, a citation of a CDC report would not include the site name. << Previous: Web page from a University site
Reference entries for a website without an author listed will include: Organizational Author. (Date). Title of page. Container or Site Name (if different than the organizational author, if it's the same--skip info here!) URL; Example website source (with elements color-coded): National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal Skin Diseases ...
In-text citations briefly identify the source of information in the body text. They correspond to a full reference entry at the end of your paper. APA in-text citations consist of the author's last name and publication year. When citing a specific part of a source, also include a page number or range, for example (Parker, 2020, p.
Provide the name of the news website in the source element of the reference. Link to the comment itself if possible. Otherwise, link to the webpage on which the comment appears. Either a full URL or a short URL is acceptable. 3. Webpage on a website with a government agency group author.
APA Style provides guidelines to help writers determine the appropriate level of citation and how to avoid plagiarism and self-plagiarism. We also provide specific guidance for in-text citation, including formats for interviews, classroom and intranet sources, and personal communications; in-text citations in general; and paraphrases and direct quotations.
Revised on January 17, 2024. APA website citations usually include the author, the publication date, the title of the page or article, the website name, and the URL. If there is no author, start the citation with the title of the article. If the page is likely to change over time, add a retrieval date. If you are citing an online version of a ...
Document from a Web site with no Author (p. 264-265; 350-352) Helpful Tip When citing sources that you find on the Internet you only need to include a retrieval date if the information you viewed is likely to change over time (p. 290).
To cite a book with no date in APA, use the core required elements: the name (s) of the author (s), the title of the book, and the publisher. Use "n.d." in place of the publication year. The table below shows how to format the in-text citation and the reference-list entry for a book with no date in APA style. In-Text Template and Citation.
When a work has no identified author, cite in text the first few words of the article title using double quotation marks, "headline- style" capitalization, and the year. ("Barcelona to Ban Burqa," 2010) Alternatively, you can integrate the citation into the sentence by means of narrative. There must be a total match between the ...
Using In-text Citation. Include an in-text citation when you refer to, summarize, paraphrase, or quote from another source. For every in-text citation in your paper, there must be a corresponding entry in your reference list. APA in-text citation style uses the author's last name and the year of publication, for example: (Field, 2005).
The in-text citation APA style provides us with a tidbit of information. Just enough to glance at it and keep on going with reading the paper. To recap, in-text citations are great because: They credit the original author of a work or information. They let readers quickly see where the information is coming from.
APA Citation Basics. When using APA format, follow the author-date method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the year of publication for the source should appear in the text, like, for example, (Jones, 1998). One complete reference for each source should appear in the reference list at the end of the paper.
Breaking down references for a web page in APA style is pretty simple. List the article title. This is the first piece of information you note, and it goes in the place of the author. Add the published date in parentheses. The date follows the format: year, month, and day, if available. Name of the website.
A short title in quotation marks, in cases in which the heading is too unwieldy to cite in full. Because there is no date and no author, your text citation would include the title (or short title) "n.d." for no date, and paragraph number (e.g., "Heuristic," n.d., para. 1). The entry in the reference list might look something like this:
For an anonymous author, your citation will look like this: " (Anonymous, 2018)" 4. Use "n.d." for no date in your citations. APA citations usually include the author and date. However, you can't include a date if one isn't there! Using "n.d." tells the reader that no date is provided on the site.
If you cite several sources by the same author or group of authors, you'll distinguish between them in your APA in-text citations using the year of publication.. If you cite multiple sources by the same author(s) at the same point, you can just write the author name(s) once and separate the different years with commas, e.g., (Smith, 2020, 2021). To distinguish between sources with the same ...
The APA manual recommends the use of the author-date citation structure for in-text citation references. This structure requires that any in-text citation (i.e., within the body of the text) be accompanied by a corresponding reference list entry. In the in-text citation provide the surname of the author but do not include suffixes such as "Jr.".
In-Text Citations: Citations are placed in the context of discussion using the author's last name and date of publication. When a work has no identified author, cite in text the first few words of the article title using double quotation marks, "headline- style" capitalization, and the year. ("Barcelona to Ban Burqa," 2010)
References provide the information necessary for readers to identify and retrieve each work cited in the text. Consistency in reference formatting allows readers to focus on the content of your reference list, discerning both the types of works you consulted and the important reference elements with ease.
Birth rates declined for females ages 15-19 from 2022 to 2023. The birth rate for teenagers ages 15-19 declined 4% from 2022 to 2023, from 13.6 to 13.1 births per 1,000 females, and was down 6% from 2021 (13.9) (Figure 2, Table 2).From 2022 to 2023, the birth rate for teenagers ages 15-17 declined 2%, from 5.6 to 5.5; there was no change in the rate from 2021 to 2022.
Report by a Group Author (Section 10.4) World Health Organization. (2014). Comprehensive implementation plan on maternal, infant and young ... American Psychological Association (7th ed.) and the Concise Guide to APA Style (7th ed.). CITE THIS HANDOUT: American Psychological Association. (2024). APA Style common reference examples guide. https ...
Secondary sources are covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Section 8.6 and the Concise Guide Section 8.6. ... If the year of publication of the primary source is known, also include it in the text citation. For example, if you read a work by Lyon et al. (2014) in which Rabbitt (1982) was cited, and you were ...
If the URL is no longer working or no longer provides readers access to the content you intend to cite, follow the guidance for works with no source. Other alphanumeric identifiers such as the International Standard Book Number (ISBN) and the International Standard Serial Number (ISSN) are not included in APA Style references.
The impact of social media and texting on students' academic writing skills (Publication No. 3683242) [Doctoral dissertation, Tennessee State University]. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global. Parenthetical citation: (Risto, 2014) Narrative citation: Risto (2014)
Narrative citations: Carey (2019), Harlan (2013), ... Credit the person who left the comment as the author using the format that appears with the comment (i.e., a real name or a username). ... Newspaper article references are covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Section 10.1 and the Concise Guide Section 10.1.