Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Parts of speech

The 8 Parts of Speech | Chart, Definition & Examples

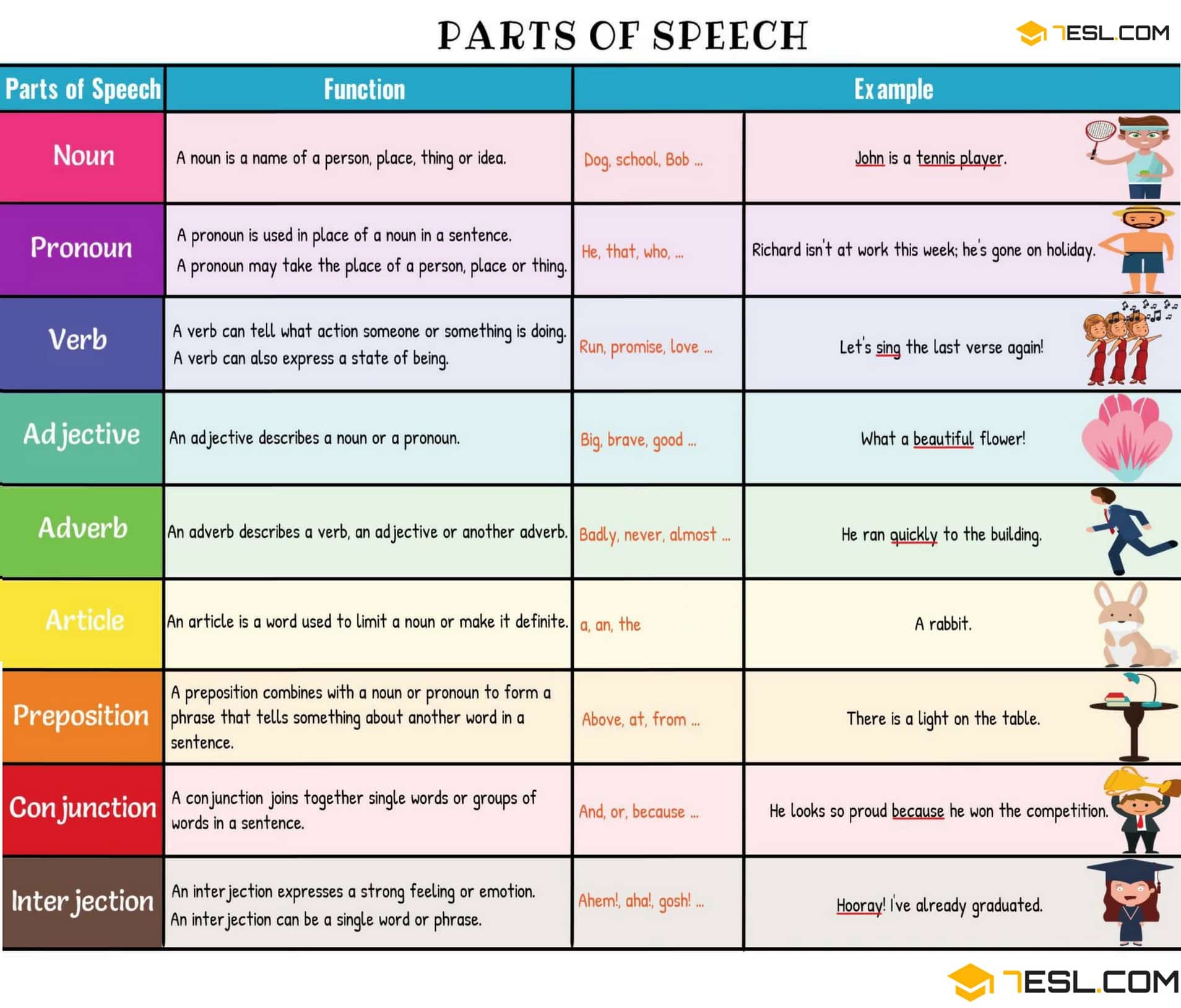
A part of speech (also called a word class ) is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence. Understanding the different parts of speech can help you analyze how words function in a sentence and improve your writing.
The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns , pronouns , verbs , adjectives , adverbs , prepositions , conjunctions , and interjections . Some modern grammars add others, such as determiners and articles .
Many words can function as different parts of speech depending on how they are used. For example, “laugh” can be a noun (e.g., “I like your laugh”) or a verb (e.g., “don’t laugh”).
Table of contents
- Prepositions
- Conjunctions
- Interjections
Other parts of speech
Interesting language articles, frequently asked questions.
A noun is a word that refers to a person, concept, place, or thing. Nouns can act as the subject of a sentence (i.e., the person or thing performing the action) or as the object of a verb (i.e., the person or thing affected by the action).
There are numerous types of nouns, including common nouns (used to refer to nonspecific people, concepts, places, or things), proper nouns (used to refer to specific people, concepts, places, or things), and collective nouns (used to refer to a group of people or things).
Ella lives in France .
Other types of nouns include countable and uncountable nouns , concrete nouns , abstract nouns , and gerunds .
Check for common mistakes
Use the best grammar checker available to check for common mistakes in your text.
Fix mistakes for free
A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun. Pronouns typically refer back to an antecedent (a previously mentioned noun) and must demonstrate correct pronoun-antecedent agreement . Like nouns, pronouns can refer to people, places, concepts, and things.
There are numerous types of pronouns, including personal pronouns (used in place of the proper name of a person), demonstrative pronouns (used to refer to specific things and indicate their relative position), and interrogative pronouns (used to introduce questions about things, people, and ownership).
That is a horrible painting!
A verb is a word that describes an action (e.g., “jump”), occurrence (e.g., “become”), or state of being (e.g., “exist”). Verbs indicate what the subject of a sentence is doing. Every complete sentence must contain at least one verb.
Verbs can change form depending on subject (e.g., first person singular), tense (e.g., simple past), mood (e.g., interrogative), and voice (e.g., passive voice ).
Regular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participle are formed by adding“-ed” to the end of the word (or “-d” if the word already ends in “e”). Irregular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participles are formed in some other way.
“I’ve already checked twice.”
“I heard that you used to sing .”
Other types of verbs include auxiliary verbs , linking verbs , modal verbs , and phrasal verbs .
An adjective is a word that describes a noun or pronoun. Adjectives can be attributive , appearing before a noun (e.g., “a red hat”), or predicative , appearing after a noun with the use of a linking verb like “to be” (e.g., “the hat is red ”).
Adjectives can also have a comparative function. Comparative adjectives compare two or more things. Superlative adjectives describe something as having the most or least of a specific characteristic.
Other types of adjectives include coordinate adjectives , participial adjectives , and denominal adjectives .
An adverb is a word that can modify a verb, adjective, adverb, or sentence. Adverbs are often formed by adding “-ly” to the end of an adjective (e.g., “slow” becomes “slowly”), although not all adverbs have this ending, and not all words with this ending are adverbs.
There are numerous types of adverbs, including adverbs of manner (used to describe how something occurs), adverbs of degree (used to indicate extent or degree), and adverbs of place (used to describe the location of an action or event).
Talia writes quite quickly.
Other types of adverbs include adverbs of frequency , adverbs of purpose , focusing adverbs , and adverbial phrases .
A preposition is a word (e.g., “at”) or phrase (e.g., “on top of”) used to show the relationship between the different parts of a sentence. Prepositions can be used to indicate aspects such as time , place , and direction .
I left the cup on the kitchen counter.
A conjunction is a word used to connect different parts of a sentence (e.g., words, phrases, or clauses).
The main types of conjunctions are coordinating conjunctions (used to connect items that are grammatically equal), subordinating conjunctions (used to introduce a dependent clause), and correlative conjunctions (used in pairs to join grammatically equal parts of a sentence).
You can choose what movie we watch because I chose the last time.
An interjection is a word or phrase used to express a feeling, give a command, or greet someone. Interjections are a grammatically independent part of speech, so they can often be excluded from a sentence without affecting the meaning.
Types of interjections include volitive interjections (used to make a demand or request), emotive interjections (used to express a feeling or reaction), cognitive interjections (used to indicate thoughts), and greetings and parting words (used at the beginning and end of a conversation).
Ouch ! I hurt my arm.
I’m, um , not sure.
The traditional classification of English words into eight parts of speech is by no means the only one or the objective truth. Grammarians have often divided them into more or fewer classes. Other commonly mentioned parts of speech include determiners and articles.
- Determiners
A determiner is a word that describes a noun by indicating quantity, possession, or relative position.
Common types of determiners include demonstrative determiners (used to indicate the relative position of a noun), possessive determiners (used to describe ownership), and quantifiers (used to indicate the quantity of a noun).
My brother is selling his old car.
Other types of determiners include distributive determiners , determiners of difference , and numbers .
An article is a word that modifies a noun by indicating whether it is specific or general.
- The definite article the is used to refer to a specific version of a noun. The can be used with all countable and uncountable nouns (e.g., “the door,” “the energy,” “the mountains”).
- The indefinite articles a and an refer to general or unspecific nouns. The indefinite articles can only be used with singular countable nouns (e.g., “a poster,” “an engine”).
There’s a concert this weekend.
If you want to know more about nouns , pronouns , verbs , and other parts of speech, make sure to check out some of our language articles with explanations and examples.
Nouns & pronouns
- Common nouns
- Proper nouns
- Collective nouns
- Personal pronouns
- Uncountable and countable nouns
- Verb tenses
- Phrasal verbs
- Types of verbs
- Active vs passive voice
- Subject-verb agreement
A is an indefinite article (along with an ). While articles can be classed as their own part of speech, they’re also considered a type of determiner .
The indefinite articles are used to introduce nonspecific countable nouns (e.g., “a dog,” “an island”).
In is primarily classed as a preposition, but it can be classed as various other parts of speech, depending on how it is used:
- Preposition (e.g., “ in the field”)
- Noun (e.g., “I have an in with that company”)
- Adjective (e.g., “Tim is part of the in crowd”)
- Adverb (e.g., “Will you be in this evening?”)
As a part of speech, and is classed as a conjunction . Specifically, it’s a coordinating conjunction .
And can be used to connect grammatically equal parts of a sentence, such as two nouns (e.g., “a cup and plate”), or two adjectives (e.g., “strong and smart”). And can also be used to connect phrases and clauses.
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked, what is a collective noun | examples & definition.
- What Is an Adjective? | Definition, Types & Examples
- Using Conjunctions | Definition, Rules & Examples
More interesting articles
- Definite and Indefinite Articles | When to Use "The", "A" or "An"
- Ending a Sentence with a Preposition | Examples & Tips
- What Are Prepositions? | List, Examples & How to Use
- What Is a Determiner? | Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Adverb? Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Interjection? | Examples, Definition & Types
"I thought AI Proofreading was useless but.."
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
The 9 Parts of Speech: Definitions and Examples
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
A part of speech is a term used in traditional grammar for one of the nine main categories into which words are classified according to their functions in sentences, such as nouns or verbs. Also known as word classes, these are the building blocks of grammar.
Every sentence you write or speak in English includes words that fall into some of the nine parts of speech. These include nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, articles/determiners, and interjections. (Some sources include only eight parts of speech and leave interjections in their own category.)
Parts of Speech
- Word types can be divided into nine parts of speech:
- prepositions
- conjunctions
- articles/determiners
- interjections
- Some words can be considered more than one part of speech, depending on context and usage.
- Interjections can form complete sentences on their own.
Learning the names of the parts of speech probably won't make you witty, healthy, wealthy, or wise. In fact, learning just the names of the parts of speech won't even make you a better writer. However, you will gain a basic understanding of sentence structure and the English language by familiarizing yourself with these labels.
Open and Closed Word Classes
The parts of speech are commonly divided into open classes (nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs) and closed classes (pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, articles/determiners, and interjections). Open classes can be altered and added to as language develops, and closed classes are pretty much set in stone. For example, new nouns are created every day, but conjunctions never change.
In contemporary linguistics , parts of speech are generally referred to as word classes or syntactic categories. The main difference is that word classes are classified according to more strict linguistic criteria. Within word classes, there is the lexical, or open class, and the function, or closed class.
The 9 Parts of Speech
Read about each part of speech below, and practice identifying each.
Nouns are a person, place, thing, or idea. They can take on a myriad of roles in a sentence, from the subject of it all to the object of an action. They are capitalized when they're the official name of something or someone, and they're called proper nouns in these cases. Examples: pirate, Caribbean, ship, freedom, Captain Jack Sparrow.
Pronouns stand in for nouns in a sentence . They are more generic versions of nouns that refer only to people. Examples: I, you, he, she, it, ours, them, who, which, anybody, ourselves.
Verbs are action words that tell what happens in a sentence. They can also show a sentence subject's state of being ( is , was ). Verbs change form based on tense (present, past) and count distinction (singular or plural). Examples: sing, dance, believes, seemed, finish, eat, drink, be, became.
Adjectives describe nouns and pronouns. They specify which one, how much, what kind, and more. Adjectives allow readers and listeners to use their senses to imagine something more clearly. Examples: hot, lazy, funny, unique, bright, beautiful, poor, smooth.
Adverbs describe verbs, adjectives, and even other adverbs. They specify when, where, how, and why something happened and to what extent or how often. Many adjectives can be turned into adjectives by adding the suffix - ly . Examples: softly, quickly, lazily, often, only, hopefully, sometimes.
Preposition
Prepositions show spatial, temporal, and role relations between a noun or pronoun and the other words in a sentence. They come at the start of a prepositional phrase , which contains a preposition and its object. Examples: up, over, against, by, for, into, close to, out of, apart from.
Conjunction
Conjunctions join words, phrases, and clauses in a sentence. There are coordinating, subordinating, and correlative conjunctions. Examples: and, but, or, so, yet.
Articles and Determiners
Articles and determiners function like adjectives by modifying nouns, but they are different than adjectives in that they are necessary for a sentence to have proper syntax. Articles and determiners specify and identify nouns, and there are indefinite and definite articles. Examples of articles: a, an, the ; examples of determiners: these, that, those, enough, much, few, which, what.
Some traditional grammars have treated articles as a distinct part of speech. Modern grammars, however, more often include articles in the category of determiners , which identify or quantify a noun. Even though they modify nouns like adjectives, articles are different in that they are essential to the proper syntax of a sentence, just as determiners are necessary to convey the meaning of a sentence, while adjectives are optional.
Interjection
Interjections are expressions that can stand on their own or be contained within sentences. These words and phrases often carry strong emotions and convey reactions. Examples: ah, whoops, ouch, yabba dabba do!
How to Determine the Part of Speech
Only interjections ( Hooray! ) have a habit of standing alone; every other part of speech must be contained within a sentence and some are even required in sentences (nouns and verbs). Other parts of speech come in many varieties and may appear just about anywhere in a sentence.
To know for sure what part of speech a word falls into, look not only at the word itself but also at its meaning, position, and use in a sentence.
For example, in the first sentence below, work functions as a noun; in the second sentence, a verb; and in the third sentence, an adjective:
- Bosco showed up for work two hours late.
- The noun work is the thing Bosco shows up for.
- He will have to work until midnight.
- The verb work is the action he must perform.
- His work permit expires next month.
- The attributive noun (or converted adjective) work modifies the noun permit .
Learning the names and uses of the basic parts of speech is just one way to understand how sentences are constructed.
Dissecting Basic Sentences
To form a basic complete sentence, you only need two elements: a noun (or pronoun standing in for a noun) and a verb. The noun acts as a subject, and the verb, by telling what action the subject is taking, acts as the predicate.
In the short sentence above, birds is the noun and fly is the verb. The sentence makes sense and gets the point across.
You can have a sentence with just one word without breaking any sentence formation rules. The short sentence below is complete because it's a verb command with an understood "you" noun.
Here, the pronoun, standing in for a noun, is implied and acts as the subject. The sentence is really saying, "(You) go!"
Constructing More Complex Sentences
Use more parts of speech to add additional information about what's happening in a sentence to make it more complex. Take the first sentence from above, for example, and incorporate more information about how and why birds fly.
- Birds fly when migrating before winter.
Birds and fly remain the noun and the verb, but now there is more description.
When is an adverb that modifies the verb fly. The word before is a little tricky because it can be either a conjunction, preposition, or adverb depending on the context. In this case, it's a preposition because it's followed by a noun. This preposition begins an adverbial phrase of time ( before winter ) that answers the question of when the birds migrate . Before is not a conjunction because it does not connect two clauses.
- What Are Word Blends?
- Figure of Speech: Definition and Examples
- Definition and Examples of Adjectives
- Subjects, Verbs, and Objects
- What Is a Rhetorical Device? Definition, List, Examples
- What Is The Speech Act Theory: Definition and Examples
- A List of Exclamations and Interjections in English
- What Is Nonverbal Communication?
- Examples and Usage of Conjunctions in English Grammar
- Linguistic Variation
- Definition and Examples of Interjections in English
- Definition and Examples of Jargon
- Understanding the Types of Verbs in English Grammar
- Complementary vs. Complimentary: How to Choose the Right Word
- Basic Grammar: What Is a Diphthong?
- Subordinating Conjunctions

Parts of Speech
What are the parts of speech, a formal definition.
Table of Contents
The Part of Speech Is Determined by the Word's Function
Are there 8 or 9 parts of speech, the nine parts of speech, (1) adjective, (3) conjunction, (4) determiner, (5) interjection, (7) preposition, (8) pronoun, why the parts of speech are important, video lesson.

- You need to dig a well . (noun)
- You look well . (adjective)
- You dance well . (adverb)
- Well , I agree. (interjection)
- My eyes will well up. (verb)
- red, happy, enormous
- Ask the boy in the red jumper.
- I live in a happy place.
- I caught a fish this morning! I mean an enormous one.
- happily, loosely, often
- They skipped happily to the counter.
- Tie the knot loosely so they can escape.
- I often walk to work.
- It is an intriguingly magic setting.
- He plays the piano extremely well.
- and, or, but
- it is a large and important city.
- Shall we run to the hills or hide in the bushes?
- I know you are lying, but I cannot prove it.
- my, those, two, many
- My dog is fine with those cats.
- There are two dogs but many cats.
- ouch, oops, eek
- Ouch , that hurt.
- Oops , it's broken.
- Eek! A mouse just ran past my foot!
- leader, town, apple
- Take me to your leader .
- I will see you in town later.
- An apple fell on his head .
- in, near, on, with
- Sarah is hiding in the box.
- I live near the train station.
- Put your hands on your head.
- She yelled with enthusiasm.
- she, we, they, that
- Joanne is smart. She is also funny.
- Our team has studied the evidence. We know the truth.
- Jack and Jill went up the hill, but they never returned.
- That is clever!
- work, be, write, exist
- Tony works down the pit now. He was unemployed.
- I will write a song for you.
- I think aliens exist .
Are you a visual learner? Do you prefer video to text? Here is a list of all our grammar videos .
Video for Each Part of Speech
The Most Important Writing Issues
The top issue related to adjectives.
| Don't write... | Do write... |
|---|---|
| very happy boy | delighted boy |
| very angry | livid |
| extremely posh hotel | luxurious hotel |
| really serious look | stern look |
The Top Issue Related to Adverbs
- Extremely annoyed, she stared menacingly at her rival.
- Infuriated, she glared at her rival.
The Top Issue Related to Conjunctions
- Burger, Fries, and a shake
- Fish, chips and peas
The Top Issue Related to Determiners
The Top Issue Related to Interjections
The top issue related to nouns, the top issue related to prepositions, the top issue related to pronouns, the top issue related to verbs.
| Unnatural (Overusing Nouns) | Natural (Using a Verb) |
|---|---|
| They are in agreement that he was in violation of several regulations. | They agree he violated several regulations. |
| She will be in attendance to present a demonstration of how the weather will have an effect on our process. | She will attend to demonstrate how the weather will affect our process. |
- Crack the parts of speech to help with learning a foreign language or to take your writing to the next level.

This page was written by Craig Shrives .
You might also like...
Help us improve....

Was something wrong with this page?

Use #gm to find us quicker .

Create a QR code for this, or any, page.
mailing list
grammar forum
teachers' zone
Confirmatory test.
This test is printable and sendable
expand to full page
show as slides
download as .doc
print as handout
send as homework
display QR code
- English Grammar
- Parts of Speech
Parts of Speech - Definition, 8 Types and Examples
In the English language , every word is called a part of speech. The role a word plays in a sentence denotes what part of speech it belongs to. Explore the definition of parts of speech, the different parts of speech and examples in this article.
Table of Contents
Parts of speech definition, different parts of speech with examples.
- Sentences Examples for the 8 Parts of Speech
A Small Exercise to Check Your Understanding of Parts of Speech
Frequently asked questions on parts of speech, what is a part of speech.
Parts of speech are among the first grammar topics we learn when we are in school or when we start our English language learning process. Parts of speech can be defined as words that perform different roles in a sentence. Some parts of speech can perform the functions of other parts of speech too.
- The Oxford Learner’s Dictionary defines parts of speech as “one of the classes into which words are divided according to their grammar, such as noun, verb, adjective, etc.”
- The Cambridge Dictionary also gives a similar definition – “One of the grammatical groups into which words are divided, such as noun, verb, and adjective”.
Parts of speech include nouns, pronouns, verbs, adverbs, adjectives, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections.
8 Parts of Speech Definitions and Examples:
1. Nouns are words that are used to name people, places, animals, ideas and things. Nouns can be classified into two main categories: Common nouns and Proper nouns . Common nouns are generic like ball, car, stick, etc., and proper nouns are more specific like Charles, The White House, The Sun, etc.
Examples of nouns used in sentences:
- She bought a pair of shoes . (thing)
- I have a pet. (animal)
- Is this your book ? (object)
- Many people have a fear of darkness . (ideas/abstract nouns)
- He is my brother . (person)
- This is my school . (place)
Also, explore Singular Nouns and Plural Nouns .
2. Pronouns are words that are used to substitute a noun in a sentence. There are different types of pronouns. Some of them are reflexive pronouns, possessive pronouns , relative pronouns and indefinite pronouns . I, he, she, it, them, his, yours, anyone, nobody, who, etc., are some of the pronouns.
Examples of pronouns used in sentences:
- I reached home at six in the evening. (1st person singular pronoun)
- Did someone see a red bag on the counter? (Indefinite pronoun)
- Is this the boy who won the first prize? (Relative pronoun)
- That is my mom. (Possessive pronoun)
- I hurt myself yesterday when we were playing cricket. (Reflexive pronoun)
3. Verbs are words that denote an action that is being performed by the noun or the subject in a sentence. They are also called action words. Some examples of verbs are read, sit, run, pick, garnish, come, pitch, etc.
Examples of verbs used in sentences:
- She plays cricket every day.
- Darshana and Arul are going to the movies.
- My friends visited me last week.
- Did you have your breakfast?
- My name is Meenakshi Kishore.
4. Adverbs are words that are used to provide more information about verbs, adjectives and other adverbs used in a sentence. There are five main types of adverbs namely, adverbs of manner , adverbs of degree , adverbs of frequency , adverbs of time and adverbs of place . Some examples of adverbs are today, quickly, randomly, early, 10 a.m. etc.
Examples of adverbs used in sentences:
- Did you come here to buy an umbrella? (Adverb of place)
- I did not go to school yesterday as I was sick. (Adverb of time)
- Savio reads the newspaper everyday . (Adverb of frequency)
- Can you please come quickly ? (Adverb of manner)
- Tony was so sleepy that he could hardly keep his eyes open during the meeting. (Adverb of degree)
5. Adjectives are words that are used to describe or provide more information about the noun or the subject in a sentence. Some examples of adjectives include good, ugly, quick, beautiful, late, etc.
Examples of adjectives used in sentences:
- The place we visited yesterday was serene .
- Did you see how big that dog was?
- The weather is pleasant today.
- The red dress you wore on your birthday was lovely.
- My brother had only one chapati for breakfast.
6. Prepositions are words that are used to link one part of the sentence to another. Prepositions show the position of the object or subject in a sentence. Some examples of prepositions are in, out, besides, in front of, below, opposite, etc.
Examples of prepositions used in sentences:
- The teacher asked the students to draw lines on the paper so that they could write in straight lines.
- The child hid his birthday presents under his bed.
- Mom asked me to go to the store near my school.
- The thieves jumped over the wall and escaped before we could reach home.
7. Conjunctions are a part of speech that is used to connect two different parts of a sentence, phrases and clauses . Some examples of conjunctions are and, or, for, yet, although, because, not only, etc.
Examples of conjunctions used in sentences:
- Meera and Jasmine had come to my birthday party.
- Jane did not go to work as she was sick.
- Unless you work hard, you cannot score good marks.
- I have not finished my project, yet I went out with my friends.
8. Interjections are words that are used to convey strong emotions or feelings. Some examples of interjections are oh, wow, alas, yippee, etc. It is always followed by an exclamation mark.
Examples of interjections used in sentences:
- Wow ! What a wonderful work of art.
- Alas ! That is really sad.
- Yippee ! We won the match.
Sentence Examples for the 8 Parts of Speech
- Noun – Tom lives in New York .
- Pronoun – Did she find the book she was looking for?
- Verb – I reached home.
- Adverb – The tea is too hot.
- Adjective – The movie was amazing .
- Preposition – The candle was kept under the table.
- Conjunction – I was at home all day, but I am feeling very tired.
- Interjection – Oh ! I forgot to turn off the stove.
Let us find out if you have understood the different parts of speech and their functions. Try identifying which part of speech the highlighted words belong to.
- My brother came home late .
- I am a good girl.
- This is the book I was looking for.
- Whoa ! This is amazing .
- The climate in Kodaikanal is very pleasant.
- Can you please pick up Dan and me on your way home?
Now, let us see if you got it right. Check your answers.
- My – Pronoun, Home – Noun, Late – Adverb
- Am – Verb, Good – Adjective
- I – Pronoun, Was looking – Verb
- Whoa – Interjection, Amazing – Adjective
- Climate – Noun, In – Preposition, Kodaikanal – Noun, Very – Adverb
- And – Conjunction, On – Preposition, Your – Pronoun
What are parts of speech?
The term ‘parts of speech’ refers to words that perform different functions in a sentence in order to give the sentence a proper meaning and structure.
How many parts of speech are there?
There are 8 parts of speech in total.
What are the 8 parts of speech?
Nouns, pronouns, verbs, adverbs, adjectives, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections are the 8 parts of speech.
| ENGLISH Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center
- Introduction
Conjunctions
Prepositions, interjections, categorizing the parts of speech.

part of speech
Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- College of Saint Rose - Parts of Speech
- Butte College - TIP Sheets - The Eight Parts of Speech
- Humanities LibreTexts - Parts of Speech
- Pressbooks Create - The Simple Math of Writing Well - Part of speech
- Table Of Contents
part of speech , lexical category to which a word is assigned based on its function in a sentence.
There are eight parts of speech in traditional English grammar: noun, pronoun, verb , adjective , adverb , conjunction, preposition , and interjection . In linguistics , parts of speech are more typically called word classes .

A noun names a person, place, thing, or idea. There are many subcategories of nouns, including common nouns, proper nouns, collective nouns, and abstract nouns.
Common nouns name basic things that can be seen and touched. Examples of common nouns include dog , banana , table , and book .
- The dog ate a banana .
- The book was on the table .
Proper nouns name specific people, places, and things, and they begin with a capital letter . Examples of proper nouns include George, New York City , Empire State Building , and Atlantic Ocean .
- George sailed the Atlantic Ocean .
- The Empire State Building is in New York City .

Collective nouns name groups of people or things. Examples of collective nouns include team , flock , litter , and batch .
- The team won the game.
- The flock flew south for the winter.
Abstract nouns name things that cannot be seen or touched. Examples of abstract nouns include happiness , truth , friendship , and beauty .
- He brings her so much happiness .
- The friendship is a strong one.
A pronoun is used in place of a noun. There are many subcategories of pronouns, including but not limited to personal pronouns, possessive pronouns, and reflexive pronouns.
Personal pronouns replace names of people, places, things, and ideas. Examples of personal pronouns include she , he , it , and they .
- They enjoyed the party.
- Mikey likes it .
Possessive pronouns replace nouns and indicate ownership. Because they modify nouns, they are also frequently categorized as adjectives. Examples of possessive pronouns include his , its , mine , and theirs .
- The house is theirs .
- The parrot knows its name.
Reflexive pronouns replace nouns when the subject and object in a sentence are the same. Examples of reflexive pronouns include myself , herself , themselves , and oneself .
- She baked a cake all by herself .
- They prepared themselves for the adventure.
A verb indicates a state of doing, being, or having. There are three main subcategories of verbs: doing verbs, being verbs, and having verbs.
Doing verbs indicate actions. Examples of doing verbs include run , wash , explain , and wonder .
- Oliver washed the windows.
- I wonder where the cat is hiding.
Being and having verbs do not indicate action and are considered relating (or linking) verbs because they connect one piece of information to another. Examples of being and having verbs include am , are , has , and own .
- We are at the store.
- John has a red baseball cap.
An adjective describes or modifies a noun or pronoun.
Adjectives provide information about the qualities or classifications of a person or thing. Examples of adjectives include tall , purple , funny , and antique .
- The Willis Tower is a tall building.
- There were several antique cars in the parade.
An adverb describes or modifies verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs.
Adverbs provide information about the manner in which things are done, as well as when, where, and why they are done. Examples of adverbs include quickly , extremely , fiercely , and yesterday .
- The boy ran quickly through the rainstorm.
- That was a fiercely competitive game yesterday.
A conjunction links words, phrases, and clauses. There are two main subcategories of conjunctions: coordinating conjunctions and subordinating conjunctions.
Coordinating conjunctions link words, phrases, and clauses that are equally important in a sentence. Examples of coordinating conjunctions include and , but , or , and so .
- The students read short stories and novels.
- Liz went to the movies but not to dinner.
Subordinating conjunctions link subordinate clauses to a sentence. Examples of subordinating conjunctions include because , although , before , and since .
- The team is cheering because it is excited.
- Henry had Swiss cheese on his burger although he preferred cheddar.
A preposition provides information about the relative position of a noun or pronoun. Prepositions can indicate direction, time, place, location, and spatial relationships of objects. Examples of prepositions include on , in , across , and after .
- The cat ran across the road.
- The pencil is in the drawer.
An interjection acts as an exclamation. Interjections typically express emotional reactions to information in an adjoining sentence. Examples of interjections include eek , wow , oops , and phew .
- Eek ! That was a huge spider.
- Oops ! I didn’t mean to slam the door.
Although the number of parts of speech is traditionally fixed at eight, some grammarians consider there to be additional parts of speech. For example, determiners (also called determinatives) modify nouns and are therefore generally considered to be adjectives, but they differ from other adjectives in that their exact meaning is supplied by context . They include articles, demonstrative pronouns, possessive pronouns, and quantifiers. Examples of determiners include the , an , that , your , and many .
Over the years grammarians have also proposed changes in how parts of speech are categorized. The 2002 edition of the Cambridge Grammar of the English Language , for example, placed pronouns as a subcategory of nouns.
Instantly enhance your writing in real-time while you type. With LanguageTool
Get started for free
Understanding the Parts of Speech in English
Yes, the parts of speech in English are extensive and complex. But we’ve made it easy for you to start learning them by gathering the most basic and essential information in this easy-to-follow and comprehensive guide.

Parts of Speech: Quick Summary
Parts of speech assign words to different categories. There are eight different types in English. Keep in mind that a word can belong to more than one part of speech.
Learn About:
- Parts of Speech
- Prepositions
- Conjunctions
- Interjections
Using the Parts of Speech Correctly In Your Writing
Knowing the parts of speech is vital when learning a new language.
When it comes to learning a new language, there are several components you should understand to truly get a grasp of the language and speak it fluently.
It’s not enough to become an expert in just one area. For instance, you can learn and memorize all the intricate grammar rules, but if you don’t practice speaking or writing colloquially, you will find it challenging to use that language in real time.
Conversely, if you don’t spend time trying to learn the rules and technicalities of a language, you’ll also find yourself struggling to use it correctly.
Think of it this way: Language is a tasty, colorful, and nutritious salad. If you fill your bowl with nothing but lettuce, your fluency will be bland, boring, and tasteless. But if you spend time cultivating other ingredients for your salad—like style, word choice, and vocabulary— then it will become a wholesome meal you can share with others.
In this blog post, we’re going to cover one of the many ingredients you’ll need to build a nourishing salad of the English language—the parts of speech.
Let’s get choppin’!
What Are the Parts of Speech in English?
The parts of speech refer to categories to which a word belongs. In English, there are eight of them : verbs , nouns, pronouns, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections.
Many English words fall into more than one part of speech category. Take the word light as an example. It can function as a verb, noun, or adjective.
Verb: Can you please light the candles?
Noun: The room was filled with a dim, warm light .
Adjective: She wore a light jacket in the cool weather.
The parts of speech in English are extensive. There’s a lot to cover in each category—much more than we can in this blog post. The information below is simply a brief overview of the basics of the parts of speech. Nevertheless, the concise explanations and accompanying example sentences will help you gain an understanding of how to use them correctly.

What Are Verbs?
Verbs are the most essential parts of speech because they move the meaning of sentences along.
A verb can show actions of the body and mind ( jump and think ), occurrences ( happen or occur ), and states of being ( be and exist ). Put differently, verbs breathe life into sentences by describing actions or indicating existence. These parts of speech can also change form to express time , person , number , voice , and mood .
There are several verb categories. A few of them are:
- Regular and irregular verbs
- Transitive and intransitive verbs
- Auxiliary verbs
A few examples of verbs include sing (an irregular action verb), have (which can be a main verb or auxiliary verb), be , which is a state of being verb, and would (another auxiliary verb).
My little sister loves to sing .
I have a dog and her name is Sweet Pea.
I will be there at 5 P.M.
I would like to travel the world someday.
Again, these are just the very basics of English verbs. There’s a lot more that you should learn to be well-versed in this part of speech, but the information above is a good place to start.
What Are Nouns?
Nouns refer to people ( John and child ), places ( store and Italy ), things ( firetruck and pen ), and ideas or concepts ( love and balance ). There are also many categories within nouns. For example, proper nouns name a specific person, place, thing, or idea. These types of nouns are always capitalized.
Olivia is turning five in a few days.
My dream is to visit Tokyo .
The Supreme Court is the highest court in the United States.
Some argue that Buddhism is a way of life, not a religion.
On the other hand, common nouns are not specific to any particular entity and are used to refer to any member of a general category.
My teacher is the smartest, most caring person I know!
I love roaming around a city I’ve never been to before.
This is my favorite book , which was recommended to me by my father.
There’s nothing more important to me than love .
Nouns can be either singular or plural. Singular nouns refer to a single entity, while plural nouns refer to multiple entities.
Can you move that chair out of the way, please? (Singular)
Can you move those chairs out of the way, please? (Plural)
While many plural nouns are formed by adding an “–s” or “–es,” others have irregular plural forms, meaning they don’t follow the typical pattern.
There was one woman waiting in line.
There were several women waiting in line.
Nouns can also be countable or uncountable . Those that are countable refer to nouns that can be counted as individual units. For example, there can be one book, two books, three books, or more. Uncountable nouns cannot be counted as individual units. Take the word water as an example. You could say I drank some water, but it would be incorrect to say I drank waters. Instead, you would say something like I drank several bottles of water.
What Are Pronouns?
A pronoun is a word that can take the place of other nouns or noun phrases. Pronouns serve the purpose of referring to nouns without having to repeat the word each time. A word (or group of words) that a pronoun refers to is called the antecedent .
Jessica went to the store, and she bought some blueberries.
In the sentence above, Jessica is the antecedent, and she is the referring pronoun. Here’s the same sentence without the proper use of a pronoun:
Jessica went to the store, and Jessica bought some blueberries.
Do you see how the use of a pronoun improves the sentence by avoiding repetitiveness?
Like all the other parts of speech we have covered, pronouns also have various categories.
Personal pronouns replace specific people or things: I, me, you, he, she, him, her, it, we, us, they, them.
When I saw them at the airport, I waved my hands up in the air so they could see me .
Possessive pronouns indicate ownership : mine, ours, yours, his, hers, theirs, whose.
I think that phone is hers .
Reflexive pronouns refer to the subject of a sentence or clause. They are used when the subject and the object of a sentence refer to the same person or thing: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves.
The iguanas sunned themselves on the roof of my car.
Intensive pronouns have the same form as reflexive pronouns and are used to emphasize or intensify the subject of a sentence.
I will take care of this situation myself .
Indefinite pronouns do not refer to specific individuals or objects but rather to a general or unspecified person, thing, or group. Some examples include someone, everybody, anything, nobody, each, something, and all.
Everybody enjoyed the party. Someone even said it was the best party they had ever attended.
Demonstrative pronouns are used to identify or point to specific pronouns: this, that, these, those.
Can you pick up those pens off the floor?
Interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions and seek information: who, whom, whose, which, what.
Who can help move these heavy boxes?
Relative pronouns connect a clause or a phrase to a noun or pronoun: who, whom, whose, which, that, what, whoever, whichever, whatever.
Christina, who is the hiring manager, is the person whom you should get in touch with.
Reciprocal pronouns are used to refer to individual parts of a plural antecedent. They indicate a mutual or reciprocal relationship between two or more people or things: each other or one another.
The cousins always giggle and share secrets with one another .
What Are Adjectives?
Adjectives modify nouns or pronouns, usually by describing, identifying, or quantifying them. They play a vital role in adding detail, precision, and imagery to English, allowing us to depict and differentiate the qualities of people, objects, places, and ideas.
The blue house sticks out compared to the other neutral-colored ones. (Describes)
That house is pretty, but I don’t like the color. (Identifies)
There were several houses I liked, but the blue one was unique. (Quantifies)
We should note that identifying or quantifying adjectives are also referred to as determiners. Additionally, articles ( a, an, the ) and numerals ( four or third ) are also used to quantify and identify adjectives.
Descriptive adjectives have other forms (known as comparative and superlative adjectives ) that allow for comparisons. For example, the comparative of the word small is smaller, while the superlative is smallest.
Proper adjectives (which are derived from proper nouns) describe specific nouns. They usually retain the same spelling or are slightly modified, but they’re always capitalized. For example, the proper noun France can be turned into the proper adjective French.
What Are Adverbs?
Adverbs are words that modify or describe verbs, adjectives, other adverbs, or entire clauses. Although many adverbs end in “–ly,” not all of them do. Also, some words that end in “–ly” are adjectives, not adverbs ( lovely ).
She dances beautifully .
In the sentence above, beautifully modifies the verb dances.
We visited an extremely tall building.
Here, the adverb extremely modifies the adjective tall.
He had to run very quickly to not miss the train.
The adverb very modifies the adverb quickly.
Interestingly , the experiment yielded unexpected results that left us baffled.
In this example, the word interestingly modifies the independent clause that comprises the rest of the sentence (which is why they’re called sentence adverbs ).
Like adjectives, adverbs can also have other forms when making comparisons. For example:
strongly, more strongly, most strongly, less strongly, least strongly
What Are Prepositions?
Prepositions provide context and establish relationships between nouns, pronouns, and other words in a sentence. They indicate time, location, direction, manner, and other vital information. Prepositions can fall into several subcategories. For instance, on can indicate physical location, but it can also be used to express time.
Place the bouquet of roses on the table.
We will meet on Monday.
There are many prepositions. A few examples include: about, above, across, after, before, behind, beneath, beside, during, except, for, from, in, inside, into, like, near, of, off, onto, past, regarding, since, through, toward, under, until, with, without.
Prepositions can contain more than one word, like according to and with regard to.
What Are Conjunctions?
Conjunctions are words that join words, phrases, or clauses together within a sentence and provide information about the relationship between those words. There are different types of conjunctions.
Coordinating conjunctions connect words, phrases, or clauses of equal importance: and, but, for, not, or, so, yet.
I like to sing, and she likes to dance.
Correlative conjunctions come in pairs and join balanced elements of a sentence: both…and, just as…so, not only…but also, either…or, neither…nor, whether…or.
You can either come with us and have fun, or stay at home and be bored.
Subordinating conjunctions connect dependent clauses to independent clauses. A few examples include: after, although, even though, since, unless, until, when , and while.
They had a great time on their stroll, even though it started raining and they got soaked.
Conjunctive adverbs are adverbs that function as conjunctions, connecting independent clauses or sentences. Examples of conjunctive adverbs are also, anyway, besides, however, meanwhile, nevertheless, otherwise, similarly, and therefore .
I really wanted to go to the party. However , I was feeling sick and decided to stay in.
I really wanted to go to the party; however , I was feeling sick and decided to stay in.
What Are Interjections?
Interjections are words that express strong emotions, sudden reactions, or exclamations. This part of speech is usually a standalone word or phrase, but even when it is part of a sentence, it does not relate grammatically to the rest of .
There are several interjections. Examples include: ahh, alas, bravo, eww, hello, please, thanks, and oops.
Ahh ! I couldn’t believe what was happening.
When it comes to improving your writing skills, understanding the parts of speech is as important as adding other ingredients besides lettuce to a salad.
The information provided above is indeed extensive, but it’s critical to learn if you want to write effectively and confidently. LanguageTool—a multilingual writing assistant—makes comprehending the parts of speech easy by detecting errors as you write.
Give it a try—it’s free!

Unleash the Professional Writer in You With LanguageTool
Go well beyond grammar and spell checking. Impress with clear, precise, and stylistically flawless writing instead.
Works on All Your Favorite Services
- Thunderbird
- Google Docs
- Microsoft Word
- Open Office
- Libre Office
We Value Your Feedback
We’ve made a mistake, forgotten about an important detail, or haven’t managed to get the point across? Let’s help each other to perfect our writing.
- Parts of Speech
- Sentence Structure
- Sentence Types
- Rules & Usage
- Punctuation
- How to Diagram
- Diagramming Index
- Diagramming Together
- Contact & FAQ
- Stream the Documentary
- Testimonials
Download your free grammar guide here.
What are the parts of speech?
Today's the day for you to learn about this important grammatical concept! But first...let's see what the parts of speech have to do with your clothes.

Imagine that it's laundry day, and you've just finished washing and drying your clothes. You dump the contents of the laundry basket onto your bed, and you begin to organize everything. You fold matching socks together, you create a pile of perfectly folded shirts that you would be proud to show Marie Kondo, and you do the same thing with your pants, jackets, and everything else.
In the same way that we organize our clothes into groups based on each item's function and features, we organize our words into categories based on each word's function and features. We call these categories of words the parts of speech .
Some people categorize words into eight parts of speech, and some people categorize them into nine parts of speech. Neither one is wrong; they're just two ways of looking at things. We'll go over these categories below. Here at English Grammar Revolution, we categorize words into eight groups, but I'll tell you about the ninth one as well.
There's one important thing for you to know before we look at these categories: most words can function as more than one part of speech . They will only do one job at a time, but they can do different things in different sentences. Look at the word love in the following sentences.
My love of grammar inspired me to make this website.
Here, love is functioning as a noun. It's the subject of the sentence.
I love you.
Now, love is acting as a verb ! It's telling us an action.
The only way we can know how to categorize a word is to look at how it's acting within a sentence.
Okay, let's check out the parts of speech!
The 8 Parts of Speech
Nouns name people, places, things, or ideas. They're important parts of our sentences because they perform important jobs (subjects, direct objects, predicate nouns, etc.).
A peacock walked through our yard .
The dog howled during the night , and it woke up our whole family .
Sometimes people get bogged down with this part of speech because there are also many subcategories of nouns. This is similar to the way that we have subcategories for our clothes. You may have a whole drawer full of pants, but you may also have different types of pants that you use for different purposes (workout pants, lounge pants, work pants, etc.). This is similar to the way that we can further categorize nouns into smaller groups.
Here are a few of the subcategories of nouns: proper nouns, common nouns , collective nouns , possessive nouns , and compound nouns.
Tip : Other parts of speech also have subcategories. If you're studying this information for the first time, ignore the subcategories and focus on learning about each broader category.
2. Pronouns
Pronouns take the place of nouns. When most people hear the word pronoun , they think of words like I, we, me, he, she, and they . These are indeed all pronouns, but they're a part of a subcategory called personal pronouns. Know that there are other kinds of pronouns out there as well. Here are some examples: myself, his, someone , and who .
Here are a few of the subcategories of pronouns: reflexive pronouns , indefinite pronouns , possessive pronouns , and relative pronouns .
When we walked across the bridge, we saw someone who knows you .
I will fix the dishwasher myself .
Verbs show actions or states of being. They are integral elements of sentences .
The shuttle will fly into space.
The loving mother comforted and soothed the baby.
In the Montessori tradition of education, they use a large red circle or ball to symbolize a verb, and they often teach children to think of verbs as a sun providing the energy of a sentence. Isn't that a lovely way to think of verbs?
I know that you're getting tired of hearing about subcategories, but linking verbs, action verbs, and helping verbs are described on the verb page here .
Modal verbs are described on that link, and you can learn even more about action verbs and linking verbs from those links.
4. Adjectives
Adjectives describe, or modify , nouns and pronouns. I like to think of them as adding color to language. It would be hard to describe a beautiful sunset or the way a touching story makes us feel without using adjectives.
The wise, handsome owl had orange eyes.
The caring father rocked the baby.
One helpful strategy for learning about and identifying adjectives is to learn how they are diagrammed . Sentence diagrams are pictures of sentences that help us see how all of the words are grammatically related. Since adjectives modify nouns and pronouns, we diagram them on slanted lines under the nouns/pronouns that they are modifying.
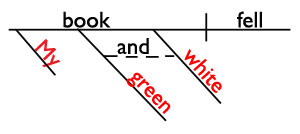
My green and white book fell.
Book is a noun. It's the subject of this sentence. My, green , and white are all adjectives describing book , so we diagram them on slanted lines underneath book . Isn't that a great way to SEE what adjectives do?
Nine Parts of Speech
When people categorize words into eight parts of speech, they say that articles/determiners ( a, an, the, this, that, etc. ) are subcategories of adjectives.
When people categorize words into nine parts of speech, they say that articles/determiners make up their own category and are not a part of the adjective category.
Adverbs modify (describe) verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs. Adverbs are similar to adjectives in that they both modify things.
The extremely cute koala hugged its mom very tightly .
The dog howled loudly .
Sentence diagrams also make it really easy to see what adverbs do. Take a look at this diagram. What do you notice about the way the adverbs are diagrammed?
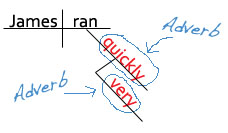
James ran very quickly.
Did you notice that the adverbs are diagrammed on slanted lines under the words that they are modifying?
Ran is a verb. Quickly is an adverb telling us more about the verb ran . Very is an adverb telling us more about the adverb quickly .
Doesn't the diagram make it easier to SEE what adverbs do?
6. Prepositions
Prepositions are probably the most difficult part of speech to explain, but people generally have an easier time understanding them when they look at lots of examples. So...let's start with some examples of commonly used prepositions!
in, for, of, off, if, until
The frog sat in the flower.
The baby cried for a long time.
I'm so convinced that memorizing some of the prepositions will be helpful to you that I'll teach you a preposition song .
Okay, now that we've looked at some examples, let's look at the definition of a preposition.
Prepositions show the relationship between a noun or a pronoun and some other word in the rest of the sentence.
Sentence diagrams will come to the rescue again to help us visualize what prepositions do. Think of prepositions as "noun hooks" or "noun bridges." In the diagram below, notice how the preposition down links the noun tree to the rest of the sentence.
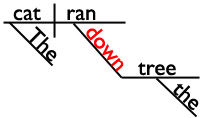
The cat ran down the tree.
Since prepositions always function as "noun hooks," they'll always be accompanied by a noun. The preposition plus its noun is called a prepositional phrase .
If you find a word from the preposition list that's not a part of a prepositional phrase, it's not functioning as a preposition. (You remember that words can function as different parts of speech , right?)
7. Conjunctions
Conjunctions join things together. They can join words or groups of words (phrases and clauses).
The hummingbird sat and waited .
The conjunction and is joining the words sat and waited .
Do you live near the park or near the hospital ?
The conjunction or is joining the phrases near the park and near the hospital.
The two conjunctions we just looked at ( and and or ) belong to a subcategory called coordinating conjunctions, but there are other subcategories of conjunctions as well. The other one that we use most often is subordinating conjunctions . Subordinating conjunctions are a little trickier to learn because they involve a more complicated concept ( dependent adverb clauses ).
For now, just know that all conjunctions, no matter what type they are, connect things together. In fact, let's LOOK at how they do this by looking at a sentence diagram.
Here is a sentence diagram showing how the coordinating conjunction and connects two clauses.

She cooked, and he cleaned.
8. Interjections
Interjections show excitement or emotion.
Wow ! That jump was amazing!
Phew , the baby finally fell asleep.
They are different from the other parts of speech in that they're not grammatically related to the rest of the sentence, and the way that we diagram them reflects that. Look at how we diagram interjections :
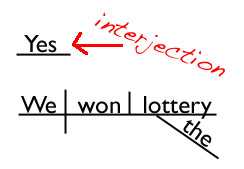
Yes ! We won the lottery!
The interjection yes sit sits there on its own line floating above the rest of the sentence. This helps show that it's not grammatically related to the other words in the sentence.
It's time to review what we covered on this page.
- We can categorize the words that we use into groups based on their functions and features. We call these groups the parts of speech.
- Many words can function as multiple parts of speech. You need to look at each word in the context of a sentence in order to say what part of speech it is.
- The eight parts of speech are nouns, pronouns, adjectives, verbs, adverbs, conjunctions, prepositions, and interjections.
- You just learned about all of the parts of speech. Give yourself a high five!
If you'd like to teach or learn grammar the easy way—with sentence diagrams—check out our Get Smart Grammar Program .
It starts from the very beginning and teaches you grammar and sentence diagramming in easy, bite-size lessons.

Hello! I'm Elizabeth O'Brien, and my goal is to get you jazzed about grammar.
This is original content from https://www.english-grammar-revolution.com/parts-of-speech.html

Our Free Guide Gives You A Fun Way
To Teach And Learn The Basics v

Elizabeth O'Brien is the creator of Grammar Revolution.
Her lessons are guaranteed to give you more confidence in your communication skills and make you smile. :)
Other Helpful Resources
- Learn more about how Montessori classrooms teach the parts of speech .
Sentences & Diagrams
Shop & log in.
|
|
|
|
Home BLOG SHOP Contact PRIVACY POLICY Your Purchases
Copyright © 2009 - 2024 Grammar Revolution. All Rights Reserved.
JOIN OUR PRIVATE FACEBOOK GROUP RSS INSTAGRAM

Parts of Speech
What is a Part of Speech?
We can categorize English words into 9 basic types called "parts of speech" or "word classes". It's quite important to recognize parts of speech. This helps you to analyze sentences and understand them. It also helps you to construct good sentences.
Parts of Speech Table
Parts of speech examples.
- Parts of Speech Quiz
This is a summary of the 9 parts of speech*. You can find more detail if you click on each part of speech.
| part of speech | function or "job" | example words | example sentences |
|---|---|---|---|
| action or state | (to) be, have, do, like, work, sing, can, must | EnglishClub a website. I EnglishClub. | |
| thing or person | pen, dog, work, music, town, London, teacher, John | This is my . He lives in my . We live in . | |
| describes a noun | good, big, red, well, interesting | My dogs are . I like dogs. | |
| limits or "determines" a noun | a/an, the, 2, some, many | I have dogs and rabbits. | |
| describes a verb, adjective or adverb | quickly, silently, well, badly, very, really | My dog eats . When he is hungry, he eats quickly. | |
| replaces a noun | I, you, he, she, some | Tara is Indian. is beautiful. | |
| links a noun to another word | to, at, after, on, but | We went school Monday. | |
| joins clauses or sentences or words | and, but, when | I like dogs I like cats. I like cats dogs. I like dogs I don't like cats. | |
| short exclamation, sometimes inserted into a sentence | oh!, ouch!, hi!, well | ! That hurts! ! How are you? , I don't know. |
- lexical Verbs ( work, like, run )
- auxiliary Verbs ( be, have, must )
- Determiners may be treated as adjectives, instead of being a separate part of speech.
Here are some examples of sentences made with different English parts of speech:
| verb |
|---|
| Stop! |
| noun | verb |
|---|---|
| John | works. |
| noun | verb | verb |
|---|---|---|
| John | is | working. |
| pronoun | verb | noun |
|---|---|---|
| She | loves | animals. |
| noun | verb | noun | adverb |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tara | speaks | English | well. |
| noun | verb | adjective | noun |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tara | speaks | good | English. |
| pronoun | verb | preposition | determiner | noun | adverb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| She | ran | to | the | station | quickly. |
| pron. | verb | adj. | noun | conjunction | pron. | verb | pron. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| She | likes | big | snakes | but | I | hate | them. |
Here is a sentence that contains every part of speech:
| interjection | pron. | conj. | det. | adj. | noun | verb | prep. | noun | adverb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Well, | she | and | my | young | John | walk | to | school | slowly. |
Words with More Than One Job
Many words in English can have more than one job, or be more than one part of speech. For example, "work" can be a verb and a noun; "but" can be a conjunction and a preposition; "well" can be an adjective, an adverb and an interjection. In addition, many nouns can act as adjectives.
To analyze the part of speech, ask yourself: "What job is this word doing in this sentence?"
In the table below you can see a few examples. Of course, there are more, even for some of the words in the table. In fact, if you look in a good dictionary you will see that the word " but " has six jobs to do:
- verb, noun, adverb, pronoun, preposition and conjunction!
| word | part of speech | example |
|---|---|---|
| work | noun | My is easy. |
| verb | I in London. | |
| but | conjunction | John came Mary didn't come. |
| preposition | Everyone came Mary. | |
| well | adjective | Are you ? |
| adverb | She speaks . | |
| interjection | ! That's expensive! | |
| afternoon | noun | We ate in the . |
| noun acting as adjective | We had tea. |
People often ask
FAQ: frequently asked parts of speech questions

Parts of Speech in English
Parts of speech are categories of words that perform similar grammatical roles in phrase and sentence structures. You might wonder what the different parts of speech are and how to identify them. This reference explains parts of speech, including nouns, verbs, pronouns, adjectives, adverbs, determiners, conjunctions, prepositions, and interjections, with examples.
You’ll also learn about open and closed word classes, how to determine a part of speech in a sentence, and their roles in simple and complex sentence constructions. This guide includes a useful picture, a video, and a quiz on parts of speech to help solidify your understanding.
Parts of Speech

What Are Parts Of Speech?
Parts of speech are word categories defined by their roles in sentence structures. These categories are organized by the functions and meanings they convey. In English, there are around ten common parts of speech: nouns , verbs , adjectives , adverbs , pronouns , prepositions , conjunctions , interjections , determiners , and articles .
Open and Closed Word Classes
Closed word classes are parts of speech that do not have newer words introduced over time. These include pronouns, conjunctions, determiners, and prepositions.
Open word classes are parts of speech that can have newer words introduced over time. These include nouns, verbs, adjectives, interjections, and adverbs.
Different Parts of Speech (with Examples)
The noun (n.).
A noun gives a name to something. There are different types of nouns like proper, collective, possessive, and common nouns.
Jeffrey, Korea, pen, New Year, dog, cat, elephant, garden, school, work, music, town, Manila, teacher, farmer, Bob, Sean, Michael, police officer, France, coffee, football, danger, happiness…
Example sentences:
- The teacher told the children to stop chattering in class.
- John is good at French but weak at History .
Common Noun : Names a general item.
- Here is a cup .
- Do you want a cake ?
Proper Noun: Names a specific item.
- The capital of England is London .
- Sarah is beautiful.
Collective Noun: Refers to a group.
- The swarm of bees was headed straight towards our picnic.
- At church on Sunday, the choir sings loudly.
Possessive Noun: Shows ownership.
- This is my dog’s ball.
- That is Sarah’s friend.
The Verb (v.)
A verb describes an action. There are three main types: action, linking, and modal verbs.
Walk, is, seem, realize, run, see, swim, stand, go, have, get, promise, invite, listen, sing, sit, laugh, walk…
- Don’t try to run before you can walk .
- Did you kiss anybody?
- Leave me alone!
Action Verb : Describes an action.
- The man walked down the street.
- I laughed at his joke.
- She ran to catch the bus before it left.
- The chef chopped the vegetables into small pieces for the salad.
Linking Verb: Connects the subject to a noun, adjective, or pronoun.
- Sarah feels cold.
- I am very tired.
- The flowers in the garden are blooming beautifully in the spring.
- The soup smells delicious and makes my mouth water.
Modal Verb: Helps the main verb and shows the speaker’s thoughts.
- I might walk to the park this afternoon.
- He can eat the last slice of cake.
- You must listen to me!
The Pronoun (pron.)
A pronoun replaces a noun. There are various types of pronouns like reflexive, indefinite, possessive, and relative pronouns.
I, me, we, you, he, she, yours, himself, its, my, that, this, those, us, who, whom
- Richard isn’t at work this week; he ‘s gone on holiday.
- Don’t tell her the truth.
- She tried it herself .
- You can’t blame him for everything .
- The woman who called yesterday wants to buy the house.
Reflexive Pronoun: Refers to self.
- I am going to keep this last cupcake for myself .
- Peter always puts himself first.
Indefinite Pronoun: Refers to a non-specific person or item.
- Can you take all ?
- I need to speak to someone about this rash on my arm.
Possessive Pronoun: Shows ownership.
- This bag is not yours , it’s mine .
- Her book is so new, while his looks vintage.
Relative Pronoun: Introduces an adjective clause.
- This is the woman who will be working with you.
- Is this the book that everyone is raving about?
The Adjective (adj.)
An adjective describes a noun or pronoun.
Beautiful, seven, cute, second, tall, blue, angry, brave, careful, healthy, little, old, generous, red, smart, two, small, tall, some, good, big, useful, interesting…
- This is a blue car.
- The small squirrel ran up the tree.
- During the thunderstorm, we saw some heavy rain.
- My mother has short hair.
- The documentary on TV last night was very interesting .
- My son has an impressive collection of toy soldiers.
- The weather is hot and sunny today.
- My vacation was exciting .
- The leaves on that tree are green and large .
The Adverb (adv.)
An adverb modifies an adjective, verb, or another adverb. Many adverbs end in -ly, but not all do.
Neatly, tomorrow, very, badly, fully, carefully, hardly, nearly, hungrily, never, quickly, silently, well, really, almost…
- This is an extremely attractive photograph.
- I have a very large pet dog.
- My car drives quickly .
- When I am running late for work, I eat my breakfast rapidly .
- The boy is crying loudly .
- She carefully preserved all his letters.
Determiners and Articles
Determiners and articles help clarify the nouns they introduce. Articles can be definite ( the ) or indefinite ( a , an ).
The, a, an, this, that, these, those, many, few, each, every, some, any, no, which, what
- The cat is sleeping on a mat.
- Can an apple be green?
- This book is very interesting.
- Each student must bring their own lunch.
The Conjunction (conj.)
A conjunction connects words, phrases, or clauses. Some common conjunctions are and , but , or , so , because , and although .
And, but, or, so, because, although, if, until, while, since, when, after, before, as
- I want to buy a sandwich and a drink.
- She was tired but happy.
- You can go to the party or stay home.
- They were late because of the traffic.
- Although it was raining, we went for a walk.
The Preposition (prep.)
A preposition shows the relationship of a noun (or pronoun) to another word. Common prepositions include at , on , in , by , with , and about .
At, on, in, by, with, about, above, below, between, during, for, from, over, under, through
- The cat is on the roof.
- She sat by the window.
- We will meet at the park in the afternoon.
- The book is about a boy with a magical power.
The Interjection (interj.)
An interjection is a word or phrase that expresses strong emotion or sudden exclamation. Common interjections include wow , ouch , oh , and hey .
Wow, ouch, oh, hey, ah, ugh, ew, hmm, yay, yikes, whoa, oops, aha, hurray, ew, oh no
- Wow ! That’s amazing!
- Ouch ! That hurt.
- Oh ! I didn’t see you there.
- Hey ! Wait for me.
- Yay ! We won the game.
In this section, you’ve learned about different parts of speech with examples and sample sentences. Each part of speech plays a unique role in creating meaningful sentences.
How To Determine A Part Of Speech In A Sentence
To determine a part of speech in a sentence, look at the word being used, its context, and what meaning it brings to the sentence structure. Here are some questions you can ask about a particular word:
- Is it a person, place, idea, name, or thing? It is a noun .
- Is the word used in place of a noun? It is a pronoun .
- Does the word convey an action, occurrence, or state of being? It is a verb .
- Does the word modify a noun? It is an adjective .
- Does the word modify a verb, adjective, or itself? It is an adverb .
- Is the word placed in front of a noun to form a modifying phrase? It is a preposition .
- Does the word link a phrase or clause? It is a conjunction .
- Is the word a quick expression of emotion? It is an interjection .
- Is the word placed before a noun to clarify it? It is a determiner or an article .
By asking these questions, you can identify the correct part of speech for any word in a sentence.
Parts of Speech and Sentence Construction
Simple/basic sentences.
In its simplest form, a sentence can have one independent clause .
For example, the sentence “I walk to the store” contains one clause.
- “I” is the subject of the clause, while “walk” is the verb.
- The ending phrase, “walk to the store” would be the verb phrase, or predicate , of the sentence.
This entire sentence “I walk to the store” is an independent clause, expresses one subject doing one action — and is known as a simple sentence .
Knowing this, apply the fact that nouns and pronouns will often be the subjects or objects of simple sentences, while verbs will convey actions. So once again:
- I (subject, pronoun)
- walk (verb)
- to (preposition)
- the (article)
- store (object, noun)
Complex Sentences
Complex sentences contain an independent clause and one or more dependent clauses. These sentences use conjunctions such as because, since, which, or who to connect clauses. Consider the structure and an example below:
- Independent Clause: She reads a book
- Dependent Clause: because she wants to learn
By combining these clauses, one forms a complex sentence: She reads a book because she wants to learn.
Other examples of complex sentences:
- Although the weather was cold, they decided to go for a hike.
- She completed her assignment before she went out with her friends.
- When you finish your homework, we can go to the movies.
- Because my coffee was too cold, I heated it in the microwave.
- If you save your money, you can buy a new bicycle.
Parts of Speech Video
Learn all parts of speech in English with a useful video lesson.
Parts Of Speech Quiz
Here are some Parts Of Speech exercises for you to practice:
A. In the sentence “I ran to the tallest tree”, what part of speech is the word “tallest”?
- A preposition
- An adjective
B. In the 2000s, the word staycation described the act of staying home for a vacation. Since “staycation” is a noun and a new word, what class of words does it belong to?
- The Open word class
- The Closed word class
- The Infinitive word class
C. In the sentence “I’ll have a few tacos”, what part of speech is the phrase “a few”?
- Interjections
- Determiners
Answers: A) 3, B) 1, C) 3
- Latest Posts
- Active vs. Passive Voice Exercises – Active vs. Passive Voice Worksheet - December 25, 2023
- Phrase Exercises – Phrase Worksheet - December 23, 2023
- Sentence Exercises – Sentence Worksheet - December 23, 2023
Have a thesis expert improve your writing
Check your thesis for plagiarism in 10 minutes, generate your apa citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Parts of speech
The 8 Parts of Speech | Definition & Examples
A part of speech (also called a word class ) is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence. Understanding the different parts of speech can help you analyse how words function in a sentence and improve your writing.
The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns , pronouns , verbs , adjectives , adverbs , prepositions , conjunctions , and interjections . Some modern grammars add others, such as determiners and articles .
Many words can function as different parts of speech depending on how they are used. For example, ‘laugh’ can be a noun (e.g., ‘I like your laugh’) or a verb (e.g., ‘don’t laugh’).
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Prepositions, conjunctions, interjections, other parts of speech, frequently asked questions.
A noun is a word that refers to a person, concept, place, or thing. Nouns can act as the subject of a sentence (i.e., the person or thing performing the action) or as the object of a verb (i.e., the person or thing affected by the action).
There are numerous types of nouns, including common nouns (used to refer to nonspecific people, concepts, places, or things), proper nouns (used to refer to specific people, concepts, places, or things), and collective nouns (used to refer to a group of people or things).
Ella lives in France .
Other types of nouns include countable and uncountable nouns , concrete nouns , abstract nouns , and gerunds .
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun. Pronouns typically refer back to an antecedent (a previously mentioned noun) and must demonstrate correct pronoun-antecedent agreement . Like nouns, pronouns can refer to people, places, concepts, and things.
There are numerous types of pronouns, including personal pronouns (used in place of the proper name of a person), demonstrative pronouns (used to refer to specific things and indicate their relative position), and interrogative pronouns (used to introduce questions about things, people, and ownership).
That is a horrible painting!
A verb is a word that describes an action (e.g., ‘jump’), occurrence (e.g., ‘become’), or state of being (e.g., ‘exist’). Verbs indicate what the subject of a sentence is doing. Every complete sentence must contain at least one verb.
Verbs can change form depending on subject (e.g., first person singular), tense (e.g., past simple ), mood (e.g., interrogative), and voice (e.g., passive voice ).
Regular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participle are formed by adding’-ed’ to the end of the word (or ‘-d’ if the word already ends in ‘e’). Irregular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participles are formed in some other way.
‘I’ve already checked twice’.
‘I heard that you used to sing ‘.
Other types of verbs include auxiliary verbs , linking verbs , modal verbs , and phrasal verbs .
An adjective is a word that describes a noun or pronoun. Adjectives can be attributive , appearing before a noun (e.g., ‘a red hat’), or predicative , appearing after a noun with the use of a linking verb like ‘to be’ (e.g., ‘the hat is red ‘).
Adjectives can also have a comparative function. Comparative adjectives compare two or more things. Superlative adjectives describe something as having the most or least of a specific characteristic.
Other types of adjectives include coordinate adjectives , participial adjectives , and denominal adjectives .
An adverb is a word that can modify a verb, adjective, adverb, or sentence. Adverbs are often formed by adding ‘-ly’ to the end of an adjective (e.g., ‘slow’ becomes ‘slowly’), although not all adverbs have this ending, and not all words with this ending are adverbs.
There are numerous types of adverbs, including adverbs of manner (used to describe how something occurs), adverbs of degree (used to indicate extent or degree), and adverbs of place (used to describe the location of an action or event).
Talia writes quite quickly.
Other types of adverbs include adverbs of frequency , adverbs of purpose , focusing adverbs , and adverbial phrases .
A preposition is a word (e.g., ‘at’) or phrase (e.g., ‘on top of’) used to show the relationship between the different parts of a sentence. Prepositions can be used to indicate aspects such as time , place , and direction .
I left the cup on the kitchen counter.
A conjunction is a word used to connect different parts of a sentence (e.g., words, phrases, or clauses).
The main types of conjunctions are coordinating conjunctions (used to connect items that are grammatically equal), subordinating conjunctions (used to introduce a dependent clause), and correlative conjunctions (used in pairs to join grammatically equal parts of a sentence).
You can choose what movie we watch because I chose the last time.
An interjection is a word or phrase used to express a feeling, give a command, or greet someone. Interjections are a grammatically independent part of speech, so they can often be excluded from a sentence without affecting the meaning.
Types of interjections include volitive interjections (used to make a demand or request), emotive interjections (used to express a feeling or reaction), cognitive interjections (used to indicate thoughts), and greetings and parting words (used at the beginning and end of a conversation).
Ouch ! I hurt my arm.
I’m, um , not sure.
The traditional classification of English words into eight parts of speech is by no means the only one or the objective truth. Grammarians have often divided them into more or fewer classes. Other commonly mentioned parts of speech include determiners and articles.
Determiners
A determiner is a word that describes a noun by indicating quantity, possession, or relative position.
Common types of determiners include demonstrative determiners (used to indicate the relative position of a noun), possessive determiners (used to describe ownership), and quantifiers (used to indicate the quantity of a noun).
My brother is selling his old car.
Other types of determiners include distributive determiners , determiners of difference , and numbers .
An article is a word that modifies a noun by indicating whether it is specific or general.
- The definite article the is used to refer to a specific version of a noun. The can be used with all countable and uncountable nouns (e.g., ‘the door’, ‘the energy’, ‘the mountains’).
- The indefinite articles a and an refer to general or unspecific nouns. The indefinite articles can only be used with singular countable nouns (e.g., ‘a poster’, ‘an engine’).
There’s a concert this weekend.
A is an indefinite article (along with an ). While articles can be classed as their own part of speech, they’re also considered a type of determiner .
The indefinite articles are used to introduce nonspecific countable nouns (e.g., ‘a dog’, ‘an island’).
In is primarily classed as a preposition, but it can be classed as various other parts of speech, depending on how it is used:
- Preposition (e.g., ‘ in the field’)
- Noun (e.g., ‘I have an in with that company’)
- Adjective (e.g., ‘Tim is part of the in crowd’)
- Adverb (e.g., ‘Will you be in this evening?’)
As a part of speech, and is classed as a conjunction . Specifically, it’s a coordinating conjunction .
And can be used to connect grammatically equal parts of a sentence, such as two nouns (e.g., ‘a cup and plate’), or two adjectives (e.g., ‘strong and smart’). And can also be used to connect phrases and clauses.
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked, what is a collective noun | examples & definition.
- What Is an Adjective? | Definition, Types & Examples
More interesting articles
- Definite and Indefinite Articles | When to Use 'The', 'A' or 'An'
- Ending a Sentence with a Preposition | Examples & Tips
- Using Conjunctions | Definition, Rules & Examples
- What Are Prepositions? | List, Examples & How to Use
- What Is a Determiner? | Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Adverb? Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Interjection? | Examples, Definition & Types
- Page Content
- Sidebar Content
- Main Navigation
- Quick links
- All TIP Sheets
The Eight Parts of Speech
- Prepositions
- Conjunctions
- Interjections
- Basic Sentence Structure
- Sentence Fragments
- Run-on Sentences and Comma Splices
- Sentence Type and Purpose
- Independent and Dependent Clauses: Coordination and Subordination
- Subject Verb Agreement
- Consistent Verb Tense
- Other Phrases: Verbal, Appositive, Absolute
- Pronoun Reference
- Relative Pronouns: Restrictive and Nonrestrictive Clauses
- Avoiding Modifier Problems
- Transitions
- Would, Should, Could
- Achieving Parallelism
- Definite and Indefinite Articles
- Two-Word Verbs
TIP Sheet THE EIGHT PARTS OF SPEECH
There are eight parts of speech in the English language: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection. The part of speech indicates how the word functions in meaning as well as grammatically within the sentence. An individual word can function as more than one part of speech when used in different circumstances. Understanding parts of speech is essential for determining the correct definition of a word when using the dictionary.
1. NOUN
- A noun is the name of a person, place, thing, or idea.
man... Butte College... house... happiness
A noun is a word for a person, place, thing, or idea. Nouns are often used with an article ( the , a , an ), but not always. Proper nouns always start with a capital letter; common nouns do not. Nouns can be singular or plural, concrete or abstract. Nouns show possession by adding 's . Nouns can function in different roles within a sentence; for example, a noun can be a subject, direct object, indirect object, subject complement, or object of a preposition.
The young girl brought me a very long letter from the teacher , and then she quickly disappeared. Oh my!
See the TIP Sheet on "Nouns" for further information.
2. PRONOUN
- A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun.
She... we... they... it
A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun. A pronoun is usually substituted for a specific noun, which is called its antecedent. In the sentence above, the antecedent for the pronoun she is the girl. Pronouns are further defined by type: personal pronouns refer to specific persons or things; possessive pronouns indicate ownership; reflexive pronouns are used to emphasize another noun or pronoun; relative pronouns introduce a subordinate clause; and demonstrative pronouns identify, point to, or refer to nouns.
The young girl brought me a very long letter from the teacher, and then she quickly disappeared. Oh my!
See the TIP Sheet on "Pronouns" for further information.
3. VERB
- A verb expresses action or being.
jump... is... write... become
The verb in a sentence expresses action or being. There is a main verb and sometimes one or more helping verbs. (" She can sing." Sing is the main verb; can is the helping verb.) A verb must agree with its subject in number (both are singular or both are plural). Verbs also take different forms to express tense.
The young girl brought me a very long letter from the teacher, and then she quickly disappeared . Oh my!
See the TIP Sheet on "Verbs" for more information.
4. ADJECTIVE
- An adjective modifies or describes a noun or pronoun.
pretty... old... blue... smart
An adjective is a word used to modify or describe a noun or a pronoun. It usually answers the question of which one, what kind, or how many. (Articles [a, an, the] are usually classified as adjectives.)
See the TIP Sheet on "Adjectives" for more information.
5. ADVERB
- An adverb modifies or describes a verb, an adjective, or another adverb.
gently... extremely... carefully... well
An adverb describes or modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb, but never a noun. It usually answers the questions of when, where, how, why, under what conditions, or to what degree. Adverbs often end in -ly.
See the TIP Sheet on "Adverbs" for more information.
6. PREPOSITION
- A preposition is a word placed before a noun or pronoun to form a phrase modifying another word in the sentence.
by... with.... about... until
(by the tree, with our friends, about the book, until tomorrow)
A preposition is a word placed before a noun or pronoun to form a phrase modifying another word in the sentence. Therefore a preposition is always part of a prepositional phrase. The prepositional phrase almost always functions as an adjective or as an adverb. The following list includes the most common prepositions:
See the TIP Sheet on "Prepositions" for more information.
7. CONJUNCTION
- A conjunction joins words, phrases, or clauses.
and... but... or... while... because
A conjunction joins words, phrases, or clauses, and indicates the relationship between the elements joined. Coordinating conjunctions connect grammatically equal elements: and, but, or, nor, for, so, yet. Subordinating conjunctions connect clauses that are not equal: because, although, while, since, etc. There are other types of conjunctions as well.
The young girl brought me a very long letter from the teacher, and then she quickly disappeared. Oh my!
See the TIP Sheet on "Conjunctions" for more information.
8. INTERJECTION
- An interjection is a word used to express emotion.
Oh!... Wow!... Oops!
An interjection is a word used to express emotion. It is often followed by an exclamation point.
The young girl brought me a very long letter from the teacher, and then she quickly disappeared. Oh my !
See the TIP Sheet on "Interjections" for more information.
Home | Calendars | Library | Bookstore | Directory | Apply Now | Search for Classes | Register | Online Classes | MyBC Portal MyBC -->
Butte College | 3536 Butte Campus Drive, Oroville CA 95965 | General Information (530) 895-2511
Parts of Speech: Definitions, Categories and Examples
By: Author English Study Online
Posted on Last updated: August 28, 2024
Sharing is caring!
In this reference, we will break down each part of speech and provide examples to help you understand their usage. We will also discuss how to identify the different parts of speech in a sentence and provide tips on how to use them correctly. Let’s get started!

Parts of Speech – Created by Englishstudyonline
Table of Contents
What is a Parts of Speech?
A part of speech is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence. These roles help you understand how words function in grammar .
There are typically eight main parts of speech in English:
- Nouns : Words that name people, places, things, or ideas.
- Pronouns : Words that replace nouns, such as he, she, it .
- Verbs : Words that describe actions or states, like run, is .
- Adjectives : Words that describe or modify nouns, like blue or quick .
Some grammars list additional parts of speech:
- Adverbs : Words that modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, such as quickly .
- Prepositions : Words that show relationships between a noun (or pronoun) and another word, like in or on .
- Conjunctions : Words that connect clauses, sentences, or words, such as and or but .
- Interjections : Words that express emotion, like wow or oops .
Some sources also include:
- Determiners/Articles : Words that modify nouns and specify which one, like the, a .
Categories of Parts of Speech
Nouns are words that represent people, places, things, or ideas. They are one of the most important parts of speech in English and are used in nearly every sentence. In this section, we will explore the different types of nouns and their functions.
- Common Nouns : General names for people, places, or things. Not capitalized unless at the start of a sentence. Examples : “book,” “city,” “teacher.”
- Proper Nouns : Specific names for people, places, or things. Always capitalized. Examples : “Harry Potter,” “New York City,” “Ms. Johnson.”
- Abstract Nouns : Names for ideas, concepts, or emotions that are intangible. Examples : “love,” “happiness,” “freedom.”
- Collective Nouns : Names for groups of people or things; can be singular or plural. Examples : “team,” “family,” “herd.”
2. Pronouns
Pronouns are words that replace nouns in a sentence. They help avoid repetition and make sentences clearer. Here are different types of pronouns in English:
- Personal Pronouns : Refer to specific people or things and can be subjects or objects. Examples : I/me, you/your/yours, he/him/his, she/her/hers, it/its.
- Demonstrative Pronouns : Point to specific people or things and indicate distance. Examples : this (near), that (far), these (plural, near), those (plural, far).
- Interrogative Pronouns : Used to ask questions. Examples : who (person), whom (person, object), whose (possession).
- Indefinite Pronouns : Refer to non-specific people or things. Examples : anybody, anyone, anything, each, either, everybody, everyone, everything.
- Action Verbs : Describe actions performed by the subject. Examples : Run, Jump, Sing, Dance, Write.
- Linking Verbs : Connect the subject to a noun, pronoun, or adjective that describes it; they do not show action. Examples : Is, Are, Was, Were, Seem.
- Helping Verbs : Work with the main verb to express tense, voice, or mood; they have no meaning on their own. Examples : Am, Is, Are, Was, Were.
4. Adjectives
Adjectives are words that describe or modify nouns or pronouns, giving more information about their qualities, quantity, or identity. Here are three types of adjectives:
- Descriptive Adjectives : Describe the characteristics or qualities of a noun or pronoun. Examples : Beautiful, Tall, Thin, Ugly, Smart, Kind. Sentence Example : “The red car is fast.” (“red” describes the color; “fast” describes the speed).
- Quantitative Adjectives : Indicate the quantity or amount of a noun or pronoun, answering “how much” or “how many.” Examples : Few, Many, Several, Some, All, No. Sentence Example : “I have two apples.” (“two” describes the number of apples).
- Demonstrative Adjectives : Point to specific nouns or pronouns, answering “which one” or “whose.” Examples : This, That, These, Those. Sentence Example : “This book is mine.” (“this” specifies the book).
Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, providing more detail about an action, adverbs of manner, adverbs of place, adverbs of time, adverbs of frequency , adverbs of degree, or intensity.
Examples of adverbs:
- I left my keys here . (Adverb of place)
- She arrived late because she missed the bus. (Adverb of time)
- James visits his grandmother weekly . (Adverb of frequency)
- Please drive carefully on the wet roads. (Adverb of manner)
- She was extremely tired after the long journey. (Adverb of degree)
6. Prepositions
Prepositions are words that show the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence, indicating position, direction, or time.
Prepositions of Time : Indicate when an action takes place. Examples :
- “At” for specific times: “at 2 pm,” “at midnight.”
- “In” for longer periods: “in the morning,” “in October.”
- “On” for dates: “on Monday,” “on July 4th.”
Prepositions of Place : Indicate where something is located. Examples :
- “In” for enclosed spaces: “in the house,” “in the car.”
- “On” for surfaces: “on the table,” “on the floor.”
- “At” for specific locations: “at the park,” “at the beach.”
Prepositions of Direction : Indicate movement from one place to another. Examples :
- “To” for movement towards: “I am going to the store.”
- “From” for movement away: “I am coming from the park.”
- “Towards” for movement in a direction: “I am walking towards the museum.”
7. Conjunctions
Conjunctions are words that connect words, phrases, or clauses in a sentence, helping to create complex sentences and showing relationships between ideas. There are three main types of conjunctions: coordinating, subordinating, and correlative.
Coordinating Conjunctions : Connect words, phrases, or independent clauses of equal importance. Remember them using FANBOYS : for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so. Examples :
- “I like pizza and pasta .”
- “He wanted to go to the beach, but it was raining.”
Subordinating Conjunctions : Connect dependent clauses to independent clauses, showing relationships like cause and effect, time, condition, or contrast. Examples : because, although, while, if, unless, since.
- “Because it was raining, we stayed inside.”
- “While I was studying, my roommate was watching TV.”
Correlative Conjunctions : Work in pairs to connect elements in a sentence, showing a relationship between them. Examples : both…and, either…or, neither…nor, not only…but also.
- “Both my sister and I like to read.”
- “Not only was he late, but he also forgot his homework.”
8. Interjections
In English grammar, interjections are words or phrases that express strong emotions or feelings. They are also known as exclamations and are one of the eight parts of speech in English. Interjections are grammatically independent from the words around them, and they can often be removed from a sentence or context without affecting its basic meaning.
Interjections can be used to express a wide range of emotions, including surprise, joy, anger, frustration, and pain. Some common examples of interjections include “ wow ,” “ ouch ,” “ yay ,” “ oh no ,” and “ oops .” They can be used to add emphasis to a sentence or to convey a particular tone or mood.
9. Articles/Determiners
In English grammar, articles and determiners are words that are used with nouns to provide more information about them. They help us to understand the context and meaning of a sentence.
There are three articles in the English language: “ the ,” “ a, ” and “ an. ” “The” is known as the definite article because it refers to a specific noun that has already been mentioned or is known to the reader. For example, “The cat is sleeping on the sofa.” In this sentence, “the” refers to a specific cat that has already been mentioned or is known to the reader.
“A” and “an” are known as indefinite articles because they refer to any member of a group or class of nouns. “A” is used before words that begin with a consonant sound, while “an” is used before words that begin with a vowel sound. For example, “I need a pen” and “She ate an apple.”
Determiners
Determiners are words that come before a noun to provide more information about it. They can include articles, as well as words like “ this ,” “ that ,” “ these ,” and “ those .”
In addition to these, there are other types of determiners such as possessive determiners (e.g. “my,” “your,” “his,” “her,” “its,” “our,” and “their”), demonstrative determiners (e.g. “this,” “that,” “these,” and “those”), and quantifying determiners (e.g. “some,” “any,” “many,” “few,” “several,” etc.).
Determiners can also be used with adjectives to provide more information about a noun. For example, “She ate the delicious apple” and “I saw that beautiful sunset.”
Examples of Parts of Speech
- Noun – The dog barked loudly.
- Pronoun – They went to the park together.
- Verb – She writes beautiful poetry.
- Adverb – He runs very quickly.
- Adjective – The red car is fast.
- Preposition – The cat is sitting on the sofa.
- Conjunction – She wanted to go for a walk, and he wanted to stay home.
- Interjection – Wow! That was an incredible performance.
Practical Exercises
Exercise 1: Identify the Part of Speech
Read each sentence and identify the underlined word’s part of speech (Noun, Pronoun, Verb, Adverb, Adjective, Preposition, Conjunction, Interjection).
- The beautiful garden is full of flowers.
- She quickly finished her homework.
- Wow! That was a great surprise.
- The cat hid under the bed.
- I want to go out, but it’s raining.
- He is a very talented musician.
- The children play in the park every evening.
- The cake is delicious .
- After lunch, we went for a walk.
- They will arrive at the airport soon.
- Interjection
- Preposition
- Conjunction
Exercise 2: Fill in the Blanks with the Correct Part of Speech
Choose the correct word from the list and fill in the blanks with the appropriate part of speech.
Word List: (and, beautiful, suddenly, them, book, Wow, under, write, she, quickly)
- The weather is so __________ today.
- I have to __________ an essay for my class.
- He ran __________ to catch the bus.
- The ball rolled __________ the table.
- They read a __________ together every night.
- She wanted to go to the park, __________ it started raining.
- Can you give this note to __________?
- __________! That was an amazing goal!
- __________ is going to the market.
- The bird flew away __________.
- beautiful (Adjective)
- write (Verb)
- quickly (Adverb)
- under (Preposition)
- book (Noun)
- and (Conjunction)
- them (Pronoun)
- Wow (Interjection)
- She (Pronoun)
- suddenly (Adverb)
- Recent Posts
- Juridical Process vs. Judicial Process: Understanding the Crucial Differences - December 14, 2023
- Compound Nouns: How to Use Them Effectively in English - November 9, 2023
- English Tenses: A Beginner’s Guide in English - November 6, 2023
The Parts of Speech – Definitions and Examples
The different parts of speech are the breakdown and classification of words in English that show their unique functions and properties. In core language, a single word can function as two or more parts of speech.
Differentiating between the 9 parts of speech is the first step to building your grammar skills and writing tools. Keep reading to learn the definitions and examples of each category!
What are the 9 Basic Parts of Speech?
A noun is any place, person, idea, or thing. Some examples of nouns include:
There are various classifications of nouns you can use in your writing. Proper nouns are specific names for places, persons, ideas, or things. Meanwhile, common nouns are generic class nouns. A possessive noun is another type of noun that demonstrates belonging.
We can also classify this part of speech as an abstract noun, concrete noun, count noun, and uncountable noun.
The placement of the noun in a sentence also determines its function. A noun can be in the nominative or objective case. The nominative functions include subject and subject complement. And the types of objects are direct object, indirect object, and object of a preposition.
A quick introduction to pronouns shows they are classes of words that take the place of nouns. Some examples of pronouns include he, that, whoever, myself.
This quick guide to pronouns shows they can be classified as:
- Personal pronoun (I, he, she, you, etc.)
- Demonstrative pronouns (that, those, these, this, etc.).
- Interrogative pronouns (what, when, why, how, etc.).
- Relative pronouns (who/whom, whose, which, etc.).
- Indefinite pronouns (anybody, everybody, somebody, everything, etc.).
- Reflexive pronouns (myself, yourself, herself, etc.).
- Intensive pronouns (myself, yourself, herself, etc.).
Pronouns can further be divided into first-person pronoun, second-person pronoun, and third-person pronoun.
A verb is a word that conveys time while showing a condition, an action, or the fact that something exists. All complete sentences should contain at least one verb unless using an interjection.
Verbs can be treated as either lexical verbs/action verbs (study, love, drink) or auxiliary verbs (seem, is, have).
A verb phrase combines verbs with linking verbs and lexical categories of verbs. Some examples include:
- Has become.
Phrasal verbs are forms of verbs that consist of two or more words. Here are some examples:
- Put up with.
When you add “up with” after the simple verb “put,” you create a brand-new verb with a new meaning. Therefore, phrasal verbs should be treated as complete verbs because of their unique definitions.
Some verbs are reflexive. A reflexive verb is where the subject and object are one since the sentence uses reflexive pronouns like “himself” or “itself.”
Whether you’re using a lexical or auxiliary verb, this part of the speech always expresses time through the different tenses. For instance, the verb “eats” is a present-tense verb, and its past form is “ate.”
4. Adjective
Another part of speech is the adjective , which modifies or describes a noun or a pronoun. It typically answers the questions “what kind,” “which one,” or “how much.” For example:
The articles “a,” “an,” and “the” are sometimes categorized as adjectives. “The” is a definite article, and “a” and “an” are indefinite articles.
Adjective classes include:
- Absolute adjectives.
- Appositive adjectives.
- Attributive adjectives.
- Predicative adjectives.
- Compound adjectives.
- Qualitative adjectives.
- Denomial adjectives.
- Participial adjectives.
- Demonstrative adjectives.
Adverbs are a word class that modifies adjectives, verbs, and fellow adverbs. One frequent adverb marker is the suffix -ly, such as “healthily,” “badly,” and “swiftly.”
But the discussion of adverbs goes beyond words that describe actions. There are also adverbs of degree, place, time, and frequency. The English language also considers “most days,” “to visit my friend,” “very loudly,” and other adverbial phrases as adverbs.
Adverbial phrases are under the phrasal categories, including verb phrases, adjective phrases, etc.
6. Conjunction
A conjunction is a word that binds words, clauses, and phrases. “And,” “but,” “because,” and “consequently” are some examples of conjunctions.
Conjunctions make it easy to construct more complex sentences because you can easily add new clauses. The category distinctions of this part of speech are:
- Coordinating conjunctions (for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so, etc.)
- Subordinating conjunctions (after, although, unless, since, if, etc.)
- Correlative conjunctions (not only… but also, either… or, etc.)
7. Preposition
Prepositions show relations of space, time, and role between nouns, pronouns, and other words. They are at the start of prepositional phrases. Here are some examples of prepositions:
- Apart from.
8. Determiner
A determiner is like an adjective because it also modifies nouns. However, these words are essential for proper syntax as opposed to adjectives. They can be classified as indefinite and definite. New grammar rules now treat articles as determiners. Examples of determiners include:
- Which.
9. Interjection
The last part of speech is the interjection which may have standalone functions in sentences. “Whoops,” “ouch,” “ah,” and “hooray” can be an entire sentence on their own.
Parts of Speech Chart
Analyzing the parts of speech is different for every individual language. Here’s an overview of the different categories in English.
| Noun | Person, thing, place, or event | She is the new . |
| Pronoun | Replaces a noun | is the new assistant. bag is missing. |
| Verb | Expresses time while demonstrating a condition, action, or the fact that something exists | She the new assistant. I what she that day. |
| Adjective | Modifies a noun or a pronoun | She is the assistant. Jane is selling her apartment. |
| Adverb | Modifies a verb, adjective, or fellow adverb. | remove your makeup. |
| Conjunction | Connects clauses, words, or sentences | I like candles I like reed diffusers. She asked me not to attend she won’t be there. |
| Preposition | Connects a noun to another word | My dog went the neighbor’s house. |
| Determiner | Determines a noun | buzzcut suits your face shape. |
| Interjection | Short exclamation | ! That was an impressive performance. |
When A Word is Also Two Different Kinds of Speech
Sometimes, words have more than one role in the English language. For example, some nouns can also act as adjectives called adjectival nouns. In the phrase “race car,” “race” modifies “car,” so its usage is as an adjective instead of a noun.
A noun can be used in verbal senses. Consider the word “work” in these sentences.
- My new work is more promising than the old one. (noun)
- Shew works in a new industry. (verb)
Open and Closed Word Classes
The two classifications of the parts of speech include open and closed classes. The open classes can be changed and added as the language changes.
- Adjectives.
Meanwhile, closed classes are parts of speech that do not change. These include:
- Prepositions.
- Conjunctions.
- Articles and determiners.
- Interjections.
In some languages, verbs and adjectives form closed classes. This closedness of verbs is common in Basque and Persian verbs .
Linguistics , or the study of language, does not recommend the label “part of speech” anymore. Instead, the discipline favors “syntactic category” or “word class.”
What Part of Speech is With?
In the stricter sense, the only use of “with” is as a preposition. You can find it before a noun or a pronoun to form prepositional phrases. Use it to show togetherness, associations, and connections between people and objects.
What Part of Speech is And?
The conjunction “and” connects words, clauses, and phrases. It can also combine sentences that need to be presented at once.
What Part of Speech is My?
“My” is a possessive pronoun that can also act as an adjective, determiner, or interjection.
Are You Using the Parts of Speech the Right Way?
This guide has shown you the nine parts of speech and their grammatical functions. By now, you should already be able to give definitions and examples of each category, so they make sense.
To correctly use the parts of speech, ask yourself, “what is the function of this word in the sentence?” Keep practicing until you master the traditional grammar rules of English!
Grammarist is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you buy via the links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no cost to you.
2024 © Grammarist, a Found First Marketing company. All rights reserved.
The 8 Parts Of Speech In English
There are eight major parts of speech .
- Nouns name persons, places, things, ideas, or qualities, e.g., Franklin, boy, Yangtze River, shoreline, Bible, desk, fear, happiness.
- Pronouns usually substitute for nouns and function as nouns, e.g., I, you, he, she, it, we, they, myself, this, that, who, which, everyone.
- Verbs express actions, occurrences, or states of being, e.g., be, become, bunt, inflate, run.
- Adjectives describe or modify nouns or pronouns, e.g., gentle, helpful, small.
- Adverbs describe or modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, e.g., almost, gently, helpfully, someday.
- Prepositions relate nouns or pronouns to other words in a sentence, e.g., about, at, down, for, of, with.
- Conjunctions link words, clauses, and phrases. There are coordinating conjunctions that link words, clauses, or phrases of equal importance, and there are subordinating conjunctions that introduce subordinate clauses and link them to main clauses.
- Interjections express feeling or command attention, either alone or in a sentence, e.g., darn, hey, oh, wow.
Some words ( adjectives , adverbs , interjections , nouns , verbs ) are productive classes allowing new members; others, with functional rather than lexical meaning ( articles , conjunctions , prepositions ) are nonproductive and have a limited number of members.
Some grammarians consider articles , quantifiers , and numerals to also be parts of speech.
Language Stories

Hobbies & Passions
Word Origins
Current Events
[ op - s uh -math ]
- By clicking "Sign Up", you are accepting Dictionary.com Terms & Conditions and Privacy policies.
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
- Phrases and Clauses
- Parts of a Sentence
- Modal Verbs
- Relative Clauses
- Confusing Words
- Online Grammar Quizzes
- Printable Grammar Worksheets
- Courses to purchase
- Grammar Book
- Grammar Blog
8 Parts of Speech
The 8 parts of speech in English are: Nouns, Adjectives, Adverbs, Verbs, Prepositions, Pronouns, Conjunctions, and Interjections.
A part of speech is a category of words that have similar grammatical functions or properties. In other words, they play similar roles in a sentence. For instance, a verb shows the action of a subject or the subject's state of being.

We'll now look in more detail at the function of each of these parts of speech.
Understanding the 8 Parts of Speech
Nouns are words used to talk about people, places, things, or ideas/concepts. Here are some examples:
- Person: The President
- Place: London
- Thing: Table
- Idea/concept: Neo-liberalism
So it may be naming something we can touch ( e.g. table; book; car ) or something we cannot touch ( e.g. Neo-liberalism; happiness; wish ).
There are both common nouns, used for classes of people, places, things, or ideas/concepts, and proper nouns, which is their given name, always with a capital letter.
Common Nouns
- political party
Proper Nouns
- Chester Avenue
Learn more about the various types of noun >>
Another of the 8 parts of speech are adjectives. They describe nouns or pronouns. They can come before or after the noun/pronoun they describe:
Absolute Adjectives
- The large shopping complex
- The excited child
- She is happy
- It was a shocking film
- Her dress was lovely
- He's a good-looking man
These are absolute adjectives , but they can also be comparative (comparing two or more things) or superlative (showing degree or quality):
Comparative Adjectives
- She's fitter than the others
- Their house is bigger
- I ran faster than you
- Cats are more agile than dogs
- Sue's more tired than Tim

Superlative Adjectives
- She's the fittest
- Their house is the biggest
- I ran the fastest
- Cats are the most agile
- Sue's the most tired
There are various other types of adjective. Learn more about the different types of adjectives >>
Adverbs modify verbs, other adverbs, and adjectives. There are adverbs of manner, time, place and degree . Here are examples of each being modified in relation to verbs, adverbs, and adjectives (the word being modified is underlined):
Adverbs Modifying Verbs
- He runs fast
- Ian quickly left the room
- She spoke slowly
Adverbs Modifying Other Adverbs
- He runs exceptionally fast
- Ian very quickly left the room
- She spoke extremely slowly
Adverbs Modifying Adjectives
- She's really excited
- He's happily married
- The elegantly designed dress is mine
Verbs form part of the predicate of a sentence.
In relation to the subject, they are used to express a physical action (e.g. walk; speak; show) or a mental action (e.g. think; feel; want). They can also express a state of being , mainly with the verb 'to be' but also some others.
Here are some examples:
Physical Action
- He ran home
- They chose the blue one
Mental Activity
- I am thinking about it
- Ian guessed the answer
- She believes in ghosts
State of Being
- She is a police woman
- They seem worried
These though are main verbs. They have many other uses in a sentence so you should read about all the types of verbs further.
Prepositions
Another of the 8 parts of speech are prepositions. These show the relationship between two words or phrases in a sentence. They precede a noun or pronoun.
Commons examples of prepositions are above, up, upon, at, before, behind, since, to, through, under, until, with, within, about, against, along, around, beside, between, down, during, below, by, except, for, from, in, into, like, near, of, off, on, toward.
In these example sentences with prepositions, the two words whose relationship is being expressed are underlined and the prepositions are in bold:
- The book is on the table
- He is the leader of the conservative party
- The boy picked up the toy under the sofa
- This is a present for your mother
Pronouns replace nouns and they prevent us from repeating the noun in a sentence. These are the types of pronouns with some examples:
- Personal e.g. I; you; they; she
- Possessive e.g. mine; yours; his; theirs
- Relative e.g. who; which; that; whom
- Demonstrative e.g. this; these; those
- Reciprocal e.g. one another; each other
- Emphatic / Reflexive e.g. myself; herself; itself; ourselves
- Interrogative e.g. what; which; whom; whose
Here are some examples of these words used in sentences:
- Martha decided she would leave
- Why don't you use his car instead of mine
- Mick is a person who learns quickly
- Shall we buy some of these ?
- They began to argue with each other
- Jenny is pleased with herself
- What time is he coming?
Conjunctions
Conjunctions are the of the 8 parts of speech responsible for joining together words, phrases, or clauses. There are three types:
- Coordinating: and; or; but; so; yet; for; nor
- Correlative: neither/nor; either/or; not only/but also
- Subordinating: e.g. although; because; while; which; where; until
Coordinating Conjunctions
Used to connect like for like words (e.g. noun+noun):
- I like apples and oranges ( 2 nouns )
- His speech was slow but effective ( 2 adjectives )
- Shall I say it loudly or quietly? ( 2 adverbs )
Or simple sentences (independent clauses):
- I find the music annoying but she finds It pleasant
- She came to the lecture late so she missed everything important
- She took her umbrella for it was raining hard
Correlative Conjunctions
Used to join alternative or equal elements:
- He felt neither happy nor sad about it
- Sue had to decide to either quit or carry on
- I went not only to Australia but also to New Zealand
Subordinating Conjunctions
Used to join subordinate clauses to main clauses:
- The government won't vote on the bill until both parties agree
- I'm still not tired although it is late
- I'll eat the dish which you don't like
Interjections
Interjections are words used to express an emotion or a sentiment such as surprise, joy, disgust, fear, excitement, pain, or enthusiasm.
They usually appear at the start of a sentence and are not connected to it grammatically. Here are some examples of interjections in sentences:
- Wow , that's an amazing score!
- Oh , I didn't know you failed the exam
- Well , we better not leave too late
- Ow , that really hurt!
- Ah , I understand now
- Oops , I've forgotten to bring the sandwiches
Learn more about interjections >>
Are there only 8 Parts of Speech?
Sometimes rather than 8 parts of speech, you may see 9 or 10 listed. This is because some people treat articles and determiners as separate categories.
However, when there are only 8 parts of speech considered (as above), this is because as these two types of word modify nouns, they are classified under adjectives.
Now practice what you have learned in our identifying parts of speech quiz
More on Sentence Structure:

Parts of a Sentence: Subject, Verbs, Objects, Predicates, Complements
The main parts of a sentence are subjects, verbs, objects, predicates, and subject complements. All of these have a specific purpose within the structure of a sentence.

Using Object Complements in a Sentence
Using object complements in a sentence enhances your ability to convey specific information about actions and their outcomes.

Types of Clauses in English Grammar - Independent and Dependent Clause
The two types of clauses in English grammar are the independent and dependent clause. Both have a subject and verb which makes them clauses, but while independent clauses express a complete thought, dependent clauses do not. This is the main distinction.

Nominalisation in English Grammar: High Level Writing Tips
Nominalisation is an important aspect of academic writing. This lesson teachers you what this is and how you can use it effectively in your writing.

Subject Complements: Predicate Adjectives and Predicate Nominatives
Here we demystify subject complements, predicate adjectives, and predicate nominatives with simple explanations and examples.

Phrases and Clauses - Building good sentences
Phrases and clauses are the key building blocks of sentences. A clause contains a subject and a verb and can express a complete thought. A phrase does not contain a subject or verb.

How to Use Either and Neither with Examples
Advice on how to use either and neither in English grammar. They can be adjectives, adverbs, pronouns and conjunctions.

Direct and Indirect Objects: The Differences
Direct and indirect objects are key parts of most sentences. A direct object is the receiver of action while indirect object identifies to or for whom or what the action of the verb is performed.

Examples of Parallelism in English Grammar
View examples of parallelism in English grammar that show you correct and incorrect parallel sentences.

Parallelism Grammar Rules (Parallel Structure)
Parallelism is about balancing the grammatical structure of words, phrases and clauses in your sentences. Parallel structure will improve your writing's coherence.
New! Comments
Any questions or comments about the grammar discussed on this page?
Post your comment here.

Sign up for free grammar tips, quizzes and lessons, straight into your inbox
Grammar Rules
Subscribe to grammar wiz:, grammar ebook.

This is an affiliate link
Recent Articles
Gerund or infinitive quiz.
Aug 11, 24 04:34 AM
Use of the Bare Infinitive
Aug 09, 24 01:59 AM
Future Continuous Tense Quiz: Yes/No Questions
Jun 29, 24 11:04 AM
Important Pages
Online Quizzes Grammar Lessons Courses Blog
Connect with Us
Search Site
Privacy Policy / Disclaimer / Terms of Use
Understanding Parts of Speech (9 Types With Examples)

What are parts of speech? In the American English language, parts-of-speech is a category to which a word is assigned in accordance with its syntactic functions. They exist under the verb , noun, pronoun, interjection , adjective , conjunction, adverb, and preposition forms.
Learn more about parts of the speech in this comprehensive worksheet…
What are parts of speech?
“Parts of speech” refers to the essential words used in sentence formation in the English language.
Every word used in a sentence structure plays an important role in defining the sentence’s meaning. These words use and placement give proper intentions in sentence structures.
Parts of speech are the basic grammar lessons taught during the primary phases of learning English.
Any word used in sentence formation falls into one of these categories for proper sentence structure.
Some of those words can be a part of one or more parts of speech. This topic further explores the essential parts of speech used in the English language.
Watch this as a video lesson
In total, there are nine categories of parts of speech
These nine parts of speech are namely: Verbs, Nouns , Adjectives, Determiners, Adverbs , Pronouns, Prepositions , Conjunctions, and Interjections.
Another additional classification is used as a part of speech, i.e. , Articles, a subprogram of determiners.
To comprehend the meaning and use of each word in the English language, it is essential to clearly understand the various parts of speech and select the right parts of speech form at the appropriate place in the sentence.
What are the 9 parts of speech with their functions?
Here are the nine parts of speech and how they impact the English language.
| Noun | name a place, person, thing, or idea. | California, man, park |
| Pronoun | Used to replace the name of a person, place, thing or idea. | He, she, it, they |
| Verb | A verb expresses what the does. | Leave, do, work put, |
| Adverb | Used to describe verb, adverb, or adjective. | Always, silently, quickly |
| Adjective | Words that are used to describe qualities or things. | Long, short, tiny, bright, dark |
| Preposition | Shows the relationship between other words in a sentence. | In, on, at, with, |
| Interjection | Words that express emotions or feelings. | Wow, oh, ah, yikes |
| Conjunction | Words that join words or groups of words together. | And, but, , , also |
‘Verbs’ are the words used in a sentence to define the action/state of action being performed. Most of the sentences in sentence formation require the inclusion of verbs.
Some examples of verbs used in the English language are Love, Break, Fall , and Cry . These are the basic forms of verbs and are known as infinitives .
Most of the verbs used have two other major forms called participles . The use of these participles is for the formation of various verb-tense combinations.
These participles define the forms of verbs concerning the time of action/performance. These verb-tense combinations can be used in two types: Active voice and passive voice .
A ‘noun’ are words used in a sentence to give recognition or the name of an object, individual, or animal.
Nouns can be sub-classified into two major categories: Common nouns , which give generic descriptor names to things, and common items, such as a bat, a bicycle , etc. The other category of nouns is Proper nouns , which have specific descriptor names to refer to a specialized object, place, or individual, such as Charley, The Empire State Building, The Telegraph , etc.
Additionally, nouns can be classified as singular nouns and plural nouns based on the number of individuals/objects.
Singular Nouns
The definition of a Singular Noun is the same as that of a noun when used commonly. It carries the same definition as the noun: “A word referring towards an individual/object/event/material/place.”
Plural Nouns
The word plural relates to “more than one in certain languages or more than two in certain languages.”
Thus singular nouns can be converted to their plural noun format when there is an implication of more than one or two objects/individuals/places.
A general Singular/Common Noun can be turned into the appropriate form of a Plural Noun by adding a ‘s’/’es’/’ ies’/’ves.’ It is also initiated by changing ‘us’ to ‘i’, ‘is’ to ‘es’ , or ‘on’ to ‘a’ .
Some common nouns do not change when interchanged between their singular and plural noun forms. Some other common nouns do not fall under plural nouns and are called irregular nouns, which are made plural by changing the spelling or adding a suffix to the word.
‘Adjectives’ are words that give a description or modify the scope of nouns/pronouns by being specific. For example, adjectives used to define a noun can be red, small, hot, common, etc.
An adjective is usually placed before a noun or after the verb that it modifies. Three forms of adjectives are used to compare similar characteristics of different individuals/objects. These three degrees of comparison are:
- Positive/Absolute form
This comparison of adjectives defines the original form of the adjective as stated in English. For example, “this candy is tasty .” This degree of comparison states that no relative subject is available for comparison.
- Comparative form
This form of the adjective gives a relative comparison between two objects performing similar actions with identical characteristics. For example, “the candy we had today is tastier than the one we received yesterday.”
- Superlative form
This form of the adjective gives the superiority declaration of one object over similar objects possessing similar characteristics. For example, “this candy is the tastiest I have ever had in the last two years .”
Adjectives can be sub-classified based on their function in sentence formation. This sub-classification is:
- Possessive Adjectives
These adjectives show/represent the possessiveness of an object. For example, mine, my, his/her, their, its, etc.
- Interrogative Adjectives
These adjectives modify the noun/pronoun by interrogation. Only a select few adjectives are available in this form. For example, whose, which, what, and where.
- Demonstrative Adjectives
These adjectives describe the current state/position of the noun/pronoun concerning space/time. For example, this, these, those, that.
- Compound Adjectives
These adjectives are a result of the combination of two or more adjectives. The resulting adjective modifies the subject in the sentence. For example, hand-dried, heavy-weighted, spike-haired, etc.
‘Determiners’ are the words placed before a noun/pronoun group terms to refer to a single/multiple things. Some commonly used determiners in English are ‘a’, ‘the’, ‘some’, ‘any’, and ‘this.’ Determiners are generally placed before descriptive adjectives . It tells the reader more about the description of the noun being referred to.
Determiners are classified into sub-categories, articles, and demonstratives.
An ‘Article’ can be either definite or indefinite. An article modifies a noun/pronoun without specifying any description of the object. In English, an example of a ‘definite article’ is the , whereas examples of two ‘indefinite articles’ are a and an .
Here, the refers to specific things or things that are identified beforehand. A or a refer to non-specific things that have not been identified beforehand.
Demonstratives
A ‘Demonstrative’ is defined as a demonstrative adjective/pronoun based on its usage in the sentence. Some examples of demonstratives are ‘this’, ‘that’, and ‘those’ .
A determiner has the same rules of use as in the case of adjectives in sentence formation. Thus, confusion takes place when carefully choosing the type of parts of speech to assign when given a choice of either a determiner or adjective.
An ‘Adverb’ defines essential information about the verb, similar to what an adjective is to a noun. It provides a descriptor for a verb used in a sentence and some cases, can also describe an adjective or another adverb.
Some adverbs used in sentences with verbs are ‘slowly’, ‘hastily’, ‘unfortunately’, and ‘angrily’.
Adverbs are further sub-classified into various types based on their application in a sentence.
- Adverbs of Time (to inform about the occurrence of a verb), For example, ‘now’, ‘tomorrow’, and ‘soon’.
- Adverbs of Manner (to describe the action of a verb), For example, ‘hastily’, ‘slowly’, and ‘minutely’.
- Adverbs of Place (to indicate the place of action of the verb),
- Adverbs of Frequency (to describe the frequency of a verb action),
- Adverbs of Degree (to describe the intensity of an action),
- Conjunctive Adverbs (are used to link/act as a conjunction to two sentences).
A ‘Pronoun’ is a word used in specifically providing an alternate name for a non/noun phrase. They are alternate words for referring to an object/individual when the requirement of a noun is unnecessary, as the noun has been mentioned previously in some parts of the sentence.
Some examples of pronouns are ‘it’, ‘he/she’, and ‘himself/herself’.
Pronouns are sub-classified into different categories based on their use in the sentence.
Some of these sub-categories are:
- Relative Pronouns (to relate a part of a sentence with the other)
- Possessive Pronouns (to show possessiveness)
- Reflexive Pronouns (to refer back to the subject of discussion)
- Demonstrative Pronouns (to refer to specific objects/individuals)
- Interrogative Pronouns (to ask questions)
- Indefinite Pronouns (to avoid reference to any specific object/individual/place)
- Personal Pronouns (to use as substitutes for proper names)
- Subject Pronouns (to assign acting on an object)
- Object Pronouns (to assign receiving action towards an object)
- Reciprocal Pronouns (to express two-way/mutual relationship)
- Preposition
A ‘Preposition’ is a word used as a connective between a noun, a noun phrase, or a pronoun with another word.
Prepositions are used in sentence formations to convey these meanings:
- To show the direction towards/of something/someone
- To refer to the period of an action taking place
- To specify the location/position of an object
- To present the space and time relationship between objects
Based on their use and function, prepositions are classified into four subtypes:
- Prepositions of Time (to indicate the happening of an action/event)
- Preposition of Place (to indicate the location of an object)
- Preposition of Direction (to indicate the direction/orientation of an object)
- Prepositions of Spatial Relationship (to indicate an object moving away/towards a source)
- Conjunction
A ‘Conjunction’ is a word that combines two/more objects and behaves as connectives in a sentence. These can appear in the beginning/middle/end of the sentence following the location of the objects.
There are three types of conjunctions used in sentence formation:
- Coordinate conjunction (to combine two independent clauses )
- Subordinate conjunction (to combine an independent with a dependent clause)
- Correlation conjunction (to combine two phrases having equal weightage)
Interjection
An ‘Interjection’ is a word to convey the expression of a variety of emotions/feelings. As such, there is no specific rule for the use of interjection and where it is to be placed.
However, in most cases, it is placed at the beginning of the sentence. For example, some of the most commonly used interjections are ‘ouch’, ‘phew’, and ‘well’.
| Noun | The howled. |
| Pronoun | It woke the baby. |
| Verb | The loving mother the child. |
| Adjective | The father rocked the baby. |
| Adverb | The dog howled |
| Preposition | The baby cried a long time. |
| Conjunction | The baby gazed at his mother father. |
| Interjection | , the baby fell back asleep. |
Parts of speech examples
Here are some examples of the parts of speech used in sentences. Note the placement and its relation with other parts of speech present in the sentence format.
- John is cutting a pipe.
- John intends to come to the office this Monday .
- Jogging regularly is good for health.
- Drinking and driving put other motorists in danger.
- Would you want to wear a suit?
- I love to sing in between classes.
See another example in the image below.
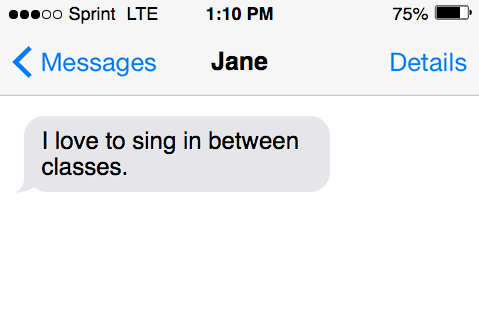
- Juno ran towards the classroom.
- The janitor requested the students to clear their lockers.
- The monkey was caged after being sedated.
- I gifted my brother a phone .
- Why did you purchase the book ?
- I misplaced the manuscript .
- Do you want to eat some ice cream ?
- Mum loved my new car .
- Daniel gifted his brother a Porsche.

- I purchased a blue suit for the reception.
- Mary purchased two oranges from the fruit seller.
- The curry is tasty .
- Juno’s brother is arrogant .
- The documentary that premiered on television was fascinating .
- Giovanni Giorgio is a great music composer.
- My house is currently under lease.
- This novel is lengthy.
- I purchased some fruits and vegetables.
- She sent me an expensive watch.
- Velma loved the dress gifted by her parents.
- Joyce and Jill watched a movie together.
- Grandma gave us materials to prepare the dessert.

- Typically , we visit Mom on Mondays.
- Don’t you taste the coffee to be too bitter?
- Do not be nervous. You will eventually get the hang of it.
- The movie I watched was very scientific.
- It is scorching hot inside the workshop.
- Can I visit the office today ?
- His aunt will be staying at the apartment for a while .
- He is the man I was referring to.
- I found my missing luggage outside the airport.

- I won’t be coming to the office in the afternoon.
- He arranged the cutlery on the table.
- Bhaskar made the dog hide under its bed.
- I enjoy strolling by the lake in the mornings.
- James and I trekked to the hilltop today.
- I stayed back home because I felt uneasy.
- He did not enjoy the yogurt , yet he finished it.

- Interjection
- Hurray! We got the funding.
- Ouch! That wound looks severe.
- Wow! You look great in the wedding gown.
- Oh my God ! I hope he is safe.
See an example in the image below.
Words with more than one job
Many parts of speech can have more than one function/job in the sentence. This improves the versatility of the words being used and makes the use more situational in its placement and conveyance of meaning.
- Myers can shift for herself (Preposition)
- Give prayers to the Almighty; for He is the one above all (Conjunction)
- We require more women to have the same vigor. (Adjective)
- More of the women died in the operating room than in the cabin. (Pronoun)
- Agatha needs to shut the gossiping and work more (Adverb)
To see how all the objects work together, see the table below.
| She | likes | big | but | I | hate | them |
Here is a chart showing the parts of speech:
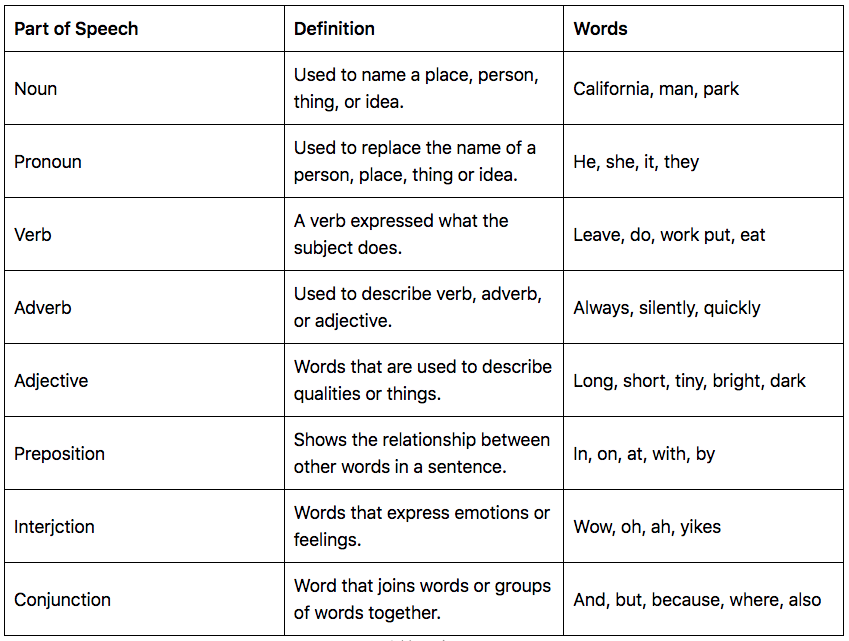
How to identify parts of speech
In sentence formation, it often becomes difficult to ascertain the parts of speech represented by each word. To help out and to make the process of identification easier, follow these steps:
- Identify any word which names an object/individual/place in a generalized form as a noun .
- To identify a specific noun, use pronouns .
- Any words which describe/identify actions/performance are verbs .
- Any word that modifies or gives a greater definition to nouns is an adjective.
- Any word that modifies or gives meaning to the actions of verbs, are adverbs.
- It is easy to pick out prepositions as they describe relationships between a noun/pronoun with other nouns/pronouns.
- Any joiner used to join two clauses is a conjunction .
- Exclamations generally follow any interjections in the text.

- Parts of speech
More parts of speech:
- Conjunctions
- Prepositions
- Possessive nouns
- Irregular plural nouns
- Proper nouns
- Concrete nouns
- Collective nouns
- Possessive and plural nouns
- Verbs: The Definitive Guide
- Nouns | Explore Definition, Examples & Types with Examples
- What Are Pronouns? Definitions and Examples
- What Are Adverbs? (with Examples)
- Interjections – Explore Meaning, Definition, Usage and Examples
- What Is A Conjunction? Types & Examples
- The 9 Parts of Speech: Definitions and Examples
- What Is a Determiner?
- The 8 Parts of Speech: Examples and Rules
- Adverbs – What is It? Explore the Meaning, Definition, Types, Usage and Examples
Inside this article
Fact checked: Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.

About the author
Dalia Y.: Dalia is an English Major and linguistics expert with an additional degree in Psychology. Dalia has featured articles on Forbes, Inc, Fast Company, Grammarly, and many more. She covers English, ESL, and all things grammar on GrammarBrain.
Core lessons
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Active Sentence
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Body Paragraph
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- Equivocation Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Gerund Phrase
- Genitive Case
- Helping Verb
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Intensifier
- Indicative Mood
- Juxtaposition
- Linking Verb
- Misplaced Modifier
- Nominative Case
- Noun Adjective
- Object Pronoun
- Object Complement
- Order of Adjectives
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Quotation Marks
- Relative Pronoun
- Reflexive Pronoun
- Reciprocal Pronoun
- Subordinating Conjunction
- Simple Future Tense
- Stative Verb
- Subjunctive
- Subject Complement
- Subject of a Sentence
- Sentence Variety
- Second Conditional
- Superlative Adjective
- Slash Symbol
- Topic Sentence
- Types of Nouns
- Types of Sentences
- Uncountable Noun
- Vowels and Consonants
Popular lessons

Stay awhile. Your weekly dose of grammar and English fun.

The world's best online resource for learning English. Understand words, phrases, slang terms, and all other variations of the English language.
- Abbreviations
- Editorial Policy

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
Understanding the 8 Parts of Speech: Definitions and Examples
General Education
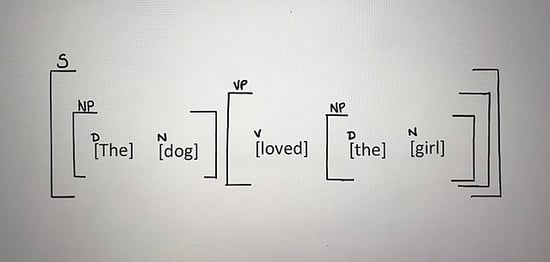
If you’re trying to learn the grammatical rules of English, you’ve probably been asked to learn the parts of speech. But what are parts of speech and how many are there? How do you know which words are classified in each part of speech?
The answers to these questions can be a bit complicated—English is a difficult language to learn and understand. Don’t fret, though! We’re going to answer each of these questions for you with a full guide to the parts of speech that explains the following:
- What the parts of speech are, including a comprehensive parts of speech list
- Parts of speech definitions for the individual parts of speech. (If you’re looking for information on a specific part of speech, you can search for it by pressing Command + F, then typing in the part of speech you’re interested in.)
- Parts of speech examples
- A ten question quiz covering parts of speech definitions and parts of speech examples
We’ve got a lot to cover, so let’s begin!
Feature Image: (Gavina S / Wikimedia Commons)

What Are Parts of Speech?
The parts of speech definitions in English can vary, but here’s a widely accepted one: a part of speech is a category of words that serve a similar grammatical purpose in sentences.
To make that definition even simpler, a part of speech is just a category for similar types of words . All of the types of words included under a single part of speech function in similar ways when they’re used properly in sentences.
In the English language, it’s commonly accepted that there are 8 parts of speech: nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, conjunctions, interjections, and prepositions. Each of these categories plays a different role in communicating meaning in the English language. Each of the eight parts of speech—which we might also call the “main classes” of speech—also have subclasses. In other words, we can think of each of the eight parts of speech as being general categories for different types within their part of speech . There are different types of nouns, different types of verbs, different types of adjectives, adverbs, pronouns...you get the idea.
And that’s an overview of what a part of speech is! Next, we’ll explain each of the 8 parts of speech—definitions and examples included for each category.

There are tons of nouns in this picture. Can you find them all?
Nouns are a class of words that refer, generally, to people and living creatures, objects, events, ideas, states of being, places, and actions. You’ve probably heard English nouns referred to as “persons, places, or things.” That definition is a little simplistic, though—while nouns do include people, places, and things, “things” is kind of a vague term. I t’s important to recognize that “things” can include physical things—like objects or belongings—and nonphysical, abstract things—like ideas, states of existence, and actions.
Since there are many different types of nouns, we’ll include several examples of nouns used in a sentence while we break down the subclasses of nouns next!
Subclasses of Nouns, Including Examples
As an open class of words, the category of “nouns” has a lot of subclasses. The most common and important subclasses of nouns are common nouns, proper nouns, concrete nouns, abstract nouns, collective nouns, and count and mass nouns. Let’s break down each of these subclasses!
Common Nouns and Proper Nouns
Common nouns are generic nouns—they don’t name specific items. They refer to people (the man, the woman), living creatures (cat, bird), objects (pen, computer, car), events (party, work), ideas (culture, freedom), states of being (beauty, integrity), and places (home, neighborhood, country) in a general way.
Proper nouns are sort of the counterpart to common nouns. Proper nouns refer to specific people, places, events, or ideas. Names are the most obvious example of proper nouns, like in these two examples:
Common noun: What state are you from?
Proper noun: I’m from Arizona .
Whereas “state” is a common noun, Arizona is a proper noun since it refers to a specific state. Whereas “the election” is a common noun, “Election Day” is a proper noun. Another way to pick out proper nouns: the first letter is often capitalized. If you’d capitalize the word in a sentence, it’s almost always a proper noun.
Concrete Nouns and Abstract Nouns
Concrete nouns are nouns that can be identified through the five senses. Concrete nouns include people, living creatures, objects, and places, since these things can be sensed in the physical world. In contrast to concrete nouns, abstract nouns are nouns that identify ideas, qualities, concepts, experiences, or states of being. Abstract nouns cannot be detected by the five senses. Here’s an example of concrete and abstract nouns used in a sentence:
Concrete noun: Could you please fix the weedeater and mow the lawn ?
Abstract noun: Aliyah was delighted to have the freedom to enjoy the art show in peace .
See the difference? A weedeater and the lawn are physical objects or things, and freedom and peace are not physical objects, though they’re “things” people experience! Despite those differences, they all count as nouns.
Collective Nouns, Count Nouns, and Mass Nouns
Nouns are often categorized based on number and amount. Collective nouns are nouns that refer to a group of something—often groups of people or a type of animal. Team , crowd , and herd are all examples of collective nouns.
Count nouns are nouns that can appear in the singular or plural form, can be modified by numbers, and can be described by quantifying determiners (e.g. many, most, more, several). For example, “bug” is a count noun. It can occur in singular form if you say, “There is a bug in the kitchen,” but it can also occur in the plural form if you say, “There are many bugs in the kitchen.” (In the case of the latter, you’d call an exterminator...which is an example of a common noun!) Any noun that can accurately occur in one of these singular or plural forms is a count noun.
Mass nouns are another type of noun that involve numbers and amount. Mass nouns are nouns that usually can’t be pluralized, counted, or quantified and still make sense grammatically. “Charisma” is an example of a mass noun (and an abstract noun!). For example, you could say, “They’ve got charisma, ” which doesn’t imply a specific amount. You couldn’t say, “They’ve got six charismas, ” or, “They’ve got several charismas .” It just doesn’t make sense!

Verbs are all about action...just like these runners.
A verb is a part of speech that, when used in a sentence, communicates an action, an occurrence, or a state of being . In sentences, verbs are the most important part of the predicate, which explains or describes what the subject of the sentence is doing or how they are being. And, guess what? All sentences contain verbs!
There are many words in the English language that are classified as verbs. A few common verbs include the words run, sing, cook, talk, and clean. These words are all verbs because they communicate an action performed by a living being. We’ll look at more specific examples of verbs as we discuss the subclasses of verbs next!
Subclasses of Verbs, Including Examples
Like nouns, verbs have several subclasses. The subclasses of verbs include copular or linking verbs, intransitive verbs, transitive verbs, and ditransitive or double transitive verbs. Let’s dive into these subclasses of verbs!
Copular or Linking Verbs
Copular verbs, or linking verbs, are verbs that link a subject with its complement in a sentence. The most familiar linking verb is probably be. Here’s a list of other common copular verbs in English: act, be, become, feel, grow, seem, smell, and taste.
So how do copular verbs work? Well, in a sentence, if we said, “Michi is ,” and left it at that, it wouldn’t make any sense. “Michi,” the subject, needs to be connected to a complement by the copular verb “is.” Instead, we could say, “Michi is leaving.” In that instance, is links the subject of the sentence to its complement.
Transitive Verbs, Intransitive Verbs, and Ditransitive Verbs
Transitive verbs are verbs that affect or act upon an object. When unattached to an object in a sentence, a transitive verb does not make sense. Here’s an example of a transitive verb attached to (and appearing before) an object in a sentence:
Please take the clothes to the dry cleaners.
In this example, “take” is a transitive verb because it requires an object—”the clothes”—to make sense. “The clothes” are the objects being taken. “Please take” wouldn’t make sense by itself, would it? That’s because the transitive verb “take,” like all transitive verbs, transfers its action onto another being or object.
Conversely, intransitive verbs don’t require an object to act upon in order to make sense in a sentence. These verbs make sense all on their own! For instance, “They ran ,” “We arrived ,” and, “The car stopped ” are all examples of sentences that contain intransitive verbs.
Finally, ditransitive verbs, or double transitive verbs, are a bit more complicated. Ditransitive verbs are verbs that are followed by two objects in a sentence . One of the objects has the action of the ditransitive verb done to it, and the other object has the action of the ditransitive verb directed towards it. Here’s an example of what that means in a sentence:
I cooked Nathan a meal.
In this example, “cooked” is a ditransitive verb because it modifies two objects: Nathan and meal . The meal has the action of “cooked” done to it, and “Nathan” has the action of the verb directed towards him.

Adjectives are descriptors that help us better understand a sentence. A common adjective type is color.
#3: Adjectives
Here’s the simplest definition of adjectives: adjectives are words that describe other words . Specifically, adjectives modify nouns and noun phrases. In sentences, adjectives appear before nouns and pronouns (they have to appear before the words they describe!).
Adjectives give more detail to nouns and pronouns by describing how a noun looks, smells, tastes, sounds, or feels, or its state of being or existence. . For example, you could say, “The girl rode her bike.” That sentence doesn’t have any adjectives in it, but you could add an adjective before both of the nouns in the sentence—”girl” and “bike”—to give more detail to the sentence. It might read like this: “The young girl rode her red bike.” You can pick out adjectives in a sentence by asking the following questions:
- Which one?
- What kind?
- How many?
- Whose’s?
We’ll look at more examples of adjectives as we explore the subclasses of adjectives next!
Subclasses of Adjectives, Including Examples
Subclasses of adjectives include adjective phrases, comparative adjectives, superlative adjectives, and determiners (which include articles, possessive adjectives, and demonstratives).
Adjective Phrases
An adjective phrase is a group of words that describe a noun or noun phrase in a sentence. Adjective phrases can appear before the noun or noun phrase in a sentence, like in this example:
The extremely fragile vase somehow did not break during the move.
In this case, extremely fragile describes the vase. On the other hand, adjective phrases can appear after the noun or noun phrase in a sentence as well:
The museum was somewhat boring.
Again, the phrase somewhat boring describes the museum. The takeaway is this: adjective phrases describe the subject of a sentence with greater detail than an individual adjective.
Comparative Adjectives and Superlative Adjectives
Comparative adjectives are used in sentences where two nouns are compared. They function to compare the differences between the two nouns that they modify. In sentences, comparative adjectives often appear in this pattern and typically end with -er. If we were to describe how comparative adjectives function as a formula, it might look something like this:
Noun (subject) + verb + comparative adjective + than + noun (object).
Here’s an example of how a comparative adjective would work in that type of sentence:
The horse was faster than the dog.
The adjective faster compares the speed of the horse to the speed of the dog. Other common comparative adjectives include words that compare distance ( higher, lower, farther ), age ( younger, older ), size and dimensions ( bigger, smaller, wider, taller, shorter ), and quality or feeling ( better, cleaner, happier, angrier ).
Superlative adjectives are adjectives that describe the extremes of a quality that applies to a subject being compared to a group of objects . Put more simply, superlative adjectives help show how extreme something is. In sentences, superlative adjectives usually appear in this structure and end in -est :
Noun (subject) + verb + the + superlative adjective + noun (object).
Here’s an example of a superlative adjective that appears in that type of sentence:
Their story was the funniest story.
In this example, the subject— story —is being compared to a group of objects—other stories. The superlative adjective “funniest” implies that this particular story is the funniest out of all the stories ever, period. Other common superlative adjectives are best, worst, craziest, and happiest... though there are many more than that!
It’s also important to know that you can often omit the object from the end of the sentence when using superlative adjectives, like this: “Their story was the funniest.” We still know that “their story” is being compared to other stories without the object at the end of the sentence.
Determiners
The last subclass of adjectives we want to look at are determiners. Determiners are words that determine what kind of reference a noun or noun phrase makes. These words are placed in front of nouns to make it clear what the noun is referring to. Determiners are an example of a part of speech subclass that contains a lot of subclasses of its own. Here is a list of the different types of determiners:
- Definite article: the
- Indefinite articles : a, an
- Demonstratives: this, that, these, those
- Pronouns and possessive determiners: my, your, his, her, its, our, their
- Quantifiers : a little, a few, many, much, most, some, any, enough
- Numbers: one, twenty, fifty
- Distributives: all, both, half, either, neither, each, every
- Difference words : other, another
- Pre-determiners: such, what, rather, quite
Here are some examples of how determiners can be used in sentences:
Definite article: Get in the car.
Demonstrative: Could you hand me that magazine?
Possessive determiner: Please put away your clothes.
Distributive: He ate all of the pie.
Though some of the words above might not seem descriptive, they actually do describe the specificity and definiteness, relationship, and quantity or amount of a noun or noun phrase. For example, the definite article “the” (a type of determiner) indicates that a noun refers to a specific thing or entity. The indefinite article “an,” on the other hand, indicates that a noun refers to a nonspecific entity.
One quick note, since English is always more complicated than it seems: while articles are most commonly classified as adjectives, they can also function as adverbs in specific situations, too. Not only that, some people are taught that determiners are their own part of speech...which means that some people are taught there are 9 parts of speech instead of 8!
It can be a little confusing, which is why we have a whole article explaining how articles function as a part of speech to help clear things up .

Adverbs can be used to answer questions like "when?" and "how long?"
Adverbs are words that modify verbs, adjectives (including determiners), clauses, prepositions, and sentences. Adverbs typically answer the questions how?, in what way?, when?, where?, and to what extent? In answering these questions, adverbs function to express frequency, degree, manner, time, place, and level of certainty . Adverbs can answer these questions in the form of single words, or in the form of adverbial phrases or adverbial clauses.
Adverbs are commonly known for being words that end in -ly, but there’s actually a bit more to adverbs than that, which we’ll dive into while we look at the subclasses of adverbs!
Subclasses Of Adverbs, Including Examples
There are many types of adverbs, but the main subclasses we’ll look at are conjunctive adverbs, and adverbs of place, time, manner, degree, and frequency.
Conjunctive Adverbs
Conjunctive adverbs look like coordinating conjunctions (which we’ll talk about later!), but they are actually their own category: conjunctive adverbs are words that connect independent clauses into a single sentence . These adverbs appear after a semicolon and before a comma in sentences, like in these two examples:
She was exhausted; nevertheless , she went for a five mile run.
They didn’t call; instead , they texted.
Though conjunctive adverbs are frequently used to create shorter sentences using a semicolon and comma, they can also appear at the beginning of sentences, like this:
He chopped the vegetables. Meanwhile, I boiled the pasta.
One thing to keep in mind is that conjunctive adverbs come with a comma. When you use them, be sure to include a comma afterward!
There are a lot of conjunctive adverbs, but some common ones include also, anyway, besides, finally, further, however, indeed, instead, meanwhile, nevertheless, next, nonetheless, now, otherwise, similarly, then, therefore, and thus.
Adverbs of Place, Time, Manner, Degree, and Frequency
There are also adverbs of place, time, manner, degree, and frequency. Each of these types of adverbs express a different kind of meaning.
Adverbs of place express where an action is done or where an event occurs. These are used after the verb, direct object, or at the end of a sentence. A sentence like “She walked outside to watch the sunset” uses outside as an adverb of place.
Adverbs of time explain when something happens. These adverbs are used at the beginning or at the end of sentences. In a sentence like “The game should be over soon,” soon functions as an adverb of time.
Adverbs of manner describe the way in which something is done or how something happens. These are the adverbs that usually end in the familiar -ly. If we were to write “She quickly finished her homework,” quickly is an adverb of manner.
Adverbs of degree tell us the extent to which something happens or occurs. If we were to say “The play was quite interesting,” quite tells us the extent of how interesting the play was. Thus, quite is an adverb of degree.
Finally, adverbs of frequency express how often something happens . In a sentence like “They never know what to do with themselves,” never is an adverb of frequency.
Five subclasses of adverbs is a lot, so we’ve organized the words that fall under each category in a nifty table for you here:
It’s important to know about these subclasses of adverbs because many of them don’t follow the old adage that adverbs end in -ly.
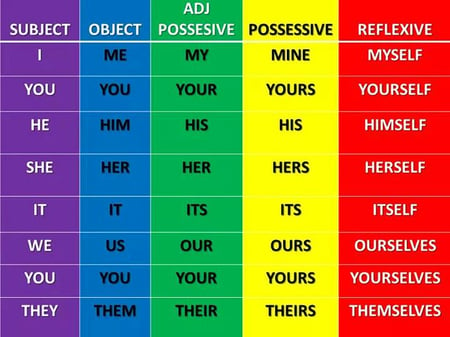
Here's a helpful list of pronouns. (Attanata / Flickr )
#5: Pronouns
Pronouns are words that can be substituted for a noun or noun phrase in a sentence . Pronouns function to make sentences less clunky by allowing people to avoid repeating nouns over and over. For example, if you were telling someone a story about your friend Destiny, you wouldn’t keep repeating their name over and over again every time you referred to them. Instead, you’d use a pronoun—like they or them—to refer to Destiny throughout the story.
Pronouns are typically short words, often only two or three letters long. The most familiar pronouns in the English language are they, she, and he. But these aren’t the only pronouns. There are many more pronouns in English that fall under different subclasses!
Subclasses of Pronouns, Including Examples
There are many subclasses of pronouns, but the most commonly used subclasses are personal pronouns, possessive pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, indefinite pronouns, and interrogative pronouns.
Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns are probably the most familiar type of pronoun. Personal pronouns include I, me, you, she, her, him, he, we, us, they, and them. These are called personal pronouns because they refer to a person! Personal pronouns can replace specific nouns in sentences, like a person’s name, or refer to specific groups of people, like in these examples:
Did you see Gia pole vault at the track meet? Her form was incredible!
The Cycling Club is meeting up at six. They said they would be at the park.
In both of the examples above, a pronoun stands in for a proper noun to avoid repetitiveness. Her replaces Gia in the first example, and they replaces the Cycling Club in the second example.
(It’s also worth noting that personal pronouns are one of the easiest ways to determine what point of view a writer is using.)
Possessive Pronouns
Possessive pronouns are used to indicate that something belongs to or is the possession of someone. The possessive pronouns fall into two categories: limiting and absolute. In a sentence, absolute possessive pronouns can be substituted for the thing that belongs to a person, and limiting pronouns cannot.
The limiting pronouns are my, your, its, his, her, our, their, and whose, and the absolute pronouns are mine, yours, his, hers, ours, and theirs . Here are examples of a limiting possessive pronoun and absolute possessive pronoun used in a sentence:
Limiting possessive pronoun: Juan is fixing his car.
In the example above, the car belongs to Juan, and his is the limiting possessive pronoun that shows the car belongs to Juan. Now, here’s an example of an absolute pronoun in a sentence:
Absolute possessive pronoun: Did you buy your tickets ? We already bought ours .
In this example, the tickets belong to whoever we is, and in the second sentence, ours is the absolute possessive pronoun standing in for the thing that “we” possess—the tickets.
Demonstrative Pronouns, Interrogative Pronouns, and Indefinite Pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns include the words that, this, these, and those. These pronouns stand in for a noun or noun phrase that has already been mentioned in a sentence or conversation. This and these are typically used to refer to objects or entities that are nearby distance-wise, and that and those usually refer to objects or entities that are farther away. Here’s an example of a demonstrative pronoun used in a sentence:
The books are stacked up in the garage. Can you put those away?
The books have already been mentioned, and those is the demonstrative pronoun that stands in to refer to them in the second sentence above. The use of those indicates that the books aren’t nearby—they’re out in the garage. Here’s another example:
Do you need shoes? Here...you can borrow these.
In this sentence, these refers to the noun shoes. Using the word these tells readers that the shoes are nearby...maybe even on the speaker’s feet!
Indefinite pronouns are used when it isn’t necessary to identify a specific person or thing . The indefinite pronouns are one, other, none, some, anybody, everybody, and no one. Here’s one example of an indefinite pronoun used in a sentence:
Promise you can keep a secret?
Of course. I won’t tell anyone.
In this example, the person speaking in the second two sentences isn’t referring to any particular people who they won’t tell the secret to. They’re saying that, in general, they won’t tell anyone . That doesn’t specify a specific number, type, or category of people who they won’t tell the secret to, which is what makes the pronoun indefinite.
Finally, interrogative pronouns are used in questions, and these pronouns include who, what, which, and whose. These pronouns are simply used to gather information about specific nouns—persons, places, and ideas. Let’s look at two examples of interrogative pronouns used in sentences:
Do you remember which glass was mine?
What time are they arriving?
In the first glass, the speaker wants to know more about which glass belongs to whom. In the second sentence, the speaker is asking for more clarity about a specific time.

Conjunctions hook phrases and clauses together so they fit like pieces of a puzzle.
#6: Conjunctions
Conjunctions are words that are used to connect words, phrases, clauses, and sentences in the English language. This function allows conjunctions to connect actions, ideas, and thoughts as well. Conjunctions are also used to make lists within sentences. (Conjunctions are also probably the most famous part of speech, since they were immortalized in the famous “Conjunction Junction” song from Schoolhouse Rock .)
You’re probably familiar with and, but, and or as conjunctions, but let’s look into some subclasses of conjunctions so you can learn about the array of conjunctions that are out there!
Subclasses of Conjunctions, Including Examples
Coordinating conjunctions, subordinating conjunctions, and correlative conjunctions are three subclasses of conjunctions. Each of these types of conjunctions functions in a different way in sentences!
Coordinating Conjunctions
Coordinating conjunctions are probably the most familiar type of conjunction. These conjunctions include the words for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so (people often recommend using the acronym FANBOYS to remember the seven coordinating conjunctions!).
Coordinating conjunctions are responsible for connecting two independent clauses in sentences, but can also be used to connect two words in a sentence. Here are two examples of coordinating conjunctions that connect two independent clauses in a sentence:
He wanted to go to the movies, but he couldn’t find his car keys.
They put on sunscreen, and they went to the beach.
Next, here are two examples of coordinating conjunctions that connect two words:
Would you like to cook or order in for dinner?
The storm was loud yet refreshing.
The two examples above show that coordinating conjunctions can connect different types of words as well. In the first example, the coordinating conjunction “or” connects two verbs; in the second example, the coordinating conjunction “yet” connects two adjectives.
But wait! Why does the first set of sentences have commas while the second set of sentences doesn’t? When using a coordinating conjunction, put a comma before the conjunction when it’s connecting two complete sentences . Otherwise, there’s no comma necessary.
Subordinating Conjunctions
Subordinating conjunctions are used to link an independent clause to a dependent clause in a sentence. This type of conjunction always appears at the beginning of a dependent clause, which means that subordinating conjunctions can appear at the beginning of a sentence or in the middle of a sentence following an independent clause. (If you’re unsure about what independent and dependent clauses are, be sure to check out our guide to compound sentences.)
Here is an example of a subordinating conjunction that appears at the beginning of a sentence:
Because we were hungry, we ordered way too much food.
Now, here’s an example of a subordinating conjunction that appears in the middle of a sentence, following an independent clause and a comma:
Rakim was scared after the power went out.
See? In the example above, the subordinating conjunction after connects the independent clause Rakim was scared to the dependent clause after the power went out. Subordinating conjunctions include (but are not limited to!) the following words: after, as, because, before, even though, one, since, unless, until, whenever, and while.
Correlative Conjunctions
Finally, correlative conjunctions are conjunctions that come in pairs, like both/and, either/or, and neither/nor. The two correlative conjunctions that come in a pair must appear in different parts of a sentence to make sense— they correlate the meaning in one part of the sentence with the meaning in another part of the sentence . Makes sense, right?
Here are two examples of correlative conjunctions used in a sentence:
We’re either going to the Farmer’s Market or the Natural Grocer’s for our shopping today.
They’re going to have to get dog treats for both Piper and Fudge.
Other pairs of correlative conjunctions include as many/as, not/but, not only/but also, rather/than, such/that, and whether/or.

Interjections are single words that express emotions that end in an exclamation point. Cool!
#7: Interjections
Interjections are words that often appear at the beginning of sentences or between sentences to express emotions or sentiments such as excitement, surprise, joy, disgust, anger, or even pain. Commonly used interjections include wow!, yikes!, ouch!, or ugh! One clue that an interjection is being used is when an exclamation point appears after a single word (but interjections don’t have to be followed by an exclamation point). And, since interjections usually express emotion or feeling, they’re often referred to as being exclamatory. Wow!
Interjections don’t come together with other parts of speech to form bigger grammatical units, like phrases or clauses. There also aren’t strict rules about where interjections should appear in relation to other sentences . While it’s common for interjections to appear before sentences that describe an action or event that the interjection helps explain, interjections can appear after sentences that contain the action they’re describing as well.
Subclasses of Interjections, Including Examples
There are two main subclasses of interjections: primary interjections and secondary interjections. Let’s take a look at these two types of interjections!
Primary Interjections
Primary interjections are single words, like oh!, wow!, or ouch! that don’t enter into the actual structure of a sentence but add to the meaning of a sentence. Here’s an example of how a primary interjection can be used before a sentence to add to the meaning of the sentence that follows it:
Ouch ! I just burned myself on that pan!
While someone who hears, I just burned myself on that pan might assume that the person who said that is now in pain, the interjection Ouch! makes it clear that burning oneself on the pan definitely was painful.
Secondary Interjections
Secondary interjections are words that have other meanings but have evolved to be used like interjections in the English language and are often exclamatory. Secondary interjections can be mixed with greetings, oaths, or swear words. In many cases, the use of secondary interjections negates the original meaning of the word that is being used as an interjection. Let’s look at a couple of examples of secondary interjections here:
Well , look what the cat dragged in!
Heck, I’d help if I could, but I’ve got to get to work.
You probably know that the words well and heck weren’t originally used as interjections in the English language. Well originally meant that something was done in a good or satisfactory way, or that a person was in good health. Over time and through repeated usage, it’s come to be used as a way to express emotion, such as surprise, anger, relief, or resignation, like in the example above.

This is a handy list of common prepositional phrases. (attanatta / Flickr)
#8: Prepositions
The last part of speech we’re going to define is the preposition. Prepositions are words that are used to connect other words in a sentence—typically nouns and verbs—and show the relationship between those words. Prepositions convey concepts such as comparison, position, place, direction, movement, time, possession, and how an action is completed.
Subclasses of Prepositions, Including Examples
The subclasses of prepositions are simple prepositions, double prepositions, participle prepositions, and prepositional phrases.
Simple Prepositions
Simple prepositions appear before and between nouns, adjectives, or adverbs in sentences to convey relationships between people, living creatures, things, or places . Here are a couple of examples of simple prepositions used in sentences:
I’ll order more ink before we run out.
Your phone was beside your wallet.
In the first example, the preposition before appears between the noun ink and the personal pronoun we to convey a relationship. In the second example, the preposition beside appears between the verb was and the possessive pronoun your.
In both examples, though, the prepositions help us understand how elements in the sentence are related to one another. In the first sentence, we know that the speaker currently has ink but needs more before it’s gone. In the second sentence, the preposition beside helps us understand how the wallet and the phone are positioned relative to one another!
Double Prepositions
Double prepositions are exactly what they sound like: two prepositions joined together into one unit to connect phrases, nouns, and pronouns with other words in a sentence. Common examples of double prepositions include outside of, because of, according to, next to, across from, and on top of. Here is an example of a double preposition in a sentence:
I thought you were sitting across from me.
You see? Across and from both function as prepositions individually. When combined together in a sentence, they create a double preposition. (Also note that the prepositions help us understand how two people— you and I— are positioned with one another through spacial relationship.)
Prepositional Phrases
Finally, prepositional phrases are groups of words that include a preposition and a noun or pronoun. Typically, the noun or pronoun that appears after the preposition in a prepositional phrase is called the object of the preposition. The object always appears at the end of the prepositional phrase. Additionally, prepositional phrases never include a verb or a subject. Here are two examples of prepositional phrases:
The cat sat under the chair .
In the example above, “under” is the preposition, and “the chair” is the noun, which functions as the object of the preposition. Here’s one more example:
We walked through the overgrown field .
Now, this example demonstrates one more thing you need to know about prepositional phrases: they can include an adjective before the object. In this example, “through” is the preposition, and “field” is the object. “Overgrown” is an adjective that modifies “the field,” and it’s quite common for adjectives to appear in prepositional phrases like the one above.
While that might sound confusing, don’t worry: the key is identifying the preposition in the first place! Once you can find the preposition, you can start looking at the words around it to see if it forms a compound preposition, a double preposition of a prepositional phrase.

10 Question Quiz: Test Your Knowledge of Parts of Speech Definitions and Examples
Since we’ve covered a lot of material about the 8 parts of speech with examples ( a lot of them!), we want to give you an opportunity to review and see what you’ve learned! While it might seem easier to just use a parts of speech finder instead of learning all this stuff, our parts of speech quiz can help you continue building your knowledge of the 8 parts of speech and master each one.
Are you ready? Here we go:
1) What are the 8 parts of speech?
a) Noun, article, adverb, antecedent, verb, adjective, conjunction, interjection b) Noun, pronoun, verb, adverb, determiner, clause, adjective, preposition c) Noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, conjunction, interjection, preposition
2) Which parts of speech have subclasses?
a) Nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs b) Nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, conjunctions, and prepositions c) All of them! There are many types of words within each part of speech.
3) What is the difference between common nouns and proper nouns?
a) Common nouns don’t refer to specific people, places, or entities, but proper nouns do refer to specific people, places, or entities. b) Common nouns refer to regular, everyday people, places, or entities, but proper nouns refer to famous people, places, or entities. c) Common nouns refer to physical entities, like people, places, and objects, but proper nouns refer to nonphysical entities, like feelings, ideas, and experiences.
4) In which of the following sentences is the emboldened word a verb?
a) He was frightened by the horror film . b) He adjusted his expectations after the first plan fell through. c) She walked briskly to get there on time.
5) Which of the following is a correct definition of adjectives, and what other part of speech do adjectives modify?
a) Adjectives are describing words, and they modify nouns and noun phrases. b) Adjectives are describing words, and they modify verbs and adverbs. c) Adjectives are describing words, and they modify nouns, verbs, and adverbs.
6) Which of the following describes the function of adverbs in sentences?
a) Adverbs express frequency, degree, manner, time, place, and level of certainty. b) Adverbs express an action performed by a subject. c) Adverbs describe nouns and noun phrases.
7) Which of the following answers contains a list of personal pronouns?
a) This, that, these, those b) I, you, me, we, he, she, him, her, they, them c) Who, what, which, whose
8) Where do interjections typically appear in a sentence?
a) Interjections can appear at the beginning of or in between sentences. b) Interjections appear at the end of sentences. c) Interjections appear in prepositional phrases.
9) Which of the following sentences contains a prepositional phrase?
a) The dog happily wagged his tail. b) The cow jumped over the moon. c) She glared, angry that he forgot the flowers.
10) Which of the following is an accurate definition of a “part of speech”?
a) A category of words that serve a similar grammatical purpose in sentences. b) A category of words that are of similar length and spelling. c) A category of words that mean the same thing.
So, how did you do? If you got 1C, 2C, 3A, 4B, 5A, 6A, 7B, 8A, 9B, and 10A, you came out on top! There’s a lot to remember where the parts of speech are concerned, and if you’re looking for more practice like our quiz, try looking around for parts of speech games or parts of speech worksheets online!

What’s Next?
You might be brushing up on your grammar so you can ace the verbal portions of the SAT or ACT. Be sure you check out our guides to the grammar you need to know before you tackle those tests! Here’s our expert guide to the grammar rules you need to know for the SAT , and this article teaches you the 14 grammar rules you’ll definitely see on the ACT.
When you have a good handle on parts of speech, it can make writing essays tons easier. Learn how knowing parts of speech can help you get a perfect 12 on the ACT Essay (or an 8/8/8 on the SAT Essay ).
While we’re on the topic of grammar: keep in mind that knowing grammar rules is only part of the battle when it comes to the verbal and written portions of the SAT and ACT. Having a good vocabulary is also important to making the perfect score ! Here are 262 vocabulary words you need to know before you tackle your standardized tests.
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!

What Are The 8 Parts of Speech? Definitions and Examples

Speaking and writing in any language involves using different parts of speech. Understanding what these parts are and how to use them correctly is important for effective communication. In English, there are 8 parts of speech, which include nouns, pronouns , verbs, adjectives , adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. In this article, we will explore each of these parts of speech in detail, along with their definitions and examples. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of the role and importance of the 8 parts of speech in English.
Content Guide
What Are Parts of Speech?
Parts of speech, also known as word classes, are categories that describe the role a word plays in a sentence. These categories help us understand how words work within sentences and how they relate to one another. In essence, parts of speech are a set of general rules that help us to form sentences that are clear, logical, and expressive. There are a total of 8 parts of speech in the English language, and each has its own set of rules.
The 8 Parts of Speech
The 8 parts of speech are:
Prepositions
- Conjunctions
- Interjections
Parts of Speech Chart
The following chart lists the 8 parts of speech—along with brief descriptions and examples.
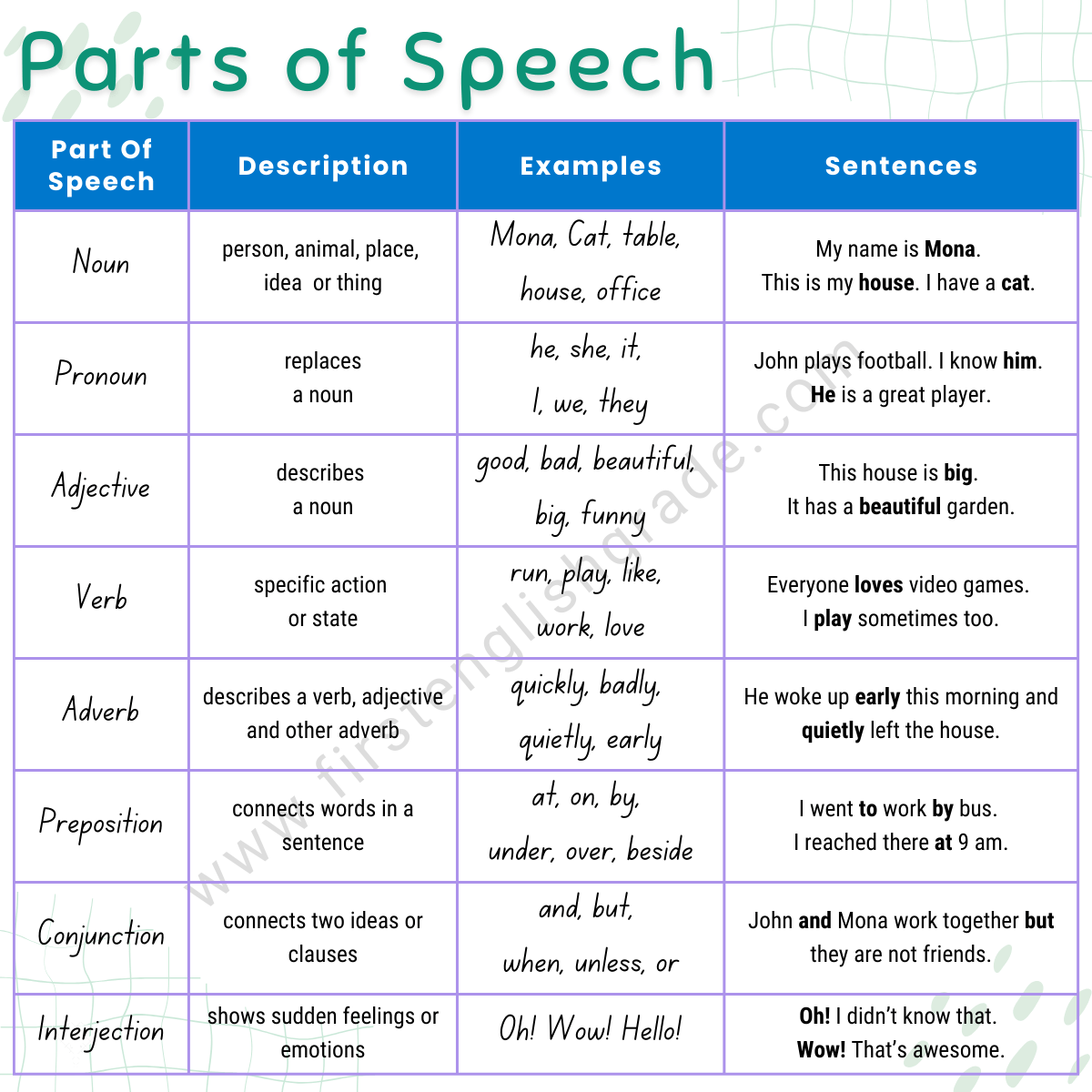
It’s time to explore them in detail. So, let’s go ahead and learn the 8 parts of speech with definitions and examples.
A noun is a word that refers to a person, animal, place, idea, or thing. For example, John, cat, dog, table, house, office, etc. In English, nouns come in many different forms, including proper nouns, which are names that refer to people or places; descriptive nouns, which describe things; and common nouns, which are words that are used to refer to a wide range of things.
Common nouns are often used to refer to everyday objects, such as “chair,” “table,” and “door.” Other common nouns are used to refer to abstract concepts, such as “love,” “hate,” and “peace.” Nouns can also be singular, plural, and neuter. A singular noun refers to one person or thing, while a plural noun refers to more than one person or thing. A neuter noun is used to refer to something that isn’t either a person or a thing.
Let’s see some examples of nouns in sentences:
Person- Her name is Amy . Place – This park is so crowded. Thing- You never sit on this chair . Animal – They have a dog .
Pronouns are words we use to replace nouns in sentences that refer to people, animals, objects, or places. Pronouns help us avoid repeating nouns while we speak or write. Words such as he, she, it, I, you, we, they, them, etc. are pronouns.
Let’s consider this paragraph without using pronouns:
Amy always wakes up early in the morning. Amy goes to the office and comes back in the afternoon. In the evening, Amy cooks dinner. After having dinner Amy goes to bed. This is Amy’s daily routine.
Did you find it a bit repetitive?
Now, when we replace the noun with pronouns, the paragraph becomes more engaging:
Amy always wakes up early in the morning. She goes to the office and comes back in the afternoon. She cooks dinner in the evening. And, after dinner, she goes to bed. This is her routine.
In this case, ‘She’ and ‘her’ are the pronouns we used instead of repeatedly mentioning Amy’s name.
Adjectives are words used to describe the person, place, or thing a noun refers to. Adjectives are often used to add extra information about a noun. It can be used to describe a person’s age, gender, or personality. Adjectives are also used to describe the quality of a noun, such as its size, shape, or color. Some examples of adjectives are tall, short, good, bad, beautiful, large, funny, sad, etc.
Let’s see some examples of adjectives in sentences:
You look beautiful in this dress. It’s pleasant weather today. He is a kind person. She looks sad today. The movie we watched yesterday was engaging .
A verb is a word that describes specific actions, or an action that is being performed. They are also called action verbs. However, not all verbs are action verbs. There are also non-action verbs that denote feelings or state of being. So, a verb can be either an action verb or a state verb. Action verbs are words such as “walk,” “run,” and “jump.” State verbs are words such as “be,” “look,” “love,” and “feel.”
Examples of verbs in sentences:
We play video games every day. They run very fast. I love pizza. He jumped off the bridge. She hates horror movies.
Adverbs describe or provide more information about verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs. They are often used to describe the way something is done, how something is done, or how something feels. Moreover, adverbs can highlight distinctions between things or actions. For instance, we use words such as “slowly” or “carefully” to describe the way something is done. We often use words such as “well” or “badly” to describe how something is done.
Some examples of adverbs are always, quickly, badly, quietly, early, slowly, etc.
He runs faster than me. Can you finish your work early ? She was badly injured while playing. Can you do it silently ? She was walking slowly towards me.
Prepositions are words that connect words in a sentence. Prepositions can be used to describe the location of something, as well as the time and manner in which something is done. The most common prepositions are: at, on, by, under, over, beside, before, after, behind, above, below, in, out, with, and without. Prepositions can also be used to indicate the relationship between two things (for example, beside means “next to”).
Prepositions are one of the most important parts of speech that you must learn to use correctly. They can make your writing clear and make your sentences more interesting.
Examples of prepositions in sentences:
My books are on the table. He leaves for home at 8 p.m. You can sit beside me. They came here after me. I travel by public transport.
Conjunction
A conjunction is a word or phrase that connects two ideas or clauses. For example, consider these sentences: “I like sports. I like music.” These are two separate sentences, but you can connect them using the conjunction “and” to say, “ I like sports and music. ” Conjunctions help make our sentences flow smoothly by joining related thoughts or actions.
There are many different types of conjunctions. Some examples of common conjunctions are: and, but, when, unless, or, nor, for, yet, although, but not, because, not only, etc.
Examples of conjunction in sentences:
I cannot go to work today because my mother is sick. My dad used to ride horses when he was young. You are likely to fail unless you work hard.
Interjection
Interjections are words that show sudden feelings or emotions such as joy, surprise, or shock. We usually use the exclamation mark (!) with interjection words.
Some examples of interjections are:
Oh! Wow! Hello! Ouch! Bravo!
Examples of interjections in sentences:
Oh! I forgot the keys. Wow! It looks great. Hello! Is anybody there?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about “Parts of Speech”
1. what are the parts of speech in english.
English has eight primary parts of speech: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, conjunctions, prepositions, and interjections.
2. Why is it important to understand parts of speech?
Understanding parts of speech is crucial for effective communication and writing. It helps you structure sentences correctly, convey your thoughts clearly, and avoid grammatical errors.
3. How can I identify the parts of speech in a sentence?
You can identify parts of speech by understanding their functions and looking for clues within the sentence. Nouns name things, verbs show actions, adjectives describe nouns, and so on. Context and practice are essential tools for identification.
4. Can words change their part of speech in different sentences?
Yes, some words can function as different parts of speech depending on their usage and context. For example, “work” can be a noun (“I have a lot of work to do”) or a verb (“I need to work hard”).
5. What’s the difference between adjectives and adverbs?
Adjectives describe nouns and answer questions like “What kind?” or “Which one?” (e.g., “red car”). Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, addressing questions like “How?” “When?” “Where?” or “To what extent?” (e.g., “She sings beautifully”).
6. How do conjunctions function in sentences?
Conjunctions connect words, phrases, or clauses to form more complex sentences. Common conjunctions are “and,” “but,” “or,” “so,” and “because.”
7. What’s the role of prepositions in sentences?
Prepositions establish connections between nouns or pronouns and other words in a sentence, indicating aspects like location, direction, time, or manner. Examples of prepositions include “in,” “on,” “under,” “with,” and “between.”
8. When should interjections be used in communication?
Interjections are used to express strong emotions or sudden exclamations. They add emotional depth to your speech or writing. For instance, “Wow, that’s amazing!” or “Ouch, that hurts!”
9. Are there any online tools to help identify parts of speech in sentences?
Yes, there are many online grammar-checking tools and apps that can analyze and label the parts of speech in a sentence. They can be useful for practice and verification.
10. How can I improve my understanding of parts of speech?
Improving your understanding of parts of speech requires practice. Analyze sentences from books, articles, or conversations. Engage in grammar exercises and quizzes. Reading widely and regularly can also help reinforce your knowledge.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Parts of Speech Overview

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A noun is a word that denotes a person, place, or thing. In a sentence, nouns answer the questions who and what.
In the sentence above, there are two nouns, dog and ball . A noun may be concrete (something you can touch, see, etc.), like the nouns in the example above, or a noun may be abstract, as in the sentences below.
The abstract concepts of integrity and love in the sentences above are both nouns. Nouns may also be proper.
Chicago , Thanksgiving , and November are all proper nouns, and they should be capitalized. (For more information on proper nouns and when to capitalize words, see our handout on Capital Letters .)
You may also visit our handout on Count and Noncount Nouns .
Learn how to spot verbs that act as nouns. Visit our handout on Verbals: Gerunds, Participles, and Infinitives .
A pronoun is a word that takes the place of a noun in a sentence.
In the sentence above, she is the pronoun. Like nouns, pronouns may be used either as subjects or as objects in a sentence.
In the example above, both she and him are pronouns; she is the subject of the sentence while him is the object. Every subject pronoun has a corresponding object form, as shown in the table below.
| I | Me |
| We | Us |
| You | You |
| She | Her |
| He | Him |
| It | It |
| They | Them |
For more information on pronouns, go to our handout on Pronouns .
To find out what part of speech are that , which , and whom ? Visit our handout on Relative Pronouns .
Articles include a , an , and the . They precede a noun or a noun phrase in a sentence.
In example 1, the article a precedes the noun house , and a also precedes the noun phrase big porch , which consists of an adjective (big) and the noun it describes (porch). In example 2, the article the precedes the noun phrase blue sweater , in which sweater is the noun and blue, the adjective.
For more information, go to our handouts on Articles: A vs. An and How to Use Articles (a/an/the) .
An adjective is a word that modifies, or describes, a noun or pronoun. Adjectives may precede nouns, or they may appear after a form of the reflexive verb to be (am, are, is, was, etc.).
In example 1, two consecutive adjectives, red and brick , both describe the noun house. In example 2, the adjective tall appears after the reflexive verb is and describes the subject, she .
For more on adjectives, go to our handouts Adjective or Adverb and How to Use Adjectives and Adverbs .
A verb is a word that denotes action, or a state of being, in a sentence.
In example 1, rides is the verb; it describes what the subject, Beth, does. In example 2, was describes Paul’s state of being and is therefore the verb.
There may be multiple verbs in a sentence, or there may be a verb phrase consisting of a verb plus a helping verb.
In example 1, the subject she performs two actions in the sentence, turned and opened . In example 2, the verb phrase is was studying .
Some words in a sentence may look like verbs but act as something else, like a noun; these are called verbals. For more information on verbs that masquerade as other parts of speech, go to our handout on Verbals: Gerunds, Participles, and Infinitives .
To learn more about conjugating verbs, visit our handouts on Verb Tenses , Irregular Verbs , and Two-Part (Phrasal) Verbs (Idioms) .
Just as adjectives modify nouns, adverbs modify, or further describe, verbs. Adverbs may also modify adjectives. (Many, though not all, adverbs end in - ly .)
In the first example, the adverb wildly modifies the verb waved . In the second example, the adverb extremely modifies the adjective bright , which describes the noun shirt . While nouns answer the questions who and what , adverbs answer the questions how , when , why , and where .
For a more detailed discussion of adverbs, visit our handout Adjective or Adverb and become an expert.
Conjunctions
A conjunction is a word that joins two independent clauses, or sentences, together.
In the examples above, both but and so are conjunctions. They join two complete sentences with the help of a comma. And, but, for, or, nor, so, and yet can all act as conjunctions.
Prepositions
Prepositions work in combination with a noun or pronoun to create phrases that modify verbs, nouns/pronouns, or adjectives. Prepositional phrases convey a spatial, temporal, or directional meaning.
There are two prepositional phrases in the example above: up the brick wall and of the house . The first prepositional phrase is an adverbial phrase, since it modifies the verb by describing where the ivy climbed. The second phrase further modifies the noun wall (the object of the first prepositional phrase) and describes which wall the ivy climbs.
For a more detailed discussion on this part of speech and its functions, click on Prepositions .
Below is a list of prepositions in the English language:
Aboard, about, above, across, after, against, along, amid, among, around, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, between, beyond, by, down, during, except, for, from, in, into, like, near, of, off, on, onto, out, over, past, since, through, throughout, to, toward, under, underneath, until, unto, up, upon, with, within, without.

Introduction to grammar
Parts of Speech
The parts of speech explain how a word is used in a sentence.
There are eight main parts of speech (also known as word classes): nouns, pronouns, adjectives, verbs, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections .
Most parts of speech can be divided into sub-classes. Prepositions can be divided into prepositions of time, prepositions of place etc. Nouns can be divided into proper nouns, common nouns, concrete nouns etc.
It is important to know that a word can sometimes be in more than one part of speech. For example with the word increase .
Increase can be a verb e.g. Prices increased and increase can also be a noun e.g. There was an increase in the number of followers.
A list of parts of speech in English grammar include the following:
A verb is used to show an action or a state of being
go, write, exist, be
A noun is a word used to refer to people, animals, objects, substances, states, events, ideas and feelings. A noun functions as a subject or object of a verb and can be modified by an adjective.
John, lion, table, freedom, love ...
3. Adjective
Adjectives are used to describe or specify a noun or pronoun
good, beautiful, nice, my ...
An adverb is used to modify a verb, adjective and other adverbs.
completely, never, there ...
A pronoun is used in the place of a noun or phrase.
I, you, he, she, it ...
6. Preposition
Prepositions are used before nouns to form a phrase that shows where, when, how and why
in, above, to, for, at ...
7. Conjunction
Conjunctions join clauses or sentences or words
and, but, when ...
8. Interjection
Interjections are used to show surprise or emotion.
oh!, Good Lord
Examples of parts of speech
Here are some examples of parts of speech: My ( adjective ) friend ( noun ) speaks ( verb ) English ( noun ) fluently ( adverb ). Oh! ( interjection ) I ( pronoun ) went ( verb ) to ( preposition ) school ( noun ) and ( conjunction ) I ( pronoun ) met ( verb ) Fred ( noun ).
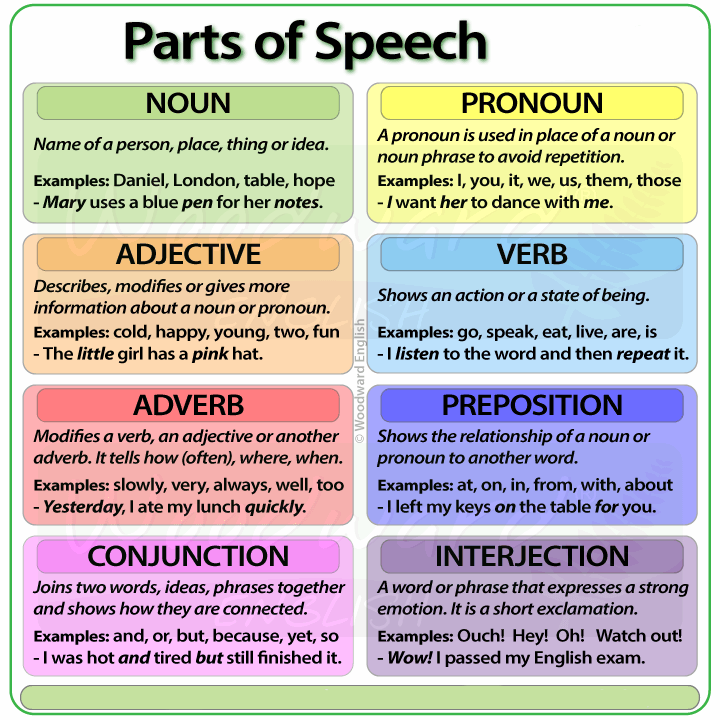
Course Curriculum
- Basic English Grammar Components 20 mins
- Auxiliary Verbs 30 mins
- Articles 20 mins
- Parts of Speech 20 mins

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn how to classify words into eight parts of speech based on their roles in sentences. Find out the definitions, categories, and examples of nouns, pronouns, adjectives, verbs, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and articles.
Learn how to identify and use the eight parts of speech in English: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. See charts, definitions, and examples for each part of speech.
Learn the names and functions of the nine main word classes in English grammar, such as nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs. See how to identify and use them in sentences with examples and practice exercises.
Learn the nine parts of speech in English with definitions, examples, and video lessons. Find out how to classify words according to their functions in sentences and why determiners are different from adjectives.
Learn what parts of speech are and how to identify them in English sentences. Find out the definitions, examples and functions of nouns, pronouns, verbs, adverbs, adjectives, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections.
Learn what a part of speech is and how to identify the eight traditional parts of speech in English grammar: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, conjunction, preposition, and interjection. Explore the subcategories and examples of each part of speech and how they function in sentences.
Learn the eight parts of speech in English and how to use them correctly in your writing. This guide covers the basics of verbs, nouns, pronouns, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections.
Learn what parts of speech are and how to categorize words into eight or nine groups based on their function and features. See examples of nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections.
Learn how to categorize English words into 9 basic types called "parts of speech" or "word classes". See examples, tables, quizzes and games to practice and test your knowledge.
Learn the definitions, examples, and roles of nouns, verbs, pronouns, adjectives, adverbs, and other parts of speech in English. Find out how to identify and use them in simple and complex sentences with a picture, a video, and a quiz.
Learn how to identify and use the eight parts of speech in English: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. See examples, types, and functions of each part of speech.
Learn the definition and examples of noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection. Find out how to use the dictionary and identify the parts of speech in sentences.
Learn the eight parts of speech in English and how to use them correctly in sentences. Find examples, definitions, and tips for nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections.
Learn the 9 basic parts of speech in English and how to identify them in sentences. See the functions, categories, and types of nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, conjunctions, prepositions, determiners, and interjections.
Learn the definitions and examples of nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Find out how some words are productive or nonproductive classes of parts of speech.
Learn the definition and function of nouns, adjectives, adverbs, verbs, prepositions, pronouns, conjunctions, and interjections. See examples of each part of speech and how they modify or join words in sentences.
Learn what parts of speech are and how they affect sentence structure in English. Explore the nine categories of parts of speech with definitions, examples, and video lessons.
Learn the definition and usage of nouns, verbs, adjectives, pronouns, adverbs, conjunctions, prepositions, and interjections. See how they modify, describe, or connect words and sentences in English.
Learn the 8 parts of speech in English with comprehensive definitions and examples. Find out how to identify nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, conjunctions, interjections, and prepositions in sentences.
Learn the 8 parts of speech in English, which are nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. See how they are used in sentences and how they describe the role and function of words in a sentence.
Learn the definitions and functions of nouns, pronouns, articles, adjectives, verbs, adverbs, conjunctions, and prepositions. See examples, tables, and links to related handouts on Purdue OWL.
Learn about the categories of words (or lexical items) that have similar grammatical properties in different languages. Compare the traditional and modern classifications of parts of speech, such as noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, preposition, conjunction, interjection, numeral, article, and determiner.
Learn the eight main parts of speech (nouns, pronouns, adjectives, verbs, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections) and their sub-classes. See examples of how to use words in different parts of speech in sentences.