

100 Words and Phrases to use in an Essay
Thomas Babb
Writing a compelling essay involves much more than simply putting your thoughts on paper. It demands the use of a precise vocabulary that not only enriches your content but also structures it in a way that is both logical and engaging. The right words and phrases can transform your essay from a basic assignment to an insightful and persuasive piece of writing.
This guide introduces you to 100 essential words and phrases recommended by expert English tutors that will help you convey your ideas more effectively. From adding information to expressing contrasts, and from illustrating examples to summarising your points, these carefully selected terms will enhance the clarity and impact of your essays.
Adding Information
When crafting an essay, integrating additional details effectively can enrich the written content and present a well-rounded argument. Here's how you can use each phrase under this category:
1. Furthermore - Use this to add weight to a point already mentioned, providing further evidence without redundancy.
2. Moreover - Similar to "furthermore," it introduces information that not only adds to the argument but enhances it.
3. Similarly - This indicates that the upcoming point shares notable characteristics with the previous one, aiding in drawing parallels.
4. Additionally - Introduces extra information or arguments that augment the current discussion.
5. Also - A simpler form of "additionally" that integrates extra facts smoothly.
6. Likewise - Indicates similarity and supports points by showing how they relate to each other in terms of qualities or actions.
7. In addition - This phrase is useful for contributing additional supportive details in a clear manner.
8. As well as - Functions to include another subject or item into your discussion without diverging from the main topic.
9. Not only... but also - A powerful structure for emphasizing not just one, but two important points, enhancing the depth of the argument.
10. Alongside - Implies that the information being added runs parallel to the already established facts, reinforcing them.
These phrases, when used correctly, help to build a strong, cohesive narrative flow in your essays, guiding the reader through a logical progression of ideas. For more on enhancing your writing with effective information addition, explore resources like Oxford Royale's Essay Writing Tips .
📈Boost your grades with our revision platform, used by 100,000+ students! 📝Access thousands of practice questions, study notes, and past papers for every subject. 📚 View IB Resources 📚 View A-Level Resources 📚 View GCSE Resources 📚 View IGCSE Resources
Introducing Examples
Introducing concrete examples is crucial in illustrating and supporting your claims effectively in an essay. Here’s how to use each word or phrase linked to this category:
11. For instance - Introduces a specific example that illuminates a broader point, helping to clarify complex ideas.
12. For example - Functions similarly to "for instance," offering a direct illustration to support or demonstrate a claim.
13. Such as - Prepares the reader for an example that is part of a larger category, typically used to list items or concepts.
14. Like - Introduces comparisons or examples in a casual and relatable manner.
15. Particularly - Highlights an example that is especially relevant to the argument, focusing attention on significant details.
16. In particular - Similar to "particularly," but often used to introduce a standout example that underscores a critical point.
17. Including - Serves to add examples to a list that may already be understood to be part of the topic being discussed.
18. Namely - Specifies and introduces exact and often multiple examples or details directly related to the point.
19. Chiefly - Points to the most important or significant examples or reasons in support of an argument.
20. Mainly - Indicates that the examples provided are the primary ones to consider, focusing on the most relevant instances.
Effective use of these phrases not only clarifies your points but also strengthens your arguments by making abstract concepts tangible. For detailed guidance on how to incorporate examples effectively in your essays, refer to academic resources like Harvard College Writing Center .
Demonstrating Contrast
IB English tutors suggest that Using contrast effectively in your essays can highlight differences that clarify your points or show alternative perspectives. Here’s how to use each phrase to demonstrate contrast:
21. Conversely - Signals a stark contrast to what has just been discussed, often introducing an opposing viewpoint.
22. However - A versatile tool to introduce a contradiction or counterpoint, breaking from the previous line of reasoning.
23. Nevertheless - Indicates persistence of a stated fact or opinion despite the contrasting information that follows.
24. On the other hand - Used to present a different perspective or an alternative to the argument previously mentioned.
25. Although - Begins a sentence where the main clause contrasts with the lesser significant, conditional clause.
26. Even though - Similar to "although," but often emphasizes a stronger degree of contrast between the conflicting elements.
27. But - A simple and direct way to introduce a contradiction to the preceding statement.
28. Yet - Suggests a contrast that is surprising or unexpected based on the previous statements.
29. Instead - Introduces an alternative action or thought in response to what has been previously discussed.
30. Rather - Used to correct or propose a different idea from what was initially stated or understood.
These phrases are essential for essays where comparing and contrasting ideas, arguments, or perspectives is necessary to deepen understanding or enhance the argument’s complexity. To learn more about using contrast in writing, visit educational resources such as Purdue Online Writing Lab .
Showing Cause and Effect
A-Level English tutors point out that effectively indicating cause and effect relationships in your essays helps clarify the reasons things happen and the consequences that follow. Here’s how to use each word or phrase to illustrate these relationships:
31. Consequently - Signals a direct result from the action or situation mentioned, highlighting the effect or outcome.
32. Therefore - Used to introduce a logical conclusion or result that follows from the reasoning presented earlier.
33. Thus - Indicates a conclusion or result that is a natural consequence of the facts previously mentioned.
34. Hence - Similar to "thus," it conveys a consequence that is a logical extension from the argument or data presented.
35. Accordingly - Shows that an action or decision is a logical response to the circumstances or facts discussed.
36. As a result - Directly points out the outcome or effect resulting from a specific cause or set of conditions.
37. This leads to - Introduces a sequence where one event or fact causes another, often used to chain multiple effects.
38. It follows that - Used when deducing a conclusion that logically arises from the preceding argument or evidence.
39. Leading to - Connects an initial action or decision directly with its consequences, highlighting a progression of events.
40. Contributing to - Indicates that the action or event adds to a situation, leading to a particular result or effect.
Mastering the use of these phrases can enhance the persuasive power of your writing by clearly linking actions and their consequences.
Adding Emphasis
Effectively emphasising key points in your essays can make your arguments more compelling and memorable. Here’s how to appropriately use each word or phrase to add emphasis:
41. Significantly - Indicates that something is of great importance or consequence, drawing the reader's attention to the gravity of the point being made.
42. Importantly - Prioritises the following information as crucial for understanding the argument or situation.
43. Indeed - Reinforces the truth of a statement, often used to confirm and agree with a previously mentioned point that might be surprising or emphatic.
44. Absolutely - A strong affirmation that leaves no doubt about the veracity or importance of the statement.
45. Definitely - Communicates certainty about a fact or opinion, strengthening the author's stance.
46. Certainly - Similar to "definitely," it expresses a high degree of assurance about the information being provided.
47. Undoubtedly - Suggests that there is no doubt about the statement, reinforcing its truth and relevance.
48. Without a doubt - A more emphatic form of "undoubtedly," eliminating any ambiguity about the point’s validity.
49. Particularly - Highlights specific information as especially significant within a broader context.
50. Especially - Used to indicate that something holds more significance than other elements, often emphasizing exceptional cases or instances.
Using these expressions strategically can enhance the persuasive impact of your writing by underscoring the most critical elements of your argument. To see more words and further explore techniques for adding emphasis in academic writing, visit resources like Cambridge Dictionary Blog .
Explaining and Clarifying
In academic essays, clearly explaining and clarifying complex ideas is essential for effective communication. IGCSE tutors and GCSE tutors suggest that each of these phrases can be used to enhance understanding:
51. That is to say - Used to introduce a rephrasing or elaboration on something that has just been stated.
52. In other words - Helps clarify a statement by expressing it in different terms for better understanding.
53. To put it another way - Similar to "in other words," it offers an alternative explanation or perspective to ensure clarity.
54. To clarify - Directly states the intent to make something clearer or to resolve any misunderstandings.
55. To explain - Introduces a detailed explanation aimed at enhancing understanding of a complex issue or point.
56. This means that - Connects a statement or idea to its implications or necessary interpretations.
57. This implies - Suggests a deeper, often unspoken consequence or meaning behind the given information.
58. Put simply - Introduces a simpler or more straightforward version of what has been discussed, making it more accessible.
59. In simpler terms - Another phrase to ease comprehension by breaking down complex concepts into basic language.
60. Thus - Concludes an explanation by summarizing the logical result or conclusion derived from the argument made.
Using these phrases effectively can help articulate intricate arguments in a more digestible format, aiding the reader’s understanding and engagement.
Summarising and Concluding
Expert IB tutors and A-Level tutors recommend that effectively summarising and concluding your essays is crucial for reinforcing your main points and providing a satisfying closure to any persuasive essay. Here’s how to use each word or phrase to effectively wrap up your discussions:
61. In conclusion - Signals the beginning of the final summary, clearly stating that the argument is drawing to a close.
62. To sum up - Introduces a concise summary of the key points discussed, often used before the final conclusion.
63. Ultimately - Indicates a final, overarching conclusion derived from the arguments and evidence presented.
64. Finally - Marks the introduction of the last point or an additional important point that concludes the discussion.
65. Lastly - Similar to "finally," it is used to introduce the final argument or point in the list.
66. To conclude - Directly states the intent to wrap up the essay, leading into a summary of the main findings.
67. In summary - Offers a recap of the essential elements discussed, reinforcing the thesis without introducing new information.
68. All things considered - Provides an overall conclusion, taking into account all the points made throughout the essay.
69. In the final analysis - Suggests a thorough consideration of all aspects discussed, leading to a concluding viewpoint.
70. After all - Implies that the conclusion takes into account all arguments and evidences previously presented.
Mastering the use of these concluding phrases ensures that your essay ends on a strong note, summarising key points and reinforcing your argument.
Discussing Similarities
Highlighting similarities effectively can enhance your argument by showing connections and parallels between ideas or topics. Here’s how to use each phrase to discuss similarities in your essays:
71. Similarly - Indicates that what follows is in alignment with the previous statement, reinforcing the connection between two points.
72. Likewise - Also used to show agreement or similarity, it confirms that the upcoming point supports the previous one in terms of characteristics or outcomes.
73. Just as - Introduces a comparison, suggesting that the situation or argument is equivalent to another.
74. As with - Used before mentioning another example, indicating that it shares properties or conditions with what has been discussed.
75. Equally - Implies that two or more elements are on the same level in terms of importance, quality, or characteristics.
76. Analogous to - Introduces a more formal comparison, indicating that one situation is comparable to another, often used in more scientific or technical discussions.
77. Comparable to - Suggests that two things can be likened to each other, providing a basis for comparison.
78. In the same way - Confirms that the action, process, or idea mirrors another, reinforcing the similarity.
79. Just like - A more casual phrase used to draw a direct comparison, making the similarity clear and understandable.
80. Similarly important - Asserts that the importance or relevance of two or more aspects is equal, emphasising their comparative significance.
Utilising these phrases allows you to effectively link concepts and arguments, showing how they complement or mirror each other, which can strengthen your overall thesis. For further reading on comparing and contrasting ideas effectively, the University of North Carolina Writing Center offers excellent resources.
Providing Alternatives
Offering alternatives in your essays can demonstrate critical thinking by showing different possibilities or approaches. Here’s how to use each word or phrase to introduce alternative ideas:
81. Alternatively - Introduces a different option or suggestion, providing another route or perspective.
82. On the contrary - Used to present a direct opposition to the previously mentioned idea, emphasising a contrasting point.
83. Rather - Suggests a preference for one choice over another, typically used to propose a different approach or opinion.
84. Conversely - Indicates a reversal of what has been previously stated, introducing an opposing viewpoint.
85. Instead - Specifies a substitute or replacement, clearly stating that one option is to be considered in place of another.
86. On the flip side - Introduces a contrasting scenario or viewpoint in a more informal manner, often used in conversational or less formal writing.
87. Rather than - Presents a comparison between two choices, highlighting a preference for one over the other.
88. As an alternative - Explicitly states the introduction of a different option or method, providing variety to the discussion.
89. Either...or - Sets up a choice between two distinct options, forcing a decision that impacts the argument’s direction.
90. Neither...nor - Used to deny two possibilities simultaneously, often restructuring the argument by excluding common options.
Incorporating these phrases allows you to explore and present multiple facets of an issue, enriching the essay’s depth and persuasiveness. For tips on effectively presenting alternative arguments, visit Harvard College Writing Center .
Expressing Conditions
Effectively expressing conditions in your essays can help outline scenarios where certain outcomes or arguments hold true. Here’s how to use each word or phrase to specify conditions:
91. If - Introduces a conditional statement, setting up a scenario where a specific result depends on a preceding condition.
92. Unless - Specifies an exception to a general rule or statement, indicating that a condition will change the outcome if not met.
93. Provided that - Sets a stipulation or requirement for a scenario to occur, emphasizing that certain conditions must be satisfied.
94. Assuming that - Suggests a hypothesis or a precondition that needs to be accepted before proceeding with an argument or conclusion.
95. In case - Prepares for a situation that might occur, setting up precautions or actions based on potential scenarios.
96. Even if - Acknowledges that even under certain circumstances, the primary argument or conclusion still holds.
97. Only if - Restricts the conditions under which a statement or outcome is valid, narrowing down the scenarios to very specific ones.
98. Whether - Presents alternatives, usually offering a choice between possibilities within the condition stated.
99. As long as - Indicates that a condition is contingent upon the duration or continuation of a specified situation.
100. Given that - Introduces a premise as a fact, assuming its truth for the sake of argument or to advance the discussion.
Final Thoughts
In crafting compelling essays, the strategic use of specific words and phrases can significantly enhance both the clarity and persuasiveness of your writing. By mastering the use of these 100 essential terms, students can effectively structure their essays, convey complex ideas, and articulate contrasts and comparisons with precision. Each category of phrases serves a unique purpose, from adding information to providing alternatives, which empowers writers to construct well-rounded arguments and engage their readers more deeply.
As you continue to refine your essay-writing skills, remember that the power of your arguments often lies in the details—the precise words and phrases you choose to express your thoughts. The power of a well crafted essay introduction and precise essay conclusion should also not be overlooked. By integrating these tools into your writing repertoire, you are better equipped to present clear, persuasive, and engaging essays that stand out in academic settings.
How can I improve my essay planning process?
Effective essay planning begins with a clear understanding of the essay question. Break down the question to identify key terms and the required response. Create an outline to organise your main points and supporting arguments logically. Consider using a mind map to visually plot connections between ideas, which can spur creative thinking. Allocate time for research, writing, and revision within your plan. Practising essay plans for different questions can enhance your ability to organise thoughts quickly and efficiently, a crucial skill especially under exam conditions.
What makes an essay introduction effective?
An effective introduction grabs the reader's attention, sets the tone, and provides a clear thesis statement. Start with a hook such as a provocative question, a startling statistic, or a compelling quote. Provide some background information to set the context, ensuring it's directly relevant to the essay's question. The thesis statement should be concise and outline your main argument or response to the question. This setup not only intrigues but also informs the reader about the essay's focus, establishing your understanding and control of the subject.
How do I choose the best evidence for my essay?
The best evidence is relevant, credible, and supports your thesis directly. Use primary sources where possible as they provide first-hand accounts that you can analyse directly. When primary sources are not available, rely on peer-reviewed journals and reputable publications. Diversify your sources to avoid over-reliance on a single type of evidence, and critically evaluate sources for bias and reliability. Properly integrating this evidence into your argument involves summarising, paraphrasing, and quoting sources while always linking back to your main argument.
How can I make my essay arguments more persuasive?
To make your arguments more persuasive, begin with a clear, assertive thesis statement. Structure your essay so each paragraph introduces a single point supporting your thesis. Use credible evidence and explain how this supports your argument. Address potential counterarguments to show the depth of your understanding and strengthen your position by demonstrating why your approach is preferable. Employing a confident but respectful tone and precise language also enhances the persuasiveness of your essay.
What are common pitfalls in essay writing to avoid?
Common pitfalls in essay writing include poor structure, weak thesis statements, and lack of coherence. Avoiding these starts with a robust plan and clear outline. Stay on topic by linking each paragraph back to your thesis statement. Avoid plagiarism by properly citing all sources. Overly complex sentence structures can confuse readers, so strive for clarity and conciseness. Finally, neglecting proofreading can leave typographical and grammatical errors, which diminish the quality of your work, so always review your essay thoroughly.
How do I manage time when writing an essay under exam conditions?
Time management in exams is crucial. Allocate about 10% of your time for planning, 80% for writing, and 10% for revising. Quickly outline your main points to structure your essay from the start. Write your body paragraphs first, as these contain the bulk of marks, then your introduction and conclusion. Keep an eye on the clock and pace yourself to ensure you have enough time to adequately develop your arguments and conclude effectively.
What are the best practices for editing and proofreading essays?
After writing your essay, take a break before you start editing to give you a fresh perspective. Read your essay aloud to catch awkward phrasing and sentences that don't flow logically. Check for consistency in tense and point of view throughout the essay. Use spell-check tools, but do not rely on them solely—manually check for homophones and commonly confused words. Consider having someone else read your work to catch errors you might have overlooked and to provide feedback on the clarity of your arguments.
How can I develop a strong thesis statement?
A strong thesis statement is clear, concise, and specific. It should express one main idea that is debatable, meaning there is potential for argument. Reflect on the essay prompt and decide on your position regarding the topic. Your thesis should guide the reader through your arguments and indicate the rationale behind your viewpoint. It serves as the backbone of your essay, so ensure it is robust and directly linked to the question asked.
How do I handle counterarguments in my essays?
Handling counterarguments effectively involves acknowledging them and then refuting them with stronger evidence or reasoning. Present them fairly and objectively, then use logical, fact-based arguments to demonstrate why your position remains valid. This not only shows critical thinking but also strengthens your original argument by showing you have considered multiple perspectives.
What is the role of a conclusion in an essay?
The conclusion of an essay should effectively summarise the main arguments discussed while reaffirming the thesis statement. It should synthesise the information presented rather than introducing new ideas. Provide a final perspective on the topic or suggest implications, further research or practical applications to leave the reader with something to ponder. A strong conclusion can reinforce your argument and leave a lasting impression on the reader.
How can I ensure my essay flows logically?
To ensure logical flow, each paragraph should seamlessly connect to the next with clear transitions. Focus on structuring paragraphs around one main idea that supports your thesis. Use transitional words and phrases to show the relationship between paragraphs. Consistency in your argumentation style and maintaining a clear focus throughout the essay will help keep your writing coherent.
What techniques help maintain reader interest throughout an essay?
To maintain reader interest, start with a strong hook in your introduction and use engaging content like relevant anecdotes, striking statistics, or interesting quotes throughout your essay. Vary your sentence structure and use active voice to keep the narrative dynamic. Also, ensure your topic is relevant and your arguments are presented with passion and clarity.
How can I integrate quotes effectively in essays?
To integrate quotes effectively, introduce the quote with a sentence that sets up its relevance to your argument, then follow the quote with analysis or interpretation that ties it back to your main point. Do not rely heavily on quotes to make your points; use them to support your arguments. Ensure that every quote is properly cited according to the required academic style guide.
What are the differences between descriptive and argumentative essays?
Descriptive essays focus on detailing a particular subject to give the reader a clear image or understanding of the topic through vivid language and sensory details. In contrast, argumentative essays aim to persuade the reader of a particular viewpoint or position using evidence and reasoning. The former is more about painting a picture, while the latter is about convincing through argument.
How can I use feedback to improve my essay writing skills?
Feedback is invaluable for improving essay writing skills. Actively seek out feedback from teachers, peers, or tutors and focus particularly on recurring themes in their comments. Reflect on this feedback critically and apply it to your future essays. Regularly revisiting and revising your work based on constructive criticism allows you to develop a more refined and effective writing style over time.
Need help from an expert?
4.93 /5 based on 486 reviews
The world’s top online tutoring provider trusted by students, parents, and schools globally.
Study and Practice for Free
Trusted by 100,000+ Students Worldwide
Achieve Top Grades in your Exams with our Free Resources.
Practice Questions, Study Notes, and Past Exam Papers for all Subjects!
Need Extra Help?
Stuck on your analytical essay? Connect with our English tutors for expert assistance in crafting a compelling analysis!

Professional tutor and Cambridge University researcher

Written by: Thomas Babb
Thomas is a PhD candidate at Oxford University. He served as an interviewer and the lead admissions test marker at Oxford, and teaches undergraduate students at Mansfield College and St Hilda’s College. He has ten years’ experience tutoring A-Level and GCSE students across a range of subjects.
Related Posts

How to Write a Narrative Essay

How to Write an Argumentative Essay

How to Write a Persuasive Essay

Hire a tutor
Please fill out the form and we'll find a tutor for you
- Select your country
- Afghanistan
- Åland Islands
- American Samoa
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bouvet Island
- British Indian Ocean Territory
- Brunei Darussalam
- Burkina Faso
- Cayman Islands
- Central African Republic
- Christmas Island
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Congo, The Democratic Republic of the
- Cook Islands
- Cote D'Ivoire
- Czech Republic
- Dominican Republic
- El Salvador
- Equatorial Guinea
- Falkland Islands (Malvinas)
- Faroe Islands
- French Guiana
- French Polynesia
- French Southern Territories
- Guinea-Bissau
- Heard Island and Mcdonald Islands
- Holy See (Vatican City State)
- Iran, Islamic Republic Of
- Isle of Man
- Korea, Democratic People'S Republic of
- Korea, Republic of
- Lao People'S Democratic Republic
- Libyan Arab Jamahiriya
- Liechtenstein
- Macedonia, The Former Yugoslav Republic of
- Marshall Islands
- Micronesia, Federated States of
- Moldova, Republic of
- Netherlands
- Netherlands Antilles
- New Caledonia
- New Zealand
- Norfolk Island
- Northern Mariana Islands
- Palestinian Territory, Occupied
- Papua New Guinea
- Philippines
- Puerto Rico
- Russian Federation
- Saint Helena
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Sao Tome and Principe
- Saudi Arabia
- Serbia and Montenegro
- Sierra Leone
- Solomon Islands
- South Africa
- South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
- Svalbard and Jan Mayen
- Switzerland
- Syrian Arab Republic
- Taiwan, Province of China
- Tanzania, United Republic of
- Timor-Leste
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Turkmenistan
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom
- United States
- United States Minor Outlying Islands
- Virgin Islands, British
- Virgin Islands, U.S.
- Wallis and Futuna
- Western Sahara

Alternatively contact us via WhatsApp, Phone Call, or Email
Words to Use in an Essay: 300 Essay Words

By Hannah Yang

Table of Contents
Words to use in the essay introduction, words to use in the body of the essay, words to use in your essay conclusion, how to improve your essay writing vocabulary.
It’s not easy to write an academic essay .
Many students struggle to word their arguments in a logical and concise way.
To make matters worse, academic essays need to adhere to a certain level of formality, so we can’t always use the same word choices in essay writing that we would use in daily life.
If you’re struggling to choose the right words for your essay, don’t worry—you’ve come to the right place!
In this article, we’ve compiled a list of over 300 words and phrases to use in the introduction, body, and conclusion of your essay.
The introduction is one of the hardest parts of an essay to write.
You have only one chance to make a first impression, and you want to hook your reader. If the introduction isn’t effective, the reader might not even bother to read the rest of the essay.
That’s why it’s important to be thoughtful and deliberate with the words you choose at the beginning of your essay.
Many students use a quote in the introductory paragraph to establish credibility and set the tone for the rest of the essay.
When you’re referencing another author or speaker, try using some of these phrases:
To use the words of X
According to X
As X states
Example: To use the words of Hillary Clinton, “You cannot have maternal health without reproductive health.”
Near the end of the introduction, you should state the thesis to explain the central point of your paper.
If you’re not sure how to introduce your thesis, try using some of these phrases:
In this essay, I will…
The purpose of this essay…
This essay discusses…
In this paper, I put forward the claim that…
There are three main arguments for…

Example: In this essay, I will explain why dress codes in public schools are detrimental to students.
After you’ve stated your thesis, it’s time to start presenting the arguments you’ll use to back up that central idea.
When you’re introducing the first of a series of arguments, you can use the following words:
First and foremost
First of all
To begin with
Example: First , consider the effects that this new social security policy would have on low-income taxpayers.
All these words and phrases will help you create a more successful introduction and convince your audience to read on.
The body of your essay is where you’ll explain your core arguments and present your evidence.
It’s important to choose words and phrases for the body of your essay that will help the reader understand your position and convince them you’ve done your research.
Let’s look at some different types of words and phrases that you can use in the body of your essay, as well as some examples of what these words look like in a sentence.
Transition Words and Phrases
Transitioning from one argument to another is crucial for a good essay.
It’s important to guide your reader from one idea to the next so they don’t get lost or feel like you’re jumping around at random.
Transition phrases and linking words show your reader you’re about to move from one argument to the next, smoothing out their reading experience. They also make your writing look more professional.
The simplest transition involves moving from one idea to a separate one that supports the same overall argument. Try using these phrases when you want to introduce a second correlating idea:
Additionally
In addition
Furthermore
Another key thing to remember
In the same way
Correspondingly
Example: Additionally , public parks increase property value because home buyers prefer houses that are located close to green, open spaces.
Another type of transition involves restating. It’s often useful to restate complex ideas in simpler terms to help the reader digest them. When you’re restating an idea, you can use the following words:
In other words
To put it another way
That is to say
To put it more simply
Example: “The research showed that 53% of students surveyed expressed a mild or strong preference for more on-campus housing. In other words , over half the students wanted more dormitory options.”
Often, you’ll need to provide examples to illustrate your point more clearly for the reader. When you’re about to give an example of something you just said, you can use the following words:
For instance
To give an illustration of
To exemplify
To demonstrate
As evidence
Example: Humans have long tried to exert control over our natural environment. For instance , engineers reversed the Chicago River in 1900, causing it to permanently flow backward.
Sometimes, you’ll need to explain the impact or consequence of something you’ve just said.
When you’re drawing a conclusion from evidence you’ve presented, try using the following words:
As a result
Accordingly
As you can see
This suggests that
It follows that
It can be seen that
For this reason
For all of those reasons
Consequently
Example: “There wasn’t enough government funding to support the rest of the physics experiment. Thus , the team was forced to shut down their experiment in 1996.”

When introducing an idea that bolsters one you’ve already stated, or adds another important aspect to that same argument, you can use the following words:
What’s more
Not only…but also
Not to mention
To say nothing of
Another key point
Example: The volcanic eruption disrupted hundreds of thousands of people. Moreover , it impacted the local flora and fauna as well, causing nearly a hundred species to go extinct.
Often, you'll want to present two sides of the same argument. When you need to compare and contrast ideas, you can use the following words:
On the one hand / on the other hand
Alternatively
In contrast to
On the contrary
By contrast
In comparison
Example: On the one hand , the Black Death was undoubtedly a tragedy because it killed millions of Europeans. On the other hand , it created better living conditions for the peasants who survived.
Finally, when you’re introducing a new angle that contradicts your previous idea, you can use the following phrases:
Having said that
Differing from
In spite of
With this in mind
Provided that
Nevertheless
Nonetheless
Notwithstanding
Example: Shakespearean plays are classic works of literature that have stood the test of time. Having said that , I would argue that Shakespeare isn’t the most accessible form of literature to teach students in the twenty-first century.
Good essays include multiple types of logic. You can use a combination of the transitions above to create a strong, clear structure throughout the body of your essay.
Strong Verbs for Academic Writing
Verbs are especially important for writing clear essays. Often, you can convey a nuanced meaning simply by choosing the right verb.
You should use strong verbs that are precise and dynamic. Whenever possible, you should use an unambiguous verb, rather than a generic verb.
For example, alter and fluctuate are stronger verbs than change , because they give the reader more descriptive detail.
Here are some useful verbs that will help make your essay shine.
Verbs that show change:
Accommodate
Verbs that relate to causing or impacting something:
Verbs that show increase:
Verbs that show decrease:
Deteriorate
Verbs that relate to parts of a whole:
Comprises of
Is composed of
Constitutes
Encompasses
Incorporates
Verbs that show a negative stance:
Misconstrue

Verbs that show a positive stance:
Substantiate
Verbs that relate to drawing conclusions from evidence:
Corroborate
Demonstrate
Verbs that relate to thinking and analysis:
Contemplate
Hypothesize
Investigate
Verbs that relate to showing information in a visual format:
Useful Adjectives and Adverbs for Academic Essays
You should use adjectives and adverbs more sparingly than verbs when writing essays, since they sometimes add unnecessary fluff to sentences.
However, choosing the right adjectives and adverbs can help add detail and sophistication to your essay.
Sometimes you'll need to use an adjective to show that a finding or argument is useful and should be taken seriously. Here are some adjectives that create positive emphasis:
Significant
Other times, you'll need to use an adjective to show that a finding or argument is harmful or ineffective. Here are some adjectives that create a negative emphasis:
Controversial
Insignificant
Questionable
Unnecessary
Unrealistic
Finally, you might need to use an adverb to lend nuance to a sentence, or to express a specific degree of certainty. Here are some examples of adverbs that are often used in essays:
Comprehensively
Exhaustively
Extensively
Respectively
Surprisingly
Using these words will help you successfully convey the key points you want to express. Once you’ve nailed the body of your essay, it’s time to move on to the conclusion.
The conclusion of your paper is important for synthesizing the arguments you’ve laid out and restating your thesis.
In your concluding paragraph, try using some of these essay words:
In conclusion
To summarize
In a nutshell
Given the above
As described
All things considered
Example: In conclusion , it’s imperative that we take action to address climate change before we lose our coral reefs forever.
In addition to simply summarizing the key points from the body of your essay, you should also add some final takeaways. Give the reader your final opinion and a bit of a food for thought.
To place emphasis on a certain point or a key fact, use these essay words:
Unquestionably
Undoubtedly
Particularly
Importantly
Conclusively
It should be noted
On the whole
Example: Ada Lovelace is unquestionably a powerful role model for young girls around the world, and more of our public school curricula should include her as a historical figure.
These concluding phrases will help you finish writing your essay in a strong, confident way.
There are many useful essay words out there that we didn't include in this article, because they are specific to certain topics.
If you're writing about biology, for example, you will need to use different terminology than if you're writing about literature.
So how do you improve your vocabulary skills?
The vocabulary you use in your academic writing is a toolkit you can build up over time, as long as you take the time to learn new words.
One way to increase your vocabulary is by looking up words you don’t know when you’re reading.
Try reading more books and academic articles in the field you’re writing about and jotting down all the new words you find. You can use these words to bolster your own essays.
You can also consult a dictionary or a thesaurus. When you’re using a word you’re not confident about, researching its meaning and common synonyms can help you make sure it belongs in your essay.
Don't be afraid of using simpler words. Good essay writing boils down to choosing the best word to convey what you need to say, not the fanciest word possible.
Finally, you can use ProWritingAid’s synonym tool or essay checker to find more precise and sophisticated vocabulary. Click on weak words in your essay to find stronger alternatives.
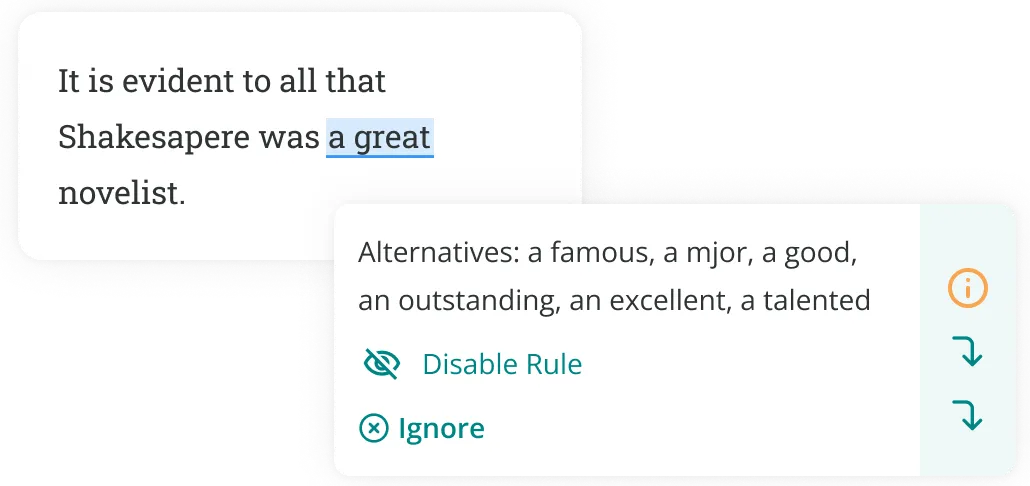
There you have it: our compilation of the best words and phrases to use in your next essay . Good luck!

Good writing = better grades
ProWritingAid will help you improve the style, strength, and clarity of all your assignments.
Hannah Yang
Hannah Yang is a speculative fiction writer who writes about all things strange and surreal. Her work has appeared in Analog Science Fiction, Apex Magazine, The Dark, and elsewhere, and two of her stories have been finalists for the Locus Award. Her favorite hobbies include watercolor painting, playing guitar, and rock climbing. You can follow her work on hannahyang.com, or subscribe to her newsletter for publication updates.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via:
39 Different Ways to Say ‘In Conclusion’ in an Essay (Rated)

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process

The phrase “In conclusion …” sounds reductive, simple and … well, just basic.
You can find better words to conclude an essay than that!
So below I’ve outlined a list of different ways to say in conclusion in an essay using a range of analysis verbs . Each one comes with an explanation of the best time to use each phrase and an example you could consider.
Read Also: How to Write a Conclusion using the 5C’s Method
List of Ways to Say ‘In Conclusion’ in an Essay
The following are the best tips I have for to say in conclusion in an essay.
1. The Weight of the Evidence Suggests…
My Rating: 10/10
Overview: This is a good concluding phrase for an evaluative essay where you need to compare two different positions on a topic then conclude by saying which one has more evidence behind it than the other.
You could also use this phrase for argumentative essays where you’ve put forward all the evidence for your particular case.
Example: “The weight of the evidence suggests that climate change is a real phenomenon.”
2. A Thoughtful Analysis would Conclude…
My Rating: 9/10
Overview: I would use this phrase in either an argumentative essay or a comparison essay. As an argument, it highlights that you think your position is the most logical.
In a comparison essay, it shows that you have (or have intended to) thoughtfully explore the issue by looking at both sides.
Example: “A thoughtful analysis would conclude that there is substantial evidence highlighting that climate change is real.”
Related Article: 17+ Great Ideas For An Essay About Yourself
3. A Balanced Assessment of the Above Information…
Overview: This phrase can be used to show that you have made a thoughtful analysis of the information you found when researching the essay. You’re telling your teacher with this phrase that you have looked at all sides of the argument before coming to your conclusion.
Example: “A balanced assessment of the above information would be that climate change exists and will have a strong impact on the world for centuries to come.”
4. Across the Board…
My Rating: 5/10
Overview: I would use this phrase in a less formal context such as in a creative discussion but would leave it out of a formal third-person essay. To me, the phrase comes across as too colloquial.
Example: “Across the board, there are scientists around the world who consistently provide evidence for human-induced climate change.”
5. Logically…
My Rating: 7/10
Overview: This phrase can be used at the beginning of any paragraph that states out a series of facts that will be backed by clear step-by-step explanations that the reader should be able to follow to a conclusion.
Example: “Logically, the rise of the automobile would speed up economic expansion in the United States. Automobiles allowed goods to flow faster around the economy.
6. After all is Said and Done…
Overview: This is a colloquial term that is more useful in a speech than written text. If you feel that the phrase ‘In conclusion,’ is too basic, then I’d also avoid this term. However, use in speech is common, so if you’re giving a speech, it may be more acceptable.
Example: “After all is said and done, it’s clear that there is more evidence to suggest that climate change is real than a hoax.”
7. All in All…
Overview: ‘All in all’ is a colloquial term that I would use in speech but not in formal academic writing. Colloquialisms can show that you have poor command of the English language. However, I would consider using this phrase in the conclusion of a debate.
Example: “All in all, our debate team has shown that there is insurmountable evidence that our side of the argument is correct.”
8. All Things Considered…
My Rating: 6/10
Overview: This term is a good way of saying ‘I have considered everything above and now my conclusion is..’ However, it is another term that’s more commonly used in speech than writing. Use it in a high school debate, but when it comes to a formal essay, I would leave it out.
Example: “All things considered, there’s no doubt in my mind that climate change is man-made.”
9. As a Final Note…
My Rating: 3/10
Overview: This phrase gives me the impression that the student doesn’t understand the point of a conclusion. It’s not to simply make a ‘final note’, but to summarize and reiterate. So, I would personally avoid this one.
Example: “As a final note, I would say that I do think the automobile was one of the greatest inventions of the 20 th Century.”
10. As Already Stated…
My Rating: 2/10
Overview: I don’t like this phrase. It gives teachers the impression that you’re going around in circles and haven’t organized your essay properly. I would particularly avoid it in the body of an essay because I always think: “If you already stated it, why are you stating it again?” Of course, the conclusion does re-state things, but it also adds value because it also summarizes them. So, add value by using a phrase such as ‘summarizing’ or ‘weighing up’ in your conclusion instead.
Example: “As already stated, I’m going to repeat myself and annoy my teacher.”
11. At present, the Best Evidence Suggests…
My Rating: 8/10
Overview: In essays where the evidence may change in the future. Most fields of study do involve some evolution over time, so this phrase acknowledges that “right now” the best evidence is one thing, but it may change in the future. It also shows that you’ve looked at the latest information on the topic.
Example: “At present, the best evidence suggests that carbon dioxide emissions from power plants is the greatest influence on climate change.”
12. At the Core of the Issue…
Overview: I personally find this phrase to be useful for most essays. It highlights that you are able to identify the most important or central point from everything you have examined. It is slightly less formal than some other phrases on this list, but I also wouldn’t consider it too colloquial for an undergraduate essay.
Example: “At the core of the issue in this essay is the fact scientists have been unable to convince the broader public of the importance of action on climate change.”
13. Despite the shortcomings of…
Overview: This phrase can be useful in an argumentative essay. It shows that there are some limitations to your argument, but , on balance you still think your position is the best. This will allow you to show critical insight and knowledge while coming to your conclusion.
Often, my students make the mistake of thinking they can only take one side in an argumentative essay. On the contrary, you should be able to highlight the limitations of your point-of-view while also stating that it’s the best.
Example: “Despite the shortcomings of globalization, this essay has found that on balance it has been good for many areas in both the developed and developing world.”
14. Finally…
My Rating: 4/10
Overview: While the phrase ‘Finally,’ does indicate that you’re coming to the end of your discussion, it is usually used at the end of a list of ideas rather than in a conclusion. It also implies that you’re adding a point rather that summing up previous points you have made.
Example: “Finally, this essay has highlighted the importance of communication between policy makers and practitioners in order to ensure good policy is put into effect.”
15. Gathering the above points together…
Overview: While this is not a phrase I personally use very often, I do believe it has the effect of indicating that you are “summing up”, which is what you want out of a conclusion.
Example: “Gathering the above points together, it is clear that the weight of evidence highlights the importance of action on climate change.”
16. Given the above information…
Overview: This phrase shows that you are considering the information in the body of the piece when coming to your conclusion. Therefore, I believe it is appropriate for starting a conclusion.
Example: “Given the above information, it is reasonable to conclude that the World Health Organization is an appropriate vehicle for achieving improved health outcomes in the developing world.”
17. In a nutshell…
Overview: This phrase means to say everything in the fewest possible words. However, it is a colloquial phrase that is best used in speech rather than formal academic writing.
Example: “In a nutshell, there are valid arguments on both sides of the debate about socialism vs capitalism.”
18. In closing…
Overview: This phrase is an appropriate synonym for ‘In conclusion’ and I would be perfectly fine with a student using this phrase in their essay. Make sure you follow-up by explaining your position based upon the weight of evidence presented in the body of your piece
Example: “In closing, there is ample evidence to suggest that liberalism has been the greatest force for progress in the past 100 years.”
19. In essence…
Overview: While the phrase ‘In essence’ does suggest you are about to sum up the core findings of your discussion, it is somewhat colloquial and is best left for speech rather than formal academic writing.
Example: “In essence, this essay has shown that cattle farming is an industry that should be protected as an essential service for our country.”
20. In review…
Overview: We usually review someone else’s work, not our own. For example, you could review a book that you read or a film you watched. So, writing “In review” as a replacement for “In conclusion” comes across a little awkward.
Example: “In review, the above information has made a compelling case for compulsory military service in the United States.”
21. In short…
Overview: Personally, I find that this phrase is used more regularly by undergraduate student. As students get more confident with their writing, they tend to use higher-rated phrases from this list. Nevertheless, I would not take grades away from a student for using this phrase.
Example: “In short, this essay has shown the importance of sustainable agriculture for securing a healthy future for our nation.”
22. In Sum…
Overview: Short for “In summary”, the phrase “In sum” sufficiently shows that you are not coming to the moment where you will sum up the essay. It is an appropriate phrase to use instead of “In conclusion”.
But remember to not just summarize but also discuss the implications of your findings in your conclusion.
Example: “In sum, this essay has shown the importance of managers in ensuring efficient operation of medium-to-large enterprises.”
23. In Summary…
Overview: In summary and in sum are the same terms which can be supplemented for “In conclusion”. You will show that you are about to summarize the points you said in the body of the essay, which is what you want from an essay.
Example: “In summary, reflection is a very important metacognitive skill that all teachers need to master in order to improve their pedagogical skills.”
24. It cannot be conclusively stated that…
Overview: While this phrase is not always be a good fit for your essay, when it is, it does show knowledge and skill in writing. You would use this phrase if you are writing an expository essay where you have decided that there is not enough evidence currently to make a firm conclusion on the issue.
Example: “It cannot be conclusively stated that the Big Bang was when the universe began. However, it is the best theory so far, and none of the other theories explored in this essay have as much evidence behind them.”
25. It is apparent that…
Overview: The term ‘ apparent ’ means that something is ‘clear’ or even ‘obvious’. So, you would use this word in an argumentative essay where you think you have put forward a very compelling argument.
Example: “It is apparent that current migration patterns in the Americas are unsustainable and causing significant harm to the most vulnerable people in our society.”
26. Last but not least…
Overview: The phrase “last but not least” is a colloquial idiom that is best used in speech rather than formal academic writing. Furthermore, when you are saying ‘last’, you mean to say you’re making your last point rather than summing up all your points you already made. So, I’d avoid this one.
Example: “Last but not least, this essay has highlighted the importance of empowering patients to exercise choice over their own medical decisions.”
27. Overall…
My Rating: 7.5/10
Overview: This phrase means ‘taking everything into account’, which sounds a lot like what you would want to do in an essay. I don’t consider it to be a top-tier choice (which is why I rated it 7), but in my opinion it is perfectly acceptable to use in an undergraduate essay.
Example: “Overall, religious liberty continues to be threatened across the world, and faces significant threats in the 21 st Century.”
28. The above points illustrate…
Overview: This phrase is a good start to a conclusion paragraph that talks about the implications of the points you made in your essay. Follow it up with a statement that defends your thesis you are putting forward in the essay.
Example: “The above points illustrate that art has had an overwhelmingly positive impact on humanity since the renaissance.”
29. The evidence presented in this essay suggests that…
Overview: I like this phrase because it highlights that you are about to gather together the evidence from the body of the essay to put forward a final thesis statement .
Example: “The evidence presented in this essay suggests that the democratic system of government is the best for securing maximum individual liberty for citizens of a nation.”
30. This essay began by stating…
Overview: This phrase is one that I teach in my YouTube mini-course as an effective one to use in an essay conclusion. If you presented an interesting fact in your introduction , you can return to that point from the beginning of the essay to provide nice symmetry in your writing.
Example: “This essay began by stating that corruption has been growing in the Western world. However, the facts collected in the body of the essay show that institutional checks and balances can sufficiently minimize this corruption in the long-term.”
31. This essay has argued…
Overview: This term can be used effectively in an argumentative essay to provide a summary of your key points. Follow it up with an outline of all your key points, and then a sentence about the implications of the points you made. See the example below.
Example: “This essay has argued that standardized tests are damaging for students’ mental health. Tests like the SATs should therefore be replaced by project-based testing in schools.”
32. To close…
Overview: This is a very literal way of saying “In conclusion”. While it’s suitable and serves its purpose, it does come across as being a sophomoric term. Consider using one of the higher-rated phrases in this list.
Example: “To close, this essay has highlighted both the pros and cons of relational dialectics theory and argued that it is not the best communication theory for the 21 st Century.”
33. To Conclude…
Overview: Like ‘to close’ and ‘in summary’, the phrase ‘to conclude’ is very similar to ‘in conclusion’. It can therefore be used as a sufficient replacement for that term. However, as with the above terms, it’s just okay and you could probably find a better phrase to use.
Example: “To conclude, this essay has highlighted that there are multiple models of communication but there is no one perfect theory to explain each situation.”
34. To make a long story short…
My Rating: 1/10
Overview: This is not a good phrase to use in an academic essay. It is a colloquialism. It also implies that you have been rambling in your writing and you could have said everything more efficiently. I would personally not use this phrase.
Example: “To make a long story short, I don’t have very good command of academic language.”
35. To Sum up…
Overview: This phrase is the same as ‘In summary’. It shows that you have made all of your points and now you’re about to bring them all together in a ‘summary’. Just remember in your conclusion that you need to do more than summarize but also talk about the implications of your findings. So you’ll need to go beyond just a summary.
Example: “In summary, there is ample evidence that linear models of communication like Lasswell’s model are not as good at explaining 21 st Century communication as circular models like the Osgood-Schramm model .”
36. Ultimately…
Overview: While this phrase does say that you are coming to a final point – also known as a conclusion – it’s also a very strong statement that might not be best to use in all situations. I usually accept this phrase from my undergraduates, but for my postgraduates I’d probably suggest simply removing it.
Example: “Ultimately, new media has been bad for the world because it has led to the spread of mistruths around the internet.”
37. Undoubtedly…
Overview: If you are using it in a debate or argumentative essay, it can be helpful. However, in a regular academic essay, I would avoid it. We call this a ‘booster’, which is a term that emphasizes certainty. Unfortunately, certainty is a difficult thing to claim, so you’re better off ‘hedging’ with phrases like ‘It appears’ or ‘The best evidence suggests’.
Example: “Undoubtedly, I know everything about this topic and am one hundred percent certain even though I’m just an undergraduate student.”
38. Weighing up the facts, this essay finds…
Overview: This statement highlights that you are looking at all of the facts both for and against your points of view. It shows you’re not just blindly following one argument but being careful about seeing things from many perspectives.
Example: “Weighing up the facts, this essay finds that reading books is important for developing critical thinking skills in childhood.”
39. With that said…
Overview: This is another phrase that I would avoid. This is a colloquialism that’s best used in speech rather than writing. It is another term that feels sophomoric and is best to avoid. Instead, use a more formal term such as: ‘Weighing up the above points, this essay finds…’
Example: “With that said, this essay disagrees with the statement that you need to go to college to get a good job.”
Do you Need to Say Anything?
Something I often tell my students is: “Can you just remove that phrase?”
Consider this sentence:
- “In conclusion, the majority of scientists concur that climate change exists.”
Would it be possible to simply say:
- “ In conclusion, The majority of scientists concur that climate change exists.”
So, I’d recommend also just considering removing that phrase altogether! Sometimes the best writing is the shortest, simplest writing that gets to the point without any redundant language at all.
How to Write an Effective Conclusion
Before I go, I’d like to bring your attention to my video on ‘how to write an effective conclusion’. I think it would really help you out given that you’re looking for help on how to write a conclusion. It’s under 5 minutes long and has helped literally thousands of students write better conclusions for their essays:
You can also check out these conclusion examples for some copy-and-paste conclusions for your own essay.
In Conclusion…
Well, I had to begin this conclusion with ‘In conclusion…’ I liked the irony in it, and I couldn’t pass up that chance.
Overall, don’t forget that concluding an essay is a way to powerfully summarize what you’ve had to say and leave the reader with a strong impression that you’ve become an authority on the topic you’re researching.
So, whether you write it as a conclusion, summary, or any other synonym for conclusion, those other ways to say in conclusion are less important than making sure that the message in your conclusion is incredibly strong.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 101 Hidden Talents Examples
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Useful Academic Expressions & Phrases For Essay Writing
These useful academic expressions , words, vocabulary and phrases will help you to write a top-notch essay. Writing an essay can be a challenging task. However it becomes simpler if it is divided into manageable pieces. There are three main parts in an essay: an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. You can easily overcome your essay writing task with these academic phrases and vocabulary for essay writing.

Phrases to Finish an Introduction Paragraph
In this essay, I will look at some of the arguments for This essay will discuss different ways of … This essay outline some of the reasons why… Let us examine both views before reaching a concrete decision. The following essay takes a look at both sides of the argument.
Vocabulary for Opinion Essay
In my opinion, I strongly agree with the idea that … I strongly disagree with the idea that … I strongly opine that… I strongly believe that… In my view… As far as I am concerned… It seems to me that… However, I strongly believe that… I oppose the view and my reasons will be explained in the following paragraphs. I will support this view with arguments in the following paragraphs. I personally believe that… Thus the advantages far outweigh the disadvantages…
Useful Expressions For Listing Your Ideas
First… First of all… Firstly… First and foremost… Initially… To begin with… To start with… In the first place…
On the one hand… Second(ly)… (do not use ‘Second of all’) Third(ly)… Then… Next… After that… And… Again… Also… Besides… Likewise… In addition… Consequently… What’s more… Furthermore… Moreover… Apart from that…
Finally… Last but not the least…
Check Also: Vocabulary for Starting Your Essay How to Write The Best Essay Ever!
Phrases to Show a Comparison in Your Essay
In the same way… Likewise… Similarly… Like the previous point… Similar to… Also… At the same time… Just as…
Useful Vocabulary and Phrases to Show Contrast
On the other hand… On the contrary… However… Nevertheless…/ Nonetheless… But… Nonetheless/ Nevertheless… Oppositely… Alternatively… Unlike… While… Whilst… Although… Though… Even though… Despite… / In spite of… In spite of the fact that… Alternatively… In contrast to this… Then again… On the other hand… Despite the fact that… Even so… Yet… Meanwhile…
Vocabulary For Expressing Condition
If… Provided that… Because of that… For this reason… Unless… Providing that… So that… In case… Whether…
Phrases for Expressing Certainty in Your Essay
Certainly… Definitely… No doubt… Of course… Doubtlessly… Without any doubt… Undoubtedly…
Vocabulary for Adding Further Information
In addition… And… Moreover… Similarly… Furthermore… Also… As well as… Besides… Even… Too… What’s more… Again… In a similar fashion… Likewise…
Expressions for Agreement & Disagreement in Your Essay
While writing your essay, as a writer you are required to show whether you agree & disagree or partially agree with a given statement or opinion.
Vocabulary for Expressing Agreement
I strongly agree… I completely agree that… I totally agree with the given idea that… I agree with the opinion that… I am quite inclined to the opinion that… I accept that… I accept the fact that… I am in agreement… I consent that…
Vocabulary for Expressing Disagreement
I disagree with the opinion that… I strongly disagree… I completely disagree with… I totally disagree with the given idea that… I disagree with the statement… I quite oppose the opinion that… I disapprove that… I totally do not accept the fact that… My own opinion contradicts… I disagree with the group of people… However, my opinion is different from…
Vocabulary for Expressing Partial Agreement
To some extent… In a way… I agree with the given statement to some extent… Up to a point, I agree… More or less… So to speak…
Essay Writing Expressions PDF
Essay Expression PDF – (download)
You May Also Like
The Eight Parts of Speech in English (PDF)

English Conversation Practice E-Books (PDF+Audio)

Types of Adverbs in English – Meaning and Examples (PDF)

50 Useful Academic Words & Phrases for Research
Like all good writing, writing an academic paper takes a certain level of skill to express your ideas and arguments in a way that is natural and that meets a level of academic sophistication. The terms, expressions, and phrases you use in your research paper must be of an appropriate level to be submitted to academic journals.
Therefore, authors need to know which verbs , nouns , and phrases to apply to create a paper that is not only easy to understand, but which conveys an understanding of academic conventions. Using the correct terminology and usage shows journal editors and fellow researchers that you are a competent writer and thinker, while using non-academic language might make them question your writing ability, as well as your critical reasoning skills.
What are academic words and phrases?
One way to understand what constitutes good academic writing is to read a lot of published research to find patterns of usage in different contexts. However, it may take an author countless hours of reading and might not be the most helpful advice when faced with an upcoming deadline on a manuscript draft.
Briefly, “academic” language includes terms, phrases, expressions, transitions, and sometimes symbols and abbreviations that help the pieces of an academic text fit together. When writing an academic text–whether it is a book report, annotated bibliography, research paper, research poster, lab report, research proposal, thesis, or manuscript for publication–authors must follow academic writing conventions. You can often find handy academic writing tips and guidelines by consulting the style manual of the text you are writing (i.e., APA Style , MLA Style , or Chicago Style ).
However, sometimes it can be helpful to have a list of academic words and expressions like the ones in this article to use as a “cheat sheet” for substituting the better term in a given context.
How to Choose the Best Academic Terms
You can think of writing “academically” as writing in a way that conveys one’s meaning effectively but concisely. For instance, while the term “take a look at” is a perfectly fine way to express an action in everyday English, a term like “analyze” would certainly be more suitable in most academic contexts. It takes up fewer words on the page and is used much more often in published academic papers.
You can use one handy guideline when choosing the most academic term: When faced with a choice between two different terms, use the Latinate version of the term. Here is a brief list of common verbs versus their academic counterparts:
| ) | |
| add up | calculate |
| carry out | execute |
| find out | discover |
| pass out | distribute |
| ask questions about | interrogate |
| make sense of | interpret |
| pass on | distribute |
Although this can be a useful tip to help academic authors, it can be difficult to memorize dozens of Latinate verbs. Using an AI paraphrasing tool or proofreading tool can help you instantly find more appropriate academic terms, so consider using such revision tools while you draft to improve your writing.
Top 50 Words and Phrases for Different Sections in a Research Paper
The “Latinate verb rule” is just one tool in your arsenal of academic writing, and there are many more out there. But to make the process of finding academic language a bit easier for you, we have compiled a list of 50 vital academic words and phrases, divided into specific categories and use cases, each with an explanation and contextual example.
Best Words and Phrases to use in an Introduction section
1. historically.
An adverb used to indicate a time perspective, especially when describing the background of a given topic.
2. In recent years
A temporal marker emphasizing recent developments, often used at the very beginning of your Introduction section.
3. It is widely acknowledged that
A “form phrase” indicating a broad consensus among researchers and/or the general public. Often used in the literature review section to build upon a foundation of established scientific knowledge.
4. There has been growing interest in
Highlights increasing attention to a topic and tells the reader why your study might be important to this field of research.
5. Preliminary observations indicate
Shares early insights or findings while hedging on making any definitive conclusions. Modal verbs like may , might , and could are often used with this expression.
6. This study aims to
Describes the goal of the research and is a form phrase very often used in the research objective or even the hypothesis of a research paper .
7. Despite its significance
Highlights the importance of a matter that might be overlooked. It is also frequently used in the rationale of the study section to show how your study’s aim and scope build on previous studies.
8. While numerous studies have focused on
Indicates the existing body of work on a topic while pointing to the shortcomings of certain aspects of that research. Helps focus the reader on the question, “What is missing from our knowledge of this topic?” This is often used alongside the statement of the problem in research papers.
9. The purpose of this research is
A form phrase that directly states the aim of the study.
10. The question arises (about/whether)
Poses a query or research problem statement for the reader to acknowledge.
Best Words and Phrases for Clarifying Information
11. in other words.
Introduces a synopsis or the rephrasing of a statement for clarity. This is often used in the Discussion section statement to explain the implications of the study .

12. That is to say
Provides clarification, similar to “in other words.”
13. To put it simply
Simplifies a complex idea, often for a more general readership.
14. To clarify
Specifically indicates to the reader a direct elaboration of a previous point.
15. More specifically
Narrows down a general statement from a broader one. Often used in the Discussion section to clarify the meaning of a specific result.
16. To elaborate
Expands on a point made previously.
17. In detail
Indicates a deeper dive into information.
Points out specifics. Similar meaning to “specifically” or “especially.”
19. This means that
Explains implications and/or interprets the meaning of the Results section .
20. Moreover
Expands a prior point to a broader one that shows the greater context or wider argument.
Best Words and Phrases for Giving Examples
21. for instance.
Provides a specific case that fits into the point being made.
22. As an illustration
Demonstrates a point in full or in part.
23. To illustrate
Shows a clear picture of the point being made.
24. For example
Presents a particular instance. Same meaning as “for instance.”
25. Such as
Lists specifics that comprise a broader category or assertion being made.
26. Including
Offers examples as part of a larger list.
27. Notably
Adverb highlighting an important example. Similar meaning to “especially.”
28. Especially
Adverb that emphasizes a significant instance.
29. In particular
Draws attention to a specific point.
30. To name a few
Indicates examples than previously mentioned are about to be named.
Best Words and Phrases for Comparing and Contrasting
31. however.
Introduces a contrasting idea.
32. On the other hand
Highlights an alternative view or fact.
33. Conversely
Indicates an opposing or reversed idea to the one just mentioned.
34. Similarly
Shows likeness or parallels between two ideas, objects, or situations.
35. Likewise
Indicates agreement with a previous point.
36. In contrast
Draws a distinction between two points.
37. Nevertheless
Introduces a contrasting point, despite what has been said.
38. Whereas
Compares two distinct entities or ideas.
Indicates a contrast between two points.
Signals an unexpected contrast.
Best Words and Phrases to use in a Conclusion section
41. in conclusion.
Signifies the beginning of the closing argument.
42. To sum up
Offers a brief summary.
43. In summary
Signals a concise recap.
44. Ultimately
Reflects the final or main point.
45. Overall
Gives a general concluding statement.
Indicates a resulting conclusion.
Demonstrates a logical conclusion.
48. Therefore
Connects a cause and its effect.
49. It can be concluded that
Clearly states a conclusion derived from the data.
50. Taking everything into consideration
Reflects on all the discussed points before concluding.
Edit Your Research Terms and Phrases Before Submission
Using these phrases in the proper places in your research papers can enhance the clarity, flow, and persuasiveness of your writing, especially in the Introduction section and Discussion section, which together make up the majority of your paper’s text in most academic domains.
However, it's vital to ensure each phrase is contextually appropriate to avoid redundancy or misinterpretation. As mentioned at the top of this article, the best way to do this is to 1) use an AI text editor , free AI paraphrase tool or AI proofreading tool while you draft to enhance your writing, and 2) consult a professional proofreading service like Wordvice, which has human editors well versed in the terminology and conventions of the specific subject area of your academic documents.
For more detailed information on using AI tools to write a research paper and the best AI tools for research , check out the Wordvice AI Blog .
- +44 (0) 207 391 9032
Recent Posts
- Practice vs. Practise: What’s the Difference?
- How Homework Builds Good Study Habits for University Students
How to Write an Article Review in Simple Steps
- Understanding Content Validity: Definition & Examples
- 10 Tips for Writing Assignments
- Easy Steps to Write a History Essay: Tips and Tricks
- How To Select the Perfect CV Writing Service
- What Is an Adjective: Types, Uses, and Examples
- How to Write a Reflective Essay
- Abstract vs. Introduction: What’s the Difference?
- Academic News
- Custom Essays
- Dissertation Writing
- Essay Marking
- Essay Writing
- Essay Writing Companies
- Model Essays
- Model Exam Answers
- Oxbridge Essays Updates
- PhD Writing
- Significant Academics
- Student News
- Study Skills
- University Applications
- University Essays
- University Life
- Writing Tips
Essay Phrases & Essay Words for Academic Writing Success
(Last updated: 10 October 2024)
Since 2006, Oxbridge Essays has been the UK’s leading paid essay-writing and dissertation service
We have helped 10,000s of undergraduate, Masters and PhD students to maximise their grades in essays, dissertations, model-exam answers, applications and other materials. If you would like a free chat about your project with one of our UK staff, then please just reach out on one of the methods below.
For the vast majority of students, essay writing doesn't always come easily. Writing at academic level is an acquired skill that can literally take years to master – indeed, many students find they only start to feel really confident writing essays just as their undergraduate course comes to an end!
If this is you, and you've come here looking for words and phrases to use in your essay, you're in the right place. We’ve pulled together a list of essential academic words you can use in the introduction, body, and conclusion of your essays .
Whilst your ideas and arguments should always be your own, borrowing some of the words and phrases listed below is a great way to articulate your ideas more effectively, and ensure that you keep your reader’s attention from start to finish.
It goes without saying (but we'll say it anyway) that there's a certain formality that comes with academic writing. Casual and conversational phrases have no place. Obviously, there are no LOLs, LMFAOs, and OMGs. But formal academic writing can be much more subtle than this, and as we've mentioned above, requires great skill.
So, to get you started on polishing your own essay writing ability, try using the words in this list as an inspirational starting point.
Words to use in your introduction
The trickiest part of academic writing often comes right at the start, with your introduction. Of course, once you’ve done your plan and have your arguments laid out, you need to actually put pen to paper (or fingers to keyboard) and begin your essay.
You need to consider that your reader doesn’t have a clue about your topic or arguments, so your first sentence must summarise these. Explain what your essay is going to talk about as though you were explaining it to a five year old – without losing the formality of your academic writing, of course! To do this, use any of the below words or phrases to help keep you on track.
1. Firstly, secondly, thirdly
Even though it sounds obvious, your argument will be clearer if you deliver the ideas in the right order. These words can help you to offer clarity and structure to the way you expose your ideas. This is an extremely effective method of presenting the facts clearly. Don’t be too rigid and feel you have to number each point, but using this system can be a good way to get an argument off the ground, and link arguments together.
2. In view of; in light of; considering
These essay phrases are useful to begin your essay. They help you pose your argument based on what other authors have said or a general concern about your research. They can also both be used when a piece of evidence sheds new light on an argument. Here’s an example: The result of the American invasion has severely impaired American interests in the Middle East, exponentially increasing popular hostility to the United States throughout the region, a factor which has proved to be a powerful recruitment tool for extremist terrorist groups (Isakhan, 2015). Considering [or In light of / In view of] the perceived resulting threat to American interests, it could be argued that the Bush administration failed to fully consider the impact of their actions before pushing forward with the war.
3. According to X; X stated that; referring to the views of X
Introducing the views of an author who has a comprehensive knowledge of your particular area of study is a crucial part of essay writing. Including a quote that fits naturally into your work can be a bit of a struggle, but these academic phrases provide a great way in.
Even though it’s fine to reference a quote in your introduction, we don’t recommend you start your essay with a direct quote. Use your own words to sum up the views you’re mentioning, for example:
As Einstein often reiterated, experiments can prove theories, but experiments don’t give birth to theories.
Rather than:
“A theory can be proved by experiment, but no path leads from experiment to the birth of a theory.” {Albert Einstein, 1954, Einstein: A Biography}.
See the difference?
And be sure to reference correctly too, when using quotes or paraphrasing someone else's words.
Adding information and flow
The flow of your essay is extremely important. You don’t want your reader to be confused by the rhythm of your writing and get distracted away from your argument, do you? No! So, we recommend using some of the following ‘flow’ words, which are guaranteed to help you articulate your ideas and arguments in a chronological and structured order.
4. Moreover; furthermore; in addition; what’s more
These types of academic phrases are perfect for expanding or adding to a point you’ve already made without interrupting the flow altogether. “Moreover”, “furthermore” and “in addition” are also great linking phrases to begin a new paragraph.
Here are some examples: The dissociation of tau protein from microtubules destabilises the latter resulting in changes to cell structure, and neuronal transport. Moreover, mitochondrial dysfunction leads to further oxidative stress causing increased levels of nitrous oxide, hydrogen peroxide and lipid peroxidases.
On the data of this trial, no treatment recommendations should be made. The patients are suspected, but not confirmed, to suffer from pneumonia. Furthermore, five days is too short a follow up time to confirm clinical cure.
5. In order to; to that end; to this end
These are helpful academic phrases to introduce an explanation or state your aim. Oftentimes your essay will have to prove how you intend to achieve your goals. By using these sentences you can easily expand on points that will add clarity to the reader.
For example: My research entailed hours of listening and recording the sound of whales in order to understand how they communicate.
Dutch tech companies offer support in the fight against the virus. To this end, an online meeting took place on Wednesday...
Even though we recommend the use of these phrases, DO NOT use them too often. You may think you sound like a real academic but it can be a sign of overwriting!
6. In other words; to put it another way; that is; to put it more simply
Complement complex ideas with simple descriptions by using these sentences. These are excellent academic phrases to improve the continuity of your essay writing. They should be used to explain a point you’ve already made in a slightly different way. Don’t use them to repeat yourself, but rather to elaborate on a certain point that needs further explanation. Or, to succinctly round up what just came before.
For example: A null hypothesis is a statement that there is no relationship between phenomena. In other words, there is no treatment effect.
Nothing could come to be in this pre-world time, “because no part of such a time possesses, as compared with any other, a distinguishing condition of existence rather than non-existence.” That is, nothing exists in this pre-world time, and so there can be nothing that causes the world to come into existence.
7. Similarly; likewise; another key fact to remember; as well as; an equally significant aspect of
These essay words are a good choice to add a piece of information that agrees with an argument or fact you just mentioned. In academic writing, it is very relevant to include points of view that concur with your opinion. This will help you to situate your research within a research context.
Also , academic words and phrases like the above are also especially useful so as not to repeat the word ‘also’ too many times. (We did that on purpose to prove our point!) Your reader will be put off by the repetitive use of simple conjunctions. The quality of your essay will drastically improve just by using academic phrases and words such as ‘similarly’, ‘as well as’, etc. Here, let us show you what we mean:
In 1996, then-transport minister Steve Norris enthused about quadrupling cycling trips by 2012. Similarly, former prime minister David Cameron promised a “cycling revolution” in 2013…
Or Renewable Energy Initiative (AREI) aims to bridge the gap of access to electricity across the continent (...). Another key fact to remember is that it must expand cost-efficient access to electricity to nearly 1 billion people.
The wording “not only… but also” is a useful way to elaborate on a similarity in your arguments but in a more striking way.
Comparing and contrasting information
Academic essays often include opposite opinions or information in order to prove a point. It is important to show all the aspects that are relevant to your research. Include facts and researchers’ views that disagree with a point of your essay to show your knowledge of your particular field of study. Below are a few words and ways of introducing alternative arguments.
8. Conversely; however; alternatively; on the contrary; on the other hand; whereas
Finding a seamless method to present an alternative perspective or theory can be hard work, but these terms and phrases can help you introduce the other side of the argument. Let's look at some examples:
89% of respondents living in joint families reported feeling financially secure. Conversely, only 64% of those who lived in nuclear families said they felt financially secure.
The first protagonist has a social role to fill in being a father to those around him, whereas the second protagonist relies on the security and knowledge offered to him by Chaplin.
“On the other hand” can also be used to make comparisons when worded together with “on the one hand.”
9. By contrast; in comparison; then again; that said; yet
These essay phrases show contrast, compare facts, and present uncertainty regarding a point in your research. “That said” and “yet” in particular will demonstrate your expertise on a topic by showing the conditions or limitations of your research area. For example:
All the tests were positive. That said, we must also consider the fact that some of them had inconclusive results.
10. Despite this; provided that; nonetheless
Use these phrases and essay words to demonstrate a positive aspect of your subject-matter regardless of lack of evidence, logic, coherence, or criticism. Again, this kind of information adds clarity and expertise to your academic writing.
A good example is:
Despite the criticism received by X, the popularity of X remains undiminished.
11. Importantly; significantly; notably; another key point
Another way to add contrast is by highlighting the relevance of a fact or opinion in the context of your research. These academic words help to introduce a sentence or paragraph that contains a very meaningful point in your essay.
Giving examples
A good piece of academic writing will always include examples. Illustrating your essay with examples will make your arguments stronger. Most of the time, examples are a way to clarify an explanation; they usually offer an image that the reader can recognise. The most common way to introduce an illustration is “for example.” However, in order not to repeat yourself here are a few other options.
12. For instance; to give an illustration of; to exemplify; to demonstrate; as evidence; to elucidate
The academic essays that are receiving top marks are the ones that back up every single point made. These academic phrases are a useful way to introduce an example. If you have a lot of examples, avoid repeating the same phrase to facilitate the readability of your essay.
Here’s an example:
‘High involvement shopping’, an experiential process described by Wu et al. (2015, p. 299) relies upon the development of an identity-based alliance between the customer and the brand. Celebrity status at Prada, for example, has created an alliance between the brand and a new generation of millennial customers.
Concluding your essay
Concluding words for essays are necessary to wrap up your argument. Your conclusion must include a brief summary of the ideas that you just exposed without being redundant. The way these ideas are expressed should lead to the final statement and core point you have arrived at in your present research.
13. In conclusion; to conclude; to summarise; in sum; in the final analysis; on close analysis
These are phrases for essays that will introduce your concluding paragraph. You can use them at the beginning of a sentence. They will show the reader that your essay is coming to an end:
On close analysis and appraisal, we see that the study by Cortis lacks essential features of the highest quality quantitative research.
14. Persuasive; compelling
Essay words like these ones can help you emphasize the most relevant arguments of your paper. Both are used in the same way: “the most persuasive/compelling argument is…”.
15. Therefore; this suggests that; it can be seen that; the consequence is
When you’re explaining the significance of the results of a piece of research, these phrases provide the perfect lead up to your explanation.
16. Above all; chiefly; especially; most significantly; it should be noted
Your summary should include the most relevant information or research factor that guided you to your conclusion. Contrary to words such as “persuasive” or “compelling”, these essay words are helpful to draw attention to an important point. For example:
The feasibility and effectiveness of my research has been proven chiefly in the last round of laboratory tests.
Film noir is, and will continue to be, highly debatable, controversial, and unmarketable – but above all, for audience members past, present and to come, extremely enjoyable as a form of screen media entertainment.
17. All things considered
This essay phrase is meant to articulate how you give reasons to your conclusions. It means that after you considered all the aspects related to your study, you have arrived to the conclusion you are demonstrating.
After mastering the use of these academic words and phrases, we guarantee you will see an immediate change in the quality of your essays. The structure will be easier to follow, and the reader’s experience will improve. You’ll also feel more confident articulating your ideas and using facts and examples. So jot them all down, and watch your essays go from ‘good’ to ‘great’!
Essay exams: how to answer ‘To what extent…’
How to write a master’s essay.
- academic writing
- writing a good essay
- writing essays
- writing tips
Writing Services
- Essay Plans
- Critical Reviews
- Literature Reviews
- Presentations
- Dissertation Title Creation
- Dissertation Proposals
- Dissertation Chapters
- PhD Proposals
- Journal Publication
- Professional CV Writing Service
- Business Proofreading Services
Editing Services
- Proofreading Service
- Editing Service
- Academic Editing Service
Additional Services
- Marking Services
- Consultation Calls
- Personal Statements
- Tutoring Services
Our Company
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Become a Writer
Terms & Policies
- Fair Use Policy
- Policy for Students in England
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Writing Service Examples
- Editing Service Examples
- Marking Service Examples
- Tutoring Service Examples
- [email protected]
- Contact Form
Payment Methods
Cryptocurrency payments.
Top List of Formal Words for Academic Writing: 101 Words To Elevate Your Writing Style
Academic writing requires a higher level of communication. Check out our list of formal words for academic writing to write on a more elevated level.
In the world of academic writing, formality is a necessity. Words that are too casual, contractions, and sometimes even second-person writing go against the rules and regulations of popular style guides like the MLA and the APA . This list of formal words for academic writing can help writers start writing more professionally.
What Are Formal Words?
Formal adjectives for academic writing, formal nouns for academic writing, formal adverbs for academic writing, formal verbs for academic writing, transition words for academic writing.

Formal words for MLA academic writing are the words writers place into their writing to make it sound like they are well-educated. These words replace commonplace words like “happy” or “buy,” giving the academic paper an elevated feel without changing the meaning of the writing.
| Acceptable | Difficult | Numerous |
| According | Discard | Notably |
| Acquisition | Discover | Observe |
| Additionally | Distribute | Occupation |
| Adequate | Donate | Omit |
| Alternatively | Effortless | Opportunity |
| Amiable | Elude | Perhaps |
| Analysis | Equipment | Permit |
| Appear | Establish | Persuade |
| Ascend | Evade | Present |
| Aspect | Exceptional | Presumption |
| Assist | Experiment | Primarily |
| Beneficial | Exploitative | Principally |
| Besides | Fabricate | Proceed |
| Cancel | Fail | Postpone |
| Cease | Firstly | Purchase |
| Challenge | Furthermore | Receive |
| Circular | However | Regard |
| Criticize | Importantly | Responsible |
| Commence | Incorrect | Seek |
| Comparably | Increase | Select |
| Complicated | Inevitable | Similarly |
| Conceive | Inform | Subject |
| Considerable | Initially | Subsequently |
| Considering | Initiative | Sufficient |
| Construct | Intermittently | Terminate |
| Contaminated | Intrinsic | Therefore |
| Controversial | Introduce | Transparent |
| Correct | Investigate | Undermine |
| Damage | Invite | Vacant |
| Decrease | Improve | Validity |
| Deficiency | Manage | Verify |
| Demonstrate | Moreover | Whereas |
| Differentiation | Negative |
Adjectives are words that describe nouns and pronouns. They have their place in academic writing, but writers do need to choose elevated descriptive words.
1. Acceptable
An acceptable outcome would be for the students to earn a passing grade on the exam.
2. Adequate
If the experiment uses an adequate amount of liquid, the result will be a polymer.
Julius Caesar thought he had an amiable relationship with Brutus, but he was proven wrong by his assassination at his former friend’s hand.
4. Beneficial
A mutually beneficial arrangement between two living organisms is called symbiosis.
5. Circular
Circular reasoning never reaches a conclusion.
6. Complicated
The complicated equation was readily solved by the mathematician.
7. Considerable
A considerable discount is available to veterans.
8. Contaminated
The contaminated solution damaged the experiment.
9. Controversial
A controversial political agreement started the war.
10. Correct
The correct answer is 85.
11. Difficult
Creating alignment between the two chemicals was a difficult challenge.
12. Effortless
The ballerina makes years of work, and challenging movements look effortless .
13. Exceptional
The outcome was exceptional .
14. Exploitative
Exploitative tax laws are often the cause of inflation.
15. Intrinsic
A gem’s intrinsic value is based on what society deems its worth.
16. Negative
Negative emotions can add to feelings of stress and anxiety.
17. Numerous
Numerous complaints against the new tax law caused lawmakers to reconsider their position.
18. Responsible
The responsible party will pay for the activities chosen.
19. Sufficient
Add a sufficient amount of salt to generate the chemical change.
20. Transparent
The chemical reaction created a transparent crystalline structure nearly as clear as glass.
The child’s vacant expression showed a lack of emotions.
Some nouns are too plain and indistinct for academic writing, but they often have synonyms that can elevate the overall piece. Consider these nouns that work well for academic works.
22. Acquisition
The acquisition of the competitor created a monopoly in the store’s small town.
23. Analysis
Upon further analysis , the experiment was a success.
All aspects of his personality were under scrutiny.
25. Challenge
The challenge of creating a unified community with different ethnic groups keeps the committee in deliberation.
Damage from the storm cost the community over $2 million.
27. Deficiency
An iron deficiency can cause feelings of exhaustion and lethargy.
28. Differentiation
Differentiation in the classroom can help students excel.
29. Equipment
Keeping equipment clean is an important part of scientific experimentation.
30. Experiment
The test subjects signed their permission to participate in the psychology experiment .
31. Incorrect
An incorrect solution to the first equation will derail the entire system of equations.
32. Inevitable
The inevitable outcome of parenting is sending children to live on their own.
33. Initiative
When the students take the initiative , projects in the classroom get done.
34. Occupation
A college degree is not required for every occupation .
35. Opportunity
When opportunity comes knocking, motivated people take action.
36. Presumption
Making the wrong presumption will lead to the wrong conclusion.
37. Subject
The subject of the experiment responded negatively to the stimuli.
38. Validity
The validity of the research became questionable when the writer’s bias showed through.
Adverbs describe verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs. Academic writing uses adverbs carefully to avoid having too many, but if your piece requires some, here are the ones you’ll want to choose.
39. According
According to the instructions, the first step is thoroughly cleaning the surface.
40. Besides
Besides the obvious plot line, a closer analysis of The Raven shows a deeper meaning of the famous poem.
41. Comparably
The crops were comparably priced, so the farmer chose the one that would grow better in his area.
42. Initially
When they initially chose the house, they were unaware it sat on a floodplain.
43. Intermittently
The rain intermittently impacted their ability to play baseball.
44. Notably
All non-essential businesses, most notably restaurants, and professional service providers, suffered impacts from COVID-19 closures.
45. Perhaps
Perhaps the most apparent reason for the choice of play for the spring performance was Shakespeare’s ongoing appeal.
46. Primarily
The aim of the new regulation is primarily to help veterans access their benefits.
47. Principally
Walter Frost was principally a poet.
48. Similarly
The two chemicals reacted similarly , except one generating heat and the other staying at the same temperature.
49. Subsequently
The increased taxes subsequently made daily life harder for the peasants.

Even verbs can be too casual. As you write, consider if one of these more formal verbs would fit your piece.
No differences between the two houses appear to be major.
The politician will ascend to the podium, calm the crowd, and deliver his speech.
The police officer will assist in stopping traffic so the parade can follow its intended path.
To cancel the agreement, both parties must sign.
The mixture will cease to bubble and fizz, and then the catalyst gets added.
55. Criticize
To criticize the dictator is to break the law in a tyrannical government.
56. Commence
The teams will commence playing after the coin toss.
57. Conceive
When the parents conceive a new idea, the attorneys will meet to discuss it.
58. Considering
For those considering adoption through the foster care system, a long list of important considerations must be made.
59. Construct
The physics class will construct bamboo stick bridges, then test their effectiveness at holding weight.
60. Decrease
Decrease the amount of acid in the solution to make it safe to touch.
61. Demonstrate
To demonstrate proper knowledge of the subject matter, students will write an essay on the topic.
62. Discard
After the reaction, discard the remaining solution safely to avoid damage to the chemistry lab.
63. Discover
The goal of the research project is to discover the most effective teaching strategy for students with ADHD.
64. Distribute
The IRS will distribute the tax rebate checks this month.
Choosing to donate to a charity can help people lower their tax burden.
Though the answer continues to elude scientists as to why the number of honey bees continues to dwindle.
67. Establish
After they establish safety for the refugees, the government will work on immigration paperwork.
The criminal continues to evade capture by the authorities.
69. Fabricate
The small workshop was not large enough to fabricate a boat.
The experiment will fail if the temperatures are not kept at a constant rate.
71. Increase
A vehicle will increase its speed more quickly if it is accelerating on a decline.
The petitioner wishes to inform the court of the change in income.
73. Introduce
The couple will introduce their parents at the wedding reception and provide a toast to each one.
74. Investigate
To investigate the crime thoroughly, the inspector asked for witness statements from everyone in the area.
To invite someone to dinner, use a formal invitation, not an electronic one.
76. Improve
The crime situation did not improve , even with more regulations.
When someone cannot manage their own problems, how can they expect to manage the problems of others?
78. Observe
To observe the changes in material, scientists will need to experiment in a well-lit room.
The recipe will fail to rise if the baker omits the baking soda.
If owners permit their dogs to roam the neighborhood without a leash, chances are high that the animals will be struck by a vehicle.
81. Persuade
The debate team tried to persuade the audience to think differently about their long-held beliefs.
82. Present
It’s important to live in the present and not dwell on the past.
83. Proceed
Pedestrians should proceed with caution through the busy intersection.
84. Postpone
The bride and groom decided to postpone their wedding date so more people could attend.
85. Purchase
A house is a major purchase that requires careful thought and consideration.
86. Receive
Receive gifts with grace and thankfulness.
When athletes regard their coach with respect, the game’s outcome is usually better.
Seek the right advice before making any legal decisions.
The scholarship committee will select winners based on academic ability and community service.
90. Terminate
To terminate the contract, read the terms carefully and follow the necessary steps and protocols.
91. Undermine
The senators tried to undermine the work of the committee because they did not agree to the proposed legislation.
Always verify sources on academic papers to ensure they are authoritative.
Academic writing needs transition words, often at the start of a paragraph or the concluding sentence of a paragraph, to guide the reader to the next idea – these words work well.
93. Additionally
Additionally, the experiment proved the thesis to be true.
94. Alternatively
Alternatively, the parents could agree to a parenting agreement outside of court.
95. Firstly
Firstly, the research study used a double-blind method to ensure little bias in the results.
96. Furthermore
Furthermore, additional research is necessary to come to a conclusion.
97. However
However, one positive outcome was weight loss for all study participants, regardless of the placebo.
98. Importantly
Most importantly, the best interests of the children are at stake.
99. Moreover
Moreover, taking additional time to decide puts the family at risk.
100. Therefore
Researchers concluded, therefore, that the asbestos was a danger to the school children.
101. Whereas
The defendant had no proof, whereas the plaintiff had plenty.
Looking for more? Check out our round-up of unusual words with beautiful meanings !

Short Essay
Short essay generator.

A short essay is a concise piece of writing, typically between 250 and 500 words, that presents a focused argument or reflection on a specific topic. Unlike longer essay writing , a short essay requires a clear, narrow topic and a precise thesis statement due to its limited length. It includes an introduction, body, and conclusion, aiming to express ideas effectively within a compact structure. Short essays often prioritize clarity, coherence, and brevity, making every sentence impactful. They are commonly used in academic settings, examinations, and other contexts where concise and well-organized responses, like a free essay , are required to convey information or opinions succinctly.
What is a Short Essay?

Download Short Essay Examples Bundle
Short Essay Format
A well-organized short essay includes three main parts: the introduction, body, and conclusion. Here’s a breakdown of each section:
1. Introduction
Purpose: The introduction presents the topic and includes a clear thesis statement to outline the essay’s main point. Length: Usually 2-3 sentences. Tips: Start with a hook to grab attention and provide some background information before stating the thesis.
Purpose: The body elaborates on the thesis, supporting it with evidence, examples, and explanations. Length: Typically 1-3 paragraphs, depending on the essay’s length. Tips: Each paragraph should focus on a single main idea that supports the thesis. Use transitions to maintain a smooth flow between paragraphs.
3. Conclusion
Purpose: The conclusion summarizes the main points and reinforces the thesis. Length: Usually 2-3 sentences. Tips: Restate the thesis in a fresh way, provide a final thought, or suggest a call to action if appropriate.
Short Essay Example
The Importance of Daily Exercise Maintaining a daily exercise routine is essential for a healthy lifestyle. Exercise not only improves physical health by reducing the risk of chronic diseases, but it also enhances mental well-being. Regular physical activity, even for just 30 minutes a day, can boost energy levels, improve mood, and increase overall life satisfaction. For instance, studies show that individuals who engage in daily exercise report higher levels of happiness and lower stress. Additionally, daily exercise promotes better sleep and cognitive function. In conclusion, incorporating daily exercise into one’s routine can lead to substantial health benefits, making it a worthwhile investment in personal well-being.
Short Essay for Students

Short Essay for Kids
Short Essay for high school Students

- Short Essay about myself for Students
- Short Essays for Class 5
- short Essays for Class 2
- Short Essay for Scholarship
- Short Essay for Job Interview
Essays usually become a channel for a person to express emotions and ideas about something or someone. A writer can be creative in presenting topics that he/she thinks is relevant and from which people can infer important lessons in life. Thus, there are many ways to write an essay .
Some of the few types of essays are informative essay , analysis essay , concept essay , reflective essay , and many more. These are all different in the way that they are written as well as their objective. Each is unique in its own way. An essay could also be written short or long, which of course, depends on the writer.
Short Narrative Essay Example

Short Essay Plan Example

Sample Narrative Essay Example

High School Narrative Essay Example

Biographical Narrative Essay Example

Free Visual Essay Example
Short Informative Essay Example

Argumentative Essay Writing

Sample Opinion Essay Example

Scholarship Essay Example

Short Expository Example

Short Narrative Essay Example

Short Argumentative Sample Example

Persuasive Short Essay Example

Descriptive Short Essay Example

College Short Essay Example

Critical Essay Example

Tips for a Short Essay
When you write a short essay, you need to remember that there are no elements to be sacrificed. Short essays draw more impact to readers because the topic is presented straightforward. You may also see essay writing examples & samples.
1. Be direct to the point.
Remember that you need to be able to make your reader get the whole point of your essay without having to say too much words. You may also check out analytical essay examples & samples.
2. Create a mind-map.
Mind-mapping helps you easily present your thoughts. Try to practice it and use to your advantage.
3. Do your research.
The key to an effective essay writing is short essay to have a substantial amount of information. Research about your topic so you can select the most important ideas to write.
Importance of Short Essay
A short essay is usually contained in just a page and not lengthy words or explanations in necessary to express the main point of the topic. Short essays are important when one is trying to present an important topic without having to write a lot of words or using multiple pages. You may also like concept essay examples & samples.
It presents just the right amount of data or knowledge necessary to feed a hungry mind. As scientific researches has put it, the mind can retain more data when the details are presented in a brief and concise manner. Some people have short attention span so you need to have the writing skills to make your point with just a few words.
How to write a short essay
Writing a short essay involves focusing on clarity and conciseness. With a limited word count, each sentence must add value and effectively convey your ideas. Follow these steps to craft a compelling short essay:
- Understand the Topic Read the prompt carefully to grasp what is required. Identify the main question or theme you need to address.
- Create a Thesis Statement Develop a clear thesis that states your main point or argument. Keep it concise , as this will guide the focus of your entire essay.
- Outline Your Essay Plan the structure : A short essay usually has an introduction, body, and conclusion. List the main points for each section. This helps maintain a logical flow.
- Write the Introduction Start with a hook to grab attention. This could be a question, fact, or a brief anecdote. Introduce your topic briefly and end with your thesis statement.
- Develop the Body Paragraphs Focus on one main idea per paragraph to ensure clarity. Use evidence or examples to support your points. This can include facts, quotes, or personal experiences. Keep paragraphs concise : Aim for around 3–5 sentences per paragraph.
- Write the Conclusion Summarize your main points briefly. Restate the thesis in a new way to reinforce your argument. End with a closing thought or a call to action, if appropriate.
- Revise and Edit Check for clarity and conciseness : Remove unnecessary words and redundant ideas. Proofread for grammar and spelling errors . Ensure your ideas flow logically , with smooth transitions between sentences and paragraphs.
Tips for writing short essays
Writing a short essay can be challenging due to the limited space available to convey your ideas. Here are some helpful tips to ensure your essay is concise, focused, and impactful:
- Be clear and specific about your main argument or point.
- Make sure your thesis is concise and sets the direction for the entire essay.
- Keep each paragraph dedicated to a single point that supports your thesis.
- Use topic sentences to introduce the paragraph’s main idea.
- Avoid unnecessary words and fluff. Get straight to the point.
- Choose words that convey your meaning accurately and efficiently.
- Even in a short essay, examples can strengthen your argument.
- Select only the most impactful evidence to support your points.
- Plan your word count for each section (introduction, body, and conclusion) to stay within the limit.
How is a Short Essay Structured?
A short essay usually includes an introduction, one or two body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Each section should be concise, with the introduction presenting the thesis, the body paragraphs supporting it, and the conclusion summarizing the main points.
How Do You Choose a Topic for a Short Essay?
Choose a focused and manageable topic that can be effectively explored within the word limit. The topic should be specific enough to allow for depth without requiring extensive background information.
What is the Purpose of a Short Essay?
The purpose of a short essay is to express a clear and concise argument, analyze a specific topic, or share insights on a subject. It encourages critical thinking and allows for concise communication of ideas.
How Do You Write a Strong Thesis for a Short Essay?
A strong thesis in a short essay should be clear, specific, and directly answer the essay prompt. It should convey the main argument or point of the essay in one or two sentences, setting the tone for the entire piece.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Write a Short Essay on the importance of teamwork.
Create a Short Essay discussing the impact of climate change.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write an essay outline | Guidelines & examples
How to Write an Essay Outline | Guidelines & Examples
Published on August 14, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
An essay outline is a way of planning the structure of your essay before you start writing. It involves writing quick summary sentences or phrases for every point you will cover in each paragraph , giving you a picture of how your argument will unfold.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Organizing your material, presentation of the outline, examples of essay outlines, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about essay outlines.
At the stage where you’re writing an essay outline, your ideas are probably still not fully formed. You should know your topic and have already done some preliminary research to find relevant sources , but now you need to shape your ideas into a structured argument.
Creating categories
Look over any information, quotes and ideas you’ve noted down from your research and consider the central point you want to make in the essay—this will be the basis of your thesis statement . Once you have an idea of your overall argument, you can begin to organize your material in a way that serves that argument.
Try to arrange your material into categories related to different aspects of your argument. If you’re writing about a literary text, you might group your ideas into themes; in a history essay, it might be several key trends or turning points from the period you’re discussing.
Three main themes or subjects is a common structure for essays. Depending on the length of the essay, you could split the themes into three body paragraphs, or three longer sections with several paragraphs covering each theme.
As you create the outline, look critically at your categories and points: Are any of them irrelevant or redundant? Make sure every topic you cover is clearly related to your thesis statement.
Order of information
When you have your material organized into several categories, consider what order they should appear in.
Your essay will always begin and end with an introduction and conclusion , but the organization of the body is up to you.
Consider these questions to order your material:
- Is there an obvious starting point for your argument?
- Is there one subject that provides an easy transition into another?
- Do some points need to be set up by discussing other points first?
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Within each paragraph, you’ll discuss a single idea related to your overall topic or argument, using several points of evidence or analysis to do so.
In your outline, you present these points as a few short numbered sentences or phrases.They can be split into sub-points when more detail is needed.
The template below shows how you might structure an outline for a five-paragraph essay.
- Thesis statement
- First piece of evidence
- Second piece of evidence
- Summary/synthesis
- Importance of topic
- Strong closing statement
You can choose whether to write your outline in full sentences or short phrases. Be consistent in your choice; don’t randomly write some points as full sentences and others as short phrases.
Examples of outlines for different types of essays are presented below: an argumentative, expository, and literary analysis essay.
Argumentative essay outline
This outline is for a short argumentative essay evaluating the internet’s impact on education. It uses short phrases to summarize each point.
Its body is split into three paragraphs, each presenting arguments about a different aspect of the internet’s effects on education.
- Importance of the internet
- Concerns about internet use
- Thesis statement: Internet use a net positive
- Data exploring this effect
- Analysis indicating it is overstated
- Students’ reading levels over time
- Why this data is questionable
- Video media
- Interactive media
- Speed and simplicity of online research
- Questions about reliability (transitioning into next topic)
- Evidence indicating its ubiquity
- Claims that it discourages engagement with academic writing
- Evidence that Wikipedia warns students not to cite it
- Argument that it introduces students to citation
- Summary of key points
- Value of digital education for students
- Need for optimism to embrace advantages of the internet
Expository essay outline
This is the outline for an expository essay describing how the invention of the printing press affected life and politics in Europe.
The paragraphs are still summarized in short phrases here, but individual points are described with full sentences.
- Claim that the printing press marks the end of the Middle Ages.
- Provide background on the low levels of literacy before the printing press.
- Present the thesis statement: The invention of the printing press increased circulation of information in Europe, paving the way for the Reformation.
- Discuss the very high levels of illiteracy in medieval Europe.
- Describe how literacy and thus knowledge and education were mainly the domain of religious and political elites.
- Indicate how this discouraged political and religious change.
- Describe the invention of the printing press in 1440 by Johannes Gutenberg.
- Show the implications of the new technology for book production.
- Describe the rapid spread of the technology and the printing of the Gutenberg Bible.
- Link to the Reformation.
- Discuss the trend for translating the Bible into vernacular languages during the years following the printing press’s invention.
- Describe Luther’s own translation of the Bible during the Reformation.
- Sketch out the large-scale effects the Reformation would have on religion and politics.
- Summarize the history described.
- Stress the significance of the printing press to the events of this period.
Literary analysis essay outline
The literary analysis essay outlined below discusses the role of theater in Jane Austen’s novel Mansfield Park .
The body of the essay is divided into three different themes, each of which is explored through examples from the book.
- Describe the theatricality of Austen’s works
- Outline the role theater plays in Mansfield Park
- Introduce the research question : How does Austen use theater to express the characters’ morality in Mansfield Park ?
- Discuss Austen’s depiction of the performance at the end of the first volume
- Discuss how Sir Bertram reacts to the acting scheme
- Introduce Austen’s use of stage direction–like details during dialogue
- Explore how these are deployed to show the characters’ self-absorption
- Discuss Austen’s description of Maria and Julia’s relationship as polite but affectionless
- Compare Mrs. Norris’s self-conceit as charitable despite her idleness
- Summarize the three themes: The acting scheme, stage directions, and the performance of morals
- Answer the research question
- Indicate areas for further study
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
You will sometimes be asked to hand in an essay outline before you start writing your essay . Your supervisor wants to see that you have a clear idea of your structure so that writing will go smoothly.
Even when you do not have to hand it in, writing an essay outline is an important part of the writing process . It’s a good idea to write one (as informally as you like) to clarify your structure for yourself whenever you are working on an essay.
If you have to hand in your essay outline , you may be given specific guidelines stating whether you have to use full sentences. If you’re not sure, ask your supervisor.
When writing an essay outline for yourself, the choice is yours. Some students find it helpful to write out their ideas in full sentences, while others prefer to summarize them in short phrases.
You should try to follow your outline as you write your essay . However, if your ideas change or it becomes clear that your structure could be better, it’s okay to depart from your essay outline . Just make sure you know why you’re doing so.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Essay Outline | Guidelines & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved October 15, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/essay-outline/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to create a structured research paper outline | example, a step-by-step guide to the writing process, how to write an argumentative essay | examples & tips, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Pardon Our Interruption
As you were browsing something about your browser made us think you were a bot. There are a few reasons this might happen:
- You've disabled JavaScript in your web browser.
- You're a power user moving through this website with super-human speed.
- You've disabled cookies in your web browser.
- A third-party browser plugin, such as Ghostery or NoScript, is preventing JavaScript from running. Additional information is available in this support article .
To regain access, please make sure that cookies and JavaScript are enabled before reloading the page.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
85. Instead - Specifies a substitute or replacement, clearly stating that one option is to be considered in place of another. 86. On the flip side - Introduces a contrasting scenario or viewpoint in a more informal manner, often used in conversational or less formal writing.
If you're struggling to choose the right words for your essay, don't worry—you've come to the right place! In this article, we've compiled a list of over 300 words and phrases to use in the introduction, body, and conclusion of your essay. Contents: Words to Use in the Essay Introduction. Words to Use in the Body of the Essay.
Most academic essays require a formal writing style because using informal writing makes it hard to edit and grade based on a standard the school or university gives. Even personal and narrative essays must stay formal. These are the words to create and enhance your introduction without losing the sense of formality in academic writing. According
Words to Start a Conclusion Paragraph. The conclusion paragraph wraps up your essay and leaves a lasting impression on the reader. It should convincingly summarize your thesis and main points. For more tips on writing a compelling conclusion, consider the following examples of ways to say "in conclusion": In summary, [topic] demonstrates…
Example: "In a nutshell, there are valid arguments on both sides of the debate about socialism vs capitalism.". 18. In closing…. My Rating: 7/10. Overview: This phrase is an appropriate synonym for 'In conclusion' and I would be perfectly fine with a student using this phrase in their essay.
Abruptly switching topics in essays can be jarring; however, transition words can smooth the change for the convenience of the reader.Moreover, you can use essay transition words to start a paragraph, sentence, or clause more naturally.Additionally, essay transition words can connect new information to the previous statement so you don't have to say everything at once.
Good sentence starters to establish cause and effect. It's common to use two different sentences to discuss a cause-and-effect relationship, as in something making something else happen. Sentence starters can make this relationship clear and show which sentence is the cause and which is the effect. As a result . . .
These useful academic expressions, words, vocabulary and phrases will help you to write a top-notch essay. Writing an essay can be a challenging task. However it becomes simpler if it is divided into manageable pieces. There are three main parts in an essay: an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. You can easily overcome your essay writing ...
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
The Oxford Phrasal Academic Lexicon (OPAL) is a set of four word lists that together provide an essential guide to the most important words and phrases to know in the field of English for Academic Purposes (EAP). This list gives around 370 important phrases for academic writing, grouped into 15 functional areas. Written phrases 1.
Provides clarification, similar to "in other words.". Example The reaction is exothermic; that is to say, it releases heat. 13. To put it simply. Simplifies a complex idea, often for a more general readership. Example The universe is vast; to put it simply, it is larger than anything we can truly imagine. 14.
33 Transition Words and Phrases. 'Besides,' 'furthermore,' 'although,' and other words to help you jump from one idea to the next. Transitional terms give writers the opportunity to prepare readers for a new idea, connecting the previous sentence to the next one. Many transitional words are nearly synonymous: words that broadly indicate that ...
in a specific or general way. Attributing claims with more or less support or certainty. Words that link ideas, helping to create a 'flow' in the writing. Many conjunctions can be used at the start of a sentence and/or. to link two short sentences into one long one. See WriteSIte for examples, exceptions and exercises.
While the words "also," "and," and "so" are used in academic writing, they are considered too informal when used at the start of a sentence. Also, a second round of testing was carried out. To fix this issue, we can either move the transition word to a different point in the sentence or use a more formal alternative.
9. By contrast; in comparison; then again; that said; yet. These essay phrases show contrast, compare facts, and present uncertainty regarding a point in your research. "That said" and "yet" in particular will demonstrate your expertise on a topic by showing the conditions or limitations of your research area.
The essay writing process consists of three main stages: Preparation: Decide on your topic, do your research, and create an essay outline. Writing: Set out your argument in the introduction, develop it with evidence in the main body, and wrap it up with a conclusion. Revision: Check your essay on the content, organization, grammar, spelling ...
They have their place in academic writing, but writers do need to choose elevated descriptive words. 1. Acceptable. An acceptable outcome would be for the students to earn a passing grade on the exam. 2. Adequate. If the experiment uses an adequate amount of liquid, the result will be a polymer. 3. Amiable.
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
A short essay is a concise piece of writing, typically between 250 and 500 words, that presents a focused argument or reflection on a specific topic. Unlike longer essay writing , a short essay requires a clear, narrow topic and a precise thesis statement due to its limited length.
Expository essay outline. Claim that the printing press marks the end of the Middle Ages. Provide background on the low levels of literacy before the printing press. Present the thesis statement: The invention of the printing press increased circulation of information in Europe, paving the way for the Reformation.
This is not a movie review! As a critical essay, a short, introductory synopsis of the film is sufficient followed by the aim or purpose of your analysis. Mentioning key themes &/or elements of the plot sets the context for your analysis and critique. Focus on a formal analysis of a key sequence/scene in the film, then turn to a critical discussion of the implicit cultural, social, or ...