
15 Questions that Teachers and Parents Can Ask Kids to Encourage Critical Thinking
By Maureen Leming
Each student walks across the graduation stage, diploma in one hand and a proverbial toolbox in the other. Inside the box is every skill and piece of knowledge they've learned throughout their childhood. The contents of this toolbox will be their building blocks to success beyond high school.
In addition to impressive classroom discoveries — like producing electricity from potatoes or building their own paper mache volcano — there's a vital skill every student should possess: critical thinking. They'll use this skill to assess, critique, and create, propelling them to thrive in the real world as they participate in engaging conversations and offer constructive solutions to real-world issues.
Fortunately, this valuable skill can be developed both inside and out of the classroom. Teachers and parents can encourage kids to think deeply and critically about the world by asking good questions. We'll explore why, as parents and teachers, the questions we ask our kids matter — and what we can be asking to help them excel.
How Questions Guide Young Students’ Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is about so much more than simply knowing the facts. Thinking critically involves applying reason and logic to assess arguments and come to your own conclusions. Instead of reciting facts or giving a textbook answer, critical thinking skills encourage students to move beyond knowing information and get to the heart of what they really think and believe.
15 Questions to Encourage Critical Thinking
What is one of the best ways to encourage critical thinking? By asking excellent questions!
We have compiled a list of 15 questions that you, as a teacher or parent, can ask to encourage kids to think outside the box. Let's dive in.
1. How Do You Know This?
Whether it was by word of mouth, classroom knowledge, or a news report, this question prompts students to consider whether their source of information is reputable.
2. How Would Your Perspective Be Different If You Were on the Opposing Side?
This question encourages kids to role-play from an opposing person’s viewpoint and discover a perspective outside their own so that they can better understand the broader situation. Extracurriculars like debate class — mandatory for all Hun middle school students — is a powerful way to accomplish this goal, as students must thoughtfully anticipate their opposition's arguments in order to counter them.
3. How Would You Solve This Problem?
Finding creative solutions to common problems is a valuable life skill. This question is the perfect opportunity to encourage young minds to wander!
4. Do You Agree or Disagree — and Why?
Choosing a side in any debate challenges students to consider both perspectives, weigh the arguments, and make an informed choice.
5. Why? Why? Why?
Just like when you were a young kid, ask why repeatedly to push students beyond a simple first, second, or even third answer, to get to the real depth. Be careful, though, not to ask them to the point of frustration — you want learning and exploring to be a positive experience.
6. How Could We Avoid This Problem in the Future?
Ask students to apply critical thinking by analyzing how they could prevent a certain issue from reoccurring.
7. Why Does It Matter?
Whether they're learning about a historical event or a mathematical concept, it's important to understand why the topic is relevant today.
8. What's Another Way to Look at This Issue?
It can be easy to learn one worldview and automatically believe it is the only, or the best, way. Challenging kids to think of a creative alternate perspective encourages them to think more broadly.
9. Can You Give Me an Example?
Inventing an example, or pulling from experience to share a real one, is an excellent way to apply critical thinking skills.
10. How Could It Have Ended Differently?
It takes some innovation and careful analysis to storyboard a different ending, considering "what could have been" rather than "what is."
11. When Will We Be Able to Tell If It Worked?
Kids will be pushed to consider what constitutes success and how it can be measured in scenarios where the results aren't set in stone.
12. Why did you ask that question?
Instead of answering a question at face value, this question encourages kids to think about what the merits of the question may be.
13. Who Would Be Affected by This?
Students as the next generation of leaders and game-changers. When making any decision, it's important to consider who will be impacted and how.
14. What Can This Story Teach Us About Our Own Lives?
From literature to social studies, students interact with all kinds of different stories. Help them take these narratives one step further by examining how it relates to their lives.
15. Why Is This a Problem?
Analyzing why something is a problem — rather than just accepting that it is — will help students develop strong problem-solving skills of their own.
The Hun School of Princeton Teaches Critical Thinking
At the Hun School of Princeton, our teachers ask these questions, and more, in combination with our student-centered learning approach that helps kids of all ages think critically about what they’re learning.
As a premier private school in Princeton, NJ , we aim to help students think deeply and develop well-rounded skill sets through immersive, problem-based learning .
Schedule a tour today to see our program in action!
Schedule a Tour

28 Critical Thinking Question Stems For Any Content Area

Guest Post by TeachThought Staff
Critical thinking isn’t a skill, nor is it content knowledge or even evidence of understanding. While it involves and requires these ideas, critical thinking is also very much a state of mind — a willingness and tendency to sit with an idea and ‘struggle wonderfully’ with it.
In critical thinking, there is no conclusion; it is constant interaction with changing circumstances and new knowledge that allows for broader vision which allows for new evidence which starts the process over again. Critical thinking has at its core raw emotion and tone. Intent.
The purpose of these stems is to help students practice this slippery ‘skill.’ By having dozens of questions written generally enough to be widely applicable, but with an inherent rigor that challenges students to think, the ability to practice thinking critically is always available.
1. What evidence can you present for/against…?
2. How does … contrast with …?
3. How could you outline or concept map…? Explain your response with examples.
4. Why is … significant? Explain your reasoning.
5. What are the advantages and disadvantages of …?
6. What is the point or ‘big idea’ of …?
7. How could you judge the accuracy of …?
8. What are the differences between … and …?
9. How is … related to …?
10. What ideas could you add to … and how would these ideas change it?
11. Describe … from the perspective of ….
12. What do you think about …? Explain your reasoning.
13. When might … be most useful and why?
14. How could you create or design a new…? Explain your thinking.
15. What solutions could you suggest the problem of …? Which might be most effective and why?
16. What might happen if you combined … and …?
17. Do you agree that …? Why or why not?
18. What information would you need to make a decision about …?
19. How could you prioritize …?
20. How is … an example of …?
21. What are the most important parts or features of …?
22. Which details of … are most important and why?
23. What patterns do you notice in …?
24. How could you classify … into a more/less general category?
25. What makes … important?
26. What criteria could you use to assess …?
27. How could … and … function together? How do they work separately and together and different ways?
28. Where is … most/least …? Explain your reasoning.
Critical Thinking Cards
In adddition to the text and cards, we’ve included a graphic below. You also can purchase them in card-format to be printed and used right away in your classroom, a sample of which you can see below.
By making them cards, they are not only easier to ‘keep around’–on your desk, on a shelf in a workstation area, or even copied and given to students– but more importantly, meaningful thinking can become a part of your daily routines. Writing prompts, reading circles, Socratic discussions and more all benefit from critical thinking, and providing students with stems is a way of supporting them as their confidence grows and their habits as thinkers develop.

ABOUT THE AUTHOR
TeachThought.com is an organization dedicated to innovation in education through the growth of innovative teachers.
LIKE THIS ARTICLE? SHARE IT ON SOCIAL:
Don't want to miss another post receive new posts via email:, more recent posts, shallow questions………can become deep.
Excerpted with permission from the third chapter of “Supercommunicators – How to Unlock the...
LEADING WITH QUESTIONS? THAT’S A GOOD QUESTION!
By Dr. Ronald Harris – Excerpted from the 11th Chapter of “340 Questions Jesus Asked” I...
START SAFE, THEN BUILD
Note from Bob: I just recently found this marvelous new book! It is a Great Read! I was delighted when...
AVOID MAKING ASSUMPTIONS
Deflect difficulty, ask the right questions, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
85 Fun Critical Thinking Questions for Kids & Teens

Have you ever thought about using fun questions to practice critical thinking?
Students may need a little guidance to think their way through questions that lack straightforward answers.
But it is that process that is important!
How the Right Questions Encourage Critical Thinking
Every parent knows how natural it is for children to ask questions.
It should be encouraged. After all, asking questions helps with critical thinking.
As they grow older, however, training them to answer questions can be equally beneficial.
Posing questions that encourage kids to analyze, compare, and evaluate information can help them develop their ability to think critically about tough topics in the future.
Of course, critical thinking questions for kids need to be age-appropriate—even better if you can mix a little fun into it!
That’s what I hope to help you with today. I’ve organized the questions below into three different ages groups:
- Upper elementary
- Middle school
- High school

Get a Question-Based Critical Thinking Exercise—Free!
Introduce critical thinking gently & easily with thought-provoking exercises.
Upper Elementary
Students in upper elementary grades can be reluctant to put themselves out there, especially with answers that seem weird.
In some cases, such hesitancy is actually fear of differing from their peers (and a barrier to critical thinking ).
But that’s exactly why it’s important to practice answering ambiguous questions.
We want our children to stand firm for their beliefs—not cave to peer pressure.
Additionally, students may feel uneasy about answering serious questions, uncertain of tackling “big” problems.
However, with careful use of creative questions for kids, it’s possible to engage even the most reluctant children in this age group.
The idea is to simply get them interested in the conversation and questions asked.
If you have an especially reserved student, try starting with the funny critical thinking questions.
Humor is a natural icebreaker that can make critical thinking questions more lighthearted and enjoyable.
Of course, most younger kids just like to be silly, so playing upon that can keep them active and engaged.
With that said, here are some great questions to get you started:
1. Someone gives you a penguin. You can’t sell it or give it away. What do you do with it?
2. What would it be like if people could fly?
3. If animals could talk, what question would you ask?
4. If you were ice cream, what kind would you be and why?
5. Do you want to travel back in time? If yes, how far back would you go? If no, why not?
6. What could you invent that would help your family?
7. If you could stay up all night, what would you do?
8. What does the man on the moon do during the day?
9. What makes something weird or normal?
10. Can you describe the tastes “salty” and “sweet” without using those words?
11. What does it feel like to ride a rollercoaster?
12. What makes a joke funny?
13. What two items would you take if you knew you would be stranded on an island and why?
14. Do you have a favorite way of laughing?
15. What noise makes you cringe and cover your ears? Why?
16. If you could be the parent for the day, what would you do?
17. If you could jump into your favorite movie and change the outcome, which one would you pick and why?
18. If you could be invisible for a day, what would you do?
19. What makes a day “perfect”?
20. If you owned a store, what kind of products would you sell?
21. If your parents were your age, would you be friends with them?
22. Would you still like your favorite food if it tasted the same as always, but now had an awful smell?
23. What would you do if you forgot to put your shoes on before leaving home?
24. Who would you be if you were a cartoon character?
25. How many hot dogs do you think you could eat in one sitting?
26. If you could breathe under water, what would you explore?
27. At what age do you think you stop being a kid?
28. If you had springs in your legs, what would you be able to do?
29. Can you describe the color blue to someone if they’re blind?
Middle School
At this point, students start to acquire more complex skills and are able to form their own conclusions based on the information they’re given.
However, we can’t expect deep philosophical debates with 12 and 13 year olds.
That said, as parent-teachers, we can certainly begin using more challenging questions to help them examine and rationalize their thought processes.
Browse the fun critical thinking questions below for students in this age range.
You might be surprised to see how receptive middle school kids can be to such thought-provoking (yet still fun) questions .
30. What would happen if it really did rain cats and dogs?
31. What does it mean to be lucky?
32. If you woke up in the middle of a dream, where would you be?
33. Is it ever okay to lie? Why or why not?
34. If you were solely responsible for creating laws, what one law would you make?
35. What makes a person a good friend?
36. What do you think is the most important skill you can take into adulthood?
37. If you had to give up lunch or dinner, which would you choose? Why?
38. How much money would you need to be considered rich?
39. If you knew you wouldn’t get caught, would you cheat on a test?
40. If you could live anywhere in the world, where would that be?
41. What is your greatest strength? How is that an asset?
42. If you had an opportunity to visit the International Space Station, would you do it?
43. Is it better to keep the peace or speak your mind?
44. Imagine yourself as your favorite animal. How would you spend your day?
45. Would you be friends with someone who didn’t have the same values as you?
46. How much screen time do you think is too much?
47. Can you describe your favorite color without naming it?
48. If you suddenly became blind, would you see things differently?
49. Would you ever go skydiving?
50. Describe the time you were the happiest in your life. Why did this make you happy?
51. If you had a million dollars, what would you do?
52. If you had to move to a new city, would you change how you present yourself to others?
53. What do you need to do in order to be famous?
54. If you could rewrite the ending of your favorite book or movie, what changes would you make?
55. How would you tackle a huge goal?
56. How would you sell ice to an eskimo in Alaska successfully?
57. What makes you unique?
High School
Critical thinking takes on an entirely different role once students reach high school.
At this age, they have a greater sense of right and wrong (and what makes things so) as well as a better understanding of the world’s challenges.
Guiding teens to delve deeper and contemplate such things is an important part of developing their reasoning and critical thinking skills.

Whether it’s fun questions about hypothetical superpowers or tough critical thinking questions about life, older teens typically have what it takes to think their way to a logical conclusion .
Of course, use your discernment as you choose discussion topics, but here are some questions to help get you started:
58. How can you avoid [common problem] in the future?
59. Do you think it’s okay to take a life in order to save 5, 10, 20 or more people?
60. If you could go back and give your younger self advice, what would it be?
61. Is it better to give or receive a gift?
62. How important is it to be financially secure? Why?
63. If it was up to you, what one rule would you change in your family?
64. What would you do if a group of friends wanted to do something that you thought was a bad idea?
65. How do you know that something is a fact rather than an opinion?
66. What would it take to get you to change your mind?
67. What’s the most important thing in your life?
68. If money were of no concern, what job would you choose and why?
69. How do you know if you’re happy?
70. Do you think euthanasia is moral?
71. What is something you can do today that you weren’t able to do a year ago?
72. Is social media a good thing or not?
73. Is it right to keep animals in a zoo?
74. How does your attitude affect your abilities?
75. What would you do if you found out a friend was doing something dangerous?
76. If you could have any superpower, what would it be? Why?
77. What will life on Earth look like in 50 years?
78. Which is more important, ending world hunger or global warming?
79. Is it a good idea to lower the voting age to 16? Why or why not?
80. If the electrical power went out today, how would you cook if using wood wasn’t an option?
81. If you could magically transport yourself to any other place, where would that be and why?
82. When should teenagers be able to stay out all night?
83. Does the number zero actually exist?
84. What defines a generous person?
85. Does an influential person influence everyone?
Feel free to print out these fun critical thinking questions and incorporate them into your homeschool week!

will your children recognize truth?
About the author.
Jordan Mitchell
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Win a personal laminator for your classroom! ✨
100+ Critical Thinking Questions for Students To Ask About Anything
Critical thinkers question everything.

In an age of “fake news” claims and constant argument about pretty much any issue, critical thinking skills are key. Teach your students that it’s vital to ask questions about everything, but that it’s also important to ask the right sorts of questions. Students can use these critical thinking questions with fiction or nonfiction texts. They’re also useful when discussing important issues or trying to understand others’ motivations in general.
“Who” Critical Thinking Questions
Questions like these help students ponder who’s involved in a story and how the actions affect them. They’ll also consider who’s telling the tale and how reliable that narrator might be.
- Is the protagonist?
- Is the antagonist?
- Caused harm?
- Is harmed as a result?
- Was the most important character?
- Is responsible?
- Is most directly affected?
- Should have won?
- Will benefit?
- Would be affected by this?

- Makes the decisions?
“What” Critical Thinking Questions
Ask questions that explore issues more deeply, including those that might not be directly answered in the text.
- Background information do I know or need to know?
- Is the main message?
- Are the defining characteristics?

- Questions or concerns do I have?
- Don’t I understand?
- Evidence supports the author’s conclusion?
- Would it be like if … ?
- Could happen if … ?
- Other outcomes might have happened?
- Questions would you have asked?
- Would you ask the author about … ?
- Was the point of … ?
- Should have happened instead?
- Is that character’s motive?
- Else could have changed the whole story?

- Can you conclude?
- Would your position have been in that situation?
- Would happen if … ?
- Makes your position stronger?
- Was the turning point?
- Is the point of the question?
- Did it mean when … ?
- Is the other side of this argument?
- Was the purpose of … ?
- Does ______ mean?
- Is the problem you are trying to solve?
- Does the evidence say?
- Assumptions are you making?
- Is a better alternative?
- Are the strengths of the argument?
- Are the weaknesses of the argument?
- Is the difference between _______ and _______?
“Where” Critical Thinking Questions
Think about where the story is set and how it affects the actions. Plus, consider where and how you can learn more.
- Would this issue be a major problem?
- Are areas for improvement?
- Did the story change?
- Would you most often find this problem?

- Are there similar situations?
- Would you go to get answers to this problem?
- Can this be improved?
- Can you get more information?
- Will this idea take us?
“When” Critical Thinking Questions
Think about timing and the effect it has on the characters or people involved.
- Is this acceptable?
- Is this unacceptable?

- Does this become a problem?
- Is the best time to take action?
- Will we be able to tell if it worked?
- Is it time to reassess?
- Should we ask for help?
- Is the best time to start?
- Is it time to stop?
- Would this benefit society?

- Has this happened before?
“Why” Critical Thinking Questions
Asking “why” might be one of the most important parts of critical thinking. Exploring and understanding motivation helps develop empathy and make sense of difficult situations.
- Is _________ happening?
- Have we allowed this to happen?
- Should people care about this issue?

- Is this a problem?
- Did the character say … ?
- Did the character do … ?
- Is this relevant?
- Did the author write this?
- Did the author decide to … ?
- Is this important?
- Did that happen?
- Is it necessary?
- Do you think I (he, she, they) asked that question?
- Is that answer the best one?
- Do we need this today?
“How” Critical Thinking Questions
Use these questions to consider how things happen and whether change is possible.
- Do we know this is true?
- Does the language used affect the story?
- Would you solve … ?
- Is this different from other situations?

- Is this similar to … ?
- Would you use … ?
- Does the location affect the story?
- Could the story have ended differently?
- Does this work?
- Could this be harmful?
- Does this connect with what I already know?
- Else could this have been handled?
- Should they have responded?

- Would you feel about … ?
- Does this change the outcome?
- Did you make that decision?
- Does this benefit you/others?
- Does this hurt you/others?
- Could this problem be avoided?
More Critical Thinking Questions
Here are more questions to help probe further and deepen understanding.
- Can you give me an example?

- Do you agree with … ?
- Can you compare this with … ?
- Can you defend the actions of … ?
- Could this be interpreted differently?
- Is the narrator reliable?
- Does it seem too good to be true?

- Is ______ a fact or an opinion?
What are your favorite critical thinking questions? Come exchange ideas on the WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook .
Plus, check out 10 tips for teaching kids to be awesome critical thinkers ., you might also like.

5 Critical Thinking Skills Every Kid Needs To Learn (And How To Teach Them)
Teach them to thoughtfully question the world around them. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256

Project-Based Learning Workshops
Inquiry Workshops
Differentiation Workshops
Objective Pluralism Workshops
Effective Online Teaching Workshops
SEL Workshops
PLC & Lesson Study Workshops
Growth Mindset Workshops
Assessment Workshops
AI in Education Workshops
Literacy Workshops
Admin/Leadership Workshops

The ThoughtStretchers Education Podcast: Does ‘Equity’ Undermine Science Education?
The thoughtstretchers education podcast: blocked but still discussing direct instruction or inquiry with anna stokke, the thoughtstretchers education podcast: helping inquiring minds learn, the thoughtstretchers education podcast: impactful instructional coaching with jim knight, the thoughtstretchers education podcast: do the science of learning and inquiry converge, the thoughtstretchers education podcast: talking inquiry with kath murdoch, the thoughtstretchers education podcast: how should we think about antiracism in education, the thoughtstretchers education podcast: a veteran teacher who rejects black and white thinking, the thoughtstretchers education podcast: a conservative vision for improving education, the thoughtstretchers education podcast: when a gop insider realizes moms for liberty claims are false, the thoughtstretchers education podcast: school desegregation in 1868 the story of susie clark, the thoughtstretchers education podcast: using thinking maps to empower project-based learning, the thoughtstretchers education podcast: hard questions about school choice, the thoughtstretchers education podcast: 2024 federal education budget advocacy, the thoughtstretchers education podcast: community-led education, overcoming the culture wars.

BLOG CATEGORIES
Differentiation
Growth Mindset
Tech Integration
Most Recent Blog Posts
Podcast Archive Page

Schedule a Call or Email Us!
Subscribe to our email newsletter.

Registration is open!
19 Types of Questions To Grow Critical Thinking
Jan 25, 2021 | Inquiry

Fostering critical thinking skills is essential for individuals to navigate the complexities of the modern world. As educators, one powerful tool at our disposal is the art of questioning. Thought-provoking questions stimulate intellectual curiosity, challenge assumptions, and encourage deeper analysis. Here are 19 types of questions designed to cultivate critical thinking in the classroom, categorized for clarity and purpose.
Categories of Questions:
1. Exploratory Questions:
- Open-ended questions: Encourage students to explore ideas without restrictive boundaries. Example: “What are the possible outcomes of this situation?”
2. Analytical Questions:
- Socratic Questions: Prompt students to analyze their own thinking processes. Example: “How did you arrive at that conclusion?”
- Comparative Questions: Encourage students to examine similarities and differences between concepts. Example: “In what ways are these two theories alike or different?”
- Cause and Effect Questions: Prompt students to consider the consequences of actions or events. Example: “What might be the repercussions if this decision is implemented?”
3. Imaginative Questions:
- Hypothetical Questions: Challenge students to think beyond the present and consider imaginary scenarios. Example: “What would happen if we reversed the roles in this situation?”
- Problem-Solving Questions: Engage students in critical thinking by presenting real-world problems. Example: “How would you address the challenges faced by the characters in this case study?”
4. Ethical Questions:
- Ethical Dilemma Questions: Foster moral reasoning by presenting ethical quandaries. Example: “If you had to choose between honesty and loyalty, which would you prioritize and why?”
5. Inference and Reflection Questions:
- Inference Questions: Encourage students to draw conclusions based on available information. Example: “What can you infer from the data provided?”
- Reflection Questions: Stimulate metacognition by prompting students to reflect on their own thought processes. Example: “How has your perspective on this topic evolved over time?”
6. Divergent Thinking Questions:
- Contradiction Questions: Encourage students to identify and resolve conflicting ideas. Example: “How can we reconcile these two seemingly contradictory viewpoints?”
- Prioritization Questions: Challenge students to determine the most significant factors in a given situation. Example: “What factors should be prioritized in making this decision?”
7. Integrative Questions:
- Interdisciplinary Questions: Encourage the integration of knowledge from multiple disciplines. Example: “How might principles from psychology and economics intersect in this context?”
8. Forward-Thinking Questions:
- Predictive Questions: Prompt students to anticipate future developments based on current trends. Example: “What might be the long-term implications of this social phenomenon?”
9. Collaborative and Metacognitive Questions:
- Collaborative Questions: Foster teamwork and collective problem-solving. Example: “How can diverse perspectives contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of this issue?”
- Meta-Questions: Encourage students to think about their thinking. Example: “What assumptions underlie your perspective, and how might they influence your conclusions?”
10. Awareness Questions:
- Bias Recognition Questions: Develop awareness of personal biases and perspectives. Example: “In what ways might your background influence your interpretation of this information?”
11. Systems Thinking Questions:
- Systemic Thinking Questions: Prompt students to consider the broader systems at play. Example: “How does this individual decision impact the larger system?”
12. Relevance and Adaptation Questions:
- Relevance Questions: Challenge students to assess the significance of information. Example: “How does this information contribute to our understanding of the main issue?”
- Adaptation Questions: Encourage flexibility in thinking by exploring alternative solutions. Example: “If the circumstances change, how might your approach to this problem evolve?”
Incorporating these diverse question types into your teaching repertoire can transform the learning experience, help create a culture of inquiry , equipping students with the invaluable skill of critical thinking. As educators, we have the power to shape not only what our students know but also how they think, empowering them to navigate the complexities of an ever-changing world with confidence and intellectual agility.

Request Workshop Info:

We'll be launching our ThoughtStretchers Community very soon!
Join our email list and you'll receive updates about the launch and events and more as we grow.
*note, this is different from our main ThoughtStretchers Education email list which is focused on our professional development work.
You have Successfully Subscribed!
Pin it on pinterest.
The Harriet W. Sheridan Center for Teaching and Learning
Questions to provoke critical thinking.
- Teaching Resources
- Classroom Practices
- Discussions and Seminars
Varying question stems can sustain engagement and promote critical thinking. The timing, sequence and clarity of questions you ask students can be as important as the type of question you ask. The table below is organized to help formulate questions provoking gradually higher levels of thinking.
Lower Levels
| Thinking Skills | Purpose | Sample Action Prompts | Example Questions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Remembering | memorize & recall facts | recognize, list, describe, identify, retrieve, name | |
| Understanding | interpret meaning | describe, generalize, explain, estimate, predict |
Higher Levels
| Thinking Skills | Purpose | Sample Action Prompts | Example Questions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Applying | apply knowledge to new situations | implement, carry out, use, apply, show, solve, hypothesize | |
| Analyzing | break down or examine information | compare, organize, deconstruct | |
| Evaluating | judge or decide according to a set of criteria | check, critique, judge, conclude, explain | |
| Creating | combine elements into a new pattern | design, construct, plan, produce |
1 From Alison King, “Inquiring Minds Really Do Want to Know: Using Questioning to Teach Critical Thinking,” Teaching of Psychology 22 (1995): 14.

85 Critical Thinking Questions to Carefully Examine Any Information
There might be affiliate links on this page, which means we get a small commission of anything you buy. As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases. Please do your own research before making any online purchase.
The ability to think critically will often determine your success in life.
Let’s face it. Every day, we are bombarded by news, social media updates, and an avalanche of information. If you take all of this at face value, it’s easy to be deceived, misled or ripped off.
That’s why it’s important to develop a mindset that focuses on critical thinking . This is a skill that needs to be developed in the classroom. But it’s also a valuable life skill.
With that in mind, the following post will share 85 critical thinking questions you can use to increase your awareness about different problems by carefully examining available information.
Let’s get started…
Table of Contents
What Are Critical Thinking Questions?
Critical thinking questions are inquiries that help you think rationally and clearly by understanding the link between different facts or ideas. These questions create a seemingly endless learning process that lets you critique, evaluate, and develop a depth of knowledge about a given subject. Moreover, you get to reinforce your viewpoints or see things in a new way.
We make decisions every day, whether at work or home. Adopting logical, rational, and practical approaches in addressing various issues requiring critical thinking is essential in decision-making. Therefore, before arriving at a decision, always ask yourself relevant questions and carefully analyze the matter’s pros and cons.
Critical Thinking Questions When in an Argument
When you make an argument using a critical thinking approach, you focus on justified claims that are valid and based on evidence. It helps one establish a strong argument.
- Do I disagree with the other person? Might the person I'm arguing with be misinformed on what they are saying?
- Would I be comfortable saying what I am telling him/her if I was in front of a group of people?
- What would happen if I lose this argument? Is engaging in this argument worth my time and energy? How will I feel if I lose?
- Is there room for ambiguity or misinterpretation? Are we arguing because I didn't make my point explicit? Should I take my time to understand his school of thought?
- Do I need some rest before saying something? Am I arguing because of other reasons other than the issues at hand? Do I need to take some time and cool down?

- Is it more important that I’m right? Am I trying to ask to prove an unnecessary point?
- Is this argument inductive, deductive, or abductive? Is it a weak or strong argument that I need to engage in? Is it compelling or sound?
- Is my opponent sincere? Given that they are wrong, are they willing to admit that they are wrong? Can they depend on available evidence, wherever it leads?
- Are my opponents only trying to shift their burden to me? What is the best way to prove them wrong without making them feel bad?
- Are the people I'm arguing with only interested in winning, or are they trying to pass some information across and help me discover the truth?
Critical Thinking Questions When Reading a Book
When you read a book, you probably ask yourself many “why” questions. Why is this a problem? Why did the character say that? Why is this important? The most challenging part of reading a book is assessing the information you are reading. These questions can help.
- If I learn only two things from this book, what will they be? How will they help me? How will I apply them in my daily life?
- What message are the authors trying to pass across? Are they making suggestions or providing evidence for their arguments?
- Given that almost every book is about solving problems, what is the most prevalent issue that the author is trying to solve?
- What is the author’s writing style? What strategy or master plan does the author employ to convey his/her main ideas throughout the book?
- Do I have background information about the book’s topic? If so, how is what the author is saying different from what I already know?
- What didn’t I understand from the book? Should I re-read the book to understand everything the writer is trying to convey?
- Which sections of the book do I love the most, and why? Generally, do I like this book? Should I look for more books that are written by the same author?
- If I had a chance to meet this book’s author, what questions would I ask him/her? What would I tell the writer about the book? Is it a great book worth recommending to your friends and family members?
- Who are the main characters of the book? If there is only one main character, what overarching goal does the character accomplish?
- In what ways did the protagonist change from the start of the book to the end? What caused the changes? Was the protagonist reckless in some ways? Which ways?
Critical Thinking Questions to Spot a Scam
Asking questions when you feel that a fraud or a scam is being presented to you is a good way to stretch your critical thinking muscles. Are you being emailed or messaged by a stranger? Or maybe there are other red flags you are unsure about. If so, ask these questions.
- Does it seem to be too good to be true? Is this stranger pushy or trying to lure me into making a poor decision?
- When trying out online dating: Is my new “friend” professing strong feelings towards me although we’ve only interacted for a few hours?
- Why is a stranger calling me to ask about my Social Security Number (SSN), personal contact information, or bank details while claiming they are from the bank or a phone company?
- When buying products online, why does the seller ask me to pay for goods using an insecure payment option like Bitcoin or money order?
- Does the email I have received have any spelling or grammatical errors? Is the language used overly formal or informal?
- If I do a quick search about the exact words of the email I received, does Google indicate it's a fraud or scam?
- Why should a stranger manipulate me using obvious questions like “Would you want to be rich or poor?” While they already know the answer?
- Is the email asking me to download an attachment? Or click a link to some insecure website?
- Is the person trying to make me feel selfish or guilty for not sending them money, whether for a donation or buying a product?
- Is the stranger portraying a sense of urgency and using pressure tactics? Are they telling me that their family member needs urgent medical attention?
Critical Thinking Questions About Your Life
It can also help to ask yourself a few critical thinking questions about your life. This way, you can gather basic information and uncover solutions to problems you might not have otherwise thought of.
- Where do I wish to be in a few years, probably two, three, or five years? What short-term and long-term goals should I set?
- What have I achieved so far from the time I set my previous goals? What should I be grateful for?
- Do I have any values that guide me in life? If so, what are these values? Am I always true to these values?
- Am I always worried about what people around me think? Can I act independently without the need to meet social expectations?
- What should people say about me at my funeral? Would they talk about how good I made them feel or how rich and flashy I was?
- If I wasn't afraid of anyone or anything, what would I have done? What if I didn't have any fear in me?
- If today was my last day, what extraordinary thing would I do? Can I do it right now?
- What should I do with the things that matter the most to me?
- What things will make the greatest difference in my future life if I take action now?
- How should I react when I feel unwanted by the people I love the most? Should I tell them?

Critical Thinking Questions for a Debate or Discussion
When you are in the middle of a debate or discussion, you need to know that what you are saying is fact, have evidence to support your claim, and position yourself as an expert in what you are saying. Here are some critical thinking questions to ask when you are in a debate or discussion.
- Is there fairness in this discussion? Is the moderator supporting one side? Do they want to make one side look stupid or wrong?
- What is the aim of this discussion? Is there a major problem that needs to be solved? If so, how can I help solve it?
- Who are the people affected by this discussion? If they were here, what would they say?
- Do my views on this discussion matter? If I raise my point, will I be redundant?
- What am I supposed to learn from this debate, and how can I use what I have learned in my daily life?
- Does the audience seem to be biased towards one side? Are they booing one side? What can I do even if it's our opponents being booed?
- Who are the discussion panel members? What views have they held about this kind of discussion or any other related discussions in the past?
- How can I make my point without being ambiguous? Before I speak, should I take down some notes to avoid any confusion during my speech?
- Am I ready to apologize if I make a mistake during the discussion? If so, what are the limits?
- What information does my team, or I need before this discussion?
Critical Thinking Questions About Lying
Admitting when you are wrong, choosing not to cheat, and sharing constructive feedback are all ways to show your honesty. Here are some critical thinking skills to ask regarding lying.
- Will the lie hurt those I am telling, or will it help them? What if being honest might cause my friend unnecessary pain?
- Should I be the one telling this person a lie, or I let someone else do it?
- Will I be the one hurt if I tell this lie? Will my friend feel I am a betrayer? Will it affect our friendship?
- Do they answer my questions in detail, or are they always trying to ignore and dodge the main problem?
- What if I ask these people the same question using different terms and wording? Will they give me the same response?
- Did the tone of my friend suddenly change after I asked him/her this question? Do they sound louder, faster, or slower compared to how they usually speak?
- Does this person have something to gain by lying to me? What is their motive?
- Does this person take a sudden pause or hesitate more than usual when responding to my question?
- When I look at these people's faces, do their facial expressions match what they say?
- Should I believe this person or not? What are my intuitions? Does it look like they are telling the truth?
- Do they blink like other days when I ask them questions? Are they always trying to avoid direct eye contact?
- Why do they seem uncomfortable when it’s just a normal conversation?
Critical Thinking Questions When Presented With a Claim
Critical thinking is much more than just evaluating whether a claim is true or not. It also means a critical thinker reflects on what follows from true claims.
- What does this claim mean, and what are its implications? What if it's a false claim?
- Which of my morals, values, or beliefs do I have to give up to accept this claim?
- Do professionals in this field agree or disagree with the claim that has been made?
- Do they have evidence to back their claim? Which is the most robust evidence to support the claim?
- What argument can I come up with to refute this claim? Or what is the best view that can support this claim?
- Who is the primary source of the claim being made? Is the basis of the claim reliable?
- Is it a claim, or it's just an opinion?
- Is the claim likely to be 100% false, true, or partially true?
- Am I allowed to refute the claim and table my evidence, or is it one-sided?
Critical Thinking Interview Questions
Critical thinking skills are valuable in any industry or field and for almost all roles. During a job interview, you will be asked questions so the potential employer can assess your skills and see how you use logic. Your critical thinking ability is just one vital part that can play into your professional development.
- Is there a time you had to convince someone to use an alternate approach to solve a problem?
- Have you ever had to make a difficult decision quickly?
- How would you handle a situation where your supervisor handled something wrong or made a mistake?
- What is one of the most difficult decisions you have ever had to make at work?
- How would you solve a disagreement between coworkers when approaching a project?
- Can you describe a time when you anticipated a problem ahead of time and took the appropriate steps to stop the problem from becoming an issue?
- If you discover a cheaper way to do something or a better solution to a problem and try to explain it to your supervisor, but they don’t understand, what do you do?
Critical Thinking Questions for Kids
We can’t leave the kids out either. Critical thinking questions for kids get them thinking and talking. It also allows a parent to get to know their child better.
- How many grains of sand do you think are on the beach?
- What would happen if it stopped raining?
- Do you think there is life on other planets?
- Should children be able to set their own bedtimes?
- How would you describe what a tree looks like without saying green or leaves?
- Can you name five different emotions?
- Can you talk for five minutes without uttering “um?”
What Are the Basic Principles of Critical Thinking?
Your critical thinking skills involve gathering complete information, understanding and defining terms, questioning the methods by which we get facts, questioning the conclusions, and looking for hidden assumptions and biases.
Additionally, we can’t expect to find all of the answers, and we need to take the time to examine the big picture of it all.
Here are the basic principles:
- Disposition: Someone with critical thinking skills is often skeptical, open-minded, and practices fair-mindedness. They can look at different viewpoints and change positions if the evidence and reason lead them to do so.
- Criteria: In order to think critically, one must also apply criteria. Certain conditions must be met before someone believes in something. The information needs to be from credible sources.
- Argument: An argument is simply a statement or proposition that is shown with supporting evidence. When you use your critical thinking skills, you identify, evaluate, and construct your argument.
- Reasoning: With critical thinking comes reasoning. You must examine logical relationships among the statements being made.
- Point of View: Critical thinkers can see things from different perspectives and different points of view.
What Are Good Analysis Questions?
Analysis is a part of critical thinking that allows you to examine something carefully. Someone with analytical skills can examine the information presented, understand what that information means, and then properly explain that information to others. Analysis in critical thinking provides more clarity on the information you process.
When analyzing, you may ask yourself, “how do I know this,” how would I solve this problem,” and “why does it matter?”
Why Is Critical Thinking an Important Skill?
Critical thinking skills allow you to express thoughts, ideas, and beliefs in a better way. It also leads to improved communication while allowing others to understand you better. Critical thinking fosters creativity and encourages out-of-the-box thinking. This is a skill that can be applied to many different areas of your life.
For example, knowing the answers to critical thinking questions for a job interview will better prepare you for the interview. Many employers, during questioning, are likely to ask you critical thinking questions to assess if you have the ability to evaluate information effectively so you can make more informed decisions.
Final Thoughts on Critical Thinking Questions
Although it's common to get torn between making two or more choices, nobody wants to make the wrong decision. The only thing you can do to avoid this is use critical thinking questions to examine your situation. The answers to these questions will help you make informed decisions and help you comprehend crucial matters in your life.
Want to learn more about critical thinking and decision-making using a real-life example? Here is how Jeff Bezos uses critical thinking to make some of the most challenging life decisions.
Finally, if you want to ask better questions, then watch this short, 20-minute course to learn how to have a great conversation with virtually anyone .


36 Question Stems Framed Around Bloom’s Taxonomy
Question stems can be used as thinking prompts for class discussions, prompting, and various forms of assessment.
Question Stems Framed Around Bloom’s Taxonomy
by TeachThought Staff
While critical thinking is a foundation rather than a brick, how you build that foundation depends on the learning process itself: exposing students to new thinking and promoting interaction with that thinking in a gradual release of responsibility approach.
Question stems can be a powerful part of that process no matter where the learner is. They can be used as metacognitive and higher-order thinking prompts for class discussions, prompting, cueing, pre-assessment, self-assessment, formative and summative assessment, etc.
See also 28 Critical Thinking Question Stems & Response Cards ($2.95)
The following graphic includes 25+ question stems framed around the early, non-revised Bloom’s Taxonomy are worth a gander.
In the ‘Knowledge’ category, question stems focus on helping students identify and recall information — these are often referred to as ‘literal’ questions, because a learner could more than likely point to a specific location in a text and say, “This is the answer.”
‘Comprehension’ question stems go a step further by prompting the students to make explain concepts or relationships in their own words, demonstrating that they can organize and select facts and ideas from within and across texts.
With ‘Application,’ students elevate their thinking by applying what they comprehend. They use facts, rules, and principles to relate their learning to other contexts, like text-to-text, text-to-world, and text-to-self connections.
In ‘Analysis,’ learners separate parts from a whole. They may categorize information, compare and contrast, or use a diagram to show relationships.
‘Synthesis’ requires students to combine ideas to form a new idea. Here, students are moving toward creation and ingenuity. They can make predictions and devise prototypes for presented problems.
Finally, ‘Evaluation’ question stems prompt students to share their own thinking, or to make judgments based on a body of evidence and/or opinion.
While this version of Bloom’s Taxonomy has since been revised, we see value in these question stems as resources to help students think more deeply, and to help teachers start them off on the right track.
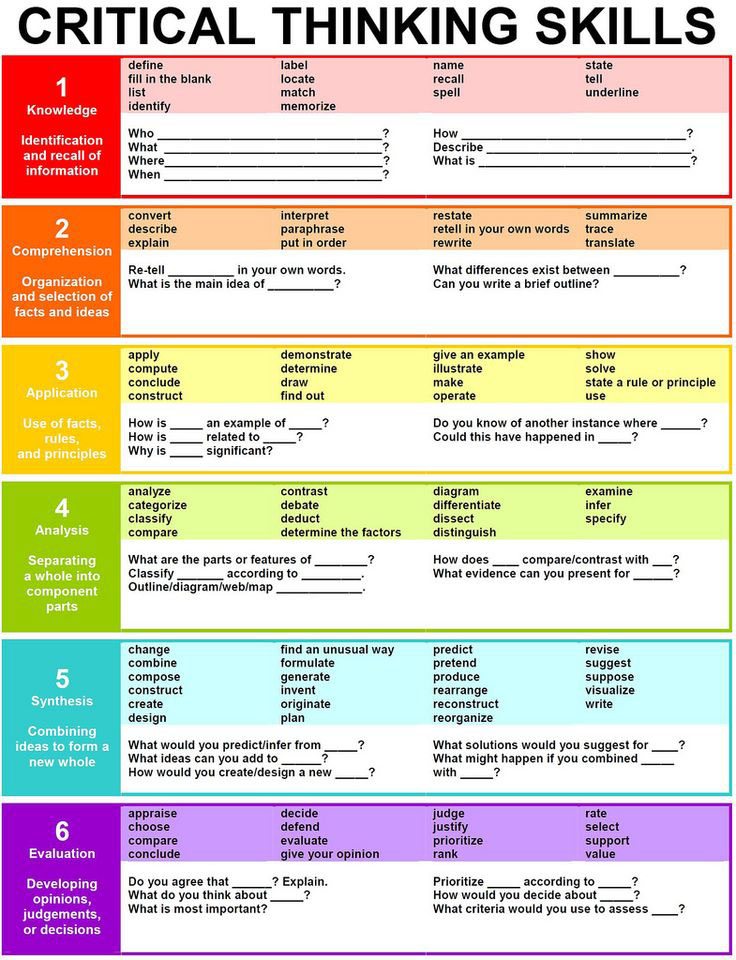
Image attribution flickr enokson
TeachThought is an organization dedicated to innovation in education through the growth of outstanding teachers.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Don't Miss a Post! Subscribe
- Guest Posts

- Educational AI
- Edtech Tools
- Edtech Apps
- Teacher Resources
- Special Education
- Edtech for Kids
- Buying Guides for Teachers

Educators Technology
Innovative EdTech for teachers, educators, parents, and students
Examples of Critical Thinking Questions for Students
By Med Kharbach, PhD | Last Update: May 22, 2024

Critical thinking is an essential cognitive skill that entails the ability to reason, analyze, synthesize, and evaluate information. It goes beyond mere acquisition of knowledge. Instead, it involves deep, reflective thought, demanding us to question our assumptions, weigh evidence, and consider consequences. It’s about making clear, reasoned judgments. In essence, critical thinking is thinking about thinking, in a manner that allows us to improve the quality of our thinking.
In our daily lives, critical thinking helps us better understand ourselves, other people, and the world around us. It aids in problem solving, aids in the formation of beliefs and opinions, and encourages curiosity and creativity.
For example, when you’re faced with a major decision like purchasing a house, critical thinking enables you to weigh the pros and cons, assess the credibility of your sources of information, consider alternative options, and make a well-informed decision.
In professional situations, critical thinking is equally important. It helps us navigate complex work situations, make informed decisions, solve problems efficiently, and think creatively. For instance, if a company faces a decline in sales, critical thinking would help diagnose the root cause of the issue, evaluate different strategies to address the problem, and make effective decisions to rectify the situation.
The importance of critical thinking is particularly crucial for students. It provides them with the necessary skills to understand complex concepts, evaluate the credibility of sources, engage in thoughtful discussions, and develop reasoned arguments. It lays the foundation for lifelong learning and the ability to adapt to an ever-changing world.
This brings us to the concept of critical thinking questions . These are questions that are specifically designed to promote critical thinking. They go beyond factual inquiries, prompting individuals to analyze, synthesize, apply, and evaluate information. Critical thinking questions challenge the conventional wisdom and encourage individuals to think deeper, questioning the why’s and how’s.
They serve as a tool to spark intellectual engagement and stimulate thoughtful and reflective responses. As we delve further into this blog post, we will explore different types of critical thinking questions and how they can be applied in various contexts.
Related: Best TED Ed Lessons on Critical Thinking
Tips on Formulating Critical Thinking Questions
Creating good critical thinking questions involves understanding the basics of inquiry and knowing how to stimulate higher order thinking. Here are some tips and steps on formulating effective critical thinking questions:
Characteristics of Good Critical Thinking Questions:
- Open-Ended: Good critical thinking questions are typically open-ended, meaning they don’t have a single, simple answer. They invite students to think deeply and come up with their unique insights.
- Thought-Provoking: Effective questions challenge assumptions and encourage students to think creatively and critically. They provoke curiosity and exploration.
- Promote Discussion: The questions should stimulate meaningful discussions. The responses to these questions should not end the conversation, but rather, foster a deeper exploration of the topic.
- Clear and Understandable: The question should be framed in such a way that it is clear and easy to understand. Confusing questions can deter students from critical thinking.
Steps to Create Effective Critical Thinking Questions:
- Identify Your Learning Goals: Start by figuring out what you want your students to learn or achieve. Your question should align with these learning goals.
- Consider the Cognitive Level: Depending on the depth of thinking you want to stimulate, frame your questions accordingly. For instance, for higher order thinking, you might want to ask analysis, evaluation, or creation questions.
- Draft Your Question: Begin drafting your question. Remember, the best questions are open-ended and require more than a yes or no answer.
- Refine Your Question: Review your question. Is it clear? Does it promote discussion? Does it align with your learning goals? Refine as necessary.
- Test Your Question: Try out your question with a few students or colleagues to see if it stimulates the kind of discussion you’re hoping for. Be open to further refining your question based on the results.
Keep in mind that the goal of asking questions is not to ‘stump’ the students, but to promote intellectual engagement and thought. The best questions often lead to more questions, igniting a passion for learning and exploration.
Types of critical thinking questions
Critical thinking questions can be divided into the following categories:
1. Analysis Questions
Analysis questions ask the respondent to break a concept or idea into its component parts for examination. These questions can help uncover underlying structures, patterns, or meanings. They often involve words like “compare”, “contrast”, “classify”, “divide”, etc.
Example: “Compare the political ideologies of democratic socialism and laissez-faire capitalism. What are the similarities and differences between them?”
2. Evaluation Questions
Evaluation questions call for the respondent to make a judgment about the value of something, based on defined criteria. They often use terms like “critique”, “justify”, “validate”, “defend”, etc.
Example: “Evaluate the effectiveness of the government’s pandemic response measures. What were the successes and shortcomings?”
3. Inference Questions
Inference questions require the respondent to go beyond what is explicitly stated and make logical conclusions or predictions based on the information provided. Key words often include “infer”, “deduce”, “predict”, “conclude”, etc.
Example: “Given the recent surge in online shopping trends, what can you infer about the future of brick-and-mortar retail stores?”
4. Application Questions
Application questions involve applying knowledge or concepts to new situations or contexts. These questions often involve “applying”, “utilizing”, “implementing”, or “executing” learned knowledge.
Example: “How would you apply the principles of conflict resolution that we studied to resolve a disagreement in your workplace?”
5. Synthesis Questions
Synthesis questions invite the respondent to combine different pieces of information, ideas, or concepts to form a new whole or propose a solution. Words often associated with these questions are “design”, “formulate”, “propose”, “create”, etc.
Example: “Based on your understanding of climate change and renewable technologies, propose a comprehensive strategy for a city to reduce its carbon footprint.”
These types of questions, when used in the appropriate contexts, can help foster a deep level of understanding and stimulate higher-level thinking.
Examples of Critical thinking Questions
Here are some examples of critical questions that you can use to stimulate students’ critical thinking skills, encouraging them to analyze, evaluate, and create new ideas based on what they’ve learned.
- What do you think would happen if…?
- Can you explain why…?
- How would you solve this problem using different strategies?
- Can you compare and contrast these two concepts?
- How can you demonstrate your understanding of this concept in a different way?
- How would you categorize these items, and why did you choose to do it that way?
- What patterns or connections do you see in the information provided?
- How might you interpret these findings from another perspective?
- Can you design a…to…?
- How would you prove or disprove this statement?
- How can we improve…?
- What would be the consequences if…?
- Can you predict the outcome if…?
- What is the relationship between…?
- How can this be applied to other situations?
- What are the possible solutions for…?
- Why do you think that… happened?
- How can we test the validity of…?
- What alternative would you suggest for…?
- How can you illustrate this concept in a diagram?
- What would you recommend, and why?
- How is this similar to…?
- Can you make a general rule about…?
- How would you evaluate…?
- What evidence do you have for your claim?
- What are the implications of…?
- How does this contradict or confirm your understanding of…?
- Can you think of an example where…?
- How would you justify…?
- What do you think is the significance of…?
In conclusion, critical thinking questions are an indispensable tool for stimulating and nurturing the intellectual capabilities of students. They’re not just questions, but sparks that ignite the curiosity, analytical ability, and problem-solving skills in a learner. They invite students to dig deeper, challenge their preconceptions, and engage with material on a more profound level.
These questions play a pivotal role in taking learning beyond the simple absorption of facts into the realm of true understanding and application. They prepare students for the complexities of the real world, honing their ability to analyze situations, make decisions, and innovate solutions.
As educators and teachers, fostering this skill in students through the strategic use of critical thinking questions should be a top priority. So, let’s continue to question, to probe, and to encourage our students to do the same, for it’s in the exploration of these questions that true learning lies.

Join our mailing list
Never miss an EdTech beat! Subscribe now for exclusive insights and resources .

Meet Med Kharbach, PhD
Dr. Med Kharbach is an influential voice in the global educational technology landscape, with an extensive background in educational studies and a decade-long experience as a K-12 teacher. Holding a Ph.D. from Mount Saint Vincent University in Halifax, Canada, he brings a unique perspective to the educational world by integrating his profound academic knowledge with his hands-on teaching experience. Dr. Kharbach's academic pursuits encompass curriculum studies, discourse analysis, language learning/teaching, language and identity, emerging literacies, educational technology, and research methodologies. His work has been presented at numerous national and international conferences and published in various esteemed academic journals.

Join our email list for exclusive EdTech content.
elttguide.com
- Premium Content
- Publications
- Lesson Plans

Asking Great Questions in the Classroom to Develop Critical Thinking

Questioning is a skill that every teacher should master. It helps students understand concepts better, and it also allows teachers to assess student understanding. In this article, I’ll teach you how to use a question prompt sheet to guide students through the process of asking questions to develop critical thinking.
Critical thinking is one of the main purposes of education. Teachers should prepare their students to think critically from the first day of school. Critical thinking helps students to lead successful, fulfilling lives and become engaged citizens.
In this article, I’m going to introduce 30 questions that you must usually ask in your classes if you want to develop your students’ critical thinking.
Before introducing these questions, let me remind you of what I’ve tackled before about critical thinking; what it is, what it involves, and some practical activities to develop it in EFL classes.
What Is Meant Of Critical Thinking?
In today’s world, critical thinking is:
- The ability to think about one’s thinking to recognize and improve it.
- The process of applying, analyzing, constructing, and evaluating information.
- Making reasoned judgments using certain criteria to judge the quality of something.
What Does Critical Thinking Involve?
- Asking questions,
- Defining a problem,
- Examining evidence,
- Analyzing assumptions and biases,
- Avoiding emotional reasoning,
- Avoiding oversimplification,
- Considering all interpretations,
- Using higher-level thinking skills; analyzing, evaluating and,
- Reaching creative solutions for problems.
Why Should You Teach & Develop Critical Thinking?
Teachers should focus mainly to develop their students’ critical thinking to help them:
- Be active receptors of the massive information that they receive nowadays.
- Solve the complex problems that they face every day.
- Make sound decisions about personal and civic affairs.
The Main Teaching Strategies To Develop Critical Thinking :
- Using ongoing classroom assessment.
- Putting students in group learning situations to get continuous support and feedback from other students.
- Presenting case studies to the class without a conclusion and using discussion and debate methods.
- Using dialogues written or oral and encouraging students to analyze them.
- Using comparisons to show the pros and cons of two things.
- Using critical thinking questions.
Critical Thinking Questions
Students don’t critically think because they are not trained to think in this way. They may be engaged in learning but critical thinking is more than simple engagement.
Lectures that provide many facts and too much memorization don’t develop critical thinking.
Critical thinking requires analytical questioning mainly for clarifications, in addition to other questions about:
- Concepts and Ideas.
- Assumptions.
- Viewpoints and perspectives.
- Information.
- Inferences and conclusions.
A good question prompt sheet will help you guide students through the questioning process. This includes providing them with a series of questions that lead up to one big question. You can do this by creating a list of questions that build toward a central idea. Then, you can add a “Why?” section at the end of each question.
A List of Critical Thinking Questions
Explore 30 Critical Thinking Questions you must ask frequently in your classes.
This Content is premium! If you are not a member yet, you can Join Us Now to read these questions and MORE of my ELT Premium Content .
Thanks For Reading
You can also join my email list not only to be notified of the latest updates on elttguide.com but also to get TWO of my products : Quick-Start Guide To Teaching Listening In The Classroom & Quick-Start Guide To Teaching Grammar In The Classroom For FREE!
Join My Email List Now (It’s FREE)!
Want to continue your elt professional development.
I offer various ELT publications on teaching English as a foreign language.
In these publications, I put the gist of my experience in TEFL for +20 years with various learners and in various environments and cultures.
The techniques and tips in these publications are sure-fire teaching methods that worked for me well and they can work for you, as well, FOR SURE.
Go ahead and get a look at these publications to know more about each one of them and the problem & challenge each one focuses on to overcome.
Then, you can get what you have an interest in. It is very easy and cheap. You can afford it and you’ll never regret it if you decide to get one of them, FOR SURE.
Now, click to get a look at my Publications
Looking for the best tefl courses your search is over, start with ita now.
The ELT training that you will receive at ITA is invaluable in that you will prepare yourself effectively as an EFL/ESL teacher.
I’m sure you will be amazed by their:
- Countless TEFL courses,
- Course structure,
- Alumni community,
- A high number of practicum hours,
- Customer service,
- Lifetime TEFL job assistance,
- Reviews and credentials.
Start now with ITA to make a difference in your TEFL journey by teaching online or abroad.
If you like this article, share it on:.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Subscribe to My Newsletter
Affiliate disclosure.
This website might have affiliate links, and if you buy something by clicking on them, the website owner could earn some money. To learn more, read the full disclosure.

Study TEFL/TESOL Online

Get 15% Discount

Visit My Video Channel

Articles Categories
- Back To School
- Brain-based ELT
- Classroom Management
- CLT Communicative Language Teaching
- Correcting Mistakes
- Develop Students' Speaking Skills
- Developing Critical Thinking
- Developing Life Skills
- ELT Snippets
- ELTT Questions & Answers
- For IELTS Exam
- Guest Posts
- Lanaguage Teaching Approaches
- Learn English
- Learning How to Learn
- Lesson Planning
- Low Achiever Students
- Online Courses
- Printables Library
- Professional Development
- Talk on Supervision
- Teach Conversations
- Teach Grammar
- Teach Language Functions
- Teach Listening Activities
- Teach Pronunciation
- Teach Reading
- Teach Vocabulary
- Teach Writing
- Teacher Wellness
- Teaching Aids
- TEFL Essential Skills
- TEFL Interview
- TEFL to Young Learners
- Testing and Assessment
- The ELT Insider
- Uncategorized
- Using Technology in EFL Classes


How To Ask Questions That Prompt Critical Thinking
Jan 1, 2021
I believe and I’ve seen some bumper stickers that would back up the idea and the fact that we are living in an international critical thinking deficit, right? Live in this world where people come to conclusions so quickly don’t really research information all that much. They take something at face value and they run with it and make decisions or maybe even worse judgments or start yelling at people because of it. In this video, we’re going to unpack how do you ask questions that promote critical thinking. And I’m going to be sharing one really brilliant strategy that I learned from Brandon Stanton, the founder of Humans Of New York, if you’re familiar with that.
Blog Note: The following is an adapted and edited transcript of one of our daily YouTube tutorials. We know sometimes it is easier to scroll through written content which is why we are publishing here. Because of that, there may be typos or phrases that seem out of context. You’ll definitely be able to get the main idea. To get the full context, visit our YouTube channel here . And if you want to watch the video on this topic specifically, you can scroll down to the bottom of this post to access it as well.
And the second strategy, I’m going to share one of my absolute favorite, I think one of the coolest practical tools in Me and Will’s book called Ask Powerful Questions Create Conversations that matter. The only kind of fluff I like is marshmallowy and sits on a sandwich. Let’s get into it.
Hearing Brandon Stanton uh speak one time. If you’re not familiar with the Humans of New York, by the way, he basically set out originally, set out to do portrait photography of 10,000 people in new york city to create this library of stories. He very simply used to… I haven’t followed him in the last like handful of months. But he used to post a picture with just a quote from that story. Now, the quote would be usually phenomenal. It would just breathe so much like depth and humanity into that 2-dimensional image that he shared. The technique of how he got there, right? Because you don’t just walk up to somebody on the street and say, “Can I take your picture and can you share this really intense beautiful quote with me so I can put it in my post today?”Right? You’ve got to actually get to there in conversation. And you’ve got to ask questions that promote really critical thought about things that potentially people have never shared out loud before that they’ve never thought deeply about. And his technique that he shared, he used the image of a spiral. He talked about spiraling down in conversation.
From Here to There
Going from, “Hey, how are you doing?” to eventually a story about their grandmother on a chair when they were 5, that really transformed their life, right? How do you go from here to here? And he used the idea of a spiral you kind of just get deeper and deeper and deeper. But you might go around, right? It’s you’re not… Oh, you’re not just like drilling straight down because that feels very invasive. To keep the conversation natural, you’re kind of spiraling down. And I love that idea in terms of promoting critical thinking. You know, if you’re familiar with the idea of socratic inquiry. Like teaching through questions. When you’re spiraling down in conversation, you start to get more specific too. You start really general and you get more specific and more specific and more specific. And one of my favorite quotes or ideas on the planet who I have no idea who said it. I can’t find it on Google. If you can, share it in the comments and I’ll like buy you a car or something. Not going to happen. But I would really love to know. But it’s this idea that specificity is the soul of narrative. I love that concept. The more specific we get, the more to the heart of story we get. And the more that we’re talking and like generalities appear, the less usefulthat is. The same is true for critical thinking.
Critical Thinking
When you’re thinking about… If you want to critically think about something contentious like the death penalty, for example. You could be thinking about this at a very surface level. But then the more specific you get into specific cases, right? And instances, that’s where story and narrative starts to really come to life and you start to be like, “Wow, I don’t I don’t know what I think anymore”, right? And that critical thinking starts to show up. My language for Brandon’s spiraling technique is to follow one curiosity path, one thread and keep bouncing to that thread. Wherever it takes you. If you spun a globe and picked a random spot, the island of newfoundland and you then zoomed in a little bit further to a park in the island of Newfoundland, and then you zoomed in a little bit further and you found there was a dog park inside that park. Then you zoomed in a little bit further and you found a dog and it’s owner. And you found out their name and you found out the type of dog and you found out how they came together and… Those are stories. But when I’m telling you about the island of Newfoundland, I’m all of a sudden a Wikipedia article, right? That’s more specific you get… You follow that curiosity path by just kind of Zooming in further. Now, the thing the cool thing with curiosity is it doesn’t work like a drill like zooming into the island of Newfoundland, you might actually find that as you’re going to the island of Newfoundland, you learn about Newfoundland dogs. And then you’re like, “Oh, wait. They were created over here.” And now you’ve got another curiosity path. Following that path down. The next tool I’m going to share with you is going to help you do that in a really practical way with one very simple word. And that word is “Why”. You might have heard of the uh this technique or this idea of the 5 whys before.
It’s a cool concept to promote design thinking, right? You ask, why are you doing something. And then you ask why are you doing that and then why are you doing that? You ask that five layers down until you get to the core or the heart. Now, that’s cool if you’re talking about ideas. But if you’re trying to promote critical thinking in people, the way that I would use this one word is by deleting it out of your vocabulary. It’s by saying drop the why. Because when I ask questions that begin with why they force people to rationalize and justify which… I can’t put this back together. But that could promote critical thinking. But it’s going to be way better if you want to promote critical thinking to start your questions with either how or what.
Those questions allow people to really expand and answer in a way that doesn’t require justification and rationalization. Because in order for critical thinking to actually happen, our brains have to be open. Barbara Fredrickson talks about the broaden and build theory and positive psychology –that when good things happen, our brains actually open up to new ideas. Whereas when we’re worried about how we’re going to pay rent and we don’t know what’s going to happen next month and we’re worried for our safety, we can do this. They can make people put up this barrier to try to protect some level of safety because it’s kind of prying for that justification. When you ask questions that begin with how or what, typically, those tend to be more open questions, they invite story. They invite explanations, they’re longer answers, they’re not closed questions that close down responses.
My invitation to you is combine Brandon Stanton’s spiraling technique of following a curiosity path by asking questions that begin with how or what over and over and over and over again until critical thinking happens. And perhaps, you can offset the critical thinking deficit that exists right now on planet earth. I’m Chad Littlefield.
Have an awesome day.
- Fundraisers
- Create You must be logged in to post onto your wall. Login | Sign up
- Saved You must be logged in to view your gallery, albums or wishlists. Login | Sign up
- Account types
- Sell resources
15 Awesome Critical Thinking Questions You Should Ask Students
Critical thinking can be difficult to teach, but it is a skill students must acquire.

Without critical thinking , students will encounter difficulty as they advance through their academic careers and may fall behind their peers. In many school environments, there is a push toward using test performance as the main marker of achievement. While standardized testing is a part of a student’s academic experience, it is just one part.
Critical thinking helps students develop analytical skills that will be useful throughout their lives. Not only during their educational years. The key to developing this skill is the use of question prompts that help them to, in essence, think for themselves. Too many students fall into the trap of believing that answers are always right or wrong, without any room for nuance or a variety of correct viewpoints.
Education resources

15 awesome critical thinking questions you should ask students
Incorporating critical thinking questions can help students think more analytically and prompt them to formulate their ideas. Great questions can be broken out into these different ways:
- Critical thinking questions start with “where.”
- Critical thinking questions start with “what.”
- Critical thinking questions start with “who.”
- Critical thinking questions start with “how.”
- Critical thinking questions start with “when.”
- Critical thinking questions start with “why.”
Take a look at these 15 awesome critical thinking questions that can help students think better:
- What else could have changed the whole story?
- What questions would you have asked?
- What is the character’s motive?
- How could the story have ended differently?
- How would you solve this problem?
- Who is the most important character?
- Who would be affected by this?
- When did the story change?
- When does this become a problem?
- Where would you most often find this problem?
- Where can you get more information?
- Why is this important?
- Why is this a problem?
- Do you agree with this outcome?
- Could this story be interpreted differently?
You will notice that none of the questions could be answered with “yes” or “no”. They are all open-ended and meant to be probing and thought-provoking. Their most effective aspect is that they will force the student to think about their interpretation or reaction rather than giving a “right” answer.
Use these questions throughout your teaching to encourage your students to think for themselves and draw conclusions. When students are only taught to memorize answers and facts, their analytical skills may not develop sufficiently. And without critical thinking skills, it will be more difficult for them to grasp more abstract concepts as they progress through each educational level.
The short story is one of the most effective vehicles for critical thinking questioning. Have the class read the same story and then gather for discussion once everyone has finished reading. Use this time to ask these questions, but allow the students to conclude. If you feel that a student is off base in their assessment, use gentle guiding statements to help steer them in the right direction. Never tell them their wrong answer or discourage them from sharing their thoughts.
The strategy behind this teaching method is to get the students to think independently and in a more grey area than close-ended questions allow. Suppose a student has a contrarian viewpoint to expound upon their idea and further discuss what events in the story caused them to think this way. With patience and guidance, your students will soon grasp the concept of critical thinking and will grow more comfortable discussing their ideas. This can be a very exciting time as a teacher, as it shows how much students are individuals and need to have their thoughts and ideas.
Related Articles
Child How to create and sell activity learning materials Creating and selling educational activity materials can be a fulfilling venture, offering both financial rewards and the satisfaction of contributing...
Art How to create and sell cooperative learning resources Selling cooperative learning resources requires a blend of educational insight, practical experience, and marketing acumen. As education continues to evolve, cooperative...
Behavior How to create and sell educational forms Creating and selling educational forms on Classful.com can be a rewarding opportunity for educators, curriculum developers, and educational content creators. Educational...
Child How to create and sell educational games Creating and selling educational games on a platform like Classful.com presents a unique opportunity for educators, game developers, and entrepreneurs...
Child How to create and sell GATE resources Creating and selling GATE resources for the Gifted and Talented Education (GATE) program involves understanding the specific needs and capabilities...
Behavior How to create and sell educational graphics Creating and selling educational graphics is a unique opportunity to support educators and enhance student learning through visual aids. Classful.com, an...
Join Our Community Today
And find out why 100k people have already joined.
Invite your friend via Facebook, Twitter or Email
Your invite has been sent

19 Short Stories and Questions For Critical Thinking
Apr 2, 2024
There have been rumblings in different online teacher groups recently about replacing novels with short stories and informational articles in middle and high school English classrooms. I have to admit I was shocked when I first read the comments because I am a book lover at heart, but since then, I’ve considered that there are several pros and cons to this approach.
Short stories and other smaller texts can provide a briefer timeline to complete tasks, and this process is helpful when there is already SO MUCH curriculum to cover. Short stories and related activities can also be more engaging for our students because of the exposure to diverse voices and themes! Using short stories and lessons provides students with amazing choices to meet their needs and preferences!
On the other hand, incorporating mainly short stories and other shorter passages means students’ already-pressed attention spans (as a result of social media influences and pervasive sources of technology) are reinforced. Plus, students miss out on the more complex stories within longer pieces of fiction that are, dare I say, life-altering! A novel can provide opportunities for sustained reading and layers for analysis that shorter pieces of literature like short stories and related texts cannot offer.
Ultimately, no matter where you find yourself on the issue, I think we can all agree that short stories and their counterparts can be vital, effective, and helpful in the modern classroom!
Continue reading for 19 Short Stories and Questions For Critical Thinking!!
Need help with Test Prep ? Check out this FREE Pack of 3 Test Prep Activities to help students achieve success on standardized tests!

Table of Contents
19 Short Stories and Questions – Suggestions for Teaching Them
You don’t need to remove all novels to be able to include short stories and smaller passages like vignettes, articles, and narratives; there’s a time and place for all genres! But if you’re thinking about ways to include more short stories and fun activities, check out this list of 19 varied short stories and critical thinking questions as well as suggestions for teaching them in middle school and high school.
1. “The Most Dangerous Game”
“The Most Dangerous Game” is one of my absolute favorite short stories and overall plots to teach! This suspenseful short story by Richard Connell follows the harrowing ordeal of Sanger Rainsford, a skilled hunter who becomes the prey of a deranged aristocrat named General Zaroff. Stranded on Zaroff’s secluded island, Rainsford must outwit the cunning general in a deadly game of survival, where the stakes are life and death.

SUGGESTIONS FOR TEACHING:
- You could focus on the setting (description of time and place) and examine how the setting changes throughout the story.
- Students could learn about the plot (major events in the story) and list the major events and evidence as they read.
- Define foreshadowing (hints for what will happen by the end of the story) and encourage students to hypothesize about what will happen after every page.
- Analyze the character development (how a character changes over time) of Rainsford and highlight his traits/actions as you read along.
CRITICAL THINKING QUESTIONS:
- How does the setting contribute to the tension and suspense in the story?
- How does the author use foreshadowing? How does the author hint at the danger Rainford is facing?
- What inferences can you make about the main character and the changes he undergoes from the beginning to the end of the story?
If you want to teach plot elements and plot analysis , check out this lesson bundle for the story , which includes comprehension quizzes and a variety of activities!
2. “An Occurrence at Owl Creek Bridge”
Ambrose Bierce’s story is a gripping tale set during the American Civil War, where a Southern civilian named Peyton Farquhar faces execution by hanging after attempting to sabotage a Union railroad bridge. As Farquhar falls through the trapdoor, time seems to stretch, and he experiences a surreal moment, only to realize his grim reality.
Integrating historical texts with other short stories and passages like “An Occurrence at Owl Creek Bridge” will make history come more alive and relevant for our students!
- Teach about irony (when the opposite occurs from what is expected) and how it plays a role throughout the story.
- Explain the term characterization (how a character is depicted) by looking at direct and indirect references while reading with your students.
- Discuss the major themes (messages) of the story and how they connect to our modern era within a Socratic Seminar.
- How does the author use characterization to convey Peyton Farquhar’s thoughts, emotions, and motivations?
- What is the purpose of irony in this story? How does its use affect the reader’s interpretation and understanding of events?
- What is the significance in our contemporary/real world of the themes of the story, including reality and fantasy, the passage of time, and the consequences of actions?
Ensure students’ understanding of the story with this set of reading questions that are perfect for state test prep, too !

3. “The Masque of the Red Death”
This chilling tale from Edgar Allan Poe is set in a secluded abbey where Prince Prospero and his wealthy guests attempt to escape a deadly plague known as the Red Death. Despite their isolation efforts, the guests are confronted with their own mortality as a mysterious figure in a blood-red mask appears.
If you have not read any short stories and poems from Poe, this story is a perfect journey into the horror genre!
- The setting (description of time and place) plays a MAJOR role in the story, so following the Prince from room to room and highlighting the imagery (description that connects to the five senses) is very important when reading.
- If you have not introduced mood (emotion intended for the reader to experience), this story is PERFECT for delineating its progression from start to finish.
- As students read, you might guide them through identifying various examples of symbolism (object, person, or place that represents something else); each room, objects within, and the “antagonist” is symbolic in some way!
- How does the author convey the tone of the story? How would you, as the reader, describe the story’s mood?
- What role does the plot structure (focus on the different rooms) play in shaping the reader’s understanding of the story?
- What is the purpose of the symbolism in the story such as the clock and the masked figure?
Check out this EASY-TO-TEACH bundle , you can practice with your students, so they will feel more confident analyzing higher-level language in “The Masque of the Red Death!”
4. “The Cask of Amontillado”
Another chilling tale from Poe is the classic story “The Cask of Amontillado.” This one is set during Carnival in an unnamed Italian city. The plot centers on a man seeking revenge on a ‘friend’ he believes has insulted him. If your students are anything like mine, they will relish the ending particularly!
This is just one more of Poe’s short stories and tales that will capture the mind of every reader!
- As you plan for this short story, be sure to encourage your students to analyze the changing setting (description of time and place); following Fortunato from scene to scene will help your students track what is really going on.
- This story is the perfect moment to teach about dialogue (conversation within someone=internal and/or between someone and someone/thing else=external); Montresor certainly means more than what he SEEMS to say!
- You might also offer a mini-lesson on the 3 types of irony and how each plays a role in the story: verbal (when a person says the opposite of what is really intended), situational (an action occurs that is the opposite from what the reader expects), and dramatic (a character expects a result, but the opposite occurs and the audience can tell what will happen)!
- Describe Montresor. What are his motives and personality?
- What inferences can you make about Montresor’s mindset based on his dialogue?
- What is the purpose of the family’s motto and the carnival atmosphere?
Check out this Short Story Activity & Quiz Bundle for Edgar Allan Poe’s “The Cask of Amontillado,” which contains questions and answers modeled after various reading standardized tests as well as pre-quiz reading comprehension questions, graphic organizers, and a writing activity to get students thinking critically about this classic short story involving REVENGE!
Want 7 more teaching ideas for one of Poe’s epic short stories and questions to go with it? Click below!

5. “To Build a Fire”
This story by Jack London describes the treacherous journey of a man through the harsh Yukon wilderness during extreme cold. Despite warnings and the company of a loyal dog, the man’s arrogance and underestimation of nature’s power lead to a tragic end.
Short stories and ideas related to survival in nature are still relevant today! Who knows when you might get lost on a hike or crashland in no man’s land?
- This story is PERFECT for a bit of literary analysis (examining the impact of various ideas, elements, or themes within a piece of literature); you could hone in on literary devices, characterization, theme, etc.!
- Integrating clips from survival shows will help students see connections to the world and extend their thinking by comparing (recognizing similarities) and contrasting (recognizing differences) varied experiences!
- Write a short narrative about surviving 24 hours in a different setting (description of time and place).
- How does the author use irony? Provide an example and explain.
- What real-world connections can be made between this story and our contemporary life?
- What is the story’s message about preparedness and respecting nature?
Grab these engaging short stories and activities to make teaching this Jack London story stress-free!
6. “The Cactus”
Told from the point of view of a young man at his former lover’s wedding, the narrator retells their story. Like most of O. Henry’s short stories and texts, this one has a twist that involves the titular cactus plant.
The ending will end in a bit of fun for your students!
- Introduce diction (word choice) and its impact within the story by hyperfocusing on specific words within the story . Students can look up definitions, locate synonyms, create their own sentences, replace the words, etc.
- Investigate twist endings (unexpected finish to a story); before reading the end of the story, ask students to guess why the girl “rejected” him. Some students may know the answer before reading it!
- Describe the main characters. What similarities and differences are evident? How does this affect the story’s action?
- What inferences can you make about Trysdale and his feelings about love and marriage?
- What are the real and symbolic meanings of the cactus?
This resource packed with questions and answers, graphic organizers, and writing activities is sure to get your students thinking about this love story driven by misconceptions.

7. “After Twenty Years”
This tale of friendship and betrayal focuses on the reunion of two old friends after twenty years apart on a New York City street corner. As they reminisce, something is revealed that demonstrates the reality of their bond as well as the choices they’ve made in life.
If you have not read O. Henry’s short stories and incorporated character analysis yet, this is your chance! The story is not long and can be completed in one to two class periods!
- Sometimes, we ask students to visualize (create a picture) in their minds, but why not give them the opportunity to use their artistic skills to draw the two characters?
- As students read, annotate for a description of each character; then, students can do a character analysis (investigation of the characters’ similarities and differences).
- What type of irony is used in the story? How does its use affect your interpretation and understanding of the story?
- How does the urban setting contribute to the mood of the story?
- What is the story’s message about friendship and loyalty?
Examine the links between loyalty and duty with this set of resources designed specifically for this O. Henry story.
8. “The Lottery”
“The Lottery” is the quintessential short story for middle school or high school English! Shirley Jackson’s “The Lottery” tells the story of an annual ritual that takes place in a seemingly idyllic town. When the townsfolk gather for the lottery drawing, a shocking turn of events demonstrates the dark side of human nature and their ties to (outdated) traditions.
- Introduce the terms suspense (uncertainty and/or excitement leading up to a major event) and tension (anxiety or uneasy feelings experienced by characters). While reading, identify evidence that relates to each of these concepts and chat/write about their impact on meaning and plot.
- Teach title (the name of the text) analysis. The title of “The Lottery” is perfect for teaching the impact of the title and audience expectations. Before reading, students may write what they believe the story will be about based on the title. After reading, students can complete a quick write responding to their previous expectations! You can do a text analysis for all short stories and poems!
- What role does the plot structure play in building suspense and tension? (Consider the revelation of the lottery’s ‘prize’ in particular.)
- What social commentary is being made through the story and its characters?
- Describe Mr. Summers, Tessie, and Old Man Warner. What does the story reveal about their role in the community and their feelings about the lottery?
Give yours elf a breath of fresh air with this NO PREP curriculum that integrates test prep within the teaching of literature by using Shirley Jackson’s quintessential story!

9. “The Pedestrian”
This Ray Bradbury story follows a lone walker in a futuristic society in which everyone else is consumed by technology, particularly the television. One evening, the walker encounters a police car that questions his unusual behavior and the end is quite unexpected! (Most of Bradbury’s short stories and texts connect to the future and technology in some way!)
- This story exemplifies Dystopian Literature (texts that include a supposedly perfect future society marred in some way by governmental or societal oppression). Using this story to introduce this type of literature is always fun for students because they will easily make connections to other dystopic short stories and poems!
- Teach about mood (the emotional impact of a story’s description/action). The goal is to get students to deepen their critical thinking skills by recognizing how the mood changes and the purpose for that change!
- How does the author use foreshadowing and suspense to build the mood of the story?
- What is the central theme of the story? How might it connect with our current world?
- What similes and metaphors does Bradbury use to describe the community and its members? What is notable about these comparisons?
With this resource about Bradbury’s “The Pedestrian,” you can just print and teach the lesson and activities with EASE!
10. “The Gift of the Magi”
This 1905 story by O. Henry relays a tale about a couple struggling to make ends meet. Throughout the story, they both figure out gifts to buy one another for Christmas and realize what love truly means!
- Review character traits (how a character is depicted internally and externally). Log the traits of each character within the story and how they are important to the meaning of the story.
- Extend (move beyond the text) critical thinking skills by encouraging students to think and write about other people. If they had $1,000 to spend on someone else, how would they spend the money and why?

- How would you describe Della and Jim, and their relationship?
- What values do the characters have, when you consider their actions and decisions?
- Explain how dramatic irony is used in the story. Is it necessary? Is it effective? Why or why not?
This tale is a great addition to your short stories and questions unit around the winter holidays! Save yourself time at that time of the year with this lesson bundle .
11. “The Monkey’s Paw”
“The Monkey’s Paw” is a classic horror story about the White family who come into possession of a mystical monkey’s paw that grants three wishes. Despite warnings, they use it and then face devastating consequences as a result.
- Teach about the elements of the horror/suspense genre (Ex. Scary movies are typically dark, stormy, surprising, morbid, etc.).
- Create a thematic statement (message relayed by the text in a complete sentence). There is no perfectly created theme (message) unless it is directly stated by the author; however, students can create a theme by supporting their ideas with evidence from the story!
- What is the main theme of the story? Or how does the author communicate the themes of greed or fate? Is one stronger than the other?
- Are Mr. and Mrs. White more alike or different from one another? How do you know?
- Should we be afraid of the unknown? What message does the story share? Do you agree or disagree?
Examine W.W. Jacobs’ classic story with this set of questions and answers along with rigorous reading and writing activities . While it is ideal for a spooky season, the story is valuable for its ability to hook readers any time of year!
12. “Lamb to the Slaughter”
This classic story with a killer plot twist is about a woman who kills her husband and gets away with murder thanks to cooking a leg of lamb!
- You could introduce the plot elements (exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, resolution), encourage students to identify major events to fit each element and write down textual evidence to support their ideas.
- Complete a film analysis (examination of film techniques and their effects) to compare/contrast the short story with the classic Alfred Hitchcock television episode.
- What is Mary Maloney’s state of mind? Does it remain the same or does it change throughout the story? Explain.
- Is the resolution of the story satisfying? Why or why not? Why do you think the author ended it as he did?
- How does irony contribute to the theme of deception in the story? Explain.
Spice up your middle school English or high school English class with this short stories and activities bundle for Dahl’s famous story!
13. “The Tell-Tale Heart”
Poe’s classic psychological thriller is narrated by an unnamed protagonist who insists on their sanity while recounting how they murdered an old man. The narrator is haunted by the sound of the victim’s beating heart, which ultimately drives him to confess to the crime despite not originally being a suspect.
- Teach symbolism (object, person, or place that represents something else) by focusing on the heart and eye . The author used these symbols in various ways!
- Investigate psychology (the study of the human mind) as a part of the story. Determine what is fact and what is fiction within the narrator’s mind.
- What does the story reveal about the human psyche?
- What is the deeper meaning of the two key symbols in the story – the beating heart and the eye of the old man?
- What role do the narrator’s inner thoughts play in the development of the plot?

This Short Story Comprehension Bundle offers quick (and effective!) ways to assess students’ learning and understanding of the story. It’s easy to use and will no doubt save you time too!
14. “The Scarlet Ibis”
Emotional short stories and their counterparts have a place as well in English classrooms! This short story by James Hurst about two brothers is a heartbreaking must-read. Through flashbacks, the unnamed narrator tells the life story of his younger sickly brother William Armstrong, who is nicknamed Doodle. And the end…well, you’ll see.
- Define and explain the purpose of a flashback (referring back to the past within a story). Think about the implications of never thinking back on the past or always thinking about the past.
- Complete a comparison chart between Doodle and the Ibis as you read along. Then, students can create a visual of each after they have ready by using their own evidence!
- What is the meaning of the story’s title and the presence of a scarlet ibis in the story?
- What is the central theme of the story? How do the events of the story support this chosen theme?
- How does the author use personification for the storm? What effect does this have on the story?
This flexible resource features critical thinking questions and answers as well as writing and reading activities for students to explore Hurst’s heartbreaking story.
15. “The Veldt”
This science fiction story by Ray Bradbury was first published as “The World the Children Made” and it is quite fitting as a title! The story focuses on a futuristic world in which a video screen can be controlled and it turns out to be more than simple virtual reality! By the story’s conclusion, the world the children made is the downfall of their parents.
- Compare and contrast “The Veldt” with “The Pedestrian,” two short stories and dystopic texts by Ray Bradbury. Analyze the similarities and differences of both short stories and create a thematic statement that connects to both texts!
- Make connections to our current reality in the 21st century. Locate research about the implications of technology on young people and integrate this information as you discuss this short story.
- How does the author address the theme of technology versus humanity in the story? Do you agree with this commentary? Why or why not?
- How does the nursery reflect the personalities of Wendy and Peter in this story?
- Do you know the story of Peter Pan and his friend Wendy? What connections can you make between it and this story by Ray Bradbury?
Ray Bradbury’s classic short stories and similar passages are the BEST to teach in middle and high school English! With so much to dive into, they are sure to be a hit with your students. Grab this set of activities to extend your students’ engagement with rigorous reading and writing activities about “The Veldt.”
16. “The Necklace”
A woman who longs for a life of luxury and elegance beyond her means faces consequences when she loses a borrowed necklace. Guy de Maupassant’s story ends with a twist that has the reader question the value of material possessions.
- I love comparing this short story with O. Henry’s “The Gift of the Magi.” You might choose to focus on the theme, characterization, setting, etc.
- Summarize (writing about the main idea with details) each chunk of the story as you read with your students. Instead of asking students to write a paragraph, you could ask students to create each summary in only one sentence.
- The story explores vanity, deception, and the consequences of striving for social status. Which theme do you think is the most important? Explain with support from the story.
- Is Mathilde Loisel a likable character? Does this change during the story? Does it matter if the reader likes her? Why or why not?
- What clues does the author provide throughout the story that foreshadow the twist at the story’s end?
Focus on the standards with this Short Story Lesson Bundle for “The Necklace” by Guy de Maupassant!
Need help with implementing activities for “The Necklace?” See below!

17. “A Vendetta”
Guy de Maupassant’s late-19th-century story is all about REVENGE. A mother is obsessed with creating a plan to avenge her son’s murder and she then puts the plan into action with a morbid outcome.
- There are so many texts that involve REVENGE! Why not use this concept as a focus for a thematic unit (texts linked to a similar concept and/or message)? You could read “A Poison Tree,” “The Cask of Amontillado,” and “Lamb to the Slaughter” as well as “A Vendetta” with the intention of writing about all 4 for a comparison/contrast paper, presentation, or seminar.
- Analyze the development (how a character changes over time) of the mother and the dog throughout the story; you might annotate for similarities and differences as well as their motivations!
- What comment is the story making about the nature (or need) for justice? Do you agree or disagree? Why or why not?
- What similes and metaphors does the author use to communicate the main character’s feelings about the vendetta?
- How does the author use details to explain the main character’s thoughts, feelings, and motivation?
Add these activities for this lesser-known work to your short story plans. It’s sure to keep things fresh for your short stories and activities unit!
18. “Thank You, Ma’am” (also known as “Thank You, M’am”)
This heartfelt story by Langston Hughes tells the story of Luella, an older woman in the neighborhood, who is nearly robbed by a young man named Roger. In response to Roger, Luella brings him back to her home and treats him with an abundance of kindness, which has a profound effect on Roger.
This tale is at the top of the list for the BEST short stories and passages for upper middle and younger high school students!
- Introduce perspective and/or point of view (how a story is told: 1st, 2nd, 3rd omniscient, 3rd limited, 3rd objective). Students might rewrite the story from another perspective or extend the story using the perspective of one of the main characters.
- Review plot elements with a focus on the exposition (introduction to the characters, setting, and conflict), climax (highest point of interest/turning point of the story), and resolution (how the story is concluded and/or resolved in some way.) You could assign an activity surrounding each concept: visualization of the scene, a journal response to the event, or a short response focused on how the element is important to the overall theme!

- Do you believe in second chances? What does the story say about second chances?
- How might the climax of the story also be seen as the turning point in Roger’s life?
- How would you describe Mrs. Luella Bates Washington Jones? Are her actions expected or unexpected in the story? Consider from Roger’s and the reader’s point of view.
Click to check out all of the details for this BUNDLE with differentiated options , which includes a Test Prep Quiz (with varied options), Venn Diagrams, Graphic Organizers, and Writing Responses!!

19. “Click Clack the Rattle Bag”
This short story by Neil Gaiman is creepy and fun in the best ways possible! The narrator is taking care of his girlfriend’s little brother and walking him to bed when the child asks for a story. Instead of the narrator sharing a story, the boy shares about the Click Clacks who drink their prey and leave behind rattling bodies. The end is too good to be missed!
Short stories and plots like those in “Click Clack the Rattle Bag” will most certainly engage even your most struggling learners!
- We all know that test prep can be tough as many reading passages are, well, boring! Why not accomplish some test prep with your students and incorporate 5 standardized test-related questions ? You could focus on theme, structure, order of events, characterization, etc.!
- Help students make inferences (acknowledging and hypothesizing about the impact of details that are not directly referenced or stated) as the scene moves along. Students can analyze the change in the setting, the little boy himself, the story the boy is telling, and specific phrases from the story.
- What details in the story contribute to its eerie atmosphere or mood? Or what figurative language devices does Neil Gaiman use to create a sense of suspense in the story?
- How does the author use ambiguity in the story? Is it effective or not? Explain.
- What inferences can you make about the relationship between the narrator and the young boy?

This “Click Clack the Rattle Bag” Quiz Pack for middle and high school students uses the Common Core standards and contains questions and answers modeled after various state standardized tests! Make teaching this amazing short story by Neil Gaiman SIMPLE & EASY!
Why should we incorporate more short stories and activities in our teaching?
While I would never advocate replacing all novels with short stories and smaller texts, there is still something to be said about spending quality time with short stories and excerpts.
Including short stories and standards-based activities is an ideal option to improve reading comprehension and develop skills, especially in middle and high school English classes!
SHORT STORIES AND ACTIVITIES RESOURCES:

This Short Stories and Test Prep Questions ULTIMATE BUNDLE with Lessons, Quizzes, and Activities uses the Common Core standards with reading comprehension QUESTIONS and ANSWERS for 18 short stories such as “The Most Dangerous Game,” “The Monkey’s Paw,” “The Tell-Tale Heart,” “After Twenty Years,” “The Gift of the Magi,” “The Veldt,” “The Lottery,” “The Pedestrian,” etc. modeled after various state reading exams.
Make teaching short stories and activities SIMPLE & EASY!
Just PRINT & TEACH with engaging short stories and lessons!!
Need more fun ideas for teaching short stories and corresponding activities? Check out my store Kristin Menke-Integrated ELA Test Prep !

Hi, I’m KRISTIN!
I primarily focus on integrating multiple disciplines and subjects. The goal is to make teaching simplified and effective!
Let's Connect
- Follow Follow
Click below to download “13 Simple Strategies to make test prep a breeze!”

40 Critical Thinking Questions for High School Students
How is electricity being produced from rainwater or do aliens exist if there are so many discoveries about them? High school students are certain to come across queries that question reality, everyday rules, general human existence, or anything out of nowhere!
Young minds are filled with an amazing potential to explore beyond their capabilities and hidden qualities. While high school students might question the existing realities of life, some students might not be aware of their imagination and thinking capacities. That is why it is important to nurture these growing minds with opportunities to question, understand, analyze, find evidence, and arrive at solutions.
In this case, critical thinking questions act as a helpful way to offer an opportunity to broaden their minds to unlimited knowledge and endless possibilities. When students are given a chance to think beyond the ordinary, they experience a sense of freedom in thinking and expressing their views.
Through critical thinking questions, they receive a wonderful chance to analyze, decode the information, and present their views without being right or wrong. Hence, the below-mentioned questions are drafted in a way to initiate abstract and informative conversations thereby boosting critical thinking.
Brain teasing critical thinking questions for high schoolers
Critical thinking skills are essential for measuring the imagination and creativity of students. High school students are likely to use the new age information and influence of others when processing their thoughts. Hence, the below-mentioned questions are a great way to channel their thoughts in a more positively empowered learning environment.
- Do you think it is okay to give up your life if you had to save someone?
- If you could go to your past, what would you change?
- What is the joy of giving for you?
- What is better – giving or receiving? Why?
- If you can change some rules of the school, which ones would you change and why?
- What if you know your future? What does it look like from your perspective?
- What if you are dragged into a situation where you disagree with others?
- What would you do if you are given a task against your willingness to complete it?
- Would you like to do – go to your past or get to know your future? Why?
- What would you choose, 1 million dollars or a lifetime free education? Why?
- What is more important to you, knowledge or money?
- How can you leverage the benefits of social media and how?
- Do you think animals should be free or kept in a zoo?
- What does life look like on the Earth 100 years from now?
- Imagine a world without mobile phones. What would you do?
- If you could choose any profession in the world, what would you choose? Why?
- Would you rather devote your life to helping others through social activities or invest in building a business?
- What is the most important matter of concern that the world needs to address?
- Do you think the voting of high school students matters in Government concerns? Why?
- Which aspect plays a major role in the success of individuals?
- If you could change any one habit of your parents, what would it be?
- If you could travel to any place in the world, where would you go? Why?
- Imagine the world is facing a major power cut issue. What would you do and how would you face the situation?
- What is more important, offering a home to the needy or offering food to the needy on an everyday basis?
- How does the number 0 change life?
- Should teenagers be allowed to make major life decisions?
- Are friendships real in today’s world?
- Does an influential person always influence others with actions and words?
- If animals could talk to you, who would you choose to talk to?
- What is the difference between happiness and achievements?
- Do you think success is the same as happiness?
- Imagine you have only 24 hours left on Earth. How would you spend it?
- What if you are given the option to reside on another planet? What would you do and how?
- Would you forgive your best friend if he/she commits a crime and is found guilty?
- If your mother and best friend are sinking in two different boats and you have the opportunity to save anyone, who would you choose? Why?
- Imagine you are stranded on an island and have access to 5 things. Which 5 things would you choose?
- Which 3 elements make a stronger nation? Why?
- What are the disadvantages of growing up? How would you tackle them?
- Would you be blind or deaf? Why?
- What if you could donate 50% of your wealth and have free food for life? What would you do?
Critical thinking in students: Why is it crucial?
High schoolers are on their way to exploring various subjects and acquiring knowledge from around the world. In such a phase, students must have the ability to think through things and make the right decision. Critical thinking empowers the brain to analyze and understand situations with complete evidence before concluding. Here’s how critical thinking shapes the life of high schoolers.
1. Develops Problem-Solving Skills
Students are sure to come across everyday problems and issues in their academic journey or personal life. While some students may develop stress, others might ignore it. However, the essence of critical thinking helps students solve these issues with intelligence. Whether it is figuring out about the project or solving an issue between friends, thinking and analyzing the possible solutions makes it easy to tackle situations.
2. Enhances Creativity
The advertisements you see every day often talk about the problem and how a product solves it. That’s exactly why you need to develop critical thinking skills. When you can identify the core issue and arrive at solutions only then can you think out of the box. Critical thinking helps students be creative with their solutions and find a way out amidst challenges.
3. Boosts Decision-Making Skills
With every project, assignment, or topic of your thesis , you need to take many decisions in the learning process. Here, critical thinking skills play a crucial role in helping you analyze, decode and disseminate information before making any decision.
4. Builds Open-mindedness
As growing individuals, it is important to be open-minded towards various problems and their suggestions. People who think critically are more likely to understand situations from different points of view. Hence, developing critical thinking skills helps you accept different perspectives and respect the opinions of others. The skill helps a long way when you need to work in a group on your projects. It is because you become capable of thinking from various perspectives.
5. Goal Setting
Success comes with proper planning and execution of tasks. However, you cannot study history if you are weak at math. Similarly, you cannot aim for a 60% growth in your academics if you have been growing at a pace of 30% in each examination. Critical thinking enables you to think practically and map your way out to reach your goals. When you think critically and practically, you can analyze your strengths and weaknesses thereby setting goals accurately.
Critical thinking indeed plays an essential role in shaping the mindset of students and exposing them to different skills simply by developing this one. As you take advantage of the critical thinking questions, know that it is important to keep questioning students to initiate conversations.
Whether it is reflective questions or would you rather-questions , these questions enable them to think beyond their imagination and dive into a world of possibilities. Apart from this, you may also involve students in interactive discussions that boost critical thinking skills.

Sananda Bhattacharya, Chief Editor of TheHighSchooler, is dedicated to enhancing operations and growth. With degrees in Literature and Asian Studies from Presidency University, Kolkata, she leverages her educational and innovative background to shape TheHighSchooler into a pivotal resource hub. Providing valuable insights, practical activities, and guidance on school life, graduation, scholarships, and more, Sananda’s leadership enriches the journey of high school students.
Explore a plethora of invaluable resources and insights tailored for high schoolers at TheHighSchooler, under the guidance of Sananda Bhattacharya’s expertise. You can follow her on Linkedin
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Published on February 10, 2018
- February 10, 2018
Critical Thinking Questions That Will Blow Your Mind

Jump to section

What would it be like if every decision you made didn’t involve your personal feelings or over-emotional reactions? What if your perspective was always balanced and decisions completely informed? Is it not time that you used critical thinking questions to become the more levelheaded, cool, and calm person you want to be?
Being a critical thinker enables you to take a neutral perspective on an idea or scenario and gives you the power of true choice. Being free from manipulation or emotional ties to your decision will allow you to make the most beneficial choice in any circumstance.
In critical thinking, we are taught to question everything. However, the question behind the question is; what questions should you be asking? Before we go into the critical matter of the exact questions, we should first look at the manner in which these critical thinking questions should be asked. After this article, you will be a wizard at asking critical thinking questions.

The Standard of Questions You Should Ask
Although the actual questions will be very important to critical thinking, the emphasis and purpose of these questions will determine how effective the questions will be. You must first know how to question before you know what and which critical thinking questions to ask.
1. Open-ended questioning
As a critical thinker, you cannot allow whomever or whatever you are questioning to give you the smallest amount of information for your questions. Yes or No answers can really drag out the process of getting the answers and information that you want.
Asking questions that will not only give you the answers you are looking for but also open up a heap more information than you were searching for. Ask open-ended questions such as the following:
- “What is the purpose of this scenario?” Instead of: “Is this the purpose of this scenario?”
- “What is your favorite thing about this scenario?” Instead of: “Is this your favorite thing about this scenario?”
2. Avoid leading questions
Being a critical thinker is about escaping your bias and seeing things outside of your personal perspective . It is thus very important to avoid leading the question, in an area you want it to go.
Keep your questions as neutral as possible and don’t allow any definitive language to creep into the question. Such as using the following:
- “What is your take on the healthiest diet there is?” Instead of: “Don’t you think the vegan diet is the healthiest diet?”
- “What is the condition of the country at the moment?” Instead of: “How bad is the condition of the country at the moment?”
3. Specify the boundaries of your questions
As much as leading a question can be a hindrance to what you want, so can leaving the question too open, and invite unnecessary information to be given. Critical thinking is about being objective, but it still needs a direction and focus in which you apply your critical thinking.
Make sure that you set up an accurate framework in which your questions can be answered. Being too broad makes the process of getting answers inefficient and drawn out. Try asking questions like:
- “Who is your favorite male tennis player in the United States?” Instead of: “Who is your favorite tennis player?”
- “If you could live anywhere in South East Asia, where would that be?” Instead of: “If you could live anywhere, where would that be?”
4. Funnel the questions until you get the answer you were looking for
When questions remain shallow, it is easy for the sources of information you are questioning to mislead and avoid giving you the information that you want.
Do not set up the path of questions beforehand, but rather make sure that you dig deeper after each question in the direction of information that you really want. Once you have your answer, then move back to broader questioning in order to get a better picture of the whole once again.
5. All the answers to your question must be based on facts and well supported from many different sources
Make sure that you don’t give into hearsay. Find the studies, the science, and ample testimonials before you accept the information that you have been given.
Look into many different and unrelated sources to see if the information matches up. Look at the other side of the argument and validate their claims.

Methods of Critical Thinking Questions
1. the 5 w’s and the h.
These are the absolute basics of critical thinking. The Who, What, Where, When, Why, and How are foundational questions that are taught over and over in journalism, investigation, and research.
They are the base from which every critical analysis should be created. You would apply these questions as follows:
- …would benefit?
- …would this harm?
- …is responsible?
- …has researched this before?
- …is the other perspective?
- …would be the challenges?
- …are the strengths?
- …is the key subject?
- …would this problem reside?
- …are there similar situations?
- …can more information be found?
- …can this be improved on?
- …is this acceptable and unacceptable?
- …could this be implemented?
- …would we be able to measure the results?
- …is it time to stop this action?
- …is this a problem?
- …is this relevant?
- …should this be known about?
- …is there a need for this?
- …is this different from anything else similar to it?
- …it functions?
- … is this the truth about it?
- …could it harm anyone?
2. Agenda and method questioning
These two areas of questioning may have already been covered through the 5 W’s and the H. However, it is beneficial to emphasize the angle from which this questioning comes.
The first one is questioning the agenda. This is aimed at figuring out how people could benefit from a situation or idea. This agenda can place all the information received in context.
For instance, if a company was contributing to a charity and their agenda was to improve their image against the damage done by that company, then the contributions would be much less charitable and much more about publicity.
Questions that would help clarify the agenda would be:
- What is the person or organization involved trying to accomplish?
- What issues or problems are raised by the person or organization involved?
- What data, what experiences, what evidence is given?
- Is the person or organization involved thinking about the environment?
- Is the person’s or organization’s thinking justified as far as we can see from our perspective?
- And how do they justify it from their perspective?
- How can we enter their perspective to appreciate what they have to say?
The second aspect of this is questioning the method. As a critical thinker, this makes the outcomes of every situation and idea questionable, which is exactly the point of critical thinking.
Too many times the outcome of a specific method is the focus of debate, without clarifying if that outcome has validity.
Questions that would help clarify the Method would be:
- I s the person or organization involved willing to fundamentally rethink their methods of creating a certain outcome?
- Has the person or organization involved thought about how the method will work going into the future?
- To what extent has the method been tested?
- Is there any other method that could be used to produce this outcome and what would be the implications of this method?
- Is the person or organization involved willing to allow this method to be tested?
- In what other situation has this method been used and how effective was it?
3. Inquiry process
The inquiry process is exactly that; a process. It does entail certain questions but the power of this process resides in the way the process is conducted.
This process is the standard of research and creates an order in which you can follow, uncovering the information that you seek. Although the terminology may change for each step of the process, the essence of what needs to be done remains the same.
The process is divided as follows:
- Ask (Pose Question)
- Investigate (Find Resources)
- Create (interpret/ Synthesise)
- Discuss (Report findings)
- Reflect (follow the process backward)
4. Bloom’s taxonomy
Bloom’s taxonomy was created by Dr. Benjamin Bloom , a psychologist in the 1950’s. Bloom’s work was to create a better form of learning through more focus on analysis and evaluation.
Bloom’s taxonomy is very much Maslow’s hierarchy of needs to critical thinking. The original Bloom’s taxonomy encompasses:
- What is the subject?
- When did it happen?
Comprehension:
- How would you compare the subject?
- Explain the subject in your own words?
Application
- What examples can you find of the subject?
- What approach would you use to solve the problem?
- What inference can you make from the information?
- How would you classify or categorize the subject?
- How would you compare the information?
- What was the value or importance of the information?
Creation or Synthesis
- Can you propose an alternative interpretation of the information?
- What might happen if you…?

Bloom’s Taxonomy has since been revised. In 2001 a group of cognitive psychologists, curriculum theorists and instructional researchers, and testing and assessment specialists change the titles of each level to make a more dynamic approach to the system.
The titles were revised to:
- Recognizing
- Recalling
- Interpreting
- Exemplifying
- Classifying
- Summarizing
- Inferring
- Comparing
- Explaining
- Executing
- Implementing
- Differentiating
- Organizing
- Attributing
- Checking
- Critiquing
- Generating
- Planning
- Producing
In the process of the revision, the authors broke the knowledge area into its own taxonomy:
Factual Knowledge
- Knowledge of terminology
- Knowledge of specific details and elements
Conceptual Knowledge
- Knowledge of classifications and categories
- Knowledge of principles and generalizations
- Knowledge of theories, models, and structures
Procedural Knowledge
- Knowledge of subject-specific skills and algorithms
- Knowledge of subject-specific techniques and methods
- Knowledge of criteria for determining when to use appropriate procedures
Metacognitive Knowledge
- Strategic Knowledge
- Knowledge about cognitive tasks, including appropriate contextual and conditional knowledge
- Self-knowledge
If you want to know more about the reasoning behind the revision click here .
5. Integral questioning
Integral theory was created by Ken Wilber (author of A Brief History of Everything ) and has become one of the most useful structures of evaluation in this era. The integral model is a reference structure in which you can objectively see all areas of a specific subject.
This method goes hand in glove with the practice of critical thinking. Applying the method into question form will bring out the following analysis:
Quadrants: this is the evaluation of each viewpoint of a certain subject.
- What does a specific person involved think or feel about the subject?
- What studies and tests have been done on the subject?
- What do the people as a whole feel or think about the subject?
- What does the industry of the subject say on the subject?
Lines: These are the areas of understanding of factors involved in the matter.
- What are the different areas of life expressed in this subject?
- What factors are involved in the situation or subject?
- To what area of understanding does is the subject appeal to?
Levels: This deals with a hierarchical standard of a certain area of the subject.
- To what level of understanding does is a subject appeal?
- How complex or advanced is this subject?
- What standard of knowledge needs to be obtained to understand this subject?
State: This refers to a fleeting state of being in which the subject can be seen in.
- In what state of mind was the person involved in when reviewing the subject?
- In what state of mind was the person involved in when the situation occurred?
- Is the information given contextual to a certain situation?
Types: This is a division of experiences based on traits that could affect perspective.
- How would someone who is completely different from the person involved perceive the situation?
- What different types of people were involved in the situation?
- How could this subject be received differently by a different cultural reference?
Question Everything
You now possess all that you need to start becoming a critical thinker and asking critical thinking questions. The only way to engrain the above processes and questions to become a critical thinker is to practice. You might need to refer to this article consistently at first, but after time you will become a natural and healthy critical thinker.
This video may help to ignite your passion for questioning everything:
Read more on critical thinking by checking out these related articles and resources:
- How to Solve the Biggest Problems With Critical Thinking
- Critical Thinking Examples That Wil Influence the World Around You
Take the next step: enroll for free

Discover Powerful Hacks to Unlock Your Superbrain to Learn Faster, Comprehend More and Forget Less
Join the foremost expert in memory improvement and brain performance, Jim Kwik, in a free masterclass that will dive into the one skill you will ever need — learning how to learn Enroll for free
Irina Yugay
You might also like

Get Started
- Try Mindvalley for Free
- Free Masterclasses
- Coaching Certifications
- Vishen Lakhiani
- The Mindvalley Show
- Partnerships
- In English 🇺🇸
- En Español 🇪🇸
- Editorial Standards
- © 2024 Mindvalley, Inc.
- English (EN)

Fact-Checking: Our Process
Mindvalley is committed to providing reliable and trustworthy content.
We rely heavily on evidence-based sources, including peer-reviewed studies and insights from recognized experts in various personal growth fields. Our goal is to keep the information we share both current and factual.
The Mindvalley fact-checking guidelines are based on:
- Content Foundation: Our articles build upon Mindvalley’s quest content, which are meticulously crafted and vetted by industry experts to ensure foundational credibility and reliability.
- Research and Sources: Our team delves into credible research, ensuring every piece is grounded in facts and evidence, offering a holistic view on personal growth topics.
- Continuous Updates: In the dynamic landscape of personal development, we are committed to keeping our content fresh. We often revisit and update our resources to stay abreast of the latest developments.
- External Contributions: We welcome insights from external contributors who share our passion for personal transformation and consciousness elevation.
- Product Recommendations and Affiliations: Recommendations come after thoughtful consideration and alignment with Mindvalley’s ethos, grounded in ethical choices.
To learn more about our dedication to reliable reporting, you can read our detailed editorial standards .
17 Types of Questions for Teachers in the Classroom

Questions are the foundation of almost any class, but knowing when to ask the right ones may require some pre-planning. Educators can use different types of questions in teaching to check on a student’s understanding, spark discussion, or help others learn from their peers.
Of course, you may have the perfect list of questions to ask, but keeping students engaged and talking can become another hurdle. We’ll go over different strategies for designing effective questions and how to handle various situations, such as incorrect answers or silence. Plus, we’ll show you how tech like Poll Everywhere can help you engage your students with interactive presentations and questions .
How to design effective and engaging questions (and get students to respond)
Keeping students engaged while you ask questions designed to measure their level of understanding is an art. Here are some steps you can take to thoughtfully craft different types of questions for your classroom:
Planning what types of questions to ask
- Choose a goal for asking questions: This helps you decide which types of questions used in teaching are best for your needs.
- Decide what course material to base questions on: It’s better to choose content you feel is important to the overall learning objectives noted in your lesson plan.
- Plan critical questions ahead of time: While it’s okay to formulate questions as the class progresses, it’s important to plan questions you deem essential to gauging students’ learning or prompting critical thinking ahead of time.
- Adapt questions to students’ knowledge levels: Make sure your questions challenge your students' understanding of newly presented topics or assess their foundational knowledge—using a diagnostic assessment before and after the semester can help gauge current knowledge.
- Use a variety of question types: Using a variety of question types—even for the same concept—can help students better grasp the course material by prompting them to think about their answers in different ways. Using Bloom’s Taxonomy to develop multiple levels of questions for the same topic is helpful.
- Anticipate possible answers: This helps you ensure the phrasing of your question isn’t too vague or misleading, as well as whether the questions match your learning objectives.
Asking questions
- Phrase questions clearly: Ensure your questions are unambiguous and are phrased logically so students don’t misunderstand or end up more confused.
- Allow time to process the question: Don’t be afraid of silence—it likely means your students are contemplating the question and thinking through their responses. You should always wait a moment for students to process the question before rephrasing or assuming they don’t understand.
- Avoid including the answer in your questions: If you’re assessing students’ comprehension, including the answer in your question defeats the purpose and likely won’t encourage engagement.
- Vary the types of questions you ask: By varying the questions you use in your teaching, you can prompt students to think about the material in different ways.
Assessing student responses
- Follow student responses with reflection: A reflective statement (e.g., “It sounds like…” or “What did you mean when you said…?”) helps you show you’re listening and double-check your understanding of the response.
- Ask students to elaborate: Similar to making a reflective statement, you can outright request that a student elaborate on their response. This can help you really dig into their level of comprehension and may also help other students who are listening in by giving them insight into their peers’ thinking processes.
- Know how you’ll handle incorrect answers: Have a game plan in place in case students answer incorrectly. This not only reduces the chance of confusion but also helps you confidently guide the discussion so students can come to the correct answer and understand why their original answer was incorrect.
- Encourage other students to chime in: Turn a one-way conversation into a discussion by inviting others to offer their opinions or state if they agree or disagree (and why).
- Use positive reinforcement: Make students feel confident and glad they responded by smiling, using positive statements, nodding, and making eye contact. This positive reinforcement can help students feel safe when responding—or when asking questions.
- Keep track of who’s responded: While some students are eager to offer their two cents, others may be more reluctant. You can create a more inclusive and inviting discussion by allowing a variety of students to share. If you teach a hybrid class, be sure to include both in-person and remote students as well.
3 strategies for addressing incorrect answers or surface-level understanding
If your students don’t respond with a satisfactory answer, you can take advantage of that time to help students understand what they got wrong and what the correct answer is. Three different strategies for guiding students to a better understanding of the topic include probing, redirecting, and refocusing.
- Probing: The probing strategy encourages students to use critical thinking to analyze their answers. This may involve uncovering relationships by comparing and contrasting different concepts, or instructors can ask students to clarify their ideas by providing examples. Additionally, educators can help students pinpoint assumptions used to justify their answers.
- Redirecting: By using redirection carefully, you can invite other students to correct a peer’s incorrect answers. This strategy also encourages more students to participate in the discussion by asking if they agree with the answer or if they can provide an example to support the answer. Just be sure to lay out ground rules before opening up a discussion based on one student’s thoughts to avoid unnecessary conflict.
- Refocusing: Instructors can refocus students if their answer doesn’t quite fit with the content being discussed. For example, let’s say you ask, “What’s one way our modern food system is making people sick?” and a student responds with, “Doesn’t it encourage us to overeat?”—you might refocus the discussion to discuss how not all calories are nutritionally equal by asking, “Yes, but what if we’re talking about not just caloric intake but nutritional intake as well?”
How to use Bloom’s Taxonomy to craft engaging questions
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a framework intended to define different levels of learning and help teachers assess student progress. You can use this concept to develop questions that assess students’ levels of understanding. According to Bloom’s Taxonomy, there are six different levels of understanding: remember, understand, apply, analyze, evaluate, and create.
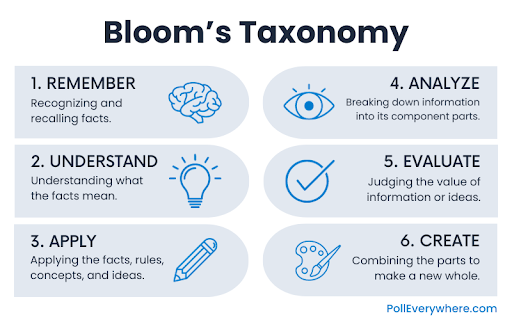
Remember, understand, and apply questions are typically used to assess learners’ comprehension to see whether anyone needs additional assistance grasping the course content. Analyze, evaluate, and create questions are more often used to encourage deeper critical thinking and problem-solving, or to spark discussions.
If you start with higher-level questions associated with the analyze, evaluate, and create levels and students aren’t sure of the answer, asking a follow-up question related to the lower levels of remember, understand, and apply can help you judge whether your learners understand the course material or not.
Here are some examples to help you craft your own questions based on Bloom’s Taxonomy:
- Can you describe ____?
- When did ____ happen?
- Which is true/false, ____ or ____?
- What does ____ mean?
- How would you show ____?
- How would you compare/contrast ____?
- What’s the main idea of ____?
- What would happen if ____?
- How would you state ____ in your own words?
- Which statements support ____?
- Do you know of another instance where ____?
- What examples can you think of to support ____?
- How would you use ____?
- How would you solve ____ using what you’ve learned?
- What questions would you ask to better understand ____?
- Why do you think ____?
- What conclusions can you draw about ____?
- Why did ____ changes occur?
- What’s the theme of ____?
- How is ____ similar to ____?
- What’s your opinion of ____ and why?
- How would you handle ____?
- Is there a better solution to ____?
- What information would you use to support the view of ____?
- Why was ____ better than ____?
- Can you see a possible solution for ____?
- What alternative can you propose for ____?
- How would you test ____?
- What would you predict is the outcome of ____?
- What new/unique uses can you come up with for ____?
What to do if students don’t respond to questions
Possibly one of the worst nightmares any instructor can have is asking a question and being met with silence. But with a few simple strategies you can turn silence into learning opportunities:
- Rephrase the question: Chances are your students don’t understand the question or aren’t sure what you’re looking for. In this case, rephrasing the question to clarify could help clear up the confusion. For example, let’s say you ask your students, “How would you define a project?” You can reword the question by asking, “In what ways are projects different from processes?”
- Prompt with information: You might be able to jog students’ memories or thinking by providing information or context. For example, if students cannot answer “How do you calculate the circumference of a circle?” you could break the question down by asking “How do you calculate the radius of a circle?”
Why is it important to use engaging questions while teaching?
At a minimum, crafting thoughtful questions can help you judge whether your class comprehends the concepts presented in the course. Additionally, strategically designing questions can improve students’ learning comprehension by helping them think critically and creatively as well as encouraging them to engage with the course content.
Questions, credibility, and feedback are all aspects of communication that can improve student engagement. A 2021 study published in the Frontiers in Psychology journal found a “strong dynamic between the aspects of academic engagement and teacher caring, credibility, feedback, and communication style.” Additionally, one study participant noted that an instructor’s credibility actually improves if they don’t always know the answers to all questions.
17 effective types of questions in teaching
Planning out your questions for each lesson also involves considering what types of questions you’ll ask. There are numerous question types and each one may elicit a different response from students. Here are some more effective types of questions to use in teaching that encourage critical thinking and creativity:
A type of rhetorical question, display questions help educators check on students’ ability to retrieve information.
- How much of the body’s oxygen consumption does the brain account for?
- Who wrote “The Faerie Queene?”
2. Referential
A referential question is used when the person asking the question doesn’t know the answer. These types of questions may be helpful to instructors when gathering student feedback about course materials and activities—or to create personal connections by checking in on how students are doing.
- Overall, do you feel this class was beneficial?
- How was your weekend?
Factual questions, also called explicit questions, call on students to answer using information pulled directly from reading assignments. Educators can use factual questions to understand whether students understand the concepts presented in the readings.
Factual questions are an essential starting point for students to expand on the information they’ve learned with critical thinking.
- Which art movement is Salvador Dali associated with?
- Who designed the Sagrada Familia in Barcelona, Spain?
4. Convergent
These types of questions ask students to pull together ideas and information from different sources and synthesize them to create a logical answer. Convergent questions are ideal for problem-solving activities.
- What was the common theme in last week’s reading?
- How would you describe this current event in one word?
5. Divergent
The opposite of convergent questions, divergent questions don’t have a single answer. These types of questions are best used to inspire creative responses and encourage students to consider different points of view, ideas, and scenarios.
- How do you think Edgar Allen Poe would have ended “The Tell-Tale Heart” if his main character didn’t confess?
- How do you think the US might be different if the assassination of John F. Kennedy never took place?
6. Evaluative
An evaluative question requires students to think of a response based on their opinion. These questions can prompt students to think critically about readings or discussions and draw connections to their own experiences or ideals.
- What do you think about Captain Ahab’s mission to find the white whale?
- Do you agree with what the author said in this paper about animal rights?
Open-ended questions are essential to prompt students to think critically about their answers. Open questions can’t be answered with a simple “Yes” or “No,” making them a powerful tool for inspiring discussion.
- What is the main purpose of the United Nations?
- What’s one major breakthrough we’ve had in science over the last 10 years?
Learn more: Marquise McGraw, Ph.D., a professional lecturer at American University, gets students involved in discussions using Poll Everywhere. Find out his personal strategies for engaging everyone —even students who are normally too shy to share—in classroom discussions.
If instructors are trying to get a student to provide more information about their answer, they can use probing questions to prompt students to clarify, justify, or elaborate on their thoughts.
- What information helped you come to that conclusion?
- Who might disagree with your answer?
9. Multiple choice
One of the most common types of questions, multiple-choice questions provide options for students to choose from when answering. Usually, multiple-choice questions have one correct answer, but alternatives include prompting students to choose the option that’s wrong out of a list of correct options or offering an “All of the above” option.
Multiple-choice questions can improve student participation by making it easier for them to respond. Tech like Poll Everywhere further enhances this accessibility by allowing students to answer using their cell phones—or answer anonymously if the instructor chooses to set up the question that way.
- Which project document includes the description, owner, source, priority, and status of product requirements? a) The project charter b) The requirements traceability matrix c) The scope management plan d) The work breakdown structure
- How are tertiary colors created? a) Mixing equal amounts of two secondary colors b) Mixing unequal amounts of two primary colors c) Mixing three primary colors d) All of the above
Focal questions encourage students to pick a side and support their position with logical reasoning. These can be helpful in inspiring students to consider alternative points of view or schools of thought.
- Do you think all US citizens should have to sign up for the draft? Why or why not?
- Do you believe it was within the right of the US Supreme Court to overturn Roe v. Wade? Why or why not?
Physicist Enrico Fermi is the namesake of the Fermi question, which requires students to estimate an answer based on limited information. You may recognize this type of question from articles covering Google’s unconventional approach to interviewing potential new employees, as Fermi questions require creative thinking and the ability to work through a problem.
- Why are manhole covers round?
- How would you explain how the internet works to a seven-year-old?
Thunk questions are intended to encourage students to pause and look at what might normally be a common, benign concept in a different light. (Fun fact: The term “thunk” is based on the irregular form of the verb “think.”)
- If your pet could talk, what would it say about you?
- What’s the difference between knowing and believing?
13. Hypothetical
Hypothetical questions use the good old “What if…” structure to prompt students to consider a scenario and how they would react or feel. Hypothetical questions inspire creativity, problem-solving, and critical thinking.
- What if Europeans never reached North or South America, how would the world be different?
- What do you think life would be like if dinosaurs never went extinct?
14. Ethical
Educators can present students with moral dilemmas using ethical questions. These types of questions don’t have a right or wrong answer but do require students to think critically about why they believe their answer is correct. Ethical questions are excellent discussion starters.
- Do you think countries should be able to claim other planets as their own?
- Should we take care of workers whose jobs are replaced by AI?
15. Application
Instructors can use application questions to encourage students to apply newly gained knowledge related to the course. By using information they’ve learned in class and applying it to real-world situations, students can achieve a higher level of comprehension.
- What are some examples of media bias you’ve seen recently?
- How would you demonstrate Newton’s first law using objects on your desk or in the classroom?
- Using what you know about cognitive bias, how would you design a website landing page that converts leads?
16. Affective
You can encourage students to engage with course content on a more personal level by using affective questions. These types of questions ask students about their feelings toward a topic and how it relates to their values.
Poll Everywhere’s numeric rating scale allows educators to present affective questions in a friendly way. Ask students to rate how they feel about an issue using a scale from one to five, then ask if anyone wants to chime in with the reasoning behind their rating to kick the discussion off.
- How do you feel about the author’s portrayal of Lenny?
- Is the use of imagination in art important to you?
These types of questions are used to gauge your students’ understanding of a topic all at the same time. By using hinge questions, you can decide whether the day’s class should continue going over the topic or if you can move on to the next lesson.
- Which of the following examples represents an allegory?
- Which of the following is an example of soft news?
3 types of ineffective questions to avoid (or use carefully)
Along with the 17 types of effective questions above, there are three more types of questions that can become problematic if not used carefully.
- Binary: Also called a closed question, a binary question is usually answered with “Yes” or No” or variations thereof. These questions typically force students to choose a side and are more effective if there’s no right or wrong answer or if you probe for additional information.
- Leading: Leading questions are problematic because they suggest the correct or desired answer. An example of a leading question is, “How satisfied were you with the class?”
- Loaded: These types of questions include an implicit assumption about the respondent. An example of a loaded question is, “How many times did you cheat on your exams during the semester?”
Poll Everywhere makes gauging student understanding effective and engaging
Getting students to participate in discussions or even ask their own questions is challenging. Designing effective questions based on your desired outcomes or learning objectives keeps you one step ahead of in-class conversations. However, you should also be ready to guide discussions back on topic if students take off on tangents or a respectful debate becomes a heated argument.
Tech like Poll Everywhere can help you present your questions in an engaging format that invites all students to participate. With the ability to ask and share any type of question using Poll Everywhere, including multiple-choice, you can quickly and easily inspire and guide discussions that all students are excited to participate in.
Related articles
The Power of a Good Question: Prompting Critical Thinking in Students

Originally published in TEACH Magazine, May/June 2023 Issue
By Sunaina Sharma
What makes a good question? We ask students questions all day long, but how do we know they are actually helping students learn and, more importantly, getting them to think? Being able to think for themselves, and especially to think critically, is one of the most important skills students will ever use—both in the classroom and beyond.
Critical thinking is the process of objectively analyzing information to form a judgment. It requires students to read, consider, observe, interpret, evaluate, reason, and conclude, but then it also requires them to articulate their position and justify it, meaning students must be able to effectively communicate their thoughts and ideas. Critical thinking is a skill that is expected of today’s 21st century learners and is a pillar of many province and state curriculum documents.
Reimagining My Questioning Style
A good question always prompts my brain to think, and I wondered if it would do the same for my students. I began to consider what would happen if I changed the types of questions I asked. Was there a way I could invite students to construct their own knowledge?
To inspire curiosity in my students, I had to start by exploring how to transform my questioning style. In my inquiry, I came upon a critical thinking skills graphic that provided examples of different levels of questions to help students learn actively. The level six questions were exactly what I was looking for. These were intellectually engaging enough to have students reflect on what they already knew, and research to understand what they didn’t, in order to seek out an answer.
I was eager to try out some of these questions for myself, so after my Grade 9 class finished reading the short story Lamb to the Slaughter by Roald Dahl, I asked the students my version of a level six critical thinking question: “We know Mary killed her husband. If you were the detective investigating the case, what would you charge her with and how would you defend your conclusion to the Crown?”
I had students break into groups to begin forming their answers. I never gave them any additional prompts or suggestions. They began talking immediately, but quickly realized that they needed more information. First, they had to figure out the legal consequences of killing someone.
Out came their prior knowledge. Students pooled together what they already knew from watching movies or television shows, then determined that they needed to know the difference between manslaughter, second-degree murder, and first-degree murder.
Out came their devices. They Googled, read, and shared the definitions they found. Once each group had a good understanding of the terms, they moved forward.
Out came their textbooks. They reread portions of the story to analyze specific plot events in light of the new definitions they had learned.
Out came their ideas. Students expressed their opinions, listened to each other, debated, disagreed, and worked towards forming a collective answer. They took notes and some even chose to mind-map or use a chart to keep track of all their ideas. We then gathered as a class to engage in a whole-group discussion so we could hear each other’s thoughts.
Out came their voices. Students communicated their answers and instinctively provided evidence from the text in support. Because of the amount of thought that went into drawing their conclusions, students referenced page numbers from the story and sources from the Internet. They were confident in their final decisions and sought to convince their peers to agree with them.
Digital Technology as a Learning Tool
After the success with my Grade 9 students, I wanted to continue refining my questioning style. I also had the idea to try and combine asking effective questions with using digital technology. My own PhD research taught me that when students use technology to construct knowledge, it engages them. As such, I developed a graphic of my own to guide me and my students:

The graphic prompted students to use technology to access outside information that would help them answer questions. In addition, the four levels aligned with the four-level rubric in the Ontario curriculum. With this simplified graphic, I continued to ask my students questions that prompted their thinking.
My Grade 11 students had been reading the graphic novel Deogratias: A Tale of Rwanda by Jean-Philippe Stassen. It is a text that has parallel storylines—one tells the tale of the main character, Deogratias, before the Rwandan genocide, and the other tells of his life afterwards. To understand the impact of the genocide on Deogratias, I engaged my students in an examination of traits he demonstrated before and after.
As students were contributing their ideas, someone called out, “After the genocide, he’s gone crazy.” I interjected and talked about the harm of that word, then asked the class to reconsider what adjective they would use to describe the main character. One student said, “I think he has PTSD.” I paused and asked everyone else what they thought. They couldn’t answer the question because they didn’t know exactly what post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) was.
I divided the students into small groups and handed each group a blank piece of paper. I had them write “Does Deogratias have PTSD?” at the top of the page, then asked them to research the symptoms of PTSD and list them on their sheet. Students began to talk with each other and some even shared stories of a family member dealing with the disorder. After sharing what they already knew and respectfully listening to their peers’ experiences, students realized they needed technology. Some grabbed their phones and others borrowed a classroom device to begin exploring and researching.
Once they accessed reliable websites, students also started flipping through the graphic novel to look for evidence they could use to prove or disprove whether Deogratias had PTSD. Again, students accessed their prior knowledge, used their technological devices, reread their book, constructed their own ideas, and shared their voices with their peers.
Here are some student responses to the question “Does Deogratias have PTSD?”

The Impact of Using Enhanced Questions
As educators, sometimes our passion for our subjects can lead us to get so focused on content that students are left wondering how their learning is relevant to the world beyond the classroom. But by reframing our questions, students are able to see the relevance of what they’re learning.
Asking students enhanced questions sparks their intellectual engagement. When we ask questions that prompt critical thinking, students are invested in choosing strategies to find the answer. They inevitably start by examining what they already know to act as a foundation for deeper learning, then they do a close reading of the text to analyze particular lines. They also use technology to deepen their learning, then form an opinion and justify that opinion with evidence.
What’s more, because they are so engaged, students are willing to share their ideas with others. They communicate, collaborate, and participate in active listening. Those are the skills I want to arm my students with because those are the skills they will use in the future.
Dr. Sunaina Sharma is an in-school program leader and secondary teacher with over 20 years’ experience teaching in the Halton District School Board. She is also an instructor and practicum advisor in a Bachelor of Education program, where she is able to share her classroom experiences with future educators.
The Art of Questioning: Techniques to Promote Critical Thinking and Inquiry
We can all agree that critical thinking is an essential skill for students to develop.
This article will provide educators with a comprehensive guide on the art of questioning - powerful techniques to promote critical thinking, inquiry, and deep learning in the classroom.
You'll discover the core principles of effective questioning, actionable strategies to engage different types of learners, as well as sample activities and assessments to put these methods into practice. Equipped with these practical tools, you can transform class discussions that foster students' natural curiosity and grow their capacity for critical thought.
Embracing the Importance of Art of Questioning
The art of questioning is a critical skill for educators to develop. Questioning techniques that promote critical thinking and inquiry-based learning lead to increased student engagement and deeper understanding. By mastering various strategic questioning approaches, teachers can stimulate complex thinking in their students.
Defining the Art of Questioning
The art of questioning refers to the teacher's ability to craft and ask meaningful questions that push students to think more critically. It goes beyond surface-level, fact-based questioning and instead focuses on stimulating analysis, evaluation, creation, connection-making, and reflection. Well-designed questions require students to tap into higher-order cognitive skills and prior knowledge to construct responses. This process mirrors real-world critical thinking and problem-solving.
Benefits of Mastering Questioning Techniques
Teachers skilled in questioning techniques reap many rewards, including:
- Increased student participation and engagement during lessons
- Development of students' critical thinking capacities
- Ability to check students' understanding and identify knowledge gaps
- Scaffolding learning to meet students at their zone of proximal development
- Encouragement of inquiry, sparking student curiosity and motivation to learn
By honing their questioning approach, teachers gain an invaluable tool for promoting deep learning.
The Role of Questioning in Early Childhood Education
Questioning plays a pivotal role in early childhood education by fostering mental activity and communities of practice. Crafting developmentally-appropriate questions allows teachers to gauge children's baseline understanding and then scaffold new concepts. This questioning facilitates theory of mind growth, as children learn to articulate their thought processes. An inquiry-based classroom also encourages participation, inclusive learning, and problem-solving. Ultimately, strategic questioning lays the foundation for critical thinking that will benefit students throughout their education.
What is the art of questioning critical thinking?
The art of questioning refers to the skill of asking thoughtful, open-ended questions that promote critical thinking , inquiry, and deeper learning. As an educator, mastering this art is key to creating an engaging classroom environment where students actively participate.
Here are some best practices around the art of questioning:
Use Open-Ended Questions
Open-ended questions allow students to explain their thought process and help teachers identify gaps in understanding. For example, asking "Why do you think the character made that decision?" lets students share their unique perspectives. Closed-ended questions that just require yes/no answers should be used sparingly.
Ask Follow-Up Questions
Asking follow-up questions based on students' responses shows you are listening and encourages them to expand upon their ideas. Phrases like "Tell me more about..." or "What makes you think that?" stimulate further discussion.
Pause After Posing Questions
Providing wait time of 3-5 seconds after asking a question gives students time to reflect and articulate a thoughtful response, rather than feeling put on the spot.
Scaffold Complex Questions
Break down multi-layered questions into smaller parts to make them more manageable. You can also give students a framework to help organize their thoughts before answering.
Encourage Multiple Perspectives
Prompt students to consider other vantage points by asking, "How might this look from X's perspective?" This builds empathy, critical analysis skills, and more inclusive thinking.
Mastering the art questioning leads to richer class discussions and unlocks students' intellectual curiosity. With practice, you'll be able to stimulate vibrant student-centered dialogue.
What questioning techniques promote critical thinking?
Asking effective questions is a skill that takes practice to develop. Here are some techniques to promote critical thinking through questioning:
Ask questions that require more than a one-word response. This encourages students to explain their reasoning and make connections. For example:
- Why do you think that?
- What evidence supports your conclusion?
- How does this relate to what we learned before?
Dig deeper into student responses by asking them to expand upon their ideas. This helps clarify understanding and uncover misconceptions. Some follow up questions include:
- Can you explain what you mean by that?
- What makes you think that?
- How does that apply to this situation?
Pause After Questions
Provide wait time of 3-5 seconds after posing a question. This gives students time to think and construct an answer, promoting deeper reflection. Resist the urge to rephrase the question or provide the answer yourself.
Scaffold Questions
Break down complex questions into smaller parts to guide student thinking while still encouraging them to do the intellectual work.
Asking thoughtful, open-ended questions takes practice but is essential for developing critical thinking skills . Start by planning 2-3 higher-order questions for each lesson and focus on truly listening to student responses. Over time, a questioning approach focused on explanation, evidence, and exploration will become second nature.
What is the art of questioning method?
The art of questioning is a teaching technique that focuses on asking strategic questions to promote critical thinking, inquiry, and meaningful learning experiences for students. It is an essential skill for educators to master in order to elicit student understanding and uncover gaps in knowledge.
Some key things to know about the art of questioning:
It checks for understanding and gets insight into students' thought processes. By asking probing questions, teachers can determine if students have truly grasped key concepts.
It activates higher-order thinking skills. Well-designed questions require students to analyze, evaluate, and create, moving beyond basic recall.
It sparks student curiosity and engagement. Thought-provoking questions pique interest in lesson topics.
It facilitates rich class discussions. Using quality questioning techniques lays the foundation for impactful dialogue.
It informs teaching strategies and adaptations. Based on student responses, teachers can clarify misconceptions or adjust the pace/complexity of lessons.
Mastering the art of questioning takes practice but is worth the effort. It transforms passive learning into an active, student-centered experience that sticks. Equipped with this vital skill, teachers can maximize critical thinking and inquiry-based learning in their classrooms.
What are the 4 main questioning techniques?
Teachers can utilize four key questioning techniques to promote critical thinking and inquiry in the classroom:
Closed Questions
Closed questions typically require short or one-word answers. They are useful for:
- Checking for understanding
- Getting students to state facts
- Reviewing material
For example, "What year did World War 2 begin?"
Open Questions
Open questions require more elaborate responses. They are effective for:
- Encouraging discussion
- Extracting deeper thinking
- Allowing students to explain concepts
For instance, "How did the Great Depression impact American society?"
Funnel Questions
Funnel questions start broad and become increasingly specific. This technique:
- Prompts recall of contextual details
- Guides students step-by-step
- Focuses thinking
An example is, "What do you know about World War 2? What were the key events leading up to it? What specific decisions by world leaders contributed to its outbreak?"
Probing Questions
Probing questions request clarification or more information. They help to:
- Draw out additional details
- Test the strength of an argument
- Determine accuracy and depth of understanding
For example, "You mentioned the Great Depression caused widespread poverty. Can you expand on the ways it impacted day-to-day life?"
Using a mix of these four questioning techniques can elicit thoughtful participation and allow teachers to effectively gauge comprehension.
sbb-itb-bb2be89
Exploring types of art of questioning.
Art of questioning refers to the teacher's ability to ask thoughtful, open-ended questions that promote critical thinking, inquiry, and engagement among students. Here we explore some key categories of questions that go beyond basic fact recall to stimulate deeper learning.
Open-Ended Questions to Foster Inquiry
Open-ended questions have no single right answer, allowing students to respond creatively within their current knowledge and experiences. Some examples:
- What do you think would happen if...?
- How might we go about solving this problem?
- What are some possible explanations for...?
Guidelines for open-ended questions:
- Ask about hypothetical situations or predictions
- Inquire about students' thought processes or reasoning
- Seek multiple diverse responses to broad issues
Probing Questions to Assess Prior Knowledge
Probing questions aim to uncover and expand upon students' existing knowledge. For instance:
- What do you already know about this topic?
- Can you explain your solution further?
Tips for probing questions:
- Ask students to elaborate or clarify their responses
- Dig deeper into the reasons behind their ideas
- Gauge their current level of understanding on a topic
Hypothetical & Speculative Questions for Mental Activity
Hypothetical and speculative questions require students to mentally engage with imaginative or puzzling scenarios. Examples:
- What do you imagine this character is thinking/feeling?
- If you could travel anywhere, where would you go?
- What might the world look like 100 years from now?
Strategies using speculative questions:
- Present imaginary situations
- Ask about unlikely or fantastical events
- Inquire about hopes, wonders, or puzzles
Synthesis & Evaluation Questions to Enhance Critical Thinking
Higher-order questions push students to analyze, evaluate, and synthesize information. For example:
- How would you compare and contrast these two stories?
- What evidence supports or contradicts this conclusion?
- What changes would you suggest to improve this process?
Techniques for using synthesis questions:
- Ask students to make connections between ideas
- Require them to assess credibility and logical consistency
- Prompt them to create novel solutions based on analysis
Thoughtful questioning is invaluable for engaging students, inspiring deeper thinking, assessing understanding, and taking learning to the next level. Match question types to desired educational outcomes.
Effective Timing and Application of Questioning Techniques
Utilizing zones of proximal development at the beginning of lesson.
At the start of a lesson, it's important to assess students' prior knowledge and understanding within their zones of proximal development. Open-ended questions that require some thought and analysis work well here, such as "What do you already know about this topic?" or "How might this connect to what we learned previously?". Allowing some think time and using gentle probing follow-ups can uncover gaps and misconceptions to address.
During Instruction: Encouraging Active Participation
While teaching new material, questions should regularly check comprehension and spur examination of ideas. "Why" and "how" questions prompt students to articulate concepts in their own words, while think-pair-share structures promote participation. Allow just enough wait time for students to gather thoughts before cold-calling. Ask students to summarize key points or apply them in novel contexts. Maintain an encouraging tone and affirm effort.
End-of-Lesson Evaluations and Inquiry
Conclude by synthesizing main points and addressing lingering questions. Open-ended questions like "What are you still wondering about?" give quieter students a chance to share. Exit tickets, short reflective writing assignments, also stimulate additional inquiry. Follow-up questions based on student responses facilitate rich discussion. Affirm participation and remind students that lingering questions present opportunities for future investigation.
Art of Questioning Activities and Games
Think-pair-share and other participatory activities.
The think-pair-share approach provides an excellent framework for questioning techniques. Students are first asked to independently think about a question or problem. They then discuss their ideas in pairs, encouraging participation from every student before ideas are shared with the whole class. Variations like think-write-pair-share add a writing component for reflection. These participatory structures promote critical thinking and inquiry through peer discussion.
Question Cycles for Continuous Learning Experience
Using a series of interrelated questions on a topic creates continuity in the learning experience. Starting with simpler questions then building up to more complex, higher-order questions logically develops student understanding. Question cycles enable connecting new information to prior knowledge, unpacking ideas, applying concepts, making evaluations, and synthesizing learning. This technique ensures questioning sequentially builds up rather than occurring in isolation.
Socratic Questioning to Challenge Theory of Mind
The Socratic method uses questioning to draw out ideas and uncover assumptions. Teachers can play "devil's advocate" to challenge students' thought processes. This develops theory of mind as students learn to see other perspectives. Socratic questioning teaches the value of intellectual humility and deep thinking. Example questions include "What do you mean when you say...?", "What evidence supports that?", "How does this tie into our earlier discussion?"
Interactive Questioning Games to Engage Students
Games put questioning techniques into action while engaging students. Examples include Quiz-Quiz-Trade with student-created questions, Question Rally with teams answering on whiteboards, Question Cards with written responses, and Question Dice promoting discussion. These games leverage friendly competition and peer involvement to motivate learning through questioning. The interactive format promotes enjoyment, attention, and participation.
Assessing the Objectives and Impact of Questioning Techniques
Developing questioning rubrics aligned with objectives.
Rubrics can be a useful tool for assessing questioning techniques and alignment with learning objectives. When developing a rubric, key aspects to consider include:
- Types of questions asked - Factual, convergent, divergent, evaluative, etc.
- Cognitive level of questions - Remember, understand, apply, analyze, evaluate, create
- Scaffolding and sequencing of questions
- Linkage to lesson objectives and goals
- Student engagement and participation
The rubric can include rating scales or descriptors across these dimensions to evaluate the art of questioning. Teachers can use the rubric for self-assessment or be observed and evaluated by others.
Gathering Insights Through Student Feedback Surveys
Conducting periodic student surveys can provide valuable perceptions into questioning approaches. Useful survey questions may cover:
- Comfort and willingness to respond to questions
- Perceived relevance of questions to learning goals
- Role of questions in promoting thinking and understanding
- Suggestions for improvement
Analyzing survey results over time can indicate whether shifts in questioning techniques have positively influenced the learning experience.
Measuring Growth in Critical Thinking with Assessments
Assessments focused on critical thinking skills can gauge the impact of improved questioning. These may include:
- Essay prompts and open-ended questions
- Scenarios to analyze that require evaluation, synthesis and creative solutions
- Individual or group projects necessitating inquiry and investigation
- Presentations demonstrating deep understanding
Comparing baseline to post-intervention assessments can quantify if questioning strategies have successfully developed critical thinking capacities.
Participatory Action Research for Professional Development
Teachers can engage in participatory action research by:
- Recording lessons and categorizing types/cognitive levels of questions asked
- Soliciting peer or mentor feedback on questioning approaches
- Setting goals for improvement and tracking progress
- Iteratively refining techniques based on evidence and collaboration
This process facilitates continuous growth and allows networking with a community of practice.
Building a Community of Practice Through Questioning
Fostering collaborative environments where educators can share best practices in questioning techniques is key to building a strong community of practice focused on the art of questioning. By creating opportunities for continuous learning and adaptation, educators can work together to advance their skills.
Fostering Collaborative Environments
- Establish routines for educators to observe each other's classrooms and provide feedback on questioning strategies
- Organize professional learning groups for educators to collaborate on developing effective questions
- Create shared online spaces for educators to exchange ideas on the art of questioning
- Promote a growth mindset culture that values inquiry and critical feedback
Sharing Best Practices in Questioning
- Host workshops for educators to demonstrate questioning techniques and activities
- Publish videos/documents highlighting examples of impactful questioning strategies in action
- Maintain forums for educators to post questions and get input from colleagues
- Enable educators to share lesson plans centered around critical thinking questions
- Encourage educators to exchange ideas on adapting questioning for different subjects
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
- Survey educators regularly on evolving needs related to questioning techniques
- Provide ongoing professional development on emerging best practices in questioning
- Establish mentoring programs for new educators to get support in questioning skills
- Promote reflection techniques for educators to assess their questioning methods
- Foster a culture of critical inquiry where questioning practices continuously improve
By taking a collaborative, growth-focused approach to the art of questioning, educators can work together in communities of practice to advance their skills and create vibrant cultures of learning in their classrooms.
Conclusion: Synthesizing the Art of Questioning for Educational Excellence
The art of questioning is a critical skill that all educators should develop. By mastering various techniques that promote critical thinking and inquiry, teachers can stimulate rich discussion, facilitate deeper learning, and empower students to analyze information.
Here are some key takeaways:
Asking open-ended questions is key to sparking curiosity and prompting students to think more critically. Closed-ended questions that have yes/no answers should be used sparingly.
Mix lower and higher-order questions. Lower-order questions assess basic understanding while higher-order questions require evaluation, synthesis and analysis.
Allow adequate wait time between questions. Give students sufficient time to process the question and develop thoughtful responses.
Scaffold complex questions by building on students' prior knowledge. Connect new ideas to concepts already familiar to them.
Encourage participation from all students with inclusive questioning strategies. Consider think-pair-share methods.
Use prompting and probing techniques to extend dialogue. Ask follow-up questions to clarify, provide evidence or expand on initial responses.
By honing expertise in thoughtful inquiry-based questioning, educators can unlock their students' potential for critical thought while creating engaging, student-centered learning environments. Continual development through communities of practice, action research and other forms of professional development can help perfect this invaluable teaching skill.
Related posts
- The Socratic Method: Engaging Students in Critical Thinking and Dialogue
- Teaching Resources for Teachers: Cultivate Critical Thinking
- Cultivating Creativity: Innovative Approaches to Encouraging Student Imagination
- How to Develop Critical Thinking Skills in Students
Best Leadership Skills for Teachers: Guiding with Confidence

Best Tech Gadgets for Teachers: Modernizing the Classroom

The Future of Education Post-Pandemic
Become a buddy..
Join 500+ teachers getting free goodies every week. 📚

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Critical Thinking Is About Asking Better Questions
- John Coleman

Six practices to sharpen your inquiry.
Critical thinking is the ability to analyze and effectively break down an issue in order to make a decision or find a solution. At the heart of critical thinking is the ability to formulate deep, different, and effective questions. For effective questioning, start by holding your hypotheses loosely. Be willing to fundamentally reconsider your initial conclusions — and do so without defensiveness. Second, listen more than you talk through active listening. Third, leave your queries open-ended, and avoid yes-or-no questions. Fourth, consider the counterintuitive to avoid falling into groupthink. Fifth, take the time to stew in a problem, rather than making decisions unnecessarily quickly. Last, ask thoughtful, even difficult, follow-ups.
Are you tackling a new and difficult problem at work? Recently promoted and trying to both understand your new role and bring a fresh perspective? Or are you new to the workforce and seeking ways to meaningfully contribute alongside your more experienced colleagues? If so, critical thinking — the ability to analyze and effectively break down an issue in order to make a decision or find a solution — will be core to your success. And at the heart of critical thinking is the ability to formulate deep, different, and effective questions.
- JC John Coleman is the author of the HBR Guide to Crafting Your Purpose . Subscribe to his free newsletter, On Purpose , or contact him at johnwilliamcoleman.com . johnwcoleman
Partner Center
- Math Resources Links
- Math in the Real World
- Differentiated Math Unlocked
- Math in the Real World Workshop
20 Math Critical Thinking Questions to Ask in Class Tomorrow
- November 20, 2023

The level of apathy towards math is only increasing as each year passes and it’s up to us as teachers to make math class more meaningful . This list of math critical thinking questions will give you a quick starting point for getting your students to think deeper about any concept or problem.
Since artificial intelligence has basically changed schooling as we once knew it, I’ve seen a lot of districts and teachers looking for ways to lean into AI rather than run from it.
The idea of memorizing formulas and regurgitating information for a test is becoming more obsolete. We can now teach our students how to use their resources to make educated decisions and solve more complex problems.
With that in mind, teachers have more opportunities to get their students thinking about the why rather than the how.
Table of Contents
Looking for more about critical thinking skills? Check out these blog posts:
- Why You Need to Be Teaching Writing in Math Class Today
- How to Teach Problem Solving for Mathematics
- Turn the Bloom’s Taxonomy Verbs into Engaging Math Activities

What skills do we actually want to teach our students?
As professionals, we talk a lot about transferable skills that can be valuable in multiple jobs, such as leadership, event planning, or effective communication. The same can be said for high school students.
It’s important to think about the skills that we want them to have before they are catapulted into the adult world.
Do you want them to be able to collaborate and communicate effectively with their peers? Maybe you would prefer that they can articulate their thoughts in a way that makes sense to someone who knows nothing about the topic.
Whatever you decide are the most essential skills your students should learn, make sure to add them into your lesson objectives.

When should I ask these math critical thinking questions?
Critical thinking doesn’t have to be complex or fill an entire lesson. There are simple ways that you can start adding these types of questions into your lessons daily!
Start small
Add specific math critical thinking questions to your warm up or exit ticket routine. This is a great way to start or end your class because your students will be able to quickly show you what they understand.
Asking deeper questions at the beginning of your class can end up leading to really great discussions and get your students talking about math.

Add critical thinking questions to word problems
Word problems and real-life applications are the perfect place to add in critical thinking questions. Real-world applications offer a more choose-your-own-adventure style assignment where your students can expand on their thought processes.
They also allow your students to get creative and think outside of the box. These problem-solving skills play a critical role in helping your students develop critical thinking abilities.
Keep reading for math critical thinking questions that can be applied to any subject or topic!
When you want your students to defend their answers.
- Explain the steps you took to solve this problem
- How do you know that your answer is correct?
- Draw a diagram to prove your solution.
- Is there a different way to solve this problem besides the one you used?
- How would you explain _______________ to a student in the grade below you?
- Why does this strategy work?
- Use evidence from the problem/data to defend your answer in complete sentences.
When you want your students to justify their opinions
- What do you think will happen when ______?
- Do you agree/disagree with _______?
- What are the similarities and differences between ________ and __________?
- What suggestions would you give to this student?
- What is the most efficient way to solve this problem?
- How did you decide on your first step for solving this problem?

When you want your students to think outside of the box
- How can ______________ be used in the real world?
- What might be a common error that a student could make when solving this problem?
- How is _____________ topic similar to _______________ (previous topic)?
- What examples can you think of that would not work with this problem solving method?
- What would happen if __________ changed?
- Create your own problem that would give a solution of ______________.
- What other math skills did you need to use to solve this problem?
Let’s Recap:
- Rather than running from AI, help your students use it as a tool to expand their thinking.
- Identify a few transferable skills that you want your students to learn and make a goal for how you can help them develop these skills.
- Add critical thinking questions to your daily warm ups or exit tickets.
- Ask your students to explain their thinking when solving a word problem.
- Get a free sample of my Algebra 1 critical thinking questions ↓
8 thoughts on “20 Math Critical Thinking Questions to Ask in Class Tomorrow”
I would love to see your free math writing prompts, but there is no place for me to sign up. thank you
Ahh sorry about that! I just updated the button link!
Pingback: How to Teach Problem Solving for Mathematics -
Pingback: 5 Ways Teaching Collaboration Can Transform Your Math Classroom
Pingback: 3 Ways Math Rubrics Will Revitalize Your Summative Assessments
Pingback: How to Use Math Stations to Teach Problem Solving Skills
Pingback: How to Seamlessly Add Critical Thinking Questions to Any Math Assessment
Pingback: 13 Math Posters and Math Classroom Ideas for High School
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- International
- Education Jobs
- Schools directory
- Resources Education Jobs Schools directory News Search

Socratic Questioning Prompts for Classroom Use.
Subject: English
Age range: 14-16
Resource type: Visual aid/Display
Last updated
1 August 2024
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

Unlock the power of critical thinking in your classroom with our vibrant and engaging Socratic Questioning Prompts resource! Designed to foster deep thinking and meaningful discussions, this resource is perfect for teachers looking to enhance their students’ analytical and reflective skills.
What’s Inside:
- Clarification Prompts: Encourage students to delve deeper into their thoughts and articulate their ideas more clearly.
- Challenging Assumptions: Help students identify and question underlying assumptions in their reasoning.
- Asking for Evidence: Guide students in supporting their arguments with concrete evidence.
- Viewpoints & Perspectives: Broaden students’ horizons by exploring alternative viewpoints and counterarguments.
- Implications & Consequences: Enable students to think about the broader impact and consequences of their ideas.
- Questioning the Question: Promote meta-cognition by encouraging students to reflect on the questions themselves and their purposes.
- Visually Appealing: Bright, colorful design that captures students’ attention and makes learning fun.
- Easy to Use: Clear, concise prompts that can be easily integrated into any lesson plan.
- Versatile Application: Ideal for various subjects including English, Philosophy, Social Studies, and more.
- Printable & Digital: High-resolution PDF that can be printed or used digitally in both physical and virtual classrooms.
- Enhance Critical Thinking: Promote deeper understanding and analysis through thoughtful questioning.
- Stimulate Engagement: Foster lively discussions that keep students engaged and interested.
- Develop Communication Skills: Improve students’ ability to articulate and defend their ideas.
- Support Differentiation: Suitable for a wide range of age groups and learning levels, making it easy to differentiate instruction.
How to Use:
- Classroom Discussions: Use the prompts to guide whole-class discussions or small group dialogues.
- Homework Assignments: Assign specific prompts for students to respond to in written form.
- Assessment Tools: Utilize the questions as formative assessment tools to gauge student understanding.
- Professional Development: Great resource for teacher training sessions to demonstrate effective questioning techniques.
Transform your classroom into a hub of inquiry and intellectual exploration with our Socratic Questioning Prompts. Purchase now and inspire your students to think critically and communicate effectively!
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
- Our Mission

54 Excellent, Low-Stakes Writing Prompts
Across grade levels, engaging and creative writing prompts encourage kids to explore their opinions, reflect on experiences, and build strong arguments.
Routine low-stakes writing should be part of every student’s literacy diet. Ungraded and low-pressure, this type of writing improves kids’ writing stamina and builds language fluency, says Rebecca Alber , an instructor at UCLA’s Graduate School of Education.
Under the right conditions, students can get ideas about a question or concept down quickly and with few parameters, then “share those thoughts, and feel just as successful as everyone else in the room,” Alber says. The goal is to help students feel empowered to communicate ideas clearly and convincingly, while increasing their confidence as writers in preparation for longer, higher-stakes writing.
Prompts are an excellent starting point—but not all prompts are created equal, writes Todd Finley , a professor of English Education at East Carolina University. Superficially clever prompts may get pencils moving but often result in writing that’s neither valuable nor memorable. To improve the quality of students’ output and their level of investment, present them with prompts that require persuasive, opinion, informative, or even creative responses—and consider incorporating some student choice in the process.
As a wrap-up, students can share their work with a partner, in small groups, or even aloud to the class. To allow everyone to fully participate in the messy work of writing and occasionally “let their scraggly emotions run free,” Finley suggests offering the option to write “personal” at the top of pages they prefer to keep private.
We combed through dozens of lists of teacher-tested prompts to find 54 thought-provoking ones that will get students—from elementary through middle and high school—thinking, reflecting, and engaging in meaningful writing.
Elementary School Prompts
- I wish my teachers knew that…
- What things do all kids know that adults do not?
- Describe a routine that you often or always do (in the morning, when you get home, Friday nights, before a game, etc.).
- You wake up tomorrow with a silly superpower that makes you famous. What is that silly power? How does it lead to you becoming an international superstar?
- What are examples of things you want versus things you need?
- Describe something that you saw in the news recently and how it made you feel.
- What is one thing you would do to make your school, town, or city a better place?
- What can we do to help people with different opinions get along better?
- If you met an alien, what three questions would you ask them?
- Which skill would you like to be good at in the future?
- You’re on a quest through a hidden underground world that no one has ever seen. What magical creatures do you come across? What do they look like, and how do they act?
- You’re the first person to ever set foot on Mars. What is it like? What do you explore first?
- I will never forget the day…
- Pretend you can trade places with someone real or imaginary, from the past or present. Describe who that person is and why you would like to trade places. Write about what you would do as that person for the day and how you would feel about it.
- Write about the kind of job you think you might like to do someday. Be sure to explain what you know about that job and why you think it would be a good fit for you.
- Would a robot make a good friend? Think about all the good and bad aspects of having a mechanical buddy. Explain why you would or would not want a robot for a friend.
- Write a story about something that happened at school one day that you want to remember for the rest of your life.
- Describe a person who influenced your life in a positive way, someone who has made a difference in your life. Explain what this person did and how it made your life different.
Middle School Prompts
- How can you tell when someone your age is feeling insecure? Are most people more insecure or anxious than they let on?
- If you starred in a television show about your life, what would the show be called? What genre would it be? (Examples: comedy, drama, thriller, romance, action-adventure, fantasy, superhero, soap opera, reality, game show, space adventure, Western, tragedy, etc.) Summarize the plot of an episode.
- Is your ethnicity an important part of your identity? How so?
- You have been selected to be principal of your school. What are five rules that every kid should follow at your school, and what do you think should happen if those rules are broken?
- What do the friends you hang out with most have in common? How are you most like them? How are you different from them?
- What contributes to someone becoming a bully? What can help stop someone from bullying?
- Should we fear failure? Explain.
- Choose an event in your life, and write about it from the perspective of someone else who was there.
- Describe a flavor (salty, sweet, bitter, etc.) to someone who has never tasted it before.
- Glass half-full/half-empty: Write about an event or situation with a positive outlook. Then write about it with a negative outlook.
- Write a texting conversation between two friends who speak every day and know each other better than anyone.
- After home and school, where do you find the strongest feeling of community?
- Should governments do more to discourage people from smoking and vaping?
- Sixth grade is a time of many changes. Describe the changes that have taken place in your life since you started sixth grade. For example, you could write about school, friends, family, or other changes. ( Teachers: Change the grade level as necessary.)
- You have a computer that can be programmed to do any of the activities you’re normally responsible for. Explain the activities you would or would not assign to the machine, and why.
- Some say the legal driving age should be lowered from 16 to 14, and some say it should be raised to 18. Explain why you think the legal driving age should be lowered to 14, raised to 18, or left as it is at 16.
- A door in your school has always been kept locked. One day, as you walk past, you discover the door is open. Write a story about what happens next.
- What would you like to tell adults in the future about being a young person during this time period?
High School Prompts
- A nonprofit hires you as a consultant to determine how best to use $20 billion to save the world. What’s your plan?
- What’s the worst thing about the internet?
- How much control over your life do you have? What makes you say that?
- Describe your ideal life 15 years from now. What is something you can do every day to reach that goal?
- What things do you conscientiously do to feed your brain?
- What are three of your most profound learning experiences? Where and when did they occur?
- Write about your day in five acts, like a Shakespearean play. If your day were a play, what would be the introduction, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution?
- You have a difficult decision to make. Describe a conversation you might have with yourself about it.
- Which beliefs and values do you think define American culture?
- Should everyone go to college?
- What’s more important, practice or performance?
- Is it my job or the teacher’s job to motivate me?
- What is the best measure of human growth?
- Pick two characters from different books you’ve read this year and have them get in an argument about something.
- Which animal would judge us the most? Write a scene (based on truth or fiction) where two or more people are doing something and being observed and criticized by animals.
- Imagine that someone says to you, “Because that’s how we’ve always done it!” Write this out as a scene. (Think: Who said it, what were the circumstances, how did you respond, etc.)
- Is voting too hard in the United States?
- Should politicians be on social media?
(Sourced from Todd Finley , We Are Teachers , TeachThought , Scholastic , Birmingham City Schools , College Transitions , The New York Times , Monte Syrie , Texthelp , and PBS/KQED’s Above the Noise )

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Ultimate Cheat Sheet For Digital Thinking by Global Digital Citizen Foundation is an excellent starting point for the 'how' behind teaching critical thinking by outlining which questions to ask. It offers 48 critical thinking questions useful for any content area or even grade level with a little re-working/re-wording. Enjoy the list!
15 Questions to Encourage Critical Thinking What is one of the best ways to encourage critical thinking? By asking excellent questions! We have compiled a list of 15 questions that you, as a teacher or parent, can ask to encourage kids to think outside the box. Let's dive in.
Writing prompts, reading circles, Socratic discussions and more all benefit from critical thinking, and providing students with stems is a way of supporting them as their confidence grows and their habits as thinkers develop.
Use these creative and fun critical thinking questions to help kids think critically. Includes engaging questions for upper elementary, middle & high school.
What are some of the most common types of questions for teaching critical thinking? This led to many dozens of answers.
Strong critical thinking skills are key. Encourage careful reading and deeper connections with this list of critical thinking questions.
Here are 19 types of questions designed to cultivate critical thinking in the classroom, categorized for clarity and purpose.
Varying question stems can sustain engagement and promote critical thinking. The timing, sequence and clarity of questions you ask students can be as important as the type of question you ask. The table below is organized to help formulate questions provoking gradually higher levels of thinking.
Here are some critical thinking questions you can use to increase your awareness about different problems and to make better decisions by carefully examining available information.
Question stems can be used as thinking prompts for class discussions, prompting, and various forms of assessment.
These are questions that are specifically designed to promote critical thinking. They go beyond factual inquiries, prompting individuals to analyze, synthesize, apply, and evaluate information. Critical thinking questions challenge the conventional wisdom and encourage individuals to think deeper, questioning the why's and how's.
Finally, I'll show you how to create and easily provide students with prompts to ask questions to develop their critical thinking.
Because in order for critical thinking to actually happen, our brains have to be open. Barbara Fredrickson talks about the broaden and build theory and positive psychology -that when good things happen, our brains actually open up to new ideas. Whereas when we're worried about how we're going to pay rent and we don't know what's going ...
15 awesome critical thinking questions you should ask students Incorporating critical thinking questions can help students think more analytically and prompt them to formulate their ideas.
Do you need go-to ideas for teaching short stories? Check out 19 Short Stories and Questions For Critical Thinking in the middle and high school classrooms!
Brain teasing critical thinking questions for high schoolers Critical thinking skills are essential for measuring the imagination and creativity of students. High school students are likely to use the new age information and influence of others when processing their thoughts.
Become a truly effective and intuitive critical thinker. Explore these approaches, methods, and questions in your research, studies, or writing.
Here are some more effective types of questions to use in teaching that encourage critical thinking and creativity: 1. Display. A type of rhetorical question, display questions help educators check on students' ability to retrieve information. Examples:
When we ask questions that prompt critical thinking, students are invested in choosing strategies to find the answer. They inevitably start by examining what they already know to act as a foundation for deeper learning, then they do a close reading of the text to analyze particular lines.
The art of questioning is a teaching technique that focuses on asking strategic questions to promote critical thinking, inquiry, and meaningful learning experiences for students. It is an essential skill for educators to master in order to elicit student understanding and uncover gaps in knowledge.
Critical thinking is the ability to analyze and effectively break down an issue in order to make a decision or find a solution. At the heart of critical thinking is the ability to formulate deep ...
Critical Thinking Questions Prompt You are an expert educator and instructional designer with expertise in crafting open-ended questions that elicit higher order thinking from your students. Your task is to create a list of [NUMBER] open-ended, critical thinking questions for [GRADE LEVEL AND SUBJECT] class on [TOPIC].
This list of math critical thinking questions will give you a quick starting point for getting your students to think deeper about any concept or problem.
Unlock the power of critical thinking in your classroom with our vibrant and engaging Socratic Questioning Prompts resource! Designed to foster deep thinking and meaningful discussions, this resource is perfect for teachers looking to enhance their students' analytical and reflective skills.
We combed through dozens of lists of teacher-tested prompts to find 54 thought-provoking ones that will get students—from elementary through middle and high school—thinking, reflecting, and engaging in meaningful writing.