
Headings identify the content within sections of a paper.
Make your headings descriptive and concise. Headings that are well formatted and clearly worded aid both visual and nonvisual readers of all abilities.

Levels of heading
There are five levels of heading in APA Style. Level 1 is the highest or main level of heading, Level 2 is a subheading of Level 1, Level 3 is a subheading of Level 2, and so on through Levels 4 and 5.
The number of headings to use in a paper depends on the length and complexity of the work.
- If only one level of heading is needed, use Level 1.
- If two levels of heading are needed, use Levels 1 and 2.
- If three levels of heading are needed, use Levels 1, 2, and 3 (and so on).
Use only the number of headings necessary to differentiate distinct sections in your paper; short student papers may not require any headings. Furthermore, avoid these common errors related to headings:
- Avoid having only one subsection heading within a section, just like in an outline.
- Do not label headings with numbers or letters.
- Double-space headings; do not switch to single spacing within headings.
- Do not add blank lines above or below headings, even if a heading falls at the end of a page.
Headings are covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Sections 2.26 and 2.27 and the Concise Guide Sections 1.25 and 1.26
Related handouts
- Heading Levels Template: Student Paper (PDF, 257KB)
- Heading Levels Template: Professional Paper (PDF, 213KB)
Format of headings
The following table demonstrates how to format headings in APA Style.
|
|
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
Text begins as a new paragraph.
|
| 2 |
Text begins as a new paragraph.
|
| 3 |
Text begins as a new paragraph.
|
| 4 | Text begins on the same line and continues as a regular paragraph.
|
| 5 | Text begins on the same line and continues as a regular paragraph.
|
Note. In title case, most words are capitalized .
Headings in the introduction
Because the first paragraphs of a paper are understood to be introductory, the heading “Introduction” is not needed. Do not begin a paper with an “Introduction” heading; the paper title at the top of the first page of text acts as a de facto Level 1 heading.
It is possible (but not required) to use headings within the introduction. For subsections within the introduction, use Level 2 headings for the first level of subsection, Level 3 for subsections of any Level 2 headings, and so on. After the introduction (regardless of whether it includes headings), use a Level 1 heading for the next main section of the paper (e.g., Method).
Creating accessible headings
Writers who use APA Style may use the automatic headings function of their word-processing program to create headings. This not only simplifies the task of formatting headings but also ensures that headings are coded appropriately in any electronic version of the paper, which aids readers who use navigation tools and assistive technologies such as screen readers.
Here are some tips on how to create headings in some common word-processing programs:
- If you use Academic Writer to write your APA Style papers, the headings menu in the Writing Center will format headings for you in 7th edition APA Style.
- Follow these headings directions from Microsoft to customize the heading formats for your future use.
- To apply Level 4 and 5 headings (which are inline headings, meaning the heading appears on the same line as paragraph text), first type the heading and a few words of the text that follows. Then highlight the text that you want to be your heading and select the appropriate heading level from the Styles menu. Only the highlighted text will be formatted as the Level 4 or 5 heading.

A step-by-step guide for creating and formatting APA Style student papers
The start of the semester is the perfect time to learn how to create and format APA Style student papers. This article walks through the formatting steps needed to create an APA Style student paper, starting with a basic setup that applies to the entire paper (margins, font, line spacing, paragraph alignment and indentation, and page headers). It then covers formatting for the major sections of a student paper: the title page, the text, tables and figures, and the reference list. Finally, it concludes by describing how to organize student papers and ways to improve their quality and presentation.
The guidelines for student paper setup are described and shown using annotated diagrams in the Student Paper Setup Guide (PDF, 3.40MB) and the A Step-by-Step Guide to APA Style Student Papers webinar . Chapter 1 of the Concise Guide to APA Style and Chapter 2 of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association describe the elements, format, and organization for student papers. Tables and figures are covered in Chapter 7 of both books. Information on paper format and tables and figures and a full sample student paper are also available on the APA Style website.
Basic setup
The guidelines for basic setup apply to the entire paper. Perform these steps when you first open your document, and then you do not have to worry about them again while writing your paper. Because these are general aspects of paper formatting, they apply to all APA Style papers, student or professional. Students should always check with their assigning instructor or institution for specific guidelines for their papers, which may be different than or in addition to APA Style guidelines.
Seventh edition APA Style was designed with modern word-processing programs in mind. Most default settings in programs such as Academic Writer, Microsoft Word, and Google Docs already comply with APA Style. This means that, for most paper elements, you do not have to make any changes to the default settings of your word-processing program. However, you may need to make a few adjustments before you begin writing.
Use 1-in. margins on all sides of the page (top, bottom, left, and right). This is usually how papers are automatically set.
Use a legible font. The default font of your word-processing program is acceptable. Many sans serif and serif fonts can be used in APA Style, including 11-point Calibri, 11-point Arial, 12-point Times New Roman, and 11-point Georgia. You can also use other fonts described on the font page of the website.
Line spacing
Double-space the entire paper including the title page, block quotations, and the reference list. This is something you usually must set using the paragraph function of your word-processing program. But once you do, you will not have to change the spacing for the entirety of your paper–just double-space everything. Do not add blank lines before or after headings. Do not add extra spacing between paragraphs. For paper sections with different line spacing, see the line spacing page.
Paragraph alignment and indentation
Align all paragraphs of text in the body of your paper to the left margin. Leave the right margin ragged. Do not use full justification. Indent the first line of every paragraph of text 0.5-in. using the tab key or the paragraph-formatting function of your word-processing program. For paper sections with different alignment and indentation, see the paragraph alignment and indentation page.
Page numbers
Put a page number in the top right of every page header , including the title page, starting with page number 1. Use the automatic page-numbering function of your word-processing program to insert the page number in the top right corner; do not type the page numbers manually. The page number is the same font and font size as the text of your paper. Student papers do not require a running head on any page, unless specifically requested by the instructor.
Title page setup
Title page elements.
APA Style has two title page formats: student and professional (for details, see title page setup ). Unless instructed otherwise, students should use the student title page format and include the following elements, in the order listed, on the title page:
- Paper title.
- Name of each author (also known as the byline).
- Affiliation for each author.
- Course number and name.
- Instructor name.
- Assignment due date.
- Page number 1 in the top right corner of the page header.
The format for the byline depends on whether the paper has one author, two authors, or three or more authors.
- When the paper has one author, write the name on its own line (e.g., Jasmine C. Hernandez).
- When the paper has two authors, write the names on the same line and separate them with the word “and” (e.g., Upton J. Wang and Natalia Dominguez).
- When the paper has three or more authors, separate the names with commas and include “and” before the final author’s name (e.g., Malia Mohamed, Jaylen T. Brown, and Nia L. Ball).
Students have an academic affiliation, which identities where they studied when the paper was written. Because students working together on a paper are usually in the same class, they will have one shared affiliation. The affiliation consists of the name of the department and the name of the college or university, separated by a comma (e.g., Department of Psychology, George Mason University). The department is that of the course to which the paper is being submitted, which may be different than the department of the student’s major. Do not include the location unless it is part of the institution’s name.
Write the course number and name and the instructor name as shown on institutional materials (e.g., the syllabus). The course number and name are often separated by a colon (e.g., PST-4510: History and Systems Psychology). Write the assignment due date in the month, date, and year format used in your country (e.g., Sept. 10, 2020).
Title page line spacing
Double-space the whole title page. Place the paper title three or four lines down from the top of the page. Add an extra double-spaced blank like between the paper title and the byline. Then, list the other title page elements on separate lines, without extra lines in between.
Title page alignment
Center all title page elements (except the right-aligned page number in the header).
Title page font
Write the title page using the same font and font size as the rest of your paper. Bold the paper title. Use standard font (i.e., no bold, no italics) for all other title page elements.
Text elements
Repeat the paper title at the top of the first page of text. Begin the paper with an introduction to provide background on the topic, cite related studies, and contextualize the paper. Use descriptive headings to identify other sections as needed (e.g., Method, Results, Discussion for quantitative research papers). Sections and headings vary depending on the paper type and its complexity. Text can include tables and figures, block quotations, headings, and footnotes.
Text line spacing
Double-space all text, including headings and section labels, paragraphs of text, and block quotations.
Text alignment
Center the paper title on the first line of the text. Indent the first line of all paragraphs 0.5-in.
Left-align the text. Leave the right margin ragged.
Block quotation alignment
Indent the whole block quotation 0.5-in. from the left margin. Double-space the block quotation, the same as other body text. Find more information on the quotations page.
Use the same font throughout the entire paper. Write body text in standard (nonbold, nonitalic) font. Bold only headings and section labels. Use italics sparingly, for instance, to highlight a key term on first use (for more information, see the italics page).
Headings format
For detailed guidance on formatting headings, including headings in the introduction of a paper, see the headings page and the headings in sample papers .
- Alignment: Center Level 1 headings. Left-align Level 2 and Level 3 headings. Indent Level 4 and Level 5 headings like a regular paragraph.
- Font: Boldface all headings. Also italicize Level 3 and Level 5 headings. Create heading styles using your word-processing program (built into AcademicWriter, available for Word via the sample papers on the APA Style website).
Tables and figures setup
Tables and figures are only included in student papers if needed for the assignment. Tables and figures share the same elements and layout. See the website for sample tables and sample figures .
Table elements
Tables include the following four elements:
- Body (rows and columns)
- Note (optional if needed to explain elements in the table)
Figure elements
Figures include the following four elements:
- Image (chart, graph, etc.)
- Note (optional if needed to explain elements in the figure)
Table line spacing
Double-space the table number and title. Single-, 1.5-, or double-space the table body (adjust as needed for readability). Double-space the table note.
Figure line spacing
Double-space the figure number and title. The default settings for spacing in figure images is usually acceptable (but adjust the spacing as needed for readability). Double-space the figure note.
Table alignment
Left-align the table number and title. Center column headings. Left-align the table itself and left-align the leftmost (stub) column. Center data in the table body if it is short or left-align the data if it is long. Left-align the table note.
Figure alignment
Left-align the figure number and title. Left-align the whole figure image. The default alignment of the program in which you created your figure is usually acceptable for axis titles and data labels. Left-align the figure note.
Bold the table number. Italicize the table title. Use the same font and font size in the table body as the text of your paper. Italicize the word “Note” at the start of the table note. Write the note in the same font and font size as the text of your paper.
Figure font
Bold the figure number. Italicize the figure title. Use a sans serif font (e.g., Calibri, Arial) in the figure image in a size between 8 to 14 points. Italicize the word “Note” at the start of the figure note. Write the note in the same font and font size as the text of your paper.
Placement of tables and figures
There are two options for the placement of tables and figures in an APA Style paper. The first option is to place all tables and figures on separate pages after the reference list. The second option is to embed each table and figure within the text after its first callout. This guide describes options for the placement of tables and figures embedded in the text. If your instructor requires tables and figures to be placed at the end of the paper, see the table and figure guidelines and the sample professional paper .
Call out (mention) the table or figure in the text before embedding it (e.g., write “see Figure 1” or “Table 1 presents”). You can place the table or figure after the callout either at the bottom of the page, at the top of the next page, or by itself on the next page. Avoid placing tables and figures in the middle of the page.
Embedding at the bottom of the page
Include a callout to the table or figure in the text before that table or figure. Add a blank double-spaced line between the text and the table or figure at the bottom of the page.
Embedding at the top of the page
Include a callout to the table in the text on the previous page before that table or figure. The table or figure then appears at the top of the next page. Add a blank double-spaced line between the end of the table or figure and the text that follows.
Embedding on its own page
Embed long tables or large figures on their own page if needed. The text continues on the next page.
Reference list setup
Reference list elements.
The reference list consists of the “References” section label and the alphabetical list of references. View reference examples on the APA Style website. Consult Chapter 10 in both the Concise Guide and Publication Manual for even more examples.
Reference list line spacing
Start the reference list at the top of a new page after the text. Double-space the entire reference list (both within and between entries).
Reference list alignment
Center the “References” label. Apply a hanging indent of 0.5-in. to all reference list entries. Create the hanging indent using your word-processing program; do not manually hit the enter and tab keys.
Reference list font
Bold the “References” label at the top of the first page of references. Use italics within reference list entries on either the title (e.g., webpages, books, reports) or on the source (e.g., journal articles, edited book chapters).
Final checks
Check page order.
- Start each section on a new page.
- Arrange pages in the following order:
- Title page (page 1).
- Text (starts on page 2).
- Reference list (starts on a new page after the text).
Check headings
- Check that headings accurately reflect the content in each section.
- Start each main section with a Level 1 heading.
- Use Level 2 headings for subsections of the introduction.
- Use the same level of heading for sections of equal importance.
- Avoid having only one subsection within a section (have two or more, or none).
Check assignment instructions
- Remember that instructors’ guidelines supersede APA Style.
- Students should check their assignment guidelines or rubric for specific content to include in their papers and to make sure they are meeting assignment requirements.
Tips for better writing
- Ask for feedback on your paper from a classmate, writing center tutor, or instructor.
- Budget time to implement suggestions.
- Use spell-check and grammar-check to identify potential errors, and then manually check those flagged.
- Proofread the paper by reading it slowly and carefully aloud to yourself.
- Consult your university writing center if you need extra help.
About the author

Undergraduate student resources
- Comprehensive Guide to Headings and Subheadings in APA 7.0

Section 1: Introduction to Headings and Subheadings in APA 7.0-
In academic writing, the use of headings and subheadings is crucial for organizing and structuring a paper. APA (American Psychological Association) style, specifically in its 7th edition, provides clear guidelines on how to effectively use headings and subheadings to enhance readability and comprehensibility of research papers, essays, and other scholarly works. This section will provide a comprehensive introduction to the importance, purpose, and benefits of using headings and subheadings in APA 7.0 format.
Purpose of Headings and Subheadings
Headings and subheadings serve as visual cues to help readers navigate through the content of a paper. They create a hierarchical structure, indicating the relationships between different sections and subsections, and aid in organizing ideas and presenting information in a logical manner. By using headings and subheadings, writers can effectively divide their work into manageable and coherent sections, making it easier for readers to comprehend and follow the main arguments and supporting details.
Importance of Headings and Subheadings
Clear and well-structured headings and subheadings are essential in academic writing for several reasons. First and foremost, they enhance the overall readability of the paper by breaking down the text into smaller, digestible chunks. This organization allows readers to quickly identify and locate specific information, especially when they are scanning or skimming through the document.
Secondly, headings and subheadings contribute to the coherence and flow of the paper. By providing a clear roadmap, they guide the reader through the main ideas, supporting evidence, and key points presented in each section. This not only improves the overall structure of the paper but also helps maintain the logical progression of thoughts and arguments.
Additionally, headings and subheadings assist both readers and writers in comprehending complex topics. They enable writers to organize their thoughts, ensuring that each section focuses on a specific aspect or theme. This organization facilitates a deeper understanding of the subject matter for both the writer during the drafting process and the reader during the consumption of the paper.
Formatting Guidelines for Headings and Subheadings
APA 7.0 provides specific rules and formatting guidelines for using headings and subheadings. These guidelines include the use of different levels of headings, capitalization rules, and placement within the paper. Understanding and adhering to these guidelines is crucial for maintaining consistency and conformity with APA style.
The APA 7.0 formatting guidelines for headings and subheadings are based on a five-level hierarchy, with each level indicating the level of importance and hierarchy of information. Level 1 headings are the highest level, followed by Level 2, Level 3, and so on. Each level has a specific formatting style, such as font size, boldness, and indentation, to differentiate it from the other levels. Furthermore, APA 7.0 also provides guidance on the appropriate use of sentence case, title case, and capitalization in headings and subheadings. For instance, Level 1 headings are typically written in sentence case and are centered and bolded. Level 2 headings are aligned to the left margin, bolded, and written in title case. To maintain clarity and consistency, APA 7.0 also provides recommendations on the number of headings to use within a paper. It suggests that at least two headings should be used in any given section, as a single heading alone may not adequately represent the content covered.
Section 2: The Purpose and Importance of Headings and Subheadings in APA 7.0
Facilitating information retrieval.
One of the primary purposes of headings and subheadings in APA 7.0 is to facilitate information retrieval for readers. When faced with a lengthy document, readers often engage in scanning or skimming techniques to locate specific information or sections of interest. Well-structured headings and subheadings act as signposts, allowing readers to quickly identify the content they are seeking without having to read the entire text. By providing a clear and organized hierarchy, headings guide readers to the main sections of a paper, while subheadings further break down the content into more specific subsections. This hierarchical structure enables readers to navigate the document with ease, locating relevant information efficiently. Thus, headings and subheadings in APA 7.0 contribute significantly to the overall accessibility and user-friendliness of academic papers.
Enhancing Readability and Comprehensibility
Headings and subheadings play a vital role in enhancing the readability and comprehensibility of academic writing. They help break up large blocks of text into smaller, digestible sections, preventing the overwhelming feeling that dense paragraphs can create. By visually separating different sections and subsections, headings and subheadings allow readers to mentally prepare for the content they are about to encounter. Additionally, headings and subheadings improve the flow and coherence of a paper. They provide a roadmap for readers, helping them understand the organization and structure of the author's arguments and supporting evidence. Well-crafted headings and subheadings enable readers to follow the logical progression of ideas and maintain a clear understanding of the paper's main points. Finally, headings and subheadings aid in the comprehension of complex topics. By breaking down the content into smaller, focused sections, readers can grasp the material more easily. Headings act as cognitive cues, preparing readers for the information presented in each section. This approach not only facilitates understanding but also allows readers to engage with the content at a deeper level, promoting knowledge retention.
Organizing and Structuring Ideas
Headings and subheadings in APA 7.0 serve as valuable tools for organizing and structuring ideas within a paper. They help writers divide their work into meaningful sections, each addressing a specific aspect or theme related to the overall topic. This organization ensures that information is presented in a coherent and logical manner, making it easier for both the writer and the reader to navigate the paper.
By using headings and subheadings, writers can create a clear outline for their work, ensuring that each section has a distinct focus. This outline acts as a framework, guiding the writer in presenting their arguments and supporting evidence in a systematic and organized way. Writers can use headings to delineate major sections or main ideas, while subheadings allow for further subcategorization and exploration of subtopics.
Furthermore, headings and subheadings assist writers in structuring their thoughts during the writing process. By providing a visual representation of the paper's organization, headings help writers maintain a coherent flow of ideas and prevent the inclusion of irrelevant or tangential information. This structured approach not only improves the overall quality of the paper but also enhances the writer's ability to communicate their ideas effectively.
Conveying the Hierarchical Relationship of Information
Another important purpose of headings and subheadings in APA 7.0 is to convey the hierarchical relationship of information. By assigning different levels to headings, the writer can indicate the relative importance and order of ideas within the paper. Higher-level headings represent broader themes or major sections, while lower-level headings address more specific subtopics or subsections. This hierarchical structure helps readers understand the organization and logical flow of the paper at a glance. It allows them to grasp the overall structure and the relationships between different sections without having to read the entire document. Additionally, the use of indentation and formatting styles for each level of heading further reinforces the hierarchical relationship and aids in visual differentiation.
Section 3: Formatting Guidelines for Headings and Subheadings in APA 7.0
Proper formatting of headings and subheadings is crucial in APA 7.0 style to ensure consistency, clarity, and readability in academic writing. This section will delve into the specific formatting guidelines provided by APA 7.0 for headings and subheadings, including the use of different levels, capitalization rules, and placement within the paper.
Levels of Headings
APA 7.0 introduces a five-level hierarchy for headings, each denoting a different level of importance and significance within the paper. These levels provide a structured framework for organizing the content and help readers understand the organization and flow of ideas. Here are the five headings in APA 7.0:
Level 1: Centered, Bold and Title Case
Text begins here.
Level 2: Left-Aligned, Bold and Title Case
Level 3: Left-Aligned, Bold, Italics, and Title Case
Level 4: Left-Aligned, Bold, Title Case, and Period. Text begins here.
Level 5: Left-Aligned, Bold, Title Case, Italics, and Period . Text begins here.
Section 4: Organizing and Structuring Your Paper
Using headings and subheadings in apa 7.0.
Organizing and structuring your paper effectively is crucial for presenting your ideas in a logical and coherent manner. Headings and subheadings in APA 7.0 play a vital role in achieving this goal by providing a clear framework for organizing your content. This section will delve into strategies and best practices for utilizing headings and subheadings to organize and structure your paper in accordance with APA 7.0 guidelines.
Preparing an Outline
Before you begin writing your paper, it is helpful to create an outline that outlines the main sections and subsections you intend to cover. An outline acts as a roadmap, allowing you to visualize the overall structure and flow of your paper. It serves as a foundation for developing meaningful headings and subheadings that accurately represent the content and facilitate logical organization. Start by identifying the major sections that your paper will include, such as introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. These major sections will serve as Level 1 headings in APA 7.0. Next, break down each major section into subsections that address specific subtopics or aspects related to the main theme. These subsections will be represented by Level 2 headings. Depending on the complexity and depth of your paper, you may further divide the subsections into sub-subsections using Level 3, Level 4, and Level 5 headings. Creating a comprehensive outline not only helps you organize your thoughts but also ensures that you cover all the necessary components of your paper. It allows you to see the relationships between different sections and subsections, enabling you to present your arguments and evidence in a logical and coherent sequence.
Maintaining Consistency and Parallelism
Consistency is key when it comes to organizing and structuring your paper using headings and subheadings. It is important to establish a consistent framework that is followed throughout the entire document. Consistency ensures that readers can easily understand the hierarchy and relationships between different sections and subsections. When creating headings and subheadings, aim for parallelism in terms of grammatical structure and formatting. Parallelism means that headings at the same level should have a similar grammatical structure and formatting style. For instance, if you choose to use noun phrases for Level 2 headings, maintain this pattern consistently across all Level 2 headings in your paper. This helps readers navigate through the content smoothly and maintain a sense of coherence. Furthermore, parallelism extends to the use of punctuation and capitalization within headings and subheadings. Maintain consistent capitalization rules, such as sentence case for Level 1 headings and title case for Level 2 headings. This uniformity enhances the visual hierarchy and clarity of your paper.
Balancing Depth and Granularity
Effective organization and structuring involve finding the right balance between depth and granularity in your headings and subheadings. Level 1 headings represent major sections and should encapsulate broad themes or concepts, providing an overview of what will be discussed within each section. Level 2 headings, as subsections, delve into more specific topics or aspects related to the main theme of the major section.
Reviewing and Revising the Organization
Organizing and structuring your paper using headings and subheadings is not a one-time task. It is an iterative process that requires regular review and revision to ensure optimal clarity and coherence. Once you have completed the initial draft of your paper, review the organization of your headings and subheadings. Ask yourself if the structure effectively reflects the flow of your ideas and supports your main argument. Consider whether the headings accurately represent the content of each section and subsection. During the review process, pay attention to transitions between sections and subsections. Ensure that the headings and subheadings create a smooth transition from one topic to another, guiding readers through the logical progression of your paper. If you notice any gaps or inconsistencies, revise and refine the organization accordingly. Additionally, seek feedback from peers, mentors, or instructors. Their fresh perspective can provide valuable insights into the clarity and effectiveness of your headings and subheadings. Incorporate their feedback and make necessary adjustments to improve the overall organization and structure of your paper.
Section 5: Common Mistakes to Avoid in Using Headings and Subheadings in APA 7.0
While using headings and subheadings in APA 7.0 can greatly improve the organization and readability of your paper, it's important to be aware of common mistakes that can compromise the effectiveness of your headings. By understanding and avoiding these mistakes, you can ensure that your headings enhance the clarity and coherence of your academic writing. This section will explore some common mistakes to avoid when using headings and subheadings in APA 7.0.
Inconsistent Formatting
One of the most common mistakes is inconsistent formatting of headings and subheadings. In APA 7.0, it is crucial to maintain consistency in capitalization, alignment, and formatting styles across headings at the same level. Inconsistencies can confuse readers and disrupt the visual hierarchy of your paper. Ensure that all Level 1 headings have the same formatting, all Level 2 headings have the same formatting, and so on. Consistency in formatting contributes to the overall professionalism and readability of your work.
Poor Alignment and Spacing
Another mistake to avoid is incorrect alignment and spacing of headings and subheadings. In APA 7.0, Level 1 headings are centered and typically start on a new page or a new line with an extra line space before and after the heading. Level 2 headings and lower-level headings, however, are left-aligned and generally require an extra line space before the heading but not after. Failure to align and space headings correctly can create confusion and disrupt the logical flow of your paper. Review APA 7.0 guidelines carefully to ensure proper alignment and spacing of your headings.
Lack of Parallelism
Parallelism, or consistent grammatical structure, is crucial when using headings and subheadings. Headings at the same level should follow a similar structure to maintain coherence and readability. For example, if you use noun phrases for Level 2 headings, ensure that all Level 2 headings follow this pattern. Lack of parallelism can make your headings appear disjointed and may confuse readers. Consistently apply parallel structure within each level of headings to create a smooth and organized flow of information.
Overcomplicating the Heading Structure
While it is important to provide a clear and hierarchical structure to your paper, overcomplicating the heading structure can lead to confusion and excessive fragmentation. Strive to find a balance between providing enough detail to cover your content effectively and avoiding an excessive number of headings and subheadings. Each heading should represent a meaningful subdivision and contribute to the overall organization and coherence of your paper. Aim for a clear and concise heading structure that guides readers without overwhelming them with excessive levels or overly specific subdivisions.
Lack of Descriptiveness
Headings and subheadings should be descriptive and informative to accurately represent the content covered within each section. Avoid using generic or ambiguous headings that do not provide a clear indication of what readers can expect to find. Vague headings can leave readers uncertain about the content or make it challenging to locate specific information within your paper. Ensure that your headings succinctly capture the main ideas or themes of each section, guiding readers through your content effectively.
Ignoring the Reader's Perspective
When creating headings and subheadings, it's important to consider the perspective of your readers. Put yourself in their shoes and think about how your headings will facilitate their understanding and navigation through your paper. Consider whether your headings effectively communicate the main points, guide readers through the logical flow of your arguments, and enable them to locate specific information easily. Ignoring the reader's perspective can result in headings that are unclear, unhelpful, or inconsistent, hindering the overall readability and comprehension of your work.
Neglecting to Revise and Edit Headings
Headings should not be an afterthought or treated as static elements in your paper. Neglecting to revise and edit your headings can lead to inaccuracies, lack of clarity, or poor alignment with the final content of your paper. As you progress through the writing process, continuously review and refine your headings to ensure they accurately represent the content and flow of your arguments. Make necessary adjustments, reword headings for better clarity, and ensure that they align with the finalized structure and organization of your paper.
Recent Posts

Creating Quarters in Stata

Renaming Variables in Stata

Adding X Lines to Graphics in Stata

The Impact of ChatGPT Hallucination on Academic Writing
Have any questions?
Our support team is ready to answer your questions.
Help Center FAQ
To mark our first year, we've slashed all our prices in half. Order now to seize this limited opportunity!
Place Your Order
Academic Editing and Proofreading
- Tips to Self-Edit Your Dissertation
- Guide to Essay Editing: Methods, Tips, & Examples
- Journal Article Proofreading: Process, Cost, & Checklist
- The A–Z of Dissertation Editing: Standard Rates & Involved Steps
- Research Paper Editing | Guide to a Perfect Research Paper
- Dissertation Proofreading | Definition & Standard Rates
- Thesis Proofreading | Definition, Importance & Standard Pricing
- Research Paper Proofreading | Definition, Significance & Standard Rates
- Essay Proofreading | Options, Cost & Checklist
- Top 10 Paper Editing Services of 2024 (Costs & Features)
- Top 10 Essay Checkers in 2024 (Free & Paid)
- Top 10 AI Proofreaders to Perfect Your Writing in 2024
- Top 10 English Correctors to Perfect Your Text in 2024
- Top 10 Essay Editing Services of 2024
- 10 Advanced AI Text Editors to Transform Writing in 2024
Academic Research
- Research Paper Outline: Templates & Examples
- How to Write a Research Paper: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Write a Lab Report: Examples from Academic Editors
- Research Methodology Guide: Writing Tips, Types, & Examples
- The 10 Best Essential Resources for Academic Research
- 100+ Useful ChatGPT Prompts for Thesis Writing in 2024
- Best ChatGPT Prompts for Academic Writing (100+ Prompts!)
- Sampling Methods Guide: Types, Strategies, and Examples
- Independent vs. Dependent Variables | Meaning & Examples
Academic Writing & Publishing
- Difference Between Paper Editing and Peer Review
- What are the different types of peer review?
- How to deal with rejection from a journal?
- Editing and Proofreading Academic Papers: A Short Guide
- How to Carry Out Secondary Research
- The Results Section of a Dissertation
- Checklist: Is my Article Ready for Submitting to Journals?
- Types of Research Articles to Boost Your Research Profile
- 8 Types of Peer Review Processes You Should Know
- The Ethics of Academic Research
- How does LaTeX based proofreading work?
- How to Improve Your Scientific Writing: A Short Guide
- Chicago Title, Cover Page & Body | Paper Format Guidelines
- How to Write a Thesis Statement: Examples & Tips
- Chicago Style Citation: Quick Guide & Examples
- The A-Z Of Publishing Your Article in A Journal
- What is Journal Article Editing? 3 Reasons You Need It
- 5 Powerful Personal Statement Examples (Template Included)
- Complete Guide to MLA Format (9th Edition)
- How to Cite a Book in APA Style | Format & Examples
- How to Start a Research Paper | Step-by-step Guide
- APA Citations Made Easy with Our Concise Guide for 2024
- A Step-by-Step Guide to APA Formatting Style (7th Edition)
- Top 10 Online Dissertation Editing Services of 2024
- Academic Writing in 2024: 5 Key Dos & Don’ts + Examples
- What Are the Standard Book Sizes for Publishing Your Book?
- MLA Works Cited Page: Quick Tips & Examples
- 2024’s Top 10 Thesis Statement Generators (Free Included!)
- Top 10 Title Page Generators for Students in 2024
- What Is an Open Access Journal? 10 Myths Busted!
- Primary vs. Secondary Sources: Definition, Types & Examples
- How To Write a College Admissions Essay That Stands Out
- How to Write a Dissertation & Thesis Conclusion (+ Examples)
- APA Journal Citation: 7 Types, In-Text Rules, & Examples
- What Is Predatory Publishing and How to Avoid It!
- What Is Plagiarism? Meaning, Types & Examples
- How to Write a Strong Dissertation & Thesis Introduction
- How to Cite a Book in MLA Format (9th Edition)
- How to Cite a Website in MLA Format | 9th Edition Rules
- 10 Best AI Conclusion Generators (Features & Pricing)
- Top 10 Academic Editing Services of 2024 [with Pricing]
- Additional Resources
- Plagiarism: How to avoid it in your thesis?
- Final Submission Checklist | Dissertation & Thesis
- 7 Useful MS Word Formatting Tips for Dissertation Writing
- How to Write a MEAL Paragraph: Writing Plan Explained in Detail
- Em Dash vs. En Dash vs. Hyphen: When to Use Which
- The 10 Best Citation Generators in 2024 | Free & Paid Plans!
- 2024’s Top 10 Self-Help Books for Better Living
- The 10 Best Free Character and Word Counters of 2024
- Citation and Referencing
- Citing References: APA, MLA, and Chicago
- How to Cite Sources in the MLA Format
- MLA Citation Examples: Cite Essays, Websites, Movies & More
- Citations and References: What Are They and Why They Matter
- APA Headings & Subheadings | Formatting Guidelines & Examples
- Formatting an APA Reference Page | Template & Examples
- Research Paper Format: APA, MLA, & Chicago Style
- How to Create an MLA Title Page | Format, Steps, & Examples
- How to Create an MLA Header | Format Guidelines & Examples
- MLA Annotated Bibliography | Guidelines and Examples
- APA Website Citation (7th Edition) Guide | Format & Examples
- APA Citation Examples: The Bible, TED Talk, PPT & More
- APA Header Format: 5 Steps & Running Head Examples
- APA Title Page Format Simplified | Examples + Free Template
- How to Write an Abstract in MLA Format: Tips & Examples
- 10 Best Free Plagiarism Checkers of 2024 [100% Free Tools]
- 5 Reasons to Cite Your Sources Properly | Avoid Plagiarism!
- Dissertation Writing Guide
- Writing a Dissertation Proposal
- The Acknowledgments Section of a Dissertation
- The Table of Contents Page of a Dissertation
- The Introduction Chapter of a Dissertation
- The Literature Review of a Dissertation
- The Only Dissertation Toolkit You’ll Ever Need!
- 5 Thesis Writing Tips for Master Procrastinators
- How to Write a Dissertation | 5 Tips from Academic Editors
- The 5 Things to Look for in a Dissertation Editing Service
- Top 10 Dissertation Editing & Proofreading Services
- Why is it important to add references to your thesis?
- Thesis Editing | Definition, Scope & Standard Rates
- Expert Formatting Tips on MS Word for Dissertations
- A 7-Step Guide on How to Choose a Dissertation Topic
- 350 Best Dissertation Topic Ideas for All Streams in 2024
- A Guide on How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- Dissertation Defense: What to Expect and How to Prepare
- Creating a Dissertation Title Page (Examples & Templates)
- Essay Writing Guide
- Essential Research Tips for Essay Writing
- What Is a Mind Map? Free Mind Map Templates & Examples
- How to Write an Essay Outline: 5 Examples & Free Template
How to Write an Essay Header: MLA and APA Essay Headers
- What Is an Essay? Structure, Parts, and Types
- How to Write an Essay in 8 Simple Steps (Examples Included)
- 8 Types of Essays | Quick Summary with Examples
- Expository Essays | Step-by-Step Manual with Examples
- Narrative Essay | Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- How to Write an Argumentative Essay (Examples Included)
- Guide to a Perfect Descriptive Essay [Examples & Outline Included]
- How to Start an Essay: 4 Introduction Paragraph Examples
- How to Write a Conclusion for an Essay (Examples Included!)
- How to Write an Impactful Personal Statement (Examples Included)
- Literary Analysis Essay: 5 Steps to a Perfect Assignment
- Compare and Contrast Essay | Quick Guide with Examples
- Top 10 Essay Writing Tools in 2024 | Plan, Write, Get Feedback
- Top AI Essay Writers in 2024: 10 Must-Haves
- 100 Best College Essay Topics & How to Pick the Perfect One!
- College Essay Format: Tips, Examples, and Free Template
- Structure of an Essay: 5 Tips to Write an Outstanding Essay
Still have questions? Leave a comment
Add Comment

Checklist: Dissertation Proposal
Enter your email id to get the downloadable right in your inbox!

Examples: Edited Papers
Need editing and proofreading services.
- Tags: Essay , Essay Editing
A header for an essay is an important part of APA or MLA formatting guidelines . In this article, we’ll find out the purpose of an essay header, how to format it, and the APA and MLA essay header variations.
A properly formatted header helps your professor quickly and easily identify your essay. In APA format , the essay header also carries a gist of your larger topic, providing the reader with basic information about your essay in one glance.
Let’s take a more detailed look at how to write a header for an essay.
Ensure top-notch essay formatting! Get started
What is a header in an essay?
A header for an essay is a line of text typically included at the top of the page. The content of the header depends on your essay header format. The MLA essay header includes your last name whereas the APA essay header includes a shortened title of your essay.
The use of a header is especially important in longer essays, as it helps professors navigate the document with ease. The page number helps them locate specific information quickly and the author’s name helps them associate each essay with the student who wrote it.
MLA essay header
The Modern Language Association (MLA), often used in literature and humanities essays, requires a specific type of header. It consists of your last name, followed by a space and then the page number. Thus, the MLA essay header helps the instructor easily associate your work with you amidst a sea of other assignments.
The header for an MLA format essay is typically placed in the top right-hand corner of each page of the document. The information is right-aligned, double-spaced, and is usually preceded by a 0.5-inch margin.
Here’s an essay header example to help you understand:
It is important to note that the MLA essay header is not the same as a title page. The title page is a separate page that includes the essay title, your name, the course title, and the date of submission. The MLA format essay header is simply a standardized way to format page numbers and your personal information within the document itself.
APA essay header
The American Psychological Association (APA) usually requires a header to be included in both student and professional essays. The APA essay header includes an abbreviated title of the essay along with the page number.
The title should be in all capital letters and should not be more than 50 characters long. It should be included on the top left corner of the page. The page number should be included opposite the title, in the top right corner of the page.
Take a look at this essay header example:
It is important to note that running head in an APA essay header is optional for students but compulsory for professionals. While the header must be present in both types of APA essays, the elements differ.
How to write a header for an essay
1. To activate the header for an essay, double-right-click on the top of the page.
If you need additional help with headers and other formatting guidelines, you can also consider working with a professional essay editing service .
Want to keep reading? Here are the newest articles we’ve worked on:
- How to Write an Essay in 8 Simple Steps
- Learn About What is an Essay and Parts of an Essay
- How to Write an Essay Outline
Frequently Asked Questions
Are the header and title exactly the same, should i use my full name in the mla header, what are running apa headers.
Found this article helpful?
Leave a Comment: Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Your vs. You’re: When to Use Your and You’re
Your organization needs a technical editor: here’s why, your guide to the best ebook readers in 2024, writing for the web: 7 expert tips for web content writing.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Get carefully curated resources about writing, editing, and publishing in the comfort of your inbox.
How to Copyright Your Book?
If you’ve thought about copyrighting your book, you’re on the right path.
© 2024 All rights reserved
- Terms of service
- Privacy policy
- Self Publishing Guide
- Pre-Publishing Steps
- Fiction Writing Tips
- Traditional Publishing
- Academic Writing and Publishing
- Partner with us
- Annual report
- Website content
- Marketing material
- Job Applicant
- Cover letter
- Resource Center
- Case studies
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Critique Report
- Writing Reports
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
MLA Format: The Ultimate Guide to Correctly Formatting Your Paper

By Hannah Yang

So you need to create an MLA heading? You’re not alone—MLA format is one of the most common styles you’ll be expected to use when you’re writing a humanities paper, whether you’re a high-school student or a PhD candidate.
Read on to learn what a correct MLA heading looks like and how to create one that works like magic.
What Is an MLA Heading?
How do you format an mla heading, what is an mla header, how do you format an mla header, headings are only the beginning, commonly asked questions about mla headers, final thoughts.
The term “MLA heading” refers to five lines of important information that appear at the top of the first page.
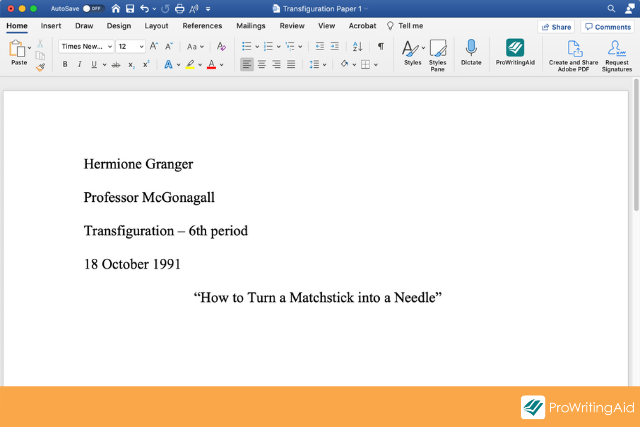
Here are two examples of what an MLA heading could look like:
Hermione Granger
Professor McGonagall
Transfiguration—6th period
18 October 1991
“How to Turn A Matchstick into a Needle”
Harry J. Potter
Prof. Remus Lupin
Defense Against the Dark Arts
4 March 1994
“Why I Think My Professor Is a Werewolf”
Why are these headings important? Well, your teacher probably collects hundreds of papers every year. If any identifying information is missing from these assignments, grading and organizing them becomes much more of a challenge.
MLA headings ensure that all key information is presented upfront. With just a glance at the first page, your teacher can easily figure out who wrote this paper, when it was submitted, and which class it was written for.

What Are the Parts of an MLA Heading?
An MLA heading should include:
- Your instructor’s name
- The name of the class
- The date the assignment is due
- The title of your paper
Your instructor may give you specific guidelines about how much detail to include in each line. For example, some teachers may ask you to refer to them by their titles, while others may ask you to use their full names. If you haven’t been given any specific instructions, don’t sweat it—any option is fine as long as it’s clear and consistent.
Follow these formatting rules for your MLA heading:
- Start each piece of information on a separate line
- Don’t use any periods, commas, or other punctuation at the end of the line
- Keep the heading double-spaced, in the same font as the rest of your paper
- Left-align the first four lines (they should start at the 1-inch margin on the left side of your paper)
- Center the title (it should appear in the middle of your paper)
- Make sure your title is in title case
Title case means that major words should be capitalized and minor words should be lowercase. Major words include nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, and any word longer than four letters. Minor words include conjunctions, prepositions, and articles.
Tip: Remember that Hermione’s “Society for the Promotion of Elfish Welfare” shortens to S.P.E.W., not S.F.T.P.O.E.W—only the major words are capitalized!

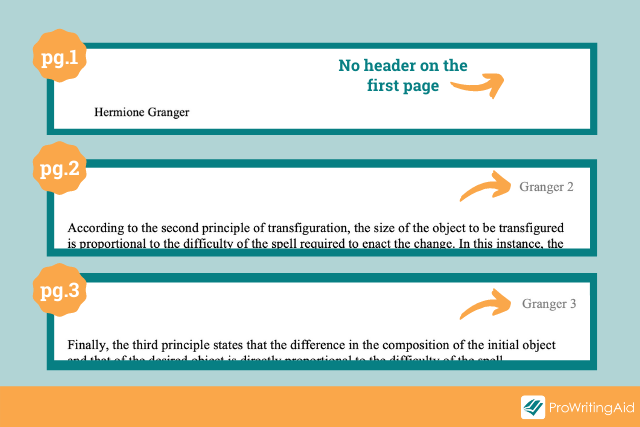
The MLA heading should only appear on the first page of your paper . But wait, you’re not done yet! In the rest of your paper, you need to include something called an MLA header at the top right corner of every page.
Think of the MLA header as a short, simple “You are here” marker that shows the reader where they are in the paper. By looking at the MLA headers, your instructor can easily understand where each page goes and which paper it belongs to.
What Are the Parts of an MLA Header?
The MLA header consists of your last name and page number.
For example, the second page of Hermione Granger’s essays would be labeled “Granger 2”, the third would be labeled “Granger 3”, and so on.
Creating MLA Headers in Microsoft Word
If you’re writing your paper in Microsoft Word, follow these steps:
- Click Insert
- Scroll down to Page Numbers and click on it
- Set the position to “Top of Page (Header)”
- Set the alignment to “Right”
- Make sure there’s no checkmark in the box for “Show number on first page”
- Click on the page number and type your last name before the number
- Set your font and font size to match the rest of your paper, if they don’t already
Creating MLA Headers in Google Docs
If you’re writing your paper in Google Docs, follow these steps:
- Scroll down to Page Numbers and hover over it
- Choose the option that sets your page number in the upper right corner
- Set your font and type size to match the rest of your paper, if they don’t already
Tip: After you create your first MLA header, save a template document for yourself that you can re-use next time, so you don’t have to follow these steps every time you write a paper!
Once you've got your headings sorted, it's time to start writing your paper. While we can't help you edit the content of your essay , ProWritingAid is here to make sure your grammar, spelling, and style is on point.
As well as checking your grammar, ProWritingAid also shows you your progress towards key goals like varied sentence structure, active voice, readability, and more. The target scores are all based on averages for real essays, so you'll always know if you're on track.
Ready to start receiving feedback before you submit your work?
Whose last name should you use in your MLA header if you’re writing a group paper?The MLA Style Guide has no specific guidelines for group projects. You should always include the names of all members of the group project in the first line of your heading, but you don’t necessarily need to do this for the header on every page. If there are only two or three authors collaborating on your paper, you can include all of your last names in the MLA header, e.g., “Granger, Potter, and Weasley 2.” If you’re part of a bigger group and it would take up too much space to include all of your last names, you can write the name that comes first in the alphabet and then add “ et al. ”, e.g., “Granger et al. 2.” (The term “et al.” is short for the Latin term “et alia”, which means “and others.” You’ll often see it used in academic papers with multiple authors.)  Should you include your class period in your MLA heading or just the class name?There’s no MLA rule about this, but when in doubt, it’s always better to err on the side of including too much information in your heading rather than not enough. If your instructor teaches more than one version of the same course, they’ll probably find it helpful if you specify the class period you’re in. You can either include your class period after the class name, e.g., “History of Magic—2nd period”, or before the class name, e.g., “2nd Period History of Magic.” What should you write in your MLA heading if you don’t have an instructor?If you have no instructor, you can explain the situation in the line where you would normally put the instructor’s name, e.g., “Independent Study” or “No Instructor.” What should you write in your MLA heading if you have multiple instructors?If you have multiple instructors, you can include both of their names in the line where you would put the instructor’s name. If you’re in a college course where you have a professor and a TA, you should choose whose name to include in the header depending on who will ultimately be reading your paper.  Should you include the date you started writing the paper or the date the paper is due?The MLA Style Guide has no specific guidelines about which date you need to put in the heading. In general, however, the best practice is to put the date the assignment is due. This is because all the papers for the same assignment will have the same due date, even if different students begin writing their assignments on different days, so it’s easier for your instructor to use the due date to determine what assignment the paper is for. Should you format the date as Day Month Year or Month Day Year?In MLA format, you should write the date in the order of Day Month Year. Instead of writing May 31 2021, for example, you would write 31 May 2021. What font should you use for your MLA heading and header?Both the heading and the header should be in the same font as the rest of your paper. If you haven’t chosen a font for your paper yet, remember that the key thing to aim for is readability. If you choose a font where your teachers have to squint to read it, or one where your teachers can’t figure out the difference between what’s italicized and what isn’t, you should rethink your choice. When in doubt, go with Times New Roman, 12 pt. It’s always a safe bet for MLA papers unless your instructor specifically tells you otherwise.  Do you need to italicize or bold the title of your MLA paper?No. There’s no need to use any special styling on the title of an MLA paper, such as bold or italics. How do you format section titles in your MLA paper?If you’re writing a paper with multiple sections, you may need to include a subtitle at the top of each section. The MLA Style Guide gives you two options for using subtitles in a paper: one-level section titles or several-level subtitles (for papers with subsections within each section). For one-level section titles, the formatting is simple. Every subtitle should look the same as the title (centered and double-spaced, with no special formatting). 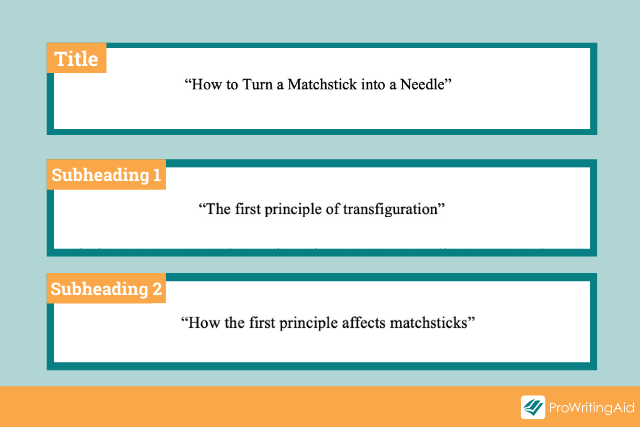 The only difference is that instead of using title case, you should capitalize only the first word of each subtitle. For example, a title would be spelled “How to Turn a Matchstick into a Needle”, while a subtitle would be spelled “How to turn a matchstick into a needle.” For several-level subtitles, you will need to format each level in a different way to show which level each section is at. You can use boldface, italics, and underlining to differentiate between levels. For example, subtitles at the highest level should be bolded, while subtitles at the next level down should be italicized. See the chart below for MLA’s suggested formats.  What is the difference between MLA format and APA format?MLA and APA are two sets of guidelines for formatting papers and citing research. MLA stands for the Modern Language Association. The MLA handbook is most often used in fields related to the humanities, such as literature, history, and philosophy. APA stands for the American Psychological Association. The APA format is most often used in fields related to the social sciences, such as psychology, sociology, and nursing. The APA manual includes a heading format similar to the MLA heading format with a few key differences, such as using a separate cover page instead of simply including the heading at the top of the first page. Both heading formats ensure that all of your papers include all your key identifying information in a clear and consistent way.  Where can you learn more about MLA style?If you have questions about how to format a specific assignment or paper, it’s always best to consult your instructor first. Your school may also have a writing center that can help you with formatting questions. In addition, Purdue has fantastic resources for all kinds of formatting topics, from MLA headings to MLA citations and everything in between. If you would like to find out more directly from the Modern Language Association, consult the MLA Style Center or the MLA Handbook (8th edition). Now you’re ready to write an MLA paper with a fantastic heading. Make sure your essay does your heading justice by checking it over with ProWritingAid. Write Better Essays Every TimeAre your teachers always pulling you up on the same errors? Maybe you're losing clarity by writing overly long sentences or using the passive voice too much? ProWritingAid helps you catch these issues in your essay before you submit it.  Be confident about grammarCheck every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send. Hannah YangHannah Yang is a speculative fiction writer who writes about all things strange and surreal. Her work has appeared in Analog Science Fiction, Apex Magazine, The Dark, and elsewhere, and two of her stories have been finalists for the Locus Award. Her favorite hobbies include watercolor painting, playing guitar, and rock climbing. You can follow her work on hannahyang.com, or subscribe to her newsletter for publication updates. Get started with ProWritingAidDrop us a line or let's stay in touch via : Learn the Standard Essay Format: MLA, APA, Chicago Styles Being able to write an essay is a vital part of any student's education. However, it's not just about linearly listing ideas. A lot of institutions will require a certain format that your paper must follow; prime examples would be one of a basic essay format like MLA, the APA, and the Chicago formats. This article will explain the differences between the MLA format, the APA format, and the Chicago format. The application of these could range from high school to college essays, and they stand as the standard of college essay formatting. EssayPro — dissertation services , that will help to make a difference! What is an Essay Format: StructureBe it an academic, informative or a specific extended essay - structure is essential. For example, the IB extended essay has very strict requirements that are followed by an assigned academic style of writing (primarily MLA, APA, or Chicago):
This outline format for an extended essay is a great example to follow when writing a research essay, and sustaining a proper research essay format - especially if it is based on the MLA guidelines. It is vital to remember that the student must keep track of their resources to apply them to each step outlined above easily. And check out some tips on how to write an essay introduction . Lost in the Labyrinth of Essay Formatting?Navigate the complexities of essay structures with ease. Let our experts guide your paper to the format it deserves! How to Format an Essay (MLA) To write an essay in MLA format, one must follow a basic set of guidelines and instructions. This is a step by step from our business essay writing service.
Essay in MLA Format ExampleMla vs. apa. Before we move on to the APA essay format, it is important to distinguish the two types of formatting. Let’s go through the similarities first:
What you need to know about the differences is not extensive, thankfully:
Alright, let’s carry over to the APA style specifics. Order an Essay Now & and We Will Cite and Format It For Free :How to format an essay (apa). The APA scheme is one of the most common college essay formats, so being familiar with its requirements is crucial. In a basic APA format structure, we can apply a similar list of guidelines as we did in the MLA section:
If you ask yourself how to format an essay, you can always turn to us and request to write or rewrite essay in APA format if you find it difficult or don't have time. Note that some teachers and professors may request deviations from some of the characteristics that the APA format originally requires, such as those listed above.  If you think: 'I want someone write a research paper for me ', you can do it at Essaypro. Essay in APA Format ExampleApa format chronobiology, chicago style. The usage of Chicago style is prevalent in academic writing that focuses on the source of origin. This means that precise citations and footnotes are key to a successful paper. Chicago Style Essay FormatThe same bullet point structure can be applied to the Chicago essay format.
 Tips for Writing an Academic PaperThere isn’t one proper way of writing a paper, but there are solid guidelines to sustain a consistent workflow. Be it a college application essay, a research paper, informative essay, etc. There is a standard essay format that you should follow. For easier access, the following outline will be divided into steps: Choose a Good TopicA lot of students struggle with picking a good topic for their essays. The topic you choose should be specific enough so you can explore it in its entirety and hit your word limit if that’s a variable you worry about. With a good topic that should not be a problem. On the other hand, it should not be so broad that some resources would outweigh the information you could squeeze into one paper. Don’t be too specific, or you will find that there is a shortage of information, but don’t be too broad or you will feel overwhelmed. Don’t hesitate to ask your instructor for help with your essay writing. Start Research as Soon as PossibleBefore you even begin writing, make sure that you are acquainted with the information that you are working with. Find compelling arguments and counterpoints, trivia, facts, etc. The sky is the limit when it comes to gathering information. Pick out Specific, Compelling ResourcesWhen you feel acquainted with the subject, you should be able to have a basic conversation on the matter. Pick out resources that have been bookmarked, saved or are very informative and start extracting information. You will need all you can get to put into the citations at the end of your paper. Stash books, websites, articles and have them ready to cite. See if you can subtract or expand your scope of research. Create an OutlineAlways have a plan. This might be the most important phase of the process. If you have a strong essay outline and you have a particular goal in mind, it’ll be easy to refer to it when you might get stuck somewhere in the middle of the paper. And since you have direct links from the research you’ve done beforehand, the progress is guaranteed to be swift. Having a list of keywords, if applicable, will surely boost the informational scope. With keywords specific to the subject matter of each section, it should be much easier to identify its direction and possible informational criteria. Write a DraftBefore you jot anything down into the body of your essay, make sure that the outline has enough information to back up whatever statement you choose to explore. Do not be afraid of letting creativity into your paper (within reason, of course) and explore the possibilities. Start with a standard 5 paragraph structure, and the content will come with time. Ask for a Peer Review of Your Academic PaperBefore you know it, the draft is done, and it’s ready to be sent out for peer review. Ask a classmate, a relative or even a specialist if they are willing to contribute. Get as much feedback as you possibly can and work on it. Final DraftBefore handing in the final draft, go over it at least one more time, focusing on smaller mistakes like grammar and punctuation. Make sure that what you wrote follows proper essay structure. Learn more about argumentative essay structure on our blog. If you need a second pair of eyes, get help from our service. Want Your Essay to Stand Out in Structure and Style? Don't let poor formatting overshadow your ideas. Find your essay on sale and ensure your paper gets the professional polish it deserves! What Is Essay Format?How to format a college essay, how to write an essay in mla format.  is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.  Online Learning ResourcesAcademic skills office, academic skills.
Using headings
Headings are standard for some written forms (e.g. report writing, case studies). However, lecturers can be divided about whether they allow/prefer you to use headings in your academic essays. Some lecturers prefer headings while others don’t want you to use headings. You will need to check your lecturer’s preference. If you do use headings, then use them wisely and correctly. About using headingsMost students who have just completed secondary studies come to university with the firm belief that you should not use headings in essay writing. The use of headings in formal writing was once restricted to business style writing, such as report writing. However, in more recent times, headings are often used in formal academic writing such as books and journals. Also, texts on the Internet are easier to read on screen if they have headings. Headings are signposts that focus the reader on the most important content in a piece of writing, and are usually connected to the set question. Provided that they are well structured, a few headings make longer pieces of writing easier to write and easier to read (for the marker). Look at headings systems in your unit reading material, and you will get a ‘feeling’ for their structure and suitability. It’s easy to see why you need a few rules to help you develop a good system of headings. Compare the following sets of headings then answer the questions that follow:
Read this description of a well-structured set of headings:
This description applies to: Correct! When you see headings set out like this, it becomes obvious that you need to create a plan for your headings before you start. Heading set 1 follows the rules and is logical, whereas Heading set 2 breaks the rules and would send the reader on a ‘chase’ to work out what the writer means. So, take a couple of minutes to work out a consistent plan for using headings and apply it to all of your essays. In general, you are expected to use headings correctly so that your writing is clear, and it is obvious that you have answered the set question. There are rules to help you to do this. Click on the links to see more details and examples. Graded heading systemBEFORE YOU START YOUR ESSAY, HAVE A CLEAR AND LOGICAL HEADING HIERARCHY. Work out a system of headings that you can use with all of your essays. Headings should be graded at levels to show a clear order of importance (e.g. level 1 – most important; level 2 – next important and so on). You will mainly use one to three levels of headings in your essay, depending on the length of your assignment. For example, most 2000 word essays may only require 3-5 level 1 headings (i.e. a level 1 heading every 2-3 pages). Remember that the aim of using headings is to keep your reader on track. Too many headings and too many levels creates confusion. When you design a heading system, show the relative importance of headings with the type size, position (e.g. centred or left justified), using boldface, underlining or capital letters. You can follow a recommended pattern or make up your own system—so long as it is clear and consistent. Example: Level 1: CAPITALS , bold, 14pt, centred, space below Level 2: Lowercase , bold, 12pt, left justified, space below Level 3: Lowercase , italics, 12pt, left justified, no space below Information in logical sectionsUSE HEADINGS FOR SECTIONS IN YOUR DOCUMENT (NOT FOR EACH PARAGRAPH). The key to working out your essay sections is to work from your question analysis. Consider the following question: Many lecturers now approve of the use of headings in academic essays. Consider whether the benefits outweigh the problems for the writers and markers. Identify and discuss the key rules for using headings appropriately in academic essays. (2000 words) Example of a heading plan for this question: Level 1 headings INTRODUCTION BENEFITS OF USING HEADINGS PROBLEMS WITH USING HEADINGS RULES TO GUIDE HEADING USAGE CONCLUSION Level 2 headings (example from one section) The heading RULES TO GUIDE HEADING USAGE could have the following level 2 headings: Heading hierarchies (3 paragraphs) Effective wording of headings (2 paragraphs) Effective wording of headings WHEN YOU DESIGN YOUR HEADINGS SYSTEM, MAKE SURE THAT THE WORDING IS CONSISTENT. Use three basic principles to word your headings:
For example:
Correct punctuation for headingsIT IS IMPORTANT THAT YOU KNOW AND APPLY PUNCTUATION RULES TO YOUR HEADINGS. Headings can be single words or short phrases and DO NOT require a full stop unless you have used a question as a heading—a question mark is then required. The use of capital letters may follow either of the following approaches provided that you are consistent:
INTRODUCE THE TOPIC OF YOUR HEADING IN THE FIRST PARAGRAPH FOLLOWING YOUR HEADING. When you place a heading in the text, it is a signpost for a section of writing. You need to begin the following paragraph with a sentence that introduces the reader to the heading topic and then announce what will be coming in that section in the essay—just as you do in the essay introduction. A heading is not part of the text of your paragraph, so you should not refer to it with a pronoun reference (e.g. this, these, that). This means that the wording of the heading matches the information of the following section. Do not make the heading part of the first sentence.
What NOT to doThere is much to learn from what is NOT wanted. Following are some of the common mistakes made in the use of headings in formal written work: Click on the links to see more details.
Headings for essay planningDesigning a good headings system is also very helpful for setting up a plan for writing as you can quickly see whether you have included and balanced all of the parts of a question. Make sure your headings match the information you signal in the outline statement of your introduction paragraph.
 Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices. 13.1 Formatting a Research PaperLearning objectives.
In this chapter, you will learn how to use APA style , the documentation and formatting style followed by the American Psychological Association, as well as MLA style , from the Modern Language Association. There are a few major formatting styles used in academic texts, including AMA, Chicago, and Turabian:
While all the formatting and citation styles have their own use and applications, in this chapter we focus our attention on the two styles you are most likely to use in your academic studies: APA and MLA. If you find that the rules of proper source documentation are difficult to keep straight, you are not alone. Writing a good research paper is, in and of itself, a major intellectual challenge. Having to follow detailed citation and formatting guidelines as well may seem like just one more task to add to an already-too-long list of requirements. Following these guidelines, however, serves several important purposes. First, it signals to your readers that your paper should be taken seriously as a student’s contribution to a given academic or professional field; it is the literary equivalent of wearing a tailored suit to a job interview. Second, it shows that you respect other people’s work enough to give them proper credit for it. Finally, it helps your reader find additional materials if he or she wishes to learn more about your topic. Furthermore, producing a letter-perfect APA-style paper need not be burdensome. Yes, it requires careful attention to detail. However, you can simplify the process if you keep these broad guidelines in mind:
 General Formatting GuidelinesThis chapter provides detailed guidelines for using the citation and formatting conventions developed by the American Psychological Association, or APA. Writers in disciplines as diverse as astrophysics, biology, psychology, and education follow APA style. The major components of a paper written in APA style are listed in the following box. These are the major components of an APA-style paper: Body, which includes the following:
All these components must be saved in one document, not as separate documents. The title page of your paper includes the following information:
List the first three elements in the order given in the previous list, centered about one third of the way down from the top of the page. Use the headers and footers tool of your word-processing program to add the header, with the title text at the left and the page number in the upper-right corner. Your title page should look like the following example.  The next page of your paper provides an abstract , or brief summary of your findings. An abstract does not need to be provided in every paper, but an abstract should be used in papers that include a hypothesis. A good abstract is concise—about one hundred fifty to two hundred fifty words—and is written in an objective, impersonal style. Your writing voice will not be as apparent here as in the body of your paper. When writing the abstract, take a just-the-facts approach, and summarize your research question and your findings in a few sentences. In Chapter 12 “Writing a Research Paper” , you read a paper written by a student named Jorge, who researched the effectiveness of low-carbohydrate diets. Read Jorge’s abstract. Note how it sums up the major ideas in his paper without going into excessive detail.  Write an abstract summarizing your paper. Briefly introduce the topic, state your findings, and sum up what conclusions you can draw from your research. Use the word count feature of your word-processing program to make sure your abstract does not exceed one hundred fifty words. Depending on your field of study, you may sometimes write research papers that present extensive primary research, such as your own experiment or survey. In your abstract, summarize your research question and your findings, and briefly indicate how your study relates to prior research in the field. Margins, Pagination, and HeadingsAPA style requirements also address specific formatting concerns, such as margins, pagination, and heading styles, within the body of the paper. Review the following APA guidelines. Use these general guidelines to format the paper:
 Begin formatting the final draft of your paper according to APA guidelines. You may work with an existing document or set up a new document if you choose. Include the following:
APA style uses section headings to organize information, making it easy for the reader to follow the writer’s train of thought and to know immediately what major topics are covered. Depending on the length and complexity of the paper, its major sections may also be divided into subsections, sub-subsections, and so on. These smaller sections, in turn, use different heading styles to indicate different levels of information. In essence, you are using headings to create a hierarchy of information. The following heading styles used in APA formatting are listed in order of greatest to least importance:
Visually, the hierarchy of information is organized as indicated in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” . Table 13.1 Section Headings
A college research paper may not use all the heading levels shown in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” , but you are likely to encounter them in academic journal articles that use APA style. For a brief paper, you may find that level 1 headings suffice. Longer or more complex papers may need level 2 headings or other lower-level headings to organize information clearly. Use your outline to craft your major section headings and determine whether any subtopics are substantial enough to require additional levels of headings. Working with the document you developed in Note 13.11 “Exercise 2” , begin setting up the heading structure of the final draft of your research paper according to APA guidelines. Include your title and at least two to three major section headings, and follow the formatting guidelines provided above. If your major sections should be broken into subsections, add those headings as well. Use your outline to help you. Because Jorge used only level 1 headings, his Exercise 3 would look like the following:
Citation GuidelinesIn-text citations. Throughout the body of your paper, include a citation whenever you quote or paraphrase material from your research sources. As you learned in Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” , the purpose of citations is twofold: to give credit to others for their ideas and to allow your reader to follow up and learn more about the topic if desired. Your in-text citations provide basic information about your source; each source you cite will have a longer entry in the references section that provides more detailed information. In-text citations must provide the name of the author or authors and the year the source was published. (When a given source does not list an individual author, you may provide the source title or the name of the organization that published the material instead.) When directly quoting a source, it is also required that you include the page number where the quote appears in your citation. This information may be included within the sentence or in a parenthetical reference at the end of the sentence, as in these examples. Epstein (2010) points out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137). Here, the writer names the source author when introducing the quote and provides the publication date in parentheses after the author’s name. The page number appears in parentheses after the closing quotation marks and before the period that ends the sentence. Addiction researchers caution that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (Epstein, 2010, p. 137). Here, the writer provides a parenthetical citation at the end of the sentence that includes the author’s name, the year of publication, and the page number separated by commas. Again, the parenthetical citation is placed after the closing quotation marks and before the period at the end of the sentence. As noted in the book Junk Food, Junk Science (Epstein, 2010, p. 137), “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive.” Here, the writer chose to mention the source title in the sentence (an optional piece of information to include) and followed the title with a parenthetical citation. Note that the parenthetical citation is placed before the comma that signals the end of the introductory phrase. David Epstein’s book Junk Food, Junk Science (2010) pointed out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137). Another variation is to introduce the author and the source title in your sentence and include the publication date and page number in parentheses within the sentence or at the end of the sentence. As long as you have included the essential information, you can choose the option that works best for that particular sentence and source. Citing a book with a single author is usually a straightforward task. Of course, your research may require that you cite many other types of sources, such as books or articles with more than one author or sources with no individual author listed. You may also need to cite sources available in both print and online and nonprint sources, such as websites and personal interviews. Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.2 “Citing and Referencing Techniques” and Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provide extensive guidelines for citing a variety of source types. Writing at WorkAPA is just one of several different styles with its own guidelines for documentation, formatting, and language usage. Depending on your field of interest, you may be exposed to additional styles, such as the following:
References ListThe brief citations included in the body of your paper correspond to the more detailed citations provided at the end of the paper in the references section. In-text citations provide basic information—the author’s name, the publication date, and the page number if necessary—while the references section provides more extensive bibliographical information. Again, this information allows your reader to follow up on the sources you cited and do additional reading about the topic if desired. The specific format of entries in the list of references varies slightly for different source types, but the entries generally include the following information:
The references page is double spaced and lists entries in alphabetical order by the author’s last name. If an entry continues for more than one line, the second line and each subsequent line are indented five spaces. Review the following example. ( Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provides extensive guidelines for formatting reference entries for different types of sources.)  In APA style, book and article titles are formatted in sentence case, not title case. Sentence case means that only the first word is capitalized, along with any proper nouns. Key Takeaways
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.  The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work Start Plagiarism Check Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper Get it proofread now Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery Configure binding now
Your Step to SuccessPlagiarism Check within 10min Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview Headings – Definition, 3 Formats & A Guide For WordHow do you like this article cancel reply. Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.  Headings immediately provide structure and help the reader to find their way around your academic writing . They start a paragraph , chapter, or page and tell you what the following content is about. Learn how to write them, how long they should be, the difference between them and titles, and much more. With this article, you will learn how to write an effective heading that will get the reader’s attention and encourage them to continue reading. Inhaltsverzeichnis
Headings in a nutshellHeadings are labels used in written content to organize and make it easier to read. They are like signs on a road, telling you what’s ahead or how to find something. In books, articles, or websites, they help break down the text into sections, each focusing on a different topic or idea. They typically come in different sizes, with the most important heading (the main title ) being the biggest, and subheadings getting smaller as they detail more specific points. This structure helps readers quickly find the information they’re interested in and understand the overall flow of the content. Definition: HeadingsWhen writing academic essays or research papers , you should maintain a logical flow of ideas throughout the work. This is when headings as textual markers come into play. They can be found in documents, web pages, and other written materials that indicate the hierarchy, structure, and organization of content. They organize text into sections and subsections, making it easier for readers to navigate information. Furthermore, they demonstrate the relative importance of different sections through varying levels, such as “Heading 1” for main titles, followed by smaller subtitles for detailed breakdowns. They enhance accessibility, allowing users, especially those with disabilities, to understand the structure of the content more easily. In web content, they also play a crucial role in search engine optimization (SEO) by helping search engines understand and rank the page content, making it more discoverable to users. Essentially, they are about structuring content to improve readability , navigability, and comprehension. Special headingsSpecial headings are specific types that serve unique purposes within a document or publication. These are typically used in academic papers, research articles, reports, or other formal documents to organize and present information in a structured manner. Here are some of the common ones:
Headings vs. titlesSection titles and titles play a crucial role in the writing process of academic works in university, school, and even work. However, these two terms serve different purposes. Read on to find out what sets them apart.
SubheadingsSubheadings, or subtitles, are titles used within a document to organize content into sections, making it easier for readers to navigate and understand the material. In an academic context, subheadings are crucial for structuring papers, reports, and articles. They help break down complex information into manageable parts, highlight key topics, and provide a clear content roadmap. Main title: The Impact of Climate Change on Marine Biodiversity Subtitle: Effects on Coral Reefs This part could delve into how rising temperatures and ocean acidification affect coral reefs, including bleaching events. Subtitle: Changes in Marine Species Distribution Here, the focus could be on how climate change alters the geographical distribution of marine species. Different style guidesThere are various style guides used by universities worldwide. However, each of them has its guidelines on formatting, etc. Below, we provide a brief overview of the three most important style guides and their specifications for formatting headlines. Note: It is important to know in advance that headline-style capitalization refers to a formatting style in which the first and last words are capitalized. Chicago StyleFor the APA style heading format, the following rules apply:
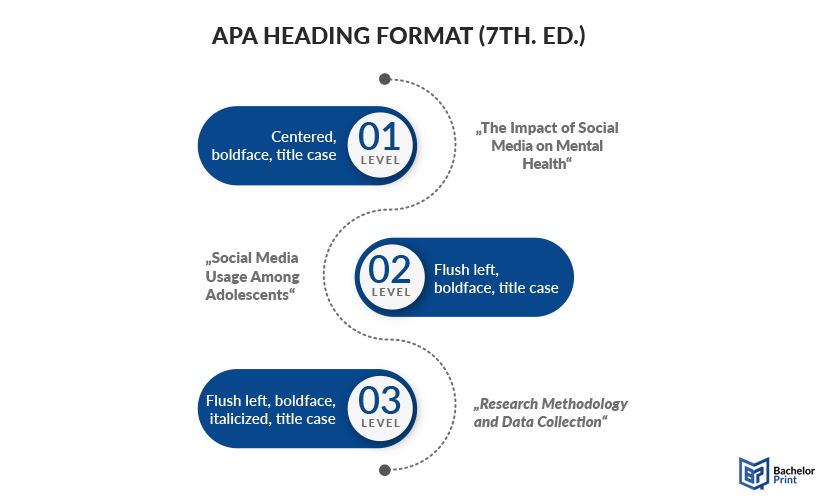 For the MLA style heading format, the following rules apply:
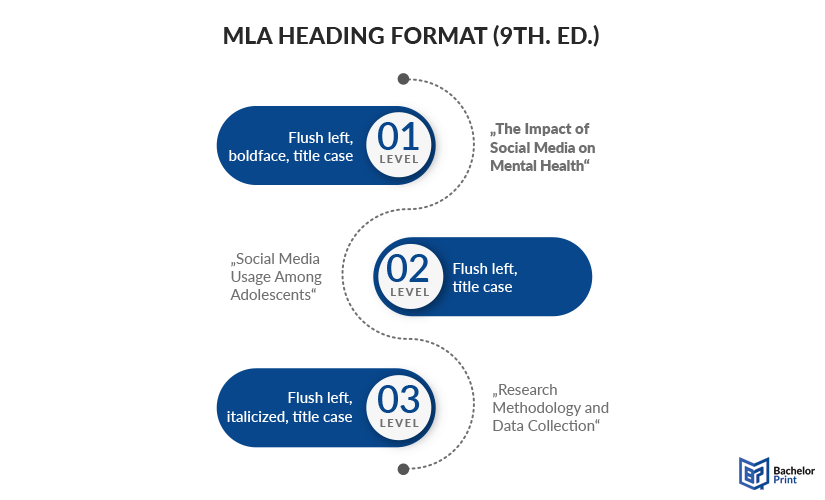 For the Chicago Style heading format, the following rules apply:
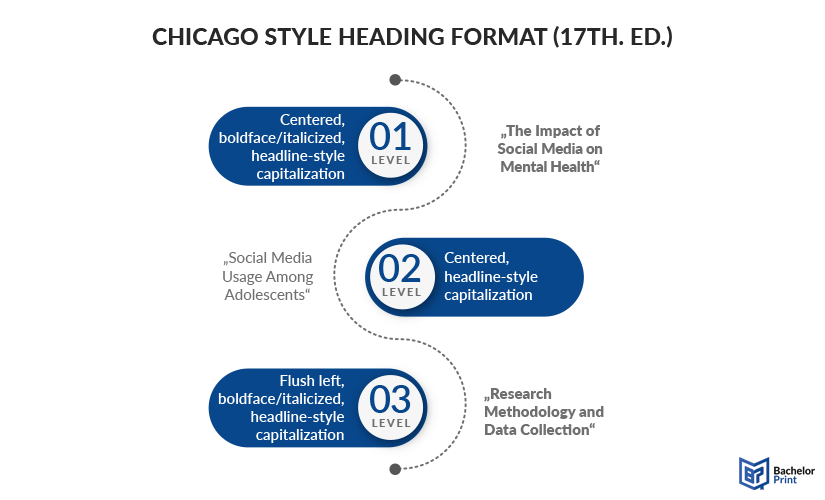 What to pay attention toThere are certain aspects, when creating a proper section title, you should pay attention to. Below, we’ll explain this and afterward you’re a pro when crafting your paper. Be descriptiveNo repetition. For your academic essays, you should incorporate some descriptive headings to provide the reader with clear information for easy understanding. When used effectively, the lecturer, or reader will peruse your document and know what it’s about simply by reading the headlines. Some tips on how to be as descriptive as possible are:
The first one is too vague and does not provide specific information about the section’s content. In contrast, the second one clearly describes the information and sets appropriate expectations for the reader. Chapters cannot have the same content; therefore, the section titles can’t be the same, too. Knowing how to write a headline that is as descriptive as possible will help arrange your ideas and give the reader an easy time. Having the same title twice can dilute your work and immensely affect your grading. Essential tips on how to write a headline without repetition are:
In the first example, it is unclear which features are being discussed in each section. The second examples are unique and refer to different paper sections, which helps in differentiating the content and improves the overall clarity. Add a heading in WordFirstly, you open up the document in Microsoft Word you’d like to create headlines for. Right at the beginning, you will see the Home tab, where you can also set the font and size. Right in the middle, you will find a fold-out column titles Styles that allows you to format your text into any headline you like (refer to the picture below). If you click on the arrow , you’ll see there are more types of section titles , if there isn’t one you like. 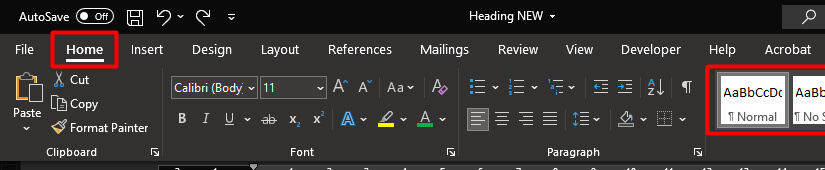 That’s how easily you format a headline in a Word document. Note: You can change the format by simply hovering over the style while marking the text. You do not have to click on the heading style to find out how it’ll look. If you want to take it one step further, you can even create your own style when folding out the Styles tab. You have two choices here. One involves changing an existing headline, whereas the other option involves creating an entirely new one.
See the images below for a visual representation. 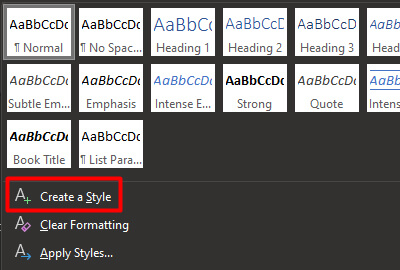 Technical terms in headingsTechnical and jargon terms used in headlines of documents may not be understandable to every reader except those familiar with the languages. An example is site language, most commonly found in search engine optimization (SEO). Different heading levels are used to communicate the site structure to Google. There are different heading ranks and they are referred to as follows:
What is a heading?A heading is a title or label used in written content to organize and indicate the structure of the information. It helps readers navigate through the text and understand its main topics and subtopics. What is an exemplary heading?Here’s an example when writing about time management techniques and strategies aimed at enhancing productivity and efficiency in various aspects of life, such as work, school, or personal activities.
What is the difference between a heading and title?
Why are headings important in writing?They convey an overview of what the entire paper is about. The reader is supposed to find out what the entire document is about by going through the sections assigned. How long should headings be?A rule of thumb is to never go past one line because it’ll be too long. A good, understandable headline for your sections or paragraphs should intrigue the reader to read more and not be too long to bore them. Extremely satisfied, excellent deal with delivery in less than 24h. The print... We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
Individual Privacy Preferences Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies. Accept all Save Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website. Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint 
by acburton | May 18, 2024 | Resources for Students , Writing Resources Think about the last time you read a really long academic article or publication for a class. When the text just seemed to drone on and on to no end, think back – weren’t you really grateful for those headings (and sometimes subheadings) that broke up the longer text, switched or elaborated on a topic, stimulated your eyesight, and gave your noggin a much needed break? I bet you were! Headings and subheadings enable longer texts and differing topics and subtopics to be clearly differentiated for your reader, yet linked in a way that can be clearly understood and appreciated. Let’s go through a few other benefits to using headings and subheadings in your writing! Incorporating headings and subheadings into your longer pieces of writing;
While headings and subheadings don’t replace the use of effective transitions , they can be used in tandem to further organize your paper, guiding your reader through your topic of choice. To use headings and subheadings appropriately, you’ll want to keep in mind three very important considerations:
The HierarchyHeadings and subheadings are represented in the form of a hierarchy, or a ranking that clearly characterizes your main topic from your subtopic or issue. The prefix “sub” in “subheading” means under or beneath so your subheading (or subissue) will always be placed underneath your heading. Use a heading whenever you are switching subjects and want to outline the main idea of a section and use subheadings to delineate the varying subsections underneath the main idea. Think of it like a pyramid structure, not in shape, but with your heading on the very top, subheading just beneath, and so on and so forth, going “deeper” into your research until you begin a new section. Citation styles, including APA format, utilize a system of “Levels” to distinguish the format of headings and subheadings as they move throughout your essay. The number of headings to use in a paper depends on the length and complexity of the work (APAStyle). In APA format, headings and subheadings are delineated into five possible levels: Level 1 is the highest or main level of heading, Level 2 is a subheading of Level 1, Level 3 is a subheading of Level 2, and so on through Levels 4 and 5 (APAStyle). Most students utilize Levels 1-3 for their work. If only one heading is needed for your assignment, use Level 1. If two levels are needed, use Levels 1 and 2 (and so on.) (APAStyle). The first image below provides a visualization of the APA heading format; the second image is an example of APA headings in a research paper from the field of education (APAStyle).  MLA in contrast emphasizes consistency over a specific style. Purdue Owl offers two examples of how to structure your essay using section headings and subheadings, although it is important to remember that while these can be used as a reference, they are by no means the rule . Remember, the goal is consistency throughout your paper. Note: Although MLA does not have specific style for headings within your paper, there is a general format used for the first page of your paper. See Purdue Owl for more information. Below, you can see two examples of acceptable headings for a paper that requires MLA formatting. The first follows a system of Levels, like what is used for APA format. The second example uses a format that numbers different sections and subsections. According to this example, Erosion and Terracing are examples of Soil Conservation, while Water Conservation and Energy Conservation require their own, main headings.  AccessibilityWhile the use of headings and subheadings work to enhance the readability of your work, without keeping accessibility in mind, your headings and subheadings can seem thorough and conducive to you, while being inaccessible and confusing to someone else. Check out these accessibility guidelines suggested by West Virginia University;
Note: Visit the Writing Center for additional help on how to format with accessibility in mind! Streefkerk, Raimo. “APA Headings and Subheadings | With Sample Paper.” Scribber, https://www.scribbr.com/apa-style/apa-headings/ . Accessed 18 May 2024. Our Newest Resources!
Additional Resources
 MLA Format Guide - 9th edition
How to Create a Header
An example of an MLA formatted header is included below.  How to Create a Works Cited PageYou can create your Works Cited page before, during, or after you write your essay. If you do not create it before, be sure to document the sources you used, including any website links, so you can go back and create your citations later. Citation format will be discussed in a later section, but this section will detail how to create a Works Cited Page.
 Other essay formatting notesWhen formatting your essay, there are a few things to keep in mind:
 Should you Include Headings and Subheadings in an Essay?If you have ever tried reading a large blob of text, then you know how hard it can be. However, it becomes easier to read when broken into headings and subheadings. Academic writings like essays have a standard of writing that must be upheld. While not every essay requires headings and subheadings, they are important for organizing your writing. Headings describe the succeeding section, while subheading gives supporting information for the heading. With that said, here is everything you need to know about headings What are Headings in Essays and Academic Papers?According to Merriam-Webster, a heading forms or serves as a head. In academic writing, headings represent what is to come in the assignment. Adding a heading will help structure a piece of writing and guide the reader throughout the content. Short pieces of writing don't always require headings. In long-form writing, each specific section should have its heading to communicate what the reader should expect clearly. Think of it as the title of that section. Since some points are more important than others, the heading chosen should be based on whether the idea you are talking about is the main point. Each heading chosen should tell the reader what the following idea is about. This is because the main points are the building blocks of the content. Make sure it is short, descriptive, and precise. You can include headings and subheadings/subtopics in an essay if it is long, but ensure that the subtopics or subheadings are relevant to the content and consistent throughout the text in a manner to contribute to your thesis statement. As a good practice, ensure that the essay headings and subheadings do not exceed 12 words. Subheadings are not recommended for short essays . However, they improve the overall structure of a long essay, help you frame and explore your topic, and enable the readers to know what to expect (they act as signposts in an essay or research paper). Heading vs. TitleHeadings and titles may look similar at a first glance, but they are not. A title represents the entire paper and explains it in clear and short phrases. It is the first thing the reader will see and determine whether they read the rest of the document. For this reason, you need to think of striking, informative, and appropriate titles. You should also write the title based on why you are writing that document. For instance, if the aim of the documents is tutorial, then the title should be task-based. On the other hand, a heading represents what each section of the paper discusses. They help guide the reader throughout the documents, which is why you should write effective headings, and they should be as descriptive as possible. Headings are a requirement in most forms of writing, but some lecturers may be divided about using them in academic essays, which is why you should confirm with them first. Headings Vs. SubheadingsHeadings are key parts of writing as they will capture the reader's attention and lure them into the document's purpose. They guide the reader to the main points of the paper. You have to set the headings apart from the body of the text by coming up with an enticing phrase. Subheadings, on the other hand, do more than grab the reader's attention; they show the different subsections of the text. They keep the reader engaged by quickly guiding them to the information they want. Headings and subheadings appear at the beginning of a section and organize the flow of the documents. In addition, they are both used to break down large blocks of text to make them more scannable. They also have a hierarchy that is Heading (H2) first, followed by subheadings (H3) and (H4) in that order. Subheadings should always come after the heading, as demonstrated. The Best Length for Headings in Academic WritingA heading can be as long as you want it to give the reader a snippet of the idea. A good rule of thumb should be no more than 70 characters. For higher level headings, like H1, H2, and H3s, they could be as low as one word, for instance, the introduction, methodology, and such. For such sections, the one word is clear enough for the reader to know what it represents. Low levels like H5 and below can be much longer and direct the reader to exactly what they are looking for. Levels of Heading in Academic WritingHeadings are an important part of academic writing as they act as a preview of the document. They guide the reader on what you are talking about, which is why you should assign different heading levels. There are five levels of headings in APA style. Level 1, Level 2, level 3, level 4, levels 5. Level 1 is the main heading, followed by level 2, its subheading, and level 3 is the subsection of level 2 in that order. Level 1 headings are your main headings and are usually typed in the center of the paper in title case and bolded. Their text beneath will always start in the next line, indented inward, just as you begin a new paragraph. These help the reader find their way through the document, read what they want and skip what they are not interested in. The length and complexity of the paper will determine how many levels you will use. If it's just a short piece of writing, you can use Level 1. If you need two headings, use level 1 and level 2. If it's a 2000-word article, research paper, term paper, or essay, you will need between 3 and 5 headings. Keep in mind that not every paragraph needs a heading. While headings can keep your work neat, too many can defeat the purpose. Also, make sure that each of the headings and subheadings has a connection to the main title. All these levels are differentiated by different styles and formats depending on the publication manual provided, which can be either APA or MLA format. Reasons to Use Headings in Academic WritingHeadings are helpful in academic writing for a myriad of reasons, including: Making Your Content More ReadableMuch information goes into academic writing to pass information to the reader. Putting all your information in a large block of text will be overwhelming and can scare away the readers. The white gaps at each heading section will offer a resting place hence a visual break. Therefore, separating the large chunks of text into manageable portions will keep your readers engaged. Outlining Your ContentHeadings serve as the structure of your writing. By dividing the large bulk of text with headings, you guide the reader through each section and what it is about. Otherwise, they won't know what it is about. Capturing the Reader's AttentionThe main aim of any heading is to hook the reader and create curiosity enough for them to continue reading through the rest of the article. Having a catchy and informative heading will entice them to read even further. Remember that readers rarely read documents from start to finish. Major headings should stand out but so should headings and subheadings if you want the readers to continue reading your paper. Finding Important InformationReaders will likely scan the essay to get a general idea of what it is about and decide if they want to read it. Well-structured headings will help them achieve that. Improving Overall QualityHeadings and subheadings improve the quality of the essay. A high-quality essay is suitable for readers and also for search engine optimization (SEO) if you intend to publish it online. Ensure to use keywords in the headings and structure them to improve visibility. Tips to Include Better Headings and SubheadingsWriting informative and precise headings and subheadings is vital if you want your writing to get the message home. You need to borrow the following tips to show that they should spend time reading your writing. Use the Right LengthThe length of your article or essay will determine how long your headings and subheadings should be. Put yourself in the reader's shoes and think of the heading you would like to read. Lengthy headings aren't attractive. Most readers want something short and precise, which is what you should do. It should only take them a few seconds to read, so be sure the length should be not more than 30 words. Make It Relevant to the Content and TopicHeadings and subheadings are essential to catch the reader's attention but are not important enough to stand independently. They represent the critical concepts and all the supporting ideas. Therefore, you need to consider the topic's relevance when determining what phrases to use in your subheading. Carefully think about each key piece of information you'd like to include in each of your sections. Then ensure that each subheading is connected to the main title or the heading. Be Clear and ConciseHeadings and subheadings tell the reader what the content is about. They are usually about five words long. Therefore, you should go directly to the point using clear language that is easy to understand. Most readers skim through the text before reading which is why you should use simple and straightforward words. Always remember that readers have questions and are looking for answers and shouldn't have to ponder what you are talking about. If your heading is clear and to the point, they won't leave to look for answers elsewhere. Place It in the Right PlaceConsider where your target audience is likely to look and where they are likely to appear. While doing this, also consider the kind of phrases they are likely to type for the specific information they want. This gives you a general idea of where to place headings and subheadings. Remember that the APA and MLA format requires that all headings be placed hierarchically. So as you choose your phrases, ensure that they align with the content's topic and flow. Consider the Formatting StyleHeading styles format your headings to make them stand out from the rest of the text. They also give your essay structure and make it more accessible to the target audience. In addition to this, headings also help in:
Remember that each heading is formatted with a different heading style located in the style section. Since you've already used H1 for the major heading, the first subheading will be H2, and the second subheading will be H3. Related Reading: How to indent an essay well. Number the Heading or Subheading if NeededPutting numbers on your heading makes it easy to scan. Top-level headings like H1 are numbered 1,2,3,4 while second-level headings, like H2, are numbered 1.1, 1.2, 1.3 Remember that even though you are numbering the headings, you need to introduce your topic in the first paragraph after the headings. Headings don't speak for themselves, so writing a few sentences restating the main idea will tell the reader what will come. Be Consistent Throughout the PaperIf you intend to use headings in your paper, ensure each section has a heading and subheading. Also, ensure they are consistent in font, size, color, indentation, etc. The style function in Microsoft Word will help create consistency in your headings. You must select the text you want to convert into a heading, then select the appropriate heading from the Style box. Avoid RepetitionAvoid repeating any phrases in your headings. Using the same heading more than once can affect the reader's comprehension of your message, negatively impacting their reaction to your essay. Sometimes you may repeat the headings without even noticing. For this reason, you should use the Find Function in MS Word or Google Docs. Another way you can check for repetition is by reading your essay out loud, and this will help you spot any headings or subheadings that have been repeated. Capitalize, Format, and Punctuate WellEffective headings are well capitalized, formatted, and punctuated. The APA style uses two styles for this, title case and sentence case. In the title case, major words are capitalized, while minor ones are lowercase. Sentence cases, on the other hand, only capitalize the proper nouns while the rest remain in lowercase. Use Automatic Heading in Word ProcessorMicrosoft Word has a built-in feature that anticipates how you want to format your document. As you begin typing, your text starts in the typical style, but when you press enter and move to a new line, the style changes to H1 with different fonts, colors, etc. If you are typing a paragraph with a small number of words and press enter and then fail to provide proper punctuation, the feature will assume you are moving to a new paragraph, and it will then automatically enter a new heading with a heading style. Use Descriptive HeadingsUse concrete and descriptive language to make your headings more effective so the reader can know what to expect in each section. Don't use function headings when writing your technical reports; these are not so predictable, and readers benefit from the headings being much more descriptive. Function headings are only used when writing pieces that need consistent structures, for instance, lab reports. An example is:
Include Technical Terms NeededTechnical terms should not be used in headings because they may be hard to understand except those who know the languages. Technical terms are primarily used in academic documents that professionals read but if not specified, avoid them. Related Read: How to write an article title in academic papers. Final WordsHeadings and subheadings are vital features in academic writing that represent the main points of a topic. The difference in formatting helps reader's the main points from the rest of the texts. Ensure you follow all the tips about including headings and subheadings in your text. Talk to your lecturer, professor, teacher, or instructor if you are unsure whether to add them to your essay. What are Headings in an Essay?Headings are markers that guide the reader through an essay by showing them what the next section is about. Like a title, they are only a few words long and are essential in structuring your content so as not to overwhelm the reader. Should I Put Headings in an Essay?Yes. It will help if you put headings in your essays to make them more readable. Essays consist of three parts: introduction, body, and conclusion. Most of them are written in a continuous, paragraphed text without the need for section headings, especially if it's a short essay. On the other hand, long-form essays need headings and subheadings to make them easy to write and read. Since most lecturers are divided about using them in academic essays, you should confirm with your tutor before you start writing. How Do I Include Subheadings in an Essay?Subheadings are mini headlines that come after the headings, and they help explain more about the headings and aid readers in skimming through the content. If you have used the first heading, H1, and need to provide more information about it, add a subheading, H2. If you have trouble deciding how to use subheadings correctly, think of them as an outline. Therefore, break down your topic into simple ideas, then use them to organize your essay. How Do You Make a Heading in an Essay or Academic Paper?You must think carefully about the aim of writing a paper and the main idea. Each heading should be clear and to the point. You don't want to mince words and possibly confuse the reader. Also, remember that headings are meant to enhance, not replace, the main topic. Ensure you set it apart from the body of the text by using H1 formatting in either Microsoft Word or Google Docs. Borrow some of the following best practices to write an effective heading:
How Do You Use Headings and Subheadings?Headings (section headings) are the title of your essay. They appear at the beginning of the page and guide the reader through your content. It is the first one your readers see before reading your essay or text. It doesn't matter whether the reader reads every word in your essay; they can still get the basic idea of your paper. Using different heading levels will help the reader navigate through the document. The headings and subheadings should be captivating enough to make an excellent first impression. When writing a subheading, keep in mind that the H2s are the headers of each header for the main section of the essay. H3s are the subsections of the main points in H2s. H4s, on the other hand, are detailed subheadings breaking down the text into more specific options. The subheadings amplify the title or heading of the essay, and they also complement the headings. They make your writing flow and should be relevant to the topic. With such an organization, you have achieved a first-class essay level. A good subheading captures the essence of the title and consistently informs the reader that they are still on an idea related to the topic. It is also short, descriptive, clear, and concise. Should Essays Have Section Headings?Yes. Just like books are divided into chapters, essays and articles should be divided into sections. Essays should have section headings because they help make your work more organized and easy to read. And within those sections, the text can be divided into subsections. Are There Specific Words to Use in Headings and Subheadings in Essays?You will probably be tempted to use more words to make your heading more concise, but this isn't a good idea. Make sure you carefully choose words that clearly describe your chosen topic. If possible, use numbers in your headings because they are like brain candy, making your work more interesting. Also, ensure you use odd numbers because they are more attractive to readers than even numbers, according to the Content Marketing institute . Avoid abbreviations, idioms, or colloquial expressions when writing headings and subheadings. How Many Headings to Use in an Essay or Academic Assignment?To be safe, only use a maximum of three headings. However, this will depend on the length of your academic assignments. Remember that headings are short phrases that introduce the topic you are writing about and make it easy for the readers to read through. So if you are writing a short essay of fewer than 1000 words, there is no need for headings. But for articles above 1000 words then, you must use them. Headings will help identify the different sections in an essay. What Are Heading Levels?Headings organize your essay in a hierarchical order. Since some points are more critical, assigning different levels will help distinguish them.  Gradecrest is a professional writing service that provides original model papers. We offer personalized services along with research materials for assistance purposes only. All the materials from our website should be used with proper references. See our Terms of Use Page for proper details. 
A Clear Guide to Headings in EssaysTable of Contents Whether to use headings in essay writing is a question of preference. Headings are standard for some written forms, such as report writing and case studies. But some lecturers prefer headings while others don’t want you to use headings in essays. You must confirm the preference of your lecturer. Let’s explore more about the basic structure of essays and using headings in your essay writing. Basic Structure of Academic Essay WritingThe majority of essays are written in continuous, flowing paragraphs without headings . At first glance, this could appear to be unorganized, yet good articles are meticulously structured. Essays usually have no section headings. Only the title page, author declaration, and reference list have a heading. The basic structure of essay writing contains three parts: IntroductionThe following five components make up a typical introduction:
You must organize the body of the essay into paragraphs. And each section should address a different aspect of the issue. However, it should also be connected to the ones before and after it in some way. This is a difficult task to master even for seasoned writers because there are a variety of effective ways to organize and combine paragraphs. There is no ideal or fixed template for a paragraph. The conclusion of a paper should not introduce any new idea or information. Typically, there should only be one paragraph in the conclusion. It combines all the main points of your essay, so you don’t need to repeat the small detail unless you are emphasizing anything. The conclusion is used to accomplish three things:
 Headings in Essay WritingIf you do use headings, make sure to do so correctly and sensibly. Headings help readers to be able to find the differences between different sections without drifting off. If you decide to use heading, then know that subheadings play an important role in your essay. It will not only capture the audience’s attention but also make the writing more visually catchy. The subheading gives the essay a more organized appearance while refocusing the reader on its important parts. This subheading will provide a hint of what to expect in the content. An essay can have subheadings if it is long enough to hold several sections with subtopics in each. However, subtitles must be compatible with the central theme and help to support the thesis of the essay. The recommended approach is to keep essay subheadings to 10 words. Using headings in essay writing is not a convention, but it is not incorrect either. Whether or not to incorporate headings in your essay depends on the lecturer’s preference. This article explains the basic pattern of essay writing and how to use headings in your essays.  Abir GhenaietAbir is a data analyst and researcher. Among her interests are artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing. As a humanitarian and educator, she actively supports women in tech and promotes diversity. Explore All Blog Title Generator ArticlesWhy are headings used in articles. As a writer, you should master everything about writing content. Your understanding of the profession reflects on the quality of…
How to Create a Good Title With Title ExamplesWhether you’re writing a blog or a feature article, you NEED a good title. With a good title, you can… Interesting Thesis Title Examples for Research PapersWriting a research paper can be daunting. What’s even more challenging is picking a suitable topic. Even after brainstorming, you… Best Tips for Writing a Great BlogAnyone who has read a blog post has taken in information from a thought leader who is a pro in… What Are Listicles? How to Start Them?List posts, also known as lists, have a bad reputation in the online world, where the value of your blog’s… How to Come up With Name Ideas for a Tech BlogDo you want to build a successful tech blog? Are you looking for great tech blog name ideas to come… What is a side heading on an essay?side heading is a short form consisting in a paragraph or in a sentence Add your answer:What is the proper heading?name date (for school) teacher, class assignment What are the characteristics of argumentative essay?uses facts and logic to convince an audience to side with a particular point of view Why shouldn't you use I in a essay?well it depends what kind of essay if its an expository then no yhur usin the info you used or reserched from a view . but you can use i if you were to say"according to the survey i took 10% liked orange juice". Do you need a contradictory paragraph in a persuasive essay?It is sometimes helpful to consider both sides of a question rather than just writing about one side, however, it is not mandatory. There are many different ways to write a persuasive essay. What are the two types of essay?Two types of essay are the descriptive essay and the argumentative essay. Top Categories How to Write a Salary Increase Letter (Example Included!) Negotiating your salary can be a key step in advancing your career and boosting your financial stability—but it can also be pretty intimidating. The good news is that with the right approach, it doesn’t have to be so scary. That's where a salary increase letter comes in. Whether you're asking for a raise due to your great performance, increased responsibilities, or changes in the market, a well-crafted letter asking for salary increment can be a powerful (and smooth) way to make your case. In this article, we'll walk you through everything you need to know about writing a salary increase letter, from understanding its purpose to tips on crafting an effective one. We'll also include sample letters and templates to help you get started. Plus, we’ve interviewed Muse career coach Jenn Smith , who shares her top advice on navigating this critical career move. Need a higher salary? Check out open jobs on The Muse for your next big move » What is a salary increase letter?A salary increase letter is a formal document that employees use to request a raise from their employer. Unlike a salary review letter—which is typically initiated by the employer to communicate pay adjustments—a salary increase letter is written by the employee seeking a boost in compensation. Writing a salary increase letter can be necessary for several reasons:
When writing a letter to request a salary increase, it's generally more effective to address it to your direct manager or your department’s director rather than HR. Your manager is more familiar with your work, contributions, and the value you bring to the team. They are also likely involved in budget decisions and have the authority to advocate for your raise. Is it OK to ask for a raise through a salary increase letter?Yes, writing a salary increase letter can be a formal and respectful way to request a raise. It allows you to clearly articulate your reasons, provide evidence of your achievements , and give your employer time to consider your request. Plus, a letter is a documented record of your request and can be reviewed by decision-makers at different levels of the organization. On the other hand, having an in-person conversation can be generally more effective. “This allows you to present your case dynamically, outlining your accomplishments, contributions, and the value you bring, and respond to questions or concerns in real-time,” Smith says, adding that a direct conversation also allows for immediate feedback. “Your manager can provide insights into decision-making, share any constraints or considerations, and offer guidance.” She also believes it’s a good idea to supplement your conversation with a follow-up email to ensure clarity and provide a reference for future discussions. How to write a salary increase letterThese tips will prepare you for writing an effective pay raise letter: 1. Research salary benchmarksConducting extensive research will strengthen your case and help you present a compelling argument. “Research industry salary benchmarks for your role, experience level, and geographic location,” Smiths says. “Use reliable sources like industry salary surveys, compensation reports, and online salary databases.” Additionally, be sure to understand your company's salary ranges, performance evaluation criteria, and typical raise percentages. 2. Choose the right timeTiming is crucial when it comes to writing a letter requesting pay increase. Making your request at the wrong time can significantly reduce your chances of success. “Typically, organizations have annual or semiannual performance review cycles,” Smiths says. “Discuss this with your manager before the performance review process starts so they can consider it as they begin budget conversations.” One common mistake she sees is “asking for a raise at an inappropriate time, such as during a company's financial downturn or immediately after a major organizational change or layoffs.” Avoid doing that at all costs. 3. Keep it clear and straightforwardBegin your letter by setting the context for your request and remind your employer of your role within the company. Clearly state your position, tenure with the company, and the purpose of the letter. 4. Detail your contributions and impactIn the main section of your letter, outline your accomplishments and contributions to the company. Highlight specific achievements, projects, or responsibilities that demonstrate your value. Provide evidence of your impact, such as performance metrics, positive feedback from clients or colleagues, and examples of how your work has benefited the company, explaining how your contributions justify the proposed raise. 5. Conclude with gratitude and reaffirmationSummarize your key points and reiterate your appreciation for the opportunity to discuss your compensation. Express gratitude for the support and experiences you have gained and reiterate your commitment to the company. This positive tone reinforces your professionalism and leaves a lasting impression. Salary increase request letter exampleHere’s a sample letter for salary increase request to show you how these tips can be put into practice: Alex Johnson 123 Elm Street Springfield, IL 62704 [email protected] July 25, 2024 Emma Thompson Director of Sales Innovative Tech Solutions 456 Maple Avenue Springfield, IL 62704 Dear Ms. Thompson, I hope you are well. I am writing to formally request a review of my current salary. I have thoroughly enjoyed working at Innovative Tech Solutions over the past three years and appreciate the opportunities for growth and development that have been provided to me. During my time here, I have consistently exceeded expectations and made significant contributions to the Sales team. For example, I spearheaded a new email marketing campaign that increased sales by 15% and successfully launched our new TechY product line, resulting in a 20% revenue boost. In addition to my core responsibilities, I have taken on new challenges, such as leading the training program for new sales representatives and managing key client accounts, which have significantly contributed to our team's success. I have also undertaken several professional development activities, including completing a certification in Advanced Sales Strategies and attending workshops on market trends, which have further enhanced my skills and ability to contribute to our team. Based on my research of industry standards and salary benchmarks for my role and experience level, I believe that an adjustment in my compensation is warranted. Therefore, I respectfully request a salary increase to $85,000. This adjustment would better reflect the value I bring to the team and align my compensation with industry standards. I am confident this increase will further motivate me to continue delivering high-quality work and contributing to the success of Innovative Tech Solutions. I am more than willing to discuss this request in person and provide any additional information that may be required. Thank you for considering my request and for your ongoing support. Sincerely, Alex Johnson Raise request letter templateNow, here's a template for a raise request letter to help guide you in drafting your own: [Your Name] [Your Address] [Email Address] [Date] [Recipient’s Name] [Recipient’s Title] [Company’s Name] [Company’s Address] Dear [recipient’s name], I hope you are well. I am writing to formally request a review of my current salary. I have thoroughly enjoyed working at [Company’s Name] over the past [number] years and appreciate the opportunities for growth and development that have been provided to me. During my time here, I have consistently exceeded expectations and made significant contributions to the [Department] team. For example, I [List your accomplishments, using quantifiable results whenever possible, such as increased sales by 15% through a new email marketing campaign; successfully launched a new product line, resulting in a 20% revenue increase; etc.]. In addition to my core responsibilities, I have taken on new challenges, such as [List additional responsibilities]. In addition to these accomplishments, I have undertaken several professional development activities, including [certifications, courses, and training programs], which have further enhanced my skills and ability to contribute to our team. Based on my research of industry standards and salary benchmarks for my role and experience level, I believe that an adjustment in my compensation is warranted. Therefore, I respectfully request a salary increase to [desired salary or salary range]. This adjustment would better reflect the value I bring to the team and align my compensation with industry standards. I am confident this increase will further motivate me to continue delivering high-quality work and contributing to the success of [Company Name]. I am more than willing to discuss this request in person and provide any additional information that may be required. Sincerely, [Your name] How often should I make a salary raise proposal ?Typically, you should ask for a raise once a year, ideally around your annual performance review. If you have taken on significant additional responsibilities or have had exceptional achievements, it might be appropriate to request a salary review sooner. However, be mindful of your company's financial health and the timing of your request. Should I wait for a performance review?Waiting for a performance review is often a good strategy, as this is a natural time for salary discussions. However, if you feel that your contributions have significantly outpaced your current compensation, you might consider requesting a meeting outside of the review cycle. Just ensure your request is well-timed and substantiated. What if the salary increase request is denied?If a salary review is denied, consider asking for specific feedback. “Work with your manager to set clear goals—create a development plan that outlines the steps you need to receive a raise,” Smith says. “Consider discussing alternative forms of compensation, which could include bonuses, additional vacation days, flexible working arrangements, and professional development opportunities.” Key takeawaysWhether you opt for a formal letter via email , a direct conversation, or a combination of both, the key is to present a well-reasoned case for your increased-salary request. When crafting your letter, keep these takeaways in mind:
Your browser is unsupportedWe recommend using the latest version of IE11, Edge, Chrome, Firefox or Safari. Information TechnologyUic’s voice on technology & innovation: thoughts on the integration of ai in education.  Last semester, we introduced UIC’s Voice on Technology & Innovation – a CIO-moderated talk series through which the UIC community of students, faculty and staff are invited to share their diverse experiences and perspectives on popular technology-focused topics. In this series, CIO Matt Riley reviewed input from various UIC community members, shared in this feature. UIC's Voice on Technology & Innovation Spring 2024 Prompt Heading link Copy linkHow has the integration of AI in education influenced your perspective on teaching and learning, and what specific benefits or challenges have you observed in harnessing AI tools within the educational environment? Thoughts from the UIC Community Heading link Copy link “It’s been one full school year since ChatGPT become a global phenomenon, and overall it turned out more or less as we expected in UIC’s writing courses. Some students — not as many as we feared, but maybe one or two in each first-year writing class — have obviously used ChatGPT to cheat by submitting entire essays, or portions of essays, that were written by the AI. Writing instructors knew to expect this, but maybe we ended up seeing fewer of these cases than we feared…or maybe more? I think most of us thought these cases would be harder to detect, and if there’s any silver lining, it seems like an attentive reader can fairly easily spot the odd AI-generated paper. A paper that’s largely AI-generated tends to stand out among two-dozen other drafts for its aberrant writing style and, in many cases, the inaccuracies and imprecisions it presents. Whatever generative AI’s benefits and affordances may be in producing outlines to essays, and summing up the internet discourse on any given topic, students need to realize that it’s never a good thing to submit AI-written text per se, without carefully vetting it for its factual content. Critical thinking is required in any given college course, and students’ own thought-labor in presenting ideas and connecting facts needs to guide their use of AI, not vice versa.” Mark Bennett Director, First-Year Writing Program community response 2 Heading link Copy link “The advent of AI technology in higher learning environments poses an opportunity for all of us who spend time in classrooms because it challenges how we consume and disseminate information. As a graduate student, the many features offered by AI-inclusive technology, such as the AI Assistant feature in Adobe products, means I can more easily navigate PDFs to find the information I need. Access to other technologies like ChatGPT or Copilot means I can get more specific results in searches for information online. My professional training allows me to discern the quality of the information I find and gives me a moral compass to address misuse concerns. The use of AI technology puts me front-center at the beginning of this new technological age. The last time I was this excited was in the 1990s when the internet was coming online. As a teaching assistant, however, I find the technology presents different circumstances that center on the issue of AI’s ethical use. In the last year, I noticed an increased use of AI among undergraduate students to fulfill homework assignments or more significant assessments. The lack of institutional support in the way of technology tools to address this issue, i.e., a SafeAssign-like application, has perpetuated the misuse of the technology and left classrooms as no-man-lands where anything and everything is now suspect. I honestly believe this does not have to be the case. As educators, we have an incredible opportunity to guide our students through this new age and grow our skill sets simultaneously. This is the perfect time to update syllabi, assignments, and assessments to reflect this new reality. I would argue that any time is the right time to do this, but the advent of AI created the perfect time to perform these upgrades en masse. As British propagandists communicated to their populace in times of war, we must keep calm and carry on.” Paul Ribera Graduate Student, Teaching Assistant, Instructor on Record community response 3 Heading link Copy link “Since AI was introduced into mainstream, I feel pressured to integrate it into my research. I am a 3rd year graduate student and would like to graduate within the next three years but now if I don’t have an AI component I think my resume will not be as competitive when applying for jobs.” Soraida Garcia Graduate Student “The ease of ChatGPT and other generative AI sites has made trust nearly impossible between instructors and students. As soon as instructors suspect the use of AI written submissions for assignments, there can be no trust between them and their students, even if the student did not use AI to complete an assignment. As both an advisor and an instructor for first-year seminar courses, I have seen how poorly prepared young people are to enter the academic environment. This technology has disrupted connections in classrooms and has impeded the ability for students to challenge themselves academically. In the same way most people use calculators to do simple math, these AI tools are reducing our capacity to do our own work, manage time effectively, and problem solve. I find it increasingly frustrating to hear that my co-workers are using AI to complete basic tasks like write a personal email to a student. ” Laura Kaczmarczyk Honors Academic Advisor and Program Specialist CIO Matt Riley Responds Heading link Copy link This Spring, we asked the UIC community how AI impacted teaching and learning throughout the 2023 to 2024 year. A mix of faculty and students answered the question, and some common themes emerged that I want to address.
For angst around available information on AI for the academic community, I would point to three perhaps underused opportunities that exist at UIC:
Colleges may also have their own guidance on AI. Please look for more information on GenAI in faculty and student newsletters when they arrive in Fall ’24. C2A Heading link Copy link
UIC's Voice on Technology & Innovation | Fall 2024 Prompt: Heading link Copy linkEnsuring the security of our digital environment is a shared responsibility. How can we enhance awareness and education about cybersecurity across the university community? What measures do you believe would contribute to a more secure online environment for both personal and professional use? Join the Conversation!Have a language expert improve your writingRun a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & TipsPublished on July 24, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023. An argumentative essay expresses an extended argument for a particular thesis statement . The author takes a clearly defined stance on their subject and builds up an evidence-based case for it. Instantly correct all language mistakes in your textUpload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes  Table of contentsWhen do you write an argumentative essay, approaches to argumentative essays, introducing your argument, the body: developing your argument, concluding your argument, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about argumentative essays. You might be assigned an argumentative essay as a writing exercise in high school or in a composition class. The prompt will often ask you to argue for one of two positions, and may include terms like “argue” or “argument.” It will frequently take the form of a question. The prompt may also be more open-ended in terms of the possible arguments you could make. Argumentative writing at college levelAt university, the vast majority of essays or papers you write will involve some form of argumentation. For example, both rhetorical analysis and literary analysis essays involve making arguments about texts. In this context, you won’t necessarily be told to write an argumentative essay—but making an evidence-based argument is an essential goal of most academic writing, and this should be your default approach unless you’re told otherwise. Examples of argumentative essay promptsAt a university level, all the prompts below imply an argumentative essay as the appropriate response. Your research should lead you to develop a specific position on the topic. The essay then argues for that position and aims to convince the reader by presenting your evidence, evaluation and analysis.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.An argumentative essay should be objective in its approach; your arguments should rely on logic and evidence, not on exaggeration or appeals to emotion. There are many possible approaches to argumentative essays, but there are two common models that can help you start outlining your arguments: The Toulmin model and the Rogerian model. Toulmin argumentsThe Toulmin model consists of four steps, which may be repeated as many times as necessary for the argument:
The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays. You don’t have to use these specific terms (grounds, warrants, rebuttals), but establishing a clear connection between your claims and the evidence supporting them is crucial in an argumentative essay. Say you’re making an argument about the effectiveness of workplace anti-discrimination measures. You might:
Rogerian argumentsThe Rogerian model also consists of four steps you might repeat throughout your essay:
This model builds up a clear picture of both sides of an argument and seeks a compromise. It is particularly useful when people tend to disagree strongly on the issue discussed, allowing you to approach opposing arguments in good faith. Say you want to argue that the internet has had a positive impact on education. You might:
You don’t necessarily have to pick one of these models—you may even use elements of both in different parts of your essay—but it’s worth considering them if you struggle to structure your arguments. Regardless of which approach you take, your essay should always be structured using an introduction , a body , and a conclusion . Like other academic essays, an argumentative essay begins with an introduction . The introduction serves to capture the reader’s interest, provide background information, present your thesis statement , and (in longer essays) to summarize the structure of the body. Hover over different parts of the example below to see how a typical introduction works. The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts is on the rise, and its role in learning is hotly debated. For many teachers who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its critical benefits for students and educators—as a uniquely comprehensive and accessible information source; a means of exposure to and engagement with different perspectives; and a highly flexible learning environment. The body of an argumentative essay is where you develop your arguments in detail. Here you’ll present evidence, analysis, and reasoning to convince the reader that your thesis statement is true. In the standard five-paragraph format for short essays, the body takes up three of your five paragraphs. In longer essays, it will be more paragraphs, and might be divided into sections with headings. Each paragraph covers its own topic, introduced with a topic sentence . Each of these topics must contribute to your overall argument; don’t include irrelevant information. This example paragraph takes a Rogerian approach: It first acknowledges the merits of the opposing position and then highlights problems with that position. Hover over different parts of the example to see how a body paragraph is constructed. A common frustration for teachers is students’ use of Wikipedia as a source in their writing. Its prevalence among students is not exaggerated; a survey found that the vast majority of the students surveyed used Wikipedia (Head & Eisenberg, 2010). An article in The Guardian stresses a common objection to its use: “a reliance on Wikipedia can discourage students from engaging with genuine academic writing” (Coomer, 2013). Teachers are clearly not mistaken in viewing Wikipedia usage as ubiquitous among their students; but the claim that it discourages engagement with academic sources requires further investigation. This point is treated as self-evident by many teachers, but Wikipedia itself explicitly encourages students to look into other sources. Its articles often provide references to academic publications and include warning notes where citations are missing; the site’s own guidelines for research make clear that it should be used as a starting point, emphasizing that users should always “read the references and check whether they really do support what the article says” (“Wikipedia:Researching with Wikipedia,” 2020). Indeed, for many students, Wikipedia is their first encounter with the concepts of citation and referencing. The use of Wikipedia therefore has a positive side that merits deeper consideration than it often receives. Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading servicesDiscover proofreading & editing An argumentative essay ends with a conclusion that summarizes and reflects on the arguments made in the body. No new arguments or evidence appear here, but in longer essays you may discuss the strengths and weaknesses of your argument and suggest topics for future research. In all conclusions, you should stress the relevance and importance of your argument. Hover over the following example to see the typical elements of a conclusion. The internet has had a major positive impact on the world of education; occasional pitfalls aside, its value is evident in numerous applications. The future of teaching lies in the possibilities the internet opens up for communication, research, and interactivity. As the popularity of distance learning shows, students value the flexibility and accessibility offered by digital education, and educators should fully embrace these advantages. The internet’s dangers, real and imaginary, have been documented exhaustively by skeptics, but the internet is here to stay; it is time to focus seriously on its potential for good. If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
College essays
(AI) Tools
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way. An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn’t have to make an original argument. Rather, it aims to explain something (e.g., a process or idea) in a clear, concise way. Expository essays are often shorter assignments and rely less on research. At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises). Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text. The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago . The majority of the essays written at university are some sort of argumentative essay . Unless otherwise specified, you can assume that the goal of any essay you’re asked to write is argumentative: To convince the reader of your position using evidence and reasoning. In composition classes you might be given assignments that specifically test your ability to write an argumentative essay. Look out for prompts including instructions like “argue,” “assess,” or “discuss” to see if this is the goal. Cite this Scribbr articleIf you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator. Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved August 7, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/argumentative-essay/ Is this article helpful? Jack CaulfieldOther students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, how to write an expository essay, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..". I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Advertisement Subscriber-only Newsletter Paul KrugmanMarket crashes happen. they don’t necessarily mean much..  By Paul Krugman Opinion Columnist On Oct. 19, 1987, Black Monday, stock prices plunged , with the Dow Jones industrial average falling 22.6 percent in a day. Many commentators rushed to explain what triggered the crash — a response to some political event, some piece of economic data or whatever. But the economist Robert J. Shiller managed to get a questionnaire out to many market participants as the crash was in progress and found that essentially nobody selling stocks explained their actions as a response to news. Instead, more or less the only important reason given for selling stocks was that … their prices were falling. In other words, the stock plunge looked like a panic that fed on itself. Shiller later won a Nobel Prize for his work on market irrationality — a prize he shared with Eugene Fama, who is famous for his theory that financial markets are extremely rational and efficient. Don’t let anyone tell you that the Swedes lack a sense of humor. I’m dating myself here, but I often think about Shiller’s work when markets go wild, as they have the past few days. Markets plunged Monday, although as I write this, they seem to be bouncing back; U.S. stock prices are still way up on the year and, for that matter, since President Biden took office in 2021. Anyway, everywhere I look, it seems that I see headlines to the effect that stocks plunged on fears of a U.S. recession — with this interpretation stated as a fact, not a guess or something some economists say. The truth, however, is that we don’t know why stocks fell. Concerns about a possible recession have certainly risen; I wrote about those concerns in my latest column . But what was true in 1987 was almost surely true in 2024, too: Most people selling stocks and other assets weren’t engaging in macroeconomic analysis; they were selling because prices were falling. It’s hard to be sure what triggered the sell-off, but it’s also not very important: Market panics can happen for many reasons, and what matters is how long they persist and whether they have serious side effects. We are having trouble retrieving the article content. Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings. Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times. Thank you for your patience while we verify access. Already a subscriber? Log in . Want all of The Times? Subscribe .  |
IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
At the outset, make a plan for how you will deal with matters of capitalization, formatting and sequencing of headings. Headings at the same level should be formatted the same. For instance, "Section 2.2" should get the same treatment as "Section 4.1". They should also have parallel structure.
There are five levels of heading in APA Style. Level 1 is the highest or main level of heading, Level 2 is a subheading of Level 1, Level 3 is a subheading of Level 2, and so on through Levels 4 and 5. The number of headings to use in a paper depends on the length and complexity of the work. If only one level of heading is needed, use Level 1.
Additional guidelines for APA headings. As well as the heading styles, there are some other guidelines to keep in mind: Double-space all text, including the headings. Use the same font for headings and body text (e.g., Times New Roman 12pt.). Don't label headings with numbers or letters. Don't add extra "enters" above or below headings.
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
For detailed guidance on formatting headings, including headings in the introduction of a paper, see the headings page and the headings in sample papers. Alignment: Center Level 1 headings. Left-align Level 2 and Level 3 headings. Indent Level 4 and Level 5 headings like a regular paragraph. Font: Boldface all headings. Also italicize Level 3 ...
Proper formatting of headings and subheadings is crucial in APA 7.0 style to ensure consistency, clarity, and readability in academic writing. This section will delve into the specific formatting guidelines provided by APA 7.0 for headings and subheadings, including the use of different levels, capitalization rules, and placement within the paper.
4. Hover over "Top of Page" and select "Plain Number 3". 5. For the MLA header, enter your last name along with the page number, both right-aligned. For the APA header, input the abbreviated version of the title in all capital letters and press the "Tab" key. MLA essay header example. APA essay header example.
Creating MLA Headers in Microsoft Word. If you're writing your paper in Microsoft Word, follow these steps: Click Insert. Scroll down to Page Numbers and click on it. Set the position to "Top of Page (Header)". Set the alignment to "Right". Make sure there's no checkmark in the box for "Show number on first page".
Otherwise, it would go in place of the text. Title. There needs to be a proper essay title format, centered and above the first line of the essay of the same font and size as the essay itself. Indentation. Just press tab (1/2 inch, just in case) Align. Align to the left-hand side, and make sure it is aligned evenly.
Using headings. Headings are standard for some written forms (e.g. report writing, case studies). However, lecturers can be divided about whether they allow/prefer you to use headings in your academic essays. Some lecturers prefer headings while others don't want you to use headings. You will need to check your lecturer's preference.
Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch. Use double-spaced text throughout your paper. Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point). Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section.
Definition: Headings. When writing academic essays or research papers, you should maintain a logical flow of ideas throughout the work.This is when headings as textual markers come into play. They can be found in documents, web pages, and other written materials that indicate the hierarchy, structure, and organization of content. They organize text into sections and subsections, making it ...
Incorporating headings and subheadings into your longer pieces of writing; Enhances the readability of your work by organizing the content in your essay and guiding your reader. Delineates subsections of a topic and provides an avenue to expanding on more complex ideas within a main idea. Demonstrates your understanding of a particular citation ...
Larger essays can be tricky for a reader to navigate. In this video, we will briefly explore how to help your reader to find their way around your essay by s...
When formatting your essay, there are a few things to keep in mind: Use the correct font as listed under the "Home" tab of this guide. Double-space your text, use 12 pt font, and use a legible font style, such as Times New Roman, Ariel, Calibri, etc., ensuring that the regular and italic font styles are distinct.
Revised on March 5, 2024. The first page of your MLA format paper starts with a four-line left-aligned header containing: Your full name. Your instructor's name. The course name and number. The date of submission. After the header, the title of the paper is centred on a new line, in title case. The header and title do not take any special ...
In academic writing, headings represent what is to come in the assignment. Adding a heading will help structure a piece of writing and guide the reader throughout the content. Short pieces of writing don't always require headings. In long-form writing, each specific section should have its heading to communicate what the reader should expect ...
A sub-heading is a short, descriptive sentence that provides information about the content of the section to which it is found. A sub-heading is used to distinguish the main points of an essay from one another. For example, i f you choose to write about 'Horses on a Beach' then your heading might say 'Movies and Horses on a Beach'.
Basic Structure of Academic Essay Writing. The majority of essays are written in continuous, flowing paragraphs without headings. At first glance, this could appear to be unorganized, yet good articles are meticulously structured. Essays usually have no section headings. Only the title page, author declaration, and reference list have a heading.
Best Answer. side heading is a short form consisting in a paragraph or in a sentence. Wiki User. ∙ 11y ago.
On the other hand, having an in-person conversation can be generally more effective. "This allows you to present your case dynamically, outlining your accomplishments, contributions, and the value you bring, and respond to questions or concerns in real-time," Smith says, adding that a direct conversation also allows for immediate feedback.
An essay is a focused piece of writing that explains, argues, describes, or narrates. In high school, you may have to write many different types of essays to develop your writing skills. Academic essays at college level are usually argumentative : you develop a clear thesis about your topic and make a case for your position using evidence ...
Carter Osborne started editing college admission essays to help pay for grad school in 2017. Now, his side hustle makes up to six figures per year and nearly doubles his income.
Last semester, we introduced UIC's Voice on Technology & Innovation - a CIO-moderated talk series through which the UIC community of students, faculty and staff are invited to share their diverse experiences and perspectives on popular technology-focused topics. In this series, CIO Matt Riley reviewed input from various UIC community members, shared in this feature.
OpenAI has a method to reliably detect when someone uses ChatGPT to write an essay or research paper. The company hasn't released it despite widespread concerns about students using artificial ...
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.
Markets plunged Monday, although as I write this, they seem to be bouncing back; U.S. stock prices are still way up on the year and, for that matter, since President Biden took office in 2021.