How to Do Market Research: The Complete Guide
Learn how to do market research with this step-by-step guide, complete with templates, tools and real-world examples.

Access best-in-class company data
Get trusted first-party funding data, revenue data and firmographics
Market research is the systematic process of gathering, analyzing and interpreting information about a specific market or industry.
What are your customers’ needs? How does your product compare to the competition? What are the emerging trends and opportunities in your industry? If these questions keep you up at night, it’s time to conduct market research.
Market research plays a pivotal role in your ability to stay competitive and relevant, helping you anticipate shifts in consumer behavior and industry dynamics. It involves gathering these insights using a wide range of techniques, from surveys and interviews to data analysis and observational studies.
In this guide, we’ll explore why market research is crucial, the various types of market research, the methods used in data collection, and how to effectively conduct market research to drive informed decision-making and success.
What is market research?
The purpose of market research is to offer valuable insight into the preferences and behaviors of your target audience, and anticipate shifts in market trends and the competitive landscape. This information helps you make data-driven decisions, develop effective strategies for your business, and maximize your chances of long-term growth.

Why is market research important?
By understanding the significance of market research, you can make sure you’re asking the right questions and using the process to your advantage. Some of the benefits of market research include:
- Informed decision-making: Market research provides you with the data and insights you need to make smart decisions for your business. It helps you identify opportunities, assess risks and tailor your strategies to meet the demands of the market. Without market research, decisions are often based on assumptions or guesswork, leading to costly mistakes.
- Customer-centric approach: A cornerstone of market research involves developing a deep understanding of customer needs and preferences. This gives you valuable insights into your target audience, helping you develop products, services and marketing campaigns that resonate with your customers.
- Competitive advantage: By conducting market research, you’ll gain a competitive edge. You’ll be able to identify gaps in the market, analyze competitor strengths and weaknesses, and position your business strategically. This enables you to create unique value propositions, differentiate yourself from competitors, and seize opportunities that others may overlook.
- Risk mitigation: Market research helps you anticipate market shifts and potential challenges. By identifying threats early, you can proactively adjust their strategies to mitigate risks and respond effectively to changing circumstances. This proactive approach is particularly valuable in volatile industries.
- Resource optimization: Conducting market research allows organizations to allocate their time, money and resources more efficiently. It ensures that investments are made in areas with the highest potential return on investment, reducing wasted resources and improving overall business performance.
- Adaptation to market trends: Markets evolve rapidly, driven by technological advancements, cultural shifts and changing consumer attitudes. Market research ensures that you stay ahead of these trends and adapt your offerings accordingly so you can avoid becoming obsolete.
As you can see, market research empowers businesses to make data-driven decisions, cater to customer needs, outperform competitors, mitigate risks, optimize resources and stay agile in a dynamic marketplace. These benefits make it a huge industry; the global market research services market is expected to grow from $76.37 billion in 2021 to $108.57 billion in 2026 . Now, let’s dig into the different types of market research that can help you achieve these benefits.
Types of market research
- Qualitative research
- Quantitative research
- Exploratory research
- Descriptive research
- Causal research
- Cross-sectional research
- Longitudinal research
Despite its advantages, 23% of organizations don’t have a clear market research strategy. Part of developing a strategy involves choosing the right type of market research for your business goals. The most commonly used approaches include:
1. Qualitative research
Qualitative research focuses on understanding the underlying motivations, attitudes and perceptions of individuals or groups. It is typically conducted through techniques like in-depth interviews, focus groups and content analysis — methods we’ll discuss further in the sections below. Qualitative research provides rich, nuanced insights that can inform product development, marketing strategies and brand positioning.
2. Quantitative research
Quantitative research, in contrast to qualitative research, involves the collection and analysis of numerical data, often through surveys, experiments and structured questionnaires. This approach allows for statistical analysis and the measurement of trends, making it suitable for large-scale market studies and hypothesis testing. While it’s worthwhile using a mix of qualitative and quantitative research, most businesses prioritize the latter because it is scientific, measurable and easily replicated across different experiments.
3. Exploratory research
Whether you’re conducting qualitative or quantitative research or a mix of both, exploratory research is often the first step. Its primary goal is to help you understand a market or problem so you can gain insights and identify potential issues or opportunities. This type of market research is less structured and is typically conducted through open-ended interviews, focus groups or secondary data analysis. Exploratory research is valuable when entering new markets or exploring new product ideas.
4. Descriptive research
As its name implies, descriptive research seeks to describe a market, population or phenomenon in detail. It involves collecting and summarizing data to answer questions about audience demographics and behaviors, market size, and current trends. Surveys, observational studies and content analysis are common methods used in descriptive research.
5. Causal research
Causal research aims to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables. It investigates whether changes in one variable result in changes in another. Experimental designs, A/B testing and regression analysis are common causal research methods. This sheds light on how specific marketing strategies or product changes impact consumer behavior.
6. Cross-sectional research
Cross-sectional market research involves collecting data from a sample of the population at a single point in time. It is used to analyze differences, relationships or trends among various groups within a population. Cross-sectional studies are helpful for market segmentation, identifying target audiences and assessing market trends at a specific moment.
7. Longitudinal research
Longitudinal research, in contrast to cross-sectional research, collects data from the same subjects over an extended period. This allows for the analysis of trends, changes and developments over time. Longitudinal studies are useful for tracking long-term developments in consumer preferences, brand loyalty and market dynamics.
Each type of market research has its strengths and weaknesses, and the method you choose depends on your specific research goals and the depth of understanding you’re aiming to achieve. In the following sections, we’ll delve into primary and secondary research approaches and specific research methods.
Primary vs. secondary market research
Market research of all types can be broadly categorized into two main approaches: primary research and secondary research. By understanding the differences between these approaches, you can better determine the most appropriate research method for your specific goals.
Primary market research
Primary research involves the collection of original data straight from the source. Typically, this involves communicating directly with your target audience — through surveys, interviews, focus groups and more — to gather information. Here are some key attributes of primary market research:
- Customized data: Primary research provides data that is tailored to your research needs. You design a custom research study and gather information specific to your goals.
- Up-to-date insights: Because primary research involves communicating with customers, the data you collect reflects the most current market conditions and consumer behaviors.
- Time-consuming and resource-intensive: Despite its advantages, primary research can be labor-intensive and costly, especially when dealing with large sample sizes or complex study designs. Whether you hire a market research consultant, agency or use an in-house team, primary research studies consume a large amount of resources and time.
Secondary market research
Secondary research, on the other hand, involves analyzing data that has already been compiled by third-party sources, such as online research tools, databases, news sites, industry reports and academic studies.

Here are the main characteristics of secondary market research:
- Cost-effective: Secondary research is generally more cost-effective than primary research since it doesn’t require building a research plan from scratch. You and your team can look at databases, websites and publications on an ongoing basis, without needing to design a custom experiment or hire a consultant.
- Leverages multiple sources: Data tools and software extract data from multiple places across the web, and then consolidate that information within a single platform. This means you’ll get a greater amount of data and a wider scope from secondary research.
- Quick to access: You can access a wide range of information rapidly — often in seconds — if you’re using online research tools and databases. Because of this, you can act on insights sooner, rather than taking the time to develop an experiment.
So, when should you use primary vs. secondary research? In practice, many market research projects incorporate both primary and secondary research to take advantage of the strengths of each approach.
One rule of thumb is to focus on secondary research to obtain background information, market trends or industry benchmarks. It is especially valuable for conducting preliminary research, competitor analysis, or when time and budget constraints are tight. Then, if you still have knowledge gaps or need to answer specific questions unique to your business model, use primary research to create a custom experiment.
Market research methods
- Surveys and questionnaires
- Focus groups
- Observational research
- Online research tools
- Experiments
- Content analysis
- Ethnographic research
How do primary and secondary research approaches translate into specific research methods? Let’s take a look at the different ways you can gather data:
1. Surveys and questionnaires
Surveys and questionnaires are popular methods for collecting structured data from a large number of respondents. They involve a set of predetermined questions that participants answer. Surveys can be conducted through various channels, including online tools, telephone interviews and in-person or online questionnaires. They are useful for gathering quantitative data and assessing customer demographics, opinions, preferences and needs. On average, customer surveys have a 33% response rate , so keep that in mind as you consider your sample size.
2. Interviews
Interviews are in-depth conversations with individuals or groups to gather qualitative insights. They can be structured (with predefined questions) or unstructured (with open-ended discussions). Interviews are valuable for exploring complex topics, uncovering motivations and obtaining detailed feedback.
3. Focus groups
The most common primary research methods are in-depth webcam interviews and focus groups. Focus groups are a small gathering of participants who discuss a specific topic or product under the guidance of a moderator. These discussions are valuable for primary market research because they reveal insights into consumer attitudes, perceptions and emotions. Focus groups are especially useful for idea generation, concept testing and understanding group dynamics within your target audience.
4. Observational research
Observational research involves observing and recording participant behavior in a natural setting. This method is particularly valuable when studying consumer behavior in physical spaces, such as retail stores or public places. In some types of observational research, participants are aware you’re watching them; in other cases, you discreetly watch consumers without their knowledge, as they use your product. Either way, observational research provides firsthand insights into how people interact with products or environments.
5. Online research tools
You and your team can do your own secondary market research using online tools. These tools include data prospecting platforms and databases, as well as online surveys, social media listening, web analytics and sentiment analysis platforms. They help you gather data from online sources, monitor industry trends, track competitors, understand consumer preferences and keep tabs on online behavior. We’ll talk more about choosing the right market research tools in the sections that follow.
6. Experiments
Market research experiments are controlled tests of variables to determine causal relationships. While experiments are often associated with scientific research, they are also used in market research to assess the impact of specific marketing strategies, product features, or pricing and packaging changes.
7. Content analysis
Content analysis involves the systematic examination of textual, visual or audio content to identify patterns, themes and trends. It’s commonly applied to customer reviews, social media posts and other forms of online content to analyze consumer opinions and sentiments.
8. Ethnographic research
Ethnographic research immerses researchers into the daily lives of consumers to understand their behavior and culture. This method is particularly valuable when studying niche markets or exploring the cultural context of consumer choices.
How to do market research
- Set clear objectives
- Identify your target audience
- Choose your research methods
- Use the right market research tools
- Collect data
- Analyze data
- Interpret your findings
- Identify opportunities and challenges
- Make informed business decisions
- Monitor and adapt
Now that you have gained insights into the various market research methods at your disposal, let’s delve into the practical aspects of how to conduct market research effectively. Here’s a quick step-by-step overview, from defining objectives to monitoring market shifts.
1. Set clear objectives
When you set clear and specific goals, you’re essentially creating a compass to guide your research questions and methodology. Start by precisely defining what you want to achieve. Are you launching a new product and want to understand its viability in the market? Are you evaluating customer satisfaction with a product redesign?
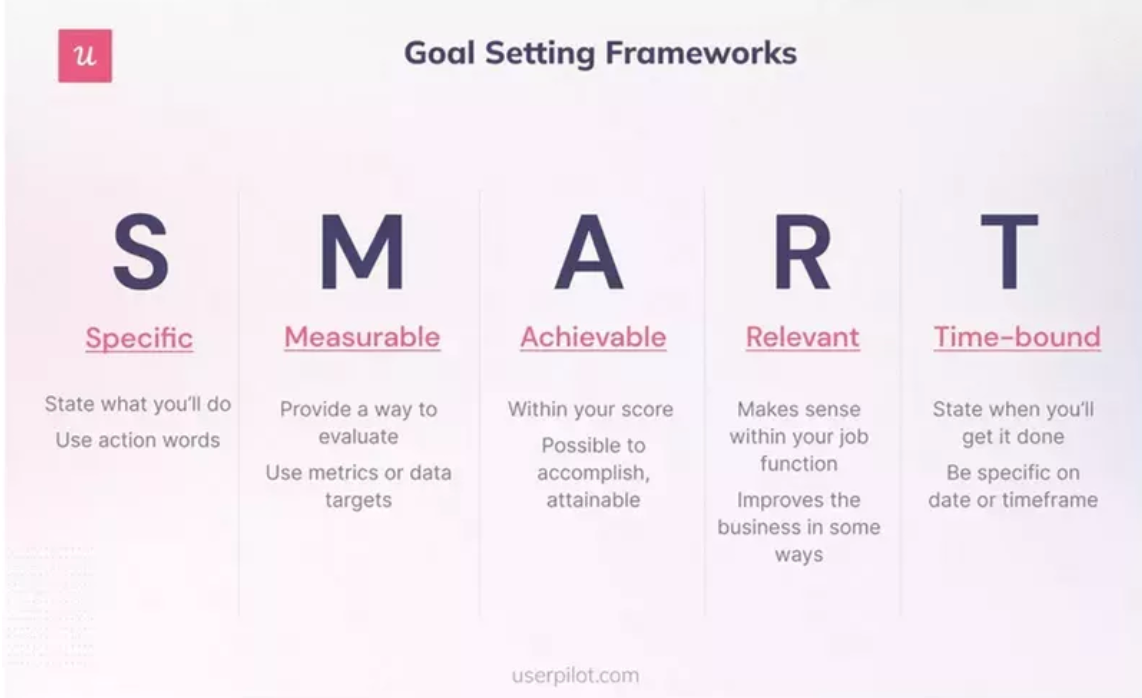
Start by creating SMART goals — objectives that are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound. Not only will this clarify your research focus from the outset, but it will also help you track progress and benchmark your success throughout the process.
You should also consult with key stakeholders and team members to ensure alignment on your research objectives before diving into data collecting. This will help you gain diverse perspectives and insights that will shape your research approach.
2. Identify your target audience
Next, you’ll need to pinpoint your target audience to determine who should be included in your research. Begin by creating detailed buyer personas or stakeholder profiles. Consider demographic factors like age, gender, income and location, but also delve into psychographics, such as interests, values and pain points.
The more specific your target audience, the more accurate and actionable your research will be. Additionally, segment your audience if your research objectives involve studying different groups, such as current customers and potential leads.
If you already have existing customers, you can also hold conversations with them to better understand your target market. From there, you can refine your buyer personas and tailor your research methods accordingly.
3. Choose your research methods
Selecting the right research methods is crucial for gathering high-quality data. Start by considering the nature of your research objectives. If you’re exploring consumer preferences, surveys and interviews can provide valuable insights. For in-depth understanding, focus groups or observational research might be suitable. Consider using a mix of quantitative and qualitative methods to gain a well-rounded perspective.
You’ll also need to consider your budget. Think about what you can realistically achieve using the time and resources available to you. If you have a fairly generous budget, you may want to try a mix of primary and secondary research approaches. If you’re doing market research for a startup , on the other hand, chances are your budget is somewhat limited. If that’s the case, try addressing your goals with secondary research tools before investing time and effort in a primary research study.
4. Use the right market research tools
Whether you’re conducting primary or secondary research, you’ll need to choose the right tools. These can help you do anything from sending surveys to customers to monitoring trends and analyzing data. Here are some examples of popular market research tools:
- Market research software: Crunchbase is a platform that provides best-in-class company data, making it valuable for market research on growing companies and industries. You can use Crunchbase to access trusted, first-party funding data, revenue data, news and firmographics, enabling you to monitor industry trends and understand customer needs.
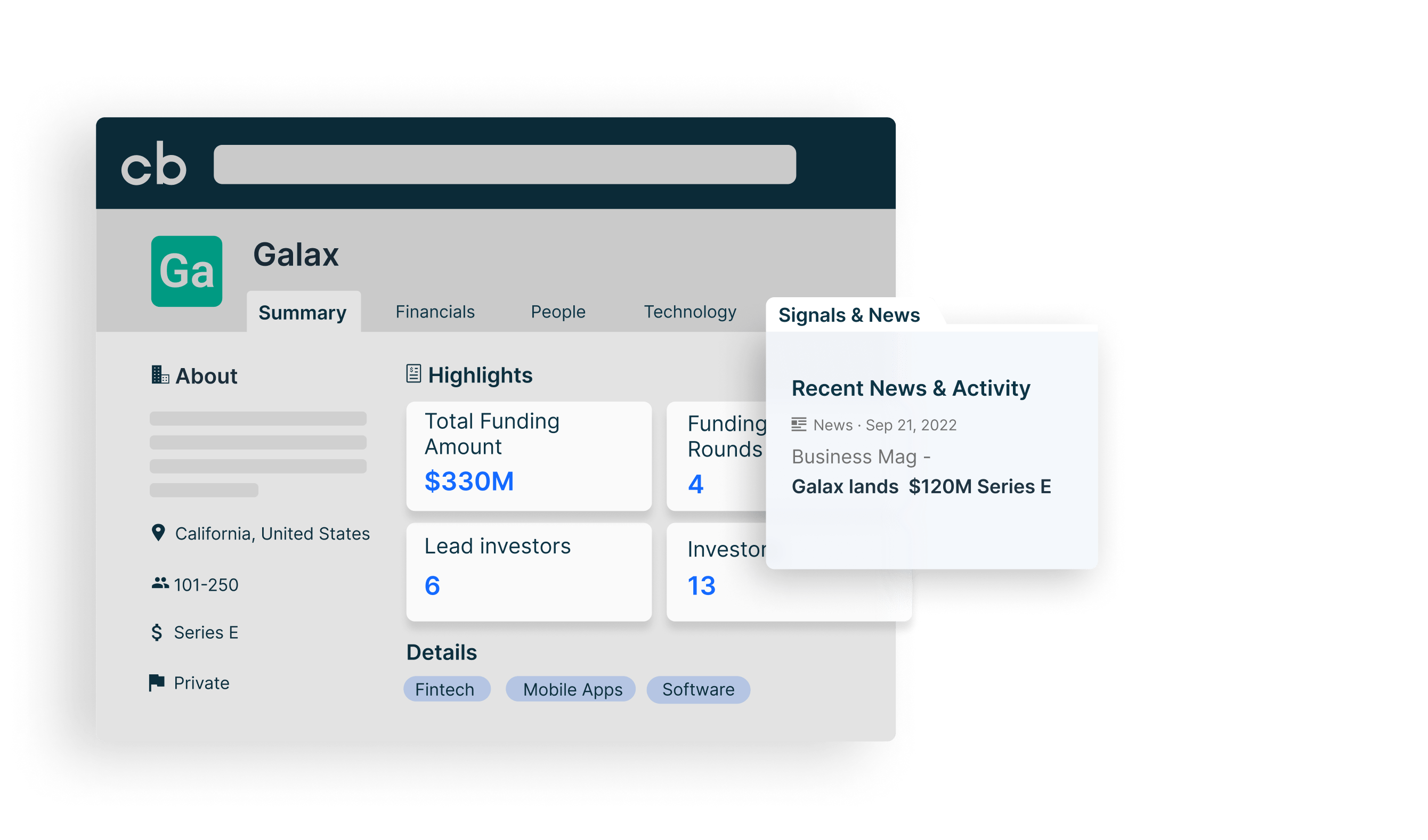
- Survey and questionnaire tools: SurveyMonkey is a widely used online survey platform that allows you to create, distribute and analyze surveys. Google Forms is a free tool that lets you create surveys and collect responses through Google Drive.
- Data analysis software: Microsoft Excel and Google Sheets are useful for conducting statistical analyses. SPSS is a powerful statistical analysis software used for data processing, analysis and reporting.
- Social listening tools: Brandwatch is a social listening and analytics platform that helps you monitor social media conversations, track sentiment and analyze trends. Mention is a media monitoring tool that allows you to track mentions of your brand, competitors and keywords across various online sources.
- Data visualization platforms: Tableau is a data visualization tool that helps you create interactive and shareable dashboards and reports. Power BI by Microsoft is a business analytics tool for creating interactive visualizations and reports.
5. Collect data
There’s an infinite amount of data you could be collecting using these tools, so you’ll need to be intentional about going after the data that aligns with your research goals. Implement your chosen research methods, whether it’s distributing surveys, conducting interviews or pulling from secondary research platforms. Pay close attention to data quality and accuracy, and stick to a standardized process to streamline data capture and reduce errors.
6. Analyze data
Once data is collected, you’ll need to analyze it systematically. Use statistical software or analysis tools to identify patterns, trends and correlations. For qualitative data, employ thematic analysis to extract common themes and insights. Visualize your findings with charts, graphs and tables to make complex data more understandable.
If you’re not proficient in data analysis, consider outsourcing or collaborating with a data analyst who can assist in processing and interpreting your data accurately.

7. Interpret your findings
Interpreting your market research findings involves understanding what the data means in the context of your objectives. Are there significant trends that uncover the answers to your initial research questions? Consider the implications of your findings on your business strategy. It’s essential to move beyond raw data and extract actionable insights that inform decision-making.
Hold a cross-functional meeting or workshop with relevant team members to collectively interpret the findings. Different perspectives can lead to more comprehensive insights and innovative solutions.
8. Identify opportunities and challenges
Use your research findings to identify potential growth opportunities and challenges within your market. What segments of your audience are underserved or overlooked? Are there emerging trends you can capitalize on? Conversely, what obstacles or competitors could hinder your progress?
Lay out this information in a clear and organized way by conducting a SWOT analysis, which stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. Jot down notes for each of these areas to provide a structured overview of gaps and hurdles in the market.
9. Make informed business decisions
Market research is only valuable if it leads to informed decisions for your company. Based on your insights, devise actionable strategies and initiatives that align with your research objectives. Whether it’s refining your product, targeting new customer segments or adjusting pricing, ensure your decisions are rooted in the data.
At this point, it’s also crucial to keep your team aligned and accountable. Create an action plan that outlines specific steps, responsibilities and timelines for implementing the recommendations derived from your research.
10. Monitor and adapt
Market research isn’t a one-time activity; it’s an ongoing process. Continuously monitor market conditions, customer behaviors and industry trends. Set up mechanisms to collect real-time data and feedback. As you gather new information, be prepared to adapt your strategies and tactics accordingly. Regularly revisiting your research ensures your business remains agile and reflects changing market dynamics and consumer preferences.
Online market research sources
As you go through the steps above, you’ll want to turn to trusted, reputable sources to gather your data. Here’s a list to get you started:
- Crunchbase: As mentioned above, Crunchbase is an online platform with an extensive dataset, allowing you to access in-depth insights on market trends, consumer behavior and competitive analysis. You can also customize your search options to tailor your research to specific industries, geographic regions or customer personas.
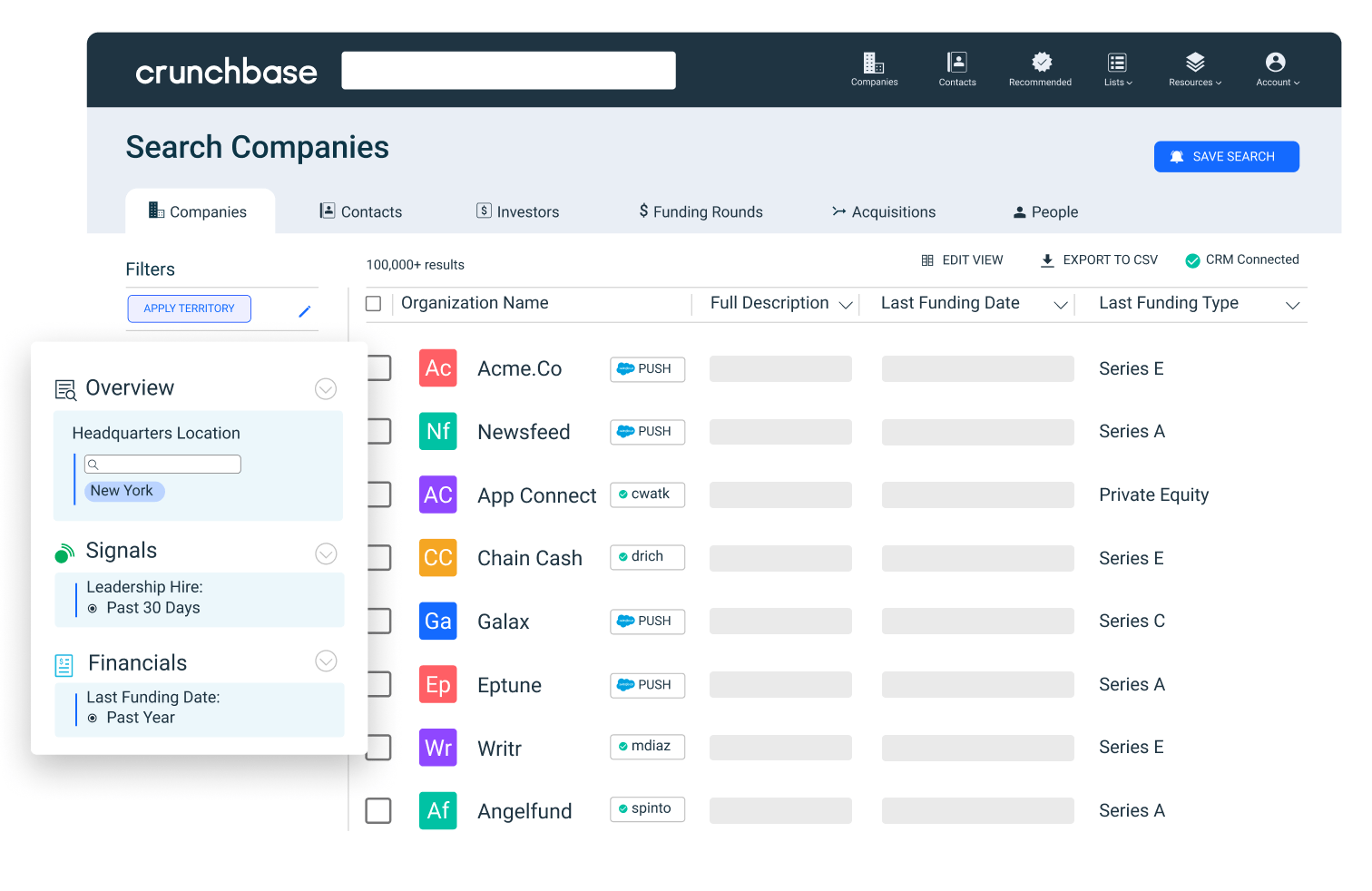
- Academic databases: Academic databases, such as ProQuest and JSTOR , are treasure troves of scholarly research papers, studies and academic journals. They offer in-depth analyses of various subjects, including market trends, consumer preferences and industry-specific insights. Researchers can access a wealth of peer-reviewed publications to gain a deeper understanding of their research topics.
- Government and NGO databases: Government agencies, nongovernmental organizations and other institutions frequently maintain databases containing valuable economic, demographic and industry-related data. These sources offer credible statistics and reports on a wide range of topics, making them essential for market researchers. Examples include the U.S. Census Bureau , the Bureau of Labor Statistics and the Pew Research Center .
- Industry reports: Industry reports and market studies are comprehensive documents prepared by research firms, industry associations and consulting companies. They provide in-depth insights into specific markets, including market size, trends, competitive analysis and consumer behavior. You can find this information by looking at relevant industry association databases; examples include the American Marketing Association and the National Retail Federation .
- Social media and online communities: Social media platforms like LinkedIn or Twitter (X) , forums such as Reddit and Quora , and review platforms such as G2 can provide real-time insights into consumer sentiment, opinions and trends.
Market research examples
At this point, you have market research tools and data sources — but how do you act on the data you gather? Let’s go over some real-world examples that illustrate the practical application of market research across various industries. These examples showcase how market research can lead to smart decision-making and successful business decisions.
Example 1: Apple’s iPhone launch
Apple ’s iconic iPhone launch in 2007 serves as a prime example of market research driving product innovation in tech. Before the iPhone’s release, Apple conducted extensive market research to understand consumer preferences, pain points and unmet needs in the mobile phone industry. This research led to the development of a touchscreen smartphone with a user-friendly interface, addressing consumer demands for a more intuitive and versatile device. The result was a revolutionary product that disrupted the market and redefined the smartphone industry.
Example 2: McDonald’s global expansion
McDonald’s successful global expansion strategy demonstrates the importance of market research when expanding into new territories. Before entering a new market, McDonald’s conducts thorough research to understand local tastes, preferences and cultural nuances. This research informs menu customization, marketing strategies and store design. For instance, in India, McDonald’s offers a menu tailored to local preferences, including vegetarian options. This market-specific approach has enabled McDonald’s to adapt and thrive in diverse global markets.
Example 3: Organic and sustainable farming
The shift toward organic and sustainable farming practices in the food industry is driven by market research that indicates increased consumer demand for healthier and environmentally friendly food options. As a result, food producers and retailers invest in sustainable sourcing and organic product lines — such as with these sustainable seafood startups — to align with this shift in consumer values.
The bottom line? Market research has multiple use cases and is a critical practice for any industry. Whether it’s launching groundbreaking products, entering new markets or responding to changing consumer preferences, you can use market research to shape successful strategies and outcomes.
Market research templates
You finally have a strong understanding of how to do market research and apply it in the real world. Before we wrap up, here are some market research templates that you can use as a starting point for your projects:
- Smartsheet competitive analysis templates : These spreadsheets can serve as a framework for gathering information about the competitive landscape and obtaining valuable lessons to apply to your business strategy.
- SurveyMonkey product survey template : Customize the questions on this survey based on what you want to learn from your target customers.
- HubSpot templates : HubSpot offers a wide range of free templates you can use for market research, business planning and more.
- SCORE templates : SCORE is a nonprofit organization that provides templates for business plans, market analysis and financial projections.
- SBA.gov : The U.S. Small Business Administration offers templates for every aspect of your business, including market research, and is particularly valuable for new startups.
Strengthen your business with market research
When conducted effectively, market research is like a guiding star. Equipped with the right tools and techniques, you can uncover valuable insights, stay competitive, foster innovation and navigate the complexities of your industry.
Throughout this guide, we’ve discussed the definition of market research, different research methods, and how to conduct it effectively. We’ve also explored various types of market research and shared practical insights and templates for getting started.
Now, it’s time to start the research process. Trust in data, listen to the market and make informed decisions that guide your company toward lasting success.
Related Articles

- Entrepreneurs
- 15 min read
What Is Competitive Analysis and How to Do It Effectively
Rebecca Strehlow, Copywriter at Crunchbase
17 Best Sales Intelligence Tools for 2024

- Market research
- 10 min read
How to Do Market Research for a Startup: Tips for Success
Jaclyn Robinson, Senior Manager of Content Marketing at Crunchbase
Search less. Close more.
Grow your revenue with Crunchbase, the all-in-one prospecting solution. Start your free trial.
How to Create a Complete Marketing Strategy in 2024 [Data + Expert Tips]
Updated: March 29, 2024
Published: October 26, 2023
Creating a marketing strategy is essential to effectively nurture your customers, improve your business’s bottom line, and increase the ROI of your efforts.

A marketing strategy is especially critical if you want to use the highest ROI trends for 2024 : short-form video and social media. To get powerful results, you must carefully weave both emerging trends and proven strategies into your plan.
Let’s dive into the critical components of a complete marketing strategy in 2024, followed by some examples for inspiration.
Table of Contents
- What is a marketing strategy?
Marketing Strategy vs. Marketing Plan
Marketing strategy components, why is a marketing strategy important, marketing strategy process, recommended resources, examples of successful marketing strategies, what to expect after following your marketing process steps, marketing strategy.
A marketing strategy covers a company’s overall approach for promoting its brand to a target audience. The process involves research, goal-setting, and positioning.
A completed marketing strategy typically includes brand objectives, target audience personas, marketing channels, key performance indicators, and more.
A marketing strategy will:
- Align your team to specific goals.
- Help you tie your efforts to business objectives.
- Allow you to identify and test what resonates with your target audience.
- Empower you to capitalize on emerging trends.
The last one is especially important. Keeping up with marketing trends is important for your strategy, but it could be a full-time job.
Why? Because almost 80% of marketers say this industry changed more in the last three years than it has in the past five decades.
Add to that the fact that 50% of marketers believe their marketing strategy in 2023 was only *somewhat effective,* which means there’s plenty of room for improvement.
In short, what worked for your marketing strategy in the past might not fly today.
A marketing strategy outlines the long-term goals and overall approach, while a marketing plan covers the specific actions and tactics to achieve those goals.
Phrased another way, marketing strategy guides the overall marketing efforts of a business. It includes goal-setting, market and competitor research, as well as messaging and positioning for a brand.
For example, say you’re creating a marketing strategy for a new fashion brand. Your strategy might target young urban professionals and position the brand as trendy and affordable.
But a marketing plan is a detailed tactical roadmap. It outlines the specific actions and tactics that should achieve the marketing strategy’s goals.
For example, the marketing plan for the fashion brand mentioned above might include:
- Targeted social media campaigns.
- Influencer partnerships.
- Online advertising timeline.
Both a marketing strategy and a marketing plan are essential for a business’s success.
To succeed in the fast-paced marketing world — and maintain a sense of relevance with your audience — it’s vital to stay ahead of the curve.
To help ease some of that uncertainty, we’re going to show you step-by-step how to create a comprehensive marketing strategy. But first, let’s go over the individual components that make up a strong marketing strategy.

Free Marketing Plan Template
Outline your company's marketing strategy in one simple, coherent plan.
- Pre-Sectioned Template
- Completely Customizable
- Example Prompts
- Professionally Designed
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
- Marketing Mix (4 Ps of Marketing)
- Marketing Objectives
- Marketing Budget
- Competitive Analysis
- Segmentation, Targeting, & Positioning
- Content Creation (Including Trending Content)
- Metrics & Key Performance Indicators
1. Marketing Mix
What is a Marketing Plan & How to Write One [+ Examples]
![marketing strategy meaning in research 6 Steps to Create an Outstanding Marketing Plan [Free Templates]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/marketingplan_20.webp)
6 Steps to Create an Outstanding Marketing Plan [Free Templates]

50 Small Business Marketing Ideas for 2024

The 2024 State of Marketing & Trends Report: Data from 1400+ Global Marketers

Mastering Social Media for Nonprofit Promotion: Insights and New Data from Experts

The AIDA Model: A Proven Framework for Converting Strangers Into Customers

Demystifying Marketing's 6 Biggest Mixed Messages of 2024 with Jasper's Head of Enterprise Marketing

The Ultimate Guide to Marketing Strategies & How to Improve Your Digital Presence

9 Pivotal Marketing Trends to Watch in 2024, According to Experts

Diving Deep Into Marketing in Construction (My Takeaways)
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
What is Marketing Research? Examples and Best Practices
12 min read

Marketing research is essentially a method utilized by companies to collect valuable information regarding their target market. Through the common practice of conducting market research, companies gather essential information that enables them to make informed decisions and develop products that resonate with consumers. It encompasses the gathering, analysis, and interpretation of data, which aids in identifying consumer demands, anticipating market trends, and staying ahead of the competition.
Exploratory research is one of the initial steps in the marketing research process. It helps businesses gain broad insights when specific information is unknown. If you are seeking insight into how marketing research can influence the trajectory of your SaaS, then you have come to the right place!
- Market research is a systematic and objective process crucial for understanding target markets, refining business strategies, and informing decisions, which includes collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data on customers, competitors, and the industry.
- Primary market research gathers specific data directly from the target audience using tools like surveys and focus groups, while secondary market research utilizes existing data from various sources to provide broader market insights.
- Effective market research combines both qualitative methods, which explore consumer motivations, and quantitative methods, which provide measurable statistics, to create comprehensive insights that guide business strategy and decision-making.
Try Userpilot and Take Your Product Marketing to the Next Level
- 14 Day Trial
- No Credit Card Required

Defining marketing research

Launching a product without knowing what your target audience wants is like walking in the dark. Market research lights the way, helping you collect, analyze, and understand information about your target market. This allows you to refine your business strategies and make decisions based on solid evidence.
Gone are the days when just intuition or subjective judgment was enough. Objective insights from market research help avoid costly mistakes and meet consumer needs by identifying trends and changes in the market. This is crucial for assessing a product’s potential success, optimizing marketing strategies, and preparing for market shifts.
Market research is a systematic approach that provides essential information, helping businesses navigate the complexities of the commercial world. Partnering with market research companies can offer additional benefits, leveraging their expertise in understanding market demands, trends, market size, economic indicators, location, market saturation, and pricing. Whether starting a new business, developing products, or updating marketing plans, understanding how to conduct effective market research is key to success.
To conduct market research effectively, businesses must determine study goals, identify target consumers, collect and analyze data, and use the findings to make informed decisions. This process is vital for evaluating past performance, measuring changes over time, and addressing specific business needs. It guides businesses in product development, marketing strategies, and overall decision-making, ensuring a better ROI and providing an eye-opening view of the market through various research methods, whether conducted in-house or outsourced.
The purpose of marketing research
Conducting marketing research is more than just gathering data; it’s about turning that data into actionable insights to refine your business strategies. This process helps you understand what motivates your customers, enabling you to tailor your products and services to minimize risks from the start. Importantly, market research plays a pivotal role in measuring and enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty, which are critical for understanding key demographics, improving user experience, designing better products, and driving customer retention. Customer satisfaction is measured as a key outcome, directly linked to the success of marketing strategies and business activities.
For SaaS product managers, market research, including competitive analysis, is crucial. It evaluates past strategies and gauges the potential success of new offerings. This research provides essential insights into brand strength, consumer behavior, and market position, which are vital for teams focused on sales, marketing, and product development.
A key aspect of market research is analyzing customer attitudes and usage. This analysis offers detailed insights into what customers want, the choices they make, and the challenges they face. It helps identify opportunities in the market and aids in formulating effective strategies for market entry.
Overall, market research equips SaaS entrepreneurs with the knowledge to meet their target audience’s needs effectively, guiding product adjustments and innovations based on informed decisions.
Key components of market research
Conducting market research is analogous to preparing a cake, requiring precise ingredients in specific quantities to achieve the intended outcome. Within this realm, necessary components consist of primary and secondary data gathering, thorough analysis, and insightful interpretation.
Primary research techniques such as exploratory studies, product evolution inquiries, estimations of market dimensions and shares, and consumer behavior examinations play a crucial role in collecting targeted information that can be directly applied. These methods afford a deeper understanding of your target demographic, allowing for customized strategy development.
In contrast, secondary research enriches the specificity of primary findings by adding wider context. It taps into external resources encompassing works from other investigators, sector-specific reports, and demographics data, which provide an expansive yet less particularized landscape view of the marketplace.
The subsequent phase involves meticulous analysis of collated data offering unbiased perspectives critical for identifying deficiencies while recognizing emerging patterns. Technological progress now facilitates examination efforts on both structured and unstructured datasets effectively addressing large-scale analytical complexities.
Ultimately, it’s through expert-led interpretation that value transcends raw figures, yielding strategies grounded in deep comprehension. Akin to decoding recipes using selected ingredients—this interpretative step enables crafting optimal business maneuvers just as one would bake their ideal confectionery creation utilizing proper culinary guidance.
Types of market research: primary and secondary
Now that you know the importance of clear research objectives, let’s explore the different types of market research and the techniques available to achieve these goals. Market research methods can be divided into two main categories: primary research and secondary research . The choice between these depends on factors like your budget, time constraints, and whether you need exploratory data or definitive answers.
Primary research involves collecting new data directly from sources. This process is like mining for precious metals, as it requires using various methods to gather fresh insights.
- Surveys (here – in-app survey templates from Userpilot ).
- Interviews.
- Focus groups.
- Product trials.
This approach gives you first-hand insight into your target audience.
Conversely, secondary research uses already established datasets of primary data – which can add depth and reinforcement to your firsthand findings.
Conducting your own market research using primary research tools can be a cost-effective strategy, allowing businesses to gather valuable insights directly and tailor their research to specific needs.
Let’s look a bit deeper into them now.
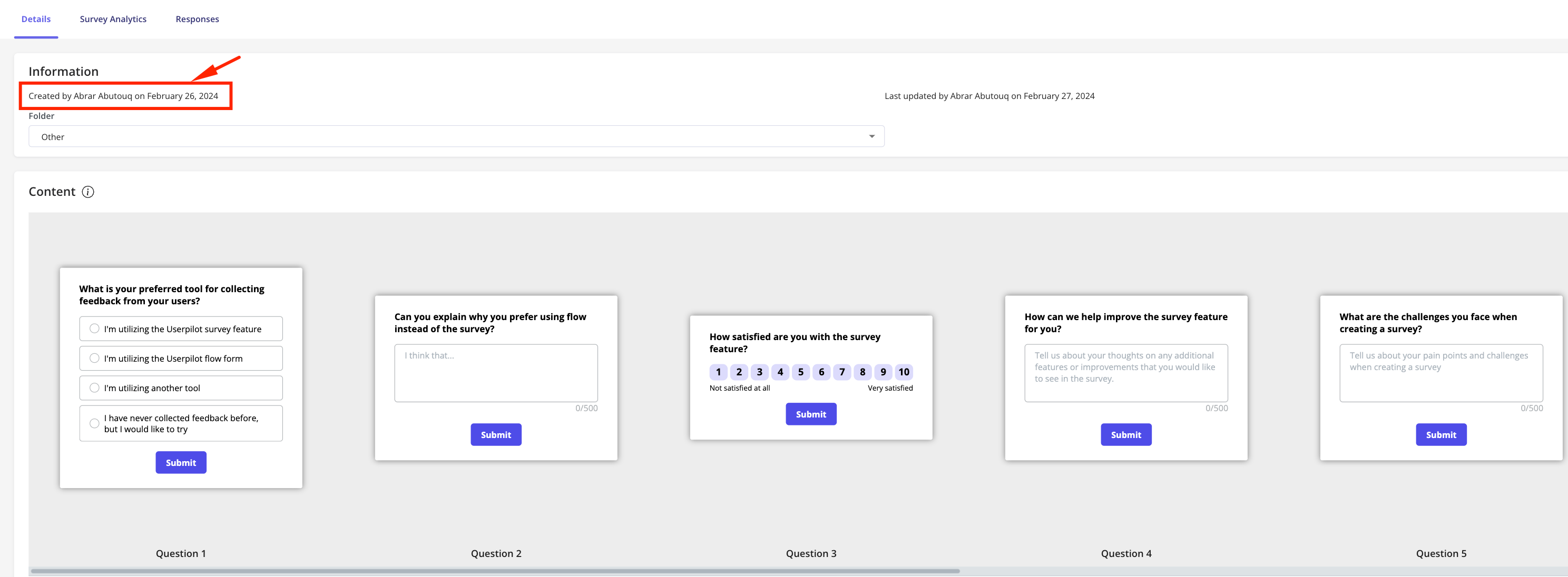
What is primary market research?
Market research uses primary market research as an essential tool. This involves collecting new data directly from your target audience using various methods, such as surveys , focus groups, and interviews.
Each method has its benefits. For example, observational studies allow you to see how consumers interact with your product.
There are many ways to conduct primary research.
Focus Groups : Hold discussions with small groups of 5 to 10 people from your target audience. These discussions can provide valuable feedback on products, perceptions of your company’s brand name, or opinions on competitors. Additionally, these discussions can help understand the characteristics, challenges, and buying habits of target customers, optimizing brand strategy.
Interviews : Have one-on-one conversations to gather detailed information from individuals in your target audience.
Surveys : These are a common tool in primary market research and can be used instead of focus groups to understand consumer attitudes. Surveys use structured questions and can reach a broad audience efficiently.
Navigating secondary market research
While marketing research using primary methods is like discovering precious metals, secondary market research technique is like using a treasure map. This approach uses data collected by others from various sources, providing a broad industry view. These sources include market analyses from agencies like Statista, historical data such as census records, and academic studies.
Secondary research provides the basic knowledge necessary for conducting primary market research goals but may lack detail on specific business questions and could also be accessible to competitors.
To make the most of secondary market research, it’s important to analyze summarized data to identify trends, rely on reputable sources for accurate data, and remain unbiased in data collection methods.
The effectiveness of secondary research depends significantly on how well the data is interpreted, ensuring that this information complements the insights from primary research.
Qualitative vs quantitative research
Market research employs both qualitative and quantitative methods, offering distinct insights that complement each other. Qualitative research aims to understand consumer behaviors and motivations through detailed analysis, while quantitative research collects measurable data for statistical analysis.
The selection of qualitative or quantitative methods should align with your research goals. If you need to uncover initial insights or explore deep consumer motivations, qualitative techniques like surveys or interviews are ideal.
On the other hand, if you need data that can be measured and analyzed for reliability, quantitative methods are more suitable.
However, these approaches don’t have to be used separately. Combining qualitative and quantitative methods in mixed-method studies allows you to capture both detailed exploratory responses and concrete numerical data. This integration offers a comprehensive view of the market, leveraging the strengths of both approaches to provide a fuller understanding of market conditions.
Implementing market research tools: Userpilot’s role
Similar to how a compass is essential for navigation at sea, businesses need appropriate instruments to carry out effective market research. Userpilot’s suite of product analytics and in-app engagement tools are critical components for this purpose.
Acting as a Buyer Persona Research instrument, Userpilot’s product analytics provide key quantitative research capabilities. This helps clearly define and comprehend the attributes and behaviors of potential customers, providing you with insights into your ICP (Ideal Customer Persona), user preferences, and product-market fit.
Beyond product analytics, Userpilot offers robust in-app engagement features such as modals and surveys that support real time collection of market research information. These interactive features work synergistically with the analytical tools to enable companies to gather detailed data and feedback crucial for informed business decision-making.
Marketing research process: Step-by-step guide
Marketing research conists of several critical stages:
- Defining precise goals.
- Delving into the knowledge of your target demographic.
- Collecting and scrutinizing data.
- Revealing insights that can be translated into tangible actions.
Following these steps allows you to gather critical information that guides business decisions.
An effective research strategy is crucial and involves:
- Properly allocating funds.
- Formulating testable hypotheses.
- Choosing appropriate methods for the study.
- Determining the number of study participants.
- Considering external variables.
A well-planned strategy ensures that your market research is focused, efficient, and produces useful outcomes.
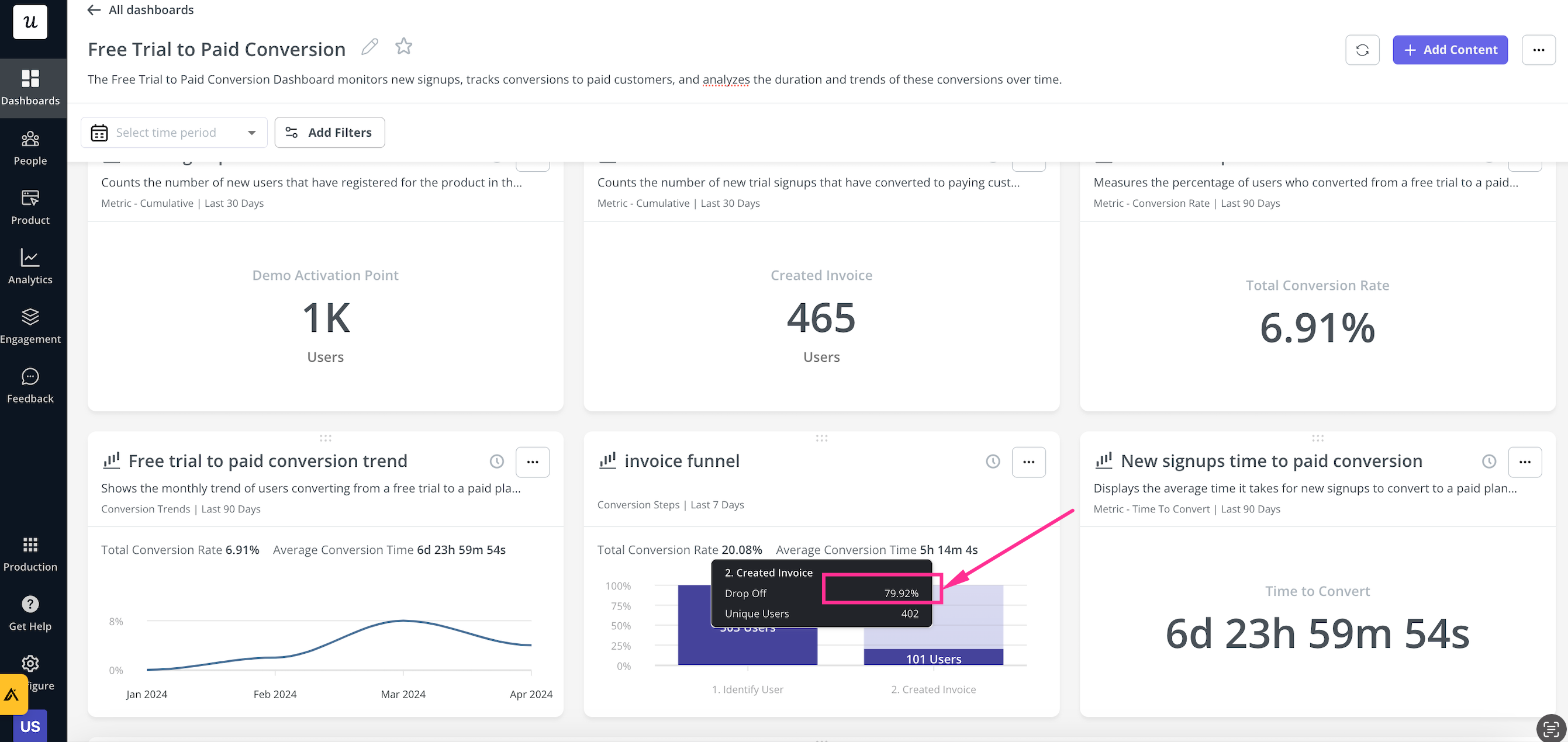
After collecting data, the next step is to analyze it. This involves comparing the data to your initial questions to draw conclusions relevant to your business strategies.
Userpilot makes your data analysis easier by providing handy analytics dashboards for key user metrics such as activation, engagement, core feature adoption, and retention out of the box:
Finally, you report the findings and the process, providing recommendations based on the evidence. This is like solving a puzzle: each piece helps to complete the overall picture.
Challenges and best practices in market research
Delving into market research comes with its own set of hurdles. Those conducting the research must deliver more profound insights within increasingly shorter timespans, and they need to cultivate strategic, continuous research methods to stay abreast of an ever-changing business landscape.
Ensuring high-quality data can be demanding due to issues such as disjointed tools or insufficient analytical expertise. New solutions like Userpilot are surfacing that make these obstacles less daunting by offering accessible and user-friendly options. Maintaining clear lines of communication with your market research team is crucial for achieving both punctuality and quality in outcomes.
The advantages of engaging in marketing research cannot be overstated.
Real-life examples of successful market research
Real-life examples of market research in the SaaS industry often showcase innovative approaches to understanding customer needs and product-market fit.
For instance, Slack, the communication platform, utilized extensive market research to identify gaps in communication tools and understand the workflows of teams. This led to the development of features that seamlessly integrated with other tools and catered to the needs of various team sizes and structures.
Another example is HubSpot, which conducted market research to understand the pain points of small to medium-sized businesses in managing customer relationships. The insights gained helped shape their all-in-one inbound marketing, sales, and service platform, which has become integral to their users’ daily operations. These examples demonstrate how SaaS companies can employ market research to inform product development, improve user experience, and strategically position themselves in a competitive market.
Choosing the right market research tools
For B2B SaaS product managers aiming to do market research, having the right set of tools can make a significant difference. Here’s a list of valuable SaaS tools that can be leveraged for effective market research:
- Userpilot : A comprehensive Product Growth Platform offering in-depth product analytics, a code-free in-app experience builder, bespoke in-app survey capabilities, and robust integration options with platforms like Salesforce and Hubspot. This tool is particularly useful for understanding user behavior, enhancing user engagement, and gathering targeted feedback.
- Qualtrics : Known for its powerful survey tools, Qualtrics helps businesses gather and analyze customer feedback effectively. Its advanced analytics features are ideal for testing market hypotheses and understanding customer sentiments.
- SurveyMonkey : A versatile tool that enables product managers to create, send, and analyze surveys quickly and easily. SurveyMonkey is suitable for gauging customer satisfaction and collecting feedback on potential new features.
- Mixpanel : Specializes in user behavior analytics, offering detailed insights into how users interact with your product. This is essential for identifying patterns and optimizing product features.
- Hotjar : Combines analytics and feedback tools to give teams insights into user behavior and preferences. Hotjar’s heatmaps and session recordings are invaluable for understanding the user experience on a deeper level.
- Tableau : A leading platform for business intelligence and data visualization, Tableau allows product managers to create comprehensive visual reports that can inform strategic decisions based on user data analysis.
Each of these tools provides unique functionalities that can assist SaaS product managers in conducting thorough market research, thereby ensuring that their products are perfectly aligned with user needs and market demands.
Measuring the impact of market research
The pivotal challenge for market research lies in demonstrating its return on investment (ROI) and overall influence on corporate success sufficiently enough to justify regular financial commitment from company leaders. The worth attributed to a market research firm hinges not only on their ability to deliver relevant and high-caliber information, but also on their pricing structures and their contribution towards propelling organizational growth.
To gauge how effectively business choices made based on market research findings succeed, various metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) are utilized. These numerical tools act as navigational aids directing enterprises toward achieving objectives while simultaneously verifying that efforts invested in conducting market analysis are yielding fruitful guidance.
Throughout our look at market research, we’ve seen its importance and impact. Our discussion covered the basics of market research, its key components, and different types, including both qualitative and quantitative methods, and the role of Userpilot’s tools. We’ve examined the details of the market research process, tackled challenges, identified best practices, and shared success stories. We also provided advice on choosing the right market research partner and how to measure the effectiveness of your market research.
In today’s data-driven world, comprehensive market research is crucial for companies that want to succeed. It acts like a guide, helping businesses navigate the complex market landscape. Start your own detailed research today, supported by insightful analytics to help you succeed.
Frequently asked questions
What is market research and why is it important.
Understanding your target market, honing business strategies, and making informed decisions are all essential components that depend heavily on effective market research. It offers objective insights to help avoid expensive errors and foresees the needs of customers .
What is the difference between primary and secondary market research?
Primary market research is characterized by the direct gathering of data, in contrast to secondary market research which leverages existing information from alternative sources for addressing research inquiries.
Such a distinction can guide you in selecting an approach that aligns with your precise needs for conducting specific research.
What are some examples of successful market research?
Examples of successful market research are evident in the operations of well-known companies such as Starbucks, Apple, and McDonald’s. They have harnessed this tool to fine-tune their business strategies and make decisions based on solid information.
By employing market research, these businesses have managed to gain insight into their customers’ desires and needs, which has contributed significantly to their success.
How can I choose the right market research partner?
Selecting an ideal market research ally involves identifying a firm that resonates with your project requirements, financial plan, and corporate goals while also verifying their track record of dependability and consistency via reviews from previous clients.
Best wishes on your endeavor!
How is the impact of market research measured?
The effectiveness of market research hinges on the precision, representativeness, and pertinence of its data, along with how successful business decisions are when they’re based on the findings from this research. These elements define the impact of the research conducted.
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Get The Insights!
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth,Management & Trends.
The coolest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends. Delivered fresh to your inbox, weekly.
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends.
You might also be interested in ...
Product marketing messaging framework: key elements & examples, product marketing strategy: definition, steps, and examples.
Aazar Ali Shad
16 Best Product Marketing Campaigns To Inspire Your Own

Strategy Studies
What is marketing strategy.
Home > Back
Specialties

In today’s fast-paced and competitive business world, having a clear and effective marketing strategy is essential for success. But what exactly is a marketing strategy, and why is it so important? In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the ins and outs of marketing strategy, from its basics to its execution, success stories, common mistakes to avoid, and what the future holds for this critical aspect of business.
Table of Contents
The Basics of Marketing Strategy
Understanding the concept of marketing.
Marketing is the process of promoting and selling products or services to a target audience. It involves various activities such as advertising, market research, product development, and customer engagement. Marketing strategy is the carefully planned approach that guides these activities to achieve specific business goals.
The role of strategy in marketing
A marketing strategy acts as a roadmap, outlining the steps a business needs to take to reach its objectives. It provides a clear direction, ensuring that marketing efforts are aligned with the overall business plan. Without a well-defined strategy, marketing can be unfocused and ineffective.
Components of a Marketing Strategy
Target audience identification.
One of the first steps in creating a marketing strategy is identifying your target audience. Who are your ideal customers? What are their needs, preferences, and behaviors? Understanding your audience is crucial for crafting messages that resonate.
Market research and analysis
Thorough market research is the foundation of a successful strategy. It involves studying your industry, competitors, and trends to make informed decisions. Market analysis helps you identify opportunities and threats.
Setting clear objectives
What do you want to achieve with your marketing efforts? Whether it’s increasing brand awareness, boosting sales, or expanding into new markets, setting clear objectives helps measure success.
Competitive analysis
Understanding your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses can help you differentiate your business. Analyze their marketing strategies to find opportunities for improvement.
Positioning and differentiation
What sets your business apart from the competition? Effective positioning and differentiation are key components of a marketing strategy. Highlight your unique selling proposition (USP) to attract customers.
Budget allocation
Allocate your marketing budget wisely. Consider the cost of various marketing channels, such as digital advertising, content marketing, or social media campaigns, and allocate resources accordingly.
Types of Marketing Strategies
Digital marketing.
Digital marketing leverages online channels like websites, social media, email, and search engines to reach customers. It’s a versatile strategy with numerous tools and tactics.
Content marketing
Content marketing involves creating and sharing valuable content to attract and engage your target audience. It’s an effective way to build brand authority and trust.
Social media marketing
Social media platforms are powerful tools for reaching a wide audience. Effective social media marketing involves consistent content sharing and engagement with followers.
Influencer marketing
Collaborating with influencers can expand your reach and credibility. Choose influencers whose values align with your brand.
Traditional marketing
Traditional marketing methods like print ads, TV commercials, and direct mail still have their place, depending on your target audience.
Guerrilla marketing
This unconventional strategy relies on creativity and imagination to capture attention. It’s often low-cost and highly memorable.
Creating an Effective Marketing Strategy
Defining your unique selling proposition (usp).
Your USP is what makes your business special. It’s the reason customers should choose you over competitors. Clearly define and communicate your USP in your marketing strategy.
Crafting a compelling value proposition
Your value proposition explains the benefits customers will receive from your product or service. It should resonate with your target audience and address their pain points.
Selecting the right marketing channels
Choose the channels that align with your target audience’s preferences. For instance, if your audience is young and tech-savvy, prioritize digital marketing.
Setting a budget and timeline
Allocate resources according to your strategy’s priorities. A budget and timeline keep your marketing efforts on track.
Executing and Monitoring the Strategy
Implementation of the strategy.
Once your strategy is in place, it’s time to put it into action. Ensure all team members understand their roles and responsibilities.
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
Establish KPIs to measure the success of your strategy. These could include website traffic, conversion rates, social media engagement, or sales figures.
Continuous monitoring and adjustment
The business landscape is ever-changing. Regularly assess your strategy’s performance and adjust it as needed to stay competitive.
Success Stories: Companies with Effective Marketing Strategies
Apple’s marketing strategy revolves around innovation, simplicity, and creating a strong emotional connection with its customers. Their product launches are highly anticipated events, showcasing the power of effective marketing.
Nike’s “Just Do It” slogan has become iconic. They’ve successfully built a brand that stands for inspiration, motivation, and athletic excellence through their marketing efforts.
Coca-Cola’s timeless branding and memorable advertising campaigns have made it one of the most recognized brands globally. Their marketing strategies focus on building an emotional connection with consumers.
Common Mistakes in Marketing Strategy
Lack of target audience clarity.
Not understanding your audience can lead to wasted resources and missed opportunities.
Neglecting market research
Skipping market research can result in poor decision-making and ineffective campaigns.
Ignoring competitors
Failing to analyze competitors can lead to being outmaneuvered in the market.

Overlooking digital opportunities
In today’s digital age, neglecting online channels can be a major oversight.
Not adapting to changing market dynamics
A rigid strategy that doesn’t adjust to market changes can hinder growth.
The Future of Marketing Strategy
Trends in marketing.
Marketing is evolving with new trends like personalized marketing, video content, and AI-driven automation.
Impact of technology and data
Advances in technology and access to data are shaping the way businesses connect with customers.
In conclusion, a well-crafted marketing strategy is the backbone of a successful business. It guides your efforts, helps you stand out in a crowded market, and drives growth. Whether you’re a small startup or a global corporation, investing in a robust marketing strategy is a key step toward achieving your business goals.
Get the Strategies
Get the latest posts delivered to your inbox for free.
Ian has marketed for some of the world's best-known brands like Hewlett-Packard, Ryder, Force Factor, and CIT Bank. His content has been downloaded 50,000+ times and viewed by over 90% of the Fortune 500. His marketing has been featured in Forbes, Inc. Magazine, Adweek, Business Insider, Seeking Alpha, Tech Crunch, Y Combinator, and Lifehacker. With over 10 startups under his belt, Ian's been described as a serial entrepreneur— a badge he wears with pride. Ian's a published author and musician and when he's not obsessively testing the next marketing idea, he can be found hanging out with family and friends north of Boston.
Subscribe to Forward Weekly
Related posts.

The Ultimate Guide to Twitter Marketing

How to Create a Winning Facebook Marketing Strategy

The Complete Guide to Instagram Marketing

The Ultimate Guide to Social Media Advertising
Leave a Reply
Get The Marketing Strategies in Your Inbox
Sign up for our 1x a week newsletter (no spam!)
Popular Posts

Get the Guide
You'll learn how to:
- Generate more demand for your product or service
- What channels to start with at first
- Strategies to maximize your lead generation
- And so much more!

Houston, we have a problem... you need to login first!
| | |
Register For This Site
A password will be e-mailed to you.
Get In-Depth Marketing Strategies
Sign up to get in-depth marketing strategies, tactics, and case studies delivered right to your inbox.
100% privacy. We will never spam you!
Copyright @ MarketingStrategy.com 2024. All Right Reserved.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case AskWhy Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Marketing research: Definition, steps, uses & advantages
What is marketing research?
Marketing research is defined as any technique or a set of practices that companies use to collect information to understand their target market better. Organizations use this data to improve their products, enhance their UX, and offer a better product to their customers. Marketing research is used to determine what the customers want, and how they react to products or features of a product.
Gather research insights
Four standard marketing research methods
The four most common marketing research methods are surveys, interviews, customer observations, and focus groups. You can research various ways without limiting yourself to just one way. Let’s dive deeper into each of these marketing research techniques.
Researchers collect responses by deploying surveys and managing data via online questionnaires or on-screen surveys at the POS. These surveys contain closed-ended and open-ended questions. They are popular and are the most widely used research techniques.
Why are online surveys popular?
Surveys are inexpensive, simple to set-up, deploy, and gather responses. It gets easy to collect multiple answers from a tailored audience group using surveys. Researchers rely on quantitative data, and online surveys provide quick responses compared to the more traditional offline methods. You can collect large amounts of data within minutes from anywhere in the world.
2. Interviews
Face-to-face or personal interviews are a more traditional way of doing marketing research. It is a slow and more expensive way of collecting responses. Researchers doing large scale marketing research do not prefer this method to collect a large number of responses. Interviews are conducted both in-person and on the telephone (CATI).
Why are interviews important?
Personal interviews may not be widely used but play a significant role in understanding precisely what the respondent feels. You can record more than just verbal responses and understand the customer better. Often, when two humans interact with each other, more information is shared because of the dialogue. Personal interviews are useful in small-scale studies, where the researcher wants to interview a specific group of local respondents. CATI’s are helpful when the respondent base is more expansive.
3. Focus groups
Focus groups or online focus groups involve several respondents who participate in discussions about a particular topic. A researcher conducts focus groups to obtain richer information. The main reason for a focus group is to hold a dialogue between various people on a particular topic of interest. Unlike interviews, focus group members are allowed to interact with each other and influence one another.
Why are focus groups impactful?
It is no secret that focus groups are hugely impactful in decision making. Researchers gain a lot of information by organizing focus groups. Often, focus groups bring up issues not foreseen by researchers. Online or video focus groups have a broad reach, and many organizations have now started creating and nurturing research communities for better respondent handling and data gathering. Direct interaction of business groups and customers positively impacts users because they feel that their voices are heard.
4. Observation
Observation, though not popular and widely used, gives intuitive feedback. Research companies organize customer observation sessions to gather information on how they engage with the product or service (or a similar competitor product or service). Feedback from people’s behavioral attitudes is a powerful tool for researchers looking to improve their products and services.
What makes observation so powerful?
Observational market research is an excellent alternative to focus groups. It’s not only an inexpensive research tool, but you will also witness people interacting with and using your product in a natural environment. The downside is that you will have to make inferences about their feelings and reactions.
LEARN ABOUT: market research trends
How to conduct marketing research
Follow these four marketing research steps to help you understand what your users think and feel about your product, service, or business.
LEARN ABOUT: Behavioral Research
1. Create simple user personas
A user persona is nothing more than a fictional character that represents a user or a customer. Understanding user personas will help you gauge how different persons react to other products and services to understand their needs. To create a persona, your questions must answer these types questions about the user or customer:
- Who are they?
- What’s their primary goal?
- What stops them from achieving that goal?
2. Conduct observational research
Use both overt and covert observation methods to observe and take notes while users use your products or a similar one.
Overt vs. covert observation
- Overt observation asks users if they will allow you to watch them use your product.
- Covert observation studies users in a natural environment without them knowing. This type of observation generally works only if you sell a product that consumers buy and use regularly. It brings in the purest observational research data as people act naturally while using the products.
3. Conduct personal interviews
One-on-one conversations with your target population allow you to explore and dig deep into their concerns, revealing answers to many questions. Here are a few tips for conducting personal interviews.
- Be a journalist and not a salesperson. Ask users about their frustrations, needs, and areas where they think they need an improvement in the product.
- Pose the ‘why’ question to dig deeper. Dive into the details to know more about their past behavior.
- Recording the conversation helps you focus on it rather than take notes simultaneously.
4. Analyze the data
The idea of conducting lean marketing research is to receive quick, actionable insight data. Analyze the information you have collected using various techniques to draw patterns into what customers like and dislike, what they want, and what they do not need. Create a simple visual representation of how people will interact with each other and the product to assess their needs in a better way.
LEARN ABOUT: Marketing Insight
Why is research so valuable?
Without research, it is impossible to gauge and understand your customers. Of course, you will have an idea of what they need and who they are and, but you must dive deeper to win their loyalty. Here is why marketing research matters:

- Attract potential customers: The primary aim of marketing research is to find ways to attract potential customers. It also helps to keep current happy and coming back for more. Understanding your customers entirely is the only way to progress. You’ll lose potential customers if you stop caring about improving your user experience.
- Answer the why’s: Marketing research gives you the answer to the ‘why.’ Make use of user analytics, big data, and reporting dashboards in marketing research to tell you what your users are thinking and why they think and act that way. For example, only marketing research can explain why customers leave you.
- Data-backed decisions: Research beats trends, assumptions, and so-called best business practices. Bad decisions are often taken due to emotional reasoning and guesswork. Focusing on customer experience by listening to your customers directs you in the right direction.
- Better planning: Research keeps you from making absurd decisions by planning in a vacuum. You might not fully gauge what your customers experience and feel while using your product. Customers may use products in a way that surprises you, and they may get confused by features that seem obvious to you. Conducting too much planning but not testing your assumptions will waste your money, time, efforts, and resources. Research helps you save up on all these factors.
LEARN ABOUT: 12 Best Tools for Researchers
Advantages of MKT research
Marketing research and user experience (UX) design help you continuously improve your product by acting on your feedback. Here are the advantages of conducting marketing research:
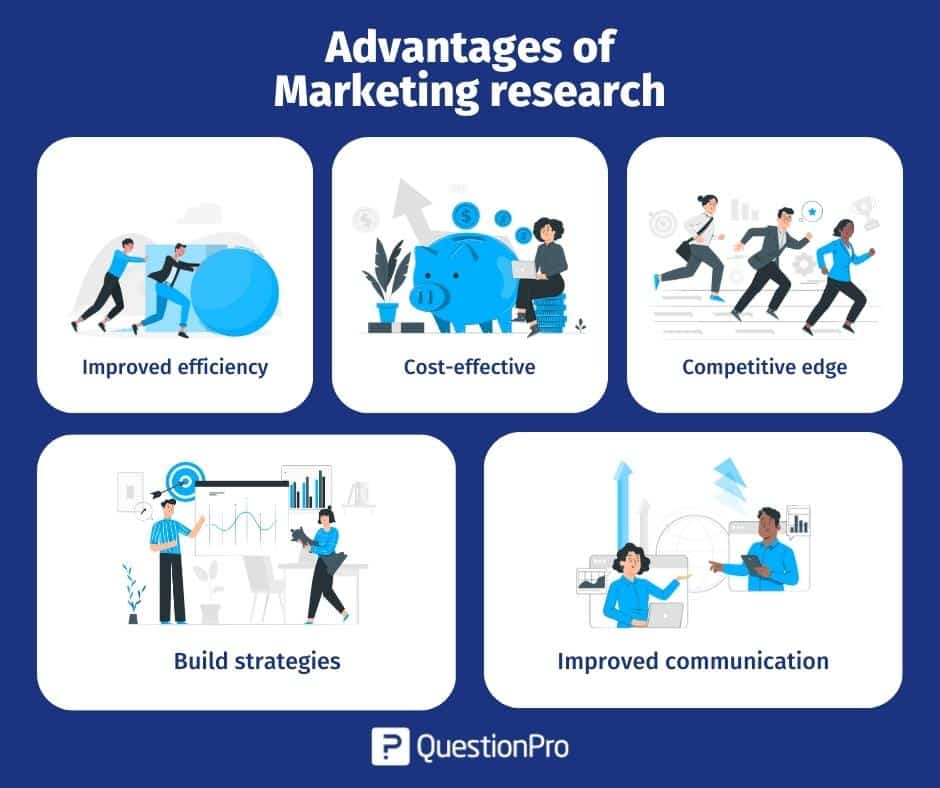
- Improved efficiency: Efficiency draws you closer to your users. You can improve the efficiency of delivering the product to the market and also increase its usability.
- Cost-effective: Marketing research helps you make the right decisions based on consumer demand, thus saving you costs in creating something that customers do not like or want.
LEARN ABOUT: Test Market Demand
- Competitive edge: Quicker, more robust insights can help you place your services and products strategically, gaining a competitive advantage over others.
- Build strategies: You can quickly build, alter, or design new approaches to attract your users and consumers.
- Improved communication: Bridge the communication gap by interacting with consumers and hearing them out. This helps consumers feel wanted and special.
- LEARN ABOUT: Market research vs marketing research
MORE LIKE THIS
Jotform vs SurveyMonkey: Which Is Best in 2024
Aug 15, 2024

360 Degree Feedback Spider Chart is Back!
Aug 14, 2024

Jotform vs Wufoo: Comparison of Features and Prices
Aug 13, 2024

Product or Service: Which is More Important? — Tuesday CX Thoughts
Other categories.
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Social media marketing strategy: definition, conceptualization, taxonomy, validation, and future agenda
- Conceptual/Theoretical Paper
- Open access
- Published: 10 June 2020
- Volume 49 , pages 51–70, ( 2021 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Fangfang Li ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4883-1730 1 ,
- Jorma Larimo 1 &
- Leonidas C. Leonidou 2
341k Accesses
266 Citations
30 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Although social media use is gaining increasing importance as a component of firms’ portfolio of strategies, scant research has systematically consolidated and extended knowledge on social media marketing strategies (SMMSs). To fill this research gap, we first define SMMS, using social media and marketing strategy dimensions. This is followed by a conceptualization of the developmental process of SMMSs, which comprises four major components, namely drivers, inputs, throughputs, and outputs. Next, we propose a taxonomy that classifies SMMSs into four types according to their strategic maturity level: social commerce strategy, social content strategy, social monitoring strategy, and social CRM strategy. We subsequently validate this taxonomy of SMMSs using information derived from prior empirical studies, as well with data collected from in-depth interviews and a quantitive survey among social media marketing managers. Finally, we suggest fruitful directions for future research based on input received from scholars specializing in the field.
Similar content being viewed by others

A Measurement Construct for Social Media: The SM Value Chain—An Abstract

The Social Media Monitoring Process and its Role in Social Media Strategy Development

A Systematic Review of Extant Literature in Social Media in the Marketing Perspective
Explore related subjects.
- Artificial Intelligence
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
The past decade has witnessed the development of complex, multifarious, and intensified interactions between firms and their customers through social media usage. On the one hand, firms are taking advantage of social media platforms to expand geographic reach to buyers (Gao et al. 2018 ), bolster brand evaluations (Naylor et al. 2012 ), and build closer connections with customers (Rapp et al. 2013 ). On the other hand, customers are increasingly empowered by social media and taking control of the marketing communication process, and they are becoming creators, collaborators, and commentators of messages (Hamilton et al. 2016 ). As the role of social media has gradually evolved from a single marketing tool to that of a marketing intelligence source (in which firms can observe, analyze, and predict customer behaviors), it has become increasingly imperative for marketers to strategically use and leverage social media to achieve competitive advantage and superior performance (Lamberton and Stephen 2016 ).
Despite widespread understanding among marketers of the need to engage customers on social media platforms, relatively few firms have properly strategized their social media appearance and involvement (Choi and Thoeni 2016 ; Griffiths and Mclean 2015 ). Rather, for most companies, the ongoing challenge is not to initiate social media campaigns, but to combine social media with their marketing strategy to engage customers in order to build valuable and long-term relationships with them (Lamberton and Stephen 2016 ; Schultz and Peltier 2013 ). However, despite the vast opportunities social media offer to companies, there is no clear definition or comprehensive framework to guide the integration of social media with marketing strategies, to gain a rigorous understanding of the nature and role of social media marketing strategies (SMMSs) (Effing and Spil 2016 ).
Although some reviews focusing on the social media phenomenon are available (e.g., Lamberton and Stephen 2016 ; Salo 2017 ), to date, an integrative evaluation effort focusing on the strategic marketing perspective of social media is missing. This is partly because the social media literature largely derives elements from widely disparate fields, such as marketing, management, consumer psychology, and computer science (Aral et al. 2013 ). Moreover, research on SMMSs mainly covers very specific, isolated, and scattered aspects, which creates confusion and limits understanding of the subject (Lamberton and Stephen 2016 ). Furthermore, research deals only tangentially with a conceptualization, operationalization, and categorization of SMMSs, which limits theory advancement and practice development (Tafesse and Wien 2018 ).
To address these problems, and also to respond to repeated pleas from scholars in the field (e.g., Aral et al. 2013 ; Guesalaga 2016 ; Moorman and Day 2016 ; Schultz and Peltier 2013 to identify appropriate strategies to leverage social media in today’s changing marketing landscape, we aim to systematically consolidate and extend the knowledge accumulated from previous research on SMMSs. Specifically, our objectives are fivefold: (1) to clearly define SMMS by blending issues derived from the social media and marketing strategy literature streams; (2) to conceptualize the process of developing SMMSs and provide a theoretical understanding of its constituent parts; (3) to provide a taxonomy of SMMSs according to their level of strategic maturity; (4) to validate the practical value of this taxonomy using information derived from previous empirical studies, as well as from primary data collection among social media marketing managers; and (5) to develop an agenda for promising areas of future research on the subject.
Our study makes three major contributions to the social media marketing literature. First, it offers a definition and a conceptualization of SMMS that help alleviate definitional deficiency and increase conceptual clarity on the subject. By focusing on the role of social connectedness and interactions in resource integration, we stress the importance of transforming social media interactions and networks into marketing resources to help achieve specific strategic goals for the firm. In this regard, we provide theoretical justification of social media from a strategic marketing perspective. Second, using customer engagement as an overarching theory, we develop a model conceptualizing the SMMS developmental process. Through an analysis of each component of this process, we emphasize the role of insights from both firms and customers to better understand the dynamics of SMMS formulation. We also suggest certain theories to specifically explain the particular role played by each of these components in developing sound SMMSs. Third, we propose a taxonomy of SMMSs based on their level of strategic maturity that can serve as the basis for developing specific marketing strategy concepts and measurement scales within a social media context. We also expect this taxonomy to provide social media marketing practitioners with fruitful insights on why to select and how to use a particular SMMS in order to achieve superior marketing results.
Defining SMMS
Although researchers have often used the term “social media marketing strategy” in their studies (e.g., Choi and Thoeni 2016 ; Kumar et al. 2013 ; Zhang et al. 2017 ), they have yet to propose a clear definition. Despite the introduction of several close terms in the past, including “social media strategy” (Aral et al. 2013 ; Effing and Spil 2016 ), “online marketing strategy” (Micu et al. 2017 ), and “strategic social media marketing” (Felix et al. 2017 ), these either fail to take into consideration the different functions/features of social media or neglect key marketing strategy issues. What is therefore required is an all-encompassing definition of SMMS that will capture two fundamental elements—namely, social media and marketing strategy. Table 1 draws a comparison between social media and marketing strategy on five dimensions (i.e., core, orientation, resource, purpose, and premise) and presents the resulting profile of SMMS.
- Social media
In a marketing context, social media are considered platforms on which people build networks and share information and/or sentiments (Kaplan and Haenlein 2010 ). With their distinctive nature of being “dynamic, interconnected, egalitarian, and interactive organisms” (Peters et al. 2013 , p. 281), social media have generated three fundamental shifts in the marketplace. First, social media enable firms and customers to connect in ways that were not possible in the past. Such connectedness is empowered by various platforms, such as social networking sites (e.g., Facebook), microblogging sites (e.g., Twitter), and content communities (e.g., YouTube), that allow social networks to build from shared interests and values (Kaplan and Haenlein 2010 ). In this regard, “social connectedness” has also been termed as “social ties” (e.g., Muller and Peres 2019 ; Quinton and Wilson 2016 ), and the strength and span of these ties determine whether they are strong or weak (Granovetter 1973 ). Prior studies have shown that tie strength is an important determinant of customer referral behaviors (e.g., Verlegh et al. 2013 ).
Second, social media have transformed the way firms and customers interact and influence each other. Social interaction involves “actions,” whether through communications or passive observations, that influence others’ choices and consumption behaviors (Chen et al. 2011 ). Nair et al. ( 2010 ) labeled such social interactions as “word-of-mouth (WOM) effect” or “contagion effects.” Muller and Peres ( 2019 ) argue that social interactions rely strongly on the social network structure and provide firms with measurable value (also referred to as “social equity”). In social media studies, researchers have long recognized the importance of social influence in affecting consumer decisions, and recent studies have shown that people’s connection patterns and the strength of social ties can signify the intensity of social interactions (e.g., Aral and Walker 2014 ; Katona et al. 2011 ).
Third, the proliferation of social media data has made it increasingly possible for companies to better manage customer relationships and enhance decision making in business (Libai et al. 2010 ). Social media data, together with other digital data, are widely characterized by the 3Vs (i.e., volume, variety, and velocity), which refer to the vast quantity of data, various sources of data, and expansive real-time data (Alharthi et al. 2017 ). A huge amount of social media data derived from different venues (e.g., social networks, blogs, forums) and in various formats (e.g., text, video, image) can now be easily extracted and usefully exploited with the aid of modern information technologies (Moe and Schweidel 2017 ). Thus, social media data can serve as an important source of customer analysis, market research, and crowdsourcing of new ideas, while capturing and creating value through social media data represents the development of a new strategic resource that can improve marketing outcomes (Gnizy 2019 ).
- Marketing strategy
According to Varadarajan ( 2010 ), a marketing strategy consists of an integrated set of decisions that helps the firm make critical choices regarding marketing activities in selected markets and segments, with the aim to create, communicate, and deliver value to customers in exchange for accomplishing its specific financial, market, and other objectives. According to the resource-based view of the firm (Barney 1991 ), organizational resources (e.g., financial, human, physical, informational, relational) help firms enhance their marketing strategies, achieve sustainable competitive advantage, and gain better performance. These resources can be either tangible or intangible and can be transformed into higher-order resources (i.e., competencies and capabilities), enabling the delivery of superior value to targeted buyers (Hunt and Morgan 1995 ; Teece and Pisano 1994 ).
Different marketing strategies can be arranged on a continuum, on which transaction marketing strategy and relationship marketing strategy represent its two ends, while in between are various mixed marketing strategies (Grönroos 1991 ). Webster ( 1992 ) notes that long-standing customer relationships should be at the core of marketing strategy, because customer interaction and engagement can be developed into valuable relational resources (Hunt et al. 2006 ). Morgan and Hunt ( 1999 ) also claim that firms capitalizing on long-term and trustworthy customer relationships can help design value-enhancing marketing strategies that will subsequently generate competitive advantages and lead to superior performance.
From a strategic marketing perspective, social media interaction entails a process that allows not only firms, but also customers to exchange resources. For example, Hollebeek et al. ( 2019 ) assert that customers can devote operant (e.g., knowledge) and operand (e.g., equipment) resources while interacting with firms. Importantly, Gummesson and Mele ( 2010 ) argue that interactions occur not simply in dyads, but also between multiple actors within a network, underscoring the critical role of network interaction in resource integration. Notably, customer-to-customer interactions are also essential, especially for the higher level of engagement behaviors (Fehrer et al. 2018 ).
Thus, social media interconnectedness and interactions (i.e., between firm–customer and between customer–customer) can be considered strategic resources, which can be further converted into marketing capabilities (Morgan and Hunt 1999 ). A case in point is social customer relationship management (CRM) capabilities, in which the firm cultivates the competency to use information generated from social media interactions to identify and develop loyal customers (Trainor et al. 2014 ). With the expanding role of social media from a single communication tool to one of gaining customer and market knowledge, marketers can strategically develop distinct resources from social media based on extant organizational resources and capabilities.
Drawing on the previous argumentation, we define SMMS as an organization’s integrated pattern of activities that, based on a careful assessment of customers’ motivations for brand-related social media use and the undertaking of deliberate engagement initiatives, transform social media connectedness (networks) and interactions (influences) into valuable strategic means to achieve desirable marketing outcomes. This definition is parsimonious because it captures the uniqueness of the social media phenomenon, takes into consideration the fundamental premises of marketing strategy, and clearly defines the scope of activities pertaining to SMMS.
Although the underlying roots of traditional marketing strategy and SMMS are similar, the two strategies have three distinctive differences: (1) as opposed to the traditional approach, which pays peripheral attention to the heterogeneity of motivations driving customer engagement, SMMS emphasizes that social media users must be motivated on intellectual, social, cultural, or other grounds to engage with firms (and perhaps more importantly with other customers) (Peters et al. 2013 ; Venkatesan 2017 ); (2) the consequences of SMMS are jointly decided by the firm and its customers (rather than by individual actors’ behaviors), and it is only when the firm and its customers interact and build relationships that social media technological platforms become real resource integrators (Singaraju et al. 2016 ; Stewart and Pavlou 2002 ); and (3) while customer value in traditional marketing strategies is narrowly defined to solely capture purchase behavior through customer lifetime value, in the case of SMMS, this value is expressed through customer engagement, comprising both direct (e.g., customer purchases) and indirect (e.g., product referrals to other customers) contributions to the value of the firm (Kumar and Pansari 2016 ; Venkatesan 2017 ).
Conceptualizing the process of developing SMMSs
The conceptualization of the process of developing SMMSs is anchored on customer engagement theory, which posits that firms need to take deliberate initiatives to motivate and empower customers to maximize their engagement value and yield superior marketing results (Harmeling et al. 2017 ). Kumar et al. ( 2010 ) distinguish between four different dimensions of customer engagement value, namely customer lifetime value, customer referral value, customer influence value, and customer knowledge value. This metric has provided a new approach for customer valuation, which can help marketers to make more effective and efficient strategic decisions that enable long-term value contributions to customers. In a social media context, this customer engagement value enables firms to capitalize on crucial customer resources (i.e., network assets, persuasion capital, knowledge stores, and creativity), of which the leverage can provide firms with a sustainable competitive advantage (Harmeling et al. 2017 ).
Customer engagement theory highlights the importance of understanding customer motivations as a prerequisite for the firm to develop effective SMMSs, because heterogeneous customer motivations resulting from different attitudes and attachments can influence their social media behaviors and inevitably SMMS outcomes (Venkatesan 2017 ). It also stresses the role of inputs from both firm (i.e., social media engagement initiatives) and customers (i.e., social media behaviors), as well as the importance of different degrees of interactivity and interconnectedness in yielding sound marketing outcomes (Harmeling et al. 2017 ). Pansari and Kumar et al. ( 2017 ) argue that firms can benefit from such customer engagement in both tangible (e.g., higher revenues, market share, profits) and intangible (e.g., feedbacks or new ideas that help to product/service development) ways.
Based on consumer engagement theory, we therefore conceive the process of developing an SMMS as consisting of four interlocking parts: (1) drivers , that is, the firm’s social media marketing objectives and the customers’ social media use motivations; (2) inputs , that is, the firm’s social media engagement initiatives and the customers’ social media behaviors; (3) throughputs , that is, the way the firm connects and interacts with customers to exchange resources and satisfy needs; and (4) outputs , that is, the resulting customer engagement outcome. Figure 1 shows this developmental process of SMMS, while Table 2 indicates the specific theoretical underpinnings of each part comprising this process.
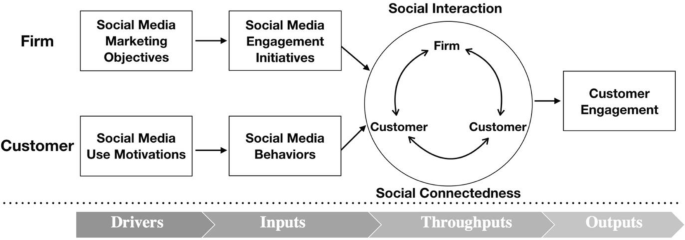
A conceptualization of the process of developing social media marketing strategies
Firms’ social media marketing objectives
Though operating in a similar context, SMMSs may differ depending on the firm’s strategic objectives (Varadarajan 2010 ). According to resource dependence theory (Pfeffer and Salancik 1978 ), the firm’s social media marketing objectives can be justified by the need to acquire external resources (which do not exist internally) that will help it accommodate the challenges of environmental contingencies. In a social media context, customers can serve as providers of resources, which can take several forms (Harmeling et al. 2017 ). Felix et al. ( 2017 ) distinguish between proactive and reactive social media marketing objectives, which can differ by the type of market targeted (e.g., B2B vs. B2C) and firm size. While for proactive objectives, firms use social media to increase brand awareness, generate online traffic, and stimulate sales, in the case of reactive objectives, the emphasis is on monitoring and analyzing customer activities.
Customers’ social media use motivations
Social media use motivations refer to various incentives that drive people’s selection and use of specific social media (Muntinga et al. 2011 ). The existence of these motivations is theoretically grounded on uses and gratifications theory (Katz et al. 1973 ), which maintains that consumers are actively and selectively involved in media usage to gratify their psychological and social needs. In a social media context, motivations can range from utilitarian and hedonic purposes (e.g., incentives, entertainment) to relational reasons (e.g., identification, brand connection) (Rohm et al. 2013 ). Muntinga et al. ( 2011 ) also categorize consumer–brand social media interactions as motivated primarily by entertainment, information, remuneration, personal identity, social interaction, and empowerment.
Firms’ social media engagement initiatives
Firms take initiatives to motivate and engage customers so that they can make voluntary contributions in return (Harmeling et al. 2017 ; Pansari and Kumar 2017 ). These firm actions can also be theoretically explained by resource dependence theory (Pfeffer and Salancik 1978 ), which argues that firms need to take initiatives to encourage customers to interact with them, to generate useful autonomous contributions that will alleviate resource shortages. Harmeling et al. ( 2017 ) identify two primary forms of a firm’s marketing initiatives to engage customers using social media: task-based and experiential. While task-based engagement initiatives encourage customer engagement behaviors with structured tasks (e.g., writing a review) and usually take place in the early stages of the firm’s social media marketing efforts, experiential engagement initiatives employ experiential events (e.g., multisensory events) to intrinsically motivate customer engagement and foster emotional attachment. Thus, firm engagement initiatives can be viewed as a continuum, where at one end, the firm uses monetary rewards to engage customers and, at the other end, the firm proactively works to deliver effective experiential incentives to motivate customer engagement.
Customers’ social media behaviors
The use of social media by customers yields different behavioral manifestations, ranging from passive (e.g., observing) to active (e.g., co-creation) (Maslowska et al. 2016 ). These customer social media behaviors can be either positive (e.g., sharing) or negative (e.g., create negative content), depending on customers’ attitudes and information processes during interactions (Dolan et al. 2016 ). Harmeling et al. ( 2017 ) characterize customers with positive behaviors as “pseudo marketers” because they contribute to firms’ marketing functions using their own resources, while those with negative behaviors may turn firm-created “hashtags” into “bashtags.” Drawing on uses and gratifications theory, Muntinga et al. ( 2011 ) also categorize customers’ brand-related behaviors in social media into three groups: consuming (e.g., reading a brand’s posts), contributing (e.g., rating products), and creating (e.g., publishing brand-related content).
Throughputs
Within the context of social media, both social connectedness and social interaction can be explained by social exchange theory, which proposes that social interactions are exchanges through which two parties acquire benefits (Blau 1964 ). Based on this theory, such a social exchange involves a sequence of interactions between firms and customers that are usually interdependent and contingent on others’ actions, with the goal to generate sound relationships (Cropanzano and Mitchell 2005 ). Thus, successful exchanges can advance interpersonal connections (referred to as social exchange relationships) with beneficial effects for the interacting parties (Cropanzano and Mitchell 2005 ).
Social connectedness
Social connectedness indicates the number of ties an individual has on social networks (Goldenberg et al. 2009 ), while Kumar et al. ( 2010 ) define connectedness with additional dimensions, including the number of connections, the strength of the connections, and the location in the network. Social media research suggests that connectedness has a significant impact on social influence. For example, Hinz et al. ( 2011 ) show that the use of “hubs” (highly connected people) in viral marketing campaigns can be eight times more successful than strategies using less connected people. Verlegh et al. ( 2013 ) also examine the impact of tie strength on making referrals in social media and confirm that people tend to interpret ambiguous information received from strong ties positively, but negatively when this information comes from weak ties.
Social interaction
Social interaction within a social media context is quite complex, as it represents multidirectional and interconnected information flows, rather than a pure firm monologue (Hennig-Thurau et al. 2013 ). This is because, on the one hand, social media have empowered customers to be equal actors in firm–customer interactions through sharing, gaming, expressing, and networking, while, on the other hand, customer–customer interactions have emerged as a growing market force, as customers can influence each other with regard to their attitudinal or behavioral changes (Peters et al. 2013 ). Chen et al. ( 2011 ) identify two types of social interactions—namely, opinion- or preference-based interactions (e.g., WOM) and action- or behavior-based interactions (e.g., observational learning)—with each requiring different strategic actions to be taken. Chahine and Malhotra ( 2018 ) also show that two-way (multiway) interaction strategies that allow reciprocity result in higher market reactions and more positive relationships.
- Customer engagement
The outputs are expressed in terms of customer engagement, which reflects the outcome of firm–customer (as well as customer–customer) connectedness and interaction in social media (Harmeling et al. 2017 ). Footnote 1 It is essentially a reflection of “the intensity of an individual’s participation in and connection with an organization’s offerings and/or organizational activities, which either the customer or the firm initiates” (Vivek et al. 2012 , p. 127). The more customers connect and interact with the firm’s activities, the higher is the level of customer engagement created (Kumar and Pansari 2016 ; Malthouse et al. 2013 ) and the higher the customer’s value addition to the firm (Pansari and Kumar 2017 ). Although the theoretical explanation of the notion of customer engagement has attracted a great deal of debate among scholars in the field, research (e.g., Brodie et al. 2011 ; Hollebeek et al. 2019 ; Kumar et al. 2019 ) has also begun adopting the service-dominant (S-D) logic (Vargo and Lusch 2004 ) because of its emphasis on customers’ interactive and value co-creation experiences in market relationships. Following the service-dominant (S-D) logic, Hollebeek et al. ( 2019 ) stress the role of customer resource integration, customer knowledge sharing, and learning as foundational in the customer engagement process, which can subsequently lead to customer individual/interpersonal operant resource development and co-creation.
Despite its pivotal role in social media marketing, extant literature has not yet attained agreement on the specific measurement of customer engagement. For example, Muntinga et al. ( 2011 ) conceptualize customer engagement in social media as comprising three stages: consuming (e.g., following, viewing content), contributing (e.g., rating, commenting), and creating (e.g., user-generated content). Maslowska et al. ( 2016 ) propose three levels of customer engagement behaviors: observing (e.g., reading content), participating (e.g., commenting on a post), and co-creating (e.g., partaking in product development). Moreover, Kumar et al. ( 2010 ) distinguish between transactional (i.e., buying the product) and non-transactional (i.e., sharing, commenting, referring, influencing) behaviors of customer engagement derived from social media connectedness and interactions.
Taxonomy of SMMSs
The distinctive differences among firms engaged in social media marketing with regard to their strategic objectives, organizational resources and capabilities, and focal industries and market structures, imply that there must also be differences in the SMMSs pursued. In this section, we first explain the criteria classifying SMMSs into different groups and then provide an analysis of their content.
Classification criteria of SMMSs
Drawing from the extant literature, we propose three important criteria that can be used to distinguish SMMSs: the nature of the firm’s strategic social media objectives with regard to using social media, the direction of interactions taking place between the firm and the customers, and the level of customer engagement achieved.
Strategic social media objectives refer to the specific organizational goals to be achieved by implementing SMMSs (Choi and Thoeni 2016 ; Felix et al. 2017 ). These can range from transactional to relational-oriented, depending on the strategist’s mental models of business–customer interactions (Rydén et al. 2015 ). Different mental models have a distinctive impact on managers’ social media sense-making, which is responsible for framing the specific role defined by social media in their marketing activities (Rydén et al. 2015 ). Rydén et al. ( 2015 ) identify four types of social media marketing objectives with four different mental models that can guide SMMSs —namely, to promote and sell (i.e., business-to-customers), to connect and collaborate (i.e., business-with-customers), to listen and learn (i.e., business-from-customers), and to empower and engage (i.e., business-for-customers).
The direction of the social media interactions can take three different forms. These include (1) one-way interaction , that is, traditional one-way communication in which the firm disseminates content (e.g., advertising) on social media and customers passively observe and react (Hoffman and Thomas 1996 ); (2) two-way interaction , that is, reciprocal and interactive communication with exchanges on social media, which can be further distinguished into firm-initiated interaction (in which the firm takes the initiative to begin the conversation) and customer participation (by liking, sharing, or commenting on the content) and customer-initiated interaction (in which the customer is the initiator of conversations by inquiring, giving feedback, or even posting negative comments about the firm, while the firm listens and responds to customer voice) (Van Noort and Willemsen 2012 ); and (3) collaborative interaction, that is, the highest level of interaction that builds on frequent and reciprocal activities in which both the firm and the customer have the power to influence each other (Joshi 2009 ).
With regard to the level of customer engagement, as noted previously, this heavily depends on the strength of connections and the intensity of interactions between the firm and the customers in social media, comprising both transactional and non-transactional elements (Kumar et al. 2010 ). Because customer engagement is the result of a dynamic and iterative process, which makes specifying the exact stage from participating to producing rather difficult (Brodie et al. 2011 ), we adopt the approach proposed by various scholars in the field (e.g., Dolan et al. 2016 ; Malthouse et al. 2013 ) to view this as a continuum, ranging from very low levels of engagement (e.g., “liking” a page) to very high levels of engagement (e.g., co-creation).
Types of SMMSs
With these three classificatory criteria, we can identify four distinct SMMSs, representing increasing levels of strategic maturity: social commerce strategy, social content strategy, social monitoring strategy, and social CRM strategy. Footnote 2 Fig. 2 illustrates this taxonomy for SMMSs, Table 3 shows the differences between these four strategies, while Appendix Table 6 provides real company examples using these strategies. In the following, we analyze each of these SMMSs by explaining their nature and characteristics, the particular role played by social media, and the specific organizational capabilities required for their adoption.
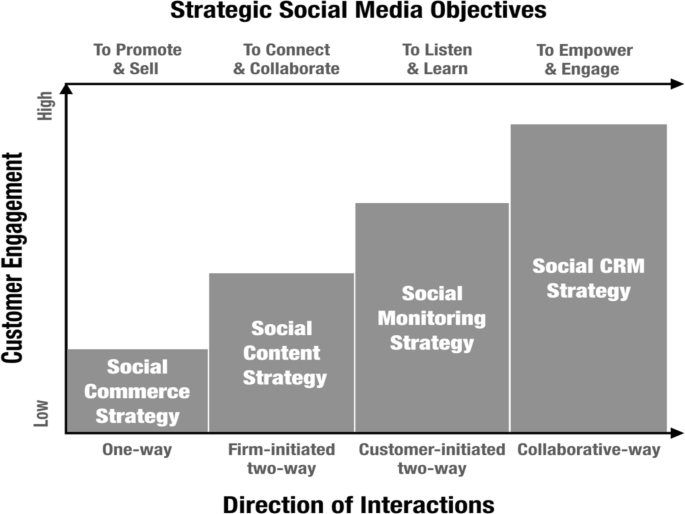
Taxonomy of social media marketing strategies
Social commerce strategy
Social commerce strategy refers to the “exchange-related activities that occur in, or are influenced by, an individual’s social network in computer-mediated social environments, whereby the activities correspond to the need recognition, pre-purchase, purchase, and post-purchase stages of a focal exchange” (Yadav et al. 2013 , p. 312). Rydén et al. ( 2015 , p. 6) claim that this way of using social media is not to create conversation and/or engagement; rather, the reasons for “the initial contact and the end purpose are to sell.” Similarly, Malthouse et al. ( 2013 ) argue that social media promotional activities do not actively engage customers because they do not make full use of the interactive role of social media. Thus, social commerce strategy can be considered as the least mature SMMS because it has a mainly transactional nature and is preoccupied with short-term goal-oriented activities (Grönroos 1994 ). It is essentially a one-way communication strategy intended to attract customers in the short run.
In this strategy, social media are claimed to be the new selling tool that has changed the way buyers and sellers interact (Marshall et al. 2012 ). They offer a new opportunity for sellers to obtain customer information and make the initial interaction with the customer more efficient (Rodriguez et al. 2012 ). Meanwhile, firms are also increasingly using social media as promising outlets for promotional/advertising purposes given their global reach (e.g., Dao et al. 2014 ; Zhang and Mao 2016 ), especially to the millennial generation (Confos and Davis 2016 ). However, as firms’ social media activities in this strategy are more transactional-oriented, customers tend to be passive and reactive. Customers contribute transactional value through purchases, but without a higher level of engagement. Therefore, we conclude that, within the context of this strategy, customers exchange their monetary resources (e.g., purchases) with the firm’s promotional offerings.
To better develop this strategy, Guesalaga ( 2016 ) highlights the need to understand the drivers of using social media in the selling process. He further stresses that personal commitment plays a crucial role in using social media as selling tools. Similarly, Järvinen and Taiminen ( 2016 ) urged for an integration of marketing with the sales department in order to gain better insights from social media marketing efforts. The importance of synergistic effects between social media and traditional media (e.g., press mentions, television, in-store promotions) has also been stressed in supporting social commerce activities (e.g., Jayson et al. 2018 ; Kumar et al. 2016 ; Stephen and Galak 2012 ). Thus, selling capabilities are crucial in this strategy, requiring the possession of adequate selling skills and the use of multiple selling channels to synergize social media effects.
Social content strategy
Social content strategy refers to “the creation and distribution of educational and/or compelling content in multiple formats to attract and/or retain customers” (Pulizzi and Barrett 2009 , p. 8). Thus, this type of SMMS aims to create and deliver timely and valuable content based on customer needs, rather than promoting products (Järvinen and Taiminen 2016 ). By attracting audiences with valuable content, the increase in customer engagement may ultimately boost product/service sales (Malthouse et al. 2013 ). Holliman and Rowley ( 2014 , p. 269) also claim that content marketing is a customer-centric strategy and describe the value of content as “being useful, relevant, compelling, and timely.” Therefore, this strategy provides a two-way communication in which firms take the initiative to deliver useful content and customers react positively to this content. The basic premises of this strategy are to create brand awareness and popularity through content virality, stimulate customer interactions, and spread positive WOM (De Vries et al. 2012 ; Swani et al. 2017 ).
Social media in this strategy have been widely used as communication tools for branding and WOM purposes (Holliman and Rowley 2014 ; Libai et al. 2013 ). On the one hand, firms generate content by their own efforts on social media (termed as ‘firm-generated’ or ‘marker-generated’ content) to actively engage consumers. On the other hand, firms encourage customers to generate the content (termed as ‘user-generated’ content) through the power of customer-to-customer interactions, as in the case of exchanging comments and sharing the brand-related content. In this way, firms provide valuable content in exchange for customer-owned resources, such as network assets and persuasion capital, to generate positive WOM and achieve a sustainable trusted brand status.
To pursue a social content strategy, firms build on capabilities focusing on how content is designed and presented (expressed in the form of a social message strategy) and how content is disseminated (expressed in the form of a seeding strategy). Thus, understanding customer engagement motivations and social media interactive characteristics is central to designing valuable content and facilitating customer interactions that would help to stimulate content sharing among customers (Malthouse et al. 2013 ). Designing compelling and valuable content in order to transform passive social media observers into active participants and collaborators is also key capability required by firms adopting this strategy (Holliman and Rowley 2014 ). Empowering customers and letting them speak for the brand is another way to engage customers with brands. Therefore, in this strategy, marketing communication capabilities are important for effective marketing content development and dissemination.
Social monitoring strategy
Social monitoring strategy refers to “a listening and response process through which marketers themselves become engaged” (Barger et al. 2016 , p. 278). In contrast with social content strategy, which is more of a “push” communication approach with content delivered, social monitoring strategy requires the firm’s active involvement in the whole communication process (from content delivery to customer response) (Barger et al. 2016 ). More specifically, social monitoring strategy is not only to observe and analyze the behaviors of customers in social media (Lamberton and Stephen 2016 ), but also to actively search for and respond to customer online needs and complaints (Van Noort and Willemsen 2012 ). A social monitoring strategy is thus characterized by a two-way communication process, in which the initiation comes from customers who comment and behave on social media, while the company takes advantage of customer behavior data to listen, learn, and react to its customers. Thus, the key objective of this strategy is to enhance customer satisfaction and cultivate stronger relationships with customers through ongoing social media listening and responding.
With today’s abundance of attitudinal and behavioral data, firms adopting this strategy use social media platforms as “tools” or “windows” to listen to customer voices and gain important market insights to support their marketing decisions (Moe and Schweidel 2017 ). Moreover, Carlson et al. ( 2018 ) argue that firms can take advantage of social media data to identify innovation opportunities and facilitate the innovation process. Hence, social media monitoring enables firms to assess consumers’ reactions, evaluate the prosperity of social media marketing initiatives, and allocate resources to different types of conversations and customer groups (Homburg et al. 2015 ). In other words, customers in this strategy are expected to be active in social media interactions, providing instantaneous and real-time feedback. This has in a way helped product development and experience improvements with resource inputs from customers’ knowledge stores.
Social monitoring strategy emphasizes the importance of carefully listening and responding to social media activities to have a better understanding of customer needs, gain critical market insights, and build stronger customer relationships (e.g., Timoshenko and Hauser 2019 ). It therefore requires firms to be actively involved in the whole communication process with customers, as customer engagement is not dependent on rewards, but is developed through the ongoing reciprocity between the firm and its customers (Barger et al. 2016 ). Thus, organizational capabilities, such as marketing sensing through effective information acquisition, interpretation and responding, are essential for the successful implementation of this strategy. More specifically, monitoring and text analysis techniques are needed to gather and capture social media data rapidly (Schweidel and Moe 2014 ). Noting the damage caused by electronic negative word of mouth (e-NWOM) on social media, firms adopting this strategy also require special capabilities to appropriately respond to customer online complaints and requests (Kim et al. 2016 ).
Social CRM strategy
Among the four SMMSs identified, social CRM strategy is characterized by the highest degree of strategic maturity, because it reflects “a philosophy and a business strategy supported by a technology platform, business rules, processes, and social characteristics, designed to engage the customer in a collaborative conversation in order to provide mutually beneficial value in a trusted and transparent business environment” (Greenberg 2009 , p. 34). The concept of social CRM is designed to combine the benefits derived from both the social media dimension (e.g., customer engagement) and the CRM dimension (e.g., customer retention) (Malthouse et al. 2013 ). In contrast with the traditional CRM approach, which assumes that customers are passive and only contribute to customer life value, social CRM strategy emphasizes the active role of customers who are empowered by social media and can make a contribution to multiple forms of value (Kumar et al. 2010 ). In brief, a social CRM strategy is a form of collaborative interaction, including firm–customer, inter-organizational, and inter-customer interactions, that are intended to engage and empower customers, so as to build mutually beneficial relationships with the firm and lead to superior performance.
Social media have become powerful enablers of CRM (Choudhury and Harrigan 2014 ). For example, Charoensukmongkol and Sasatanun ( 2017 ) argue that the integration of social media and CRM provides a possibility for firms to segment their customers based on similar characteristics, and can customize marketing offerings to the specific preferences of individual customers. With social CRM strategy, firms can enhance the likelihood of customer engagement through one-to-one social media interactions. Customers at this stage are collaborative and interactive in value creation, such as voluntarily providing innovative ideas and collaborating with brands (Jaakkola and Alexander 2014 ). Hence, besides resource like network assets, persuasion capital, and knowledge stores, engaged customers also contribute their creativity resource for value co-creation.
Social CRM capability is “a firm-level capability and refers to a firm’s competency in generating, integrating, and responding to information obtained from customer interactions that are facilitated by social media technologies” (Trainor et al. 2014 , p. 271). Therefore, firms should be extremely creative to combine social media data with its CRM system, as well as to link the massive social media data on customer activities to other data sources (e.g., customer service records) to generate better customer-learning and innovation opportunities (Choudhury and Harrigan 2014 ; Moe and Schweidel 2017 ). Social CRM strategy also emphasizes the significance of reciprocal information sharing and collaborations that are supported by the firm’s culture and commitment, operational resources, and cross-functional cooperation (Malthouse et al. 2013 ; Schultz and Peltier 2013 ). To sum up, social CRM capabilities, organizational learning capabilities connected with relationship management and innovation are essential prerequisites to building an effective social CRM strategy.
Validation of proposed SMMSs
Using the previously developed classification of SMMSs (i.e., social commerce strategy, social content strategy, social monitoring strategy, and social CRM strategy) as a basis, we reviewed the pertinent literature to collate useful knowledge supporting the content of each of these strategies. Table 4 provides a summary of the key empirical insights derived from the extant studies reviewed, together with resulting managerial lessons.
To validate the practical usefulness of our proposed classificatory framework of SMMSs, we first conducted a series of in-depth interviews with 15 social media marketing practitioners, who had their own firm/brand accounts on social media platforms, at least one year of social media marketing experience, and at least three years’ experience in their current organization (see Web Appendix 1 ). Interviewees represented companies located in China (8 companies), Finland (5 companies), and Sweden (2 companies) and involved in a variety of industries (e.g., digital tech, tourism, food, sport). All interviews were based on a specially designed guide (which was sent to participants in advance to prepare them for the interview) and were audiotaped and subsequently transcribed verbatim (see Web Appendix 2 ).
The main findings of this qualitative study are the following: (1) social media are mainly used as a key marketing channel to achieve business objectives, which, however, differentiates in terms of product-market type, organization size, and managerial mindset; (2) distinct differences exist across organizations in terms of their social media initiatives to deliver content, generate reactions, and develop social CRM; (3) there are marked variations in customer engagement levels across participant firms, resulting from the adoption of different SMMSs; (4) the firm’s propensity to use a specific SMMSs is enhanced by infrastructures, systems, and technologies that help to actively search, access, and integrate data from different sources, as well as facilitate the sharing and coordination of activities with customers; and (5) the adoption of a specific SMMS does not follow a sequential pattern in terms of strategic maturity development, but rather, depends on the firm’s strategic objectives, its willingness to commit the required resources, and the deployment of appropriate organizational capabilities.
To further confirm the existence of differences in profile characteristics among the four types of SMMSs, we conducted an electronic survey among a sample of 52 U.S. social media marketing managers who were randomly selected. For this purpose, we designed a structured questionnaire incorporating the key parameters related to SMMSs, namely firms’ strategic objectives, firms’ engagement initiatives, customers’ social media behaviors, social media resources and capabilities required, direction of interactions, and customer engagement levels (see Web Appendix 3 ).
Specifically, we found that: (1) each of the four SMMSs emphasize different types of strategic objectives, ranging from promoting and selling, in the case of social commerce strategy, to empowering and engaging in social CRM strategy; (2) experiential engagement initiatives geared to customer engagement were more evident at the advanced level, as opposed to the lower level strategies; (3) passive customer social media behaviors were more characteristic of the social commerce strategy, while more active customer behaviors were observed in the case of social CRM strategy; (4) the more advanced the maturity of the SMMS employed, the higher the level customer engagement, as well as the higher requirements in terms of organizational resources and specialized capabilities; and (5) one-way interaction was associated more with social commerce strategy, two-way interaction was more evident in the social content strategy and the social monitoring strategy, and collaborative interaction was a dominant feature in the social CRM strategy (see Web Appendix 4 ).
Future research directions
While the extant research offers insightful information and increased knowledge on SMMSs, there is still plenty of room to expand this field of research with other issues, especially given the rapidly changing developments in social media marketing practice. To gain a more accurate picture about the future of research on the subject, we sought the opinions of academic experts in the field through an electronically conducted survey among authors of academic journal articles written on the subject. We specifically asked them: (1) to suggest the three most important areas that research on SMMSs should focus on in the future; (2) within each of the areas suggested, to indicate three specific topics that need to be addressed more; and (3) within each topic, to illustrate analytical issues that warrant particular attention (see Web Appendix 5 ). Altogether, we received input from 43 social media marketing scholars who suggested 6 broad areas, 13 specific topics, and 82 focal issues for future research, which are presented in Table 5 .
Among the research issues proposed, finding appropriate metrics to measure performance in SMMSs seems to be an area to which top priority should be given. This is because performance is the ultimate outcome of these strategies, for which there is still little understanding due to the idiosyncratic nature of social media as a marketing tool (e.g., Beckers et al. 2017 ; Trainor et al. 2014 ). In particular, it is important to shed light on both short-term and long-term performance, as well as its effectiveness, efficiency, and adaptiveness aspects (e.g., Barger et al. 2016 ). Another key priority area stressed by experts in the field involves integrating to a greater extent various strategic issues regarding each of the marketing-mix elements in a social media context. This would help achieve better coordination between traditional and online marketing tools (e.g., Kolsarici and Vakratsas 2018 ; Kumar et al. 2017 ).
Respondents in our academic survey also stressed the evolutionary nature of knowledge with regard to each of the four SMMSs and proposed multiple issues for each of them. Particular attention should be paid to how inputs from customers and firms are interrelated in each of these strategies, taking into consideration the central role played by customer engagement behaviors and firm initiatives (e.g., Sheng 2019 ). Respondents also pinpointed the need for more emphasis on social CRM strategy (which is relatively under-researched), while there should also be a closer assessment of new developments in both marketing (e.g., concepts and tools) and social media (e.g., technologies and platforms) that can lead to the emergence of new types of SMMSs (e.g., Ahani et al. 2017 ; Choudhury and Harrigan 2014 ).
Respondents also noted that up to now the preparatory phase for designing SMMSs has been overlooked, and that therefore there is a need to shed more light on this because of its decisive role in achieving positive results. For example, issues relating to market/competitor analysis, macro-environmental scanning, and target marketing should be carefully studied in conjunction with formulating sound SMMSs, to better exploit opportunities and neutralize threats in a social media context (e.g., De Vries et al. 2017 ). By contrast, our survey among scholars in the field stressed the crucial nature of issues relating to SMMS implementation and control, which are of equal, or even greater, importance than those of strategy formulation (e.g., Järvinen and Taiminen 2016 ). The academics also indicated that, by their very nature, social media transcend national boundaries, thus leaving plenty of room to investigate the international ramifications of SMMSs, using cross-cultural research (e.g., Johnston et al. 2018 ).
Implications and conclusions
Theoretical implications.
Given the limited research on SMMSs, this study has several important theoretical implications. First, we are taking a step in this new theoretical direction by providing a workable definition and conceptualization of SMMS that combines both social media and marketing strategy dimensions. The study complements and extends previous research (e.g., Harmeling et al. 2017 ; Singaraju et al. 2016 ) that emphasized the value of social media as resource integrator in exchanging customer-owned resources, which can provide researchers with new angles to address the issue of integrating social media with marketing strategy. Such integrative efforts can have a meaningful long-term impact on building a new theory (or theories) of social media marketing. They also point to a deeper theoretical understanding of the roles played by resource identification, utilization, and reconfiguration in a SMMS context.
We have also extended the idea of “social interaction” and “social connectedness” in a social media context, which is critical because the power of a customer enabled by social media connections and interactions is of paramount importance in explaining the significance of SMMSs (Hennig-Thurau et al. 2013 ). More importantly, our study suggests that firms should take the initiative to motivate and engage customers, which will lead to wider and more extensive interactions. In particular, we show that a firm can leverage its social media usage through the use of different engagement initiatives to enforce customer interactivity and interconnectedness. Such enquiries can provide useful theoretical insights into the strategic marketing role played by social media in today’s highly digitalized and globalized world.
We are also furthering the customer engagement literature by proposing an SMMS developmental process. As firm–customer relationships evolve in a social media era, it is critical to identify those factors that have an impact on customer engagement. Although prior studies (e.g., Harmeling et al. 2017 ; Pansari and Kumar 2017 ) have demonstrated the engagement value contributed by customers and the need for engagement initiatives taken by firms, we are extending this idea to provide a more holistic view by highlighting the role of insights from both firms and customers to better understand the dynamics of SMMS formulation. We also suggest certain theories to specifically explain the role played by each of the components of the process in developing sound SMMSs. We capture the unique characteristics of social media by suggesting that these networks and interactions are tightly interrelated with the outcome of SMMS, which is customer engagement. Our proposed SMMS developmental process may therefore provide critical input for new studies focusing on customer engagement research.
Finally, we build on various criteria to distinguish among four SMMSs, each representing a different level of strategic maturity. We show that a SMMS is not homogeneous, but needs to be understood in a wider, more nuanced way, as having different strategies relying on different goals and deriving insights from firms and their customers, ultimately leading to different customer engagement levels. In this regard, the identification of the key SMMSs stemming from our analysis can serve as the basis for developing specific marketing strategy constructs and scales within a social media context. We also indicate that different SMMSs can be implemented and yield superior competitive advantage only when the firm is in a position to devote to it the right amount and type of resources and capabilities (e.g., Gao et al. 2018 ; Kumar and Pansari 2016 ).
Managerial implications
Our study also has serious implications for managers. First, our analysis revealed that the ever-changing digital landscape on a global scale calls for a reassessment of the ways to strategically manage brands and customers in a social media context. This requires companies to understand the different goals for using social media and to develop their strategies accordingly. As a starting point, firms could explore customer motivations for using social media and effectively deploy the necessary resources to accommodate these motivations. They should also think carefully about how to engage customers when implementing their marketing strategies, because social media become resource integrators only when customers interact with and provide information on them (Singaraju et al. 2016 ).
Managers need to set objectives at the outset to guide the effective development, implementation, and control of SMMSs. Our study suggests four key SMMSs achieving different business goals. For example, the goal of social commerce strategy is to attract customers with transactional interests, that of social content strategy and social monitoring strategy is to deliver valuable content and service to customers, and that of social CRM strategy is to build mutually beneficial customer relationships by integrating social media data with current organizational processes. Unfortunately, many companies, especially smaller ones, tend to create their social media presence for a single purpose only: to disseminate massive commercial information on their social media web pages in the hope of attracting customers, even though these customers may find commercially intensive content annoying.
This study also suggests that social media investments should focus on the integration of social media platforms with internal company systems to build special social media capabilities (i.e., creating, combining, and reacting to information obtained from customer interactions on social media). Such capabilities are vital in developing a sustainable competitive advantage, superior market and financial performance. However, to achieve this, firms must have the right organizational structural and cultural transformation, as well as substantial management commitment and continuous investment.
Lastly, social media have become powerful tools for CRM, helping to transform it from traditional one-way interaction to collaborative interaction. This implies that customer engagement means not only encouraging customer engagement on social media, but also proactively learning from and collaborating with customers. As Pansari and Kumar et al. ( 2017 ) indicate, customer engagement can contribute both directly (e.g., purchase) and indirectly (e.g., customer knowledge value) to the firm. Therefore, interacting with customers via social media provides tremendous opportunities for firms to learn more about their customers and opens up new possibilities for product/service co-creation.
Conclusions
The exploding use of social media in the past decade has underscored the need for guidance on how to build SMMSs that foster relationships with customers, advance customer engagement, and increase marketing performance. However, a comprehensive definition, conceptualization, and framework to guide the analysis and development of SMMSs are lacking. This can be attributed to the recent introduction of social media as a strategic marketing tool, while both academics and practitioners still lack the necessary knowledge on how to convert social media data into actionable strategic marketing tools (Moe and Schweidel 2017 ). This insufficiency also stems from the fact that the adoption of more advanced SMMSs requires the possession of specific organizational capabilities that can be used to leverage social media, with the support of a culture that encourages breaking free from obsolete mindsets, emphasizing employee skills with intelligence in data and customer analytical insights, and operational excellence in organizational structure and business processes (Malthouse et al. 2013 ).
Our study takes the first step toward addressing this issue and provides useful guidelines for leveraging social media use in strategic marketing. In particular, we provide a systematic consolidation and extension of the extant pertinent SMMS literature to offer a robust definition, conceptualization, taxonomy, and validation of SMMSs. Specifically, we have amply demonstrated that the mere use of social media alone does not generate customer value, which instead is attained through the generation of connections and interactions between the firm and its customers, as well as among customers themselves. These generated social networks and influences can subsequently be used strategically for resource transformation and exchanges between the interacting parties. Our conceptualization of the SMMS developmental process also suggests that firms first need to recognize customers’ motivations to engage in brand-related social media activities and encourage their voluntary contributions.
Although the four SMMSs identified in our study (i.e., social commerce strategy, social content strategy, social monitoring strategy, and social CRM strategy) denote progressing levels of strategic maturity, their adoption does not follow a sequential pattern. As our validation procedures revealed, this will be determined by the firm’s strategic objectives, resources, and capabilities. Moreover, the success of the various SMMSs will depend on the firm’s ability to identify and leverage customer-owned resources, as in the case of transforming customers from passive receivers of the firm’s social media offerings to active value contributors. It will also depend on the firm’s willingness to allocate resources in order to foster collaborative conversations, develop appropriate responses, and enhance customer relationships. These will all ultimately help to build a sustainable competitive advantage and enhance business performance.
Although in our conceptualization of the process of developing SMMSs we treat customer engagement as the output of this process, we fully acknowledge that firms’ ultimate objective to engage in social media marketing activities is to improve their market (e.g., customer equity) and financial (e.g., revenues) performance. In fact, extant social media marketing research (e.g., Kumar et al. 2010 ; Kumar and Pansari 2016 ; Harmeling et al. 2017 ) repeatedly stresses the conducive role of customer engagement in ensuring high performance results.
SMMSs are difficult to operationalize by focusing solely on the elements of the marketing mix (i.e., product, price, distribution, and promotion), mainly because many other important parameters are involved in their conceptualization, such as relationship management, market development, and business innovation issues. However, each SMMS seems to have a different marketing mix focus, with social commerce strategy emphasizing advertising and sales, social content strategy emphasizing branding and communication, social monitoring strategy emphasizing service and product development, and social CRM strategy emphasizing customer management and innovation.
Acommerce (2019). How L’Oréal uses e-commerce’s social commerce to simplify transaction and increase customer engagement. Available at https://www.acommerce.asia/case-study-loreal-social-commerce/ .
Ahani, A., Rahim, N. Z. A., & Nilashi, M. (2017). Forecasting social CRM adoption in SMEs: A combined SEM-neural network method. Computers in Human Behavior, 75 , 560–578.
Article Google Scholar
Alharthi, A., Krotov, V., & Bowman, M. (2017). Addressing barriers to big data. Business Horizons, 60 (3), 285–292.
Aral, S., & Walker, D. (2014). Tie strength, embeddedness, and social influence: A large-scale networked experiment. Management Science, 60 (6), 1352–1370.
Aral, S., Dellarocas, C., & Godes, D. (2013). Social media and business transformation: A framework for research. Information Systems Research, 24 (1), 3–13.
Barger, V., Peltier, J. W., & Schultz, D. E. (2016). Social media and consumer engagement: A review and research agenda. Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing, 10 (4), 268–287.
Barney, J. (1991). Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. Journal of Management, 17 , 99–120.
Beckers, S. F. M., van Doorn, J., & Verhoef, P. C. (2017). Good, better, engaged? The effect of company-initiated customer engagement behavior on shareholder value. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 46 (3), 366–383.
Blau, P. (1964). Exchange and power in social life . New York: Wiley.
Google Scholar
Brodie, R. J., Hollebeek, L. D., Juric, B., & Ilic, A. (2011). Customer engagement: Conceptual domain, fundamental propositions, and implications for research. Journal of Service Research, 14 (3), 252–271.
Carlson, J., Rahman, M., Voola, R., & De Vries, N. (2018). Customer engagement behaviors in social media: Capturing innovation opportunities. Journal of Services Marketing, 32 (1), 83–94.
Chahine, S., & Malhotra, N. K. (2018). Impact of social media strategies on stock price: The case of twitter. European Journal of Marketing, 52 (7–8), 1526–1549.
Charoensukmongkol, P., & Sasatanun, P. (2017). Social media use for CRM and business performance satisfaction: The moderating roles of social skills and social media sales intensity. Asia Pacific Management Review, 22 (1), 25–34.
Chen, Y., Wang, Q., & Xie, J. (2011). Online social interactions: A natural experiment on word of mouth versus observational learning. Journal of Marketing Research, 48 (2), 238–254.
Choi, Y., & Thoeni, A. (2016). Social media: Is this the new organizational stepchild? European Business Review, 28 (1), 21–38.
Choudhury, M. M., & Harrigan, P. (2014). CRM to social CRM: The integration of new technologies into customer relationship management. Journal of Strategic Marketing, 22 (2), 149–176.
Confos, N., & Davis, T. (2016). Young consumer-brand relationship building potential using digital marketing. European Journal of Marketing, 50 (11), 1993–2017.
Cropanzano, R., & Mitchell, M. S. (2005). Social exchange theory: An interdisciplinary review. Journal of Management, 31 (6), 874–900.
Dao, W. V. T., Le, A. N. H., Cheng, J. M. S., & Chen, D. C. (2014). Social media advertising value: The case of transitional economies in Southeast Asia. International Journal of Advertising, 33 (2), 271–294.
De Vries, L., Gensler, S., & Leeflang, P. S. H. (2012). Popularity of brand posts on brand fan pages: An investigation of the effects of social media marketing. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 26 (2), 83–91.
De Vries, L., Gensler, S., & Leeflang, P. S. H. (2017). Effects of traditional advertising and social messages on brand-building metrics and customer acquisition. Journal of Marketing, 81 (5), 1–15.
Dolan, R., Conduit, J., Fahy, J., & Goodman, S. (2016). Social media engagement behavior: A uses and gratifications perspective. Journal of Strategic Marketing, 24 (3–4), 261–277.
Effing, R., & Spil, T. A. M. (2016). The social strategy cone: Towards a framework for evaluating social media strategies. International Journal of Information Management, 36 (1), 1–8.
Fehrer, J. A., Woratschek, H., Germelmann, C. C., & Brodie, R. J. (2018). Dynamics and drivers of customer engagement: Within the dyad and beyond. Journal of Service Management, 29 (3), 443–467.
Felix, R., Rauschnabel, P. A., & Hinsch, C. (2017). Elements of strategic social media marketing: A holistic framework. Journal of Business Research, 70 , 118–126.
Gao, H., Tate, M., Zhang, H., Chen, S., & Liang, B. (2018). Social media ties strategy in international branding: An application of resource-based theory. Journal of International Marketing, 26 (3), 45–69.
Gnizy, I. (2019). Big data and its strategic path to value in international firms. International Marketing Review, 36 (3), 318–341.
Goldenberg, J., Han, S., Lehmann, D. R., & Hong, J. W. (2009). The role of hubs in the adoption process. Journal of Marketing, 73 (2), 1–13.
Granovetter, M. S. (1973). The strength of weak ties. American Journal of Sociology, 78 (6), 1360–1380.
Greenberg, P. (2009). CRM at the speed of light: Social CRM strategies, tools, and techniques for engaging consumers . New York: McGraw-Hill Osborne Media.
Griffith, G. (2016). Get to know customers better by monitoring social media sentiment. Available at https://www.raconteur.net/business-innovation/get-to-know-customers-better-by-monitoring-social-media-sentiment .
Griffiths, M., & Mclean, R. (2015). Unleashing corporate communications via social media: A UK study of brand management and conversations with customers. Journal of Customer Behavior, 14 (2), 147–162.
Grönroos, C. (1991). The marketing strategy continuum: Towards a marketing concept for the 1990s. Management Decision, 29 (1), 72–76.
Grönroos, C. (1994). From marketing mix to relationship marketing. Management Decision, 32 (2), 4–20.
Guesalaga, R. (2016). The use of social media in sales: Individual and organizational antecedents, and the role of customer engagement in social media. Industrial Marketing Management, 54 , 71–79.
Gummesson, E., & Mele, C. (2010). Marketing as value co-creation through network interaction and resource integration. Journal of Business Market Management, 4 (4), 181–198.
Hamilton, M., Kaltcheva, V. D., & Rohm, A. J. (2016). Social media and value creation: The role of interaction satisfaction and interaction immersion. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 36 , 121–133.
Harmeling, C. M., Moffett, J. W., Arnold, M. J., & Carlson, B. D. (2017). Toward a theory of customer engagement marketing. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 45 (3), 312–335.
Hennig-Thurau, T., Hofacker, C. F., & Bloching, B. (2013). Marketing the pinball way: Understanding how social media change the generation of value for consumers and companies. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 27 (4), 237–241.
Hinz, O., Skiera, B., Barrot, C., & Becker, J. U. (2011). Seeding strategies for viral marketing: An empirical comparison. Journal of Marketing, 75 (6), 55–71.
Hoffman, D. L., & Thomas, P. N. (1996). Marketing in hypermedia computer-mediated environments: Conceptual foundations. Journal of Marketing, 60 (3), 50–69.
Hollebeek, L. D., Srivastava, R. K., & Chen, T. (2019). S-D logic-informed customer engagement: Integrative framework, revised fundamental propositions, and application to CRM. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 47 , 161–185.
Holliman, G., & Rowley, J. (2014). Business to business digital content marketing: Marketers’ perceptions of best practice. Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing, 8 (4), 269–293.
Homburg, C., Ehm, L., & Artz, M. (2015). Measuring and managing consumer sentiment in an online community environment. Journal of Marketing Research, 52 (5), 629–641.
Hunt, S. D., & Morgan, R. M. (1995). The comparative advantage theory of competition. Journal of Marketing, 59 (2), 1–15.
Hunt, S. D., Arnett, D. B., & Madhavaram, S. (2006). The explanatory foundations of relationship marketing theory. Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing, 21 (2), 72–87.
Jaakkola, E., & Alexander, M. (2014). The role of customer engagement behavior in value co-creation: A service system perspective. Journal of Service Research, 17 (3), 247–261.
Järvinen, J., & Taiminen, H. (2016). Harnessing marketing automation for B2B content marketing. Industrial Marketing Management, 54 , 164–175.
Jayson, R., Block, M. P., & Chen, Y. (2018). How synergy effects of paid and digital owned media influence brand sales considerations for marketers when balancing media spend. Journal of Advertising Research, 58 (1), 77–89.
Johnston, W. J., Khalil, S., Le, A. N. H., & Cheng, J. M. S. (2018). Behavioral implications of international social media advertising: An investigation of intervening and contingency factors. Journal of International Marketing, 26 (2), 43–61.
Joshi, A. W. (2009). Continuous supplier performance improvement: Effects of collaborative communication and control. Journal of Marketing, 73 (1), 133–150.
Kaplan, A. M., & Haenlein, M. (2010). Users of the world, unite! The challenges and opportunities of social media. Business Horizons, 53 (1), 59–68.
Katona, Z., Zubcsek, P. P., & Sarvary, M. (2011). Network effects and personal influences: The diffusion of an online social network. Journal of Marketing Research, 48 (3), 425–443.
Katz, E., Gurevitch, M., & Haas, H. (1973). On the use of mass media for important things. American Sociological Review, 38 , 164–181.
Kim, S. J., Wang, R. J. H., Maslowska, E., & Malthouse, E. C. (2016). “Understanding a fury in your words”: The effects of posting and viewing electronic negative word-of-mouth on purchase behaviors. Computers in Human Behavior, 54 , 511–521.
Kolsarici, C., & Vakratsas, D. (2018). Synergistic, antagonistic, and asymmetric media interactions. Journal of Advertising, 47 (3), 282–300.
Kumar, V., & Pansari, A. (2016). Competitive advantage through engagement. Journal of Marketing Research, 53 (4), 497–514.
Kumar, V., Aksoy, L., Donkers, B., Venkatesan, R., Wiesel, T., & Tillmans, S. (2010). Undervalued or overvalued customers: Capturing total customer engagement value. Journal of Service Research, 13 (3), 297–310.
Kumar, V., Bhaskaran, V., Mirchandani, R., & Shah, M. (2013). Creating a measurable social media marketing strategy: Increasing the value and ROI of intangibles and tangibles for hokey pokey. Marketing Science, 32 (2), 194–212.
Kumar, A., Bezawada, R., Rishika, R., Janakiraman, R., & Kannan, P. K. (2016). From social to sale: The effects of firm-generated content in social media on customer behavior. Journal of Marketing, 80 (1), 7–25.
Kumar, V., Choi, J. W. B., & Greene, M. (2017). Synergistic effects of social media and traditional marketing on brand sales: Capturing the time-varying effects. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 45 (2), 268–288.
Kumar, V., Rajan, B., Gupta, S., & Dalla Pozza, I. (2019). Customer engagement in service. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 47 (1), 138–160.
Lamberton, C., & Stephen, A. T. (2016). A thematic exploration of digital, social media, and mobile marketing: Research evolution from 2000 to 2015 and an agenda for future inquiry. Journal of Marketing, 80 (6), 146–172.
Libai, B., Bolton, R., Bugel, M. S., de Ruyter, K., Gotz, O., Risselada, H., & Stephen, A. T. (2010). Customer-to-customer interactions: Broadening the scope of word of mouth research. Journal of Service Research, 13 (3), 267–282.
Libai, B., Muller, E., & Peres, R. (2013). Decomposing the value of word-of-mouth seeding programs: Acceleration versus expansion. Journal of Marketing Research, 50 (2), 161–176.
Malthouse, E. C., Haenlein, M., Skiera, B., Wege, E., & Zhang, M. (2013). Managing customer relationships in the social media era: Introducing the social CRM house. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 27 (4), 270–280.
Marshall, G. W., Moncrief, W. C., Rudd, J. M., & Lee, N. (2012). Revolution in sales : The impact of social media and related technology on the selling environment. Journal of Personal Selling & Sales Management, 32 (3), 349–363.
Maslowska, E., Malthouse, E. C., & Collinger, T. (2016). The customer engagement ecosystem. Journal of Marketing Management, 32 (5–6), 469–501.
Micu, A., Micu, A. E., Geru, M., & Lixandroiu, R. C. (2017). Analyzing user sentiment in social media: Implications for online marketing strategy. Psychology & Marketing, 34 (12), 1094–1100.
Moe, W. W., & Schweidel, D. A. (2017). Opportunities for innovation in social media analytics. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 34 (5), 697–702.
Moorman, C., & Day, G. S. (2016). Organizing for marketing excellence. Journal of Marketing, 80 (6), 6–35.
Morgan, R. M., & Hunt, S. (1999). Relationship-based competitive advantage: The role of relationship marketing in marketing strategy. Journal of Business Research, 46 (3), 281–290.
Muller, E., & Peres, R. (2019). The effect of social networks structure on innovation performance: A review and directions for research. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 36 (1), 3–19.
Muntinga, D. G., Moorman, M., & Smit, E. G. (2011). Introducing COBRAs: Exploring motivations for brand-related social media use. International Journal of Advertising, 30 (1), 13–46.
Nair, H. S., Manchanda, P., & Bhatia, T. (2010). Asymmetric social interactions in physician prescription behavior: The role of opinion leaders. Journal of Marketing Research, 47 (5), 883–895.
Naylor, R. W., Lamberton, C. P., & West, P. M. (2012). Beyond the “like” button: The impact of mere virtual presence on brand evaluations and purchase intentions in social media settings. Journal of Marketing, 76 (6), 105–120.
Pansari, A., & Kumar, V. (2017). Customer engagement: The construct, antecedents, and consequences. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 45 (3), 294–311.
Peters, K., Chen, Y., Kaplan, A. M., Ognibeni, B., & Pauwels, K. (2013). Social media metrics - a framework and guidelines for managing social media. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 27 (4), 281–298.
Pfeffer, J., & Salancik, G. (1978). The external control of organizations: A resource dependence perspective . New York: Harper & Row.
Pulizzi, J., & Barrett, N. (2009). Get content, get customers: Turn prospects into buyers with content marketing . New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Quinton, S., & Wilson, D. (2016). Tensions and ties in social media networks: Towards a model of understanding business relationship development and business performance enhancement through the use of LinkedIn. Industrial Marketing Management, 54 , 15–24.
Rapp, A., Beitelspacher, L. S., Grewal, D., & Hughes, D. E. (2013). Understanding social media effects across seller, retailer, and consumer interactions. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 41 (5), 547–566.
Ravi, K. (2018). Six ways Nike built a strong brand on social media. Available at https://blog.unmetric.com/nike-social-media .
Robert, Y. (2018). How Asos is making E-commerce all-inclusive. Available at https://www.forbes.com/sites/yolarobert1/2018/10/23/now-trending-how-asos-is-making-e-commerce-all-inclusive/#37e9d67b297d .
Rodriguez, M., Peterson, R. M., & Krishnan, V. (2012). Social media’s influence on business-to-business sales performance. Journal of Personal Selling & Sales Management, 32 , 365–378.
Rohm, A., Kaltcheva, V. D., & Milne, G. R. (2013). A mixed-method approach to examining brand-consumer interactions driven by social media. Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing, 7 (4), 295–311.
Rydén, P., Ringberg, T., & Wilke, R. (2015). How managers’ shared mental models of business-customer interactions create different sensemaking of social media. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 31 , 1–16.
Saldanha, F. P., Cohendet, P., & Pozzebon, M. (2014). Challenging the stage-gate model in crowdsourcing: The case of fiat Mio in Brazil. Technology Innovation Management Review, 4 (9), 28–35.
Salo, J. (2017). Social media research in the industrial marketing field: Review of literature and future research directions. Industrial Marketing Management, 66 , 115–129.
Schultz, D. E., & Peltier, J. (2013). Social media’s slippery slope: Challenges, opportunities and future research directions. Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing, 7 (2), 86–99.
Schweidel, D. A., & Moe, W. W. (2014). Listening in on social media: A joint model of sentiment and venue format choice. Journal of Marketing Research, 51 (4), 387–402.
Sheng, J. (2019). Being active in online communications: Firm responsiveness and customer engagement behavior. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 46 , 40–51.
Singaraju, S. P., Nguyen, Q. A., Niininen, O., & Sullivan-Mort, G. (2016). Social media and value co-creation in multi-stakeholder systems: A resource integration approach. Industrial Marketing Management, 54 , 44–55.
Stampler, L. (2013). How Dove’s “Real Beauty Sketches” became the most viral video ad of all time. Available at https://www.businessinsider.com/how-doves-real-beauty-sketches-became-the-most-viral-ad-video-of-all-time-2013-5?r=US&IR=T .
Stephen, A. T., & Galak, J. (2012). The effects of traditional and social earned media on sales: A study of a microlending marketplace. Journal of Marketing Research, 49 (5), 624–639.
Stewart, D. W., & Pavlou, P. A. (2002). From consumer response to active consumer: Measuring the effectiveness of interactive media. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 30 (4), 376–396.
Swani, K., Milne, G. R., Brown, B. P., Assaf, A. G., & Donthu, N. (2017). What messages to post? Evaluating the popularity of social media communications in business versus consumer markets. Industrial Marketing Management, 62 , 77–87.
Tafesse, W., & Wien, A. (2018). Implementing social media marketing strategically: An empirical assessment. Journal of Marketing Management, 34 (9–10), 732–749.
Teece, D., & Pisano, G. (1994). The dynamic capabilities of firms: An introduction. Industrial and Corporate Change, 3 (3), 537–556.
Timoshenko, A., & Hauser, J. R. (2019). Identifying customer needs from user-generated content. Marketing Science, 38 (1), 1–20.
Trainor, K. J., Andzulis, J., Rapp, A., & Agnihotri, R. (2014). Social media technology usage and customer relationship performance: A capabilities-based examination of social CRM. Journal of Business Research, 67 (6), 1201–1208.
Van Noort, G., & Willemsen, L. M. (2012). Online damage control: The effects of proactive versus reactive webcare interventions in consumer-generated and brand-generated platforms. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 26 (3), 131–140.
Varadarajan, R. (2010). Strategic marketing and marketing strategy: Domain, definition, fundamental issues and foundational premises. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 38 (2), 119–140.
Vargo, S., & Lusch, R. (2004). Evolving to a new dominant logic for marketing. Journal of Marketing, 68 (1), 1–17.
Venkatesan, R. (2017). Executing on a customer engagement strategy. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 45 (3), 289–293.
Verlegh, P. W. J., Ryu, G., Tuk, M. A., & Feick, L. (2013). Receiver responses to rewarded referrals: The motive inferences framework. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 41 (6), 669–682.
Vivek, S. D., Beatty, S. E., & Morgan, R. M. (2012). Customer engagement: Exploring customer relationships beyond purchase. Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice, 20 (2), 127–145.
Waldo, L. (2014). Hertz hands the social media keys over from marketing, to customer care. Available at http://futurecare.today/news/hertz-hands-the-social-media-keys-over-from-marketing-to-customer-care/#sthash.0t3MYPZq.M2vFKOV9.dpbs .
Wang, X. F. (2017). Case study: Increasing customers’ loyalty with social CRM. Available at https://go.forrester.com/blogs/17-01-23 - case_study_increasing_customers_loyalty_with_social_crm/ .
Webster, F. E. (1992). The changing role of marketing in the corporation. Journal of Marketing, 56 (4), 1–17.
Yadav, M. S., de Valck, K., Hennig-Thurau, T., Hoffman, D. L., & Spann, M. (2013). Social commerce: A contingency framework for assessing marketing potential. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 27 (4), 311–323.
Zhang, J., & Mao, E. (2016). From online motivations to ad clicks and to behavioral intentions: An empirical study of consumer response to social media advertising. Psychology and Marketing, 33 (3), 155–164.
Zhang, Y., Moe, W. W., & Schweidel, D. A. (2017). Modeling the role of message content and influencers in social media rebroadcasting. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 34 (1), 100–119.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Editor, the Area Editor, and the three anonymous Reviewers for their constructive comments, insightful suggestions, and supportive guidance provided during the review process.
Open access funding provided by University of Vaasa (UVA).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Marketing and Communication, University of Vaasa, P.O. Box 700, FI-65101, Vaasa, Finland
Fangfang Li & Jorma Larimo
Department of Business and Public Administration, School of Economics and Management, University of Cyprus, 1 University Road, P.O. Box 20537, CY-1678, Nicosia, Cyprus
Leonidas C. Leonidou
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Fangfang Li .
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rajkumar Venkatesan served as Area Editor for this article.
Electronic supplementary material
(DOCX 26.6 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Li, F., Larimo, J. & Leonidou, L.C. Social media marketing strategy: definition, conceptualization, taxonomy, validation, and future agenda. J. of the Acad. Mark. Sci. 49 , 51–70 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-020-00733-3
Download citation
Received : 11 December 2018
Accepted : 20 May 2020
Published : 10 June 2020
Issue Date : January 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-020-00733-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Social media marketing strategy
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Send us an email
How to do market research: The complete guide for your brand
Written by by Jacqueline Zote
Published on April 13, 2023
Reading time 10 minutes
Blindly putting out content or products and hoping for the best is a thing of the past. Not only is it a waste of time and energy, but you’re wasting valuable marketing dollars in the process. Now you have a wealth of tools and data at your disposal, allowing you to develop data-driven marketing strategies . That’s where market research comes in, allowing you to uncover valuable insights to inform your business decisions.
Conducting market research not only helps you better understand how to sell to customers but also stand out from your competition. In this guide, we break down everything you need to know about market research and how doing your homework can help you grow your business.
Table of contents:
What is market research?
Why is market research important, types of market research, where to conduct market research.
- Steps for conducting market research
- Tools to use for market research
Market research is the process of gathering information surrounding your business opportunities. It identifies key information to better understand your audience. This includes insights related to customer personas and even trends shaping your industry.
Taking time out of your schedule to conduct research is crucial for your brand health. Here are some of the key benefits of market research:
Understand your customers’ motivations and pain points
Most marketers are out of touch with what their customers want. Moreover, these marketers are missing key information on what products their audience wants to buy.
Simply put, you can’t run a business if you don’t know what motivates your customers.
And spoiler alert: Your customers’ wants and needs change. Your customers’ behaviors today might be night and day from what they were a few years ago.
Market research holds the key to understanding your customers better. It helps you uncover their key pain points and motivations and understand how they shape their interests and behavior.
Figure out how to position your brand
Positioning is becoming increasingly important as more and more brands enter the marketplace. Market research enables you to spot opportunities to define yourself against your competitors.
Maybe you’re able to emphasize a lower price point. Perhaps your product has a feature that’s one of a kind. Finding those opportunities goes hand in hand with researching your market.
Maintain a strong pulse on your industry at large
Today’s marketing world evolves at a rate that’s difficult to keep up with.
Fresh products. Up-and-coming brands. New marketing tools. Consumers get bombarded with sales messages from all angles. This can be confusing and overwhelming.
By monitoring market trends, you can figure out the best tactics for reaching your target audience.
Not everyone conducts market research for the same reason. While some may want to understand their audience better, others may want to see how their competitors are doing. As such, there are different types of market research you can conduct depending on your goal.
Interview-based market research allows for one-on-one interactions. This helps the conversation to flow naturally, making it easier to add context. Whether this takes place in person or virtually, it enables you to gather more in-depth qualitative data.
Buyer persona research
Buyer persona research lets you take a closer look at the people who make up your target audience. You can discover the needs, challenges and pain points of each buyer persona to understand what they need from your business. This will then allow you to craft products or campaigns to resonate better with each persona.
Pricing research
In this type of research, brands compare similar products or services with a particular focus on pricing. They look at how much those products or services typically sell for so they can get more competitive with their pricing strategy.
Competitive analysis research
Competitor analysis gives you a realistic understanding of where you stand in the market and how your competitors are doing. You can use this analysis to find out what’s working in your industry and which competitors to watch out for. It even gives you an idea of how well those competitors are meeting consumer needs.
Depending on the competitor analysis tool you use, you can get as granular as you need with your research. For instance, Sprout Social lets you analyze your competitors’ social strategies. You can see what types of content they’re posting and even benchmark your growth against theirs.
Brand awareness research
Conducting brand awareness research allows you to assess your brand’s standing in the market. It tells you how well-known your brand is among your target audience and what they associate with it. This can help you gauge people’s sentiments toward your brand and whether you need to rebrand or reposition.
If you don’t know where to start with your research, you’re in the right place.
There’s no shortage of market research methods out there. In this section, we’ve highlighted research channels for small and big businesses alike.
Considering that Google sees a staggering 8.5 billion searches each day, there’s perhaps no better place to start.
A quick Google search is a potential goldmine for all sorts of questions to kick off your market research. Who’s ranking for keywords related to your industry? Which products and pieces of content are the hottest right now? Who’s running ads related to your business?
For example, Google Product Listing Ads can help highlight all of the above for B2C brands.

The same applies to B2B brands looking to keep tabs on who’s running industry-related ads and ranking for keyword terms too.

There’s no denying that email represents both an aggressive and effective marketing channel for marketers today. Case in point, 44% of online shoppers consider email as the most influential channel in their buying decisions.
Looking through industry and competitor emails is a brilliant way to learn more about your market. For example, what types of offers and deals are your competitors running? How often are they sending emails?

Email is also invaluable for gathering information directly from your customers. This survey message from Asana is a great example of how to pick your customers’ brains to figure out how you can improve your quality of service.

Industry journals, reports and blogs
Don’t neglect the importance of big-picture market research when it comes to tactics and marketing channels to explore. Look to marketing resources such as reports and blogs as well as industry journals
Keeping your ear to the ground on new trends and technologies is a smart move for any business. Sites such as Statista, Marketing Charts, AdWeek and Emarketer are treasure troves of up-to-date data and news for marketers.
And of course, there’s the Sprout Insights blog . And invaluable resources like The Sprout Social Index™ can keep you updated on the latest social trends.
Social media
If you want to learn more about your target market, look no further than social media. Social offers a place to discover what your customers want to see in future products or which brands are killin’ it. In fact, social media is become more important for businesses than ever with the level of data available.
It represents a massive repository of real-time data and insights that are instantly accessible. Brand monitoring and social listening are effective ways to conduct social media research . You can even be more direct with your approach. Ask questions directly or even poll your audience to understand their needs and preferences.

The 5 steps for how to do market research
Now that we’ve covered the why and where, it’s time to get into the practical aspects of market research. Here are five essential steps on how to do market research effectively.
Step 1: Identify your research topic
First off, what are you researching about? What do you want to find out? Narrow down on a specific research topic so you can start with a clear idea of what to look for.
For example, you may want to learn more about how well your product features are satisfying the needs of existing users. This might potentially lead to feature updates and improvements. Or it might even result in new feature introductions.
Similarly, your research topic may be related to your product or service launch or customer experience. Or you may want to conduct research for an upcoming marketing campaign.
Step 2: Choose a buyer persona to engage
If you’re planning to focus your research on a specific type of audience, decide which buyer persona you want to engage. This persona group will serve as a representative sample of your target audience.
Engaging a specific group of audience lets you streamline your research efforts. As such, it can be a much more effective and organized approach than researching thousands (if not millions) of individuals.
You may be directing your research toward existing users of your product. To get even more granular, you may want to focus on users who have been familiar with the product for at least a year, for example.
Step 3: Start collecting data
The next step is one of the most critical as it involves collecting the data you need for your research. Before you begin, make sure you’ve chosen the right research methods that will uncover the type of data you need. This largely depends on your research topic and goals.
Remember that you don’t necessarily have to stick to one research method. You may use a combination of qualitative and quantitative approaches. So for example, you could use interviews to supplement the data from your surveys. Or you may stick to insights from your social listening efforts.
To keep things consistent, let’s look at this in the context of the example from earlier. Perhaps you can send out a survey to your existing users asking them a bunch of questions. This might include questions like which features they use the most and how often they use them. You can get them to choose an answer from one to five and collect quantitative data.
Plus, for qualitative insights, you could even include a few open-ended questions with the option to write their answers. For instance, you might ask them if there’s any improvement they wish to see in your product.
Step 4: Analyze results
Once you have all the data you need, it’s time to analyze it keeping your research topic in mind. This involves trying to interpret the data to look for a wider meaning, particularly in relation to your research goal.
So let’s say a large percentage of responses were four or five in the satisfaction rating. This means your existing users are mostly satisfied with your current product features. On the other hand, if the responses were mostly ones and twos, you may look for opportunities to improve. The responses to your open-ended questions can give you further context as to why people are disappointed.
Step 5: Make decisions for your business
Now it’s time to take your findings and turn them into actionable insights for your business. In this final step, you need to decide how you want to move forward with your new market insight.
What did you find in your research that would require action? How can you put those findings to good use?
The market research tools you should be using
To wrap things up, let’s talk about the various tools available to conduct speedy, in-depth market research. These tools are essential for conducting market research faster and more efficiently.
Social listening and analytics
Social analytics tools like Sprout can help you keep track of engagement across social media. This goes beyond your own engagement data but also includes that of your competitors. Considering how quickly social media moves, using a third-party analytics tool is ideal. It allows you to make sense of your social data at a glance and ensure that you’re never missing out on important trends.

Email marketing research tools
Keeping track of brand emails is a good idea for any brand looking to stand out in its audience’s inbox.
Tools such as MailCharts , Really Good Emails and Milled can show you how different brands run their email campaigns.
Meanwhile, tools like Owletter allow you to monitor metrics such as frequency and send-timing. These metrics can help you understand email marketing strategies among competing brands.
Content marketing research
If you’re looking to conduct research on content marketing, tools such as BuzzSumo can be of great help. This tool shows you the top-performing industry content based on keywords. Here you can see relevant industry sites and influencers as well as which brands in your industry are scoring the most buzz. It shows you exactly which pieces of content are ranking well in terms of engagements and shares and on which social networks.

SEO and keyword tracking
Monitoring industry keywords is a great way to uncover competitors. It can also help you discover opportunities to advertise your products via organic search. Tools such as Ahrefs provide a comprehensive keyword report to help you see how your search efforts stack up against the competition.

Competitor comparison template
For the sake of organizing your market research, consider creating a competitive matrix. The idea is to highlight how you stack up side-by-side against others in your market. Use a social media competitive analysis template to track your competitors’ social presence. That way, you can easily compare tactics, messaging and performance. Once you understand your strengths and weaknesses next to your competitors, you’ll find opportunities as well.
Customer persona creator
Finally, customer personas represent a place where all of your market research comes together. You’d need to create a profile of your ideal customer that you can easily refer to. Tools like Xtensio can help in outlining your customer motivations and demographics as you zero in on your target market.

Build a solid market research strategy
Having a deeper understanding of the market gives you leverage in a sea of competitors. Use the steps and market research tools we shared above to build an effective market research strategy.
But keep in mind that the accuracy of your research findings depends on the quality of data collected. Turn to Sprout’s social media analytics tools to uncover heaps of high-quality data across social networks.
- Marketing Disciplines
- Social Media Strategy
Social media RFPs: The best questions to include (plus a template)
Template: Essential Questions to Ask in Your Social Media Management Software RFP
- Team Collaboration
How to build a marketing tech stack that scales your business
- Customer Experience
Brand trust: What it is and why it matters
- Now on slide
Build and grow stronger relationships on social
Sprout Social helps you understand and reach your audience, engage your community and measure performance with the only all-in-one social media management platform built for connection.
What Is Marketing Strategy? – Examples, Components, & Planning

A strategy is like a map that helps you reach your goals using a predefined route. Marketers use such strategies to fulfil their marketing objectives. These marketing strategies connect the dots of a marketing plan to help the business reach the target customers using apt channels and aid business growth in the long run.
Marketing strategies are essential elements of a business. In fact, they are the deciding factor of the business’s success and failure in the long run.
But first, what is a marketing strategy, and why is it important?
What Is Marketing Strategy?
A marketing strategy is the combination of all the business’s decisions and actions to increase sales and achieve a sustainable competitive advantage by understanding and fulfilling the needs and wants of the customers.
This definition of marketing strategy stands on three key pillars. These are:
- What: Marketing strategy is the overall game plan or the roadmap marketers use to achieve a business’s marketing objectives and goals.
- Why: It aims to achieve a unique market position backed by a sustainable competitive advantage that results in more sales and profits for the business.
- How: Every marketing strategy works directly or indirectly by fulfilling the needs and wants of the customers.
In simple terms, a marketing strategy is an achievable and actionable focused set of steps devised by marketers to achieve a marketing objective.
Importance Of Marketing Strategy
Every marketing plan derives its form from a set of marketing strategies it uses. These marketing strategies play an essential role in the marketing mix of a business.
- Helps achieve marketing objectives: Marketing strategies lay down a set of steps to achieve marketing objectives focused on fulfilling the business’s short term and long term marketing goals.
- Provides direction: Marketing strategies set roadmaps that includes apt steps towards achieving goals. This roadmap gives direction and ensures that the business doesn’t stray away from the set of listed steps.
- Ensures coordination: The set of steps ensures coordination and avoids confusion among different business departments that work together to achieve the same goals.
- Reduces Wastage: Marketing strategies ensure optimum resource use by reducing duplication of work and appropriate allocation of limited resources.
- Ensures better control: It decides on the path to be followed and interim goals to be achieved. Hence, it becomes easier for marketers to control the marketing activities and ensure they are going according to the plans.
Components Of A Marketing Strategy
Even though there are numerous types of marketing strategies, all of them consists of these six components.
- Target Market: It is the customer segment to whom all the marketing activities are directed.
- Business Offering: The product or service offered by the business.
- Competitive Advantage: The value proposition that separates the company from the competition.
- Goal: A milestone that decides whether the marketing strategy was successful or not.
- Communication strategy: How the company plans to communicate the marketing message to the target market. It includes communication channels and tactics to get more traction and conversion.
- KPI: Key performance indicators measure the business’s performance and progress in the strategic marketing areas associated with its success.
Marketing Strategy Vs Marketing Plan Vs Marketing Tactic
Marketing strategy is a subset of a marketing plan that defines marketing goals and objectives and elaborates on how the business intends to achieve them.
Marketing strategy outlines the roadmap of how to achieve the goals and objectives defined by the marketing plan.
Marketing tactic, on the other hand, constitutes the actions taken to support the strategy.
That is, if getting 10,000 followers on Instagram is a marketing goal defined in the marketing plan, the marketing strategy will define the set of steps a brand will take to achieve this goal. The steps may include one post and two posts a day. However, a marketing tactic would be the content of posts and stories that the brand will use to support the strategy.
What Are The 4 Ps and 7ps Of Marketing Strategy?
Each marketing strategy stands on some key pillars required to market an offering to the customers. These include four key pillars and three additional pillars.
The four pillars of a marketing strategy are:
- Product: the tangible, physical good or intangible service being marketed;
- Price: how much the customer pays to buy the product;
- Place: where and through what channels can the customer purchase the product;
- Promotion: how the business promotes its product to the customers.
The three additional Ps of a marketing strategy include:
- People: Thebusiness’s human resource that enables it to deliver the offering to the customer.
- Process: The series of actions involved in delivering the offering to the final consumer.
- Physical Evidence: The tangible elements surrounding the product and the physical environment where the product or service is provided to the customers.
A business develops its marketing strategy only after considering these seven Ps of marketing.
Marketing Strategies Examples
Every business in the market employs some form of marketing strategy to achieve sustainable competitive advantage and increase its sales. Some of the renowned marketing strategy examples include:

Aldi is a renowned discount supermarket operating in over 18 countries. The company sells highly discounted products that are up to 50% less pricey as compared to competitors.
While the marketing plan sets the objective to sell products at a highly discounted price, the marketing strategy makes Aldi’s business model unique.
The company believes in a no-frills experience and limits its inventory to only important items with high sales volume. Moreover, 90% of the brands within the store are in-store brands which allow the company to source most of its products from local vendors.

TikTok is a short-video powered social media platform that makes it easy for users to create and share short videos across the internet. In its initial days, the company used Instagram and other social media channels to get more users onboard. The company placed its logo within the user-generated content and made sharing videos on Instagram and other social media platforms super easy.
So, whenever a user shared a TikTok video on Instagram, their friends got triggered by FOMO as to what this platform was and downloaded the app just to try it. This made the company gain its initial users.
How To Develop A Marketing Strategy
Marketing strategy builds a roadmap that leads a business from the current scenario to the desired scenario. But developing a marketing strategy isn’t as easy as it seems. It requires a marketer to hop through six different steps.
Identify the Goals and Objectives
Every market strategy stems from the core goals defined in a marketing plan. The goals can be big or small, quantitative or qualitative, and short term or long term. But they give structure to the set of steps that a market strategy defines.
Conduct A Market Analysis
Before developing a marketing strategy, a marketer should analyse the current situation of the market. This includes –
- Who is the target customer?
- What is the buyer persona?
- Who are the current players in the market?
- How do they market their offerings?
- What are the shortcomings in the current market scenario?
- What needs are not yet fulfilled?
- What positioning strategies are not yet capitalised on?
Once the business gets the answer to these questions, developing a marketing strategy and capitalising on the value proposition becomes easy.
Identify The Competitive Advantage
Competitive advantage is the benefit that sets the business apart from the other market players. It is usually powered by the business’s unique value proposition and is the factor the business capitalises on to fulfil its marketing objectives.
Lay Down The Set Of Steps
Once the marketer is well versed with the market’s current situation – what is missing from the market and how can they capitalise on their competitive advantage to fill the gap, it becomes easy to lay down the steps to achieve the goals.
For example, if a business is looking to increase its number of paying users and the market analysis proves that its existing customers are loyal and would appreciate rewards, it can make use of a referral marketing strategy to reward its existing users for bringing in new users on board.
Go On, Tell Us What You Think!
Did we miss something? Come on! Tell us what you think of this article in the comments section.
A startup consultant, digital marketer, traveller, and philomath. Aashish has worked with over 20 startups and successfully helped them ideate, raise money, and succeed. When not working, he can be found hiking, camping, and stargazing.
Related Posts:

- Sales +1 (800) 646-0520
- Online Survey Tool (DIY)
- Survey Design
- Survey Distribution
- Survey Participation
- Data Management
- All Features
- Enterprise Feedback
- Take a Tour
- Form Builder
- Customer Experience Overview
- Omnichannel Experience
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Analytics
- Customer Journey
- Alerts and Action
- Employee Experience Overview
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Pulse
- HR Analytics
- Help Desk Ticketing
- Closing the Loop
- Automation and Integration
- Managed Services
- Survey Templates
From design to distribution to data, our comprehensive solution is both intuitive and powerful.
- Customer Service
- Market Research
- Risk Assessment
- Event Planning
- Legal and Compliance
- Resident Satisfaction
- Credit Union
- Financial Services
- Travel & Hospitality
- Higher Education
- Manufacturing
Our top-tier certifications and practices ensure your data privacy and security every step of the way.
Professionally designed questionnaires for a wide range of projects allow you to go live in no time.
Our powerful, flexible solutions serve clients across industries and around the world. Their success is our success.
- See Case Studies
Enabling individuals and small teams to create and manage professional-looking surveys, forms, and polls.
Empowering businesses to gather and analyze feedback through a comprehensive platform that supports secure collaboration.
Enabling companies to improve customer experience and loyalty by examining trends and drivers across the customer journey.
Transforming always-on feedback collection into a streamlined triage and follow-up flow to close the loop efficiently.
Helping organizations to listen more deeply to their employees to uncover key drivers that impact engagement and retention.
- SogoConnect
- Video Library
- Latest Release
- Sign Up Free Sign Up Free
- Request a Demo Request a Demo
The 11-Minute Marketing Research Process Guide You Need for 2024
Estimated Reading Time : 9 mins
Is marketing research relevant for data-led marketers? How does it impact business success in today’s digital-first environment? Why do top marketers rely on it to maximize customer engagement? Do traditional market research surveys still serve as effective channels?
In this article, we decode the ideal marketing research process for the modern, tech-savvy marketer. Got 11 minutes? Dive into this step-by-step guide to approaching marketing research from processes that add CX value to benefits that maximize customer lifecycle value.
What is market research?
We’d say 99% of marketing is understanding the human behind the customer. And marketing research helps you decode things that make this human tick. It lets you explore the many factors that influence your customer; similar to mapping the customer experience across touchpoints.
Effective market research tools and methods help you with the precise insights you need to get an edge in the market – right from competition sentiment to ideal product pricing. Over the years, marketing research has even been synonymous with stellar business insights and even turnarounds.
Take, for instance, the case of LEGO. After struggling to stay profitable in 2003, the toy manufacturer was able to recapture the imagination of customers owing to high-impact market research .
Contrary to what many digital-first marketers think, marketing research isn’t limited to large companies with giant budgets. Whether you are an established mid-size firm or a team of two, consistent marketing research is key to engaging and winning your customers. Don’t worry about investing and training resources.
Depending on your immediate to mid-term priorities, you can choose to limit your marketing research . This may mean understanding evolving pricing sensibilities. Or you may want to narrow down your research to the top 3 purchase triggers for Gen Zs. Using intelligent marketing research tools and methods , you can develop a process ecosystem that is not resource or skill-intensive which will help you find out why you should conduct a market research survey .
The efficacy of your marketing research is shaped by a single factor – the emotional intelligence and design quotient of your marketing research surveys. The metrics and methods you use to analyze customer responses come a close second.
Top benefits of marketing research
Before you get down to developing your marketing research process, you must weigh the top benefits. This lets you arrive at the business value you stand to get from the exercise
Benefit #1 – Retain customer trust
Your customer’s needs and expectations are changing faster than ever. And a growing percentage of them expect brands and businesses to keep pace. As personalization becomes integral to Customer Experience (CX), customers want to do business with companies that put them first.
When a business fails to deliver on this expectation, it loses customer trust. This demands that you invest in a CX-focused marketing research ecosystem. By using effective market research tools and conducting on-point market research surveys , you stand to gain deep, impactful insights into every customer’s psyche. When you leverage these insights to engage with the customer across touchpoints, you earn their trust.
Benefit #2 – Win the ‘speed-to-market’ race
Being the first to own a category or introduce a breakthrough offering always comes with a massive advantage – you can gain a huge market share and forge strong customer relationships before the competition kicks in.
Whether you are weeks away from launching a new offering or want to know the viability of expanding to a new category, market research lets you know where you stand in the context of your competition. This works to your advantage – alter your launch strategy… get your pricing right…invite pre-orders. It lets you build a go-to-market strategy that is far more likely to succeed.
Benefit #3 – Build a strong brand
It takes more than a great product or a powerful marketing campaign to make customers fall in love with your brand. Following a marketing research process consistently gives you access to the many facets that customers will value in your brand. When you engage customers across markets, you arrive at a gold mine of research. It helps you build a brand that caters to the emotional and rational needs of customers.
Right from your innovation and product design team to your sales and finance teams, everyone aligns with a perspective that is rooted in market reality. For instance, it can help you understand how the market is keeping up with customer-first pricing in a subscription economy.
Benefit #4 – Pivot at the right time
The decision to scale or innovate, when implemented in isolation, can be dangerous for profitability. On the other hand, investing in a marketing research process lets you gain significant business velocity
With tech and AI disrupting markets in the most unimaginable ways, strategic market research methods help you move your business in the direction of changing customer needs. The Fujifilm pivot to new verticals outside of film photography remains an industry favorite example in this context. Your marketing research exercise may even point you in the direction of an unconventional collaboration. This makes it critical to approach the process with an open mind.
The marketing research process
The process you deploy can define the success of your marketing research exercise. It also helps everyone on the team see the value in investing and aligning with the preferred method and the results.
Here are some step-by-step examples of the marketing research process :
- Identify your marketing research goal(s)
- Define the type of marketing research
- Design your research framework and methods
- Map your sample cohorts
- Onboard partners and tools
- Gather data and insights
- Action change
Have you ever wondered what top marketers do differently to get the most out of their marketing research? They act upon micro insights without a moment’s delay. This is often key to staying ahead of competitors as well as retaining customer confidence. How? By investing in marketing research and survey tools that make sense of data for them.
Types of marketing research with examples
Depending on your business and marketing goal, you can choose one or a mix of marketing research designs to build your research framework.
Primary research
Secondary research, exploratory research, descriptive research, causal research, putting your marketing research results to work.
Ready to build your marketing research process? Learn how SogoCX can help you build an integrated ecosystem.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the marketing research process.
Depending on the goal and scale of the research, every marketer’s process may differ. But in essence, it involves taking a structured, step-wise approach to gain deep, precise insights into various or specific market dynamics.
What is the role of marketing research?
In a highly dynamic business environment, market research ensures you are in sync with changing customer preferences, evolving stakeholder sentiment, competitor strength, and other external factors. It allows you to resolve a marketing challenge or unlock new opportunities, depending on your business priority.
Why is the marketing research process important?
Adopting a marketing research process makes it quicker and easier for everyone on your team to action research and act swiftly on the findings. A step-wise framework ensures the results are credible and relevant. This greatly increases the chances of thriving in an immensely competitive market. It can also enable you to compare results each time on a couple of common metrics even if every research’s primary goal is unique.
What are the 7 steps in the marketing research process?
Many marketers choose to create their own steps and framework to arrive at a marketing research process. Broadly, these align to the below 7 steps:
Recent Posts
- The Power of Brand Loyalty In Today’s Marketplace: Study Results August 9, 2024
- The 11-Minute Marketing Research Process Guide You Need for 2024 July 23, 2024
- 5 Communication Styles in the Workplace You Need to Know July 18, 2024
- New Hire Onboarding Survey Questions to Improve Employee Experience and Retention July 17, 2024
- Buyer Journey vs. Customer Journey: Key Differences and Why They Matter July 16, 2024
Subscribe for tips and insights to drive better decisions!
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
- Anti-Spam Policy
- Data & Security
- Get 7 Days Free
GQG Partners Inc Chess Depository Interest
| Morningstar Rating for Stocks | Fair Value | Economic Moat | Capital Allocation |
|---|---|---|---|
| A$7.41 | Lxfx | Wplqghwx |
GQG Has Strong Results but Market Not Pricing in Mean Reversion

Business Strategy and Outlook
GQG Partners is a boutique manager of listed equities. As of July 2024, GQG manages around USD 156 billion for institutional, wholesale and subadvised clients.
Free Trial of Morningstar Investor
Get our analysts’ objective, in-depth, and continuous investment coverage of GQG so you can make buy / sell decisions free of market noise.
Sponsor Center
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Target Market?
- Defining a Product's Target Market
- 4 Target Markets
Why Are Target Markets Important?
What are market segments, target market and product sales.
- Target Market FAQs
The Bottom Line
- Marketing Essentials
Target Market: Definition, Purpose, Examples, Market Segments
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Group1805-3b9f749674f0434184ef75020339bd35.jpg)
Investopedia / Mira Norian
A target market is a group of people that have been identified as the most likely potential customers for a product because of their shared characteristics, such as age, income, and lifestyle.
Identifying the target market is a key part of the decision-making process when a company designs, packages, and advertises its product.
Key Takeaways
- A target market is a group of customers with shared demographics who have been identified as the most likely buyers of a company's product or service.
- Identifying the target market is important in the development and implementation of a successful marketing plan for any new product.
- The target market also can inform a product's specifications, packaging, and distribution.
How Do I Define My Product's Target Market?
Part of creating a new product is envisioning the consumers who will buy it.
A new product must satisfy a need or solve a problem—or both. That need or problem is probably not universal (unless it reaches the level of indoor plumbing). More likely, it is needed by a subset of consumers, such as environmentally-conscious vegetarians, science nerds, or outdoor enthusiasts. It may appeal to a teenager or a middle-aged professional, a bargain-hunter or a snob.
Envisioning your likely target market is part of the process of creating and refining a product and informs decisions about its packaging, marketing, and placement.
What Are the 4 Target Markets?
Market researchers use activity, interest, and opinion (AIO) surveys to construct psychographic profiles of their target customers. Marketing professionals divide consumers into four major segments:
Demographic : These are the main characteristics that define your target market. Everyone can be identified as belonging to a specific age group, income level, gender, occupation, and education level.
Geographic : This segment is increasingly relevant in the era of globalization. Regional preferences need to be taken into account.
Psychographic : This segment goes beyond the basics of demographics to consider lifestyle, attitudes, interests, and values.
Behavioral : This is the one segment that relies on research into the decisions of a company's current customers. New products may be introduced based on research into the proven appeal of past products.
What Is an Example of a Target Market?
Each of the four target markets can be used to consider who the customer is for a new product.
For example, there are an estimated 49,773 Italian restaurants in the U.S. Clearly, they have enormous appeal.
But a corner pizza joint might appeal mostly—although by no means entirely—to a younger and more budget-conscious consumer, while an old-fashioned white tablecloth place might be frequented by older individuals and families who live in the neighborhood. Meanwhile, a newer venue down the street might cater to an upscale and trend-conscious crowd who will travel a good distance for the restaurant's innovative menu and fancy wine list.
In each successful case, a savvy business person has consciously considered the ideal target market for the restaurant and has tweaked the menu, decor, and advertising strategy to appeal to that market.
Few products today are designed to appeal to absolutely everyone. The Aveda Rosemary Mint Bath Bar, available for $26 per bar at Aveda beauty stores, is marketed to the upscale and eco-conscious woman who will pay extra for quality. Clé de Peau Beauté Synactif Soap retails for $110 a bar and is marketed to wealthy, fashion-conscious women who are willing to pay a premium for a luxury product. An eight-pack of Dial soap costs $11.49 at CVS, and it is known to get the job done.
Part of the success of selling a good or service is knowing whom it will appeal to and who will ultimately buy it. Its user base can grow over time through additional marketing, advertising, and word of mouth.
That's why businesses spend a lot of time and money in defining their initial target markets, and why they follow through with special offers, social media campaigns , and specialized advertising.
Dividing a target market into segments means grouping the population according to the key characteristics that drive their spending decisions. Some of these are gender, age, income level, race, education level, religion, marital status, and geographic location.
Consumers with the same demographics tend to value the same products and services, which is why narrowing down the segments is one of the most important factors in determining target markets.
For example, people who fall into a higher income bracket may be more likely to buy specialty coffee from Starbucks instead of relying on Dunkin' Donuts. The parent companies of both of these brands need to know that in order to decide where to locate their stores, where to stock their products, and where to advertise their brand.
A business may have more than one target market—a primary target market, which is the main focus, and a secondary target market, which is smaller but has growth potential. Toy commercials are targeted directly to children, and their parents are the secondary market.
Identifying the target market is an essential part of a product development plan, along with manufacturing, distribution, price, and promotion planning. The target market determines significant factors about the product itself. A company may tweak certain aspects of a product, such as the amount of sugar in a soft drink or the style of the packaging, so that it appeals more to consumers in its target group.
As a company’s product sales grow, it may expand its target market internationally. International expansion allows a company to reach a broader subset of its target market in other regions of the world.
In addition to international expansion, a company may find its domestic target market expands as its products gain more traction in the marketplace. Expanding a product's target market is a revenue opportunity worth pursuing.
How Detailed Should a Target Market Be?
It depends. Broadly speaking, a product may be designed for a mass market or a niche market, and a niche market can be a very small group indeed, especially in a product's early introductory phase.
Some carbonated beverages aim for a practically universal market. Coca-Cola had to branch out to 200 markets abroad to continue growing its customer base. Gatorade is owned by Pepsi Cola, but the brand is positioned as a drink for athletes. The soda brand Poppi, which is branded as a healthy, sparkling, prebiotic soda with real fruit juice and gut health and immunity benefits, is clearly aimed at a younger, healthier, and more trend-conscious target market.
Consider a casual apparel company that is working to build its distribution channels abroad. In order to determine where its apparel will be most successful, it conducts some research to identify its primary target market. It discovers that the people most likely to buy its products are middle-class women between the ages of 35 and 55 who live in cold climates.
It's reasonable for the company to focus its advertising efforts on northern European websites that have a strong female audience. But first, the company may consider how its apparel can be most attractive to that target market. It may revise its styles and colors and tweak its advertising strategy to optimize its appeal to this new prospective market.
What Is the Purpose of a Target Market?
A target market defines a product as well as vice versa. Once a target market is identified, it can influence a product's design, packaging, price, promotion, and distribution. A product aimed at men won't be packaged in pink plastic. A luxury cosmetic won't be sold in a pharmacy. An expensive pair of shoes comes with a branded cloth drawstring bag as well as a shoebox. All of those factors are signals to the target audience that they have found the right product.
Identifying the target market is part of the process of creating and refining a new product.
A target market can be translated into a profile of the consumer to whom a product is most likely to appeal. The profile considers four main characteristics of that person: demographic, geographic, psychographic, and behavioral. These characteristics help determine who might purchase a company's product.
IBISWorld. " Italian Restaurants in the U.S. - Number of Businesses ."
Aveda. " Rosemary Mint Bath Bar ."
Cle de Peau. " Synactif Soap ."
CVS. " Dial Antibacterial Deodorant Bar Soap, White ."
Coca-Cola Australia. " Coca-Cola: From Start-Up to Global Enterprise ."
Pepsico Partners. " Gatorade ."
DrinkPoppi. " Home ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Market-Segmenation-76c1fe9e48ff4906bc2a565bb67c6862.png)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Marketing Strategy
Marketing Strategies
- January 2006
- In book: Marketing Management: International Perspectives (pp.81-98)
- Edition: 1st
- Publisher: Vijay Nicole Publishing, Chennai (India)

- Université de Fribourg
Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations

- Chiaki Iwai

- Yağmur Özyer
- Başak Değerli
- Alper Değerli

- H. A. Iliyasu
- ELECTR POW SYST RES

- J MARKETING

- J RETAILING

- Kevin Lane Keller

- M.E. Porter
- G. M. Stalker
- HARVARD BUS REV
- FOREIGN AFF
- William Diebold
- Michael E. Porter

- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up
| You might be using an unsupported or outdated browser. To get the best possible experience please use the latest version of Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Microsoft Edge to view this website. |
Social Media Marketing Strategy Tips For 2024

Published: Aug 15, 2024, 8:25am

Table of Contents
What is social media marketing, why social media marketing is important, 11 tips to build your social media marketing strategy, bottom line, frequently asked questions (faqs).
Social media marketing was born in the mid-2000s with the rise of platforms such as MySpace, Facebook and Twitter, but did not start hitting its stride until Facebook introduced “Facebook Flyers Pro” in 2007. Since then, it has revolutionized the marketing landscape by allowing companies to reach an unprecedented amount of potential customers worldwide.
But how exactly do businesses harness the power of the 5 billion-plus people using social media? In this article, we will dive into what exactly social media marketing is, why it is important and provide tips for you to up your social media marketing strategy in 2024.
Social media marketing is all about using social media platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, X and TikTok to chat with your audience, get your brand recognized and increase sales. It involves creating posts, images and videos that your audience will love, interact with and share. This method capitalizes on the interactive nature of social media to foster engagement, allow businesses to showcase their products and build a community around their brand. Creating an effective social media marketing campaign requires setting clear objectives, choosing the right social media platform or platforms, using analytics tools to track performance and adjusting strategies accordingly.
Traditional marketing methods such as print ads, television commercials and billboards often hoped to grab interested customers from a broad reach. The digital age of social media marketing has ushered in an era of personalization and precision targeting. Social media allows businesses to gather insights into user behavior, preferences, disinterests and online activities. Marketers can then create social media campaigns that target the direct audience that they want to attract. This new level of personalization has transformed the way businesses interact with their audiences.
Featured Partners
Sprout Social
Standard $199/seat/month; Professional $299/seat/month; Advanced $399/seat/month *pricing is based on annual subscriptions
30 day free trial (all plans)
Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, LinkedIn, Youtube, TikTok, Pinterest, Reddit, Tumblr, Yelp!, Glassdoor, Trip Advisor, Google My Business, and more

On Sprout Social's Website
Professional $99/month; Team $249/month *pricing based on annual subscriptions
Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, LinkedIn, YouTube, TikTok, Pinterest, Threads (beta), Google Business Profile and more

On Hootsuite's Website
Social media marketing is a game-changer for businesses because it allows you to reach so many people around the world in real time. It is no wonder why so many businesses have ditched old-school marketing strategies such as billboards or radio spots in exchange for comprehensive social media campaigns. Some of the biggest advantages of social media marketing include:
- Increase brand awareness: You can expand your brand’s awareness by consistently posting on social media sites. This is especially useful for small or new businesses to be able to introduce themselves and their business personality to a new audience.
- Drive traffic: Creating intriguing content with compelling calls to action can drive followers to visit your website. You can funnel users directly from your social media platform to your website by including tailored links in your posts, stories or reels. For example, promoting a new blog post on X with a “Read Now” button can bring followers onto your site.
- Generate leads: Social media platforms provide tools for lead generation such as Instagram’s “Swipe Up” feature or LinkedIn’s lead-generation forms. Let’s say you’ve launched a new e-book. You can gather new leads to expand your email list by advertising the e-book on Facebook and attaching a direct download link in exchange for an email address.
- Real-time discovery of industry trends: Social media serves as a live feed for market patterns and trends. You can capitalize on viral topics by watching trending hashtags or popular discussion points within your industry.
- Cost-effective: In comparison to traditional marketing channels such as print or TV ads, social media marketing offers ways to publicize your product without spending a fortune. Social media marketing can be completely free if you do not have a marketing budget. You can, however, leverage your reach through sponsored content or ads on platforms such as Facebook, Instagram and LinkedIn.
- Humanize your brand: Consumers appreciate brands with authentic personalities. You can create a relatable brand by sharing “behind-the-scenes” content or telling your company’s story through posts or stories. For example, Patagonia regularly shares posts highlighting its commitment to environmental conservation, which strongly resonates with its customer base.
At first glance, social media marketing might appear straightforward, but to truly make an impact it requires more than just a few posts online every now and again. Along with any successful marketing strategy, it involves meticulous planning, consistent content creation, thorough analysis and strategic adjustments. Here are 12 tips on building a comprehensive social media marketing strategy to help you harness the full potential of social media for your business.
- Set S.M.A.R.T., relevant goals: Before starting your social media marketing strategy, make sure to set S.M.A.R.T. goals. S.M.A.R.T. stands for specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound. Begin by outlining clear, actionable goals using this criterion. For instance, instead of vaguely aiming to “increase sales,” strive to “increase sales by 15% over the next quarter through social media referral traffic.” This will provide a precise path for your strategy.In addition, set goals that are relevant to your business. Do you want to increase brand awareness? Do you want to increase your social media footprint? Do you want to drive traffic to your website? Reach, impressions and engagement rate are among the 13 essential social media metrics to measure in 2024 . Make sure the goals you set are relevant to your business’s objectives.
- Identify target audience: Before you begin, it is important to know who you are talking to. Create a sketch of your ideal customer. Describe their demographic traits including age, location and gender as well as psychographic traits such as interests, problems and values. If you deal in luxury watches, your audience likely consists of older, affluent individuals with an interest in style and status. Or if you have a boutique yoga studio, your ideal audience is probably a woman between 25 and 50 who prioritizes health and wellness.
- Choose the right platforms: The big seven social media platforms are Facebook, X, Instagram, TikTok, YouTube, Pinterest and LinkedIn. Each platform attracts a different type of audience. Analyze where your core audience spends the most time online and target those platforms. For example, if your brand caters to professionals or B2B clients, LinkedIn may prove more beneficial than TikTok.
- Create valuable content: Never publish content just to post something. Always create content that your audience will find beneficial. Aim to inform, engage or inspire. For a fitness brand, this might include workout tips, healthy recipes or motivational posts. In addition, it is a good idea to occasionally incorporate interactive elements such as Q&As, polls or challenges to engage your audience actively and foster a sense of community.
- Consistent branding: Maintain uniform design elements such as logo and brand colors and voice, whether it is formal or casual across platforms. This consistency will help with brand recognition.
- Use visual content: As the old saying goes, a picture is with a thousand words. Make use of visuals—photos, infographics or videos—to increase engagement. Leverage visual storytelling in order to convey your brand’s personality. For example, a bakery might post mouthwatering photos of its cupcakes or a step-by-step video tutorial on dough kneading. Additionally, incorporating user-generated content such as customer photos or reviews can add authenticity to your feed.
- Automate scheduling: Use social media management tools to schedule posts in advance. Not only will this help you save time, it will also ensure your content is delivered on a consistent basis. A regular posting schedule helps keep your brand’s presence fresh in the minds of your audience. Buffer, Hootsuite and Zoho Social are three of the best social media management software platforms on the market.
- Engage actively: Join conversations and reply promptly to comments. Don’t be afraid to show a human side to your interactions. Chipotle, for instance, has more than 30 million followers on social media. The company is renowned for its witty, engaging responses in its social media interactions.
- Collaborate with influencers: Partner with relevant influencers to get your brand in front of new eyes. Collaborating with these partners can help you tap into specific communities and boost your credibility by leveraging the trust they’ve established with their followers. A children’s clothing brand might collaborate with parenting bloggers while a new restaurant might collaborate with a local food blogger.
- Analyze and adapt: Use analytics tools to track your performance. If Instagram Stories drive more engagement than regular posts, for instance, shift your focus accordingly. This data-driven approach allows you to understand your audience better so you can tailor your strategy for maximum impact.
- Monitor trends: Social media trends evolve rapidly. Keeping up to date can unlock new avenues—be it new features such as Instagram Reels or trends such as the sustainability movement—to align your strategy with broader user behavior. Adapting to the latest trend helps keep you relevant and can even open doors to innovative methods of customer engagement and user-generated content.
Since its inception in the early 2000s, social media has revolutionized the marketing landscape by offering businesses an unprecedented ability to reach audiences, prioritize personalization and build real-time connections between brands and consumers. It helps businesses ramp up brand visibility, drives traffic, pulls in potential leads and catches the wave of trending topics—all while being budget-friendly. If your business wants to ride the social media wave, you should focus on creating clear and achievable goals, targeting your ideal audience and creating valuable content. Mix in some smart scheduling tools, actively engage with your followers and use analytics to continually fine-tune your strategies and you can significantly amplify your brand’s online impact.
What are the five Ps of social media marketing?
The five Ps of marketing—Product, Price, Promotion, Place and People—form the cornerstone of marketing strategies. “Product” refers to what a company sells, whether it is tangible goods or intangible services. “Price” is the cost consumers are willing to pay. “Promotion” is all communicative tactics used including advertising, PR or social media engagement. “Place” is the channels or physical locations where the product or service is sold. “People” refers to everyone involved in the business including customers, employees, vendors and partners.
What are the seven Cs of social media marketing?
The seven Cs of social media marketing are the guiding principles for building a robust social media marketing plan. They include “Community,” referring to the group of people your brand brings together, while “Collaboration” and “Communication” refer to the value of working alongside users and other brands to collaborate and share valuable insights. “Constraints” acknowledge the limitations that social media platforms can present to marketers. “Connectivity” and “Channels” focus on establishing a seamless link between social media platforms and choosing the right mediums to reach your target audience. “Content” is central to attracting an audience through relevant, engaging and high-quality content.
What is the golden rule of social media marketing?
The golden rule of social media marketing is to foster genuine interactions that build trust and community. Crafting content that initiates conversations enables brands to spark conversations and build a community. This strategy emphasizes authentic connection with the audience to help brands achieve enduring marketing success through active participation.
- Best SEO Software For Small Business
- Best Social Media Management Software
- Best Email Marketing Software
- Best SEO Services For Small Business
- Best Mass Texting Services
- Best Mailchimp Alternatives
- Best ActiveCampaign Alternatives
- Top SEMRush Alternatives
- Top ahrefs Alternatives
- Hootsuite Review
- MailerLite Review
- ActiveCampaign Review
- Constant Contact Review
- Sprout Social Review
- SEMRush Review
- Mailchimp Review
- Small Business Marketing
- What Is Marketing?
- What Is Digital Marketing?
- Digital Marketing Strategy Guide
- Digital Marketing Tips
- Search Engine Marketing Guide
- SEO Marketing Guide
- Social Media Marketing
- Content Marketing
- PPC Advertising Guide
- Tips For Generating Leads Online
- The 4 Ps Of Marketing
- How To Get More Followers On Instagram
- How To Start A Podcast
- E-Commerce SEO
- WordPress SEO Guide
Next Up In Marketing
- Best SEO Tools & Software
- Best Social Media Management Tools
- Best SEO Services
- Best Chatbots

Best Search Engines To Use In 2024
What Is Incident Response? Definition & Best Practices
What Is An IT Audit? Definition And Best Practices
How To Do Keyword Research For SEO
What Is Computer Networking?
SITE123 Review 2024: Features, Pros And Cons
Jennifer Simonson draws on two decades as a journalist covering everything from local economic developement to small business marketing. Beyond writing, she tested entrepreneurial waters by launching a mobile massage service, a content marketing firm and an e-commerce venture. These experiences enriched her understanding of small business management and marketing strategies. Today, she channels this first-hand knowledge into her articles for Forbes Advisor.
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Auto Racing
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
What are carry trades and how did they contribute to this week’s global market mayhem?
Currency traders watch monitors near a screen, back, showing the Korea Composite Stock Price Index (KOSPI), top left, and the foreign exchange rate between U.S. dollar and South Korean won, top center, at the foreign exchange dealing room of the KEB Hana Bank headquarters in Seoul, South Korea, Tuesday, Aug. 6, 2024. (AP Photo/Ahn Young-joon)

- Copy Link copied
BANGKOK (AP) — The mayhem that swept across world markets this week was partly caused by a market strategy known as the “carry trade.”
Japan’s benchmark Nikkei 225 plunged 12.4% on Monday and markets in Europe and North America suffered outsized losses as traders sold stocks to help cover rising risks from investments made using cheaply financed funds borrowed mostly in Japanese yen.
Markets recovered much of their losses on Tuesday. But the damage lingers.
They were jolted by a combination of factors, including dread of a possible recession in the United States, the world’s largest economy, and worries that technology shares have shot way too high this year.
But the scale of the declines was exaggerated by the rush to sell U.S. dollars due to carry trade deals that had helped drive markets to record levels.
What are carry trades?
Carry trades involve borrowing at low cost in one currency to achieve higher returns from investments in another currency. One of the most recent examples has been to borrow Japanese yen, expecting the currency to remain cheap against the U.S. dollar and for Japanese interest rates to remain low. The borrowed funds would then be invested in U.S. stocks and Treasury bonds in anticipation of a higher return.
Why have traders been unwinding their carry trades?
The key factor behind a carry trade is a difference in interest rates. The Bank of Japan has kept interest rates at or near zero for years, trying to encourage more spending and spur economic growth. Last week, it raised its main interest rate from nearly zero . Higher interest rates tend to boost the value of a nation’s currency, and the Japanese yen surged against the U.S. dollar. Traders scrambled to sell higher risk, dollar-denominated assets to cover suddenly higher borrowing costs, plus losses from foreign exchange rate changes and losses in asset values as share prices plunged. Also, hedge funds that conduct carry trades use computer models to help maximize their returns versus their risks. They needed to sell shares to maintain acceptable risk profiles.
Why do carry trades have an outsized impact on markets?
Carry trades tend to make the most sense when foreign exchange rates are relatively stable and investors can tap into higher yielding market opportunities, like the recent runups of stock prices in places like the United States. The recent market upheavals obliged traders to cover their debts by buying yen and other carry trade currencies and selling relatively more of the higher risk assets they bought under more favorable conditions. Also, carry trades are very lucrative when stocks or other investments are rising, but losses can snowball when thousands of traders are pressured to sell stocks or other assets all at once. “A massive global carry trade unwind was the spark that lit the fuse for this market Armageddon,” Stephen Innes of SPI Asset Management said. “One defining characteristic of these self-perpetuating market melts is the vicious cycle where a sell-off increases realized volatility.”
What’s the future risk from carry trades?
The gap between the main interest rate in Japan, now at 0.25%, and the Federal Reserve’s benchmark rate of 5%-5.25% is still wide but is likely to narrow as the Fed cuts rates and Japan raises its rates. Financial markets appeared to have calmed Tuesday, with Japan’s Nikkei 225 index gaining 10.2% and other markets mostly higher. Analysts are divided over whether this bout of volatility in the markets has passed or if there is more to come. Regardless, carry trades have been used for decades. They contributed to a meltdown in Iceland’s financial sector in 2007-2008 where investors borrowed in yen or Swiss francs to take advantage of high Icelandic interest rates. During this latest market upset, Mexico, another focus of the yen carry trade, has seen its peso fall more than 6%. The popular but potentially complicated trading strategy is likely to remain a wild card for investors, especially in times of high market volatility.


IMAGES
COMMENTS
Marketing strategy is a construct that lies at the conceptual heart of the field of strategic marketing and is central to the practice of marketing. It is also the area within which many of the most pressing current challenges identified by marketers and CMOs arise. We develop a new conceptualization of the domain and sub-domains of marketing strategy and use this lens to assess the current ...
Abstract. Marketing strategy is a construct that lies at the conceptual heart of the field of strategic marketing and is central to the practice of marketing. It is also the area within which many ...
A marketing strategy is a business's overall game plan for reaching consumers and turning them into customers.. The key word in the above definition is "game plan". Entering a market with a product is like starting a new game. Since you're new to the game, you don't know the rules, and you don't know who you're playing against.
Example 2: McDonald's global expansion. McDonald's successful global expansion strategy demonstrates the importance of market research when expanding into new territories. Before entering a new market, McDonald's conducts thorough research to understand local tastes, preferences and cultural nuances.
Marketing Strategy: A marketing strategy is a business' overall game plan for reaching people and turning them into customers of the product or service that the business provides. The marketing ...
2. Create a Research Plan. Once you have found the problem you want to solve, the next step is to start building a research plan. If you haven't developed a marketing research plan before, the task can be intimidating. To help you out, here are some approaches you can use for your research.
This SMART goal guide can help you with more effective goal-setting. 3. Identify your target audience and create buyer personas. To create an effective marketing strategy, you need to understand who your ideal customers are. Take a look at your market research to understand your target audience and market landscape.
Marketing research is essentially a method utilized by companies to collect valuable information regarding their target market. Through the common practice of conducting market research, companies gather essential information that enables them to make informed decisions and develop products that resonate with consumers. It encompasses the gathering, analysis, and interpretation of data, which ...
A marketing strategy acts as a roadmap, outlining the steps a business needs to take to reach its objectives. It provides a clear direction, ensuring that marketing efforts are aligned with the overall business plan. Without a well-defined strategy, marketing can be unfocused and ineffective.
It also prop oses a definition. for marketing strategy, the focal organ izational strategy. construct of the field, and enumerates a number of. foundation al premises of market ing strategy. The ...
commonly employed non-rational. processes of strategy making. — that the content of strong marketing. strategies is, to a useful degree, well. defined by the extant literature. This. content ...
Marketing research is defined as any technique or a set of practices that companies use to collect information to understand their target market better. Organizations use this data to improve their products, enhance their UX, and offer a better product to their customers. Marketing research is used to determine what the customers want, and how ...
Although social media use is gaining increasing importance as a component of firms' portfolio of strategies, scant research has systematically consolidated and extended knowledge on social media marketing strategies (SMMSs). To fill this research gap, we first define SMMS, using social media and marketing strategy dimensions. This is followed by a conceptualization of the developmental ...
Explore our product to learn how SurveyMonkey can work for you. Get data-driven insights from a global leader in online surveys. Integrate with 100+ apps and plug-ins to get more done. Build and customize online forms to collect info and payments. Create better surveys and spot insights quickly with built-in AI.
Social media can influence marketing strategy in several ways. For example, social media can help to formulate a marketing strategy that expands its geographical reach, because of its power to enhance connections and provide two-way conversations (Li et al., 2021).
specific objectives: (a) to develop a framework through which to assess the current state of. research conducted within marketing strategy; (b) to illuminate and illustrate the "state of. knowledge" in core sub-domains of marketing strategy development and execution; and (c), to.
Build a solid market research strategy. Having a deeper understanding of the market gives you leverage in a sea of competitors. Use the steps and market research tools we shared above to build an effective market research strategy. But keep in mind that the accuracy of your research findings depends on the quality of data collected.
Here are some best practices for market research: 1. Define your research objectives: Clearly articulate the goals and purpose of your research. Identify the specific information you need to gather, such as customer insights, market size, competitor analysis, or product feedback. 2.
1. Have your market research data ready. It's crucial to build your marketing strategy on data, not assumptions. You're probably not developing and launching a product into the marketplace without market research —or at least you shouldn't be. Market research is an essential part of marketing and a topic on its own.
This definition of marketing strategy stands on three key pillars. These are: What: Marketing strategy is the overall game plan or the roadmap marketers use to achieve a business's marketing objectives and goals. ... Our philosophy is to research, curate, and provide the best startup feeds and resources to help you succeed in your venture. ...
A marketing strategy is an overview of how a business or organization will articulate its value proposition to its customers. Generally, a marketing strategy outlines business goals, target market, buyer personas, competitors, and value for customers. It provides a long-term vision for overall marketing efforts, often looking many years ahead.
Identify your marketing research goal(s) You might be surprised how many digital-first marketers tend to miss this crucial step in their marketing research process. Unlike digital marketing, marketing research demands you to gather and analyze data with a clear goal (and even a hypothesis) in sight. Depending on the business scope, you may choose to limit your research to a primary goal or add ...
Morningstar is an investment research company offering mutual fund, ETF, and stock analysis, ratings, and data, and portfolio tools. Discover actionable insights today.
Target Market: A target market is the market a company wants to sell its products and services to, and it includes a targeted set of customers for whom it directs its marketing efforts ...
Following Sudharshan (1995), we define a firm's. marketing strategy as the development of and decisions about a firm's relationships with its. key stakeholders, its offerings, resource ...
Social media marketing is a game-changer for businesses because it allows you to reach so many people around the world in real time. It is no wonder why so many businesses have ditched old-school ...
BANGKOK (AP) — The mayhem that swept across world markets this week was partly caused by a market strategy known as the "carry trade." Japan's benchmark Nikkei 225 plunged 12.4% on Monday and markets in Europe and North America suffered outsized losses as traders sold stocks to help cover rising risks from investments made using cheaply financed funds borrowed mostly in Japanese yen.
While the allure of high returns from volatile assets like technology stocks can be tempting, many investors prefer a more stable strategy that allows them to minimize risk and preserve wealth over time. Conservative investment strategies are popular with those nearing retirement or saving for a significant financial milestone — or simply anyone preferring a lower-risk investment strategy.