Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches


pink flowers
255 templates

15 templates

62 templates

49 templates

rio de janeiro
16 templates

39 templates
X-Ray Style Disease
It seems that you like this template, x-ray style disease presentation, free google slides theme, powerpoint template, and canva presentation template.
Need to prepare a presentation where X-rays are the protagonists? Look no further. Here's the perfect proposal for you. This template is inspired by X-ray illustrations, with blue color, traditionally associated with health topics, as it conveys reliability. You can use it to talk about certain diseases or to explain the science behind an X-ray. Resources such as infographics, tables, charts, graphs or maps that we have included will help you to do so.
Features of this template
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- 28 different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics such as graphs, maps, tables, timelines and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides, Canva, and Microsoft PowerPoint
- 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all types of screens
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the free resources used
How can I use the template?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute?
Combines with:
This template can be combined with this other one to create the perfect presentation:

Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?

Register for free and start downloading now
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access


Basics of Chest X-Ray
Oct 15, 2014
4.41k likes | 14.97k Views
Basics of Chest X-Ray. Outline. CXR Basics Types of CXR PA vs. AP Films Obtaining Images Systematic method to reading CXR Common Signs Examples. Chest X-ray (CXR) Basics. A standard chest X-ray consists of a PA Image Lateral Image Images read together AP for supine patients
Share Presentation
- pulmonary edema
- examples pericardial effusion
- signs solitary pulmonary nodule

Presentation Transcript
Outline • CXR Basics • Types of CXR • PA vs. AP Films • Obtaining Images • Systematic method to reading CXR • Common Signs • Examples
Chest X-ray (CXR) Basics • A standard chest X-ray consists of a • PA Image • Lateral Image • Images read together • AP for supine patients • Lots of information available on a CXR • Be systematic with your reading • Always compare to prior studies if possible
Basics of X-Rays • X-Rays are part of the light spectrum • Unlike visible light, x-rays pass through the human body • Pass through lungs without much interference • Difficult to pass through bones • Place film cassette on other side of patient and capture the shadow
Basics of X-Ray • Organs absorb X-rays differently and thus their shadow on the film is different • Bone: high absorption (film appears white) • Tissue: moderate absorption (film appears grey) • Air/Lungs: little absorption (film appears black)
Types of CXRs • PA and Lateral • Patient facing cassette • X-ray 6 feet away • Supine AP • X-ray 40 inches away • Magnifies anterior structures and pulmonary vasculature 101 cm 1.83 m
Comparing Chest X-rays Protocols PA AP Note heart enlarged, lung fields not as clear • Preferred method
PA Image • PA Film • Read as if patient is facing you (Patient’s left side is on the right of the X-ray)
Lateral Image • Obtained with patient’s left side against the cassette. • Minimizes heart silhouette magnification
Assessing Film Technique • Inspiration • Penetration • Rotation
Inspiration • Image should be at full inspiration • Diaphragm at level of 8-10 rib • Allows reader to see intrapulmonary structures Poor Inspiration mimics RML Infiltrate Same patient with proper inspiration
Penetration • Amount of radiation required for a quality image • PA film: should barely see thoracic spine disc spaces • Lateral: spine should appear darker as move cadually Examples of adequately penetrated images
Penetration Overpenetrated Underpenetrated
Rotation • Patient should be flat against the cassette • Rotation of the patient will alter appearance of mediastinum • Observe rotation by comparing location of clavicular heads • Should be equal distance from spinous process of thoracic vertebral bodies
Rotation Normal Rotated to the Right
Mass vs. Infiltrate Mass Infiltrate
Lobes and Fissures: PA Film A: Minor Fissure between RML and RLL B: Upper and lower boundaries of major fissures
Lobes and Fissures: Lateral A: Minor Fissure R Lung B: Major Fissure R Lung B: Major Fissure L Lung
CXR Anatomy
How to Read an X-Ray Part 1 • Patient Data (Name, history, age, sex) • Technique (PA vs. AP, rotation, penetration, etc) • Trachea: midline or deviated, any masses? • Lungs: masses, infiltrates? • Costophrenic angles should be sharp (if not = effusions) • Silhouette signs, air-bronchograms, pulmonary edema • Pulmonary vessels: enlarged?
How to Read an X-Ray Part 2 • Hilar Region: masses or lymphadenopathy • Heart: enlarged, abnormal shape • Pleura: effusion, thickening, calcification • Bones: fractures or masses • ICU Films: looks for line and tube placement
How to Read an X-Ray Part 3 • It is best to focus on a small area of the film and then scan rather than look at the whole film at once
Signs: Silhouette Sign • Loss of lung/soft tissue interface caused by mass, fluid, or infiltrate in the normally air filled lung • Commonly applied to heart, aorta, chest wall, and diaphram borders with lung • Location of silhouette sign helps to localize pathology Lose Right Heart and Lung border = RML
Signs: Air Bronchogram • Tubular outline of an airway made visible by filling of the surrounding alveoli by fluid or inflammatory exudates • Causes • Pulmonary edema • Lung Consolidation • Severe Interstitial Disease • Neoplasm
Signs: Solitary Pulmonary Nodule • Can be innocuous or potentially fatal lung cancer • Always compare to prior films for growth • Nodules with irregular borders are suspicious
Conclusions • Lots of information in a chest x-ray • Always read the film in the same order • Never skip to the most prominent abnormality, you will miss a small (but potentially important finding) • Compare to priors if possible • We will finish with some examples of common pathology
Examples: Atelectasis • Collapse or incomplete expansion of alveoli • Causes: • Endobronchial lesions (mucous plug or tumor) • Extrinsic compression (mass, lymph node) • Peripheral compression (pleural effusion) • Linear density on CXR
Examples: Pulmonary Edema • Cephalization of pulmonary vessels (arrow) • Kerley B Lines • Peribronchial cuffing • “Bat Wing” Appearance • Increased Cardiac Size (arrow)
Examples: Pneumonia • Airspace disease and consolidation • CXR Findings • Airspace opacity • Lobar consolidation • Interstitial opacities
Differentiating Atelectasis from Pneumonia Atelectasis Pneumonia Normal or increased volume No shift Consolidation, air space process Not centered at hilum Air bronchograms • Volume Loss • Associated ipsilateral shift • Linear, wedge shaped • Apex at hilum • Air bronchograms
Examples: TB • TB can be seen as consolidation, cavitation, fibrosis, adenopathy, or pleural effusion depending on stage of infection
Examples: Pleural Effusions Fluid in Costophrenic Angle Blunting of Costophrenic Angles
Examples: Pneumothorax (PTX) • Air inside the thoracic cavity but outside the lung • PTX appears as air without lung markings in least dependent area of chest
Examples: Hemopneumothorax Lung Air Fluid
Examples: Interstitial Lung Disease • Hazy ground glass opacification • Volume Loss • Linear opacities bilaterally • “Honeycomb lung”
Examples: COPD and Emphysema • Diffuse hyperinflation • Flattened diaphragms • Increased retrosternal space • Bullae
Examples: Rib Fractures • Can you find the rib fracture?
Examples: Pericardial Effusion
Examples: Hiatal Hernia Gastric Bubble
Hilar Enlargement Enlarged Pulmonary Artery Hilar Adenopathy
- More by User

Chest X-Ray Review
Chest X-Ray Review. SYMPTOMS : Bad or persistent cough Chest pain Chest injury Coughing up blood Fever Shortness of breath S/P fall. Why order a CXR?. Pleural effusion Pneumothorax Hemothorax Pulmonary embolus Trauma Monitoring chest drainage TB. Lung cancer Chest pain (MI?)
2.52k views • 33 slides

Chest X-ray Interpretation Quiz
Chest X-ray Interpretation Quiz. CXR Quiz!. Fourteen questions Need 80% correct (12 of 14) to pass Will go in training folder Good luck!!. 1. Which lobe is involved?. 2. Is the lingula or lower lobe involved?. 3. Effusion or Collapse?. 4. Effusion or Collapse?.
5.01k views • 17 slides

Chest X-ray Path correlation
Chest X-ray Path correlation. Normal structures Densities Genesis of abnormal densities Localization Pathological correlation Steps in evaluation of CXR. Left. RV. RA. LV. LA. Densities. Hemorrhage. Hem. Localization. Lobar distribution Air bronchogram Silouhette sign
1.25k views • 72 slides

Chest X – Ray : Heart Failure
Chest X – Ray : Heart Failure. Dr.Juan A.Venter Dept.Imaging Sciences Universitas Hospital. Causes:PVH /Pulmonary Oedema. Left Ventricular Failiure Left Ventricular Outflow Obstruction Mitral Valve Disease Left Atrial Myxoma Fibrosing Mediastinitis
644 views • 26 slides

Chest X-Ray Basic Interpretation
Chest X-Ray Basic Interpretation. Dr. Shujauddin S Rahimi Senior Registrar Department of Radio-Diagnosis.
3.22k views • 46 slides

Approach to viewing Chest x-ray Basics A.J. Chandrasekhar
Approach to viewing Chest x-ray Basics A.J. Chandrasekhar. Created : 10/28/2003 Reviewed 12/20/2010. Is the film centered Is it PA or AP film Is it exposed properly Is it a good inspiration film. Is this film centered?. Difficult to evaluate the position of mediastinum
697 views • 48 slides
Basic Chest X-Ray Interpretation
Basic Chest X-Ray Interpretation. Deb Updegraff, C.N.S., PICU. X-rays- describe radiation which is part of the spectrum which includes visible light, gamma rays and cosmic radiation. Unlike visible light, radiation passes through stuff. When you shine a beam of X-Ray at a person
882 views • 39 slides

Principles of Chest X-Ray Interpretation
Principles of Chest X-Ray Interpretation. Dr Rod Taylor Consultant Respiratory Physician. Different from us…. Only Two Choices. Hmmn! There are far too many white bits!. That’s funny - this one’s got too many black bits!. Chest X-ray. P. = important radiological principle.
2.12k views • 81 slides

Basics of Chest X-Ray. AFAMS Residency Orientation April 16, 2012. Outline. CXR Basics Types of CXR PA vs. AP Films Obtaining Images Systematic method to reading CXR Common Signs Examples. Chest X-ray (CXR) Basics. A standard chest X-ray consists of a PA Image Lateral Image
1.96k views • 41 slides


The Chest X-Ray
The Chest X-Ray. For: Nottingham SCRUBS 26 th August 2006 Presented by: Matthew. Objectives:. Basic Radiology 101 Film Interpretation Appreciate the role radiology plays Artifacts in X-Rays. Contents:. Densities Techniques Anatomy CXR Interpretation Common Pathologies Questions.
1.32k views • 74 slides

Normal chest X-ray
Normal chest X-ray. Dr.Ahmed Refaey. MBBCh, MS, FRCR. How do you look at chest x ray?. Avoid tunnel vision. * bones ; lesions or fractures * soft tissue ; mastectomy or soft tissue tumors. * trachea ; position & caliber * hila : lymphadenopathy * mediastinum contour : ? mass
1.55k views • 82 slides
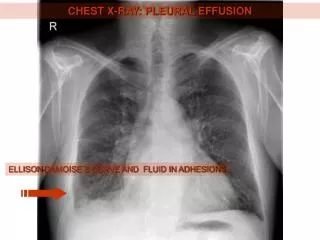
CHEST X-RAY: PLEURAL EFFUSION
CHEST X-RAY: PLEURAL EFFUSION. ELLISON-DAMOISE´S CURVE AND FLUID IN ADHESIONS. CHEST X-RAY: PNEUMONIA. PARENCHYMAL CONSOLIDATION. CHEST X-RAY: LEFT-SIDED HEART FAILURE. DILATED LUNG HILUM. KERLEY´S LINES. HEART ENLARGEMENT. CHEST X-RAY: PNEUMOTHORAX. CENTRAL VENOUS CATHETER.
2.06k views • 50 slides

LECTYRE OF THE CHEST X-RAY
LECTYRE OF THE CHEST X-RAY. A.WEISS M.D D.E.S , Chirurgie Générale, Viscérale et Laparoscopique A.F.S/A.F.S.A/DU - FRANCE. Aims. Basics . Best exam results . Appreciate the role radiology plays . Instil an interest in radiology. Contents. Densities Techniques Anatomy
1.08k views • 78 slides
The Chest X-Ray. Dr Mohamed El Safwany, MD. Intended learning outcome. The student should learn at the end of this lecture Clinical aspects of Chest X ray. Aims:. Basics Best exam results Appreciate the role radiology plays. Contents:. Densities Techniques Anatomy CXR Interpretation
1.58k views • 75 slides
Chest X-ray Interpretation
Chest X-ray Interpretation. Bucky Boaz, ARNP-C. Introduction. Routinely obtained Pulmonary specialist consultation Inherent physical exam limitations Chest x-ray limitations Physical exam and chest x-ray provide compliment. Essentials Before Getting Started. Exposure Overexposure
3.24k views • 101 slides
Chest X-Ray Interpretation
Chest X-Ray Interpretation. For beginners. Why take x rays ?. How are chest x rays taken ?. What do they show ?. Rules for reading chest xrays………. 1. Know the patient. 2. Check the technical stuff. 3. Look at the bones. 4. Lungs. 5. Heart. 6. Hardware. Technical info. Name, Age.
1.4k views • 26 slides

Chest X-ray
Esam Alhamad, MD,FCCP, FACP Division of Pulmonary Medicine College of Medicine. Chest X-ray. Is this film centered?. Why do you have to know whether it is PA or AP film. ?. Is this a PA or AP film?. Is the exposure appropriate?. Mediastinal Masses. Anterior mediastinal masses (4Ts)
1.16k views • 41 slides

Chest X-ray. PA vs AP. Lateral Decubitus. Turn off stray lights, optimize room lighting, view images in order Patient Data (name history #, age, sex, old films) Routine Technique: AP/PA, exposure, rotation, supine or erect Trachea: midline or deviated, caliber, mass
727 views • 37 slides

CHEST X-RAY
CHEST X-RAY. The plain CXR is the most commonly performed imaging exam because: Cardio-pulmonary disease is common The exam is quick, easy to do, cheap, with low radiation exposure (a PA CXR gives only about 3-days-worth of radiation exposure we get anyway from natural sources)
1.29k views • 57 slides

The Chest X-Ray. For: Nottingham SCRUBS 26 th August 2006 Presented by: Matthew. Aims:. Basics Best exam results Appreciate the role radiology plays ? Instil an interest in radiology. Contents:. Densities Techniques Anatomy CXR Interpretation Common Pathologies Questions.
1.1k views • 74 slides

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
8.1 PRODUCTION AND CHARACTERISTICS OF X-RAYS
Published by Joella Porter Modified over 9 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "8.1 PRODUCTION AND CHARACTERISTICS OF X-RAYS"— Presentation transcript:

Advanced Biomedical Imaging Lecture 3

X-ray tube.

Formation Characteristics

The X-Ray Tube Bushong Ch 7.

X-Ray Interaction with Matter & Human Biology

{ Projection Radiography Chapter 5 (in more detail)

Resident Physics Lectures

X-ray tube and detection of X-rays Lecture 5. Reminder: The rough schematics of an X-ray tube filament cathod target anode photon flux e-e- electron kinetic.

FRCR: Physics Lectures Diagnostic Radiology

ACVR Artifacts Artifacts of Diagnostic Radiology

ENTC 4390 PRODUCTION OF X RAYS.

Radiation Physics II.
Medical Imaging X-Rays I.

BME 560 Medical Imaging: X-ray, CT, and Nuclear Methods X-ray Instrumentation Part 1.

BME 560 Medical Imaging: X-ray, CT, and Nuclear Methods
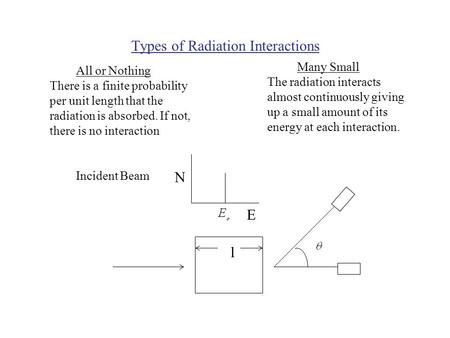
Types of Radiation Interactions All or Nothing Many Small There is a finite probability per unit length that the radiation is absorbed. If not, there is.
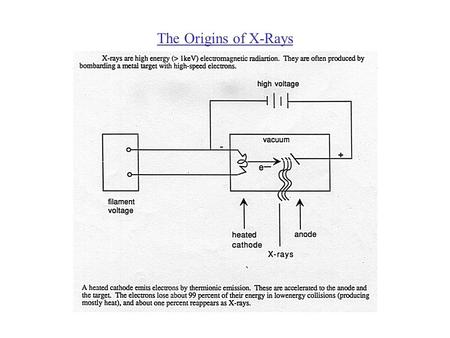
The Origins of X-Rays. The X-Ray Spectrum The X-Ray Spectrum (Changes in Voltage) The characteristic lines are a result of electrons ejecting orbital.

Factors affecting the X-Ray output

X-Ray Production & Emission

About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
Junior doctors & students menu
Chest X-rays for Medical Students
A superb guide to CXRs for students
Abdominal X-rays for Medical Students
A superb guide to AXRs for students
Radiology B a s i c s
Ultrasound and CT e-learning for junior doctors and students
Join 10k+ newsletter subscribers
Please note: Your email address will never be shared with any 3rd parties. It will only be used for Radiology Cafe communications. Emails are sent less than once a month on average. Read our Privacy policy for more details.
How to present an X-ray
A short guide to help you improve your presentation of radiographsin an exam situation or on the ward
The purpose of this guide isn’t to teach you what you’re going to see, but how you should say it! Guides to help you get through looking at images systematically can be found elsewhere; our aim is to improve your presentation skills.
Opening line
Imagine you’re sat in an OSCE. You are presented with a radiograph and invited to comment on it. How might you start presenting? Just as you wouldn’t jump straight to the heart sounds when presenting a cardiovascular exam, so you shouldn’t jump straight to the interesting bit of the image.
An opening line of:
“frontal chest radiograph of an adult patient”
…can virtually never be wrong. This is often enough as an opening line, but you could expand if you can with the details you’re given – especially if you are given some of the patient’s history. For example:
“frontal chest radiograph of an adult male patient with shortness of breath”
For the first radiograph you see, it’s good to briefly demonstrate you know what an adequate radiograph looks like. DO NOT SPENT LONG DOING THIS (10 seconds at most). Some medical schools do not award any marks for talking about the adequacy of a radiograph so whatever you do, do not spend much time on this! The interesting bit is describing the pathology on the radiograph itself. On your second or subsequent radiograph during a station, if the image is clearly adequate, simply stick with your single opening line and proceed to the lungs.
There are broadly 3 categories of adequacy to assess:
- Rotation: are the clavicles equidistant from the spinous processes?
- Penetration: can you see the spine through the heart?
- Expansion: The anterior aspect of the 6 th rib (the sloping ones) should meet the diaphragm near the mid-clavicular line. You should be able to see the apices and costophrenic angles.

So you might introduce the above radiograph as follows:
“frontal chest radiograph of an adult female patient. It is not rotated, with good penetration and good expansion of the lungs, although the tips of the costophrenic angles are not included on this radiograph”
As a note of caution, some medical schools do not award any marks for talking about the adequacy of a radiograph so whatever you do, do not spend much time on this! The interesting bit is describing the pathology on the radiograph itself. On your second or subsequent radiograph during a station, if the image is clearly adequate, simply stick with your single opening line and proceed to the lungs.
Main abnormality
So you’ve made it to the lungs and something looks wrong. This almost always means there is opacity (whiteness) where there shouldn’t be. Describe this in terms of appearance and location.
Is the opacity:
- Patchy – hard to draw round properly, heterogeneous (e.g. pulmonary oedema)

- Dense – very white so that you can barely see structures through it (e.g. pleural effusion)

- Rounded – discrete, round(ish) in shape (e.g. a mass lesion in the lung)

Then ask yourself, where is the lesion located?
The lung lobes overlap significantly on a frontal chest radiograph, so it is hard to place an abnormality in a specific lobe when viewed only from the front. A solution to this is to split the lung into zones – upper zone is above the heart, mid-zone is level with the top half of the heart, and lower zone is below that. It is also worth looking under the diaphragms and behind the heart for subtle, ‘hidden’ lesions.
Ok, so now think how you might describe the abnormality in the radiograph we showed you at the start.
“there is a solitary rounded opacity in the left upper zone”
Review areas
To complete your assessment of a radiograph, particularly if it’s your first of a session, it’s worth quickly summarising the rest of the radiograph to show you have assessed everything. If the abnormality is in the lungs, you might also comment on:
- The heart: is it enlarged?
- The diaphragm: can you see any free gas?
- The bones: are there any fractures?
So for our radiograph:
“the heart is not enlarged, there is no free air below the diaphragm, and there are no fractures identified”
Put everything above together and you’ll have had 30 seconds or so to think up a differential diagnosis to put the icing on your presentation:
“this could represent a primary lung malignancy, but might also be a metastasis”
Finally, finish by saying what you would do next:
“I would like to request a CT chest to further evaluate the lesion and look for evidence of malignancy”
So that’s it!
Stick to these basic rules and you will go a long way in your exams and when presenting on the ward. Good luck!
- Christopher Clarke
- Last updated: 10 October 2021
Interview & application
Radiology trainees, junior doctors & students.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
X-rays, also known as X-radiations, are a form of ionizing electromagnetic radiation discovered in 1895 by Wilhelm Röntgen. They have wavelengths between 0.01 to 10 nanometers. X-rays are used widely in medical diagnostics to image bone fractures and other injuries or medical conditions.
The document discusses x-rays, how they produce images, and their risks and benefits. It explains that x-rays are electromagnetic waves that can pass through tissues at different levels, exposing film to create internal images of the body.
xray -basics ppt. XRay-Basics discusses the production of x-rays through interactions between electrons and matter. X-rays are produced when electrons collide with a metal target, such as a tungsten anode. This results in bremsstrahlung radiation and characteristic radiation.
X-rays and Diagnostic Radiology. Learning Outcomes. 53.1 Explain how x-rays are used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. 53.2 Compare invasive and noninvasive diagnostic procedures. 53.3 Carry out the medical assistant’s role in x-ray and diagnostic radiology testing. Slideshow...
X-rays are produced in a generator by the interaction of an electron beam with a Tungsten target. The X-rays are emitted from the generator as a beam and travel through a patient. Tissues absorb (attenuate) some of the x-rays, while others pass through and hit the cassette.
X-Ray Style Disease Presentation. Free Google Slides theme, PowerPoint template, and Canva presentation template. Need to prepare a presentation where X-rays are the protagonists? Look no further. Here's the perfect proposal for you.
Chest X-ray (CXR) Basics • A standard chest X-ray consists of a • PA Image • Lateral Image • Images read together • AP for supine patients • Lots of information available on a CXR • Be systematic with your reading • Always compare to prior studies if possible.
The X-ray Imaging System - ppt download. Published by Johnathan Randall Modified over 9 years ago. Embed. Download presentation. Presentation on theme: "The X-ray Imaging System"— Presentation transcript: 1 The X-ray Imaging System. Week 4-5.
X-rays are one of the main diagnostical tools in medicine since its discovery by Wilhelm Roentgen in Current estimates show that there are approximately 650 medical and dental X-ray examinations per 1000 patients per year. X-rays are produced when high energetic electrons interact with matter.
Stick to these basic rules and you will go a long way in your exams and when presenting on the ward. Good luck! Guide to improving your presentation of radiographs in an exam situation or on the ward. The purpose of this page is not to teach you what you’re going to see, but how to say it.