- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences

How Apple Is Organized for Innovation
- Joel M. Podolny
- Morten T. Hansen

When Steve Jobs returned to Apple, in 1997, it had a conventional structure for a company of its size and scope. It was divided into business units, each with its own P&L responsibilities. Believing that conventional management had stifled innovation, Jobs laid off the general managers of all the business units (in a single day), put the entire company under one P&L, and combined the disparate functional departments of the business units into one functional organization. Although such a structure is common for small entrepreneurial firms, Apple—remarkably—retains it today, even though the company is nearly 40 times as large in terms of revenue and far more complex than it was in 1997. In this article the authors discuss the innovation benefits and leadership challenges of Apple’s distinctive and ever-evolving organizational model in the belief that it may be useful for other companies competing in rapidly changing environments.
It’s about experts leading experts.
Idea in Brief
The challenge.
Major companies competing in many industries struggle to stay abreast of rapidly changing technologies.
One Major Cause
They are typically organized into business units, each with its own set of functions. Thus the key decision makers—the unit leaders—lack a deep understanding of all the domains that answer to them.
The Apple Model
The company is organized around functions, and expertise aligns with decision rights. Leaders are cross-functionally collaborative and deeply knowledgeable about details.
Apple is well-known for its innovations in hardware, software, and services. Thanks to them, it grew from some 8,000 employees and $7 billion in revenue in 1997, the year Steve Jobs returned, to 137,000 employees and $260 billion in revenue in 2019. Much less well-known are the organizational design and the associated leadership model that have played a crucial role in the company’s innovation success.
- Joel M. Podolny is the dean and vice president of Apple University in Cupertino, California. The former dean of the Yale School of Management, Podolny was a professor at Harvard Business School and the Stanford Graduate School of Business.
- MH Morten T. Hansen is a professor at the University of California, Berkeley, and a faculty member at Apple University, Apple. He is the author of Great at Work and Collaboration and coauthor of Great by Choice . He was named one of the top management thinkers in the world by the Thinkers50 in 2019. MortentHansen
Partner Center

- International Marketing
Apple’s Global Strategy: Simplicity, Innovation, and Adaptability
- January 19, 2024
- LinkedIn 29
Table of Contents
Delving into apple’s global strategy, apple’s core values and the simplicity mantra, apple’s global branding strategy, apple’s global marketing strategy, case studies, apple’s global tax strategy.
- The Cornerstones of Apple’s Global Strateg
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, Apple stands as a beacon of innovation and design, captivating consumers worldwide with its sleek products and user-centric approach. With a global presence spanning over 150 countries and an estimated $383.29 billion in revenue in 2023, according to Statista , Apple’s success is a testament to its astute global strategy , a harmonious blend of differentiation, adaptability, and unwavering commitment to quality.
Apple’s global strategy is rooted in the concept of “differentiation,” a strategic approach that sets it apart from its competitors. By consistently pushing the boundaries of innovation, Apple has carved a niche for itself, offering products that are not only technologically advanced but also aesthetically pleasing and user-friendly . This differentiation has allowed Apple to capture a loyal customer base and establish a strong brand identity across the globe .
Apple’s global strategy has evolved over time, adapting to the changing dynamics of the international market. In its early days, the company focused heavily on innovation, relentlessly pursuing cutting-edge technologies and groundbreaking designs. However, as the company matured, it recognized the importance of customer experience and began placing a greater emphasis on this aspect . Today, Apple’s global strategy is a seamless blend of innovation and customer focus, ensuring that its products and services align with the needs and preferences of consumers worldwide.
At the heart of Apple’s global success lies a set of core values that permeate every aspect of the company’s operations , from product design to marketing campaigns. These values, deeply rooted in the company’s identity, guide Apple’s approach to innovation, customer experience, and global expansion.
- Accessibility: Apple strives to make its products and services accessible to everyone, regardless of their physical or cognitive abilities. This commitment is evident in features like VoiceOver , which provides spoken feedback for visually impaired users, and AssistiveTouch , which allows users with limited mobility to control devices with gestures.
- Educational Support: Apple recognizes the transformative power of technology in education and actively supports initiatives that promote digital literacy and learning. The company’s initiatives include Apple Teacher certification programs, curriculum resources, and educational apps that enhance teaching and learning.
- Carbon Neutrality: Apple is committed to reducing its environmental impact and is working towards becoming carbon neutral by 2030 . The company has implemented numerous initiatives to minimize its carbon footprint, including transitioning to renewable energy sources, designing energy-efficient products, and recycling materials.
- Inclusive Work Environment: Apple is committed to creating a diverse and inclusive workplace where everyone is valued and respected. The company has implemented policies and programs that promote diversity hiring, provide equal opportunities for advancement, and foster a culture of inclusion.
- Privacy: Apple is a staunch advocate for user privacy and believes that individuals should have control over their personal data. The company has implemented robust privacy protections in its products and services, including encryption, data minimization, and transparency.
- Equity and Justice: Apple is committed to promoting equity and justice in its operations and throughout the world. The company supports initiatives that address social and economic inequalities, promotes human rights, and advocates for environmental sustainability.
- Supplier Responsibility: Apple is committed to ensuring that its suppliers adhere to high ethical standards and treat their workers with respect. The company has established stringent supplier codes of conduct and conducts regular audits to monitor compliance.
These core values, collectively, form the foundation of Apple’s global strategy. They guide the company’s product design, marketing campaigns, and customer service interactions , ensuring that Apple delivers products and experiences that are not only technologically advanced but also aligned with its values of simplicity, accessibility, and inclusivity.
Simplicity is a cornerstone of Apple’s design philosophy, evident in the clean aesthetics, intuitive interfaces, and user-friendly features of its products. This emphasis on simplicity has resonated with consumers worldwide , making Apple products accessible to a broad audience and fostering a loyal customer base.
By upholding its core values and embracing simplicity, Apple has not only achieved global success but also established itself as a role model for other companies seeking to build a sustainable and ethical business model.
Apple’s global branding strategy is a delicate balance of standardization and adaptation, ensuring that the company maintains a consistent brand identity while also resonating with consumers in diverse cultures and markets. On the one hand, Apple strives to project a unified brand image, conveying its core values of innovation, simplicity, and elegance across all its products, marketing campaigns, and customer interactions. This standardization helps reinforce Apple’s reputation for quality and consistency, fostering brand loyalty and recognition worldwide.
On the other hand, Apple recognizes the need to adapt its branding to local markets and cultures. This adaptability is evident in the company’s product offerings, marketing messages, and customer support. For instance, Apple has developed localized versions of its products with features and specifications tailored to specific regions . Additionally, the company’s marketing campaigns often incorporate cultural nuances and local references to connect with consumers on a deeper level.
Apple’s ability to balance standardization and adaptation has been a key factor in its global success. By maintaining a consistent brand identity, the company has built a strong foundation of brand recognition and loyalty . However, by adapting to local markets, Apple has been able to cater to the needs and preferences of consumers in different parts of the world, expanding its reach and deepening its customer base.
Examples of Apple’s Standardization
- Unifying Brand Elements: Apple employs a consistent design language across its products, including clean aesthetics, minimalist interfaces, and sleek silhouettes. This consistent visual language helps establish a cohesive brand identity.
- Global Marketing Campaigns: Apple’s marketing campaigns often feature universal themes of innovation, creativity, and personal empowerment, appealing to a global audience.
- Seamless Customer Experience: Apple’s customer support is available in multiple languages, and the company’s online store can be accessed in over 40 countries, ensuring a consistent experience for customers worldwide.
Examples of Apple’s Adaptation
- Localization of Products: Apple offers localized versions of its products, such as the iPhone and iPad, with features and specifications tailored to specific regions. For instance, the iPhone SE 2020 is optimized for Indian consumers with support for two SIM cards and regional cellular bands.
- Culturally Sensitive Marketing: Apple’s marketing campaigns often incorporate cultural nuances and local references to connect with consumers on a deeper level. For example, the company’s “ Shot on iPhone ” campaign features images captured by photographers from around the world, showcasing the diversity of visual storytelling.
- Localized Customer Support: Apple provides customer support in multiple languages and offers localized resources, such as online FAQs and tutorials, tailored to specific regions. The company also partners with local businesses to offer personalized support services.
Apple’s success in balancing standardization and adaptation is a testament to its understanding of the complexities of global branding. By striking this delicate balance, the company has been able to maintain a strong brand identity while also resonating with consumers in diverse markets , solidifying its position as one of the world’s most recognizable brands.
Apple’s global marketing strategy is a multifaceted approach that revolves around four key pillars: wide acceptance, brand value, competitive advantage, and low imitation . These pillars are intertwined, working together to propel Apple’s success in the global marketplace.
Wide Acceptance
Apple’s products have achieved widespread acceptance worldwide, attracting a loyal customer base across diverse demographics and regions . This widespread appeal is attributed to several factors, including:
- Innovative Designs: Apple consistently pushes the boundaries of design, creating products that are both aesthetically pleasing and user-friendly. The company’s sleek, minimalist aesthetic has become synonymous with Apple’s brand identity.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Apple’s products are renowned for their intuitive interfaces, making them easy to navigate and use for people of all technical backgrounds.
- Effective Marketing Campaigns: Apple’s marketing campaigns are known for their creativity and emotional appeal, resonating with consumers on a personal level. The company often uses storytelling and cultural references to connect with diverse audiences.
Brand Value
Apple has built a strong brand value over the years, characterized by perceptions of quality, innovation, and premium craftsmanship . This brand value has been instrumental in attracting consumers and fostering brand loyalty.
- Reputation for Quality: Apple is consistently rated among the most reliable and durable consumer electronics brands. This reputation for quality has earned the company a loyal following among consumers who value long-lasting products.
- Innovation: Apple is renowned for its pioneering spirit, consistently introducing innovative products that redefine the technological landscape. This focus on innovation has helped maintain Apple’s cutting-edge reputation and attract early adopters.
- Premium Branding: Apple’s products are positioned in the premium segment of the market , commanding higher prices than its competitors. This premium positioning contributes to the company’s brand value and reinforces its image as a luxury brand.
Competitive Advantage
Apple maintains a competitive advantage in the global market through a combination of factors, including:
- Strategic Product Differentiation: Apple differentiates its products from competitors through unique features, design elements, and user experiences. This differentiation strategy has helped the company carve out a distinct niche in the market.
- Focus on Customer Experience: Apple prioritizes customer satisfaction, creating a seamless and personalized experience for its users. This focus on customer experience has helped foster brand loyalty and attract new customers.
- Global Retail Presence: Apple has a strong global retail presence, with over 500 stores in 23 countries, as per Statista . This extensive retail network provides consumers with easy access to Apple products and services.
Low Imitation
Despite facing intense competition from numerous technology giants, Apple has been able to maintain a relatively low level of imitation . This is due to several factors, including:
- Continuous Innovation: Apple’s relentless pursuit of innovation makes it difficult for competitors to replicate its products and services.
- Strengthened Intellectual Property Protection: Apple has a robust intellectual property portfolio, providing legal protection for its innovative designs and technologies.
- Brand Loyalty: Apple’s loyal customer base is less susceptible to imitation, as they are often willing to pay a premium for Apple products due to their brand loyalty and trust in the company.
Apple’s successful global marketing strategy is a testament to its ability to balance innovation, brand value, competitive advantage, and low imitation. By consistently delivering high-quality products, cultivating a strong brand reputation, and prioritizing customer experience, Apple has cemented its position as one of the world’s leading technology companies .
Apple’s remarkable global success is evident in its ability to penetrate and dominate markets as diverse as China and India. These two countries represent two of the world’s most populous and rapidly growing economies, offering significant opportunities for technology companies. Apple’s success in these markets is a testament to its ability to adapt its global strategy to local conditions and preferences .
China has become Apple’s second-largest market , with over 190 million active iPhones in use as of 2023 ( Statista , 2023). Apple’s success in China can be attributed to several factors, including:
- Pricing Strategy: Apple has adopted a tiered pricing strategy in China, offering a wider range of products at lower price points to cater to a broader range of consumers.
- Distribution Channels: Apple has established a strong network of authorized resellers and retail stores in China, making its products readily available to consumers across the country.
- Partnerships with Local Businesses: Apple has partnered with Chinese telecommunications companies, e-commerce platforms, and content providers to expand its reach and customer base.
- Localization: Apple has made sure to localize its products , marketing campaigns, and customer support for the Chinese market, ensuring that they resonate with local consumers.
Despite facing challenges such as piracy and counterfeiting, Apple has successfully established itself as a premium brand in China . The company’s commitment to innovation, design, and customer experience has resonated with Chinese consumers, who are increasingly embracing technology.
India is another key market for Apple, with a growing middle class and increasing smartphone penetration. Apple’s strategy in India has focused on tailoring its products and services to the specific needs and preferences of Indian consumers .
- Price Sensitivity: Apple has introduced more affordable iPhone models in India, such as the iPhone SE, to attract price-conscious consumers.
- Online Sales: Apple has heavily invested in its online presence in India, making it easier for consumers to purchase its products online.
- Partnerships with Local Businesses: Apple has partnered with Indian e-commerce platforms, mobile carriers, and banks to expand its distribution reach and payment options.
- Localization: Apple’s localization strategy for the Indian market has included the adaptation of its products, marketing campaigns, and customer support, including the development of Hindi-language versions of its software.
Apple’s success in India has been gradual but steady. The company has faced challenges such as competition from local smartphone brands and a lack of brand recognition in rural areas. However, Apple’s commitment to innovation and adaptation has helped it gain traction in this emerging market .
Apple’s global success has been accompanied by scrutiny over its tax practices, particularly its use of a subsidiary company in Ireland to minimize its global tax liability. This strategy, known as “ Double Irish with a Dutch Sandwich ,” has allowed Apple to shift profits offshore, effectively reducing its tax payments in the United States and other countries .
While Apple has defended its tax strategy, arguing that it complies with all applicable laws, it has faced criticism from governments, tax experts, and consumer advocacy groups . Critics argue that Apple’s tax practices amount to corporate tax avoidance, depriving governments of revenue that could be used for public services.
Advantages of Apple’s Tax Strategy
Apple’s tax strategy has several potential advantages for the company, including:
- Reduced Tax Burden: By shifting profits offshore, Apple can effectively reduce its tax payments, which can boost its profitability and financial returns to shareholders.
- Increased Competitiveness: Lowering tax costs can give Apple a competitive advantage over other companies, allowing it to invest more in research and development, marketing, and product development.
- Enhanced Shareholder Value: By reducing its tax burden and increasing profitability, Apple can improve its financial performance and boost shareholder value.
Disadvantages of Apple’s Tax Strategy
Apple’s tax strategy has also been criticized for several potential disadvantages, including:
- Public Image Concerns: Apple’s tax practices have tarnished its public image, raising concerns about corporate social responsibility and ethical behavior.
- Legal Challenges: Governments and tax authorities around the world have been investigating Apple’s tax strategy, and the company faces potential legal challenges that could lead to fines and penalties.
- Political Fallout: Apple’s tax practices have created political tensions, with some countries considering imposing stricter tax laws to prevent multinational corporations from shifting profits offshore.
A Balancing Act
Apple’s global tax strategy has been a source of controversy, highlighting the delicate balance between corporate profitability and societal responsibility . While the company may benefit financially from its tax practices, it also faces reputational risks and potential legal repercussions. Apple must carefully navigate this complex landscape to maintain its global success while addressing concerns about its ethical conduct.
The Cornerstones of Apple’s Global Strategy
Apple’s journey to becoming one of the world’s most recognizable and successful companies is a testament to its ability to balance simplicity, innovation, and adaptability. From its early days as a niche computer manufacturer to its current status as a global technology powerhouse, Apple has consistently demonstrated its knack for understanding and meeting the evolving needs of consumers worldwide .
Apple’s core values, particularly its emphasis on simplicity, have permeated every aspect of its business. The company’s products are renowned for their user-friendly interfaces and intuitive designs , making them accessible to a wide range of users, regardless of their technical expertise. This commitment to simplicity extends to Apple’s marketing campaigns, which often use storytelling and emotional appeals to resonate with consumers on a personal level.
Apple’s unwavering focus on innovation has been another driving force behind its global success. The company has consistently pushed the boundaries of technology, introducing groundbreaking products that have transformed the way people interact with the digital world . From the revolutionary iPhone to the sleek AirPods, Apple has consistently redefined the standards for innovation in the technology industry.
Alongside innovation and simplicity, Apple has also demonstrated remarkable adaptability in its global expansion . The company has successfully tailored its products, marketing strategies, and customer support to suit the unique needs and preferences of different cultures. This adaptability has been crucial in Apple’s ability to penetrate and dominate markets as diverse as China and India, where local competitors pose significant challenges.
Apple’s approach to globalization is not without its critics. The company’s tax strategy, which has been the subject of intense scrutiny, has raised concerns about corporate social responsibility and ethical behavior. As Apple continues to expand its global footprint, it will need to address these concerns and demonstrate its commitment to operating responsibly and ethically in all the markets it serves.
Looking to the future, Apple faces a number of challenges and opportunities. The company will need to continue to innovate and adapt to the ever-changing technological landscape . It will also need to navigate the complexities of global markets, ensuring that its products and services remain relevant and appealing to consumers worldwide.
Apple’s journey to global success is a compelling case study in how a company can build a strong brand and establish a lasting presence in the international arena. By embracing simplicity, innovation, and adaptability, Apple has demonstrated that it has the vision and resilience to continue to thrive in an increasingly competitive and interconnected world .
As Apple embarks on the next chapter of its global journey, it remains to be seen how the company will navigate the evolving landscape of technology, consumerism, and globalization. However, one thing is certain: Apple’s commitment to innovation and its ability to understand the needs of consumers worldwide will continue to be key drivers of its success in the years to come.

Privacy Preferences
When you visit our website, it may store information through your browser from specific services, usually in the form of cookies. Here you can change your Privacy preferences. It is worth noting that blocking some types of cookies may impact your experience on our website and the services we are able to offer.
About Stanford GSB
- The Leadership
- Dean’s Updates
- School News & History
- Commencement
- Business, Government & Society
- Centers & Institutes
- Center for Entrepreneurial Studies
- Center for Social Innovation
- Stanford Seed
About the Experience
- Learning at Stanford GSB
- Experiential Learning
- Guest Speakers
- Entrepreneurship
- Social Innovation
- Communication
- Life at Stanford GSB
- Collaborative Environment
- Activities & Organizations
- Student Services
- Housing Options
- International Students
Full-Time Degree Programs
- Why Stanford MBA
- Academic Experience
- Financial Aid
- Why Stanford MSx
- Research Fellows Program
- See All Programs
Non-Degree & Certificate Programs
- Executive Education
- Stanford Executive Program
- Programs for Organizations
- The Difference
- Online Programs
- Stanford LEAD
- Seed Transformation Program
- Aspire Program
- Seed Spark Program
- Faculty Profiles
- Academic Areas
- Awards & Honors
- Conferences
Faculty Research
- Publications
- Working Papers
- Case Studies
Research Hub
- Research Labs & Initiatives
- Business Library
- Data, Analytics & Research Computing
- Behavioral Lab
Research Labs
- Cities, Housing & Society Lab
- Golub Capital Social Impact Lab
Research Initiatives
- Corporate Governance Research Initiative
- Corporations and Society Initiative
- Policy and Innovation Initiative
- Rapid Decarbonization Initiative
- Stanford Latino Entrepreneurship Initiative
- Value Chain Innovation Initiative
- Venture Capital Initiative
- Career & Success
- Climate & Sustainability
- Corporate Governance
- Culture & Society
- Finance & Investing
- Government & Politics
- Leadership & Management
- Markets and Trade
- Operations & Logistics
- Opportunity & Access
- Technology & AI
- Opinion & Analysis
- Email Newsletter
Welcome, Alumni
- Communities
- Digital Communities & Tools
- Regional Chapters
- Women’s Programs
- Identity Chapters
- Find Your Reunion
- Career Resources
- Job Search Resources
- Career & Life Transitions
- Programs & Webinars
- Career Video Library
- Alumni Education
- Research Resources
- Volunteering
- Alumni News
- Class Notes
- Alumni Voices
- Contact Alumni Relations
- Upcoming Events
Admission Events & Information Sessions
- MBA Program
- MSx Program
- PhD Program
- Alumni Events
- All Other Events
- Operations, Information & Technology
- Organizational Behavior
- Political Economy
- Classical Liberalism
- The Eddie Lunch
- Accounting Summer Camp
- California Econometrics Conference
- California Quantitative Marketing PhD Conference
- California School Conference
- China India Insights Conference
- Homo economicus, Evolving
- Political Economics (2023–24)
- Scaling Geologic Storage of CO2 (2023–24)
- A Resilient Pacific: Building Connections, Envisioning Solutions
- Adaptation and Innovation
- Changing Climate
- Civil Society
- Climate Impact Summit
- Climate Science
- Corporate Carbon Disclosures
- Earth’s Seafloor
- Environmental Justice
- Operations and Information Technology
- Organizations
- Sustainability Reporting and Control
- Taking the Pulse of the Planet
- Urban Infrastructure
- Watershed Restoration
- Junior Faculty Workshop on Financial Regulation and Banking
- Ken Singleton Celebration
- Marketing Camp
- Quantitative Marketing PhD Alumni Conference
- Presentations
- Theory and Inference in Accounting Research
- Stanford Closer Look Series
- Quick Guides
- Core Concepts
- Journal Articles
- Glossary of Terms
- Faculty & Staff
- Researchers & Students
- Research Approach
- Charitable Giving
- Financial Health
- Government Services
- Workers & Careers
- Short Course
- Adaptive & Iterative Experimentation
- Incentive Design
- Social Sciences & Behavioral Nudges
- Bandit Experiment Application
- Conferences & Events
- Get Involved
- Reading Materials
- Teaching & Curriculum
- Energy Entrepreneurship
- Faculty & Affiliates
- SOLE Report
- Responsible Supply Chains
- Current Study Usage
- Pre-Registration Information
- Participate in a Study
The Rise of Apple
Learning objective.

- See the Current DEI Report
- Supporting Data
- Research & Insights
- Share Your Thoughts
- Search Fund Primer
- Affiliated Faculty
- Faculty Advisors
- Louis W. Foster Resource Center
- Defining Social Innovation
- Impact Compass
- Global Health Innovation Insights
- Faculty Affiliates
- Student Awards & Certificates
- Changemakers
- Dean Jonathan Levin
- Dean Garth Saloner
- Dean Robert Joss
- Dean Michael Spence
- Dean Robert Jaedicke
- Dean Rene McPherson
- Dean Arjay Miller
- Dean Ernest Arbuckle
- Dean Jacob Hugh Jackson
- Dean Willard Hotchkiss
- Faculty in Memoriam
- Stanford GSB Firsts
- Class of 2024 Candidates
- Certificate & Award Recipients
- Dean’s Remarks
- Keynote Address
- Teaching Approach
- Analysis and Measurement of Impact
- The Corporate Entrepreneur: Startup in a Grown-Up Enterprise
- Data-Driven Impact
- Designing Experiments for Impact
- Digital Marketing
- The Founder’s Right Hand
- Marketing for Measurable Change
- Product Management
- Public Policy Lab: Financial Challenges Facing US Cities
- Public Policy Lab: Homelessness in California
- Lab Features
- Curricular Integration
- View From The Top
- Formation of New Ventures
- Managing Growing Enterprises
- Startup Garage
- Explore Beyond the Classroom
- Stanford Venture Studio
- Summer Program
- Workshops & Events
- The Five Lenses of Entrepreneurship
- Leadership Labs
- Executive Challenge
- Arbuckle Leadership Fellows Program
- Selection Process
- Training Schedule
- Time Commitment
- Learning Expectations
- Post-Training Opportunities
- Who Should Apply
- Introductory T-Groups
- Leadership for Society Program
- Certificate
- 2024 Awardees
- 2023 Awardees
- 2022 Awardees
- 2021 Awardees
- 2020 Awardees
- 2019 Awardees
- 2018 Awardees
- Social Management Immersion Fund
- Stanford Impact Founder Fellowships
- Stanford Impact Leader Prizes
- Social Entrepreneurship
- Stanford GSB Impact Fund
- Economic Development
- Energy & Environment
- Stanford GSB Residences
- Environmental Leadership
- Stanford GSB Artwork
- A Closer Look
- California & the Bay Area
- Voices of Stanford GSB
- Business & Beneficial Technology
- Business & Sustainability
- Business & Free Markets
- Business, Government, and Society Forum
- Second Year
- Global Experiences
- JD/MBA Joint Degree
- MA Education/MBA Joint Degree
- MD/MBA Dual Degree
- MPP/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Computer Science/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Electrical Engineering/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Environment and Resources (E-IPER)/MBA Joint Degree
- Academic Calendar
- Clubs & Activities
- LGBTQ+ Students
- Military Veterans
- Minorities & People of Color
- Partners & Families
- Students with Disabilities
- Student Support
- Residential Life
- Student Voices
- MBA Alumni Voices
- A Week in the Life
- Career Support
- Employment Outcomes
- Cost of Attendance
- Knight-Hennessy Scholars Program
- Yellow Ribbon Program
- BOLD Fellows Fund
- Application Process
- Loan Forgiveness
- Contact the Financial Aid Office
- Evaluation Criteria
- GMAT & GRE
- English Language Proficiency
- Personal Information, Activities & Awards
- Professional Experience
- Letters of Recommendation
- Optional Short Answer Questions
- Application Fee
- Reapplication
- Deferred Enrollment
- Joint & Dual Degrees
- Entering Class Profile
- Event Schedule
- Ambassadors
- New & Noteworthy
- Ask a Question
- See Why Stanford MSx
- Is MSx Right for You?
- MSx Stories
- Leadership Development
- How You Will Learn
- Admission Events
- Personal Information
- GMAT, GRE & EA
- English Proficiency Tests
- Career Change
- Career Advancement
- Daycare, Schools & Camps
- U.S. Citizens and Permanent Residents
- Requirements
- Requirements: Behavioral
- Requirements: Quantitative
- Requirements: Macro
- Requirements: Micro
- Annual Evaluations
- Field Examination
- Research Activities
- Research Papers
- Dissertation
- Oral Examination
- Current Students
- Education & CV
- International Applicants
- Statement of Purpose
- Reapplicants
- Application Fee Waiver
- Deadline & Decisions
- Job Market Candidates
- Academic Placements
- Stay in Touch
- Faculty Mentors
- Current Fellows
- Standard Track
- Fellowship & Benefits
- Group Enrollment
- Program Formats
- Developing a Program
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Strategic Transformation
- Program Experience
- Contact Client Services
- Campus Experience
- Live Online Experience
- Silicon Valley & Bay Area
- Digital Credentials
- Faculty Spotlights
- Participant Spotlights
- Eligibility
- International Participants
- Stanford Ignite
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Founding Donors
- Location Information
- Participant Profile
- Network Membership
- Program Impact
- Collaborators
- Entrepreneur Profiles
- Company Spotlights
- Seed Transformation Network
- Responsibilities
- Current Coaches
- How to Apply
- Meet the Consultants
- Meet the Interns
- Intern Profiles
- Collaborate
- Research Library
- News & Insights
- Program Contacts
- Databases & Datasets
- Research Guides
- Consultations
- Research Workshops
- Career Research
- Research Data Services
- Course Reserves
- Course Research Guides
- Material Loan Periods
- Fines & Other Charges
- Document Delivery
- Interlibrary Loan
- Equipment Checkout
- Print & Scan
- MBA & MSx Students
- PhD Students
- Other Stanford Students
- Faculty Assistants
- Research Assistants
- Stanford GSB Alumni
- Telling Our Story
- Staff Directory
- Site Registration
- Alumni Directory
- Alumni Email
- Privacy Settings & My Profile
- Success Stories
- The Story of Circles
- Support Women’s Circles
- Stanford Women on Boards Initiative
- Alumnae Spotlights
- Insights & Research
- Industry & Professional
- Entrepreneurial Commitment Group
- Recent Alumni
- Half-Century Club
- Fall Reunions
- Spring Reunions
- MBA 25th Reunion
- Half-Century Club Reunion
- Faculty Lectures
- Ernest C. Arbuckle Award
- Alison Elliott Exceptional Achievement Award
- ENCORE Award
- Excellence in Leadership Award
- John W. Gardner Volunteer Leadership Award
- Robert K. Jaedicke Faculty Award
- Jack McDonald Military Service Appreciation Award
- Jerry I. Porras Latino Leadership Award
- Tapestry Award
- Student & Alumni Events
- Executive Recruiters
- Interviewing
- Land the Perfect Job with LinkedIn
- Negotiating
- Elevator Pitch
- Email Best Practices
- Resumes & Cover Letters
- Self-Assessment
- Whitney Birdwell Ball
- Margaret Brooks
- Bryn Panee Burkhart
- Margaret Chan
- Ricki Frankel
- Peter Gandolfo
- Cindy W. Greig
- Natalie Guillen
- Carly Janson
- Sloan Klein
- Sherri Appel Lassila
- Stuart Meyer
- Tanisha Parrish
- Virginia Roberson
- Philippe Taieb
- Michael Takagawa
- Terra Winston
- Johanna Wise
- Debbie Wolter
- Rebecca Zucker
- Complimentary Coaching
- Changing Careers
- Work-Life Integration
- Career Breaks
- Flexible Work
- Encore Careers
- Join a Board
- D&B Hoovers
- Data Axle (ReferenceUSA)
- EBSCO Business Source
- Global Newsstream
- Market Share Reporter
- ProQuest One Business
- RKMA Market Research Handbook Series
- Student Clubs
- Entrepreneurial Students
- Stanford GSB Trust
- Alumni Community
- How to Volunteer
- Springboard Sessions
- Consulting Projects
- 2020 – 2029
- 2010 – 2019
- 2000 – 2009
- 1990 – 1999
- 1980 – 1989
- 1970 – 1979
- 1960 – 1969
- 1950 – 1959
- 1940 – 1949
- Service Areas
- ACT History
- ACT Awards Celebration
- ACT Governance Structure
- Building Leadership for ACT
- Individual Leadership Positions
- Leadership Role Overview
- Purpose of the ACT Management Board
- Contact ACT
- Business & Nonprofit Communities
- Reunion Volunteers
- Ways to Give
- Fiscal Year Report
- Business School Fund Leadership Council
- Planned Giving Options
- Planned Giving Benefits
- Planned Gifts and Reunions
- Legacy Partners
- Giving News & Stories
- Giving Deadlines
- Development Staff
- Submit Class Notes
- Class Secretaries
- Board of Directors
- Health Care
- Sustainability
- Class Takeaways
- All Else Equal: Making Better Decisions
- If/Then: Business, Leadership, Society
- Grit & Growth
- Think Fast, Talk Smart
- Spring 2022
- Spring 2021
- Autumn 2020
- Summer 2020
- Winter 2020
- In the Media
- For Journalists
- DCI Fellows
- Other Auditors
- Academic Calendar & Deadlines
- Course Materials
- Entrepreneurial Resources
- Campus Drive Grove
- Campus Drive Lawn
- CEMEX Auditorium
- King Community Court
- Seawell Family Boardroom
- Stanford GSB Bowl
- Stanford Investors Common
- Town Square
- Vidalakis Courtyard
- Vidalakis Dining Hall
- Catering Services
- Policies & Guidelines
- Reservations
- Contact Faculty Recruiting
- Lecturer Positions
- Postdoctoral Positions
- Accommodations
- CMC-Managed Interviews
- Recruiter-Managed Interviews
- Virtual Interviews
- Campus & Virtual
- Search for Candidates
- Think Globally
- Recruiting Calendar
- Recruiting Policies
- Full-Time Employment
- Summer Employment
- Entrepreneurial Summer Program
- Global Management Immersion Experience
- Social-Purpose Summer Internships
- Process Overview
- Project Types
- Client Eligibility Criteria
- Client Screening
- ACT Leadership
- Social Innovation & Nonprofit Management Resources
- Develop Your Organization’s Talent
- Centers & Initiatives
- Student Fellowships
Organizational Analysis (A Case Study of Apple Inc.)

- Lincoln University New Zealand
Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up
Table of Contents
Apple target audience , marketing strategy of apple, 5 key takeaways from apple marketing strategy, a case study on apple marketing strategy.

Breaking through with several inventions in the world of technology, Apple Inc. has been carving infinite milestones ever since its inception. Even though its innovations speak for themselves, this highly-valued giant corporation has invested heavily in its marketing team to soar high up as a tech maestro. Apple Inc. realized the role of brand marketing in the success of a venture from the start as a crucial way to connect with its target audience. This brand's marketing is so vigorously carried out and well-thought that it is often an inspiration and a place of research for marketing professionals. Here we bring you a well-curated case study on Apple's marketing strategy, the key takeaways to learn from this venture, and how to incorporate the same in your business and marketing strategies.
Become a Certified Marketing Expert in 8 Months
To understand its key strategies for marketing Apple products, let's first understand what Apple's target audience is like. Apple's target audience consists of middle-class and upper-class users who can pay higher for products that provide them with an incredible user experience. This means that these users have a higher disposable income and are willing to pay more for as high-priced products as Apple's.
Let's take a look at Apple's target audience with this comprehensive analysis sourced from Business Research Methodology's report on Apple Segmentation :
| Areas | Urban |
| Gender | All |
| Age | 20-45 |
| Life phase | Bachelors to Married both |
| Earnings | High |
| Jobs | Working professionals, managers & executive level workers |
Besides this primary classification, Apple also explicitly targets professionals working in specialized software like music, video, photography and all kinds of design careers. These working professionals prefer Adobe’s Final Cut, Photoshop and related editing software which work well with Macbooks and IPads than other operating systems.
Even better, business professionals prefer Apple products such as iPods and Macbooks for their day-to-day work. Products like iPads and Macbooks are lighter and portable, so they are often selected by students (upper-class), educational institutions and teaching.
Now coming to the marketing strategy of Apple, it is a combination of well-designed products with the right user experience, promotional campaigns, distribution, and pricing. Let’s take a look at all these features of Apple marketing strategy in detail:
Focus on Finer User Experience
Apple’s branding strategy is based on its stylish, more straightforward and lush products that focus on providing a user interface that is very simple to use and learn. They are lighter, easy to carry as well as durable. This minimal look and user experience makes it a perfect sell to its target audience, which comes from the middle to upper class.
Suave Yet Simple Advertising
Storytelling is such an essential part of every Apple ad as well as a marketing campaign. Often these ads focus on minimal design as well as high-quality images. They are either blended with music or a simple story. Apple consciously ensures that its advertising and marketing don’t use too much jargon or filler language in its ads. Instead, it shines a light on the product to let it speak for itself without showing what the price is like or using complicated words for its features.
Targeting the Right Markets
Apple is excellent at tapping into its target audiences like a genuine tech witch who knows their aspirations, preferences and pain points! Its market research is always on-point and crystal clear in its products, curation, and features.
Here are the major critical takeaways from Apple Marketing Strategy:
- Tapping into your target markets and audience is the key to curating and selling user experiences that value the preferences of its people.
- With simplicity and finesse in design, the right products with minimal designs and features can create a perfect impact for your brand.
- Incorporating emotion in your advertising and marketing can also help you connect with your audience better.
- Don’t exaggerate the copy and conceptualizing of your advertising and marketing campaigns and prefer the “less is more” approach. Create shorter yet emotional and empathetic ads to captivate your target audience.
- When you create an international brand value through quality and minimal, sophisticated design, you don’t need to compete in terms of price. Instead, your price will set you apart for your user experience and design features.
Become a millennial Digital Marketer in just 6 months. Enroll now for our PGP in Digital Marketing course in collaboration with Purdue University!
Thus, we hope we have helped you understand what Apple’s marketing strategy is about! Want to read more case studies about top brands and their marketing strategies? Join Simplilearn’s specialized PGP Digital Marketing certification in collaboration with Meta Blueprint and Harvard Publishing. This certification can help you level up your career in digital marketing through case studies, industry projects, masterclasses from industry experts, ad marketing tools from Facebook, Google, and related marketing tools.
Our Digital Marketing Courses Duration And Fees
Digital Marketing Courses typically range from a few weeks to several months, with fees varying based on program and institution.
| Program Name | Duration | Fees |
|---|---|---|
| Cohort Starts: | 8 Months | € 1,699 |
| Cohort Starts: | 8 Months | € 999 |
Recommended Reads
Digital Marketing Career Guide: A Playbook to Becoming a Digital Marketing Specialist
Apple Interview Questions 2024
12 Powerful Instagram Marketing Strategies To Follow in 2021
Introductory Digital Marketing Guide
Walmart Marketing Strategy
What is Digital Marketing and How Does It Work?
Get Affiliated Certifications with Live Class programs
Post graduate program in digital marketing.
- Joint Purdue-Simplilearn Digital Marketer Certificate
- Become eligible to be part of the Purdue University Alumni Association
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.

- About / Contact
- Privacy Policy
- Alphabetical List of Companies
- Business Analysis Topics
Apple’s Company Culture: An Organizational Analysis

Apple’s organizational culture is a key factor in the continuing success of its business. The consumer electronics company’s organizational or corporate culture establishes and maintains the business philosophy, core values, beliefs, and related behaviors among employees. This business analysis case shows that Apple has a work culture that motivates human resources to support strategic objectives for competitiveness. For example, the company’s cultural traits are aligned with the drive for innovation, which is a major factor that determines business competitiveness in the information technology, online services, and consumer electronics industries. With this company culture, business operations facilitate the fulfillment of Apple’s mission and vision . Through the leadership of Tim Cook, the company continues to enhance its cultural characteristics to maximize human resource support for business relevance in various markets around the world. Apple shapes its business culture and uses it as a tool for strategic management and multinational business success.
Apple’s company culture strengthens competitive advantages over other firms in various industries. The company’s products compete with the consumer electronics and online services of Google (Alphabet) , Samsung , Microsoft , Amazon , and Sony . Also, Apple TV Plus competes with the video streaming services of Disney , Facebook (Meta) , and Netflix . These competitors impose a strong external force that influences strategic management among firms in the industry, as illustrated in the Five Forces analysis of Apple Inc . As a result, cultural traits must reinforce the iPhone maker’s business competitive advantages through its workforce. It can be argued that Apple partially achieves this strategic objective through the effects of its organizational culture on workers’ behavior and job performance.
Apple’s Culture Type and Traits
Apple has an organizational culture for creative innovation . The company’s cultural features focus on maintaining a high level of innovation that involves workers’ creativity and a mindset that challenges conventions and standards, such as in consumer electronics design. Apple’s IT business depends on cultural support and coherence, which are determinants of competitiveness and industry leadership, especially in addressing aggressive and rapid technological innovation and product development. The following are the main characteristics of Apple’s culture:
- Top-notch excellence
- Moderate combativeness
Top-notch Excellence . Apple’s organizational culture comes with a human resource policy of hiring only the best of the best in the labor market. Steve Jobs was known to fire employees who did not meet his expectations. This tradition continues under Tim Cook. Such a tradition maintains and reinforces a company culture that promotes, appreciates, and expects top-notch excellence among the technology company’s employees. This cultural trait is also institutionalized in Apple’s organization. For example, the company has programs that recognize and reward excellence among workers in software design. Excellence is emphasized as a critical success factor in the business, especially in product design and development, which is a major growth strategy described in Apple’s competitive strategy and growth strategies .
Creativity . This cultural trait pertains to creating new ideas that help improve the technology business and its products. Apple’s management favors creativity among employees’ knowledge, skills, and abilities. This characteristic of the work culture enables the company to ensure sufficient creativity, especially among employees involved in consumer electronics product design and development processes. Creativity is observable in the design and features of iPhones, Macs, iPads, and other products included in Apple’s marketing mix (4Ps) . Along with creativity, originality is also culturally emphasized as a way of maximizing the company’s intellectual properties, such as patents for new mobile devices. In this regard, the organizational culture helps maintain Apple’s capacity to satisfy and exceed customers’ expectations and preferences.
Innovation . Apple’s company culture supports rapid innovation. The technology business is frequently appraised as one of the most innovative companies in the world. Based on this cultural trait, Apple trains and motivates its employees to innovate in terms of individual work performance and idea contributions for product development, design, and other processes. The work culture facilitates rapid innovation, which is at the heart of Apple’s operations management . Rapid innovation ensures that the company continues to introduce new products that are profitable and attractive to target customers in the global consumer electronics and Internet services market.
Secrecy . Apple has a secretive organizational culture. This cultural characteristic defines the MacBook maker’s human resource development and management practices. Secrecy is part of the company’s strategy to prevent theft of proprietary information or intellectual property, such as designs for the next generations of the iPhone. It is also a strategic management approach that enables Apple Inc. to maximize its leading edge against competitors. Through the company culture, employees are motivated and expected to keep business information within the technology business organization. This cultural trait is reinforced through Apple’s organizational structure (business structure) and related policies, rules, and employment contracts that prohibit the disclosure of information, such as technological breakthroughs in the company’s consumer electronics. In this context, Apple’s work culture helps protect the business from corporate espionage and the negative effects of employee poaching.
Moderate Combativeness . Apple’s company culture has moderate combativeness. This feature is linked to Steve Jobs and his combative approach to leadership. He was known to randomly challenge employees to ensure that they have what it takes to work at Apple. Today, under Tim Cook’s leadership, the company has been changing its corporate culture to a more sociable and a less combative one. Nonetheless, combativeness remains a major influence in the technology business. Apple’s business culture exhibits a moderate degree of combativeness that presents challenges that motivate employees to enhance their output.
Apple’s Organizational Culture: Advantages, Disadvantages, Recommendations
Advantages and Benefits . The combination of top-notch excellence, creativity, and innovation in Apple’s organizational culture supports the company’s industry leadership. The business is widely regarded as a leader in terms of innovation and product design, especially in consumer electronics. These cultural characteristics empower Apple and its human resources to stand out and stay ahead of competitors. This company culture enables success and competitive advantages, as well as the further strengthening of the company’s brand, which is one of the key business strengths shown in the SWOT analysis of Apple Inc . Creativity and excellence are especially important in the company’s rapid innovation processes for continuous competitiveness and business development despite aggressive competition with Samsung and other firms.
Drawbacks and Weaknesses . Apple’s corporate culture brings challenges because of the emphasis on secrecy and the moderate degree of combativeness. An atmosphere of secrecy can limit rapport among workers, while moderate combativeness has the potential to limit or reduce employees’ morale. These cultural issues can reduce business effectiveness and increase employee turnover. Apple Inc. can address this situation by modifying its organizational culture to reduce combativeness, but not necessarily remove it. This recommendation focuses on reducing the disadvantages of combativeness, without eliminating the benefits of combative approaches in the technology company’s operations. Also, Apple can integrate new cultural traits to keep the business relevant, given trends and changes in the information technology, cloud services, digital content distribution, and consumer electronics industries’ environment.
- Choi, Y., Ingram, P., & Han, S. W. (2023). Cultural breadth and embeddedness: The individual adoption of organizational culture as a determinant of creativity. Administrative Science Quarterly, 68 (2), 429-464.
- Apple Inc. – Inclusion & Diversity .
- Apple Inc. – Life at Apple .
- Apple Inc. – Work at Apple .
- Dyer, C. (2023). The Power of Company Culture: How any business can build a culture that improves productivity, performance and profits . Kogan Page Publishers.
- Zhang, W., Zeng, X., Liang, H., Xue, Y., & Cao, X. (2023). Understanding how organizational culture affects innovation performance: A management context perspective. Sustainability, 15 (8), 6644.
- Copyright by Panmore Institute - All rights reserved.
- This article may not be reproduced, distributed, or mirrored without written permission from Panmore Institute and its author/s.
- Educators, Researchers, and Students: You are permitted to quote or paraphrase parts of this article (not the entire article) for educational or research purposes, as long as the article is properly cited and referenced together with its URL/link.

Apple Case Study – How Steve Jobs built Apple around simplicity

This article is written by Graham Robertson, the founder of Beloved Brands
Brand Toolkit
Our Apple case study starts with 𝘁𝗵𝗲 𝗱𝗮𝘆 𝗦𝘁𝗲𝘃𝗲 𝗝𝗼𝗯𝘀 𝗿𝗲𝘁𝘂𝗿𝗻𝗲𝗱 𝘁𝗼 𝗔𝗽𝗽𝗹𝗲. This is the starting point that 𝘁𝗿𝗮𝗻𝘀𝗳𝗼𝗿𝗺𝗲𝗱 𝗔𝗽𝗽𝗹𝗲 𝗶𝗻𝘁𝗼 𝗼𝗻𝗲 𝗼𝗳 𝘁𝗼𝗱𝗮𝘆’𝘀 𝗺𝗼𝘀𝘁 𝗮𝗱𝗺𝗶𝗿𝗲𝗱 𝗯𝗿𝗮𝗻𝗱 s . Steve Jobs recognized that consumers were frustrated by how all the other technology brands designed their products in a lab without any thought for the consumer. Steve Jobs made the most significant contribution to the Apple brand strategy by starting with the consumer experience and then working back to the technology. The Apple brand positioning builds everything around the idea that “Apple makes technology so simple that everyone can be part of the future.”
Moreover, we witnessed the most incredible decade that any company has ever seen, with Apple launching iTunes, iPod, iMac, the MacBook Pro, MacBook Air, iPhone, and the iPad.
If you are a marketer looking to improve your knowledge by looking at what Apple has done so well, our Apple case study will teach plenty of lessons for using a brand idea to inspire and steer everyone who works on the brand. At every step of the Apple brand strategy, we will provide a link to click on and learn how the process can work on your brand.
If you are a fan of Apple, click on this link to view their best store locations: Apple Store locations . Or come see some of their best advertising: Apple Advertising .

Apple Case Study - Table of Contents
Building the apple brand.
Our Apple case study will show how to develop Apple’s brand positioning statement and plan . Then, I will show how Steve Jobs pushed to stretch their “simplicity” brand idea across their company. Everyone who works behind the scenes knows their role in delivering simplicity.
Simplicity drives all Apple advertising.
In the 1980s, Apple started with “technology for the rest of us” when they took on IBM. And they continued that attack with “I’m a Mac” ads that took on Microsoft. Simplicity drives Apple’s innovation. Steve Jobs pushed for great advertising.
The beauty of Apple is how they take complex technology and simplify it so consumers can do more with Apple products.
The Apple brand strategy even drives their retail stores. Their Genius bar helps answer technology questions. They allow consumers to play with their products. Apple salespeople are trained to avoid “geek speak.”
The return of Steve Jobs
After Steve Jobs returned in 1997, he shifted the focus to rebuilding around the brand idea of “Apple makes technology so simple that everyone can be part of the future.” Jobs came in with a consumer-first approach in a market dominated by an obsession with gadgets, bits, and bytes. At the heart of our Apple case study is the use of the brand idea of simplicity and its impact on the brand strategy.

Undoubtedly, simplicity is one of the values Steve Jobs held very close to his heart. For example, he built simplicity into everything Apple did and everything it stood for. Even over the last decade, Apple is still following the Steve Jobs playbook.
Apple Brand Positioning - how they use 'simplicity'
The apple brand positioning builds everything behind the “simplicity” brand idea..
We use our consumer benefit ladder to find differentiation. Importantly, turn your brand’s features into consumer benefits. Stop thinking about what your brand does. And, start thinking about what your consumer gets. That’s when the Apple brand positioning statement comes alive.
Functional consumer benefits.
To help brand leaders kickstart their brand positioning work, I have created 12 functional zones that expand to over 50 potential functional benefits. For instance, as you look through the list, gravitate to the functional benefits you think will fit your consumers’ needs and differentiate your brand by looking for words where your brand does it better than competitors. While you might start with our words, try to layer in your own creative language with the specific category or consumer language.
Emotional consumer benefits.
Below is a list of 40 potential emotional benefits that help build an emotional brand positioning statement that differentiates your brand. Importantly, you want to own one emotional space in the consumer’s heart as much as you own the rational space in the consumer’s mind.
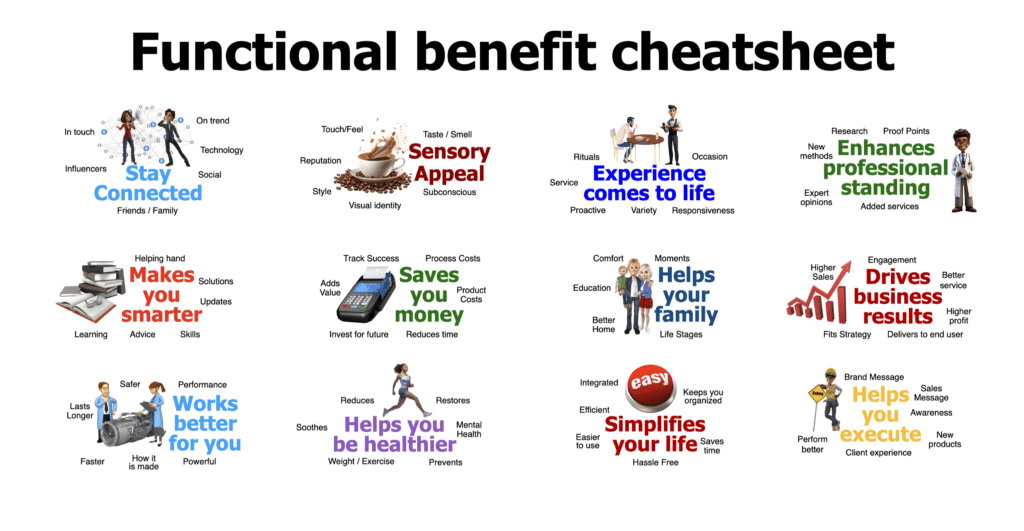
To illustrate, click on our Consumer Benefit Cheatsheet to build the Apple brand positioning .
Choosing the right benefit clusters for Apple
Using our brand positioning process, the Apple brand positioning narrows in on the brand’s potential benefit clusters of the functional and emotional benefits.
What Apple does: best features
- Intuitive and easy to use: Apple allows everyone to do more and get more from their devices.
- Stylish designs: Fashion-forward designed so that people want to show them off.
- Integrated technology: All devices, software, and services work harmoniously, enhancing user experience.
- Fresh innovation: Apple customers always have access to cutting-edge features and advancements.
What Apple consumers get: functional benefits
- Simplifies your life: Hassle free, easier to use, integrated.
- Sensory Appeal: Touch/feel, subconscious, and style.
- Experience: Responsiveness, rituals, and service.
How Apple consumers feel: emotional benefits
- Feel free: Alive, excited, exhilarating.
- Get noticed: Cool, trendy, popular, and playful.
- Optimism: Successful, inspired, and motivated.
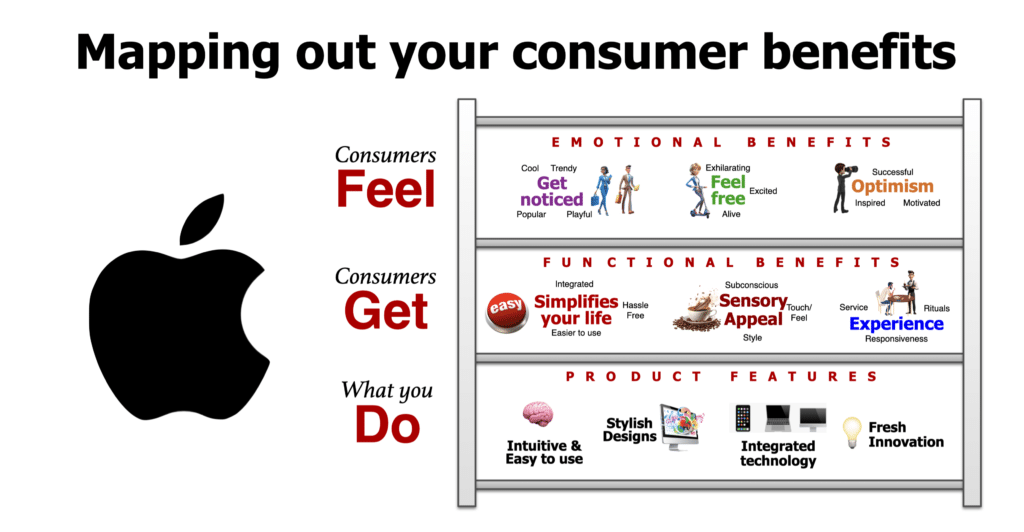
To illustrate, click on our Consumer Benefit ladder we use to build the Apple brand positioning .
Apple Brand positioning statement
Once everything is settled, the overall Apple brand positioning statement focuses on simplifying technology to help you feel smarter so you can do more with every device.
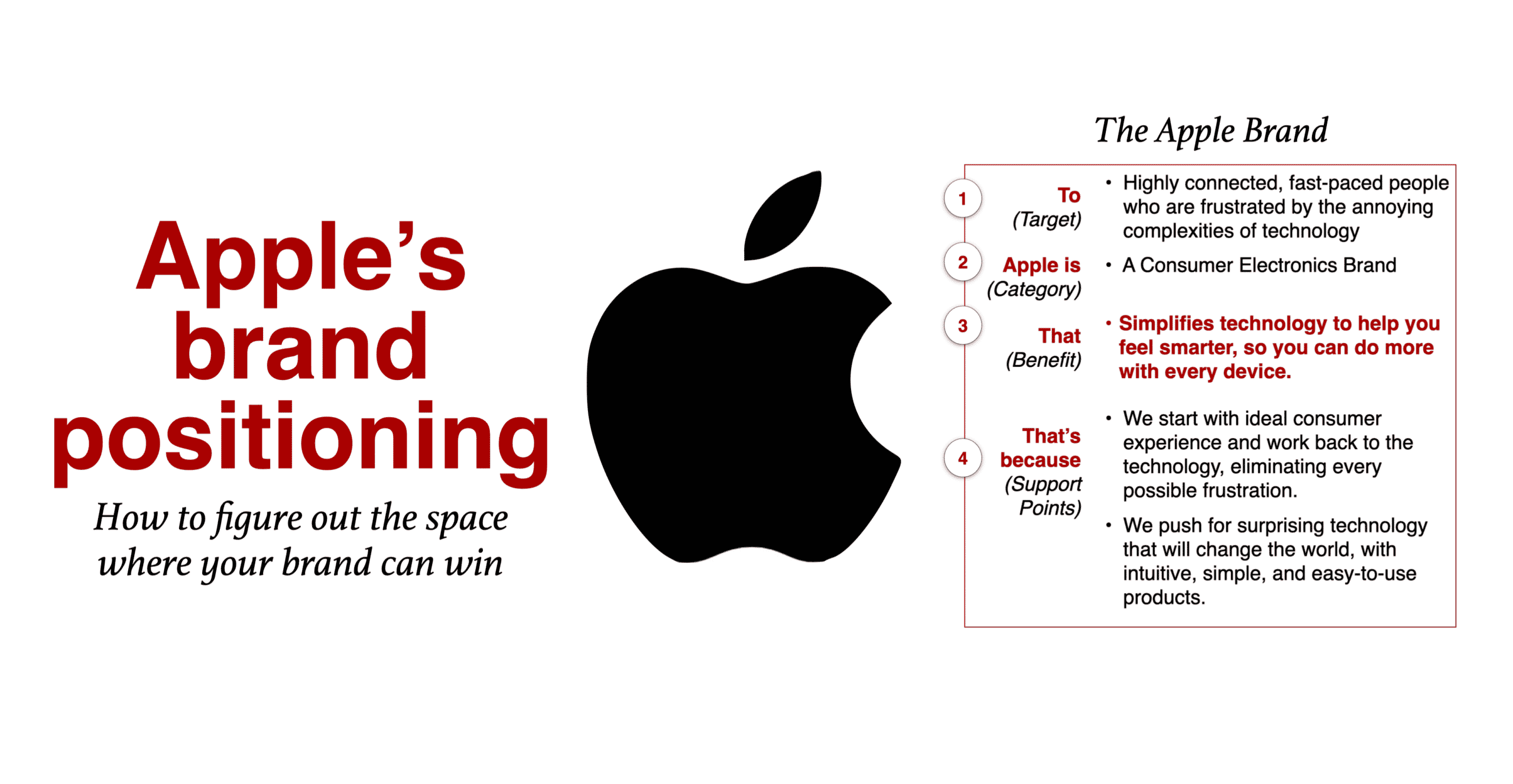
To illustrate, click on the Apple Brand Positioning Statement . You can zoom in, download it, or share it.

Old school brand positioning vs new school
When brand positioning began in the 1970s and 80s, the goal was to stay single-minded and focused and even get down to one word. For example, Volvo was about SAFETY. I still believe in that thinking for marketing communications. If all Volvo does is “safety,” no one would pay $50,000 to $70,000 USD for their cars. The additional benefits earn extra money for the comfortable leather seats, stylish design, and high-quality radio.
However, as brands have matured, the brand positioning should drive product innovation, the purchase moment, and the ideal consumer experience. One word might not be enough. Now, we can see brands can own a cluster of benefits.
Below, we can see the cluster of benefits, both functional and emotional, to create a word cloud for Apple. These words can show up as support communications to the ‘simplicity’ idea. Moreover, these words should appear in product design, in-store layout, people management, and consumer experience. These words should drive every part of the Apple brand strategy.
In a similar vein, the pharmaceutical industry has also adapted its marketing strategies to meet the changing demands and expectations of consumers. Take, for example, Motilium, a medication used to treat nausea and vomiting. As brand positioning evolves, the marketing for Motilium not only highlights its effectiveness but also emphasizes convenience and accessibility by promoting the option to buy Motilium online ( reference ). This adaptation ensures that the messaging is not just about the functional benefit of symptom relief but also about making the purchase process as easy as possible for the consumer, aligning with modern expectations of convenience and immediate availability.
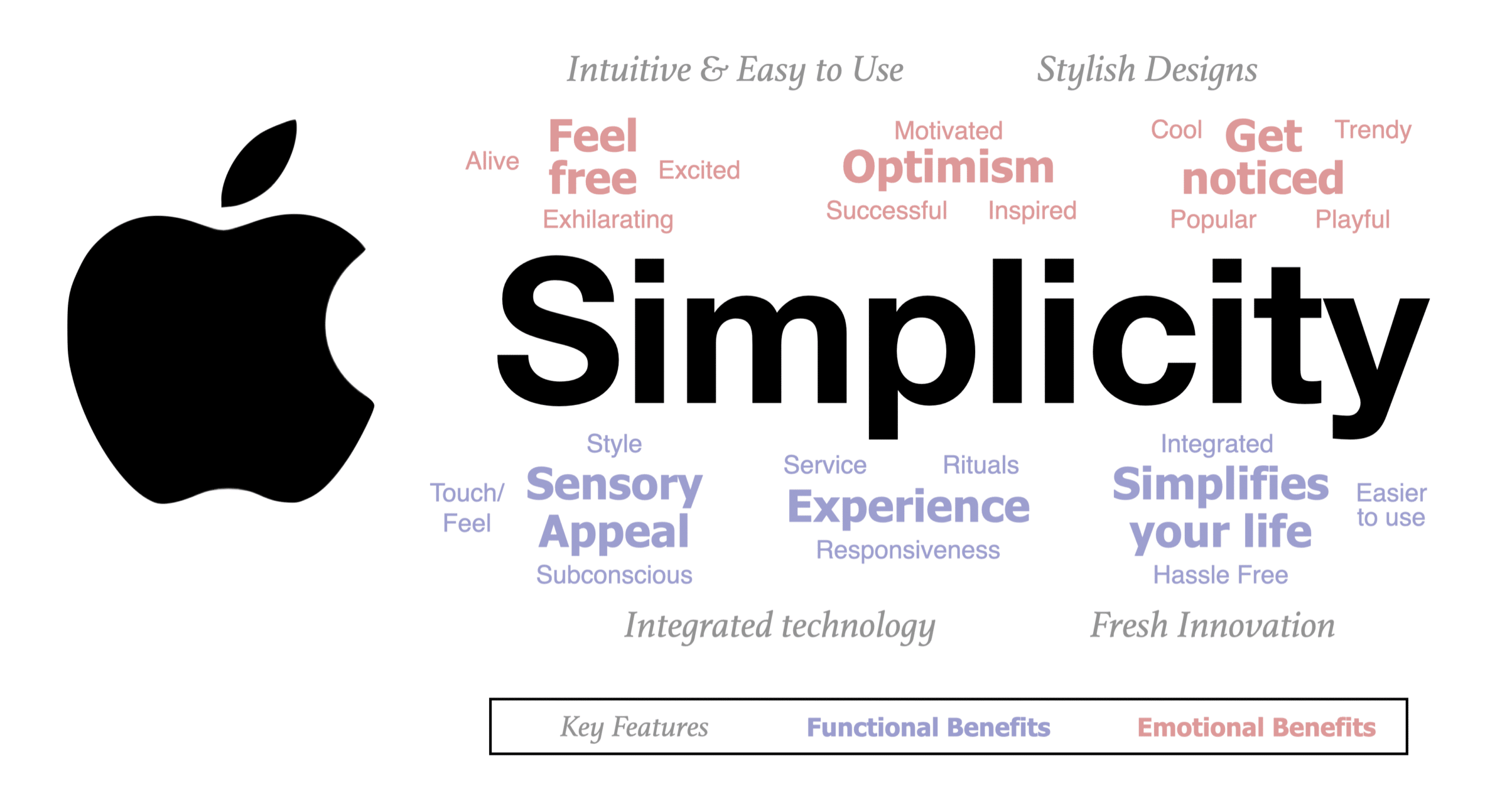
To illustrate, click on our Cluster of Consumer Benefits that we use to build the Apple brand positioning .
Beloved Brands Marketing Training
To view, use the arrow to see our Beloved Brands Marketing Training program video.
It's time to elevate your marketing team's performance with our Beloved Brands Marketing Training program.
Our marketing training makes your marketers smarter with brand analytics, strategic thinking, brand positioning, brand plans, and marketing execution.
Building Apple's brand idea
Everyone seems to call the short-form description of a brand by different names; brand DNA, big idea, brand essence or shout from the mountain. I keep it simple by calling it the brand idea. To win in the marketplace, your brand idea must be interesting, simple, unique, inspiring, motivating, and ownable.
I created a brand idea blueprint with five ideas that surround it.
On the internal brand soul side, describe the products and services and the cultural inspiration, which is the internal rallying cry to everyone who works on the brand. On the external brand reputation side, define the ideal consumer reputation and the reputation among necessary influencers or partners. The brand role acts as a bridge between the internal and external sides.
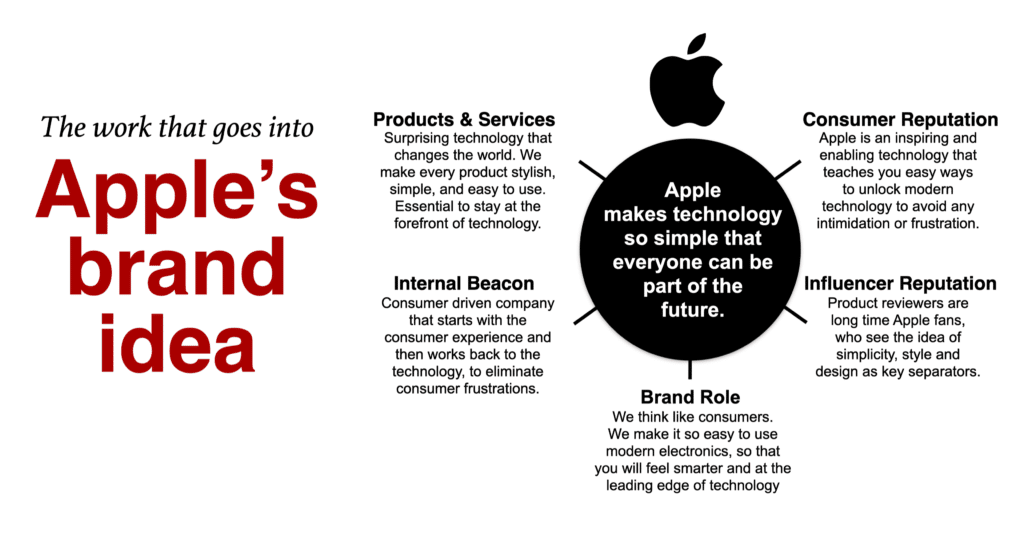
To illustrate, click on the Apple Brand Idea we use to build upon the Apple brand positioning .
The Apple case study uses the brand idea for Apple is “making technology so simple that everyone can be part of the future.” Most importantly, Steve Jobs insisted they take a consumer-first mentality as they transformed leading technology advancements into “consumer-accessible” technology, helping fuel the perception among the mass audience that Apple is an innovative leader.
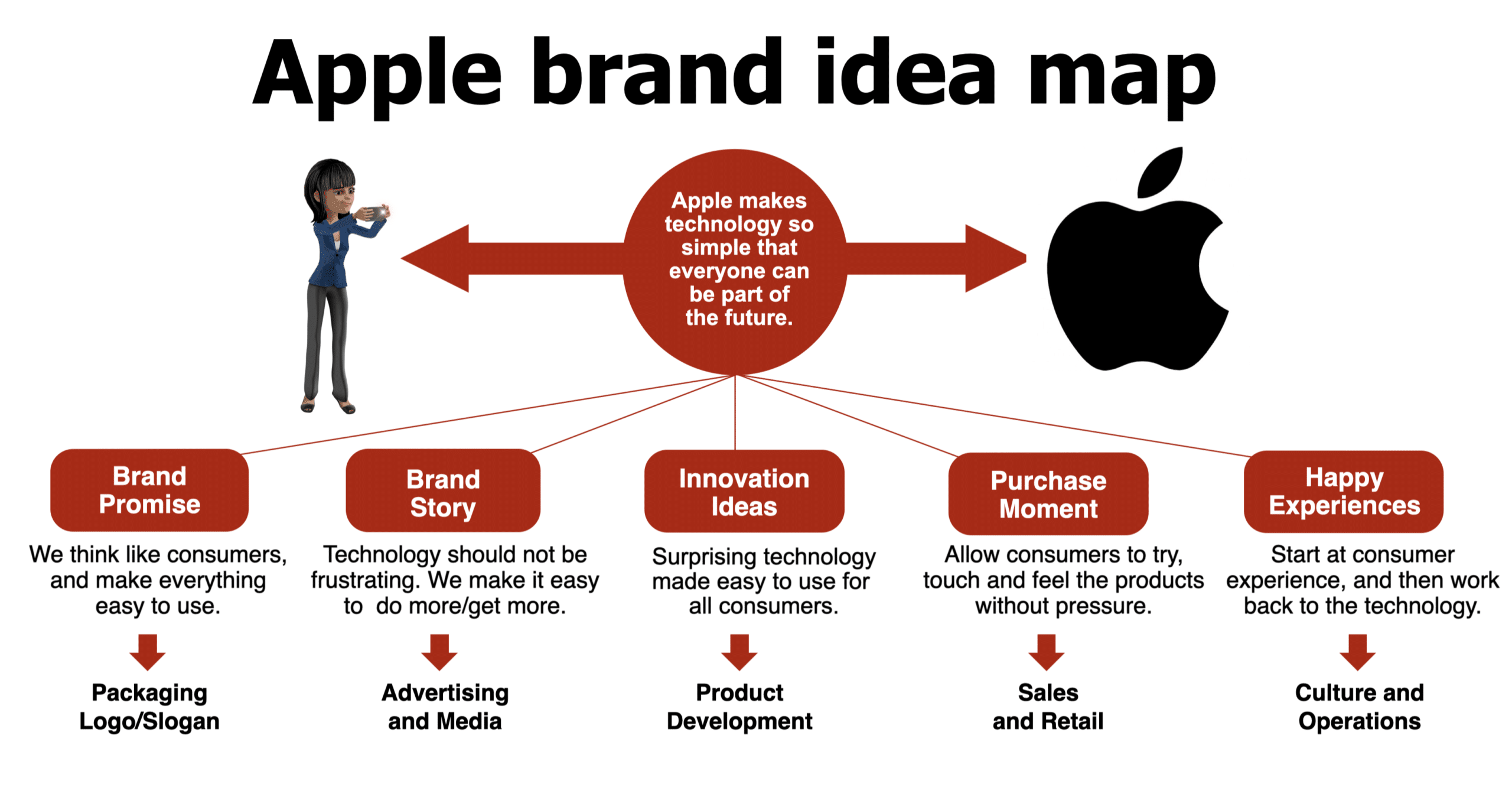
To illustrate, click on the Apple Brand Idea Map we use to build upon the Apple brand positioning .
Apple Case Study - video
Our apple case study is part of our beloved brands mini mba. take a look..
Below is an example video (30 minutes) from our Beloved Brands Mini MBA. We use the Apple case study to demonstrate the Apple brand positioning tools.
To view the Beloved Brands Mini MBA video , use the ▶️ button to play.
Apple's Brand Key Model
A Brand Key model is a tool from consumer marketing that allows marketers to lay out their brand’s unique selling proposition (USP) elements on one page. This article will go through the Brand Key model with nine elements that build the USP. And, with each element, we will show you the work you need to do.
Below is the Brand Key example for the Apple brand. It brings to life Apple’s unique selling proposition of simplicity. To read more on brand key models, click this link: Using a Brand Key Model to Define your Brand’s USP.
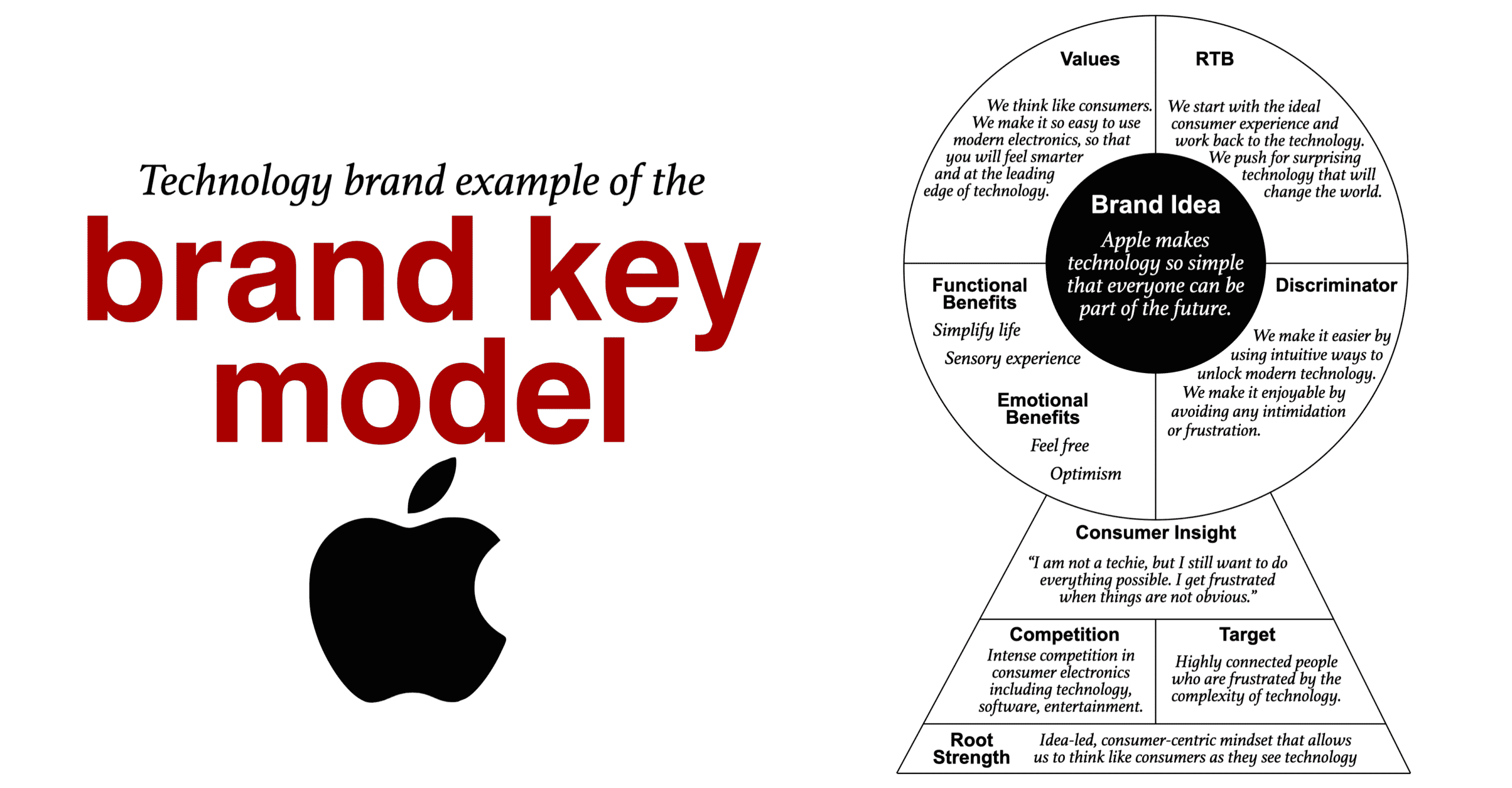
To illustrate, click on the Apple Brand Key we use to express the Apple brand positioning .
Our best posts
Click on any story below to read the more.
Use Apple's brand idea as a lens to see the problems not delivering
Apple has done a great job taking that simple brand idea and stretching it across its brand story through advertising and its innovation plan (as they have entered many new technology categories).
They have also used their brand idea to guide how they manage the purchase moment (to make sure their retail outlets are easy for consumers) and how they create happy experiences. And, when they don’t nail the ideal consumer experience, they go out of their way to help. They also have the genius bar and on-site lessons, which help increase consumers’ knowledge.
The other beauty of having a crystal clear brand idea is that everything that goes against that brand idea almost acts like an obvious virus. Below are four examples of where Apple is missing out on “simplicity,” which puts the brand idea at risk. Above all, these should trigger action plans to build into your brand plan. In pointing out these flaws within our Apple case study, I am yet to see Apple take action.
I wonder what Steve Jobs would think of these flaws.
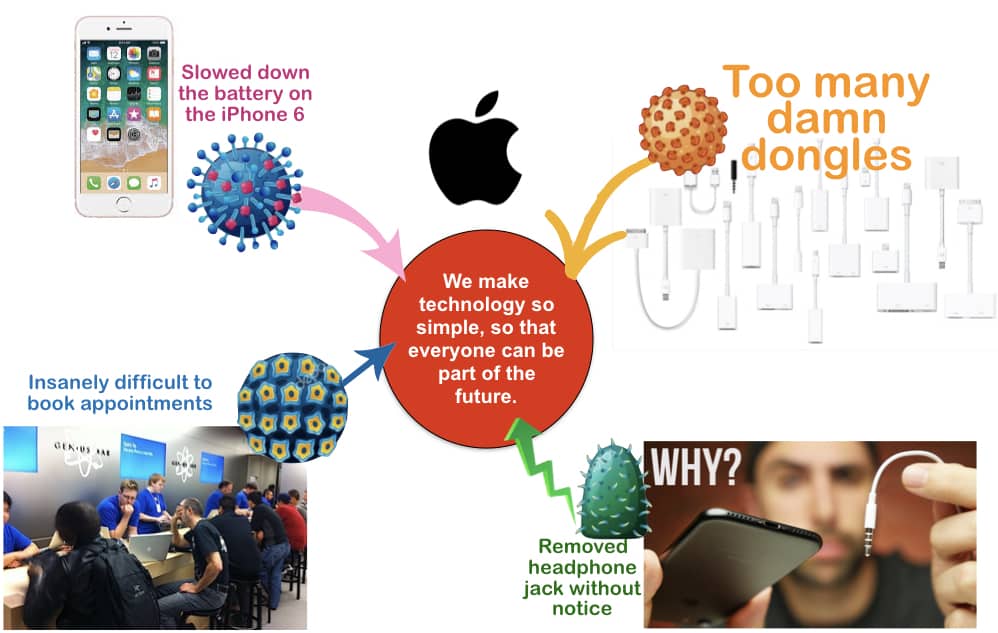
To illustrate, click on the Apple Case Study diagram to show where they go aga inst the Apple brand positioning.
Apple brand strategy
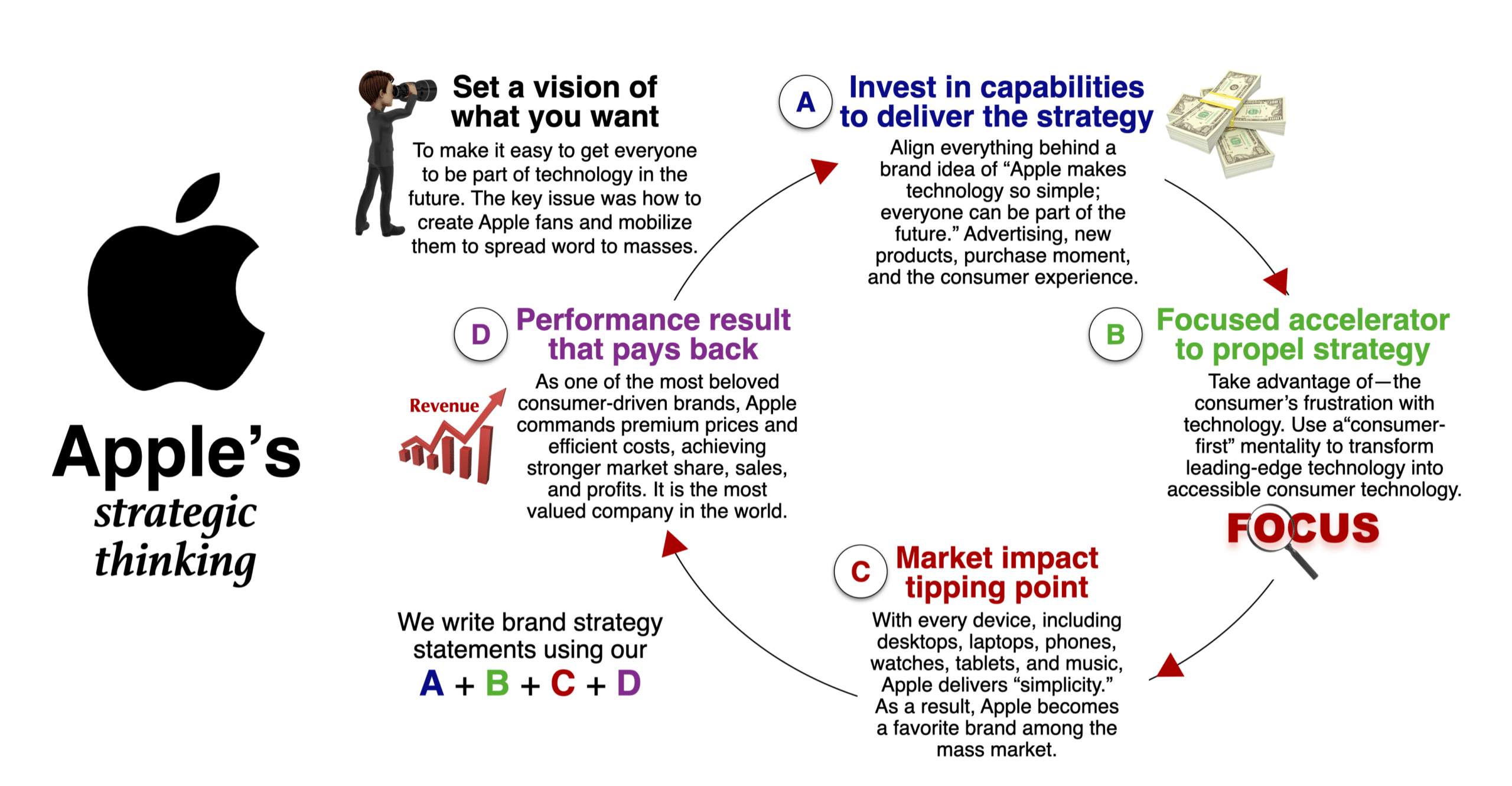
How the five elements of smart strategic thinking sets up apple's famous turnaround plan:, 1. set a vision of what you want..
To start our Apple case study, their vision is to make it easy for everyone to be part of technology in the future. The main issue was creating brand fans and then mobilizing them to spread the word to the masses.
2. Invest resources in a strategic program.
Next, Apple invested and aligned everything behind the Apple brand positioning and brand idea: “Apple makes technology so simple; everyone can be part of the future.” They use this brand idea at every touchpoint, including the brand positioning, communication, innovation, purchase moment, and experience.

3. Focus on an identified opportunity.
For decades, Apple consistently focused on empathizing with—and taking advantage of—the consumer’s frustration with technology. In the 1980s, they attacked IBM’s personal computers as too complicated. In 2005, they used “I’m a Mac, and I’m a PC” advertising to attack Microsoft. Each time, it used its “consumer-first” mentality to transform leading-edge technology into accessible consumer technology.
4. Leverage a breakthrough market impact.
Above all, the Apple brand strategy takes a fast-follower stance that takes current technology and makes it simple to use. Every platform, including desktops, laptops, phones, watches, tablets, and music streaming, delivers the brand idea of simplicity. They deploy high-profile launch hype to use vocal advocates to spread the word to their friends.
5. Performance result that pays back.
Most importantly, Apple created a consumer bond with its brand fans to enter new categories. On top of that, it is now the most beloved consumer-driven brand, with premium prices, stronger market share, sales, and profits. The Apple brand strategy used brand love to help drive a remarkable 40x revenue growth over ten years, skyrocketing from $5.7 billion in 2005 to $240 billion in 2015. This rapid growth helps cover the high costs of advertising and R&D, giving them very healthy operating margins, up over 35%. All this strategic effort has increased their market capitalization by over $1 trillion.
To illustrate, click on the Apple Brand Strategy diagram . You can zoom in, download it, or share it.
Apple brand plan
We are going to build out a Brand Strategy Roadmap that can steer the brand for the next three to five years. And, we’ll show a one-page Annual Brand Plan. We’ll show the rough brand plan work you can do.

To illustrate, click on the Apple Brand Strategy Roadmap . You can zoom in, download it, or share it.
The rough brand plan for Apple
With the Apple case study, our strategic thinking model sets up the core elements of the Apple brand strategy:
Apple wants everyone in the world to be part of the future.
Continue aggressive sales growth, geographic expansion into China, and launch a major new consumer-friendly technology each year.
Key issues:
- How do we convey Mac’s superior user experience versus the traditional PC?
- How do we enter the music industry and increase the availability of online music to support our iPod?
Strategies:
- Apple will launch a full communications assault to challenge the PC/Microsoft Windows dominant position by finding flaws in the PC to contrast with Mac computers’ simplicity to steal significant market share by enticing frustrated PC consumers to buy a Mac.
- Apple will launch a full assault against the entire music industry with a disruptive innovator stance to show how iTunes provides higher quality digital music on your iPod much cheaper, faster, and smarter than CDs to gain an entry point into the music industry.
- TV advertising to highlight new features and challenge competitors.
- Launch innovation each year, including phones, tablets, online music, watches, and personal computers.
- Launch specific products for China. Increase retail space around the world. Build out the e-commerce program.

To illustrate, click on the Apple Brand Plan example that brings the Apple brand positioning to life.
Apple advertising
Advertising has delivered “simplicity” since the 1970s.
Apple’s advertising has been relatively consistent for over 40 years and incredibly connected with consumers. As Steve Jobs was launching Apple, the early print ads of the 1970s talked about how we designed the computer, so you don’t have to worry about the details.

Steve Jobs pushed for the “1984” TV ad for the Mackintosh launch that spoke about freedom from machines. Although the message was a little ahead of its time, it fit with simplicity. Above all, the brilliance of the side-by-side “I’m a Mac, and I’m a PC” TV ads epitomized the brand idea by making the PC seem overly complicated and frustrating while setting up the Mac as the simple alternative. These ads really express the Apple brand positioning statement.
Take a look at some of "I'm a Mac" TV ads. Enjoy!
To illustrate, click the ▶️ button to see the Apple brand advertising that brings the Apple brand positioning to life .
Apple innovation
Building product innovation around simplicity.
Apple has taken many failed technology ideas like online music, tablets, or mp3 players and turned them into consumer-friendly platforms such as iTunes, iPads, and iPods. With each new product, Apple uses launch hype to generate excitement to spark the enthusiasm of the early adopters who spread the word. Also, Apple has successfully taken its cherished brand fans into new categories.
The combination of Johnny Ives and Steve Jobs created many great Apple products.
Learn how to make innovation decisions.

Video on Apple's product innovation philosophy
To view the Apple brand innovation philosophy use the ▶️ button to play.
Apple retail
Purchasing apple products is very simple, including its own retail store experience.
Retail stores are a significant part of the Apple Case Study.
Steve Jobs saw a vision for retail to help Apple use simplicity to manage the purchase moment through its retail stores, ensuring the experience is simple and straightforward. All staff carry a credit card machine and complete the transaction very quickly. No lines or cash registers.
Simplicity shines through the store layout, with the genius bar for one-on-one tech questions and support and the training area to teach classes. The brand also displays every Apple product to allow consumers to take them for a test drive. It’s all about delivering the consumer experience that Steve Jobs loved so much.
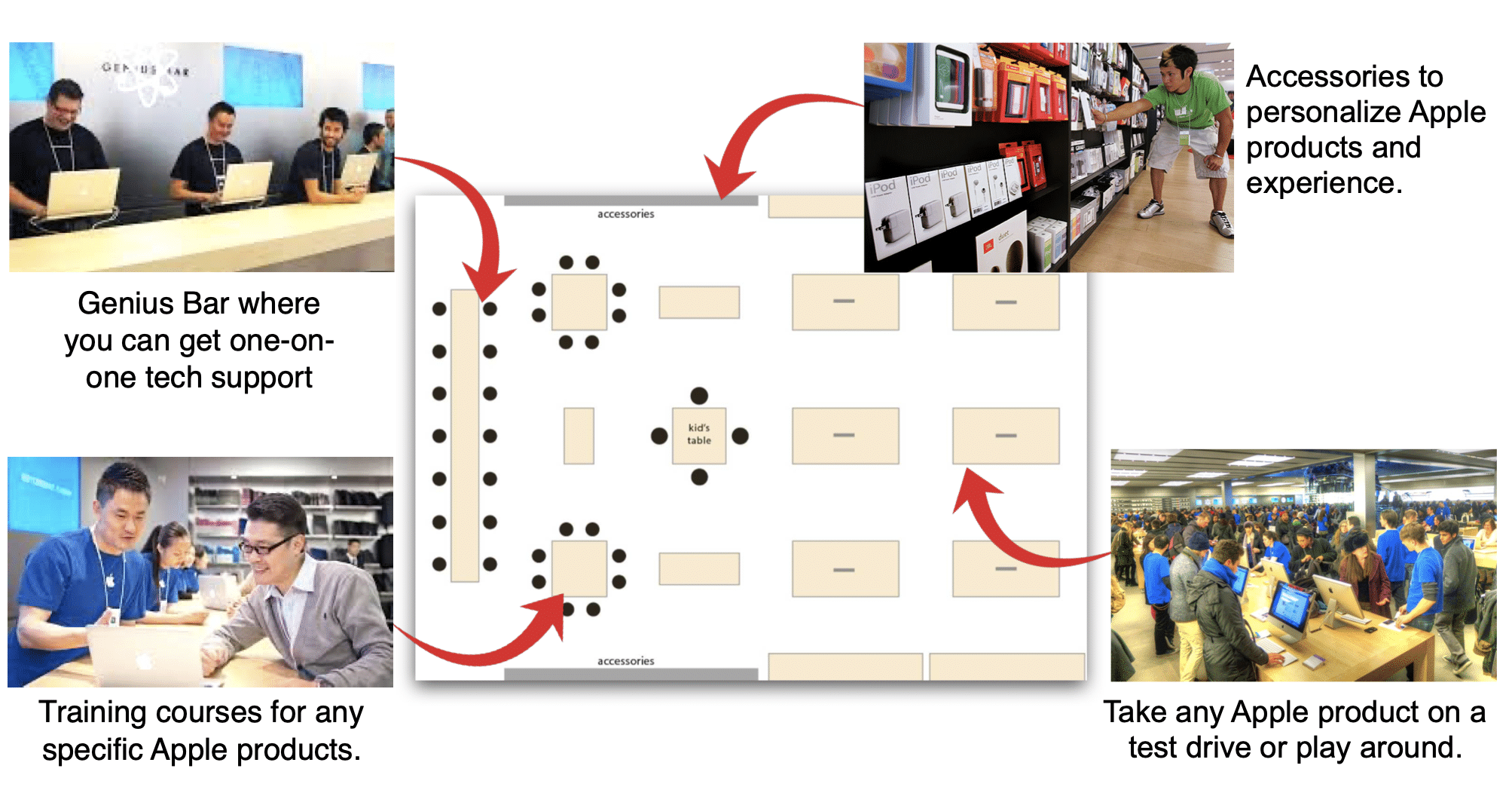
To illustrate, click on the Apple Store Layout. You can zoom in, download it, or share it.
Even when Apple products are in other stores, the brand has used its power with that retailer to create a distinct store-within-a-store concept, replicating a similar look and experience from Apple’s retail locations.
Fifth Avenue Apple store in NYC

Tower Theater Apple store in LA

To illustrate, click on the Apple Store examples. You can zoom in, download it, or share it.
Apple in Singapore
Milan Apple store

Apple consumer experience
Obsessing about the consumer experience.
As Steve Jobs famously said, “You have to start with the customer experience and work backward to the technology.” Apple even believes opening your Apple products should be like unwrapping a gift.
Steve Jobs wanted the consumer to be able to use any Apple product right away rather than spending hours loading software or setting up their machine. Regarding product integration, Apple products work together, and they work the same way, which makes it very simple for consumers when they move from one Apple product to another.
Next time you are in a brainstorming session, try to think like Steve Jobs.
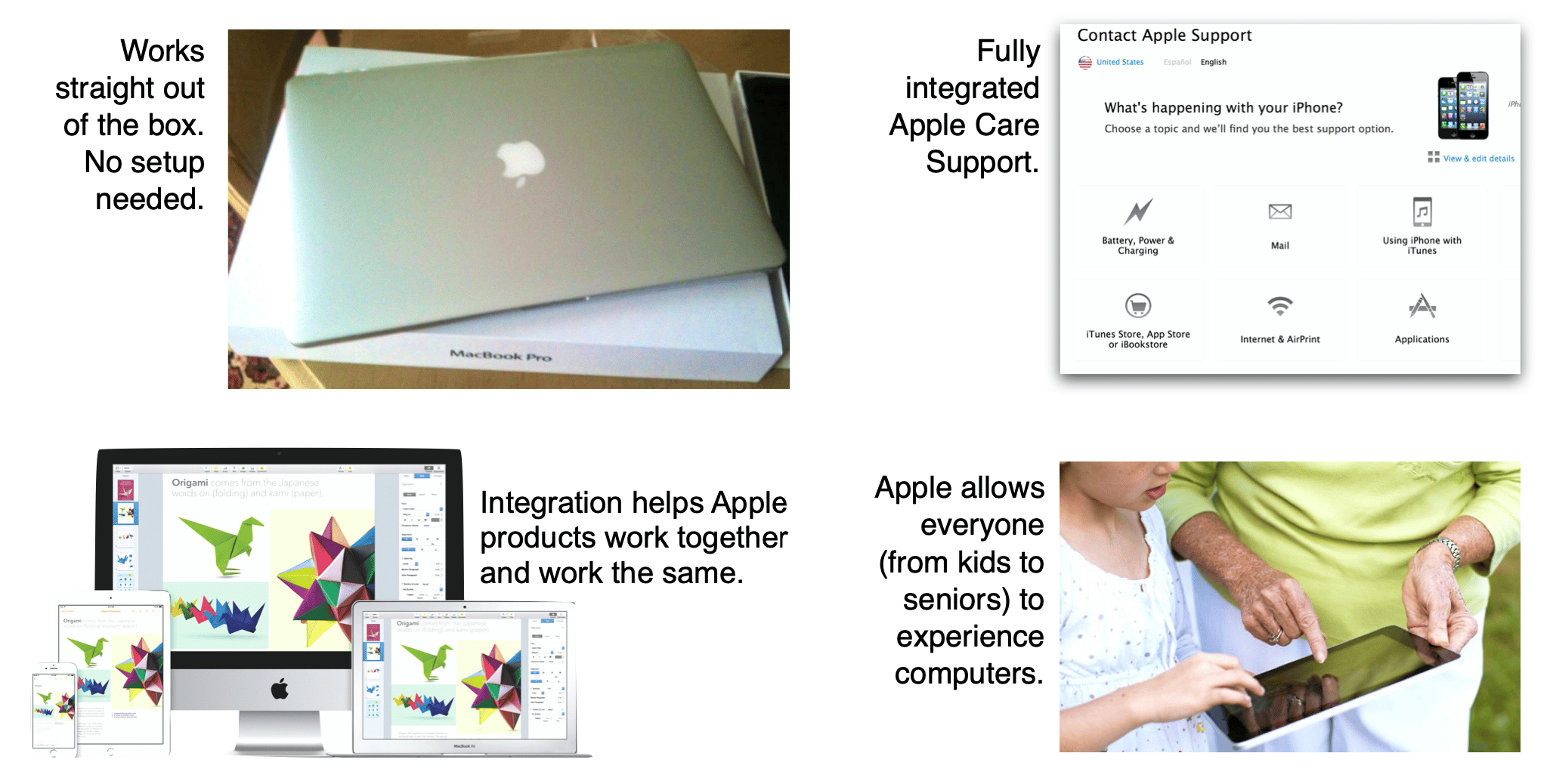
To illustrate, click on the Apple Consumer Experience . You can zoom in, download it, or share it.
The power of the Apple brand - how loyalty drives profit
How apple's brand love leads to increased power.
As we continue our Apple case study, let’s look at the power and profit Apple generates through brand love.
As they achieved an extremely tight bond with loyal followers, they used the tight consumer bond to generate brand power that they quietly wield in the market. Apple’s retail network generates twice the sales per square foot of any retailer worldwide, yet it is a very soft-sell environment.
I was recently on a double-decker bus tour of New York City, and when the bus went past the 5th Avenue Apple flagship store, half the bus stood up to take a photo. And they have such power over the supplier network with an array of engineers following extremely tight procedures.
Also, they have power over the media, generating over $2 billion worth of free media each year. Moreover, Apple fans often want to work at Apple, giving up lucrative jobs to be part of the brand.
Smartphone loyalty scores
Below, we can see the loyalty scores of the various smartphones. Apple leads the way with over 90% loyalty, moving from one model to the next. Samsung’s loyalty is below 70%. And LG has fallen to 32%. At LG’s level, you constantly need to source new consumers. That’s an extremely expensive way to manage your brand.
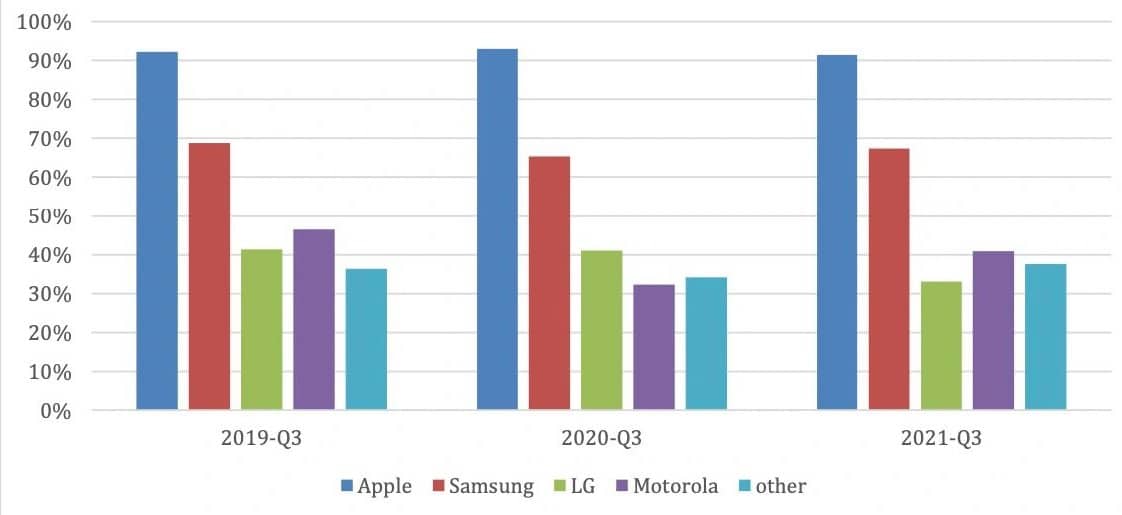
To illustrate, click on the Apple Case Study diagram . You can zoom in, download it, or share it.
Whoever says loyalty does not exist has not talked with Apple consumers. Apple significantly outperforms its competitors and uses that loyalty to drive future sales.
Apple's prices continue to increase
As Apple’s loyalty holds strong, they can increase their prices with each model. Loyal consumers are less price sensitive. This translates the Apple brand strategy into added profits. Steve Jobs used hype marketing to create a very tight bond with consumers.
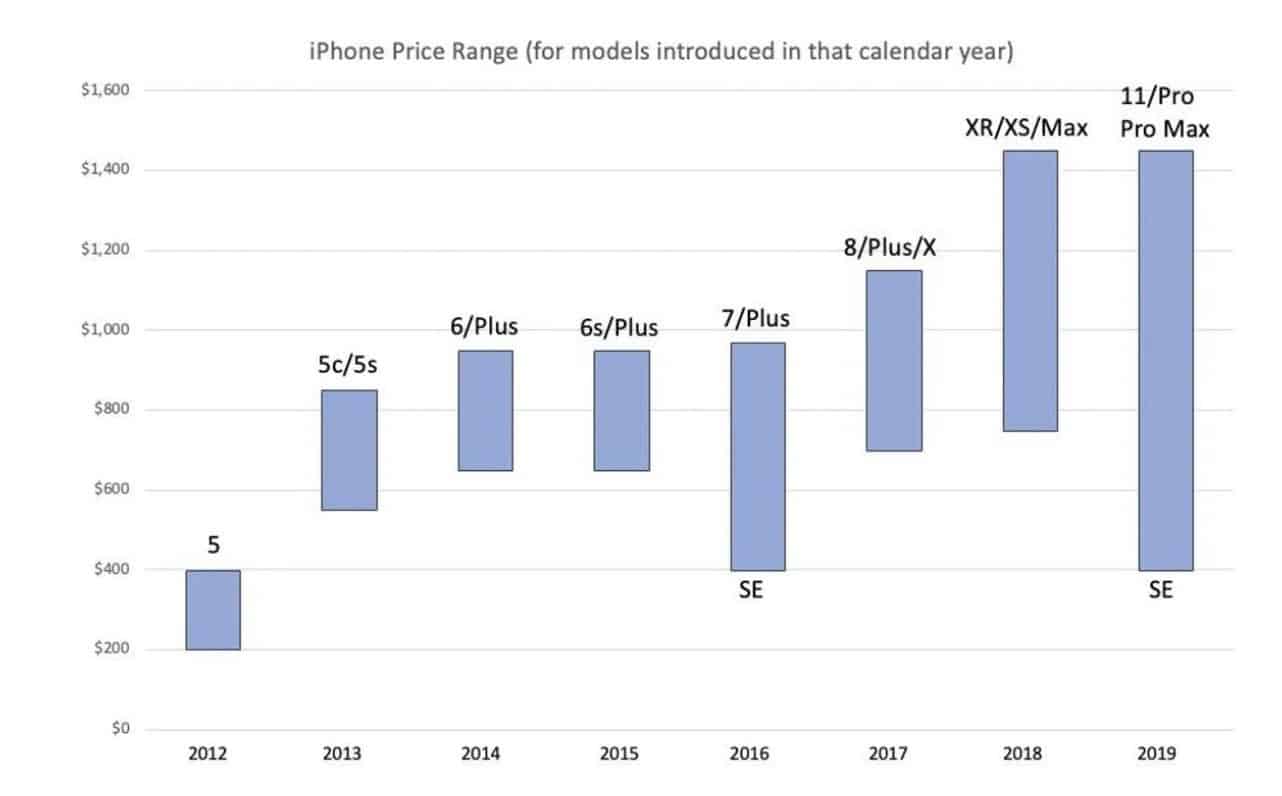
We can see how Apple uses power over its consumers to increase prices each year. Their iPhones deliver 40% profit margins, 4x higher than their competitor’s profits.
How Apple's brand power leads to increased profit
The Apple brand strategy extrapolates the power they generate into profit , with their incredible financial performance over the last 15 years. And they generate significant price premiums, relatively lower cost of goods, and moderate marketing spend ratios. Most importantly, this keeps their margins healthy for a technology firm.
Furthermore, Apple has entered many new categories over the past 15 years. Each time, their army of loyal fans has followed, moving into laptops, phones, tablets, and the music business. In each segment, they continue to gain market share to drive volumes.
Finally, the higher margins and volumes make for a beautiful profit statement.
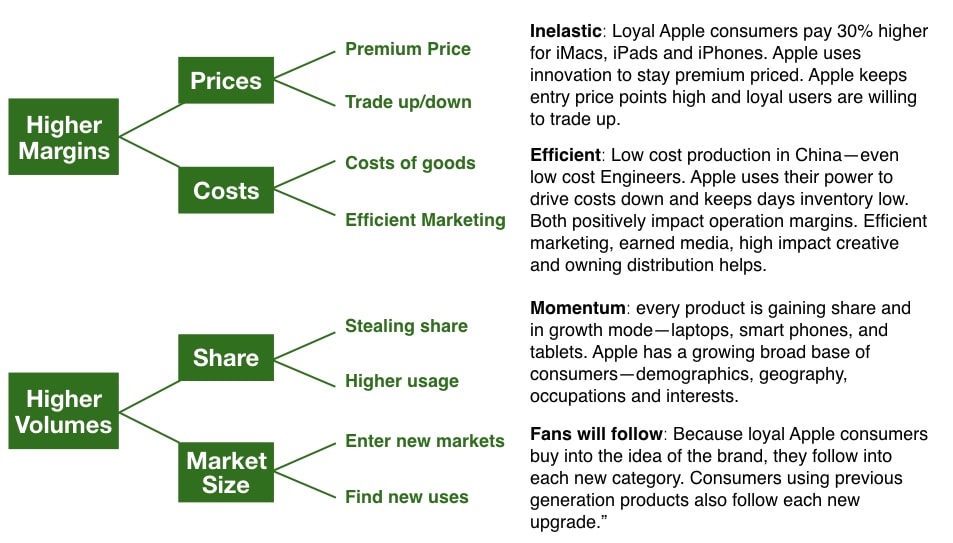
We can use our eight ways that a brand can drive profit to see the impact of the magic of the Apple brand on profits. Apple uses price, cost control, entry into new categories, and driving market share in each category.
Even though Apple gives the perception of an extremely friendly brand that is on the side of the consumer, they are now a huge mass market corporate brand, with a market capitalization of $500-600 billion, which is 2-3 times the value of companies like Coke, Procter & Gamble, Pfizer, and IBM.
So, if you invested a mere $10,000 in 2005, you would have $240,000 a decade later. The Apple case study is indeed a glorious look at the vision of Steve Jobs.
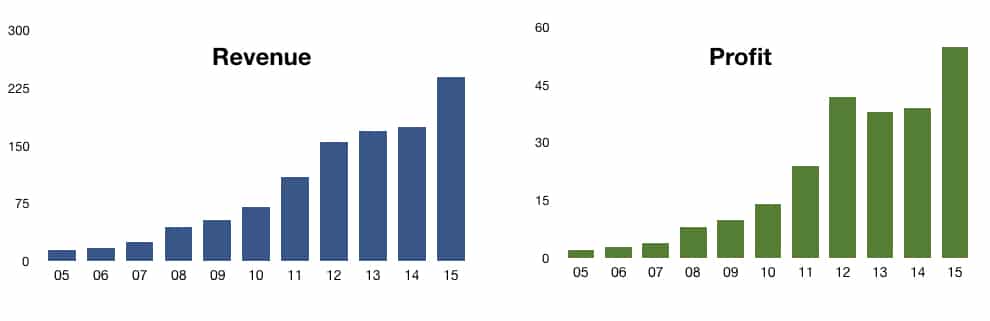
To conclude our case study, we can see how Apple uses its brand strategy to drive loyalty, revenue, and profitability each year. Their P&L is a thing of beauty.
Apple turns their brand love into higher power and profits

Graham Robertson
Email questions
Call 416 885 3911, follow us on linkedin, beloved brands book.

Beloved Brands Marketing Training Video
Elevate your team’s performance with our marketing training. The smarter they are, the greater your brand growth will be.

Click to read more

Find the template that fits your brand. Each of our templates is available for consumer, B2B, healthcare, or retailer brands.

Contact Information
Email: [email protected]
Phone: 416–885–3911
Search our site for any marketing topic
M a r k e t i n g B o o k
beloved brands
The playbook for how to create a brand your consumers will love.

With our Beloved Brands playbook , you will learn to think strategically, define your brand positioning, write a marketing plan, make execution decisions, and analyze your brand. Our readers tell us they reach for Beloved Brands as a reference tool to help them with the day-to-day management of their brand. We are proud that 89% of online reviewers have rated Beloved Brands a 5-star. As a result, Beloved Brands has been a #1 bestseller in brand management. We also have the B2B Brands playbook and our Healthcare Brands playbook .
Marketing Training
The smarter your team, the better the results you will see!
As a marketing team leader, you know that your team’s success is essential for your company’s growth. Our Beloved Brands marketing training gives your team the skills they need to make strategic decisions, produce exceptional work, and drive business growth. They will learn to define brand positioning, write effective plans, improve brief writing, make informed execution decisions, and analyze their brand’s performance.

We have designed our marketing training program to build the fundamental skills to help your team reach their full potential. We will work with your team to help them learn to take on Strategic Thinking, Brand Positioning, Marketing Planning, Marketing Execution, and Brand Analytics.

Popular Posts
Brand Positioning
Marketing Plans
Brand Strategy Roadmap
Creative Briefs
Marketing Career
Brand Key Model
Brand Toolkit for B2B
Brand Toolkit for Healthcare
Marketing Plan Template
Brand Plan template
Positioning template
Brand Consulting
Beloved Brands
Healthcare Brands
416 885 3911
[email protected]
MBA Knowledge Base
Business • Management • Technology
Home » Management Case Studies » Case Study: The Business Strategy of Apple
Case Study: The Business Strategy of Apple
Apple Inc is a multinational American company that design and sells computer software, consumer gadgets and personal computers. It was co-founded by Steve Jobs , Steve Wozniak and Ronald Wayne. Apple Inc is well-known for being innovative as they kept on producing new innovations from the first Apple computer Macintosh to the more recent iPhone and iPad series.
Today Apple Inc. is very well known in the world because of their advanced technology in products such as iPods, iPhone, Macbooks, Apple TV and other professional software. All the high tech products provide consumers with a better living standard in many different ways. Moreover, Apple Inc’s dominant position in the global market has changed the trend of consumer usage of electronic appliances such as in virtual communication. People will never need to carry multiple devices where each one only offers a handful of functions. Furthermore, Apple also created a substantial value in highly competitive market and industry which help them to achieve competitive advantages in an industry with stiff competition. In addition, it resolves the other external factors that present difficulty challenges to Apple Inc. Therefore, now Apple Inc is known as a strong company and the market leader in industry. Now, let us discuss about the current expansion strategy that used by Apple that make the company has greater success in marketplace.

The first strategy that use by Apple Inc for their current expansion strategy is creating innovative idea that slightly different from the competitors that already exists in market and industry. In order to make the company more innovative, Steve Jobs focused innovation on competitive pressure and value proposition by stressing his management style on customer center innovation and customer experience. As CEO in Apple, Steve Jobs carefully evaluated competitive pressure and opportunity in market place by continuously pursuit customer experience innovation. He also focused their business and IT strategy on customer center experience. It means that Apple will be more focused on looking outwards, market and business drivers rather than at the products or services that already exist. Steve Jobs focused on this strategy because the customers can help the company to understand what customers need and scarcity of the people so that he can use the feedbacks as inspiration to deeply investigate and then to create more innovative, creative and highly advanced technological product or services that can fulfill the needs of the customers. Therefore, Apple products design is always attractive and elegant compared to those existing competitors. Apple products like iPods and iPhones are good examples that show the innovation of Apple Company by creating digital lifestyle .
The second strategy applied by Apple is differentiation . Apple is using Macintosh as operating software whereas other personal computer’s producers are using Windows. The differentiation in operating software gives Apple a competitive advantage in the personal computer industry. Macbook users are satisfied with Macintosh performance because it is very energy saving where the processor will automatically “close” those programs which are not in use when it is in standby mode. On the other hand, Windows does not have such technology. Thus, Windows’ users might have to charge the laptop more often due to the battery consumption is higher than Macintosh.
In terms of applications and software, Appstore provides a platform for customers to download software and applications according to categories. It is easy to search for any application or software by using Appstore. iTunes allow consumers to categorize and download songs easily . By using iTunes, consumers can choose their preferable album cover for their songs. They can also “synchronize” and update the songs in their iPhone with a laptop. Besides that, iTunes also allow consumers to transfer photos from iPhones to PCs.
As for pricing, Apple is using skimming pricing strategy where they set high selling price for their products. However, there are still a lot of loyal customers who prefer to spend more money on Apple products. This is due to the self esteem where consumers feel good by carrying Apple products because it somehow shows their status as being up-to-date and their taste is better than others. Some customers think that Apple products are not cheap but also not high-priced products because the value of Apple products bring to them is never disappointing.
In a nutshell, the key to Apple’s success is down to creating a unique product with the ability for it to be customized to suit each individual’s needs.
Related posts:
- Case Study on Apple’s Business Strategies
- Case Study: Sony’s Business Strategy and It’s Failure
- Case Study: Business Strategy of Sony Corporation
- Case Study: Business Strategy Analysis of Wal-Mart
- Case Study of Papa John’s: Quality as a Core Business Strategy
- Case Study: Delta Airlines Successful Business Turnaround Strategy
- Case Study: Marketing Strategy Analysis of Apple iPad
- Case Study of Apple: Competitive Advantage Through Innovation
- Case Study of Apple Inc: An Apple for Your Enterprise
- Case Study: Kellogg’s Business Strategy
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Case Study: Experimentation as a Path to Business Transformation | Kate Goodine (Senior Director of Marketing and Product Analytics at Shutterstock) The Data Storytellers Podcast
On this episode of The Data Storytellers podcast, Kate Goodine joins Laszlo Mucsi to discuss the transformative power of building a culture of experimentation in business. We explore leadership strategies for fostering innovation, overcoming barriers to data-driven decision-making, and the journey from hypothesis to impactful business outcomes. Learn how to drive organizational change and build a cohesive data-driven culture. Connect with us: • Website: https://thedatastorytellers.com/ • LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/the-data-storytellers • Spotify: https://open.spotify.com/show/2N0vZtHZHgod4Tll2LX2xa • YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCz9e56lhYUfORiOHMiLlPmA • Apple Podcast: https://podcasts.apple.com/gb/podcast/the-data-storytellers-podcast/id1493766476 Chapters: 00:00 - Introduction to Kate Goodine and her background 06:00 - The importance of building a culture of experimentation 13:15 - Strategies for overcoming barriers to data-driven decision making 20:30 - Transforming business through analytics and experimentation 28:45 - The power of hypothesis testing in driving innovation 36:00 - Leadership strategies for fostering a culture of innovation 44:15 - Building a data-driven culture from the ground up 52:30 - Case studies on successful data-driven transformations 58:45 - Final thoughts and conclusions on data-driven innovation
- Episode Website
- More Episodes
- The Data Storytellers Podcast
Top Podcasts In Business
Apple Enterprise Resources
Resources. for all things apple..
Learn about the latest technologies to drive transformation within your organization.
Augmented Reality in Business
Learn about the capabilities, impact, and use cases of AR so you can power all-new workflows.
Download the guide (PDF)
Mac Adoption Blueprint
Understand how to guide conversations within your organization about the benefits of Mac.
Download the blueprint (PDF)
Mac Employees Communications Guide
Build awareness as you roll out Mac, and create a plan for success.
Productivity
Give every employee the tools they need to be their most creative and productive — anywhere they work.
Business Apps Getting Started Guide
Productivity is built right in. Discover some of the amazing apps that Apple runs to get the job done.
Employee Choice Guide
Discover why choice makes employees more effective, engaged, and productive.
It’s easier than ever to deploy, manage, and secure Apple devices for your business — no matter the size. Learn how to start the process.
Apple Platform Deployment
Read the in-depth guide to the ultraflexible options you have in deploying Apple products.
Visit Apple Platform Deployment
iOS and iPadOS Deployment Overview
Step-by-step guidance on deploying iPhone and iPad, for a number of ownership scenarios.
Apple Business Manager User Guide
An in-depth guide to the benefits and features provided by Apple Business Manager.
Read the Apple Business Manager User Guide
Apple Platform Security
Find out about the features and frameworks that protect hardware, software, data, and users.
Visit Apple Platform Security
Apple Platform Certifications
Deep-dive into third-party security certifications we engage with to provide security assurance.
Visit Apple Platform Certifications
IDC Report on Mac Security in Enterprise
Learn about top trends and the importance of security endpoints.
Download the report (PDF)
Learn how Apple can boost productivity while lowering costs over your product life cycle — from management to repairs to energy savings.
The Total Economic Impact™ Of Mac In Enterprise
Learn more about cost savings and business benefits enabled by Mac devices in Enterprise. *
Visit the Forrester TEI study
Apple offers flexible models to meet your organization’s needs for employee training, support, and more.
AppleCare Professional Support
Compare services from AppleCare to support your help desk, integration efforts, and hardware.
Visit AppleCare Professional Support
Apple Professional Training for IT
Get started with expert online training to certify your IT team.
Visit Apple Professional Training
Apple Professional Training for Developers
Get started with expert online training to certify your developers.
AppleSeed for IT
Test beta software, access test plans, and provide feedback.
Visit AppleSeed for IT
Apple for Enterprise
Explore more.
- Apple at Work
- Small Business
Shop products
- Apple Vision Pro
- Success Stories
- Apple Business Manager
- Harvard Business School →
- Faculty & Research →
- May 2015 (Revised October 2015)
- HBS Case Collection
Apple Inc. in 2015
- Format: Print
- | Language: English
- | Pages: 30
About The Author
David B. Yoffie
Related work.
- Faculty Research
- Apple Inc. in 2015 By: David B. Yoffie
- Apple Inc. in 2015 By: David B. Yoffie and Eric Baldwin
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Times Insider
The Apple of One Business Reporter’s Eye
Since 2022, Tripp Mickle has covered news surrounding one of the biggest technology companies in Silicon Valley.

By Josh Ocampo
Times Insider explains who we are and what we do and delivers behind-the-scenes insights into how our journalism comes together.
Some journalists have broad beats — animals , the entire state of California , even the cosmos .
Tripp Mickle, however, focuses on just one company: Apple. But there’s still more than enough to write about. Since joining the Business desk at The New York Times in April 2022, Mr. Mickle has reported on Apple’s flashy new Vision Pro headset , its foray into artificial intelligence and the ongoing antitrust case against the company , which has been accused by U.S. regulators of running a smartphone monopoly.
Despite having a specific beat, Mr. Mickle’s work still finds a wide audience. “It’s this incredible company that has such influence in our lives,” Mr. Mickle said in an interview. “And it’s a fortress of secrecy.”
Before writing for The Times, he dabbled in other topics, including NASCAR for Sports Business Journal, and the tobacco and alcohol industries for The Wall Street Journal. It was during his time at The Journal that Mr. Mickle decided to take a bite of the Apple beat.
In a phone conversation from his home in the Glen Park district of San Francisco, Mr. Mickle discussed how his beat has changed over the years and his experience staking out the offices of OpenAI. These are edited excerpts.
What made you decide to become a journalist?
I’ve wanted to become a journalist since I was in the fifth grade. I had a teacher who gave ribbons to students at the end of the year that tried to predict what you would pursue professionally in the future. Some of the ribbons were jokes, and some of them were serious. I was really obsessed with current events, and I liked writing, so she gave me a ribbon that read “future editor at The New York Times.” That became a point of direction for me as I looked out on the horizon and tried to figure out what to do.
Can you explain your beat to readers?
I cover Apple and now, Nvidia. One of the most fascinating things about the technology industry is that, without fail, it changes almost every three years thematically. There was a period when the major theme was regulators scrutinizing big tech firms. Now the entire tech industry has changed because of the introduction of ChatGPT and the rush to develop generative A.I.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
Business Ethics: Kant, Virtue, and the Nexus of Duty
Foundations and case studies, publisher description.
This book offers students a philosophical introduction to the ethical foundations of business management. It combines lessons from Kant with virtue ethics and also touches upon additional approaches such as utilitarianism. At the core of the book lies the concept of the “nexus of imperfect managerial duty.” This consists of the creation and reinforcement of virtuous managerial teams, engagement of discourse among all stakeholders, and pursuit of business responsibilities including the creative efforts necessary for modern organizations. A variety of special problems in managerial ethics are also explored, such as the ethics of managerial paternalism, fairness in stakeholder negotiations, devolution of business into scandalous corruption, and the role of boycotts in society’s shaping of managerial duties. Case illustrations of these applications are presented throughout the book including in chapter appendices. A series of brief-answer questions, essay questions, and discussion questions are presented at the end of each chapter. Links to relevant video presentations of lectures applicable for each chapter are also provided.
More Books by Richard M. Robinson
Other books in this series.
More From Forbes
Rng: bridging the gap between sustainability and profitability.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Sergey Buchin is the Founder and CEO of IRBISIO Cleantech Infrastructure Fund.
The renewable natural gas (RNG) market in the United States holds immense promise as a potential opportunity to address climate change and stimulate economic development. RNG is a dependable energy source that can be seamlessly integrated with traditional natural gas, reducing carbon emissions in municipalities and the corporate, education and transportation sectors. This industry has experienced significant growth , driven by government initiatives encouraging environmental sustainability and fostering innovation.
I believe the RNG market in the U.S. presents great potential for farmers, investors and forward-thinking enterprises. As someone who heads a cleantech infrastructure fund that researches the latest investment opportunities in green energy, I will demonstrate how, by delving into this growing industry, we can uncover various possibilities and obstacles that need to be tackled to attain RNG's full potential.
Understanding The Potential Of RNG
Given the vast number of potential production sites in the U.S., such as landfills, food waste and agricultural byproducts, RNG has the potential to make a significant impact in the energy sector. According to the American Biogas Council , there are over 15,000 potential biogas production sites in the United States, which include dairy, poultry and swine farms; water resource recovery facilities; food scrap-only systems; and landfills that are currently flaring their gas.
If fully developed, these biogas systems have the potential to generate a staggering 103 billion kilowatt hours of electricity per year. This could have a significant impact on reducing emissions, equivalent to "removing 117 million passenger vehicles from the road." The initial capital investment for RNG projects is quite substantial, amounting to approximately $37.5 billion over 20 years; however, the implementation of these projects has the potential to generate around $45 billion in capital investment, as well as 374,000 short-term construction jobs and 25,000 permanent jobs.
Apple iPhone 16, iPhone 16 Pro Release Date: New Report Reveals Extraordinary Strategy
Nasa urges public to leave the city for the perseid meteor shower this weekend, hbo reveals when ‘house of the dragon’ will come to an end.
RNG development has accelerated due to new technologies and innovative approaches. Key areas include biodigester efficiency, feedstock preprocessing and biogas upgrading technologies. Research in anaerobic digestion and methane capture also offers potential for industry transformation.
Case Study: Successful Outcomes In RNG
Smithfield Foods, a prominent player in the pork industry, has effectively executed RNG projects on multiple farms. Through the capture of methane from hog manure, Smithfield effectively decreases greenhouse gas emissions and also generates extra revenue. They have partnered with Dominion Energy on four initiatives aimed at significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions from U.S. farms. These projects are projected to have a substantial impact, reducing 2.5 million metric tons of CO2e over 10 years .
Other companies are also proving the worth of RNG as a viable and growing investment. In California, the Calgren Dairy Fuels project converts methane from dairy manure into renewable natural gas, which is then injected into the natural gas pipeline. This project not only reduces greenhouse gas emissions but also provides a sustainable energy source for local communities. According to the EPA , such agricultural-based anaerobic digestion (AD) biogas systems are becoming increasingly popular, showcasing the potential for significant environmental and economic benefits.
Addressing The Current Challenges
Despite its potential, the RNG industry has several challenges. One important element to getting the most out of RNG is the use of biodigesters. Biodigesters are sealed systems that create ideal conditions for controlled anaerobic digestion, resulting in the production of biogas. They play an important role in converting organic waste into RNG, effectively minimizing odors and generating valuable byproducts such as fertilizers. However, issues like the cost and limited availability of biodigesters and the use of less efficient technologies, such as covered lagoon systems, can prevent the efficient capture of biogas. There are also significant barriers when it comes to logistical challenges such as feedstock collection, transportation and integrating RNG into existing natural gas pipelines.
I believe that tackling these challenges will require significant investments in infrastructure, advancements in technology and bolstering support for these technologies, along with raising awareness. In addition, the support of the government and industry associations is important for the progress of RNG projects. Implementing policies that support pipeline construction and offer financial incentives could greatly speed up the adoption of RNG. For example, farmers and waste management companies can be provided with economic incentives in the form of lower waste management costs and the opportunity to generate additional revenue through the sale of RNG, green credits, CO2 and other byproducts.
The development of RNG is also greatly influenced by ongoing and upcoming political and regulatory changes. Government initiatives and specific laws that support RNG, such as the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) and Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS) , have a significant impact on shaping the market. Having a good grasp of these regulations and using them to your advantage can give you a strategic edge in the RNG sector. Organizations like the American Biogas Council are working toward advocating for supportive legislation and offering resources and education.
I believe that in order for us to see the full potential of the RNG market, investors, policymakers and industry leaders should come together to establish a conducive environment for the development of RNG. Emphasizing the importance of research, advocating for regulatory frameworks, and promoting public-private partnerships can help us achieve a cleaner and more sustainable energy future. For those who are passionate about promoting clean energy, consider actively participating in discussions, staying updated on regulatory changes and investing in cutting-edge technologies as the RNG sector continues to expand.
The road to a sustainable energy future is filled with obstacles, but I believe that the potential benefits will make it a worthwhile endeavor.
Forbes Business Council is the foremost growth and networking organization for business owners and leaders. Do I qualify?

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions

COMMENTS
Apple is well-known for its innovations in hardware, software, and services. Thanks to them, it grew from some 8,000 employees and $7 billion in revenue in 1997, the year Steve Jobs returned, to ...
Apple's journey to global success is a compelling case study in how a company can build a strong brand and establish a lasting presence in the international arena. By embracing simplicity, innovation, and adaptability, Apple has demonstrated that it has the vision and resilience to continue to thrive in an increasingly competitive and ...
Dean, Apple University Morten T. Hansen Faculty, Apple University AUTHORS FOR ARTICLE REPRINTS CALL 800-988-0886 OR 617-783-7500, OR VISIT HBR.ORG Harvard Business Review November-December 2020 3 This article is made available to you with compliments of Apple Inc for your personal use. Further posting, copying or distribution is not permitted.
Abstract. After a decade as CEO, Tim Cook is facing one of his biggest strategic transitions of his tenure. While Apple had performed spectacularly well under Cook, Apple's core business was maturing. Sales of iPhones, iPads, and Macs were flat or down. However, Apple's new hardware—Apple Watch and Airpods—as well as services were growing ...
This case explores the sources of Apple's competitive advantages, the sustainability of the iPhone, the efficacy of Apple's strategy as a walled garden, and the pros and cons of building a service business largely built around the iPhone. ... Harvard Business School Case 724-419, November 2023. Educators;
The Rise of Apple. By William P. Barnett, Debra Schifrin. 2016 | Case No. SM260 | Length 12 pgs. Between 2000 and 2016 Apple introduced a number of new products and services that dramatically expanded the company's scope well beyond its traditional market position in computers. Over that period, the direction of the company changed and ...
After a decade as CEO, Tim Cook is facing one of his biggest strategic transitions of his tenure. While Apple had performed spectacularly well under Cook, Apple's core business was maturing. Sales of iPhones, iPads, and Macs were flat or down. However, Apple's new hardware-Apple Watch and Airpods-as well as services were growing rapidly. This case explores Apple's history and Cook's strategic ...
Apple's core business—the iPhone—continued to deliver spectacular results. In addition, Cook was aggressively introducing new products, ranging from Apple Watch to HomePod. Cook also had the world's biggest balance sheet to invest in new technologies and markets. ... Harvard Business School Case 718-439, May 2018. (Revised December 2019 ...
This case focuses on the supply chain strategy of Apple Inc. (Apple). Set in early 2020, it provides a detailed description of the company's supply chain network and capabilities. Data in the case allows students to develop an understanding of Apple's source of competitiveness and to gain insights into the management of a large, complex global supply chain network that focused on the ...
The case is set in September 2019 and the protagonist is Tim Cook, the CEO at Apple, Inc. In 2019, Apple had revenues of $260 billion; yet, net revenues were down by 7 percent over the same period. Much of the decline in Apple's revenues is a result of decreased sales of the iPhone, which contributed 62 (!) percent of Apple's total revenues in 2018, and declined to 54 percent in 2019. The case ...
Abstract. The essential components of carrying out an organizational analysis (a case study on Apple Inc) include evaluating external factors that can affect the organization's performance as well ...
Fees. Post Graduate Program in Digital Marketing. Cohort Starts: 28 Aug, 2024. 8 Months. $ 3,000. Digital Marketing Specialist. 8 Months. $ 1,649. Here we bring you a well-curated case study on Apple's marketing strategy, the key takeaways to learn from this venture, and how to incorporate the same in your business and marketing strategies.
Apple's Culture Type and Traits. Apple has an organizational culture for creative innovation. The company's cultural features focus on maintaining a high level of innovation that involves workers' creativity and a mindset that challenges conventions and standards, such as in consumer electronics design. Apple's IT business depends on ...
Headquartered in Cupertino, California, Apple Inc. has experienced many successes throughout. their business history. Apple's journey to success has not been without ethical challenges along. the way. Apple's success can be seen from their stock price, up from $3.30 per share in 1997 to. $320 per share in 2020.
Apple case study shows how Steve Jobs used simplicity as the Apple brand strategy and Apple brand positioning to drive Apple's success. Home Training ... and drive business growth. They will learn to define brand positioning, write effective plans, improve brief writing, make informed execution decisions, and analyze their brand's performance
Apple case study Operations Cost leadership Forming partnerships with Foxconn in China, etc, to minimise costs as cost of production such as labour and materials are significantly lower in china Economies of scale - achieved by Foxconn as it is the largest contracts manufacturer of electronics and produces on a large scale
Describes Apple's approach to innovation, management, and design thinking. For several years, Apple has been ranked as the most innovative company in the world, but how it has achieved such success remains mysterious because of the company's obsession with secrecy. This note considers the ingredients of Apple's success and its quest to develop ...
Case Study on Apple's Business Strategies. Apple was founded by Steve Jobs and Stephen Wozniak in 1976; Apple Computers revolutionized the personal computer industry. Apple Computers Inc is considered to be one of the innovators in the computer industry. It brought about different changes to the industry; these changes are still visible in ...
Case Study: The Business Strategy of Apple. Apple Inc is a multinational American company that design and sells computer software, consumer gadgets and personal computers. It was co-founded by Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak and Ronald Wayne. Apple Inc is well-known for being innovative as they kept on producing new innovations from the first Apple ...
20:30 - Transforming business through analytics and experimentation 28:45 - The power of hypothesis testing in driving innovation 36:00 - Leadership strategies for fostering a culture of innovation 44:15 - Building a data-driven culture from the ground up 52:30 - Case studies on successful data-driven transformations
Business Studies - Case Study Notes - Topic 1: Operations Role of operations management Strategic role of operations management - cost leadership, good/service differentiation Cost leadership: Apple reduces its operations costs by forming a partnership with manufacturers such as Foxconn in China.
Visit Apple Platform Deployment. iOS and iPadOS Deployment Overview. Step-by-step guidance on deploying iPhone and iPad, for a number of ownership scenarios. Download the guide (PDF) Apple Business Manager User Guide. An in-depth guide to the benefits and features provided by Apple Business Manager. Read the Apple Business Manager User Guide
Abstract. At the end of 2014, Apple Inc. recorded the most profitable quarter of any firm in history, and its market capitalization soon topped $700 billion. 'Apple Inc in 2015' explores the history of Apple, its successes under Jobs, its continued growth under Tim Cook, and the challenges facing the company in 2015.
Since joining the Business desk at The New York Times in April 2022, Mr. Mickle has reported on Apple's flashy new Vision Pro headset, its foray into artificial intelligence and the ongoing ...
Case illustrations of these applications are presented throughout the book including in chapter appendices. A series of brief-answer questions, essay questions, and discussion questions are presented at the end of each chapter. Links to relevant video presentations of lectures applicable for each chapter are also provided.
Apple iPhone 16, iPhone 16 Pro Release Date: New Report Reveals Extraordinary Strategy ... Case Study: Successful Outcomes In RNG. ... Forbes Business Council is the foremost growth and networking ...