Can You Start a Research Paper with a Story
Quick Navigation

Common information you need to know about a research paper
If you want to start a research paper, first of all, you have to understand what is it about? It is academic writing that is based on researchers who were made by the person on a particular topic. Also, it can include analysis and interpretations. A research paper can be of different types and variations. It doesn’t matter what type of work you are doing – a term paper, a master’s thesis or a doctoral dissertation – all of them can be made in a research form.
Now, you have to ask yourself – how to write a really nice and strong research paper?
- A topic. It is the first thing. Choose the best one, a catchy topic that will make people interested in your text. Also, if you choose a topic which you like, then people will feel your attitude to it.
- You have to surf the internet a lot. Of course, your topic is just yours, but to get the more new information you have to know the previous one and have a huge background.
- Don’t forget that your introduction should have a strong thesis statement as each research papers require it.
- Make an outline of the paper. It has to consist of the title page, abstract, introduction that has to include some background information about the topic. Also, you have to make a strong body and divide it into sections. Finish with the conclusion, references, and tables (figures, appendix if it is needed for your topic).
- After making an outline, you have to organize all the information. Think critically to use only good and useful information. Choose reliable sources with checked thoughts.
- Now you can start writing! But bear in mind that this stage is not the last, as here you make only your first draft.
- After that reread the draft, and make sure it corresponds to the outline you made before. Also, check on errors and mistakes.
- Finally, type the final paper.
Can you start a research paper with a story?
This is a very common question students have, as we all think that a story will take much space and as a result, we will have fewer things to write. Let’s find it out together.
When you start writing a research paper you have to remember that the best variants to start will be the next ones:
1. Writing definitions
Exactly here we clarify all unknown words and things the audience might face while reading your text. So, if your paper is dedicated to some specialized topic which has a lot of unfamiliar words for the common reader, write definitions to make the reading process easier and more interesting. You may start an introduction with defining a central word or phrase which is used most of all in the text. But please, don’t use the definition if it will not give any needed information to the reader.
2. Adding an Anecdote or Quotation
If you use this method, it will make the reading process easier. What happens to you when you appear in a new company and see that people say jokes and simply have fun? You feel relaxed. The same is here – start with an anecdote. Can you start a research paper with a personal story? Yes, you definitely can. You may use a piece of the story from a legend or myth or even your own example.
3. Creating a Contrast
The good thing is to start with a point you disagree with. For example, you may start with a sentence describing that breastfeeding up to three years old is not good for mental health of the child; they make a transition with a word like “however” or “but,” and explain your point of view with researchers you made before.
Also, read about how to use notecards for research papers.
Starting a research paper process
Writing texts, especially catchy introductions can be a hard thing. Sometimes it even frustrates. But it doesn’t need to be like that if you will plan your paper very good. What can go wrong if you will make an outline and draft with all needed information, personal stories, or the ones from books? Just stay focus. You can do everything with your text, even to start it with a story. Look at the pieces of advice below to understand how will be better to begin each part of the paper:
- In the beginning, you have a chance to introduce your topic and grab your reader’s attention. Bear in mind the next thing – never starts with words like “In this paper, I will” or “This paper is about.” This is not cool, really. Start with something strong! Is your research connected to some fact, story or interesting quotation? Then use it! Even anecdote is a good variant to begin the text.
- And as you see, yes, you may start with the story, but make it precise, concrete and the one which will grab.
- The middle sentences of the introduction have to inform all the various points of view your paper might have.
All the previous information is needed to be written in accordance to be relevant to the thesis statement. It has to show the overall idea of the essay and show your personal point of view. It has to be concrete and precise. Also, it has no problem to be no longer than one sentence.
Now, look at the example of an introductory paragraph for a paper we wrote. We started the paper with a fact, then presented each main point of the paper and then ended with the thesis statement.
Comics have been part of America since the 1930’s, and their appeal has survived to the present day. Graphic novels are comics in a trade paperback format – the story is told both through text and through images. Graphic novels first appeared on the scene in 1978 and are steadily becoming mainstream in American culture (Maureen Mooney, 2002). In recent years, much debate has been stirred regarding whether or not graphic novels have a place within a library’s collection. To most, comics and graphic novels are silly, violent and chauvinistic. However comics are no longer simply men in tights – many graphic novels deal with current issues, serious subjects, and learning.
So, now you can cope with such a complicated task as writing a research paper. All that you need is to follow some rules and pick the best voice of the future creation. Do not hesitate and try different ways to grab readers’ attention; one of them is a story. Be brave and start with your own experience; perhaps it will help your target audience to realize the aim and plot of the paper better.
To sum it up, now you know the answer to the question if you can start a research paper with a story? You may write it but make sure that the story will be interesting to the reader, and will grab his attention.
Save Time On Research and Writing
Hire a Pro to Write You a 100% Plagiarism-Free
It will be useful to read
It's possible to submit essay on time.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Webinar Transcripts: What About Me? Using Personal Experience in Academic Writing
What about me using personal experience in academic writing.
Presented October 31, 2018
View the webinar recording
Last updated 12/11/2018
Visual: Slide changes to the following: Housekeeping
- Will be available online within 24 hours.
- Polls, files, and links are interactive.
- Now: Use the Q&A box.
- Later: Send to [email protected] or visit our Live Chat Hours .
- Ask in the Q&A box.
- Choose “Help” in the upper right-hand corner of the webinar room
Audio: All right. Well, hello, everyone and thank you so much for joining us today. My name is Beth Nastachowski and I am the Manager of Multimedia Writing instruction here at the Writing Center and I'm just getting us started here with a couple of quick housekeeping notes before I hand this session over to our presenter today, Claire
A couple of things to keep in mind, the first is I have started the recording for the webinar. I'll be posting the regarding in the webinar archive and you can access that later if you have to leave for any reason during the session or if you would like to come back and review the session or access the slides, you can do that from the recording.
I also like to note here that we record all of the webinars in the Writing Center, so if you ever see a webinar being presented live and you can't attend or if you're looking for help on a particular writing topic, we have those recordings available for you 24/7 so you can just take a look at the archive in the categories there to find a recording that would be useful for you
We also hope that you'll interact with us throughout the session, so I know Claire has lots of polls and the chats she'll be using throughout the session, so make sure to interact with her and your fellow students there
But also note that the links throughout the slides that Claire has are also interactive, so you can click on the links and it will open up in a new tab on your browser, and can you also download the slides that she has here in the Files Pod that’s at the bottom right‑hand corner and can you download those slides and they'll save to your computer as well
Finally, we also have a Q&A Box on the right‑hand side of the screen so I'll monitor that box throughout the session and would be happy to answer any questions or respond to any comments that you have, so do let me know as soon as you have a question or comment, I'm happy to hear from you and I know Claire will be stopping for questions and comments to address those aloud throughout certain points of the presentation as well
However, at the very end of the session if we get to a point where we need to close out the session because we're out of time and you still have questions, please feel free to email us or visit the Live Chat Hours and we're happy to respond to you there and I'll display this information at the end of the session as well
Alright. Actually, this is our final point here. If you have any questions or have any technical issues, feel free to let me know in the Q&A Box, I have a couple of tips and tricks I can give you, but the Help Button at the top right‑hand corner is really the place to go if you have any significant issues.
Visual: Slide changes to the title of the webinar, “ What About Me? Using Personal Experience in Academic Writing ” and the speakers name and information: Claire Helakoski, Writing Instructor, Walden University Writing Center.
Audio: Alright, and so with that, Claire, I will hand it over to you.
Claire: Thanks so much, Beth. Hi, everyone, I'm Claire Helakoski a writing instructor here at the Walden Writing Center and I’m coming in from Grand Rapids, Michigan today to present What About Me? Using Personal Experience in Academic Writing today, and also Happy Halloween to those of you that celebrate it.
Visual: Slide changes to the following: Learning Objectives
After this session, you will be able to:
- Identify the benefits and drawbacks of using personal experience in writing
- Determine the situations when using personal experience is appropriate
- Integrate personal experience effectively
- Access additional resources
Audio: All right. So first I want to go over our learning objectives today which are that after the session you'll be able to identify the benefits and drawbacks of using personal experience in your academic writing, determine the situations where using personal experience is appropriate, integrate personal experience effectively, and access additional resources.
Visual: Slide changes to the following: Caveat
We are specifically talking about
personal experience in coursework ,
meaning discussion posts or weekly
assignments .
Doctoral studies are a whole other thing!
Audio: All right, and I do want to start with a caveat that I'm specifically talking about personal experience in coursework, so discussion posts, or weekly assignments. Doctoral studies are a very different things and if you are beyond your coursework and just working on your doctoral study, this presentation may not be as beneficial to you at your current stage since it does get a little more specific and the requirements are a little bit different in those aspects of your writing.
So today we're going to really focus on that coursework discussion post, weekly paper assignments.
Visual: Slide changes to the following: Walden Students
- Are at an advantage!
- In previous education institutions
- In careers in their chosen field of study
- In military , family , or volunteer situations
Audio: All right. So Walden students are at an advantage for talking about personal experience because most of you are already working in your fields or have previous education and careers in your field of study, even if you're not working in that now, you've had some sort of career most likely, and I'm just speaking broadly and statistically here, but also through military family or volunteer situations, our students from my experience, tend to be very passionate and knowledgeable about their topics and that means you're at an advantage to have all of these great personal experiences to inform that passion and your coursework as it applies to your current job, future job, or past work that you've done.
Where does that experience go?
What does it count for?
Audio: So, we might wonder where does that experience go, right, because we're often kind of told to pull back on the personal experience in our coursework. So where does it go? Where does it end up sort of counting for? Sorry. I thought there was a pop‑up there.
That experience doesn't go anywhere in a sense that it's there, it is valuable, it is important, it has informed your decision to pursue your degree and there are many assignments that I have personally seen in the Writing Center that will let you kind of tap into that and express it in your coursework. It doesn't count for anything as far as, you know, a grade or something like that, but it's beneficial because it gives you that sort of starting point, that jumping off place to begin your work, right.
A lot of times even if you're starting an assignment that's not really meant to explore personal experience, you might think of a personal experience that you've had had and decide to pursue that topic, so it counts in a sense that you're mentally kind of already engaged with your subject, you’re invested in it, and that gives you a starting point for any type of writing you're going to do for your coursework.
Visual: Slide changes to the following: Poll: How convinced are you?
Paragraph A
By and large, substance abuse in the United States begins during adolescence. The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (2013) stated that on an average day 881,684 adolescents smoke cigarettes, 646,707 smoke marijuana, and 457,672 drink alcohol. Adult addicts typically report beginning substance use in adolescence. In fact, one in four Americans who started using addictive substances in their teens are addicted now, compared to one in 25 who began using after the age of 21 (National Center on Addiction and Substance Abuse, 2011). When teens engage in substance use, their behavior impacts their adult lives.
Paragraph B
By and large, substance abuse in the United States begins during adolescence. As a school paraprofessional, I know this is a problem. I see teenagers every day in the high school library who are drunk or high. Just this past year, five separate students got into serious car accidents (with injuries) due to substance use. We actually have to employ drug-sniffing dogs in the school as well. These teens do not get the help they need, and so addiction becomes something they struggle with as adults as well.
Audio: So, we're going to start with a little poll here. We have Paragraph A and Paragraph B, so I'd like you to read them both and note which option you're most convinced by, and I'm going to not read these aloud because I think it would take longer than you guys reading them through, but I will give you a couple minutes to read them through and consider which of them you find most convincing and then let us know in the poll.
[silence as students respond]
I see the answers still trickling in here. I'm going to give you another minute to go ahead and respond if you have not and then we'll talk over our responses.
All right. It looks like the responses have kind of stopped trickling in so I'm going to go ahead and talk about each of these options. So, a lot of you, most of you, chose Paragraph A and that is probably because we have a lot of great statistics in Paragraph A, right. We're focusing on this kind of overall issue, we have proof that it is an issue, really specific proof, right. We're talking about numbers and statistics, and then we kind of explain what all of that means at the end there. Whereas in Paragraph B, we have kind of the same topic, right. So, we're still talking about substance use in teenagers, but this one is talking about what this writer sees in their work every day. They see these things happening, and they do have some specifics like the five separate students and what's going on in their school, and they have a kind of the same takeaway or opinion, which is that addiction is an issue and, you know, something kind of needs to be done.
So, they really are about the same topic, but Paragraph A is likely a little more convincing to the wider majority of people because it's more neutral, it has facts and statistics, you know, from all over really because it's from the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Organization and so it's a big study by an established organization. And in Paragraph B while these personal experiences are great and they definitely do speak to an issue at this person's school, so if that was the assignment, then this would probably be appropriate, but if we're talking about this as a whole issue for the country or like a larger health issue, then talking about it more globally with more global statistics is going to be effective there and a little bit more convincing for an outside reader who isn't a member of this Paragraph B person's school.
Visual: Slide changes to the following: Academic Writing
Readers expect
- to see research-based evidence* supporting statements even if the writer has expertise in the area
- to be persuaded through logic and reasoning
*information from course readings, books, scholarly journals, trusted websites
The need for research doesn’t mean your own knowledge is unimportant or wrong
Audio: All right. So as I kind of went over, in academic writing, readers expect to see that research‑based evidence which supports statements even if the writer has expertise in the area, so because none of us are doctors in our field yet, we aren't considered experts in our area, even though we most likely have experiences that inform us on our topic and we might have really great things to say about it, but we're not considered experts yet. And in academic writing, even the experts are still going to find that research‑based evidence to help support what they're saying. So that's just a general expectation of academic writing, and it's one of the things that separates it from other types of writing that you may have done in the past or that you may see in other fields.
Readers also expect to be persuaded through logic and reasoning rather than sort of emotional appeals or those other, you know, tools that people will use in online articles or, you know, commercials and things like that that are really overly persuasive and personal and have lots of emotion. That's not quite the right tone for that academic writing, that scholarly writing. It's not a wrong technique, but it should be saved for different arenas, different places where you're going to write. In academic writing, you want to be logical, objective, fact based, and by evidence, I mean information from your course readings, from books, scholarly journals, trusted website, so research you're doing that's been done by other people in your field and is supported and reviewed.
All right. As I've kind of gone over as well, the need for research doesn't mean your own knowledge is unimportant or wrong. It just means that you need to be a little bit careful about when and where you use that personal knowledge in your course writing because a lot of times it won't meet reader expectation, so while it can inform what you're going to write about, you'll want to use that information to fuel your research, for example.
And as we'll go over in a little bit, there are assignments that specifically ask for your own experiences, opinions, and ideas and so you can look out for those as well.
Visual: Slide changes to the following: When is personal experience okay?
- In the research process
- Thinking ● Researching ● Thinking ● Researching ● Writing
Audio: All right, so as I've sort of gone over, you might be wondering when is personal experience okay? As I mentioned in the research process, we're kind of getting you started and personal experience is a great tool, a really beneficial tool to give you a jumping off point. Like in our paragraph example, this writing has seen these issues with teenage addiction in their school so they can say, I know this is an issue and I don't think it's just an issue in my school so what I want to do is think about that issue, research that issue, and then end up writing about that issue.
And your research and thinking and writing process may go back and forth, and it probably should, right. You think of an idea, do a little research to see what's out there, think about it again, do I have enough points, do I maybe need more, is it maybe going in a different direction than I thought? Maybe do a little more research, and then start your writing. And informing that with your personal experience to help get you started for something that you observe or something that you already know to be true can be really beneficial as a jumping off point for your research.
Visual: Slide changes to the following: Type of Assignments
- Assignment instructions might use the term “you” as in “What do you think will be most useful to you…”
- Assignment instructions might say, “Demonstrate your learning…” or “Refer to specific experiences in your workplace…”
- Assignment instructions might say, “Select a topic based on something you have seen, heard, or experienced…”
- Assignment instructions might say, “Describe your educational and professional background…”
Audio: So in your assignments, you may have some assignments, as I mentioned, that are going to ask for you to talk about personal experience and that is a great, great use of personal experience and a place where personal experience is not only okay but it's asked for and it's expected, and one of the key words you can look for in your assignment prompt is you, so look out for assignment prompts that use the word "you." What would you do? What do you think? What experience do you have in this field? And what would you do in this situation? Lots of "you" there but, of course, you're going to use "I," you're going to use your personal experience in those situations.
So, here’s a few that come up. An example in a reflection paper or a post, what do you think will be most useful to you? Right, reflection means you're going to talk about your experience, it's kind of inherent to reflecting on your own writing and ideas.
In a prior learning narrative, the assignment instructions might say something like, demonstrate your learning, refer to experiences in your workplace. I've seen a lot like that so obviously those are really good places to bring out that personal experience.
The assignment instructions might say something like, select a topic based on something you have seen, heard, or experienced. Or I've seen papers that deal with, you know, for example, different leadership styles or something like that and it will ask if you've had any experience with a prior manager that exhibited one of these leadership styles. Those are great places to use that personal experience. And in your professional development plan, if you write one of those, you'll definitely write about personal experience because the assignment instructions will say something like, describe your educational and professional background. So those are all wonderful places to use that personal experience and where you're being asked to use that personal experience.
So, don't feel like we're saying never, ever, ever use personal experience. You're going to have to use your judgment, and that's kind of what this webinar is to help you do, right. So, in your research process, personal experience can be helpful. In assignments that are using "you" and not just this week "you've read," but like asking questions of what do you think, what would you do in your workplace? Those are great questions where you could use some of the experience that you may have.
Visual: Slide changes to the following: To Illustrate a Theory
According to the theory of caring, nurses should be sensitive facilitators of a healing environment (Watson, 1979). I demonstrate this when I talk to patients in a calm voice, listen attentively to their needs, and limit the amount of visitors and noise.
Systems theory looks at a system holistically, with the parts working together (Janson, 2015). An example of this interdependence in my organization is…
Audio: And Sometimes talking about illustrating a theory could be a good place to introduce personal experience as well. Here is an example. According to the theory of caring, nurses should be sensitive facilitators of a healing environment. I demonstrate this when I talk to patients in a calm voice, listen attentively to their needs, and limit the amount of visitors and noise.
So, this assignment probably has something to do with talking about nursing theories and how you do or do not implement them in your nursing practice, right. So, they probably used "you" in the assignment somewhere, but it's not just all personal reflection. It's talking about the reading, talking about how you use these tools, so that's a great place to use that personal experience in a nice specific concrete way.
Here is another example. Systems theory looks at a system holistically with the parts working together and an example of this interdependence in my organization is, and again here we've probably been asked to write about your organization or a past experience in your workplace in the assignment prompt, but when you're combining that with research, demonstrating that theory with personal experience can be really beneficial and helpful for readers because you have that nice evidence and then a concrete example.
Visual: Slide changes to the following: Benefits of Personal Experience
- better understanding
- stronger connection with the material
- perhaps more confidence
- more interesting
- helpful to see an example from an insider perspective
Audio: All right, so the benefits of personal experience for you are that better understanding of your topic, a stronger connection with the material. I mentioned that passion before. And maybe more confidence writing about it because you know for sure that this is an issue, this is something that's going on, this is something you've noticed, you've experienced, and so you can go into it with confidence into your research that there is going to be something out there that supports what you've seen and what you've experienced or what practices you have in your workplace.
For your reader, adding that personal experience where appropriate can be more interesting and helpful to see those examples from an insider perspective. As you all know, I'm sure, excuse me. ‑‑ as you all know I'm sure, reading just about theories can be a little dry, so having those concrete examples of what that looks like in practice can be much more engaging for readers.
Visual: Slide changes to the following: Questions
Audio: All right. Let's pause for a moment to see if we have any questions.
Beth: Thanks so much, Claire. Something just came in here. Oh, yeah, so you just said this I think a little bit, but could you talk a little more and kind of address the question that the student had had on whether they can use first person in their personal experience when discussing personal experience, and specifically maybe tips for using first person in those cases too. Does that make sense?
Claire: Yes, it does. That's a great question. So, I know that some of you have probably heard beyond just don't use personal experience but you may have heard don't use "I," right, which is the first person. So, don't use "I," but using "I" isn't incorrect per APA, and I'll go over this a little about bit later, but the kinds of "I" statements you want to avoid are those I believe, I feel, I think statements. Unless of course your writing a personal reflection of some kind in which case those would be appropriate. But when you’re talking about personal experience you’re going to have to use "I," right. That just makes sense, it would be really weird to say something like, this this writer has experienced. Instead just say, in my workplace I have done this, I exemplify this theory when I do this really focusing on actions you've taken or things that you've observed in your workplace through the use of "I" is going to be much clearer for the readers and help them out. So, using "I" is not inappropriate for personal experience. It's really those other kind of more feeling‑based statements that you really want to watch out for.
Beth: Thank you so much, Claire. I think you just covered a little bit of examples of when to use that first person, and so I think we're good for now. Yeah. I'll keep watching out for more questions, but I think that covers it for now.
Claire: Thanks, Beth, and yeah, we will go can over some examples of using "I" a little bit further on in this presentation too, so you can look for that or look forward to that, sorry.
Visual: Slide changes to the following: When is using personal experience inappropriate?
- Avoid generalizing
- Our schools are failing. Parents want more individualized support for their children in the classroom.
- My daughter texts constantly, which shows that teenagers use cell phones more than they did in the past.
Audio: All right. So, when is using personal experience inappropriate? So, we talked about when it's appropriate, right, during your research process, when your assignment specifically asked for that reflection, that background information, or when you're exemplifying a theory in an assignment which has kind of asked for how you connect to the source reading for that week.
Right, so those are all great places and appropriate places to use that first person and that personal experience.
When using personal experience is inappropriate is using it as evidence in an argument, it's kind of like our Paragraph B from earlier. I noticed this at my school so all teenagers should go through drug testing and that's just too general, right. It's not backed up enough. You want to avoid generalizing. Personal experience can lead to those generalizations, so here are some examples.
Our schools are failing, parents want more individualized support for their children in the classroom, and so this is just really vague, right? This first one, it's really vague and how do I know that schools are failing, whose opinion is this, it's just the writer's opinion and that's probably not enough to say that our schools are failing, like they might be an authority on if their own school is failing, but that's a whole big other ‑‑ I assume they're talking about schools in the United States but they could be talking about the whole world, so it's important to be really specific and use that evidence to avoid those generalizations.
Our second example is my daughter texts constantly which shows that teenagers use cell phones more than they did in the past. So again, this observation, we can't expand it out to all teenagers or all schools or all anything from one personal experience, right? Even our own hospital or at our own high school that our daughter attends, we would have to actually do research and do some kind of study to make this type of statement because otherwise somebody could say anything they wanted, right. I could say, online students are lazy, which I know to be very untrue since I work with Walden students all the time, but I could just say that if we didn't need to have that evidence, if I was just going to use my own personal biased opinion, I could say whatever I wanted. I could say something like that and I wouldn't need to go find any research. I would just say it like it's true and move on, so to avoid that, to have that credibility, you want to have that research to back up statements and avoid using that personal experience, those personal observations, and stating them as facts that extend beyond your own observation.
Visual: Slide changes to the following: Problems with Using Only Experience
- How does one person’s experience compete with verified and reported research involving many people?
- No foundation of knowledge
- No practice with library skills, research, and using sources
Audio: The problems with using only your personal experience in your work are that it's not a very convincing argument. As I sort of just explained, one person's experience, how does that compete with verified research involving many people or across many states or years. You know, one person's opinion just isn't as strong as that. There isn't a clear foundation of knowledge if you're only using personal experience, then you're not explaining, you know, how you contribute to the conversation that's already happening on this topic and that's one of my favorite, favorite things about academic writing is that we're constantly contributing to the conversations that are already happening in our field. And if it's just your opinion and you’re not taking into account what other people have already said or are saying on your topic, then you're not coming off as having a foundation of knowledge or really contributing to that conversation.
Also, the problem with only using experience is you won't get practice with those library skills, research, and using sources effectively. And you're going to need those skills as you progress through your programs, even if maybe you don't need them on your first few discussion posts, for example, you will need them throughout your program and to succeed in your fields.
Visual: Slide changes to the following: Example of Effective Integration
By and large, substance abuse in the United States begins during adolescence. The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (2013) stated that on an average day 881,684 adolescents smoke cigarettes, 646,707 smoke marijuana, and 457,672 drink alcohol. Adult addicts typically report beginning substance use in adolescence. In fact, one in four Americans who started using addictive substances in their teens are addicted now, compared to one in 25 who began using after the age of 21 (National Center on Addiction and Substance Abuse, 2011). To address this pattern, school districts should implement prevention and intervention programs.
At my high school in suburban Atlanta, I helped create Clean Matters. The program follows the National Institute on Drug Abuse principles of …
Audio: All right. So, I want to talk about an example of that effective integration of personal experience with research, so this isn't only research, right, it's personal experience and research.
By and large, substance abuse in the United States begins during adolescents. The substance abuse and mental health services administration stated that on average, an average day, oh, man I'm so bad at reading numbers aloud. This many adolescents smoked cigarettes, marijuana, and drank alcohol. Adult addicts typically report beginning substance use in adolescence, and in fact one in four Americans who started using addictive substances in their teens are addicted now compared to 1 in 25 who began using at the age of 21. To address this pattern, school districts should implement prevention intervention programs. At my high school in suburban Atlanta, I helped create Clean Matters and the program follows the National Institute on Drug abuse Principles of ‑‑
So here you can see that we have this great effective paragraph, and this is that you might recognize as our Paragraph A from earlier, and so we have this effective paragraph that has lots of information from a source. We have a clear takeaway at the end, right? We're saying this is information that is true, here is what this means, this is an issue, it needs to be addressed, right? And here is what we can do.
Then we have an example of what someone is doing already, so for example I've seen some paper assignments that say something like establish your health issue, discuss what your community is doing to combat this issue, for example.
So, this would be a great place to establish your issue using that research and then include what you're doing in your community, especially if you do have that personal involvement and the assignment asked about your community, then this is a good place to use that personal experience and talk about the campaign that you personally worked on.
Visual: Slide changes to the following: Chat
Chat: Did the author effectively
integrate their personal experience in this reflection paper?
Being an active listener is probably the most challenging part of my face-to-face communication. Although I choose my responses wisely and use skills such as validation and empathic listening, I struggle to be an active listener and easily get distracted by mental noises and perceptual biases. Active listeners are “people who focus on the moment, are aware of interactions as they unfold, respond appropriately, and are aware of distractions” (Dobkin & Pace, 2006, p. 98). To strengthen this skill, I must practice clearing my mind and eliminating distractions so I can fully focus on the messages I am receiving.
Audio: All right, so let's do another practice, now that we've done through an example of that effective integration. Did the author here effectively integrate their personal experience in this reflection paper, and why or why not? I will read it aloud for you. Being an active listening is probably the most challenging part of my face‑to‑face communication. Although, I choose my responses wisely and use skills such as validation and empathic listening, I struggle to be an active listener and easily get distracted by mental noises and perceptual biases Active listeners are people who focus on the moment, are, aware of interactions, respond appropriately and are aware of interactions. To strengthen this skill, I must practice clearing my mind and eliminating distraction so I can fully focus on the message I am receiving.
Go ahead and take a minute and then tell us what you think in the chat box.
[silence as students type]
I can see some people are still typing. I'll give you another minute to go ahead and finish up with your response here.
All right. It looks like our contributors have dried up, so I'm going to go ahead and talk over. If you're still typing, go ahead and keep typing and I'll just begin our discussion.
So, a lot of you said that you did think that this was effective in general because we do have some source information that we're dealing with here and we are tying that in to our personal experience. A few of you suggested having the evidence sort of earlier in the paragraph to help support the observations that the writer is making a little bit sooner rather than necessarily beginning with a personal, a sentence of personal experience. And you know, I think it really depends on what the assignment is, right, which is always the answer with personal experience. What is the assignment? This assignment is probably one that I've seen where you take some sort of, you know, assessment or quiz about your skills and then write a reflection about how you scored and what you can do to have kind of like an improvement plan, so that's what I'm guessing this is here.
And in that case, right, it probably is fine to have that personal experience right away in the paragraph because this is a more personal reflective type of assignment, but it's a good thing to keep in mind that you may want to start with an overall what is this paragraph really going to be about, what is the bigger kind of connection, think about your thesis, and then if there are personal details to add to have them a little bit later can be very effective as well.
So great observations, everybody. Thank you for participating.
Visual: Slide changes to the following: Tips for Effectively Using Personal Experience
Audio: All right, so now we're going to go through some tips for effectively using that personal experience.
Visual: Slide changes to the following: Effective Integration Tips
DO use the first-person point of view.
- Helps you avoid referring to yourself in the third person or passive voice.
- Unclear: In this writer’s role as an executive assistant, this writer compiles reports on financial transactions.
- Appropriate: In my role as an executive assistant, I compile reports on financial transactions.
Audio: All right, so as we sort of mentioned before with the questions about using "I," you use that first‑person point of view for your first‑person experience, right. It helps avoid referring to yourself in the third person or in passive voice, which can be very confusing for readers.
An example is in this writer's role an as executive assistant this writer compiles reports on financial transactions. That's not only repetitive, but it's a little confusing because in academic writing, right, we write about what other writers think all the time, so if I'm a reader and I'm seeing this, I'm thinking, okay, by this writer, do they mean the researcher they were just talking about in the last paragraph? Who do they mean? Who were they talking about exactly? So that can be really unclear. Whereas, in my role as an executive assistant I compile reports on financial transactions. There is nothing wrong with using first person in that way, right, because it's not biased, it's not opinionated, it's explaining what you do in your role so there is nothing inappropriate about that per APA.
This blog on including relevant details might be helpful!
DO stay on task.
- Ask yourself: Is this experience directly related to the assignment? How much does the reader really need to know?
- Too Much: I want to pursue a degree in social work at Walden. My stepfather kicked me out of the house when I was 14, and I became homeless. On the streets, I was scared and hungry and had to steal or beg to get by. I don’t want other teens to suffer like I did for many years.
- Appropriate: I want to pursue a degree in social work at Walden. The experience of being homeless as a teenager has made me empathetic toward other people in similar situations.
Audio: All right. You do want to stay on task, so what I see sometimes is even in those assignments that are asking for you to write about your own experience, I see some students get a little bit carried away and I know why because you're so excited to be able to write about that personal experience, to be able to share that you might end up getting kind of off topic and maybe sharing more than is strictly needed for the assignment, so you want to stay focused. You want to ask, is this experience directly related to the assignment? How much does the reader really need to know?
So here is an example. I want to pursue a degree in social work at Walden. My step‑father kicked me out of the house when I was 14 and I became homeless. On the streets I was scared and hungry and had to steal or beg to get by and I don't want other teens to suffer like I did for many years. So, do we need all of that information to understand why this person wants to pursue a degree at Walden?
We can probably cut it down, right. I want to pursue a degree in social work at Walden. The experience of being homeless as a teenager has made me empathetic towards other people in similar situations. So, we're taking the ideas and we're sort of paraphrasing ourselves, right. We're shrinking it down and we're focusing on what the point is, what's the importance of these personal details, what's the takeaway for the reader.
And I have a blog post on including relevant details that I wrote for these specific situations, so you can click that active link or if you're watching this as a recording, you can download the slides and you'll be able to review it there as well, so that has some more detailed examples if this sounds like something you maybe do.
DO Use an objective, formal, nonjudgmental voice (even if the content is very personal).
- Ask yourself: Is this voice appropriate for a professional context?
- Too casual: In my opinion, the students were behaving like brats. I couldn’t even get their attention to take attendance! I had to…
- Appropriate: One day at preschool, the students were particularly rambunctious. It was difficult to take attendance, so I …
Audio: Do remain objective, formal and nonjudgmental even if the content is very personal. Ask yourself, is this voice appropriate for professional context. And when I think of a professional context, I like to imagine that you are writing a letter to a person in your field who you greatly respect but have never met in person, so that might be a helpful visual for some of you, really thinking about that tone. You want to be formal, you want to be direct, you want to seem smart, right, so you want to avoid being overly emotional or, you know, judgmental potentially or opinionated.
Example is in my opinion; the students were behaving like brats. I couldn't even get their attention to take attendance, so here is that less appropriate use of "I" that we sort of talked about before, right. My opinion, so unless the prompt specifically asks for your opinion, then you shouldn't have statements like "in my opinion" or "I believe" and then we have, I couldn't even get their attention to take attendance, so we're just kind of complaining, right.
Instead, we can write one day at preschool the students were particularly rambunctious and so it was difficult to take attendance, so really, we're saying the same thing here but we just tweaked it. We made it more objective, more observable, and something you can think about is, if someone was watching you in your situation, would they find your description effective to paint the picture that they saw, right? Whereas like, students were behaving like brats, that's really subjective. Whereas, the students were energetic or rambunctious that's something that someone could easily observe if they were standing outside of the classroom and they could tell it was difficult for you to take attendance, but I couldn't even get their attention is very personal, that's drawing on not only your personal experience of what happened but you're sort of mental and emotional state while it was happening, so that's another thing to help you kind of focus in on remaining objective and clear, is to think about, am I portraying what happened or am I portraying my emotional response to what happened?
DO NOT wear “experience blinders.”
- Remain open
- Consult other sources and viewpoints, even contradictory ones
- Instead: Provide a citation for personal experience
Audio: All right. Don't wear those experience blinders. Remain open. Think about, you know, someone might say your experience just doesn't belong in this paper, you know, and that's not saying that your experience doesn't matter or isn't important or they're not informed and knowledgeable and intelligent about your topic. It's just, you know, it may not be for the assignment or it might just not match kind of that formal scholarly academic tone.
You can consult other sources and viewpoints, even contradictory ones on your topic, to help maintain that kind of neutral tone throughout even if you think you already have an opinion on it, and you can provide a citation instead of just your personal experience, right. You can provide a citation if you have written about it before, for example, or if you're drawing from your personal experience and you want to go look up something that mirrors what you experienced.
Chat: How would you pair personal
experience with this quote from an article?
Write 1-2 sentences.
“About 75% of the online students surveyed
indicated that they were more engaged in courses
that included images, video, and audio” (Sherman
& MacKenzie, 2015, p. 31).
Audio: All right. So here we have our last practice, so how would you pair personal experience with this quote from an article? And assume that this is appropriate, right, your assignment has asked you to pair personal experience, and so here is a quote. About 75% of the online students surveyed indicated they were more engaged in courses that included images, video, and audio. So, what's your personal experience that connects with this quotation? Write one to two sentences in the Chat Box and then we'll talk about some of them.
I'm seeing some great responses so far and I'm going to go ahead and give you guys another minute or so before we talk over these.
All right. I'm going to go ahead and start talking about a few of the examples that I pulled, but if you're still typing, please go ahead and continue typing.
All right, so one example is "I experience better engagement in courses when I start an online degree with Walden University, images, videos, and webinar and presentations helped me stay focused. So, that pairs nicely with our evidence because they found 75% of students were more engaged by this type of content, right, and so this person is adding to that by saying that they agree, right, and that they give some specifics as to what that looked like here at Walden, so that's a great use of personal experience.
All right. We have sort of an introduction, which was from teaching, information, literacy, and public speaking, my experience is that ‑‑ so that's a great introduction to kind of, what your experience was with that engaging content. I would caution you here to not then just have the quotation, right. Because your experience isn't that 75% of online students surveyed indicated their engagement, right. Your experience is that you also were more engaged by those image, video, and audio, right. You can only speak to your own experience and that's something that wasn't in this presentation, but which is important to think about. You don't want to pair a citation with an "I" statement because it doesn't make sense, right. That writer, Sherman and Mackenzie they didn't write about you. They wrote about subjects in their study. So, pairing with an "I" statement is confusing to readers and you want to make that statement separate from the evidence and show how it connects but you don't want to mash it together in the same sentence.
All right. In my experience as an online student, images, video, and audio have been beneficial in keeping me engaged in online courses. So that’s great, right? That's similar to the first one I read, having the nice specifics and they're agreeing with the statistics and supporting them with their own experience.
Personally, I find my attention is drawn to an attraction eye catching image or video, and right so again we're just kind of agreeing with that source information.
Here’s another one that kind of takes what is an "I" statement or personal statement and goes a little bit too far out from their own experience. From personal experience the use of video and images are imperative for effective learning. The only person you really have authority to say that about is yourself, right. So, from personal experience, the uses of videos are imperative for my learning to be effective is something that you are definitely qualified and should say, right, if that's true here, that would be a great use of personal experience. But you don't want to say, I also, like I agree and this is true for everybody. You don't want to go beyond yourself.
Research has proven that a good number of online students are engaged with video and audio learning experiences, and so that's more of a paraphrase of this quotation, right. That's not personal experience. It's not saying that I had this experience that is supported by this research, right, so there were so many great examples there and I really appreciate your input, and it just shows that this is a skill and it takes time and practice and it is way easier when it's an assignment you have in front of you and you know exactly what personal experience you want to use.
But I'm going to go ahead and move on so that we have time for questions at the end.
Visual: Slide changes to the following: Additional Resources
- Avoiding Bias web page
- All About Audience podcast episode
- Why You Shouldn’t Wiki blog post
- APA blog post on personal experience
- Prior Learning Portfolio web page (UG students)
Audio: All right. So, I promise to use some additional resources at the beginning of this presentation and here are some great ones. We have an Avoiding Bias web page. We have all about audience podcast episode. We also have a podcast episode called Objectivity and Passion that is really good if you feel or if someone is saying that you are too emotional or too passionate about your topic, or you're getting a little opinionated, that's a good one too.
Why You Shouldn't use Wikipedia Blog Post we have an APA, APA has a blog post on personal experience, and for undergraduate students, there is a Prior Learning Portfolio web page to assist you.
Visual: Slide changes to the following: Questions: Ask Now or Later
[email protected] • Live Chat Hours
Learn More:
Check out the recorded webinars “What Is Academic Writing?”
and “Writing Effective Academic Paragraphs”
Audio: And before I turn it over for questions, I also wanted to note that I think a paper review, which I don't think was linked on a previous page, but a paper review is a really great resource too when you're using this personal experience and you're not sure if you are telling too much or, you know, if you're being too passionate about your topic or how well you're integrating that personal experience with those resources. You can send in your paper for a paper review through our paper review system, My Pass, and a writing instructor like myself will read it, give you feedback, and then attach a draft with comments and links in it the day of or day after your scheduled appointment. So that can be really useful and just let us know on your appointment form that you're kind of nervous about using personal experience effectively or would like some assistance with that, and we will focus on that in your review.
All right. Do we have any lingering questions, Beth?
Beth: Yeah. Thanks so much, Claire. Thank you so much. That was all fantastic first off. But we did have a question from a student who was saying, you know, what if their assignment is asking for their personal experience but they're just not coming up with ideas, like they're kind of having writer's block in that area. Do you have any strategies to help students generate ideas from their own personal experience?
Claire: That's a good question. Yeah, it can certainly be challenging, you know, especially if you're being asked, for example, if you're changing career paths and then you're being asked to sort of write about your experience in that career area. Because I have seen some assignments that are like that so I can see why it would be hard to sort of come up with an experience.
If you're really struggling and your faculty has kind of asked you to talk through a scenario or a leadership situation and you're just not coming up with one, then I would definitely reach out to your faculty and see if maybe you can use a scenario from some reading or talk through something like that because that can happen, right, where you just don't really have an experience that fits the bill.
As far as where you definitely know you have experiences, but you're kind of struggling to figure out which one to talk about, or you feel like there are too many, or you just don't know where to start, I would definitely try free writing, which is where, you know, you ask yourself about the topic and you just write for a given amount of time, so I usually start with like 10 minutes, and you just write about that topic, everything you can remember, everything you can think about related to that topic and your experience, and that can really help like jog your memory and focus in on specific events that might be helpful, but definitely, you know, especially if you're coming back to school from a ‑‑ from a while outside of school, then you might not remember a really clear memory to use for a specific example, and in that case I would definitely just ask your faculty and let them know what's going on because they're not trying to trip you up with that. They're just playing on how a lot of Walden students have relevant, current kind of experiences in their field and they're not meaning for you to not be able to complete the assignment.
Beth: That's fantastic, Claire. Can I provide maybe one other idea? I was just thinking of something that's just something I was thinking about.
Claire: Yeah
Beth: Depending on your assignment too, it's also helpful to sometimes read, I don't know, like other more popular research or just like do a Google Search on a topic. Maybe you know, the theoretical peer review journal articles you're reading about a topic just don't help you connect that top wick your own experience, maybe it's like a leadership style or something, but reading an article about leadership styles in a more informal publication that you wouldn't cite in your paper but that could help you generate ideas, that can sometimes sort of make it more real for you. That's been helpful for me in the past sometimes. I don't know, I just wanted to throw that out there as well. I hope that's okay.
Claire: Yeah, no. That's a great idea too. It doesn't have to be research to like spark your ideas. Maybe you want to go watch a TED Talk or you know find an infographic, Beth loves infographics, so find an infographic or find, you know, a little like life hacker article that kind of breaks it down.
Beth: Something yeah. I like that, and I know this is like, it felt so blasphemous when I just read it but sometimes it will even say go to the Wikipedia page on the topic, you won't cite the Wikipedia page but you might generate ideas from it or find other research that's cited on the page too, so yeah.
Okay. No other questions, Claire, that are coming in. Do you have any last thoughts you want to leave everyone with before we kind of wrap up?
Claire: Just, you know, make sure you're looking over your assignment really carefully when you're deciding if you want to use personal experience or not. And if you are ever unsure, ask your faculty. It is their job and they will know if they want personal experience or not in that paper and they will be able to tell you really clearly if you're not sure.
Beth: Perfect. Thank you so much, Claire. I'm seeing lots of thanks coming into the Q&A Box. Thank you, thank you everyone for attending, if you have any more questions, make sure to reach out and we hope to see you at another webinar coming up soon. Thanks, everyone.
- Previous Page: Welcome to the Writing Center
- Next Page: What Is Academic Writing?
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
Starting Your Research Paper: Writing an Introductory Paragraph
- Choosing Your Topic
- Define Keywords
- Planning Your Paper
- Writing an Introductory Paragraph
The Dreaded Introductory Paragraph
Writing the introductory paragraph can be a frustrating and slow process -- but it doesn't have to be. If you planned your paper out, then most of the introductory paragraph is already written. Now you just need a beginning and an end.
| for writing thesis statements. |
Here's an introductory paragraph for a paper I wrote. I started the paper with a factoid, then presented each main point of my paper and then ended with my thesis statement.
Breakdown:
| 1st Sentence | I lead with a quick factoid about comics. | |
| 2nd & 3rd | These sentences define graphic novels and gives a brief history. This is also how the body of my paper starts. | |
| 4rd Sentence | This sentence introduces the current issue. See how I gave the history first and now give the current issue? That's flow. | |
| 5th Sentence | Since I was pro-graphic novels, I gave the opposing (con) side first. Remember if you're picking a side, you give the other side first and then your side. | |
| 6th Sentence | Now I can give my pro-graphic novel argument. | |
| 7th Sentence | This further expands my pro-graphic novel argument. | |
| 8th Sentence | This is my thesis statement. |
- << Previous: Planning Your Paper
- Last Updated: Feb 12, 2024 12:16 PM
- URL: https://libguides.astate.edu/papers


- my research
- contributions and comments
the personal narrative in the thesis introduction
So you are going to write a personal narrative as the introduction to your thesis. Not everyone has – or wants – to do this. But some do, or they want to. But in some disciplines – and places – it seems to be almost mandatory to begin the thesis with a few pages which are about yourself. In other places and disciplines to do so would be unthinkable.
Why do people want – or are required – to write a personal narrative? Well there are at least three reasons – any or all of:
- The personal narrative is intended to locate the researche r so that examiners can see how the researcher’s actual life and/or work experience might influence the research, for better or worse. The narrative enacts the (epistemological) position that no research is neutral and all research is written from somewhere, and where matters. Of course, understanding something about the researchers’ experiences can raise questions for examiners about potential blank and blind spots and the need for researcher reflexivity.
- The personal narrative is intended to show how the research question arises from the personal life or professional work experience of the researcher . In applied fields for instance it is not uncommon for doctoral researchers to find the mandate for their research in their professional context. They know from their direct experience that a particular kind of research would be valuable and useful and so their thesis reports a piece of work which does just this. And researchers do often end up researching something that is directly related to their life experience. They have a child or friend with… or they have experienced… Alternatively, the research may be a continuation of a scholarly interest formed earlier.
- The personal narrative is intended to lay the ground work for a claim for professional knowledge. In applied fields, and often in professional doctorates, people draw on their own experience as part of the data. For instance a headteacher might use their experience of school budgeting to advantage, a midwife use the need to work both emotionally as well as on the body, and so on. (This is sometimes called working with Mode 2 knowledge as the knowing arises from experience in work settings or working on applied problems).
It is helpful to understand the reasons for writing a personal narrative as these will explicitly guide the choice of what information to include and exclude. No introductory narrative will be comprehensive – it’s not a biography, but a carefully chosen set of information put together in narrative form.

Once upon a time I dreamed of being a researcher…
So we might say to friends for example – I am the first person in my family to get to university . But we might write in our introductory thesis narrative – I grew up at a time when it was possible for young people to enter higher education in larger numbers than ever before. I, and some of my peers, were the first in our families to go to university . We might say – My parents wanted me to do well and so I did . We might write this or perhaps – Because my parents belonged to that section of the working class that believed strongly in the power of education, and regretted not being able to go further in their own schooling, I was positioned at the outset to take advantage of the opportunities that schooling offered. And so on.
It’s important in the introductory thesis personal narrative to hold what we usually say to ourselves up to some critical scrutiny and to make the connections to the following research very clear. Don’t leave it up to the examiners to guess these connections.
Just to show you what I mean here are a couple of paragraphs from my own PhD which looked at the changes in South Australian schools after a major national poverty funding programme was stopped. The introduction to the thesis begins with a brief historical snapshot of schools in Australia and then says something about the particular poverty reform programme that was abandoned. I then go on to write about myself. I trace my own work history and the way it was tangled up with the particular programme in question and then say:
I have lived in the educational, political, social and cultural changes of the postwar period, lived in the struggles for equity and the permanent improvement of schooling for working class children and young people. I have not been the central figure in these events, but I have been there. My identity, my sense of self, is therefore strongly connected with the location of this research text, not only geographically, but also in its politics. This is no disinterested piece of scholarship but rather is another phase in an ongoing career. This research grows from my commitment to social justice and an abiding anger at the ways in which particular classed, raced and gendered students do not benefit from their schooling, whereas other students who are already privileged seem to gain even greater benefits.
While I am unequivocal about the axiological positioning of this research, I am also alert to the dangers that such a ‘will to truth’ and insider solipsism might bring. Even in this brief introduction I have used terms that are hardly innocent bystanders – words such as class, gender, race, advantage, justice and education. Both my story, and the troubled lexicon of sociology, are subtexts in this research.
Now I’m certainly not suggesting that you follow this as a model. There are things about these two paragraphs that I wish I could rewrite. Darn it, I can’t. So don’t copy it please. But I hope this exposure of my former self does serve to illustrate one of very many ways in which a researcher can connect their personal narrative with their research, signaling as they do that they also know the potential problems that might arise for their research from this tangle. You need to find your own way to do this – but you do need to do it if you are personal narrative bound.
The personal narrative as thesis introduction needs to work for you and not to present you as someone who might as well be telling a tale in the pub to their mates. The narrative needs to serve a purpose and show you as a reflective situated scholar.
Share this:
About pat thomson
9 responses to the personal narrative in the thesis introduction.
Styles and academic (fashions) conventions change, Pat, and as you so correctly note, any introductory foray into the realm of locating the researcher has to work. It has to work, not just for the writer, but also as a contribution that persuades the examiners. Reflexivity has become an ‘OK’ thing to weave into a thesis but I’m bound to say that from the innards of a Psychology Department in the early 1990s, I was seen as something of a deviant (in psychological terms you understand) because not only did I use a mixed methods approach for gathering data, but I also used the first person singular whenever I needed to emphasise or underscore a point I was writing about.
My approach, at that time, was not the done thing but over the years, it has became quite acceptable. The use of I was a way of placing the writer/researcher at the core of an academic argument – the proprietor so to speak.
Now, though, people use advanced organisers far more extensively than even you did in your thesis: they say what they will be doing and then they do it. Such a strategy was not encouraged in the early 1990s and I guess in time, current conventions of allowing “…I will…” may inevitably shift yet again. But the important point, and one you that you make, is that the personal narrative has to be scholarly because it is, after all, but a part of an assessment tool that will be appraised by three appointed examiners. And only one of those chosen three should be a first time examiner.
I think in some Psych Departments this would still not be acceptable so you were clearly a trail blazer in this area in your discipline. And… sorry if I wasn’t clear – the question, anticipation of argument and the outline of the thesis all come after the personal narrative if there is one. This is either as a separate chapter if the narrative is particularly lengthy, or as separate sections if it’s quite short. The narrative of course doesn’t substitute for any of these. The introductory chapter often concludes with what I call the Outline of the thesis to come.
Yes, I agree with you, Pat, on all sorts of planes. I was not so much a trail-blazer but an obstinate researcher who had something to say in what I know would be the most appropriate way. They changed the rules for appointing examiners at the UNE after one of them, a psych person from UQ, could not grasp the possibility of mixed methods but that’s another story. Many of my own students have included in their first chapter, the kind of personal scene and person introducing narrative you spoke of and frankly, I encourage that. And yes, it must be pertinent. As well, the traditional outline is always included.
As a throwaway comment, I’m back in Australia doing a one year stint at the UNSW trying to morph academics into becoming teachers who can engage their students. One of my kids had twins so we decided to leave our research retreat at Woodhill Part for the year and help them out with their premature babies so a job at UNSW became a very convenient way of doing that. Any rate, my point is that at a colloquium for Education PhD and Masters students yesterday, I mentioned both your blog and that by Inger to the students. Few had heard of it and I suspect that even fewer staff were aware of it. There’s a pressing need, still, to guide supervisors in the art and science of supervision (paraphrased from the late Malcolm Knowles).
Thanks so much for this, Pat. I’ve just been re-reading the second chapter of Shawn Wilson’s Research is Ceremony, where something like this happens. The personal narrative is in the form of a letter to his sons, and it’s in a different font to the other parts of the chapter that contain a different kind of commentary on the practice of research, that we could loosely think of as “professional narrative”. What works for me is that neither is subordinated to the other: both have powerful reasons for being told in the way that they are told, and in the final paragraph both narratives come together to address the reader on the purpose of the book, and its unflinching ethical goal. Your post is so timely for me as I’m getting ready to introduce these ideas of personal narrative to undergraduate researchers next week. (Next week? Yikes.)
Thanks for the heads up in the Wilson text. I hadn’t sent I, I’m a bit out of touch with Australian publications 😦
Pingback: the business of self presentation | patter
Reblogged this on CTS at LCC and commented: So you are going to write a personal narrative as the introduction to your thesis. Not everyone has – or wants – to do this. But some do, or they want to. But in some disciplines – and places – it seems to be almost mandatory to begin the thesis with a few pages which are about yourself. In other places and disciplines to do so would be unthinkable.
The personal narrative is intended to locate the researcher so that examiners can see how the researcher’s actual life and/or work experience might influence the research, for better or worse. The narrative enacts the (epistemological) position that no research is neutral and all research is written from somewhere, and where matters. Of course, understanding something about the researchers’ experiences can raise questions for examiners about potential blank and blind spots and the need for researcher reflexivity. The personal narrative is intended to show how the research question arises from the personal life or professional work experience of the researcher. In applied fields for instance it is not uncommon for doctoral researchers to find the mandate for their research in their professional context. They know from their direct experience that a particular kind of research would be valuable and useful and so their thesis reports a piece of work which does just this. And researchers do often end up researching something that is directly related to their life experience. They have a child or friend with… or they have experienced… Alternatively, the research may be a continuation of a scholarly interest formed earlier. The personal narrative is intended to lay the ground work for a claim for professional knowledge. In applied fields, and often in professional doctorates, people draw on their own experience as part of the data. For instance a headteacher might use their experience of school budgeting to advantage, a midwife use the need to work both emotionally as well as on the body, and so on. (This is sometimes called working with Mode 2 knowledge as the knowing arises from experience in work settings or working on applied problems).
Pat – though this has been posted for some time, I’m thankful it’s still up! In my proposal defense, my committee suggested adding in ‘my story’ as I am coming to the research with a practitioner first mindset, which was coming across in my writing but not implicitly said. They suggested adding it, to which I thought they were thinking full on Autoethnography kind of stuff but insisted that’s not the case. Your post and looking at your full dissertation has been a huge help in understanding how I can include my ‘practitioner heart’ in my quantitative dissertation. Many thanks for sharing your knowledge.
I’m glad it was helpful.
Leave a comment Cancel reply
- Search for:
Follow Blog via Email
Enter your email address to follow this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
Email Address:

patter on facebook
Recent Posts
- Category is – “limitations” Part One
- Getting over bad/limited advice – journal article introductions
- what do you do for your reader?
- on bad writing advice, again
- do you read – or talk – your conference paper?
- your conference paper – already published or work in progress?
- a musing on email signatures
- creativity and giving up on knowing it all
- white ants and research education
- Anticipation
- research as creative practice – possibility thinking
- research as – is – creative practice

SEE MY CURATED POSTS ON WAKELET
Top posts & pages.
- writing a bio-note
- aims and objectives - what's the difference?
- avoiding the laundry list literature review
- I can't find anything written on my topic... really?
- headings and subheadings – it helps to be specific
- writing the thesis – the theoretical framework
- 20 reading journal prompts
- five ways to structure a literature review
- connecting chapters/chapter conclusions
- Entries feed
- Comments feed
- WordPress.com

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Critique Report
- Writing Reports
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
Telling the Story of Yourself: 6 Steps to Writing Personal Narratives

By Jennifer Xue

Table of Contents
Why do we write personal narratives, 6 guidelines for writing personal narrative essays, inspiring personal narratives, examples of personal narrative essays, tell your story.
First off, you might be wondering: what is a personal narrative? In short, personal narratives are stories we tell about ourselves that focus on our growth, lessons learned, and reflections on our experiences.
From stories about inspirational figures we heard as children to any essay, article, or exercise where we're asked to express opinions on a situation, thing, or individual—personal narratives are everywhere.
According to Psychology Today, personal narratives allow authors to feel and release pains, while savouring moments of strength and resilience. Such emotions provide an avenue for both authors and readers to connect while supporting healing in the process.
That all sounds great. But when it comes to putting the words down on paper, we often end up with a list of experiences and no real structure to tie them together.
In this article, we'll discuss what a personal narrative essay is further, learn the 6 steps to writing one, and look at some examples of great personal narratives.
As readers, we're fascinated by memoirs, autobiographies, and long-form personal narrative articles, as they provide a glimpse into the authors' thought processes, ideas, and feelings. But you don't have to be writing your whole life story to create a personal narrative.
You might be a student writing an admissions essay , or be trying to tell your professional story in a cover letter. Regardless of your purpose, your narrative will focus on personal growth, reflections, and lessons.
Personal narratives help us connect with other people's stories due to their easy-to-digest format and because humans are empathising creatures.
We can better understand how others feel and think when we were told stories that allow us to see the world from their perspectives. The author's "I think" and "I feel" instantaneously become ours, as the brain doesn't know whether what we read is real or imaginary.
In her best-selling book Wired for Story, Lisa Cron explains that the human brain craves tales as it's hard-wired through evolution to learn what happens next. Since the brain doesn't know whether what you are reading is actual or not, we can register the moral of the story cognitively and affectively.
In academia, a narrative essay tells a story which is experiential, anecdotal, or personal. It allows the author to creatively express their thoughts, feelings, ideas, and opinions. Its length can be anywhere from a few paragraphs to hundreds of pages.
Outside of academia, personal narratives are known as a form of journalism or non-fiction works called "narrative journalism." Even highly prestigious publications like the New York Times and Time magazine have sections dedicated to personal narratives. The New Yorke is a magazine dedicated solely to this genre.
The New York Times holds personal narrative essay contests. The winners are selected because they:
had a clear narrative arc with a conflict and a main character who changed in some way. They artfully balanced the action of the story with reflection on what it meant to the writer. They took risks, like including dialogue or playing with punctuation, sentence structure and word choice to develop a strong voice. And, perhaps most important, they focused on a specific moment or theme – a conversation, a trip to the mall, a speech tournament, a hospital visit – instead of trying to sum up the writer’s life in 600 words.
In a nutshell, a personal narrative can cover any reflective and contemplative subject with a strong voice and a unique perspective, including uncommon private values. It's written in first person and the story encompasses a specific moment in time worthy of a discussion.
Writing a personal narrative essay involves both objectivity and subjectivity. You'll need to be objective enough to recognise the importance of an event or a situation to explore and write about. On the other hand, you must be subjective enough to inject private thoughts and feelings to make your point.
With personal narratives, you are both the muse and the creator – you have control over how your story is told. However, like any other type of writing, it comes with guidelines.
1. Write Your Personal Narrative as a Story
As a story, it must include an introduction, characters, plot, setting, climax, anti-climax (if any), and conclusion. Another way to approach it is by structuring it with an introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction should set the tone, while the body should focus on the key point(s) you want to get across. The conclusion can tell the reader what lessons you have learned from the story you've just told.
2. Give Your Personal Narrative a Clear Purpose
Your narrative essay should reflect your unique perspective on life. This is a lot harder than it sounds. You need to establish your perspective, the key things you want your reader to take away, and your tone of voice. It's a good idea to have a set purpose in mind for the narrative before you start writing.
Let's say you want to write about how you manage depression without taking any medicine. This could go in any number of ways, but isolating a purpose will help you focus your writing and choose which stories to tell. Are you advocating for a holistic approach, or do you want to describe your emotional experience for people thinking of trying it?
Having this focus will allow you to put your own unique take on what you did (and didn't do, if applicable), what changed you, and the lessons learned along the way.
3. Show, Don't Tell
It's a narration, so the narrative should show readers what happened, instead of telling them. As well as being a storyteller, the author should take part as one of the characters. Keep this in mind when writing, as the way you shape your perspective can have a big impact on how your reader sees your overarching plot. Don't slip into just explaining everything that happened because it happened to you. Show your reader with action.
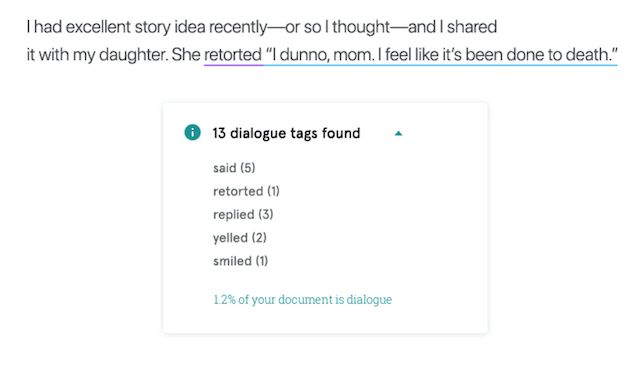
You can check for instances of telling rather than showing with ProWritingAid. For example, instead of:
"You never let me do anything!" I cried disdainfully.
"You never let me do anything!" To this day, my mother swears that the glare I levelled at her as I spat those words out could have soured milk.
Using ProWritingAid will help you find these instances in your manuscript and edit them without spending hours trawling through your work yourself.
4. Use "I," But Don't Overuse It
You, the author, take ownership of the story, so the first person pronoun "I" is used throughout. However, you shouldn't overuse it, as it'd make it sound too self-centred and redundant.
ProWritingAid can also help you here – the Style Report will tell you if you've started too many sentences with "I", and show you how to introduce more variation in your writing.
5. Pay Attention to Tenses
Tense is key to understanding. Personal narratives mostly tell the story of events that happened in the past, so many authors choose to use the past tense. This helps separate out your current, narrating voice and your past self who you are narrating. If you're writing in the present tense, make sure that you keep it consistent throughout.

6. Make Your Conclusion Satisfying
Satisfy your readers by giving them an unforgettable closing scene. The body of the narration should build up the plot to climax. This doesn't have to be something incredible or shocking, just something that helps give an interesting take on your story.
The takeaways or the lessons learned should be written without lecturing. Whenever possible, continue to show rather than tell. Don't say what you learned, narrate what you do differently now. This will help the moral of your story shine through without being too preachy.
GoodReads is a great starting point for selecting read-worthy personal narrative books. Here are five of my favourites.
Owl Moon by Jane Yolen
Jane Yolen, the author of 386 books, wrote this poetic story about a daughter and her father who went owling. Instead of learning about owls, Yolen invites readers to contemplate the meaning of gentleness and hope.
Night by Elie Wiesel
Elie Wiesel was a teenager when he and his family were sent to Auschwitz concentration camp in 1944. This Holocaust memoir has a strong message that such horrific events should never be repeated.
The Diary of a Young Girl by Anne Frank
This classic is a must-read by young and old alike. It's a remarkable diary by a 13-year-old Jewish girl who hid inside a secret annexe of an old building during the Nazi occupation of the Netherlands in 1942.
The Year of Magical Thinking by Joan Didion
This is a personal narrative written by a brave author renowned for her clarity, passion, and honesty. Didion shares how in December 2003, she lost her husband of 40 years to a massive heart attack and dealt with the acute illness of her only daughter. She speaks about grief, memories, illness, and hope.
Educated by Tara Westover
Author Tara Westover was raised by survivalist parents. She didn't go to school until 17 years of age, which later took her to Harvard and Cambridge. It's a story about the struggle for quest for knowledge and self-reinvention.
Narrative and personal narrative journalism are gaining more popularity these days. You can find distinguished personal narratives all over the web.
Curating the best of the best of personal narratives and narrative essays from all over the web. Some are award-winning articles.
Narratively
Long-form writing to celebrate humanity through storytelling. It publishes personal narrative essays written to provoke, inspire, and reflect, touching lesser-known and overlooked subjects.
Narrative Magazine
It publishes non,fiction narratives, poetry, and fiction. Among its contributors is Frank Conroy, the author of Stop-Time , a memoir that has never been out of print since 1967.
Thought Catalog
Aimed at Generation Z, it publishes personal narrative essays on self-improvement, family, friendship, romance, and others.
Personal narratives will continue to be popular as our brains are wired for stories. We love reading about others and telling stories of ourselves, as they bring satisfaction and a better understanding of the world around us.
Personal narratives make us better humans. Enjoy telling yours!

Write like a bestselling author
Love writing? ProWritingAid will help you improve the style, strength, and clarity of your stories.
Jennifer Xue
Jennifer Xue is an award-winning e-book author with 2,500+ articles and 100+ e-books/reports published under her belt. She also taught 50+ college-level essay and paper writing classes. Her byline has appeared in Forbes, Fortune, Cosmopolitan, Esquire, Business.com, Business2Community, Addicted2Success, Good Men Project, and others. Her blog is JenniferXue.com. Follow her on Twitter @jenxuewrites].
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :

- Request new password
- Create a new account
Doing Research in Counselling and Psychotherapy
Student resources, using personal experience as a basis for research: autoethnography.
Autoethnography is quite different from other genres of research, in being based in first-person writing and reflection on personal experience. Carrying out an autoethnographic study not only has the potential to contribute to the research literature – it can also be highly personally meaningful, and provide a distinctive vantage point from which it is possible to see other types of research in a fresh way.
To appreciate what is involved in autoethnographic research it is necessary to try it out on yourself. This set of reflexive writing tasks provide suggestions about how to make a start with this kind of process. It is not necessary to complete all the writing exercises, or to begin with the first one – better to scan through the options and engage with the ones that strike a chord.
Articles on ethical issues in autoethnographic research are available in the Chapter 5 section of these online resources.
Papers on engaging in autoethnographic inquiry
These papers on psychotherapeutic topics illustrate different styles of autoethnographic inquiry, and different writing techniques. When reading them, make notes about those elements of each paper that could be usefully incorporated into your own study, and these elements that would be inappropriate.
Douglass, B.G. & Moustakas, C. (1985) Heuristic inquiry: the internal search to know. Journal of Humanistic Psychology, 25, 39 – 55.
Heuristic inquiry was an important precursor of autoethnography – this article highlights aspects of the study of personal experience that are not always given enough emphasis in the contemporary autoethnographic literature
Chang, H. (2016). Autoethnography in health research: growing pains? Qualitative Health Research, 26, 443 – 451.
A useful discussion of current trends in autoethnography
Harder, R., Nicol, J. J., & Martin, S. L. (2020). " The power of personal experiences": post-publication experiences of researchers using autobiographical data. The Qualitative Report , 25(1), 238 – 254.
Autoethnographic work is personally highly revealing – this study explores how experienced autoethnographic researchers evaluate the impact this has had on them
Wall, S. (2006) An autoethnography on learning about autoethnography. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 5, 146 – 160.
Wall, S. (2008) Easier said than done: writing an autoethnography. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 7, 38 – 53.
Many researchers have found these papers – which tell the story of conducting an autoethnographic study – useful in terms of their own development
Exemplar autoethnographic articles
Asfeldt, M., & Beames, S. (2017). Trusting the journey: Embracing the unpredictable and difficult to measure nature of wilderness educational expeditions. Journal of Experiential Education , 40(1), 72 – 86.
Brooks, C.F. (2011). Social performance and secret ritual: battling against Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Qualitative Health Research, 21, 249 – 261.
Fox, R. (2014). Are those germs in your pocket, or am I just crazy to see you? An autoethnographic consideration of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Qualitative Inquiry , 20(8), 966 – 975.
Matthews, A. (2019). Writing through grief: Using autoethnography to help process grief after the death of a loved one. Methodological Innovations , 12(3), 1 –10 .
The Writing Planet

50 % off on all orders
How to Write a Short Story Research Paper

What Exactly Is A Story?
Our capacity for feeling and our ability to remember are both enhanced by the telling of stories, which are essentially built into our brains. But what is a story exactly? The more people you ask for definitions, the more you will obtain. The basic format of the majority of Hollywood dramas consists of one main character living her life until she meets a predicament. There will be ups and downs, culminating in a large event such as a fight or a party. The action begins when she seeks to resolve the issue. Things are ultimately resolved in some fashion. We observe how our protagonist’s life has changed as a result of the novel’s events.

Whether you are writing a research paper for a high school or college-level class, the process of researching a short story is generally the same, although a college instructor will likely want additional information. Before investigating the short story, thoroughly read it and make any necessary notes. Creating your research paper allows you to have a deeper understanding of the short story and share your discoveries with the reader.
Read any handouts or notes you’ve prepared on the particular requirements for the next research paper. Pay particular attention to the required word/page count and the type of works mentioned page in terms of both structure and quantity of sources. Additionally, you should keep track of whether your instructor requires a specified number of primary sources in addition to secondary sources. Determine which, if any, of your sources may be located online.
- Find a quiet place to read and reread the required short story . Take notes carefully as you read.
- Seek comments about the story you want to create. You should find a number of reviews on the subject at your institution’s library or at your community’s public library. Although various short story assessments are available online, be sure that any web resource you use to compose your research report is credible. In general, academic sources are reputable. Reference libraries that provide access to sources are useful while conducting research; however, you may need a university ID number to access these online resources.
- Examine the testimonials in detail. Occasionally, annotations appear beneath the actual text when an authority provides definitions and explanations of what a certain word or paragraph means. In general, a scholar of the author and the work will read the text from a broader perspective, drawing judgments about where the author drew inspiration from other writers’ works or in creating a particular character or the narrative’s main theme.
- Write your paper using the sources you’ve selected to support the assertions you intend to make in your research report. Utilize your own notes to recall what you observed while reading the tale.
If you have just been told that you need to write a research paper and are feeling apprehensive, we are confident that the following strategies will assist you. First and foremost, whether you are searching for or attempting to comprehend a topic, consult to your professor. Do not be concerned! You constantly undertake research. Consider the most recent time you made a significant purchase, selected a school, or went to the movies. You may have conversed with pals, read product or movie reviews, visited a college campus, or test-driven a car. Academic research is comparable; however, procedures and sources may vary.
A Guide to Writing a Short Story Research Paper
·â â â â â â â select an engaging question.
Your instructor or professor will either allow you to select your own topic, provide you with a selection of topics to pick from or assign you one. In any case, select a topic or component of your topic that you find interesting. Approach your studies with a critical frame of mind. Critical does not mean “finding defects,” but rather a perceptive and discriminating attitude.
·       Be precise
Construct your question to extract information on the “who, what, where, why, and how” of your problem. Too general subjects should be avoided. An expansive topic will make it tough to limit your research. Consider your research question to be both an anchor and an umbrella: your “who” and “how” questions are your anchor, and it’s up to you to keep everything in control under the protection of your research umbrella.
·       Pay Close Attention to Your Thesis Statement
How has global warming harmed the earth is an example of a too-broad thesis statement. How has global warming impacted marine life in the Pacific Ocean? This is an example of a debatable thesis statement.
·       Make Your Question Challenging
Along with a specific question, your topic should be engaging enough to hold the reader’s interest. Individuals will only be compelled to continue reading if simply a yes or no response is required.
·       Primary and Secondary Data Collection
Begin your search for information that can assist you in answering your question. A research paper may need the utilization of both primary and secondary materials. Primary research requires working with genuine materials or obtaining data in the field. Secondary research is finding out what others have found out about a topic.
·       Support Your Question with a Choice of Sources
Secondary research materials can be acquired in a number of different methods. Utilize the databases within the library. Consider newspapers and periodicals. Visit websites with caution; be certain they are trustworthy. If the domain ends in “.org,” “.gov,” or “.edu,” this is a good (but not foolproof) indicator.
·       Conduct Refined Keyword Research
Although search engines vary, the following guidelines apply to the majority of them.
·       Take Notes While Reading
Using note cards to record pertinent quotations and paraphrases is an excellent method for organizing your thoughts. Make a note of the source’s title, author, and page number to avoid future citation problems!
·       Create a Draft
Create an outline and begin writing your first draught of the paper. The use of an outline might help you keep everything “under the umbrella.” Consider your introduction, the arguments you will make, the sequence in which you will make them, and your planned conclusion. Create a preliminary draught. Before beginning a rewrite, you should set the document aside for at least twenty-four hours and have someone else review it.
·       Finish With the Final Revision
Rewrite your paper in light of your reflection and comments. Remember to proofread carefully for spelling and punctuation errors. Check the correctness of your Works Cited (or References) page as well.
Purpose of Story Research Paper
Consequently, what is the objective of a story research paper ? This style of paper is meant to demonstrate the researcher’s capacity to comprehend, analyze, and interpret the subject matter. Here are some recommendations on how to begin preparing and writing an outstanding research paper on a story.
How to Write a Research Paper on a Story
1.â â â â read the book twice.
Read the book attentively and have a dictionary and a notebook on hand, if required. Only take notes when something captures your attention or merits highlighting. Remember to record each note’s page number. Try to rest in between readings and record your initial impressions of the book when you’ve completed it. It might be useful in the future.
2.    Choose the Subjects You Will Emphasize In Your Paper
Ensure that your research piece concentrates on certain subjects. For instance, you may opt to emphasize the book’s characters or the plot’s content. This will make outlining your thoughts and writing your research report much simpler.
3.    Plan the Structure of Your Paper
It typically consists of an introductory paragraph, a body that highlights the book’s themes, and a conclusion that summarizes the last issues. Consider extending the main body to many paragraphs or chapters.
4.    Consider the Main Points of Each Paragraph
Before writing, choose a statement for each paragraph that emphasizes the key ideas and shows the approach you will emphasize in your own research paper.
In addition, include any citations or references you desire to emphasize while building paragraphs. Utilize headers and subheadings to simplify your work. Remember that these notes are intended just for your personal use, and organize your thoughts accordingly.
Now that we’ve discussed how to write a story-based research paper let’s examine the structure of your paper.
·       Introduction
The first paragraph explains the book and the major topics you uncovered throughout your research. In addition to a summary of the storyline and an introduction to the main characters, the introduction of a research paper should also include a brief synopsis of the plot and an overview of the main characters. In this section, you should introduce both your research topic and the essential concept of history.
·       The Report’s Primary Content
Make this the first paragraph in which you illustrate your thesis by focusing on one aspect or theme of the story. To illustrate the most crucial components of the story in relation to your plot, you may describe specific situations or include direct quotations. Include any relevant research you’ve conducted about the author, historical era, or gender to bolster your arguments.
Draw the major characters in the story and explain their origins and characteristics. Describe in a few sentences the tension that exists at the beginning of the tale. Discuss the character’s journey and the resolution of the dilemma. Focus on the significant events that shaped the story’s conclusion with little specifics. Consider any lessons or realizations the protagonist learned toward the end of the narrative.
·       Conclusions
Your book report should conclude with a summary of how your thorough method pertains to the entire plot. Three or four phrases that link the relevance of your detailed method to the overarching tale, conflict, and character stance should conclude your paper. Due to the fact that the broad viewpoint frequently involves analysis and critique, conclude the paper with a concluding statement that indicates what you gained from reading the book or a conclusive statement that reveals your ultimate opinion on the idea examined.
Bring the overview of the book to a close by discussing the conclusion and offering your comments or ideas about the text. You must demonstrate comprehension of the author’s message in three to five sentences. To explain the value of the book to you, describe a relationship between it and your personal experiences. The conclusion also affords you the chance to write a succinct evaluation of the book, indicating why you liked or hated it.
·       Go Over Your Paper Again
After you have completed your research paper , you should proofread it. Take a break and delegate your task to someone else. People who are reading the work for the first time typically discover errors that the authors should have made.
When asking a friend to critique your work, the question about his own impressions of the content. Ask direct inquiries and expect direct responses. Inquire as to whether the buddy liked or hated the work, whether reading the paper inspired them to read the book, whether the writing was flowing, etc.
The Bottom Line
We hope our suggestions were helpful. Internet searches for terms such as “ how to write a good research paper on a book ” might complement your understanding of writing a research paper on a story or a book.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How to write a short paper research?
The format of a normal five-paragraph short paper is as follows: introduction (1 paragraph), thesis, major body (3 paragraphs), and conclusion (1 paragraph). This allows your work to be more extensively organised and simpler to understand. Even if you’re writing a brief essay, first impressions are important.
- What should a short research paper include?
Typically, a complete APA-style research paper describing an experimental study would include a Title page, Abstract, Introduction, Methods, Results, Discussion, and References section. In addition to figures and tables, many will also include an appendix or appendices.
Previous Posts

Write My Research Paper for Me to get an ‘A ‘ grade?

Research Paper Help – Professional Writing Assistance

What Is The Difference Between Research Paper and Essay
- Translation
Academic writing style: Telling a story in your research paper
By charlesworth author services.
- Charlesworth Author Services
- 25 February, 2022
Academic writing can often be somewhat drab. Make no mistake – it isn’t supposed to entertain, it’s supposed to inform. However, that doesn’t mean that it can’t be engaging . Building your research paper around a narrative format can help the reader (from the editor who views your initial submission to the final reader) follow the ‘story’ of what you’re bringing across more easily, thus enabling them to absorb the information more readily. Here, we discuss the benefits of telling a story in your research paper and share some pointers for doing it well.
Telling a story in your paper: Explained and exemplified
When we say ‘narrative’, we don’t necessarily mean ‘write in the style of your favourite author’. A narrative, in the context of academic writing, is a central thread that runs through each of your result pieces . The idea is to have a beginning, a middle and an end to your paper, thereby providing the reader with structure and a satisfying progression through the paper .
Why is this important?
Consider the following example:
Western blot results suggested the presence of the protein of interest. Structural analysis confirmed the protein’s folded structure to include disulphide bonds.
The above example is a matter-of-fact statement of results.
Now, consider this example:
To determine whether our protein of interest was present, a western blot was performed, suggesting its presence in the sample. Further structural analysis revealed the presence of disulphide bonds.
This example improves on the first statement by reframing it as a progression of events, giving the impression of a development occurring with every new piece of data generated , rather than a simple collection of data. By restructuring the information this way, the second example also ties the rationale into the sentence , giving the reader context for what they are about to read.
How to write your paper as a story: Basics
A complete illustration of writing your research paper as a story or narrative is beyond the scope of this article. So, here, we provide some basic tips.
What you need to do
You’ll need a beginning, a middle and an end . Oftentimes this can be a helpful way of structuring your paper when you are about to commence writing , as it can help you obtain an idea about the overall form that you think would be ideal for it.
Also, try not to simply retell your entire process chronologically, but rather in terms of rationale . For example…
One piece of data led you to another question, which would in turn have directed you towards interrogating yet another aspect, and so on.
This leads the reader through your process and will help them to understand why you progressed the way you did .
What you need to avoid
It is not uncommon to have to reappraise your data when the time comes to write your paper. However, be aware that using a narrative structure and voice could lead you to omit certain experiments because they might not fit with the ‘story’ . There are cases where this is fine, because perhaps a specific experiment or method isn’t particularly relevant. However, be aware that there can be a fine line between this and ‘cherry picking data’ , which can be regarded as misconduct and/or an unethical practice .
Also try to avoid using too many personal pronouns . There are instances, disciplines and journals in which this may be acceptable. Just ensure that your writing does not start coming across as too informal or even unprofessional, and that you still adhere to the overall tone of your chosen journal.
Integrating a narrative structure into your paper is a stylistic choice that can help your reader follow your thought processes and make sense of your overall progression, from forming the hypothesis through to testing that hypothesis. The more you are able to engage your audience using your writing and tools like this, the more they will engage with your work , which is the ultimate goal of publication .
Charlesworth Author Services , a trusted brand supporting the world’s leading academic publishers, institutions and authors since 1928.
To know more about our services, visit: Our Services
Visit our new Researcher Education Portal that offers articles and webinars covering all aspects of your research to publication journey! And sign up for our newsletter on the Portal to stay updated on all essential researcher knowledge and information!
Register now: Researcher Education Portal
Maximise your publication success with Charlesworth Author Services.
Share with your colleagues
Scientific Editing Services
Sign up – stay updated.
We use cookies to offer you a personalized experience. By continuing to use this website, you consent to the use of cookies in accordance with our Cookie Policy.
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Is it okay to discuss personal experiences or observations in literature review?
Is it okay to discuss personal experiences or observations in literature review as long as they are relevant and contribute to the presentation of the summary of literature?
In other words, I am not intending to reference or cite any of my experiences as a source, but rather, I am seeking to use my experiences to essentially add to the research story.
For instance,
The Blah Blah theory by Smith (2010) suggests A, B, and C. I experienced event M and I observed event N, which may potentially be manifestations of the phenomenon described in the Blah Blah theory, with event M being a possible example of A and event N being an example of C.
Something to this extent.
Many of the papers I have read primarily use examples from their studies or hypothetical scenarios to explain models/theories, but I have only ran across personal experience examples in textbooks and not in academic review papers or theses.
- writing-style
- literature-review
- Maybe its just a matter of taste, but I prefer to read articles/thesis that are "streamlined" and not the story with personal experience. (Don't get me wrong, I also enjoy to read stories about research and failed attempts, but not as articles or thesis, but, e.g. as blog post or in popular science books.) – Dirk Commented Mar 28, 2017 at 7:04
- Can you put the personal anecdote in as a footnote or endnote? – trikeprof Commented Mar 29, 2017 at 13:21
Although you didn't quite ask it this way, I see two parts to your question, and I will offer answers accordingly: "Is it okay to discuss personal experiences or observations in academic writing ?" and "Is there any difference when it comes to literature reviews?"
Is it okay to discuss personal experiences or observations in academic writing ?
Although it is controversial (some people will tell you never to include personal experiences), I think there is a place for personal experiences. But first, you need to understand why this is generally frowned on.
Everyone has personal experiences and everyone has different ways to interpret them. Anyone can write a magazine or blog article sharing their personal experiences. That's just their opinion, which the reader could take as good or bad. What separates an academic article from such opinions is that academic writing is usually expected to be fairly objective (tries to take a disinterested third-party perspective) and critical (takes nothing at face value, but tries to dig under the surface to understand what is really going on from multiple non-obvious perspectives). (One notable exception to this is critical social theory, which does not necessarily try to be objective, but nonetheless strongly emphasizes being critical.)
So, where do personal experiences fit in here? Most of the time, they are not objective (by definition) and all too often, they are insufficiently critical. This is why they are often frowned on. However, I believe they could be helpful and acceptable if the writer considers their own personal experiences this way: "What makes my personal experience more outstanding than other random personal experiences related to this phenomenon?" If there is nothing particularly outstanding about it (e.g. it merely serves to illustrate the point, as do other people's experiences), then it is best not to mention it, since such a mention would weaken an otherwise strong academic argument. But if it is unique or original (e.g., the entire study is propelled by the fact that the writer's personal experiences contradict the dominant scholarly discourse), then it is definitely worth mentioning. However, in such cases, the writer should try to describe their experience as objectively as possible and should be critical in not accepting their own interpretations of their experience at face value. When presented properly, such personal experiences can strengthen the credibility of the writer.
Is there any difference when it comes to literature reviews?
I believe the principle I laid out for academic writing in general also applies to literature reviews. However, there are two levels or two aspects to a literature review that you need to distinguish in this case:
Including your personal experiences as part of the "literature" being reviewed: NO. Your personal experiences are not "literature". "Literature" means published works (by "published" I include grey literature such as working papers; I also include non-scholarly practitioner publications). It does not include unpublished, unwritten anecdotes. That is at best to be considered primary research, which is never part of "literature" being reviewed in a literature review. (Don't misunderstand me; you are certainly free to supplement a literature review with original primary research if you want to, but you just have to clearly distinguish that from the "review" part of the article or chapter.)
Including your personal experiences as part of the introduction or discussion of your literature review: In this case, since you are clearly not presenting your own experiences as part of the "literature" being reviewed, then my comments above apply. I see no problem with this if it is done properly. But again, this is controversial; "controversial" means that your supervisor or journal editor might disagree, and so you might have to drop it regardless.
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged writing writing-style literature-review ..
- Featured on Meta
- We've made changes to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy - July 2024
- Announcing a change to the data-dump process
Hot Network Questions
- Why is a datetime value returned that matches the predicate value when using greater than comparison
- Does space dust fall on the roof of my house and if so can I detect it with a cheap home microscope?
- How could ocean liners survive in a major capacity after large jet airliners become common?
- What's wrong with constructions like "Dragons are big, green, and eat people."?
- ebproof: How can I force a big prooftree across the margins of the page?
- Can I add a PCIe card to a motherboard without rebooting, safely?
- What are examples of moral principles in religions that secular ethical systems find hard to accept or justify and why?
- Who checks and balances SCOTUS?
- Pseudo One Time Pad against Computational Unbounded Adversary
- What are the guidelines regarding Mass outside of a Church setting?
- How is clang able to evaluate loops without getting stuck in an infinite loop?
- Land comes in tapped but untapped?
- Lexicographically earliest permutation of the initial segment of nonnegative integers subject to divisibility constraints
- What is the English word for "tableau" in the context of the theatre?
- Replace infinitely many digits of Pi, with the same digit. Is this new number irrational?
- Public flight from Quito (UIO) to Lago Agrio Airport (LGQ)
- Coupon Collector vs. Geometric Distribution: Catching All 150 Pokémon
- Why do many CVT cars appear to index gears during normal automatic operation?
- What is this usage of 回った?
- What role can scrum master have/take when product owners differ from opinion?
- What is the most economical way to fly small planes?
- Groups killed by centralizing one element
- Regression with dummy/control variables added leading to insignificant independent variable
- Running the plot of Final Fantasy X
Research Stories
Research stories share your research in a way that is understandable and interesting to a non-expert, public audience. Unlike a research report, a research story focuses on telling the narrative of your process, the significance of your research to others, and your personal engagement with your research. This handout will help you frame your research in an engaging way.
Story Structure
The overall structure of a research story is slightly different than a general research report. Scientific reports usually summarize a completed research project, which is why they emphasize the methods and results as separate sections. A research story, however, can describe completed research or research that is still in process. As such, the methods and results are briefly described in one section called the research process. Instead, a story format emphasizes the introduction and discussion, where most of your story will take place.
Catchy Introductions
Your introduction should be catchy to establish a story-like tone that can be carried throughout the rest of the document. A good research story introduction establishes the importance and relevance of the topic and gradually incorporates the scientific aspects. The next two examples are from Napoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules that Changed History , which discusses scientific concepts in an engaging, story form.
Consider the opening sentences from Napoleon's Buttons :
In June 1812, Napoleon's army was 600,000 strong. By early December, however, the once proud Grande Armee numbered fewer than 10,000. The tattered remnants of Napoleon's forces had crossed the Berezina River, near Borisov in western Russia, on the long road of retreat from Moscow. —Jay Burreson and Penny Le Couteur, Napoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules that Changed History
You'll notice that the story does not jump into the science immediately. Instead, it uses history to identify the topic's significance and draw the reader in. Two paragraphs later, the authors draw the audience towards the science of the book:
What caused the downfall of the greatest army Napoleon had led? Why did Napoleon's soldiers, victorious in previous battles, falter in the Russian campaign? One of the strangest theories to be advanced can be captured by paraphrasing an old nursery rhyme: "all for the want of a button." Surprising as it may seem, the disintegration of Napoleon's army may be traceable to something as small as the disintegration of a button - a tin button, to be exact, the kind that fastened everything from the greatcoats of Napoleon's officers to the trousers and jackets of his foot soldiers. When temperatures drop, shiny metallic tin starts to change into a crumbly nonmetallic gray powder - still tin, but with a different structural form. —Jay Burreson and Penny Le Couteur, Napoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules that Changed History
Here is an additional example from the first-place winner of the 2015 Science Writing Contest. The author vividly describes a scene that immediately establishes the importance of studying acid rain and draws the reader into their story.
Dead fish. Blistered skin. Statues with their faces grotesquely weathered. For many Americans, these are the images that come to mind when we hear the words "acid rain." Many of us are vaguely aware of the danger of this phenomenon—yet few people fully understand how acid rain forms and why it has such devastating effects. Recently, scientists have found that acid rain is even changing the way microbes interact with their soil environment, altering nutrient cycles and changing ecosystems from the ground up. —Hannah Devens, "Unearthing a Legacy: Acid Rain's Effects on Nutrient Cycles in Forest Ecosystems," 1st Place Winner of the 2015 Science Writing Contest
Research Process
Whether your research has been completed or not, describing your research process makes your topic and hypotheses/conclusions more clear to readers. The process can include the methods you have used or are considering, your results if they have been collected, or the types of results you are hoping to collect based on your methodology or hypotheses.
The following example describes the research process in a story format:
We are using several techniques to test the effects of calcium levels on microbial respiration. To measure the amount of carbon respiration in each sample, we are using a method in which the carbon dioxide emitted from the soil microbes reacts with a solution so we can capture it in solid form. We are also distinguishing between leaf litter and soil organic matter as carbon sources for the microbes by analyzing chemical signatures in the captured solid. More carbon emitted from a sample would indicate that its microbes respired at a higher rate, recycling more rapidly from the organic form. When we compare the amounts of carbon with the amounts of calcium in the soil samples, we hope to see a relationship that will tell us more about how calcium is affecting microbial respiration of organic matter in the soil. —Hannah Devens, "Unearthing a Legacy: Acid Rain's Effects on Nutrient Cycles in Forest Ecosystems," 1st Place Winner of the 2015 Science Writing Contest
The author had not completed their research, but they described their methodology for conducting research, articulating their goals for analysis and the potential results. You can be at any stage of your research as long as you creatively and engagingly tell the story of your research and its significance.
Your discussion, then, can discuss your results (if you have already analyzed your data), or the next steps for your research and the information they might reveal. The discussion should still inform your general audience about the importance of such research (and potential future research).
The following example is a discussion section from a research story:
This experiment has important implications for the future of ecology. Many people believe that acid rain's effects have been largely reversed by the passage of the Clean Air Acts of 1970 and 1990 (Hubbard Brook Research Foundation, 2001). These acts required a reduction in emissions of sulfur dioxide, an important contributor to acid rain. However, nutrients continue to be depleted from soils in the Northeast (such as those tested in the HBEF). While rates of depletion have slowed substantially, results show that acid rain's nutrient leaching abilities have continued decades after such environmental legislation was passed. A legacy of acid deposition has been left in soils because the depletion of calcium and other nutrients from soils has not been reversed even where deposition has been markedly reduced. If we can better pin down the dynamics of nutrient-microbial relationships, we may be one step closer to understanding how to help damaged ecosystems recover from the ravages of acid rain and other human-caused disturbances. —Hannah Devens, "Unearthing a Legacy: Acid Rain's Effects on Nutrient Cycles in Forest Ecosystems," 1st Place Winner of the 2015 Science Writing Contest
The author discusses why we should care about this research, why it matters to us. While the author had not yet finished their experiment, they were still able to discuss the potential implications of their work.
Audience and Tone
A research story is written for a general (rather than scientific) audience, so pay attention to your language choices. Note the differences in language use and audience awareness in the next two examples on acid rain.
The first example is from a scientific article published in the journal Science. The author takes a formal approach in order to appear professional and credible with other specialists in their field. The writer uses terms like "biogeochemistry of sulfur," "nitrogen," and "sulfuric acid" without explanation or context, because their audience is already familiar with these concepts. They also dive right into the problem at hand.
Research on the effects of acid rain in the United States and Europe has focused primarily on the biogeochemistry of sulfur, and to a lesser extent on that of nitrogen. The emphasis was because sulfuric acid is the dominant acid in precipitation throughout the eastern United States and Europe where acid rain is a serious environmental problem. —G.E. Likens, C.T Driscoll, and D.C. Buso, "Long-Term Effects of Acid Rain: Response and Recovery of a Forest Ecosystem" .
The second example is from a research story on acid rain. The author uses first-person "we" to relate to audiences unfamiliar with the topic and uses familiar or creative words to catch readers' interest, such as "business," "noxious," and "spew," while still incorporating the science aspects of "acid rain," "water," "oxygen," and "acidic compounds." This writer begins with background information on her topic by clearly and simply explaining what acid rain is and how it forms.
One of the main contributors to acid rain is a business we can't live without: the fossil fuel industry. The issue begins with the noxious gases that coal-burning power plants spew into the air (Hubbard Brook Research Foundation, 2001). Once in the atmosphere, these emissions interact with water and oxygen to form acidic compounds that eventually fall to the earth as acid rain. —Hannah Devens, "Unearthing a Legacy: Acid Rain's Effects on Nutrient Cycles in Forest Ecosystems," 1st Place Winner of the 2015 Science Writing Contest
As mentioned earlier, you want to establish an engaging tone in the beginning that will last throughout the rest of the story. Tone can have an important effect on your audience's experience with and interpretation of your voice and story. Consider the following types of tone:
- Conversational
The following examples model what different kinds of tone look like; it's up to you to write in a tone that works for the story you are telling.
The excerpt below from a New York Times article on Global Warming adopts a serious and stern tone. The seriousness of death statistics attempts to draw compassion from the audience and persuade them to take a stance on global warming. A stern tone reinforces the seriousness of this issue and its effect on others.
The question is important because while a gradual increase in average temperatures can have profound ecological consequences, it is weather extremes that have the greatest effect on human society. A 1995 heat wave in Chicago killed hundreds of people, and a 2003 heatwave in Europe killed an estimated 70,000. Scientists believe both were made more likely by the human emissions that are warming the planet, and heat on that scale will become commonplace if emissions are allowed to continue unabated. For now, though, such heat extremes — Chicago temperatures were near or above 100 degrees for four days running that July — are still rare, which makes them difficult to study in a statistical sense. —Justin Gillis, "New Study Links Weather Extremes to Global Warming"
For those familiar with Edgar Allen Poe, the next passage establishes an excited yet terrified tone. Phrases such as "I gasped for breath" and "as if excited to fury by the observations of the men" establishes an excitable, frantic tone, while "they were making a mockery of my horror" establishes the feeling of terror.
No doubt I now grew very pale; --but I talked more fluently, and with a heightened voice. Yet the sound increased --and what could I do? It was a low, dull, quick sound --much such a sound as a watch makes when enveloped in cotton. I gasped for breath --and yet the officers heard it not. I talked more quickly --more vehemently; but the noise steadily increased. I arose and argued about trifles, in a high key and with violent gesticulations; but the noise steadily increased. Why would they not be gone? I paced the floor to and fro with heavy strides, as if excited to fury by the observations of the men --but the noise steadily increased. Oh God! what could I do? I foamed --I raved --I swore! I swung the chair upon which I had been sitting, and grated it upon the boards, but the noise arose over all and continually increased. It grew louder --louder --louder! And still the men chatted pleasantly, and smiled. Was it possible they heard not? Almighty God! --no, no! They heard! --they suspected! --they knew! --they were making a mockery of my horror!-this I thought, and this I think. But anything was better than this agony! Anything was more tolerable than this derision! I could bear those hypocritical smiles no longer! I felt that I must scream or die! and now --again! --hark! louder! louder! louder! louder! —Edgar Allen Poe, "The Tell-Tale Heart"
The next piece by Hemingway is sparsely written, so the tone is very calm, reserved, and content. It does not raise alarm; rather, it describes and clearly paints a picture for readers. However, it is not as exciting as the previous example.
It was very late and everyone had left the cafe except an old man who sat in the shadow the leaves of the tree made against the electric light. In the day time the street was dusty, but at night the dew settled the dust and the old man liked to sit late because he was deaf and now at night it was quiet and he felt the difference. The two waiters inside the cafe knew that the old man was a little drunk, and while he was a good client they knew that if he became too drunk he would leave without paying, so they kept watch on him. —Ernest Hemmingway, "A Clean, Well-Lighted Place"
This next example by Dickens also implies a darker, more terrified tone with words such as "evil," "forlorn," "clammy," and "unwholesome."
There was a steaming mist in all the hollows, and it had roamed in its forlornness up the hill, like an evil spirit, seeking rest and finding none. A clammy and intensely cold mist, it made its slow way through the air in ripples that visibly followed and overspread one another, as the waves of an unwholesome sea might do. It was dense enough to shut out everything from the light of the coach-lamps but these its own workings, and a few yards of road; and the reek of the labouring horses steamed into it, as if they had made it all. —Charles Dickens, A Tale of Two Cities
Use Active Voice and Get Personal
Take action in your writing! Don't let "the passive voice be avoided by good writers": let "good writers avoid passive voice." Active voice can help drive your story along and keep your reader intrigued. It can show action being done, progress being made, and the persons contributing to scientific efforts. Here are some examples of how passive voice might be revised in active voice:
My first lab report will always be remembered by me. (passive) I'll always remember my first lab report. (active)
Examination of patients was accomplished by me. (passive) I examined patients. (active)
Here's a way to remember active versus passive voice: if you can insert "by zombies" after the verb, then you're using passive voice. For example:
I was run over by a truck. (You could say "I was run over by zombies" so this sentence is passive.) A truck ran me over. (It would not make sense to say "A truck ran me over by zombies" so this sentence is active.)
501 E. High Street Oxford, OH 45056
- Online: Miami Online
- Main Operator 513-529-1809
- Office of Admission 513-529-2531
- Vine Hotline 513-529-6400
- Emergency Info https://miamioh.edu/emergency
1601 University Blvd. Hamilton, OH 45011
- Online: E-Campus
- Main Operator 513-785-3000
- Office of Admission 513-785-3111
- Campus Status Line 513-785-3077
- Emergency Info https://miamioh.edu/regionals/emergency
4200 N. University Blvd. Middletown, OH 45042
- Main Operator 513-727-3200
- Office of Admission 513-727-3216
- Campus Status 513-727-3477
7847 VOA Park Dr. (Corner of VOA Park Dr. and Cox Rd.) West Chester, OH 45069
- Main Operator 513-895-8862
- From Middletown 513-217-8862
Chateau de Differdange 1, Impasse du Chateau, L-4524 Differdange Grand Duchy of Luxembourg
- Main Operator 011-352-582222-1
- Email [email protected]
- Website https://miamioh.edu/luxembourg
217-222 MacMillan Hall 501 E. Spring St. Oxford, OH 45056, USA
- Main Operator 513-529-8600
Initiatives
- Miami THRIVE Strategic Plan
- Miami Rise Strategic Plan
- Boldly Creative
- Annual Report
- Moon Shot for Equity
- Miami and Ohio
- Majors, Minors, and Programs
- Inclusive Excellence
- Employment Opportunities
- University Safety and Security
- Parking, Directions, and Maps
- Equal Opportunity
- Consumer Information
- Land Acknowledgement
- Privacy Statement
- Title IX Statement
- Report an Accessibility Issue
- Annual Security and Fire Safety Report
- Report a Problem with this Website
- Policy Library
- Have your assignments done by seasoned writers. 24/7
- Contact us:
- +1 (213) 221-0069
- [email protected]

How to Use Personal Experience in Research Paper or Essay

Personal Experience In Research Writing
Personal experience in academic writing involves using things that you know based on your personal encounter to write your research paper.
One should avoid using personal experience to write an academic paper unless instructed to do so. Suppose you do so, then you should never cite yourself on the reference page.

Some instructions may prompt you to write an essay based on personal experience. Such instances may compel you to write from your personal knowledge as an account for your past encounters over the same topic.
Can you Use Personal Experience in an Essay?
In most of the essays and papers that people write, it is highly recommended that one avoids the use of first-person language. In our guide to writing good essays , we explained that the third person is preferred for academic work.
However, it can be used when doing personal stories or experiences. But can is it possible?

In practice, you can use personal experience in an essay if it is a personal narrative essay or it adds value to the paper by supporting the arguments.
Also, you can use your personal experience to write your academic paper as long as you are writing anything that is relevant to your research.
The only harm about such an essay is that your experience might sound biased because you will be only covering one side of the story based on your perception of the subject.
Students can use the personal story well through a catchy introduction.
Inquire from the instructor to offer you more directions about the topic. However, write something that you can remember as long as you have rich facts about it.
People Also Read: Can Research Paper be Argumentative: How to write research arguments
How to Use Personal Experience in a Research Paper
When you are crafting your easy using your personal experience, ensure you use the first-person narrative. Such a story includes the experiences you had with books, situations, and people.
For you to write such a story well, you should find a great topic. That includes thinking of the events in your life encounters that can make a great story.
Furthermore, you should think of an event that ever happened to you. Besides, you can think of special experiences you had with friends, and how the encounter changed your relationship with that specific person.
The right personal experience essay uses emotions to connect with the reader. Such an approach provokes the empathic response. Most significantly, you can use sensory details when describing scenes to connect with your readers well.
Even better, use vivid details and imagery to promote specificity and enhance the picture of the story you are narrating.

Structure of the Essay

Before you begin to write, brainstorm and jot down a few notes. Develop an outline to create the direction of the essay story.
Like other essays, you should use the introduction, the body, and a conclusion. Let your introduction paragraph capture the reader’s attention.
In other words, it should be dramatic. Your essay should allow the audience to know the essence of your point of view.
Let the body of this essay inform the reader with clear pictures of what occurred and how you felt about it.
Let the story flow chronologically or group the facts according to their importance. Use the final paragraph to wrap up and state the key highlights of the story.
Make it Engaging
The right narrative needs one to use interesting information engagingly. Record yourself narrating the story to assist you in organizing the story engagingly. Furthermore, you are free to use dialogue or anecdotes. For that reason, think about what other people within your story said.
Moreover, you should use transition words for better sentence connections. Again, you should vary the sentence structures to make them more interesting. Make the words as lively and as descriptive as possible.
People Also Read: Can Research Paper Use Bullet Points: when & How to Use them
The Value of Personal Experience
We use personal experience to connect your artwork with your readers since they are human and they would prefer real stories. You will become more realistic when you describe emotions, feelings, and events that happened to you.
Your wealth of personal experience in a specific field will offer you a great advantage when you want to connect all the facts into a useful story.
People Also Read: What is a Background in an Essay: Introducing Information
Reinforcing your Writing Skills
Some students may have brilliant ideas and fail to capture them on paper properly. Some seek to write personal issues but also want to remove first-person language from their writing. This is not good.
However, you can sharpen your writing skills in this aspect. One can use the following tips to make your personal research paper readable and more appealing:

1. Sharpen grammar
The readability and clarity of your content will rely on grammar.
For that reason, you should polish your spelling, grammar skills, and punctuation daily.
Moreover, you should practice regularly and make the essay more appealing.
2. Expand Vocabulary
It can be helpful if you expand your vocabulary to describe your events successfully. Using better word choice enable the writer to connect with the topic well.
3. Have a Diary
Having a personal diary helps you by boosting your memory about past memorable events. That ensures that you do not lose hold of something important that happened in your past encounter.
4. Systematize it
Make your narration appear systematic to improve the flow. For example, you can divide your experiences in particular importance, emotions, events, people, and so on.
5. Interpret your feelings
It is not a walkover for one to remember every feeling he or she encountered when particular events happened. One should try to analyze and interpret them for better and more effective delivery when writing about personal experiences.
Can you Cite yourself or Personal Experience?

You cannot cite yourself or reference your personal experience because it is your own narration and not data, facts, or external information. Ideally, one does not need to cite personal experiences when using any writing style whether APA or MLA.
It will be unprofessional if you cite yourself in your research paper. Such an experience is your voice which you are bringing to the paper.
Choose the relevant essay based on your essay.
People Also Read: Best Research Paper Font and Size: Best Styles for an Essay
Instances when to use Personal Experience in a Research Paper
There are many instances when you have to apply personal narrations in an essay. In these instances, the use of first language is important. Let us explore them.
1. Personal essays
You can use personal essays in academic writing to engage readers. It makes your writing to be credible and authentic because you will be engaging readers with your writing voice. Some stories are better told when given from personal encounters.
The secret lies in choosing the most relevant topic that is exciting and triggers the right emotions and keeps your audience glued to it. You can include some dialogue to make it more engaging and interesting.
2. Required by the instructions
Some situations may prompt your professor to offer students instructions that compel them to write a research paper based on a personal encounter. Here, you have to follow the instructions to the latter for you to deliver and earn a good score well.
One way of winning the heart of your professor is to stick to the given instructions. You should relate your past events with the topic at hand and use it to connect with your readers in an engaging manner.
3. Personal Research Report
When you are doing research that involves your personal encounter, you will have to capture those events that can reveal the theme of your topic well.
Of course, it is an account of your perception concerning what you went through to shape your new understanding of the event.
A personal research report cannot be about someone’s also experience. It states the details of what you encountered while handling the most memorable situations.
4. Ethnography Reports
Such a report is qualitative research where you will immerse yourself in the organization or community and observe their interactions and behavior. The narrator of the story must use his perception to account for particular issues that he may be tackling in the essay.
Ethnography helps the author to give first-hand information about the interactions and behavior of the people in a specific culture.
When you immerse yourself in a particular social environment, you will have more access to the right and authentic information you may fail to get by simply asking.
We use ethnography as a flexible and open method to offer a rich narrative and account for a specific culture. As a researcher, you have to look for facts in that particular community in various settings.

When not handling complex essays and academic writing tasks, Josh is busy advising students on how to pass assignments. In spare time, he loves playing football or walking with his dog around the park.
Related posts

Titles for Essay about Yourself
Good Titles for Essays about yourself: 31 Personal Essay Topics

How to Write a Diagnostic Essay
How to Write a Diagnostic Essay: Meaning and Topics Example

How Scantron Detects Cheating
Scantron Cheating: How it Detects Cheating and Tricks Students Use
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Applying to graduate school
- How to Write Your Personal Statement | Strategies & Examples
How to Write Your Personal Statement | Strategies & Examples
Published on February 12, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on July 3, 2023.
A personal statement is a short essay of around 500–1,000 words, in which you tell a compelling story about who you are, what drives you, and why you’re applying.
To write a successful personal statement for a graduate school application , don’t just summarize your experience; instead, craft a focused narrative in your own voice. Aim to demonstrate three things:
- Your personality: what are your interests, values, and motivations?
- Your talents: what can you bring to the program?
- Your goals: what do you hope the program will do for you?
This article guides you through some winning strategies to build a strong, well-structured personal statement for a master’s or PhD application. You can download the full examples below.
Urban Planning Psychology History
Table of contents
Getting started with your personal statement, the introduction: start with an attention-grabbing opening, the main body: craft your narrative, the conclusion: look ahead, revising, editing, and proofreading your personal statement, frequently asked questions, other interesting articles.
Before you start writing, the first step is to understand exactly what’s expected of you. If the application gives you a question or prompt for your personal statement, the most important thing is to respond to it directly.
For example, you might be asked to focus on the development of your personal identity; challenges you have faced in your life; or your career motivations. This will shape your focus and emphasis—but you still need to find your own unique approach to answering it.
There’s no universal template for a personal statement; it’s your chance to be creative and let your own voice shine through. But there are strategies you can use to build a compelling, well-structured story.
The first paragraph of your personal statement should set the tone and lead smoothly into the story you want to tell.
Strategy 1: Open with a concrete scene
An effective way to catch the reader’s attention is to set up a scene that illustrates something about your character and interests. If you’re stuck, try thinking about:
- A personal experience that changed your perspective
- A story from your family’s history
- A memorable teacher or learning experience
- An unusual or unexpected encounter
To write an effective scene, try to go beyond straightforward description; start with an intriguing sentence that pulls the reader in, and give concrete details to create a convincing atmosphere.
Strategy 2: Open with your motivations
To emphasize your enthusiasm and commitment, you can start by explaining your interest in the subject you want to study or the career path you want to follow.
Just stating that it interests you isn’t enough: first, you need to figure out why you’re interested in this field:
- Is it a longstanding passion or a recent discovery?
- Does it come naturally or have you had to work hard at it?
- How does it fit into the rest of your life?
- What do you think it contributes to society?
Tips for the introduction
- Don’t start on a cliche: avoid phrases like “Ever since I was a child…” or “For as long as I can remember…”
- Do save the introduction for last. If you’re struggling to come up with a strong opening, leave it aside, and note down any interesting ideas that occur to you as you write the rest of the personal statement.
Once you’ve set up the main themes of your personal statement, you’ll delve into more detail about your experiences and motivations.
To structure the body of your personal statement, there are various strategies you can use.
Strategy 1: Describe your development over time
One of the simplest strategies is to give a chronological overview of key experiences that have led you to apply for graduate school.
- What first sparked your interest in the field?
- Which classes, assignments, classmates, internships, or other activities helped you develop your knowledge and skills?
- Where do you want to go next? How does this program fit into your future plans?
Don’t try to include absolutely everything you’ve done—pick out highlights that are relevant to your application. Aim to craft a compelling narrative that shows how you’ve changed and actively developed yourself.
My interest in psychology was first sparked early in my high school career. Though somewhat scientifically inclined, I found that what interested me most was not the equations we learned about in physics and chemistry, but the motivations and perceptions of my fellow students, and the subtle social dynamics that I observed inside and outside the classroom. I wanted to learn how our identities, beliefs, and behaviours are shaped through our interactions with others, so I decided to major in Social Psychology. My undergraduate studies deepened my understanding of, and fascination with, the interplay between an individual mind and its social context.During my studies, I acquired a solid foundation of knowledge about concepts like social influence and group dynamics, but I also took classes on various topics not strictly related to my major. I was particularly interested in how other fields intersect with psychology—the classes I took on media studies, biology, and literature all enhanced my understanding of psychological concepts by providing different lenses through which to look at the issues involved.
Strategy 2: Own your challenges and obstacles
If your path to graduate school hasn’t been easy or straightforward, you can turn this into a strength, and structure your personal statement as a story of overcoming obstacles.
- Is your social, cultural or economic background underrepresented in the field? Show how your experiences will contribute a unique perspective.
- Do you have gaps in your resume or lower-than-ideal grades? Explain the challenges you faced and how you dealt with them.
Don’t focus too heavily on negatives, but use them to highlight your positive qualities. Resilience, resourcefulness and perseverance make you a promising graduate school candidate.
Growing up working class, urban decay becomes depressingly familiar. The sight of a row of abandoned houses does not surprise me, but it continues to bother me. Since high school, I have been determined to pursue a career in urban planning. While people of my background experience the consequences of urban planning decisions first-hand, we are underrepresented in the field itself. Ironically, given my motivation, my economic background has made my studies challenging. I was fortunate enough to be awarded a scholarship for my undergraduate studies, but after graduation I took jobs in unrelated fields to help support my parents. In the three years since, I have not lost my ambition. Now I am keen to resume my studies, and I believe I can bring an invaluable perspective to the table: that of the people most impacted by the decisions of urban planners.
Strategy 3: Demonstrate your knowledge of the field
Especially if you’re applying for a PhD or another research-focused program, it’s a good idea to show your familiarity with the subject and the department. Your personal statement can focus on the area you want to specialize in and reflect on why it matters to you.
- Reflect on the topics or themes that you’ve focused on in your studies. What draws you to them?
- Discuss any academic achievements, influential teachers, or other highlights of your education.
- Talk about the questions you’d like to explore in your research and why you think they’re important.
The personal statement isn’t a research proposal , so don’t go overboard on detail—but it’s a great opportunity to show your enthusiasm for the field and your capacity for original thinking.
In applying for this research program, my intention is to build on the multidisciplinary approach I have taken in my studies so far, combining knowledge from disparate fields of study to better understand psychological concepts and issues. The Media Psychology program stands out to me as the perfect environment for this kind of research, given its researchers’ openness to collaboration across diverse fields. I am impressed by the department’s innovative interdisciplinary projects that focus on the shifting landscape of media and technology, and I hope that my own work can follow a similarly trailblazing approach. More specifically, I want to develop my understanding of the intersection of psychology and media studies, and explore how media psychology theories and methods might be applied to neurodivergent minds. I am interested not only in media psychology but also in psychological disorders, and how the two interact. This is something I touched on during my undergraduate studies and that I’m excited to delve into further.
Strategy 4: Discuss your professional ambitions
Especially if you’re applying for a more professionally-oriented program (such as an MBA), it’s a good idea to focus on concrete goals and how the program will help you achieve them.
- If your career is just getting started, show how your character is suited to the field, and explain how graduate school will help you develop your talents.
- If you have already worked in the profession, show what you’ve achieved so far, and explain how the program will allow you to take the next step.
- If you are planning a career change, explain what has driven this decision and how your existing experience will help you succeed.
Don’t just state the position you want to achieve. You should demonstrate that you’ve put plenty of thought into your career plans and show why you’re well-suited to this profession.
One thing that fascinated me about the field during my undergraduate studies was the sheer number of different elements whose interactions constitute a person’s experience of an urban environment. Any number of factors could transform the scene I described at the beginning: What if there were no bus route? Better community outreach in the neighborhood? Worse law enforcement? More or fewer jobs available in the area? Some of these factors are out of the hands of an urban planner, but without taking them all into consideration, the planner has an incomplete picture of their task. Through further study I hope to develop my understanding of how these disparate elements combine and interact to create the urban environment. I am interested in the social, psychological and political effects our surroundings have on our lives. My studies will allow me to work on projects directly affecting the kinds of working-class urban communities I know well. I believe I can bring my own experiences, as well as my education, to bear upon the problem of improving infrastructure and quality of life in these communities.
Tips for the main body
- Don’t rehash your resume by trying to summarize everything you’ve done so far; the personal statement isn’t about listing your academic or professional experience, but about reflecting, evaluating, and relating it to broader themes.
- Do make your statements into stories: Instead of saying you’re hard-working and self-motivated, write about your internship where you took the initiative to start a new project. Instead of saying you’ve always loved reading, reflect on a novel or poem that changed your perspective.
Your conclusion should bring the focus back to the program and what you hope to get out of it, whether that’s developing practical skills, exploring intellectual questions, or both.
Emphasize the fit with your specific interests, showing why this program would be the best way to achieve your aims.
Strategy 1: What do you want to know?
If you’re applying for a more academic or research-focused program, end on a note of curiosity: what do you hope to learn, and why do you think this is the best place to learn it?
If there are specific classes or faculty members that you’re excited to learn from, this is the place to express your enthusiasm.
Strategy 2: What do you want to do?
If you’re applying for a program that focuses more on professional training, your conclusion can look to your career aspirations: what role do you want to play in society, and why is this program the best choice to help you get there?
Tips for the conclusion
- Don’t summarize what you’ve already said. You have limited space in a personal statement, so use it wisely!
- Do think bigger than yourself: try to express how your individual aspirations relate to your local community, your academic field, or society more broadly. It’s not just about what you’ll get out of graduate school, but about what you’ll be able to give back.
You’ll be expected to do a lot of writing in graduate school, so make a good first impression: leave yourself plenty of time to revise and polish the text.
Your style doesn’t have to be as formal as other kinds of academic writing, but it should be clear, direct and coherent. Make sure that each paragraph flows smoothly from the last, using topic sentences and transitions to create clear connections between each part.
Don’t be afraid to rewrite and restructure as much as necessary. Since you have a lot of freedom in the structure of a personal statement, you can experiment and move information around to see what works best.
Finally, it’s essential to carefully proofread your personal statement and fix any language errors. Before you submit your application, consider investing in professional personal statement editing . For $150, you have the peace of mind that your personal statement is grammatically correct, strong in term of your arguments, and free of awkward mistakes.
A statement of purpose is usually more formal, focusing on your academic or professional goals. It shouldn’t include anything that isn’t directly relevant to the application.
A personal statement can often be more creative. It might tell a story that isn’t directly related to the application, but that shows something about your personality, values, and motivations.
However, both types of document have the same overall goal: to demonstrate your potential as a graduate student and s how why you’re a great match for the program.
The typical length of a personal statement for graduate school applications is between 500 and 1,000 words.
Different programs have different requirements, so always check if there’s a minimum or maximum length and stick to the guidelines. If there is no recommended word count, aim for no more than 1-2 pages.
If you’re applying to multiple graduate school programs, you should tailor your personal statement to each application.
Some applications provide a prompt or question. In this case, you might have to write a new personal statement from scratch: the most important task is to respond to what you have been asked.
If there’s no prompt or guidelines, you can re-use the same idea for your personal statement – but change the details wherever relevant, making sure to emphasize why you’re applying to this specific program.
If the application also includes other essays, such as a statement of purpose , you might have to revise your personal statement to avoid repeating the same information.
If you want to know more about college essays , academic writing , and AI tools , make sure to check out some of our other language articles with explanations, examples, and quizzes.
College essays
- College essay examples
- College essay format
- College essay style
- College essay length
- Diversity essays
- Scholarship essays
Academic writing
- Writing process
- Avoiding repetition
- Literature review
- Conceptual framework
- Dissertation outline
- Thesis acknowledgements
- Burned or burnt
- Canceled or cancelled
- Dreamt or dreamed
- Gray or grey
- Theater vs theatre
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, July 03). How to Write Your Personal Statement | Strategies & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 5, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/graduate-school/personal-statement/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a graduate school resume | template & example, how (and who) to ask for a letter of recommendation, master's vs phd | a complete guide to the differences, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- Have your assignments done by seasoned writers. 24/7. Contact us:
- +1 (213) 221-0069
- [email protected]

Can a Research Paper have Personal Experience or Narrative

_Personal Experience in essays
A research paper is a type of academic writing that has a comprehensive analysis, inquiries, and argument of a different research that is independent. Even though the paper has similarities with academic essays, it entails detailed assignments and is usually longer.
Through a research paper, lecturers are able to know the learner’s writing skills and their level of scholarly research. As a student, you ought to show a strong knowledge of the topic given. In addition, analyze all available sources, then put your own contribution to the discussion of the topic.

For a research paper to be complete, writers must understand the topic by analyzing the assignment sheet. If there is any confusion, seek clarification from the lecturer to know more about the assignment’s goal, the formatting specifications, the deadline, and how to submit it.
Can a Research Paper Have Personal Experience?
A personal experience can be included in your research paper as long as it is relevant to the research topic you are working on.
The main goal is to ensure that the reader will connect to an event of your own life experience. In this case, putting a personal experience into a research paper requires the use of descriptive language.

Including personal experience is beneficial to both the reader and the writer. For instance, the writer feels more confident and will better understand the paper.
As a writer, the experience you include will also create a stronger connection with the writing.
On the other hand, the experience in a research paper will make the reader have an exciting time and enjoy going through your work. He or she will view your research paper from an insider perspective.
As usual, a lecturer can find it boring to read dry theories with no sense of humour. By adding a personal experience, you spice up the monotony of the paper.
The concrete life examples you include in your paper as personal experiences can engage the reader and make your piece more interesting to reward.
You will have more confidence when writing a personal experience in a research paper. This is because you are writing down an issue you know or are going on in your life. It will be easier to get support and backup because you are writing about something you experienced.
It could be an event you noticed or past practices that have taken place in your workplace.
When is Personal Experience Needed in Essay Writing
As a student, you will face paper writing cases that will specifically require you to include your own opinions, ideas, and real-life experiences. Personal experience is necessary in the research process.
Use personal experience if you are dealing with an assignment that has precisely asked for the reflection. If there is a situation that will need you to exemplify a particular theory, a personal experience will make the writing have a perfect flow.
These are some of the appropriate instances and places in your paper that will need personal experience.
Writing a Personal Essay

In order to effectively integrate your personal experience in your paper, always use the first-person point of view. This will help to connect with the reader directly.
In this way, your paper will be void of passive voice.
Also, you will avoid the chances of referring to yourself in a third-person perspective which can confuse the reader.
It is important to note that writing in the first-person language is not necessarily inappropriate if it is not opinionated or biased.
All you are required to do is stay on point and focus on experiences that are related to the assignment given.
Students are advised not to be too excited or get carried away about writing a personal experience so they do not go off-topic.
You can end up sharing more experiences than what was required in the assignment.
When it comes to the voice, be very objective and formal. A non-judgmental voice is very appropriate for a personal experience in a research paper.
Be formal and speak directly to the reader. Similarly, avoid sounding emotional even when giving an experience that may have bad memories or is affecting your life.
When writing a personal experience, it is also essential to remain open. You can consult different sources and viewpoints concerning your topic but make sure that your tone remains neutral.
How to Include a Personal Experience in a Research Paper
Primarily, it is important to choose a good personal topic that goes in line with the assignment you have been given.
Try to recall events in your life that can make a great story that depicts the research paper topic you have in hand. You can think of something you learned or a past event that happened to you.
Also, remind yourself of your special experiences with family members or friends.
The use of a personal story helps to draw the reader to the ideas you have included in the paper.

After ultimately finishing your personal experience story, citing is not necessary in your reference page.
This will make your work easier because even in-text citation in the article body is not necessary.
The experience you include is a life involvement and part of your voice and therefore does not need any citation.
You simply have to come up with your own experience; hence research or a source is unnecessary.
Below are brainstorming ideas you can use to come up with a good personal experience for your research paper:
- A past moment in the office or home when you were embarrassed.
- A major event that was small but very significant and life-changing.
- The sudden end of past relationships or events.
- A perfect relationship experience with a close person such as a parent, grandparents, or even friends.
- An encounter with a person who changed your life.
- The beginning of something new in your life
Instances When to Avoid Personal Narrative
Personal experience should not be used as evidence in your argument.
Curriculum theorists and even renowned researchers will not hesitate to give low grades on a paper that has personal experience used as evidence. All in all, that is the only area where using your own experience is discouraged in research writing.
Your personal feelings, beliefs, and experience can boost a student’s involvement in learning and have a better understanding of the subject matter.
The numerous advantages of including a personal experience in a research paper cannot be ignored. Your research paper will be accepted as long as you have followed all the guidelines provided.
Stylistic and linguistic grounds are among the reasons that can cause your paper to be rejected. A well-expressed personal experience, when put in a competently researched paper, will boost the chances of your manuscript being accepted for publication.
Students invest a lot of money, time, and effort in doing research, and it can be traumatizing and quite discouraging to have your paper rejected. As a student, writing a perfect research paper may be difficult, especially if you are doing it for the first time.
Revise your final research paper and ensure you choose the correct topic for a personal story. In this way, you will be able to create a good impression on your lecturer and boost your chances of earning higher grades.
Top-notch study papers portray a vivid picture of significant personal experiences that can move the reader and make the research paper more interesting.

James Lotta
Related posts.

How Edgenuity Checks for Plagiarism
Edgenuity Cheating: Detecting Cheating, Plagiarism and Tabs

Do Colleges Share Essays
Do Colleges Share Essays: Can I Reuse for New Applications

Passing ISSA Final Exam
Issa Final Exam Cheat Sheet: Tips to Study and Pass Issa
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Start a Personal Narrative
Last Updated: October 4, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Grant Faulkner, MA . Grant Faulkner is the Executive Director of National Novel Writing Month (NaNoWriMo) and the co-founder of 100 Word Story, a literary magazine. Grant has published two books on writing and has been published in The New York Times and Writer’s Digest. He co-hosts Write-minded, a weekly podcast on writing and publishing, and has a M.A. in Creative Writing from San Francisco State University. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 111,395 times.
A personal narrative also called a personal essay, should engagingly tell a personal story. You may be writing a personal narrative for a college application, for a class, or your enjoyment. A good personal narrative will entertain the reader and offer insight into an idea or theme. To get started on a personal narrative, choose a story idea, and structure the essay so you know where you’re headed. Then, craft a strong opening for the narrative to draw your reader in.
Choosing a Story Idea for the Narrative

- Choose an event that feels full of meaning and significance to you personally. These events usually make the best story ideas for a personal narrative.
- For example, if your narrative focuses on your intended career path as a teacher, you could write a narrative about how a youth coaching experience showed you the importance of making a positive impact on children.
- Alternatively, if you’re writing about how you came to choose a college major in medical science, your narrative could focus on a wonderful volunteer experience you had as a child that made you want to help other people.

- For instance, you may pick an experience where you lost an important match, only to learn the value of failing and do better. Or you may choose an experience where you made a moral decision to help someone, which then leads to positive outcomes for you and the person.

- For example, you may choose a theme like love and use it to explore your experience of love growing up in a family with two fathers. Or you may choose a theme like freedom and use to explore your struggles with freedom as a refugee.
Structuring the Narrative

- You may need to use a mixture of tenses throughout the narrative. For instance, the answer to the prompt or the narrative you discuss may be written in the present tense, while an anecdote or narration of a story may be written in the past tense, as it has already happened.

- The thesis statement in a narrative essay can explore the events of the story in a brief way. Or it can tell the reader about the moral or lesson learned through the personal experience. You can also present the main theme in the essay in the thesis statement.
- For example, if you are writing an essay about your personal experience as a refugee, you may have a thesis statement that presents the theme of freedom. You may write, “My journey is just one of many. We all came to a new country carrying nothing more than hope and memories of the past.”

- For example, you may have three supporting body paragraphs where you tell your narrative based on the theme of your essay. You may start with your experience of “freedom” in your home country in the first paragraph, followed by your experience of the same theme in your new country in the second paragraph.

- For example, you may end the essay by stating the lesson or moral you learned from the personal experience. Or you may note how the experience has positively affected your life now.
Creating a Strong Opening for the Narrative

- The hook is usually not longer than 1 to 2 sentences. It starts your introductory paragraph and can take the form of a scene, question, interesting fact or statement, or even an anecdote.

- For example, you may wish, “I huddled under my Disney Princess bed cover as my father banged on my bedroom door. As I listened to his muffled screams, I wondered if it was possible to simply disappear, away from my lonely home life and my failing high school grades.”

- For example, you may start with a question like, “Have you ever wondered how it might feel to leave your home forever?” or “Have you ever felt like a stranger in your own country?”

- For example, you may start with an interesting fact about lawnmowers if your narrative is about how mowing lawns as a kid taught you the value of hard work. Or you may choose a funny statement about winning and losing if your essay is about learning how to accept failure.

- For example, if you are writing about learning how to accept failure, you may start with an anecdote about your father telling you not to lose a softball game as a kid.
- Or if you are writing about your personal experiences as a refugee, you may use an anecdote on a moment of acceptance you experienced in your new country.
Expert Q&A

- Don’t forget to revise your essay and make any necessary changes! Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://grammar.yourdictionary.com/grammar-rules-and-tips/tips-for-writing-a-personal-narrative-essay.html
- ↑ https://www.kibin.com/essay-writing-blog/how-to-start-a-narrative-essay/
- ↑ Grant Faulkner, MA. Professional Writer. Expert Interview. 8 January 2019.
- ↑ http://www.artsyqr.com/crafting-a-personal-narrative-essay-starting-out/
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Leona Holder
Aug 11, 2020
Did this article help you?
Jovie Simpkins
May 19, 2020
Brandi McWhirter
Jul 29, 2020
Braden Kramer
Sep 12, 2020
Alissia Ramey
Jan 18, 2021

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
- Page Content
- Sidebar Content
- Main Navigation
- Quick links
- All TIP Sheets
- Writing a Summary
- Writing Paragraphs
- Writing an Analogy
- Writing a Descriptive Essay
- Writing a Persuasive Essay
- Writing a Compare/Contrast Paper
- Writing Cause and Effect Papers
- Writing a Process Paper
- Writing a Classification Paper
- Definitions of Writing Terms
- How to Write Clearly
- Active and Passive Voice
- Developing a Thesis and Supporting Arguments
Writing Introductions & Conclusions
- How to Structure an Essay: Avoiding Six Weaknesses in Papers
- Writing Book Reports
- Writing about Literature
- Writing about Non-Fiction Books
- Poetry: Meter and Related Topics
- Revising and Editing
- Proofreading
TIP Sheet WRITING INTRODUCTIONS & CONCLUSIONS
Even when you know everything about your paper's topic, it's hard to know how to create a "hook" that makes a reader want to read it. And how in the world do you end satisfactorily? The fact is that many of us anguish over our intros and conclusions. The problem of introductions and conclusions is really one problem. They are linked, not only in anguish but in content; they are almost mirror images of each other.
First, however, there are two common misconceptions to dispel. Your thesis is not an introduction. An introductory paragraph starts with a "hook," which leads into the thesis. You do need an introduction as well as a thesis. Second, a simple restatement of your thesis is not a conclusion. To create that satisfying sense of finality in your conclusion, you must revisit the stuff of your introduction. If you start with a story, return to the story. If you start with a definition, return to the definition, even if only to contradict it.
From the TIP Sheet "How to Start (and Complete) a Research Paper," you already know to start writing your paper in the middle, with the thesis statement and body. When you are ready to finish with the introduction and conclusion, choose from several strategies:
- Illustrate : Show instead of tell.
- Challenge : Raise reader expectations.
- Quote : Make use of the wordsmiths.
- Compare/contrast: Evoke familiarity by comparing or create tension and expectation by contrasting.
- Define : Define-or redefine in a unique way.
- Make a provocative statement : Offer an amazing statistic or personal insight.
Illustrate An illustration can be as simple as a personal story or anecdote . It's natural to think of a personal anecdote as an introduction to a personal narrative, but stories and anecdotes can be effective introductions to any kind of paper. The following anecdote introduces a research paper on vegetarian and vegan diets. The conclusion returns briefly to the story:
Introduction: We took our sons fishing in the spillway next to the dam one moonlit night. In the hush of the night, one of them hooked a small trout. But when the landed fish screamed aloud, my son fled the scene in horror and has never eaten flesh since.
Conclusion: People adopt vegetarian and vegan diets for different reasons, not all of them out of horror, as my son did. Whatever their reasons, they are finding more options in grocery stores, restaurants, and cookbooks than ever before.
An example taken from local or world news events is another kind of illustration. This is the introduction and conclusion to a paper on urban growth problems in California:
Introduction: The Chico city council recently approved six hundred new homes to go in on the east side of the city. The impacts this development will have are likely to be extreme, illustrating the problems all California cities face in managing growth.
Conclusion: How well Chico will cope with the increased traffic, pressure on schools, and impacts to the watershed is yet to be seen. But Chico is not alone in having to find solutions soon.
A composite illustration is a fiction that you create in order to make a point. (Composite means including a bit of this and a bit of that.) The advantage of a composite illustration is that it can be perfectly crafted to fit your point. A composite can illustrate extreme examples that are possible though not likely ("Suppose that..."), or distant consequences that are possible but not yet observed.
An analogy is an extended comparison between one thing and another (the development of a balanced state budget compared with a shopping list, perhaps). If you come up with an apt analogy, it can be very effective; however, a so-so analogy is better abandoned sooner than later. You are better off with a good story than with a mediocre analogy. For more on analogies, see the TIP Sheet, "Writing an Analogy."
Challenge A challenge raises reader expectations and creates tension. A challenging opening statement is effective for a thesis that calls for changes to be made in public policies or personal actions, such as in persuasive essays and argument or analysis papers:
Introduction Chances are, if you live outside city limits in any of California's twenty-one rural counties, you couldn't use public transportation if you wanted to. There isn't any.
Conclusion: Sure, Californians need to get over their love affairs with their cars, but having a better system of public transportation in place would help. Then, perhaps, I could get from rural Durham to rural Oroville, where I live, without putting yet another car on the road.
A question is another type of challenge:
Introduction: Does it make sense to prohibit minors from carrying calamine lotion with them at school without two kinds of written permission, and yet allow them to leave campus without parental knowledge or consent for invasive medical procedures?
Conclusion: Even more than many of the zero-tolerance laws in place in our schools, this one should be ditched. Does it make sense? Clearly it doesn't.
Note that a question is an introductory strategy , not a thesis statement. A thesis statement should answer the question, and in some detail-not just "yes" or "no."
Quote Make good use of the wordsmiths of history. Online quotation banks, usually searchable by topic, are a great source for quotations on practically any subject. You have some latitude in how you choose a quote for an introduction; it can be offbeat or unexpected. In the following example, an unusual quote by Albert Einstein is used to introduce an essay on restricting cell phone use while driving:
Introduction: Albert Einstein once said, "Any man who can drive safely while kissing a pretty girl is simply not giving the kiss the attention it deserves."
Conclusion: It doesn't take an Einstein to realize that cell phones are not the first, nor will they be the last, driving distraction. We don't need more restrictions on cell phones; we just need better drivers.
Song lyrics or familiar sayings sometimes make good introductions, but avoid clichés such as "Haste makes waste." If a familiar saying draws on jargon or sayings familiar only to a particular group, you have to provide the context for those who are unfamiliar with that group:
Introduction: Computer programmers have a saying: "Garbage in, garbage out."
Conclusion: The next time you read the results of the latest poll, consider the polling method, the sample, and the source, and remember, "Garbage in, garbage out."
Compare or contrast Comparison shows similarities and creates a sense of familiarity. Contrast shows differences and creates tension and expectation. You do not have to be writing a compare/contrast paper to use this as an introduction strategy. For example, this is a contrast intro to a personal narrative:
Introduction: When I was seven, I thought my father was all-powerful and could do no wrong. When I was seventeen, I thought he was a jerk.
Conclusion: My father wasn't the god he seemed when I was seven, but he was sure a lot better and wiser than I thought he was when I was seventeen.
Define A definition can make a good introduction. You don't have to be writing a definition paper to use definition as an introduction strategy. You can use a standard dictionary if you want, but consider using books of quotations or online quotation banks for more interesting definitions:
Introduction: Here is how Ambrose Bierce defines a conservative: " Conservative. noun. A statesman who is enamored of existing evils, as distinguished from a liberal, who wishes to replace them with others. "
Conclusion: In the matter of agricultural subsidies, we are better off sticking with existing evils than replacing them with others that promise far worse results.
Another interesting use of definition is to use it as a starting point to re-define something in your own terms:
Introduction: Webster says friendship is mutual feelings of trust, affection, assistance, and approval between people. However, I say friendship sometimes is knowing when to walk away.
Conclusion: Walking away that day was the biggest favor Mai ever did for me.
Make a provocative or startling statement If the provocative statement is someone else's, treat it as a quotation. If the provocative statement is statistical , make sure you cite the source. If you have a way with words or an insight all your own, by all means use that:
Introduction: It is ridiculous and immoral to allow congressmen to give themselves pay raises.
Conclusion: Restricting the ability of congressmen to vote themselves raises would go a long way to restoring morality and a sense of public service to public servants.
As you can see, introductions and conclusions are closely linked. Once you decide on a strategy, try simply over-writing the introduction (as one student we know regularly did) and then split off part of it to use as the conclusion. When you begin to think of introductions and conclusions as two pieces of a single puzzle, you will probably find them much easier to write.
Home | Calendars | Library | Bookstore | Directory | Apply Now | Search for Classes | Register | Online Classes | MyBC Portal MyBC -->
Butte College | 3536 Butte Campus Drive, Oroville CA 95965 | General Information (530) 895-2511
How can I use my own personal experiences as a reference in my research paper?
It is very tempting to want to use things that we know based on our own personal experiences in a research paper. However, unless we are considered to be recognized experts on the subject, it is unwise to use our personal experiences as evidence in a research paper. It is better to find outside evidence to support what we know to be true or have personally experienced.
If it is not possible to find outside evidence, then you will have to construct your paper in such a way as to show your reader that you are an expert on the topic. You would need to lay out your credentials for the reader so that the reader will be able to trust the undocumented evidence that you are providing. This can be risky and is not recommended for research based papers. But even if you do use your own experiences, you would not add yourself to your References page.
Sometimes you will be assigned to write a paper that is based on your experiences or on your reaction to a piece of writing, in these instances it would be appropriate to write about yourself and your personal knowledge. However, you would still never cite yourself as a source on your References page.
For assistance with APA citations, visit the APA Help guide.
Thank you for using ASK US. For further assistance, please contact your Baker librarians .
- Last Updated Oct 26, 2021
- Views 54066
- Answered By Baker Librarians
FAQ Actions
- Share on Facebook
Comments (0)
We'll answer you within 3 hours m - f 8:00 am - 4:00 pm..
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
11 Weaving Personal Experience into Academic Writing
Marjorie Stewart
“Warp and Weft” uses the metaphor of weaving to demonstrate one way of using personal and narrative writing within academic essays. Rather than debate whether narrative is appropriate for academic writing, it addresses the question of when is it appropriate and how it can be done effectively, focusing on helping writers decide when the use of personal experience is appropriate for their purpose, how to make personal experience and narrative pull its weight in the essay, and how the ability to incorporate personal experience can translate into the ability to incorporate research.
The essay is structured as an example of the use of personal experience as well as a how-to guide. “Warp and Weft” contains a discussion of three students who incorporated narrative in their essays in three ways: as a structural frame, as an example when the research topic and personal experience overlap, and as a tool for discovery. Students will benefit from the peer-written examples as well as the use of the personal in the essay itself.
Like many students, I worked my way through college with a retail job. [1] I was luckier than many of my classmates: I found a job at a hip little boutique called Rebecca: A Gallery of Wearable Art in the trendy part of town. We carried many styles of hand-made clothing, jewelry, and accessories, but our most important merchandise was that made by Rebecca herself. Rebecca was a weaver who made hand-woven clothing and scarves. Her loom took up half of the back room and she wove while I waited on customers. When one fabric came off the loom, Anne, the seamstress, would begin to cut and sew while Rebecca set up the loom for the next design. She created her patterns then transferred them into a computer program that told her how to thread the yarn onto the loom to produce the pattern. She threaded the warp, the yarn that runs lengthwise, onto the loom. The weft (formerly known as woof) was placed on bobbins that fed the shuttle. The act of weaving was moving the shuttle with the weft through the warp to create the weave.
So what, you might well ask. So what does this have to do with writing?
Many of you have been taught not to use the word “I” in your academic writing; not to include anything that does not directly relate to that mysterious thing called a “thesis statement;” and not to include anything personal in your writing. The opening of this essay has broken all of those so-called rules – it contains a personal story, told in the first person, that at first glance seems unrelated to the topic of writing. However, in this essay, I – yes, “I” – am here to help you step away from those rules and to use personal stories effectively in your academic writing.
The first consideration is whether using personal narrative is appropriate for your project. My story of working in Rebecca’s shop is useful here – it is intended to attract the attention of the readers and to establish and explain the extended metaphor of weaving. However, if I were writing an essay for my art history class about the evolution of weaving techniques and equipment, my story would seem out of place, as I only have experience with one step in that evolution, and that experience is of an observer rather than a participant.
Your composition professor will likely talk to you about the rhetorical situation of any piece of writing. Stated simply (perhaps too simply), the rhetorical situation – the writer, the audience, and the purpose of the writing – affects the way the message is presented. In my hypothetical art history essay, the narrative would confuse the reader as to the purpose of the project and distract from the actual message of the paper. Often in writing classes it seems that your audience is specifically your professor and secondarily, perhaps, your classmates. Given the essays you will read about in this chapter, imagine the larger audiences that the student writers might have been addressing. Consider carefully whether personal narrative belongs in papers you are writing for history, biology, or business classes.
In addition to your specific rhetorical situation, of course, you should always comply with your professors’ guidelines for each assignment. “No first-person narratives” is a clear statement that personal stories are not appropriate in that classroom.
However, once you have established that your narrative is appropriate for your purpose and audience, what next? It is my purpose to help you incorporate narrative effectively, and to do that, I will use examples from three of my students in a first-year course, a course designed to help writers bridge the gap between high school and college writing. I am also using the example of this essay itself. Consider my story about Rebecca. I am using her weaving, her design of warp and weft, as a metaphor for the kind of writing this essay is going to talk about. I will also use the story as a frame – talking about weaving in the introduction, the conclusion, and perhaps in the transitions.
Personal Story As Frame
Using a personal story as a frame for your essay can be an effective way to draw your reader into your ideas and then to help them reinterpret those ideas in the end. Perhaps, like me, you’re working in a retail job. Perhaps it’s in a big box store instead of my artsy boutique, and you’re wondering if you’d be happier somewhere else, or you’re thinking, please, hand-woven clothing? You sell electronics, important, functional electronics.
Just as I began with the story of my time at Rebecca, Lynn Z. Bloom began a conference presentation with a story from her classroom, and then commented, “Such stories, even brief ones, make us want to hear more, and to tell our own right back. They get us where they live. All writing is personal, whether it sounds that way or not, if the writer has a stake in the work” (1). One of my goals in telling the story of Rebecca is to make you want to hear more, and to make you want to tell your own. The human mind is a giant filing cabinet of stories, and when you hear one, you go to the appropriate file drawer – in this case R for Retail Employment – and pull out your own.
There are many stories in that drawer, however, and it’s important that you choose the right ones. Because my metaphor of writing as weaving is central to my topic, I haven’t included lots of other great stories that came out of my time at Rebecca. I didn’t talk about the great gyros we used to get from Mike and Tony’s across the street, or about how the changing nature of the neighborhood made Rebecca worry whether she had chosen the right location for the store, or about the great artists who came in for trunk shows of their work. I focused on the loom, the weaving. And as the framework for this essay, I consider the story of the loom to be the warp, the yarn threaded on the loom in advance. I will thread my shuttle with the examples of my students’ writing and weave them through.
The first example, Callie Harding’s “The Life of a Choir Director’s Child,” does the opposite. Her topic – the need for better education about religion in America – is the warp, and her childhood stories are woven though to show the reader how this topic became so important to her. Her stories give the readers context and help them connect with her.
Personal Story as Context
Telling a personal story can help your reader understand why you are writing about the topic you have chosen, and why you have come to care so deeply about it. Callie’s childhood experience of travelling from church to church where her parents worked as choir directors gave her an understanding of many religions, and she uses those stories to show how that has helped her be a more compassionate, thoughtful, and sensitive person.
Her paper starts this way:
When I was a child, I didn’t spend much time on playgrounds or with the backyard swing set. I didn’t look forward to dance class or soccer practice every week. Instead, most of my time was spent in the pews of a church with a My Little Pony figure that was weaving its way through a jungle of hymnals and pew Bibles. My playground was a cathedral with the somewhat harmonious voices from the volunteer choir echoing off the stone floor over the magnificent pipe organ. At the front of the choir was either my mother or father . . . Yes, I was the child of choir directors. (Harding 1)
Callie goes on to explain that her family moved from a non-denominational Christian church to a Jewish synagogue; the First Church of Christ, Scientist; a Catholic Church, and finally, a small Lutheran church. “What religion are we?” she asks. This is how she tries to answer her question:
My mother spent a while with the Hindu faith before marrying my father and converting to Mormonism. We are also deeply into our Native American background and practice their cultural and religious ceremonies. Add the fact that we had many friends from many religions and cultures and you can tell that I had one of the most openly religious households on the block. (Harding 1-2)
Callie then moves very nicely into her research on how to encourage religious tolerance through education. She contrasts her experience in a fundamentalist Christian high school to a school district in Modesto, California where all ninth graders take a semester-long world religion course. She writes about the importance of helping all children understand and celebrate diversity of religion and points to her own experiences as an example of the positive effect this has on them. As part of her research, Callie interviewed her mother about her diverse upbringing. While her mother called it a “happy accident,” she also explained to Callie how she stood up to her very Mormon father to make sure Callie and her sister were free to find their own beliefs.
As I was studying Callie’s essay, I took three highlighters and circled each paragraph: pink for Callie’s personal story; yellow for Callie’s presentation and discussion of her research, and green for the information from her interview with her mother. This is the result:
- Paragraphs 1-3 – Callie’s personal story
- Paragraphs 4-6 – discussion of research
- Paragraph 7 – Callie’s story
- Paragraphs 8-9 – discussion of research
- Paragraph 10 – Callie’s interview with her mother
- Paragraph 11 – Callie’s story
- Paragraph 12 – Callie’s interview with her mother
- Paragraphs 13-14 – Callie’s personal story
It wasn’t until I did that exercise with the markers that I realized how smoothly Callie had incorporated the three elements of her writing. As I’ve done in this essay, Callie framed her story with the personal. She also used it within the essay to focus and reflect on her research findings. Marking your essay the same way can help you see if you have the right balance between the personal and the more traditionally academic portions of your paper.
While Callie used her personal stories to provide context to the issue of religion in education, she also used her own background to show herself as an example of someone for whom a broad religious education proved beneficial. In “A Life Lost,” student Melynda Goodfellow used her personal story as an example.
Personal Story as Example
Melynda chose to write about teen suicide, certainly an important topic, but one that far too often leads to a patchwork of statistics and distant narratives, more a report than an essay with heart. Sadly, Melynda had reason to care deeply about her topic: her cousin Jared killed himself with an overdose of prescription pain medication.
Melynda started her essay with a simple story of a typical Friday night, getting ready to go the high school football game, where her brother would be playing in the band. This night, however, was special, because her cousin had just moved into town and her boyfriend would be meeting him for the first time. Choosing to open with a typical activity – going to the football game – but giving it special meaning was particularly effective for Melynda. I encourage writers to ask themselves the first Passover question: Why is this night different from all other nights? This is the question asked by the youngest child at the beginning of the Seder to start telling the story of the Passover. It also serves the beginning writer well: If this night, this football game, isn’t special in any way, then it isn’t the story to use in your essay. Melynda’s football game is different from all others because her cousin will be there to meet her boyfriend.
Although the atmosphere is festive, Melynda shows us with foreshadowing that this is not a typical Friday night lights story. She writes that Jared moved because “he wanted to get away from the lifestyle that he was living back home. He wanted a kind of fresh start.” She connects herself to the characters of her brother and her cousin through the band: she had been in band, her brother is performing with the band at the football game, and her cousin is excited about returning to school and joining the band himself. Throughout the narrative part of her essay, Melynda shows Jared as sad and desperate, yet looking forward to his fresh start.
Melynda tells the story in a straightforward, chronological way from the evening of the football game through her cousin’s death and funeral. Her use of personal experience is different from mine and Callie’s because the majority of her paper is that narrative. The structure of her paper is very different: where Callie went back and forth between the story and the research, Melynda began with the story and introduced the research at the end. The first three pages of Melynda’s six-page essay are the story of her friendship with Jared that fall, and how she becomes his confidant. Pages four and five are the story of how she heard of his death. It is only at the end of her essay that she introduces the statistics that show that suicide is “the third leading cause of death in people ages 15 to 24” (Goodfellow 6). Her conclusion, shortly after that statistic, reads:
I never in a million years would have thought something like this would happen in my family. I knew that mental health problems run in the family, but I believed everyone knew where to get help. We knew that suicide wasn’t an option and that we had each other if nothing else. As tragic as it may sound, this event brought our whole family back together. Any quarrels or grudges anyone had seemed to dissipate that day. Ironically, one of the things that Jared wanted the most was for the family to just forget their differences and get along. (Goodfellow 9)
This ending refocuses Melynda’s readers on the personal meaning of the impersonal statistic.
In his book Living the Narrative Life: Stories as a Tool for Meaning Making , Gian Pagnucci writes, “I think, actually, that stories can help us get at the truth even if there isn’t a firm truth to be had.” (51) And in Writing to Change the World , Mary Phipher says:
Research shows that storytelling not only engages all of the senses, it triggers activity on both the left and the right sides of the brain . . . . People attend, remember, and are transformed by stories which are meaning-filled units of ideas, the verbal equivalent of mother’s milk. (11)
Melynda works at getting at the true story of her cousin’s death, making meaning of it, even though there is no firm truth or solid meaning to be had there. The truth she arrives at, however, is more powerful than the “just the facts” approach because the story lingers with her readers in a way statistics can’t.
Another thing Melynda does that makes her essay different from mine, and Callie’s, is her inclusion of dialogue. I think she makes especially good use of it in her essay, something that is often difficult for writers at all levels. Here she shows us how she learned of Jared’s death:
“What is it?” I said when I picked the phone up. “It’s about time you answered your phone! I’ve been calling you for over an hour,” my mom said. “Well?” “It’s Jared. He’s in the hospital. He overdosed.” “Oh, my God . . . Is he okay? I’ll be right there. I’m leaving work now.” “No. Don’t come here. There’s nothing you can do. He’s dead.” (Goodfellow 4)
Recreating dialogue can be challenging – a year after her cousin’s death, can Melynda be certain that these were the exact words that she and her mother spoke? Probably not, but she can show her readers the tension in the moment – her mother’s anger that she didn’t pick up, her desire to be with Jared, and her mother’s postponing of the awful news. Dialogue also can be used to pick up the pace of the story – the light look of it on the page helps readers’ eyes move over it quickly, getting a lot of information from a few carefully-chosen words.
There are significant structural differences between Melynda’s essay and Callie’s. Callie’s is split almost evenly between personal experience and research; Melynda’s is about 85% personal story. The third student, Ethelin Ekwa, uses personal story in an even larger portion of her essay, which is entitled “Ethelin Ekwa: An Autobiography.” Although the title might lead you to believe that the essay is only, or just, or simply, personal narrative, Ethelin uses the story of her life to explore her ethnic heritage, her life as a single mother, and her determination to make the most of her artistic and musical talents. She tells the story of her life as a way of understanding her place in the world at the time of the writing.
Personal Story as Discovery
Ethelin’s essay can be seen as an example of Donald M. Murray’ beliefs about writing: “We write to think – to be surprised by what appears on the page; to explore our world with language; to discover meaning that teaches us and may be worth sharing with others …. . . we write to know what we want to say.” (3). Although my students always write multiple drafts of all of their essays, Ethelin wrote more than usual – at least four significant revisions before the final draft that she submitted in her portfolio. She was a frequent visitor at our writers’ center as she worked through the paper. Somewhere in an intermediate draft, she found her frame: a quotation from Ani Difranco’s song “Out of Habit:” “Art is why I get up in the morning.” That idea led her Ethelin to her conclusion: “I cannot imagine a day without the ability to create in unconventional ways” (Ekwa 9). In the eight and a half pages in between, she tells the story of her life.
In Callie and Melynda’s essays, there is a very clear separation between personal experience, research material, and the writers’ commentary on those elements. The weaving, to continue the metaphor, is done in larger blocks of color. Ethelin’s essay has a more subtle pattern. Every paragraph contains some detail of her life – where she was born, who her parents were, where she lived – but also has a reference to her life-long desire to be an artist. She talks about her work as a writer and poet; as a singer and musician; and as a photographer and visual artist.
Ethelin’s background is intriguing – her parents moved from Cameroon, West Africa to France and then to Texas, where she was born, the youngest of five children. She has lived in Europe and Africa, and she went to school in France and Cameroon. Here is how she introduces herself in the second paragraph:
My birth name is Ethelin Ekwa. I am also known as Obsolete by my artist friends and as Krysty by my close personal friends. I am an artist, a mother, a photographer and a lover of all things. I am an American-born citizen with Cameroonian and French origins. I am 30 years old and I currently reside in North Braddock. (Ekwa 1)
Ethelin’s identity is tied to her arts from the very beginning, and every story from her life is wrapped around those arts. When, at 22, she becomes a single mother, her priorities change, but she never gives up: “When I got pregnant, I put singing, painting, and drawing on hold . . . I had more pressing matters to take care of and there just was not time for art” (Ekwa 3). Soon, though, she tells us that she made a new friend who introduced her to digital photography, and by the time her daughter was two years old, she had her own photography business up and running.
While Melynda chose one special night to tell about at the start of her essay, Ethelin chose many events from her life, all of them important, life-changing events. Reading Ethelin’s essay, I can almost see Rebecca’s shuttle flying back and forth across the loom, the turn at each side another event that pulls Ethelin back into the world of art. When the weaver turns the shuttle at the edge of the warp, the weft creates a finished edge that prevents the fabric from fraying or unraveling called a selvage. The turns in Ethelin’s story create a sense that her life, which is sometimes unplanned and chaotic, still has something that keeps it from unraveling, and that something is her artistic nature.
Tying Up Loose Ends
The examples from my students’ essays can help you understand how to use personal experience in your academic writing. But how do you know when to use it? When is it acceptable and appropriate? Gian Pagnucci asserts, “Narrative ideology is built on a trust in confusion, a letting go of certainty and clarity that can ultimately lead to understanding” (53); that stories have a “piercing clarity” (17), and that “the drive to narrate experience is, if not instinctive, then at the very least quintessentially human” (41). He also warns that the academic world is not always welcoming of personal experience. I know many of my colleagues are not willing to trust in confusion – their entire careers, and even their lives, have been built on the quest for knowledge and certainty.
If your composition professor has asked you to read this chapter, it’s a pretty safe bet that you may use personal experiences in your writing for that class. Even in that setting, however, there are times when it is more effective than others. Using the examples of the essays I’ve quoted from and the guidelines given in the beginning of this chapter, here are some tips on when to use your personal experience in your essays:
- When, like Callie and Melynda, your experiences have inspired a passionate opinion on your topic
- When, like Ethelin, your personal experiences constantly point back to your central idea
- When, like me, your personal experiences provide a strong and extended metaphor for your subject
- When, like all of the writers, your personal experience provides a structure or framework for your essay
The expression “tying up the loose ends” comes from weaving and other fabric arts. When the yarn in the shuttle is changed, the new yarn is tied to the old at the selvage. Those threads are later woven into the fabric so that they don’t show, and so that the connection is tight. When your rough draft is done, it’s time to take the fabric off the loom and make sure your weave is tight. At that point, ask yourself these questions to be sure you are using your experience appropriately and effectively in your essay:
- What percentage of your essay is personal experience, and how does that match up with the nature of the assignment? Callie’s essay was written in response to an assignment that required more research than the one Ethelin was responding to, so it included less personal writing.
- Have you included only the personal stories that directly relate to your topic, your attitude towards your topic, or your controlling idea?
- Are your selvages tight? Do the moves you make between personal story and research and analysis make sense, or is the fabric of your essay likely to unravel?
- Is the resulting pattern appropriate to your project? Are you working in large blocks of color, like Callie and Melynda, or the subtler tweed of Ethelin’s essay?
I started this essay in Rebecca’s shop and tried to weave the metaphor inspired there through this essay. In the process, I realized another advantage to using personal stories in academic writing: I hadn’t thought about Rebecca and Anne, about Mike and Tony’s gyros, about the bright creative atmosphere in the gallery and in the neighborhood for a long time. Accessing those stories from the filing cabinet in my brain was inspirational. My stories from Rebecca are mostly fun or funny. Your stories, like mine and the writers quoted here, are a mix of light and dark, funny and serious. I encourage you to open the file cabinet and find the stories that will make your readers remember similar times.
Works Cited
Bloom, Lynn Z. “That Way Be Monsters: Myths and Bugaboos about Teaching Personal Writing.” CCCC 51st Annual Meeting, Minneapolis, MN, Apr. 2000.
DiFranco, Ani. “Out of Habit.” Ani DiFranco , Righteous Babe Records, 1990. Ekwa, Ethelin. “Ethelin Ekwa: An Autobiography.” 3 Aug. 2009. Composition and Language I, Art Institute of Pittsburgh, student paper.
Goodfellow, Melynda. “A Life Lost.” 3 Aug. 2009. Composition and Language I, Art Institute of Pittsburgh, student paper.
Harding, Callie. “The Life of a Choir Director’s Child.” 3 Aug. 2009. Composition and Language I, Art Institute of Pittsburgh, student paper.
Murray, Donald M. A Writer Teaches Writing . Rev. 2nd ed. Cengage, 2003.
Pagnucci, Gian. Living the Narrative Life: Stories as a Tool for Meaning Making . Heinemann, 2004.
Pipher, Mary. Writing to Change the World . Riverhead Books, 2006.
Teacher Resources for Weaving Personal Experience into Academic Writing by Marjorie Stewart
Overview and teaching strategies.
This essay is useful for faculty teaching the research-based essays that are frequently the concentration in a second semester composition course in a two-term first year writing sequence. Instructors who encourage a personal connection to the research topic will find this essay helpful in guiding students as to when and how they might use their personal narratives in their academic research essays.
The questions below are designed to stimulate discussion and to move students from thinking academically about this genre to delving into their own lives for experiences they are inspired to research and learn more.
Often the attitude towards personal narrative, held by teachers and students alike, is that it is a beginning genre and an ice breaker that is designed as a stepping stone to real or more important ways of writing. This essay instead subscribes to the theory that personal narrative is, as Gian Pagnucci says, “if not instinctive, then at the very least quintessentially human” (41). My experience working with students on this kind of essay is that they are eager to both tell their own stories and to research the issues that inform those stories.
- Marjorie Stewart claims that our minds are filing cabinets of stories. Do her stories, or the stories of her students, remind you of stories of your own? How does this chain of stories help us make sense of our experiences?
- Has there ever been a time when you wanted to include personal experience in a writing project but were discouraged or forbidden to by an instructor? Why did you feel the story was important? What might have motivated the instructor?
- Are their personal stories you are eager to include in an essay? What about stories that you would be uneasy revealing? How do you, and how do other writers, decide which stories they wish to share?
- Work with an essay, either assigned in class or one you are familiar with in which the author uses personal experience. Compare it to an article on the same topic with no personal writing. Which do your respond to more, and why? Does the personal writing help you understand the writer, or does it get in the way of your intellectual understanding of the topic?
Essay Resources
If you have a favorite example of a well-mixed narrative research essay, by all means, use it. If you are using a book with good examples, you might assign one as companion reading to “Warp and Weft.” I also recommend many essays published as creative nonfiction, especially those from The Creative Nonfiction Foundation, at creativenonfiction.org. One of my favorites is “Rachel at Work: Enclosed, A Mother’s Report” by Jane Bernstein, published in Creative Nonfiction and anthologized in their collection True Stories, Well Told .
- This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) and are subject to the Writing Spaces Terms of Use. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ , email [email protected] , or send a letter to Creative Commons, PO Box 1866, Mountain View, CA 94042, USA. To view the Writing Spaces Terms of Use, visit http://writingspaces.org/terms-of-use . ↵
Weaving Personal Experience into Academic Writing Copyright © 2020 by Marjorie Stewart is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

How to Start a Research Project: Choosing a Topic
- Choosing a Topic
Beginning Your Research Project
You have an assignment coming up in class. You need to write a research paper, create an annotated bibliography, or make a presentation. These are just some research projects you may need to do.
This guide will show you different ways to start a research project. When following this guide, please consider 3 concepts:
- Center your personal research interests - What are you interested in?
- Take as long on each step as you would like.
- Skip steps and repeat steps as you need.
Starting from Nothing: The Mind Map
A mind map is a visual way of building a topic into a research question .
A topic is the basic idea that interests you. This is the idea that sparks your research. A topic could be "barbeque," "The Cold War," "flightless birds," or "the common cold." If you are having trouble choosing a topic , review the class syllabus or canvas modules. Find a topic covered in class that you can see yourself spending time with.
A research question is the focus of your research project. It is the thesis of your paper or the point of your presentation.
Work with us through the mind map steps to build your own research question .
To create a mind map , you will need to be able to write or type text, and the text must also be rearrangeable.
- Start with an idea like "Kitchen Design". Place your idea in the center.

- Surround your central idea with related concepts. I wrote all the kinds of kitchens I could think of. I could have also chosen to list appliances or design themes instead.

- Out of the kitchen-types, I was most drawn to "Hospital Kitchens". I then added concepts around "Hospital Kitchens". These concepts can be moved to also combined with other ideas.

- I also thought more about "Home Kitchens". I combined, "Kitchen Safety", "Consumer Preferences", and "Advertisements."

- My final version of my mind map example is very small. Don't worry if you have many more ideas and need more time rearranging your cards and planning.
I have identified two different starting research questions by combining my concepts:
- How could hospital managers design hospital kitchens to be safer for employees?
- How do kitchen appliance manufacturers advertise the safety of their products to consumers?
Research Questions
A research question is the focus of your research project. It is the thesis of your paper or the point of your presentation. Here are some requirements of a good research question:
- Research questions cannot be answered with "yes" or "no".
- Research questions can be researched.
- A small research paper shouldn't have a research question with a giant scope: How does preventative healthcare get planned?
- A small research paper should have a research question with a manageable scope: How do preventative care programs for type II diabetes in Alabaman clinics get advertised?
In this example, we narrowed the scope of our initial research question in a few ways:
- Type: "Preventative care" was limited to - "type II diabetes"
- Place: We had no initial location limit. We limited ourselves to "Alabaman clinics"
- Action: "Planned" was defined as "advertised"
Sometimes, research questions need to change slightly after you have done some research. If you were not able to find any useful resources for the example research question, then you could try changing the scope. If you cannot find anything specific to Alabaman clinics, then you could change that part of your research question to "United States clinics" or "Alabaman healthcare providers."
Still stuck? Please check Monash University's Developing Research Questions guide .
Turning your Research Question into a Search
Useful links.
- Purdue OWL: Choosing a Topic This handout provides detailed information about how to write research papers including discussing research papers as a genre, choosing topics, and finding sources.
- UNC: Brainstorming This handout discusses techniques that will help you start writing a paper and continue writing through the challenges of the revising process. Brainstorming can help you choose a topic, develop an approach to a topic, or deepen your understanding of the topic’s potential.
- University Writing Center Schedule a session with a tutor at the University Writing Center.
- Next: JSTOR >>
- Last Updated: Aug 6, 2024 12:46 PM
- URL: https://libguides.southalabama.edu/start-research
Get the Reddit app
A place to get help for any type of paper in high school/college level English courses.
Starting a research paper with a personal story help.
I'm a freshman in high school and our quarter project is writing an argumentative research paper on the topic of our choice. My topic that I chose was that "The United States military should be decreased so that its funds can be allocated elsewhere." the part I need help with is my introductory paragraph. Our teacher told us about the 5 main ways to start a paper: joke, question, facts, background info, and (the one she want us to use) personal story. So how can I write a "personal" story about military expenditure, specifically reducing it? Is there a better way I can start my paper?
TL;DR Personal story about military expenditure?
By continuing, you agree to our User Agreement and acknowledge that you understand the Privacy Policy .
Enter the 6-digit code from your authenticator app
You’ve set up two-factor authentication for this account.
Enter a 6-digit backup code
Create your username and password.
Reddit is anonymous, so your username is what you’ll go by here. Choose wisely—because once you get a name, you can’t change it.
Reset your password
Enter your email address or username and we’ll send you a link to reset your password
Check your inbox
An email with a link to reset your password was sent to the email address associated with your account
Choose a Reddit account to continue
Money blog: House price prediction from major lender after rate cut; secret code to get free crumpets
Welcome to the Money blog, your place for personal finance and consumer news and tips. Leave a comment on any of the stories we're covering below.
Wednesday 7 August 2024 14:09, UK
- The secret code word that will get you free crumpets
- Oil giant to help staff escape abusive relationships after boss allegations
- Here's how much grandparents would earn a year if they were paid for helping with the kids
- Stock market continues slow recovery after meltdown
Essential reads
- Will 'the greatest chocolate bar ever' return? We asked Cadbury's...
- Cheap Eats: Where you've (probably) been going wrong with green curry
- Explained : US recession could be 'huge' for global economy
- Is equity release ever a good idea?
- Aldi's new copycat is much cheaper but what do nutritionists think?
- Where kids can eat for free or cheap
- Money Problem : 'I cancelled booking and they won't give me refund without 14 days' notice'
- Basically... Wills
- Best of the Money blog - an archive of features
Ask a question or make a comment
Halifax predicts house prices will increase for the rest of the year.
Lower mortgage rates and potential base rate reductions will push up asking prices, said the bank's head of mortgages, Amanda Bryden.
The average price rose by £2,200 from June to July, Halifax found, following three relatively flat months and putting the average house at £291,268.
"Last week's Bank of England base rate cut, which follows recent reductions in mortgage rates, is encouraging for those looking to remortgage, purchase a first home or move along the housing ladder," said Ms Bryden.
Rates were lowered from 5.25% to 5% on Thursday - the first cut in more than four years.
"Against the backdrop of lower mortgage rates and potential further base rate reductions, we anticipate house prices to continue a modest upward trend throughout the remainder of this year," Ms Bryden said.
Holly Tomlinson, a financial planner at wealth manager Quilter, said she expected the autumn to be a busier period for the market, as indecisive sellers are encouraged by the direction in which rates are going.
Purplebricks chief executive Sam Mitchell agreed: "With lenders already slashing mortgage rates in response to last week’s decision, buyers are beginning to move ahead with purchasing decisions they have been putting off for months."
A supermarket cafe is giving away free crumpets - if you know the password.
Ask for "Ellen" at a Morrisons Cafe and you can get a free portion of Warburtons crumpets with a choice of six toppings.
The offer, named after Warburton's founder, Ellen Warburton, is available until 25 August or while stock lasts.
How to get your free crumpets
Just ask for "Ellen" at the till, and you'll receive two crumpets with either honey, banana, chocolate spread, jam and butter, marmalade, or maple-flavoured syrup.
Vegan spread is available on request, according to Warburtons, which has teamed up with Morrisons over the summer holidays.
There is no minimum spend and the freebie is available in all cafes - but customers can only get one portion per person each day.
Morrisons told Money Saving Expert that there are 100,000 portions available - which cost 99p before they were removed from its cafe menus.
A major bank has created a series of deepfake videos to warn customers how realistic they have become.
Santander has posted the videos, featuring its fraud lead Chris Ainsley and influencer Timi Merriman-Johnson, on social media to raise awareness of a method of fraud increasingly available to criminals.
Deepfakes can be videos, sounds or images of real people that have been digitally manipulated through artificial intelligence to convincingly misrepresent a person or organisation.
"Generative AI is developing at breakneck speed, and we know it's 'when' rather than 'if' we start to see an influx of scams with deepfakes lurking behind them," said Mr Ainsley.
"We already know fraudsters flood social media with fake investment opportunities and bogus love interests, and unfortunately, it's highly likely that deepfakes will begin to be used to create even more convincing scams of these types."
Just 17% of people are confident they could easily identify a deepfake video, found an Opinium survey of 2,000 people for Santander in July.
Almost Six in 10 people said they are already more suspicious of what they see or hear because of deepfakes.
Here are Santander's top tips to spot a deepfake:
- Deepfakes are likely to be used in investment scams and impersonation fraud, such as romance scams.
- Look out for imperfections like blurring around the mouth, less blinking than normal, or odd reflections.
- Context is important. Ask: Is this too good to be true? If this is real, why is everyone not doing this? If this is legitimate, why are they asking me to lie to my family or my bank?
By Daniel Binns, business reporter
The stock market in London is continuing to slowly recover this morning following Monday's global falls.
The FTSE 100 is up 0.9%, while the FTSE 250 has gained 0.7%.
Banks and financial institutions are among the top gainers, including NatWest, which is up 2.5%, Standard Chartered, which has risen 2.9%, and Lloyds Banking Group, which has increased by 2%.
Fallers include bottling company Coca-Cola HBC - which is a partner of the global drinks firm - down 2.4%.
It comes despite the company upgrading its profit and revenue forecast for the year.
Hotel giant IHG, which owns brands including Holiday Inn, is also down 1.8% despite positive second quarter results published yesterday.
Oil prices are also gradually creeping back up following falls last week.
A barrel of the benchmark Brent crude will currently set you back just over $76.5 (£60), a rise of 0.3%.
On the currency markets, £1 buys $1.27 US or €1.16 this morning.
Read more on what caused Monday's US recession fears here...
Many families rely on grandparents for childcare, and most are happy to oblige.
Their reward is often simply spending valuable time with their grandkids and making memories - but what if they actually got paid?
A new tool by SunLife , a financial services company used by people later in life, allows grandparents to input all the hours of "parenting" they do - from taxiing to cooking to days spent babysitting.
We had a go - answering each question in what we presumed could be a typical scenario. Our fictional grandparent did two hours each of taxiing, cooking and cleaning for their grandkids, and 18 hours (roughly two working days) of babysitting a week.
For this, SunLife estimates a salary of £15,864 would be appropriate.
SunLife recently polled more than 2,000 grandparents and found there has been a rise in the number being relied upon to look after grandchildren during the school holidays and on inset days.
More than four in 10 (43%) now provide "holiday" care and are giving up 18 hours a week on average - up from 16.54 hours last year and equivalent to almost three days a week.
BP will offer staff who are trapped in abusive relationships free emergency accommodation.
The oil and gas company will pay up to the value of £1,500 for those trying to escape an abusive partner as part of its new domestic abuse policy.
It will also provide employees with legal advice and 10 days extra paid leave for meeting with lawyers or visits to court.
In a document seen by The Telegraph , BP noted that employees in abusive relationships could be "subjected by perpetrators to economic abuse, controlling working hours, or demanding that salary is paid into a specific bank account".
It said this could affect productivity and also lead to unplanned absences.
The policy comes after allegations about former boss Bernard Looney's "personal relationships with colleagues".
Mr Looney left his role as chief executive of the British energy giant after he was said to have failed to fully disclose details of the relationships as required by the company.
BP said at the time last year that Mr Looney was standing down "with immediate effect" and that he accepted he was not fully transparent in his previous disclosures.
"He did not provide details of all relationships and accepts he was obligated to make more complete disclosure," they said.
There is no suggestion that Mr Looney was ever involved in any abusive relationships.
Every Wednesday we ask Michelin chefs to pick their favourite Cheap Eats where they live and when they cook at home. This week we speak to award-winning Michael Wignall, of the one-star The Angel at Hetton, in Skipton in the Yorkshire Dales.
Hi Michael, can you tell us your favourite places in North Yorkshire where you can get a meal for two for less than £40?
If I ever go cycling with the kids on the mountain bike Ye Olde Naked Man , in Settle, is on one of our routes.
We go over the tops - it's 12 miles over the tops of the Yorkshire Dales - then drop into Settle.
I've always taken the kids there, whether that's for a hot chocolate and cake or sandwich.
It's so nice, really popular (for good reason), and right in the middle of Settle, a lovely little town.
If I'm on my own on the road bike and do a big cycle, say 30 to 50 miles, it's on the way home and just before a horrific climb in the area - 20% gradient - I stop at The Naked Man and psych myself up for it. Even my friends stop there for caffeine and a bite to eat before the last journey.
It's in a great location, opposite the market square and a traditional, old-school place that I love. The food is very reasonable, and the service is brilliant.
Paradise Food , at Daleside Nurseries, is another option. The chef here is lovely, and we go back a long way. It started as a pop-up at garden centre, and is now a full-time restaurant.
They've had a really colourful career, a great chef, which is reflected at Paradise. They're hard working and have core values that I really respect, and I just love coming here for a great meal. It is super popular.
Rind , at Courtyard Dairy, is just over the tops, out of Settle and towards the Lake District.
They are very famous and do our cheese for us. The team is super passionate, and a few years ago extended the cheese shop and built a pizzeria (among other things, like a museum). It is so good here, very cool and the views are just stunning.
Our restaurant manager is Italian, and even she raves about it! That's when you know it's good.
The toppings are a bit different, and it's only 15 minutes away so we do visit often.
What is your go-to cheap eat to cook at home when you have a night in?
A green curry is my "go-to".
Here are my recipe tips:
- Keep lemongrass in the freezer so you always have it on hand; buy a fresh bunch of it to start and then put any left-over in the freezer;
- When cooking rice - use a quality rice and don't skimp on it. Wash it thoroughly at least 10 times until clear;
- Use a good quality coconut milk/coconut block. I use a whole tin of milk and then about a quarter of a block of coconut cream;
- Use a good quality fresh lime in the last few minutes. Grate the zest and squeeze the juice in. Doing it last will mean you don't split the milk;
- Use fresh chillies, not dried. They aren't expensive and not processed and give a much better flavour;
- Like with the lemongrass, use fresh Kaffir lime leaf and keep it in the freezer. It is a bit expensive but makes all the difference.
In short - buy good quality, fresh ingredients!
We've spoken to lots of top chefs - check out their cheap eats from around the country here...
By Jenness Mitchell , Scotland reporter
Edinburgh Festival Fringe is officially under way - one of the greatest celebrations of arts and culture, and increasingly one of the most expensive to enjoy.
Earlier this year, comedian Jason Manford branded the city's accommodation prices an "absolute joke".
He posted on X in April: "No idea how anyone starting out is managing to get up there and showcase their talents!"
Manford called it "pure greed".
Though I'm not from Edinburgh, I try to go every year - like many Scots, I'll go for the day, so don't incur accommodation costs.
But even then, is it still as affordable as I remember it from years ago?
The Money team gave me a budget of £20 to see if I could eat, get a drink and take in a show. Could it be done?
I thought I'd get the easiest bit out of the way first - a drink. I set myself a £2 budget.
I searched high and low for a drink from a vendor to meet my budget - most coffees started at £3, the cheapest beer I spotted was £6, and the best cocktail offer was breaking £10.
I had two options - something bog standard from a local store or supermarket, or try my luck getting a bartender to whip up something in exchange for my final two coins.
Happily, the staff working at the pop-up Bar Bados near to the Underbelly George Square venue were in the festival mood and delivered a dream of a drink.
I don't really know what it was but it didn't have alcohol and still tasted of sunshine.
Disclaimer: Had I not been a Sky News journalist with my press pass, I most likely would have had to buy a cheaper drink from a local shop.
With food trucks on every corner as well as restaurants, cafes and gastro pubs, you're spoiled for choice when it comes to what you want to eat in Edinburgh.
The city has a vibrant local food and drink culture which attracts visitors from around the globe.
During the Fringe, Innis & Gunn is taking over The Mound with a one-stop hub featuring music, comedy, food and drink.
Fancy a pizza? Wanderers Kneaded will take care of you. Want something that tastes like summer? Fred's Backyard BBQ will have the grill fired up. You can even wash your food down with a pint of Innis & Gunn or a G&T from Edinburgh Gin.
But, I opted for The Tap on the corner of the Novotel building on Lauriston Place. I ordered the avocado toast for £7.
To be fair, I had chalked up around 20,000 steps around the city by that point - so any meal would have been a winner, but it was delicious.
I had £11 left and I admit that seeing something memorable on this budget is tricky but it was enough to get me into I Wish You Well - The Gwyneth Paltrow Ski-Trial Musical.
It tells the "mostly" true story of the high-profile civil court case in which the Oscar-winning actress was accused of crashing into a man while skiing - and, no lies, it was one of the best things I've ever seen at the Fringe.
The production has been choreographed by Dame Arlene Phillips of Strictly Come Dancing fame, and former The X Factor star Diana Vickers captivated the crowd in the lead role.
I didn't have any change, and maybe have enjoyed the day slightly less with a Ribena instead of my made-just-for-me mocktail, but it can be done.
Domino's Pizza expects to see a hit to its profits after recording a drop in orders over the first half of the year.
The company, which holds the US chain's master franchise in the UK and Ireland, said it expected its new expected adjusted annual core profit to be at the lower end of market expectations after a "slow start to the year".
Total orders were down 0.9% to 35.1 million in the six months to the end of June, although the firm said they had been picking up notably since May and increased by 0.6% in the second quarter.
The company also forecasted that its overall profit for the year would be between £144m to £149m, at the lower end of market expectations.
After it downgraded its predictions for the year, the company's shares fell as low as 8% during trading on the FTSE 250 today.
The food group also announced it was aiming to continue expanding by opening 70 branches across the UK this year and said its average delivery time had been cut to 24 minutes between April and June - shaving one minute off its time in the previous quarter.
Sainsbury's is set to integrate AI technology into its self-checkout machines.
Features on 22,500 checkouts will enable them to identify specific items quickly and spot when a "suspicious" item has appeared in the checkout shelf.
The Next Generation Checkout Systems (NCRs), which use a function called Picklist, will also enable staff to approve transactions remotely rather than going to each till - which the supermarket hopes will save time and boost efficiency.
Sainsbury's will also receive real time data with each transaction and hope to bring in personalised promotions.
When unstaffed tills were introduced, it was hoped they would provide convenience and speed, but over the years a number of problems have arisen, with technology at times going wrong, long queues and theft.
In bringing in AI, Sainsbury's hopes to address these concerns.
Clodagh Moriarty, its chief retail and technology director, told The Grocer the AI technology would "unlock new capabilities".
"This is driving us to the next level and delivers for customers, colleagues and shareholders," she said.
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free

Advertisement
Supported by
Britain’s Violent Riots: What We Know
The country was bracing for more unrest, with fresh protests planned after a weekend of demonstrations turned into anti-immigrant riots.
- Share full article

By The New York Times
The authorities in Britain were bracing for more potential unrest on Wednesday after days of violent rioting spurred by disinformation around a deadly stabbing rampage.
Protests over the weekend devolved into violence in more than a dozen towns and cities, and with messages on social media calling for wider protests and counterprotests on Wednesday, the British authorities were on high alert.
Prime Minister Keir Starmer’s cabinet held emergency meetings to discuss what has become the first crisis of his recently elected government, and thousands of police officers fanned out across the country.
Here’s what we know as the country girds for more potential violence.
Where has the unrest taken place?
Protesters over the weekend took to the streets of a dozen cities across Britain, most of them in England. Trouble broke out from Aldershot in the south to Sunderland in the north and Liverpool in the west. Belfast, in Northern Ireland, was also drawn into the fray.
In some cases, the protesters were merely unruly, but in others the violence was far more pronounced.
Where arrests have been reported
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This is a very common question students have, as we all think that a story will take much space and as a result, we will have fewer things to write. Let's find it out together. When you start writing a research paper you have to remember that the best variants to start will be the next ones: 1. Writing definitions.
Maybe do a little more research, and then start your writing. And informing that with your personal experience to help get you started for something that you observe or something that you already know to be true can be really beneficial as a jumping off point for your research. ... You're going to have to use your judgment, and that's kind of ...
Personal Story As Frame Using a personal story as a frame for your essay can be an effective way to draw your reader into your ideas and then to help them reinterpret those ideas in the end. Perhaps, like me, you're working in a retail job. Perhaps it's in a big box store instead of my artsy boutique, and you're wondering if
Start strong. In your research, have you come across an odd factoid or interesting quote? Try starting your paper with that. How about starting with an anecdotal story or humor? Middle Sentences : The middle sentences cover the different points in your paper. If you've already planned which order to write the points in the paper, you already ...
General Use of I or We. It is totally acceptable to write in the first person in an APA Style paper. If you did something, say, "I did it"—there's no reason to hide your own agency by saying "the author [meaning you] did X" or to convolute things by using the passive "X was done [meaning done by you].". If you're writing a ...
The personal narrative is intended to locate the researche r so that examiners can see how the researcher's actual life and/or work experience might influence the research, for better or worse. The narrative enacts the (epistemological) position that no research is neutral and all research is written from somewhere, and where matters.
However, like any other type of writing, it comes with guidelines. 1. Write Your Personal Narrative as a Story. As a story, it must include an introduction, characters, plot, setting, climax, anti-climax (if any), and conclusion. Another way to approach it is by structuring it with an introduction, body, and conclusion.
by John McLeod. Using Personal Experience as a Basis for Research: Autoethnography. Autoethnography is quite different from other genres of research, in being based in first-person writing and reflection on personal experience. Carrying out an autoethnographic study not only has the potential to contribute to the research literature - it can ...
The first-person voice can make a science story more engaging or relatable. However, not every article will benefit from a personal touch, and putting one's own experiences on the page may be uncomfortable, particularly for writers new to the style. By knowing when and how to insert themselves into their stories, though, science writers can successfully use their life experiences to create ...
2.    Choose the Subjects You Will Emphasize In Your Paper. Ensure that your research piece concentrates on certain subjects. For instance, you may opt to emphasize the book's characters or the plot's content. This will make outlining your thoughts and writing your research report much simpler.
Telling a story in your paper: Explained and exemplified. When we say 'narrative', we don't necessarily mean 'write in the style of your favourite author'. A narrative, in the context of academic writing, is a central thread that runs through each of your result pieces. The idea is to have a beginning, a middle and an end to your ...
Although it is controversial (some people will tell you never to include personal experiences), I think there is a place for personal experiences. But first, you need to understand why this is generally frowned on. Everyone has personal experiences and everyone has different ways to interpret them. Anyone can write a magazine or blog article ...
Research stories share your research in a way that is understandable and interesting to a non-expert, public audience. Unlike a research report, a research story focuses on telling the narrative of your process, the significance of your research to others, and your personal engagement with your research. This handout will help you frame your ...
How to Use Personal Experience in a Research Paper. When you are crafting your easy using your personal experience, ensure you use the first-person narrative. Such a story includes the experiences you had with books, situations, and people. For you to write such a story well, you should find a great topic. That includes thinking of the events ...
Strategy 1: Open with a concrete scene. An effective way to catch the reader's attention is to set up a scene that illustrates something about your character and interests. If you're stuck, try thinking about: A personal experience that changed your perspective. A story from your family's history.
A personal experience can be included in your research paper as long as it is relevant to the research topic you are working on. The main goal is to ensure that the reader will connect to an event of your own life experience. In this case, putting a personal experience into a research paper requires the use of descriptive language.
It starts your introductory paragraph and can take the form of a scene, question, interesting fact or statement, or even an anecdote. 2. Set the scene to offer specific details and strong imagery. One way you can open the personal narrative is to start right in the scene, with the "I" in action.
An illustration can be as simple as a personal story or anecdote. It's natural to think of a personal anecdote as an introduction to a personal narrative, but stories and anecdotes can be effective introductions to any kind of paper. The following anecdote introduces a research paper on vegetarian and vegan diets. The conclusion returns briefly ...
Make details specific and interesting. Make your descriptions of the setting, characters, and action concrete and specific. For example: Step-by-step instructions with many examples. How to choose your topic and how to organize effectively so you can write a personal experience essay quickly.
Answer. It is very tempting to want to use things that we know based on our own personal experiences in a research paper. However, unless we are considered to be recognized experts on the subject, it is unwise to use our personal experiences as evidence in a research paper. It is better to find outside evidence to support what we know to be ...
The essay is structured as an example of the use of personal experience as well as a how-to guide. "Warp and Weft" contains a discussion of three students who incorporated narrative in their essays in three ways: as a structural frame, as an example when the research topic and personal experience overlap, and as a tool for discovery.
A mind map is a visual way of building a topic into a research question.. A topic is the basic idea that interests you. This is the idea that sparks your research. A topic could be "barbeque," "The Cold War," "flightless birds," or "the common cold." If you are having trouble choosing a topic, review the class syllabus or canvas modules.Find a topic covered in class that you can see yourself ...
Starting a research paper with a personal story help. I'm a freshman in high school and our quarter project is writing an argumentative research paper on the topic of our choice. My topic that I chose was that "The United States military should be decreased so that its funds can be allocated elsewhere."
Welcome to the Money blog. We'll have our usual personal finance and consumer news and tips, as well as all the latest on turbulence on the stock market. Leave a comment on any of the stories we ...
The country begins a new week on edge after anti-immigrant riots, fanned by disinformation from the far right, broke out in cities across Britain. By The New York Times After a weekend of violent ...