- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences

What the Case Study Method Really Teaches
- Nitin Nohria

Seven meta-skills that stick even if the cases fade from memory.
It’s been 100 years since Harvard Business School began using the case study method. Beyond teaching specific subject matter, the case study method excels in instilling meta-skills in students. This article explains the importance of seven such skills: preparation, discernment, bias recognition, judgement, collaboration, curiosity, and self-confidence.
During my decade as dean of Harvard Business School, I spent hundreds of hours talking with our alumni. To enliven these conversations, I relied on a favorite question: “What was the most important thing you learned from your time in our MBA program?”
- Nitin Nohria is the George F. Baker Jr. and Distinguished Service University Professor. He served as the 10th dean of Harvard Business School, from 2010 to 2020.
Partner Center
Why Directing is the Heart of Successful Management?
In the intricate world of management, there is one role that stands out as the heartbeat of any organization – the director. Often hailed as the driving force behind success, a director possesses a unique set of skills that sets them apart from other management positions. With their ability to navigate complexities, inspire teams, and make strategic decisions, it is no wonder why directing is considered the heart of management. From the boardroom to the factory floor, the director orchestrates the symphony of tasks, ensuring that every aspect of the organization is working harmoniously towards a common goal. This crucial role requires a delicate balance of leadership, vision, and adaptability. It is the director’s responsibility to not only steer the ship in the right direction but also to motivate and guide their team members to reach their full potential. With their finger on the pulse of the company, directors are the driving force that propels organizations towards success.
Table of Contents
The Role of Directing in the Management Process
Directing is an essential function of management that involves guiding and supervising individuals and teams to achieve organizational goals. It encompasses a wide range of activities, including setting objectives, allocating resources, providing guidance and support, and evaluating performance. The director plays a pivotal role in ensuring that the organization’s vision, mission, and values are effectively communicated and understood by all employees. By providing clear direction and guidance, directors empower their teams to perform at their best and contribute to the overall success of the organization.
Furthermore, directing involves the allocation of resources to ensure that the organization’s goals can be achieved effectively and efficiently. Directors must make strategic decisions regarding the allocation of financial, human, and technological resources, taking into consideration the organization’s priorities and constraints. This requires a deep understanding of the organization’s capabilities and needs, as well as the ability to prioritize and make informed decisions. By effectively managing resources, directors enable their teams to work efficiently and maximize their productivity.
Key Functions of Directing in an Organization
Effective directing encompasses several key functions that are vital for the success of an organization. These functions include:
Importance of Effective Directing for Organizational Success
Furthermore, effective directing fosters a positive work culture and enhances employee engagement and job satisfaction. When employees feel valued, supported, and empowered, they are more likely to be motivated and committed to their work. This leads to higher levels of productivity, creativity, and innovation, which are crucial for organizational growth and competitiveness.
Additionally, effective directing helps to foster collaboration and teamwork within the organization. By providing clear direction and coordinating activities, directors enable different departments and teams to work together towards common goals. This collaboration leads to better communication, improved problem-solving, and increased efficiency.
In summary, effective directing is crucial for organizational success. It provides the necessary guidance, support, and direction to ensure that the organization’s resources are utilized effectively and efficiently. It fosters a positive work culture, enhances employee engagement, and promotes collaboration and teamwork. Moreover, effective directing enables organizations to adapt to changes in the business environment and seize new opportunities.
Directing vs. Other Management Functions (Planning, Organizing, Controlling)
While directing is considered the heart of management, it is important to recognize its relationship with other management functions, namely planning, organizing, and controlling. Each of these functions plays a critical role in the overall management process, and they are closely interconnected.
Tools and Techniques Used in Directing
Directors utilize various tools and techniques to effectively direct their teams and achieve organizational goals. These tools and techniques help streamline communication, enhance decision-making, and improve overall performance. Some common tools and techniques used in directing include:
These are just a few examples of the tools and techniques used in directing. Directors must select and adapt these tools and techniques based on the unique needs and challenges of their organization. The key is to ensure that these tools and techniques align with the organization’s goals, values, and culture, and support the overall directing process.
Characteristics of Effective Directing
Challenges in implementing effective directing.
Implementing effective directing can be challenging due to various factors. Some common challenges include:
These are just a few examples of the challenges directors may face in implementing effective directing. Overcoming these challenges requires strong leadership skills, adaptability, and a commitment to continuous improvement.
Case Studies of Successful Directing in Organizations
Case study 1: company x – driving innovation and growth.
Company X is a technology company that operates in a highly competitive market. The director of the company recognized the need to foster innovation and drive growth to stay ahead of the competition.
Related Posts:
- Introduction, Meaning, Importance and Principles of Directing
Directing is the heart of management function. All other functions of management such as planning, organizing, and staffing have no importance without directing. Leadership , motivation, supervision , communication are various aspects of directing. Let us study the importance and principles of directing.
Suggested Videos
Directing refers to a process or technique of instructing, guiding, inspiring, counselling, overseeing and leading people towards the accomplishment of organizational goals. It is a continuous managerial process that goes on throughout the life of the organization . Main characteristics of Directing are as follows:
1. Initiates Action
A directing function is performed by the managers along with planning , staffing, organizing and controlling in order to discharge their duties in the organization. While other functions prepare a platform for action, directing initiates action.
Browse more Topics under Directing
- Elements of Direction
- Communications
2. Pervasive Function
Directing takes place at every level of the organization. Wherever there is a superior-subordinate relationship, directing exists as every manager provides guidance and inspiration to his subordinates.
4. Continuous Activity
It is a continuous function as it continues throughout the life of organization irrespective of the changes in the managers or employees .
5. Descending Order of Hierarchy
Directing flows from a top level of management to the bottom level. Every manager exercises this function on his immediate subordinate.
6. Human Factor
Since all employees are different and behave differently in different situations, it becomes important for the managers to tackle the situations appropriately. Thus, directing is a significant function that gets the work done by the employees and increases the growth of the organization.
(Source: qsstudy)
Explore more about Directing
- Communication
- Elements of Directing
Each and every action in an organization is initiated only through directing. The managers direct the subordinates about what to do, how to do when to do and also see to it that their instructions are properly followed.
2. Ingrates Efforts
Directing integrates the efforts of all the employees and departments through persuasive leadership and effective communication towards the accomplishment of organizational goals.
3. Motivates Employees
A manager identifies the potential and abilities of its subordinates and helps them to give their best. He also motivates them by offering them financial and non-financial incentives to improve their performance.
4. Provides Stability
Stability is significant in the growth of any organization. Effective directing develops co-operation and commitment among the employees and creates a balance among various departments and groups.
5. Coping up with the Changes
Employees have a tendency to resist any kind of change in the organization. But, adapting the environmental changes is necessary for the growth of the organization. A manager through motivation , proper communication and leadership can make the employees understand the nature and contents of change and also the positive aftermaths of the change. This will help in a smooth adaptation of the changes without any friction between the management and employees.
6. Effective Utilization of Resources
It involves defining the duties and responsibilities of every subordinate clearly thereby avoiding wastages, duplication of efforts, etc. and utilizing the resources of men, machine, materials, and money in the maximum possible way. It helps in reducing costs and increasing profits.
Read the Elements of Directing here .
Principles of Directing
1. maximum individual contribution.
One of the main principles of directing is the contribution of individuals. Management should adopt such directing policies that motivate the employees to contribute their maximum potential for the attainment of organizational goals.
2. Harmony of Objectives
Sometimes there is a conflict between the organizational objectives and individual objectives. For example, the organization wants profits to increase and to retain its major share, whereas, the employees may perceive that they should get a major share as a bonus as they have worked really hard for it.
Here, directing has an important role to play in establishing harmony and coordination between the objectives of both the parties.
3. Unity of Command
This principle states that a subordinate should receive instructions from only one superior at a time. If he receives instructions from more than one superiors at the same time, it will create confusion, conflict, and disorder in the organization and also he will not be able to prioritize his work.
4. Appropriate Direction Technique
Among the principles of directing, this one states that appropriate direction techniques should be used to supervise, lead, communicate and motivate the employees based on their needs, capabilities, attitudes and other situational variables.
5. Managerial Communication
According to this principle, it should be seen that the instructions are clearly conveyed to the employees and it should be ensured that they have understood the same meaning as was intended to be communicated.
6. Use of Informal Organization
Within every formal organization, there exists an informal group or organization. The manager should identify those groups and use them to communicate information. There should be a free flow of information among the seniors and the subordinates as an effective exchange of information are really important for the growth of an organization.
7. Leadership
Managers should possess a good leadership quality to influence the subordinates and make them work according to their wish. It is one of the important principles of directing.
8. Follow Through
As per this principle, managers are required to monitor the extent to which the policies, procedures, and instructions are followed by the subordinates. If there is any problem in implementation, then the suitable modifications can be made.
Solved Question for You
Q: Direction takes place at all levels of management. True or False?
Ans: The statement is true. Every manager of the organisation performs some function of directing. From top executives to low-level managers all give direction to their subordinates.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- New QB365-SLMS
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships

Class 12th Business Studies - Directing Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023
By QB365 on 08 Sep, 2022
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 12 Business Studies Subject - Directing, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Directing case study questions with answer key.
12th Standard CBSE
Final Semester - June 2015
Business Studies
Mr. Sunil Diali is a safety officer in a reputed PSU sector ECL. He supervises the workers towards the predetermined goals of the organisation and directs how to eradicate unsafe practices of inundation, fire breakouts, existence of inflammable gases etc. On one such instances there was huge fire breakout in the underground mines and the workers morale was down and demotivated because of several risk hazards. Mr. Diali observed the whole situation and consulted with all his workers and constantly monitored, guided and inspired them to integrate their efforts and accept the situation as a challenge and take adequate safety measures for fire extinguish and subsidizing its effects. Thereby, production turnover was outstanding and out performed other subsidiaries.Mr.Diali was recognised with Bravery Award from CIL. 1. Mr. Diali worked towards predetermined goals of the organization . Which important function of directing is addressed here?
2. Mr. Diali consulted with all his workers, he listened to their opinions. Which form of leadership is identified here?
3. Braveryawardis form of non-financial incentives.
4. Under Maslow’s hierarchy need theory which need of Mr. Diali has been met through respect and recognition among other employees?
*****************************************
Directing case study questions with answer key answer keys.
1. (b) Initiates action 2. (c) Democratic 3. (d) Employee recognition 4. (c) Esteem needs
Related 12th Standard CBSE Business Studies Materials
12th standard cbse syllabus & materials, cbse 12th physics wave optics chapter case study question with answers, cbse 12th physics ray optics and optical instruments chapter case study question with answers, cbse 12th physics nuclei chapter case study question with answers, cbse 12th physics moving charges and magnetism chapter case study question with answers, cbse 12th physics electromagnetic induction chapter case study question with answers, cbse 12th physics atoms chapter case study question with answers, 12th physics alternating current chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th maths vector algebra chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th maths three dimensional geometry chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th maths probability chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th maths linear programming chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th maths differential equations chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th maths continuity and differentiability chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th maths application of integrals chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th chemistry the d and f block elements chapter case study question with answers cbse.

Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

12th Standard CBSE Study Materials

12th Standard CBSE Subjects


Notes of Ch 7 Directing| Class 12th Business Studies
Summary and notes of ch 7 directing| class 12th business studies .
| Unsatisfied Need ↓ Tension ↓ Drivers ↓ Search Behaviours ↓ Satisfied Need ↓ Reduction of Tension |
Contact Form
CBSE Class 12 Case Studies In Business Studies – Directing
DIRECTING Directing: Definition Directing refers to the process of instructing, guiding, counselling, motivating and leading people in the organisation for the purpose of achieving organisational goals.
Importance of Directing
- Directing helps to initiate action by people in the organisation towards attainment of desired objectives.
- Directing integrates employees’ efforts in the organisation in such a way that it contributes to the organisational performance.
- Directing guides employees to fully realise their potential through effective communication, motivation and leadership.
- Directing facilitates introduction of needed changes in the organisation as it helps to reduce employees’ resistance and develop an environment which is conducive to introducing changes in the organisation.
- Effective directing helps to bring stability and balance in the organisation since it encourages cooperation and commitment.
Features of Directing
- Directing initiates action in the organisation as it is an executive function of management.
- Directing takes place at every level of management wherever superior – subordinate relations exist.
- Directing is a continuous process and is carried on till an organisation ceases to exist.
- Directing flows from top to bottom as it is first initiated at top level and flows to the bottom through organisational hierarchy.
Elements of Directing
- Supervision
- Communication
SUPERVISION Supervision: Definition Supervision is the process of overseeing the work of a subordinate by his superior.
Importance of Supervision
- A good supervisor acts as a guide, friend and philosopher to the workers.
- Supervisor acts as a link between workers and management.
- Supervisor plays a crucial role in maintaining group unity among workers placed under his control.
- Supervisor ensures performance of work according to the targets set and motivates the workers effectively.
- Supervisor provides good on-the-job training to the workers and employees.
- A supervisor with good leadership qualities can build up high morale among workers.
- A good supervisor analyses the work performed and gives feedback to the workers.
MOTIVATION Motivation: Definition Motivation is the process of stimulating people to action to accomplish desired goals.
Importance of Motivation
- Motivation helps to improve the performance of both the employees as well as the organisation.
- Motivation helps to mould negative or indifferent attitudes of employees into positive attitudes for the benefit of theorganisation.
- Motivation helps to reduce the employee turnover and leads to reduction in the cost to be incurred on new recruitment and training.
- Motivation helps managers to introduce changes within the organisation smoothly without much resistance from their subordinates.
- Motivation helps to reduce absenteeism in the organisation as work becomes a source of pleasure and workers attend to the work regularly.
Features of Motivation
- Motivation is an internal feeling as it relates to the urge, drives, desires, or needs of human beings.
- Motivation produces goal directed behaviour.
- Motivation can be either positive or negative.
- Motivation is a comolex nrocess as the individuals may differ in their perceptions and reactions. expectations,
Abraham Maslow’s Need Hierarchy Theory of Motivation
- Basic Physiological Needs refer to the needs that are most basic in the hierarchy like hunger, thirst, shelter etc. which can be fulfilled by basic salary.
- Safety/Security Needs refer to the needs to get security and protection from physical and emotional harm which can be fulfilled through job security, stability of income, pension plans etc.
- Affiliation/Belonging Needs refer to the needs that relate to affection, sense of belongingness, acceptance and friendship which can be fulfilled through team work, kindness etc.
- Esteem Needs include factors such as self-respect, autonomy status, recognition and attention which can be fulfilled by giving praise and recognition, offering promotions etc.
- Self-Actualisation Needs refer to the drive to become what one is capable of becoming which can be fulfilled by providing challenging work and giving them flexibility and autonomy in their jobs .
INCENTIVES Incentive: Definition Incentive means all measures which are used to motivate people to improve performance.
Types of Financial Incentives
- Pay and allowances
- Productivity linked wage incentives
- Profit Sharing
- Co-partnership/ Stock option
- Retirement Benefits
- Perquisites
Types of Incentives
- Financial incentives refers to incentives which are in direct monetary form.
- Non-financial incentives mainly focus on psychological, social and emotional needs.
Types of Non-financial Incentives
- Organisational Climate
- Career Advancement Opportunity
- Job Enrichment
- Employee Recognition programmes
- Job security
- Employee participation
- Employee Empowerment
LEADERSHIP Leadership: Definition Leadership is the process of influencing the behaviour of people by making them strive voluntarily towards achievement of organisational goals.
Importance of Leadership
- It helps to bring about a positive change in the behaviour of the employees for the benefit Of the organisation.
- It helps to maintain good personal relations and also helps the followers in fulfilling their needs.
- It helps to introduce the required changes in the organisation smoothly.
- It helps to resolve the conflicts within the organisation effectively without leading to any disruptions in working of the organisation.
- It facilitates training of subordinates by the leader.
Features of Leadership
- Leadership shows the ability of an individual to influence others.
- Leadership seeks to bring about a desired change in the behaviour of others.
- Leadership reflects the interpersonal relations between leaders and followers.
- Leadership is an effective tool to achieve common goals of the drganisation.
- Leadership is a continuous process.
Styles of Leadership
- Autocratic leadership
- Democratic leadership
- Laissez-faire
COMMUNICATION Communication: Definition Communication is defined as a process of exchange of ideas, views, facts, feelings etc., between or among people to create common understanding.
Importance of Communication
- Acts as basis of coordination among departments, activities and persons in the organisation
- Helps in smooth working of an enterprise as all organisational interactions depend on communica tions.
- Acts as basis of decision making as it provides the information needed for decision making.
- Increases managerial efficiency as it lubricates the entire organisation and keeps the organisation at work with efficiency.
- Promotes cooperation and industrial peace as the two way communication promotes cooperation and mutual understanding between the management and workers.
- Effective communication helps to establish effective leadership.
- Boosts morale and provides motivation to the employees and managers to achieve higher goals.
Elements Involved in Communication Process
- Sender refers to a person who conveys his thoughts or ideas to the receiver.
- Message is the content of ideas, feelings, suggestions, order etc., intended to be communicated.
- Encoding refers to the process of converting the message into communication symbols such as words, pictures, gestures etc.,
- Media is the path through which encoded message is transmitted to receiver through a face to face interaction, phone call, internet
- Decoding is the process of converting encoded symbols of the sender.
- Receiver refers to the person who receives communication of the sender.
- Feedback includes all those actions of receiver indicating that he has received and understood message of sender.
- Noise means some obstruction to communication
Types of Formal Communication Networks
- Upwards (from subordinate to his superior)
- Downward (froma superior to his subordinate) Horizontal
- Takes place between one division and another
- Informal communication is generally referred to as the ‘Grapevine’ because it spreads throughout the organisation with its branches going out in all directions in complete disregard to the levels of au thority.
BARRIERS TO COMMUNICATION IN THE ORGANISATIONS Semantic Barriers
- Badly expressed massage
- Symbols with different meanings
- Faulty translations
- Unclarified assumptions
- Technical jargon
- Body language and gesture decoding
Organisational Barriers
- Organisational policy
- Rules and regulations
- Complexity in organisation structure
- Organisational facilities
Psychological Barriers
- Premature evaluation
- Lack of attention
- Loss by transmission and poor retention
Personal Barriers
- Fear of challenge to authority
- Lack of confidence of superior on his subordinates
- Unwillingness to communicate
- Lack of proper incentives
Ways of Improving Communication Effectiveness
- Clarifying the ideas before communication
- Communicate according to the needs of receiver
- Consult others before communicating
- Be aware of languages, tone and content of message
- Convey things of help and value to listeners
- Ensure proper feedback
- Follow up communications
- Be a good listener
LATEST CBSE QUESTIONS
Question 1. Give the meaning of ‘motivation’ as an element of directing. (CBSE, Delhi 2017) Answer: Motivation is the process of stimulating people to action to accomplish desired goals.
Question 2. Explain briefly any three functions performed by a supervisor. (CBSE, Delhi 2017) Answer: The three functions performed by the supervisor are stated below:
- Supervisor maintains day-to-day contact and maintains friendly relations with workers and acts as a guide, friend and philosopher to them.
- Supervisor provides good on the-job training to the workers and employees and helps to build efficient team of workers.
- A good supervisor analyses the work performed and gives feedback to the workers. He suggests ways and means of developing work skills.
Question 3. Umang Gupta is the Managing Director of Denver Ltd. The company had established a good name for itself and had been doing well. It was known for timely completion of orders. The Production Manager, Ms. Kanta was efficiently handling the processing of order and had a team of fourteen motivated employees working under her. Everything was going on well. Unfortunately she met with an accident. Umang knew that in the absence of Ms. Kanta, the company may not be able to meet the deadlines. He also knew that not meeting the deadlines may lead to customer dissatisfaction with the risk of loss of business and goodwill. So, he had a meeting with his employees in which accurate the speedy processing of orders was planned. Everybody agreed to work as team because the behaviour of Umang Gupta was positive towards the employees of the organisation. Hence everyone put in extra time and efforts and the targets were met on time. Not only this, Umang visited Ms. Kanta and advised her to take sufficient rest.
- Identify the leadership style of Umang Gupta and draw a diagram depicting the style.
- State any two values highlighted by the behaviour of Umang Gupta. (CBSE, Delhi 2017)
- Responsibility
- Participation
Question 4. Explain any three points that highlight the importance of directing function of management. (CBSE, Delhi 2017) Answer: The three points that highlight the importance of directing function of management are described below:
- Initiate action: Directing helps to initiate action by people in the organisation towards attainment of desired objectives. It is the first execution function of management.
- Integrates employees efforts: Directing seeks to integrate the individual efforts of employees in the organisation towards the realisation of the organisational goals.
- Helps to realise their potential: Directing provides effective guidance, motivation and leadership to the employees so as to enable them to realise their potential and capabilities.
Question 5. Explain briefly any three measures to overcome the communication barriers. (CBSE, Delhi 2017) Answer: The three measures to overcome the communication barriers:
- Communicate according to the needs of receiver: For effective communication it is important that the message should be adjusted according to the education and understanding levels of the receiver.
- Be aware of languages, tone and content of message: The contents of the message, tone, language used, manner in which the message is to be communicated are the important aspects of effective communication.
- Ensure proper feedback: Inorder to ensure the success of communication, questions may be asked regarding the message conveyed. Thus the communication process may be improved by the feedback received to make ensure that the receiver has understood the sender’s ideas clearly.
Question 6. Explain briefly any three semantic barriers to communication. (CBSE, OD 2017) Answer: Semantic barriers are the ones that arise due to the problems and hinderances in the process of encoding and decoding of message into words. The three types of semantic barriers are described below:
- Badly expressed message: Many a times due to inadequate vocabulary, usage of wrong words, omission of required words etc. the sender may not be able to convey the intended meaning to the receiver.
- Faulty translations: Many a times a message has to be translated in an easily understandable language keeping in view the needs of the receiver. However, the message may not be conveyed in the desired manner if the translator is not proficient in both the languages and mistakes may happen which is likely to change the meaning of messages due to use of inappropriate words.
- Technical jargon: In order to communicate effectively it is important that the words used are easily understandable by the receiver. However, many a times it has been observed that the specialists may use technical terminology which cannot be comprehended by the receivers in the desired manner.
Question 7. Explain briefly any three organisational barriers to communication. (CBSE, OD 2017) Answer: Organisation barriers includes the factors related to organisation structure, rules and regulation, authority responsibility relationships etc. which are likely to hinder the smooth flow of communication within the organisation. The three types of organizational barriers are described below:
- Organisational policy: The effectiveness of communications within the organization is likely to be adversely affected if the organizational policy either explicitly or implicitly restricts the free flow of communication within the organization like if an organization is highly centralized.
- Status: The subordinates may not be able to express themselves freely if their superior being status conscious prefers to maintain a distance with them. This kind of an attitude of the superior tends to create a psychological distance between them.
- Organisational facilities: If an organization provides facilities like frequent meetings, suggestion box, complaint box, social and cultural gathering, transparency in operations and so on in order to facilitate free flow of communication it will lead to better management. This approach will foster smooth, clear and timely communications.
Question 8. Explain briefly any three personal barriers to communication. (CBSE, OD 2017) Answer: The personal barriers arise as a result of the personal outlook of both sender and receiver that may exert influence on effective communication. The three personal barriers to communication are described below:
- Tear of challenge to authority: At times a superior may tend to withhold or suppress such communication which he feels is likely to have an adverse affect on his authority.
- Lack of confidence of superior on his subordinates: A superior is unlikely to seek any advise from his subordinates if he lacks confidence on their competencies.
- Unwillingness to communicate: Many a times, a subordinate may withhold any communication deliberately if he feels its disclosure is likely to affect his/her interests adversely.
Question 9. Why is it said that directing takes place where ever superior subordinate relationship exists? (CBSE, Sample Paper, 2017) Answer: In every organisation, directing function is performed by every manager regardless of the level of management from top executive to supervisor. Therefore, it is said that directing takes place wherever superior subordinate relations exist .
Question 10. M/s Beta Ltd. deals in consumer goods. It employs 100 workers and 10 operative managers who give guidance and support to the workers while operating the machinery. The company has a policy of granting leave as per the requirement of the workers. Workers 3 H 3 are generally granted leave on festivals and special occasions. Recently on Puja festival, it received a big order. Workers are keen to take Puja holidays while management is pressing hard for overtime. This matter was placed before the Personnel Manager who called the meeting of operative managers and workers to inform them about the changes in the incentive plan which states payment of double wages for working overtime and triple wages for working on holidays. Workers without any pressure voluntarily took limited holidays and were able to increase their earning by working overtime and on holidays. During Board of Directors meeting, Personnel Manager was asked to update the management for achieving higher output, meeting timely supplies without any confrontation with workers. Personnel Manager replied, “I just used a carrot with no sticks approach”. (CBSE, Sample Paper, 2017) By quoting the lines from above paragraph state any two elements of directing. Answer: The two elements of directing being discussed in the above paragraph are outlined below:
- Supervision: Supervision is the process of overseeing the work of the subordinates and giving instructions to ensure optimum utilisation of resources and achievement of work targets. Supervision-” it employs 10 operating managers ……………….. support to the workers.”
- Motivation: Motivation is the process of stimulating people to action to accomplish desired goals. Motivation-“to pay double wages for working overtime and triple wages for working on holidays”.
Question 11. Describe briefly Maslow’s need hierarchy theory of motivation. (CBSE, Sample Paper, 2017) Answer: The various types of needs that exist in a hierarchy within every human being are stated below:
- Basic Physiological Needs: These needs are most basic in the hierarchy and are linked to primary needs like hunger, thirst, shelter etc. These needs of employees may be fulfilled by providing basic salary and the necessary breaks to use the washroom and eat food.
- Safety/Security Needs: These needs offer security and protection from physical and emotional harm. Job security and safe working conditions may be offered to the employees for the fulfillment of these needs.
- Affiliation/Belonging Needs: These needs refer to affection, sense of belongingness, acceptance and friendship. By encouraging cooperative teamwork and by being-an accessible and kind superiors these needs of employees may be fulfilled.
- Esteem Needs: These include factors such as self-respect, autonomy, status, recognition and attention. By giving praise and recognition when the employee does well and offering promotion these needs of the employee may be fulfilled.
- Self Actualisation Needs: It is the highest level of need in the hierarchy. It refers to the drive to become what one is capable of becoming. These needs include growth, self-fulfilment and achievement of goals. By providing challenging work and giving them flexibility and autonomy in their jobs, these needs of the employees may be fulfilled.
Question 12. Prateek is working in a multinational company in Noida. He was running a temperature for the last many days. When his blood was tested, he was found to be positive for malaria. He was admitted in a hospital and a blood transfusion was advised by the doctors as his condition was very serious. One of his colleagues sent a text message to his superior, Mr. B. Chatterjee. Mr. B. Chatterjee immediately sent a text message to the employees of the organisation requesting them to donate blood for Prateek. When the General Manager came to know about it, he ordered for fumigation in the company premises and cleaning the surroundings.
- From the above paragraph, quote lines that indicate formal and informal communication.
- State any two features of informal communication.
- Identify any two values that are being communicated to society in the above case. (CBSE, OD 2016)
- Informal communication: “One of his colleagues sent a text message to his superior, Mr. B. Chatterjee. Mr. B. Chatterjee immediately sent a text message to the employees of the organisation requesting them to donate blood for Prateek.” Formal communication: “When the general manger came to know about it, he ordered for fumigation in the company premises and cleaning surroundings.”
- The grapevine/ informal communication spreads very fast and sometimes gets distorted.
- It is very difficult to detect the source of such communication.
- Cleanliness
Question 13. Mr. Shubhendu Bose is the owner of Bikmac Enterprises carrying on the business of manufacturing various kinds of biscuits. There was a lot of discontentment in the organisation and the targets were not being met. He asked his son, Naval, who had recently completed his MBA, to find out the reason. Naval found that all the decision-making of the enterprise were in the hands of his father. His father didn’t believe in his employees. As a result, both the employer and the employees were not able to understand each others’ messages in the same sense. Thus, the employees were not happy and targets were not met.
- Identify any two communication barriers because of which Bikmac Enterprises was not able to achieve its target.
- State one more barrier each of the types identified in (1) above. (CBSE, Delhi 2016)
- Organisational barriers: Organisational Policy If the organisational policy, is not supportive to free flow of communication, it may hamper effectiveness of communications. Like in the above case Naval found that all the decision making power of the organisation was highly centralised as it was in hands of his father only.
- Psychological barriers: Distrust Sometimes if there is lack of trust between the parties, they cannot understand each other’s message in the same sense. Like in the above case Naval found out that his father didn’t believe in his employees.
- Organisational barriers: Status: Sometimes a status conscious manager also may not allow his subordinates to express their feelings freely. This kind of an attitude may create psychological distance between him and his subordinates. Psychological barriers: Premature evaluation: Sometimes people tend to evaluate the meaning of message even before the sender completes his message on the basis of their own judgement, experience etc.
Question 14. Mr. Fernandes is the owner of Unibie Enterprises, carrying on the business of manufactur¬ing electrical appliances. There is a lot of discontentment in the organisation and targets are not being met. He asked his son, Michel, who has recently completed his MBA to find out the reason. Michel found that all the decision-making of the enterprise were in the hands of his father. Moreover, his father did not have confidence in the competency of the employees. Thus, the employees were not happy.
- Identify any two communication barriers because of which Unibie Enterprise was not able to achieve its target.
- State one more barrier each of the types identified in part (1) above. (CBSE, OD 2016)
- Organisational barriers: Organisational policy If the organisational policy, is not supportive to free flow of communication, it may hamper effectiveness of communications. Like in the above case Michel found that all the decision making power of the organisation was highly centralised as it was in hands of his father only.
- Personal barriers: Lack of confidence of superior in the subordinate: The personal factors of both sender and receiver may exert influence on effective communication and they may not be able to understand each other’s message in the same sense. Like in the above case Michel found out that his father didn’t have confidence in the competency of the employees.
- Organisational barriers: Status: Sometimes a status conscious manager also may not allow his subordinates to express their feelings freely. This kind of an attitude may create psychological distance between him and his subordinates. Personal barriers: Pear of challenge to authority: If a superior may withhold or suppress the communication that he may perceive is likely to have an adverse affect on his authority.
Question 15. Alfa Ltd. was dealing in renewable energy services. To get the business, the team leader and his team used to travel to different states to give presentations to the clients. As per the policy of the company, the team leader used to travel by air whereas his team travelled by road/train. It was not only time-consuming but also forced the female team members to travel alone at times. As a result, the subordinates were not acting in a desired manner to achieve the organisational goals. The CEO of the company came to know about it. He called the team leader, discussed the matter with him and decided to change the travel policy of the company. It was decided that in future, all the members including the leader would travel together and usefully utilise the travelling time in discussion about the presentation to be given to the clients. This made a positive impact and every member of the team started acting in a manner as desired by the team leader. State the features of the element of the function of management used by the CEO. (CBSE, OD 2016) Answer: The CEO Alfa Ltd. has used Motivation, which is an element of directing function of management in order to deal with the situation effectively. The features of motivation are explained below:
- Motivation is an internal feeling: An urge, drives, or needs of human being, which are internal, but likely to influence human behaviour.
- Motivation produces goal directed behaviour: A motivated employees is likely to act in a desired manner and contribute effectively.
- Motivation can be either positive or negative: Positive motivation can be provided through rewards like increase in pay, promotion, recognition etc. Negative motivation involves use of negative means like punishment, stopping increments, threatening etc. which also may prompt a person to act in the desired way.
Question 16. Samita had been working as an assistant manager with Johnson Enterprises for the last ten years. She was very popular amongst her colleagues because of her commitment and dedication towards work. When the manager senior to her retired, all her colleagues thought that now Samita would be promoted. But to everyone’s surprise, the vacant post was filled by an outsider, Mrs. Rita. Samita felt demoralised and her performance started declining. She would absent herself often and could not meet her targets. Mrs. Rita was a good leader who would not only instruct her subordinates but would also guide and inspire them. She notices Samita’s behaviour and felt that her performance could be improved. She started involving Samita in the decision-making issues related to the organisation and made her a part of a high level joint-management committee. Samita was now punctual in office and her performance started improving.
- Identify the function of management being performed by Mrs. Rita.
- Name the element of the above function of management which helped Rita improve Samita’s behaviour.
- State any three features of the element identified in (2) above. (CBSE, Delhi 2015)
- Mrs. Rita has performed the directing function of management.
- Mrs. Rita has been able to improve Samita’s behaviour with the help of motivation which is an element of directing.
- Motivation is an internal feeling: An urge, drives, or needs of human being, which are internal, but are likely to influence human behaviour.
- Motivation can be either positive or negative: Positive motivation can be provided through rewards like increase in pay, promotion, recognition etc., Negative motivation involves use of negative means like punishment, stopping increments, threatening etc. which also may prompt a person to act in the desired way.
Question 17. Jaideep recently joined as the Managing Director of Tivori Ltd., an apparel designing company. He observed that the company had a number of experienced fashion designers on its payroll. They regularly offered useful suggestions which were neither appreciated nor rewarded by the company. Instead, the company outsourced its services to some renowned fashion designers and paid them a good compensation for their services. Because of this, the employees felt disheartened and stopped giving useful suggestions.
- Identify the communication barrier discussed above.
- State the category of this communication barrier.
- Explain any other communication barriers of the same category. (CBSE, OD 2015)
- The communication barrier discussed in the above paragraph is Lack of proper incentives
- It is a type of personal barrier.
- Fear of challenge to authority: If a superior may withhold or suppress the communication which he perceives is likely to adversely affect his authority..
- Lack of confidence of superior on his subordinates: A superior may not seek the advice or opinions of their subordinates if he / she do not have confidence on their competency.
- Unwillingness to communicate: Sometimes, subordinates may deliberately with hold any communication with their superiors, if they perceive that it may adversely affect their personal interests.
Question 18. Neeraj, a sales representative of Omida. Ltd. has changed seven jobs in the last one year. He is a hardworking person but is not able to finalise deals with customers due to his inadequate vocabulary and omission of needed words. Sometimes, he uses wrong words because of which the intended meaning is not conveyed. All this creates a misunderstandings between him and his clients.
- Explain any other communication barriers of the same category. (CBSE, Delhi 2015)
- The communication barrier discussed above is badly expressed message.
- This kind of barrier falls in the category of semantic barriers.
- Symbols with different meanings: Sometimes, a word may have several meanings. The communication will be effective only if the receiver perceives it in the same manner as intended by communicator.
- Faulty translations: Many a times it has been noted that if the translator is not proficient with both the languages, mistakes may creep in causing different meanings to the communication.
- Technical jargon: It is usually seen that specialists use technical jargon while explaining something. If the persons with whom they are communicating are not specialists in the concerned field, they may not be able to understand the actual meaning of many such words.
- Body language and gesture decoding: While speaking, one may tend to move his/her body in a certain manner. If there is no match between what is said and what is expressed in body movements, communications may be wrongly perceived by the receiver.
Question 19. Pramod was a supervisor at ‘Annapurna Aata’ factory. The factory was producing 200 quintals of aata every day. His job was to make sure that the work went on smoothly and there was no interruption in production. He was a good leader who would give orders only after consulting his subordinates and work-out the policies with the acceptance of the group. Identify and describe the leadership style being adopted by Pramod. (CBSE, Delhi 2015) Answer: As a supervisor of ‘Annapurna Atta/ Pramod has adopted the democratic style of leadership. Democratic leadership is also known as participative leadership. In this type of leadership style, the members of the group take a more participative role in the decision-making process. Everyone is given the opportunity to participate, ideas are exchanged freely, and discussion is encouraged. It is one of the most effective style of leadership and leads to higher productivity, better contributions from group members, and increased group morale.
Question 20. Rahim was working in an enterprise on a daily wages basis. It was difficult for him to fulfill the basic needs of his family. His daughter fell ill. He had no money for his daughter’s treatment. To meet the expenses of her treatment, he participated in a cycle race and won the prize money. The cycle company offered him a permanent pensionable job which he happily accepted.
- By quoting lines from the above paragraph, identify the needs of Rahim that are satisfied by the offer of the cycle company.
- Also, explain two other needs of Rahim followed by above that are still to be satisfied. (CBSE, Delhi 2014)
- The physiological needs and safety needs of Rahim are being satisfied by the offer of the company.
- Affiliation/Belonging Needs: These needs refer to affection, sense of belongingness, acceptance and friendship. The organisation, by encouraging cooperative teamwork and by having accessible and kind superiors, can fulfill these needs of its employees.
- Esteem Needs: These include factors such as self-respect, autonomy status, recognition and attention. The organisation,by giving praise and recognition when the employees do well, and offering promotions, can fulfill these needs of its employees.
Question 21. Ankur is working as a production manager in an organisation. His subordinate, Saurabh, discussed with him a method of production which will reduce the cost of production. But due to some domestic problems and Ankur’s mind being pre-occupied, he is not in a position to understand the message. Saurabh got disappointed by this. Identify the factor which acts as communication barrier. Explain three other factors of the same group of communication barriers. (CBSE, OD 2012) Answer: Ankur is not in a position to understand the message due to lack of attention. It is a type of psychological barrier. The preoccupied mind of the receiver leads to non-listening of a message which acts as a major psychological barrier. Some of the other psychological barriers are described below:
- Premature evaluation: Sometimes people tend to evaluate the meaning of a message on the basis of their own judgement, experience etc., even before the sender completes his message. This may lead to misinterpretation of the message.
- Loss by transmission and poor retention: When communication passes through various levels, successive transmissions of the message result in the loss of information or transmission of inaccurate information. Also, sometimes due to poor retention, people cannot retain the information for a long time if they are inattentive or not interested.
- Distrust: If the communicator and communicator not trust each other, it may act as a barrier. This is because if they do not believe each other, they may not understand each other’s message in the desired sense.
Question 22. Rakesh is working under his superior Neeraj. He always communicate useful ideas and suggestions to his superior regarding the reduction of cost, improvements in the product, etc. Neeraj implements his suggestions and has always found favourable results but he never appreciates Rakesh for his suggestions. Now, Rakesh decides not to communicate any suggestion or idea to Neeraj. Identify the factor which acts as a communication barrier. Explain three other factors of the same group of communication barriers. (CBSE, Delhi 2012) Answer: Due to the lack of proper incentives, Rakesh has decided not to communicate any suggestion or idea to Neeraj. If there is no motivation or incentive for communication, subordinates may not take initiative to communicate. It is a type of personal barrier. Sometimes the personal factors of both the sender and the receiver may exert influence on effective communication. A few of these are discussed below:
- Fear of challenge to authority: A superior may withhold or suppress the communication which he perceives is likely to adversely affect his authority.
- Lack of confidence of superior in his subordinates: A superior may not seek the advice or opinions of his/her subordinates if he/she does not have confidence on their competency.
- Unwillingness to communicate: Sometimes, subordinates may deliberately withhold any communication with their superiors if they perceive that it may adversely affect their personal interests.
Question 23. Ayasha Ltd. assured their employees that in spite of the recession, no workers will be retrenched from their jobs.
- Name and explain the type of incentive offered to the employees.
- Explain one more incentive of the same category. (CBSE, Delhi 2010)
- The type of incentive offered to the employees is job security. It is a non-financial incentive. In order to fulfill their safety needs, the employees want certain stability about future income and work. As a result they feel motivated and give better job performance. However, it has been observed many a times that when people feel that they are not likely to lose their jobs, they may become complacent.
- The other incentive of this category is employee participation. It is a means by which the employees may be involved in the decision making process of the issues related to them. The sense of participation motivates them to contribute positively towards their job performance.
Question 24. Rajat, a sales manager, achieved his sales targets one month in advance. This achievement was displayed on the notice board and a certificate for the best performance was awarded to him by the CEO of the company.
- Name the incentive provided to Rajat.
- Identify the type of incentive.
- List two other incentives of the type identified in part (2). (CBSE, 2008)
- Recognition is the incentive provided to Rajat.
- It is a type of non-financial incentive.
- The two other types of non-financial incentives are job security and status.
Question 25. Mohan and Sohan are friends working in Surya Ltd. as Production Manager and Sales Manger respectively. In an interdepartmental meeting, Sohan informed Mohan about a change in the marketing policy of the company. Identify the type of communication used in the above example. (CBSE, 2008) Answer: Formal communication is being used in the above example.
ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS
Question 1. Post demonetisation, bank employees have been experiencing hectic long working hours, which has been highly praised by all. Banks chalked out a compensation plan for their employees, who have been working long hours like offering compensatory “off-days” in lieu of holidays on which the employees worked , giving “additional money” to the employees and so on. Reshma (42), who has been working with a nationalized bank for seven years, said, ” We have worked tirelessly to meet customer’s demands,”. Moreover she added that “There were several circulars from the head office and RBI. We had to go through them thoroughly and adhere to all the instructions. It is also important to ensure transactions go smoothly and we solve customer-staff disputes,” In context of the above case:
- Identify the human need of Reshma as per Maslow’s need hierarchy theory which was affected due to demonitisation.
- Identify the type of incentives which were provided to the bank employees for assuming their responsibility diligently.
- State any two values which the banks are propagating towards their customers.
- The human need of Reshma as per Maslow’s need hierarchy theory of which was affected due to demonitisation is described below: Basis physiological needs: These needs are most basic in the hierarchy and are linked to primary needs like hunger, thirst, shelter etc.
- Both monetary and non-monetary incentive were being provided to the bank employees for assuming their responsibility diligently.
- Customer satisfaction
Question 2. Roshan is the chief chef of ‘Khidmat7 restaurant located in the city of Bangaluru. The place is known for its exquisite Mughlai cuisine especially mutton biryani and kababs. All the food is prepared under Roshan’s purview. The various activities in the kitchen are initiated in accordance to his instructions. He is very clear and specific in issuing instructions to his subordinates in order to ensure smooth working of the department. He personally oversees the method followed by the chefs for preparation of each dish. He misses no opportunity to praise his subordinates for their good work. All his team members feel very happy and satisfied under his direction. He provides constant guidance to them in order to improve upon its taste and presentation and also encourages them to innovate and be more creative in their work. In the above context:
- Identify the various elements of directing mentioned in the above paragraph by quoting lines from the paragraph.
- Describe briefly any two points to highlight the importance of directing as a function of management.
- Communication: “He is very clear and specific in issuing instructions to his subordinates in order to ensure smooth working of the department.” Supervision-. “He personally oversees the method followed by the chefs for preparation of each dish.”
- Leadership: “He provides constant guidance to them in order to improve upon its taste and presentation and also encourages them to innovate and be more creative in their work.”
- Motivation: “He misses no opportunity to praise his subordinates for their good work.”
- Initiates action: Directing helps to initiate action by people in the organisation towards attainment of desired objectives. It is the first execution function of management.
- Integrates employees’ efforts: Directing seeks to integrate the individual efforts of employees in the organisation towards the realisation of the organisational goals.
- Helps to realise their potential: Directing provides effective guidance, motivation and leadership to the employees so as to enable them to realise their potential and capabilities, (any two)
Question 3. Anurag has joined as a supervisor in a hospital. He realises that the support staff workers are not working up to their full potential. Due to a constant conflict with the management on wages, they have developed an indifferent attitude towards it. The workers have become lazy and tend to avoid work. Moreover, there are a few internal differences amongst the workers. In order to motivate them he starts giving them praise and encouragement as a result of which the workers slowly start showing improvements in their work performance. In the above context:
- Define the term supervision.
- What are the challenges that Anurag is facing as a supervisor? Outline the role he needs to play in overcoming them.
- The term supervision consists of two words i.e. ‘super’ which means over and above and ‘vision’ which means the art of seeing objects. Supervision is the process of overseeing the work of a subordinate by his superior.
- As a link between workers and management, he has to work towards resolving the conflicts between management and workers. He should convey the management’s ideas to the workers on one hand and workers’ problems to the management on the other.
- He should strive to maintain harmony among the workers by helping to clear out the internal difference among them.
- He has to ensure that the performance of work in the hospital is according to the targets set. He has to assume the responsibility for task achievement and motivates his workers effectively.
Question 4. Neeraj has been working as a sewing machine operator in an export house for the past ten years. His basic work is to seam the parts of a garment together, and attach buttons, hooks, zippers, and accessories to produce clothing. Considering the fact that Neeraj is an experienced operator, he is well versed with the fundamentals of industrial production and possesses good communication skills. The plant superintendent in the factory recommends Neeraj’s name to the production manager for the post of supervisor which will fall vacant after a month on the retirement of the present supervisor. Consequently, Neeraj is assigned the post of supervisor and his salary is increased accordingly. Moreover, as per the policy of the export house, he is offered free medical aid and education to his two children. In context of the above case:
- Identify the type of source of recruitment used by the export house to fill up the post of supervisor. Give any two advantages of using this source.
- Identify the types of financial incentives offered to Neeraj by quoting lines from the paragraph.
- Employees are motivated to improve their performance: When employees are promoted internally from within an organisation, it has a positive impact on their commitment and loyalty and they tend remain satisfied with their jobs. Also, it may lead to a chain of promotion at lower levels in the organisation. As a result,it motivates the employees to improve their performance through learning and practice.
- Internal recruitment simplifies the process of selection and placement: The candidates can be appraised more perfectly and economically as that are already working in the organisation. As the candidates are already known to the organisation, it is considered to be a more reliable method of recruitment.
- Pay and allowances: “his salary is increased accordingly.”
- Perquisites: “as per the policy of the export house, he is offered free medical aid and education to his two children.”
Question 5. After completing his bachelor’s in computer science, Abhijeet joined an IT consultancy firm. He observed there that the senior management more often communicated failures than successes. They rarely shared any good news related to the growth of the firm or give any recognition to its employees for their extraordinary contributions towards the firm. As a result, Abhijeet never felt encouraged enough to work up to his full potential and started exploring other avenues for employment. In the context of the above case:
- Identify and explain the element of directing in the absence of which the employees don’t feel encouraged to work.
- State the importance of this element as identified in part (1) by giving any two suitable points
- The element of directing being referred to is motivation.
- Improves performance: Motivation helps to improve the performance of both the employees as well as the organisation. This is because motivated employees contribute their maximum efforts for organisational goals.
- Reduces employee turnover: Motivation helps to reduce employee turnover and thereby saves the cost of new recruitment and training. This is due to the fact that the managers identify the motivational needs of employees and provide suitable incentives. Consequently the employees feel satisfied and may not think of leaving the organisation.
Question 6. Atuliya has started his own consultancy firm under the name ‘Happy Go Lucky’ after working for five years in a company as a wedding planner. Considering the fact that he is into a labour intensive business and motivation is a complex process, Atulia wants to offer such rewards and benefits that will help to fulfill the various needs of the employees and will inspire them to give their best to the organisation. In the context of the above case:
- Why is motivation considered to be a complex process?
- Name the various types of needs that exist in a hierarchy within every human being. Also, suggest any two suitable incentives for each of these that Atulia may offer to his employees.
- Motivation is considered to be a complex process as the individuals may differ in their expectations, perceptions and reactions. Therefore, the same type of motivation may not have uniform effect on all the persons.
- Basic Physiological Needs: These needs are most basic in the hierarchy and are linked to primary needs like hunger, thirst, shelter etc. Atulia may fulfill these needs of his employees by providing basic salary and the necessary breaks to use the bathroom and eat and/or drink.
- Safety/Security Needs: These needs offer security and protection from physical and emotional harm. Atulia may offer job security and safe working conditions to his employees for the fulfillment of these needs.
- Affiliation/Belonging Needs: These needs refer to affection, sense of belongingness, acceptance and friendship. Atulia, by encouraging cooperative teamwork and by being an accessible and kind manager, can fulfill these needs of his employees.
- Esteem Needs: These include factors such as self-respect, autonomy, status, recognition and attention. Atulia may give praise and recognition when the employee does well, and offer promotions to fulfill these needs of his employees.
- Self Actualisation Needs: It is the highest level of need in the hierarchy. It refers to the drive to become what one is capable of becoming. These needs include growth, self-fulfilment and achievement of goals. Atulia, by providing challenging work and giving them flexibility and autonomy in their jobs, may fulfill these needs of his employees.
Question 7. Sunidhi has started a designer studio in the basement of her residence after completing her masters in fashion designing. She has appointed ten employees to take care of the various aspects of the work. She interacts regularly with each employee to tell exactly what is expected of him/her and what he/she needs to do to be regarded as a’ good performer. At the same time she allows a free work environment wherein the employees openly chit chat with each other in order to fulfil their social and emotional needs. Sometimes, these interactions also lead to spreading rumours which are not authentic. In the context of the above case:
- Name and explain the two types of communication being referred to in the above paragraph.
- How does effective communication increases managerial efficiency?
- Formal communication: The communication that flows through official channels de¬signed in the organisation structure is called formal communication. This corn- munication may take place between a subordinate and superior or among same team employees or managers. Usually a written record of such communications is maintained, recorded and filed in the office. Formal communication may be further classified as – Vertical and Horizontal.
- Informal communication: Informal communication is the type of communication that takes place without following the formal lines of communication. It is generally referred to as the ‘grapevine’ because it spreads throughout the organisation with its branches going out in all directions in utter disregard to the levels of authority. The informal communication arises out of needs of employees to exchange their views, which cannot be done through formal channels.
- Effective communication increases managerial efficiency by lubricating the working of the entire organisation through quick and effective performance of managerial functions. It enables the management to express the goals and targets, issue instructions, allocate jobs and responsibilities and look after the performance of subordinates.
Question 8. Gagan has joined as a Managing Director of True Help Ltd., a company engaged in the business of providing road side assistance to the vehicle owners. He was previously working in an automobile company. As a part of the joining incentive, the company has allotted him 400 shares of the company. In context of the above case:
- Identify the type of source of recruitment used by True Help Ltd. to fill up the post of Managing Director.
- Identify the type of financial incentive offered to Gagan. Also, state any one other method that can be used to offer financial incentives to the employees.
- External source of recruitment has been used by True Help Ltd. to fill up the post of Managing Director.
- Co-partnership/ Stock option is the type of financial incentive offered to Gagan. The other method that can be used to offer financial incentives to the employees is Bonus. Bonus is an incentive offered over and above the wages/ salary to the employees
Question 9. Yash has set up a small scale manufacturing unit for making different varieties of low cost detergents. In order to market his product he has employed a team of five salesmen. Each salesman has been assigned specific areas in the city. He holds a meeting every month for determining the objectives to achieved during the coming month. A sales target is pre¬determined for each month which is mutually agreed by both Yash and his sales team. If the salesmen succeeds in reaching this target a bonus is paid out to all of them along with the monthly salary. In context of the above case:
- What style of leadership is adopted by Yash? Explain by quoting lines from the para.
- Name the type of non financial incentive being offered to the salesmen by seeking their involvement in deciding the monthly targets of the firm.
- The democratic style of leadership is adopted by Yash. A democratic leader encourages his subordinates to participate in the process of decision making. Thereby, the manager is able to motivate his subordinates to perform their best, as they themselves have set the goals. “A sales target is pre-determined for each month which is mutually agreed by both Yash and his sales team.”
- Employee participation is the type of non financial incentive that is being offered to the salesmen by seeking their involvement in deciding the monthly targets of the firm.
Question 10. Priyank works as a banquet manager in a hotel. He feels highly motivated at his job because the work that is assigned to him frequently involves variety of challenges. He is given more autonomy and responsibility and provided with ample opportunities for personal growth and a meaningful work experience. In context of the above case:
- Define the term ‘motivation’.
- What are the measures used to motivate the employees to improve performance known as? Give its classification.
- Identify the type of non-financial incentive being offered to Priyank.
- Motivation refers to the process of stimulating people to action to achieve desired goals.
- The measures used to motivate the employees to improve performance are known as incentives. These incentives may be broadly classified as financial and non-financial.
- Job Enrichment is the type of non-financial incentive being offered to Priyank.
Question 11. Google Inc. is an American multinational corporation that is best known for running one of the largest search engines on the World Wide Web (WWW). Every day, 200 million people use it. Google was named the 2014 “Best Company to Work For” by the Great Place to Work Institute and Fortune Magazine. The organization topped the’list for the fifth time. The company hosts employee forums on all fridays where there is an examination of the 20 most asked questions. Moreover, its employees can make use of any of a number of channels of expression to communicate their ideas and thoughts. Channels include Google+ conversations, a wide variety of surveys, Fixits (24 hour sprints wholly dedicated to fixing a specific problem) and even direct emails to any of the Google leaders. In the above context:
- Identify the type of communication barrier being overcome by Google Inc. by providing a number of channels of expression to their employees to communicate their ideas and thoughts.
- Briefly explain any two other types of communication barriers.
- Organisational barrier is being overcome by providing organisation facilities through a number of channels of expression to their employees to communicate their ideas and thoughts.
- Psychological barriers: Sometimes the emotional or psychological factors act as barriers to communicators. Thus, the state of mind of both sender and receiver of communication reflects in effective communication. For example, premature evaluation, distrust etc.
- Semantic barriers: These barriers are concerned with problems and obstructions in the process of encoding and decoding of message into words or impressions. Normally, such barriers result on account of use of wrong words, faulty translations, different interpretations etc.
Question 12. Nikhil runs a small dhabba on the Jaipur highway. He is very rigid and follows a strict policy of punishment like cutting the salary, stopping increments or giving job termination threats to his workers for any kind of discrepancies in their work. He does not seek advice or opinions from his workers, as he does not have any confidence on the competence of his workers. Also, the workers are not willing to offer useful suggestions as they do not expect any motivation or incentive for taking such initiatives. As a result, the labour turnover is high and his business has been adversely affected. In the above context:
- Name and explain the style of leadership adopted by Nikhil.
- Identify the various human needs of workers that are being overlooked by Nikhil as per the Maslow’s need hierarchy theory of motivation.
- Identify the type of communication barrier created by Nikhil due to which the workers suppress their need to communicate with him.
- The autocratic style of leadership has been adopted by Nikhil. An autocratic leader expects strict compliance from his subordinates with regard to the orders and instructions given by him. Therefore, it involves only one-way communication.
- Basic Physiological Needs: These needs are most basic in the hierarchy and are linked to primary needs like hunger, thirst, shelter etc.
- Safety/Security Needs: These needs offer security and protection from physical and emotional harm.
- Lack of confidence of superior on his subordinates: If superiors do not have confidence on the competency of their subordinates, they may not seek their advice or opinions.
- Lack of proper incentives: If there is no motivation or incentive for communication, subordinates may not take initiative to communicate. For example, if there is no reward or appreciation for a good suggestion, the subordinates may not be willing to offer useful suggestions.
Question 13. After pursuing a course in gemmology from Australia, Raj started a workshop in Surat to supplement his father’s jewellery business in Delhi. He is used to speaking in English but the local skilled workers understand only Hindi and Gujarati. Hence, he started facing problems in the work due to miscommunications between him and the workers. As a result, he is not able to get the jewellery designs made in the desired manner and getting them redesigned turns out to be very expensive. In the context of the above case:
- Define the term ‘communication’.
- Identify the type of communication barrier being referred to in the above paragraph.
- Suggest any four measures by which he can improve his communication effectiveness.
- Communication is a process by which people create and share information with one another in order to reach common understanding.
- Semantic barrier is being referred to in the above paragraph.
- Communicate according to the needs of receiver: Raj should adjust his communication according to the education and understanding levels of his subordinates.
- Be aware of languages, tone and content of message: The contents of the message, tone, and language used and the manner in which the message is to be communicated are the important aspects of effective communication.
- Ensure proper feedback: He may ensure the success of communication by asking questions regarding the message conveyed. Thus the communication process may be improved by the feedback received to ensure that the workers have understood his ideas clearly.
- Follow up communications: He should do a regular follow up and review on the instructions given to the workers. Such follow up measures help in removing hurdles, if any, in implementing the instructions.
Case Studies in Business Studies Business Studies Case Studies Business Studies Commerce
One thought on “ CBSE Class 12 Case Studies In Business Studies – Directing ”
Extremely useful . God bless you.
Comments are closed.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
Directing Class 12 Notes CBSE Business Studies Chapter 7 (Free PDF Download)
- Revision Notes
- Business Studies
- Chapter 7 Directing

Revision Notes for CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 7 - Free PDF Download
Class 12 Commerce NCERT Business Studies comprises excellent chapters aiming at developing knowledge related to many aspects of business management and an organization. It helps students to learn how a business is run and where they have to concentrate. The 7 th chapter of Class 12 Business Studies is Directing. This chapter elaborates on how businessmen should lead a team to take their business to a new level. This is where the students of Class 12 will need the assistance of Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 7 Revision Notes by Vedantu.
Chapter 7 of Class 12 Business Studies Notes focuses on how a person will direct a team, guide the team members, manage their productivity, give instructions, motivate, and lead the staff to achieve a goal together. The subject experts at Vedantu are aware of the CBSE guidelines and also know where the students generally need help. These notes are prepared to resolve the queries arising in their minds and help them to quickly revise the chapter before an exam. You can also download Directing Class 12 Business Studies Revision Notes PDF and use them at your convenience to make your study schedule better and flexible.
Download CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Revision Notes 2024-25 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 12 Business studies revision notes for other chapters:
CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Notes | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Chapter 7 - Directing Notes |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Related Chapters
Access Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 7 - Directing Notes
Directing is the process in which a superior provides instructions, guidance and counselling to its subordinate so as to motivate and lead them for the successful achievement of objectives.
Characteristics of Directing
Initiates action: Directing initiates action through instructions supervision and motivation to achieve goals.
All pervasive: Directing takes place in every organization, and at every level of management.
Continuous process: Directing is a continuous process and takes place throughout the life of an organization.
Flows downward: Directing flows downward from superior to subordinate.
Importance of Directing
Initiates action: Directing helps to initiate action towards attainment of desired objective.
Integrates efforts: It integrates individual efforts as group effort to achieve organizational objectives.
Provide leadership and motivation; Directing motivates and provides effective leadership to employees to realise their full potential.
Brings changes: Directing introduces changes in the organization through proper communication, motivation and leadership.
Maintain stability: Balance and stability in the organization could be maintained through effective directing.
Principles of Directing
Maximum individual contribution: Through effective directing a manager must help the employee to realise his full potential, and contribute maximum towards the achievement of organizational goals.
Harmony of objectives: Through effective directing, managers must provide harmony between employee’s individual objectives and organizational objectives.
Unity of command: Employees must get instructions and direction from one superior for effective directing.
Appropriateness of direction technique : A manager must choose different direction tools according to the situation for effective direction.
Managerial communication: Communication should be in accordance with subordinate need for effective direction.
Use of informal organization: For effective direction managers should use informal organization for building cordial relationships with subordinates.
Leadership: A manager must possess good leadership qualities to influence subordinates.
Follow through: Manager must review employee’s performance for effective directing.
Elements of direction
These are grouped into four categories:
Supervision
Communication.
Supervision involves overseeing and guiding the efforts of human and other resources with an objective to accomplish the desired objectives.
It means overseeing what is being done by subordinates and giving instruction to ensure optimum utilisation of resources and achievement of work targets.
Importance of Supervision
Supervisor maintains friendly relationships with workers.
Connects management plans and ideas to workers and represents workers grievances and problems to management.
Helps to maintain unity amongst workers.
By giving instructions and motivating workers helps in achievement of targets.
Provides training to the workers and builds them as an efficient and skilled team of workers.
Helps in bringing out untapped energies of employees and builds up high morale.
Suggests ways and means to develop new skills.
A stimulator used by managers to make people act in a desired way to achieve organizational goals.
The Related terms in motivation are:
Motive: It is the inner state of an individual which directs his behaviour towards a goal.
Motivation: It is the process of stimulating people into action.
Motivators: These are The techniques used for motivating people.
Features of Motivation
Motivation is an internal feeling: It is the urge or desire to satisfy needs or wants which influences human behavior.
Motivation produces goal-directed behaviour: All actions are directed to achieve specific goals.
Motivation may be positive or negative: Positive motivators are like high salaries that influence constructively while negative motivators are like punishments that inculcates fear in the employees.
Motivation is a complex process: It involves dealing with people of different types and expectations.
Motivation Process
Unsatisfied need
Tension
Drives
Search behavior
Satisfied need
Reduction of tension
Unsatisfied Want: The motivation process begins with an individual's unsatisfied need.
Tension: As the desire goes unsatisfied, frustration builds up in the individual's mind.
Motives/Drives: Frustration motivates the individual to seek out alternatives to meet his needs.
Search Behaviour: He selects one of several options and begins acting in accordance with it.
Satisfied Needs: After a period of time, he evaluates whether or not his need has been met.
Reduced Tension: Once the need is met, the individual's frustration and tension are relieved.
Example: Assume a person wishes to advance in his or her career. This makes him uneasy, and he begins to look for other ways to advance in his career. He may consider working harder and bettering his performance. After consistently working hard, he may receive recognition and a promotion, which will finally satisfy his desire and alleviate his frustration.
Importance of Motivation
Improves Performance : It satisfies employee’s needs resulting in higher level of performance contributing towards organizational goals.
Develops a positive attitude: Motivation techniques eliminate negativity and create a desire to realize maximum potential.
Reduces employee turnover: A satisfied employee prefers to remain loyal to the organization leading to a lesser number of people quitting the organization.
Reduces absenteeism: Motivation helps to make the workplace a source of pleasure and provides the workers with a pleasant experience resulting in increased level of commitment from employees towards work.
Brings change smoothly: A motivated staff accepts changes with much lesser resistance.
Maslow's Need Hierarchy Theory of Motivation
This theory was given by Abraham Maslow in 1943, and is based on human needs.
Assumptions
Satisfaction of needs influences people's behaviour.
Needs are in hierarchical order.
Once need is satisfied only, the next higher need can motivate individuals.
Satisfaction of lower-level needs motivates to move to the next level of need.
Hierarchy of needs
According to Maslow need hierarchy theory, employees need and wants can be categorised as a hierarchy of five needs:
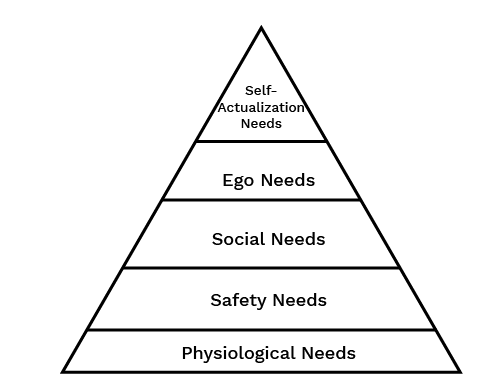
Basic Physiological Needs: It includes basic needs like hunger, thirst, shelter, sleep, etc.
Safety/ Security Needs: It includes needs of security and protection like job security, etc.
Affiliation/ Social/ Belonging Needs : It includes needs like affection, sense of belongingness, friendship, etc.
Esteem Needs: It includes needs like self respect autonomy, status, recognition, etc.
Self Actualization Needs: It includes needs that drive to realize a dream.
Financial and Non Financial Incentives
Incentives are the means to satisfy an employee's needs and motives. These can be:
Non-Financial
Financial Incentives
Incentives offered to employees which are either in direct monetary form or can be valued in monetary terms.

Types of Financial Incentives
Pay and allowances: These include salary, dearness allowance and other allowances paid to employees.
Productivity linked wage incentives: Wages paid at different rates to increase productivity.
Bonus: Incentive offered above the wages or salary.
Profit Sharing: Providing a fixed percentage of profit to employees.
Co-partnership/ Stock option: Shares offered to employees at a price which is lower than the market price.
Retirement benefits: Benefits offered after retirement such as provident fund, pension, etc.
Perquisites: Benefits over and above the salary offered such as car allowance, housing, medical aid, etc.
Non-Financial Incentives
Incentives which are given to provide psychological and emotional satisfaction rather than monetary satisfaction.
Types of Non-Financial Incentives
Status: It is the level of authority, responsibility and recognition an employee commands in the organization.
Organizational climate: Characteristics influencing an individual's behaviour such as individual autonomy, reward orientation, consideration to employees, etc.
Career advancement opportunity: Opportunities of growth and development in the organization to the higher level.
Job enrichment: It refers to a variety of work offered to challenge the knowledge and skills of highly motivated employees.
Employee recognition programmes: It involves recognising and appreciating the contribution of employees in public.
Job security: It refers to the certainty and stability offered in a job about future income and work.
Employee participation: Involvement of employees in the decision making process, seeking their advice or suggestions.
Employee empowerment: Opportunities provided to employees to take decisions independently and perform jobs assigned to them.
Leadership is the process of influencing the behaviour of people in such a way that they voluntarily work towards the achievement of organizational objectives.
Features of Leadership
It is the ability of an individual to influence others.
It tries to transform the behaviour of the subordinates.
It indicates interpersonal relationship between leader and followers.
It is exercised to achieve organizational goals.
It is a continuous process.
Importance of Leadership
It influences people's behavior to have a positive attitude.
It provides opportunities to subordinates to fulfill their needs and wants and build confidence.
It helps employees in understanding the need for changes and introduction of changes smoothly.
It clarifies and eliminates conflicts effectively through healthy discussions.
It trains and develops employees to handle managerial work.
Qualities of a Good Leader
Physical features: Should be fit and presentable with positive energy.
Knowledge: Should have required knowledge and competence.
Integrity: Must possess a high level of integrity and honesty.
Initiative: Should grab opportunity and use it to the advantage of organization.
Communication skills: Must possess skill to communicate and convince people effectively.
Motivation skills: Should motivate the individuals to improve their performance.
Self confidence: Should have a high level of confidence to handle difficult situations.
Decisiveness: Should be decisive and remain firm on decisions.
Social skills: Should be social and friendly with his colleagues and subordinates.
Leadership Styles
Autocratic leadership: in this style of leadership, a leader takes all the decisions on his own and gives orders to his or her subordinate to implement them.
Democratic leadership: In this style of leadership a leader takes decisions after consulting with subordinates and encourages them to participate in decision making.
Laissez faire leader: In this style of leadership a leader gives freedom to his subordinate to take decisions and execute work assigned to them and the leader acts as observer or guide.
It is the process of exchange of information between two or more people with an aim to create common understanding.
Elements of Communication Process
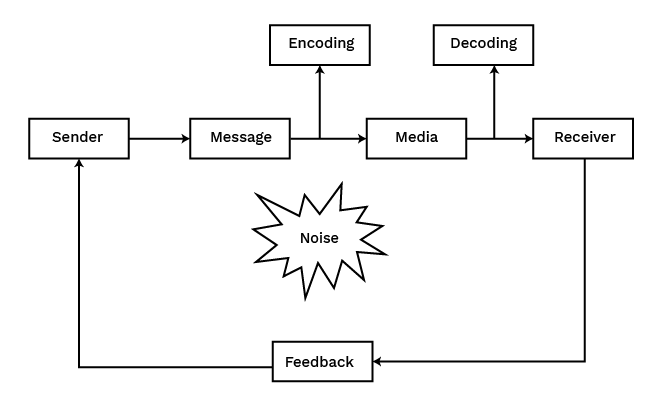
Sender: The person who conveys his thoughts or ideas.
Message: Content intended to be communicated.
Encoding: Process of converting message into communication.
Media: Path through which an encoded message is transmitted to the receiver.
Decoding: It is the process of converting the encoded message in a readable format.
Receiver: The person who receives a communication message from the sender.
Feedback: It refers to the information or suggestions provided by the receiver to the sender in context to the communication or message he received.
Noise: The hindrances and obstruction to communication.
Importance of Communication
Basis of coordination: Acts as a basis to coordinate their efforts of employees by explaining organizational goals.
Smooth working of an enterprise: It makes interaction among all individuals possible helping smooth and unrestricted working of an enterprise.
Basis of decision making: Communication acts as a medium for providing information needed for decision making.
Increases managerial efficiency: Helps managers to convey important information to subordinates to enable them to perform with efficiency.
Cooperation and industrial peace: The two way communication promotes cooperation and mutual understanding between the management and workers.
Effective leadership: Effective communication enables a manager to lead and influence his or her subordinate.
Boosts morale and provides motivation: Managers understand and satisfy employees' needs and motives by effective communication.
Formal and Informal Communication
The process of communication within an organization may be
Formal or
Formal communication
It flows through official channels designed in the organization chart to communicate official information between employees.
Formal communication is classified as:
Vertical communication: It is the formal two-way communication between superior and subordinate and the communication flows upward or downward.
Horizontal communication: It is the formal two-way communication between employees working at the same level of authority.
Formal Communication Networks
Single chain: Communication flows from superior to his immediate subordinate.
Wheel: Superior acts as a hub of information and all subordinates communicate through the superior only.
Circular: Employees communicate with his or her adjoining people.
Free flow: All employees are free to communicate with each other without any restrictions.
Inverted V: An employee communicates with his or her immediate superior but may also communicate with his/her superior’s superior.
Informal communication
Communication between employees who are not officially related to each other is called informal communication, this type of communication may flow in any direction thus it is also called 'grapevine'.
The informal communication spreads information rapidly and sometimes generates rumors.
Grapevine Network
Grapevine communication, also known as informal communication, is a communication that develops as a result of social interaction among employees and spreads without following the formal communication path. The types of grapevine communication networks are as follows.
Single Strand Network: An employee communicates with other employees in sequence. That is, one person communicates with another, who then communicates with yet another. Hence, information is passed through a line of persons.
Gossip Network: In a gossip network, one person spreads information to a large number of people. An employee communicates with all on a selective basis. Such as gossip about the new employee who recently joined the organization etc.
Probability Network: In a probability network, an individual shares information with other people at random. That is, the individual is unconcerned about who he shares the information with.
Cluster Network: Information in this network is first shared between two people who trust each other. One of them then passes the information on to another, who then passes it on to another, and so the information spreads.
Barriers to Communication
A. Semantic Barriers:
Problems and obstructions in the encoding and decoding of messages into words or impressions.
Reasons of semantic barriers are:
Badly expressed message: It involves the message with inadequate vocabulary, use of wrong words, omission of important words, or framing the message improperly, etc., that may distort the understanding and readability of the message.
Symbols with different meanings: Words with multiple meanings may change the intended meaning of the message, such as idol and idle, the word value having two meanings(price and importance), deer and dear.
Faulty translations: Incorrect translations may change the meaning of the message. For example, the meaning of certain words may change in a translation of an instruction from English to Hindi.
Unclarified assumptions: Sender and receiver may follow different assumptions while understanding the message resulting in different understanding of the message.
Technical jargon: Meaning of a message may not be clear if technical words are used in the communication with the workers who may not be familiar. For example the word drawings have separate meanings for a commerce person and a person from non-commerce background.
Body language and gesture decoding: Mismatch between body movement or gestures may convey wrong meaning. As in your face expression reveals anger, while your hand movements reveal otherwise.
B. Psychological Barriers:
Sender or receiver's state of mind may influence the meaning of the message.
Reasons of psychological barriers are:
Premature evaluation: Judgemental or biased nature of the receiver may result in premature evaluation. For example the listener/receiver may assume in advance that his boss is going to shout at him, this may lead to biasness in listening.
Lack of attention: Sender's or receiver’s pre-occupation of mind with other thoughts may result in ineffective communication.
Loss by transmission and poor retention : Passing of messages through various levels of communication and poor retention may result in transmission of inaccurate information.
Distrust: Distrust between sender or receiver may distort information.
C. Organizational Barriers:
Organizational authority relationships, rules and regulations, may result in communication barriers.
Reasons of organizational barriers are:
Organizational policy: Policies may not support free flow of communication.
Rules and regulations: Strict rules and regulations may result in delay of information, such as following a certain path for communication etc.
Status: A status conscious manager, hampering the effectiveness of communication between him and his subordinates.
Complexity in organizational structure: organization with too many levels may result in delay or distort of communication due to several filter points.
Organizational facilities: Improper facilities may affect free flow of communication and may create problems. A free and effective flow of communication requires the presence of certain organizational facilities such as social gatherings, complaint boxes, and transparency in operations, etc. The absence of such facilities hinders the flow of information
D. Personal Barriers:
These barriers arise due to the personal factors on the part of both, the sender and the receiver which may affect effective communication.
Reasons of personal barriers are:
Fear of challenge to authority : Superior may not share any information with the subordinates that may affect his authority.
Lack of confidence of superior on his subordinates : Sometimes superiors aren’t confident enough about their subordinates, and hence he may not welcome any take suggestions or opinions given by the subordinates.
Unwillingness to communicate: Subordinates unwillingness to communicate with their superiors may lead to ineffective communication.
Lack of proper incentives: Lack of incentives may discourage employees from taking initiative or sharing information.
Measures to Improve Communication Effectiveness
Clarify the ideas before communication: Superiors must have a clear and detailed understanding of the message before it is communicated to the subordinates.
Communicate according to the needs of the receiver : Sender must consider receiver's education, knowledge and understanding level while communicating message.
Consult others before communicating : Superiors must involve subordinates while taking decisions and making plans for effective communication.
Be aware of languages, tone and content of message: Sender must use proper language and tone while transmitting message to the receiver.
Convey things of help and value to listeners: Sender must consider the interests and needs of the receiver while transmitting messages.
Ensure proper feedback: Feedback from receiver ensures that the message is received or understood with the same intended meaning.
Communicate for present as well as future: Superiors must communicate with the subordinates about the present and future goals of the organization.
Follow ups: Regular follow ups and reviews make communication effective.
Be a good listener: Communicator must be a patient and attentive listening to understand the receiver’s problem related to understanding and implementing message
Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 7 Revision Notes: Summary
In this chapter, you will study the different characteristics of directing. You will learn what comprises directing and what an owner of a business should do. It can also be followed by any person holding a responsible position. The study of this chapter is absolutely important for those who are willing to work someday with a big company. Learning managerial and directing skills from the early phase of professional life is quite beneficial for all. To learn this chapter better, you will find Class 12 Business Studies Revision Notes Solution Chapter 7 very convenient. Let us check what you will find in these revision notes on directing.
These revision notes begin with the description of ‘directing’. Its characteristics are properly explained one after the other in an organized way. Every characteristic of directing has been explained with examples so that you can correlate it with real-life situations. The NCERT solutions Chapter 7 Class 12 Business Studies Revision Notes will help you grab the concepts better and will also help you understand how to answer a question in the exams. After explaining the features and traits of directing, you will then proceed to the next section where you will study the importance of directing in a business organization. You will find out how important it is to direct a team and start working on a plan. As per Class 12 Business Studies Directing Revision Notes, directing initiates the action as planned. It integrates the employees together. In fact, the efforts of all team members will be consolidated to give a fruitful output during and at the end of a task. It is important to direct a team to motivate them. A director will have to supervise, as well as, monitor a team’s performance on a regular basis. It is the responsibility of the director to stabilize the operations and bring balance to the organization.
On proceeding further, the Class 12 Revision Notes Chapter 7 will describe the principles followed while directing a team of employees. It will describe how a director needs to bring harmony and everyone in the team is accountable to report to the head/boss/director. In fact, every employee will move in the direction as guided by the director. Follow the Business Studies Class 12 Chapter 7 Revision Notes to find more principles that make directing more effective. Here you will learn how communication, motivation, leadership skills, and supervision can yield surprising results when incorporated into a directing process.
What are the Benefits of Referring to Vedantu’s Revision Notes for Class 12 CBSE Business Studies Chapter 7 - Directing
Provides quick, clear summaries of key concepts.
Simplifies complex topics for better understanding.
Efficient tool for last-minute exam prep.
Enhances retention of crucial information.
Supports effective exam preparation with key points and tips.
Saves time by consolidating information.
Prioritizes important topics and questions.
Offers practical examples for real-world connections.
Boosts student confidence for exams.
For an enhanced comprehension of this subject, NCERT - Class 12 Chapter 7 “Directing” thoughtfully prepared by experienced educators at Vedantu is your invaluable companion. These notes break down the complexities of Directing into easily digestible sections, helping you grasp new concepts and navigate through questions effortlessly quickly in the last minute as well. By immersing yourself in these notes, you not only prepare for your studies more efficiently but also develop a profound understanding of the subject matter.
Chapter-wise Revision Notes on Class 12 Business Studies
Chapter 1 - Nature and Significance of Management Notes
Chapter 2 - Principles of Management Notes
Chapter 3 - Business Environment Notes
Chapter 4 - Planning Notes
Chapter 5 - Organising Notes
Chapter 6 - Staffing Notes
Chapter 8 - Controlling Notes
Chapter 9 - Financial Management Notes
Chapter 10 - Financial Markets Notes
Chapter 11 - Marketing Notes
Chapter 12 - Consumer Protection Notes
Chapter 13 - Entrepreneurship Development Notes
Class 12 Subject-wise Revision Notes
Class 12 Maths Revision Notes
Class 12 Physics Revision Notes
Class 12 Chemistry Revision Notes
Class 12 Biology Revision Notes
Class 12 Business Studies Revision Notes
Class 12 Economics Revision Notes
Subject-wise Solutions for Class 12
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 English
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Accountancy

FAQs on Directing Class 12 Notes CBSE Business Studies Chapter 7 (Free PDF Download)
1. What is the Meaning of Directing?
Directing is the process where a person will take command of a team and guide, motivate, supervise, and encourage the members of the team s to complete a task or achieve a goal. Check the revision notes on Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 7 to find complete details on directing.
2. What are the Important Features of Directing?
If you follow the NCERT Class 12 Revision Notes Business Studies Chapter 7 solution, you will find out that the features of directing are its continuity, pervasiveness, human factor, creativity, executive level, and delegation functioning. To understand these features elaborately, you can refer to the explanation provided in the revision notes.
3. Why is the Importance of Directing?
While going through the revision notes provided above, you will understand that every business needs proper directing. Directing is performed by the managers and executives with experience to assist a team to achieve a goal or complete a task in order to achieve desired outcomes.
4. What do you mean by direct?
The concept of directing is to give instructions, motivation and guidance to the staff of an organization so they work hard and diligently to achieve their organisational goals. This task of directing is assigned to the manager of the organization along with statistical planning. Directing is a continuous process that is initiated from the top position in the hierarchy of organisations and flows to the bottom of the hierarchy. Directing is an essential part to run an organisation successfully. Vedantu offers complete solutions for this chapter for free.
5. What are the features of directing?
Directing is a prominent part of organisations for its proper functioning. Some of the essential features of directing are;
It initiates a plan of action in the firm. Along with planning and controlling the environment of the firm, the manager must direct the firm.
It is a continuous process to ensure stability in the organisation and to make sure that every organisational goal is met.
Directing occurs vertically in an organisation i.e. the process of directing flows from the position at the top in the hierarchy and finishes at the bottom in the hierarchy.
6. What is planning?
The process of dedicating a particular period of time for certain work or objective can be defined as planning. Planning is to decide beforehand about your plan of action for the near future or the future in general. Planning also includes the process of considering various plans of action to attain a certain goal and to decide, which one will be effective and efficient to follow. You can go through NCERT solutions from Vedantu for further explanation of the concept of planning and related topics in class 11 chapter 7.
7. What are elements of the communication process?
Communication is a process of sending and receiving new ideas, views, feelings etc. Some of the essential elements of communication are sender, message, encoding, media, deciding, receiver feedback and noise. All these elements are essential for effective and successful communication. Commuting if directions and instructions are essential to complete any given task. Managers need to include all these elements in their communication skills. For further explanation of the role of communication, you can visit Vedantu's official website or download the Vedantu app.
8. What is the importance of supervision?
Supervision connects the workers of the organisation and helps to work in sync. The role of a good supervisor is to be a guide, friend and philosopher of the workers of the organisation. A supervisor must explain the organization's new policies to the workers and tell workers' problems to the manager. A good supervisor must ensure that each worker is working to the best of their ability and there's no feud among the workers. A supervisor should provide on the job training to its workers.
Study Materials for Class 12
myCBSEguide
- Directing class 12 Notes...
- Directing class 12 Notes Business Studies
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
CBSE class 12 Business Studies Directing class 12 Notes Business Studies in PDF are available for free download in myCBSEguide mobile app. The best app for CBSE students now provides Directing class 12 Notes Business Studies latest chapter wise notes for quick preparation of CBSE board exams and school based annual examinations. Class 12 Business Studies notes on chapter 7 Directing are also available for download in CBSE Guide website.
CBSE Guide Directing class 12 Notes Business Studies
CBSE guide notes are the comprehensive notes which covers the latest syllabus of CBSE and NCERT. It includes all the topics given in NCERT class 12 Business Studies text book. Users can download CBSE guide quick revision notes from myCBSEguide mobile app and my CBSE guide website.
12 Business Studies notes Chapter 7 Directing
Download CBSE class 12th revision notes for chapter 7 Directing in PDF format for free. Download revision notes for Directing class 12 Notes and score high in exams. These are the Directing class 12 Notes Business Studies prepared by team of expert teachers. The revision notes help you revise the whole chapter 7 in minutes. Revision notes in exam days is one of the best tips recommended by teachers during exam days.
Download Revision Notes as PDF
CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Revision Notes CHAPTER – 7 Directing class 12 Notes Business Studies
Meaning: Directing means giving instructions, guiding, counseling, motivating and leading the staff in an organization in doing work to achieve Organizational goals. Directing is a key managerial function to be performed by the manager along with planning, organizing, staffing and controlling. From top executive to supervisor performs the function of directing and it takes place accordingly wherever superior – subordinate relations exist.Directing is a continuous process initiated at top level and flows to the bottom through organizational hierarchy.
Direction has got following characteristics:
1. Pervasive Function- Directing is required at all levels of organization. Every manager provides guidance and inspiration to his subordinates. 2. Continuous Activity- Direction is a continuous activity as it continuous throughout the life of organization. 3. Human Factor- Directing function is related to subordinates and therefore it is related to human factor. Since human factor is complex and behaviour is unpredictable, direction function becomes important. 4. Creative Activity- Direction function helps in converting plans into performance. Without this function, people become inactive and physical resources are meaningless. 5. Executive Function- Direction function is carried out by all managers and executives at all levels throughout the working of an enterprise, a subordinate receives instructions from his superior only. 6. Delegate Function- Direction is supposed to be a function dealing with human beings. Human behaviour is unpredictable by nature and conditioning the people’s behaviour towards the goals of the enterprise is what the executive does in this function. Therefore, it is termed as having delicacy in it to tackle human behaviour.
1. Initiates Action: It helps to initiate action by the people in the organization towards attainment of desired objectives. The employees start working only when they get instructions and directions from their superiors. It is the directing function which starts actual work to convert plans into results. 2. Integrates Employee’s Efforts: All the activities of the organization are interrelated so it is necessary to coordinate all the activities. It integrates the activities of subordinates by supervision, guidance and counselling. 3. Means of motivation: It motivates the subordinates to work efficiently and to contribute their maximum efforts towards the achievement of organizational goals. 4. Facilitates change: Employees often resist changes due to fear of adverse effects on their employment and promotion. Directing facilitates adjustment in the organization to cope with changes in the environment. 5. Stability and balance in the organization: Managers while performing directing function instruct, guide, supervise and inspire their subordinates in a manner that they are able to strike a balance between individual and organizational interests.
Principles of Effective Direction:
Effective direction leads to greater contribution of subordinates to organization goals. The directing function of management can be effective only when certain well accepted principles are followed.
The following are the basic principles of effective direction:
1. Harmony of Objectives:
It is an essential function of management to make the people realize the objectives of the group and direct their efforts towards the achievement of their objectives. The interest of the group must always prevail over individual interest. The principle implies harmony of personal interest and common interest..
2. Unity of Command:
This principle states that one person should receive orders from only one superior, in other words, one person should be accountable to only one boss. If one person is under more than one boss then there can be contradictory orders and the subordinate fails to understand whose order to be followed. In the absence of unity of command, the authority is undermined, discipline weakened, loyalty divided and confusion and delays are caused.
3. Unity of Direction:
To have effective direction, there should be one head and one plan for a group of activities having the same objectives. In other words, each group of activities having the same objectives must have one plan of action and must be under the control of one supervisor.
4. Direct Supervision:
The directing function of management becomes more effective if the superior maintains direct personal contact with his subordinates. Direct supervision infuses a sense of participation among subordinates that encourages them to put in their best to achieve the organizational goals and develop an effective system of feed-back of information.
5. Participative or Democratic Management:
The function of directing becomes more effective if participative or democratic style of management is followed. According to this principle, the superior must act according to the mutual consent and the decisions reached after consulting the subordinates. It provides necessary motivation to the workers by ensuring their participation and acceptance of work methods.
6. Effective Communication:
To have effective direction, it is very essential to have an effective communication system which provides for free flow of ideas, information, suggestions, complaints and grievances.
7. Follow-up:
In order to make direction effective, a manager has to continuously direct, guide, motivate and lead his subordinates. A manager has not only to issue orders and instructions but also to follow-up the performance so as to ensure that work is being performed as desired. He should intelligently oversee his subordinates at work and correct them whenever they go wrong.
(i) Supervision- implies overseeing the work of subordinates by their superiors. It is the act of watching & directing work & workers.
(ii) Motivation- means inspiring, stimulating or encouraging the sub-ordinates with zeal to work. Positive, negative, monetary, non-monetary incentives may be used for this purpose.
(iii) Leadership- may be defined as a process by which manager guides and influences the work of subordinates in desired direction.
(iv) Communications- is the process of passing information, experience, opinion etc from one person to another. It is a bridge of understanding.
1. Supervision, as an element of directing:
process of guiding the efforts of employees and other resources to accomplish desired objectives.
Overseeing people at work
Involves instructing, observing, monitoring and guiding employees.
Carried out at all levels but more important at the lower levels therefore the term ‘Supervisor’is used at the operativeslevel of management
I. Importance of Supervision/Role of a Supervisor/Functions
1. Link between workers and management because the supervisor explains management policies to workers and brings workers problems to the notice of the management.
2. Ensures issuing Instructions: To make sure that the instructions are communicated to each and every employee.
3. Facilities Control: Control means match between actual and planned output. It ensures checking on the methods in use and progress of work according to planned schedule.
4. Maintenance of discipline: The strict supervision and guidance of supervisor encourages the employees and workers to be more disciplined in the activities.
Under the guidance of superior the workers follow a fixed or strict timetable and execute the plans in right directions.
5. Feedback: The supervisors are directly dealing with the subordinates. As a result, feedback in the form of suggestions, grievances keep coming to the management. It improves quality management decisions and revision of plans & policies.
6. Improved Motivation: A supervisor with good leadership qualities can build up high morale among workers. The relationship with the supervisor is a very good incentive to improve the motivation level of the employees while guiding the employees, the supervisors encourage the subordinates to perform to their best capacities.
7. Optimum utilization of resources: All the activities are under the observation of supervisor so less wastage and optimum utilization of resources is possible.
II. Motivation
i. Incitement or inducement to act/move.
ii. Process of stimulating people to action to accomplish desired goals.
• Three key terms = motive, motivation, motivators
Motive :inner state that energizes, activates and directs behaviour towards goals.
Arises out of unsatisfied needs = causes restlessness.
Motivation : Process of stimulating people to action + Depend on satisfying needs of people.
Motivators: Technique used to motivate people.Egs. = pay, bonus, promotion, recognition etc.
1. Psychological Phenomenon: Motivation is an internal feeling which means it cannot be forced on employees. The internal feeling such as need, desire, aspiration etc. influence human behaviour to behave in a particular manner.
2. Goal Directed Behaviour: It induces people to behave in such a manner so that they can achieve their goals. A motivated person works towards the achievement of desired goals.
3. Motivation can be either positive or Negative: Positive motivation means inspiring people to work better and appreciating a work that is well done e.g., pay increase promotion recognition. Negative motivation means forcing people to work by threatening or punishing them. e.g., issue of memo, demotion, stopping increments etc.
4.Complex Process: It is a complex and difficult process. Individuals differ in their needs and wants and moreover human needs change from time to time.
5. Continuous Process: Human needs are unlimited and so they keep on changing continuously, satisfaction of one need gives rise to another. As soon as one need is satisfied another need arises. So managers have to continuously perform the function of motivation.
Maslow‟s Hierarchy Of Needs: Maslow‘s need hierarchy is considered to be fundamental to the understanding of motivation and plays an important role in motivation.
• People have a wide range of needs like physiological needs, social needs, safety needs, esteem needs and self actualisation needs which motivate them to work.
• The manager must understand the needs and wants of people in order to motivate them and improve their performance levels.
• For the satisfaction of these needs, managers must offer different incentives (monetary and non-monetary).
| NEED | Examples Of Need (Individual Example) | Management Can Satisfy This Need By (Organizational Example) |
| 1. Basic Physiological Needs | Most basic in the hierarchy and corresponds to primary needs. Hunger, thirst, shelter, sleep. | Offer monetary incentives e.g. Good salary/wages and comfortable working conditions |
| 2. Safety/Security Needs | Security and protection from physical and emotional harm, stability of Income etc. | Offer job security, pension, insurance etc |
| 3. Affiliation/Belonging Needs | Refer to affection, sense of belongingness, acceptance and friendship | The firm can encourage team building and permit the workers to opportunity to interact socially and so develop cordial relations with colleagues |
| 4. Esteem Needs | Include factors such as self-respect, autonomy status, recognition and attention | Recognize good performance, provide opportunity for employees to feel a sense of accomplishment, provide important job titles etc |
| 5. Self Actualisation Needs | The drive to become what one is capable of becoming. These needs include growth, self-fulfillment and achievement of goals. | Offer the freedom to take decisions, providing them with opportunity to learn things, encouraging creativity, leading to achievement of goals etc. |
Financial and Non-Financial Incentives: Incentive means all measures which are used to motivate people to improve performance.
| Financial incentives = directly in money form or measurable in monetary terms. 1. Pay and allowance 2. Productivity linked incentive schemes 3. Bonus 4. Profit sharing 5. Co-partnership/Stock options 6. Retirement benefits 7. Perquisites | Non-financial incentives= main emphasis is to provide psychological and emotional satisfaction. Not measurable in monetary terms. 1. Status 2. Organizational climate 3. Career advancement opportunities 4. Job enrichment 5. Employee recognition programmes 6. Job security 7. Employee participation 8. Employee empowerment |
III. Leadership
Leadership is the activity of influencing people to strive willingly for mutual objectives. Managers at all levels are expected to be the leaders of their subordinates. Leadership indicates the ability of an individual to maintain good interpersonal relations with followers and motivate them to contribute for achieving organizational objectives. It is a process of interaction between the leader and his followers. It helps in persuading employees to work cooperatively and enthusiastically towards common goals.
Importance of Leadership:
1. Makes people contribute positively:
• Influences behaviour and makes people contribute positively and produce good results.
2. Creates congenial work environment:
• Maintains personal relations, helps followers fulfil their needs+ provides confidence, support and encouragement.
3. Introduces change:
• Persuades, clarifies and inspires people to accept changes.
• So overcomes resistance to change with minimum discontent..
4. Handles conflict
• Does not allow adverse effects .
• Allows followers to express their feelings and disagreements and gives suitable clarifications.
5. Trains subordinates:
• Builds up successors and helps in smooth succession process.
Qualities Of A Good Leader:
1. Physical features – appearance, personality, heath and endurance inspires followers to work with the same tempo. 2. Knowledge – knowledge and competence to instruct and influence subordinates. 3. Integrity – the leader should be a role model regarding ethics, values, integrity and honesty. 4. Initiative – grab opportunities instead of waiting for them. 5. Communication – capacity to explain his ideas and also be a good listener, teacher, counselor and persuader. 6. Motivation skills – understand followers needs and devise suitable means to satisfy them. 7. Self-confidence – so that he can provide confidence to followers 8. Decisiveness – should be firm and not change opinions frequently 9. Social skills – sociable, friendly and maintain good relations with followers.
Styles of Leadership
Leadership styles refer to a leader’s behaviour. Behavioural pattern which the leader reflects in his role as a leader is often described as the style of leadership.
A Leadership style is the result of the leader’s philosophy, personality, experience and value system. It also depends upon the type of followers and the atmosphere revealing in the organization.
Different types of leadership style are:
1. Autocratic leadership 2. Participative leadership/Democratic 3. Free rein leadership/Laissez Faire
A leader may use all styles over a period of time but one style tends to predominate as his normal way of using power.
l. Autocratic or Authoritarian Leader
An autocratic leader gives orders and insists that they are obeyed. He determines the policies for the group without consulting them. He does not give information about future plans but simply tells the group what immediate steps they must take. Under this style, all decision making power is centralized in the leader. He does not give the subordinates any freedom to influence his decisions.
It is like “bossing people around.” This style should normally be used on rare occasion.
It is best applied to situations where there is little time for group decision making or where the leader is the most knowledgeable member of the group.
2. Democratic or Participative Leader
A democratic leader gives order only after consulting the group and works out the policies with the acceptance of the group.
He never asks people to do things without working out the long term plans on which they are working. He favours decision making by the group as shown in the diagram.
It works best in situations where group members are skilled and eager to share their knowledge.
It is also important to have plenty of time to allow people to contribute, develop a plan and then vote on the best course of action.
This style should NOT he used when:
In situations where roles are unclear or time is of the essence, democratic leadership can lead to communication failures and incomplete projects.
3. Laissez Faire or Free Rein Leader
Communication
It is transfer of information from the sender to the receiver with the information being understood by the receiver. Communication plays key role in the success of a manager. Directing abilities of manager mainly depend upon his communication skills. That is why organization always emphasizes on improving communication skills of managers as well as employees. Communication is important for the directing function because all other elements of directing become possible only when there is adequate communication.
Elements of Communication Process
1. Sender: Who conveys his thoughts or ideas.
2. Message: Ideas, feelings, suggestions, order etc.
3. Encoding: Converting the message into communication symbols such as words/pictures etc.
4. Media: Path/Channel through which encoded message is transmitted to receiver e.g., face to face, phone call, internet etc.
5. Decoding: Converting encoded symbols of the sender.
6. Receiver: Who receives communication of the sender.
7. Feedback: All those actions of receiver indicating that he has received and understood the message of the sender.
8. Noise: Some obstruction or hindrance to communication like poor telephone connection, inattentive receiver.
Importance of Communication
1. Facilitates Coordination: between interrelated departments and sections thus creating a unity of purpose and action.
2. Provides data necessary for decision makings: When information is effectively and efficiently communicated to management.
3. Increases managerial efficiency: Every individual in the organization is assigned a job or task. The employee must know clearly who has to report to whom, what part of total job they are expected to perform and what are their decisions. The clarity comes only with smooth flow of communication which keeps the organization at work with efficiency.
4. Promotes cooperation and Industrial Peace: The two-way communication promotes cooperation and mutual understanding between the management and workers and brings peace in the organization.
5. Establishes effective leadership: Effective communication helps to influence subordinates. while influencing, a leader should possess good communication skills.
If there is two-way information flow between the superior and subordinates then there will be positive reaction of employees.
Communication taking place within an organization may be broadly classified into two categories.
| Formal communication 1.Official communication following the chain of command 2.Is concerned with official matters 3. May be written/oral but generally recorded and filed. 4.Directions = 5.Popular communication networks are: | Informal Communication: 1.Takes place outside the official channels – 2. May be work related or other matters – 3.Arises out of social interactions – 4.Grapevine: 5.Types = |
Difference between Formal and Informal Communication
| Basis | Formal Communication | Informal communication |
| 1. Meaning | Follows the official chain of command. | Between individuals and groups are not officially recognized. |
| 2. Channel | Through a definite path. | No definite path. |
| 3. Speed | Slow: because all information has to pass through an established scalar chain. | Very fast-Cuts across all the official channels. |
| 4. Nature | More rigid and cannot be modified. | Flexible and varies from individual to individual. |
| 5. Expression | It is mostly expressed in the written form. | It mostly tends to be oral. |
Barriers to Effective Communication
Semantic Barriers: Concerned with problems and obstructions in the process of encoding or decoding of message into words or impressions. Semantic barriers are as follows:
1. Badly expressed message: Sometimes intended meaning may not be conveyed. 2. Words with different meanings confuses the receiver. 3. Faulty translations may transfer wrong messages. 4. Unclarified assumption: Different interpretations may result in confusion. 5. Technical Jargon: Technical words may not be understood by the workers.
Psychological/Emotional barriers
1. Premature evaluation- judgement before listening leads to misunderstanding. 2. Lack of attention/poor listening may disappoint the employees. 3. Loss by transmission and poor retention: When oral communication passes through various levels it destroys the structure of the message or leads to transmission of inaccurate message. 4. Distrust: If the parties do not believe each other. They cannot understand each other’s message in its original sense.
Organizational Barriers
Factors related to organization structure:
1. If organizational policy does not support free flow of information it creates problem. 2. Rules and regulations: Rigid rules and regulations may lead to red tapism and delay of action. 3. Status conscious managers may not allow subordinates to express their feelings freely. 4. Complexity in organization structure results in delay and distortion.
Personal Barriers: of superiors and subordinates.
1. Fear of challenge to authority may withhold or suppress a particular communication. 2. Lack of confidence of superior in his subordinates. 3. Unwillingness to communicate. e.g., fear of punishment/demotion. 4. Lack of proper incentives stops the subordinates to offer useful suggestions.
Improving Communication Effectiveness
1. Clarify the ideas before communication. 2. Communicate according to the needs of receiver. 3. Consult others before communicating. 4. Be aware of language, tone and content of message. 5. Ensure proper feedback. Feedback provides opportunity for suggestions and criticism. 6. Follow up communication helps to remove hurdles, misunderstanding of information given by managers to subordination. 7. Be a good listener.
- CBSE Revision notes (PDF Download) Free
- CBSE Revision notes for Class 12 Business Studies PDF
- CBSE Revision notes Class 12 Business Studies – CBSE
- CBSE Revisions notes and Key Points Class 12 Business Studies
- Summary of the NCERT books all chapters in Business Studies class 12
- Short notes for CBSE class 12th Business Studies
- Key notes and chapter summary of Business Studies class 12
- Quick revision notes for CBSE board exams
CBSE Class-12 Revision Notes and Key Points
Directing class 12 Notes Business Studies. CBSE quick revision note for class-12 Business Studies, Chemistry, Math’s, Biology and other subject are very helpful to revise the whole syllabus during exam days. The revision notes covers all important formulas and concepts given in the chapter. Even if you wish to have an overview of a chapter, quick revision notes are here to do if for you. These notes will certainly save your time during stressful exam days.
- Revision Notes for class-12 Physics
- Revision Notes for class-12 Chemistry
- Revision Notes for class-12 Mathematics
- Revision Notes for class-12 Biology
- Revision Notes for class-12 Accountancy
- Revision Notes for class-12 Economics
- Revision Notes for class-12 Business Studies
- Revision Notes for class-12 Computer Science
- Revision Notes for class-12 Informatics Practices
- Revision Notes for class-12 English Core
- Revision Notes for class-12 History
- Revision Notes for class-12 Physical Education
To download Directing class 12 Notes Business Studies, sample paper for class 12 Physics, Chemistry, Biology, History, Political Science, Economics, Geography, Computer Science, Home Science, Accountancy, Business Studies and Home Science; do check myCBSEguide app or website. myCBSEguide provides sample papers with solution, test papers for chapter-wise practice, NCERT solutions, NCERT Exemplar solutions, quick revision notes for ready reference, CBSE guess papers and CBSE important question papers. Sample Paper all are made available through the best app for CBSE students and myCBSEguide website
- Nature and Significance of Management class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Principles of Management class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Business Environment class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Planning class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Organizing class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Staffing class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Controlling class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Financial Management class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Financial Markets class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Marketing Management class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Consumer Protection class 12 Notes Business Studies
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
1 thought on “directing class 12 notes business studies”.
Its a nice site to see the notes but I have ask you for the brief notes not long notes It’s so long after seeing the notes I am thinking that I should read Directing chapter from my copy not from the sites available in the Internet so just provide brief notes instead of long notes to the students.
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Case Studies - Directing | Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? |
Q. 1. Ayesha Ltd. Assured their employees that in spite of recession no worker will be retrenched from the job.
(i) Name and explain the type of incentive offered to the employees.
(ii) Explain one more incentive of the same category.
Ans. (i) Job security
(ii) Explain one more incentive of the same category.
- Employee’s recognition.
- Organizational climate.
Q. 2. Blue Birds Ltd. Offers to its employees issue of shares at a price which is less than the market price.
Ans. (i) Co-partnership/Stock option.
(ii) Other incentives: (a) Pay and allowance, (b) Bonus.
Q. 3. ABC Ltd. Is not able to achieve its objective on analyzing, they found that employees were not given their best, so he decided to announce an incentive plain, which offers various incentives to employee workers at different level for achieving their target.
(i) Which element of directing is used by manager?
(ii) Suggest incentive suitable for:
- Employees operating at lower level.
- Employees operating at higher level.
Ans. (i) Motivation is missing.
(ii) (a) Lower level: offer monetary incentives.
(b) Higher level: non-monetary incentive.
Q. 4. Mr. John faced lot of problems regarding the policy on teaching. He directly consulted the principal about his problem ignoring the Headmistress who is immediate superior of Mr. John as he feels more free to communicate with principal.
(i) Name the pattern of communication followed by Mr. John.
(ii) State any other two patters.
Ans. (i) Mr. John is following inverted ‘V’ pattern.
(ii) Other two pattern:
- Wheel pattern, (b) Chain pattern.
Q. 5. Is directing required at planning stage? Name the element of directing function under which:
(i) the superiors oversee the activities of their subordinates.
(ii) the superiors assure the subordinates that their needs will be taken care of.
(iii) the superior attempts to influence the behavior of people at work towards the realization of specified goals.
(iv) the superior share information with the subordinates in order to reach common understanding. (3 Marks)
Ans. No, directing is not required at planning stage since it is an executive function. It initiates action in the organization while other functions of management (planning, organizing, staffing and controlling) just prepare a setting for action.
- Supervision (ii) Motivation (iii) Leadership (iv) Communication.
Q. 6. Amit and Mikki are working in the same organization but in different departments. One day at lunch time Mikki informed Amit that due to computerization some people are going to be retrenched from the organization.
Name which type of communication is this. State any two limitations of this type of communication. (3 Marks)
Ans. Informal Communication
Limitations:
- The grapevine/informal communication spreads rapidly and sometimes gets distorted. It is very difficult to detect the source of such communication.
- It also leads to generate rumours. People’s behavior is affected by rumours and informal discussion and sometimes may hamper work environment.
Q. 7. You are working at the middle level of management. Your superior, a top management personnel, sent a message for you which you received and well understood. Is the communication process complete? Give reason. (3 Marks)
Ans. No, the communication process is not complete unless and until feedback is given to the superior. Feedback includes all those actions of the receiver indicating that he has received and understood the message of sender. So, I must respond to communication to improve its effectiveness, e. g., by giving a reply to letter, giving reactions to the message, etc.
Q. 8. Rakesh is working under his superior Neeraj. He always communicates useful ideas and suggestions to his superior regarding reduction of cost, improvement in the product, etc. Neeraj implements his suggestions and has always found favourable results, but he never appreciates Rakesh for his suggestions. Now Rakesh decided not to communicate any suggestion or idea to Neeraj. Identify the factor which acts as a communication barrier. (1 Marks)
Ans. Lack of proper incentives (Personal Barriers to Communication)
Q.9. Ankur is working as a production manager in an organization. His subordinate Saurabh discussed with hi a method o production which will reduce the cost of production. But due to some domestic problems and Ankur’s mind being pre-occupied he is not in a position to understand the message. Saurabh got disappointed by this. Identify the factor which acts as a communication barrier. (1 Marks)
Ans. Lack of attention (Psychological/Emotional Barriers to Communication)
Q.10. Rajat a Sales Manager, achieved his sales target one moth in advance. This achievement as displayed on the notice board and the CEO of the Company awarded a certificate for the best performance to him. Name the incentive provided to Rajat. (1 Marks)
Ans. The incentive provided to Rajat is – ‘Recognition’.
Q. 11. A behavior study was done on total of 100 employees of an organization. Group A (of 50 employees) were appreciated by the manager for their work and initiative for new idea. All these employees were given option of flexible working hours and were paid wages at a higher piece rate. On the other hand, Group B (of remaining 50 employees) was criticized for their poor performance. Their increments were stopped and they were paid wages at a lower piece rate.
(a) Identify and explain the feature of motivation highlighted in the above case.
(b) What type of leadership is followed by the manager? Justify your answer. (4 Marks)
- Motivation can be either positive or negative. Positive motivation provides positive rewards like increase in pay, promotion, recognition, etc. Negative motivation uses negative means like punishment, stopping increments, threatening, etc.
- Autocratic leadership style.
The leader’s following is based on the assumption that reward or punishment both can be given depending upon the result.
Q. 12. In a company, Mr. Kshitij always explains management policies to workers and brings workers’ problems to the notice of management. At what post does Mr. Kshitij work in this company? (1 Marks)
Ans. Mr. Kshitij is supervisor in the company as he acts as a link between workers and management.
Q. 13. Prachi is working in an MNC. She has been given an option to buy the shares of the company at an amount less than the market price because of her performance as an incentive. Identify which incentive is being given to her. (1 Marks)
Ans. Co-partnership/Stock option.
Q. 14. Ms. Snigdha, Production Manager and Mr. Sarthak, Marketing manager of an electronics company are not on talking terms with each other. Because of that they do not transfer complete information to each other.
(a) Identify the element of directing which becomes ineffective due to the behavior of the managers.
(b) Also, explain the factor which led to their such behavior. (3 Marks)
Ans. (a) Communication
- Distrust (Psychological barrier)
Distrust between sender and receiver causes failure of communication.If they do not believe each other, they cannot understand each other’s message in its original sense.
Q. 15. Huma is working in a company on a permanent basis. As per job agreement she had to work for 8 hours a day and was free to work overtime. Huma worked overtime, due to which she fell ill and had to take leave from her work. No one showed concern and enquired about her health. She realized that she was fulfilling only some of her needs while some other needs still remained to be fulfilled.
(i) By quoting the lines from the above para, identify the needs of Huma which she is able to fulfil.
(ii) Also explain two other needs of Huma followed by the above needs, which still remained to be satisfied.
- ‘Huma is working in a company on a permanent basis’.
According to above line Huma is able to fulfil her following needs:
(a) Physiological needs(b) Safety or Security needs
(ii) Needs of Huma which still remained to be satisfied are:
- Affiliation Need: It refers to the need for affection, since to belongingness, acceptance and friendship.
- Esteem Need: It refers to the need for self-respect, autonomy, status, recognition and attention.
Q. 16. Mr. Nath, a recently appointed production manager of Suntech Ltd. Has decided to produce jute bags instead of plastic bags as these are banned by the government. He set a target of producing 1000 jute bags a day. It was reported that the employees were not able to achieve the target. After analysis he found that employees were demotivated and not putting in their best for achieving the target. Mr. Nath’s beaviour is good towards the employees. His attitude is always positive. So he announced various incentive schemes for the employees like;
- Installing award or certificate for best performance.
- Rewarding an employee for giving valuable suggestion.
- Congratulating the employees for good performance.
- Identify the functions of management highlighted in the above paragraph.
- State the ‘incentive’ under which the employees are motivated.
- State any two values which the production manager wants to communicate to the society by his work and behavior.
- Directing and Controlling
- Employee recognition programme (non-monetary incentive)
- Sensitivity of environment
- Good behavior towards employees.
Q. 17. NOTICE
A meeting of all supervisors is scheduled on 20 th August, 2016
This notice was placed on the notice board in the reception area of XYZ Ltd. But it did not mention clear specification regarding the time of meeting. Which barrier of communication is referred to here? Explain any two other forms of barriers to effective communication under the same category. (5 Marks)
Ans. Badly expressed message (Semantic barriers) – Use of wrong words, omission of needed words, inadequate vocabulary, etc.
- Symbols with different meanings: A work may have several meanings. For example, consider these three sentences where the work ‘value’ is used:
- What is the value of this ring?
- I value our friendship.
- What is the value of learning compute skills?
Wrong perception by the receiver leads to communication problems.
- Faulty translations: Sometimes, the communications originally drafted in one language (say, English) need to be translated to the language understandable to workers (say, Hindi). If the translator is not proficient with both the languages, communication becomes ineffective.
Q. 18. Mr. Sandeep is the marketing manager of a company manufacturing designer clothes. One day, in the morning while leaving home he had a quarrel with a person in his neighbourhood on some issue. That person is a criminal who could abuse his family members. Mr. Sandeep, on that day, is very worried and angry too on the behavior of the neighood person. On that day, a meeting was held by a team of marketing and design experts to ensure that whatever is produced is according to market demand and tastes and fashion of the customers. But Mr. Sandeep could not pay attention to the discussion between them.
(a) Identify the type of barriers to communication mentioned in the above para. Justify your answer.
(b) Explain any two such barriers to communication .
- Psychological barriers.
These are related to the state of mind of both sender and receiver of communication.For example, a worried person cannot communicate properly and an angry receiver cannot understand the real meaning of message.
‘Mr. Sandeep is very worried and angry on that day.So he could not pay attention to the discussion in the meeting.’
- Psychological barriers to communication:
- Lack of attention: the pre-occupied mind of receiver and the resulting non-listening of message acts as a major psychological barrier.
- Premature evaluation : Sometimes people form a judgement before the sender completes his message, which causes failure of communication.
Q. 19. Mrs. Rajlaxmi is working as the Human Resource Cosultant in a firm manufacturing cosmetic, which is facing a problem of high employee urnover. The CED of the company has invited suggestions from her for retaining the talented employees & reducing the employee turnover. Mrs. Rajlaxmi recommends that the good employees be rewarded in a way that it creates a feeling of ownership among the employees and at the same time makes them contribute towards the growth of the organization.
(a) Identify the incentive and explain its type, which has been suggested by Mrs. Rajlaxmi to the CEO of the company.
(b) Also explain any two other incentives of the same type.
- Financial incentive.
Co-Partnership/Stock Option
- Other financial incentives:
- Pay and allowances: For every employee, salary is the basic financial incentive. It includes basic pay, dearness allowance and other allowance. Pay hike and increments improve performance level of employees.
- Profit sharing: Employees are given a share in the profits of the organization. This motives them to improve their performance and contributes to increase in profits of the organization.
Q. 20. Mr. Bhuvan is the marketing manager of the company manufacturing designer clothes. One day in the morning while leaving home, he had a quarrel with the person in the neighbourhood. That person abused his family and threaten to harm the family. Mr. Bhuvan got very upset and worried. On the same day a meeting was organized in the office to finalise the design according to market demand and taste the fashion of the customers. Mr. Bhuvan could not pay attention to the discussion as he was thinking about the quarrel only.
(a) Identify the type of barrier to communication mention in the above para.
(b) State any other two barriers of same category.
- Psychological barrier Lack of attention.
- (i)Premature evaluation
(ii) Loss by poor retention.
Q. 21. Rajiv is working as Personal Manager in a company. The specialty of the company is that financial position of all the employees is good. The employees working here are honest punctual and hardworking. The CEO of the company asked him to suggest a method of motivation. The CEO asked him to suggest a method which is happily accepted by all the employees.
Rajiv spoke to many employees in this connection. Some employees suggested give more importance to individual autonomy, another suggested good performance should be appreciated another group suggested to award, certificate, trophies to recognize the good performance. Mr. Rajiv mixed all and suggested a method of motivation to CEO. The CEO happily accepted that and it was immediately implemented. With in few days the company’s growth rate appeared to have become fast.
- Identify the functions of management indicate in the above paragraph.
- Which motivation methods were suggested by different group of employees.
- Which motivation method combine all the above stated and was suggested by personal manager.
- (i) Recognition
(ii) Autonomy
- (i) Ethical behavior
(ii) Motivating employees
(iii) Taking Suggestions from employing.
Q. 22. Pramod was a supervisor at a ‘Annapurna Aata’ factory. The factory was producing 200 quintals of Aata every day. His job was to make sure that the work goes on smoothly and there was no interruption in production. He was a good leader who would give orders only after consulting his subordinates and work out the policies with the acceptance of the group.
Identify and describe the leadership style being adopted by Pramod.
Ans. Democratic style of leadership.
- A democratic leader favours decision making by the group. This improves the attitude of the employees towards their jobs and the organization thereby increasing their morale.
- Using this style is of mutual benefit – it allows them (subordinates) to become part of the team and helps leaders (seniors) to make better decisions.
Q. 23. Neeraj, a sales representative of ‘Omida Ltd’ has changed seven jobs in the last one year. He is a hard working person but is not able to finalise deals with the customer due to his inadequate vocabulary and omission of needed words. Sometimes he uses wrong words because of which intended meaning is not conveyed. All this created a mis-understanding between him and his cliens.
(a) Identify the communication barrier discussed above.
(b) State the category of this communication barrier.
(c) Explain any other communication barrier of the same category.
- Badly expressed message
- Semantic barrier, which arises from problems and obstructions in the process of encoding and decoding of message into words or impressions.
- Technical jargon; Specialists use technical language or jargon while explaining to the workings, e.g., tariff, quotas, etc. therefore, they may not understand the actual meaning of many such words.
Q. 24. Smita had been working as an assistant manager with ‘Johnson Enterprises’ for the last ten years. She was very popular amongst her colleagues because of her commitment and dedication towards the work. When the manager senior to her retired, all her colleagues thought that now Smita would be promoted. But to everyone’s surprise the vacant post was filled by an outsider, Mrs. Rita. Smita felt demoralized and her performance started declining. She would abstain herself often and could not meet her targets.
Mrs. Rita was a good leader, who would not only instruct her subordinates but would also guide and inspire them. She noticed Smita’s hebaviour and felt that her performance could be improved. She started involving Smita in decision making-issues related to the organization and made her a part of high level joint-management committed. Smita was now punctual in office and her performance started improving.
- Identify the function of management being performed by Rita.
- Name the element of the above function of management which helped Rita to improve Smita;s behavior.
- State any three features of the element identified in (ii) above.
- Features of motivation:
- Motivation is an internal feeling: The urge, desires, aspirations or needs of people, which are internal, influence human behavior.
- Motivation produces goal-directed behavior: For example, if the employee is interested in promotion, it helps to produce a behavior to improve performance.
- Motivation can be either positive or negative: Positive motivation provides positive rewards like increase in pay, promotion, recognition, etc. negative motivation uses negative means like punishment, stopping increments, threatening, etc.
Q. 25. Rahim was working in an enterprise on daily wages basis. It was difficult for him to fulfill the basic needs of his family. His daughter fell ill. He had no money for his daughter’s treatment. To meet the expenses of her treatment, he participated in a cycle race and won the prize money. The cycle company offered him a permanent pensionable job which he happily accepted.
(i) By quoting the lines from the above para identify the needs of Rahim that are satisfied by the offer of cycle company.
(ii) Also, explain two other needs of Rahim followed by above that are still to be satisfied.
- Needs of Rahim that are satisfied by the offer of cycle company are Physiological and safety/security needs.
‘The cycle company offered him a permanent pensionable job’.
- The other needs followed by the above stated needs that are still to be satisfied are:
- Affiliation/Belongingness needs: These needs refer to the need for affection, sense of belonging, acceptance and friendship.
- Esteem needs: These needs refer to the need for self-respect, autonomy status, recognition, etc.
Q. 26.Y Ltd. Is a bank functioning in India. It is planning to diversify into insurance business. Lately, the government of India has allowed the private sector to gain entry in the insurance business. Previously, it was the prerogative of LIC and GIC to do insurance business. But now with liberalization of the economy and to make the field competitive other companies have been given licences to start insurance business under the regulation of ‘Insurance regulatory and development Authority’.
Y Ltd. Plans to recruit high quality employees and agents and exercise effective direction to capture a substantial part of life and non-life insurance business.
- Identify how the company can supervise its employees and agents effectively.
- What financial and non-financial incentives can the company use for employees and agents separately to motivate them?
- How can the company ensure that higher order needs i.e., esteem and self actualization as specified by Maslow are met?
- How can the company follow formal communication system?
- How can informal communication help to supplement formal communication?
- The company will appoint supervisors who will provide on the job training to the employees and agents. They will maintain group unity and ensure that the company gets enough insurance business.
- To the employees, the company can give pay and allowances, bonus, retirement benefits, perquisites (e.g., car allowance),recognisation, promotion, job security etc. to motivate them for higher performance.
To the agents, the company can give the following incentives:
- Profit sharing
- Stock option (i.e., giving company’s share at a price less than market price)
- Productivity linked salary (i.e., higher salary for getting more insurance business)
- Participation in decision – making.
- By giving recognition, autonomy status, etc. and providing growth and self-fulfillment opportunities, the company ensures that higher order needs-esteem and self actualization needs are met.
- The company can follow formal communication system by ensuring that all communication flows through official channels designed in the organization chart (i.e., through Scalar chain).
- Information communication network (i.e., grapevine) can be used by the company to transmit information to know he reactions of the employees and agents to the company’s decisions and policies. Grapevine channels can carry insurance market information rapidly.
Q. 27. Prateek is working in a multinational company in Noida. He was running a temperature for the last many days. When his blood was tested, he was found to be positive for malaria. He was admitted in a hospital and a blood transfusion was advised by the doctors as his condition was very serious. One of his colleagues sent a text message to his superior, Mr. B. Chatterjee. Mr. B. Chatterjee immediately sent a text message to the employees of the organization requesting them to donate blood for Prateek. When the General Manager came t o know about it, he ordered for fumigation in the company premises and cleaning the surroundings.
- From the above paragraph, quote lines that indicate formal and informal communication.
- State any two features of informal communication.
- Identify any two values that are being communicated to society in the above case.
- (i) Informal communication: “One of his colleagues sent a text message to his superior, Mr. B. Chatterjee. Mr. B. Chatterjee immediately sent a text message to the employees of the organization requesting them to donate blood for Prateek.”
(ii) Formal communication: “When the general manager came to know about it, he ordered for fumigation in the company premises and cleaning surroundings.”
- The features of informal communication are as follows:
- The grapevine/informal communication spreads very fast and sometimes gets distorted.
- It is very difficult to detect the source of such communication.
- The two values that are being communicated to the society are:
- Cleanliness
Q. 28. Roshan is the chief of ‘Khidmat’ restaurant located in the city of Bangaluru. The place is known for its exquisite Mughlai cuisine especially mutton briyani and kababs. All the food is prepared under Roshan’s purview. The various activities in the kitchen are initiated in accordance to his instructions. He is very clear and specific in issuing instructions to his subordinates in order to ensure smooth working of the department. He personally oversees the method followed by the chefs for preparation of each dish. He misses no opportunity to praise his subordinates for their good work. All his team members feel very happy and satisfied under his direction. He provides constant guidance to them in order to improve upon its taste and presentation and also encourages them to innovate and be more creative in their work.
In the above context:
- Identify the various elements of directing mentioned in the above paragraph by quoting lines from the paragraph.
- Describe briefly any two points to highlight the importance of directing as a function of management.
- The various elements of directing mentioned in the above paragraph are as follows:
- Communication: ‘He is very clear and specific in issuing instructions to his subordinates in order to ensure smooth working of the department.”
- Supervision: “He personally oversees the method followed by the chefs for preparation of each dish.”
- Leadership: “He provides constant guidance to them in order to improve upon its taste and presentation and also encourages them to innovate and be more creative in their work.”
- Motivation: “He misses no opportunity to praise his subordinates for their good work.”
- The importance of directing as a function of management is described below:
- Initiates action: Directing helps to initiate action by people in the organization towards attainment of desired objectives. It is the first execution function of management.
- Integrates employees’ efforts: Directing seeks to integrate the individual efforts of employees in the organization towards the realization of the organizational goals.
- Helps to realize their potential: Directing provides effective guidance, motivation and leadership to the employees so as to enable them to realize their potential and capabilities. (any two)
Q. 29. Neeraj has been working as a sewing machine operator in an export house for the past ten years. His basic work is to seam the parts of a garment together, and attach buttons, hooks, zippers, and accessories to produce clothing. Considering the fact that Neeraj is an experienced operator, he is well versed with the fundamentals of industrial production and possesses good communication skills. The plant superintendent in the factory recommends Neeraj’s name to the production manager for the post of supervisor which will fall vacant after a month on the retirement of the present supervisor. Consequently, Neeraj is assigned the post of supervisor and his salary is increased accordingly. Moreover, as per the policy of the export house, he is offered free medical aid and education to his two children.
In the context of the above case:
- Identify the type of source of recruitment used by the export house to fill up the post of supervisor. Give any two advantages of using this source.
- Identify the types of financial incentives offered to Neeraj by quoting lines from the paragraph.
- The internal source of recruitment has been used by the export house to fill up the post of supervisor through promotion. The two advantages of using internal source of recruitment are stated below.
- Employees are motivated to improve their performance: When employees are promoted internally from within an organization, it has a positive impact on their commitment and loyalty and they tend remain satisfied with their jobs. Also, it may lead to a chain of promotion at lower levels in the organization. As a result, it motivates the employees to improve their performance through learning and practice.
- Internal recruitment simplifies the process of selection and placement: The candidates can be appraised more perfectly and economically as that are already working in the organization. As the candidates are already known to the organization, it is considered to be a more reliable method of recruitment.
- The types of financial incentives offered to Neeraj are as follows:
- Pay and allowances: “his salary is increased accordingly.”
- Perquisites: “as per the policy of the export house, he is offered free medical aid and education to his two children.”
Q. 30. Sunidhi has started a designer studio in the basement of her residence after completing her masters in fashion designing. She has appointed ten employees to take care of the various aspects of the work. She interacts regularly with each employee to tell exactly what is expected of him/.her and what he/she needs to do to be regarded as a good performer. At the same time she allows a free work environment wherein the employees openly chit chat with each other in order to fulfil their social and emotional needs. Sometimes, these interactions also lead to spreading rumours which are not authentic.
- Name and explain the two types of communication being referred to in the above paragraph.
- How does effective communication increases managerial efficiency?
- The two types of communication being referred to in the above paragraph are formal communication and informal communication.
- Formal communication: The communication that flows through official channels designed in the organization structure is called formal communication. This communication may take place between a subordinate and superior or among same team employees or managers. Usually a written record of such communications is maintained, recorded and filed in the office. Formal communication may be further classified as – Vertical and Horizontal.
- Informal communication: Informal communication is the type of communication that takes place without following the formal lines of communication. It is generally referred to as the ‘grapevine’ because it spreads throughout the organization with its branches going out in all directions in utter disregard to the levels of authority. The informal communication arises out of needs of employees to exchange their views, which cannot be done through formal channels.
- Effective communication increases managerial efficiency by lubricating the working of the entire organization through quick and effective performance of managerial functions. It enables the management to express the goals and targets, issue instructions, allocate jobs and responsibilities and look after the performance of subordinates.
Q. 31. Gagan has joined as a Managing Director of True Help Ltd., a company engaged in the business of providing road side assistance to the vehicle owners. He was previously working in an automobile company. As a part of the joining incentive, the company has allotted him 400 shares of the company.
In context of the above case:
- Identify the type of source of recruitment used by True Help Ltd. to fill up the post of Managing Director.
- Identify the type of financial incentive offered to Gagan. Also, state any one other method that can be used to offer financial incentives to the employees.
- External source of recruitment has been used by True Help Ltd. to fill up the post of Managing Director.
- Co-partnership/ Stock option is the type of financial incentive offered to Gagan.
The other method that can be used to offer financial incentives to the employees is Bonus. Bonus is an incentive offered over and above the wages/ salary to the employees.
Q. 32. Mr. Naresh is working as a Production Manager in Vohra Ltd. His subordinates are mostly engineers and qualified technicians.
As a manager, he is very strict, does not listen to any suggestions or feedbacks given by his subordinates. He expects them to following his instructions without any questions and does not allow them to give suggestions.
- What leadership style does the manager follow?
- Is such a leadership style beneficial for the company? Explain.
- State any one value being overlooked by him? (4 marks)
- Autocratic leadership
- This leadership style is effective in getting productivity in many situations like in a factory where the supervisor is responsible for production on time and has to ensure labour productivity. Quick decision-making is also facilitated.
- Value overlooked:
- Respect for other’s opinion
- Initiative (any one)
| |205 docs|49 tests |
Top Courses for Commerce
FAQs on Case Studies - Directing - Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is Directing Commerce? |
| 2. What are some of the services provided by Directing Commerce? |
| 3. How can Directing Commerce help businesses increase their sales? |
| 4. Does Directing Commerce only work with e-commerce businesses? |
| 5. How does Directing Commerce stay up-to-date with the latest trends in digital marketing? |
| Views | |
| Rating | |
| Last updated |
shortcuts and tricks
Past year papers, previous year questions with solutions, important questions, semester notes, objective type questions, study material, mock tests for examination, case studies - directing | business studies (bst) class 12 - commerce, video lectures, practice quizzes, extra questions, viva questions, sample paper.

Case Studies - Directing Free PDF Download
Importance of case studies - directing, case studies - directing notes, case studies - directing commerce questions, study case studies - directing on the app.
| cation olution |
| Join the 10M+ students on EduRev |
Welcome Back
Create your account for free.
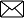
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country, practice & revise.
- Sample Paper
- Question Paper
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Books
- NCERT Audio Books
- NCERT Exempler
- Model Papers
- Past Year Question Paper
- Writing Skill Format
- RD Sharma Solutions
- HC Verma Solutions
- CG Board Solutions
- UP Board Solutions
- Careers Opportunities
- Courses & Career
- Courses after 12th
Home » 12th Class » Class 12 Business Studies Notes for Directing (PDF) – Study Material
Class 12 Business Studies Notes for Directing (PDF) – Study Material
Class 12 Business Studies Directing – Get here the Notes, Question & Practice Paper of Class 12 Business Studies for topic Directing Notes. Directing Notes for Class 12 Business Studies are here. You can download the Directing Notes PDF to study all the topics in this chapter. Moreover the class 12 Business Studies notes include chapter summary, definitions, examples, and key pointers for Directing . Thus if you are studying class Business Studies (व्यवसाय अध्ययन), then the Directing notes will help you easily understand the topic and ace it.
Class 12 Business Studies Notes for Directing
Directing is a critical part in the study of Business Studies . In India, it is taught in class. Therefore the class 12 Notes for Business Studies topic Directing have been compiled by teachers and field experts. They explain the complete chapter of Directing in one-shot . Whether you are studying the topic Directing to complete your class syllabus, or for any competitive exam like JEE , NEET , UPSC, you can simply refer these notes to complete the chapter in one-shot!
Directing Notes Download Link – Click Here to Download PDF
Directing Notes for Class 12 Business Studies PDF
The PDF of Directing class 12 notes is as follows. You can view the document here and also download it to use it anytime for future reference whenever you want to brush up your concepts of Business Studies.

Candidates who are ambitious to qualify the Class 12 with good score can check this article for Notes, Study Material, Practice Paper. Above we provided the link to access the Notes , Important Question and Practice Paper of Class 12 Business Studies for topic Directing.
All Topics Class 12 Business Studies Notes
Chapter wise notes for Business Studies (व्यवसाय अध्ययन) are given below.
- Business Environment
- Consumer Protection
- Controlling
- Financial Management
- Financial Markets
- Marketing Management
- Nature and Significance of Management
- Principles of Management
Class 12 Notes for All Subjects
- Class 12 Biology Notes
- Class 12 Business Studies Notes
- Class 12 Chemistry Notes
- Class 12 Economics Notes
- Class 12 English Notes
- Class 12 Geography Notes
- Class 12 Maths Notes
- Class 12 Physics Notes
- Class 12 Sociology Notes
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies Directing
The Directing notes here help you solve the questions and answers . Also, you can complete the class 12 Directing worksheet using the same. In addition you will also tackle CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Important Questions with these class 12 notes .
However if you still need help, then you can use the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies Directing to get all the answers. Directing solutions contain questions, answers, and steps to solve all questions.
Notes for All Classes
- Class 7 Notes
- Class 8 Notes
- Class 9 Notes
- Class 10 Notes
- Class 11 Notes
- Class 12 Notes
Directing Notes for Class 12 Business Studies – An Overview
Class 12 Directing Notes for All Boards
You can use the class 12 Business Studies notes of Directing for all boards.
The education boards in India for which Directing notes are relevant are – CBSE, CISCE, AHSEC, CHSE Odisha, CGBSE, HBSE, HPBOSE, PUE Karnataka, MSBSHSE, PSEB, RBSE, TBSE, UPMSP, UBSE, BIEAP, BSEB, GBSHSE, GSEB, JAC, JKBOSE, KBPE, MBOSE, MBSE, MPBSE, NBSE, DGE TN, TSBIE, COHSEM, WBCHSE .
Therefore you can refer to these notes as CBSE, CISCE, AHSEC, CHSE Odisha, CGBSE, HBSE, HPBOSE, PUE Karnataka, MSBSHSE, PSEB, RBSE, TBSE, UPMSP, UBSE, BIEAP, BSEB, GBSHSE, GSEB, JAC, JKBOSE, KBPE, MBOSE, MBSE, MPBSE, NBSE, DGE TN, TSBIE, COHSEM, WBCHSE notes for class Class 12 / Class / Business Studies for the topic Directing.
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel .
Class 11 Political Science Notes for The Legislature (PDF) – Study Material
Class 12 chemistry notes for amines (pdf) – study material, related posts.

AP Inter 2nd Year Previous Year Question Papers – Download PDF Andhra Pradesh Board PYQP
Ap inter 2nd year kannada question paper | ap pyqp pdf download, ap inter 2nd year oriya question paper | ap pyqp pdf download, ap inter 2nd year persian question paper | ap pyqp pdf download, leave a reply cancel reply, cbse board quick links.
- CBSE Date Sheet
- CBSE Result
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Sample Papers
- CBSE Question Papers
- CBSE Practice Papers
CISCE Board Quick Links
- CISCE Time Table
- CISCE Results
- CISCE Specimen Papers
- CISCE Syllabus
- CISCE Question Papers
Class Wise Study Material
Board exams 2023.
- Solved Sample Papers
- Revision Notes
- State Board
Study Material
- Class Notes
- Courses After Class 12th
- JEE Main 2024
- Fashion & Design
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
© 2019 aglasem.com
Discover more from AglaSem Schools
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
Important Questions for CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Concept, Characteristics, Importance and Elements of Directing
December 8, 2019 by Sastry CBSE
Directing Important Questions for CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Concept, Characteristics, Importance and Elements of Directing
1.Concept of Directing It refers to the process of instructing, guiding, counselling, motivating and leading people in the organisation through effective communication so that their efforts result in achievement of organisational objectives.
2. Definition of Directing According to Ernest Dale, ‘Directing is telling people what to do and seeing that they do it to the best of their ability’.
3. Features or Characteristics of Directing
- Initiates action
- A pervasive function
- A continuous process
- It flows from top to bottom
4. Importance of Directing
- Helps to initiate action
- Integrates employees’ efforts
- Improves efficiency
- Helps to bring stability and balance in the organisation
- Facilitates introduction of needed changes in the organisation
5. Elements of Directing
- Supervision
- Communication
Previous Years Examination Questions
1 Mark Questions 1. Explain in one sentence how directing initiates action in management. (Compartment 2014; Delhi 2011) Ans. Directing initiates action by ordering employees to attain the desired goal of an organisation.
2. What is meant by directing? (Delhi 2009) Ans. Directing is the process of instructing, guiding and inspiring people in the organisation to achieve its objectives.
3. Give any two elements of directing. (All India 2009) Ans. (i) Supervision (ii) leadership.
4. State the element of directing which helps in implementing the principle of scalar chain. (HOTS; All India 2008) Ans. Communication helps in implementing the principle of scalar chain.
5. State any one characteristic of directing. (Delhi 2008C) Ans. Directing helps to initiate action by the people in the organisation towards attainment of desired objectives. 3 Marks Question
6. How directing helps in efficient and effective functioning of the organisation? Explain by giving any three points. (Delhi 2014) Ans. Directing helps in efficient and effective functioning of management because: (i) It integrates employees Directing integrates employees’ efforts in the organisation in such a way that every individual’s efforts contributes to the welfare of the organisation. Thus, it ensures that employees work efficiently for the attainment of goals. (ii) It improves efficiency Directing guides employees to fully realise their potentials and capabilities. Through this function, managers utilise the potential of employees and persuade them to work with the best of their ability and contribute their maximum efforts towards the achievement of organisational objectives. (iii) It facilitates change Business environment is changing very frequently, but the people generally have a tendency to resist change. In this context, directing helps manager to persuade his subordinates to carry out changes from time to time to cope with changes in the environment as the changes are necessary to adapt and it is the need of modern business 4 / 5 Marks Questions
7. Exxplain the meaning and any three characteristics of directing. (All India 2010) Ans. Directing refers to the process of instructing, guiding, counselling, motivating and leading people in the organisation through effective communication, so that their efforts result in achievement of organisational objectives. Characteristics of directing are as follows: (i) Initiating process It involves giving orders and instructions to the employees and thereby decisions are converted into actions. (ii) Pervasive function The directing function is performed by all managers at all levels to achieve the organisational goals. (iii) A continuous process It is an activity that takes place throughout the life of an organisation, irrespective of people occupying managerial position.
8. Directing is the heart of the management process. Do you agree? Give any four reasons in support of your answer. (HOTS; Delhi 2010c, 2009; All India 2010) Ans. Yes, I do agree with this statement. Directing may be regarded as the heart of the management process; Its importance may be explained under the following points (i) Initiates action Directing helps to initiate action by people in the organisation towards attainment of desired objectives, e.g. if a supervisor guides his subordinates and clarifies their doubts in performing a task, it will help workers to achieve work targets given to them. (ii) Integrates employees’ efforts Directing integrates employees’ efforts in the organisation in such a way that every individual effort contributes to the attainment of organisational objectives. Thus, it ensures that the individuals work for organisational goals. (iii)Improves efficiency Directing guides employees to fully realise their potential and capabilities by motivating and providing effective leadership. A good leader can always identify the potential of his employees and motivate them to extract work up to their potential. (iv)Brings balance and stability in the organisation Effective directing helps to bring stability and balance in the organisation since, it fosters cooperation and commitment among the people and helps to achieve balance among various group activities and the departments.
9. Directing is not required at all in management of organisation. Do you agree? Give two reasons in support of your answer. (HOTS; Delhi 2008) Ans . No, I do not agree with the above statement. Directing is required in organisation as it initiates the action of people towards attainment of desired goals. Reasons (i) Initiates action Directing helps to initiate action by people in the organisation towards attainment of desired objectives, e.g. if a supervisor guides his subordinates and clarifies their doubts in performing a task, it will help workers to achieve work targets given to them. (ii) Integrates employees’ efforts Directing integrates employees’ efforts in the organisation in such a way that every individual effort contributes to the attainment of organisational objectives. Thus, it ensures that the individuals work for organisational goals. (iii)Improves efficiency Directing guides employees to fully realise their potential and capabilities by motivating and providing effective leadership. A good leader can always identify the potential of his employees and motivate them to extract work up to their potential. (iv)Brings balance and stability in the organisation Effective directing helps to bring stability and balance in the organisation since, it fosters cooperation and commitment among the people and helps to achieve balance among various group activities and the departments. 6 Marks Question
10. Explain how directing helps in effective and efficient functioning of the organisation. (Compartment 2014) or What is meant by directing as a function of management? Describe any four points of its importance. (Delhi 2012) or ‘Every action in the organisation is initiated through directing’. Explain any four points of importance of directing in the light of this statement. (All India 2012) Ans. Directing refers to the process of instructing, guiding, counselling, motivating and leading people in the organisation through effective communication so that their efforts result in achievement of organisational objectives. The scope of directing is very wide. It consists of all those activities by which a manager influences the behaviour of his subordinates to secure desired performance from them. According to William Newman, ‘Directing deals with the steps, a manager takes to get subordinates and others to carry out plans’. Importance of directing Its importance may be explained under the following points (i) Initiates action Directing helps to initiate action by people in the organisation towards attainment of desired objectives, e.g. if a supervisor guides his subordinates and clarifies their doubts in performing a task, it will help workers to achieve work targets given to them. (ii) Integrates employees’ efforts Directing integrates employees’ efforts in the organisation in such a way that every individual effort contributes to the attainment of organisational objectives. Thus, it ensures that the individuals work for organisational goals. (iii)Improves efficiency Directing guides employees to fully realise their potential and capabilities by motivating and providing effective leadership. A good leader can always identify the potential of his employees and motivate them to extract work up to their potential. (iv)Brings balance and stability in the organisation Effective directing helps to bring stability and balance in the organisation since, it fosters cooperation and commitment among the people and helps to achieve balance among various group activities and the departments.
Important Questions for Class 12 Business Studies Class 12 Business Studies NCERT Solutions Home Page
Free Resources
NCERT Solutions
Quick Resources
CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free
Directing Class 12 Business Studies Notes and Questions
Please refer to Directing Class 12 Business Studies notes and questions with solutions below. These revision notes and important examination questions have been prepared based on the latest Business Studies books for Class 12 . You can go through the questions and solutions below which will help you to get better marks in your examinations.
Class 12 Business Studies Directing Notes and Questions
Q. 1. Ayesha Ltd. Assured their employees that in spite of recession no worker will be retrenched from the job. (i) Name and explain the type of incentive offered to the employees. (ii) Explain one more incentive of the same category. Ans. (i) Job security (ii) Explain one more incentive of the same category. 1. Employee’s recognition. 2. Organizational climate. Q. 2. Blue Birds Ltd. Offers to its employees issue of shares at a price which is less than the market price. (i) Name and explain the type of incentive offered to the employees. (ii) Explain one more incentive of the same category. Ans. (i) Co-partnership/Stock option. (ii) Other incentives: (a) Pay and allowance, (b) Bonus. Q. 3. ABC Ltd. Is not able to achieve its objective on analyzing, they found that employees were not given their best, so he decided to announce an incentive plain, which offers various incentives to employee workers at different level for achieving their target. (i) Which element of directing is used by manager? (ii) Suggest incentive suitable for: 1. Employees operating at lower level. 2. Employees operating at higher level. Ans. (i) Motivation is missing. (ii) (a) Lower level: offer monetary incentives. (b) Higher level: non-monetary incentive. Q. 4. Mr. John faced lot of problems regarding the policy on teaching. He directly consulted the principal about his problem ignoring the Headmistress who is immediate superior of Mr. John as he feels more free to communicate with principal. (i) Name the pattern of communication followed by Mr. John. (ii) State any other two patters. Ans. (i) Mr. John is following inverted ‘V’ pattern. (ii) Other two pattern: 1. Wheel pattern, (b) Chain pattern. Q. 5. Is directing required at planning stage? Name the element of directing function under which: (i) the superiors oversee the activities of their subordinates. (ii) the superiors assure the subordinates that their needs will be taken care of. (iii) the superior attempts to influence the behavior of people at work towards the realization of specified goals. (iv) the superior share information with the subordinates in order to reach common understanding. Ans. No, directing is not required at planning stage since it is an executive function. It initiates action in the organization while other functions of management (planning, organizing, staffing and controlling) just prepare a setting for action. 1. Supervision (ii) Motivation (iii) Leadership (iv) Communication. Q. 6. Amit and Mikki are working in the same organization but in different departments. One day at lunch time Mikki informed Amit that due to computerization some people are going to be retrenched from the organization. Name which type of communication is this. State any two limitations of this type of communication. Ans. Informal Communication Limitations: 1. The grapevine/informal communication spreads rapidly and sometimes gets distorted. It is very difficult to detect the source of such communication. 2. It also leads to generate rumours. People’s behavior is affected by rumours and informal discussion and sometimes may hamper work environment. Q. 7. You are working at the middle level of management. Your superior, a top management personnel, sent a message for you which you received and well understood. Is the communication process complete? Give reason. Ans. No, the communication process is not complete unless and until feedback is given to the superior. Feedback includes all those actions of the receiver indicating that he has received and understood the message of sender. So, I must respond to communication to improve its effectiveness, e. g., by giving a reply to letter, giving reactions to the message, etc. Q. 8. Rakesh is working under his superior Neeraj. He always communicates useful ideas and suggestions to his superior regarding reduction of cost, improvement in the product, etc. Neeraj implements his suggestions and has always found favourable results, but he never appreciates Rakesh for his suggestions. Now Rakesh decided not to communicate any suggestion or idea to Neeraj. Identify the factor which acts as a communication barrier. Ans. Lack of proper incentives (Personal Barriers to Communication) Q.9. Ankur is working as a production manager in an organization. His subordinate Saurabh discussed with hi a method o production which will reduce the cost of production. But due to some domestic problems and Ankur’s mind being pre-occupied he is not in a position to understand the message. Saurabh got disappointed by this. Identify the factor which acts as a communication barrier. Ans. Lack of attention (Psychological/Emotional Barriers to Communication) Q.10. Rajat a Sales Manager, achieved his sales target one moth in advance. This achievement as displayed on the notice board and the CEO of the Company awarded a certificate for the best performance to him. Name the incentive provided to Rajat. Ans. The incentive provided to Rajat is – ‘Recognition’. Q. 11. A behavior study was done on total of 100 employees of an organization. Group A (of 50 employees) were appreciated by the manager for their work and initiative for new idea. All these employees were given option of flexible working hours and were paid wages at a higher piece rate. On the other hand, Group B (of remaining 50 employees) was criticized for their poor performance. Their increments were stopped and they were paid wages at a lower piece rate. (a) Identify and explain the feature of motivation highlighted in the above case. (b) What type of leadership is followed by the manager? Justify your answer. Ans. 1. Motivation can be either positive or negative. Positive motivation provides positive rewards like increase in pay, promotion, recognition, etc. Negative motivation uses negative means like punishment, stopping increments, threatening, etc. 2. Autocratic leadership style. The leader’s following is based on the assumption that reward or punishment both can be given depending upon the result. Q. 12. In a company, Mr. Kshitij always explains management policies to workers and brings workers’ problems to the notice of management. At what post does Mr. Kshitij work in this company? Ans. Mr. Kshitij is supervisor in the company as he acts as a link between workers and management. Q. 13. Prachi is working in an MNC. She has been given an option to buy the shares of the company at an amount less than the market price because of her performance as an incentive. Identify which incentive is being given to her. Ans. Co-partnership/Stock option. Q. 14. Ms. Snigdha, Production Manager and Mr. Sarthak, Marketing manager of an electronics company are not on talking terms with each other. Because of that they do not transfer complete information to each other. (a) Identify the element of directing which becomes ineffective due to the behavior of the managers. (b) Also, explain the factor which led to their such behavior. Ans. (a) Communication 1. Distrust (Psychological barrier) Distrust between sender and receiver causes failure of communication.If they do not believe each other, they cannot understand each other’s message in its original sense. Q. 15. Huma is working in a company on a permanent basis. As per job agreement she had to work for 8 hours a day and was free to work overtime. Huma worked overtime, due to which she fell ill and had to take leave from her work. No one showed concern and enquired about her health. She realized that she was fulfilling only some of her needs while some other needs still remained to be fulfilled. (i) By quoting the lines from the above para, identify the needs of Huma which she is able to fulfil. (ii) Also explain two other needs of Huma followed by the above needs, which still remained to be satisfied. Ans. 1. ‘Huma is working in a company on a permanent basis’. According to above line Huma is able to fulfil her following needs: (a) Physiological needs(b) Safety or Security needs (ii) Needs of Huma which still remained to be satisfied are: 1. Affiliation Need: It refers to the need for affection, since to belongingness, acceptance and friendship. 2. Esteem Need: It refers to the need for self-respect, autonomy, status, recognition and attention. Q. 16. Mr. Nath, a recently appointed production manager of Suntech Ltd. Has decided to produce jute bags instead of plastic bags as these are banned by the government. He set a target of producing 1000 jute bags a day. It was reported that the employees were not able to achieve the target. After analysis he found that employees were demotivated and not putting in their best for achieving the target. Mr. Nath’s beaviour is good towards the employees. His attitude is always positive. So he announced various incentive schemes for the employees like; ● Installing award or certificate for best performance. ● Rewarding an employee for giving valuable suggestion. ● Congratulating the employees for good performance. 1. Identify the functions of management highlighted in the above paragraph. 2. State the ‘incentive’ under which the employees are motivated. 3. State any two values which the production manager wants to communicate to the society by his work and behavior. Ans. 1. Directing and Controlling 2. Employee recognition programme (non-monetary incentive) 3. Vale: ● Sensitivity of environment ● Good behavior towards employees. Q. 17. NOTICE A meeting of all supervisors is scheduled on 20 th August, 2016 This notice was placed on the notice board in the reception area of XYZ Ltd. But it did not mention clear specification regarding the time of meeting. Which barrier of communication is referred to here? Explain any two other forms of barriers to effective communication under the same category. Ans. Badly expressed message (Semantic barriers) – Use of wrong words, omission of needed words, inadequate vocabulary, etc. 1. Symbols with different meanings: A work may have several meanings. For example, consider these three sentences where the work ‘value’ is used: ● What is the value of this ring? ● I value our friendship. ● What is the value of learning compute skills? Wrong perception by the receiver leads to communication problems. 1. Faulty translations: Sometimes, the communications originally drafted in one language (say, English) need to be translated to the language understandable to workers (say, Hindi). If the translator is not proficient with both the languages, communication becomes ineffective. Q. 18. Mr. Sandeep is the marketing manager of a company manufacturing designer clothes. One day, in the morning while leaving home he had a quarrel with a person in his neighborhood on some issue. That person is a criminal who could abuse his family members. Mr. Sandeep, on that day, is very worried and angry too on the behavior of the neighood person. On that day, a meeting was held by a team of marketing and design experts to ensure that whatever is produced is according to market demand and tastes and fashion of the customers. But Mr. Sandeep could not pay attention to the discussion between them. (a) Identify the type of barriers to communication mentioned in the above para. Justify your answer. (b) Explain any two such barriers to communication. Ans. 1. Psychological barriers. These are related to the state of mind of both sender and receiver of communication.For example, a worried person cannot communicate properly and an angry receiver cannot understand the real meaning of message. ‘Mr. Sandeep is very worried and angry on that day.So he could not pay attention to the discussion in the meeting.’ Psychological barriers to communication: 1. Lack of attention: the pre-occupied mind of receiver and the resulting non-listening of message acts as a major psychological barrier. 2. Premature evaluation : Sometimes people form a judgement before the sender completes his message, which causes failure of communication. Q. 19. Mrs. Rajlaxmi is working as the Human Resource Cosultant in a firm manufacturing cosmetic, which is facing a problem of high employee urnover. The CED of the company has invited suggestions from her for retaining the talented employees & reducing the employee turnover. Mrs. Rajlaxmi recommends that the good employees be rewarded in a way that it creates a feeling of ownership among the employees and at the same time makes them contribute towards the growth of the organization. (a) Identify the incentive and explain its type, which has been suggested by Mrs. Rajlaxmi to the CEO of the company. (b) Also explain any two other incentives of the same type. Ans. 1. Financial incentive. Co-Partnership/Stock Option Other financial incentives: 1. Pay and allowances: For every employee, salary is the basic financial incentive. It includes basic pay, dearness allowance and other allowance. Pay hike and increments improve performance level of employees. 2. Profit sharing: Employees are given a share in the profits of the organization. This motives them to improve their performance and contributes to increase in profits of the organization. Q. 20. Mr. Bhuvan is the marketing manager of the company manufacturing designer clothes. One day in the morning while leaving home, he had a quarrel with the person in the neighbourhood. That person abused his family and threaten to harm the family. Mr. Bhuvan got very upset and worried. On the same day a meeting was organized in the office to finalise the design according to market demand and taste the fashion of the customers. Mr. Bhuvan could not pay attention to the discussion as he was thinking about the quarrel only. (a) Identify the type of barrier to communication mention in the above para. (b) State any other two barriers of same category. Ans. 1. Psychological barrier Lack of attention. 2. (i)Premature evaluation (ii) Loss by poor retention. Q. 21. Rajiv is working as Personal Manager in a company. The specialty of the company is that financial position of all the employees is good. The employees working here are honest punctual and hardworking. The CEO of the company asked him to suggest a method of motivation. The CEO asked him to suggest a method which is happily accepted by all the employees. Rajiv spoke to many employees in this connection. Some employees suggested give more importance to individual autonomy, another suggested good performance should be appreciated another group suggested to award, certificate, trophies to recognize the good performance. Mr. Rajiv mixed all and suggested a method of motivation to CEO. The CEO happily accepted that and it was immediately implemented. With in few days the company’s growth rate appeared to have become fast. 1. Identify the functions of management indicate in the above paragraph. 2. Which motivation methods were suggested by different group of employees. 3. Which motivation method combine all the above stated and was suggested by personal manager. Ans. 1. Directing. 2. (i) Recognition (ii) Autonomy 1. Organizational climate. 2. (i) Ethical behavior (ii) Motivating employees (iii) Taking Suggestions from employing. Q. 22. Pramod was a supervisor at a ‘Annapurna Aata’ factory. The factory was producing 200 quintals of Aata every day. His job was to make sure that the work goes on smoothly and there was no interruption in production. He was a good leader who would give orders only after consulting his subordinates and work out the policies with the acceptance of the group. Identify and describe the leadership style being adopted by Pramod. Ans. Democratic style of leadership. ● A democratic leader favours decision making by the group. This improves the attitude of the employees towards their jobs and the organization thereby increasing their morale. ● Using this style is of mutual benefit – it allows them (subordinates) to become part of the team and helps leaders (seniors) to make better decisions. Q. 23. Neeraj, a sales representative of ‘Omida Ltd’ has changed seven jobs in the last one year. He is a hard working person but is not able to finalise deals with the customer due to his inadequate vocabulary and omission of needed words. Sometimes he uses wrong words because of which intended meaning is not conveyed. All this created a mis-understanding between him and his cliens. (a) Identify the communication barrier discussed above. (b) State the category of this communication barrier. (c) Explain any other communication barrier of the same category. Ans. 1. Badly expressed message 2. Semantic barrier, which arises from problems and obstructions in the process of encoding and decoding of message into words or impressions. 3. Technical jargon; Specialists use technical language or jargon while explaining to the workings, e.g., tariff, quotas, etc. therefore, they may not understand the actual meaning of many such words. Q. 24. Smita had been working as an assistant manager with ‘Johnson Enterprises’ for the last ten years. She was very popular amongst her colleagues because of her commitment and dedication towards the work. When the manager senior to her retired, all her colleagues thought that now Smita would be promoted. But to everyone’s surprise the vacant post was filled by an outsider, Mrs. Rita. Smita felt demoralized and her performance started declining. She would abstain herself often and could not meet her targets. Mrs. Rita was a good leader, who would not only instruct her subordinates but would also guide and inspire them. She noticed Smita’s hebaviour and felt that her performance could be improved. She started involving Smita in decision making-issues related to the organization and made her a part of high level joint-management committed. Smita was now punctual in office and her performance started improving. 1. Identify the function of management being performed by Rita. 2. Name the element of the above function of management which helped Rita to improve Smita;s behavior. 3. State any three features of the element identified in (ii) above. Ans. 1. Directing 2. Motivation 3. Features of motivation: 1. Motivation is an internal feeling: The urge, desires, aspirations or needs of people, which are internal, influence human behavior. 2. Motivation produces goal-directed behavior: For example, if the employee is interested in promotion, it helps to produce a behavior to improve performance. 3. Motivation can be either positive or negative: Positive motivation provides positive rewards like increase in pay, promotion, recognition, etc. negative motivation uses negative means like punishment, stopping increments, threatening, etc. Q. 25. Rahim was working in an enterprise on daily wages basis. It was difficult for him to fulfill the basic needs of his family. His daughter fell ill. He had no money for his daughter’s treatment. To meet the expenses of her treatment, he participated in a cycle race and won the prize money. The cycle company offered him a permanent pensionable job which he happily accepted. (i) By quoting the lines from the above para identify the needs of Rahim that are satisfied by the offer of cycle company. (ii) Also, explain two other needs of Rahim followed by above that are still to be satisfied. Ans. 1. Needs of Rahim that are satisfied by the offer of cycle company are Physiological and safety/security needs. ‘The cycle company offered him a permanent pensionable job’. 1. The other needs followed by the above stated needs that are still to be satisfied are: 1. Affiliation/Belongingness needs: These needs refer to the need for affection, sense of belonging, acceptance and friendship. 2. Esteem needs: These needs refer to the need for self-respect, autonomy status, recognition, etc. Q. 26.Y Ltd. Is a bank functioning in India. It is planning to diversify into insurance business. Lately, the government of India has allowed the private sector to gain entry in the insurance business. Previously, it was the prerogative of LIC and GIC to do insurance business. But now with liberalization of the economy and to make the field competitive other companies have been given licences to start insurance business under the regulation of ‘Insurance regulatory and development Authority’. Y Ltd. Plans to recruit high quality employees and agents and exercise effective direction to capture a substantial part of life and non-life insurance business. 1. Identify how the company can supervise its employees and agents effectively. 2. What financial and non-financial incentives can the company use for employees and agents separately to motivate them? 3. How can the company ensure that higher order needs i.e., esteem and self actualization as specified by Maslow are met? 4. How can the company follow formal communication system? 5. How can informal communication help to supplement formal communication? Ans. 1. The company will appoint supervisors who will provide on the job training to the employees and agents. They will maintain group unity and ensure that the company gets enough insurance business. 2. To the employees, the company can give pay and allowances, bonus, retirement benefits, perquisites (e.g., car allowance),recognisation, promotion, job security etc. to motivate them for higher performance. To the agents, the company can give the following incentives: 1. Profit sharing 2. Stock option (i.e., giving company’s share at a price less than market price) 3. Productivity linked salary (i.e., higher salary for getting more insurance business) 4. Participation in decision – making. 1. By giving recognition, autonomy status, etc. and providing growth and self-fulfillmentopportunities, the company ensures that higher order needs-esteem and self actualization needs are met. 2. The company can follow formal communication system by ensuring that all communication flows through official channels designed in the organization chart (i.e., through Scalar chain). 3. Information communication network (i.e., grapevine) can be used by the company to transmit information to know he reactions of the employees and agents to the company’s decisions and policies. Grapevine channels can carry insurance market information rapidly. Q. 27. Prateek is working in a multinational company in Noida. He was running a temperature for the last many days. When his blood was tested, he was found to be positive for malaria. He was admitted in a hospital and a blood transfusion was advised by the doctors as his condition was very serious. One of his colleagues sent a text message to his superior, Mr. B. Chatterjee. Mr. B. Chatterjee immediately sent a text message to the employees of the organization requesting them to donate blood for Prateek. When the General Manager came t o know about it, he ordered for fumigation in the company premises and cleaning the surroundings. 1. From the above paragraph, quote lines that indicate formal and informal communication. 2. State any two features of informal communication. 3. Identify any two values that are being communicated to society in the above case. Ans. 1. (i) Informal communication: “One of his colleagues sent a text message to his superior, Mr. B. Chatterjee. Mr. B. Chatterjee immediately sent a text message to the employees of the organization requesting them to donate blood for Prateek.” (ii) Formal communication: “When the general manager came to know about it, he ordered for fumigation in the company premises and cleaning surroundings.” The features of informal communication are as follows: 1. The grapevine/informal communication spreads very fast and sometimes gets distorted. 2. It is very difficult to detect the source of such communication. . The two values that are being communicated to the society are: 1. Humanity 2. Cleanliness Q. 28. Roshan is the chief of ‘Khidmat’ restaurant located in the city of Bangaluru. The place is known for its exquisite Mughlai cuisine especially mutton briyani and kababs. All the food is prepared under Roshan’s purview. The various activities in the kitchen are initiated in accordance to his instructions. He is very clear and specific in issuing instructions to his subordinates in order to ensure smooth working of the department. He personally oversees the method followed by the chefs for preparation of each dish. He misses no opportunity to praise his subordinates for their good work. All his team members feel very happy and satisfied under his direction. He provides constant guidance to them in order to improve upon its taste and presentation and also encourages them to innovate and be more creative in their work. In the above context: 1. Identify the various elements of directing mentioned in the above paragraph by quoting lines from the paragraph. 2. Describe briefly any two points to highlight the importance of directing as a function of management. Ans. 1. The various elements of directing mentioned in the above paragraph are as follows: 1. Communication: ‘He is very clear and specific in issuing instructions to his subordinates in order to ensure smooth working of the department.” 2. Supervision: “He personally oversees the method followed by the chefs for preparation of each dish.” 3. Leadership: “He provides constant guidance to them in order to improve upon its taste and presentation and also encourages them to innovate and be more creative in their work.” 4. Motivation: “He misses no opportunity to praise his subordinates for their good work.” The importance of directing as a function of management is described below: 1. Initiates action: Directing helps to initiate action by people in the organization towards attainment of desired objectives. It is the first execution function of management. 2. Integrates employees’ efforts: Directing seeks to integrate the individual efforts of employees in the organization towards the realization of the organizational goals. 3. Helps to realize their potential: Directing provides effective guidance, motivation and leadership to the employees so as to enable them to realize their potential and capabilities. (any two) Q. 29. Neeraj has been working as a sewing machine operator in an export house for the past ten years. His basic work is to seam the parts of a garment together, and attach buttons, hooks, zippers, and accessories to produce clothing. Considering the fact that Neeraj is an experienced operator, he is well versed with the fundamentals of industrial production and possesses good communication skills. The plant superintendent in the factory recommends Neeraj’s name to the production manager for the post of supervisor which will fall vacant after a month on the retirement of the present supervisor. Consequently, Neeraj is assigned the post of supervisor and his salary is increased accordingly. Moreover, as per the policy of the export house, he is offered free medical aid and education to his two children. In the context of the above case: 1. Identify the type of source of recruitment used by the export house to fill up the post of supervisor. Give any two advantages of using this source. 2. Identify the types of financial incentives offered to Neeraj by quoting lines from the paragraph. Ans. 1. The internal source of recruitment has been used by the export house to fill up the post of supervisor through promotion. The two advantages of using internal source of recruitment are stated below. 1. Employees are motivated to improve their performance: When employees are promoted internally from within an organization, it has a positive impact on their commitment and loyalty and they tend remain satisfied with their jobs. Also, it may lead to a chain of promotion at lower levels in the organization. As a result, it motivates the employees to improve their performance through learning and practice. 2. Internal recruitment simplifies the process of selection and placement: The candidates can be appraised more perfectly and economically as that are already working in the organization. As the candidates are already known to the organization, it is considered to be a more reliable method of recruitment. The types of financial incentives offered to Neeraj are as follows: 1. Pay and allowances: “his salary is increased accordingly.” 2. Perquisites: “as per the policy of the export house, he is offered free medical aid and education to his two children.” Q. 30. Sunidhi has started a designer studio in the basement of her residence after completing her masters in fashion designing. She has appointed ten employees to take care of the various aspects of the work. She interacts regularly with each employee to tell exactly what is expected of him/.her and what he/she needs to do to be regarded as a good performer. At the same time she allows a free work environment wherein the employees openly chit chat with each other in order to fulfil their social and emotional needs. Sometimes, these interactions also lead to spreading rumours which are not authentic. In the context of the above case: 1. Name and explain the two types of communication being referred to in the above paragraph. 2. How does effective communication increases managerial efficiency? Ans. 1. The two types of communication being referred to in the above paragraph are formal communication and informal communication. 1. Formal communication: The communication that flows through official channels designed in the organization structure is called formal communication. This communication may take place between a subordinate and superior or among same team employees or managers. Usually a written record of such communications is maintained, recorded and filed in the office. Formal communication may be further classified as – Vertical and Horizontal. 2. Informal communication: Informal communication is the type of communication that takes place without following the formal lines of communication. It is generally referred to as the ‘grapevine’ because it spreads throughout the organization with its branches going out in all directions in utter disregard to the levels of authority. The informal communication arises out of needs of employees to exchange their views, which cannot be done through formal channels. 1. Effective communication increases managerial efficiency by lubricating the working of the entire organization through quick and effective performance of managerial functions. It enables the management to express the goals and targets, issue instructions, allocate jobs and responsibilities and look after the performance of subordinates. Q. 31. Gagan has joined as a Managing Director of True Help Ltd., a company engaged in the business of providing road side assistance to the vehicle owners. He was previously working in an automobile company. As a part of the joining incentive, the company has allotted him 400 shares of the company. In context of the above case: 1. Identify the type of source of recruitment used by True Help Ltd. to fill up the post of Managing Director. 2. Identify the type of financial incentive offered to Gagan. Also, state any one other method that can be used to offer financial incentives to the employees. Ans. 1. External source of recruitment has been used by True Help Ltd. to fill up the post of Managing Director. 2. Co-partnership/ Stock option is the type of financial incentive offered to Gagan. The other method that can be used to offer financial incentives to the employees is Bonus. Bonus is an incentive offered over and above the wages/ salary to the employees. Q. 32. Mr. Naresh is working as a Production Manager in Vohra Ltd. His subordinates are mostly engineers and qualified technicians. As a manager, he is very strict, does not listen to any suggestions or feedbacks given by his subordinates. He expects them to following his instructions without any questions and does not allow them to give suggestions. 1. What leadership style does the manager follow? 2. Is such a leadership style beneficial for the company? Explain. 3. State any one value being overlooked by him? Ans. 1. Autocratic leadership 2. This leadership style is effective in getting productivity in many situations like in a factory where the supervisor is responsible for production on time and has to ensure labour productivity. Quick decision-making is also facilitated. 3. Value overlooked: ● Respect for other’s opinion ● Initiative
Important Notes for NCERT Class 12 Business Studies Chapter Directing
Meaning Directing as a function of management, refers to the process of instructing, guiding counselling, motivating and leading people in the organisation to achieve its objectives. It does not mean only instructions but also include supervising the employees when they are performing the job, motivating them to perform more efficiently and leading them towards the achievement of organisational goal. Features: 1. Directing initiate action: The other functions of management prepare a setting for action, but directing initiates action in the organisation. 2. Directing takes place at every level of Management: – Every manager from top executive to supervisor performs the function of directing. 3. Directing is a continuous process of supervision, communication, leadership and motivation, It takes place throughout the life of the organisation. 4. Directing flows from top to bottom: – It is first initiated at the top level and flows to the bottom through organisational hierarchy. Importance: 1. Initiates Action: It helps to initiate action by people in the organisation towards attainment of desired objectives. The employees start working only when they get instructions and directions from their superiors. It is the directing function which starts actual work to convert plans into results. 2. Integrate Employee s Efforts: – All the activities of the organisation are interrelated so it in necessary to coordinate all the activities. It integrates the activities of subordinates by supervision, guidance and counselling. 3. Means of motivation – It motivates the subordinates to work efficiently and to contribute their maximum efforts towards the achievement of organisational goals. 4. Facilitates change: – Employees often resist changes due to fear of adverse effects on their employment and promotion. Directing facilitate adjustment in the organisation to cope with changes in the environment. 5. Stability and Balance in the organisation: – It helps to achieve balance between individual interests of employees and organisational interests.
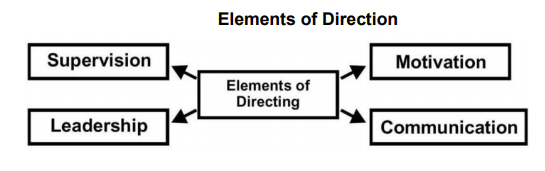
1. Supervision – It means observing the subordinates at work to see that they are working in according with plans and to help them in solving their problems. The important thing in supervision is it involves face to face contact between superior and subordinates. Supervisor position is immediately above the worker. Motivations :- Meaning :- It is the process of stimulating people to act to their best ability to accomplish desired goals. It depends upon satisfying needs of people. Leadership – Leadership is the activity of influencing people to strive willingly for mutual objectives. Managers at all levels are expected to the leaders of their subordinates. Different types of Leadership styles:- 1. Autocratic or Authoritarian Leader. 2. Democratic or Participative Leader. 3. Laissez Faire or Free Rein Leader. Communication – It is transfer of information from the sender to the receiver with the information being understood by the receiver.
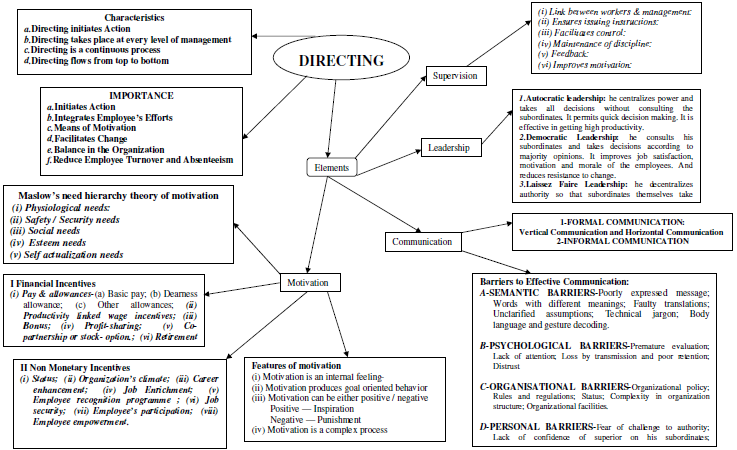
We hope the above Directing Class 12 Business Studies are useful for you. If you have any questions then post them in the comments section below. Our teachers will provide you an answer. Also refer to MCQ Questions for Class 12 Business Studies
Related Posts

Sectors Of Indian Economy Class 10 Social Science Notes and Questions

CBSE Class 10 English The Hundred Dresses II Summary

Foreign Exchange Rate and Balance of Payments Class 12 Economics Notes and Questions
1 thought on “ directing class 12 business studies notes and questions ”.
I loved this technique it gives such a clear view of things. This way of explaining makes understanding much better as you understand the scenario as well as its solution to the problems. In any organization, it is important that it has good leaders so that they direct their employees towards achieving goals in a correct manner.
Comments are closed.
Directing – CBSE Notes for Class 12 Business Studies

Directing – CBSE Notes for Class 12 Business Studies
CBSE Notes CBSE Notes Business Studies NCERT Solutions Business Studies
