While Sandel argues that pursuing perfection through genetic engineering would decrease our sense of humility, he claims that the sense of solidarity we would lose is also important.
This thesis summarizes several points in Sandel’s argument, but it does not make a claim about how we should understand his argument. A reader who read Sandel’s argument would not also need to read an essay based on this descriptive thesis.

Broad thesis (arguable, but difficult to support with evidence)
Michael Sandel’s arguments about genetic engineering do not take into consideration all the relevant issues.
This is an arguable claim because it would be possible to argue against it by saying that Michael Sandel’s arguments do take all of the relevant issues into consideration. But the claim is too broad. Because the thesis does not specify which “issues” it is focused on—or why it matters if they are considered—readers won’t know what the rest of the essay will argue, and the writer won’t know what to focus on. If there is a particular issue that Sandel does not address, then a more specific version of the thesis would include that issue—hand an explanation of why it is important.
Arguable thesis with analytical claim
While Sandel argues persuasively that our instinct to “remake” (54) ourselves into something ever more perfect is a problem, his belief that we can always draw a line between what is medically necessary and what makes us simply “better than well” (51) is less convincing.
This is an arguable analytical claim. To argue for this claim, the essay writer will need to show how evidence from the article itself points to this interpretation. It’s also a reasonable scope for a thesis because it can be supported with evidence available in the text and is neither too broad nor too narrow.
Arguable thesis with normative claim
Given Sandel’s argument against genetic enhancement, we should not allow parents to decide on using Human Growth Hormone for their children.
This thesis tells us what we should do about a particular issue discussed in Sandel’s article, but it does not tell us how we should understand Sandel’s argument.
Questions to ask about your thesis
- Is the thesis truly arguable? Does it speak to a genuine dilemma in the source, or would most readers automatically agree with it?
- Is the thesis too obvious? Again, would most or all readers agree with it without needing to see your argument?
- Is the thesis complex enough to require a whole essay's worth of argument?
- Is the thesis supportable with evidence from the text rather than with generalizations or outside research?
- Would anyone want to read a paper in which this thesis was developed? That is, can you explain what this paper is adding to our understanding of a problem, question, or topic?
- picture_as_pdf Thesis
- Privacy Policy

Home » Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
Table of contents.

Definition:
Thesis is a scholarly document that presents a student’s original research and findings on a particular topic or question. It is usually written as a requirement for a graduate degree program and is intended to demonstrate the student’s mastery of the subject matter and their ability to conduct independent research.
History of Thesis
The concept of a thesis can be traced back to ancient Greece, where it was used as a way for students to demonstrate their knowledge of a particular subject. However, the modern form of the thesis as a scholarly document used to earn a degree is a relatively recent development.
The origin of the modern thesis can be traced back to medieval universities in Europe. During this time, students were required to present a “disputation” in which they would defend a particular thesis in front of their peers and faculty members. These disputations served as a way to demonstrate the student’s mastery of the subject matter and were often the final requirement for earning a degree.
In the 17th century, the concept of the thesis was formalized further with the creation of the modern research university. Students were now required to complete a research project and present their findings in a written document, which would serve as the basis for their degree.
The modern thesis as we know it today has evolved over time, with different disciplines and institutions adopting their own standards and formats. However, the basic elements of a thesis – original research, a clear research question, a thorough review of the literature, and a well-argued conclusion – remain the same.
Structure of Thesis
The structure of a thesis may vary slightly depending on the specific requirements of the institution, department, or field of study, but generally, it follows a specific format.
Here’s a breakdown of the structure of a thesis:
This is the first page of the thesis that includes the title of the thesis, the name of the author, the name of the institution, the department, the date, and any other relevant information required by the institution.
This is a brief summary of the thesis that provides an overview of the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions.
This page provides a list of all the chapters and sections in the thesis and their page numbers.
Introduction
This chapter provides an overview of the research question, the context of the research, and the purpose of the study. The introduction should also outline the methodology and the scope of the research.
Literature Review
This chapter provides a critical analysis of the relevant literature on the research topic. It should demonstrate the gap in the existing knowledge and justify the need for the research.
Methodology
This chapter provides a detailed description of the research methods used to gather and analyze data. It should explain the research design, the sampling method, data collection techniques, and data analysis procedures.
This chapter presents the findings of the research. It should include tables, graphs, and charts to illustrate the results.
This chapter interprets the results and relates them to the research question. It should explain the significance of the findings and their implications for the research topic.
This chapter summarizes the key findings and the main conclusions of the research. It should also provide recommendations for future research.
This section provides a list of all the sources cited in the thesis. The citation style may vary depending on the requirements of the institution or the field of study.
This section includes any additional material that supports the research, such as raw data, survey questionnaires, or other relevant documents.
How to write Thesis
Here are some steps to help you write a thesis:
- Choose a Topic: The first step in writing a thesis is to choose a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. You should also consider the scope of the topic and the availability of resources for research.
- Develop a Research Question: Once you have chosen a topic, you need to develop a research question that you will answer in your thesis. The research question should be specific, clear, and feasible.
- Conduct a Literature Review: Before you start your research, you need to conduct a literature review to identify the existing knowledge and gaps in the field. This will help you refine your research question and develop a research methodology.
- Develop a Research Methodology: Once you have refined your research question, you need to develop a research methodology that includes the research design, data collection methods, and data analysis procedures.
- Collect and Analyze Data: After developing your research methodology, you need to collect and analyze data. This may involve conducting surveys, interviews, experiments, or analyzing existing data.
- Write the Thesis: Once you have analyzed the data, you need to write the thesis. The thesis should follow a specific structure that includes an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, conclusion, and references.
- Edit and Proofread: After completing the thesis, you need to edit and proofread it carefully. You should also have someone else review it to ensure that it is clear, concise, and free of errors.
- Submit the Thesis: Finally, you need to submit the thesis to your academic advisor or committee for review and evaluation.
Example of Thesis
Example of Thesis template for Students:
Title of Thesis
Table of Contents:
Chapter 1: Introduction
Chapter 2: Literature Review
Chapter 3: Research Methodology
Chapter 4: Results
Chapter 5: Discussion
Chapter 6: Conclusion
References:
Appendices:
Note: That’s just a basic template, but it should give you an idea of the structure and content that a typical thesis might include. Be sure to consult with your department or supervisor for any specific formatting requirements they may have. Good luck with your thesis!
Application of Thesis
Thesis is an important academic document that serves several purposes. Here are some of the applications of thesis:
- Academic Requirement: A thesis is a requirement for many academic programs, especially at the graduate level. It is an essential component of the evaluation process and demonstrates the student’s ability to conduct original research and contribute to the knowledge in their field.
- Career Advancement: A thesis can also help in career advancement. Employers often value candidates who have completed a thesis as it demonstrates their research skills, critical thinking abilities, and their dedication to their field of study.
- Publication : A thesis can serve as a basis for future publications in academic journals, books, or conference proceedings. It provides the researcher with an opportunity to present their research to a wider audience and contribute to the body of knowledge in their field.
- Personal Development: Writing a thesis is a challenging task that requires time, dedication, and perseverance. It provides the student with an opportunity to develop critical thinking, research, and writing skills that are essential for their personal and professional development.
- Impact on Society: The findings of a thesis can have an impact on society by addressing important issues, providing insights into complex problems, and contributing to the development of policies and practices.
Purpose of Thesis
The purpose of a thesis is to present original research findings in a clear and organized manner. It is a formal document that demonstrates a student’s ability to conduct independent research and contribute to the knowledge in their field of study. The primary purposes of a thesis are:
- To Contribute to Knowledge: The main purpose of a thesis is to contribute to the knowledge in a particular field of study. By conducting original research and presenting their findings, the student adds new insights and perspectives to the existing body of knowledge.
- To Demonstrate Research Skills: A thesis is an opportunity for the student to demonstrate their research skills. This includes the ability to formulate a research question, design a research methodology, collect and analyze data, and draw conclusions based on their findings.
- To Develop Critical Thinking: Writing a thesis requires critical thinking and analysis. The student must evaluate existing literature and identify gaps in the field, as well as develop and defend their own ideas.
- To Provide Evidence of Competence : A thesis provides evidence of the student’s competence in their field of study. It demonstrates their ability to apply theoretical concepts to real-world problems, and their ability to communicate their ideas effectively.
- To Facilitate Career Advancement : Completing a thesis can help the student advance their career by demonstrating their research skills and dedication to their field of study. It can also provide a basis for future publications, presentations, or research projects.
When to Write Thesis
The timing for writing a thesis depends on the specific requirements of the academic program or institution. In most cases, the opportunity to write a thesis is typically offered at the graduate level, but there may be exceptions.
Generally, students should plan to write their thesis during the final year of their graduate program. This allows sufficient time for conducting research, analyzing data, and writing the thesis. It is important to start planning the thesis early and to identify a research topic and research advisor as soon as possible.
In some cases, students may be able to write a thesis as part of an undergraduate program or as an independent research project outside of an academic program. In such cases, it is important to consult with faculty advisors or mentors to ensure that the research is appropriately designed and executed.
It is important to note that the process of writing a thesis can be time-consuming and requires a significant amount of effort and dedication. It is important to plan accordingly and to allocate sufficient time for conducting research, analyzing data, and writing the thesis.
Characteristics of Thesis
The characteristics of a thesis vary depending on the specific academic program or institution. However, some general characteristics of a thesis include:
- Originality : A thesis should present original research findings or insights. It should demonstrate the student’s ability to conduct independent research and contribute to the knowledge in their field of study.
- Clarity : A thesis should be clear and concise. It should present the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions in a logical and organized manner. It should also be well-written, with proper grammar, spelling, and punctuation.
- Research-Based: A thesis should be based on rigorous research, which involves collecting and analyzing data from various sources. The research should be well-designed, with appropriate research methods and techniques.
- Evidence-Based : A thesis should be based on evidence, which means that all claims made in the thesis should be supported by data or literature. The evidence should be properly cited using appropriate citation styles.
- Critical Thinking: A thesis should demonstrate the student’s ability to critically analyze and evaluate information. It should present the student’s own ideas and arguments, and engage with existing literature in the field.
- Academic Style : A thesis should adhere to the conventions of academic writing. It should be well-structured, with clear headings and subheadings, and should use appropriate academic language.
Advantages of Thesis
There are several advantages to writing a thesis, including:
- Development of Research Skills: Writing a thesis requires extensive research and analytical skills. It helps to develop the student’s research skills, including the ability to formulate research questions, design and execute research methodologies, collect and analyze data, and draw conclusions based on their findings.
- Contribution to Knowledge: Writing a thesis provides an opportunity for the student to contribute to the knowledge in their field of study. By conducting original research, they can add new insights and perspectives to the existing body of knowledge.
- Preparation for Future Research: Completing a thesis prepares the student for future research projects. It provides them with the necessary skills to design and execute research methodologies, analyze data, and draw conclusions based on their findings.
- Career Advancement: Writing a thesis can help to advance the student’s career. It demonstrates their research skills and dedication to their field of study, and provides a basis for future publications, presentations, or research projects.
- Personal Growth: Completing a thesis can be a challenging and rewarding experience. It requires dedication, hard work, and perseverance. It can help the student to develop self-confidence, independence, and a sense of accomplishment.
Limitations of Thesis
There are also some limitations to writing a thesis, including:
- Time and Resources: Writing a thesis requires a significant amount of time and resources. It can be a time-consuming and expensive process, as it may involve conducting original research, analyzing data, and producing a lengthy document.
- Narrow Focus: A thesis is typically focused on a specific research question or topic, which may limit the student’s exposure to other areas within their field of study.
- Limited Audience: A thesis is usually only read by a small number of people, such as the student’s thesis advisor and committee members. This limits the potential impact of the research findings.
- Lack of Real-World Application : Some thesis topics may be highly theoretical or academic in nature, which may limit their practical application in the real world.
- Pressure and Stress : Writing a thesis can be a stressful and pressure-filled experience, as it may involve meeting strict deadlines, conducting original research, and producing a high-quality document.
- Potential for Isolation: Writing a thesis can be a solitary experience, as the student may spend a significant amount of time working independently on their research and writing.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Informed Consent in Research – Types, Templates...

Research Methodology – Types, Examples and...

What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and...

Research Results Section – Writing Guide and...

Research Recommendations – Examples and Writing...

Research Topics – Ideas and Examples
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Tips for Writing Your Thesis Statement
1. Determine what kind of paper you are writing:
- An analytical paper breaks down an issue or an idea into its component parts, evaluates the issue or idea, and presents this breakdown and evaluation to the audience.
- An expository (explanatory) paper explains something to the audience.
- An argumentative paper makes a claim about a topic and justifies this claim with specific evidence. The claim could be an opinion, a policy proposal, an evaluation, a cause-and-effect statement, or an interpretation. The goal of the argumentative paper is to convince the audience that the claim is true based on the evidence provided.
If you are writing a text that does not fall under these three categories (e.g., a narrative), a thesis statement somewhere in the first paragraph could still be helpful to your reader.
2. Your thesis statement should be specific—it should cover only what you will discuss in your paper and should be supported with specific evidence.
3. The thesis statement usually appears at the end of the first paragraph of a paper.
4. Your topic may change as you write, so you may need to revise your thesis statement to reflect exactly what you have discussed in the paper.
Thesis Statement Examples
Example of an analytical thesis statement:
The paper that follows should:
- Explain the analysis of the college admission process
- Explain the challenge facing admissions counselors
Example of an expository (explanatory) thesis statement:
- Explain how students spend their time studying, attending class, and socializing with peers
Example of an argumentative thesis statement:
- Present an argument and give evidence to support the claim that students should pursue community projects before entering college
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
How to Write a Strong Thesis Statement: 4 Steps + Examples

What’s Covered:
What is the purpose of a thesis statement, writing a good thesis statement: 4 steps, common pitfalls to avoid, where to get your essay edited for free.
When you set out to write an essay, there has to be some kind of point to it, right? Otherwise, your essay would just be a big jumble of word salad that makes absolutely no sense. An essay needs a central point that ties into everything else. That main point is called a thesis statement, and it’s the core of any essay or research paper.
You may hear about Master degree candidates writing a thesis, and that is an entire paper–not to be confused with the thesis statement, which is typically one sentence that contains your paper’s focus.
Read on to learn more about thesis statements and how to write them. We’ve also included some solid examples for you to reference.
Typically the last sentence of your introductory paragraph, the thesis statement serves as the roadmap for your essay. When your reader gets to the thesis statement, they should have a clear outline of your main point, as well as the information you’ll be presenting in order to either prove or support your point.
The thesis statement should not be confused for a topic sentence , which is the first sentence of every paragraph in your essay. If you need help writing topic sentences, numerous resources are available. Topic sentences should go along with your thesis statement, though.
Since the thesis statement is the most important sentence of your entire essay or paper, it’s imperative that you get this part right. Otherwise, your paper will not have a good flow and will seem disjointed. That’s why it’s vital not to rush through developing one. It’s a methodical process with steps that you need to follow in order to create the best thesis statement possible.
Step 1: Decide what kind of paper you’re writing
When you’re assigned an essay, there are several different types you may get. Argumentative essays are designed to get the reader to agree with you on a topic. Informative or expository essays present information to the reader. Analytical essays offer up a point and then expand on it by analyzing relevant information. Thesis statements can look and sound different based on the type of paper you’re writing. For example:
- Argumentative: The United States needs a viable third political party to decrease bipartisanship, increase options, and help reduce corruption in government.
- Informative: The Libertarian party has thrown off elections before by gaining enough support in states to get on the ballot and by taking away crucial votes from candidates.
- Analytical: An analysis of past presidential elections shows that while third party votes may have been the minority, they did affect the outcome of the elections in 2020, 2016, and beyond.
Step 2: Figure out what point you want to make
Once you know what type of paper you’re writing, you then need to figure out the point you want to make with your thesis statement, and subsequently, your paper. In other words, you need to decide to answer a question about something, such as:
- What impact did reality TV have on American society?
- How has the musical Hamilton affected perception of American history?
- Why do I want to major in [chosen major here]?
If you have an argumentative essay, then you will be writing about an opinion. To make it easier, you may want to choose an opinion that you feel passionate about so that you’re writing about something that interests you. For example, if you have an interest in preserving the environment, you may want to choose a topic that relates to that.
If you’re writing your college essay and they ask why you want to attend that school, you may want to have a main point and back it up with information, something along the lines of:
“Attending Harvard University would benefit me both academically and professionally, as it would give me a strong knowledge base upon which to build my career, develop my network, and hopefully give me an advantage in my chosen field.”
Step 3: Determine what information you’ll use to back up your point
Once you have the point you want to make, you need to figure out how you plan to back it up throughout the rest of your essay. Without this information, it will be hard to either prove or argue the main point of your thesis statement. If you decide to write about the Hamilton example, you may decide to address any falsehoods that the writer put into the musical, such as:
“The musical Hamilton, while accurate in many ways, leaves out key parts of American history, presents a nationalist view of founding fathers, and downplays the racism of the times.”
Once you’ve written your initial working thesis statement, you’ll then need to get information to back that up. For example, the musical completely leaves out Benjamin Franklin, portrays the founding fathers in a nationalist way that is too complimentary, and shows Hamilton as a staunch abolitionist despite the fact that his family likely did own slaves.
Step 4: Revise and refine your thesis statement before you start writing
Read through your thesis statement several times before you begin to compose your full essay. You need to make sure the statement is ironclad, since it is the foundation of the entire paper. Edit it or have a peer review it for you to make sure everything makes sense and that you feel like you can truly write a paper on the topic. Once you’ve done that, you can then begin writing your paper.
When writing a thesis statement, there are some common pitfalls you should avoid so that your paper can be as solid as possible. Make sure you always edit the thesis statement before you do anything else. You also want to ensure that the thesis statement is clear and concise. Don’t make your reader hunt for your point. Finally, put your thesis statement at the end of the first paragraph and have your introduction flow toward that statement. Your reader will expect to find your statement in its traditional spot.
If you’re having trouble getting started, or need some guidance on your essay, there are tools available that can help you. CollegeVine offers a free peer essay review tool where one of your peers can read through your essay and provide you with valuable feedback. Getting essay feedback from a peer can help you wow your instructor or college admissions officer with an impactful essay that effectively illustrates your point.

Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

What is a Theoretical Framework? How to Write It (with Examples)

Theoretical framework 1,2 is the structure that supports and describes a theory. A theory is a set of interrelated concepts and definitions that present a systematic view of phenomena by describing the relationship among the variables for explaining these phenomena. A theory is developed after a long research process and explains the existence of a research problem in a study. A theoretical framework guides the research process like a roadmap for the research study and helps researchers clearly interpret their findings by providing a structure for organizing data and developing conclusions.
A theoretical framework in research is an important part of a manuscript and should be presented in the first section. It shows an understanding of the theories and concepts relevant to the research and helps limit the scope of the research.
Table of Contents
What is a theoretical framework ?
A theoretical framework in research can be defined as a set of concepts, theories, ideas, and assumptions that help you understand a specific phenomenon or problem. It can be considered a blueprint that is borrowed by researchers to develop their own research inquiry. A theoretical framework in research helps researchers design and conduct their research and analyze and interpret their findings. It explains the relationship between variables, identifies gaps in existing knowledge, and guides the development of research questions, hypotheses, and methodologies to address that gap.

Now that you know the answer to ‘ What is a theoretical framework? ’, check the following table that lists the different types of theoretical frameworks in research: 3
Developing a theoretical framework in research can help in the following situations: 4
- When conducting research on complex phenomena because a theoretical framework helps organize the research questions, hypotheses, and findings
- When the research problem requires a deeper understanding of the underlying concepts
- When conducting research that seeks to address a specific gap in knowledge
- When conducting research that involves the analysis of existing theories
Summarizing existing literature for theoretical frameworks is easy. Get our Research Ideation pack
Importance of a theoretical framework
The purpose of theoretical framework s is to support you in the following ways during the research process: 2
- Provide a structure for the complete research process
- Assist researchers in incorporating formal theories into their study as a guide
- Provide a broad guideline to maintain the research focus
- Guide the selection of research methods, data collection, and data analysis
- Help understand the relationships between different concepts and develop hypotheses and research questions
- Address gaps in existing literature
- Analyze the data collected and draw meaningful conclusions and make the findings more generalizable
Theoretical vs. Conceptual framework
While a theoretical framework covers the theoretical aspect of your study, that is, the various theories that can guide your research, a conceptual framework defines the variables for your study and presents how they relate to each other. The conceptual framework is developed before collecting the data. However, both frameworks help in understanding the research problem and guide the development, collection, and analysis of the research.
The following table lists some differences between conceptual and theoretical frameworks . 5

How to write a theoretical framework
The following general steps can help those wondering how to write a theoretical framework: 2
- Identify and define the key concepts clearly and organize them into a suitable structure.
- Use appropriate terminology and define all key terms to ensure consistency.
- Identify the relationships between concepts and provide a logical and coherent structure.
- Develop hypotheses that can be tested through data collection and analysis.
- Keep it concise and focused with clear and specific aims.
Write a theoretical framework 2x faster. Get our Manuscript Writing pack

Examples of a theoretical framework
Here are two examples of a theoretical framework. 6,7
Example 1 .
An insurance company is facing a challenge cross-selling its products. The sales department indicates that most customers have just one policy, although the company offers over 10 unique policies. The company would want its customers to purchase more than one policy since most customers are purchasing policies from other companies.
Objective : To sell more insurance products to existing customers.
Problem : Many customers are purchasing additional policies from other companies.
Research question : How can customer product awareness be improved to increase cross-selling of insurance products?
Sub-questions: What is the relationship between product awareness and sales? Which factors determine product awareness?
Since “product awareness” is the main focus in this study, the theoretical framework should analyze this concept and study previous literature on this subject and propose theories that discuss the relationship between product awareness and its improvement in sales of other products.
Example 2 .
A company is facing a continued decline in its sales and profitability. The main reason for the decline in the profitability is poor services, which have resulted in a high level of dissatisfaction among customers and consequently a decline in customer loyalty. The management is planning to concentrate on clients’ satisfaction and customer loyalty.
Objective: To provide better service to customers and increase customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Problem: Continued decrease in sales and profitability.
Research question: How can customer satisfaction help in increasing sales and profitability?
Sub-questions: What is the relationship between customer loyalty and sales? Which factors influence the level of satisfaction gained by customers?
Since customer satisfaction, loyalty, profitability, and sales are the important topics in this example, the theoretical framework should focus on these concepts.
Benefits of a theoretical framework
There are several benefits of a theoretical framework in research: 2
- Provides a structured approach allowing researchers to organize their thoughts in a coherent way.
- Helps to identify gaps in knowledge highlighting areas where further research is needed.
- Increases research efficiency by providing a clear direction for research and focusing efforts on relevant data.
- Improves the quality of research by providing a rigorous and systematic approach to research, which can increase the likelihood of producing valid and reliable results.
- Provides a basis for comparison by providing a common language and conceptual framework for researchers to compare their findings with other research in the field, facilitating the exchange of ideas and the development of new knowledge.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. How do I develop a theoretical framework ? 7
A1. The following steps can be used for developing a theoretical framework :
- Identify the research problem and research questions by clearly defining the problem that the research aims to address and identifying the specific questions that the research aims to answer.
- Review the existing literature to identify the key concepts that have been studied previously. These concepts should be clearly defined and organized into a structure.
- Develop propositions that describe the relationships between the concepts. These propositions should be based on the existing literature and should be testable.
- Develop hypotheses that can be tested through data collection and analysis.
- Test the theoretical framework through data collection and analysis to determine whether the framework is valid and reliable.
Q2. How do I know if I have developed a good theoretical framework or not? 8
A2. The following checklist could help you answer this question:
- Is my theoretical framework clearly seen as emerging from my literature review?
- Is it the result of my analysis of the main theories previously studied in my same research field?
- Does it represent or is it relevant to the most current state of theoretical knowledge on my topic?
- Does the theoretical framework in research present a logical, coherent, and analytical structure that will support my data analysis?
- Do the different parts of the theory help analyze the relationships among the variables in my research?
- Does the theoretical framework target how I will answer my research questions or test the hypotheses?
- Have I documented every source I have used in developing this theoretical framework ?
- Is my theoretical framework a model, a table, a figure, or a description?
- Have I explained why this is the appropriate theoretical framework for my data analysis?
Q3. Can I use multiple theoretical frameworks in a single study?
A3. Using multiple theoretical frameworks in a single study is acceptable as long as each theory is clearly defined and related to the study. Each theory should also be discussed individually. This approach may, however, be tedious and effort intensive. Therefore, multiple theoretical frameworks should be used only if absolutely necessary for the study.
Q4. Is it necessary to include a theoretical framework in every research study?
A4. The theoretical framework connects researchers to existing knowledge. So, including a theoretical framework would help researchers get a clear idea about the research process and help structure their study effectively by clearly defining an objective, a research problem, and a research question.
Q5. Can a theoretical framework be developed for qualitative research?
A5. Yes, a theoretical framework can be developed for qualitative research. However, qualitative research methods may or may not involve a theory developed beforehand. In these studies, a theoretical framework can guide the study and help develop a theory during the data analysis phase. This resulting framework uses inductive reasoning. The outcome of this inductive approach can be referred to as an emergent theoretical framework . This method helps researchers develop a theory inductively, which explains a phenomenon without a guiding framework at the outset.

Q6. What is the main difference between a literature review and a theoretical framework ?
A6. A literature review explores already existing studies about a specific topic in order to highlight a gap, which becomes the focus of the current research study. A theoretical framework can be considered the next step in the process, in which the researcher plans a specific conceptual and analytical approach to address the identified gap in the research.
Theoretical frameworks are thus important components of the research process and researchers should therefore devote ample amount of time to develop a solid theoretical framework so that it can effectively guide their research in a suitable direction. We hope this article has provided a good insight into the concept of theoretical frameworks in research and their benefits.
References
- Organizing academic research papers: Theoretical framework. Sacred Heart University library. Accessed August 4, 2023. https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803&p=185919#:~:text=The%20theoretical%20framework%20is%20the,research%20problem%20under%20study%20exists .
- Salomao A. Understanding what is theoretical framework. Mind the Graph website. Accessed August 5, 2023. https://mindthegraph.com/blog/what-is-theoretical-framework/
- Theoretical framework—Types, examples, and writing guide. Research Method website. Accessed August 6, 2023. https://researchmethod.net/theoretical-framework/
- Grant C., Osanloo A. Understanding, selecting, and integrating a theoretical framework in dissertation research: Creating the blueprint for your “house.” Administrative Issues Journal : Connecting Education, Practice, and Research; 4(2):12-26. 2014. Accessed August 7, 2023. https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1058505.pdf
- Difference between conceptual framework and theoretical framework. MIM Learnovate website. Accessed August 7, 2023. https://mimlearnovate.com/difference-between-conceptual-framework-and-theoretical-framework/
- Example of a theoretical framework—Thesis & dissertation. BacherlorPrint website. Accessed August 6, 2023. https://www.bachelorprint.com/dissertation/example-of-a-theoretical-framework/
- Sample theoretical framework in dissertation and thesis—Overview and example. Students assignment help website. Accessed August 6, 2023. https://www.studentsassignmenthelp.co.uk/blogs/sample-dissertation-theoretical-framework/#Example_of_the_theoretical_framework
- Kivunja C. Distinguishing between theory, theoretical framework, and conceptual framework: A systematic review of lessons from the field. Accessed August 8, 2023. https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1198682.pdf
Editage All Access is a subscription-based platform that unifies the best AI tools and services designed to speed up, simplify, and streamline every step of a researcher’s journey. The Editage All Access Pack is a one-of-a-kind subscription that unlocks full access to an AI writing assistant, literature recommender, journal finder, scientific illustration tool, and exclusive discounts on professional publication services from Editage.
Based on 22+ years of experience in academia, Editage All Access empowers researchers to put their best research forward and move closer to success. Explore our top AI Tools pack, AI Tools + Publication Services pack, or Build Your Own Plan. Find everything a researcher needs to succeed, all in one place – Get All Access now starting at just $14 a month !
Related Posts

Paperpal Review: Key Features, Pricing Plans, and How-to-Use

How to Structure a Dissertation?

Conceptual and Theoretical Frameworks for Thesis Studies: What you must know

A theoretical framework is a conceptual model that provides a systematic and structured way of thinking about a research problem or question. It helps to identify key variables and the relationships between them and to guide the selection and interpretation of data. Theoretical frameworks draw on existing theories and research and can be used to develop new hypotheses or test existing ones. They provide a foundation for research design, data collection, and analysis and can help to ensure that research is relevant, rigorous, and coherent. Theoretical frameworks are common in many disciplines, including social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities, and are essential for building knowledge and advancing understanding in a field.
This article explains the importance of frameworks in a thesis study and the differences between conceptual frameworks and theoretical frameworks. It provides guidelines on how to write a thesis framework, definitions of variable types, and examples of framework types.
What is a research framework and why do I need one?
When planning your thesis study, you need to justify your research and explain its design to your readers. This is called the research framework.
When planning your thesis study, you need to justify your research and explain its design to your readers. This is called the research framework. Think of it as the foundation of a building. A good building needs a strong foundation. Similarly, your research needs to be supported by reviewing and explaining the existing knowledge in the field, describing how your research study will fit within or contribute to the existing literature (e.g., it could challenge or test an existing theory or address a knowledge gap), and informing the reader how your study design aligns with your thesis question or hypothesis.
Important components of the framework are a literature review of recent studies associated with your thesis topic as well as theories/models used in your field of research. The literature review acts as a filtering tool to select appropriate thesis questions and guide data collection, analysis, and interpretation of your findings. Think broadly! Apart from reviewing relevant published papers in your field of research, also explore theories that you have come across in your undergraduate courses, other published thesis studies, encyclopedias, and handbooks.
There are two types of research frameworks: theoretical and conceptual .
What is a conceptual framework?
A conceptual framework is a written or visual representation that explains the study variables and their relationships with each other. The starting point is a literature review of existing studies and theories about your topic.
Steps to develop a conceptual framework
- Clarify your study topic by identifying and defining key concepts in your thesis problem statement and thesis question. Essentially, your thesis should address a knowledge gap.
- Perform a literature review to provide a background to interpret and explain the study findings. Also, draw on empirical knowledge that you have gained from personal experience.
- Identify crucial variables from the literature review and your empirical knowledge, classify them as dependent or independent variables, and define them.
- Brainstorm all the possible factors that could affect each dependent variable.
- Propose relationships among the variables and determine any associations that exist between all variables.
- Use a flowchart or tree diagram to present your conceptual framework.
Types of variables
When developing a conceptual framework, you will need to identify the following:
- Independent variables
- Dependent variables
- Moderating variables
- Mediating variables
- Control variables
First, identify the independent (cause) and dependent (effect) variables in your study. Then, identify variables that influence this relationship, such as moderating variables, mediating variables, and control variables. A moderating variable changes the relationship between independent and dependent variables when its value increases or decreases. A mediating variable links independent and dependent variables to better explain the relationship between them. A control variable could potentially impact the cause-and-effect relationship but is kept constant throughout the study so that its effects on the findings/outcomes can be ruled out.
Example of a conceptual framework
You want to investigate the hours spent exercising (cause) on childhood obesity (effect).

Now, you need to consider moderating variables that affect the cause-and-effect relationship. In our example, the amount of junk food eaten would affect the level of obesity.

Next, you need to consider mediating variables. In our example, the maximum heart rate during exercise would affect the child’s weight.

Finally, you need to consider control variables. In this example, because we do not want to investigate the role of age in obesity, we can use this as a control variable. Thus, the study subjects would be children of a specific age (e.g., aged 6–10 years).

What is a theoretical framework?
A theoretical framework provides a general framework for data analysis. It defines the concepts used and explains existing theories and models in your field of research.
A theoretical framework provides a general framework for data analysis. It defines the concepts used and explains existing theories and models in your field of research. It also explains any assumptions that were used to inform your approach and your choice of specific rationales. Theoretical frameworks are often used in the fields of social sciences.
Purpose of a theoretical framework
- Test and challenge existing theories
- Establish orderly connections between observations and facts
- Predict and control situations
- Develop hypotheses
Steps to develop a theoretical framework
- Identify and define key concepts in your thesis problem statement and thesis question.
- Explain and evaluate existing theories by writing a literature review that describes the concepts, models, and theories that support your study.
- Choose the theory that best explains the relationships between the key variables in your study.
- Explain how your research study fills a knowledge gap or fits into existing studies (e.g., testing if an established theory applies to your thesis context).
- Discuss the relevance of any theoretical assumptions and limitations.
A thesis topic can be approached from a variety of angles, depending on the theories used.
- In psychology, a behavioral approach would use different methods and assumptions compared with a cognitive approach when treating anxiety.
- In literature, a book could be analyzed using different literary theories, such as Marxism or poststructuralism.
Structuring a theoretical framework
The structure of a theoretical framework is fluid, and there are no specific rules that need to be followed, as long as it is clearly and logically presented.
The theoretical framework is a natural extension of your literature review. The literature review should identify gaps in the field of your research, and reviewing existing theories will help to determine how these can be addressed. The structure of a theoretical framework is fluid, and there are no specific rules that need to be followed, as long as it is clearly and logically presented. The theoretical framework is sometimes integrated into the literature review chapter of a thesis, but it can also be included as a separate chapter, depending on the complexity of the theories.
Example of a theoretical framework
The sales staff at Company X are unmotivated and struggling to meet their monthly targets. Some members of the management team believe that this could be achieved by implementing a comprehensive product-training program, but others believe that introducing a sales commission structure will help.
Company X is not achieving their monthly sales targets
To increase monthly sales.
Research question:
How can Company X motivate their sales team to achieve its monthly sales targets?
Sub-questions:
- Why do the sales staff feel unmotivated?
- What is the relationship between motivation and monetary rewards?
- Do the sales staff feel that they have sufficient product knowledge?
Theoretical framework:
A literature search will need to be performed to understand the background of the many different theories of motivation in psychology. For example, Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs (basic human needs—physiological, safety, love/belonging, esteem, and self-actualization—have to be fulfilled before one can live up to their true potential), Vroom’s Theory of Expectancy (people decide upon their actions based on the outcomes they expect), and Locke’s Goal-Setting Theory (goals are a key driver of one’s behavior). These theories would need to be investigated to determine which would be the best approach to increase the motivation of the sales staff in Company X so that the monthly sales targets are met.
A robust conceptual or theoretical framework is crucial when writing a thesis/dissertation. It defines your research gap, identifies your approach, and guides the interpretation of your results.
A thesis is the most important document you will write during your academic studies. For professional thesis editing and thesis proofreading services, check out Enago's Thesis Editing service s for more information.
Editor’s pick
Get free updates.
Subscribe to our newsletter for regular insights from the research and publishing industry!
What type of framework is used in the Humanities and Social Sciences (HSS) domain? +
Theoretical frameworks are typically used in the HSS domain, while conceptual frameworks are used in the Sciences domain.
What is the difference between mediating versus moderating variables? +
The difference between mediators and moderators can be confusing. A moderating variable is unaffected by the independent variable and can increase or decrease the strength of the relationship between the independent and dependent variables. A mediating variable is affected by the independent variable and can explain the relationship between the independent and dependent variables. T he statistical correlation between the independent and dependent variables is higher when the mediating variable is excluded.
What software should I use to present my conceptual framework? +
The software program Creately provides some useful templates that can help you get started. Other recommended programs are SmartDraw , Inkscape , and diagrams.net .

Thesis Statements
What this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can craft or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence near the beginning of your paper (most often, at the end of the first paragraph) that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I create a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis” that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following :
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question. If the prompt isn’t phrased as a question, try to rephrase it. For example, “Discuss the effect of X on Y” can be rephrased as “What is the effect of X on Y?”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is likely to be “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s okay to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on contemporary communication, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: “Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.” Looking back at your notes, you might start with this working thesis:
Social media impacts public awareness in both positive and negative ways.
You can use the questions above to help you revise this general statement into a stronger thesis.
- Do I answer the question? You can analyze this if you rephrase “discuss the impact” as “what is the impact?” This way, you can see that you’ve answered the question only very generally with the vague “positive and negative ways.”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not likely. Only people who maintain that social media has a solely positive or solely negative impact could disagree.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? No. What are the positive effects? What are the negative effects?
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? No. Why are they positive? How are they positive? What are their causes? Why are they negative? How are they negative? What are their causes?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? No. Why should anyone care about the positive and/or negative impact of social media?
After thinking about your answers to these questions, you decide to focus on the one impact you feel strongly about and have strong evidence for:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
This version is a much stronger thesis! It answers the question, takes a specific position that others can challenge, and it gives a sense of why it matters.
Let’s try another. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
You begin to analyze your thesis:
- Do I answer the question? No. The prompt asks you to analyze some aspect of the novel. Your working thesis is a statement of general appreciation for the entire novel.
Think about aspects of the novel that are important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
- Do I answer the question? Yes!
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not really. This contrast is well-known and accepted.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? It’s getting there–you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation. However, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? Not yet. Compare scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions and anything else that seems interesting.
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?”
After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Ramage, John D., John C. Bean, and June Johnson. 2018. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing , 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Ruszkiewicz, John J., Christy Friend, Daniel Seward, and Maxine Hairston. 2010. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers , 9th ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a thesis statement + examples

What is a thesis statement?
Is a thesis statement a question, how do you write a good thesis statement, how do i know if my thesis statement is good, examples of thesis statements, helpful resources on how to write a thesis statement, frequently asked questions about writing a thesis statement, related articles.
A thesis statement is the main argument of your paper or thesis.
The thesis statement is one of the most important elements of any piece of academic writing . It is a brief statement of your paper’s main argument. Essentially, you are stating what you will be writing about.
You can see your thesis statement as an answer to a question. While it also contains the question, it should really give an answer to the question with new information and not just restate or reiterate it.
Your thesis statement is part of your introduction. Learn more about how to write a good thesis introduction in our introduction guide .
A thesis statement is not a question. A statement must be arguable and provable through evidence and analysis. While your thesis might stem from a research question, it should be in the form of a statement.
Tip: A thesis statement is typically 1-2 sentences. For a longer project like a thesis, the statement may be several sentences or a paragraph.
A good thesis statement needs to do the following:
- Condense the main idea of your thesis into one or two sentences.
- Answer your project’s main research question.
- Clearly state your position in relation to the topic .
- Make an argument that requires support or evidence.
Once you have written down a thesis statement, check if it fulfills the following criteria:
- Your statement needs to be provable by evidence. As an argument, a thesis statement needs to be debatable.
- Your statement needs to be precise. Do not give away too much information in the thesis statement and do not load it with unnecessary information.
- Your statement cannot say that one solution is simply right or simply wrong as a matter of fact. You should draw upon verified facts to persuade the reader of your solution, but you cannot just declare something as right or wrong.
As previously mentioned, your thesis statement should answer a question.
If the question is:
What do you think the City of New York should do to reduce traffic congestion?
A good thesis statement restates the question and answers it:
In this paper, I will argue that the City of New York should focus on providing exclusive lanes for public transport and adaptive traffic signals to reduce traffic congestion by the year 2035.
Here is another example. If the question is:
How can we end poverty?
A good thesis statement should give more than one solution to the problem in question:
In this paper, I will argue that introducing universal basic income can help reduce poverty and positively impact the way we work.
- The Writing Center of the University of North Carolina has a list of questions to ask to see if your thesis is strong .
A thesis statement is part of the introduction of your paper. It is usually found in the first or second paragraph to let the reader know your research purpose from the beginning.
In general, a thesis statement should have one or two sentences. But the length really depends on the overall length of your project. Take a look at our guide about the length of thesis statements for more insight on this topic.
Here is a list of Thesis Statement Examples that will help you understand better how to write them.
Every good essay should include a thesis statement as part of its introduction, no matter the academic level. Of course, if you are a high school student you are not expected to have the same type of thesis as a PhD student.
Here is a great YouTube tutorial showing How To Write An Essay: Thesis Statements .

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
Published on 15 September 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on 25 September 2024.
A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a PhD program in the UK.
Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Indeed, alongside a dissertation , it is the longest piece of writing students typically complete. It relies on your ability to conduct research from start to finish: designing your research , collecting data , developing a robust analysis, drawing strong conclusions , and writing concisely .
Thesis template
You can also download our full thesis template in the format of your choice below. Our template includes a ready-made table of contents , as well as guidance for what each chapter should include. It’s easy to make it your own, and can help you get started.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template
Make your writing flawless in 1 upload
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
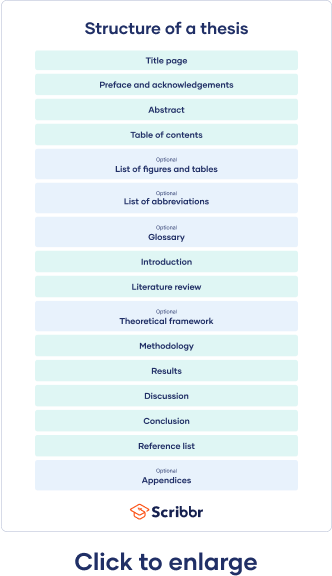
Thesis vs. thesis statement, how to structure a thesis, acknowledgements or preface, list of figures and tables, list of abbreviations, introduction, literature review, methodology, reference list, proofreading and editing, defending your thesis, frequently asked questions about theses.
You may have heard the word thesis as a standalone term or as a component of academic writing called a thesis statement . Keep in mind that these are two very different things.
- A thesis statement is a very common component of an essay, particularly in the humanities. It usually comprises 1 or 2 sentences in the introduction of your essay , and should clearly and concisely summarise the central points of your academic essay .
- A thesis is a long-form piece of academic writing, often taking more than a full semester to complete. It is generally a degree requirement to complete a PhD program.
- In many countries, particularly the UK, a dissertation is generally written at the bachelor’s or master’s level.
- In the US, a dissertation is generally written as a final step toward obtaining a PhD.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Upload my document
The final structure of your thesis depends on a variety of components, such as:
- Your discipline
- Your theoretical approach
Humanities theses are often structured more like a longer-form essay . Just like in an essay, you build an argument to support a central thesis.
In both hard and social sciences, theses typically include an introduction , literature review , methodology section , results section , discussion section , and conclusion section . These are each presented in their own dedicated section or chapter. In some cases, you might want to add an appendix .
Thesis examples
We’ve compiled a short list of thesis examples to help you get started.
- Example thesis #1: ‘Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the “Noble Savage” on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807’ by Suchait Kahlon.
- Example thesis #2: ‘A Fistful of Genomes: Adventures in Comparative Genomics of Seed-Free Plants’ by David Wickell.
The very first page of your thesis contains all necessary identifying information, including:
- Your full title
- Your full name
- Your department
- Your institution and degree program
- Your submission date.
Sometimes the title page also includes your student ID, the name of your supervisor, or the university’s logo. Check out your university’s guidelines if you’re not sure.
Read more about title pages
The acknowledgements section is usually optional. Its main point is to allow you to thank everyone who helped you in your thesis journey, such as supervisors, friends, or family. You can also choose to write a preface , but it’s typically one or the other, not both.
Read more about acknowledgements Read more about prefaces
An abstract is a short summary of your thesis. Usually a maximum of 300 words long, it’s should include brief descriptions of your research objectives , methods, results, and conclusions. Though it may seem short, it introduces your work to your audience, serving as a first impression of your thesis.
Read more about abstracts
A table of contents lists all of your sections, plus their corresponding page numbers and subheadings if you have them. This helps your reader seamlessly navigate your document.
Your table of contents should include all the major parts of your thesis. In particular, don’t forget the the appendices. If you used heading styles, it’s easy to generate an automatic table Microsoft Word.
Read more about tables of contents
While not mandatory, if you used a lot of tables and/or figures, it’s nice to include a list of them to help guide your reader. It’s also easy to generate one of these in Word: just use the ‘Insert Caption’ feature.
Read more about lists of figures and tables
If you have used a lot of industry- or field-specific abbreviations in your thesis, you should include them in an alphabetised list of abbreviations . This way, your readers can easily look up any meanings they aren’t familiar with.
Read more about lists of abbreviations
Relatedly, if you find yourself using a lot of very specialised or field-specific terms that may not be familiar to your reader, consider including a glossary . Alphabetise the terms you want to include with a brief definition.
Read more about glossaries
An introduction sets up the topic, purpose, and relevance of your thesis, as well as expectations for your reader. This should:
- Ground your research topic , sharing any background information your reader may need
- Define the scope of your work
- Introduce any existing research on your topic, situating your work within a broader problem or debate
- State your research question(s)
- Outline (briefly) how the remainder of your work will proceed
In other words, your introduction should clearly and concisely show your reader the “what, why, and how” of your research.
Read more about introductions
A literature review helps you gain a robust understanding of any extant academic work on your topic, encompassing:
- Selecting relevant sources
- Determining the credibility of your sources
- Critically evaluating each of your sources
- Drawing connections between sources, including any themes, patterns, conflicts, or gaps
A literature review is not merely a summary of existing work. Rather, your literature review should ultimately lead to a clear justification for your own research, perhaps via:
- Addressing a gap in the literature
- Building on existing knowledge to draw new conclusions
- Exploring a new theoretical or methodological approach
- Introducing a new solution to an unresolved problem
- Definitively advocating for one side of a theoretical debate
Read more about literature reviews
Theoretical framework
Your literature review can often form the basis for your theoretical framework, but these are not the same thing. A theoretical framework defines and analyses the concepts and theories that your research hinges on.
Read more about theoretical frameworks
Your methodology chapter shows your reader how you conducted your research. It should be written clearly and methodically, easily allowing your reader to critically assess the credibility of your argument. Furthermore, your methods section should convince your reader that your method was the best way to answer your research question.
A methodology section should generally include:
- Your overall approach ( quantitative vs. qualitative )
- Your research methods (e.g., a longitudinal study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., interviews or a controlled experiment
- Any tools or materials you used (e.g., computer software)
- The data analysis methods you chose (e.g., statistical analysis , discourse analysis )
- A strong, but not defensive justification of your methods
Read more about methodology sections
Your results section should highlight what your methodology discovered. These two sections work in tandem, but shouldn’t repeat each other. While your results section can include hypotheses or themes, don’t include any speculation or new arguments here.
Your results section should:
- State each (relevant) result with any (relevant) descriptive statistics (e.g., mean , standard deviation ) and inferential statistics (e.g., test statistics , p values )
- Explain how each result relates to the research question
- Determine whether the hypothesis was supported
Additional data (like raw numbers or interview transcripts ) can be included as an appendix . You can include tables and figures, but only if they help the reader better understand your results.
Read more about results sections
Your discussion section is where you can interpret your results in detail. Did they meet your expectations? How well do they fit within the framework that you built? You can refer back to any relevant source material to situate your results within your field, but leave most of that analysis in your literature review.
For any unexpected results, offer explanations or alternative interpretations of your data.
Read more about discussion sections
Your thesis conclusion should concisely answer your main research question. It should leave your reader with an ultra-clear understanding of your central argument, and emphasise what your research specifically has contributed to your field.
Why does your research matter? What recommendations for future research do you have? Lastly, wrap up your work with any concluding remarks.
Read more about conclusions
In order to avoid plagiarism , don’t forget to include a full reference list at the end of your thesis, citing the sources that you used. Choose one citation style and follow it consistently throughout your thesis, taking note of the formatting requirements of each style.
Which style you choose is often set by your department or your field, but common styles include MLA , Chicago , and APA.
Create APA citations Create MLA citations
In order to stay clear and concise, your thesis should include the most essential information needed to answer your research question. However, chances are you have many contributing documents, like interview transcripts or survey questions . These can be added as appendices , to save space in the main body.
Read more about appendices
Once you’re done writing, the next part of your editing process begins. Leave plenty of time for proofreading and editing prior to submission. Nothing looks worse than grammar mistakes or sloppy spelling errors!
Consider using a professional thesis editing service to make sure your final project is perfect.
Once you’ve submitted your final product, it’s common practice to have a thesis defense, an oral component of your finished work. This is scheduled by your advisor or committee, and usually entails a presentation and Q&A session.
After your defense, your committee will meet to determine if you deserve any departmental honors or accolades. However, keep in mind that defenses are usually just a formality. If there are any serious issues with your work, these should be resolved with your advisor way before a defense.
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation shouldn’t take up more than 5-7% of your overall word count.
When you mention different chapters within your text, it’s considered best to use Roman numerals for most citation styles. However, the most important thing here is to remain consistent whenever using numbers in your dissertation .
If you only used a few abbreviations in your thesis or dissertation, you don’t necessarily need to include a list of abbreviations .
If your abbreviations are numerous, or if you think they won’t be known to your audience, it’s never a bad idea to add one. They can also improve readability, minimising confusion about abbreviations unfamiliar to your reader.
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical first steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organise your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
Generally, an outline contains information on the different sections included in your thesis or dissertation, such as:
- Your anticipated title
- Your abstract
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review, research methods, avenues for future research, etc.)
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
George, T. (2024, September 25). What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 21 October 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/thesis-ultimate-guide/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, dissertation & thesis outline | example & free templates, how to write a thesis or dissertation conclusion, how to write a thesis or dissertation introduction.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Revised on April 16, 2024. A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
A thesis is an in-depth research study that identifies a particular topic of inquiry and presents a clear argument or perspective about that topic using evidence and logic. Writing a thesis showcases your ability of critical thinking, gathering evidence, and making a compelling argument. Integral to these competencies is thorough research ...
Thesis. Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic. Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore ...
Updated on April 13, 2023 Academic Writing. A thesis statement is a sentence in a paper or essay (in the opening paragraph) that introduces the main topic to the reader. As one of the first things your reader sees, your thesis statement is one of the most important sentences in your entire paper—but also one of the hardest to write!
Thesis. Definition: Thesis is a scholarly document that presents a student's original research and findings on a particular topic or question. It is usually written as a requirement for a graduate degree program and is intended to demonstrate the student's mastery of the subject matter and their ability to conduct independent research.
An analytical paper breaks down an issue or an idea into its component parts, evaluates the issue or idea, and presents this breakdown and evaluation to the audience.; An expository (explanatory) paper explains something to the audience.; An argumentative paper makes a claim about a topic and justifies this claim with specific evidence. The claim could be an opinion, a policy proposal, an ...
Thesis Statement Types & Models Blinn College - Bryan Writing Center Spring 2023 Page 4 of 4 10. Rhetorical Analysis Argument What it does: Examines the organization and effectiveness of a written or visual argument. Include in your thesis: Author's or artist's name, title of the work, topic of the analyzed work, analyzed work's claim, your claim (whether the rhetoric is effective ...
Format of the Thesis. In form, the thesis is a lengthy experimental, design, or theoretical report, with a problem-method-results-discussionstructure. This recurrenthypothetico-deductive pattern of developing a thesis to solve a problem and then constructing amethodology and testing for results is common in research writing.
Step 4: Revise and refine your thesis statement before you start writing. Read through your thesis statement several times before you begin to compose your full essay. You need to make sure the statement is ironclad, since it is the foundation of the entire paper. Edit it or have a peer review it for you to make sure everything makes sense and ...
A theoretical framework guides the research process like a roadmap for the study, so you need to get this right. Theoretical framework 1,2 is the structure that supports and describes a theory. A theory is a set of interrelated concepts and definitions that present a systematic view of phenomena by describing the relationship among the variables for explaining these phenomena.
Conclusion. A robust conceptual or theoretical framework is crucial when writing a thesis/dissertation. It defines your research gap, identifies your approach, and guides the interpretation of your results. A thesis is the most important document you will write during your academic studies.
Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates. Published on June 7, 2022 by Tegan George.Revised on November 21, 2023. A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical early steps in your writing process.It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding the specifics of your dissertation topic and showcasing its relevance to ...
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
It is a brief statement of your paper's main argument. Essentially, you are stating what you will be writing about. Organize your papers in one place. Try Paperpile. No credit card needed. Get 30 days free. You can see your thesis statement as an answer to a question. While it also contains the question, it should really give an answer to the ...
The term thesis comes from the Greek word θέσις, meaning "something put forth", and refers to an intellectual proposition. Dissertation comes from the Latin dissertātiō, meaning "discussion". Aristotle was the first philosopher to define the term thesis.. A 'thesis' is a supposition of some eminent philosopher that conflicts with the general opinion...for to take notice when any ...
A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a PhD program in the UK. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Indeed, alongside a dissertation, it is the longest piece of writing students typically complete. It relies on your ability to conduct research from start to ...
Developing a conceptual framework in research. Step 1: Choose your research question. Step 2: Select your independent and dependent variables. Step 3: Visualize your cause-and-effect relationship. Step 4: Identify other influencing variables. Frequently asked questions about conceptual models.
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program. Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you've ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating ...
The boutique claims in its mission statement that it wants to sell not only a product, but also a feeling. As a result, unconscious comparison will play an important role in the satisfaction of its customers. Thomassen's definition is therefore more relevant. Thomassen's Customer Satisfaction Model