

Class 12 Maths: Case Study of Chapter 6 Applications of Derivatives PDF Download
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: 12 board / Class 12
- Post comments: 0 Comments
In Class 12 Boards there will be Case studies and Passage Based Questions will be asked, So practice these types of questions. Study Rate is always there to help you. Free PDF Download of CBSE Class 12 Mathematics Chapter 6 Applications of Derivatives Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers were Prepared Based on Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 12 Maths Applications of Derivatives to know their preparation level.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 12 Maths Paper, There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Applications of Derivatives Case Study Questions With answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 12 Mathematics Chapter 6 Applications of Derivatives
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
(i) To construct a garden using 200 ft of fencing, we need to maximize its
| (a) volume | (b) area | (c) perimeter | (d) length of the side |
Answer: (b) area
(ii) If x denote the length of side of garden perpendicular to brick wall and y denote the length, of side parallel to brick wall, then find the relation representing total amount of fencing wire.
| (a) x+2y=150 | (b) x+2y=50 | (c) y+2x=200 | (d) y+2x=100 |
Answer: (c) y+2x=200
(iii) Area of the garden as a function of x, say A(x), can be represented as
| (a) 200 + 2x | (b) x – 2x | (c) 200x – 2x | (d) 200-x |
Answer: (c) 200x – 2×2
(iv) Maximum value of A(x) occurs at x equals
| (a) 50 ft | (b) 30 ft | (c) 26ft | (d) 31 ft |
Answer: (a) 50 ft
(v) Maximum area of garden will be
| (a) 2500sq.ft | (b) 4000sq.ft | (c) 5000sq.ft | (d) 6000 sq. ft |
Answer: (c) 5000sq.ft
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 6 Applications of Derivatives with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries of CBSE Class 12 Mathematics Applications of Derivatives Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible. By Team Study Rate

You Might Also Like
Class 12 physics assertion reason questions chapter 5 magnetism and matter, mcq class 12 english my mother at sixty-six questions with answers english poem 1, mcq questions for class 12 physics with answers chapter wise pdf download, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

The Topper Combo Flashcards
- Contains the Latest NCERT in just 350 flashcards.
- Colourful and Interactive
- Summarised Important reactions according to the latest PYQs of NEET(UG) and JEE
No thanks, I’m not interested!
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 12 Maths Applications of Derivatives Free PDF

Mere Bacchon, you must practice the CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 12 Maths Applications of Derivatives in order to fully complete your preparation . They are very very important from exam point of view. These tricky Case Study Based Questions can act as a villain in your heroic exams! I have made sure the questions (along with the solutions) prepare you fully for the upcoming exams. To download the latest CBSE Case Study Questions , just click ‘ Download PDF ’.
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 12 Maths Applications of Derivatives PDF
Checkout our case study questions for other chapters.
- Chapter 4 Determinants Case Study Questions
- Chapter 5 Continuity and Differentiability Case Study Questions
- Chapter 7 Integrals Case Study Questions
- Chapter 8 Applications of Integrals Case Study Questions
How should I study for my upcoming exams?
First, learn to sit for at least 2 hours at a stretch
Solve every question of NCERT by hand, without looking at the solution.
Solve NCERT Exemplar (if available)
Sit through chapter wise FULLY INVIGILATED TESTS
Practice MCQ Questions (Very Important)
Practice Assertion Reason & Case Study Based Questions
Sit through FULLY INVIGILATED TESTS involving MCQs. Assertion reason & Case Study Based Questions
After Completing everything mentioned above, Sit for atleast 6 full syllabus TESTS.
Comments are closed.
Contact Form
Privacy Policy
Class 12 CBSE A.O.D ML AGGARWAL Case Study
Please select, case-study-1 a political party placed an order to a screen printer for the printing of party's slogan on a rectangular cloth sheets. a margin of 2.5 cm along length and 1 cm along width of cloth was left. the pictorial view of the slogan in shown below: if the total area of cloth is 640 cm2, based on the above information, answer the following questions: (i) the length and the breadth (in cm) of the rectangular part on which the slogan is printed respectively are (a)x-2.5, y-1 (b) x-5,y-2 (c) x-2,y-5 (d) x-5,y-1 (ii) the relation between x and y is (a) (x-2.5)(y-1)=640 (b) (x-5)(y-2)=640 (c) xy=640 (d) (x-2)(y-5)= (iii) area 'a' of cloth on which slogan matter was written is given by (a) 650-2x-3200/x (b) 650+2x+ 3200/x (c) 600-2x-3200/x (d) 600 +2x + 3200/x (iv) what is the value of x for which the printing area is maximum (a) 16 cm (b) 40 cm (c) 14 cm (d) 11 cm (v) what is the value of 'a' when printing of slogan is done on maximum area (a) 640 cm² (b) 418 cm² (c) 490 cm² (d) none of these.

Case-study-2 Saloni has a piece of tin rectangular in shape as shown in the diagram given below. She is going to cut squares from each corners and fold up the sides to form an open box. Based on the above information, answer the following questions: (i) If x is the side of square cut off from each corner of the sheet, then what is the length of open box? (a) 45-x (b) 45-2x (c) 45 +2x (d) none of these (ii) What is width of open box? (a) 24-x (b) 24+ x (c) 24-2x (d) none of these (iii) Volume 'V' of open box is given by (a) V = (45-x)(24-x) x (b) V=(45+x)(24+x) x (c) V=(45+2x) (24+2x) x (d) V=(45-2x)(24-2x) x (iv) What should be the side of square to be cut off so that the volume of box is maximum? (a) 18 cm (b) 5 cm (c) both (a) and (b) (d) none of these (v) The maximum value of V (in cm³) is (a) 5400 (b) 4200 (c) 3600 (d) 2450

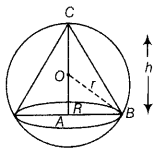
Case-study-3 A company is planning to launch a new product and decides to pack the new product in closed right circular cylindrical cans of volume 432 πcm³. The cans are to be made from tin sheet. The company tried different options. Based on the above information, answer the following questions: (i) If 7 cm is the radius of the base of the cylinder and h cm is height, then (a) rh=216 (b) r(r+h)=216 (c) rh² = 432 (d) r 2 h=432 (ii) If S cm² is the surface area of the closed cylindrical can, then (a) S= 2π (r 2 +432/r) (b) S= π (r 2 +864/r) (c) S= π (r 2 +432/r) (d) S= 432π/r (iii) For S to be minimum r is equal to (a) 3 cm (b) 6 cm (c) 8 cm (d) 12 cm (iv) Minimum surface area of cylindrical can is (a) 54 πcm 2 (b) 108 πcm² (c) 216 πcm² (d) none of these (v) The relation between the radius and the height of cylindrical area is (a) height is equal to radius of base (b) height is equal to twice the radius of base (c) radius is equal to twice the height (d) radius is two-third of the height.

Case-study-4 A factory owner wants to construct a tank with rectangular base and rectangular sides, open at the top, so that its depth is 2 m and capacity is 8 m³. The building of the tank costs ₹250 per square metre for the base and ₹180 per square metre for the sides. Based on the above information, answer the following questions: (i) If the length and the breadth of the rectangular base of the tank are x metres and mimiy metres respectively, then the relation between x and y is (a)x+y=4 (b) xy=4 (c) xy=8 (d) xy+x+y=4 (ii) The cost of construction of the sides of the tank is (a) ₹180 (x+y) (b) ₹360 (x+y) (c) ₹720 (x + y) (d) ₹1120 (x+y) (iii) If C (in ₹) is the cost of construction of the tank, then C as a function of x is (d) C= 1120 + 720 (x+4/x) (b) C=720+1120 (x+4/x) (c) C=1120+360 (x+4/x) (d) C=1120+180 (x+4/x) (iv) The cost of construction of the tank is least when the value of x is (a) 1 (b) 3 /2 (c) 2 (d) 3 (v) The least cost of construction of the tank is (a) ₹2000 (b) ₹3000 (c)₹3600 (d) ₹4000

Case-study-5 A carpenter has a wire of length 28 m. He wants to cut into two pieces, one of the two pieces is to be made into a square and other into a circle. Based on the above information, answer the following questions: (i)If x metres wire is used in making a square, then what is the expression of combined area A? (ii) What is the length of radius for minimum combined area? (a) 28/π+4 (b) 112/π+4 (c) 14/π+4 (d) none of these (iii) What is the length of circular part? (a) 28/π+4 (b) 14/π+4 (c) 14π/π+4 (d) 28π/π+4 (iv) What is the length of square part? (a) 112/π+4 (b) 112π/π+4 (c) 14π/π+4 (d) 28/π+4 (v) The minimum combined area of square and circle is (a) 196/π+4 m 2 (b) 196/(π+4) 2 m 2 (c) 196/π-4 m 2 (d) none of these

Case-study-6 A firm has the cost function C(x)=x 3 /3-7x 2 + 111x +50 and demand function x = 100-p. Based on the above information, answer the following questions: (i) The total revenue function is (a) R(x) = x²-100x (b) R(x) = 100x-x 2 (c) R(x) = 100-x (d) none of these (ii) The total profit function is (a)-x 3 /3 +6x²-11x-50 (b)-x 3 /3-6x²-11x+50 (c)x 3 /3+6x²-11x+50 (d) -x 3 /3-6x²-11x+50 (iii) The value of x for which profit is maximum is (a) 8 (b) 9 (c) 10 (d) 11 (iv) The maximum profit is (a) ₹133.11 (b) ₹113.31 (c) ₹111.33 (d) ₹133.11 (b) The marginal revenue when x = 10 units is (a) 900 (b) 80 (c) 90 (d) 800
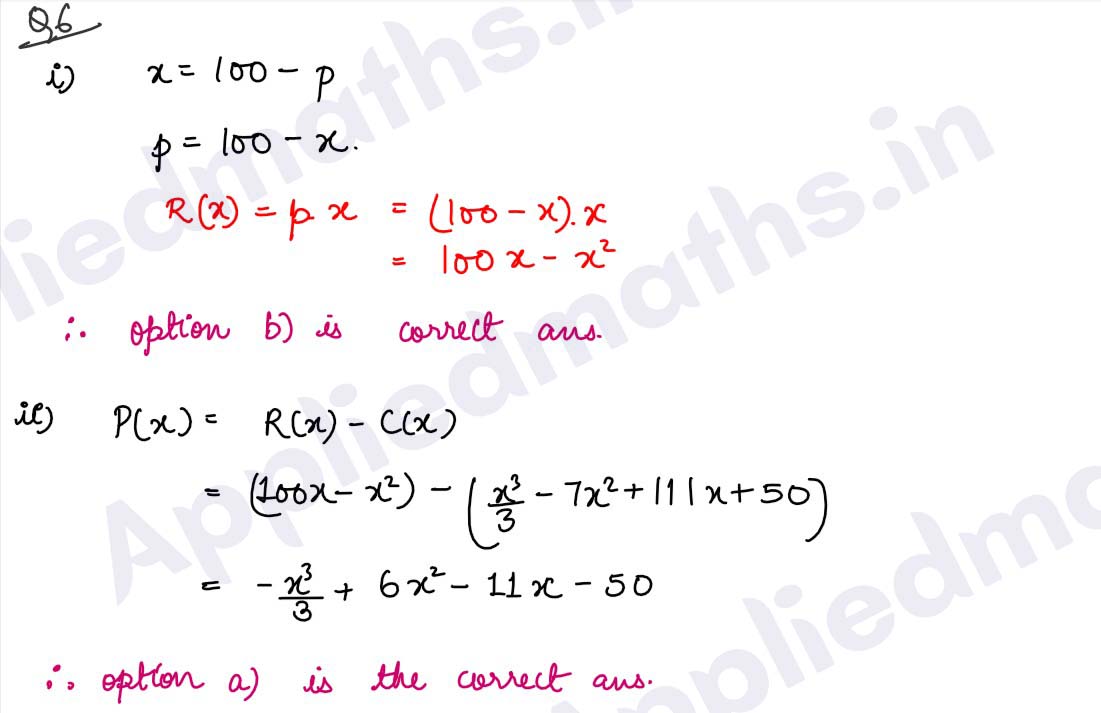
Case-study-7 The average cost function associated with producing and marketing x units of an item is given by 50 AC=2x-11 + 50/x Based on the above information, answer the following questions: (i) The total cost function is (a) C(x)=2x²-11x+50 (b) C(x)=2- 50/x 2 (c) C(x)=2x- 50/x (d) C(x)=2x²+11x-50 (ii) The marginal cost function is (a) MC=4x+ 11 (b) MC=4x-11 (c) MC = 2 + 50/x 2 (d) MC= 100/x 3 (iii) The marginal cost when x = 4 units is (a) ₹5 (b) ₹27 (c) ₹18 (d) ₹13 (iv) The range of values of x for which AC is increasing is (a) x (b) x>-5 (c) x (d) x>5 (v) The range of values of x for which total cost is decreasing is (a) x ≤ 11/4 (b) x ≥ 11/4 (c) x (d) x>-11/4

- Neet Online Test Pack
12th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் subjects.

கணினி பயன்பாடுகள்

கணினி அறிவியல்
வணிகக் கணிதம் மற்றும் புள்ளியியல்.

கணினி தொழில்நுட்பம்

கணக்குப்பதிவியல்

English Subjects

Computer Science

Business Maths and Statistics

Accountancy

Computer Applications

Computer Technology

11th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

9th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

Social Science

சமூக அறிவியல்
6th standard stateboard question papers & study material.

10th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

7th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

8th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

கணிதம் - old

12th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

Introductory Micro and Macroeconomics

Business Studies

Indian Society

Physical Education

Bio Technology

Engineering Graphics

Entrepreneurship

Hindi Elective

Home Science

Legal Studies

Political Science

11th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

Mathematics

Enterprenership

Applied Mathematics
10th standard cbse subject question paper & study material.

9th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

8th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

7th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

6th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

School Exams

Tamil Nadu State Board Exams

Scholarship Exams

Study Materials , News and Scholarships

Stateboard Tamil Nadu


Free Online Tests

Educational News

Scholarships

Entrance Exams India

Video Materials

12th Standard CBSE
Class 12th Maths - Application of Derivatives Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023

Class 12th Maths - Application of Derivatives Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023 Study Materials Sep-08 , 2022
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 12 Maths Subject - Application of Derivatives, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.

A PHP Error was encountered
Severity: Warning
Message: in_array() expects parameter 2 to be array, null given
Filename: material/details.php
Line Number: 1436
Message: Use of undefined constant EXAM - assumed 'EXAM' (this will throw an Error in a future version of PHP)
Line Number: 1438
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Application of derivatives case study questions with answer key.
Final Semester - June 2015
(ii) Volume of the open box formed by folding up the cutting corner can be expressed as
(iii) The values of x for which \(\begin{equation} \frac{d V}{d x}=0 \end{equation}\) ,are
(iv) Megha is interested in maximising the volume of the box. So, what should be the side of the square to be cut off so that the volume of the box is maximum?
| ( |
(v) The maximum value of the volume is
(ii) If x denote the length of side of garden perpendicular to brick wall and y denote the length, of side parallel to brick wall, then find the relation representing total amount of fencing wire.
(iii) Area of the garden as a function of x, say A(x), can be represented as
(iv) Maximum value of A(x) occurs at x equals
(v) Maximum area of garden will be
| ( | |
(ii) Revenue R as a function of x can be represented as
| - 60x - 24000 | + 60x + 24000 |
| + 40x - 16000 | - 60x - 14000 |
(iii) Find the number of days after 1stJuly, when Shyams father attain maximum revenue.
(iv) On which day should Shyam's father harvest the onions to maximise his revenue?
| uly | July | July | July |
(v) Maximum revenue is equal to
An owner of an electric bi~e rental company have determined that if they charge customers Rs. x per day to rent a bike, where 50 Rs. x Rs. 200, then number of bikes (n), they rent per day can be shown by linear function n(x) = 2000 - 10x. If they charge Rs. 50 per day or less, they will rent all their bikes. If they charge Rs. 200 or more per day, they will not rent any bike. Based on the above information, answer the following questions.
(ii) If R(x) denote the revenue, then maximum value of R(x) occur when x equals
(iii) At x = 260, the revenue collected by the company is
(iv) The number of bikes rented per day, if x = 105 is
(v) Maximum revenue collected by company is
(ii) If x represent the number of apartments which are not rented, then the profit expressed as a function of x is
(iii) If P = 10500, then N =
(iv) If P = 11,000, then the profit is
(ii) The range of x is
(iii) The value of xfor which revenue is maximum, is
(iv) When the revenue is maximum, the price of the ticket is
(v) How any spectators should be present to maximize the revenue?
| (a) \(2 \pi r^{2}\) | (b) \(\sqrt{\frac{500}{\pi}} \mathrm{cm}\) | (c) \(\sqrt[3]{\frac{1500}{\pi}} \mathrm{cm}\) | (d) \(2 \pi r^{2}+\frac{6000}{r}\) |
(ii) The radius that will minimize the cost of the material to manufacture the tin can is
(iii) The height thatt will minimize the cost of the material to manufacture the tin can is
(iv) If the cost of material used to manufacture the tin can is Rs.100/m 2 and \(\sqrt[3]{\frac{1500}{\pi}} \approx 7.8\) then minimum cost is approximately
(v) To minimize the cost of the material used to manufacture the tin can, we need to minimize the
(ii) The relation between a and b is given by
| (c) |
(iii) Area of poster in terms of b is given by
(iv) The value of b, so that area of the poster is minimized, is
(v) The value of a, so that area of the poster is minimized, is
(i) In order to make a least expensive water tank, Nitin need to minimize its
(ii) Total cost of tank as a function of h can' be' represented as
| \(c(h)=100 h+320+\frac{1600}{h}\) |
(iii) Range of h is
(iv) Value of h at which c(h) is minimum, is
(v) The cost ofleast expensive tank is
(ii) If sum of the surface areas of box and ball are given to be constant k 2 , then x is equal to
(iii) The radius of the ball, when S is minimum, is
(iv) Relation between length of the box and radius of the ball can be represented as
(v) Minimum value of S is
(ii) If C(x) denote the maintenance cost function, then maximum value of C(x) occur at x =
(iii) The maximum value of C(x) would be
(iv) The number of apartments, that the complex should have in order to minimize the maintenance cost, is
(v) If the minimum maintenance cost is attain, then the maintenance cost for each apartment would be
| (a) Area of outer rectangle | (b) Area of inner rectangle |
| (c) Area of top border | (d) None of these |
(ii) If x is the length of the outer rectangle, then area of inner rectangle in terms of x is
(iii) Find the range of x.
(iv) If area of inner rectangle is m~imum, then x is equal to
(v) If area of inner rectangle is maximum, then length and breadth of this rectangle are respectively
(ii) If magazine company increases Rs.500 as annual charges, then R is equal to
(iv) What amount of increase in annual charges will bring maximum revenue?
| b) \(\frac{1000}{\left(600-x^{2}\right)}+\frac{125}{x^{2}}\) |
(ii) The maximum value of x can not be
(iii) The rainimum value of x can not be
(iv) If l(x) denote the combined light intensity, then lex) will be minimum when x =
(v) The darkest spot between the two lights is
| + 2xy) m | + 4xy) m | + 2xy) m | + 8xy) m |
(ii) The relation between x and y is
| y = 32 | = 32 | y = 32 |
(iii) The outer surface area of tank will be minimum when depth of tank is equal to
| of its width | of its width |
(iv) The cost of material will be least when width of tank is equal to
(v) If cost of aluminium sheet is Rs.360/m 2 , then the minimum cost for the construction of tank will be
| ,y-7 | ,y+7) | + 7) | ,x-7) |
(ii) Distance (say D) between Arun and Manita will be
| + 2x + 3) | +x |
(iii) For which real value(s) of x, first derivative of D 2 w.r.t. 'x' will Vanish?
(iv) Find the position of Arun when Manita will hit the paper hall.
(v) The minimum value of D is
| - y = 10 | + y =10 | + 1 = 100 | - y = 100 |
(ii) The area (A) of green grass, in terms of x, is given by
(iii) The maximum value of A is
(iv) The value oflength of rectangle, when A is maximum, is
(v) The area of gravelling path is
(ii) The length PQ is
(iii) Let there be a quantity S such that S = Rp 2 + RQ 2 , then S is given by
| - 40x - 1140 | + 40x + 1140 | - 40x + 1140 | + 40x - 1140 |
(iv) Find the value of x for which value of S is minimum.
(v) For minimum value of S, find the value of PR and RQ
(ii) The area (A) of the window can be given by
(iii) Rohan is interested in maximizing the area of the whole window, for this to happen, the value of x should be
(iv) Maximum area of the window is
(v) For maximum value of A, the breadth of rectangular part of the window is
| + y = p |
(ii) The area (A) of the rectangular region, as a function of x, can be expressed as
| ( |
(iii) School's manager is interested in maximising the area of floor 'A' for this to be happen, the value of x should be
(iv) The value of y, for which the area of floor is maximum is
(v) Maximum area of floor is
*****************************************
- Previous Class 12th Maths - Three Dimensional Geometry Case Study Questions and Answers 2...
- Next Class 12th Maths - Linear Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023
Reviews & Comments about Class 12th Maths - Application of Derivatives Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023

Write your Comment

12th Standard CBSE Maths Videos
CBSE 12th Maths Sample Model Question Paper with Answer Key 2023
12th Standard CBSE Maths Usefull Links

- 10th Standard
Other 12th Standard CBSE Subjects

Other 12th Standard CBSE Maths Study material
Class 12th maths - three dimensional geometry ... click to view, class 12th maths - linear case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023 click to view, class 12th maths - probability case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023 click to view, class 12th maths - vector algebra case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023 click to view, class 12th maths - differential equations case ... click to view, class 12th maths - application of integrals ... click to view, class 12th maths - application of derivatives ... click to view, class 12th maths - continuity and differentiability ... click to view, class 12th maths - determinants case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023 click to view, class 12th maths - matrices case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023 click to view, class 12th maths - relations and functions ... click to view, test click to view, 12th standard cbse mathematics public model question paper iv 2019 - 2020 click to view, 12th standard cbse mathematics public model question paper iii 2019 - 2020 click to view, 12th standard cbse mathematics public model question paper ii 2019 - 2020 click to view, register & get the solution for class 12th maths - application of derivatives case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023.
- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
Case Based Questions (MCQ)
- Miscellaneous
- NCERT Exemplar - MCQs
- Tangents and Normals (using Differentiation)
- Approximations (using Differentiation)
Question 6 - Case Based Questions (MCQ) - Chapter 6 Class 12 Application of Derivatives
Last updated at April 16, 2024 by Teachoo
There is a bridge whose length of three sides of a trapezium other than base are equal to 10 cm.
Based on the above information answer the following:.
This question is inspired from Example 37 - Chapter 6 Class 12 (AOD) - Maths

What is the value of DP?
(a) √( 100 - x 2 ) , (b) √( x 2 - 100 ), (c) 100 - x 2 , (d) x 2 − 100.

What is the area of trapezium A(x)?
(a) (x - 10 )√( 100 - x 2 ) , (b) ( x + 10) √( 100 - x 2 ), (c) ( x - 10 ) (100 - x 2 ), (d) ( x + 10)(100 - x 2 ).

If A'(x) = 0, then what are the values of x?
(a) 5,-10 , (b) - 5, 10, (c) - 5,-10 .

What is the value of maximum Area?
(a) 75 √2 cm 2 , (b) 75 √3 cm 2, (c) 75 √5 cm 2 , (d) 75 √7 cm 2 .

Question There is a bridge whose length of three sides of a trapezium other than base are equal to 10 cm. Based on the above information answer the following: Question 1 What is the value of DP? (A) √(100−𝑥^2 ) (B) √(𝑥^2−100) (C) 100−𝑥^2 (D)〖 𝑥〗^2 − 100 In Δ ADP By Pythagoras theorem DP2 + AP2 = AD2 DP2 + x2 = 102 DP2 + x2 = 100 DP2 = 100 – 𝑥2 DP = √(𝟏𝟎𝟎 −𝒙𝟐) So, the correct answer is (A) Question 2 What is the area of trapezium A(x)? (A) (𝑥 −10)√(100−𝑥^2 ) (B) (𝑥+10)√(100−𝑥^2 ) (C) (𝑥−10)(100−𝑥^2) (D) (𝑥+10)(100−𝑥^2 ") " Let A be the area of trapezium ABCD A = 1/2 (Sum of parallel sides) × (Height) A = 𝟏/𝟐 (DC + AB) × DP A = 1/2 (10+2𝑥+10) (√(100−𝑥2)) A = 1/2 (2𝑥+20) (√(100−𝑥2)) A = (𝒙+𝟏𝟎) (√(𝟏𝟎𝟎−𝒙𝟐)) So, the correct answer is (B) Question 3 If A'(x) = 0, then what are the values of x? (A) 5,−10 (B) −5, 10 (C) −5,−10 (D) 5,10 A = (𝒙+𝟏𝟎) (√(𝟏𝟎𝟎−𝒙𝟐)) Since A has a square root It will be difficult to differentiate Let Z = A2 = (𝑥+10)^2 (100−𝑥2) Where A'(x) = 0, there Z’(x) = 0 So, the correct answer is (A) Differentiating Z Z =(𝑥+10)^2 " " (100−𝑥2) Differentiating w.r.t. x Z’ = 𝑑((𝑥 + 10)^2 " " (100 − 𝑥2))/𝑑𝑘 Using product rule As (𝑢𝑣)′ = u’v + v’u Z’ = [(𝑥 + 10)^2 ]^′ (100 − 𝑥^2 )+(𝑥 + 10)^2 " " (100 − 𝑥^2 )^′ Z’ = 2(𝑥 + 10)(100 − 𝑥^2 )−2𝑥(𝑥 + 10)^2 Z’ = 2(𝑥 + 10)[100 − 𝑥^2−𝑥(𝑥+10)] Z’ = 2(𝑥 + 10)[100 − 𝑥^2−𝑥^2−10𝑥] Z’ = 2(𝑥 + 10)[−2𝑥^2−10𝑥+100] Z’ = −𝟒(𝒙 + 𝟏𝟎)[𝒙^𝟐+𝟓𝒙+𝟓𝟎] Putting 𝒅𝒁/𝒅𝒙=𝟎 −4(𝑥 + 10)[𝑥^2+5𝑥+50] =0 (𝑥 + 10)[𝑥^2+5𝑥+50] =0 (𝑥 + 10) [𝑥2+10𝑥−5𝑥−50]=0 (𝑥 + 10) [𝑥(𝑥+10)−5(𝑥+10)]=0 (𝒙 + 𝟏𝟎)(𝒙−𝟓)(𝒙+𝟏𝟎)=𝟎 So, 𝑥=𝟓 & 𝒙=−𝟏𝟎 So, the correct answer is (A) Question 4 What is the value of maximum Area? (A) 75 √2 cm^2 (B) 75 √3 cm^2 (C) 75 √5 cm^2 (D) 75 √7 cm^2 We know that Z’(x) = 0 at x = 5, −10 Since x is length, it cannot be negative ∴ x = 5 Finding sign of Z’’ for x = 5 Now, Z’ = −4(𝑥 + 10)[𝑥^2+5𝑥+50] Z’ = −4[𝑥(𝑥^2+5𝑥+50)+10(𝑥^2+5𝑥+50)] Z’ = −4[𝑥^3+5𝑥^2+50𝑥+10𝑥^2+50𝑥+500] Z’ = −𝟒[𝒙^𝟑+𝟏𝟓𝒙^𝟐+𝟏𝟎𝟎𝒙+𝟓𝟎𝟎] Differentiating w.r.t x Z’’ = 𝑑(−4[𝒙^𝟑 + 𝟏𝟓𝒙^𝟐 + 𝟏𝟎𝟎𝒙 + 𝟓𝟎𝟎])/𝑑𝑘 Z’’ =−4[3𝑥^2+15 × 2𝑥+100] Z’’ =−4[3𝑥^2+30𝑥+100] Putting x = 5 Z’’ (5) = −4[3(5^2) +30(5) +100] = −4 × 375 = −1500 < 0 Hence, 𝑥 = 5 is point of Maxima ∴ Z is Maximum at 𝑥 = 5 That means, Area A is maximum when x = 5 Finding maximum area of trapezium A = (𝑥+10) √(100−𝑥2) = (5+10) √(100−(5)2) = (15) √(100−25) = 15 √75 = 75√𝟑 cm2 So, the correct answer is (C)

Davneet Singh
Davneet Singh has done his B.Tech from Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur. He has been teaching from the past 14 years. He provides courses for Maths, Science, Social Science, Physics, Chemistry, Computer Science at Teachoo.
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
Application of Derivatives Class 12 Maths Important Questions Chapter 6
July 14, 2022 by Sastry CBSE
Get access to Class 12 Maths Important Questions Chapter 6 Application of Derivatives, Application of Derivatives Class 12 Important Questions with Solutions Previous Year Questions will help the students to score good marks in the board examination.
Application of Derivatives Class 12 Important Questions with Solutions Previous Year Questions
Rate Measure, Increasing-Decreasing Functions and Approximation
Question 1. The total cost C(x) associated with the production of x units of an item is given by C(x) = 0.005x 3 – 0.02x 2 + 30x + 5000. Find the marginal cost when 3 units are produced, where by marginal cost we mean the instantaneous rate of change of total cost at any level of output. (CBSE 2018) Answer: We have, C(x) = 0.005x 3 – 0.02x 2 + 30x + 5000 Clearly, the marginal cost, MC (x) = \(\frac{d}{d x}\)C(x) = \(\frac{d}{d x}\)(0.005x 3 – 0.02x 2 + 30x + 500) = 0.005 × 3x 2 – 0.02 × 2x + 30 + 0 = 0.015x 2 – 0.04x + 30
Now, marginal cost when 3 units arei produced MC(3)= 0.015(9) – 0.04(3) + 30 = 0135 – 0.12 + 30= 30.015
Question 2. The total revenue received from the sale of x units of a product is given by R(x) = 3x 2 + 36x + 5 in rupees. Find the marginal revenue when x = 5, where by marginal revenue we mean the rate of change of total revenue with respect to the number of items sold at an instant. (CBSE 2018 C) Answer: Marginal Rcvcnuc (MR) = \(\frac{d R}{d x}=\frac{d}{d x}\)(3x 2 + 36x + 5) = 6x + 36 ∴ When x = 5 Marginai Revenue (MR) = 6 × 5 + 36 = 66
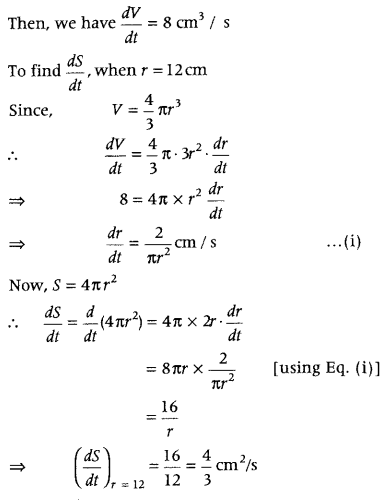
Question 4. Show that the function f(x) = x 3 – 3x 2 + 6x – 100 is increasing on R. (All India 2017) Answer: Given, f(x) = x 3 – 3x 2 + 6x – 100 On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get f'(x) = 3x 2 – 6x + 6 = 3x 2 – 6x + 3 + 3 = 3(x 2 – 2x + 1) + 3 = 3(x – 1) 2 + 3 > 0 ∴ f'(x) > 0 This show that function f(x) is increasing on R. Hence proved.
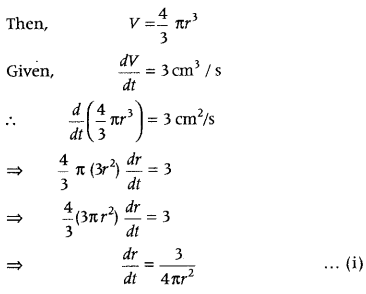
Question 6. Show that the function f(x) = 4x 3 – 18x 2 + 27x – 7 is always increasing on R. (Delhi 2017) Answer: We have, f(x) = 4x 3 – 18x 2 + 27x – 7 On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get f(x) = 12x 2 – 36x + 27 ⇒ f'(x) = 3(4x 2 -12x + 9) ⇒ f'(x) = 3(2x – 3) 2 ⇒ f(x) > 0 ⇒ For any x ∈ R, (2x – 3) 2 > 0 Since, a perfect square number cannot be negative. ∴ Given function f(x) is an increasing function on R.
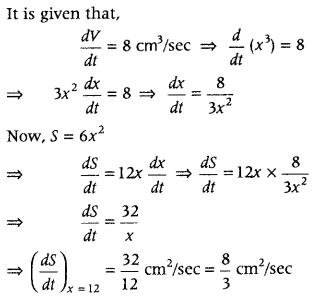
Question 9. Find the intervals in which the function f(x) = -2x 3 – 9x 2 – 12x + 1 is (i) strictly increasing (ii) strictly decreasing, (CBSE 201B C) Answer: Given, f(x) = -2x 3 – 9x 2 – 12x + 1 On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get f'(x) = – 6x 2 – 18x – 12 ⇒ f'(x) = – 6(x 2 + 3x + 2) ⇒ f'(x) = – 6(x 2 + 2x + x + 2) ⇒ – 6 [x(x + 2) + 1 (x + 2)] ⇒ – 6 (x + 2) (x + 1)
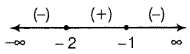
| Interval | Sign of f'(x) F’(x) = -6(x + 2)(x + 1) | Nature of function |
| (-∞, -2) | (-) (-) (-) = (-) < 0 | Strictly decreasing |
| (-2, -1) | (-) (+) (-) = (+) > 0 | Strictly increasing |
| (-1, ∞) | (-) (+) (+) = (-) < 0 | Strictly decreasing |
Hence, f(x) is strictly increasing in the interval (- 2, -1) and f(x) is strictly decreasing in the interval (- ∞, – 2) ∪ (-1, ∞).
Question 10. The length x of a rectangle is decreasing at the rate of 5 cm/min and the width y is increasing at the rate of 4 cm/min. When x = 8 cm and y = 6 cm, find the rate of change of (i) the perimeter. (ii) area of rectangle. (All India 2017) Answer: Using the relation, perimeter of rectangle, P = 2(x + y) and area of rectangle, A = xy, differentiate both sides with respect to t and put them in rate of change value and get the result. Given that length x of a rectangle is decreasing at the rate of 5 cm/min. ∴ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = – 5cm/min ………..(i) Also, the breadth y of rectangle is increasing at the rate of 4 cm/min. ∴ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 4 cm/min ……(ii)
(i) Here, we have to find rate of change of perimeter, i.e. dP/dt and we know that, perimeter P = 2 (x + y)
On differentiating both sides w.r.t. t, we get \(\frac{d P}{d t}\) = 2\(\left(\frac{d x}{d t}+\frac{d y}{d t}\right)\) ⇒ \(\frac{d P}{d t}\) = 2(-5 + 4) = 2(-1) = -2cm/min [from Eqs. (i) and (ii)] Hence, perimeter of rectangle is decreasing at the rate 2 cm/min.
(ii) Here, we have to find rate of change of area \(\frac{d A}{d t}\) We know that, area of rectangle A = xy On differentiating both sides w.r.t. t, we get \(\frac{d A}{d t}=x \cdot \frac{d y}{d t}+y \cdot \frac{d x}{d t}\) [by using product rule of derivative]
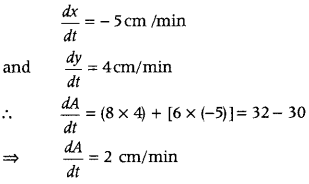
Question 11. The side of an equilateral triangle is increasing at the rate of 2 cm/s. At what rate is its area increasing, when the side 22. of the triangle is 20 cm? (Delhi 2015) Answer: Let a be the side of an equilateral triangle and A be the area of an equilateral triangle. Then, \(\frac{d a}{d x}\) = 2 cm/s
We know that, area of an equilateral triangle, A = \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}\)a 2
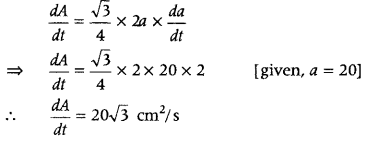
Question 12. Find the intervals in which the function f(x) = 3x 4 – 4x 3 – 12x 2 + 5 is (i) strictly increasing. (ii) strictly decreasing. (Delhi 2014) Answer: First, find the first derivative and put equal to zero, we get different values of x and then divide the real line into disjoint intervals. Further check sign of f(x) in a given interval, if f'(x) > 0, then it is strictly increasing and if f'(x) < 0, then it is strictly decreasing. f(x) = 3x 4 – 4x 3 – 12x 2 + 5 On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get f'(x) = 12x 3 -12x 2 – 24x For strictly increasing or strictly decreasing, put f'(x) = 0, we get 12x 3 – 12x 2 – 24x = 0 ⇒ 12x [x 2 – 2x + x – 2] = 0 12x (x + 1) (x – 2) = 0 ∴ x = 0, -1 or 2 Now, we find intervals in which f(x) is strictly increasing or strictly decreasing.
| Interval | f’(x) = 12x(x + 1)(x – 2) | Sign of f’(x) |
| x < – 1 | (-) (-) (-) | – ve |
| – 1 < x < 0 | (-) (+) (-) | + ve |
| 0 < x < 2 | (+) (+) (-) | – ve |
| x > 2 | (+) (+) (+) | + ve |
We know that, a function f(x) is said to be strictly increasing , if f'(x) > 0 and it is said to be strictly decreasing , if f'(x) < 0. So, the given function f(x) is (i) strictly increasing on the intervals (-1, 0) and (2, ∞). (ii) strictly decreasing on the intervals (-∞, -1) and (0, 2).
Question 13. Find the intervals in which the function given by ; f(x) = \(\frac{3}{10}\) x 4 – \(\frac{4}{5}\)x 3 – 3x 2 + \(\frac{36x}{5}\) + 11 is (i) strictly increasing. (ii) strictly decreasing. (All India 2014C) Answer: (i) Strictly increasing in (-2, 1) and (3, ∞). (ii) Strictly decreasing in (-∞,- 2) and (1, 3).
Question 14. The sides of an equilateral triangle are increasing at the rate of 2 cm/s. Find the rate at which the area increases, when the side is 10 cm? (All India 2014C) Answer: 10√ 3 cm 2 /s
Question 15. Find the value(s) of x for which y = [x(x – 2)] 2 is an increasing function. (All India 2014; Delhi 2010) Answer: Given function is y = [x(x – 2)] 2 = [x 2 – 2x] 2 . On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 2(x 2 – 2x) – (x 2 – 2x) = 2(x 2 – 2x) (2x – 2) = 4x(x – 2) (x -1)
On putting \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 0, we get 4x(x – 2)(x – 1) = 0 ⇒ x = 0, 1 and 2
Now, we find interval in which f(x) is strictly increasing or strictly decreasing.
| Interval | \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 4x(x – 2)(x – 1) | Sign of f’(x) |
| (-∞, 0) | (-) (-) (-) | – ve |
| (0, 1) | (-) (+) (-) | + ve |
| (1, 2) | (+) (+) (-) | – ve |
| (2, ∞) | (+) (+) (+) | + ve |
Hence, y is strictly increasing in (0, 1) and (2, ∞). Also, y is a polynomial function, so it continuous at x = 0, 1 and 2. Hence, y is increasing in [0, 1] ∪ [2, ∞).
Question 16. Using differentials, find the approximate value of (3.968) 3/2 . (Delhi 2014C) Answer: Let y = f(x) = (x) 3/2 On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get Let x = 4 and x + Δx = 3.968 Then, Δx = -0.032 Now, f(x+ Δx) 3/2 ≈ f(x) + f'(x)Δx (x+ Δx) 3/2 ≈ (x) 3/2 + \(\frac{3}{2}\).(x) 1/2 .(-0.032) ⇒ (4 – 0.032) 3/2 ≈ (4) 3/2 + \(\frac{3}{2}\)(4) 1/2 (-0.032) [put x = 4] ⇒ (3.968) 3/2 ≈ 8 + \(\frac{3}{2}\) .2.(-0.032) ⇒ (39368) 3/2 ≈ 8 – 0.096 ⇒ (3.968) 3/2 ≈ 7.904
Question 17. Find the intervals in which the function f(x) = \(\frac{3}{2}\) x 4 – 4x 3 – 45x 2 + 51 is (i) strictly increasing. (ii) strictly decreasing. (Foreign 2014C) Answer: (i) Strictly increasing in (-3, 0) and (5, ∞). (ii) Strictly decreasing in (-∞,- 3) and (0,5).
Question 18. Find the approximate value of f(3.02), upto 2 places of decimal, where f(x) = 3x 2 + 15x + 3. (Foreign 2014) Answer: First, split 3.02 into two parts x and Ax, so that x + Δx = 3.02 and f(x + Δx) = f(3.02) Now, write f(x + Δx) = f(x) + Δx . f'(x) and use this result to find the required value. Given function is f(x) = 3x 2 + 15x + 3 On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get f'(x) = 6x + 15 Let x = 3 and Δx = 0.02 So that f(x + Δx) – f(302) By using f(x + Δx) ~ f(x)+ Δx f'(x), we get f(x + Δx) = 3x 2 + 15x + 3 + (6x + 15) Δx f(3 + 0.02) = 3(3) 2 + 15(3) + 3+ [6(3) + 15] (0.02) = 27 + 45 + 3 + 33(0.02) = 75 + 0.66 = 75.66 Hence, f (3.02) ≈ 75.66
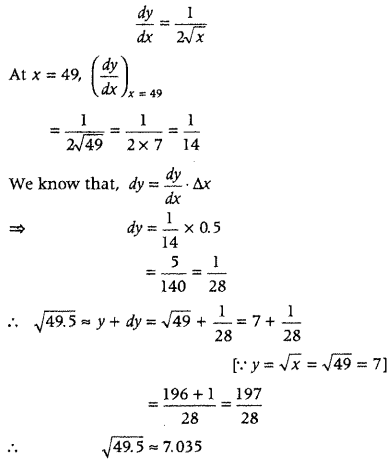
Hence, the function is (i) increasing in [0, \(\frac{\pi}{4}\)] and [\(\frac{5\pi}{4}\), 2π] (ii) decreasing in \(\left[\frac{\pi}{4}, \frac{5 \pi}{4}\right]\)
Question 23. Find the intervals in which the function given by f(x) = x 4 – 8x 3 + 22x 2 – 24x + 21 is (i) increasing, (ii) decreasing. (All Delhi 2012C) Answer: Given function is f(x) = x 4 – 8x 3 + 22x 2 – 24x + 21 On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get f(x) = 4x 3 – 24x 2 + 44x – 24 = 4(x 3 – 6x 2 + 11 x – 6) = 4(x – 1) (x 2 – 5x + 6) = 4(x – 1) (x – 2) (x – 3) Put f'(x) = 0 ⇒ 4(x – 1)(x – 2)(x – 3) = 0 ⇒ x = 1, 2, 3 So, the possible intervals are (-∞, 1), (1, 2), (2, 3) and (3, ∞). For interval (- ∞, 1), f'(x) < 0 For interval (1, 2), f'(x) > 0 For interval (2, 3), f'(x) < 0 For interval (3, ∞), f'(x) > 0.
Also, as f(x) is a polynomial function, so it is continuous at x = 1, 2, 3…………. Hence, (i) function increases in [1, 2] and [3, ∞). (ii) function decreases in (-∞, 1 ] and [2, 3]
Question 24. Sand is pouring from the pipe at the rate of 12 cm3/s. The falling sand forms a cone on a ground in such a way that the height of cone is always one-sixth of radius of the base. How fast is the height of sand 5 cone increasing when the height is 4 cm? (Delhi 2011) Answer: Let V be the volume of cone, h be the height and r be the radius of base of the cone. Given, \(\frac{d V}{d t}\) = 12 cm 3 /s ……(i)
Also, height of cone = \(\frac{1}{6}\) × (radius of base of cone) ∴ h = \(\frac{1}{6}\)r or r = 6h ………..(ii)
We know that, volume of cone is given by V = \(\frac{1}{3}\)πr 2 h …(iii)
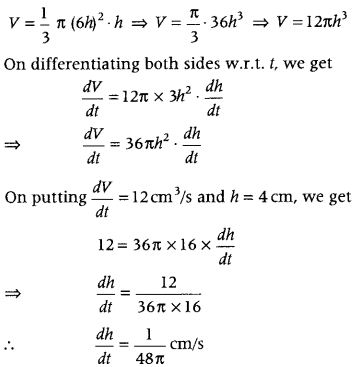
Question 25. If the radius of sphere is measured as t 9 cm with an error of 0.03 cm, then find the approximate error in calculating its surface area. (All India 2011) Answer: Let S be the surface area, r be the radius of the sphere. Given, r = 9 cm Then, dr = Approximate error in radius r = 0.03 cm and dS = Approximate error in surface area Now, we know that surface area of sphere is given by S = 4πr 2 On differentiating both sides w.r.t. r, we get \(\frac{d S}{d r}\) = 4π × 2r = 8πr dS = 8πr × dr ⇒ dS = 8π × 9 × 0.03 [∵ r = 9 cm and dr = 0.03 cm ] ⇒ dS = 72 × 0.03π ∴ dS = 2.16π cm 2 /cm Hence, approximate error in surface area is 2.16π cm 2 /cm.
Question 26. Find the intervals in which the function f(x) = sin x + cos x, 0 ≤ x ≤ 2π is strictly l increasing and strictly decreasing. (Foreign 2011) Answer: Strictly increasing in the intervals [0, \(\frac{\pi}{4}\)) and (\(\frac{5 \pi}{4}\), 2] strictly decreasing in the intervals \(\left(\frac{\pi}{4}, \frac{5 \pi}{4}\right)\)
Question 27. Show that the function f(x) = x 3 – 3x 2 + 3x, x ∈ R is increasing on R. (All India 2011C) Answer: We know that, a continuous function y = f(x) is said to be increasing on R, if \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) ≥ 0, ∀ x ∈ R. Given, y = x 3 – 3x 2 + 3x
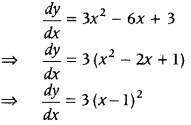
Question 28. Find the intervals in which the function f(x) = (x – 1 ) 3 (x – 2) 2 is (i) increasing, (ii) decreasing. (All India 2011C) Answer: Given, f(x) = (x – 1 ) 3 (x – 2) 2
On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get f'(x) = (x – 1) 3 .\(\frac{d}{d x}\)(x – 2) 2 + (x – 2) 2 .\(\frac{d}{d x}\)(x – 1) 3 ⇒ f'(x) = (x – 1) 3 – 2(x – 2)+ (x – 2) 2 3(x – 1) 2 = (x – 1) 2 (x – 2)[2(x – 1) + 3(x – 2)] = (x – 1) 2 (x – 2) (2x – 2 + 3x – 6) ⇒ f’(x) = (x – 1) 2 (x – 2){3x – 8)
Now, put f'(x) = 0 ⇒ (x – 1) 2 (x – 2) (5x – 8) = 0 Either (x – 1) 2 = 0 or x – 2 = 0 or 5x – 8 = 0 ∴ x = 1, \(\frac{8}{5}\), 2 Now, we find intervals and check in which interval f(x) is strictly increasing and strictly decreasing.
| Interval | f’(x) = (x – 1) (x – 2)(5x – 8) | Sign of f’(x) |
| x < 1 | (+) (-) (-) | +ve |
| 1 < x < \(\frac{8}{5}\) | (+) (-) (-) | + ve |
| \(\frac{8}{5}\) < x < 2 | (+) (-) (+) | – ve |
| x > 2 | (+) (+) (+) | + ve |
We know that, a function f(x) is said to be an strictly increasing function, if f'(x) > 0 and strictly decreasing, if f'(x) < 0. So, the given function f(x) is increasing on the intervals (-∞, 1) (1, \(\frac{8}{5}\)) and (2, ∞) and decreasing on continuous at x = 1, -, 2 Hence, f(x) is (i) increasing on intervals I (ii) decreasing on interval Note: Every strictly increasing (strictly decreasing) function is incresing (decreasing) but converse need not be true.
Question 29. Find the intervals in which the function f(x) = 2x 3 + 9x 2 + 12x + 20 is (i) increasing (ii) decreasing. (Delhi 2011c) Answer: Given function is f(x) = 2x 3 + 9x 2 + 12x + 20 On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get f(x) = 6x 2 + 18x + 12 Put f'(x) = 0, we get 6x 2 + 18x + 12 = 0 ⇒ 6(x 2 + 3x + 2) = 0 ⇒ 6 (x + 1) (x + 2) = 0 ⇒ (x + 1) (x + 2) = 0 ⇒ x + 1= 0 or x + 2 = 0 x = – 2, -1 Now, we find intervals and check in which interval f(x) is strictly increasing and strictly decreasing.
| Interval | f’(x) = 6(x + 1)(x + 2) | Sign of f’(x) |
| x < -2 | (+) (-) (-) | + ve |
| -2 < x < -1 | (+) (-) (+) | – ve |
| x > -1 | (+) (+) (+) | + ve |
We know that, a function f(x) is said to be an strictly increasing function, if f'(x) > 0 and strictly decreasing, if f'(x) < 0. So, given function is increasing on intervals (-∞,- 2) and (-1, ∞) and decreasing on interval (-2, -1). Since, f(x) is a polynomial function, so it is continuous at x = -1, – 2. Hence, given function is (i) increasing on intervals (-∞, – 2] and [-1, ∞). (ii) decreasing on interval [-2,-1 ].
Question 30. Find the intervals in which the function f(x) = 2x 3 – 9x 2 + 12x -15 is (i) increasing. (ii) decreasing. (Delhi 2011c) Answer: (i) The function increasing on intervals (- ∞, 1]and [2, ∞). (ii) The function decreasing on interval [1, 2]
Question 31. Find the intervals in which the function f(x) = 2x 3 – 15x 2 + 36x + 17 is increasing or decreasing. (All India 2010c) Answer: The function increasing on (- ∞, 2] and [3, ∞) and decreasing on [2, 3]
Question 32. Find the intervals in which the function f(x) = 2x 3 – 9x 2 + 12x + 15 is (i) increasing. (ii) decreasing. (All India 2010C) Answer: (i) The function increasing on (- ∞,1] and [2, ∞). (ii) The function decreasing on [1, 2]
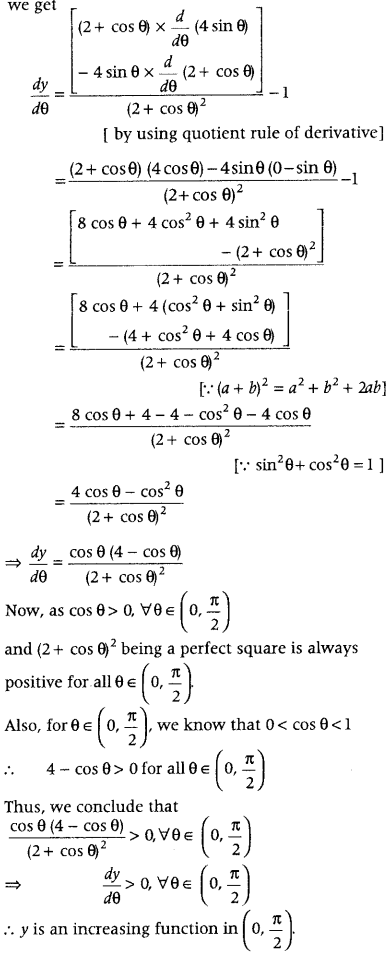
Question 34. Find the intervals in which the function f(x) = sin 3x – cos 3x, 0 < x < π, is strictly increasing or strictly decreasing. (Delhi 2016) Answer: Given, f(x) = sin 3x – cos 3x, 0 < x < π On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get f'(x) = 3cos 3x + 3sin 3x
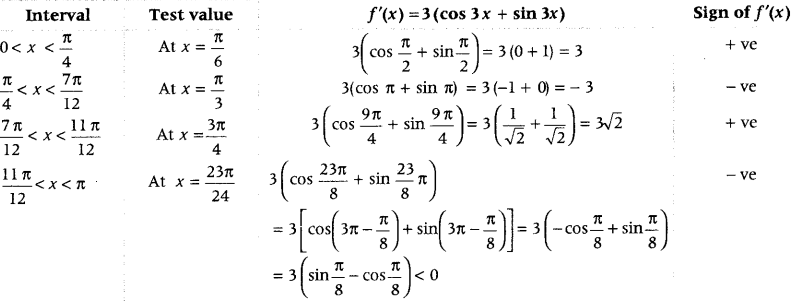
While f'(x) < 0 in \(\frac{\pi}{4}\) < x < \(\frac{7\pi}{12}\) and \(\frac{11 \pi}{12}\) < x < π So, f(x) is strictly decreasing in the intervals \(\left(\frac{\pi}{4}, \frac{7 \pi}{12}\right)\) and (\(\frac{11 \pi}{12}\), π)
Question 35. Prove that the function f defined by f(x) = x 2 – x + 1 is neither increasing nor decreasing in (-1, 1). Hence, find the intervals in which f(x) is (i) strictly increasing. (ii) strictly decreasing. (Delhi 2014C) Answer: Given function is f(x) = x 2 – x + 1. On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get f'(x) = 2x – 1 On putting f'(x) = 0 ⇒ 2x – 1 = 0 ⇒ x = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Now, we find intervals in which f(x) is strictly increasing or strictly decreasing.
| Interval | f'(x) = (2x – 1) | Sign of f'(x) |
| x < \(\frac{1}{2}\) | (-) | -ve |
| x > \(\frac{1}{2}\) | (+) | +ve |
Here, f(x) is strictly increasing on (\(\frac{1}{2}\), ∞) and f(x) is strictly decreasing on (- ∞, \(\frac{1}{2}\)) ⇒ f(x) is strictly increasing on (\(\frac{1}{2}\), 1) and f(x) is strictly decreasing on (-1, \(\frac{1}{2}\)) ∴ f'(x) does not have same sign throughout the interval (-1, 1). Thus, f(x) is neither increasing nor decreasing in (-1, 1).
Question 36. Find the intervals in which the function f(x) = 20 – 9x + 6x 2 – x 3 is (i) strictly increasing. (ii) strictly decreasing. (All India 2010) Answer: Given function is f(x) = 20 – 9x + 6x 2 – x 3 . On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get f'(x) = – 9 + 12x – 3x 2 On putting f'(x) = 0, we get -9 + 12x – 3x 2 = 0 ⇒ -3(x 2 – 4x + 3) = 0 ⇒ -3(x – 1)(x – 3) = 0 ⇒ (x – 1)(x – 3) = 0 ⇒ x – 1 = 0 or x – 3 = 0 ⇒ x = 1 or 3 Now, we find intervals in which f(x) is strictly increasing or strictly decreasing.
| Interval | F(x) = – 3 (x -1) (x – 3) | Sign of f'(x) |
| x < 1 | (-) (-) (-) | – ve |
| 1< x < 3 | (-) (+) (-) | + ve |
| x > 3 | (-) (+) (+) | – ve |
We know that, a function f(x) is said to be strictly increasing when f'(x) > 0 and it is said to be strictly decreasing, if f'(x) < 0. So, the given function f(x) is (i) strictly increasing on the interval (1, 3) and (ii) strictly decreasing on the intervals (-∞, 1) and (3, ∞).
Tangents and Normals
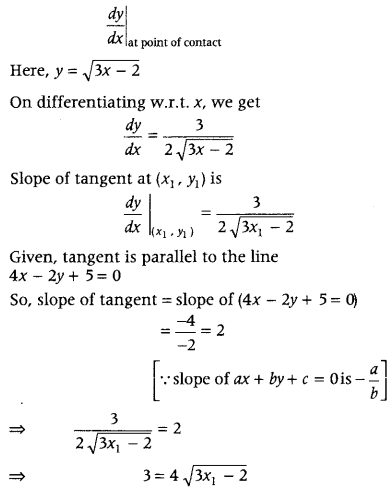
Since, point (x 1 , y 1 ) is on the curv, therefore y 1 = \(\sqrt{3 x_{1}-2}\) ⇒ y 1 = \(\sqrt{3 \times \frac{41}{48}-2}=\frac{3}{4}\) Hence, the point is (x 1 , y 1 )
Now, equation of the tangent is given by y – y 1 = m(x – x 1 ) ⇒ y – \(\frac{3}{4}\) = 2(x – \(\frac{41}{48}\)) ⇒ \(\frac{4 y-3}{4}=\frac{48 x-41}{24}\) ⇒ \(\frac{24}{4}\)(4y – 3) = 48x – 41 ⇒ 6(4y – 3) = 48x – 41 ⇒ 48x – 41 – 24y + 18 = 0 ⇒ 48x – 24y = 23, which is the required equation of the tangent.
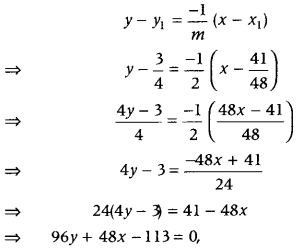
On differentiating w.r.t. x, we get 2x = 4\(\frac{d y}{d x}\) ⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}=\frac{2 x}{4}=\frac{x}{2}\)
Slope of normal = \(-\frac{1}{\frac{d y}{d x}}=-\frac{1}{\frac{x}{2}}=-\frac{2}{x}\) Let (h, k) be the point where normal and curve intersect.
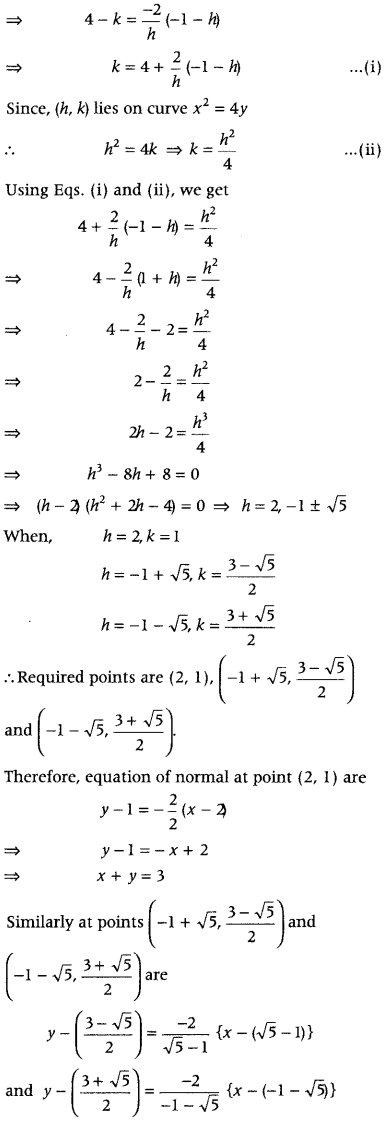
Question 3. Find the equations of the tangent and the normal to the curve 16x 2 + 9y 2 = 145 at the point (x 1 , y 1 ), where x 1 = 2 and y 1 > 0. (CBSE 2018) Answer: Given equation of curve is 16x 2 + 9y 2 = 145 Clearly, when x = 2, then 16(2) 2 + 9y 2 =145 9y 2 = 145 – 64 ⇒ 9y 2 = 81 ⇒ y 2 = 9 ⇒ y = ±3 [taking square root on both sides] But it is given that y 1 > 0 y = 3
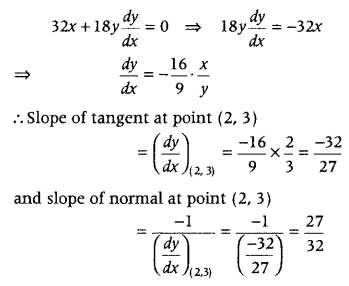
Question 4. Find the angle of intersection of the curves x 2 + y 2 = 4 and (x – 2) 2 + y 2 = 4, at the point in the first quadrant. (CBSE 2018C) Answer: Given curves are x 2 + y 2 = 4 and (x – 2) 2 + y 2 = 4 From Eqs. (i) and (ii), we get x 2 + 4 – 4x + y 2 = 4 ⇒ 4 – 4x = 0 ⇒ x = 1
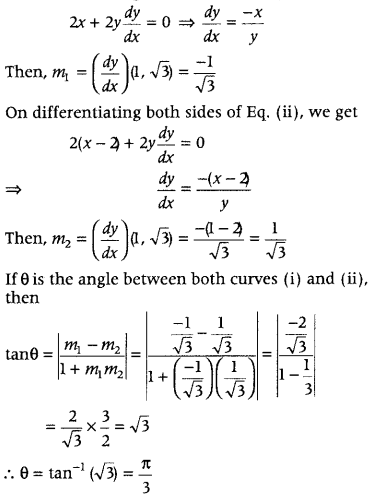
Question 6. Find the equation of tangents to the curve y = x 3 + 2x – 4 which are perpendicular to the line x + 14y – 3 = 0. (All India 2016) Answer: Given equation of curve is y = x 3 + 2x – 4
On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 3x 2 + 2
∴ The slope of required tangent is m 1 = \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 3x 2 + 2
Now, slope of line x + 14y – 3 = 0 or y = \(-\frac{x}{14}+\frac{3}{14}\) is m 2 = \(-\frac{1}{14}\)
Since, the required tangent is perpendicular to the line x + 14y -3=0. ∴ m 1 m 2 = -1 ⇒ (3x 2 + 2) × \(\left(-\frac{1}{14}\right)\) = -1 ⇒ 3x 2 + 2 = 14 ⇒ 3x 2 = 12 ⇒ x 2 = 4 ⇒ x =± 2
When x = 2, then y = 2 3 + 2 × 2- 4= 8 + 4 – 4 = 8
When x = – 2, then y = (-2) 3 + 2 × (-2) – 4 = -8 – 4 – 4 = -16 ∴ Points of contact are (2, 8) and (- 2, -16).
Now, equation of tangent at point (2, 8) is ⇒ y – 8 = \(\left(\frac{d y}{d x}\right)_{(2,8)}\) (x – 2) ⇒ y – 8 = ( 3 × 2 2 + 2)(x – 2) ⇒ y – 8 = 14(x – 2) ⇒ y = 14x – 20
and equation of tangent at point (- 2, -16) is ⇒ y + 16 = \(\frac{d y}{d x}_{(-2,-16)}\) (x + 2) ⇒ y + 16 = [3 (- 2) 2 + 2](x + 2) ⇒ y + 16 = 14 (x + 2) ⇒ y = 14x + 12 Hence, the required equation of tangents are y = 14x – 20 and y = 14x + 12
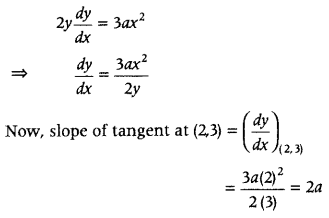
Question 8. Find the point on the curve 9y 2 = x 3 , where the normal to the curve makes equal intercepts on the axes. (Foreign 2015) Answer: Given curve is 9y 2 = x 3 …(i) On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get 9 × 2y\(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 3x 2 ⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}=\frac{3 x^{2}}{18 y}=\frac{x^{2}}{6 y}\) Let (x 1 , y 1 ) be the required point on the curve (i).

Question 9. Find the equations of the tangent and normal to the curves x = a sin 3 θ and y = a cos 3 θ at θ = \(\frac{\pi}{4}\). (Delhi 2014) Answer: Given, x = a sin 3 θ On differentiating both sides w.r.t. θ, we get \(\frac{d x}{d \theta}\) = a(3sin 2 θ cos θ) ⇒ \(\frac{d x}{d \theta}\) = 3a sin 2 θ cos θ and y = a cos 3 θ
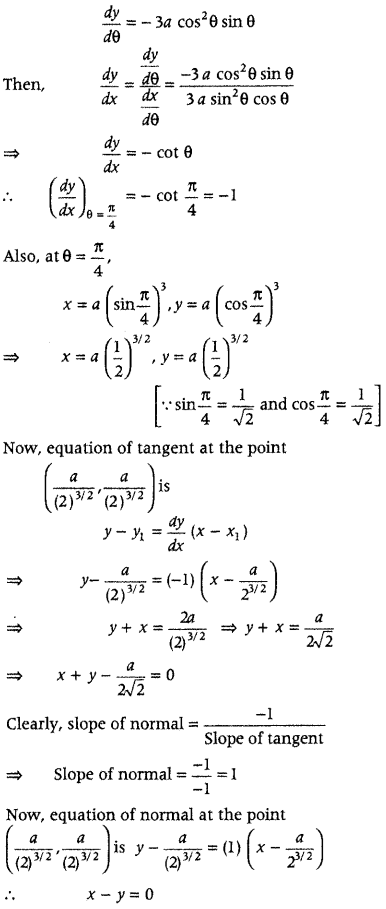
Question 10. Find the equations of the tangent and normal to the curves \(\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}-\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}\) = 1 at the point (√2a, b). (Delhi 2014) Answer: Given equation of curves is \(\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}-\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}\) = 1
On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get \(\frac{2 x}{a^{2}}-\frac{2 y}{b^{2}} \cdot \frac{d y}{d x}\) = 0 ⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}=\frac{b^{2} x}{a^{2} y}\)
Slope of the tangent at point (√2a, b) is \(\left(\frac{d y}{d x}\right)_{(\sqrt{2} a, b)}=\frac{\sqrt{2} a b^{2}}{b a^{2}}=\frac{\sqrt{2} b}{a}\)
Hence, the equation of the tangent at point (√2a, b) is y – b = \(\frac{\sqrt{2} b}{a}\)(x – √2a) ⇒ a (y- b) = √2 b (x – √2a) ⇒ ay – ab = √2 bx – 2ab ⇒ √2bx – ay – ab = 0
Now, the slope of the normal at point (√2a, b) = \(\frac{-1}{\text { Slope of tangent }}=\frac{-1}{\sqrt{2} b / a}\)
Hence, the equation of the normal at point(√2a, b) is (y – b) = \(-\frac{a}{\sqrt{2} b}\)(x – √2a) ⇒ √2b(y – b) = -a (x – √2a) ⇒ √2 by – √2 b 2 = -ax + √2 a 2 ∴ ax + √2by – √2 (a 2 + b 2 ) = 0
Question 11. Find the points on curve y = x 3 – 11x + 5 at which equation of tangent is y = x – 11. (Delhi 2012C) Answer: First, find the slope of tangent to the given curve and of given equation of tangent, then equate them to get value of x. Put value of x in given curve to find required points.
Given, equation of curve is y = x 3 – 11x + 5 ………(i)
Slope of the tangent at any point (x, y) is given by \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 3x – 11 ………….(ii)
Also, slope of the tangent y = x – 11 is 1. ∴ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 1 ⇒ 3x 2 – 11 = 1 [frpm Eq. (i)] ⇒ 3x 2 = 12 ⇒ x 2 = 4 ⇒ x = ±2
When x = 2, then y = (2) 3 -11(2) + 5 = 8 – 22 + 5 = – 9 When x = – 2, then y = (-2) 3 -11 (-2) + 5 = -8 + 22 + 5 = 19 Since, the points (-2, 19) does not lies on the line y = x – 1 Hence, the required points on the curve are (2, -9).
Question 12. Find the points on the curve x 2 + y 2 – 2x – 3 = 0 at which tangent is parallel to X-axis. (Delhi 2011) Answer: As tangent is parallel to X-axis, put \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 0 and find value of x from it. Then, put this value of x in the equation of the given curve and find value of y.
Given equation of curve is x 2 + y 2 – 2x – 3 = 0
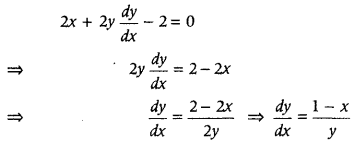
On putting \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 0, we get 1 – x = 0 ⇒ x = 1 Now, on putting x = 1 in Eq. (i), we get 1 + y 2 – 2 – 3 = 0 y 2 = 4 ⇒ y = ±2 Hence, the required points are (1, 2) and (1, -2).
Question 13. Find the points on the curve y = x 3 at which the slope of the tangent is equal to y-coordinate of the point. (Foreign 2011) Answer: First, determine the derivative and put \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = y and then find the value of x from it. Further, put this value of x in the equation of the given curve and find the value of y.
Given equation of curve is y = x 3 . …….(i) On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 3x 2
∴ Slope of tangent at any point (x, y) is \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 3x 2
Now, given that Slope of tangent = y-coordinate of the point ⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = y ⇒ 3x 2 = y [∵\(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 3x 2 ] ⇒ 3x 2 = x 3 [∵ y = x 3 ] ⇒ 3x 2 – x 3 = 0 ⇒ x 3 (3 – x) = 0 ⇒ Either x 2 = 0 or 3 – x = 0 x = 0, 3
Now, on putting x = 0 and 3 in Eq. (i), we get y = (0) 3 = 0 [at x = 0] and y = (3) 3 = 27 Hence, the required points are (0, 0) and (3, 27).
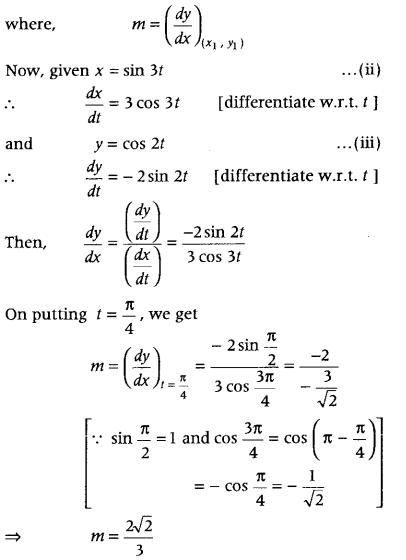
Question 17. Find the equation of tangent to the curve y = x 4 – 6x 3 + 13x 2 – 10x + 5 at point x = 1, y = 0. (Delhi 2011C) Answer: Given equation of curve is y = x 4 – 6x 3 + 13x 2 – 10x + 5
On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 4x 3 – 18x 2 + 26x – 10
Slope of a tangent at point (1, 0) is m = \(\left[\frac{d y}{d x}\right]_{x=1}\) = 4 – 18 + 26 – 10 = 2
∴ Equation of tangent at point (1,0) having slope 2 is y – 0 = 2(x – 1) ⇒ y = 2x – 2 Hence, required equation of tangent is 2x – y = 2
Question 18. Find the points on the curve y = [x(x – 2)] 2 , where the tangent is parallel to X-axis. (Delhi 2010) Answer: We have to find the points on the given curve where the tangent is parallel to X-axis. We know that, when a tangent is parallel to X-axis, then \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 0 ⇒ \(\frac{d}{d x}\)(x 2 – 2x) 2 = 0 ⇒ 2(x 2 – 2x)(2x – 2) = 0 ⇒ x = 0, 1, 2 When x = 0, then y = [0(-2)] 2 = 0 When x = 1, then y = [1 – 2(1)] 2 = 1 When x = 2, then y = [2 2 – 2 × 2] 2 = 0 Hence, the tangent is parallel to X-axis at the points (0, 0), (1, 1) and (2, 0).
Question 19. Find the equation of tangent to the curve y = \(\frac{x-7}{x^{2}-5 x+6}\) at the point, where it cuts the X-axis. (All India 2010C, 2010) Answer: Given equation of curves is y = \(\frac{x-7}{x^{2}-5 x+6}\) ……….(i)
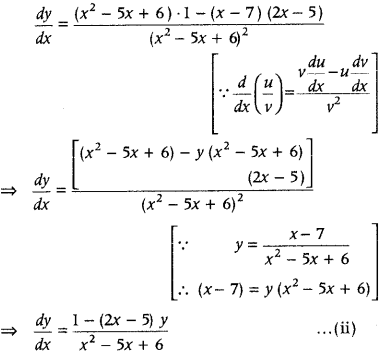
Hence, the required equation of tangent passing through the point (7, 0) having slope 1/20 is y – o = \(\frac{1}{20}\)(x – 7) ⇒ 20y = x – 7 ∴ x – 20y = 7
Question 20. Find the equations of the normal to the curve y = x 3 + 2x + 6, which are parallel to line x + 14y + 4 = 0. (Delhi 2010) Answer: First, find the slope of normal to curve, i.e. \(\frac{-1}{d y / d x}\) and put them equal to the slope of line, simplify them and find the values of x and y. Further, use the equation y – y 1 = Slope of normal (x – x 1 ).
Given equation of curve is y = x 2 + 2x + 6 ……..(i) and the given equation of line is x + 14y + 4= 0
On differentiating both sides of Eq. (i) w.r.t. x, we get \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 3x 2 + 2 Slope of normal = \(\frac{-1}{\left(\frac{d y}{d x}\right)}=\frac{-1}{3 x^{2}+2}\)
Also, slope of the line x + 14y + 4 = 0 is – \(\frac{1}{14}\) [∵ slope of the line Ax + By + C = 0 is – \(\frac{A}{B}\)] We know that, if two lines are parallel, then their slopes are equal. ∴ \(-\frac{1}{3 x^{2}+2}=-\frac{1}{14}\) ⇒ 3x 2 + 2 = 14 ⇒ 3x 2 = 12 ⇒ x 2 = 4 ⇒ x = ± 2
When x = 2, then from Eq. (i), y = (2) 3 + 2(2) + 6 = 8 + 4 + 6 = 18 and when x = – 2, then from Eq. (i), y = (-2) 3 + 2(-2) + 6 = -8 – 4 + 6 = – 6
∴ Normal passes through (2, 18) and (-2, -6). Also, slope of normal = – \(\frac{1}{14}\) Hence, equation of normal at point (2, 18) is y – 18 = – \(\frac{1}{14}\)(x – 2) ⇒ 14y – 252 = – x + 2 ⇒ x + 14 y = 254
and equation of normal at point (-2, -6) is y + 6 = – \(\frac{1}{14}\) (x + 2) ⇒ 14y + 84 = -x – 2 ⇒ x + 14y = -86 Hence, the two equations of normal are x + 14y = 254 and x + 14y = – 86.
Question 21. Find the angle of intersection of the curves y 2 = 4ax and x 2 = 4by. (Foreign 2016) Answer: Given equations of curves are y 2 = 4ax …(i) and x 2 = 4 by … (ii) Clearly, the angle of intersection of curves (i) and (ii) is the angle between the tangents to the curves at the point of intersection. So, let us first find the intersection point of given curves.
On substituting the value of y from Eq. (ii) in Eq. (i), we get \(\left(\frac{x^{2}}{4 b}\right)^{2}\) = 4ax ⇒ \(\frac{x^{4}}{16 b^{2}}\) = 4ax ⇒ x 4 = 64ab 2 x ⇒ x 4 – 64ab 2 x = 0 ⇒ x(x 2 – 64ab 2 ) = 0 x = 0 or x = 4a 1/3 b 2/3 Clearly, when x = 0, then from Eq. (i), y = 0 and when x = 4a 1/3 b 2/3 , then from Eq. (i), y 2 =16a 4/3 b 2/3 ⇒ y = 4a 2/3 b 1/3
Thus, the points of intersection are (0, 0) and (4a 1/3 b 2/3 , 4a 2/3 b 1/3 ). Now, let us find the angle of intersection at (0, 0) and (4a 1/3 b 2/3 , 4a 2/3 b 1/3 ). Let be the slope of tangent to the curve (i) and m 2 be the slope of tangent to the curve (ii).
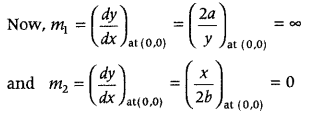
On squaring and adding Eqs. (iii) and (iv), we get cos 2 (x 1 + y 1 ) + sin 2 (x 1 + y 1 ) = 1 + y 1 2 1 + y 2 1 = 1 ⇒ y 2 1 = o ⇒ y 1 = o
On putting y 1 = 0 in Eq. (iii), we get cosx 1 = 0 ⇒ x 1 = \(\frac{\pi}{2}, \frac{3 \pi}{2}, \frac{-\pi}{2}, \frac{-3 \pi}{2}\) [∵ -2π ≤ x ≤ 2π] But only x 1 = \(\frac{\pi}{2}\) and \(\frac{-3 \pi}{2}\) satisfy Eq. (iv).
Hence, the points of contact are (\(\frac{\pi}{2}\), o) and (\(\frac{-3 \pi}{2}\), 0) ∴ Equations of tangents are y – 0 = –\(\frac{1}{2}\)(x – \(\frac{\pi}{2}\)) and y -0 = –\(\frac{1}{2}\)(x + \(\frac{-3 \pi}{2}\))
Question 23. Find the value of p for which the curves x 2 = 9p (9 – y) and x 2 = p (y + 1) cut each other at right angles. (All India 2015) Answer: Given equations of curves are x 2 = 9p (9 – y) …….(i) and x 2 = p (y + 1) ………….(ii)
As, these curves cut each other at right angle, therefore their tangent at point of intersection are perpendicular to each other. So, let us first find the point of intersection and slope of tangents to the curves. From Eqs. (i) and (ii), we get 9p(9 – y) =p(y + 1) ∴ 9(9 – y) = y + 1 [∵ p ≠ 0, as if p = 0, then curves becomes straight, which will be parallel] ⇒ 81 – 9y = y + 1 ⇒ 80 = 10y ⇒ y = 8
On substituting the value of yin Eq. (i),we get x 2 = 9p ⇒ x = + 3 Thus, the point of intersection are (3√p, 8) and (-3√p, 8)
Now, consider Eq.(i),we get \(\frac{x^{2}}{9 p}\) = 9 – y ⇒ y = 9 – \(\frac{x^{2}}{9 p}\)
On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get \(\frac{d y}{d x}=\frac{-2 x}{9 p}\) ……(iii)
From Eq. (ii), we get \(\frac{x^{2}}{p}\) = y + 1 ⇒ y = \(\frac{x^{2}}{p}\) – 1
On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get \(\frac{d y}{d x}=\frac{2 x}{p}\) ………(iv)
Now, for intersection point (3√p, 8), we have slope of tangent to the first curve = \(\frac{-2(3 \sqrt{p})}{9 p}=\frac{-6 \sqrt{p}}{9 p}\) [using Eq. (iii)]
and slope of tangent to the second curve = \(\frac{2(3 \sqrt{p})}{p}=\frac{6 \sqrt{p}}{p}\) [using Eq. (iv)]
∵ Tangents are perpendicular to each other. Then, Slope of first curve x Slope of second curve = -1 ∴ \(\frac{-6 \sqrt{p}}{9 p} \times \frac{6 \sqrt{p}}{p}\) = -1 ⇒ \(\frac{4}{p}\) = 1 ⇒ p = 4
And for intersection point (3√p, 8), we have slope of tangent to the first curve = \(\frac{-2(-3 \sqrt{p})}{9 p}=\frac{6 \sqrt{p}}{9 p}\) [using Eq. (iii)]
and slope of tangent to the second curve = \(\frac{2(-3 \sqrt{p})}{p}=\frac{-6 \sqrt{p}}{p}\) [using Eq. (iv)]
Tangents are perpendicular to each other. Then, \(\frac{6 \sqrt{p}}{9 p} \times \frac{-6 \sqrt{p}}{p}\) = -1 [∵ m 1 m 2 = -1] ⇒ \(\frac{4}{p}\) = 1 ⇒ p = 4 Hence, the value of p is 4.
Question 24. Find the equations of the tangent to the curve y = x 2 – 2x + 7 which is (i) parallel to the line 2x – y + 9 = 0. (ii) perpendicular to the line 5y – 15x = 13. (Delhi 2014C) Answer: Given equation of curve is y = x 2 – 2x + 7
On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 2x – 2
(i) Given, equation of the line is 2x – y + 9 = 0 ⇒ y = 2x + 9 which is of the form y = mx + c.
∴ Slope of the line is m = 2 If a tangent is parallel to the line, then slope of tangent is equal to the slope of the line. Therefore, \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = m ⇒ 2x – 2 = 2 ⇒ x = 2 When x = 2, then from Eq. (i), we get y = 2 2 – 2 × 2 + 7 ⇒ y = 7 The point on the given curve at which tangent is parallel to given line is (2, 7) and the equation of the tangent is y – 7 = 2(x – 2) [∵ y – y 1 =m(x- x 1 )] ⇒ 2x – y + 3 = 0 Hence, the equation of the tangent line to the given curve which is parallel to line 2x – y + 9 = 0 is y – 2x – 3 = 0.
(ii) The equation of the given line is 5y – 15x = 13 ⇒ y = \(\frac{15 x+13}{5}\) = 3x + \(\frac{13}{5}\) which is of the form y = mx + c
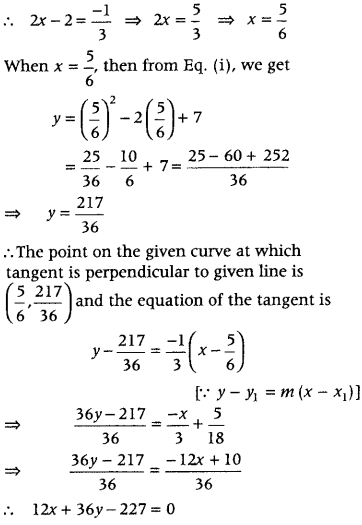
Question 25. Find the equation of the normal at a point on the curve x 2 = 4y, which passes through the point (1, 2). Also, find the equation of the corresponding tangent. (Delhi 2013) Answer: Given curve is x 2 = 4y. On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x,we get 2x = 4\(\frac{d y}{d x}\) ⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) Let (h, k) be the coordinates of the point of contact of the normal to the curve x2 = 4y. Then, slope of the tangent at (h, k) is given by \(\left(\frac{d y}{d x}\right)_{(h, k)}=\frac{h}{2}\) and slope of the normal ay (h, k) = \(\frac{-1}{d y / d x}=\frac{-2}{h}\)
Therefore, the equation of normal at (h, k) is y – k = \(\frac{-2}{h}\)(x – h) ………….(i) [∵ Equation of normal in slope form is y – y 1 = \(\frac{-1}{m}\)(x – x 1 )] Since, it passes through the point (1, 2), so on putting x =1 and y = 2, we get 2 – k = \(\frac{-2}{h}\)(1 – h) ⇒ k = 2 + Since, (h, k) also lies on the curve x 2 = 4y, therefore h 2 = 4k ………(iii)
On solving Eqs.(ii) and (iii), we get h = 2 and k = 1
Substituting the values of h and k in Eq.(i), the required equation of normal is y – 1 = \(\frac{-2}{2}\)(x – 2) ⇒ x + y = 3
Now, equation of tangent at (h, k) is y – k = \(\frac{h}{2}\)(x – h)
On putting h = 2 and k = 1, we get y – 1 = \(\frac{2}{2}\)(x – 2) ⇒ y – 1 = x – 2 ∴ y = x – 1
Question 26. Find the equations of tangents to the curve 3x 2 – y 2 = 8, which passes through the point [\(\frac{4}{3}\), 0 ]. (All India 2013) Answer: First, differentiate the given curve with respect to x and determine \(\frac{d y}{d x}\). Then, find the equation of tangent at (x, y,}. Now, as this equation is passes through given point (x0, y0), so this point will satisfy the tangent and curve also. Further, simplify it and get the required equations of tangent.
Given equation of curve is 3x 2 – y 2 = 8
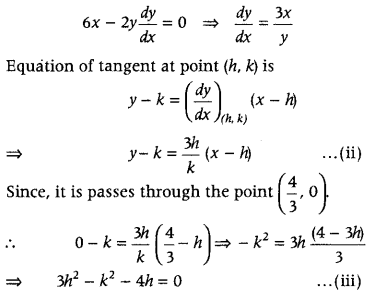
Now, on solving Eqs. (iii) and (iv), we get 4h = 8 ⇒ h = 2
On putting h = 2 in Eq. (iv), we get 3 (2) 2 – k 2 = 8 ⇒ k 2 = 4 ⇒ k = ±2
Now, putting the values of h and k in Eq. (h), we get ⇒ y = (±2) = \(\frac{3(2)}{\pm 2}\)(x – 2) ⇒ y + 2 = ±3(x – 2) ⇒ y = ± 3(x – 2) ± 2 ⇒ y = ± {3(x – 2) + 2} ⇒ y = ± (3x – 6 + 2) ⇒ y = ± (3x – 4) Hence, y = – 3x + 4 and y = 3x – 4 are two required equations of tangent.
Question 27. Find all the points on the curve y = 4x 3 – 2x 5 at which the tangent passes through the origin. (Delhi 2013C) Answer: Given curve is y = 4x 3 – 2x 5 . ………(i)
Let any point on the curve be (x 1 ,y 1 ). So, it satisfies Eq. (i). ∴ y 1 = 4x 1 3 – 2x 1 5 ………(ii)
On differentiating both sides of Eq. (i), we get \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 12x 2 – 10x 4
Equation of tangent at point (x 1 , y 1 ) is y – y 1 = \(\left(\frac{d y}{d x}\right)_{\left(x_{1}, y_{1}\right)}\) (x – x 1 ) ⇒ y – y 1 = [12(x 1 ) 2 – 10(x 1 ) 4 ](x – x 1 )
Since, it passes through the origin. ∴ 0 – y 1 = (12x 1 2 – 10x 1 4 )(0 – x 1 ) ⇒ y 1 = (12x 1 2 – 10x 1 4 )x 1 ………(iii)
From Eqs. (ii) and (iii), we get (12x 2 1 – 10x 4 1 )x 1 = 4x 1 3 – 2x 1 5 ⇒ 2x 1 3 (6 – 5x 1 2 ) = 2x 1 3 (2 – x 1 2 ) ⇒ 2x 1 3 (4 – 4x 1 2 ) = 0 ⇒ x 1 = 0 or 4 – 4x 1 2 = 0 ∴ x 1 = 0 or x 1 = 1
On putting the values of x, = 0,1 and -1 respectively in Eq. (ii), we get At x 1 = 0, y 1 = 0 At x 1 = 1, y 1 = 4(1) 3 -2(1) 5 = 4 – 2 = 2 and at x 1 = (-1), y 1 = 4(-1) 3 – 2(-1) 5 = 4 (-1) – 2 (-1) = -4+ 2 = -2 Hence, all points on the curve at which the tangent passes through origin, are (0, 0), (1, 2) and (-1,-2).
Question 28. Prove that the curves x = y 2 and xy = k cut at the right angles, if 8k 2 = 1. (Delhi 2013C) Answer: Given equations of curves are x = y 2 …(i) and xy = k …(ii)
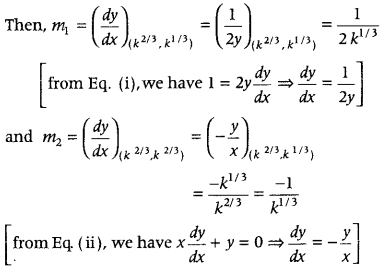
On cubing both sides, we get 8k 2 = 1 Hence Proved.
Question 29. Prove that all normals to the curves x = a cos t + at sin t and y = a sin t – at cos t are at a constant distance ‘a’ from the origin. (All India 2013C) Answer: Given equations of curves are x = a cost + at sin t and y = asin t – at cost
On differentiating x and y separately w.r.t. t, we get \(\frac{d x}{d t}\) = -asin t + a(t cost + sin t) = -a sin t + a tcos t+ a sin t = at cost and \(\frac{d y}{d t}\) = acos t – a[t(-sin t) + cos t)] = a cost + at sin t – acost = at sin t
Now \(\frac{d y}{d x}=\frac{\frac{d y}{d t}}{\frac{d x}{d t}}=\frac{a t \sin t}{a t \cos t}\) = tan t = Slope of normal at any point t = \(\frac{-1}{\tan t}\) = -cot t
Now, equation of normal at any point t is given by y – (asin t – at cos t) = – cot t[x – (a cos t + atsint)] ⇒ y – asin t + at cos t = \(\frac{-\cos t}{\sin t}\) (x – acost – at sin t) ⇒ y sint – a sin 2 t + at cost sint = -x cost + acos 2 t + at sint cost ⇒ x cost + y sint = a(cos 2 t + sin 2 t) ⇒ x cost + ysint = a [∵ sin 2 θ + cos 2 θ = 1] ∴ xcos t + ysin t – a = 0 Now, the distance of normal from the origin is given by \(\frac{|0 \cdot \cos t+0 \cdot \sin t-a|}{\sqrt{\cos ^{2} t+\sin ^{2} t}}=\frac{|-a|}{\sqrt{1}}\) = a
Question 30. Find the equations of tangent and normal to the curve x = 1 – cos θ, y = θ – sin θ at θ = \(\frac{\pi}{4}\) Answer: First, differentiate the given curve with respect to and then determine \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) at θ = \(\frac{\pi}{4}\). Further, use the formula, equation of tangent at (x 1 , y 1 ) is y – y 1 = m(x – x 1 ) and equation of normal at (x 1 , y 1 ) is y – y 1 = –\(\frac{1}{m}\) (x – x 1 ).
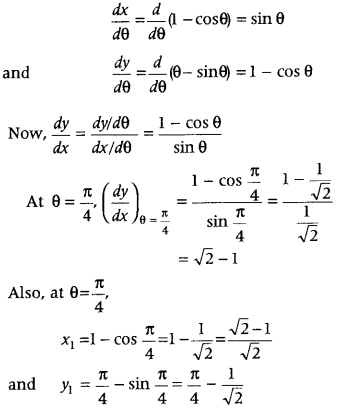
Maxima and Minima
Question 2. The sum of the perimeters of a circle and square is k, where k is some constant. Prove that the sum of their areas is least, when the side of the square is double the radius of the circle. (Delhi 2014C) Answer: Let r be the radius of circle and x be the side of a square. Then, given that Perimeter of square + Perimeter of circle = k (constant) i.e. 4x + 2πr = k ⇒ x = \(\frac{k-2 \pi r}{4}\) ……(i)
Let A denotes the sum of their areas. ∴ Area, A = area of a square + area of circle ∴ A = x 2 + πr 2 …(ii)
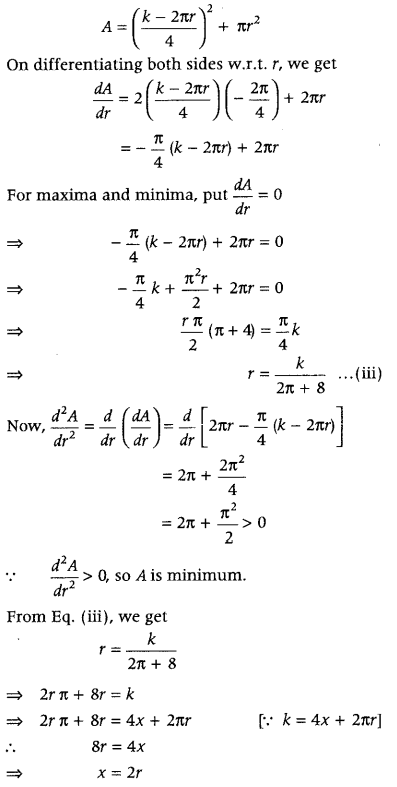
Question 3. A tank with rectangular base and rectangular sides, open at the top is to be constructed, so that its depth is 2 m and volume is 8 m 3 . If building of tank cost ₹ 70 per sq m for the base and ₹ 45 per sq m for sides. What is the cost of least expensive tank? (Delhi 2019) Answer: Let x m be the length, y m be the breadth and h=2m be the depth of the tank. Let ₹ H be the total cost for building the tank. Now, given that h = 2 m and volume of tank = 8 m 3 . Clearly, area of the rectangular base of the tank = length × breadth = xy m 2
and the area of the four rectangular sides = 2 (length + breadth) × height = 2 (x + y) × 2= 4 (x + y) m 2
∴ Total cost, H = 70 × xy + 45 × 4 (x + y) ⇒ H = 70xy + 180 (x + y) …………(i)
Also, volume of tank = 8 m 3 ⇒ l × b × h = 8 ⇒ x × y × 2 = 8 ⇒ y = \(\frac{4}{x}\) …..(ii)
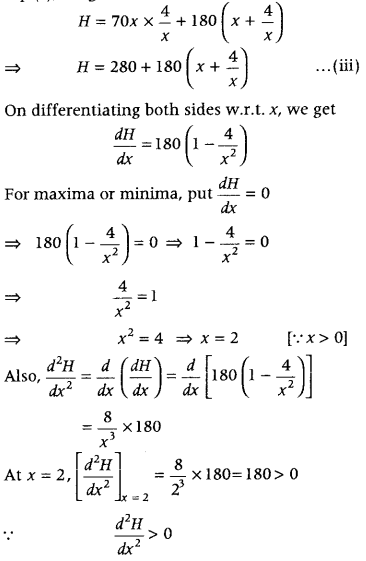
Question 6. Show that the altitude of the right circular cone of maximum volume that can he inscribed in a sphere of radius r is \(\frac{4r}{3}\) Also, find the maximum volume in terms of volume of the sphere. (Delhi 2019, 2016) Or Show that the altitude of the right circular cone of maximum volume that can be inscribed in a sphere of radius r is \(\frac{4r}{3}\). Also, show that the maximum volume of the cone is \(\frac{8}{27}\) of the volume of the sphere. (All India 2014) Answer: Let R be the radius and h be the height of the cone, which inscribed in a sphere of radius r. ∴ OA = h – r
In ΔOAB, by Pythagoras theorem, we have r 2 = R 2 + (h – r) 2 ⇒ r = R 2 + h 2 + r 2 – 2rh ⇒ R 2 = 2rh – h 2 ……….(i)
Note that, to admit maximum light, area of window should be maximum. Here, area of window A = area of rectangle + area of semicircular region = 2x × y + \(\frac{1}{2}\)πx 2 ⇒ A = 2x\(\left(\frac{10-x(\pi+2)}{2}\right)\) + \(\frac{1}{2}\) πx 2 [from Eq. (i)] ⇒ A = 10x – x 2 (π + 2) + \(\frac{1}{2}\) πx 2
On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get dA \(\frac{d A}{d x}\) = 10 – 2x (π + 2) + πx = 10- 2x π – 4x + πx = 10 – πx – 4x ……(iii)
For maximum, Put \(\frac{d A}{d x}\) = 0 ⇒ 10 = πx + 4x ⇒ x = \(\frac{10}{\pi+4}\)
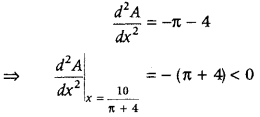
Question 8. Show that the surface area of a closed cuboid with square base and given volume is minimum, when it is a cube. (All India 2017) Answer: Let V be the fixed volume of a closed cuboid with length x, breadth x and height y. Then, V = x × x × y ⇒ y = \(\frac{V}{x^{2}}\) …………(i)
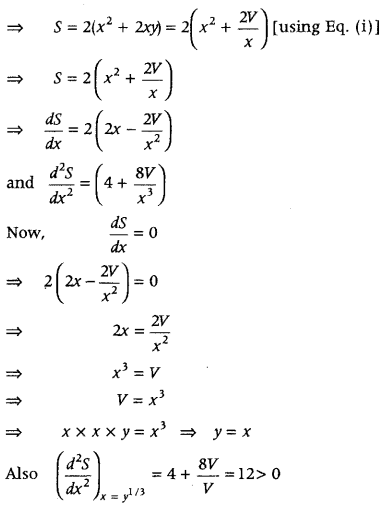
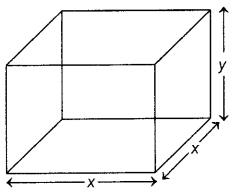
Let C denotes the cost of the box. C = 2x 2 × 5 + 4xy × 2.50 = 10x 2 + 10xy = 10x (x + y) = 10x(x + \(\frac{1024}{x^{2}}\)) = 10x 2 + \(\frac{10240}{x}\) ……..(i)
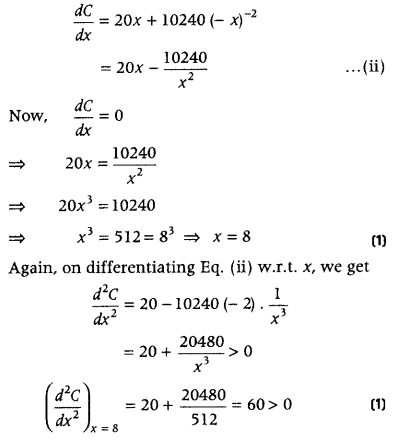
Now, when θ = tan -1 √2, then tan 2 θ = 2 ⇒ sin 2 θ = 2cos 2 θ
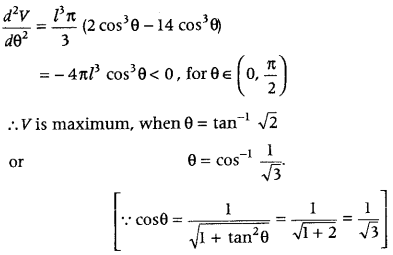
Now, perimeter (P) of ΔABC = AB + BC + AC = AE + BE + BD + DC + AF + FC = (AE +AF) + (BE + BD + DC + FC) = 2AE + 4BD …(i)
Consider ΔOEA, in this we have AE = \(\frac{O E}{\tan \theta}=\frac{r}{\tan \theta}\) and OA = \(\frac{r}{\sin \theta}\) and in ΔADB we have BD = AD tan θ = (AO + OD) tanθ = [\(\frac{r}{\sin \theta}\) + r)tan θ Now, P = 2.\(\frac{r}{\sin \theta}\) + 4(\(\frac{r}{\sin \theta}\) + r)tan θ [From Eq. (i)] ⇒ P(θ) = r(2 cot θ + 4 sec θ + 4 tan θ) …….(ii)
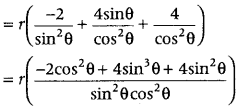
Question 15. Find the local maxima and local minima of the function f(x) = sin x – cos x, 0 ≤ x ≤ 2π. Also, find the local maximum and local minimum values. (Delhi 2015) Answer: We have, f(x) = sin x – cos x, 0< x < 2π On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get f'(x) = cosx + sinx ……….(i) For local maximum and local minimum, Put f'(x) = 0, i.e. cosx + sinx = 0 ⇒ cosx = – sinx ⇒ tanx = -1 ⇒ x = π – \(\frac{\pi}{4}\) or 2π – \(\frac{\pi}{4}\) ⇒ x = \(\frac{3 \pi}{4}\) or \(\frac{7 \pi}{4}\)
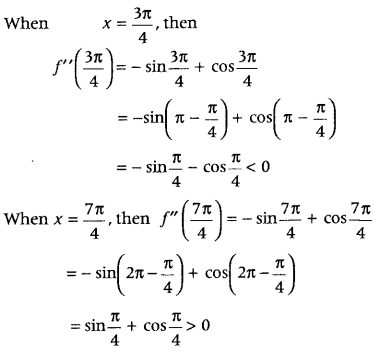
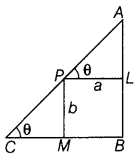
Question 18. A point on the hypotenuse of a right triangle is at distances a and b from the sides of the triangle. Show that the minimum length of the hypotenuse is (a 2/3 + b 2/3 ) 3/2 . (Delhi 2015C) Answer: Let P be a point on the hypotenuse AC of right angled ΔABC. Such that PL ⊥ AB and PL = a and PM ⊥ BC and PM = b. Let ∠APL = ∠ACB = 6 [say] Then, AP = a sec θ, PC = b cosec θ
Let l be the length of the hypotenuse, then l = AP + PC ⇒ l = a sec θ + b cosec θ, 0 < θ< \(\frac{\pi}{2}\)
On putting V 2 = 2π 2 r 6 /9 in Eq. (i), we get 2π 2 r 6 = π 2 r 4 h 2 ⇒ 2r 2 = h 2 ⇒ h = √2r ⇒ \(\frac{h}{r}\) = √2 ⇒ cot θ = √2 [from the figure, cot θ = \(\frac{h}{r}\).] ∴ θ = cot -1 √2 Hence, the semi-vertical angle of the right circular cone of given volume and least curved surface area is cot -1 √2. Hence proved.
Note: If square of any area is maximum (or minimum), then area is also maximum (or minimum).
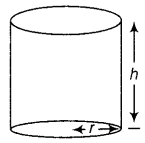
Question 29. Show that the right circular cone of least curved surface and given volume has an altitude equal to √2 times the radius of the base. (Delhi 2011) Answer: Let C denotes the curved surface area, r be the radius of base, h be the height and V be the volume of right circular cone. We know that, volume of cone is given by V = \(\frac{1}{3}\)πr 2 h ⇒ h = \(\frac{3 V}{\pi r^{2}}\) …(i) Also, the curved surface area of cone is given by C = ml, where l = \(\sqrt{r^{2}+h^{2}}\) is the slant height of cone. ∴ C = πr\(\sqrt{r^{2}+h^{2}}\)

Let A be the area of rectangle. ∴ A = (2x) (2y) [∵ area of rectangle = length x breadth] ⇒ A = 4 xy ⇒ A = 4x\(\sqrt{b^{2}-x^{2}}\) [∵ y = \(\sqrt{b^{2}-x^{2}}\)]

Question 32. Show that of all the rectangles with a given perimeter, the square has the largest area. (Delhi 2011) Answer: Let x and y be the lengths of two sides of a rectangle. Again, let P denotes its perimeter and A be the area of rectangle. Then, P = 2 (x + y) [∵ perimeter of rectangle = 2(l + b)] ⇒ P = 2x + 2y ⇒ y = \(\frac{P-2 x}{2}\) …..(i)
We know that, area of rectangle is given by A = xy ⇒ A = x\(\left(\frac{P-2 x}{2}\right)\) [by using Eq. (i)] ⇒ A = \(\left(\frac{P-2 x}{2}\right)\)
On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get \(\frac{d A}{d x}=\frac{P-4 x}{2}\)
For maxima or minima, put \(\frac{d A}{d x}\) = 0 ⇒ \(\frac{P-4 x}{2}\) = 0 ⇒ P = 4x ⇒ 2x + 2y = 4x [∵ P = 2x + 2y] ⇒ x = y
So, the rectangle is a square. Also, \(\frac{d^{2} A}{d x^{2}}=\frac{d}{d x}\left(\frac{P-4 x}{2}\right)\) = \(-\frac{4}{2}\) = -2 < 0 ⇒ A is maximum. Hence, area is maximum, when rectangle is a square. Hence proved.
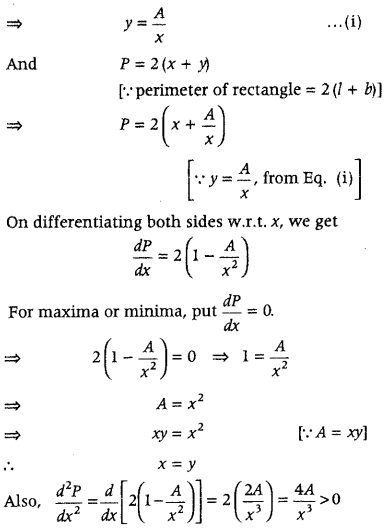
Question 35. Find the point on the curve y 2 = 2x which is at a minimum distance from the point (1, 4). (All India 2011) Answer: First, consider any point on the curve, use the, formula of distance between two points. Then, square both sides and eliminate one variable with i the help of given equation. Further, apply concept : of maxima and minima to find the required point.
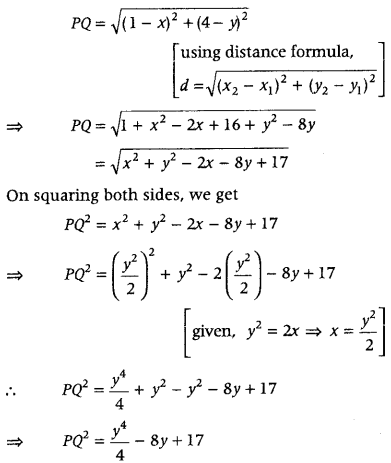
On differentiating both sides w.r.t. y, we get \(\frac{d Z}{d y}=\frac{4 y^{3}}{4}\) – 8 = y 3 – 8
For maxima or minima, put \(\frac{d Z}{d y}\) = 0 ⇒ y 3 – 8 = 0 ⇒ y 3 = 8 ⇒ y = 2 Also, \(\frac{d^{2} Z}{d y^{2}}=\frac{d}{d y}\)(y 3 – 8) = 3y 2
On putting y = 2, we get \(\left(\frac{d^{2} Z}{d y^{2}}\right)_{y=2}\) = 3(2) 2 = 12 >0 \(\frac{d^{2} Z}{d y^{2}}\) > 0
∴ Z is minimum and therefore PQ is also minimum as Z = PQ 2 . On putting y = 2 in the given equation, i.e. y 2 = 2x, we get (2) 2 = 2x ⇒ 4 = 2x ⇒ x = 2 Hence, the point which is at a minimum distance from point (1, 4) is P (2, 2).
Question 36. A wire of length 28 m is to be cut into two pieces. One of the two pieces is to be made into a square and the other into a circle. What should be the lengths of two pieces, so that the combined area of circle and square is minimum? (All India 2010) Answer: First, find length of circular part (or its circumference) and calculate the length of square part (or its perimeter). Add these two terms and equate it to 28 m and apply second derivative test to check minimum.
Let x m be the side of the square and r be the radius of circular part. Then, Length of square part = perimeter of square = 4 × Side = 4 × and length of circular part = circumference of circle = 2πr Given, length of wire = 28 ⇒ 4x + 2πr = 28 ⇒ 2x + πr = 14 ∴ x = \(\frac{14-\pi r}{2}\) ……(i)
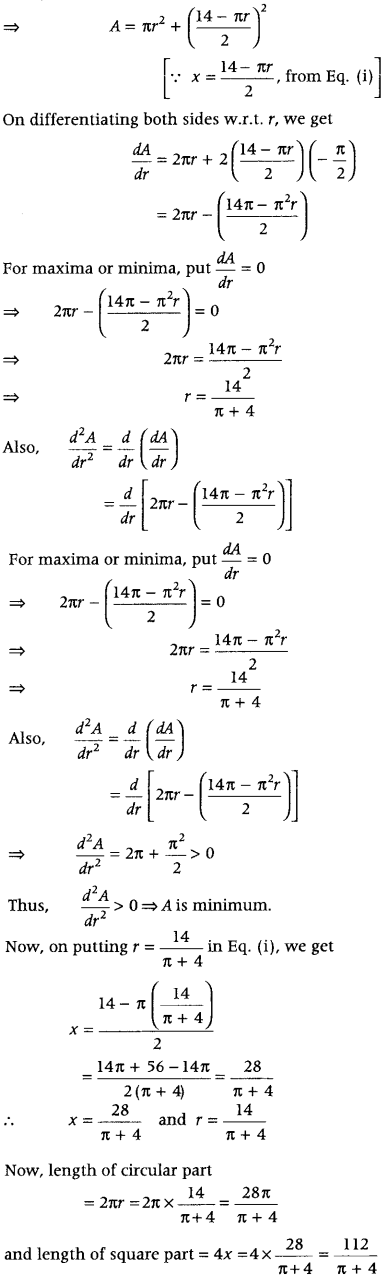
Question 37. Show that the volume of the largest cone that can be inscribed in a sphere of radius R is \(\frac{8}{27}\) of the volume of the sphere. (Delhi 2010C) Answer: Let R be the radius and h be the height of the cone, which inscribed in a sphere of radius r. ∴ OA = h – r
Question 38. Find the maximum area of an isosceles triangle inscribed in the ellipse \(\frac{x^{2}}{25}+\frac{y^{2}}{16}\) = 1, with its vertex at one end of the major axis. (Delhi 2010c) Answer: Given equation of ellipse is \(\frac{x^{2}}{25}+\frac{y^{2}}{16}\) = 1
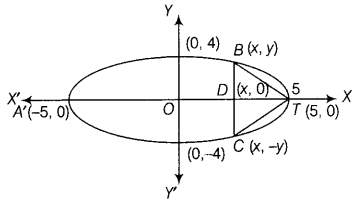
Note: If A 2 is maximum/minimum, then A is also maximum/minimum.
Question 39. Show that the right circular cylinder, open at the top and of given surface area and maximum volume is such that its height is equal to the radius of the base. (Delhi 2010) Answer: Let V be the volume, S be the total surface area of a right circular cylinder which is open at the top. Again, let r be the radius of base and h be the height. Now, S = 2πrh + πr 2 [∵ cylinder is open at top] ⇒ h = \(\frac{S-\pi r^{2}}{2 \pi r}\) ……….(i)

Free Resources
NCERT Solutions
Quick Resources

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- Question Bank
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- Toppers Notes
- Most Repeated Question
- Diagram Based Question
- Study Planner
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- BCECE Previous Year Paper
- JCECE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension
- Logical Reasoning & Data Interpretation
- CAT Mock Test
- CAT Important Question
- CAT Vocabulary
- CAT English Grammar
- MBA General Knowledge
- CAT Mind Map
- CAT Study Planner
- CMAT Mock Test
- SRCC GBO Mock Test
- SRCC GBO PYQs
- XAT Mock Test
- SNAP Mock Test
- IIFT Mock Test
- MAT Mock Test
- CUET PG Mock Test
- CUET PG PYQs
- MAH CET Mock Test
- MAH CET PYQs
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam

SHARING IS CARING If our Website helped you a little, then kindly spread our voice using Social Networks. Spread our word to your readers, friends, teachers, students & all those close ones who deserve to know what you know now.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences
- Integrals 3 September, 2024, 11:00 am
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions 3 September, 2024, 11:00 am
- Relations And Functions 14 April, 2021, 6:25 pm
- Matrices 14 April, 2021, 6:25 pm
- Determinants 14 April, 2021, 6:25 pm
- Continuity And Differentiability 14 April, 2021, 6:25 pm
- Application Of Derivatives 14 April, 2021, 6:25 pm
- Application Of Integrals 14 April, 2021, 6:25 pm
- Differential Equations 14 April, 2021, 6:25 pm

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

myCBSEguide
- Mathematics
- Class 12 Maths Case...
Class 12 Maths Case Study Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
Class 12 Maths question paper will have 1-2 Case Study Questions. These questions will carry 5 MCQs and students will attempt any four of them. As all of these are only MCQs, it is easy to score good marks with a little practice. Class 12 Maths Case Study Questions are available on the myCBSEguide App and Student Dashboard .
Why Case Studies in CBSE Syllabus?
CBSE has introduced case study questions in the CBSE curriculum recently. The purpose was to make students ready to face real-life challenges with the knowledge acquired in their classrooms. It means, there was a need to connect theories with practicals. Whatsoever the students are learning, they must know how to apply it in their day-to-day life. That’s why CBSE is emphasizing case studies and competency-based education .
Case Study Questions in Maths
Let’s have a look over the class 12 Mathematics sample question paper issued by CBSE, New Delhi. Question numbers 17 and 18 are case study questions.
Focus on concepts
If you go through each MCQ there, you will find that the theme/case study is common but the questions are based on different concepts related to the theme. It means, that if you have done ample practice on the various concepts, you can solve all these MCQs in minutes.
Easy Questions with a Practical Approach
The difficulty level of the questions is average or say easy in some cases. On the other hand, you get four options to choose from. So, you get two levels of support to get full marks with very little effort.
Practice Questions Regularly
Most of the time we feel that it’s easy and neglect it. But in the end, we have to pay for this negligence. This may happen here too. Although it’s easy to score good marks on the case study questions if you don’t practice such questions, you may lose your marks. So, we suggest students should practice at least 30-40 such questions before writing the board exam.
12 Maths Case-Based Questions
We are giving you some examples of case study questions here. We have arranged hundreds of such questions chapter-wise on the myCBSEguide App. It is the complete guide for CBSE students. You can download the myCBSEguide App and get more case study questions there.
Case Study Question – 1
- A is a diagonal matrix
- A is a scalar matrix
- A is a zero matrix
- A is a square matrix
- If A and B are two matrices such that AB = B and BA = A, then B 2 is equal to
Case Study Question – 2
- 4(x 3 – 24x 2 + 144x)
- 4(x 3 – 34x 2 + 244x)
- x 3 – 24x 2 + 144x
- 4x 3 – 24x 2 + 144x
- Local maxima at x = c 1
- Local minima at x = c 1
- Neither maxima nor minima at x = c 1
- None of these
Case Study Questions Matrices -1
Answer Key:
Case Study Questions Matrices – 2
Read the case study carefully and answer any four out of the following questions: Once a mathematics teacher drew a triangle ABC on the blackboard. Now he asked Jose,” If I increase AB by 11 cm and decrease the side BC by 11 cm, then what type of triangle it would be?” Jose said, “It will become an equilateral triangle.”
Again teacher asked Suraj,” If I multiply the side AB by 4 then what will be the relation of this with side AC?” Suraj said it will be 10 cm more than the three times AC.
Find the sides of the triangle using the matrix method and answer the following questions:
- (a) 3 × 3
Case Study Questions Determinants – 01
DETERMINANTS: A determinant is a square array of numbers (written within a pair of vertical lines) that represents a certain sum of products. We can solve a system of equations using determinants, but it becomes very tedious for large systems. We will only do 2 × 2 and 3 × 3 systems using determinants. Using the properties of determinants solve the problem given below and answer the questions that follow:
Three shopkeepers Ram Lal, Shyam Lal, and Ghansham are using polythene bags, handmade bags (prepared by prisoners), and newspaper envelopes as carrying bags. It is found that the shopkeepers Ram Lal, Shyam Lal, and Ghansham are using (20,30,40), (30,40,20), and (40,20,30) polythene bags, handmade bags, and newspapers envelopes respectively. The shopkeeper’s Ram Lal, Shyam Lal, and Ghansham spent ₹250, ₹270, and ₹200 on these carry bags respectively.
- (b) Shyam Lal
- (a) Ram Lal
Case Study Questions Determinants – 02
Case study questions application of derivatives.
- R(x) = -x 2 + 200x + 150000
- R(x) = x 2 – 200x – 140000
- R(x) = 200x 2 + x + 150000
- R(x) = -x 2 + 100 x + 100000
- R'(x) > 0
- R'(x) < 0
- R”(x) = 0
- (a) -x 2 + 200x + 150000
- (a) R'(x) = 0
- (c) 257, -63
Case Study Questions Vector Algebra
- tan−1(5/12)
- tan−1(12/3)
- (b) 130 m/s
- (a) tan−1(5/12)
- (b) 170 m/s
More Case Study Questions
These are only some samples. If you wish to get more case study questions for CBSE class 12 maths, install the myCBSEguide App. It has class 12 Maths chapter-wise case studies with solutions.
12 Maths Exam pattern
Question Paper Design of CBSE class 12 maths is as below. It clearly shows that 20% weightage will be given to HOTS questions. Whereas 55% of questions will be easy to solve.
| 1. | Exhibit memory of previously learned material by recalling facts, terms, basic concepts, and answers. Demonstrate understanding of facts and ideas by organizing, comparing, translating, interpreting, giving descriptions, and stating main ideas | 44 | 55 |
| 2. | Solve problems to new situations by applying acquired knowledge, facts, techniques and rules in a different way. | 20 | 25 |
| 3. | Examine and break information into parts by identifying motives or causes. Make inferences and find evidence to support generalizations | 16 | 20 |
| Present and defend opinions by making judgments about information, the validity of ideas, or quality of work based on a set of criteria. | |||
| Compile information together in a different way by combining elements in a new pattern or proposing alternative solutions | |||
| 80 | 100 |
- No. chapter-wise weightage. Care to be taken to cover all the chapters
- Suitable internal variations may be made for generating various templates keeping the overall weightage to different forms of questions and typology of questions the same.
Choice(s): There will be no overall choice in the question paper. However, 33% of internal choices will be given in all the sections
| Periodic Tests ( Best 2 out of 3 tests conducted) | 10 Marks |
| Mathematics Activities | 10 Marks |
12 Maths Prescribed Books
- Mathematics Part I – Textbook for Class XII, NCERT Publication
- Mathematics Part II – Textbook for Class XII, NCERT Publication
- Mathematics Exemplar Problem for Class XII, Published by NCERT
- Mathematics Lab Manual class XII, published by NCERT
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- CBSE Reduced Syllabus Class 10 (2020-21)
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Sample Paper 2020-21
- Case Study Class 10 Maths Questions
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
1 thought on “Class 12 Maths Case Study Questions”
plz provide solutions too
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
The Site is down as we are performing important server maintenance, during which time the server will be unavailable for approximately 24 hours. Please hold off on any critical actions until we are finished. As always your feedback is appreciated.

- Study Packages
- NCERT Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Online Test

- Questions Bank
- Mathematics
- Applications of Derivatives
- Test Series
- Ncert Solutions
- Solved Papers
- Current Affairs
- JEE Main & Advanced
- Pre-Primary
- MP State Exams
- UP State Exams
- Rajasthan State Exams
- Jharkhand State Exams
- Chhattisgarh State Exams
- Bihar State Exams
- Haryana State Exams
- Gujarat State Exams
- MH State Exams
- Himachal State Exams
- Delhi State Exams
- Uttarakhand State Exams
- Punjab State Exams
- J&K State Exams
12th Class Mathematics Applications of Derivatives Question Bank
Done case based (mcqs) - applications of derivatives total questions - 15.

| Directions: (1 - 5) |
| The Relation between the height of the plant (y in cm) with respect to exposure to sunlight is governed by following equation \[y=4x-\frac{1}{2}{{x}^{2}}\] where x is the number of days exposed to sunlight. |
A) \[4x-\frac{1}{2}{{x}^{2}}\] done clear
B) \[4\text{ }-\text{ }x\] done clear
C) \[\text{x }-\text{ 4}\] done clear
D) \[x-\frac{1}{2}{{x}^{2}}\] done clear
question_answer 2) What is the number of days it will take for the plant to grow to the maximum height?
A) 4 done clear
B) 6 done clear
C) 7 done clear
D) 10 done clear
question_answer 3) What is the maximum height of the plant?
A) 12 cm done clear
B) 10 cm done clear
C) 8 cm done clear
D) 6 cm done clear
question_answer 4) What will be the height of the plant after 2 days?
A) 4 cm done clear
B) 6 cm done clear
D) 10 cm done clear
question_answer 5) If the height of the plant is 7/2 cm, the number of days it has been exposed to the sunlight is
A) 2 done clear
B) 3 done clear
C) 4 done clear
D) 1 done clear
| Directions (6 - 10) |
| \[P(x)=-5{{x}^{2}}+125x+37500\] is the total profit function of a company, where x is the production of the company. |
A) 37500 done clear
B) 12.5 done clear
C) -12.5 done clear
D) -37500 done clear
question_answer 7) What will be the maximum profit?
A) Rs 38,28,125 done clear
B) Rs 38281.25 done clear
C) Rs 39,000 done clear
D) None. done clear
question_answer 8) Check in which interval the profit is strictly increasing.
A) \[\left( 12.5,\infty \right)\] done clear
B) for all real numbers done clear
C) for all positive real numbers done clear
D) (0, 12.5) done clear
question_answer 9) When the production is 2 units what will be the profit of the company?
B) 37,730 done clear
C) 37,770 done clear
D) None done clear
question_answer 10) What will be production of the company when the profit is Rs 38250?
A) 15 done clear
B) 30 done clear
C) 2 done clear
D) data is not sufficient to find done clear
| Directions: (11 - 15) |
| The shape of a toy is given as \[f(x)=6(2{{x}^{4}}-{{x}^{2}}).\]To make the toy beautiful 2 sticks which are perpendicular to each other were placed at a point (2, 3), above the toy. |
A) \[\pm \frac{1}{4}\] done clear
B) \[\pm \frac{1}{2}\] done clear
C) ±1 done clear
question_answer 12) Find the slope of the normal based on the position of the stick
A) 360 done clear
B) -360 done clear
C) \[\frac{1}{360}\] done clear
D) \[-\frac{1}{360}\] done clear
question_answer 13) What will be the equation of the tangent at the critical point if it passes through (2, 3)?
A) \[x+360y=1082\] done clear
B) \[y=360x-717\] done clear
C) \[x=717y+360\] done clear
D) none of these done clear
question_answer 14) Find the second order derivative of the function at x =5.
A) 598 done clear
B) 1176 done clear
C) 3588 done clear
D) 3312 done clear
question_answer 15) At which of the following intervals will \[f\text{ }\left( x \right)\]be strictly increasing?
A) \[\left( -\infty ,\text{ }-1/2 \right)\cup \text{ }\left( 1/2,\text{ }\infty \right)\] done clear
B) \[\left( -1/2,\,\,0 \right)\cup \left( 1/2,\text{ }\infty \right)\] done clear
C) \[\left( 0,\,\,1/2 \right)\cup \left( 1/2,\text{ }\infty \right)\] done clear
D) \[\left( -\infty ,\,-\,1/2 \right)\cup \left( 0,\text{ 1/2} \right)\] done clear
Study Package

Case Based (MCQs) - Applications of Derivatives
Related question.

Reset Password.
OTP has been sent to your mobile number and is valid for one hour
Mobile Number Verified
Your mobile number is verified.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The case study on Application Of Derivatives Class 12 Maths with solutions in PDF helps students tackle questions that appear confusing or difficult to answer. The answers to the Application Of Derivatives case study questions are very easy to grasp from the PDF - download links are given on this page.
Free PDF Download of CBSE Class 12 Mathematics Chapter 6 Applications of Derivatives Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers were Prepared Based on Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 12 Maths Applications of Derivatives to know their preparation level. Download Books for Boards. Join our Telegram Channel, there you ...
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 12 Maths, and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
Mere Bacchon, you must practice the CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 12 Maths Applications of Derivatives in order to fully complete your preparation.They are very very important from exam point of view. These tricky Case Study Based Questions can act as a villain in your heroic exams! I have made sure the questions (along with the solutions) prepare you fully for the upcoming exams.
Case-study-4 A factory owner wants to construct a tank with rectangular base and rectangular sides, open at the top, so that its depth is 2 m and capacity is 8 m³. The building of the tank costs ₹250 per square metre for the base and ₹180 per square metre for the sides.
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 12 Maths Subject - Application of Derivatives, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.
Class 12th Maths - Application of Derivatives Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023 - Complete list of 12th Standard CBSE question papers, syllabus, exam tips, study material, previous year exam question papers, centum tips, formula, answer keys, solutions etc..
CASE STUDY | CASE BASED QUESTIONS | APPLICATION OF DERIVATIVES CLASS 12 MATS 2023-24OSWAL GURUKUL SAMPLE PAPERBuy Link Amazon - https://www.amazon.in/stores/...
Application Of Derivatives Class 12 Objective Questions By Harsh Sir. Solve Class 12 Maths Application Of Derivatives Objective Questions With Vedantu Math. ...
We learned Derivatives in the last chapter, in Chapter 5 Class 12. In this Chapter we will learn the applications of those derivatives. The topics in the chapter include. Finding rate of change. Checking if a function is increasing or decreasing in an interval. Checking if a function is increasing or decreasing in whole domain.
#casestudyquestions #casestudyquestionsforclass12mathIn this video you will learn how to solve case study questions of class 12 math's board exams as per lat...
Question 6 - Case Based Questions (MCQ) - Chapter 6 Class 12 Application of Derivatives Last updated at April 16, 2024 by Teachoo. There is a bridge whose length of three sides of a trapezium other than base are equal to 10 cm. Based on the above information answer the following: This ...
Application of Derivatives Class 12 Important Questions with Solutions Previous Year Questions. Rate Measure, Increasing-Decreasing Functions and Approximation. Question 1. The total cost C (x) associated with the production of x units of an item is given by C (x) = 0.005x 3 - 0.02x 2 + 30x + 5000.
Spread our word to your readers, friends, teachers, students & all those close ones who deserve to know what you know now. Case Study on Application Of Derivatives Class 12 Maths: Here, you will get Case Study Questions on Class 12 Application Of Derivatives PDF at free of cost. Along with you can also download Application Of Derivatives case ...
Case Study Questions Application of Derivatives. A telephone company in a town has 500 subscribers on its list and collects fixed charges of 300 per subscriber per year. The company proposes to increase the annual subscription and it is believed that for every increase of 1 one subscriber will discontinue the service.
Important Questions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 6 - Applications of Derivatives are provided here. The questions are taken as per the syllabus of the CBSE board. These important questions help the students to secure good marks in the class 12 board examination. The important questions provided here covers 1 mark, 2 marks, 4 marks, and 6 marks.
Case Study Based Questions | Application of Derivatives | AOD #k2institute #maths #maths10th #k2institute #learnwithk2institute #experientiallearningatk2inst...
Free Question Bank for 12th Class Mathematics Applications of Derivatives Case Based (MCQs) - Derivatives. Customer Care : 6267349244. Toggle navigation 0 . 0 . Railways; UPSC; CET; Banking; CUET; SSC; ... Study Packages Question Bank Online Test Rajasthan State Exams ; Videos Sample Papers Study Packages Question Bank Online Test
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 12 Maths, and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams - Complete list of 12th Standard CBSE question papers, syllabus, exam tips, study material, previous year exam question papers, centum ...
Free Question Bank for 12th Class Mathematics Applications of Derivatives Case Based (MCQs) - Applications of Derivatives. Customer Care : 6267349244. Toggle navigation 0 . 0 . Railways; ... Study Packages Question Bank Online Test Rajasthan State Exams ; Videos Sample Papers Study Packages Question Bank Online Test
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
Aug 15, 2021 • 1h 2m • 140 views. In this Session , Vishal Mahajan discuss the Application of Derivatives .This Session will be beneficial Of Class 12 & all aspirants preparing for Competitive Exams.This session will be Conducted in English & Hindi and notes will be provided in English.
For Enquiries, please contact: 050 571 8643. Home. Class XI. Class XII. Contact. LoginRegister. Class XII - Case Study Questions - APPLICATION OF DERIVATIVES. Case Study Questions - APPLICATION OF DERIVATIVES. AOD CASE STUDY QUESTIONS.