Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples

What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples
Published on January 27, 2023 by Tegan George . Revised on January 12, 2024.
Table of contents
Types of action research, action research models, examples of action research, action research vs. traditional research, advantages and disadvantages of action research, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about action research.
There are 2 common types of action research: participatory action research and practical action research.
- Participatory action research emphasizes that participants should be members of the community being studied, empowering those directly affected by outcomes of said research. In this method, participants are effectively co-researchers, with their lived experiences considered formative to the research process.
- Practical action research focuses more on how research is conducted and is designed to address and solve specific issues.
Both types of action research are more focused on increasing the capacity and ability of future practitioners than contributing to a theoretical body of knowledge.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Action research is often reflected in 3 action research models: operational (sometimes called technical), collaboration, and critical reflection.
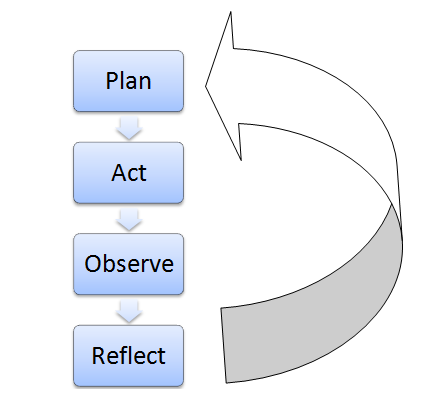
- Operational (or technical) action research is usually visualized like a spiral following a series of steps, such as “planning → acting → observing → reflecting.”
- Collaboration action research is more community-based, focused on building a network of similar individuals (e.g., college professors in a given geographic area) and compiling learnings from iterated feedback cycles.
- Critical reflection action research serves to contextualize systemic processes that are already ongoing (e.g., working retroactively to analyze existing school systems by questioning why certain practices were put into place and developed the way they did).
Action research is often used in fields like education because of its iterative and flexible style.
After the information was collected, the students were asked where they thought ramps or other accessibility measures would be best utilized, and the suggestions were sent to school administrators. Example: Practical action research Science teachers at your city’s high school have been witnessing a year-over-year decline in standardized test scores in chemistry. In seeking the source of this issue, they studied how concepts are taught in depth, focusing on the methods, tools, and approaches used by each teacher.
Action research differs sharply from other types of research in that it seeks to produce actionable processes over the course of the research rather than contributing to existing knowledge or drawing conclusions from datasets. In this way, action research is formative , not summative , and is conducted in an ongoing, iterative way.
| Action research | Traditional research | |
|---|---|---|
| and findings | ||
| and seeking between variables | ||
As such, action research is different in purpose, context, and significance and is a good fit for those seeking to implement systemic change.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Action research comes with advantages and disadvantages.
- Action research is highly adaptable , allowing researchers to mold their analysis to their individual needs and implement practical individual-level changes.
- Action research provides an immediate and actionable path forward for solving entrenched issues, rather than suggesting complicated, longer-term solutions rooted in complex data.
- Done correctly, action research can be very empowering , informing social change and allowing participants to effect that change in ways meaningful to their communities.
Disadvantages
- Due to their flexibility, action research studies are plagued by very limited generalizability and are very difficult to replicate . They are often not considered theoretically rigorous due to the power the researcher holds in drawing conclusions.
- Action research can be complicated to structure in an ethical manner . Participants may feel pressured to participate or to participate in a certain way.
- Action research is at high risk for research biases such as selection bias , social desirability bias , or other types of cognitive biases .
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Action research is conducted in order to solve a particular issue immediately, while case studies are often conducted over a longer period of time and focus more on observing and analyzing a particular ongoing phenomenon.
Action research is focused on solving a problem or informing individual and community-based knowledge in a way that impacts teaching, learning, and other related processes. It is less focused on contributing theoretical input, instead producing actionable input.
Action research is particularly popular with educators as a form of systematic inquiry because it prioritizes reflection and bridges the gap between theory and practice. Educators are able to simultaneously investigate an issue as they solve it, and the method is very iterative and flexible.
A cycle of inquiry is another name for action research . It is usually visualized in a spiral shape following a series of steps, such as “planning → acting → observing → reflecting.”
Sources in this article
We strongly encourage students to use sources in their work. You can cite our article (APA Style) or take a deep dive into the articles below.
George, T. (2024, January 12). What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved September 16, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/action-research/
Cohen, L., Manion, L., & Morrison, K. (2017). Research methods in education (8th edition). Routledge.
Naughton, G. M. (2001). Action research (1st edition). Routledge.
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, what is an observational study | guide & examples, primary research | definition, types, & examples, guide to experimental design | overview, steps, & examples, what is your plagiarism score.

Action Research: Steps, Benefits, and Tips

Introduction
History of action research, what is the definition of action research, types of action research, conducting action research.
Action research is an approach to qualitative inquiry in social science research that involves the search for practical solutions to everyday issues. Rooted in real-world problems, it seeks not just to understand but also to act, bringing about positive change in specific contexts. Often distinguished by its collaborative nature, the action research process goes beyond traditional research paradigms by emphasizing the involvement of those being studied in resolving social conflicts and effecting positive change.
The value of action research lies not just in its outcomes, but also in the process itself, where stakeholders become active participants rather than mere subjects. In this article, we'll examine action research in depth, shedding light on its history, principles, and types of action research.

Tracing its roots back to the mid-20th century, Kurt Lewin developed classical action research as a response to traditional research methods in the social sciences that often sidelined the very communities they studied. Proponents of action research championed the idea that research should not just be an observational exercise but an actionable one that involves devising practical solutions. Advocates believed in the idea of research leading to immediate social action, emphasizing the importance of involving the community in the process.
Applications for action research
Over the years, action research has evolved and diversified. From its early applications in social psychology and organizational development, it has branched out into various fields such as education, healthcare, and community development, informing questions around improving schools, minority problems, and more. This growth wasn't just in application, but also in its methodologies.
How is action research different?
Like all research methodologies, effective action research generates knowledge. However, action research stands apart in its commitment to instigate tangible change. Traditional research often places emphasis on passive observation , employing data collection methods primarily to contribute to broader theoretical frameworks . In contrast, action research is inherently proactive, intertwining the acts of observing and acting.

The primary goal isn't just to understand a problem but to solve or alleviate it. Action researchers partner closely with communities, ensuring that the research process directly benefits those involved. This collaboration often leads to immediate interventions, tweaks, or solutions applied in real-time, marking a departure from other forms of research that might wait until the end of a study to make recommendations.
This proactive, change-driven nature makes action research particularly impactful in settings where immediate change is not just beneficial but essential.
Action research is best understood as a systematic approach to cooperative inquiry. Unlike traditional research methodologies that might primarily focus on generating knowledge, action research emphasizes producing actionable solutions for pressing real-world challenges.
This form of research undertakes a cyclic and reflective journey, typically cycling through stages of planning , acting, observing, and reflecting. A defining characteristic of action research is the collaborative spirit it embodies, often dissolving the rigid distinction between the researcher and the researched, leading to mutual learning and shared outcomes.
Advantages of action research
One of the foremost benefits of action research is the immediacy of its application. Since the research is embedded within real-world issues, any findings or solutions derived can often be integrated straightaway, catalyzing prompt improvements within the concerned community or organization. This immediacy is coupled with the empowering nature of the methodology. Participants aren't mere subjects; they actively shape the research process, giving them a tangible sense of ownership over both the research journey and its eventual outcomes.
Moreover, the inherent adaptability of action research allows researchers to tweak their approaches responsively based on live feedback. This ensures the research remains rooted in the evolving context, capturing the nuances of the situation and making any necessary adjustments. Lastly, this form of research tends to offer a comprehensive understanding of the issue at hand, harmonizing socially constructed theoretical knowledge with hands-on insights, leading to a richer, more textured understanding.

Disadvantages of action research
Like any methodology, action research isn't devoid of challenges. Its iterative nature, while beneficial, can extend timelines. Researchers might find themselves engaged in multiple cycles of observation, reflection, and action before arriving at a satisfactory conclusion. The intimate involvement of the researcher with the research participants , although crucial for collaboration, opens doors to potential conflicts. Through collaborative problem solving, disagreements can lead to richer and more nuanced solutions, but it can take considerable time and effort.
Another limitation stems from its focus on a specific context: results derived from a particular action research project might not always resonate or be applicable in a different context or with a different group. Lastly, the depth of collaboration this methodology demands means all stakeholders need to be deeply invested, and such a level of commitment might not always be feasible.
Examples of action research
To illustrate, let's consider a few scenarios. Imagine a classroom where a teacher observes dwindling student participation. Instead of sticking to conventional methods, the teacher experiments with introducing group-based activities. As the outcomes unfold, the teacher continually refines the approach based on student feedback, eventually leading to a teaching strategy that rejuvenates student engagement.
In a healthcare context, hospital staff who recognize growing patient anxiety related to certain procedures might innovate by introducing a new patient-informing protocol. As they study the effects of this change, they could, through iterations, sculpt a procedure that diminishes patient anxiety.
Similarly, in the realm of community development, a community grappling with the absence of child-friendly public spaces might collaborate with local authorities to conceptualize a park. As they monitor its utilization and societal impact, continual feedback could refine the park's infrastructure and design.
Contemporary action research, while grounded in the core principles of collaboration, reflection, and change, has seen various adaptations tailored to the specific needs of different contexts and fields. These adaptations have led to the emergence of distinct types of action research, each with its unique emphasis and approach.
Collaborative action research
Collaborative action research emphasizes the joint efforts of professionals, often from the same field, working together to address common concerns or challenges. In this approach, there's a strong emphasis on shared responsibility, mutual respect, and co-learning. For example, a group of classroom teachers might collaboratively investigate methods to improve student literacy, pooling their expertise and resources to devise, implement, and refine strategies for improving teaching.
Participatory action research
Participatory action research (PAR) goes a step further in dissolving the barriers between the researcher and the researched. It actively involves community members or stakeholders not just as participants, but as equal partners in the entire research process. PAR is deeply democratic and seeks to empower participants, fostering a sense of agency and ownership. For instance, a participatory research project might involve local residents in studying and addressing community health concerns, ensuring that the research process and outcomes are both informed by and beneficial to the community itself.
Educational action research
Educational action research is tailored specifically to practical educational contexts. Here, educators take on the dual role of teacher and researcher, seeking to improve teaching practices, curricula, classroom dynamics, or educational evaluation. This type of research is cyclical, with educators implementing changes, observing outcomes, and reflecting on results to continually enhance the educational experience. An example might be a teacher studying the impact of technology integration in her classroom, adjusting strategies based on student feedback and learning outcomes.

Community-based action research
Another noteworthy type is community-based action research, which focuses primarily on community development and well-being. Rooted in the principles of social justice, this approach emphasizes the collective power of community members to identify, study, and address their challenges. It's particularly powerful in grassroots movements and local development projects where community insights and collaboration drive meaningful, sustainable change.
Key insights and critical reflection through research with ATLAS.ti
Organize all your data analysis and insights with our powerful interface. Download a free trial today.
Engaging in action research is both an enlightening and transformative journey, rooted in practicality yet deeply connected to theory. For those embarking on this path, understanding the essentials of an action research study and the significance of a research cycle is paramount.
Understanding the action research cycle
At the heart of action research is its cycle, a structured yet adaptable framework guiding the research. This cycle embodies the iterative nature of action research, emphasizing that learning and change evolve through repetition and reflection.
The typical stages include:
- Identifying a problem : This is the starting point where the action researcher pinpoints a pressing issue or challenge that demands attention.
- Planning : Here, the researcher devises an action research strategy aimed at addressing the identified problem. In action research, network resources, participant consultation, and the literature review are core components in planning.
- Action : The planned strategies are then implemented in this stage. This 'action' phase is where theoretical knowledge meets practical application.
- Observation : Post-implementation, the researcher observes the outcomes and effects of the action. This stage ensures that the research remains grounded in the real-world context.
- Critical reflection : This part of the cycle involves analyzing the observed results to draw conclusions about their effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
- Revision : Based on the insights from reflection, the initial plan is revised, marking the beginning of another cycle.
Rigorous research and iteration
It's essential to understand that while action research is deeply practical, it doesn't sacrifice rigor . The cyclical process ensures that the research remains thorough and robust. Each iteration of the cycle in an action research project refines the approach, drawing it closer to an effective solution.
The role of the action researcher
The action researcher stands at the nexus of theory and practice. Not just an observer, the researcher actively engages with the study's participants, collaboratively navigating through the research cycle by conducting interviews, participant observations, and member checking . This close involvement ensures that the study remains relevant, timely, and responsive.

Drawing conclusions and informing theory
As the research progresses through multiple iterations of data collection and data analysis , drawing conclusions becomes an integral aspect. These conclusions, while immediately beneficial in addressing the practical issue at hand, also serve a broader purpose. They inform theory, enriching the academic discourse and providing valuable insights for future research.
Identifying actionable insights
Keep in mind that action research should facilitate implications for professional practice as well as space for systematic inquiry. As you draw conclusions about the knowledge generated from action research, consider how this knowledge can create new forms of solutions to the pressing concern you set out to address.

Collecting data and analyzing data starts with ATLAS.ti
Download a free trial of our intuitive software to make the most of your research.


- Section 2: Home
- Developing the Quantitative Research Design
- Qualitative Descriptive Design
- Design and Development Research (DDR) For Instructional Design
- Qualitative Narrative Inquiry Research
- Action Research Resource
What is Action Research?
Considerations, creating a plan of action.
- Case Study Design in an Applied Doctorate
- SAGE Research Methods
- Research Examples (SAGE) This link opens in a new window
- Dataset Examples (SAGE) This link opens in a new window
- IRB Resource Center This link opens in a new window
Action research is a qualitative method that focuses on solving problems in social systems, such as schools and other organizations. The emphasis is on solving the presenting problem by generating knowledge and taking action within the social system in which the problem is located. The goal is to generate shared knowledge of how to address the problem by bridging the theory-practice gap (Bourner & Brook, 2019). A general definition of action research is the following: “Action research brings together action and reflection, as well as theory and practice, in participation with others, in the pursuit of practical solutions to issues of pressing concern” (Bradbury, 2015, p. 1). Johnson (2019) defines action research in the field of education as “the process of studying a school, classroom, or teacher-learning situation with the purpose of understanding and improving the quality of actions or instruction” (p.255).
Origins of Action Research
Kurt Lewin is typically credited with being the primary developer of Action Research in the 1940s. Lewin stated that action research can “transform…unrelated individuals, frequently opposed in their outlook and their interests, into cooperative teams, not on the basis of sweetness but on the basis of readiness to face difficulties realistically, to apply honest fact-finding, and to work together to overcome them” (1946, p.211).
Sample Action Research Topics
Some sample action research topics might be the following:
- Examining how classroom teachers perceive and implement new strategies in the classroom--How is the strategy being used? How do students respond to the strategy? How does the strategy inform and change classroom practices? Does the new skill improve test scores? Do classroom teachers perceive the strategy as effective for student learning?
- Examining how students are learning a particular content or objectives--What seems to be effective in enhancing student learning? What skills need to be reinforced? How do students respond to the new content? What is the ability of students to understand the new content?
- Examining how education stakeholders (administrator, parents, teachers, students, etc.) make decisions as members of the school’s improvement team--How are different stakeholders encouraged to participate? How is power distributed? How is equity demonstrated? How is each voice valued? How are priorities and initiatives determined? How does the team evaluate its processes to determine effectiveness?
- Examining the actions that school staff take to create an inclusive and welcoming school climate--Who makes and implements the actions taken to create the school climate? Do members of the school community (teachers, staff, students) view the school climate as inclusive? Do members of the school community feel welcome in the school? How are members of the school community encouraged to become involved in school activities? What actions can school staff take to help others feel a part of the school community?
- Examining the perceptions of teachers with regard to the learning strategies that are more effective with special populations, such as special education students, English Language Learners, etc.—What strategies are perceived to be more effective? How do teachers plan instructionally for unique learners such as special education students or English Language Learners? How do teachers deal with the challenges presented by unique learners such as special education students or English Language Learners? What supports do teachers need (e.g., professional development, training, coaching) to more effectively deliver instruction to unique learners such as special education students or English Language Learners?
Remember—The goal of action research is to find out how individuals perceive and act in a situation so the researcher can develop a plan of action to improve the educational organization. While these topics listed here can be explored using other research designs, action research is the design to use if the outcome is to develop a plan of action for addressing and improving upon a situation in the educational organization.
Considerations for Determining Whether to Use Action Research in an Applied Dissertation
- When considering action research, first determine the problem and the change that needs to occur as a result of addressing the problem (i.e., research problem and research purpose). Remember, the goal of action research is to change how individuals address a particular problem or situation in a way that results in improved practices.
- If the study will be conducted at a school site or educational organization, you may need site permission. Determine whether site permission will be given to conduct the study.
- Consider the individuals who will be part of the data collection (e.g., teachers, administrators, parents, other school staff, etc.). Will there be a representative sample willing to participate in the research?
- If students will be part of the study, does parent consent and student assent need to be obtained?
- As you develop your data collection plan, also consider the timeline for data collection. Is it feasible? For example, if you will be collecting data in a school, consider winter and summer breaks, school events, testing schedules, etc.
- As you develop your data collection plan, consult with your dissertation chair, Subject Matter Expert, NU Academic Success Center, and the NU IRB for resources and guidance.
- Action research is not an experimental design, so you are not trying to accept or reject a hypothesis. There are no independent or dependent variables. It is not generalizable to a larger setting. The goal is to understand what is occurring in the educational setting so that a plan of action can be developed for improved practices.
Considerations for Action Research
Below are some things to consider when developing your applied dissertation proposal using Action Research (adapted from Johnson, 2019):
- Research Topic and Research Problem -- Decide the topic to be studied and then identify the problem by defining the issue in the learning environment. Use references from current peer-reviewed literature for support.
- Purpose of the Study —What need to be different or improved as a result of the study?
- Research Questions —The questions developed should focus on “how” or “what” and explore individuals’ experiences, beliefs, and perceptions.
- Theoretical Framework -- What are the existing theories (theoretical framework) or concepts (conceptual framework) that can be used to support the research. How does existing theory link to what is happening in the educational environment with regard to the topic? What theories have been used to support similar topics in previous research?
- Literature Review -- Examine the literature, focusing on peer-reviewed studies published in journal within the last five years, with the exception of seminal works. What about the topic has already been explored and examined? What were the findings, implications, and limitations of previous research? What is missing from the literature on the topic? How will your proposed research address the gap in the literature?
- Data Collection —Who will be part of the sample for data collection? What data will be collected from the individuals in the study (e.g., semi-structured interviews, surveys, etc.)? What are the educational artifacts and documents that need to be collected (e.g., teacher less plans, student portfolios, student grades, etc.)? How will they be collected and during what timeframe? (Note--A list of sample data collection methods appears under the heading of “Sample Instrumentation.”)
- Data Analysis —Determine how the data will be analyzed. Some types of analyses that are frequently used for action research include thematic analysis and content analysis.
- Implications —What conclusions can be drawn based upon the findings? How do the findings relate to the existing literature and inform theory in the field of education?
- Recommendations for Practice--Create a Plan of Action— This is a critical step in action research. A plan of action is created based upon the data analysis, findings, and implications. In the Applied Dissertation, this Plan of Action is included with the Recommendations for Practice. The includes specific steps that individuals should take to change practices; recommendations for how those changes will occur (e.g., professional development, training, school improvement planning, committees to develop guidelines and policies, curriculum review committee, etc.); and methods to evaluate the plan’s effectiveness.
- Recommendations for Research —What should future research focus on? What type of studies need to be conducted to build upon or further explore your findings.
- Professional Presentation or Defense —This is where the findings will be presented in a professional presentation or defense as the culmination of your research.
Adapted from Johnson (2019).
Considerations for Sampling and Data Collection
Below are some tips for sampling, sample size, data collection, and instrumentation for Action Research:
Sampling and Sample Size
Action research uses non-probability sampling. This is most commonly means a purposive sampling method that includes specific inclusion and exclusion criteria. However, convenience sampling can also be used (e.g., a teacher’s classroom).
Critical Concepts in Data Collection
Triangulation- - Dosemagen and Schwalbach (2019) discussed the importance of triangulation in Action Research which enhances the trustworthiness by providing multiple sources of data to analyze and confirm evidence for findings.
Trustworthiness —Trustworthiness assures that research findings are fulfill four critical elements—credibility, dependability, transferability, and confirmability. Reflect on the following: Are there multiple sources of data? How have you ensured credibility, dependability, transferability, and confirmability? Have the assumptions, limitations, and delimitations of the study been identified and explained? Was the sample a representative sample for the study? Did any individuals leave the study before it ended? How have you controlled researcher biases and beliefs? Are you drawing conclusions that are not supported by data? Have all possible themes been considered? Have you identified other studies with similar results?
Sample Instrumentation
Below are some of the possible methods for collecting action research data:
- Pre- and Post-Surveys for students and/or staff
- Staff Perception Surveys and Questionnaires
- Semi-Structured Interviews
- Focus Groups
- Observations
- Document analysis
- Student work samples
- Classroom artifacts, such as teacher lesson plans, rubrics, checklists, etc.
- Attendance records
- Discipline data
- Journals from students and/or staff
- Portfolios from students and/or staff
A benefit of Action Research is its potential to influence educational practice. Many educators are, by nature of the profession, reflective, inquisitive, and action-oriented. The ultimate outcome of Action Research is to create a plan of action using the research findings to inform future educational practice. A Plan of Action is not meant to be a one-size fits all plan. Instead, it is mean to include specific data-driven and research-based recommendations that result from a detailed analysis of the data, the study findings, and implications of the Action Research study. An effective Plan of Action includes an evaluation component and opportunities for professional educator reflection that allows for authentic discussion aimed at continuous improvement.
When developing a Plan of Action, the following should be considered:
- How can this situation be approached differently in the future?
- What should change in terms of practice?
- What are the specific steps that individuals should take to change practices?
- What is needed to implement the changes being recommended (professional development, training, materials, resources, planning committees, school improvement planning, etc.)?
- How will the effectiveness of the implemented changes be evaluated?
- How will opportunities for professional educator reflection be built into the Action Plan?
Sample Action Research Studies
Anderson, A. J. (2020). A qualitative systematic review of youth participatory action research implementation in U.S. high schools. A merican Journal of Community Psychology, 65 (1/2), 242–257. https://onlinelibrary-wiley-com.proxy1.ncu.edu/doi/epdf/10.1002/ajcp.12389
Ayvaz, Ü., & Durmuş, S.(2021). Fostering mathematical creativity with problem posing activities: An action research with gifted students. Thinking Skills and Creativity, 40. https://proxy1.ncu.edu/login?url=https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=edselp&AN=S1871187121000614&site=eds-live
Bellino, M. J. (2018). Closing information gaps in Kakuma Refugee Camp: A youth participatory action research study. American Journal of Community Psychology, 62 (3/4), 492–507. https://proxy1.ncu.edu/login?url=https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=ofs&AN=133626988&site=eds-live
Beneyto, M., Castillo, J., Collet-Sabé, J., & Tort, A. (2019). Can schools become an inclusive space shared by all families? Learnings and debates from an action research project in Catalonia. Educational Action Research, 27 (2), 210–226. https://proxy1.ncu.edu/login?url=https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=ehh&AN=135671904&site=eds-live
Bilican, K., Senler, B., & Karısan, D. (2021). Fostering teacher educators’ professional development through collaborative action research. International Journal of Progressive Education, 17 (2), 459–472. https://proxy1.ncu.edu/login?url=https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=ehh&AN=149828364&site=eds-live
Black, G. L. (2021). Implementing action research in a teacher preparation program: Opportunities and limitations. Canadian Journal of Action Research, 21 (2), 47–71. https://proxy1.ncu.edu/login?url=https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=ehh&AN=149682611&site=eds-live
Bozkuş, K., & Bayrak, C. (2019). The Application of the dynamic teacher professional development through experimental action research. International Electronic Journal of Elementary Education, 11 (4), 335–352. https://proxy1.ncu.edu/login?url=https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=ehh&AN=135580911&site=eds-live
Christ, T. W. (2018). Mixed methods action research in special education: An overview of a grant-funded model demonstration project. Research in the Schools, 25( 2), 77–88. https://proxy1.ncu.edu/login?url=https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=ehh&AN=135047248&site=eds-live
Jakhelln, R., & Pörn, M. (2019). Challenges in supporting and assessing bachelor’s theses based on action research in initial teacher education. Educational Action Research, 27 (5), 726–741. https://proxy1.ncu.edu/login?url=https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=ehh&AN=140234116&site=eds-live
Klima Ronen, I. (2020). Action research as a methodology for professional development in leading an educational process. Studies in Educational Evaluation, 64 . https://proxy1.ncu.edu/login?url=https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=edselp&AN=S0191491X19302159&site=eds-live
Messiou, K. (2019). Collaborative action research: facilitating inclusion in schools. Educational Action Research, 27 (2), 197–209. https://proxy1.ncu.edu/login?url=https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=ehh&AN=135671898&site=eds-live
Mitchell, D. E. (2018). Say it loud: An action research project examining the afrivisual and africology, Looking for alternative African American community college teaching strategies. Journal of Pan African Studies, 12 (4), 364–487. https://proxy1.ncu.edu/login?url=https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=ofs&AN=133155045&site=eds-live
Pentón Herrera, L. J. (2018). Action research as a tool for professional development in the K-12 ELT classroom. TESL Canada Journal, 35 (2), 128–139. https://proxy1.ncu.edu/login?url=https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=ofs&AN=135033158&site=eds-live
Rodriguez, R., Macias, R. L., Perez-Garcia, R., Landeros, G., & Martinez, A. (2018). Action research at the intersection of structural and family violence in an immigrant Latino community: a youth-led study. Journal of Family Violence, 33 (8), 587–596. https://proxy1.ncu.edu/login?url=https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=ccm&AN=132323375&site=eds-live
Vaughan, M., Boerum, C., & Whitehead, L. (2019). Action research in doctoral coursework: Perceptions of independent research experiences. International Journal for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning, 13 . https://proxy1.ncu.edu/login?url=https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=edsdoj&AN=edsdoj.17aa0c2976c44a0991e69b2a7b4f321&site=eds-live
Sample Journals for Action Research
Educational Action Research
Canadian Journal of Action Research
Sample Resource Videos
Call-Cummings, M. (2017). Researching racism in schools using participatory action research [Video]. Sage Research Methods http://proxy1.ncu.edu/login?URL=https://methods.sagepub.com/video/researching-racism-in-schools-using-participatory-action-research
Fine, M. (2016). Michelle Fine discusses community based participatory action research [Video]. Sage Knowledge. http://proxy1.ncu.edu/login?URL=https://sk-sagepub-com.proxy1.ncu.edu/video/michelle-fine-discusses-community-based-participatory-action-research
Getz, C., Yamamura, E., & Tillapaugh. (2017). Action Research in Education. [Video]. You Tube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X2tso4klYu8
Bradbury, H. (Ed.). (2015). The handbook of action research (3rd edition). Sage.
Bradbury, H., Lewis, R. & Embury, D.C. (2019). Education action research: With and for the next generation. In C.A. Mertler (Ed.), The Wiley handbook of action research in education (1st edition). John Wiley and Sons. https://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/nu/reader.action?docID=5683581&ppg=205
Bourner, T., & Brook, C. (2019). Comparing and contrasting action research and action learning. In C.A. Mertler (Ed.), The Wiley handbook of action research in education (1st edition). John Wiley and Sons. https://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/nu/reader.action?docID=5683581&ppg=205
Bradbury, H. (2015). The Sage handbook of action research . Sage. https://www-doi-org.proxy1.ncu.edu/10.4135/9781473921290
Dosemagen, D.M. & Schwalback, E.M. (2019). Legitimacy of and value in action research. In C.A. Mertler (Ed.), The Wiley handbook of action research in education (1st edition). John Wiley and Sons. https://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/nu/reader.action?docID=5683581&ppg=205
Johnson, A. (2019). Action research for teacher professional development. In C.A. Mertler (Ed.), The Wiley handbook of action research in education (1st edition). John Wiley and Sons. https://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/nu/reader.action?docID=5683581&ppg=205
Lewin, K. (1946). Action research and minority problems. In G.W. Lewin (Ed.), Resolving social conflicts: Selected papers on group dynamics (compiled in 1948). Harper and Row.
Mertler, C. A. (Ed.). (2019). The Wiley handbook of action research in education. John Wiley and Sons. https://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/nu/detail.action?docID=5683581
- << Previous: Qualitative Narrative Inquiry Research
- Next: Case Study Design in an Applied Doctorate >>
- Last Updated: Jul 28, 2023 8:05 AM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/c.php?g=1013605

© Copyright 2024 National University. All Rights Reserved.
Privacy Policy | Consumer Information

Research Methods and Design
- Action Research
- Case Study Design
- Literature Review
- Quantitative Research Methods
- Qualitative Research Methods
- Mixed Methods Study
- Indigenous Research and Ethics This link opens in a new window
- Identifying Empirical Research Articles This link opens in a new window
- Research Ethics and Quality
- Data Literacy
- Get Help with Writing Assignments
Action research
A type of applied research designed to find the most effective way to bring about a desired social change or to solve a practical problem, usually in collaboration with those being researched.
SAGE Research Methods Videos
How do you define action research.
Professor David Coghlan explains action research as an approach that crosses many academic disciplines yet has a shared focus on taking action to address a problem. He describes the difference between this approach and empirical scientific approaches, particularly highlighting the challenge of getting action research to be taken seriously by academic journals
Dr. Nataliya Ivankova defines action research as using systematic research principles to address an issue in everyday life. She delineates the six steps of action research, and illustrates the concept using an anti-diabetes project in an urban area.
This is just one segment in a whole series about action research. You can find the rest of the series in our SAGE database, Research Methods:
Videos covering research methods and statistics
Further Reading
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Case Study Design >>
- Last Updated: May 7, 2024 9:51 AM
CityU Home - CityU Catalog

- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case AskWhy Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research Research Tools and Apps
Action Research: What it is, Stages & Examples

The best way to get things accomplished is to do it yourself. This statement is utilized in corporations, community projects, and national governments. These organizations are relying on action research to cope with their continuously changing and unstable environments as they function in a more interdependent world.
In practical educational contexts, this involves using systematic inquiry and reflective practice to address real-world challenges, improve teaching and learning, enhance student engagement, and drive positive changes within the educational system.
This post outlines the definition of action research, its stages, and some examples.
Content Index
What is action research?
Stages of action research, the steps to conducting action research, examples of action research, advantages and disadvantages of action research.
Action research is a strategy that tries to find realistic solutions to organizations’ difficulties and issues. It is similar to applied research.
Action research refers basically learning by doing. First, a problem is identified, then some actions are taken to address it, then how well the efforts worked are measured, and if the results are not satisfactory, the steps are applied again.
It can be put into three different groups:
- Positivist: This type of research is also called “classical action research.” It considers research a social experiment. This research is used to test theories in the actual world.
- Interpretive: This kind of research is called “contemporary action research.” It thinks that business reality is socially made, and when doing this research, it focuses on the details of local and organizational factors.
- Critical: This action research cycle takes a critical reflection approach to corporate systems and tries to enhance them.
All research is about learning new things. Collaborative action research contributes knowledge based on investigations in particular and frequently useful circumstances. It starts with identifying a problem. After that, the research process is followed by the below stages:
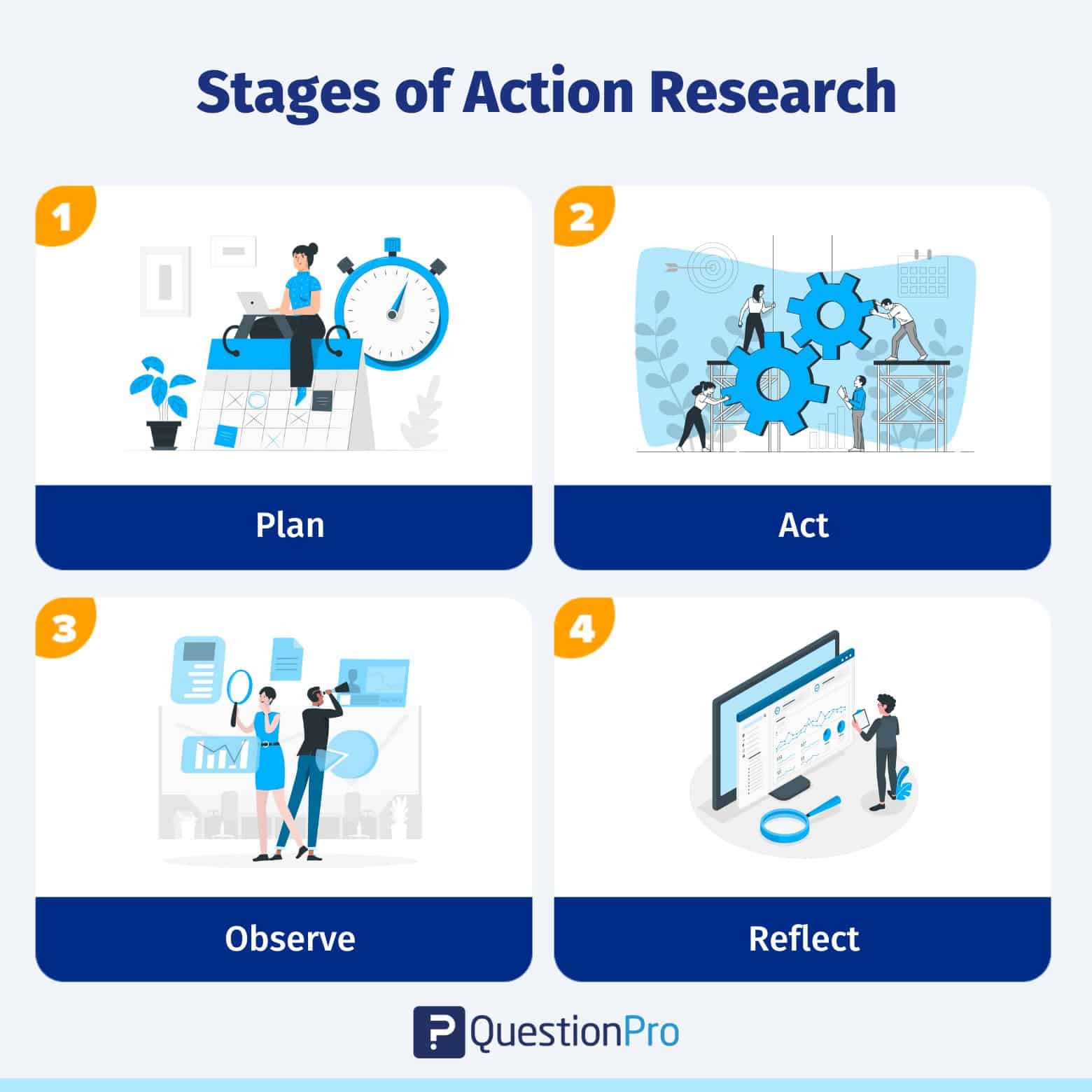
Stage 1: Plan
For an action research project to go well, the researcher needs to plan it well. After coming up with an educational research topic or question after a research study, the first step is to develop an action plan to guide the research process. The research design aims to address the study’s question. The research strategy outlines what to undertake, when, and how.
Stage 2: Act
The next step is implementing the plan and gathering data. At this point, the researcher must select how to collect and organize research data . The researcher also needs to examine all tools and equipment before collecting data to ensure they are relevant, valid, and comprehensive.
Stage 3: Observe
Data observation is vital to any investigation. The action researcher needs to review the project’s goals and expectations before data observation. This is the final step before drawing conclusions and taking action.
Different kinds of graphs, charts, and networks can be used to represent the data. It assists in making judgments or progressing to the next stage of observing.
Stage 4: Reflect
This step involves applying a prospective solution and observing the results. It’s essential to see if the possible solution found through research can really solve the problem being studied.
The researcher must explore alternative ideas when the action research project’s solutions fail to solve the problem.
Action research is a systematic approach researchers, educators, and practitioners use to identify and address problems or challenges within a specific context. It involves a cyclical process of planning, implementing, reflecting, and adjusting actions based on the data collected. Here are the general steps involved in conducting an action research process:
Identify the action research question or problem
Clearly define the issue or problem you want to address through your research. It should be specific, actionable, and relevant to your working context.
Review existing knowledge
Conduct a literature review to understand what research has already been done on the topic. This will help you gain insights, identify gaps, and inform your research design.
Plan the research
Develop a research plan outlining your study’s objectives, methods, data collection tools, and timeline. Determine the scope of your research and the participants or stakeholders involved.
Collect data
Implement your research plan by collecting relevant data. This can involve various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, document analysis, or focus groups. Ensure that your data collection methods align with your research objectives and allow you to gather the necessary information.
Analyze the data
Once you have collected the data, analyze it using appropriate qualitative or quantitative techniques. Look for patterns, themes, or trends in the data that can help you understand the problem better.
Reflect on the findings
Reflect on the analyzed data and interpret the results in the context of your research question. Consider the implications and possible solutions that emerge from the data analysis. This reflection phase is crucial for generating insights and understanding the underlying factors contributing to the problem.
Develop an action plan
Based on your analysis and reflection, develop an action plan that outlines the steps you will take to address the identified problem. The plan should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART goals). Consider involving relevant stakeholders in planning to ensure their buy-in and support.
Implement the action plan
Put your action plan into practice by implementing the identified strategies or interventions. This may involve making changes to existing practices, introducing new approaches, or testing alternative solutions. Document the implementation process and any modifications made along the way.
Evaluate and monitor progress
Continuously monitor and evaluate the impact of your actions. Collect additional data, assess the effectiveness of the interventions, and measure progress towards your goals. This evaluation will help you determine if your actions have the desired effects and inform any necessary adjustments.
Reflect and iterate
Reflect on the outcomes of your actions and the evaluation results. Consider what worked well, what did not, and why. Use this information to refine your approach, make necessary adjustments, and plan for the next cycle of action research if needed.
Remember that participatory action research is an iterative process, and multiple cycles may be required to achieve significant improvements or solutions to the identified problem. Each cycle builds on the insights gained from the previous one, fostering continuous learning and improvement.
Explore Insightfully Contextual Inquiry in Qualitative Research
Here are two real-life examples of action research.
Action research initiatives are frequently situation-specific. Still, other researchers can adapt the techniques. The example is from a researcher’s (Franklin, 1994) report about a project encouraging nature tourism in the Caribbean.
In 1991, this was launched to study how nature tourism may be implemented on the four Windward Islands in the Caribbean: St. Lucia, Grenada, Dominica, and St. Vincent.
For environmental protection, a government-led action study determined that the consultation process needs to involve numerous stakeholders, including commercial enterprises.
First, two researchers undertook the study and held search conferences on each island. The search conferences resulted in suggestions and action plans for local community nature tourism sub-projects.
Several islands formed advisory groups and launched national awareness and community projects. Regional project meetings were held to discuss experiences, self-evaluations, and strategies. Creating a documentary about a local initiative helped build community. And the study was a success, leading to a number of changes in the area.
Lau and Hayward (1997) employed action research to analyze Internet-based collaborative work groups.
Over two years, the researchers facilitated three action research problem -solving cycles with 15 teachers, project personnel, and 25 health practitioners from diverse areas. The goal was to see how Internet-based communications might affect their virtual workgroup.
First, expectations were defined, technology was provided, and a bespoke workgroup system was developed. Participants suggested shorter, more dispersed training sessions with project-specific instructions.
The second phase saw the system’s complete deployment. The final cycle witnessed system stability and virtual group formation. The key lesson was that the learning curve was poorly misjudged, with frustrations only marginally met by phone-based technical help. According to the researchers, the absence of high-quality online material about community healthcare was harmful.
Role clarity, connection building, knowledge sharing, resource assistance, and experiential learning are vital for virtual group growth. More study is required on how group support systems might assist groups in engaging with their external environment and boost group members’ learning.
Action research has both good and bad points.
- It is very flexible, so researchers can change their analyses to fit their needs and make individual changes.
- It offers a quick and easy way to solve problems that have been going on for a long time instead of complicated, long-term solutions based on complex facts.
- If It is done right, it can be very powerful because it can lead to social change and give people the tools to make that change in ways that are important to their communities.
Disadvantages
- These studies have a hard time being generalized and are hard to repeat because they are so flexible. Because the researcher has the power to draw conclusions, they are often not thought to be theoretically sound.
- Setting up an action study in an ethical way can be hard. People may feel like they have to take part or take part in a certain way.
- It is prone to research errors like selection bias , social desirability bias, and other cognitive biases.
LEARN ABOUT: Self-Selection Bias
This post discusses how action research generates knowledge, its steps, and real-life examples. It is very applicable to the field of research and has a high level of relevance. We can only state that the purpose of this research is to comprehend an issue and find a solution to it.
At QuestionPro, we give researchers tools for collecting data, like our survey software, and a library of insights for any long-term study. Go to the Insight Hub if you want to see a demo or learn more about it.
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ’s)
Action research is a systematic approach to inquiry that involves identifying a problem or challenge in a practical context, implementing interventions or changes, collecting and analyzing data, and using the findings to inform decision-making and drive positive change.
Action research can be conducted by various individuals or groups, including teachers, administrators, researchers, and educational practitioners. It is often carried out by those directly involved in the educational setting where the research takes place.
The steps of action research typically include identifying a problem, reviewing relevant literature, designing interventions or changes, collecting and analyzing data, reflecting on findings, and implementing improvements based on the results.
MORE LIKE THIS

Participant Engagement: Strategies + Improving Interaction
Sep 12, 2024

Employee Recognition Programs: A Complete Guide
Sep 11, 2024
A guide to conducting agile qualitative research for rapid insights with Digsite

Cultural Insights: What it is, Importance + How to Collect?
Sep 10, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence

Action Research
Action research can be defined as “an approach in which the action researcher and a client collaborate in the diagnosis of the problem and in the development of a solution based on the diagnosis” [1] . In other words, one of the main characteristic traits of action research relates to collaboration between researcher and member of organisation in order to solve organizational problems.
Action study assumes social world to be constantly changing, both, researcher and research being one part of that change. [2] Generally, action researches can be divided into three categories: positivist, interpretive and critical.
Positivist approach to action research , also known as ‘classical action research’ perceives research as a social experiment. Accordingly, action research is accepted as a method to test hypotheses in a real world environment.
Interpretive action research , also known as ‘contemporary action research’ perceives business reality as socially constructed and focuses on specifications of local and organisational factors when conducting the action research.
Critical action research is a specific type of action research that adopts critical approach towards business processes and aims for improvements.
The following features of action research need to be taken into account when considering its suitability for any given study:
- It is applied in order to improve specific practices. Action research is based on action, evaluation and critical analysis of practices based on collected data in order to introduce improvements in relevant practices.
- This type of research is facilitated by participation and collaboration of number of individuals with a common purpose
- Such a research focuses on specific situations and their context
Advantages of Action Research
- High level of practical relevance of the business research;
- Can be used with quantitative, as well as, qualitative data;
- Possibility to gain in-depth knowledge about the problem.
Disadvantages of Action Research
- Difficulties in distinguishing between action and research and ensure the application of both;
- Delays in completion of action research due to a wide range of reasons are not rare occurrences
- Lack of repeatability and rigour
It is important to make a clear distinction between action research and consulting. Specifically, action research is greater than consulting in a way that action research includes both action and research, whereas business activities of consulting are limited action without the research.
Action Research Spiral
Action study is a participatory study consisting of spiral of following self-reflective cycles:
- Planning in order to initiate change
- Implementing the change (acting) and observing the process of implementation and consequences
- Reflecting on processes of change and re-planning
- Acting and observing
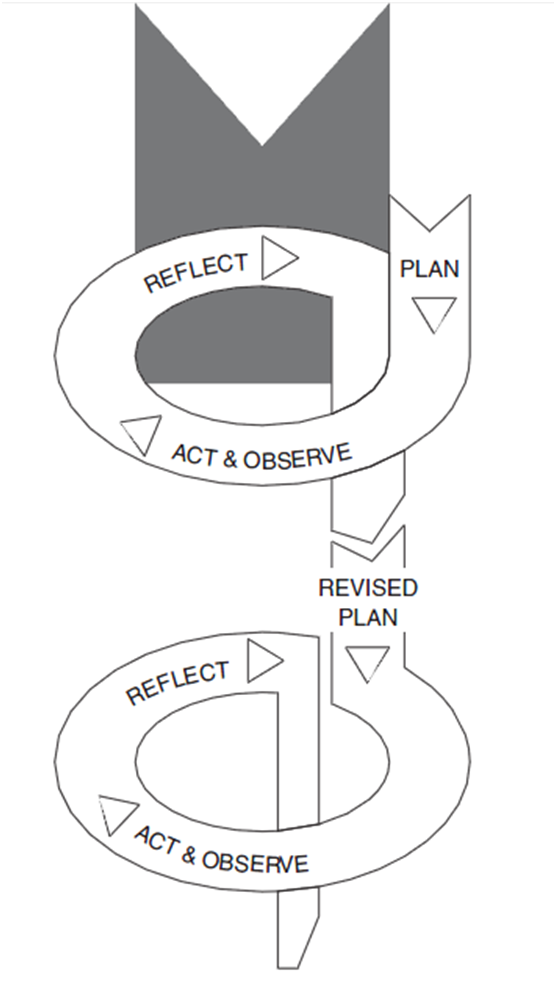
Kemmis and McTaggart (2000) do acknowledge that individual stages specified in Action Research Spiral model may overlap, and initial plan developed for the research may become obselete in short duration of time due to a range of factors.
The main advantage of Action Research Spiral model relates to the opportunity of analysing the phenomenon in a greater depth each time, consequently resulting in grater level of understanding of the problem.
Disadvantages of Action Research Spiral model include its assumption each process takes long time to be completed which may not always be the case.
My e-book, The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Dissertation in Business Studies: a step by step assistance offers practical assistance to complete a dissertation with minimum or no stress. The e-book covers all stages of writing a dissertation starting from the selection to the research area to submitting the completed version of the work within the deadline.

References
[1] Bryman, A. & Bell, E. (2011) “Business Research Methods” 3 rd edition, Oxford University Press
[2] Collis, J. & Hussey, R. (2003) “Business Research. A Practical Guide for Undergraduate and Graduate Students” 2nd edition, Palgrave Macmillan
Action Research
- Reference work entry
- First Online: 01 January 2023
- Cite this reference work entry

- David Coghlan 2
584 Accesses
Action research is an approach to research which aims at both taking action and creating knowledge or theory about that action as the action unfolds. It starts with everyday experience and is concerned with the development of living knowledge. Its characteristics are that it generates practical knowledge in the pursuit of worthwhile purposes; it is participative and democratic as its participants work together in the present tense in defining the questions they wish to explore, the methodology for that exploration, and its application through cycles of action and reflection. In this vein they are agents of change and coresearchers in knowledge generation and not merely passive subjects as in traditional research. In this vein, action research can be understood as a social science of the possible as the collective action is focused on creating a desired future in whatever context the action research is located.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others


Action Research As an Ethics Praxis Method
Banks, S., & Brydon-Miller, M. (2018). Ethics in participatory research for health and social well-being . Abingdon: Routledge.
Book Google Scholar
Bradbury, H. (2015). The Sage handbook of action research (3rd ed.). Sage: London.
Bradbury, H., Mirvis, P., Neilsen, E., & Pasmore, W. (2008). Action research at work: Creating the future following the path from Lewin. In P. Reason & H. Bradbury (Eds.), The Sage handbook of action research (2nd ed., pp. 77–92). London: Sage.
Chapter Google Scholar
Bradbury, H., Roth, J., & Gearty, M. (2015). The practice of learning history: Local and open approaches. In H. Bradbury (Ed.), The Sage handbook of action research (3rd ed., pp. 17–30). London: Sage.
Brydon-Miller, M., Greenwood, D., & Maguire, P. (2003). Why action research? Action Research, 1 (1), 9–28.034201[1476–7503(200307)1:1].
Article Google Scholar
Chevalier, J. M., & Buckles, D. J. (2019). Participatory action research. Theory and methods for engaged inquiry (2nd ed.). Abingdon: Routledge.
Coghlan, D. (2010). Seeking common ground in the diversity and diffusion of action research and collaborative management research action modalities: Toward a general empirical method. In W.A. Pasmore, A.B.. (Rami) Shani and R.W. Woodman (Eds.), Research in organizational change and development (vol 18, pp. 149–181). Bingley: Emerald.
Google Scholar
Coghlan, D. (2016). Retrieving the philosophy of practical knowing for action research. International Journal of Action Research, 12 , 84–107. https://doi.org/10.1688/IJAR-2016-01 .
Coghlan, D. (2019). Doing action research in your own organization (5th ed.). London: Sage.
Coghlan, D., & Brydon-Miller, M. (2014). The Sage encyclopedia of action research . London: Sage.
Coghlan, D., & Shani, A.B.. (Rami). (2017). Inquiring in the present tense: The dynamic mechanism of action research. Journal of Change Management , 17, 121–137. https://doi.org/10.1080/14697017.2017.1301045 .
Coghlan, D., Shani, A.B.. (Rami), & Hay, G.W. (2019). Toward a social science philosophy of organization development and change. In D.A. Noumair & A.B.. (Rami) Shani (eds.). Research in organizational change and development (Vol. 27, pp. 1–29). Bingley: Emerald.
Gearty, M., & Coghlan, D. (2018). The first-, second- and third-person dynamics of learning history. Systemic Practice & Action Research., 31 , 463–478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11213-017-9436-5 .
Greenwood, D., & Levin, M. (2007). Introduction to action research (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Heron, J., & Reason, P. (1997). A participatory inquiry paradigm. Qualitative Inquiry, 3 , 274–294.
Heron, J., & Reason, P. (2008). Extending epistemology within a cooperative inquiry. In P. Reason & H. Bradbury (Eds.), The Sage handbook of action research (2nd ed., pp. 366–380). London: Sage.
Huxham, C. (2003). Actionresearch as a methodology for theory development. Policy and Politics, 31 (2), 239–248. https://doi.org/10.1332/030557303765371726 .
Koshy, E., Koshy, V., & Waterman, H. (2011). Action research in healthcare . London: Sage.
Lonergan, B. J. (2005). Dimensions of meaning. In B. J. Lonergan (Ed.), The collected work of Bernard Lonergan (Vol. 4, pp. 232–244). Toronto: Toronto University Press.
Marshall, J. (2016). First person action research: Living life as inquiry . London: Sage.
Owen, R., Bessant, J., & Heintz, M. (2013). Responsible innovation: Managing the responsible emergence of science and innovation in society . London: Wiley.
Pasmore, W. A. (2001). Action research in the workplace: The socio-technical perspective. In P. Reason & H. Bradbury (Eds.), The handbook of action research (pp. 38–47). London: Sage.
Revans, R. W. (1971). Developing effective managers . London: Longmans.
Revans, R. (1998). ABC of action learning . London: Lemos& Crane.
Schein, E. H. (2013). Humble inquiry: The gentle art of asking instead of telling . Oakland: Berrett-Kohler.
Shani, A.B.. (Rami), & Coghlan, D. (2019). Action research in business and management: A reflective review. Action Research . https://doi.org/10.1177/1476750319852147 .
Susman, G. I., & Evered, R. D. (1978). An assessment of the scientific merits of action research. Administrative Science Quarterly, 23 , 582–601. https://doi.org/10.2307/2392581 .
Torbert, W. R., & Associates. (2004). Action inquiry . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Whitney, D., & Trosten-Bloom, A. (2010). The power of appreciative inquiry: A practical guide to positive change . Oakland: Berrett-Kohler.
Williamson, G., & Bellman, L. (2012). Action research in nursing and healthcare . London: Sage.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Trinity Business School, University of Dublin Trinity College, Dublin, Ireland
David Coghlan
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to David Coghlan .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Dublin City University, Dublin, Ireland
Vlad Petre Glăveanu
Section Editor information
Webster University Geneva, Geneva, Switzerland
Richard Randell
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Coghlan, D. (2022). Action Research. In: Glăveanu, V.P. (eds) The Palgrave Encyclopedia of the Possible. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-90913-0_180
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-90913-0_180
Published : 26 January 2023
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-90912-3
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-90913-0
eBook Packages : Behavioral Science and Psychology Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
Share this entry
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Research Methodologies Guide
- Action Research
- Bibliometrics
- Case Studies
- Content Analysis
- Digital Scholarship This link opens in a new window
- Documentary
- Ethnography
- Focus Groups
- Grounded Theory
- Life Histories/Autobiographies
- Longitudinal
- Participant Observation
- Qualitative Research (General)
- Quasi-Experimental Design
- Usability Studies
Action Re search
Acti on research is defined by O'Leary (2007) as
"Research strategies that tackle real-world problems in participatory, collaborative, and cyclical ways in order to produce both knowledge and action."
It refers to a type of research methodology which works toward a kind of change (whether social or professional). Because its goals are oriented toward change rather than knowledge-gathering alone, active research studies are often based in everyday issues, and concern themselves with the creation of practical solutions to these problems.
Elements of action research studies include:
- Identify a problem
- Research the problem and its probable causes
- Develop a response to the problem
- Implement the proposed solution
- Observe the implementation of the solution
- Reflect on the results (and start over, if necessary)
For more in-depth information, browse the resources below:
Where to Start
Below, a few tools and online guides that can help you start your action research project are listed. These include free online resources and resources available only through ISU Library.
- Action Research Handout [pdf] From the University of Pittsburgh, this handout defines action research, how it can be carried out, and common features of this type of research.
Online Resources
- YouTube - What is Action Research? This video reviews action research as it is used in education.
- Action Research - Informal Education From the encyclopedia of information education, this is another helpful article on action research, featuring different ways of describing it.
- Action research - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Wikipedia can be a useful place to start your research- check the citations at the bottom of the article for more information.
- Center for Collaborative Action Research A website for collaboration in action research.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Bibliometrics >>
- Last Updated: Sep 11, 2024 11:05 AM
- URL: https://instr.iastate.libguides.com/researchmethods

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 7: Action Research
Darshini Ayton
Learning outcomes
Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to:
- Explain the purpose of an action research approach.
- Explain the action research cycle.
- Describe action research characteristics.
What is action research?
The key concept in action research is change or action .
Action research (also known as ‘participatory action research’) aligns well with the practice of health and social care because researchers and practitioners in this discipline work with people and communities in holistic and relational ways to understand the history, culture and context of the setting. Action research aims to understand the setting and improve it through change or action. 1 This method has its roots in activism and advocacy and is focused on solutions. It is practical and deals with real-world problems and issues. Action research often undergoes phases in seeking to understand the problem, plan a solution, implement the solution and then reflect on or evaluate the solution, cyclically and iteratively. Action research is used in the practice of health and social care because it has two fundamental aims: to improve and to involve. This chapter outlines how this is evident, using examples from the research literature (see Table 7.1.).
Action research as involvement
Action research is a collaborative process between researchers and community members. This process is a core component of action research and represents a significant shift from typical research methods. Through action research, those who are being researched become the researchers, with close consideration given to power dynamics. The research participants become partners in the research and are involved in identifying and prioritising the research area, designing and undertaking data collection, conducting data analysis, and interpreting and disseminating the results. 1 The research partners may be provided with support and training to enable them to undertake these activities and to promote empowerment and capacity building (see examples following). Patient and public involvement in research and healthcare improvement (known in Australia as ‘consumer and community involvement’), has led to action research gaining popularity as a research design that captures the ‘living knowledge’ with, for and by people and communities throughout the research journey.
As an example, in the project Relationships Matter for Youth ‘Aging Out’ of Care, 2 Doucet and colleagues aimed to examine relationships that matter to young people in care and how these relationships can be nurtured and supported over time. The project is a collaborative participatory action research study incorporating photovoice (see Chapter 17 for more information on photovoice). Eight young people, formerly in care and from diverse backgrounds, were recruited to the study. The lead researcher highlighted their own lived experience of the child welfare system and a consciousness of the power dynamics at play. The lead researcher created processes within the project to ensure the youth co-researchers were empowered to share their experiences and that the research team members were working with the youth co-researchers and not for them. These processes included three months of weekly facilitated group discussions, shared meals before project commencement and group outings and community engagement during the project to encourage connection, bonding and trust. The youth co-researchers were provided with photography training and digital cameras. Data collection included the youth co-researchers submitting 6–7 photographs with responses to the following questions for photo contextualisation:
- What does this photograph mean to you? Why is this photo, in particular, most significant to you?
- How do you see this photo as a reflection of the issue of supportive long-term relationships – and one that is relevant to you as a former youth in care in your community?
- What is the relationship between the content of the photo and how you perceive the community or the world around you? What recommendation for change in your community is associated with this photo? 2(para22)
The photographs were showcased at an exhibition that was open to the community; those in attendance included policymakers, advocates and community representatives. The change documented through this project was one of social transformation for the community and self-transformation and healing for the individuals.
Action research as improvement
Action research can be practitioner-led, whereby the study investigates problems identified by the practitioner with the goal of understanding and improving practice over time. Improvement can be both social improvement and healthcare improvement. Healthcare improvement, in particular quality (of healthcare) improvement, has been the focus of clinical practice, research, education and advocacy for more than 30 years. The two main frameworks guiding healthcare and quality improvement efforts are the Plan, Do, Study, Act (PDSA) cycle and Learning Health Systems. 3 Both of these frameworks lend themselves to action research. For example, the PDSA cycle is guided by three overarching questions:
- What are we trying to accomplish?
- How will we know that a change is an improvement?
- What change can we make that will result in improvement? 4(Figure1)
Learning Health Systems is another approach to quality improvement that has gained popularity over the past decade. Data collected by health services (e.g. patient data, health records, laboratory results) are used for knowledge creation in continuous and rapid cycles of study, feedback and practice change. 5 A Learning Health Systems framework incorporates systems science, data science, research methods for real-world contexts, implementation science, participatory research and quality improvement approaches.
Van Heerden and colleagues adopted an action research study to transform the practice and environment of neonatal care in the maternity section of a district hospital in South Africa. The study Strategies to sustain a quality improvement initiative in neonatal resuscitation 6 was conducted in three cycles. Cycle 1 was a situation analysis that explored and described the existing practices and factors influencing neonatal resuscitation and mortality in the hospital through administering questionnaires with nurses (n=69); a focus group with nine doctors; and an analysis of hospital records. A nominal group discussion (structured group discussion including prioritisation) was conducted with 10 managers and staff, followed by a reflective meeting with the project’s steering committee. Cycle 2 developed and implemented strategies to sustain a quality improvement initiative. The strategies addressed training, equipment and stock, staff attitudes, staff shortages, transport transfer for critically ill neonates, and protocols. Cycle 3 was an evaluation of change and sustainability after the implementation of strategies (Cycle 2) and involved the analysis of hospital record data, repeat questionnaire with nurses (n=40), focus group discussion with 10 doctors, steering committee and management members, followed by reflective meetings with the steering committee. Qualitative data was analysed through open coding, and quantitative data was analysed descriptively. The neonatal mortality rate declined (yet still needed to improve) and the implementation strategies facilitated change that led to improvement and practice transformation.
Action research as a methodology or an approach
There is debate as to whether action research is a methodology or an approach, since several different research methods and methodologies can be used. For example, multiple forms of data collection can be utilized, including quantitative data from surveys or medical records, to inform the identification and understanding of the problem and evaluation of the solution. Action research can also draw on descriptive qualitative research, quantitative cross-sectional studies, case studies (see Chapter 8 ), ethnography ( Chapter 9 ) and grounded theory ( Chapter 10 ). Action research can therefore take a purely qualitative approach, or can take a mixed-methods approach. See Table 7.1. for examples of action research studies.
Advantages and disadvantages of action research
Action research addresses practical problems, drawing on principles of empowerment, capacity-building and participation. The research problem to be addressed is typically identified by the community, and the solutions are for the community. The research participants are collaborators in the research process. The examples presented in this chapter demonstrate how the research collaborators and co-researchers received training and support to lead elements of the project. Another advantage of action research is that it is a continuous cycle of development. Hence, the approach is iterative and the full solution can take multiple cycles and iterations to develop and sustain. 7,8
Since action research is fundamentally about relationships and integrating research into the real world, studies can take years to result in a solution. It is important to be able to adapt and be flexible in response to community and stakeholder needs and contexts. The research can therefore be constrained by what is practical and also ethical within the setting. This may limit the scope and scale of the research and compromise its rigour. Action research can also create unanticipated work for community members and participants because they are not usually involved in research in this way, and thus training may be required, as well as remuneration for time and experience. 7,8
| Middleton, 2021 | Taylor, 2015 | |
| 'To provide a critical analysis of the continuous process required to engender a collaborative effort towards developing socially just community sports programs.' | 'To identify the factors affecting telehealth adoption, and to test solutions to address prioritised areas for improvement and expansion.' | |
| This project was initiated by staff at the YMCA. Hence, it was community initiated and led. The YMCA team wanted to improve the sports program for forced migrant young people resettled in their community. The young people were provided with a one-year free membership; however many families did not renew this after the free period. The research team believed that an action research approach in which they worked alongside forced migrant young people would extend to the young people’s family members also benefiting from sports involvement. The YMCA team had a staff member with lived experience of being an asylum seeker and the manager knew about YMCA programs that could benefit from an action research approach. | To improve the adoption of telehealth aligned with the principles of plan do study act (PDSA) quality improvement process.Phase 1: Qualitative in-depth case studyPhase 2: Action research – researchers worked in partnership with participants at each site to plan, test and evaluate solutions to telehealth adoption. | |
| YMCA in Northeastern Ontario, Canada | Four community nursing settings using telehealth to monitor the symptoms of patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) and Chronic Health Failure, United Kingdom | |
| Relationships between the research team, YMCA team and young people were developed through meetings, shared meals, community encounters, Facebook group and visits to the homes of the young people.33 forced migrant young people from 15 families became collaborators in the study. The average age was 13 years.Get-to-know-you interviews were conducted, incorporating art and interviewing techniques – ‘draw any images and/or symbols that meaningfully depicted personal stories related to playing sport in Canada’, which was followed by interpreting events. The team then co-developed creative non-fiction polyphonic vignettes – these were shared with the young people and families and the YMCA and research teams for feedback. | Recruitment via site collaborators and local telehealth champions. All case study participants were invited to take part in the action research component if interested. 57 staff (community matrons, nurse specialists, frontline clinical and support staff, clinical leads and service managers, and other managers) and 1 patient. Total participants: 58.Phase 2: Action research component.Workshop 1 – develop an implementation plan (plan component of the PDSA cycle). Phase 1 case study findings presented. 3–6 actions were identified.An Action Inquiry Group (AIG) was established for each action with members responsible for implementation (DO) and review of progress and learning (STUDY).Workshop 2 – review and reflect on work and extend, refine or discontinue the plan. (ACT) | |
| Reflexive thematic analysis | Thematic analysis using framework analysis | |
| Themes are not presented in this article as it focuses on the process of the action research project. | Seven main action areas were identified (see subheadings in the article) |
Action research is a research design in which researchers and community members work together to identify problems, design and implement solutions and evaluate the impact of these solutions. Change or action is a core component of this research design.
- Baum F, MacDougall C, Smith D. Participatory action research. J Epidemiol Community Health . 2006;60(10):854-857. doi:10.1136/jech.2004.028662
- Doucet M, Pratt H, Dzhenganin M, Read J. Nothing About Us Without Us: Using Participatory Action Research (PAR) and arts-based methods as empowerment and social justice tools in doing research with youth ‘aging out’ of care. Child Abuse Negl . 2022;130:105358. doi: 10.1016/j.chiabu.2021.105358
- Taylor J, Coates E, Wessels B, Mountain G, Hawley MS. Implementing solutions to improve and expand telehealth adoption: participatory action research in four community healthcare settings. BMC Health Serv Res . 2015;15:529. doi:10.1186/s12913-015-1195-3
- Taylor MJ, McNicholas C, Nicolay C, Darzi A, Bell D, Reed JE. Systematic review of the application of the plan-do-study-act method to improve quality in healthcare. BMJ Qual Saf . 2014;23(4):290-298. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2013-001862
- Menear M, Blanchette MA, Demers-Payette O, Roy D. A framework for value-creating learning health systems. Health Res Policy Syst . 2019;17(1):79. doi:10.1186/s12961-019-0477-3
- Van Heerden C, Maree C, Janse Van Rensburg ES. Strategies to sustain a quality improvement initiative in neonatal resuscitation. Afr J Prim Health Care Fam Med . 2016;8(2):a958. doi:10.4102/phcfm.v8i2.958
- Liamputtong P. Qualitative Research Methods . 5th ed. Oxford University Press; 2020.
- Liamputtong P, Ezzy D. Qualitative Research Methods: A Health Focus . Oxford University Press; 1999.
- Middleton TRF, Schinke RJ, Lefebvre D, Habra B, Coholic D, Giffin C. Critically examining a community-based participatory action research project with forced migrant youth. Sport Soc . 2021;25(2):418-433. doi:10.1080/17430437.2022.2017619
Qualitative Research – a practical guide for health and social care researchers and practitioners Copyright © 2023 by Darshini Ayton is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Instant insights, infinite possibilities
What is action research?
Last updated
26 April 2023
Reviewed by
Cathy Heath
This research approach is often used in education, social work, healthcare, and community development.
Analyze action research
Dovetail streamlines action research analysis to help you uncover and share actionable insights
- What are the main types of action research?
Technical action research
This type of action research focuses on improving the efficiency and effectiveness of a system or process. It is often used in organizational contexts, such as businesses or government agencies, to address specific issues or improve operations.
In technical action research, the research process typically involves a systematic analysis of the existing system or process to identify areas of inefficiency or opportunity for improvement. This analysis may include collecting and analyzing data, observing work practices, conducting interviews with employees or other stakeholders, and/or reviewing documentation.
Collaboration action research
Collaborative action research seeks to empower stakeholders and give them a voice in the research process. It’s about working together to identify issues, create solutions, and implement change. This approach is typically used in community-based research, where community members and organizations are actively involved in the research process.
Collaborative action research is characterized by a high degree of participation, communication, and cooperation between researchers and stakeholders. The goal is to create a sense of ownership and commitment among all participants, leading to more sustainable and effective outcomes.
Critical reflection action research
This type of action research aims to create a space for marginalized voices to be heard and to address the power imbalances that exist between different stakeholders . It seeks to challenge the dominant power structures and social injustices that exist within a particular context.
This research also emphasizes the importance of reflecting on the underlying assumptions and values that drive research and decision-making processes.
Critical reflection action research involves a continuous process of questioning and reflection. This helps researchers gain a deeper understanding of the complexities and nuances of the context they are working in.
Through this research process, researchers can identify and challenge assumptions, beliefs, and practices that perpetuate social inequalities and injustices.
- What is the main purpose of action research?
The primary purpose of action research is to drive change and improvement within a particular context or situation. It aims to address real-world problems and challenges by involving stakeholders in the research process, encouraging collaboration and reflection, and using data to inform decision-making.
Action research emphasizes practical solutions over theoretical abstractions, and its goal is to create meaningful and sustainable change that benefits everyone involved.
Using a cyclical process of planning, acting, observing, and reflecting, action research enables stakeholders to learn and adapt continually and to make ongoing improvements based on their experiences and insights.
Overall, action research is a powerful tool for driving positive change and promoting continuous learning and improvement in various contexts.
- What are the tools of action research?
Action research typically involves a range of tools and techniques that help researchers gather and analyze data.
Here are some commonly used tools for action research:
Surveys and questionnaires
These are structured and often include closed-ended questions with predetermined response options. These tools help understand a population's experiences, opinions, and attitudes toward a particular issue or topic.
Document analysis
This involves analyzing written documents such as reports, policies, and procedures to gather qualitative data .
Observations
This involves systematically watching and recording phenomena, such as behaviors or interactions, in their natural setting to collect data.
Asking people questions during interviews is one way to gather qualitative information about their perspectives or experiences.
Case studies
This method deeply understands a particular person, group, or situation. It involves collecting data through various sources, such as interviews, observations, and document analysis, to form a comprehensive picture of the situation being studied.
- How is action research different from other methods?
Action research is distinct from other research methodologies because it focuses on producing actionable insights that lead to practical solutions.
Unlike other forms of research that tend to emphasize the generation of abstract theories or empirical models, action research emphasizes the active engagement of stakeholders in problem-solving activities that can result in a substantial change in real-world situations.
This approach strongly emphasizes collaboration, co-creation, and participatory processes to empower individuals and organizations to take ownership of their challenges and work towards sustainable, impactful solutions.
By prioritizing the needs and perspectives of those directly affected by a problem, action research can help bridge the gap between theory and practice and create meaningful, impactful, and sustainable change.
- What research method is used in action research?
Action research uses a process that allows researchers to implement changes and observe the effects of those changes in real-life situations.
This research methodology is grounded in the idea that the best solutions come from those who are most impacted by the issue. The participants are actively involved in the research process, collaborating with the researcher to develop solutions that work in their unique context.
Using participatory methods and data collection tools ensures that the data gathered is accurate and reflects the participants' perspectives. This can include surveys , questionnaires , interviews, and observations .
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 22 August 2024
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 August 2024
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
the encyclopaedia of pedagogy and informal education

What is action research and how do we do it?
In this article, we explore the development of some different traditions of action research and provide an introductory guide to the literature., contents : what is action research · origins · the decline and rediscovery of action research · undertaking action research · conclusion · further reading · how to cite this article . see, also: research for practice ..
In the literature, discussion of action research tends to fall into two distinctive camps. The British tradition – especially that linked to education – tends to view action research as research-oriented toward the enhancement of direct practice. For example, Carr and Kemmis provide a classic definition:
Action research is simply a form of self-reflective enquiry undertaken by participants in social situations in order to improve the rationality and justice of their own practices, their understanding of these practices, and the situations in which the practices are carried out (Carr and Kemmis 1986: 162).
Many people are drawn to this understanding of action research because it is firmly located in the realm of the practitioner – it is tied to self-reflection. As a way of working it is very close to the notion of reflective practice coined by Donald Schön (1983).
The second tradition, perhaps more widely approached within the social welfare field – and most certainly the broader understanding in the USA is of action research as ‘the systematic collection of information that is designed to bring about social change’ (Bogdan and Biklen 1992: 223). Bogdan and Biklen continue by saying that its practitioners marshal evidence or data to expose unjust practices or environmental dangers and recommend actions for change. In many respects, for them, it is linked into traditions of citizen’s action and community organizing. The practitioner is actively involved in the cause for which the research is conducted. For others, it is such commitment is a necessary part of being a practitioner or member of a community of practice. Thus, various projects designed to enhance practice within youth work, for example, such as the detached work reported on by Goetschius and Tash (1967) could be talked of as action research.
Kurt Lewin is generally credited as the person who coined the term ‘action research’:
The research needed for social practice can best be characterized as research for social management or social engineering. It is a type of action-research, a comparative research on the conditions and effects of various forms of social action, and research leading to social action. Research that produces nothing but books will not suffice (Lewin 1946, reproduced in Lewin 1948: 202-3)
His approach involves a spiral of steps, ‘each of which is composed of a circle of planning, action and fact-finding about the result of the action’ ( ibid. : 206). The basic cycle involves the following:
This is how Lewin describes the initial cycle:
The first step then is to examine the idea carefully in the light of the means available. Frequently more fact-finding about the situation is required. If this first period of planning is successful, two items emerge: namely, “an overall plan” of how to reach the objective and secondly, a decision in regard to the first step of action. Usually this planning has also somewhat modified the original idea. ( ibid. : 205)
The next step is ‘composed of a circle of planning, executing, and reconnaissance or fact-finding for the purpose of evaluating the results of the second step, and preparing the rational basis for planning the third step, and for perhaps modifying again the overall plan’ ( ibid. : 206). What we can see here is an approach to research that is oriented to problem-solving in social and organizational settings, and that has a form that parallels Dewey’s conception of learning from experience.
The approach, as presented, does take a fairly sequential form – and it is open to a literal interpretation. Following it can lead to practice that is ‘correct’ rather than ‘good’ – as we will see. It can also be argued that the model itself places insufficient emphasis on analysis at key points. Elliott (1991: 70), for example, believed that the basic model allows those who use it to assume that the ‘general idea’ can be fixed in advance, ‘that “reconnaissance” is merely fact-finding, and that “implementation” is a fairly straightforward process’. As might be expected there was some questioning as to whether this was ‘real’ research. There were questions around action research’s partisan nature – the fact that it served particular causes.
The decline and rediscovery of action research
Action research did suffer a decline in favour during the 1960s because of its association with radical political activism (Stringer 2007: 9). There were, and are, questions concerning its rigour, and the training of those undertaking it. However, as Bogdan and Biklen (1992: 223) point out, research is a frame of mind – ‘a perspective that people take toward objects and activities’. Once we have satisfied ourselves that the collection of information is systematic and that any interpretations made have a proper regard for satisfying truth claims, then much of the critique aimed at action research disappears. In some of Lewin’s earlier work on action research (e.g. Lewin and Grabbe 1945), there was a tension between providing a rational basis for change through research, and the recognition that individuals are constrained in their ability to change by their cultural and social perceptions, and the systems of which they are a part. Having ‘correct knowledge’ does not of itself lead to change, attention also needs to be paid to the ‘matrix of cultural and psychic forces’ through which the subject is constituted (Winter 1987: 48).
Subsequently, action research has gained a significant foothold both within the realm of community-based, and participatory action research; and as a form of practice-oriented to the improvement of educative encounters (e.g. Carr and Kemmis 1986).
Exhibit 1: Stringer on community-based action research
A fundamental premise of community-based action research is that it commences with an interest in the problems of a group, a community, or an organization. Its purpose is to assist people in extending their understanding of their situation and thus resolving problems that confront them….
Community-based action research is always enacted through an explicit set of social values. In modern, democratic social contexts, it is seen as a process of inquiry that has the following characteristics:
• It is democratic , enabling the participation of all people.
• It is equitable , acknowledging people’s equality of worth.
• It is liberating , providing freedom from oppressive, debilitating conditions.
• It is life enhancing , enabling the expression of people’s full human potential.
(Stringer 1999: 9-10)
Undertaking action research
As Thomas (2017: 154) put it, the central aim is change, ‘and the emphasis is on problem-solving in whatever way is appropriate’. It can be seen as a conversation rather more than a technique (McNiff et. al. ). It is about people ‘thinking for themselves and making their own choices, asking themselves what they should do and accepting the consequences of their own actions’ (Thomas 2009: 113).
The action research process works through three basic phases:
Look -building a picture and gathering information. When evaluating we define and describe the problem to be investigated and the context in which it is set. We also describe what all the participants (educators, group members, managers etc.) have been doing.
Think – interpreting and explaining. When evaluating we analyse and interpret the situation. We reflect on what participants have been doing. We look at areas of success and any deficiencies, issues or problems.
Act – resolving issues and problems. In evaluation we judge the worth, effectiveness, appropriateness, and outcomes of those activities. We act to formulate solutions to any problems. (Stringer 1999: 18; 43-44;160)
The use of action research to deepen and develop classroom practice has grown into a strong tradition of practice (one of the first examples being the work of Stephen Corey in 1949). For some, there is an insistence that action research must be collaborative and entail groupwork.
Action research is a form of collective self-reflective enquiry undertaken by participants in social situations in order to improve the rationality and justice of their own social or educational practices, as well as their understanding of those practices and the situations in which the practices are carried out… The approach is only action research when it is collaborative, though it is important to realise that action research of the group is achieved through the critically examined action of individual group members. (Kemmis and McTaggart 1988: 5-6)
Just why it must be collective is open to some question and debate (Webb 1996), but there is an important point here concerning the commitments and orientations of those involved in action research.
One of the legacies Kurt Lewin left us is the ‘action research spiral’ – and with it there is the danger that action research becomes little more than a procedure. It is a mistake, according to McTaggart (1996: 248) to think that following the action research spiral constitutes ‘doing action research’. He continues, ‘Action research is not a ‘method’ or a ‘procedure’ for research but a series of commitments to observe and problematize through practice a series of principles for conducting social enquiry’. It is his argument that Lewin has been misunderstood or, rather, misused. When set in historical context, while Lewin does talk about action research as a method, he is stressing a contrast between this form of interpretative practice and more traditional empirical-analytic research. The notion of a spiral may be a useful teaching device – but it is all too easy to slip into using it as the template for practice (McTaggart 1996: 249).
Further reading
This select, annotated bibliography has been designed to give a flavour of the possibilities of action research and includes some useful guides to practice. As ever, if you have suggestions about areas or specific texts for inclusion, I’d like to hear from you.
Explorations of action research
Atweh, B., Kemmis, S. and Weeks, P. (eds.) (1998) Action Research in Practice: Partnership for Social Justice in Education, London: Routledge. Presents a collection of stories from action research projects in schools and a university. The book begins with theme chapters discussing action research, social justice and partnerships in research. The case study chapters cover topics such as: school environment – how to make a school a healthier place to be; parents – how to involve them more in decision-making; students as action researchers; gender – how to promote gender equity in schools; writing up action research projects.
Carr, W. and Kemmis, S. (1986) Becoming Critical. Education, knowledge and action research , Lewes: Falmer. Influential book that provides a good account of ‘action research’ in education. Chapters on teachers, researchers and curriculum; the natural scientific view of educational theory and practice; the interpretative view of educational theory and practice; theory and practice – redefining the problem; a critical approach to theory and practice; towards a critical educational science; action research as critical education science; educational research, educational reform and the role of the profession.
Carson, T. R. and Sumara, D. J. (ed.) (1997) Action Research as a Living Practice , New York: Peter Lang. 140 pages. Book draws on a wide range of sources to develop an understanding of action research. Explores action research as a lived practice, ‘that asks the researcher to not only investigate the subject at hand but, as well, to provide some account of the way in which the investigation both shapes and is shaped by the investigator.
Dadds, M. (1995) Passionate Enquiry and School Development. A story about action research , London: Falmer. 192 + ix pages. Examines three action research studies undertaken by a teacher and how they related to work in school – how she did the research, the problems she experienced, her feelings, the impact on her feelings and ideas, and some of the outcomes. In his introduction, John Elliot comments that the book is ‘the most readable, thoughtful, and detailed study of the potential of action-research in professional education that I have read’.
Ghaye, T. and Wakefield, P. (eds.) CARN Critical Conversations. Book one: the role of the self in action , Bournemouth: Hyde Publications. 146 + xiii pages. Collection of five pieces from the Classroom Action Research Network. Chapters on: dialectical forms; graduate medical education – research’s outer limits; democratic education; managing action research; writing up.
McNiff, J. (1993) Teaching as Learning: An Action Research Approach , London: Routledge. Argues that educational knowledge is created by individual teachers as they attempt to express their own values in their professional lives. Sets out familiar action research model: identifying a problem, devising, implementing and evaluating a solution and modifying practice. Includes advice on how working in this way can aid the professional development of action researcher and practitioner.
Quigley, B. A. and Kuhne, G. W. (eds.) (1997) Creating Practical Knowledge Through Action Research, San Fransisco: Jossey Bass. Guide to action research that outlines the action research process, provides a project planner, and presents examples to show how action research can yield improvements in six different settings, including a hospital, a university and a literacy education program.
Plummer, G. and Edwards, G. (eds.) CARN Critical Conversations. Book two: dimensions of action research – people, practice and power , Bournemouth: Hyde Publications. 142 + xvii pages. Collection of five pieces from the Classroom Action Research Network. Chapters on: exchanging letters and collaborative research; diary writing; personal and professional learning – on teaching and self-knowledge; anti-racist approaches; psychodynamic group theory in action research.
Whyte, W. F. (ed.) (1991) Participatory Action Research , Newbury Park: Sage. 247 pages. Chapters explore the development of participatory action research and its relation with action science and examine its usages in various agricultural and industrial settings
Zuber-Skerritt, O. (ed.) (1996) New Directions in Action Research , London; Falmer Press. 266 + xii pages. A useful collection that explores principles and procedures for critical action research; problems and suggested solutions; and postmodernism and critical action research.
Action research guides
Coghlan, D. and Brannick, D. (2000) Doing Action Research in your own Organization, London: Sage. 128 pages. Popular introduction. Part one covers the basics of action research including the action research cycle, the role of the ‘insider’ action researcher and the complexities of undertaking action research within your own organisation. Part two looks at the implementation of the action research project (including managing internal politics and the ethics and politics of action research). New edition due late 2004.
Elliot, J. (1991) Action Research for Educational Change , Buckingham: Open University Press. 163 + x pages Collection of various articles written by Elliot in which he develops his own particular interpretation of action research as a form of teacher professional development. In some ways close to a form of ‘reflective practice’. Chapter 6, ‘A practical guide to action research’ – builds a staged model on Lewin’s work and on developments by writers such as Kemmis.
Johnson, A. P. (2007) A short guide to action research 3e. Allyn and Bacon. Popular step by step guide for master’s work.
Macintyre, C. (2002) The Art of the Action Research in the Classroom , London: David Fulton. 138 pages. Includes sections on action research, the role of literature, formulating a research question, gathering data, analysing data and writing a dissertation. Useful and readable guide for students.
McNiff, J., Whitehead, J., Lomax, P. (2003) You and Your Action Research Project , London: Routledge. Practical guidance on doing an action research project.Takes the practitioner-researcher through the various stages of a project. Each section of the book is supported by case studies
Stringer, E. T. (2007) Action Research: A handbook for practitioners 3e , Newbury Park, ca.: Sage. 304 pages. Sets community-based action research in context and develops a model. Chapters on information gathering, interpretation, resolving issues; legitimacy etc. See, also Stringer’s (2003) Action Research in Education , Prentice-Hall.
Winter, R. (1989) Learning From Experience. Principles and practice in action research , Lewes: Falmer Press. 200 + 10 pages. Introduces the idea of action research; the basic process; theoretical issues; and provides six principles for the conduct of action research. Includes examples of action research. Further chapters on from principles to practice; the learner’s experience; and research topics and personal interests.
Action research in informal education
Usher, R., Bryant, I. and Johnston, R. (1997) Adult Education and the Postmodern Challenge. Learning beyond the limits , London: Routledge. 248 + xvi pages. Has some interesting chapters that relate to action research: on reflective practice; changing paradigms and traditions of research; new approaches to research; writing and learning about research.
Other references
Bogdan, R. and Biklen, S. K. (1992) Qualitative Research For Education , Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
Goetschius, G. and Tash, J. (1967) Working with the Unattached , London: Routledge and Kegan Paul.
McTaggart, R. (1996) ‘Issues for participatory action researchers’ in O. Zuber-Skerritt (ed.) New Directions in Action Research , London: Falmer Press.
McNiff, J., Lomax, P. and Whitehead, J. (2003) You and Your Action Research Project 2e. London: Routledge.
Thomas, G. (2017). How to do your Research Project. A guide for students in education and applied social sciences . 3e. London: Sage.
Acknowledgements : spiral by Michèle C. | flickr ccbyncnd2 licence
How to cite this article : Smith, M. K. (1996; 2001, 2007, 2017) What is action research and how do we do it?’, The encyclopedia of pedagogy and informal education. [ https://infed.org/mobi/action-research/ . Retrieved: insert date] .
© Mark K. Smith 1996; 2001, 2007, 2017
- Search Menu
Sign in through your institution
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Numismatics
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Social History
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Acquisition
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Media
- Music and Religion
- Music and Culture
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Meta-Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Legal System - Costs and Funding
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Restitution
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Ethics
- Business Strategy
- Business History
- Business and Technology
- Business and Government
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Social Issues in Business and Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic History
- Economic Systems
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Social Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Sustainability
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- Ethnic Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Theory
- Politics and Law
- Politics of Development
- Public Policy
- Public Administration
- Qualitative Political Methodology
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Disability Studies
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous chapter
- Next chapter >
24 Action Research
- Published: December 2015
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
This chapter on action research describes the orchestration of cyclical processes of action and research that mutually inform each other. The conceptual foundations of action research are explained, and a case is made for action research’s utility as a framework for knowledge generation in collaboration with community organizations. Although action research is often conducted using qualitative methods, this chapter makes a case for methodological pluralism. Principles for designing and conducting mixed methods action research are provided, drawing specifically on an example of an ongoing collaboration with a community organizing network working on multiple issues, including immigration and transit.
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
- Add your ORCID iD
Institutional access
Sign in with a library card.
- Sign in with username/password
- Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
| Month: | Total Views: |
|---|---|
| October 2022 | 1 |
| November 2022 | 3 |
| December 2022 | 4 |
| January 2023 | 2 |
| February 2023 | 4 |
| March 2023 | 4 |
| April 2023 | 1 |
| May 2023 | 1 |
| June 2023 | 2 |
| July 2023 | 2 |
| August 2023 | 1 |
| September 2023 | 2 |
| October 2023 | 2 |
| November 2023 | 2 |
| December 2023 | 4 |
| April 2024 | 1 |
| May 2024 | 5 |
| June 2024 | 1 |
| July 2024 | 1 |
| September 2024 | 4 |
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

How to... Carry out action research
Action research is a research strategy which combines research with action and participation in the field. As a method, it goes back to the period immediately post the Second World War (see "The history of action research", below) and has become increasingly popular over the last few years, along with other qualitative methods, as people come to see the value in collecting rich data by disparate means. It is a form of applied research, and is particularly useful in developing theory about practice.
On this page
What is action research, research design and data collection, exposing action research, action research resources.
"Action research can be described as a family of research methodologies which pursue action (or change) and research (or understanding) at the same time. In most of its forms it does this by:
- using a cyclic or spiral process which alternates between action and critical reflection, and
- in the later cycles, continuously refining methods, data and interpretation in the light of the understanding developed in the earlier cycles.
It is thus an emergent process which takes shape as understanding increases; it is an iterative process which converges towards a better understanding of what happens.
In most of its forms it is also participative (among other reasons, change is usually easier to achieve when those affected by the change are involved) and qualitative."
From Dick, B. (1999), "What is action research?". Available online at http://www.scu.edu.au/schools/gcm/ar/whatisar.htm
The normal position of the researcher is detached, scientific, standing outside events and diligently recording them. A number of methods may be used – questionnaire, focus group, interviews, observation, etc. – but it is generally the researcher who controls data gathering for purposes that affect their research rather than the participants' agenda. In other words, the subjects are passive in research terms: they may either be unaware of being "watched" or unconcerned about the data used from their interview or survey.
In action research, however, people are not just subjects but partners in the research process. The research arises not out of a question from an external individual, but as a shared process of reflection between the researcher and the participants; the latter help gather data in relation to their own questions; research results are fed back to them directly to improve the situation that was the subject of the research.
The learning so acquired goes not only to answer a research question, but also to solve an organisational problem, or at least to take forward and deepen the organisation's understanding of itself.
However much confined to the organisation are the interests of the participants, the researcher will have broader concerns. He or she is seeking and creating knowledge which relates not just to the project itself, but which can be applied to other projects, in other contexts, and which can add to practice and theory itself. Good action research, like any good research, seeks a broad influence.
The context of action research is almost always the organisation: most action research studies are case studies. They are very often linked with a change agenda, via the creation of deeper knowledge and understanding about a particular social or organisational issue, in order to improve a particular situation.
Below are two examples of research projects that deliberately set out to change rather than just observe:
- In " Operationalizing the concept of value – an action research-based model " Naslund et al. (2006) looked at the concept of value within an organisation, principally at a global corporation which leads in the packaging supply field. The data were collected in the organisation by means of document studies, informal surveys, observations and interviews. The object was to help people in the organisation look at their ways of working and overcome any resistance to better ways of doing things.
- In " Performance measurement action research " Moss et al . (2007) describe how the Centre for Facilities Management worked with a provider of estates and facilities management to a major UK government department. It used action research to create an improved performance measurement system for the organisation.
In "conventional" research, the researcher either takes a snapshot of what is going on in an organisation at a particular time, or does a longitudinal study. In action research the participant as well as the researcher reflects on actions, while the researcher is equally concerned to see organisational change as to have research hypotheses substantiated.
In " The impact of e-resources at Bournemouth University 2004/2006 " Beard et al. provide the following definition of action research:
"Action research … seeks to bring together action and reflection, theory and practice, in participation with others, in pursuit of practical solutions to issues of pressing concern to people (Reason, P. and Bradbury, H. (2001), Handbook of Action Research , Sage, London, p. 1)."
In " The quality of an action research thesis in the social sciences " Zuber-Skerrit and Fletcher (2007) quote the following definition of action research which was first given at a 1989 symposium in Brisbane:
"If yours is a situation in which:
- people reflect and improve (or develop) their own work and their own situations;
- by tightly interlinking their reflection and action; and
- also making their experience public not only to other participants but also to other persons interested in and concerned about the work and the situation, i.e. their public theories and practices of the work and the situation;
and if yours is a situation in which there is increasingly:
- data gathering by participants themselves (or with the help of others) in relation to their own questions;
- participation (in problem posing and in answering questions) in decision making;
- power sharing and the relative suspension of hierarchical ways of working, in a conscious move towards social and industrial democracy;
- collaboration among members of the group as a 'critical community';
- self-reflection, self-evaluation and self-management by autonomous and responsible persons and groups;
- progressive (and public) learning by doing and making mistakes in a 'self-reflective spiral' of planning, acting, observing, reflective planning, etc.; and
- reflection that supports the idea of the '(self-)reflective practitioner';
then yours is a situation in which action research is occurring."
The history of action research
The concept of action research goes back to the German psychologist Kurt Lewin (1890-1947). As a Jew and a leftist, Lewin was forced in the 1930s to flee Hitler's Germany for the USA, where he did much to develop our contemporary ideas of change. He was particularly (and understandably) concerned with social justice and racial discrimination, seeing the latter as linked with problems of management and gatekeepers who determined what was and wasn't done. He believed that efforts for change should be focused on the group, which should challenge group norms and processes.
The concept of action research grew out of Lewin's strong social convictions – research would be linked with action to create a change process over organisational issues directly experienced by practitioners. Good research, Lewin claimed, should produce real change and not just end up in books (he was writing in an era well before the dominance of the top US journals with their "scientific" approach or the UK Research Assessment Exercise).
A particularly good account of Lewin's contribution to action research theory is given in Adams and McNicholas (2007).
In order to produce this change, the researcher needed to witness events at first hand as a partner in the process, to become truly involved in the system. His or her role is not only to document, but also to facilitate the process of reflection and enquiry.
A group of university researchers worked in partnership with the local high schools to help the latter determine what were the factors that led to pupils staying longer in school. They used a method of "appreciative inquiry", which is looking for the best and building on it. The positive environment thus created encourages and stimulates learning (Calabrese, 2006).
Action research has also been taken up in Latin America, by Paolo Friere and Orlando Fals Borda, and is currently a popular research methodology all over the world with a burgeoning literature, especially over the last two decades.
Applications of action research
According to Gapp and Fisher (2006) action research presents:
"a very effective alternative to social science research methods in that it is: practical, participative and collaborative, emancipatory, interpretive and critical. The process of action research is very effective in identifying creative solutions".
As described above, and because of its participatory and organisational nature, action research is much identified with change, whether as an actual change initiative, observation of change process or seeking to manage change in an organisation. Part of its strength here lies in its ability to take interaction with participants further than with normal research, yielding deeper understanding of individuals and drawing down more illuminating data. Equally it helps participants themselves to gain deeper understanding by reflecting on their experience.
Action research can also be strongly linked with action learning – learning from experience, particularly in an organisational context. As the researchers participate in the organisation, they create an impetus for learning as members of the organisation reflect on their experiences.
In Scandinavia, the "dialogue conference" has been in use for 30 years, and involves creating a public forum for participation and dialogue organised according to principles of respect and democracy. " Developmental magic? Two takes on a dialogue conference " (Philips and Huzzard, 2007) explores the use of this technique in action research to facilitate change within health organisations, taking on themes of visions, challenges, ideas and plans for future work.
Action research was used as a tool to try and understand the management of change in an organisation, the organisation being a university and the change being the wide scale adoption of electronic resources, as described by Beard et al. (2007).
Action research is common in research which looks at social issues, such as ethnicity, equality and the environment. Another application is in educational research, its popularity here being no doubt due to the obvious need to improve practice.
An EC funded project wanted to examine the question, would new migrants be more likely to work for the NHS if they had a better command of English and related material? This was researched through a number of focus groups comprising health service workers and non-working minority groups. Material was also created and trialled with a number of groups of learners.
Finally, there is an obvious attraction for action research for part-time management students looking for a way of integrating their studies with their work, many of whom use their project as a way of solving a workplace issue and carrying out some consultancy.
Adams, C.A and McNicholas, P. (2007) " Making a difference. Sustainability reporting, accountability and organisational change ", Accounting, Auditing & Accountability Journal , Vol. 20 No. 3, pp. 382-402.
Beard, J., Dale, P. and Hutchins, J. (2007), " The impact of e-resources at Bournemouth University 2004/2006 ", Performance Measurement and Metrics , Vol. 8 No. 1, pp. 7-17.
Calabrese, R.L. (2006), " Building social capital through the use of an appreciative inquiry theoretical perspective in a school and university partnership ", International Journal of Education Management , Vol. 20 No. 3, pp. 173-182.
Gapp, R. and Fisher, R. (2006), " Achieving excellence through innovative approaches to student involvement in course evaluation within the tertiary education sector ", Quality Assurance in Education , Vol. 14 No. 2, pp. 156-166.
Moss, Q.Z., Alho, J. and Alexander, K. (2007), " Performance measurement action research ", Journal of Facilities Management , Vol. 5 No. 4, pp. 290-300.
Naslund, D. , Olsson, A. and Karlsson, S. (2006), " Operationalizing the concept of value – an action research-based model ", The Learning Organization , Vol. 13 No. 3, pp. 300-332.
Philips, M.E. and Huzzard, T. (2007), " Developmental magic? Two takes on a dialogue conference ", Journal of Organizational Change Management , Vol. 20 No. 1, pp. 8-25.
Zuber-Skerrit, O. and Fletcher, M. (2007), " The quality of an action research thesis in the social sciences ", Quality Assurance in Education, Vol. 15 No. 4, pp. 413-436.
Like any research approach, action research has its own development cycle, its links with theory, what may rather grandly be termed its epistemological stance (i.e. whether it aims to build on or build theory) and its preferred data collection methods. This is all part of research design, and this section will look at how to design an action research project in a thorough and effective way.
Link with participants
As we saw in the previous section, what really distinguishes action research from other forms of research is that the participants have a much more direct role. This will influence the design from start to finish. For example participants will:
- need to be involved in the planning process, in order to ensure that the research asks questions that are relevant to their concern,
- possibly have a hand in data gathering, and definitely an interest in the results,
- look for practice related, as opposed to research, outcomes, and a change in their own practice.
Action research has been compared with consulting in that it is concerned with development of practice; the difference is that it is cyclical rather than linear, the cyclical element being concerned with reflection, designed not only to improve practice but also to generate theory. The time-scale is often longer, and the budget larger.
The theoretical connection
For all that action research is concerned with improvements to practice, the theoretical angle is also important as all research seeks to build theory.
Action research is generally inductive rather than deductive – that is, the data collection builds rather than tests theory. The researcher may start with a particular theoretical position, but should be open to what the research yields, and to open reflection.
This openness, however, does not negate the importance of immersing oneself in the relevant literature, both content and methodology, in order to give a context to the problem.
The unique nature of action research interventions, and their non repeatability, means that they are not good for rigorous theory testing. On the other hand, they are good at testing theoretical frameworks, or theories as related to other theories. Hence their usefulness in organisation studies, where such frameworks apply.
The important thing is for the particular research to have results which extend beyond the confines of the particular project and have a general application, whether as a test of theoretical frameworks as described above, as theory which informs more robust practice, or a tool, model, or method which can be used in a range of situations.
In " Making a difference. Sustainability reporting, accountability and organisational change " Adams and McNicholas (2007) conclude their study of sustainability reporting thus:
"Our study has shown that, through action research, academics can assist organisations in bringing about improvements to their sustainability reporting processes, accountability and sustainability performance. Action research might also contribute to academic literature and theorising by improving our understanding of: what drives organisations to provide an account of their sustainability performance; what determines the level of accountability attained; the complex nature of the interactions and relationships between organisations and their stakeholders on sustainability issues; and the manner in which sustainability reporting processes impact on organisational change towards improved sustainability performance."
In " Action research as culture change tool " Marcinkoniene and Kekäle describe a programme of change in post-communist Baltic schools. They use the literature to describe the prevalent culture, and conclude that it would be possible to apply a similar action research intervention in other post-communist states, where schools are likely to have a similar culture.
Action research takes the researcher and the organisation through a cyclical process of deepening understanding, both of the organisational problem and the research question, in which reflection happens not just at the beginning and the end, but throughout the process. This reflection yields a greater sense of empowerment for participants, who feel themselves more in charge of decision-making processes and more able to see problems clearly.
The iterative nature of the reflection process makes action research similar to grounded theory, which involves going back into the field after looking at data with a clearer understanding of the key issues, and developing further understanding through more research.
In " The quality of an action research thesis in the social sciences " Zuber-Skerrit quotes her own theoretical framework of action research – the CRASP model. Action research is:
- C ritical (and self-critical) collaborative enquiry by
- R eflective practitioners being
- A ccountable and making the results of their enquiry public,
- S elf-evaluating their practice and engaged in
- P articipative problem-solving and continuing professional development.
Collecting data – multiple sources of evidence
The great advantage of the case study (and most action research, as we have seen, takes place in a case study environment) is that it can yield data from many different sources. Many action research studies use a combination of artefacts, document studies, surveys, interviews, focus groups, discussions, participant observation, group work, performance measurement. In addition, hard data may be available as in the following example.
Adams and McNicholas (2007) report on the data collection methods, which supplemented discussion, observations in meetings and interviews, with hard data such as operational statistics, financial accounts, marketing reports, sustainability reports, as well as detailed study of the website, annual reports etc.
The most striking thing about action research, however, is that much of the data is supplied by the individuals themselves as part of feedback on how the object of data collection helps them in their work and lives.
In " Prioritizing tactical quality improvement: An action research study " Hales et al. (2006) describe the testing of a method for improving decision making at the shop-floor level. The method was tried out on the shop-floor with interviews being conducted with users and observation of people using it.
Andersen et al . (2006) describe how the researchers were involved in bringing about changes in a bank, and deployed a number of methods to identify shortcomings and suggest improvements, including:
- interviews with all employees in the bank;
- observation of employees' interaction with customers in customer meetings and other situations;
- interviews with customers, both those observed in interactions with service personnel and those who had not been in contact with the bank in a while;
- performance measurement of some key factors, e.g. customer flow in the bank office;
- group work among the bank employees to analyse problem areas and develop improvements; and
- the use of tools like business process analysis, root cause analysis, and similar techniques to shed light on problem areas.
Beard et al. (2007) used action research because it was participatory, encouraging researchers to seek views which they did through online questionnaires and subsequent interviews with a number of participants, and which they triangulated with data on online use.
Gapp and Fisher (2006) describe how the traditional course evaluation questionnaires were supplemented by focus groups as an additional way of finding out how to improve the course.
Andersen, B., Henriksen, B. and Aarseth, W. (2006), " Holistic performance management: an integrated framework ", International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management , Vol. 55 No. 1, pp. 61-78.
Hales, D.N., Siha, S.M. and McKnew, J.I. (2006), " Prioritizing tactical quality improvement: An action research study ", International Journal of Operations and Production Management , Vol. 26 No. 8, pp. 866-881.
Marcinkoniene, R. and Kekäle, T. (2007), " Action research as culture change tool ", Baltic Journal of Management , Vol. 2 No. 1, pp. 97-109.
The advantages of action research will have become clear. It allows the researcher to work on a problem, not only yielding answers to the problem but also informing theory. It empowers participants, enables change, and creates opportunities for organisational learning. It yields rich data from multiple sources. It creates solid theory about practice, and hence leads to improvements.
Despite these benefits, action research is not without its limitations and critics. The latter point to the lack of validity and generalisability, on the ground that the intervention is a one off and not repeatable. Perhaps more seriously, however, is the fact that it is not perceived as mainstream, and will therefore not be welcomed by the gatekeepers of the all important mainstream international journals.
Despite these benefits, action research is not without its limitations and critics. The latter point to the lack of validity and generalisability, on the ground that the intervention is a one off and not repeatable. Perhaps more seriously, however, is the fact that it is not perceived as mainstream, and will therefore not be welcomed by the gate keepers of the all important mainstream international journals.
How to improve the validity of action research
Validity can be ensured by applying rigour in the research methodology and design. In particular:
- Using the relevant literature, both method and content, to situate the problem, and then to reflect on findings.
- Using measures and methods that are well respected in the literature.
- Using standard tools to increase reliability – for example a written protocol for interviews.
- Writing up the research in a well argued and well documented manner.
The case study approach, and focus on the particular (organisation, problem, etc.) encourages multiple sources of data. This in itself increases validity, as evidence is coming from a range of sources, and allows for triangulation – checking of one source against another.
At the end of their article, " The impact of e-resources at Bournemouth University 2004/2006 ", Beard et al. comment:
"Action research has proved to be an appropriate methodology for this type of research, as it allows quantitative and qualitative data to be used and learning to occur through action and reflection. Triangulation enables the views of a diverse community of academics and students to be considered alongside data from management information systems".
Triangulation in action research, however, is not merely a matter of being able to check one set of results against another; it is also possible to check differences in data from observation, personal accounts, etc. over the passage of time. However, the researcher here is looking for difference, not similarity, and for the opportunity to reflect on the different perspectives the former reveals.
Validity is also increased by having several researchers on the project, which gives greater objectivity. Hales et al. (2006) describe how they tested a method one of them had developed for improving tactical decision making. They used multiple sources of evidence – including open-ended interviews with senior managers, supervisors and workers, and observation – as a way of validating data, and four researchers to increase objectivity. The first author developed the method, the second and fourth authors conducted the interviews, which were analysed by the third, who also reviewed research logs. Three of the authors carried on participant observation.
Dissemination
Dissemination is obviously an excellent way of generalising research. According to Eden and Huxham (2002), action research calls for book length, owing to the incremental nature of theory development, the need to provide background and the complexity of the data itself. Doherty and Manfredi (2006) believe that despite the growing popularity of action research, it is disdained by "mainstream" management journals which favour more traditional methodologies.
Failure to benefit from the top publication outlets (i.e. top American journals) hits both UK and US based scholars. The former are in hock to the Research Assessment Exercise, which provides top ratings for international (and mostly American) journals which promote a conventional, positivist, research ethos, and in any case treats with suspicion any research that is not mainstream. The latter can only receive tenure if they publish in the aforementioned top journals. For a young scholar, doing action research can be just too much of a risk.
That notwithstanding, much action research does get published in journals – for example, a fulltext search for the phrase "action research" in Emerald's database yielded over 1,300 entries (search as of January 2008).
Students using action research as a method for a doctoral thesis may also experience problems, taking longer to complete, and having difficulty finding a supervisor who understands (Zuber-Skerrit and Fletcher, 2007). According to the latter, a good action research thesis should solve a real and complex problem, benefit from top level commitment in the organisation the student is researching in, and the reflection should be to find out what is the gap in knowledge that will earn the doctorate.
There is quite a bit of advice on writing an action research thesis, as will be explained in Section 4 "Action research resources".
Zuber-Skerrit and Fletcher (2007) advise that a quality action research thesis is one which:
- solves a real, complex problem – it is necessary to get the cooperation of top level management,
- contributes to both practical and theoretical knowledge –- above all, identifying a gap.
This quality is achieved by:
- a carefully designed, explained and justified methodology,
- an original contribution which provides relevant support and validation and which is well argued,
- the use of relevant literature, both methodological and content, aligned to the topic,
- a clear, concise and accurate piece of writing, free from errors.
Eden, C. and Huxham, C. (2002), "Action research" in Partington, D (Ed.), Essential Skills for Management Research , Sage Publications, London.
Doherty, L. and Manfredi, S. (2006), ' Action research to develop work-life balance in a UK university ', Women in Management Review , Vol. 21 No. 3, pp. 241-259.
There are a number of web resources on action research. Undoubtedly the best is that from Southern Cross University.
A substantial collection of action research resources presented by Bob Dick of Southern Cross University. It contains AREOL, an online course in action research, many useful papers on topics such as evaluation, using particular techniques and processes etc. There is also a section on writing an action research thesis, as well as abstracts of completed AR theses.
Has a lot of useful publications, including doctoral and masters' theses, as well as some useful papers including an introductory chapter from the Handbook of Action Research .
This site rates low on usability and is a hotchpotch of assorted items, but it does provide links to theses as well as a paper aimed at new action researchers: http://www.jeanmcniff.com/booklet1.html .
A professional network of action researchers, based at Manchester Metropolitan University, with publications and a discussion list.
A series of links which relates to action research in an educational context.
Southern Cross University – Bob Dick
Centre for action research in professional practice (university of bath), jack whitehead's pages at the university of bath – actionresearch.net, the collaborative action research network, action research at queen's university.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples
What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples
Published on 27 January 2023 by Tegan George . Revised on 21 April 2023.
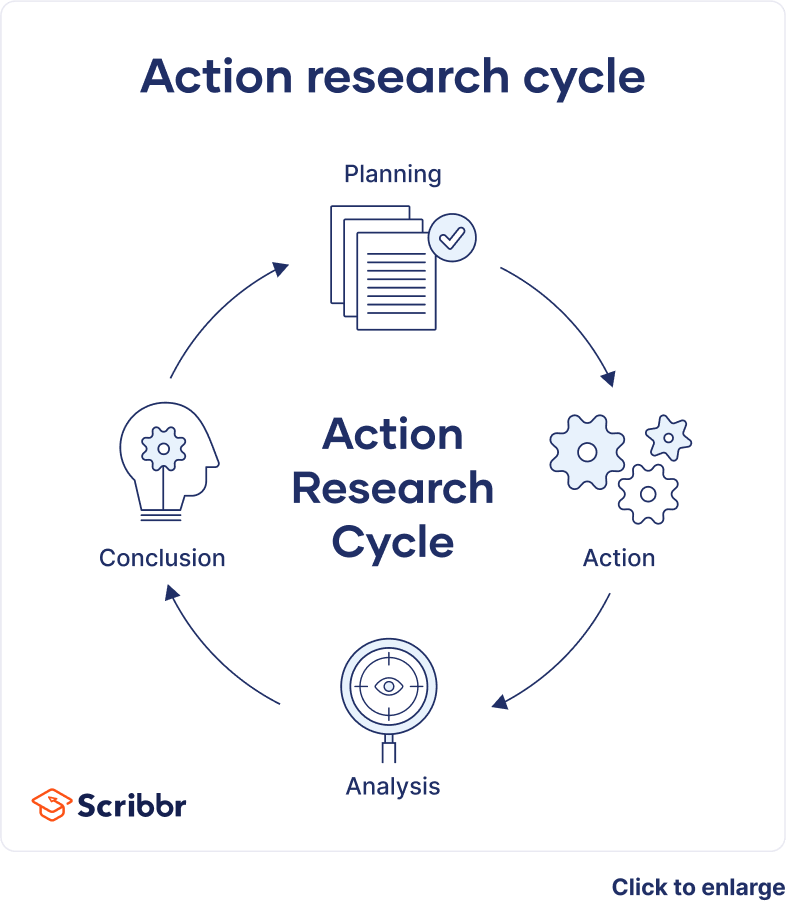
Table of contents
Types of action research, action research models, examples of action research, action research vs. traditional research, advantages and disadvantages of action research, frequently asked questions about action research.
There are 2 common types of action research: participatory action research and practical action research.
- Participatory action research emphasises that participants should be members of the community being studied, empowering those directly affected by outcomes of said research. In this method, participants are effectively co-researchers, with their lived experiences considered formative to the research process.
- Practical action research focuses more on how research is conducted and is designed to address and solve specific issues.
Both types of action research are more focused on increasing the capacity and ability of future practitioners than contributing to a theoretical body of knowledge.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Action research is often reflected in 3 action research models: operational (sometimes called technical), collaboration, and critical reflection.
- Operational (or technical) action research is usually visualised like a spiral following a series of steps, such as “planning → acting → observing → reflecting.”
- Collaboration action research is more community-based, focused on building a network of similar individuals (e.g., college professors in a given geographic area) and compiling learnings from iterated feedback cycles.
- Critical reflection action research serves to contextualise systemic processes that are already ongoing (e.g., working retroactively to analyse existing school systems by questioning why certain practices were put into place and developed the way they did).
Action research is often used in fields like education because of its iterative and flexible style.
After the information was collected, the students were asked where they thought ramps or other accessibility measures would be best utilised, and the suggestions were sent to school administrators. Example: Practical action research Science teachers at your city’s high school have been witnessing a year-over-year decline in standardised test scores in chemistry. In seeking the source of this issue, they studied how concepts are taught in depth, focusing on the methods, tools, and approaches used by each teacher.
Action research differs sharply from other types of research in that it seeks to produce actionable processes over the course of the research rather than contributing to existing knowledge or drawing conclusions from datasets. In this way, action research is formative , not summative , and is conducted in an ongoing, iterative way.
| Action research | Traditional research | |
|---|---|---|
| and findings | ||
| and seeking between variables | ||
As such, action research is different in purpose, context, and significance and is a good fit for those seeking to implement systemic change.
Action research comes with advantages and disadvantages.
- Action research is highly adaptable , allowing researchers to mould their analysis to their individual needs and implement practical individual-level changes.
- Action research provides an immediate and actionable path forward for solving entrenched issues, rather than suggesting complicated, longer-term solutions rooted in complex data.
- Done correctly, action research can be very empowering , informing social change and allowing participants to effect that change in ways meaningful to their communities.
Disadvantages
- Due to their flexibility, action research studies are plagued by very limited generalisability and are very difficult to replicate . They are often not considered theoretically rigorous due to the power the researcher holds in drawing conclusions.
- Action research can be complicated to structure in an ethical manner . Participants may feel pressured to participate or to participate in a certain way.
- Action research is at high risk for research biases such as selection bias , social desirability bias , or other types of cognitive biases .
Action research is conducted in order to solve a particular issue immediately, while case studies are often conducted over a longer period of time and focus more on observing and analyzing a particular ongoing phenomenon.
Action research is focused on solving a problem or informing individual and community-based knowledge in a way that impacts teaching, learning, and other related processes. It is less focused on contributing theoretical input, instead producing actionable input.
Action research is particularly popular with educators as a form of systematic inquiry because it prioritizes reflection and bridges the gap between theory and practice. Educators are able to simultaneously investigate an issue as they solve it, and the method is very iterative and flexible.
A cycle of inquiry is another name for action research . It is usually visualized in a spiral shape following a series of steps, such as “planning → acting → observing → reflecting.”
Sources for this article
We strongly encourage students to use sources in their work. You can cite our article (APA Style) or take a deep dive into the articles below.
George, T. (2023, April 21). What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 16 September 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/action-research-cycle/
Cohen, L., Manion, L., & Morrison, K. (2017). Research methods in education (8th edition). Routledge.
Naughton, G. M. (2001). Action research (1st edition). Routledge.
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, primary research | definition, types, & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, what is an observational study | guide & examples.
- Social Science
- Qualitative Social Research
- Action Research
Action research: Collecting and analysing data
- November 2018
- Conference: IATEFL Research SIG webinar
- At: Sydney, Australia

- University of Technology Sydney
Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations

- P Rebolledo

- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Action research is a research method that aims to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue. In other words, as its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time. It was first coined as a term in 1944 by MIT professor Kurt Lewin.A highly interactive method, action research is often used in the social sciences, particularly in educational settings.
History of action research. Tracing its roots back to the mid-20th century, Kurt Lewin developed classical action research as a response to traditional research methods in the social sciences that often sidelined the very communities they studied. Proponents of action research championed the idea that research should not just be an observational exercise but an actionable one that involves ...
Action research is a qualitative method that focuses on solving problems in social systems, such as schools and other organizations. The emphasis is on solving the presenting problem by generating knowledge and taking action within the social system in which the problem is located. The goal is to generate shared knowledge of how to address the ...
Action Learning and Action Research by Ortrun Zuber-Skerritt (Editor); Lesley Wood (Editor) ISBN: 9781787695382 Action Research (AR) is an ideal methodology to enable practical and emancipatory outcomes, as well as to generate relevant and authentic theory.
Stage 1: Plan. For an action research project to go well, the researcher needs to plan it well. After coming up with an educational research topic or question after a research study, the first step is to develop an action plan to guide the research process. The research design aims to address the study's question.
Action research can be defined as "an approach in which the action researcher and a client collaborate in the diagnosis of the problem and in the development of a solution based on the diagnosis".In other words, one of the main characteristic traits of action research relates to collaboration between researcher and member of organisation in order to solve organizational problems.
Summary. Action research is a term used to describe a family of related approaches that integrate theory and action with a goal of addressing important organizational, community, and social issues together with those who experience them. It focuses on the creation of areas for collaborative learning and the design, enactment and evaluation of ...
Action Research refers to a research method that involves actively engaging in problem-solving activities and reflecting on the process. It emphasizes the use of suitable techniques, high-quality data analysis, and the involvement of key stakeholders in the research process. ... The example used in the action research model below (Du Toit, 2009 ...
Action research is a philosophy and methodology of research generally applied in the social sciences. It seeks transformative change through the simultaneous process of taking action and doing research, which are linked together by critical reflection. ... After seven decades of action research development, many methods have evolved that adjust ...
Action research is defined as a "research method for systematically and intentionally studying issues related to practice" (Manfra, 2019, p. 3). Emerging from the field of education, action research provides a framework through which educators can approach real-life and classroom-based problems. ... Applied: Action research can be used for ...
As the name suggests, action research is an approach to research which aims at both taking action and creating knowledge or theory about that action as the action unfolds. It rejects the notion that research must be value free in order to be credible, in favor an explicitly socially engaged and democratic practice (Brydon-Miller et al. 2003).
search. Action research is defined by O'Leary (2007) as. "Research strategies that tackle real-world problems in participatory, collaborative, and cyclical ways in order to produce both knowledge and action." It refers to a type of research methodology which works toward a kind of change (whether social or professional).
Action research is used in the practice of health and social care because it has two fundamental aims: to improve and to involve. This chapter outlines how this is evident, using examples from the research literature (see Table 7.1.). Action research as involvement. Action research is a collaborative process between researchers and community ...
Action research is a participatory approach to research that emphasizes collaboration between researchers and individuals or groups to identify problems, develop solutions, and implement changes. It is a method of inquiry driven by a desire to reflect upon and improve practice rather than generate knowledge. This research approach is often used in education, social work, healthcare, and ...
Action and Participatory Action Research Methodologies and Methods. The SAGE Handbook of Action Research Third Edition (2015) by Hilary Bradbury. The third edition of The SAGE Handbook of Action Research presents an updated version of the bestselling text, including new chapters covering emerging areas in healthcare, social work, education and international development, as well as an expanded ...
%PDF-1.4 %âãÏÓ 468 0 obj > endobj xref 468 58 0000000016 00000 n 0000002619 00000 n 0000002768 00000 n 0000003326 00000 n 0000003470 00000 n 0000003642 00000 n 0000004175 00000 n 0000004744 00000 n 0000004856 00000 n 0000004970 00000 n 0000005244 00000 n 0000005860 00000 n 0000006135 00000 n 0000006703 00000 n 0000007504 00000 n 0000008262 00000 n 0000008687 00000 n 0000008801 00000 n ...
The use of action research to deepen and develop classroom practice has grown into a strong tradition of practice (one of the first examples being the work of Stephen Corey in 1949). ... He continues, 'Action research is not a 'method' or a 'procedure' for research but a series of commitments to observe and problematize through ...
Action research shifts the paradigm of contemporary educational reform by emphasizing inquiry and placing teachers at the center of research-into-practice. ... In Flood J., Lapp D., Squire J. R. (Eds.), Methods of research on teaching the English language arts: The Methodology chapters From the Handbook of Research on Teaching the English ...
The conceptual foundations of action research are explained, and a case is made for action research's utility as a framework for knowledge generation in collaboration with community organizations. Although action research is often conducted using qualitative methods, this chapter makes a case for methodological pluralism.
As an applied research methodologist, she teaches courses in qualitative, mixed methods, and action research. Her research interests focus on using mixed methods within a translational research framework. Nancy Wingo, PhD, MA, is an assistant professor in the School of Nursing at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, where she teaches ...
Action research is a research strategy which combines research with action and participation in the field. As a method, it goes back to the period immediately post the Second World War (see "The history of action research", below) and has become increasingly popular over the last few years, along with other qualitative methods, as people come to see the value in collecting rich data by ...
Action research is a research method that aims to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue. In other words, as its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time. It was first coined as a term in 1944 by MIT professor Kurt Lewin. A highly interactive method, action research is often used in the social ...
The 'observing' stage of action research involves collecting data, for example via surveys, focus groups, interviews, observations, reflective journal writing, and/or assessments. For language ...