Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples

What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples
Published on January 27, 2023 by Tegan George . Revised on January 12, 2024.
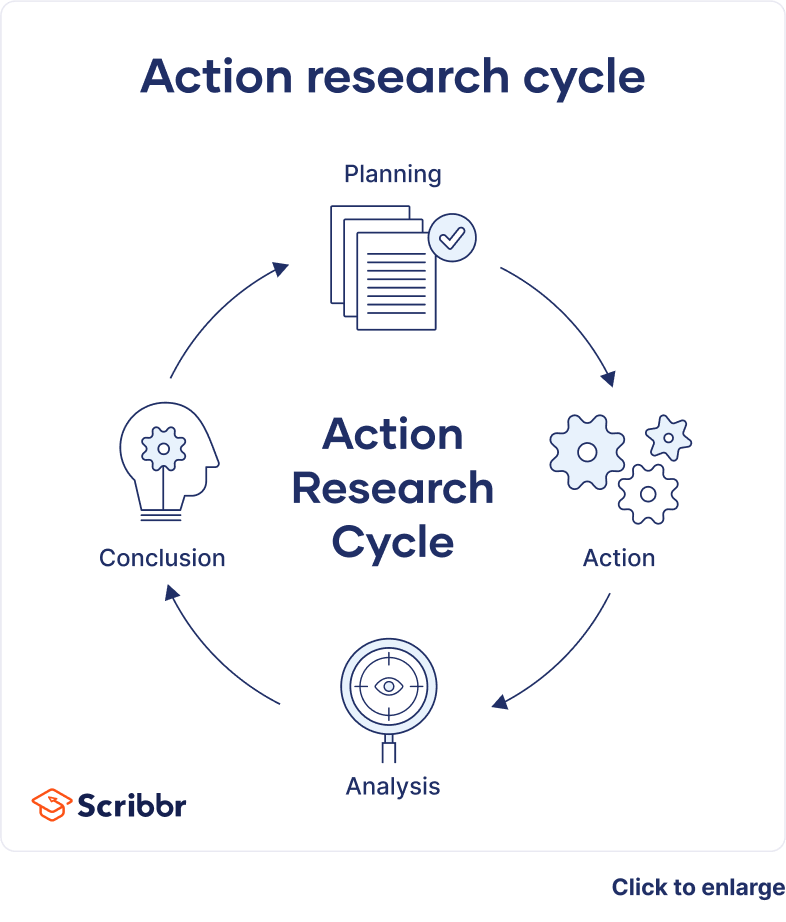
Table of contents
Types of action research, action research models, examples of action research, action research vs. traditional research, advantages and disadvantages of action research, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about action research.
There are 2 common types of action research: participatory action research and practical action research.
- Participatory action research emphasizes that participants should be members of the community being studied, empowering those directly affected by outcomes of said research. In this method, participants are effectively co-researchers, with their lived experiences considered formative to the research process.
- Practical action research focuses more on how research is conducted and is designed to address and solve specific issues.
Both types of action research are more focused on increasing the capacity and ability of future practitioners than contributing to a theoretical body of knowledge.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Action research is often reflected in 3 action research models: operational (sometimes called technical), collaboration, and critical reflection.
- Operational (or technical) action research is usually visualized like a spiral following a series of steps, such as “planning → acting → observing → reflecting.”
- Collaboration action research is more community-based, focused on building a network of similar individuals (e.g., college professors in a given geographic area) and compiling learnings from iterated feedback cycles.
- Critical reflection action research serves to contextualize systemic processes that are already ongoing (e.g., working retroactively to analyze existing school systems by questioning why certain practices were put into place and developed the way they did).
Action research is often used in fields like education because of its iterative and flexible style.
After the information was collected, the students were asked where they thought ramps or other accessibility measures would be best utilized, and the suggestions were sent to school administrators. Example: Practical action research Science teachers at your city’s high school have been witnessing a year-over-year decline in standardized test scores in chemistry. In seeking the source of this issue, they studied how concepts are taught in depth, focusing on the methods, tools, and approaches used by each teacher.
Action research differs sharply from other types of research in that it seeks to produce actionable processes over the course of the research rather than contributing to existing knowledge or drawing conclusions from datasets. In this way, action research is formative , not summative , and is conducted in an ongoing, iterative way.
| Action research | Traditional research | |
|---|---|---|
| and findings | ||
| and seeking between variables | ||
As such, action research is different in purpose, context, and significance and is a good fit for those seeking to implement systemic change.
Action research comes with advantages and disadvantages.
- Action research is highly adaptable , allowing researchers to mold their analysis to their individual needs and implement practical individual-level changes.
- Action research provides an immediate and actionable path forward for solving entrenched issues, rather than suggesting complicated, longer-term solutions rooted in complex data.
- Done correctly, action research can be very empowering , informing social change and allowing participants to effect that change in ways meaningful to their communities.
Disadvantages
- Due to their flexibility, action research studies are plagued by very limited generalizability and are very difficult to replicate . They are often not considered theoretically rigorous due to the power the researcher holds in drawing conclusions.
- Action research can be complicated to structure in an ethical manner . Participants may feel pressured to participate or to participate in a certain way.
- Action research is at high risk for research biases such as selection bias , social desirability bias , or other types of cognitive biases .
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Action research is conducted in order to solve a particular issue immediately, while case studies are often conducted over a longer period of time and focus more on observing and analyzing a particular ongoing phenomenon.
Action research is focused on solving a problem or informing individual and community-based knowledge in a way that impacts teaching, learning, and other related processes. It is less focused on contributing theoretical input, instead producing actionable input.
Action research is particularly popular with educators as a form of systematic inquiry because it prioritizes reflection and bridges the gap between theory and practice. Educators are able to simultaneously investigate an issue as they solve it, and the method is very iterative and flexible.
A cycle of inquiry is another name for action research . It is usually visualized in a spiral shape following a series of steps, such as “planning → acting → observing → reflecting.”
Sources in this article
We strongly encourage students to use sources in their work. You can cite our article (APA Style) or take a deep dive into the articles below.
George, T. (2024, January 12). What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 12, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/action-research/
Cohen, L., Manion, L., & Morrison, K. (2017). Research methods in education (8th edition). Routledge.
Naughton, G. M. (2001). Action research (1st edition). Routledge.
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, what is an observational study | guide & examples, primary research | definition, types, & examples, guide to experimental design | overview, steps, & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
- Tools and Resources
- Customer Services
- Original Language Spotlight
- Alternative and Non-formal Education
- Cognition, Emotion, and Learning
- Curriculum and Pedagogy
- Education and Society
- Education, Change, and Development
- Education, Cultures, and Ethnicities
- Education, Gender, and Sexualities
- Education, Health, and Social Services
- Educational Administration and Leadership
- Educational History
- Educational Politics and Policy
- Educational Purposes and Ideals
- Educational Systems
- Educational Theories and Philosophies
- Globalization, Economics, and Education
- Languages and Literacies
- Professional Learning and Development
- Research and Assessment Methods
- Technology and Education
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Article contents
Action research.
- Eileen S. Johnson Eileen S. Johnson Oakland University
- https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190264093.013.696
- Published online: 29 May 2020
Action research has become a common practice among educational administrators. The term “action research” was first coined by Kurt Lewin in the 1930s, although teachers and school administrators have long engaged in the process described by and formally named by Lewin. Alternatively known as practitioner research, self-study, action science, site-based inquiry, emancipatory praxis, etc., action research is essentially a collaborative, democratic, and participatory approach to systematic inquiry into a problem of practice within a local context. Action research has become prevalent in many fields and disciplines, including education, health sciences, nursing, social work, and anthropology. This prevalence can be understood in the way action research lends itself to action-based inquiry, participation, collaboration, and the development of solutions to problems of everyday practice in local contexts. In particular, action research has become commonplace in educational administration preparation programs due to its alignment and natural fit with the nature of education and the decision making and action planning necessary within local school contexts. Although there is not one prescribed way to engage in action research, and there are multiple approaches to action research, it generally follows a systematic and cyclical pattern of reflection, planning, action, observation, and data collection, evaluation that then repeats in an iterative and ongoing manner. The goal of action research is not to add to a general body of knowledge but, rather, to inform local practice, engage in professional learning, build a community practice, solve a problem or understand a process or phenomenon within a particular context, or empower participants to generate self-knowledge.
- action research cycle
- educational practice
- historical trends
- philosophical assumptions
- variations of action research
You do not currently have access to this article
Please login to access the full content.
Access to the full content requires a subscription
Printed from Oxford Research Encyclopedias, Education. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a single article for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice).
date: 14 August 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [185.148.24.167]
- 185.148.24.167
Character limit 500 /500
Our websites may use cookies to personalize and enhance your experience. By continuing without changing your cookie settings, you agree to this collection. For more information, please see our University Websites Privacy Notice .
Neag School of Education
Educational Research Basics by Del Siegle
Action research.
An Introduction to Action Research Jeanne H. Purcell, Ph.D.
Your Options
- Review Related Literature
- Examine the Impact of an Experimental Treatment
- Monitor Change
- Identify Present Practices
- Describe Beliefs and Attitudes
Action Research Is…
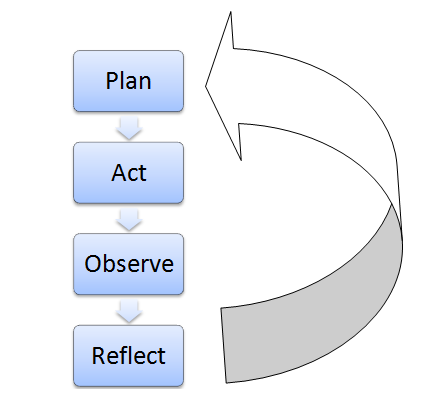
- Action research is a three-step spiral process of (1) planning which involves fact-finding, (2) taking action, and (3) fact-finding about the results of the action. (Lewin, 1947)
- Action research is a process by which practitioners attempt to study their problems scientifically in order to guide, correct, and evaluate their decisions and action. (Corey, 1953).
- Action research in education is study conducted by colleagues in a school setting of the results of their activities to improve instruction. (Glickman, 1990)
- Action research is a fancy way of saying Let’s study what s happening at our school and decide how to make it a better place. (Calhoun,1994)
Conditions That Support Action Research
- A faculty where a majority of teachers wish to improve some aspect (s) of education in their school.
- Common agreement about how collective decisions will be made and implemented.
- A team that is willing to lead the initiative.
- Study groups that meet regularly.
- A basic knowledge of the action research cycle and the rationale for its use.
- Someone to provide technical assistance and/or support.
The Action Research Cycle
- Identify an area of interest/problem.
- Identify data to be collected, the format for the results, and a timeline.
- Collect and organize the data.
- Analyze and interpret the data.
- Decide upon the action to be taken.
- Evaluate the success of the action.
Collecting Data: Sources
Existing Sources
- Attendance at PTO meetings
- + and – parent communications
- Office referrals
- Special program enrollment
- Standardized scores
Inventive Sources
- Interviews with parents
- Library use, by grade, class
- Minutes of meetings
- Nature and amount of in-school assistance related to the innovation
- Number of books read
- Observation journals
- Record of peer observations
- Student journals
- Teacher journals
- Videotapes of students: whole class instruction
- Videotapes of students: Differentiated instruction
- Writing samples
Collecting Data: From Whom?
- From everyone when we are concerned about each student’s performance.
- From a sample when we need to increase our understanding while limiting our expenditure of time and energy; more in-depth interviews or observations may follow.
Collecting Data: How Often?
- At regular intervals
- At critical points
Collecting Data: Guidelines
- Use both existing and inventive data sources.
- Use multiple data sources.
- Collect data regularly.
- Seek help, if necessary.
Organizing Data
- Keep it simple.
- Disaggregate numbers from interviews and other qualitative types of data.
- Plan plenty of time to look over and organize the data.
- Seek technical assistance if needed.
Analyzing Data
- What important points do they data reveal?
- What patterns/trends do you note? What might be some possible explanations?
- Do the data vary by sources? Why might the variations exist?
- Are there any results that are different from what you expected? What might be some hypotheses to explain the difference (s)?
- What actions appear to be indicated?
Taking Action
- Do the data warrant action?
- What might se some short-term actions?
- What might be some long-term actions?
- How will we know if our actions have been effective?
- What benchmarks might we expect to see along the way to effectiveness ?
Action Plans
- Target date
- Responsibility
- Evidence of Effectiveness
Action Research Handout
Bibliography
Brubacher, J. W., Case, C. W., & Reagan, T. G. (1994). Becoming a reflective educator . Thousand Oaks: CA: Corwin Press.
Burnaford, G., Fischer, J., & Hobson, D. (1996). Teachers doing research . Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Calhoun, Emily (1994). How to use action research in the self-renewing school . Alexandria, VA: ASCD.
Corey, S. M. (1953). Action research to improve school practices . New York: Teachers College Press.
Glickman, C. D. (1990). Supervision of instruction: A developmental approach . Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
Hubbard, R. S. & Power, B. M. (1993). The art of classroom inquiry . Portsmouth, NH: Heineman.
Lewin, K. (1947). Group decisions and social change. In Readings in social psychology . (Eds. T M. Newcomb and E. L. Hartley). New York: Henry Holt.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
2 Action Research as a Process for Professional Learning and Leadership
ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS
- What is the role of action research in professional learning and leadership?
- What are the educational contexts that action research takes place?
- What are the critiques of action research as a methodology?
- What are the basic stages of an action research project?
In the previous chapter, we were able to explore the idea of action research, the purpose of action research, and the theoretical underpinnings of action research. Hopefully, you now have a good understanding of the landscape of action research and the contours in which it can take shape in educational contexts. It is important to emphasize that the primary aim of conducting action research in an educational context is to study and improve upon an educator’s, or group of educators’, practice. This chapter will explore some of the practical aspects of action research, in particular, the forethought and planning required to engage in a successful action research experience.
As we begin to transition from the theoretical to the more practical aspects of action research, we want to provide a few questions to consider:
- How does the epistemological, ontological, and theoretical basis of action research fit with your pedagogical philosophy in the classroom? Will using action research require any paradigmatic shifts in how you approach your pedagogy?
- What are the pedagogical benefits of using action research in your educational context?
- What are the most significant affordances and challenges of using action research in your educational context?
After considering the questions above, we think it is important from a practical standpoint to consider and situate action research as part of an educator’s responsibility to professional learning and leadership.
Action Research as Professional Learning and Leadership
Thus far, we have made the case that action research is a useful methodology for educators because it formalizes a process you already use to improve your pedagogy; but how does it benefit you as a professional and your professional identity? In Becoming Critical Carr and Kemmis (2003) list characteristics of action research that make it integral to critical professional learning for educators. We have summarized their five characteristics of action research as a methodology for educators:
Five Characteristics of Action Research as a Methodology for Educators
- action research rejects positivist notions of rationality, objectivity, and truth and instead has an openness to competing possibilities for effective pedagogical practice in educational contexts;
- action research employs educators’ reflective and interpretive categories, and uses the language of educators as a basis for educators to explore and develop their own pedagogical theorizing;
- action research allows educators’ unrealized self-understandings to be discerned by analyzing their own practices and understandings;
- action research connects reflection to action, enabling educators to overcome barriers to pedagogical change through awareness of social and systemic factors influencing their educational context;
- action research involves deep consideration of theory and practice and to demonstrate this critically self-reflective action, researchers develop and organize knowledge in which truth is evidenced through its relation to practice.
To synthesize these five characteristics in terms of practical knowledge, we think it is important to now consider a “so what?” type of question. After learning these characteristics, why would an educator engage in action research for the purpose of professional learning or leadership? The following five principles correspond to the five characteristics above:
Why an Educator would Engage in Action Research
- the development of an educator’s pedagogy is not about developing a set of “surefire” technical competencies; it is concerned with finding the most effective practices for the students in their educational context;
- one way for educators to be consistently informed on pedagogy and increase their skills is through actively being involved in a culture of inquiry that dually relies on the latest educational research and their own classroom to spark new inquiry;
- by doing action research, educators are engaged in the process of hypothesizing, theorizing, and developing self-knowledge related specifically to their practice;
- when educators engage in action research, they develop agency and gain control of knowledge, and address questions for themselves, instead of being subservient to the knowledge enacted on their educational context;
- when educators are engaged in research, educators are naturally engaged in educational theorizing because they are reflecting on practice systematically and critically, to close the distance between educational theory practice, which many educators feel (Hopkins, 2003).
Professional learning in education takes many forms. Action research is unique in the realm of professional learning because it is tailored to the educator’s real time pedagogical foci, issues, or needs. Professional learning opportunities often fail to meet the expectations of educators because they are meant for large groups of teachers, either based on a school, topic, subject, or course. Even at the course level of professional learning, while the content may be the same for each teacher, the students and educational context are different for each teacher – which creates unique challenges that educators want to address through their professional learning. One advantage of traditional professional learning sessions is the group aspect, or collaborative thinking that takes place. Action research is flexible enough that collaborative inquiry could be part of the process, and educators could include colleagues as part of their research. In many ways, action research not only contributes to professional learning, but also provides professional leadership to colleagues.
Professional leadership in education, or teacher leadership, also takes many forms. Danielson (2007) lists teacher leadership in her framework for teaching, as one of several professional responsibilities for educators. Educators who engage in action research and share their findings, are working to impact professional learning, and subsequently student learning, beyond their classrooms. Engaged educators who attain and continue to receive recognition in the teaching profession invest a lot of time and energy to stay informed and further develop their skills. Danielson (2007) notes that these educators are in a prime position to exercise leadership among their colleagues. Often times educators view conferences and professional learning sessions as the only opportunities to further develop their skills and become leaders among their colleagues. However, Danielson (2007) goes on to describe a distinguished educator as someone who engages in a combination of seeking “out opportunities for professional development and makes a systematic effort to conduct action research” (105). In this way, professional learning is a part of the action research process that engages educators in reflection and conversations outside of their educational context, while also potentially providing an alternative lens to analyze their data.
Data-driven decision making by administrators, teachers, and teams of educators, often facilitated by teacher leaders, is a prevalent practice in schools that impacts educator performance and student learning. This sort of professional learning through collaborative inquiry provides vital contextual data to improve pedagogy in classrooms and throughout the school. Sagor (2010) defines collaborative action research as ”the team inquiry process, when a group of individuals who are a part of a specific PLC, grade-level, or teacher learning team engage in inquiry and research.” These teams can become a means for collaboratively engaging in action research and developing data that is relative to the school. Data is most valuable to an educational context when it is deeply relatable and relevant to the specific educational context. Data specifically related to the educational context can increase a school’s capacity to focus on curricular and instructional strategies with the greatest potential to support student learning. In an effort to spark professional leadership, and as we discuss the process of action research in future chapters, please discuss with colleagues the potential action research projects in your own classroom and think about how to leverage those toward your school’s PLC, professional learning, or school-wide improvement plans. Thinking about your action research in this way adds another layer of purpose and makes action research a truly valuable process for improvement throughout your educational context.
What Will Action Look Like in My Classroom?
Now that we have discussed the relevance of action research for professional learning and leadership, it may be a little easier to conceptualize an action research project, or perhaps you already have an idea ready to start. O’Leary (2004) provides a useful list of processes related to action research that could help you think about your initial plans. Here are some questions to think about related to the processes of an action research project:
- Does it address a practical problems(s)? Educators typically identify a practical problem in their educational context that has multiple possible ways to be addressed. The impetus to improve professional practice prioritizes change.
- Does it generate knowledge? Generating knowledge promotes change. By addressing this practical problem, you will generate knowledge.
- Does it enact changes in your pedagogy/classroom/school? The changes generated by the knowledge will be useful to enact change relatively close to the conclusion of the research project.
- Is it participatory? Action research is participatory, and the primary researcher is involved in the action, potentially along with other researchers and stakeholders.
- Could it be a cyclical process? Action research is a cyclical process that results from emerging knowledge. Once better situational understanding is gained through research, a change can be implemented and researched again, resulting in an evaluative practice that reciprocates between informed action and critical reflection.
I want to emphasize that this is one of interpretations of the processes involved in the action research process, and you should adapt these basic processes to fit your needs as an educator and researcher. These processes will also become clearer in purpose as we discuss the contexts for action research.
The Contexts for Considering Action Research
Action research can take place in many professional settings and contexts. As we think about some of those contexts we will focus on the most common in educational settings. I have also provided some examples for research in each context.
Improving Classroom Practice
These projects are conducted by educators in their classroom context and focus on pedagogical, curricular, or instructional aspects of their practice. Examples could include:
- How can Socratic questioning improve engagement in class discussions?
- Who participates more in my class?
- How can integrated social studies and ELA lessons improve students’ reading scores?
- Will learning diaries in mathematics lessons enhance students’ conceptual understanding?
- How can Flipgrid help connect student interests to content standards?
Examining an Educational Theme
These projects allow educators to examine new ideas or themes that they have encountered in professional learning opportunities. Examples could include:
- How can I implement personalized learning in my classroom?
- Can I integrate all subjects into a problem-based inquiry project?
- In what ways do Breakout Box activities prepare students for content-based learning?
- Do exercise balls help students focus longer while sitting at their seats?
Educational Context Focus
These projects focus on interaction between humans and the ecological space of the context. Examples could include:
- How can using non-letter grades improve communication with parents?
- How can we increase engagement at parent meetings?
- Does going outside and doing yoga improve student focus in the afternoon?
- What is the effect of eliminating homework?
- Does presenting to community members, outside the school community, improve engagement or motivation for group projects?
- What anti-bullying strategies reduce verbal teasing?
Implementing a New Initiative Based on Policy or Research
These projects are sparked by new policy or research data or are related to district or state-wide initiatives. These are often group or collaborative projects. Examples could include:
- What are the best methods to prepare teachers for a school-wide one-to-one device launch?
- Do weekly meetings help support first-year teachers?
- Adopting the new formative assessment framework for inquiry-based learning.
Critiques of Action Research
Action research is a fairly new form of acceptable educational research; therefore, educators should be aware of some of the common critiques you may hear when presenting or sharing your research. These critiques can also be easily dealt with in the planning and development of your action research project. The following are three of the most common critiques of action research.
Critique #1: Action research lacks rigor and trustworthiness in comparison to other methodologies…
The rigor of a research project is shaped by the manner in which data collection and analysis are conducted in the research process. For example, rigor can develop in data collection by using a variety of research methods to collect data (discussed further in Chapter 6). Sharing data with critical friends and colleagues, or triangulating the data, would demonstrate rigor in the data analysis process. Issues of trustworthiness are raised around the question: Can you be/maintain objectivity when you are conducting research on your own practice? Trustworthiness can be viewed as the strength of the inference made possible by the given research study. Trustworthiness can be achieved primarily through triangulation of data (multiple sources of data) and a clear description of context, participants, processes, and analysis which allows for transferability as a reader. Maintaining a rigorous data collection and analysis process will help with trustworthiness, but also being clear in your epistemological stance and positionality from the beginning of the project also contributes to trustworthiness. Rigor and trustworthiness can easily be addressed through developing a research plan and sticking to it. Adherence to ethical research (IRB) will also add to trustworthiness, we will discuss this in a later chapter.
Critique #2: Action research findings are not generalizable to other educational contexts…
Generalizability is often a concern for quantitative researchers who are trying to solve problems across large portions of the population. Simply put, the action researcher is not concerned with generalizable data that can provide answers to other educators in different contexts (However, it is great if this happens!). The action researcher is primarily concerned with generating knowledge based on the actions within their own situated context. Action research findings are generalizable only within specific situations and within that specific educational context, which is described and considered as part of the research process. Sharing findings could be applicable to educators who are interested or who are in similar circumstances, either locally, nationally, or globally.
Critique #3: Action research is based on a deficit model…
The problem-solving nature of action research may give an appearance that it is based on a deficit model. This is not necessarily the case; however, if researchers are not conscious of deficit thinking or deficit models of thinking, it is possible to engage in action research based on perceived student deficits. From my perspective, developing strategies for solving a problem within a situation with the sole purpose of improving practice is not rooted in deficit thinking, especially if they really generate knowledge. Regardless, researchers need to be aware of deficit thinking and make sure their research questions do not rely on assumptions about students’ weaknesses based on demographic groupings.
What’s Ahead? Thinking about the Stages of Action Research
The models of action research presented in Chapter 1 all described action research as a cyclical process. It is exciting to think about a cyclical process of professional learning to improve your practice; however, it can also be overwhelming to think about the process. We think it is helpful to have some awareness of what may happen during the project, represented in distinct stages, to provide an overview of the whole process. This will help you plan more efficiently, but we think it is also important to be flexible and understand that your project does not always need to follow that order. Here is what to expect:
- Identifying a topic in the educational context
- Reviewing related literature
- Revising the topic
- Developing a research question
- Plan research activities
- Collect data
- Analyze data
- Action implementation
- Reflection on action
- Report, share, or document.
Each of these steps has some brief considerations, yet I would like to discuss these steps in three broad areas of focus due to the overlap of these considerations.
Topic Development
- Researching in Action
Action Implications
Identifying and developing a topic that is important and relevant to your practice is vitally essential. Your topic not only shapes the area of educational knowledge you will contribute to, but it will also shape your research question. It is usually helpful to identify and write down three to five potential topics. In addition to writing the topic down, describe why each topic is important or relevant to you, your practice, your students, and/or your educational context. Then, if you are still having a hard time deciding on a topic, write down the intended benefits for you, your practice, your students, and/or your educational context. It may also be helpful to discuss your ideas with others, to help focus your thoughts and provide another perspective on the feasibility of completing a study on a particular topic, its relevance and implications for practice.
Once you have identified a topic, it is important to conduct a literature review (discussed fully in Chapter 3) to find out what the field of education has researched in regards to your topic. This will help you understand what we know and don’t know about your topic. Once you have conducted a thorough literature review you will feel capable of potentially revising your topic to reflect the knowledge base, and possibly narrow the scope of your project for your own purposes.
Lastly, you will be able to develop a research question (discussed fully in Chapter 4) based on your topic, the reviewed literature, and your intended outcomes.
Researching Action
After you have thoroughly vetted a topic and developed a research question, you will be ready to begin the process of researching your topic in your educational context. In consideration of your research question, you can begin to plan your research activities—when and how you will conduct the research in your educational context (Chapter 4). This will include a timeline of activities. You will then begin planning your data collection (Chapter 5) methods and fit those into your timeline. You will also need to think about a proposed process, or order for analyzing your data. This may seem strange; however, it helps contribute to the rigor and validity of your study to have a plan that fits within your epistemological stance.
Once your plan is set, you can begin the data collection process. After data collection, you can begin the analysis of the data (Chapter 6).
After you have analyzed your data, you should have some indication as to implications for your research question. You will have the opportunity to reflect on the research, take action, and eventually share or report your findings. Many of you will have reason to change an action in your educational context, whether it is the following week, the next semester, or next school year. This is where the cyclical process of action research can take shape.
Action Research in Action: A Vignette
As a classroom teacher, I was often engaged in action research without realizing it, and typically this process began from reflection. As a graduate student, weekly reflections on the required readings in my Teachers as Researchers course prompted me to identify issues in my classroom to address, either through pedagogical changes or adjustments to my curriculum. In a less formal way, action research naturally emerged as part of my yearly evaluations with administration. In one particular year, after reflecting on my own practice, I realized (rather, admitted) that my junior-level English students did not enjoy our classroom novel studies, resulting in a lack of engagement and poor performance for many of them. The ‘start and stop’ method—where students read a chapter, then stop to either discuss the chapter or take a quiz—did not replicate how people read books, and it is no wonder that it destroyed my students’ desire to engage with the novels they were assigned. This is where action research emerged—I established a driving question for my own classroom problem: How can I adapt whole novel studies to reflect the natural reading process, take into account each students’ reading level, and improve overall reading performance and engagement?
The next step in this process was to find research that already existed on whole novel studies in the classroom and use that information as a catalyst for my own research. I read several examples of alternative methods to whole novel studies, but most of what I could find was based on a middle school classroom. This was good news! It meant, on a large scale, my action research would have a place in the broad educational context by filling an existing void in the information available to classroom teachers. On a small scale, this meant other teachers in my own department could benefit from what I design since a lack of resources exists in this area.
After reading several examples of alternative methods, I adapted the practices that seemed to fit best with my own students and created my own version of how to work with whole novels in the high school English classroom. I implemented this method in two different courses, one of which was considered an ‘advanced’ course, with students at all different reading levels. I tracked their progress in multiple ways and recorded the information on spreadsheets for future use. After a successful first attempt at changing my practice, I presented the findings to my colleagues at a department meeting, and many adapted my method to use in their own classrooms.
Though this example of action research does not reflect a formalized project, it speaks to how teachers naturally engage in the process of questioning and problem-solving to create change for their students. It also demonstrates the value in what teachers discover in their own classrooms. Researchers are often criticized for being too far removed from classroom practice to really understand what teachers need; but teacher researchers have the opportunity to be their own guide and to potentially influence teacher praxis in positive and practical ways.
Action Research Copyright © by J. Spencer Clark; Suzanne Porath; Julie Thiele; and Morgan Jobe is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Action Research
Action research can be defined as “an approach in which the action researcher and a client collaborate in the diagnosis of the problem and in the development of a solution based on the diagnosis” [1] . In other words, one of the main characteristic traits of action research relates to collaboration between researcher and member of organisation in order to solve organizational problems.
Action study assumes social world to be constantly changing, both, researcher and research being one part of that change. [2] Generally, action researches can be divided into three categories: positivist, interpretive and critical.
Positivist approach to action research , also known as ‘classical action research’ perceives research as a social experiment. Accordingly, action research is accepted as a method to test hypotheses in a real world environment.
Interpretive action research , also known as ‘contemporary action research’ perceives business reality as socially constructed and focuses on specifications of local and organisational factors when conducting the action research.
Critical action research is a specific type of action research that adopts critical approach towards business processes and aims for improvements.
The following features of action research need to be taken into account when considering its suitability for any given study:
- It is applied in order to improve specific practices. Action research is based on action, evaluation and critical analysis of practices based on collected data in order to introduce improvements in relevant practices.
- This type of research is facilitated by participation and collaboration of number of individuals with a common purpose
- Such a research focuses on specific situations and their context
Advantages of Action Research
- High level of practical relevance of the business research;
- Can be used with quantitative, as well as, qualitative data;
- Possibility to gain in-depth knowledge about the problem.
Disadvantages of Action Research
- Difficulties in distinguishing between action and research and ensure the application of both;
- Delays in completion of action research due to a wide range of reasons are not rare occurrences
- Lack of repeatability and rigour
It is important to make a clear distinction between action research and consulting. Specifically, action research is greater than consulting in a way that action research includes both action and research, whereas business activities of consulting are limited action without the research.
Action Research Spiral
Action study is a participatory study consisting of spiral of following self-reflective cycles:
- Planning in order to initiate change
- Implementing the change (acting) and observing the process of implementation and consequences
- Reflecting on processes of change and re-planning
- Acting and observing
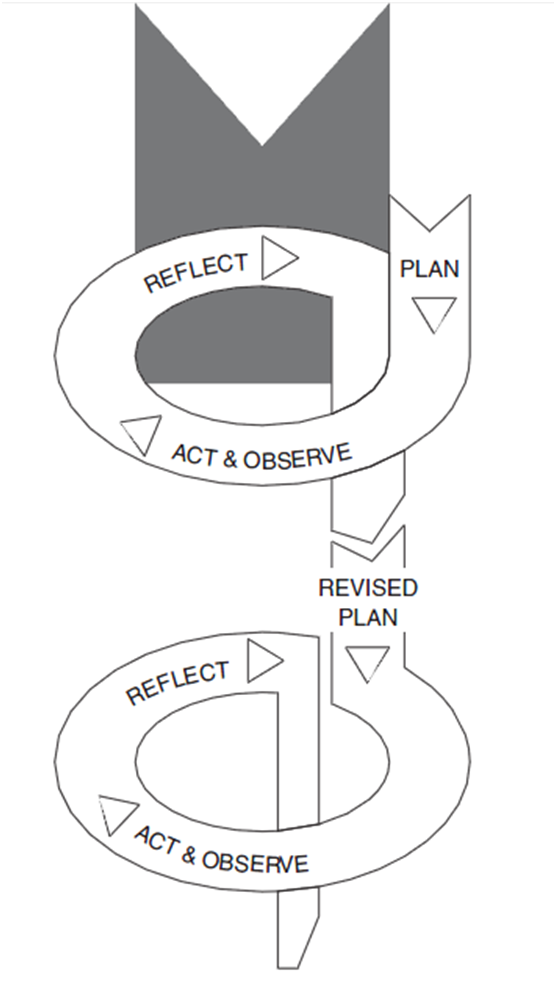
Kemmis and McTaggart (2000) do acknowledge that individual stages specified in Action Research Spiral model may overlap, and initial plan developed for the research may become obselete in short duration of time due to a range of factors.
The main advantage of Action Research Spiral model relates to the opportunity of analysing the phenomenon in a greater depth each time, consequently resulting in grater level of understanding of the problem.
Disadvantages of Action Research Spiral model include its assumption each process takes long time to be completed which may not always be the case.
My e-book, The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Dissertation in Business Studies: a step by step assistance offers practical assistance to complete a dissertation with minimum or no stress. The e-book covers all stages of writing a dissertation starting from the selection to the research area to submitting the completed version of the work within the deadline.

References
[1] Bryman, A. & Bell, E. (2011) “Business Research Methods” 3 rd edition, Oxford University Press
[2] Collis, J. & Hussey, R. (2003) “Business Research. A Practical Guide for Undergraduate and Graduate Students” 2nd edition, Palgrave Macmillan

Linking Research to Action: A Simple Guide to Writing an Action Research Report
What Is Action Research, and Why Do We Do It?
Action research is any research into practice undertaken by those involved in that practice, with the primary goal of encouraging continued reflection and making improvement. It can be done in any professional field, including medicine, nursing, social work, psychology, and education. Action research is particularly popular in the field of education. When it comes to teaching, practitioners may be interested in trying out different teaching methods in the classroom, but are unsure of their effectiveness. Action research provides an opportunity to explore the effectiveness of a particular teaching practice, the development of a curriculum, or your students’ learning, hence making continual improvement possible. In other words, the use of an interactive action-and-research process enables practitioners to get an idea of what they and their learners really do inside of the classroom, not merely what they think they can do. By doing this, it is hoped that both the teaching and the learning occurring in the classroom can be better tailored to fit the learners’ needs.
You may be wondering how action research differs from traditional research. The term itself already suggests that it is concerned with both “action” and “research,” as well as the association between the two. Kurt Lewin (1890-1947), a famous psychologist who coined this term, believed that there was “no action without research; no research without action” (Marrow, 1969, p.163). It is certainly possible, and perhaps commonplace, for people to try to have one without the other, but the unique combination of the two is what distinguishes action research from most other forms of enquiry. Traditional research emphasizes the review of prior research, rigorous control of the research design, and generalizable and preferably statistically significant results, all of which help examine the theoretical significance of the issue. Action research, with its emphasis on the insider’s perspective and the practical significance of a current issue, may instead allow less representative sampling, looser procedures, and the presentation of raw data and statistically insignificant results.
What Should We Include in an Action Research Report?
The components put into an action research report largely coincide with the steps used in the action research process. This process usually starts with a question or an observation about a current problem. After identifying the problem area and narrowing it down to make it more manageable for research, the development process continues as you devise an action plan to investigate your question. This will involve gathering data and evidence to support your solution. Common data collection methods include observation of individual or group behavior, taking audio or video recordings, distributing questionnaires or surveys, conducting interviews, asking for peer observations and comments, taking field notes, writing journals, and studying the work samples of your own and your target participants. You may choose to use more than one of these data collection methods. After you have selected your method and are analyzing the data you have collected, you will also reflect upon your entire process of action research. You may have a better solution to your question now, due to the increase of your available evidence. You may also think about the steps you will try next, or decide that the practice needs to be observed again with modifications. If so, the whole action research process starts all over again.
In brief, action research is more like a cyclical process, with the reflection upon your action and research findings affecting changes in your practice, which may lead to extended questions and further action. This brings us back to the essential steps of action research: identifying the problem, devising an action plan, implementing the plan, and finally, observing and reflecting upon the process. Your action research report should comprise all of these essential steps. Feldman and Weiss (n.d.) summarized them as five structural elements, which do not have to be written in a particular order. Your report should:
- Describe the context where the action research takes place. This could be, for example, the school in which you teach. Both features of the school and the population associated with it (e.g., students and parents) would be illustrated as well.
- Contain a statement of your research focus. This would explain where your research questions come from, the problem you intend to investigate, and the goals you want to achieve. You may also mention prior research studies you have read that are related to your action research study.
- Detail the method(s) used. This part includes the procedures you used to collect data, types of data in your report, and justification of your used strategies.
- Highlight the research findings. This is the part in which you observe and reflect upon your practice. By analyzing the evidence you have gathered, you will come to understand whether the initial problem has been solved or not, and what research you have yet to accomplish.
- Suggest implications. You may discuss how the findings of your research will affect your future practice, or explain any new research plans you have that have been inspired by this report’s action research.
The overall structure of your paper will actually look more or less the same as what we commonly see in traditional research papers.
What Else Do We Need to Pay Attention to?
We discussed the major differences between action research and traditional research in the beginning of this article. Due to the difference in the focus of an action research report, the language style used may not be the same as what we normally see or use in a standard research report. Although both kinds of research, both action and traditional, can be published in academic journals, action research may also be published and delivered in brief reports or on websites for a broader, non-academic audience. Instead of using the formal style of scientific research, you may find it more suitable to write in the first person and use a narrative style while documenting your details of the research process.
However, this does not forbid using an academic writing style, which undeniably enhances the credibility of a report. According to Johnson (2002), even though personal thoughts and observations are valued and recorded along the way, an action research report should not be written in a highly subjective manner. A personal, reflective writing style does not necessarily mean that descriptions are unfair or dishonest, but statements with value judgments, highly charged language, and emotional buzzwords are best avoided.
Furthermore, documenting every detail used in the process of research does not necessitate writing a lengthy report. The purpose of giving sufficient details is to let other practitioners trace your train of thought, learn from your examples, and possibly be able to duplicate your steps of research. This is why writing a clear report that does not bore or confuse your readers is essential.
Lastly, You May Ask, Why Do We Bother to Even Write an Action Research Report?
It sounds paradoxical that while practitioners tend to have a great deal of knowledge at their disposal, often they do not communicate their insights to others. Take education as an example: It is both regrettable and regressive if every teacher, no matter how professional he or she might be, only teaches in the way they were taught and fails to understand what their peer teachers know about their practice. Writing an action research report provides you with the chance to reflect upon your own practice, make substantiated claims linking research to action, and document action and ideas as they take place. The results can then be kept, both for the sake of your own future reference, and to also make the most of your insights through the act of sharing with your professional peers.
Feldman, A., & Weiss, T. (n.d.). Suggestions for writing the action research report . Retrieved from http://people.umass.edu/~afeldman/ARreadingmaterials/WritingARReport.html
Johnson, A. P. (2002). A short guide to action research . Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
Marrow, A. J. (1969). The practical theorist: The life and work of Kurt Lewin . New York, NY: Basic Books.
Tiffany Ip is a lecturer at Hong Kong Baptist University. She gained a PhD in neurolinguistics after completing her Bachelor’s degree in psychology and linguistics. She strives to utilize her knowledge to translate brain research findings into practical classroom instruction.
Breadcrumbs Section. Click here to navigate to respective pages.

ACTION RESEARCH RATIONALE AND PLANNING: DEVELOPING A FRAMEWORK FOR TEACHER INQUIRY
DOI link for ACTION RESEARCH RATIONALE AND PLANNING: DEVELOPING A FRAMEWORK FOR TEACHER INQUIRY
Click here to navigate to parent product.
I like to try to find ways into a subject that will catch everybody’s
interests…. I like to see the most productive of questions get born out
of laughter, and the most frustrating of brick walls give way to an idea
that has been there all along.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Taylor & Francis Online
- Taylor & Francis Group
- Students/Researchers
- Librarians/Institutions
Connect with us
Registered in England & Wales No. 3099067 5 Howick Place | London | SW1P 1WG © 2024 Informa UK Limited
Action Research
Cite this chapter.

- Anne Burns 3
6770 Accesses
10 Citations
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others

Altrichter, H., Posch, P., & Somekh, B. (1993). Teachers investigate their work. An introduction to the methods of action research . London: Routledge.
Google Scholar
Bailey, A., Rey, L., & Rosado, N. (2007). Understanding practices: Bridging the gap between what teachers do and what students know. In H. M. McGarrell (Ed.), Language teacher research in the Americas (pp. 7–24). Alexandria: TESOL.
Bailey, K. M. (1990). The use of diary studies in teacher education programs. In J. C. Richards & D. Nunan, Second language teacher education (pp.215–226). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Bailey, K. M., Curtis, A., & Nunan, D. 2001 Pursuing professional development: The self as source . Boston: Heinle & Heinle.
Burns, A. (1999). Collaborative action research for English language teachers . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Burns, A. (2000). Facilitating collaborative action research: Some insights from the AMEP. Prospect 15(3), 23–34.
Burns, A. (2005). Action research . In E. Hinkel (Ed.), Handbook of research in second language teaching and learning (pp.241–256). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Burns, A. (2007). Action research: Contributions and further directions in ELT. In J. Cummins & C. Davison (Eds.), International handbook of English (pp. 987–1002). New York: Springer.
Burton, J. I., & Carroll, M. (Eds.). (2001). Journal writing . Alexandria, VA: TESOL.
Carr, W., & Kemmis, S. (1986). Becoming critical: Knowing through action research . London: Falmer Press.
Fischer, J. C. (2001). Action research rationale and planning: Developing a framework for teache r inquiry. In G. Burnaford, J. C. Fischer, & D. Hobson (Eds.), Teachers doing research: The power of action through inquiry (pp. 29–48). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Freeman, D., & Johnson, K. E. (1998). Reconceptualizing the knowledge-base of language teacher education. TESOL Quarterly 32(3), 397–418.
Article Google Scholar
Kemmis, S., & McTaggart, R. (1986). The action research planner . Geelong, Victoria: Deakin University Press.
Krueger, R. A., & Casey, M. A. (2000). Focus groups: A practical guide for applied research . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
Book Google Scholar
LeCompte, M. D., & Goetz, J. P. 1984 Ethnography and qualitative design in educational research . New York: Academic Press.
McKay, S. L. (2006). Researching second language classrooms . Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Patton, M. Q. (1990). Qualitative evaluation and research methods . Newbury Park, CA: Sage Publications.
Progoff, I. (1975). At a journal workshop: The basic text and guide for using the Intensive Journal process . New York: Dialogue House Library.
Richards, K. (2003). Qualitative inquiry in TESOL . Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan.
Richards, J. C., & Farrell, T. S. C. 2005 Professional development for language teachers . New York: Cambridge University Press.
Roach, K. (2008). Teaching literacy to deaf adults: Maxims for mapping uncharted territory. In A. Burns & J. Burton (Eds.), Language teacher research in Australia and New Zealand (pp. 181–198). Alexandria: TESOL.
Rochsantiningsih, D. (2005). Enhancing professional development of Indonesian high school teachers through action research . Unpublished PhD thesis, Macquarie University: Sydney.
Samway, K. D. (1994). But it’s hard to keep fieldnotes while also teaching. TESOL Journal 4(1), 47–48.
Schwalbach, E. M. 2003 Value and validity in action research. A guidebook for reflective practitioners . Lanham, MD: The Scarecrow Press.
Somekh, B. (1993). Quality in educational research: The contribution of classroom teachers. In J. Edge & K. Richards (Eds.), Teachers develop teachers’ research (pp. 26–38). London: Heinemann.
Troudi, S. (2007). Negotiating with multiple resisters. In C. Coombe & L. Barlow (Eds.), Language teacher research in the Middle East (pp.161–172). Alexandria: TESOL.
Zeichner, K. M., & Liston, D. P. (1996). Reflective teaching. An introduction . Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Macquarie University, Sydney, Australia
Anne Burns ( Chair Professor in the Department of Linguistics and the former Dean of Linguistics and Psychology )
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar

Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Sugiyama Jogakuen University, Japan
Juanita Heigham
Nanzan University, Japan
Robert A. Croker
Copyright information
© 2009 Anne Burns
About this chapter
Burns, A. (2009). Action Research. In: Heigham, J., Croker, R.A. (eds) Qualitative Research in Applied Linguistics. Palgrave Macmillan, London. https://doi.org/10.1057/9780230239517_6
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/9780230239517_6
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, London
Print ISBN : 978-0-230-21953-3
Online ISBN : 978-0-230-23951-7
eBook Packages : Palgrave Language & Linguistics Collection Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write the Rationale of the Study in Research (Examples)
What is the Rationale of the Study?
The rationale of the study is the justification for taking on a given study. It explains the reason the study was conducted or should be conducted. This means the study rationale should explain to the reader or examiner why the study is/was necessary. It is also sometimes called the “purpose” or “justification” of a study. While this is not difficult to grasp in itself, you might wonder how the rationale of the study is different from your research question or from the statement of the problem of your study, and how it fits into the rest of your thesis or research paper.
The rationale of the study links the background of the study to your specific research question and justifies the need for the latter on the basis of the former. In brief, you first provide and discuss existing data on the topic, and then you tell the reader, based on the background evidence you just presented, where you identified gaps or issues and why you think it is important to address those. The problem statement, lastly, is the formulation of the specific research question you choose to investigate, following logically from your rationale, and the approach you are planning to use to do that.
Table of Contents:
How to write a rationale for a research paper , how do you justify the need for a research study.
- Study Rationale Example: Where Does It Go In Your Paper?
The basis for writing a research rationale is preliminary data or a clear description of an observation. If you are doing basic/theoretical research, then a literature review will help you identify gaps in current knowledge. In applied/practical research, you base your rationale on an existing issue with a certain process (e.g., vaccine proof registration) or practice (e.g., patient treatment) that is well documented and needs to be addressed. By presenting the reader with earlier evidence or observations, you can (and have to) convince them that you are not just repeating what other people have already done or said and that your ideas are not coming out of thin air.
Once you have explained where you are coming from, you should justify the need for doing additional research–this is essentially the rationale of your study. Finally, when you have convinced the reader of the purpose of your work, you can end your introduction section with the statement of the problem of your research that contains clear aims and objectives and also briefly describes (and justifies) your methodological approach.
When is the Rationale for Research Written?
The author can present the study rationale both before and after the research is conducted.
- Before conducting research : The study rationale is a central component of the research proposal . It represents the plan of your work, constructed before the study is actually executed.
- Once research has been conducted : After the study is completed, the rationale is presented in a research article or PhD dissertation to explain why you focused on this specific research question. When writing the study rationale for this purpose, the author should link the rationale of the research to the aims and outcomes of the study.
What to Include in the Study Rationale
Although every study rationale is different and discusses different specific elements of a study’s method or approach, there are some elements that should be included to write a good rationale. Make sure to touch on the following:
- A summary of conclusions from your review of the relevant literature
- What is currently unknown (gaps in knowledge)
- Inconclusive or contested results from previous studies on the same or similar topic
- The necessity to improve or build on previous research, such as to improve methodology or utilize newer techniques and/or technologies
There are different types of limitations that you can use to justify the need for your study. In applied/practical research, the justification for investigating something is always that an existing process/practice has a problem or is not satisfactory. Let’s say, for example, that people in a certain country/city/community commonly complain about hospital care on weekends (not enough staff, not enough attention, no decisions being made), but you looked into it and realized that nobody ever investigated whether these perceived problems are actually based on objective shortages/non-availabilities of care or whether the lower numbers of patients who are treated during weekends are commensurate with the provided services.
In this case, “lack of data” is your justification for digging deeper into the problem. Or, if it is obvious that there is a shortage of staff and provided services on weekends, you could decide to investigate which of the usual procedures are skipped during weekends as a result and what the negative consequences are.
In basic/theoretical research, lack of knowledge is of course a common and accepted justification for additional research—but make sure that it is not your only motivation. “Nobody has ever done this” is only a convincing reason for a study if you explain to the reader why you think we should know more about this specific phenomenon. If there is earlier research but you think it has limitations, then those can usually be classified into “methodological”, “contextual”, and “conceptual” limitations. To identify such limitations, you can ask specific questions and let those questions guide you when you explain to the reader why your study was necessary:
Methodological limitations
- Did earlier studies try but failed to measure/identify a specific phenomenon?
- Was earlier research based on incorrect conceptualizations of variables?
- Were earlier studies based on questionable operationalizations of key concepts?
- Did earlier studies use questionable or inappropriate research designs?
Contextual limitations
- Have recent changes in the studied problem made previous studies irrelevant?
- Are you studying a new/particular context that previous findings do not apply to?
Conceptual limitations
- Do previous findings only make sense within a specific framework or ideology?
Study Rationale Examples
Let’s look at an example from one of our earlier articles on the statement of the problem to clarify how your rationale fits into your introduction section. This is a very short introduction for a practical research study on the challenges of online learning. Your introduction might be much longer (especially the context/background section), and this example does not contain any sources (which you will have to provide for all claims you make and all earlier studies you cite)—but please pay attention to how the background presentation , rationale, and problem statement blend into each other in a logical way so that the reader can follow and has no reason to question your motivation or the foundation of your research.
Background presentation
Since the beginning of the Covid pandemic, most educational institutions around the world have transitioned to a fully online study model, at least during peak times of infections and social distancing measures. This transition has not been easy and even two years into the pandemic, problems with online teaching and studying persist (reference needed) .
While the increasing gap between those with access to technology and equipment and those without access has been determined to be one of the main challenges (reference needed) , others claim that online learning offers more opportunities for many students by breaking down barriers of location and distance (reference needed) .
Rationale of the study
Since teachers and students cannot wait for circumstances to go back to normal, the measures that schools and universities have implemented during the last two years, their advantages and disadvantages, and the impact of those measures on students’ progress, satisfaction, and well-being need to be understood so that improvements can be made and demographics that have been left behind can receive the support they need as soon as possible.
Statement of the problem
To identify what changes in the learning environment were considered the most challenging and how those changes relate to a variety of student outcome measures, we conducted surveys and interviews among teachers and students at ten institutions of higher education in four different major cities, two in the US (New York and Chicago), one in South Korea (Seoul), and one in the UK (London). Responses were analyzed with a focus on different student demographics and how they might have been affected differently by the current situation.
How long is a study rationale?
In a research article bound for journal publication, your rationale should not be longer than a few sentences (no longer than one brief paragraph). A dissertation or thesis usually allows for a longer description; depending on the length and nature of your document, this could be up to a couple of paragraphs in length. A completely novel or unconventional approach might warrant a longer and more detailed justification than an approach that slightly deviates from well-established methods and approaches.
Consider Using Professional Academic Editing Services
Now that you know how to write the rationale of the study for a research proposal or paper, you should make use of Wordvice AI’s free AI Grammar Checker , or receive professional academic proofreading services from Wordvice, including research paper editing services and manuscript editing services to polish your submitted research documents.
You can also find many more articles, for example on writing the other parts of your research paper , on choosing a title , or on making sure you understand and adhere to the author instructions before you submit to a journal, on the Wordvice academic resources pages.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Action research is a research method that aims to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue. In other words, as its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time. It was first coined as a term in 1944 by MIT professor Kurt Lewin.A highly interactive method, action research is often used in the social sciences, particularly in educational settings.
Action research is a process for improving educational practice. Its methods involve action, evaluation, and reflection. It is a process to gather evidence to implement change in practices. Action research is participative and collaborative. It is undertaken by individuals with a common purpose.
tioners. Examples of action research projects undertaken by healthcare practitioners in a range of situations are provided later in this chapter. The development of action research: a brief background Whether the reader is a novice or is progressing with an action research project, it would be useful to be aware of how action research has devel-
Action research shifts the paradigm of contemporary educational reform by emphasizing inquiry and placing teachers at the center of research-into-practice. By situating teachers as learners, action research offers a systematic and intentional approach to changing teaching. When working as part of a community of practice, action researchers ...
etc.) whose effects need to be better understood. The researchers develop a viable plan for collecting the. The researchers develop a viable plan for collecting the data. necessary data. needed to illuminate the implementation of the operative theory. The researchers implement the new theory of action and.
Action research is a growing tradition for improving teachers' practice and students' learning outcomes, and it draws from a variety of methods for collecting and analysing data. In this article ...
Summary. Action research has become a common practice among educational administrators. The term "action research" was first coined by Kurt Lewin in the 1930s, although teachers and school administrators have long engaged in the process described by and formally named by Lewin. Alternatively known as practitioner research, self-study ...
Action Research is fundamentally concerned with change. It is an inherently normative project. It tries to provide resources for the research participants to collaboratively change their situation toward a subjectively felt and objectively visible improvement of their living conditions.
As the name suggests, action research is an approach to research which aims at both taking action and creating knowledge or theory about that action as the action unfolds. It rejects the notion that research must be value free in order to be credible, in favor an explicitly socially engaged and democratic practice (Brydon-Miller et al. 2003 ).
participatory action research action research and feminsim appreciative inquiry Introduction Simply put, action research is a process by which change is achieved and new knowledge about a situation is generated. These two objectives go hand-in-hand to a greater or lesser degree in most action research studies: it is difficult
Tripp Action research: a methodological introduction 2. 2005 draft of a paper to be published in Educação e Pesquisa University of São PauloUSP. administration (Collier), community development ...
Action research has come to be understood as a global family of related approaches that integrates theory and practice with a goal of addressing important organizational, community, and social issues together with those who experience them (Bradbury, 2015; Brydon-Miller & Coghlan, 2014).It focuses on the creation of areas for collaborative learning and the design, enactment, and evaluation of ...
A basic knowledge of the action research cycle and the rationale for its use. Someone to provide technical assistance and/or support. The Action Research Cycle. Identify an area of interest/problem. Identify data to be collected, the format for the results, and a timeline. Collect and organize the data. Analyze and interpret the data. Decide ...
The action research process described in this paper incorporates traditional outcome assessment where students produce some end product (projects, papers, presentations, exams, etc.), as well as, faculty and students' perspectives of the impact the learning activity had on the learning process. The purpose of this paper is to encourage ...
What Is Action Research? 1. Since there is "action", this implies that there will be some kind of active investigation of whatever is seen to be the problem to be fixed, the puzzle to be considered, the question to be answered, or the issue to be addressed. 2. Since there is "action", there must be an agent, that is, someone performing ...
Sagor (2010) defines collaborative action research as "the team inquiry process, when a group of individuals who are a part of a specific PLC, grade-level, or teacher learning team engage in inquiry and research.". These teams can become a means for collaboratively engaging in action research and developing data that is relative to the school.
The first part of the paper positions the action research movement in the context of other research and development concepts and describes its rationale and some basic quality criteria. Action research is regarded as an umbrella term defined by two generic characteristics: substantial practitioner control of both the practice situation ...
Definition. Action research is a form of enquiry that integrates theory and action to address real life problems. It enables practitioners to systematically evaluate and improve their practice. The number of types of action researches has multiplied over the last 50 years (Fourali 2016 ) or so and, accordingly, so did the number of definitions ...
Action research can be defined as "an approach in which the action researcher and a client collaborate in the diagnosis of the problem and in the development of a solution based on the diagnosis".In other words, one of the main characteristic traits of action research relates to collaboration between researcher and member of organisation in order to solve organizational problems.
This brings us back to the essential steps of action research: identifying the problem, devising an action plan, implementing the plan, and finally, observing and reflecting upon the process. Your action research report should comprise all of these essential steps. Feldman and Weiss (n.d.) summarized them as five structural elements, which do ...
Book Teachers Doing Research. Edition 2nd Edition. First Published 2000. Imprint Routledge. Pages 16. eBook ISBN 9781410605641.
Action research rationale and planning: Developing a framework for teache r inquiry. In G. Burnaford, J. C. Fischer, & D. Hobson (Eds.), Teachers doing research: The power of action through inquiry (pp. 29-48). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. Google Scholar
The rationale of the study is the justification for taking on a given study. It explains the reason the study was conducted or should be conducted. This means the study rationale should explain to the reader or examiner why the study is/was necessary. It is also sometimes called the "purpose" or "justification" of a study.