
- Notre histoire
- Gouvernance
- Nos engagements
- Centre de conférences
- Enseignement
- Innovation et transfert de technologie
- Plan stratégique 2019-2023
- Comment nous soutenir ?
- Pourquoi nous soutenir ?
- Pasteur et vous
- Covid-19 : merci pour votre soutien !
- Espace Donateur
- Infos pratiques
- Consultations
- Vaccination
- Préparer votre voyage
- Fiches maladies
- Rechercher dans le journal
- Documents de presse
- Ressources pour la presse
- Nos recherches sur Sars-Cov-2
- Actualités Covid-19
- Fiche Maladie Covid-19
- L'Institut Pasteur
- Nos missions
- Nous soutenir
- Centre médical
- Le journal de la recherche
- Espace presse
- Tout sur SARS-CoV-2 / Covid-19 à l'Institut Pasteur
- Centre d'enseignement
- Programmes et cours
- Startup Awareness
- Hébergements
- Toute l'actualité
- Centres nationaux de référence
- Centres collaborateurs de l'OMS
- Centre de Ressources Biologiques
- Centres collaborateurs de l’OMSA
- Coopérations
- Programmes internationaux
- Appels à propositions
- Bourses et mobilité
- Pasteur Network
- Qui sommes-nous ?
- Partenariats industriels
- Partenariats avec des investisseurs
- Label Carnot
- Pourquoi nous rejoindre
- Nos offres d'emploi
- Votre arrivée
- Pasteuriens et Alumni
- Bibliothèque
- Photothèque
- Publications scientifiques
- Suivre l'Institut Pasteur sur Facebook
- Suivre l'Institut Pasteur sur LinkedIn
- Suivre l'Institut Pasteur sur Twitter
- Suivre l'Institut Pasteur sur Youtube
- Suivre l'Institut Pasteur sur Instagram
- Santé publique
- International
- Faites un don


Mpox (anciennement variole du singe)

Le Mpox est un virus initialement présent chez l’animal, notamment chez des rongeurs en Afrique, et qui circule désormais chez l’être humain ; on parle ainsi de zoonose émergente. La maladie causée par ce virus porte le même nom, Mpox (anciennement appelée variole de singe ou monkeypox), et se présente comme une forme atténuée de la variole humaine, avec des symptômes moins graves et une létalité plus faible (nombre de morts sur le nombre de personnes atteintes).
De petites flambées épidémiques localisées ont régulièrement eu lieu ces dernières années en Afrique centrale et de l’Ouest. Ces émergences ont été étudiées et surveillées jusqu’à l’émergence mondiale de la maladie, observée en mai 2022.
Au début des années 1980, suite à l’éradication mondiale de la variole humaine, la vaccination antivariolique a été arrêtée. Les personnes ainsi vaccinées sont partiellement protégées face au virus Mpox ; il existe en effet une immunité croisée entre le virus Mpox et le virus de la variole humaine.
En juillet 2022, l’Organisation mondiale de la santé (OMS) a déclaré une première fois que l’épidémie de Mpox est une urgence de santé publique de portée internationale (USPPI) suite à sa propagation « extraordinaire » dans plus de 75 pays non endémiques (régions où la maladie n’existe pas en permanence).
Le 14 août 2024, devant la recrudescence du Mpox en République Démocratique du Congo et dans plusieurs pays voisins, ainsi que l’apparition d’une nouvelle souche virale possiblement plus transmissible (clade 1b), l’OMS déclare une deuxième USPPI.
87972 CAS DANS LE MONDE ENTRE LE 1ER JANVIER 2022 ET LE 19 JUIN 2023
52 CAS EN FRANCE EN 2023
Quelles sont les causes ?
Le virus Mpox est un virus à ADN double brin (environ 200 kilobases), de la famille des Poxviridés et du genre Orthopoxvirus . Il est apparenté au virus responsable de la variole humaine, une maladie déclarée éradiquée, grâce à la vaccination, en 1980.
Le virus Mpox a été isolé pour la première fois en 1958, au sein d’une colonie de singes à Copenhague, au Danemark. Ces singes présentaient des lésions cutanées qui évoquaient la variole humaine. D’où le nom de variole du singe, attribué à cette maladie.
Bien qu’on l’appelle encore fréquemment variole *du singe*, ce n’est pas via les singes que cette maladie se transmet à l’humain, mais à partir des rongeurs (voir ci-dessous le paragraphe « Comment se transmet la maladie »). L’OMS privilégie depuis fin 2022 la dénomination “Mpox".
On distingue deux principaux types du virus Mpox :
- le clade 1 : souche “historique” du virus, présent dans le Bassin du Congo en Afrique Centrale. Le clade 1b provient du clade 1.
- le clade 2 présent en Afrique de l’Ouest. Le virus qui circule actuellement en Europe, le clade 2b, provient du clade 2 impliqué dans l’épidémie du Nigéria.
Comment se transmet la maladie ?
Le Mpox est une zoonose, c’est-à-dire une maladie transmise de l’animal à l’humain.
Le Mpox se transmet à l’humain à partir des rongeurs (par exemple, en Afrique, les écureuils de forêt ou rat de Gambie). Toutefois, le réservoir animal n’a pas encore été formellement identifié. D’après une étude publiée en 2021 par l’Institut Pasteur, concernant la variole du singe en République centrafricaine, l’histoire génomique suggère de multiples introductions depuis des réservoirs animaux forestiers.
La transmission du virus Mpox chez l’humain se fait :
- principalement par contact avec les lésions cutanées contenant des particules virales ou les muqueuses de personnes infectées
- soit par contact direct avec des animaux infectés,
- soit de façon indirecte via des matériaux contaminés (comme la literie ou les surfaces).
- Elle pourrait peut-être se faire aussi via les gouttelettes respiratoires d’une personne infectée.
Quels sont les symptômes ?
La présentation clinique du Mpox est une forme atténuée de la variole humaine, dont l’éradication à l’échelle mondiale a été déclarée en 1980.
Toutefois, le Mpox est moins contagieux que la variole humaine et entraîne une maladie plus bénigne.
Historiquement, en Afrique, le Mpox se manifeste ainsi :
- une période d’incubation d’en moyenne 12 jours, avant la survenue des premiers symptômes ;
- généralement un syndrome fébrile (courbatures, céphalées, fatigue, etc.), durant 1 à 4 jours ; le sujet est contagieux dès l’apparition des premiers symptômes (voir fiche DGS à destination des professionnels de santé ) ;
- puis une phase éruptive, durant 2 à 4 semaines, avec des éruptions cutanées sous forme de petites tâches (éruptions maculopapulaires évoluant vers pustules, vésicules et croûtes), qui atteignent l’ensemble du corps dont la paume des mains et la plante des pieds, avec un gonflement des ganglions lymphatiques.
L’épidémie qui a sévi à partir de mai 2022 en Europe, liée au clade 2b – et qui s’est étendue ensuite dans le reste du monde – montre des éruptions cutanées plus localisées, souvent sur les zones génitales ou péri-anales (Voir la fiche "Monkeypox" sur le site de Santé publique France ).
Les symptômes durent de 2 à 4 semaines et la personne malade guérit en général spontanément. Des complications peuvent survenir telles que : surinfections cutanées, septicémie, encéphalites, ou atteintes cornéennes. Elles peuvent mener à des formes graves de la maladie. L’OMS rapporte sur son site un taux de létalité d’environ 3 à 6 % en 2022 concernant les épidémies en Afrique, la létalité semblant plus importante avec la souche d’Afrique centrale (clade 1) et en contexte endémique. Il faut savoir que la létalité est très dépendante de l’âge des patients (élevée chez les moins de 5 ans, notamment les enfants dénutris et/ou déshydratés), de la présence d’un déficit immunitaire (infection par le VIH) et surtout de la qualité de la prise en charge hospitalière. Ainsi, dans le contexte de l’épidémie mondiale en 2022, la létalité était beaucoup plus faible, de l’ordre de 0,2%.
Comment diagnostiquer l’infection ?
Le diagnostic du Mpox est réalisé d’abord cliniquement par des médecins spécialisés (infectiologues, dermatologues). Il est ensuite confirmé en laboratoire par PCR en temps réel sur écouvillon oropharyngé et sur écouvillon de pustule.
Le diagnostic du Mpox doit prendre en considération d’autres maladies éruptives : en particulier la varicelle , mais aussi la rougeole, les infections bactériennes cutanées, la syphilis, l’herpès, etc.
Quels sont les traitements ?
Un agent antiviral, le Tecovirimat, initialement conçu pour le traitement de la variole, a été utilisé pour le traitement du Mpox lors de l’épidémie de 2022-2023. Ce traitement n’est indiqué que dans les formes sévères de la maladie, et est administré le plus précocement possible pour une durée de 15 jours par voie orale. Son efficacité clinique nécessite d’être déterminée de façon robuste.
La Haute Autorité de santé (HAS) propose sur son site des réponses rapides à l’attention des professionnels de santé, concernant l’infection par le virus Mpox et la prise en charge en médecine de premier recours.
En savoir plus avec les recommandations de la HAS
Comment prévenir la maladie ?
Dans les zones endémiques (en Afrique), la principale stratégie de prévention du Mpox consiste à limiter les interfaces humains/faune sauvage , donc sensibiliser et informer les populations aux facteurs de risque de transmission zoonotique (par les animaux) et ainsi diminuer les risques de transmission de l’animal vers l’humain. Au-delà, il faut agir sur la réduction de facteurs participant eux aussi à la survenue d’épidémie tels que la pauvreté, à travers la dépendance à la viande de brousse comme source protéique et la densité et la promiscuité dans les foyers, ou les conflits militaires induisant des déplacements de populations.
Plus généralement, pour limiter la transmission interhumaine, la stratégie de prévention repose sur l’information et la sensibilisation :
- sensibiliser les populations aux facteurs de risque de transmission : éviter contacts cutanés avec des personnes malades ou du matériel contaminé (lire plus haut),
- informer les populations à risque et les professionnels de santé.
Le développement de tests rapides de diagnostic permettra d’améliorer le diagnostic et prévenir la transmission interhumaine.
Plusieurs vaccins sont disponibles contre le Mpox.
Les vaccins antivarioliques , employés dans le cadre du programme d’éradication de la variole dans les années 1970, offrent une protection croisée contre le Mpox. D’autres vaccins ont également été mis au point plus récemment et présentent moins d’effets indésirables.
Certains pays proposent un vaccin aux personnes susceptibles d’être à risque, comme les personnels de laboratoires, les agents de santé, etc. En France, la Haute Autorité de santé a recommandé dans son avis du 7 juillet 2022 qu’une vaccination préventive soit proposée aux personnes les plus exposées au virus, à savoir les hommes ayant des relations sexuelles avec des hommes, propriétaires de lieux de consommation sexuelle, et professionnels du sexe.
Qui est touché ?
Le Mpox est une maladie infectieuse émergente, identifiée pour la première fois chez l’être humain en 1970 en République démocratique du Congo (RDC). Ensuite, la plupart des cas ont été signalés dans les régions rurales et isolées, et les zones de forêts tropicales humides d’Afrique centrale et d’Afrique de l’Ouest.
La fréquence des flambées épidémiques, et leurs tailles dans les populations humaines, ont régulièrement augmenté ces dernières années. La propagation géographique du Mpox s’est étendue au-delà des forêts d’Afrique centrale, vers des zones de savane ou des zones urbaines, et jusqu’à d’autres parties du monde où des cas ont été importés.
Ce schéma de transmission s’explique en partie par le déclin mondial de l’immunité post-vaccination antivariolique, suite à l’arrêt de cette vaccination, dans les années 1980 (voir l’analyse rétrospective de l’Institut Pasteur en juillet 2020 ).
Cependant, d’autres facteurs, qui ont été sujets à une évolution ces 30 dernières années, sont également impliqués : changements majeurs d’usage des terres, déforestation massive, urbanisation croissante, destructions d’habitat de faune sauvage, pertes de biodiversité. Ces pressions sur les écosystèmes dues à l’activité humaine entrainent une majoration des interfaces humains/faune sauvage, ainsi que la modification des structures et dynamiques des communautés animales.
Depuis quelques années, on assiste à un changement du profil épidémiologique des patients en Afrique, alors que le virus est retrouvé de plus en plus souvent en zone urbaine :
- Au Nigéria, il s’agit depuis 2017 d’une population majoritairement masculine, d’âge sexuellement actif, avec une proportion non négligeable de patients infectés par le VIH. Le clade infectant, appelé 2b, est celui qui a été retrouvé par la suite lors de la pandémie mondiale de 2022, qui a majoritairement touché les hommes ayant des relations sexuelles avec des hommes (HSH). Cette pandémie, 87972 cas et 147 décès dans 110 pays, a amené l’OMS à déclarer pour la première fois une urgence de santé publique de portée internationale (USPPI) le 23 juillet 2022. Les mesures de prévention relayées par les milieux associatifs vers les populations à risque, ainsi que la vaccination, ont permis d’enrayer cette première pandémie, même si le virus continue à circuler à bas bruit (52 cas notifiés en France en 2023, 107 lors du premier semestre 2024 ).
- En RDC, où le nombre de cas est en constante augmentation depuis deux ans, et où une épidémie particulièrement importante sévit dans la partie est du pays (le Kivu). La majorité des cas sont des adultes jeunes, beaucoup travaillant dans les zones minières, et également des professionnelles du sexe, suggérant une transmission sexuelle active du virus dans ces communautés. Le clade 1b, impliqué dans ces transmissions, a depuis été retrouvé dans plusieurs pays d’Afrique de l’Est où le virus ne circulait pas auparavant (notamment le Rwanda, le Burundi, l’Ouganda et le Kenya). C’est cette circulation active du virus en Afrique de l’Est, et la présence d’un nouveau clade dont on ne connait pas encore la transmissibilité et la létalité, qui a amené l’OMS à déclarer une deuxième USPPI le 14 août 2024.
Voir la fiche maladie de l’OMS
Obtenir des informations sur le Mpox sur le site de l'Assurance Maladie
Obtenir des informations sur le nombre de cas de Mpox en France et dans le monde sur le site de Santé publique France
- Esports World Cup
- Scores en direct
- Accueil Football
- Calendrier/Résultats
- Ligue des champions
- Premier League
- Toutes les compétitions
- Accueil Tennis
- Calendrier ATP
- Calendrier WTA
- Accueil Cyclisme
- Courses en direct
- Tour de France
- Tour d'Espagne
- Dare to Dream
- Accueil Sports d'hiver
- Tous les sports
- Accueil JO Paris 2024
- Olympic Channel
- Mon Paris Olympique
- Accueil Rugby
- Coupe du monde
- Champions Cup
- Accueil e-Sports
- Accueil Athlétisme
- Ligue de Diamant
- Ch. Monde outdoor
- Ch. Monde indoor
- Accueil Auto-Moto
- Goodyear Ready For Anything
- Accueil Basketball
- Betclic Élite
- Toutes les Ligues
- Accueil Boxe
- Accueil Cyclisme sur piste
- UCI Track Champions League
- Accueil Cyclo-cross
- Accueil Equitation
- Accueil Formule 1
- Classements
- Accueil Golf
- World Ranking
- DP World Tour
- Accueil Handball
- Championnats du Monde
- Championnat d'Europe
- Accueil Judo
- Accueil MotoGP
- Classements Moto GP
- Accueil Natation
- Championnats du monde
- Paris, la vie sportive
- Accueil Snooker
- Northern Ireland Open
- Tous les championnats
- Accueil Speedway
- Accueil Sports universitaires
- Accueil Triathlon
- Accueil UCI TCL
- Classement messieurs
- Classement dames
- Accueil Volleyball
- Marmara SpikeLigue
- Ligue des Champions
- Ligue Mondiale
La 41e et dernière journée de l’EWC a vu les champions de Rocket League, ESL R1 et PUBG : Battlegrounds être couronnés
/dnl.eurosport.com/sd/img/placeholder/eurosport_logo_1x1.png)
Publié 27/08/2024 à 06:32 GMT+2
Beaucoup d’émotions et de matchs intenses lors de la dernière journée de l’EWC avec la suite et fin des tournois de Rocket League, ESL R1 et PUBG : Battlegrounds. Certaines finales ont même dû se jouer plus tôt afin de ne pas empiéter sur la cérémonie de clôture qui était prévue pour le soir même.
Crédit: Eurosport
Rocket League
Team falcons entre dans l’histoire en remportant la coupe du monde d’e-sport.
il y a une heure
- Team Redline – 100 pts
- Team Vitality – 72 pts
- Porsche Coanda Esports — 51 pts
- Guild Esports — 48 pts
- Williams Esports — 46 pts
- MOUZ — 32 pts
PUBG : Battlegrounds
Cérémonie de clôture de l’ewc 2024 : fin d’un évènement historique.
Hier à 06:16
ECW – J40 : en route pour les finales de Rocket League, ESL R1 et PUBG Battlegrounds
26/08/2024 à 10:52
Riyad, capitale mondiale de l’e-sport : présentation de « Saudi Vision 2030 »
24/08/2024 à 16:25
Delivering presentations

LESSON SET OVERVIEW
With this lesson set, your students will:
- learn dos and don’ts of presenting ,
- discuss different structures and types of presentations (e.g. elevator pitch);
- learn and practise signposting language (e.g. to start, elaborate, make a connection, recap, deviate),
- watch a video about virtual presentations ,
- consolidate their knowledge by doing a few revision exercises and preparing mini presentations .
These three lessons were designed to introduce language useful for going through business presentation and practise using it in controlled scenarios to finally do presentations on different topics in the final lesson.
This is a lesson set. Use the lessons in the set in the suggested order. Learn more about sets here.
Each lesson in the set is also a standalone lesson.

How to nail that presentation
The first lesson in this set includes a video about how to nail a virtual presentation . Apart from the tips, in this lesson students also learn the types of presentations such as an elevator pitch, team briefing, roadmap presentation , etc. and their structures.

Moving through your presentation
Students learn the phrases to start, elaborate, make a connection, recap, deviate , etc. You can revise the vocabulary and the tips from the first lesson by encouraging students to use them in the first discussion question in ex. 1 (slide 3) , as well as in ex. 8 and ex. 11 (slide 45 and slide 51) of this lesson.

Presentation: putting skills into action
In the last lesson of this set, students consolidate their knowledge by doing a few revision exercises (ex. 1-4 / slides 3-12) and preparing mini presentations based on the information they receive.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Browse other sets for this level

Let’s get down to business! – new B2/C1 Business English students
This lesson set is designed to give you an opportunity to learn more about your new B2/C1 Business English students and to assess their level of English.

First things first – new B2/C1 students
This lesson set is designed to give you an opportunity to learn more about your new B2/C1 students and to assess their level of English.

Discussing social media
In this lesson set, students not only discuss different aspects of social media but revise and practise useful grammar and vocabulary

Expressing likelihood
In the first lesson, students learn language to express likelihood. In the second lesson, they practise the target language while talking about a topic of interest.

Learning to say ‘no’
This lesson set focuses on ways to say ‘no’ and the importance of protecting personal boundaries. It focuses on introducing and practising appropriate functional language.

Getting things done
This lesson set focuses on ways to be productive letting students learn useful vocabulary and structures and practise them in multiple activities.

Revising conditionals
With this lesson set, your students will review three types of conditional sentences during 2 lessons. Each lesson in the set requires some pre-class student work (watching a video or reading an article).

Talking about advantages and disadvantages
In the first lesson, students learn language to talk about advantages and disadvantages. In the second lesson, they practise the target language while talking about a topic of interest.

Storytelling
The set was created to provide revision and practice of three past tenses (Past Simple, Past Continuous, Past Perfect) and let students practise storytelling.
Is there a minimum subscription period if I choose a monthly subscription?
What currencies can i pay in for my subscription, how can i edit an e-lesson plan.
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
Your browser is not supported
Sorry but it looks as if your browser is out of date. To get the best experience using our site we recommend that you upgrade or switch browsers.
Find a solution
- Skip to main content
- Skip to navigation
- Macmillan English
- Onestopenglish
- Digital Shop

- Back to parent navigation item
- Sample material
- Amazing World of Animals
- Amazing World of Food
- Arts and Crafts
- Mathematics
- Transport and Communication
- Teaching Tools
- Sustainable Development and Global Citizenship
- Support for Teaching Children
- Vocabulary & Phonics
- Spelling Bee Games
- Phonics & Sounds
- The Alphabet
- Onestop Phonics: The Alphabet
- Alphabet Booklet
- Interactive Flashcards
- Warmers & Fillers
- Young Learner Games
- Stories and Poems
- Fillers & Pastimes
- Fun Fillers
- Ready for School!
- Topics & Themes
- Young Learner Topics
- Young Learner Festivals
- Festival Worksheets
- Art and Architecture
- Business and Tourism
- Geography and the Environment
- Information Technology
- Science and Nature
- Topic-based Listening Lessons
- Cambridge English
- Cambridge English: Preliminary (PET)
- Cambridge English: First (FCE)
- Cambridge English: Proficiency (CPE)
- Cambridge English: Advanced (CAE)
- General English
- News Lessons
- Topics and Themes
- Beyond (BrE)
- Beyond: Arts and Media
- Beyond: Knowledge
- Go Beyond (AmE)
- Go Beyond: Arts & Media
- Go Beyond: Knowledge
- Impressions
- Macmillan Readers
- A Time to Travel
- Life & School
- Skills for Problem Solving
- Digital Skills for Teens
- Support for Teaching Teenagers
- Games Teaching Materials
- Business and ESP
- Business Lesson Plans
- Business Skills Bank
- Business Top Trumps
- Elementary Business Lessons
- HR Management
- Let's Talk Business
- Business News Lessons
- ESP Lesson Plans
- Career Readiness
- Professional Communication Skills
- Cambridge English: Business (BEC)
- Everyday Life
- Celebrations
- Live from...
- Live from London
- Discussion Cards
- Writing Lesson Plans
- Life Skills
- Support for Teaching Adults
- Vocabulary Lesson Plans
- Language for...
- Vocabulary Teaching Materials
- Macmillan Dictionary Blog
- Vocabulary Infographics
- Kahoot! Quizzes
- Blog Articles
- Professional Development
- Lesson Share
- Methodology: Projects and Activities
- Methodology: Tips for Teachers
- Methodology: The World of ELT
- Advancing Learning
- Online Teaching
- More from navigation items
Business Skills Bank: Giving Presentations
By Tim Bowen
This Business skills lesson plan by Tim Bowen presents common features of presentations and practises useful language for putting together and giving presentations.
Lesson length: 60-75 mins
Materials: Worksheets 1-5
Subsidiary aims: Listening (or reading) for specific information, discussion of what makes a good presentation.
Business Skills Bank: Giving presentations—Worksheets
Business skills bank: giving presentations—teacher's notes, presentations part 1, presentations part 2.
- British English
- Business / ESP
- Intermediate
- Lesson Plan / Teacher's Notes
- Pre-Intermediate
- Printable Worksheet
- Up to 90 mins
- Upper-Intermediate
- Whole Class
Related articles

Business Skills Bank: Meetings
Sara Helm introduces a short series of lessons for business professionals on meetings skills and the type of functional language needed to conduct meetings in English.
Business skills bank: Preparing for a first meeting: Part 3
By Sara Helm
In this lesson students participate in a business meeting, while the teacher observes and takes notes for a performance review.
Business skills bank: Preparing for a first meeting: Part 2
A lesson to help review and practise language for leading and participating in meetings.
3 Readers' comments
Only registered users can comment on this article., more from business lesson plans.

Live from London: Business—Negotiations
By Pete Clements
Watch authentic London office workers describe the ways to conduct successful negotiations and the skills good negotiators need. Now Interactive!

Live from London: Business — Dress codes
Watch authentic London office workers giving advice on the best ways to dress to impress. Try the new Interactive Worksheets!

Live from London: Business — Emails
By Bryan Goodman-Stephens
Watch authentic London office workers explain how they use emails and phones to communicate in their companies. Now with Interactive Worksheets!
Join onestopenglish today
With more than 700,000 registered users in over 100 countries around the world, Onestopenglish is the number one resource site for English language teachers, providing access to thousands of resources, including lesson plans, worksheets, audio, video and flashcards.
- Connect with us on Facebook
- Connect with us on Twitter
- Connect with us on Youtube
Onestopenglish is a teacher resource site, part of Macmillan Education, one of the world’s leading publishers of English language teaching materials.
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie policy
- Manage cookies
©Macmillan Education Limited 2023. Company number: 1755588 VAT number: 199440621
Site powered by Webvision Cloud
Teaching Effective Presentation Skills to ESL/EFL Students
This article discusses some practical techniques that ESL/EFL teachers can use in teaching effective academic presentation skills. It is suggested that macro organization, micro organization, thesis and support, strategies to involve the audience, response to audience input, non-verbal communication, use of visual materials, and pacing should be taught explicitly to the students.
Introduction
Macro organization, micro organization, thesis and support, strategies to involve the audience, response to the audience input, non-verbal communication, use of visual materials.

- Become an Affiliate
- Join our Team
- Online Platform Tutorial
- TEFL Courses
- Contact Us / FAQ
Forgot Username or Password
- Active vs. Passive Voice
- Adverbial Clauses
- Adverbial Phrases
- Be Going To Statements
- Be Going To Wh Questions
- Be Going To Yes/No Questions
- Be Going To & Present Continuous
- Comparatives
- Superlatives
- Comparatives & Superlatives
- Zero Conditional
- First Conditional
- Second Conditional
- Third Conditional
- Mixed Conditionals
- Future Continuous
- Future Continuous vs. Future Perfect
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect Simple
- Future Simple
- Future Tenses
- Future Time Clauses
- Gerunds & Infinitives
- Have Got & Has Got
- I wish & If only
- Imperatives
- Irregular Verbs
- Narrative Tenses
- Noun Clauses
- Noun Phrases
- Passive Voice
- Past Continuous
- Past Perfect
- Past Perfect Continuous
- Past Perfect Simple & Continuous
- Past Simple Affirmative & Negative
- Past Simple Passive
- Past Simple Regular Verbs
- Past Simple Was and Were
- Past Simple Wh Questions
- Past Simple Yes/No Questions
- Past Simple vs. Past Continuous
- Past Simple vs. Present Perfect
- Past Tense Review
- Present Continuous
- Present Perfect
- Present Perfect Continuous
- Present Perfect - Ever and Never
- Present Perfect - For and Since
- Present Perfect - Just, Yet & Already
- Present Simple Affirmative & Negative
- Present Simple Passive
- Present Simple vs. Present Continuous
- Present Simple vs. Present Perfect
- Present Simple Wh Questions
- Present Simple Yes/No Questions
- Present Tense Review
- Question Words
- Relative Clauses
- Reported Speech
- Subject-Verb Agreement
- Tag Questions
- There is & There are
- Wh Questions
- Abstract Nouns
- Adjective-Noun Collocations
- Adjectives of Feeling & Emotion
- Adjectives of Opinion
- Adjectives of Quantity
- Adjective Opposites
- Adjective Order
- Adjective-Preposition Collocations
- -ed and -ing Adjectives
- Adverb-Adjective Collocations
- Adverb Order
- Adverbs of Affirmation & Negation
- Adverbs of Degree
- Adverbs of Frequency
- Adverbs of Manner
- Adverbs of Place
- Adverbs of Time
- Articles - a, an, the
- Causative Verbs
- Collective Nouns
- Common & Proper Nouns
- Compound Adjectives
- Compound Nouns
- Concrete Nouns
- Conjunctions
- Countable & Uncountable Nouns
- Demonstrative Adjectives
- Demonstrative Pronouns
- Dependent Prepositions
- Indefinite Pronouns
- Intensifiers & Mitigators
- Interjections
- Modal Verbs of Ability
- Modals of Deduction & Speculation
- Modals of Necessity
- Modals of Obligation & Prohibition
- Modals of Possibility & Certainty
- Onomatopoeia
- Parts of Speech
- Phrasal Verbs
- Possessives
- Prepositions of Movement
- Prepositions of Place
- Prepositions of Time
- Proper Adjectives
- Quantifiers
- Reflexive Pronouns
- Sense Verbs and Adjectives
- Singular & Plural Nouns
- So and Such
- Subject & Object Pronouns
- Too and Enough
- Transition Words
- Verb-Noun Collocations
- Agreeing & Disagreeing
- Asking Permission
- At the Dentist's
- At the Doctor's
- Being Polite
- Classroom Language
- Complaining & Apologizing
- Complimenting
- Critical Thinking & Problem Solving
- Describing Character & Personality
- Describing People's Appearance
- Describing Places
- Describing Things
- Etiquette and Manners
- Getting Around
- Getting to Know You
- Giving Advice
- Giving Directions
- Giving Opinions
- Giving Personal Information
- Greetings & Introductions
- Indirect Questions
- Likes and Dislikes
- Making Arrangements
- Making Decisions
- Making Excuses
- Making Invitations
- Making Offers & Promises
- Making Requests
- Making Suggestions
- Online Communication
- Ordering Food & Drink
- Social Media
- Telephoning
- Times and Dates
- British English vs. American English
- Cities, Towns & Places
- Clothes & Fashion
- Computers & Smartphones
- Countries & Nationalities
- Crime, Law & Punishment
- Cultural Celebrations
- Daily Routines
- Everyday Objects
- Family & Relationships
- Food & Drink
- Going Out & Entertainment
- Health & Fitness
- Hobbies & Free Time
- Houses, Rooms & Furniture
- Jobs & the Workplace
- Love, Romance & Dating
- Modes of Transport
- Parts of the Body
- Reading Comprehension
- Shapes & Measurements
- The Natural World
- Time Expressions
- TV & Film
- Valentine's Day
- Academic Collocations
- Academic Phrasal Verbs
- Academic Reading Comprehension
- AWL Sublist 1 & 2
- Cause and Effect Essays
- Compare and Contrast Essays
- Discussion Essays
- Discussion Skills
- Discussions Practice
- Essay Writing
- Paragraph Writing
- Persuasive Essays
- Presentation Skills
- Problem Solution Essays
- Punctuation
- Reading Skills
- Referenced Essays
- Study Skills
- The Writing Process
- Business Collocations
- Business Emails
- Business Idioms
- Business Meetings
- Business Negotiations
- Business Phrasal Verbs
- Closing a Presentation
- Describing Graphs & Charts
- Presentation Language & Structure
- Resumes, CVs & Email Cover Letters
- Starting a Presentation
- Talking about Companies
- Talking About Jobs
- Answer Games
- Brainstorming Games
- Category Games
- Classic Childhood Games
- Counting Games
- Describing Games
- Drawing Games
- Drilling Activity Games
- First Day of Class Games
- Flashcard Games
- Grammar Games
- Hangman Games
- Listening Games
- Miming Games
- Music Games
- Question & Answer Games
- Sentence Race Games
- Spelling Games
- TV Game Shows
- Vocabulary Games
- Word Association Games
- Yes/No Question Games
- Classroom Interaction Patterns
- Classroom Management
- Concept Checking
- Cultural Awareness
- Developing Students' Listening Skills
- Developing Students' Reading Skills
- Developing Students' Speaking Skills
- Eliciting Techniques
- ESL Dictations
- How to Introduce a Lesson
- How to Use Music in ESL Class
- Lesson Planning
- Making Teaching Materials Relevant
- Problems Learning English
- Teaching English Idioms
- Teaching English Vocabulary
- Teaching Large Classes
- Teaching Mixed-Ability Classes
- Teaching Small Classes
- The First Day of Class
- Using Correction in Class
- Using Song Gap Fills
- Online Membership
- ESL Essentials eBook Series
Presentation Skills EAP Worksheets and Activities
- Intermediate ( B1 )
- Upper-intermediate ( B2 )

4-3-2 Presentation Fluency
Eap presentation fluency practice - speaking activity: giving a short presentation, freer practice, fluency practice - pair work - intermediate (b1) - 30 minutes.

Presentation Language
Eap presentation language worksheet - reading and writing exercises: unscrambling, writing phrases - speaking activity - preparing and delivering a presentation - pair work - intermediate (b1) - 40 minutes.

Present with Style
Eap academic presentation skills worksheet - reading and writing exercises: matching, categorising, ranking, identifying, rewriting sentences - intermediate (b1) - 45 minutes.

Impromptu Speech Practice
Eap presentation skills worksheet - reading and writing exercises: identifying, matching, brainstorming, creating an outline - speaking activity: presenting - group work - upper-intermediate (b2) - 45 minutes.

Presentation Preparation and Practice
Eap academic presentation skills worksheet - reading and writing: ordering, matching, identifying, gap-fill - speaking: delivering a presentation - group work - upper-intermediate (b2) - 60 minutes.

Sign up for our monthly newsletter and keep up-to-date with our latest resources, news and website features.
You have successfully joined our subscriber list.
Latest Free Resources
Upper-intermediate (B2)
Elementary (A1-A2)
Latest Member Resources
Talking about companies, here's what our members are saying....
There are a lot of resources that are useful for teaching English. I downloaded the games which are handy and use them in my classes. With the games, my students never skip class or feel tired to learn English. The resources for teaching English helped my students progress in grammar, vocabulary, writing and comprehension. They also helped me a lot to guide my students to learn in a practical way.
I am an ESOL teacher, and the resources have helped my classes enormously. In particular, the speaking activities were a great help for my intermediate students before their exam. The website is user-friendly, and I will continue to utilise the resources - next term is reading and comprehension, so I will be looking for more resources from you. Thank you for such helpful activities and worksheets. They save me a lot of time in class preparation.
Teach This is an absolutely brilliant website, offering a vast amount of high-quality content, much of it free. Everyone involved in its creation deserves commendation. The leadership's vision has my deepest respect and gratitude. It's undoubtedly the best resource for English teachers, with its clear layout, easy navigation, concise messaging, and lack of invasive advertising - rare qualities that Teach This has perfected.
When I need to add or change an activity from my school’s curriculum, I always turn to TeachThis. While our curriculum is usually very good, it sometimes doesn’t fit well with my students. With TeachThis, I can easily find activities that match my topic and level, and the resources make my classes more interesting and varied. I look forward to the monthly newsletter and exploring new materials for inspiration. Please keep it up!
I like the efficiency and organization of the website. The resources cater to various levels with topic-based options for higher levels. The worksheets are very engaging and the answer keys are particularly helpful for teacher. The resources are also highly specific to levels and outcomes, making planning much easier. Finding what I need is simple and time-saving with the keyword search feature. Everything is clear and straightforward.
The easy and ready-to-go materials have helped me a lot during the last few years. Most of all I like the grammar games that activate my pupils and keep them engaged. My lessons have become way more playful and varied. Additionally, I like the grammar worksheets which I use to consolidate what I have worked on during class. The website is very user-friendly, and I have never had any difficulties finding what I was looking for.
A friend told me about the site, and it's awesome. I have found the Business English resources especially engaging and relevant for my students as the materials help them understand business writing and terms. My teaching experience has also improved from using the games on the site as they allow me to teach in a fun way. The user experience is outstanding. Great job!
I found Teach-This a long time ago when I started teaching. It's always had great resources. I really appreciate the grammar materials, board games, and group activities. They've saved me lots of time on lesson planning. The materials are easy to use and understand, making my job much simpler. The best thing is that many resources can be downloaded for free. I've used it for around 8 years, and it consistently offers great content.
I use the resources from the Games Section as part of my daily 30-minute morning warm-up activities, and I've received rave reviews for using them. The games help me maintain student interest and participation and leave the students feeling happy and awake. I like everything about the site, and customer support is very effective as they respond in time.
Teach-This is one of the best EFL websites I've found. It's extremely user-friendly, and I always find what I need quickly. I like the design, and the content is fun, engaging and original. I am very thankful for all your work and generosity by making some resources free. I always recommend this website to my fellow teachers. Your work is really helpful, and I value it enormously.
I like the grammar-focused resources the most as they save me time. The resources also inspire me. If I see an interesting grammar activity, I often rework it for other grammar rules. I like the fact that I simply pay a flat fee, and I can download whatever I want. Teach-This really is a great timesaver. I know that if I am in need of resources for my students, I can go to Teach-This and find something interesting.
Getting familiar with the site and how to use the resources is not difficult. I found the writing skills resources to be the most valuable as they have enhanced my teaching of this skill. The website is elaborate and full of all types of resources to help me teach English. When I contacted customer support, they were super-fast to deal with my enquiry. So overall, I recommend it.
I have found the grammar and vocabulary resources the most valuable. They have improved my teaching experience because they are easy to use and well-organized. The materials are very engaging for my students. The website is also very user-friendly. The best thing about Teach-This is that it offers ready-made worksheets for busy teachers, and the content is well-organized and full of information.
I'm really glad I found the Teach-This website. The materials in the General English section have proven to be really helpful and made my classes more engaging. The materials are well-structured and cover a wide range of topics, making it easy to keep my students interested and motivated. Overall, my experience using your resources has been great.
My first impression of the website was that it was amazing. The games and activities have really improved my teaching. The resources are engaging and relevant to my students’ needs, and I find the website easy to use and navigate. Thanks.
I discovered the site on Google when I was searching for question games and reading activities. It has been very helpful. The activities are awesome and have benefited me and my students by making my classes more fun. I am now less stressed about preparing for classes as the ready-made resources offer me everything I need. I give the site five out of five for user-friendliness. It is very easy to navigate and find what I need.
I would like to thank you for making a fantastic website. I particularly enjoy teaching the functional language materials, which have been very helpful in my classes. The resources have significantly improved my students' communication skills in daily life, so it was rewarding to see them benefit in this way. It feels great to be able to make a difference in my students' lives. Please keep up the good work.
- Have got & Has got
- Adverbs of Affirmation and Negation
- Concrete nouns
- Sense Verbs & Adjectives
- AWL Sublist 1 and 2
- Talking about Jobs
- TEFL Certification & Courses
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
Blog > English Presentation Structure (Introduction, Closing) & useful Phrases
English Presentation Structure (Introduction, Closing) & useful Phrases
02.21.20 • #powerpoint #presentation #english.
When giving a presentation in english, there are certain guidelines you should follow. Maybe you haven't got a lot of experience presenting - or you would simply like to refresh your already existing knowledge - we're here to teach you the basics about presenting and provide you with a free list of useful phrases and the basic structure you can in your presentation!
1. Structure
The general structure of a presentation is the following:
- Introduction
It is up to you to design these three parts. Using videos or everyday-examples can be a great way to introduce the audience to the topic. The important thing is that you capture the audience's attention from the beginning by making an interesting introduction. The main part is where you present your topic, ideally divided into sections. You can be creative with it - incorporate images, videos, stories or interactive polls . We generally recommend using different kinds of elements, as that makes the presentation more lively. Make sure your main part is well structured, so your audience can follow. In the conclusion, you should give a short summary of the points you made without adding any new information. You can also make an appeal to your audience in the end.
2. Useful Phrases
Here you'll find several phrases that you'll need in every presentation. Of course, you should adapt them and use them in a context that is suitable for your setting. The phrases are divided into subcategories so you can find what you're looking for more easily.

Starting your Presentation
In your introduction, you should:
Welcome your audience
Good morning/afternoon/evening everyone!
Ladies and gentlemen, I welcome you to my presentation about...
Introduce yourself
I am ... (from company ...) and today I would like to introduce you to the topic of ...
My name is ... and I am going to talk about ... today.
Icebreakers (for audience engagement)
Icebreaker polls are an amazing way to engage your audience instantly. They function as a fun and playful element at the beginning, giving you the perfect start you need to give a successful presentation. Click here to read our detailed post about icebreaker polls!
Mention the presentation topic and the reason for giving the presentation
I am grateful to be here today and tell you you about...
I would like to take this opportunity to talk about ...
I am here today to talk to you about ...
The reason why I am here today to talk about ... is ...
The purpose of this presentation is to ...
My goal today is to ...
Hopefully, by the end of the presentation, you will all know more about ...
Give a short overview of the content
To make it as understandable as possible, I divided my presentation into ... parts. In the first part, I will concentrate on ..., the second part will be about ..., ...
First of all, I will give you a short introduction, then we will move on to ...
... and finally, I will give you some insights to ...

Here are a few phrases that you could use during the whole presentation, but especially in the main part.
Engage your audience
In order to raise the audience's attention and improve their engagement, it is extremely important to make contact with them. A great way to do so is by adding interactive elements such as polls. If you would like to know more about this topic, read our article on How To Boost Audience Engagement . You can also use a software like SlideLizard , which allows you to conduct live polls, do Q&A sessions with your audience, share your resources and many more benefits that take your presentation to the next level.
Please raise your hand if you ...
Have you ever thought about ... ?
I would like to do a poll about ...
Please ask any questions as soon as they arrive.
On one hand, … on the other hand…
Comparing … with …, we can see that…
Clearly, … makes more sense than …
Whereas Option A is …, Option B is …
Making new points
Firstly,… Secondly,…
What also has to be mentioned is…
Next, I would like to bring up the topic of…
That being said, now we are going to take a look at…
Let's move on to the next topic.
On the next slide,…
The last thing I would like to mention is…

We made a whole blog post about how to pose questions in your presentation: The Right Way to do a Question Slide .
Talking about images or videos
In this image you can clearly see that ...
We are now going to take a look at a picture/video of ...
I'm going to show you a video by ... about ... now.
I've prepared a video about ...
Talking about statistics and charts
I am now addressing this graph that refers to the results of study XY.
In the graph on this slide, you can see that ...
The average is at ...
This graph clearly shows that the majority ...
According to this graph, the focus should be on ...
What that study tells us for practice is that we should ...
Emphasizing
I would like to emphasize the importance of ...
Moreover, it has to be said that ...
I want to stress the importance of ...
We always have to remember that ...
This is of high significance because ...
That part is especially important because ...
When something goes wrong
I am sorry, but it seems like the projector isn't working.
Could someone please help me with ...?
Is anybody here who knows how to ...?
Could someone give me a hand with ...
I would like to apologize for ...
I apologize for the technical problems, we are going to continue in a minute.
I am sorry for the inconvenience.
End of Presentation
In the conclusion, you should...
Sum up the main points
In conclusion I can say that…
To sum up the main points,…
With all mentioned aspects taken into consideration, I can say that…
Make an appeal
So please, in the future, try to be conscious about...
Please take a moment to think about...
I would like to encourage you to...
Thank your audience and say goodbye
It was a pleasure being here today.
Thank you for listening and goodbye.
Thank you for being such a great, engaged audience. Goodbye.
Thank you so much for listening, see you next time.
What is the structure of a presentation?
Your presentations should always have an Introduction, a Main part and a Conclusion.
What is a good way to begin a presentation?
You can start by introducing yourself, giving an overview of your topic, telling a little story or showing the audience an introductory video or image.
What are good phrases to use in English presentations?
There are many phrases that will make your presentation a lot more professional. Our blog post gives you a detailed overview.
Related articles
About the author.

Pia Lehner-Mittermaier
Pia works in Marketing as a graphic designer and writer at SlideLizard. She uses her vivid imagination and creativity to produce good content.
Get 1 Month for free!
Do you want to make your presentations more interactive.
With SlideLizard you can engage your audience with live polls, questions and feedback . Directly within your PowerPoint Presentation. Learn more

Top blog articles More posts

Elegant Architecture - Free PowerPoint Template

How to add a Countdown Timer in PowerPoint
Get started with Live Polls, Q&A and slides
for your PowerPoint Presentations
The big SlideLizard presentation glossary
Hybrid event.
When an event consist of both virtual and in-person parts, this is called a hybrid event. This type of event is popular as it combines the benefits of both online and live events.
Break-out-Room
In live online training, it is sometimes useful to divide the students into small groups for certain exercises, as it would be impossible to have conversations at the same time. Break-out-rooms are used so that people can talk to each other without disturbing the others. When the exercise is over, they are sent back to the main room.
Audience Demographics
Audience Demographics are the characteristics of listeners like age, gender, cultural backgrounds, group affiliations and educational level. The speaker has to consider all these characteristics when adapting to an audience.
Informative Presentations
An information presentation is created when no solution is currently available. Facts, data and figures or study results are presented and current processes are described.
Be the first to know!
The latest SlideLizard news, articles, and resources, sent straight to your inbox.
- or follow us on -
We use cookies to personalize content and analyze traffic to our website. You can choose to accept only cookies that are necessary for the website to function or to also allow tracking cookies. For more information, please see our privacy policy .
Cookie Settings
Necessary cookies are required for the proper functioning of the website. These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website.
Analytical cookies are used to understand how visitors interact with the website. These cookies help provide information about the number of visitors, etc.
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Terms and Conditions
- British Council Global
- Accessibility
© 2024 British Council
- Mini English Lessons
- Business English
How to Ace Your Business Presentation in English
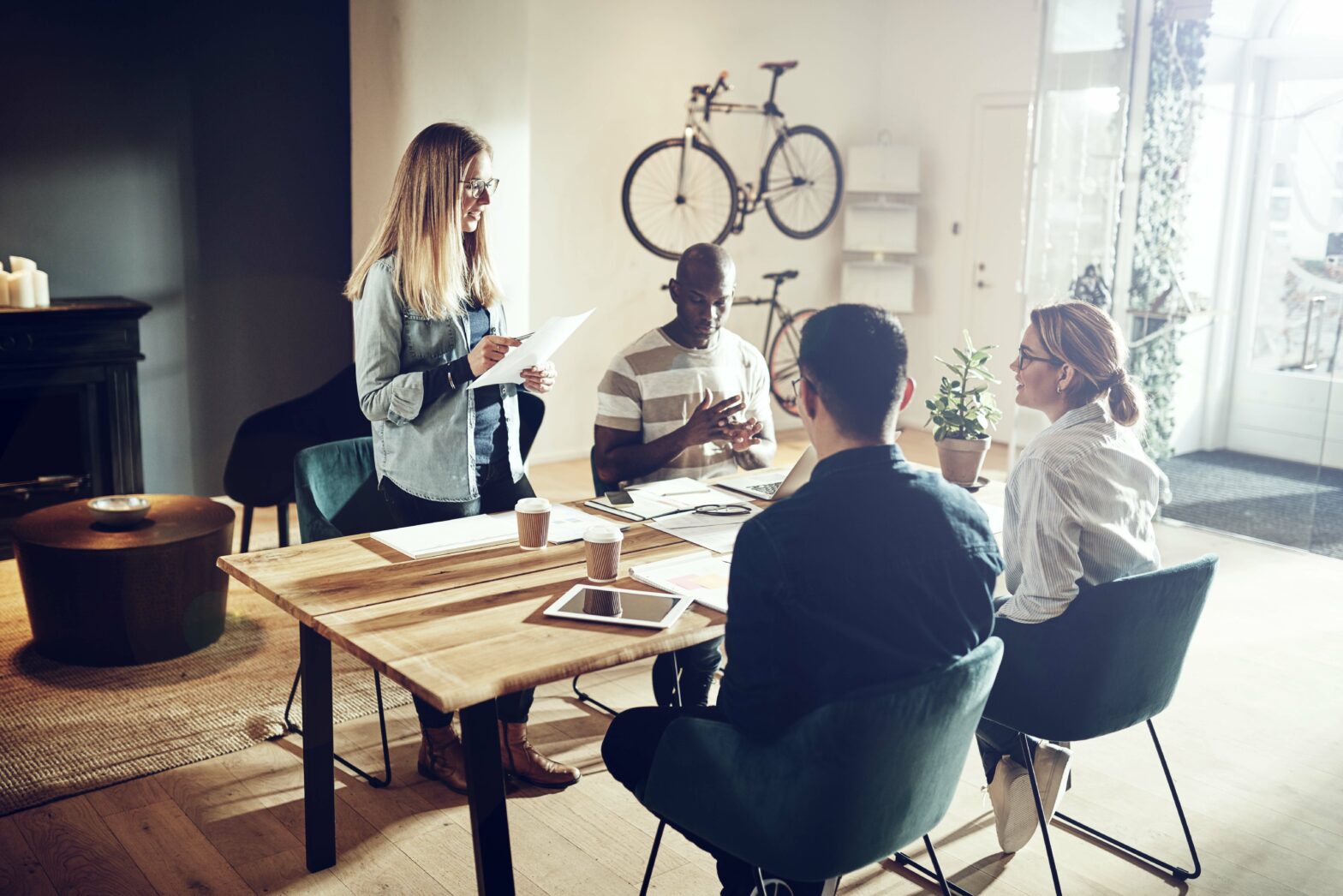

So, you need to make a business presentation in English.
First of all, congratulations! To be in your position, you must have invested a huge amount of time and effort in your English language skills. You should be proud.
That said, we totally understand that giving a presentation in a second language can be a challenge. You may be worried that your audience won’t understand your accent. Perhaps you are wondering whether you need to use specific vocabulary. Maybe you’re not sure how best to handle questions from your audience.
If this sounds like you, don’t worry. In this post, we’re going to run through our top tips for acing your business presentation in English. Even if you’ve already made a few presentations in the language, we’re sure you’ll find these suggestions helpful.
So, read on to learn more. And before we start, let us wish you the very best of luck in delivering your next presentation.
Understand your audience
As with all forms of communication, it’s vital that you understand who your audience is. Even in the business world, you can find yourself speaking to very different groups of people.
For example, if you are giving a presentation to members of another company, you would certainly be more formal than when you give a presentation to members of your own team. In each case, you need to think about what your audience will expect from your presentation.
So, before you write a word, ask yourself these questions about your audience. Who are they? What interests them? What do they need to know? What do you want them to do as a result of your presentation?
One useful tip for writing your presentation is to imagine your audience is a single person. It’s easier to write convincingly if you have a single person in mind. Try it!

Mind your language
Most audiences will expect you to give your presentation using formal Business English . Don’t make the mistake of confusing Business English with business jargon .
Successful Business English uses language that is simple, direct, professional and easy to understand. Business jargon on the other hand, relies on obscure phrases, clichés, and acronyms. In many cases, business jargon is complex, not very precise and a barrier to good communication .
We have some useful resources on Business English on this page . However, if in doubt, keep the language of your presentation as simple and clear as possible. It’s also a good idea to use sentences with the active, rather than the passive voice. This allows you to use fewer words, which makes your sentences shorter and more engaging.
To give an example, this is a sentence in the passive voice:
The interview was failed by over one third of applicants.
Now compare this sentence, which is in the active voice.
Over one-third of applicants failed the interview.
To learn more about the active and the passive voice, check out this explainer from the British Council.
Practise, practise, practise
If English isn’t your first language, it’s more important than ever to practise your presentation before delivering it. By practising, you’ll feel more comfortable using English in a business setting. You’ll be able to work on any words or phrases you find difficult to pronounce, or you can change them to words or phrases you are more comfortable with.
Ideally, you should practise giving your presentation in front of someone else. That way you can get useful feedback on what works well, and what doesn’t. If that’s not possible, make a video of yourself giving your presentation. When you see yourself on screen, it will give you helpful insights into ways you can improve your delivery.
Don’t forget to introduce yourself
It may sound obvious, but don’t forget to introduce yourself at the very beginning of your presentation. It not only breaks the ice , but it’s an opportunity to get the audience on your side. If you are presenting to native English speakers, you may wish to tell them that English is not your first language – but don’t apologise for it! If anything, your audience will be impressed that you can give a presentation in a second language.
Have a clear structure
When people learn to teach in the UK, they are often told to structure their lessons in this simple way:
- Say what you’re going to say
- Say what you’ve said
In other words, introduce the session by explaining what you intend to talk about. This sets the audience’s expectations – they know what’s going to happen.
You then use main part of the session to make your presentation. There are many effective ways of doing this, and we’ll cover some of these soon.
Finally, finish by summarising the most important points of your presentation. This helps your audience to remember them clearly.
One other tip, if you plan to let the audience ask questions, it’s a good idea to tell them you’d prefer to answer them at the end of the presentation. This will discourage them from interrupting your presentation at the wrong moment.
Use storytelling
People love stories. If you can capture your audience’s imagination with a story, you can make a very powerful impression.
For example, imagine you are giving a presentation about how to commission new advertisements for your company. You want to make the point that good copywriting as just as important as good visual design.
You can either make your point directly, like this:
“Successful adverts rely on good writing as well as good design. If you change the wording of an advert, it can often result in extra sales – or fewer. Therefore, the words we choose are as important as the images we use.”.
Or you could begin with a story, like this:
“I want you to imagine it’s the year 1907. A man called Louis Victor Eytinge is in prison, convicted of murder. He’s a drug addict, suffering from tuberculosis. He’s unlikely to live, never mind get out of jail. Yet, by 1923 he walked free into a well-paid advertising job and a career as a Hollywood screenwriter. How? He had written his way to freedom. I want to use his story to show you why, if we want successful adverts, we need to commission powerful writing as well as good design.”
Which version of the presentation would you rather listen to?!
Remember pace and pitch
One useful tip for acing your business presentations in English is to vary the pace and pitch of your delivery.
While you don’t want to speak too fast, it’s a good idea to use a different pace for different parts of your presentation. For example, when you want to communicate a key point, speaking more slowly will help people understand that you think it is important.
Equally, it’s a good idea to vary the pitch of your voice. Try and keep this as natural as possible, but experiment with using a higher pitch when asking questions and a lower pitch when beginning your sentences. One good way to learn how to vary your pitch is to listen to UK news broadcasts – news presenters are expert at varying the tone of their voice to keep listeners interested.
Add a call to action
Most business presentations are given for a specific purpose. You may want to convince another company to work with you. Or you may want to convince your own firm to invest in a new kind of product. You may simply be explaining to colleagues how a new training scheme will work.
Whatever the purpose of your presentation, always remember to tell your audience what you want them to do. This is a ‘call to action’. Do you want your audience to email you their ideas? Or send you a funding proposal? Or arrange a meeting?
No matter what you need your audience to do, don’t forget to tell them. And at the very end, be sure to thank them for their time!
More business presentation tips
There are many other tips we could share with you on how to ace a business presentation in English. For example, it’s never a good idea to read your presentation from a piece of paper – it’s not engaging and it means you can’t easily make eye contact. It’s also tempting to rely too heavily on visual aids like PowerPoint, but if you get it wrong your audience will read your slides instead of listening to you. On the other hand, it can really engage an audience if you ask them to work together in small groups to share ideas or solve problems.
However you choose to make your presentation, if you prepare well, speak clearly and work hard to connect with your audience, you are very likely to succeed. And if you’d like to improve your presentation skills even further, why not try live online classes with English Online ? They can help you succeed in any career where using English is essential.
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Related Posts

Employability Skills: How to Ace Competency-Based Interview Questions
Learn how to navigate competency-based interview questions confidently and effectively with this helpful guide to using the STAR method. Advertisement Advertisement What are competency-based […]

- Social English
Your Ultimate Guide to Adapting Communication Styles to Different Situations
Ever found yourself wondering why a well-intended message didn’t land as expected? Or perhaps you’ve been on the receiving end of conversations that just […]

From Conflict to Collaboration: How to Manage Difficult Conversations at Work
Addressing challenging discussions at work is rarely enjoyable, but it’s something we all encounter sooner or later. These conversations have a big impact on […]
Get Exclusive access to offers and promotions
Enter your email address below to join the english online mailing list..
Personal details will be held by the British Council and will only be used in relation to your request. Please read our terms of use for more information.

Mini-Presentation Prompts
€ 2.60
Access all our ESL Resources

This Mini-Presentation Task features eight topics, including prompts to help your ESL students prepare for the task. The students do each presentation with a different student, ensuring they get lots of speaking practice. There is also an optional vocabulary brainstorming task to help the students prepare.
Topics include my hometown, my best friend, sports and hobbies I like, and more.
We have a teacher’s copy (including teacher’s notes) and a student version, which you can email to your class for online lessons.
Level: This is most suited to A 1/A2- level students.
For best results when printing our PDFs, open and print them through Adobe Acrobat. https://get.adobe.com/reader /
Hundreds of ESL lesson plans, worksheets, and activities for adult and teen lessons!
You may also like….
‘All about You’ Questions

Mini-Presentation Activity

Conversation Questions (A1)

Conversation Questions (A2)
Related products.

Talk for a Minute: ‘How to’ Topics

Present Simple vs. Continuous: Exercise

Talking about Football

Summertime Bundle

Talk for a Minute: School & Study
BACK-TO-SCHOOL SALE! 30% OFF A 12-MONTH MEMBERSHIP: €27.95 x
BACK TO SCHOOL SALE!
Access our full library of esl resources, 12-month membership, already a member, buy now and extend your membership.
© TEFL Lessons
My English Language
English language resources for efl students and teachers.

PPP Technique in TEFL
Presentation, practice and production.
The PPP technique in teaching is a common way to introduce students to new words and concepts. This can be especially useful in the EFL classroom. The PPP method in English teaching is a three-step lesson plan and teaching approach that helps the student learn, understand and practice new vocabulary.
The three stages of a PPP lesson
There are three stages in a PPP TEFL lesson.
Firstly, the teacher presents the new word, an event which involves the presentation of pronunciation and spelling in context.
Next, the teacher allows the students to practice the new word in a controlled setting, making sure the student has understood the vocabulary and usage properly.
Lastly comes the production stage, where there is a period of less-controlled practice and an informal assessment of learning. This is where the students get chance to use the new word or phrase in an original way and to relate it to their knowledge and experiences.
These three stages of a PPP lesson help the student to consolidate the new word in their mental vocabulary bank.
The sequence of a PPP lesson in EFL teaching
This EFL teaching method of presentation, practice and production is an approach that follows a definite sequence:
- The teacher presents the new vocabulary and explains the form of the language in a meaningful context.
- The students practise this new vocabulary through controlled activities such as worksheets or question and answer activities to check comprehension.
- The students use or produce what they have learned in a communicative activity such as a role-play, communication game, or question and answer session.
Teaching English using the PPP technique
Each stage of the Presentation, Practice and Production lesson must be planned well to be effective. However, the PPP method in TEFL is a highly flexible approach to teaching and there are many different activities a teacher can employ for each stage.
Presentation can include mime, drawing and audio. In fact, it is a good idea to try to engage with the students’ different senses to get across the meaning of the new word, using visual, kinaesthetic (movement) and audio techniques.
It is also important to make sure that students have understood the new word before encouraging them to practise it. It is often fun and highly effective for students to play games to practise vocabulary and to produce it.
Current debate about the PPP technique in TEFL
In recent times, there has been increasing debate surrounding the PPP method of teaching, with many critics asking if teachers should be using the PPP technique so often in the EFL classroom.
Some critics of the PPP method in TEFL think it can be too formal and structured, with too little focus on student interaction. However, we think the PPP technique in EFL teaching offers a very flexible base from which to construct a lesson that is highly student-centred.
For ideas on ways to present new vocabulary and check comprehension , and activities which allow students to practice and produce their vocabulary , please browse this PPP teaching section.
- Is the PPP method old fashioned or is it still a useful and effective way to teach?
- Do you use the PPP technique in TEFL?
- What is your favourite way to present new vocabulary?
Let us know your thoughts in the comments box below.
9 thoughts on “ PPP Technique in TEFL ”
may I know who is the actual founder of PPP technique?
Sorry Sifa, we don’t know who originally developed the PPP technique. Can any readers help?
Yes, it was Jeremy Harmer. 😉
Thanks for this information, Miri! If any readers want to check out Jeremy Harmer’s explorations of the PPP technique, you can read more in his book: ‘How to Teach English’, published by Longman.
Catherine may you please help me with the same book by Jeremy Harmer, on soft copy I will highly appreciate it.
Hi Grace, Jeremy Harmer’s book can be found online to read or download at academia.edu.
It PPP useful and used in teaching reading?
Hi Muharram, thanks for your question. Yes the PPP method can be used to teach all areas of language, including reading.
In this type of lesson, any new target words would be presented in the early part of the class (pre-reading) before the student meets the vocabulary within a longer written text. While reading the text during the ‘practice’ stage, students should be able to identify the individual ideas expressed and understand how the new words are used in context.
After reading, students can analyse the material and discuss the text, hold a questions/answer session or write about it in the production stage. This helps them deepen their understanding and test their reading comprehension. I hope this gives you a few ideas – I’ll be adding more details about using the PPP method to teach reading and writing soon.
Can somebody help me with these questions of Unit 3 i-to-i (180 hour units) please:
Match the description to the stages to make a complete PPP lesson. The aim of the lesson is expressing past habits with ‘used to’ + infinitive. For example, When I was younger, I used to watch cartoons.
The teacher repeats the model sentence with natural linking, stress and intonation. The class repeats.
1)Teacher asks, “Did he play football in the past?” (Yes) “Does he play football now?” (No).
2)Teacher says ‘used to’ + infinitive can be used to talk about things we regularly did in the past, but don’t do now.
3)The students answer conversation questions about their childhood to introduce them to the topic.
4)The teacher asks some individuals how many people share their thoughts on living in London and corrects some errors if they are made.
5)The learners use the target language to talk about how their lives are different now they live in London and compare their country’s cultures to the UK.
6)The teacher writes the model sentence on the board. When I was younger, he used to play football. Draws a box round ‘used to’ and writes ‘infinitive’ over play.
7)Learners choose an activity they enjoyed as children then walk round the class asking if other people used to do the same thing. For example, Did you use to watch cartoons?
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- How to Teach
Presentation Ideas for ESL Students
- By Hall Houston
Imagine a student standing in front of the class delivering a presentation. The student looks out and sees students playing on their smart phones, chatting, giggling, even one student sleeping. How might this affect the student’s ability to give a presentation?
I always enjoy watching student presentations, seeing students demonstrating their increasing fluency in English, as well as practicing their presentation skills. I teach at a university in Taiwan , and I think most students enjoy the opportunity to develop their English and presentation skills simultaneously. Their English level takes a big step forward as they rehearse and deliver their presentation. Also, mastering the art of giving a presentation is something that will benefit them later on in their academic and professional careers.
However, I’m disappointed to see students chatting and looking at their phones instead of rewarding their classmates with their full attention. While one might think that this is exclusively a problem associated with younger students, I have seen adult students who cannot quiet down and focus on another students’ presentation.
Over the years, I’ve developed a number of solutions to this problem. I want to share with you some ways to maximize student’s attention during group presentations. If student inattention is a common occurrence in your teaching context, perhaps you might consider one or more of these options:
1) Address the subject
During a lesson, point out that it’s very rude for an audience member not to give their complete attention when someone is giving a presentation. Work together with your students to create a list of good and bad audience behavior on the board. You can show them the list of good audience behavior again, right before presentations start.
2) Demonstrate rude behavior
Bring a student to the front of the class for a role play . Ask the student to tell you a story about their childhood. As they speak to you, yawn, look around, play on your smart phone, sigh, give every sign that you don’t really care. When the student finishes, ask the speaker how he felt about your behavior. Ask the class if you were being a good listener. Next, repeat the role play, but choose a student to take your place and ask this student to demonstrate good listener behavior.
3) Teach the presenters
Teach your students techniques that increase student involvement that they can put to use during their presentations. One powerful technique is interacting directly with the audience by moving around, speaking directly to audience members, and asking questions. Another technique is to start off with an intriguing question or short quiz, leaving everyone eager to hear the answers. These techniques could be taught to the students several weeks before they present. You can give a short presentation to demonstrate a technique, then choose a student to model the technique for the class.
4) Carrots and sticks
Consider giving rewards or punishments to students based on how much they pay attention. You can offer a small prize to the student who is the most focused when others are presenting or tell students you will deduct points for students who don’t pay attention.
5) Move the students around
Before presentations begin, make sure that the first few rows of seats are completely full. Also, put students into pairs to break up groups that can’t help chatting away when they’re together.
6) Active participation
Assign a task that heightens involvement in the presentation. You can give the audience a rubric to follow each time a group presents. Students watch and listen, then assess each group. Alternatively, you can insist that everyone ask a question at the end of each presentation, thus encouraging everyone to pay strict attention.
When groups are presenting, scan the class from time to time. If you see students who are not paying attention, make eye contact and gesture for them to watch the presentation . However, overuse of this technique can result in spending too much time disciplining and ultimately missing out on the presentations.
While these techniques might not completely eliminate student inattention, they will definitely make students more aware of the relationship between audience and presenters, and help them improve at both roles.
What are your thoughts? What presentation ideas for ESL students can you offer ?
Related Topics
- Presentations
Hall Houston
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Related Articles

Learning Language Online: Reflections And Reviews

The Growth Mindset and Language Learning

Teach Future Simple and The 5 Ps

Teaching English for Job Hunting
Privacy overview.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Join Our Newsletter

Business English Lesson plan- Giving a Presentation (ESA Framework)

Type of Lesson: Integrated skills (Listening integrated to speaking, pronunciation and vocabulary using authentic material. Theme: giving presentations)
Aims: To identify the characteristics of a good and bad presentation To introduce vocabulary related to presentations To review sentence stress and intonation patterns for effective presentations.
Outcome: By the end of the lesson, students will be able to give a sales presentation about their companies’ new product.
Read: 5 Great Activities to Use with Your Business English Students!
Read: How to Conduct a Needs Analysis for Your Business English Class
Assumptions: Students have a wide range of vocabulary related to the business field. They are able to articulate full sentences using complex and compound sentences. They are aware of how important intonation is when delivering a message. They are able to differentiate intonation patterns. They will already know many adjectives that are used to describe the product they sell at their company, as they will have used them in their own language while performing sales pitches. They have prior experience in giving presentations in their own language and have given presentations in previous ESL classes. They are familiar with the structure of a presentation: introduction, overview, state points, state results and conclusions, summarize, and close.
– Save $100 with the TESOL Diploma and Teaching Business English Specialist Package! –
Students background information: Students are to give a sales presentation about their companies’ new product at a business conference. They are well established sales people in Japan and this will be their first time presenting their product in an overseas environment.
Anticipated Problems and Solutions: Students may not be able to recall some ‘great speakers’. In this case, the teacher will suggest people such as Martin Luther King Jr., Steve Jobs, etc. They may have difficulty using proper intonation in certain phrases; this will be solved by demonstration and drilling. They may also have problems with some pronunciation in the intonation exercise. The teacher will be around to assist students with their individual needs.
Aids/Materials: YouTube video “Enhancing Your Presentation Skills”; a vocabulary presentation worksheet; stress and intonation worksheet; Steve Jobs iphone 2007 presentation YouTube Time: approx. 150 minutes
ENGAGE – Business English Lesson Plan
– Learn to create Business English lesson plans online! –
Aim: to introduce the topic of giving presentations and to outline skills and characteristics that lead to a good presentation. Techniques used: questionnaire; discussion; brainstorming Skills: speaking and listening Interactive Pattern: SS Time: 10 minutes
Aids/Materials: handouts with questions/board
Put students into pairs and have them discuss the following questions:
1. What are the characteristics of a great speech/presentation? 2. Who are the greatest speakers that you can think of? 3. Who do you need to give presentations to as a part of your job? What are they about?
Once students have finished discussing in pairs, have an entire class feedback and have students brainstorm the characteristics of a great speech are. (Examples of ideas that will be elicited: eye contact, clear voice, positive body language, etc.).
STUDY – Business English Lesson Plan
20-hour Teaching Business English Course Only $199!
Step 1: introduce words and phrases related to giving presentations Techniques: Gap-filling Skills: Reading and speaking Interactive Patterns: T-S; SS Time: 5-10 minutes
Aids/Materials: Vocabulary: Presentation Language worksheet.
Students will be given a ‘Vocabulary: Presentation Language’ worksheet that uses words and phrases suitable for presentations. They are to work in pairs in order to fill in the blanks of the passage. After students have completed this activity, the teacher will take it up as a whole class and discuss any vocabulary words they were unsure of.
Vocabulary: Presentation Language
Complete the following presentation excerpts using the words below.
after that finally illustrate outline to start with then describe specifically purpose sum up thank tell you
Good morning, everybody. I hope you are all doing well today and I’d like to _______ you all for being here. Today I am here to __________ about our latest product, and more _________ about how it works and what it does. I’d also like to __________ the products’ features and __________ inform you about where you can get it and how. ____________, I’d like to briefly __________ our current marketing policy in Canada. ________, I’ll __________ some of the problems we have encountered in our market share. ___________, I’ll ________ our progress this year and continue on with our main _______ for being here; the product.
Answer Key: thank, tell you, specifically, illustrate, finally, to start with, describe, then, outline, after that, sum up, purpose
Step 2: To identify how important intonation is in delivering a sound presentation Techniques: Elicitation Skills: Listening and speaking Interactive Patterns: T-S Time: 5 minutes Aids/Materials: Vocabulary: Presentation Language worksheet
The teacher will read the excerpt twice. T will ask the students to listen carefully and identify the differences. The first time, T will read it using proper sentence stress (stressing content words: nouns, main verbs, adjectives, adverbs), intonation and tone of voice. The second time, T will read it in a monotone voice. Then T will elicit the difference and which one is more effective and why: T: “Which speech was more effective?” S: “The first one” T: “Why?” S: (Possible answers) “You used expression, your voice changed, you sounded enthusiastic. In the second reading, your sounded dull, boring.”
Read: How to Use the Communicative Approach
Read: How to Use Task-based Learning
ACTIVATE – Business English Lesson Plan
Aim: Practice intonation patterns Techniques: reading aloud Skills: speaking and pronunciation Interactive Patterns: SS Time: 10 minutes
Aids/Materials: “Good and Bad Stress and Intonation” from UsingEnglish.com
The teacher will hand out the worksheet “Good and Bad Stress and Intonation”. Students will work in partners to practice saying the sixteen sentences with both good and bad intonation. The back of the worksheet provides helpful tips in how to express the sentences in the best and worst ways possible. Once students have finished practicing with a partner, they will go over each sentence as a whole class. The teacher will correct them where necessary
Step 1: Aim: to identify characteristics of effective presentations. Technique: note-taking, listen for main ideas Skills: listening and speaking Interactive patterns: S and SS Time: 10-15 minutes Aids/Materials: YouTube video “Enhancing Your Presentation Skills- Killer Presentations” by Doug Jeffries. (about 7:18 minutes)
The teacher will play the video twice to ensure students have a full understanding of the content. Students are responsible for noting at least five presentation skills that Doug Jeffries mentions in the video (Making your audience comfortable, establishing eye contact, ‘power of the pause’, body language/gestures, effective content). They will then go over and discuss the importance of each point as a whole class. For example:
T: “Why is establishing eye contact important when giving a presentation?” S: “It engages the viewer and allows them to know that you are speaking directly to them”
The teacher will now ask students if they know who Steve Jobs was and what he was responsible for.
T will tell the students that they will now watch a presentation by Steve Jobs and they have to discuss the following questions:
– Can you identify any of the presentation skills described by Doug Jeffries in Steve Jobs’ video?
– What makes Steve Jobs’ iphone 2007 launch presentation effective? (Possible answers: visuals, timing of speech accompanied by visuals, clear voice, confidence, knowledge of product).
– How does he keep the audience engaged? (Possible answers: movement, gestures, tone/pitch, humour, repetition (“re-invent, revolutionary”)
T will ask students to take a closer look at Steve Jobs’ presentation. T will direct them to identify any words they think made his presentation effective; words he repeated, words that they think helped to describe/promote his product. Students should pick out certain adjectives such as revolutionary, life-changing, re-invent, magic, etc. T will write students’ answers on the board and then ask them to think of other vocabulary words they could use to sell a product, focusing on a product that the company they work for sells. “If you were to sell your company’s new product in a presentation like Steve Jobs’, what type of words would you use to engage the audience and make them want to buy your product? Come up with as many adjectives as you can to promote your product.” Students will compile an individual list. Once they have finished their lists, they will discuss their adjectives together as a class. T will write their ideas on the board, adding to the list that we compiled from Steve Jobs’ presentation and give the students time to copy any of the adjectives that they wish to use for their presentations into their notes.
Aim: Students will create a presentation with the assistance of ICT tools (PowerPoint/Camtasia) to sell a product to their classmates using appropriate vocabulary and body language. Techniques: collaborative writing and discussion Skills: Speaking, listening, reading and writing Aids/Materials: computers with Camtasia program and Microsoft PowerPoint Interactive Pattern: SSS Time: approx. 50 min.
For the final stage of the lesson, T will tell students that they are going to create a presentation, much like the one they viewed in the Steve Jobs video, using ICT tools (Camtasia or Powerpoint) to sell a product of their choice. The product must be something they are fully aware of as they will not have much time to research.
T will briefly go over the main stages of a presentation. Students’ presentation must follow this format: introduction, overview, state point, state results, summarize, and close.
Other points to remember to use in their presentations are: -use of vocabulary (adjectives and phrases) to describe the product -body language, gestures and intonation -synchronization of their speech with the slideshow presentation
After each student presents, the rest of the class will give them feedback regarding their presentation (both good and bad) and what they need to work on for a real life sales presentation scenario.
Adapted from lesson plan by 120-hour TEFL certificate graduate.
Take a TESOL course with Teaching Business English specialist!
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
The Presentation
Most presentations are divided into 3 main parts (+ questions):
As a general rule in communication, repetition is valuable. In presentations, there is a golden rule about repetition:
- Say what you are going to say...
- then say what you have just said.
In other words, use the three parts of your presentation to reinforce your message. In the introduction, you tell your audience what your message is going to be. In the body, you tell your audience your real message. In the conclusion, you summarize what your message was.
We will now consider each of these parts in more detail.
Introduction
The introduction is a very important - perhaps the most important - part of your presentation. This is the first impression that your audience have of you. You should concentrate on getting your introduction right. You should use the introduction to:
- welcome your audience
- introduce your subject
- outline the structure of your presentation
- give instructions about questions
The following table shows examples of language for each of these functions. You may need to modify the language as appropriate.
The body is the 'real' presentation. If the introduction was well prepared and delivered, you will now be 'in control'. You will be relaxed and confident.
The body should be well structured, divided up logically, with plenty of carefully spaced visuals.
Remember these key points while delivering the body of your presentation:
- do not hurry
- be enthusiastic
- give time on visuals
- maintain eye contact
- modulate your voice
- look friendly
- keep to your structure
- use your notes
- signpost throughout
- remain polite when dealing with difficult questions
Use the conclusion to:
- (Give recommendations if appropriate)
- Thank your audience
- Invite questions
Questions are a good opportunity for you to interact with your audience. It may be helpful for you to try to predict what questions will be asked so that you can prepare your response in advance. You may wish to accept questions at any time during your presentation, or to keep a time for questions after your presentation. Normally, it's your decision, and you should make it clear during the introduction. Be polite with all questioners, even if they ask difficult questions. They are showing interest in what you have to say and they deserve attention. Sometimes you can reformulate a question. Or answer the question with another question. Or even ask for comment from the rest of the audience.

15 Speaking Projects And Activities For ESL Students
I don’t think I am sticking my neck out too much by saying that most ESL students enjoy speaking activities more than typical reading, writing and listening activities. Tending to be more dynamic, true to life and fun, a good speaking activity can really enhance an ESL student’s fluency and confidence.
Here, I am going to offer you a series of ESL speaking projects that you can adapt and use for your ESL students. Let’s go:
Infomercial Activities
This is one of my favorite speaking projects by far. Show students some typical adverts from a shopping channel; I like to show some of the funnier products just for giggles and to encourage students minds to wander, take a look at this compilation to see what I mean.
Next, I ask students usually in pairs to come up with their own completely original product to sell on an infomercial. If students struggle to come up with a completely new product you can suggest they add a new twist to arnold product, or make a new product based on a combination of two or more others.
For example, in the past I have had: microwave televisions, hair dryers that double as vacuum cleaners and laptops that double as portable stoves.
I tend to also do a language lesson based around the language of selling and persuasion so that when students make their infomercial they will send realistic and they often like to know some of the sales phrases, tactics and strategies that are used in real life.
Just for fun, you can tell students that they have a certain amount of money to spend and after they have seen all the infomercials they get to spend it. Sales can be recorded and you can see which idea/pair has made the most money and are the winner!
Presentations
Give students a presentation of a topic of your choosing, perhaps your own hobby and model the format and language that you want the students to use.
I tend to share slides with the student with the title of each slide already inserted. Students then have to fill the space with suitable information for that slide.
So, for example, if I wanted my students to present their own hobbies then I would probably have six slides titled with questions:
What is my favorite hobby? Why did I start this hobby? What have I achieved doing this hobby? Who do I do this hobby with? What will I do next in this hobby? Other interesting info about my hobby.
Students then fill the slides full of pictures that relate to the question and then they talk about these to the group and answer questions.
Some students always want to write out a script for a presentation which I let them do on the understanding that they can’t actually read it when they present. I allow them to write it out just so they can build up some confidence in what they are going to say and check the language accuracy of it.
I do usually place sentence starters and linking words on posters behind the audience so that the presenter always has some support if needs be.
Of course, this could also be done as a recorded video task. I sometimes ask students to record a voice over on top of the slides. This can then be converted into a video format for sharing later.
A few other simple presentation topic titles for ESL students that could be used are: My Best Friend, Who Am I?, My Pets, My Future Career, My Family, The Last Celebration I want to, Why I am a fan of __________ (insert name of whatever they are a fan of).
At this point you might also want to read one of my popular article about how to make your students speak English , here
Hot Seat ing
Become an expert – As it sounds. Students spent a certain amount of time researching a topic that either they choose or that is given to them. They are then to become that character and the rest of the group has to ask them questions to find out as much as they can about them in a set amount of time.
You can award points for correct questions being asked and for grammatically correct sentences in response. Personally I like to do this at the beginning of a new topic and direct students to research different famous people.
For example, if we are going to be covering the topic of Travel as in the IGCSE ESL then I have students research characters, such as: Dr Livingstone, Joe Simpson, Ernest Shackleton, Amelia Earhart, Ranulf Fiennes, and so on.
I often have students create a mini glossary for their characters as well which other students can refer to as they are quizzing the character.
This activity is best for intermediate level and above students and even then you may need to provide texts at a suitable level for students to be able to access, otherwise students end up on Wikipedia reading very difficult text.
You can have the group make notes and write summaries of each character for homework if you also wish to work on summary writing skills.
Recommended reading: 15 Research Projects For ESL Students
The Detective Game
For this activity you make up a crime that occurred in a given location, the more gruesome the better and if you can personalise it to your location and environment more the better.
Divide the group into smaller groups of three or four people and then ask them to create their alibis for the morning, afternoon, or evening in question. These people are the suspects.
One group, however, is assigned as being the investigators and they individually quiz different suspects one to one to try and find inconsistencies in their group’s stories. This forces each group to consider exactly what they were doing, where and with whom very carefully and in great detail.
After interviewing as many members of each group and making notes about inconsistencies between group members the investigators then confer with each other to decide upon which group’ alibi is the most inconsistent. This group are then sent to jail.
Whilst the investigators are discussing this, the suspects discuss which investigator was the best at questioning them and finding out the inconsistencies. The suspects will then announce who this person is, and they earn a promotion. Finally, the investigators announce the losing group which will go to prison.
This ‘game’ has got real legs and could go in so many different directions, so don’t be afraid to improvise and have fun with this one.
Drama Activities
Acting out a chapter of a book. Pretty much as it sounds. Read through a chapter of a book with students or have them read it for homework before letting groups act out the chapter, or a scene from it.
This works well even if they all act out the same scene as each group will learn from the last and the acting/performance and language should get increasingly better throughout. Alternatively arrange it so that each group acts out the following scene to the last group and so the full story is told.
Storyboard and act out the student’s own story. Rather than act out a book, you could have students plan out a story, or at least part of a story on a storyboard. This can give a greater sense of ownership, achievement and ‘buy in’ from the students.
What happened next. Read the opening of a book and as a ‘cliffhanger is reached’ pause and have students work together to act out the ending of the story or the next scene at least.
This also works well with videos from YouTube, crime videos work well as do Walt Disney cartoons – even with adult learners for some reason!
You might also be interested in reading my helpful article on how to get your students speaking fluently , here.
Mind Map ping
Vocabulary relationships. Engage students in a subject which contains lots of relationships of cause and effect. Basically, you need to pick a topic and analyse what the different factors were that affected the main decision or characters involved.
In the centre of your mind map place the decision or a character that was made and then arrange influencing factors around this.
The larger the circle each factor is in and the closer it is to the centre of the paper the stronger the influence is. Students then need to explain their mind map and the relationships to the group. Others can question and agree/ disagree with them.
Topics can range from serious issues from history through to celebrity scandals, or even plots in a movie, such as, why did celebrity couple X and Y get divorced, or why did actor x decide to y in the movie xyz. Obviously, you can let the students self select these issues for greater interest.
Backs To The Board
A timeless classic not so much a speaking project but this can be developed into a full lesson’s worth of speaking and it works for groups of all sizes. It is excellent for reviewing vocabulary at the end of a project or to see what students know at the beginning of a topic.
Simply split the group into teams of no more than five and have one member of the group come to the front and sit with their back to the board.
The other members of the group form a ‘u’ shape around the person, or, rather than being sat literally against the board groups can be sat at tables with just one student having their back to the board.
All you then need to do is to write a word on the board and the students facing the board have to get the person not facing the board to say the word without literally telling them the word. They should be encouraged to use definitions, synonyms and examples of the word where possible.
Depending on numbers, students can just shout out when they think they have the answer, or with large groups I make the students raise their hand if they think they have the answer.
The danger with debates is that to the teacher they may seem boring, or at least they do to me but have to remind myself that just because I have done the debates dozens of times, they haven’t and even the most overdone/boring sounding debates may go down like fireworks with some groups.
With that in mind here are a few of the more traditional/boring debates for your students to get their teeth into:
Which is better, country life or city life?
Should animal testing be allowed?
Should school uniforms be gotten rid of
Are cats better than dogs?
Should women be paid as much as men?
Online learning is better than classroom learning
Does money equal success in life?
I also like to see if there is something going on in the students view of the world that is worth debating. For example, in Thailand the debate over whether Korean pop music is better than Thai pop music is a popular one.
I have had colleagues dive into debates about serious political topics with higher level students which have worked really well.
However, some topics are just too hot to handle and you don’t know who you are upsetting so be careful what topics you do debate, you never know who is listening, or who is going to offense at any of your personal views that you may let slip!
Here is a good resource for more ESL debate ideas .
Book And Movie Review s
This is pretty much as it sounds. I like to set a reading task for students over a holiday break and when they return they have to submit a video review of the book or movie they watched/read.
I usually show them a good movie review for ideas and ask them to follow the same format. Something like this review of Kung Fu Panda . This goes along the lines of: background information, main characters, plot explanation, favorite moments, final recommendation.
I’ve also done this with higher level groups for documentaries but with enough support and speaking frames pre intermediate students can engage well with this activity.
Conversation Question s
Don’t underestimate the value of pure lists of conversation questions. Students are often happy to just ‘have a chat’ and use the English that they do know.
It is great for their confidence and fluency, as well as requiring zero lesson prep, which is always a nice thing. Just be sure to rotate speaking partners to avoid students getting bored with the same partners and used to different accents.
Sometimes, depending on ability and interest levels I will teach three or four idioms at the beginning of the lesson and set the task of trying to naturally drop them into conversation later on.
There are lot of good sources of conversation questions, here are a couple: eslconversationquestions.com and esldiscussions.com .
ESL Exam Preparation Material
Some students are hugely motivated by doing well in exams such as the IELTS test, and IGCSE ESL speaking tests. Exam boards for tests such as these produce a plethora of practise material that is often available for free online and ready to be use.
My students particularly enjoy the IELTS speaking part 2 task where they are required to speak about a given topic and are given three bullet points to talk about. They are given one minute to prepare their ideas before they have to speak on their own for two minutes.
If you think your students might enjoy this then here are some good sources of free IELTS style questions: IELTS IDP and ielts-exam.net , and for IGCSE ESL speaking questions check out the role play paper here.
The added bonus of these activities is that there is always a grading criteria ready to be used so you can grade students and give them real reasons why they scored a certain level and what they need to do to score higher in the future.
Here are the IELTS speaking criteria for example which clearly spells out what is expected of students at different levels.
Finger Puppet Shows
One really good way to get shy students speaking I have found to introduce sock puppets. As silly as it sounds, there is something about using a puppet that takes away the pressure on the speaker and frees them up to speak.
Whether it is the element of hilarity of speaking sock or the fact that people are generally looking at the sock rather than the person it seems to work well.
Depending on the ability level I will either give pairs of students scripts to act out with puppets. They can introduce their own props as well to make it even more funny. Alternatively, I will do this as an improv.
I will read out a situation, for example, one of you has lost their passport at the airport. Then the students have to act out this scenes as best as they can.
Switch partners and introduce more situations and watch the energy level of the room pick up!
By the end of the lesson you may well notice previously shy students speaking confidently with other students having been drawn into the magic of sock puppets! A great little speaking project.
Role Plays With Idioms
I use this lesson pattern quite regularly and it works well. I start off with student matching idioms to meanings and then to example sentences with the idioms missing.
After going through these answers and doing any teaching necessary to aid understanding I will then hand out a dialogue but with all the sentences jumbled up.
Students then have to unjumble the conversation which contains one or more of the idioms being used in a natural way. Next, they read the dialogue through taking different roles each and then doing the dialogue again without looking at the words.
Next, students are given the task of creating their own dialogues using at least one of the idioms in an appropriate way. Students write out the dialogues, rehearse them and then act them out for the group.
You can also do this with phrasal verbs but either way it works out well and the routine can be used again when you are a bit short of material or are having a hangover day!
Barrier Activities
One favourite of mine that never fails to stimulate plenty of language use is to simply create your own barrier exercise. I like to get a nice chunky newspaper article related to what we are learning and then go through each paragraph and remove key details, such as: names, dates, place names, times, location etcetera…
I create two versions of this, the first one will have words missing from odd number paragraphs and the second copy will have words missing from even number paragraphs.
This prevents it from becoming confusing and make sure to keep one master version with no details missing and if you have time highlight the missing words in red so it is easy for students to check later.
Once the missing word copies are ready you can divide the class into two halves distributing sheet A to one half and sheet B to the other half. Allow them to work in groups at this point to work out what questions they need to ask the other half of the group in order to get the missing details filled in.
If you think this will be too difficult for them you can provide the questions in a jumbled up format so they have to rearrange them to make the questions,, or even give them the questions but they have to work out the order in which to ask them to correspond to the paragraph order.
After this preparation period students can then pair up with someone from the opposite half of the group to take turns asking and answering each other’s questions.
Make sure that students do not show each other their articles and simply just sit and copy the answers, clearly this simply defeats the whale point of the exercise.
Before starting this I also pre teach any tricky vocabulary that I know is going to come up in the article just to make sure the final questions and answer session goes without too much stopping and starting to ask about vocabulary.
After students have got the answers then you can either display the answers on an overhead projector, or send students back to their original half of the group to see if they have all gotten the same answers.
Jigsaw Reading
This is another easy way to get students involved in the language and speaking. Select a relevant article related to the topic you are studying and chop it up into paragraphs. Hand out A4 paper with a simple one column table with as many boxes as there are paragraphs.
Hand out the paragraphs to the students considering which paragraphs are more difficult and should go to the higher level learners and which are slightly easier and can go to the lower ability students.
Individually, students now summarise in their own words as far as possible their paragraphs and write the summary in a box in the table. Following this students pair up with students who had a different paragraph and they then read out their summaries whilst the other students make notes of it.
Rotate partners so that everyone can get every paragraph and after the first couple of times students have read their summaries, force students to turn over their paper and explain their paragraph from memory.
After the first couple of goes they should be able to do this and by the time they have explained to everyone in the group they should be reeling off their summary very comfortably.
A Word On Differentiation …
There is a lot of fun to be had for the students in the above activities but it is important to not forget that some students will require more support than others. Just asking students to do a role play with no support may be too much for some.
Always consider using speaking frames, having sentence starters placed around the room, ‘useful language’ handouts, and always show a clear model of what it is you are expecting the students to produce.
If you can tick those boxes then your speaking lesson will go that bit more smoothly.
All the best with your ESL speaking projects!
Recent Posts
Can I Teach IELTS Without a Certificate or Qualifications?
The IELTS test is a key part of many non-native speakers' journey into entering a university in a native English-speaking country, such as the UK, or Canada. Teaching IELTS is a great way to gain...
How Bad Grammar Can Change Meaning (Real Examples)
Many people dismiss grammar as being unimportant. They claim that grammar adds little meaning to communication and is an unnecessary complication. Although grammar may change over time, it is still a...

COMMENTS
Nous sommes dès lors très fiers de pouvoir accueillir David Brozak comme nouveau directeur technique de notre club. Pierre se concentrera lui sur son rôle de manager de la Ligue A.
Retrouvez toutes les informations sur Mpox : transmission, causes, symptômes, diagnostic, traitement, prévention, épidémiologie...
La dernière journée de la Coupe du monde était consacrée aux finales de Rocket League, ESL R1 et PUBG : Battlegrounds. Voici les résultats.
Il est autorisé aux examens et aux concours. Sous forme d'un dépliant maniable et facile à consulter, le Plan Comptable Général Nathan 2025 donne la liste intégrale des comptes classés par couleur pour un meilleur repérage : -Les comptes de bilan : les classes 1 à 5. -Les comptes de gestion : les classes 6 et 7.
Step into the world of presentations with this handy lesson! Students explore vocabulary for structuring presentations, read the text of a presentation and watch a video on how to communicate ideas clearly.
They listen to a business presentation and identify and practise a range of functional language for structuring presentations. The lesson includes vocabulary development and a presentation activity which can be extended to include preparation of slides with visual aids.
develop skills in structuring a presentation. In this lesson, students explore vocabulary for presentations (e.g. I'm going to tell you about…, As you can see…, I'd like to turn to…, etc.), practise using it and discuss their perspectives on presentations.
It's not easy to give a good oral presentation but these tips will help you. Here are our top tips for oral presentations. Do: Use the planning time to prepare what you're going to say. If you are allowed to have a note card, write short notes in point form. Use more formal language. Use short, simple sentences to express your ideas clearly.
With this lesson set, your students will: learn dos and don'ts of presenting, discuss different structures and types of presentations (e.g. elevator pitch); learn and practise signposting language (e.g. to start, elaborate, make a connection, recap, deviate), watch a video about virtual presentations,
Structure your presentation into introduction, body, conclusion and questions. Write notes based on keywords. Rehearse your presentation several times and modify it as necessary.
This Business skills lesson plan by Tim Bowen presents common features of presentations and practises useful language for putting together and giving presentations. Lesson length: 60-75 mins. Materials: Worksheets 1-5.
This article discusses some practical techniques that ESL/EFL teachers can use in teaching effective academic presentation skills. It is suggested that macro organization, micro organization, thesis and support, strategies to involve the audience, response to audience input, non-verbal communication, use of visual materials, and pacing should ...
Participants discuss some different presentation techniques and introductory activities, which are tested in TKT Module 1 Part 3. They consider the advantages of some of these activities and do a practice task
Presentations are a great way to have students practise all language systems areas (vocabulary, grammar, discourse and phonology) and skills (speaking, reading, writing and listening). They also build confidence, and presenting is a skill that most people will need in the world of work.
Among the key aspects of a successful oral presentation are: having a firm idea of what your audience already knows, careful presentation and rehearsal, making clear the structure of your talk clear, and dealing effectively with questions.
Presentation skills EAP worksheets and activities to help teach your students how to deliver academic presentations by focusing on key language and skills.
Learn professional phrases and a good presentation structure. From outline to introduction, wording and closing section: Learn how to create exceptional PowerPoint presentations for work, university and school!
Most business presentations are given for a specific purpose. You may want to convince another company to work with you. Or you may want to convince your own firm to invest in a new kind of product. You may simply be explaining to colleagues how a new training scheme will work.
This Mini-Presentation Task features 8 topics, including prompts to help your students prepare for and do a presentation. Get 100's of ESL resources here!
The PPP technique in EFL teaching uses a 3 step lesson plan to help students learn, understand and practice new vocabulary. Presentation, practice and production.
Teach your students techniques that increase student involvement that they can put to use during their presentations. One powerful technique is interacting directly with the audience by moving around, speaking directly to audience members, and asking questions. Another technique is to start off with an intriguing question or short quiz, leaving ...
Aim: to introduce the topic of giving presentations and to outline skills and characteristics that lead to a good presentation. Techniques used: questionnaire; discussion; brainstorming Skills: speaking and listening
Most presentations are divided into three main parts: introduction, body and conclusion. Presentations in English for ESL learners.
Presentations. Give students a presentation of a topic of your choosing, perhaps your own hobby and model the format and language that you want the students to use. I tend to share slides with the student with the title of each slide already inserted. Students then have to fill the space with suitable information for that slide.