Rubric Best Practices, Examples, and Templates
A rubric is a scoring tool that identifies the different criteria relevant to an assignment, assessment, or learning outcome and states the possible levels of achievement in a specific, clear, and objective way. Use rubrics to assess project-based student work including essays, group projects, creative endeavors, and oral presentations.
Rubrics can help instructors communicate expectations to students and assess student work fairly, consistently and efficiently. Rubrics can provide students with informative feedback on their strengths and weaknesses so that they can reflect on their performance and work on areas that need improvement.

How to Get Started
Best practices, moodle how-to guides.
- Workshop Recording (Spring 2024)
- Workshop Registration
Step 1: Analyze the assignment
The first step in the rubric creation process is to analyze the assignment or assessment for which you are creating a rubric. To do this, consider the following questions:
- What is the purpose of the assignment and your feedback? What do you want students to demonstrate through the completion of this assignment (i.e. what are the learning objectives measured by it)? Is it a summative assessment, or will students use the feedback to create an improved product?
- Does the assignment break down into different or smaller tasks? Are these tasks equally important as the main assignment?
- What would an “excellent” assignment look like? An “acceptable” assignment? One that still needs major work?
- How detailed do you want the feedback you give students to be? Do you want/need to give them a grade?
Step 2: Decide what kind of rubric you will use
Types of rubrics: holistic, analytic/descriptive, single-point
Holistic Rubric. A holistic rubric includes all the criteria (such as clarity, organization, mechanics, etc.) to be considered together and included in a single evaluation. With a holistic rubric, the rater or grader assigns a single score based on an overall judgment of the student’s work, using descriptions of each performance level to assign the score.
Advantages of holistic rubrics:
- Can p lace an emphasis on what learners can demonstrate rather than what they cannot
- Save grader time by minimizing the number of evaluations to be made for each student
- Can be used consistently across raters, provided they have all been trained
Disadvantages of holistic rubrics:
- Provide less specific feedback than analytic/descriptive rubrics
- Can be difficult to choose a score when a student’s work is at varying levels across the criteria
- Any weighting of c riteria cannot be indicated in the rubric
Analytic/Descriptive Rubric . An analytic or descriptive rubric often takes the form of a table with the criteria listed in the left column and with levels of performance listed across the top row. Each cell contains a description of what the specified criterion looks like at a given level of performance. Each of the criteria is scored individually.
Advantages of analytic rubrics:
- Provide detailed feedback on areas of strength or weakness
- Each criterion can be weighted to reflect its relative importance
Disadvantages of analytic rubrics:
- More time-consuming to create and use than a holistic rubric
- May not be used consistently across raters unless the cells are well defined
- May result in giving less personalized feedback
Single-Point Rubric . A single-point rubric is breaks down the components of an assignment into different criteria, but instead of describing different levels of performance, only the “proficient” level is described. Feedback space is provided for instructors to give individualized comments to help students improve and/or show where they excelled beyond the proficiency descriptors.
Advantages of single-point rubrics:
- Easier to create than an analytic/descriptive rubric
- Perhaps more likely that students will read the descriptors
- Areas of concern and excellence are open-ended
- May removes a focus on the grade/points
- May increase student creativity in project-based assignments
Disadvantage of analytic rubrics: Requires more work for instructors writing feedback
Step 3 (Optional): Look for templates and examples.
You might Google, “Rubric for persuasive essay at the college level” and see if there are any publicly available examples to start from. Ask your colleagues if they have used a rubric for a similar assignment. Some examples are also available at the end of this article. These rubrics can be a great starting point for you, but consider steps 3, 4, and 5 below to ensure that the rubric matches your assignment description, learning objectives and expectations.
Step 4: Define the assignment criteria
Make a list of the knowledge and skills are you measuring with the assignment/assessment Refer to your stated learning objectives, the assignment instructions, past examples of student work, etc. for help.
Helpful strategies for defining grading criteria:
- Collaborate with co-instructors, teaching assistants, and other colleagues
- Brainstorm and discuss with students
- Can they be observed and measured?
- Are they important and essential?
- Are they distinct from other criteria?
- Are they phrased in precise, unambiguous language?
- Revise the criteria as needed
- Consider whether some are more important than others, and how you will weight them.
Step 5: Design the rating scale
Most ratings scales include between 3 and 5 levels. Consider the following questions when designing your rating scale:
- Given what students are able to demonstrate in this assignment/assessment, what are the possible levels of achievement?
- How many levels would you like to include (more levels means more detailed descriptions)
- Will you use numbers and/or descriptive labels for each level of performance? (for example 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 and/or Exceeds expectations, Accomplished, Proficient, Developing, Beginning, etc.)
- Don’t use too many columns, and recognize that some criteria can have more columns that others . The rubric needs to be comprehensible and organized. Pick the right amount of columns so that the criteria flow logically and naturally across levels.
Step 6: Write descriptions for each level of the rating scale
Artificial Intelligence tools like Chat GPT have proven to be useful tools for creating a rubric. You will want to engineer your prompt that you provide the AI assistant to ensure you get what you want. For example, you might provide the assignment description, the criteria you feel are important, and the number of levels of performance you want in your prompt. Use the results as a starting point, and adjust the descriptions as needed.
Building a rubric from scratch
For a single-point rubric , describe what would be considered “proficient,” i.e. B-level work, and provide that description. You might also include suggestions for students outside of the actual rubric about how they might surpass proficient-level work.
For analytic and holistic rubrics , c reate statements of expected performance at each level of the rubric.
- Consider what descriptor is appropriate for each criteria, e.g., presence vs absence, complete vs incomplete, many vs none, major vs minor, consistent vs inconsistent, always vs never. If you have an indicator described in one level, it will need to be described in each level.
- You might start with the top/exemplary level. What does it look like when a student has achieved excellence for each/every criterion? Then, look at the “bottom” level. What does it look like when a student has not achieved the learning goals in any way? Then, complete the in-between levels.
- For an analytic rubric , do this for each particular criterion of the rubric so that every cell in the table is filled. These descriptions help students understand your expectations and their performance in regard to those expectations.
Well-written descriptions:
- Describe observable and measurable behavior
- Use parallel language across the scale
- Indicate the degree to which the standards are met
Step 7: Create your rubric
Create your rubric in a table or spreadsheet in Word, Google Docs, Sheets, etc., and then transfer it by typing it into Moodle. You can also use online tools to create the rubric, but you will still have to type the criteria, indicators, levels, etc., into Moodle. Rubric creators: Rubistar , iRubric
Step 8: Pilot-test your rubric
Prior to implementing your rubric on a live course, obtain feedback from:
- Teacher assistants
Try out your new rubric on a sample of student work. After you pilot-test your rubric, analyze the results to consider its effectiveness and revise accordingly.
- Limit the rubric to a single page for reading and grading ease
- Use parallel language . Use similar language and syntax/wording from column to column. Make sure that the rubric can be easily read from left to right or vice versa.
- Use student-friendly language . Make sure the language is learning-level appropriate. If you use academic language or concepts, you will need to teach those concepts.
- Share and discuss the rubric with your students . Students should understand that the rubric is there to help them learn, reflect, and self-assess. If students use a rubric, they will understand the expectations and their relevance to learning.
- Consider scalability and reusability of rubrics. Create rubric templates that you can alter as needed for multiple assignments.
- Maximize the descriptiveness of your language. Avoid words like “good” and “excellent.” For example, instead of saying, “uses excellent sources,” you might describe what makes a resource excellent so that students will know. You might also consider reducing the reliance on quantity, such as a number of allowable misspelled words. Focus instead, for example, on how distracting any spelling errors are.
Example of an analytic rubric for a final paper
| Above Average (4) | Sufficient (3) | Developing (2) | Needs improvement (1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Thesis supported by relevant information and ideas | The central purpose of the student work is clear and supporting ideas always are always well-focused. Details are relevant, enrich the work. | The central purpose of the student work is clear and ideas are almost always focused in a way that supports the thesis. Relevant details illustrate the author’s ideas. | The central purpose of the student work is identified. Ideas are mostly focused in a way that supports the thesis. | The purpose of the student work is not well-defined. A number of central ideas do not support the thesis. Thoughts appear disconnected. |
| (Sequencing of elements/ ideas) | Information and ideas are presented in a logical sequence which flows naturally and is engaging to the audience. | Information and ideas are presented in a logical sequence which is followed by the reader with little or no difficulty. | Information and ideas are presented in an order that the audience can mostly follow. | Information and ideas are poorly sequenced. The audience has difficulty following the thread of thought. |
| (Correctness of grammar and spelling) | Minimal to no distracting errors in grammar and spelling. | The readability of the work is only slightly interrupted by spelling and/or grammatical errors. | Grammatical and/or spelling errors distract from the work. | The readability of the work is seriously hampered by spelling and/or grammatical errors. |
Example of a holistic rubric for a final paper
| The audience is able to easily identify the central message of the work and is engaged by the paper’s clear focus and relevant details. Information is presented logically and naturally. There are minimal to no distracting errors in grammar and spelling. : The audience is easily able to identify the focus of the student work which is supported by relevant ideas and supporting details. Information is presented in a logical manner that is easily followed. The readability of the work is only slightly interrupted by errors. : The audience can identify the central purpose of the student work without little difficulty and supporting ideas are present and clear. The information is presented in an orderly fashion that can be followed with little difficulty. Grammatical and spelling errors distract from the work. : The audience cannot clearly or easily identify the central ideas or purpose of the student work. Information is presented in a disorganized fashion causing the audience to have difficulty following the author’s ideas. The readability of the work is seriously hampered by errors. |
Single-Point Rubric
| Advanced (evidence of exceeding standards) | Criteria described a proficient level | Concerns (things that need work) |
|---|---|---|
| Criteria #1: Description reflecting achievement of proficient level of performance | ||
| Criteria #2: Description reflecting achievement of proficient level of performance | ||
| Criteria #3: Description reflecting achievement of proficient level of performance | ||
| Criteria #4: Description reflecting achievement of proficient level of performance | ||
| 90-100 points | 80-90 points | <80 points |
More examples:
- Single Point Rubric Template ( variation )
- Analytic Rubric Template make a copy to edit
- A Rubric for Rubrics
- Bank of Online Discussion Rubrics in different formats
- Mathematical Presentations Descriptive Rubric
- Math Proof Assessment Rubric
- Kansas State Sample Rubrics
- Design Single Point Rubric
Technology Tools: Rubrics in Moodle
- Moodle Docs: Rubrics
- Moodle Docs: Grading Guide (use for single-point rubrics)
Tools with rubrics (other than Moodle)
- Google Assignments
- Turnitin Assignments: Rubric or Grading Form
Other resources
- DePaul University (n.d.). Rubrics .
- Gonzalez, J. (2014). Know your terms: Holistic, Analytic, and Single-Point Rubrics . Cult of Pedagogy.
- Goodrich, H. (1996). Understanding rubrics . Teaching for Authentic Student Performance, 54 (4), 14-17. Retrieved from
- Miller, A. (2012). Tame the beast: tips for designing and using rubrics.
- Ragupathi, K., Lee, A. (2020). Beyond Fairness and Consistency in Grading: The Role of Rubrics in Higher Education. In: Sanger, C., Gleason, N. (eds) Diversity and Inclusion in Global Higher Education. Palgrave Macmillan, Singapore.
Center for Excellence in Teaching
Home > Resources > Academic essay rubric
Academic essay rubric
This is a grading rubric an instructor uses to assess students’ work on this type of assignment. It is a sample rubric that needs to be edited to reflect the specifics of a particular assignment.
Download this file
Download this file [63.33 KB]
Back to Resources Page

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
SAT Essay Rubric: Full Analysis and Writing Strategies

We're about to dive deep into the details of that least beloved* of SAT sections, the SAT essay . Prepare for a discussion of the SAT essay rubric and how the SAT essay is graded based on that. I'll break down what each item on the rubric means and what you need to do to meet those requirements.
On the SAT, the last section you'll encounter is the (optional) essay. You have 50 minutes to read a passage, analyze the author's argument, and write an essay. If you don’t write on the assignment, plagiarize, or don't use your own original work, you'll get a 0 on your essay. Otherwise, your essay scoring is done by two graders - each one grades you on a scale of 1-4 in Reading, Analysis, and Writing, for a total essay score out of 8 in each of those three areas . But how do these graders assign your writing a numerical grade? By using an essay scoring guide, or rubric.
*may not actually be the least belovèd.
Feature image credit: Day 148: the end of time by Bruce Guenter , used under CC BY 2.0 /Cropped from original.
UPDATE: SAT Essay No Longer Offered
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});.
In January 2021, the College Board announced that after June 2021, it would no longer offer the Essay portion of the SAT (except at schools who opt in during School Day Testing). It is now no longer possible to take the SAT Essay, unless your school is one of the small number who choose to offer it during SAT School Day Testing.
While most colleges had already made SAT Essay scores optional, this move by the College Board means no colleges now require the SAT Essay. It will also likely lead to additional college application changes such not looking at essay scores at all for the SAT or ACT, as well as potentially requiring additional writing samples for placement.
What does the end of the SAT Essay mean for your college applications? Check out our article on the College Board's SAT Essay decision for everything you need to know.
The Complete SAT Essay Grading Rubric: Item-by-Item Breakdown
Based on the CollegeBoard’s stated Reading, Analysis, and Writing criteria, I've created the below charts (for easier comparison across score points). For the purpose of going deeper into just what the SAT is looking for in your essay, I've then broken down each category further (with examples).
The information in all three charts is taken from the College Board site .
The biggest change to the SAT essay (and the thing that really distinguishes it from the ACT essay) is that you are required to read and analyze a text , then write about your analysis of the author's argument in your essay. Your "Reading" grade on the SAT essay reflects how well you were able to demonstrate your understanding of the text and the author's argument in your essay.
|
|
|
|
(Inadequate) | The response demonstrates little or no comprehension of the source text. The response fails to show an understanding of the text’s central idea(s), and may include only details without reference to central idea(s). The response may contain numerous errors of fact and/or interpretation with regard to the text. The response makes little or no use of textual evidence (quotations, paraphrases, or both), demonstrating little or no understanding of the source text. |
|
(Partial) | The response demonstrates some comprehension of the source text. The response shows an understanding of the text’s central idea(s) but not of important details. The response may contain errors of fact and/or interpretation with regard to the text. The response makes limited and/or haphazard use of textual evidence (quotations, paraphrases, or both), demonstrating some understanding of the source text. |
|
(Proficient) | The response demonstrates effective comprehension of the source text. The response shows an understanding of the text’s central idea(s) and important details. The response is free of substantive errors of fact and interpretation with regard to the text. The response makes appropriate use of textual evidence (quotations, paraphrases, or both), demonstrating an understanding of the source text. |
|
(Advanced) | The response demonstrates thorough comprehension of the source text. The response shows an understanding of the text’s central idea(s) and of most important details and how they interrelate, demonstrating a comprehensive understanding of the text. The response is free of errors of fact or interpretation with regard to the text. The response makes skillful use of textual evidence (quotations, paraphrases, or both), demonstrating a complete understanding of the source text. |
You'll need to show your understanding of the text on two different levels: the surface level of getting your facts right and the deeper level of getting the relationship of the details and the central ideas right.
Surface Level: Factual Accuracy
One of the most important ways you can show you've actually read the passage is making sure you stick to what is said in the text . If you’re writing about things the author didn’t say, or things that contradict other things the author said, your argument will be fundamentally flawed.
For instance, take this quotation from a (made-up) passage about why a hot dog is not a sandwich:
“The fact that you can’t, or wouldn’t, cut a hot dog in half and eat it that way, proves that a hot dog is once and for all NOT a sandwich”
Here's an example of a factually inaccurate paraphrasing of this quotation:
The author builds his argument by discussing how, since hot-dogs are often served cut in half, this makes them different from sandwiches.
The paraphrase contradicts the passage, and so would negatively affect your reading score. Now let's look at an accurate paraphrasing of the quotation:
The author builds his argument by discussing how, since hot-dogs are never served cut in half, they are therefore different from sandwiches.
It's also important to be faithful to the text when you're using direct quotations from the passage. Misquoting or badly paraphrasing the author’s words weakens your essay, because the evidence you’re using to support your points is faulty.
Higher Level: Understanding of Central Ideas
The next step beyond being factually accurate about the passage is showing that you understand the central ideas of the text and how details of the passage relate back to this central idea.
Why does this matter? In order to be able to explain why the author is persuasive, you need to be able to explain the structure of the argument. And you can’t deconstruct the author's argument if you don’t understand the central idea of the passage and how the details relate to it.
Here's an example of a statement about our fictional "hot dogs are sandwiches" passage that shows understanding of the central idea of the passage:
Hodgman’s third primary defense of why hot dogs are not sandwiches is that a hot dog is not a subset of any other type of food. He uses the analogy of asking the question “is cereal milk a broth, sauce, or gravy?” to show that making such a comparison between hot dogs and sandwiches is patently illogical.
The above statement takes one step beyond merely being factually accurate to explain the relation between different parts of the passage (in this case, the relation between the "what is cereal milk?" analogy and the hot dog/sandwich debate).
Of course, if you want to score well in all three essay areas, you’ll need to do more in your essay than merely summarizing the author’s argument. This leads directly into the next grading area of the SAT Essay.
The items covered under this criterion are the most important when it comes to writing a strong essay. You can use well-spelled vocabulary in sentences with varied structure all you want, but if you don't analyze the author's argument, demonstrate critical thinking, and support your position, you will not get a high Analysis score .
|
|
|
|
(Inadequate) | The response offers little or no analysis or ineffective analysis of the source text and demonstrates little or no understanding of the analytic task. The response identifies without explanation some aspects of the author’s use of evidence, reasoning, and/or stylistic and persuasive elements, and/or feature(s) of the student’s choosing, Or numerous aspects of the response’s analysis are unwarranted based on the text. The response contains little or no support for claim(s) or point(s) made, or support is largely irrelevant. The response may not focus on features of the text that are relevant to addressing the task, Or the response offers no discernible analysis (e.g., is largely or exclusively summary). |
|
(Partial) | The response offers limited analysis of the source text and demonstrates only partial understanding of the analytical task. The response identifies and attempts to describe the author’s use of evidence, reasoning, and/or stylistic and persuasive elements, and/or feature(s) of the student’s own choosing, but merely asserts rather than explains their importance, or one or more aspects of the response’s analysis are unwarranted based on the text. The response contains little or no support for claim(s) or point(s) made. The response may lack a clear focus on those features of the text that are most relevant to addressing the task. |
|
(Proficient) | The response offers an effective analysis of the source text and demonstrates an understanding of the analytical task. The response competently evaluates the author’s use of evidence, reasoning, and/or stylistic and persuasive elements, and/or feature(s) of the student’s own choosing. The response contains relevant and sufficient support for claim(s) or point(s) made. The response focuses primarily on those features of the text that are most relevant to addressing the task. |
|
(Advanced) | The response offers an insightful analysis of the source text and demonstrates a sophisticated understanding of the analytical task. The response offers a thorough, well-considered evaluation of the author’s use of evidence, reasoning, and/or stylistic and persuasive elements, and/or feature(s) of the student’s own choosing. The response contains relevant, sufficient, and strategically chosen support for claim(s) or point(s) made. The response focuses consistently on those features of the text that are most relevant to addressing the task. |
Because this category is so important, I've broken it down even further into its two different (but equally important) component parts to make sure everything is as clearly explained as possible.
Part I: Critical Thinking (Logic)
Critical thinking, also known as critical reasoning, also known as logic, is the skill that SAT essay graders are really looking to see displayed in the essay. You need to be able to evaluate and analyze the claim put forward in the prompt. This is where a lot of students may get tripped up, because they think “oh, well, if I can just write a lot, then I’ll do well.” While there is some truth to the assertion that longer essays tend to score higher , if you don’t display critical thinking you won’t be able to get a top score on your essay.
What do I mean by critical thinking? Let's take the previous prompt example:
Write an essay in which you explain how Hodgman builds an argument to persuade his audience that the hot dog cannot, and never should be, considered a sandwich.
An answer to this prompt that does not display critical thinking (and would fall into a 1 or 2 on the rubric) would be something like:
The author argues that hot dogs aren’t sandwiches, which is persuasive to the reader.
While this does evaluate the prompt (by providing a statement that the author's claim "is persuasive to the reader"), there is no corresponding analysis. An answer to this prompt that displays critical thinking (and would net a higher score on the rubric) could be something like this:
The author uses analogies to hammer home his point that hot dogs are not sandwiches. Because the readers will readily believe the first part of the analogy is true, they will be more likely to accept that the second part (that hot dogs aren't sandwiches) is true as well.
See the difference? Critical thinking involves reasoning your way through a situation (analysis) as well as making a judgement (evaluation) . On the SAT essay, however, you can’t just stop at abstract critical reasoning - analysis involves one more crucial step...
Part II: Examples, Reasons, and Other Evidence (Support)
The other piece of the puzzle (apparently this is a tiny puzzle) is making sure you are able to back up your point of view and critical thinking with concrete evidence . The SAT essay rubric says that the best (that is, 4-scoring) essay uses “ relevant, sufficient, and strategically chosen support for claim(s) or point(s) made. ” This means you can’t just stick to abstract reasoning like this:
That explanation is a good starting point, but if you don't back up your point of view with quoted or paraphrased information from the text to support your discussion of the way the author builds his/her argument, you will not be able to get above a 3 on the Analysis portion of the essay (and possibly the Reading portion as well, if you don't show you've read the passage). Let's take a look of an example of how you might support an interpretation of the author's effect on the reader using facts from the passage :
The author’s reference to the Biblical story about King Solomon elevates the debate about hot dogs from a petty squabble between friends to a life-or-death disagreement. The reader cannot help but see the parallels between the two situations and thus find themselves agreeing with the author on this point.
Does the author's reference to King Solomon actually "elevate the debate," causing the reader to agree with the author? From the sentences above, it certainly seems plausible that it might. While your facts do need to be correct, you get a little more leeway with your interpretations of how the author’s persuasive techniques might affect the audience. As long as you can make a convincing argument for the effect a technique the author uses might have on the reader, you’ll be good.

Say whaaat?! #tbt by tradlands , used under CC BY 2.0 /Cropped and color-adjusted from original.
Did I just blow your mind? Read more about the secrets the SAT doesn’t want you to know in this article .
Your Writing score on the SAT essay is not just a reflection of your grasp of the conventions of written English (although it is that as well). You'll also need to be focused, organized, and precise.
|
|
|
|
(Inadequate) | The response demonstrates little or no cohesion and inadequate skill in the use and control of language. The response may lack a clear central claim or controlling idea. The response lacks a recognizable introduction and conclusion. The response does not have a discernible progression of ideas. The response lacks variety in sentence structures; sentence structures may be repetitive. The response demonstrates general and vague word choice; word choice may be poor or inaccurate. The response may lack a formal style and objective tone. The response shows a weak control of the conventions of standard written English and may contain numerous errors that undermine the quality of writing. |
|
(Partial) | The response demonstrates little or no cohesion and limited skill in the use and control of language. The response may lack a clear central claim or controlling idea or may deviate from the claim or idea over the course of the response. The response may include an ineffective introduction and/or conclusion. The response may demonstrate some progression of ideas within paragraphs but not throughout the response. The response has limited variety in sentence structures; sentence structures may be repetitive. The response demonstrates general or vague word choice; word choice may be repetitive. The response may deviate noticeably from a formal style and objective tone. The response shows a limited control of the conventions of standard written English and contains errors that detract from the quality of writing and may impede understanding. |
|
(Proficient) | The response is mostly cohesive and demonstrates effective use and control of language. The response includes a central claim or implicit controlling idea. The response includes an effective introduction and conclusion. The response demonstrates a clear progression of ideas both within paragraphs and throughout the essay. The response has variety in sentence structures. The response demonstrates some precise word choice. The response maintains a formal style and objective tone. The response shows a good control of the conventions of standard written English and is free of significant errors that detract from the quality of writing. |
|
(Advanced) | The response is cohesive and demonstrates a highly effective use and command of language. The response includes a precise central claim. The response includes a skillful introduction and conclusion. The response demonstrates a deliberate and highly effective progression of ideas both within paragraphs and throughout the essay. The response has a wide variety in sentence structures. The response demonstrates a consistent use of precise word choice. The response maintains a formal style and objective tone. The response shows a strong command of the conventions of standard written English and is free or virtually free of errors. |
Because there's a lot of different factors that go into calculating your Writing score, I've divided the discussion of this rubric area into five separate items:
Precise Central Claim
Organization, vocab and word choice, sentence structure, grammar, etc..
One of the most basic rules of the SAT essay is that you need to express a clear opinion on the "assignment" (the prompt) . While in school (and everywhere else in life, pretty much) you’re encouraged to take into account all sides of a topic, it behooves you to NOT do this on the SAT essay. Why? Because you only have 50 minutes to read the passage, analyze the author's argument, and write the essay, there's no way you can discuss every single way in which the author builds his/her argument, every single detail of the passage, or a nuanced argument about what works and what doesn't work.
Instead, I recommend focusing your discussion on a few key ways the author is successful in persuading his/her audience of his/her claim.
Let’s go back to the assignment we've been using as an example throughout this article:
"Write an essay in which you explain how Hodgman builds an argument to persuade his audience that the hot dog cannot, and never should be, considered a sandwich."
Your instinct (trained from many years of schooling) might be to answer:
"There are a variety of ways in which the author builds his argument."
This is a nice, vague statement that leaves you a lot of wiggle room. If you disagree with the author, it's also a way of avoiding having to say that the author is persuasive. Don't fall into this trap! You do not necessarily have to agree with the author's claim in order to analyze how the author persuades his/her readers that the claim is true.
Here's an example of a precise central claim about the example assignment:
The author effectively builds his argument that hot dogs are not sandwiches by using logic, allusions to history and mythology, and factual evidence.
In contrast to the vague claim that "There are a variety of ways in which the author builds his argument," this thesis both specifies what the author's argument is and the ways in which he builds the argument (that you'll be discussing in the essay).
While it's extremely important to make sure your essay has a clear point of view, strong critical reasoning, and support for your position, that's not enough to get you a top score. You need to make sure that your essay "demonstrates a deliberate and highly effective progression of ideas both within paragraphs and throughout the essay."
What does this mean? Part of the way you can make sure your essay is "well organized" has to do with following standard essay construction points. Don't write your essay in one huge paragraph; instead, include an introduction (with your thesis stating your point of view), body paragraphs (one for each example, usually), and a conclusion. This structure might seem boring, but it really works to keep your essay organized, and the more clearly organized your essay is, the easier it will be for the essay grader to understand your critical reasoning.
The second part of this criteria has to do with keeping your essay focused, making sure it contains "a deliberate and highly effective progression of ideas." You can't just say "well, I have an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion, so I guess my essay is organized" and expect to get a 4/4 on your essay. You need to make sure that each paragraph is also organized . Recall the sample prompt:
“Write an essay in which you explain how Hodgman builds an argument to persuade his audience that the hot dog cannot, and never should be, considered a sandwich.”
And our hypothetical thesis:
Let's say that you're writing the paragraph about the author's use of logic to persuade his reader that hot dogs aren't sandwiches. You should NOT just list ways that the author is logical in support of his claim, then explain why logic in general is an effective persuasive device. While your points might all be valid, your essay would be better served by connecting each instance of logic in the passage with an explanation of how that example of logic persuades the reader to agree with the author.
Above all, it is imperative that you make your thesis (your central claim) clear in the opening paragraph of your essay - this helps the grader keep track of your argument. There's no reason you’d want to make following your reasoning more difficult for the person grading your essay (unless you’re cranky and don’t want to do well on the essay. Listen, I don’t want to tell you how to live your life).
In your essay, you should use a wide array of vocabulary (and use it correctly). An essay that scores a 4 in Writing on the grading rubric “demonstrates a consistent use of precise word choice.”
You’re allowed a few errors, even on a 4-scoring essay, so you can sometimes get away with misusing a word or two. In general, though, it’s best to stick to using words you are certain you not only know the meaning of, but also know how to use. If you’ve been studying up on vocab, make sure you practice using the words you’ve learned in sentences, and have those sentences checked by someone who is good at writing (in English), before you use those words in an SAT essay.
Creating elegant, non-awkward sentences is the thing I struggle most with under time pressure. For instance, here’s my first try at the previous sentence: “Making sure a sentence structure makes sense is the thing that I have the most problems with when I’m writing in a short amount of time” (hahaha NOPE - way too convoluted and wordy, self). As another example, take a look at these two excerpts from the hypothetical essay discussing how the author persuaded his readers that a hot dog is not a sandwich:
Score of 2: "The author makes his point by critiquing the argument against him. The author pointed out the logical fallacy of saying a hot dog was a sandwich because it was meat "sandwiched" between two breads. The author thus persuades the reader his point makes sense to be agreed with and convinces them."
The above sentences lack variety in structure (they all begin with the words "the author"), and the last sentence has serious flaws in its structure (it makes no sense).
Score of 4: "The author's rigorous examination of his opponent's position invites the reader, too, to consider this issue seriously. By laying out his reasoning, step by step, Hodgman makes it easy for the reader to follow along with his train of thought and arrive at the same destination that he has. This destination is Hodgman's claim that a hot dog is not a sandwich."
The above sentences demonstrate variety in sentence structure (they don't all begin with the same word and don't have the same underlying structure) that presumably forward the point of the essay.
In general, if you're doing well in all the other Writing areas, your sentence structures will also naturally vary. If you're really worried that your sentences are not varied enough, however, my advice for working on "demonstrating meaningful variety in sentence structure" (without ending up with terribly worded sentences) is twofold:
- Read over what you’ve written before you hand it in and change any wordings that seem awkward, clunky, or just plain incorrect.
- As you’re doing practice essays, have a friend, family member, or teacher who is good at (English) writing look over your essays and point out any issues that arise.
This part of the Writing grade is all about the nitty gritty details of writing: grammar, punctuation, and spelling . It's rare that an essay with serious flaws in this area can score a 4/4 in Reading, Analysis, or Writing, because such persistent errors often "interfere with meaning" (that is, persistent errors make it difficult for the grader to understand what you're trying to get across).
On the other hand, if they occur in small quantities, grammar/punctuation/spelling errors are also the things that are most likely to be overlooked. If two essays are otherwise of equal quality, but one writer misspells "definitely" as "definately" and the other writer fails to explain how one of her examples supports her thesis, the first writer will receive a higher essay score. It's only when poor grammar, use of punctuation, and spelling start to make it difficult to understand your essay that the graders start penalizing you.
My advice for working on this rubric area is the same advice as for sentence structure: look over what you’ve written to double check for mistakes, and ask someone who’s good at writing to look over your practice essays and point out your errors. If you're really struggling with spelling, simply typing up your (handwritten) essay into a program like Microsoft Word and running spellcheck can alert you to problems. We've also got a great set of articles up on our blog about SAT Writing questions that may help you better understand any grammatical errors you are making.
How Do I Use The SAT Essay Grading Rubric?
Now that you understand the SAT essay rubric, how can you use it in your SAT prep? There are a couple of different ways.
Use The SAT Essay Rubric To...Shape Your Essays
Since you know what the SAT is looking for in an essay, you can now use that knowledge to guide what you write about in your essays!
A tale from my youth: when I was preparing to take the SAT for the first time, I did not really know what the essay was looking for, and assumed that since I was a good writer, I’d be fine.
Not true! The most important part of the SAT essay is using specific examples from the passage and explaining how they convince the reader of the author's point. By reading this article and realizing there's more to the essay than "being a strong writer," you’re already doing better than high school me.

Change the object in that girl’s left hand from a mirror to a textbook and you have a pretty good sketch of what my junior year of high school looked like.
Use The SAT Essay Rubric To...Grade Your Practice Essays
The SAT can’t exactly give you an answer key to the essay. Even when an example of an essay that scored a particular score is provided, that essay will probably use different examples than you did, make different arguments, maybe even argue different interpretations of the text...making it difficult to compare the two. The SAT essay rubric is the next best thing to an answer key for the essay - use it as a lens through which to view and assess your essay.
Of course, you don’t have the time to become an expert SAT essay grader - that’s not your job. You just have to apply the rubric as best as you can to your essays and work on fixing your weak areas . For the sentence structure, grammar, usage, and mechanics stuff I highly recommend asking a friend, teacher, or family member who is really good at (English) writing to take a look over your practice essays and point out the mistakes.
If you really want custom feedback on your practice essays from experienced essay graders, may I also suggest the PrepScholar test prep platform ? I manage the essay grading and so happen to know quite a bit about the essay part of this platform, which gives you both an essay grade and custom feedback for each essay you complete. Learn more about how it all works here .
What’s Next?
Are you so excited by this article that you want to read even more articles on the SAT essay? Of course you are. Don't worry, I’ve got you covered. Learn how to write an SAT essay step-by-step and read about the 6 types of SAT essay prompts .
Want to go even more in depth with the SAT essay? We have a complete list of past SAT essay prompts as well as tips and strategies for how to get a 12 on the SAT essay .
Still not satisfied? Maybe a five-day free trial of our very own PrepScholar test prep platform (which includes essay practice and feedback) is just what you need.
Trying to figure out whether the old or new SAT essay is better for you? Take a look at our article on the new SAT essay assignment to find out!
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Laura graduated magna cum laude from Wellesley College with a BA in Music and Psychology, and earned a Master's degree in Composition from the Longy School of Music of Bard College. She scored 99 percentile scores on the SAT and GRE and loves advising students on how to excel in high school.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
University Writing Program
- Collaborative Writing
- Writing for Metacognition
- Supporting Multilingual Writers
- Alternatives to Grading
- Making Feedback Matter
- Peer Review
- Responding to Multilingual Writers’ Texts
- Model Library
Written by Arthur Russell
Just about every discussion of rubrics begins with a caveat: writing rubrics are not a substitute for writing instruction. Rubrics are tools for communicating grading criteria and assessing student progress. Rubrics take a variety of forms, from grids to checklists , and measure a range of writing tasks, from conceptual design to sentence-level considerations.
As with any assessment tool, a rubric’s effectiveness is entirely dependent upon its design and its deployment in the classroom. Whatever form rubrics take, the criteria for assessment must be legible to all students—if students cannot decipher our rubrics, they are not useful.
When effectively integrated with writing instruction, rubrics can help instructors clarify their own expectations for written work, isolate specific elements as targets of instruction, and provide meaningful feedback and coaching to students. Well-designed rubrics will draw program learning outcomes, assignment prompts, course instruction and assessment into alignment.
Starting Points
Course rubrics vs. assignment rubrics.
Instructors may choose to use a standard rubric for evaluating all written work completed in a course. Course rubrics provide instructors and students a shared language for communicating the values and expectations of written work over the course of an entire semester. Best practices suggest that establishing grading criteria with students well in advance helps instructors compose focused, revision-oriented feedback on drafts and final papers and better coach student writers. When deploying course rubrics in writing-intensive courses, consider using them to guide peer review and self-evaluation processes with students. The more often students work with established criteria, the more likely they are to respond to and incorporate feedback in future projects.
At the same time, not every assignment needs to assess every aspect of the writing process every time. Particularly early in the semester, instructors may develop assignment-specific rubrics that target one or two standards. Prioritizing a specific learning objective or writing process in an assignment rubric allows instructors to concentrate time spent on in-class writing instruction and encourages students to develop targeted aspects of their writing processes.
Developing Evaluation Criteria
- Establish clear categories. What specific learning objectives (i.e. critical and creative thinking, inquiry and analysis) and writing processes (i.e. summary, synthesis, source analysis, argument and response) are most critical to success for each assignment?
- Establish observable and measurable criteria of success. For example, consider what counts for “clarity” in written work. For a research paper, clarity might attend to purpose: a successful paper will have a well-defined purpose (thesis, takeaway), integrate and explain evidence to support all claims, and pay careful attention to purpose, context, and audience.
- Adopt student-friendly language. When using academic terminology and discipline-specific concepts, be sure to define and discuss these concepts with students. When in doubt , VALUE rubrics are excellent models of clearly defined learning objective and distinguishing criteria.
Sticking Points: Writing Rubrics in the Disciplines
Even the most carefully planned rubrics are not self-evident. The language we have adopted for writing assessment is itself a potential obstacle to student learning and success . What we count for “clarity” or “accuracy” or “insight” in academic writing, for instance, is likely shaped by our disciplinary expectations and measured by the standards of our respective fields. What counts for “good writing” is more subjective than our rubrics may suggest. Similarly, students arrive in our courses with their own understanding and experiences of academic writing that may or may not be reflected in our assignment prompts.
Defining the terms for success with students in class and in conference will go a long way toward bridging these gaps. We might even use rubrics as conversation starters, not only as an occasion to communicate our expectations for written work, but also as an opportunity to demystify the rhetorical contexts of discipline-specific writing with students.
Helpful Resources
For a short introduction to rubric design, the Creating Rubrics guide developed by Louise Pasternack (2014) for the Center for Teaching Excellence and Innovation is an excellent resource. The step-by-step tutorials developed by North Carolina State University and DePaul Teaching Commons are especially useful for instructors preparing rubrics from scratch. On the use of rubrics for writing instruction and assignments in particular, Heidi Andrade’s “Teaching with Rubrics: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly” provides an instructive overview of the benefits and drawbacks of using rubrics. For a more in-depth introduction (with sample rubrics), Melzer and Bean’s “Using Rubrics to Develop and Apply Grading Criteria” in Engaging Ideas is essential reading.
Cited and Recommended Sources
- Andrade, Heidi Goodrich. “Teaching with Rubrics: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly.” College Teaching , vol. 53, no. 1, 2005, pp. 27–30, http://www.jstor.org/stable/27559213
- Athon, Amanda. “Designing Rubrics to Foster Students’ Diverse Language Backgrounds.” Journal of Basic Writing , vol. 38, No.1, 2019, pp. 78–103, https://doi.org/10.37514/JBW-J.2019.38.1.05
- Bennett, Cary. “Assessment Rubrics: Thinking inside the Boxes.” Learning and Teaching: The International Journal of Higher Education in the Social Sciences , vol. 9, no. 1, 2016, pp. 50–72, http://www.jstor.org/stable/24718020
- Broad, Bob. What We Really Value: Beyond Rubrics in Teaching and Assessing Writing . University Press of Colorado, 2003. https://doi-org.proxy1.library.jhu.edu/10.2307/j.ctt46nxvm
- Melzer, Dan, and John C. Bean. Engaging Ideas: The Professor’s Guide to Integrating Writing, Critical Thinking, and Active Learning in the Classroom . 3rd ed., Jossey-Bass, 2021 (esp. pp. 253-277), https://ebookcentral-proquest-com.proxy1.library.jhu.edu/lib/jhu/detail.action?docID=6632622
- Pasternack, Louise. “Creating Rubrics,” The Innovative Instructor Blog , Center for Teaching Excellence and Innovation, Johns Hopkins University, 21 Nov. 2014.
- Reynders, G., et al. “Rubrics to assess critical thinking and information processing in undergraduate STEM courses.” International Journal of STEM Education vol. 7, no. 9, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-020-00208-5
- Turley, Eric D., and Chris W. Gallagher. “On the ‘Uses’ of Rubrics: Reframing the Great Rubric Debate.” The English Journal , vol. 97, no. 4, 2008, pp. 87–92, http://www.jstor.org/stable/30047253
- Wiggins, Grant. “The Constant Danger of Sacrificing Validity to Reliability: Making Writing Assessment Serve Writers.” Assessing Writing , vol. 1, no. 1, 1994, pp. 129-139, https://doi.org/10.1016/1075-2935(94)90008-6
Essay Rubric

About this printout
This rubric delineates specific expectations about an essay assignment to students and provides a means of assessing completed student essays.
Teaching with this printout
More ideas to try.
Grading rubrics can be of great benefit to both you and your students. For you, a rubric saves time and decreases subjectivity. Specific criteria are explicitly stated, facilitating the grading process and increasing your objectivity. For students, the use of grading rubrics helps them to meet or exceed expectations, to view the grading process as being “fair,” and to set goals for future learning. In order to help your students meet or exceed expectations of the assignment, be sure to discuss the rubric with your students when you assign an essay. It is helpful to show them examples of written pieces that meet and do not meet the expectations. As an added benefit, because the criteria are explicitly stated, the use of the rubric decreases the likelihood that students will argue about the grade they receive. The explicitness of the expectations helps students know exactly why they lost points on the assignment and aids them in setting goals for future improvement.
- Routinely have students score peers’ essays using the rubric as the assessment tool. This increases their level of awareness of the traits that distinguish successful essays from those that fail to meet the criteria. Have peer editors use the Reviewer’s Comments section to add any praise, constructive criticism, or questions.
- Alter some expectations or add additional traits on the rubric as needed. Students’ needs may necessitate making more rigorous criteria for advanced learners or less stringent guidelines for younger or special needs students. Furthermore, the content area for which the essay is written may require some alterations to the rubric. In social studies, for example, an essay about geographical landforms and their effect on the culture of a region might necessitate additional criteria about the use of specific terminology.
- After you and your students have used the rubric, have them work in groups to make suggested alterations to the rubric to more precisely match their needs or the parameters of a particular writing assignment.
- Print this resource
Explore Resources by Grade
- Kindergarten K

- Houston Community College
- Eagle Online

- Nicole Antoine
Essay Writing Rubric
Essay Writing Assignment Scoring Rubric ( 100 points possible )
| ( points possible) |
|
|
| II. Method of organization is well-suited to topic |
| (50 points possible) Too much information distracts the focus of the paper Essay does not address assignment prompt |
|
|
| IV. Examples in essay are ample support for thesis Examples in essay need more support for thesis |
|
|
| V. Examples are specific and concrete. Examples are somewhat nonspecific and/or abstract. |
|
|
| VI. Interest level of essay is superior. |
|
|
| VII. Introduction and conclusion are interesting and balanced. |
| (30 points possible) |
|
|
| IX. Essay exhibits correct spelling. |
|
|
| X. Essay is written in appropriate point of view and format. Point of view and format are inappropriate for essay. |
Eberly Center
Teaching excellence & educational innovation, grading and performance rubrics, what are rubrics.
A rubric is a scoring tool that explicitly represents the performance expectations for an assignment or piece of work. A rubric divides the assigned work into component parts and provides clear descriptions of the characteristics of the work associated with each component, at varying levels of mastery. Rubrics can be used for a wide array of assignments: papers, projects, oral presentations, artistic performances, group projects, etc. Rubrics can be used as scoring or grading guides, to provide formative feedback to support and guide ongoing learning efforts, or both.
Advantages of Using Rubrics
Using a rubric provides several advantages to both instructors and students. Grading according to an explicit and descriptive set of criteria that is designed to reflect the weighted importance of the objectives of the assignment helps ensure that the instructor’s grading standards don’t change over time. Grading consistency is difficult to maintain over time because of fatigue, shifting standards based on prior experience, or intrusion of other criteria. Furthermore, rubrics can reduce the time spent grading by reducing uncertainty and by allowing instructors to refer to the rubric description associated with a score rather than having to write long comments. Finally, grading rubrics are invaluable in large courses that have multiple graders (other instructors, teaching assistants, etc.) because they can help ensure consistency across graders and reduce the systematic bias that can be introduced between graders.
Used more formatively, rubrics can help instructors get a clearer picture of the strengths and weaknesses of their class. By recording the component scores and tallying up the number of students scoring below an acceptable level on each component, instructors can identify those skills or concepts that need more instructional time and student effort.
Grading rubrics are also valuable to students. A rubric can help instructors communicate to students the specific requirements and acceptable performance standards of an assignment. When rubrics are given to students with the assignment description, they can help students monitor and assess their progress as they work toward clearly indicated goals. When assignments are scored and returned with the rubric, students can more easily recognize the strengths and weaknesses of their work and direct their efforts accordingly.
Examples of Rubrics
Here are links to a diverse set of rubrics designed by Carnegie Mellon faculty and faculty at other institutions. Although your particular field of study and type of assessment activity may not be represented currently, viewing a rubric that is designed for a similar activity may provide you with ideas on how to divide your task into components and how to describe the varying levels of mastery.
Paper Assignments
- Example 1: Philosophy Paper This rubric was designed for student papers in a range of philosophy courses, CMU.
- Example 2: Psychology Assignment Short, concept application homework assignment in cognitive psychology, CMU.
- Example 3: Anthropology Writing Assignments This rubric was designed for a series of short writing assignments in anthropology, CMU.
- Example 4: History Research Paper . This rubric was designed for essays and research papers in history, CMU.
- Example 1: Capstone Project in Design This rubric describes the components and standard of performance from the research phase to the final presentation for a senior capstone project in the School of Design, CMU.
- Example 2: Engineering Design Project This rubric describes performance standards on three aspects of a team project: Research and Design, Communication, and Team Work.
Oral Presentations
- Example 1: Oral Exam This rubric describes a set of components and standards for assessing performance on an oral exam in an upper-division history course, CMU.
- Example 2: Oral Communication
- Example 3: Group Presentations This rubric describes a set of components and standards for assessing group presentations in a history course, CMU.
Class Participation/Contributions
- Example 1: Discussion Class This rubric assesses the quality of student contributions to class discussions. This is appropriate for an undergraduate-level course, CMU.
- Example 2: Advanced Seminar This rubric is designed for assessing discussion performance in an advanced undergraduate or graduate seminar.
Essay Rubric: Grading Students Correctly
- Icon Calendar 10 July 2024
- Icon Page 2897 words
- Icon Clock 14 min read
Lectures and tutors provide specific requirements for students to meet when writing essays. Basically, an essay rubric helps tutors to analyze an overall quality of compositions written by students. In this case, a rubric refers to a scoring guide used to evaluate performance based on a set of criteria and standards. As such, useful marking schemes make an analysis process simple for lecturers as they focus on specific concepts related to a writing process. Moreover, an assessment table lists and organizes all of the criteria into one convenient paper. In other instances, students use assessment tables to enhance their writing skills by examining various requirements. Then, different types of essay rubrics vary from one educational level to another. Essentially, Master’s and Ph.D. grading schemes focus on examining complex thesis statements and other writing mechanics. However, high school evaluation tables examine basic writing concepts. In turn, guidelines on a common format for writing a good essay rubric and corresponding examples provided in this article can help students to evaluate their papers before submitting them to their teachers.
General Aspects
An essay rubric refers to a way for teachers to assess students’ composition writing skills and abilities. Basically, an evaluation scheme provides specific criteria to grade assignments. Moreover, the three basic elements of an essay rubric are criteria, performance levels, and descriptors. In this case, teachers use assessment guidelines to save time when evaluating and grading various papers. Hence, learners must use an essay rubric effectively to achieve desired goals and grades, while its general example is:
What Is an Essay Rubric and Its Purpose
According to its definition, an essay rubric is a structured evaluation tool that educators use to grade students’ compositions in a fair and consistent manner. The main purpose of an essay rubric in writing is to ensure consistent and fair grading by clearly defining what constitutes excellent, good, average, and poor performance (DeVries, 2023). This tool specifies a key criteria for grading various aspects of a written text, including a clarity of a thesis statement, an overall quality of a main argument, an organization of ideas, a particular use of evidence, and a correctness of grammar and mechanics. Moreover, an assessment grading helps students to understand their strengths to be proud of and weaknesses to be pointed out and guides them in improving their writing skills (Taylor et al., 2024). For teachers, such an assessment simplifies a grading process, making it more efficient and less subjective by providing a clear standard to follow. By using an essay rubric, both teachers and students can engage in a transparent, structured, and constructive evaluation process, enhancing an overall educational experience (Stevens & Levi, 2023). In turn, the length of an essay rubric depends on academic levels, types of papers, and specific requirements, while general guidelines are:
High School
- Length: 1-2 pages
- Word Count: 300-600 words
- Length: 1-3 pages
- Word Count: 300-900 words
University (Undergraduate)
- Length: 2-4 pages
- Word Count: 600-1,200 words
Master’s
- Length: 2-5 pages
- Word Count: 600-1,500 words
- Length: 3-6 pages
- Word Count: 900-1,800 words

| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Thesis Statement | A well-defined thesis statement is crucial as it sets a particular direction and purpose of an essay, making it clear what a writer intends to argue or explain. |
| Introduction | An introduction captures a reader’s interest and provides a framework for what a paper will cover, setting up a stage for arguments or ideas that follow after an opening paragraph. |
| Content | High-quality content demonstrates thorough understanding and research on a specific topic, providing valuable and relevant information that supports a thesis. |
| Organization | Effective organization ensures author’s ideas are presented in a clear, well-structure, and logical order, enhancing readability and an overall flow of a central argument. |
| Evidence and Support | Providing strong evidence and detailed analysis is essential for backing up main arguments, adding credibility and depth to a final document. |
| Conclusion | A strong conclusion ties all the main numbers together, reflects on potential implications of arguments, and reinforces a thesis, leaving a lasting impression on a reader. |
| Grammar and Mechanics | Proper grammar, spelling, and punctuation are vital for clarity and professionalism, making a whole text easy to read and understand. |
| Style and Tone | Correctness in writing style and author’s tone appropriate to a paper’s purpose and audience enhances an overall effectiveness of a particular text and engages a reader. |
| Citations and References | Accurate and complete citations and references are crucial for giving credit to sources, avoiding plagiarism, and allowing readers to follow up on the research. |
Note: Some elements of an essay rubric can be added, deled, or combined with each other because different types of papers, their requirements, and instructors’ choices affect a final assessment. To format an essay rubric, people create a table with criteria listed in rows, performance levels in columns, and detailed descriptors in each cell explaining principal expectations for each level of performance (Steven & Levi, 2023). Besides, the five main criteria in a rubric are thesis statement, content, organization, evidence and support, and grammar and mechanics. In turn, a good essay rubric is clear, specific, aligned with learning objectives, and provides detailed, consistent descriptors for each performance level.
Steps How to Write an Essay Rubric
In writing, the key elements of an essay rubric are clear criteria, defined performance levels, and detailed descriptors for each evaluation.
- Identify a Specific Purpose and Goals: Determine main objectives of an essay’s assignment and consider what skills and knowledge you want students to demonstrate.
- List a Key Criteria: Identify essential components that need to be evaluated, such as thesis statement, introduction, content, organization, evidence and support, conclusion, grammar and mechanics, writing style and tone, and citations and references.
- Define Performance Levels: Decide on a particular scale you will use to measure performance (e.g., Excellent, Good, Fair, Poor) and ensure each level is distinct and clearly defined.
- Create Descriptors for Each Criterion: Write detailed descriptions for what constitutes each level of performance for every criterion and be specific about what is expected at each level to avoid misunderstanding.
- Assign Number Values: Determine a specific range for each criterion and performance level and allocate numbers in a way that reflects an actual importance of each criterion in an overall assessment.
- Review and Revise: Examine a complete rubric to ensure it is comprehensive and clear and adjust any descriptions or number values that seem unclear or disproportionate.
- Test a Working Essay Rubric: Apply a grading scheme to a few sample compositions to see if it effectively differentiates between different levels of performance and make adjustments as necessary.
- Involve Peers for Feedback: Share marking criteria with colleagues or peers for feedback and insights on clarity and fairness that you might have overlooked.
- Provide Examples: Include examples of complete papers or writing excerpts at each performance level and help students to understand what is expected for grading.
- Communicate With Students: Share a complete rubric with students before they begin an assignment and explain each criterion and performance level so they understand how their work will be evaluated and what they need to do to achieve highest marks.
Essay Rubric Example
Organization
Excellent/8 points: A submitted essay contains stiff topic sentences and a controlled organization.
Very Good/6 points: A paper contains a logical and appropriate organization. An author uses clear topic sentences.
Average/4 points: A composition contains a logical and appropriate organization. An author uses clear topic sentences.
Needs Improvement/2 points: A provided text has an inconsistent organization.
Unacceptable/0 (zero): A complete document shows an absence of a planned organization.
Grade: ___ .
Excellent/8 points: A submitted essay shows the absence of a planned organization.
Very Good/6 points: A paper contains precise and varied sentence structures and word choices.
Average/4 points: A composition follows a limited but mostly correct sentence structure. There are different sentence structures and word choices.
Needs Improvement/2 points: A provided text contains several awkward and unclear sentences. There are some problems with word choices.
Unacceptable/0 (zero): An author does not have apparent control over sentence structures and word choice.
Excellent/8 points: An essay’s content appears sophisticated and contains well-developed ideas.
Very Good/6 points: A paper’s content appears illustrative and balanced.
Average/4 points: A composition contains unbalanced content that requires more analysis.
Needs Improvement/2 points: A provided text contains a lot of research information without analysis or commentary.
Unacceptable/0 (zero): A complete document lacks relevant content and does not fit the thesis statement. Essay rubric rules are not followed.
Excellent/8 points: A submitted essay contains a clearly stated and focused thesis statement.
Very Good/6 points: A paper comprises a clearly stated argument. However, a particular focus would have been sharper.
Average/4 points: A thesis statement phrasing sounds simple and lacks complexity. An author does not word the thesis correctly.
Needs Improvement/2 points: A thesis statement requires a clear objective and does not fit the theme in a paper’s content.
Unacceptable/0 (zero): A thesis statement is not evident in an introduction paragraph.
Excellent/8 points: A submitted is clear and focused. An overall work holds a reader’s attention. Besides, relevant details and quotes enrich a thesis statement.
Very Good/6 points: A paper is mostly focused and contains a few useful details and quotes.
Average/4 points: An author begins a composition by defining an assigned topic. However, a particular development of ideas appears general.
Needs Improvement/2 points: An author fails to define an assigned topic well or focuses on several issues.
Unacceptable/0 (zero): A complete document lacks a clear sense of a purpose or thesis statement. Readers have to make suggestions based on sketchy or missing ideas to understand an intended meaning. Essay rubric requirements are missed.
Sentence Fluency
Excellent/8 points: A submitted essay has a natural flow, rhythm, and cadence. Its sentences are well-built and have a wide-ranging and robust structure that enhances reading.
Very Good/6 points: Presented ideas mostly flow and motivate a compelling reading.
Average/4 points: A composition hums along with a balanced beat but tends to be more businesslike than musical. Besides, a particular flow of ideas tends to become more mechanical than fluid.
Needs Improvement/2 points: A provided text appears irregular and hard to read.
Unacceptable/0 (zero): Readers have to go through a complete document several times to give this paper a fair interpretive reading.
Conventions
Excellent/8 points: An author demonstrates proper use of standard writing conventions, like spelling, punctuation, capitalization, grammar, usage, and paragraphing. A person also uses correct protocols in a way that improves an overall readability of an essay.
Very Good/6 points: An author demonstrates proper writing conventions and uses them correctly. One can read a paper with ease, and errors are rare. Few touch-ups can make a submitted composition ready for publishing.
Average/4 points: An author shows reasonable control over a short range of standard writing rules. A person also handles all the conventions and enhances readability. Writing errors in a presented composition tend to distract and impair legibility.
Needs Improvement/2 points: An author makes an effort to use various conventions, including spelling, punctuation, capitalization, grammar usage, and paragraphing. A provided text contains multiple errors.
Unacceptable/0 (zero): An author makes repetitive errors in spelling, punctuation, capitalization, grammar, usage, and paragraphing. Some mistakes distract readers and make it hard to understand discussed concepts. Essay rubric rules are not covered.
Presentation
Excellent/8 points: A particular form and presentation of a text enhance an overall readability of an essay and its flow of ideas.
Very Good/6 points: A chosen format has few mistakes and is easy to read.
Average/4 points: An author’s message is understandable in this format.
Needs Improvement/2 points: An author’s message is only comprehensible infrequently, and a provided text appears disorganized.
Unacceptable/0 (zero): Readers receive a distorted message due to difficulties connecting to a presentation of an entire text.
Final Grade: ___ .
Grading Scheme
- A+ = 60+ points
- F = less than 9
Differences in Education Levels
An overall quality of various types of texts changes at different education levels. In writing, an essay rubric works by providing a structured framework with specific criteria and performance levels to consistently evaluate and grade a finished paper. For instance, college students must write miscellaneous papers when compared to high school learners (Harrington et al., 2021). In this case, assessment criteria will change for these different education levels. For example, university and college compositions should have a debatable thesis statement with varying points of view (Mewburn et al., 2021). However, high school compositions should have simple phrases as thesis statements. Then, other requirements in a marking rubric will be more straightforward for high school students (DeVries, 2023). For Master’s and Ph.D. works, a writing criteria presented in a scoring evaluation should focus on examining a paper’s complexity. In turn, compositions for these two categories should have thesis statements that demonstrate a detailed analysis of defined topics that advance knowledge in a specific area of study.
Recommendations
When observing any essay rubric, people should remember to ensure clarity and specificity in each criterion and performance level. This clarity helps both an evaluator and a student to understand principal expectations and how a written document will be assessed (Ozfidan & Mitchell, 2022). Consistency in language and terminology across an essay rubric is crucial to avoid confusion and maintain fairness. Further on, it is essential to align a working scheme with learning objectives and goals of an essay’s assignment, ensuring all key components, such as thesis, content, organization, and grammar, are covered comprehensively (Stevens & Levi, 2023). Evaluators should also be aware of the weighting and scoring distribution, making sure they accurately reflect an actual importance of each criterion. Moreover, testing a rubric on sample essays before finalizing it can help to identify any mistakes or imbalances in scores. Essentially, providing concrete examples or descriptions for each performance level can guide students in understanding what is expected for each grade (Taylor et al., 2024). In turn, an essay rubric should be reviewed, revised, and updated after each educational year to remain relevant and aligned with current academic standards. Lastly, sharing and explaining grading assessment with students before they start their composition fosters transparency and helps them to put more of their efforts into meeting defined criteria, ultimately improving their writing and learning experience in general.
Common Mistakes
- Lack of Specificity: Descriptions for each criterion and performance level are too vague, leading to ambiguity and confusion for both graders and students.
- Overcomplicating a Rubric: Including too many criteria or overly complex descriptions that make a scoring assessment difficult to use effectively.
- Unbalanced Weighting: Assigning disproportionate number values to different criteria, which can mislead an overall assessment and not accurately reflect an actual importance of each component.
- Inconsistent Language: Using inconsistent terminology or descriptors across performance levels, which can confuse users and make a rubric less reliable.
- Not Aligning With Objectives: Failing to align a particular criteria and performance levels with specific goals and learning outcomes of an assignment.
- Omitting Key Components: Leaving out important criteria that are essential for evaluating a paper comprehensively, such as citations or a conclusion part.
- Lack of Examples: Not providing examples or concrete descriptions of what constitutes each performance level, making it harder for students to understand expectations.
- Ignoring Grammar and Mechanics: Overlooking an actual importance of grammar, spelling, and punctuation, which are crucial for clear and professional writing.
- Not Updating an Essay Rubric: Using outdated rubrics that do not reflect current educational standards or specific assignment needs.
- Insufficient Testing: Failing to test a grading scheme on some sample documents to ensure it effectively differentiates between levels of performance and provides fair assessments.
Essay rubrics help teachers, instructors, professors, and tutors to analyze an overall quality of compositions written by students. Basically, an assessment scheme makes an analysis process simple for lecturers, and it lists and organizes all of the criteria into one convenient paper. In other instances, students use such evaluation tools to improve their writing skills. However, they vary from one educational level to the other. Master’s and Ph.D. assessment schemes focus on examining complex thesis statements and other writing mechanics. However, high school grading criteria examine basic writing concepts. As such, the following are some of the tips that one must consider when preparing any rubric.
- Include all mechanics that relate to essay writing.
- Cover different requirements and their relevant grades.
- Follow clear and understandable statements.
DeVries, B. A. (2023). Literacy assessment and intervention for classroom teachers . Routledge.
Harrington, E. R., Lofgren, I. E., Gottschalk Druschke, C., Karraker, N. E., Reynolds, N., & McWilliams, S. R. (2021). Training graduate students in multiple genres of public and academic science writing: An assessment using an adaptable, interdisciplinary rubric. Frontiers in Environmental Science , 9 , 1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2021.715409
Mewburn, I., Firth, K., & Lehmann, S. (2021). Level up your essays: How to get better grades at university . NewSouth.
Ozfidan, B., & Mitchell, C. (2022). Assessment of students’ argumentative writing: A rubric development. Journal of Ethnic and Cultural Studies , 9 (2), 121–133. https://doi.org/10.29333/ejecs/1064
Stevens, D. D., & Levi, A. (2023). Introduction to rubrics: An assessment tool to save grading time, convey effective feedback, and promote student learning . Routledge, Taylor & Francis Group.
Taylor, B., Kisby, F., & Reedy, A. (2024). Rubrics in higher education: An exploration of undergraduate students’ understanding and perspectives. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education , 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2023.2299330
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles

How to Cite a Newspaper Article in APA 7 With Examples
- Icon Calendar 12 October 2020
- Icon Page 754 words

"Who Am I" Essay Examples & Student Guidelines
- Icon Calendar 10 October 2020
- Icon Page 5309 words
Rubric Design
Main navigation, articulating your assessment values.
Reading, commenting on, and then assigning a grade to a piece of student writing requires intense attention and difficult judgment calls. Some faculty dread “the stack.” Students may share the faculty’s dim view of writing assessment, perceiving it as highly subjective. They wonder why one faculty member values evidence and correctness before all else, while another seeks a vaguely defined originality.
Writing rubrics can help address the concerns of both faculty and students by making writing assessment more efficient, consistent, and public. Whether it is called a grading rubric, a grading sheet, or a scoring guide, a writing assignment rubric lists criteria by which the writing is graded.
Why create a writing rubric?
- It makes your tacit rhetorical knowledge explicit
- It articulates community- and discipline-specific standards of excellence
- It links the grade you give the assignment to the criteria
- It can make your grading more efficient, consistent, and fair as you can read and comment with your criteria in mind
- It can help you reverse engineer your course: once you have the rubrics created, you can align your readings, activities, and lectures with the rubrics to set your students up for success
- It can help your students produce writing that you look forward to reading
How to create a writing rubric
Create a rubric at the same time you create the assignment. It will help you explain to the students what your goals are for the assignment.
- Consider your purpose: do you need a rubric that addresses the standards for all the writing in the course? Or do you need to address the writing requirements and standards for just one assignment? Task-specific rubrics are written to help teachers assess individual assignments or genres, whereas generic rubrics are written to help teachers assess multiple assignments.
- Begin by listing the important qualities of the writing that will be produced in response to a particular assignment. It may be helpful to have several examples of excellent versions of the assignment in front of you: what writing elements do they all have in common? Among other things, these may include features of the argument, such as a main claim or thesis; use and presentation of sources, including visuals; and formatting guidelines such as the requirement of a works cited.
- Then consider how the criteria will be weighted in grading. Perhaps all criteria are equally important, or perhaps there are two or three that all students must achieve to earn a passing grade. Decide what best fits the class and requirements of the assignment.
Consider involving students in Steps 2 and 3. A class session devoted to developing a rubric can provoke many important discussions about the ways the features of the language serve the purpose of the writing. And when students themselves work to describe the writing they are expected to produce, they are more likely to achieve it.
At this point, you will need to decide if you want to create a holistic or an analytic rubric. There is much debate about these two approaches to assessment.
Comparing Holistic and Analytic Rubrics
Holistic scoring .
Holistic scoring aims to rate overall proficiency in a given student writing sample. It is often used in large-scale writing program assessment and impromptu classroom writing for diagnostic purposes.
General tenets to holistic scoring:
- Responding to drafts is part of evaluation
- Responses do not focus on grammar and mechanics during drafting and there is little correction
- Marginal comments are kept to 2-3 per page with summative comments at end
- End commentary attends to students’ overall performance across learning objectives as articulated in the assignment
- Response language aims to foster students’ self-assessment
Holistic rubrics emphasize what students do well and generally increase efficiency; they may also be more valid because scoring includes authentic, personal reaction of the reader. But holistic sores won’t tell a student how they’ve progressed relative to previous assignments and may be rater-dependent, reducing reliability. (For a summary of advantages and disadvantages of holistic scoring, see Becker, 2011, p. 116.)
Here is an example of a partial holistic rubric:
Summary meets all the criteria. The writer understands the article thoroughly. The main points in the article appear in the summary with all main points proportionately developed. The summary should be as comprehensive as possible and should be as comprehensive as possible and should read smoothly, with appropriate transitions between ideas. Sentences should be clear, without vagueness or ambiguity and without grammatical or mechanical errors.
A complete holistic rubric for a research paper (authored by Jonah Willihnganz) can be downloaded here.
Analytic Scoring
Analytic scoring makes explicit the contribution to the final grade of each element of writing. For example, an instructor may choose to give 30 points for an essay whose ideas are sufficiently complex, that marshals good reasons in support of a thesis, and whose argument is logical; and 20 points for well-constructed sentences and careful copy editing.
General tenets to analytic scoring:
- Reflect emphases in your teaching and communicate the learning goals for the course
- Emphasize student performance across criterion, which are established as central to the assignment in advance, usually on an assignment sheet
- Typically take a quantitative approach, providing a scaled set of points for each criterion
- Make the analytic framework available to students before they write
Advantages of an analytic rubric include ease of training raters and improved reliability. Meanwhile, writers often can more easily diagnose the strengths and weaknesses of their work. But analytic rubrics can be time-consuming to produce, and raters may judge the writing holistically anyway. Moreover, many readers believe that writing traits cannot be separated. (For a summary of the advantages and disadvantages of analytic scoring, see Becker, 2011, p. 115.)
For example, a partial analytic rubric for a single trait, “addresses a significant issue”:
- Excellent: Elegantly establishes the current problem, why it matters, to whom
- Above Average: Identifies the problem; explains why it matters and to whom
- Competent: Describes topic but relevance unclear or cursory
- Developing: Unclear issue and relevance
A complete analytic rubric for a research paper can be downloaded here. In WIM courses, this language should be revised to name specific disciplinary conventions.
Whichever type of rubric you write, your goal is to avoid pushing students into prescriptive formulas and limiting thinking (e.g., “each paragraph has five sentences”). By carefully describing the writing you want to read, you give students a clear target, and, as Ed White puts it, “describe the ongoing work of the class” (75).
Writing rubrics contribute meaningfully to the teaching of writing. Think of them as a coaching aide. In class and in conferences, you can use the language of the rubric to help you move past generic statements about what makes good writing good to statements about what constitutes success on the assignment and in the genre or discourse community. The rubric articulates what you are asking students to produce on the page; once that work is accomplished, you can turn your attention to explaining how students can achieve it.
Works Cited
Becker, Anthony. “Examining Rubrics Used to Measure Writing Performance in U.S. Intensive English Programs.” The CATESOL Journal 22.1 (2010/2011):113-30. Web.
White, Edward M. Teaching and Assessing Writing . Proquest Info and Learning, 1985. Print.
Further Resources
CCCC Committee on Assessment. “Writing Assessment: A Position Statement.” November 2006 (Revised March 2009). Conference on College Composition and Communication. Web.
Gallagher, Chris W. “Assess Locally, Validate Globally: Heuristics for Validating Local Writing Assessments.” Writing Program Administration 34.1 (2010): 10-32. Web.
Huot, Brian. (Re)Articulating Writing Assessment for Teaching and Learning. Logan: Utah State UP, 2002. Print.
Kelly-Reilly, Diane, and Peggy O’Neil, eds. Journal of Writing Assessment. Web.
McKee, Heidi A., and Dànielle Nicole DeVoss DeVoss, Eds. Digital Writing Assessment & Evaluation. Logan, UT: Computers and Composition Digital Press/Utah State University Press, 2013. Web.
O’Neill, Peggy, Cindy Moore, and Brian Huot. A Guide to College Writing Assessment . Logan: Utah State UP, 2009. Print.
Sommers, Nancy. Responding to Student Writers . Macmillan Higher Education, 2013.
Straub, Richard. “Responding, Really Responding to Other Students’ Writing.” The Subject is Writing: Essays by Teachers and Students. Ed. Wendy Bishop. Boynton/Cook, 1999. Web.
White, Edward M., and Cassie A. Wright. Assigning, Responding, Evaluating: A Writing Teacher’s Guide . 5th ed. Bedford/St. Martin’s, 2015. Print.
- Units and Programs
Make a Gift
Rubrics & Checklists
Grading criteria can be very simple or complex. They can analyze discrete elements of performance or describe general traits that define papers in a given grade range. You can use them to set up a scoring sheet for grading final drafts, and to create revision-oriented checklists to speed up commenting on early drafts of projects. By far the best way to clarify grading criteria is to look at one or more sample pieces of writing, asking students to apply the criteria, and discussing their judgments as a class.
Analytical approaches to grading
Analytical rubrics assign a specific point value to each attribute of a project (for example: thesis, evidence, logic, discussion, development, grammar, spelling, and formatting). They may be arranged graphically as grids, sliding scales, or checklists. You can weight categories to reflect issues of more or less concern, such as stressing the quality of a student’s thesis more than spelling skills. Analytical grade scales allow very detailed assessment of multi-faceted projects, but the more detailed they are, the longer they take to develop, fine-tune, and use. They also are more likely to elicit “bean-counting” responses from students, who want to know why they “lost” five points for comma splices when a fellow student was only penalized three points for spelling errors. Some instructors and students dislike what can feel like a lack of flexibility in analytical assessment.

Holistic approaches to grading
Holistic grading rubrics typically focus on larger skill sets demonstrated in the writing. They can be as detailed or as general as you like. Ideally, the descriptions will use specific language, but not overload students with information. Assigning holistic grades often speeds up the grading process, and many instructors feel holistic grades best reflect the inseparability of mechanics and ideas. But without good performance level descriptions, holistic grades can frustrate students, because they don’t convey a lot of information.
Creating your own criteria
Analytical and holistic elements can be combined in a single set of grading criteria. Use the arrangement that best fits the way you think as you are grading, and makes the most sense in terms of the particular assignment you are creating.
Also, when writing the criteria, use language that reflects your strengths and the way you grade. If you don’t have an encyclopedic knowledge of grammar errors, judge a paper’s “coherence and readability” rather than “number of sentence boundary errors.”
Here we have collected samples of grading criteria, checklists, and rubrics developed by writing instructors in different fields. We will be adding to this list fairly regularly, but of there is a specific type of rubric you would like to see that we have not yet added, please contact our office.
Rough Draft Revision Checklist This checklist for providing comments on students’ early drafts of writing projects was designed for a causal analysis paper in a freshman-level composition course. It analyzes the draft across four performance areas: Claim or thesis, logic and reasoning, support and development, and organization and mechanics. The weaknesses most commonly seen in causal draft papers are described, with additional space left for comments in each section (the additional spaces are ideal for noting a draft’s strengths).
Holistic Grading Criteria These criteria were developed by Dr. David Barndollar for a sophomore-level English course. Here, the descriptions are grouped by grade performance level (A, B, C, D, and F) with the same five concerns addressed at each level: quality of ideas, development and organization, language and word choice, mechanics, and style.
Analytical Grading Outline This grade sheet is adapted from one devised by Dr. Ruth Franks for a long research paper in her Biology 325L class. This highly-detailed rubric apportions 300 points for various performance categories. Dr. Franks was the winner of the 2003-3004 SWC Award for Writing Instruction.
Scaled Analytical Rubric This very simple grade sheet was used by Dr. Susan Schorn for giving final grades on short papers in a rhetoric class. General performance descriptors are scaled to the point range for each criterion. The criteria on this grade sheet are not described here, but they map to more extensive criteria students received in the course syllabus and paper assignment. Note that space is left under each criterion for instructor comments.
Grading Grid Dr. Joanna Migrock devised a criteria grid or table for assessing all assignments in a first-year composition class. Five performance areas are delineated: Purpose, Content, Audience, Organization, and Mechanics. Four performance levels are then described for each area. This grid could be used as is to give revision-oriented feedback on drafts; with the addition of grade weightings at each performance level, it could also be used to grade final drafts.
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Win a $500 Oriental Trading Gift Card ✨
15 Helpful Scoring Rubric Examples for All Grades and Subjects
In the end, they actually make grading easier.

When it comes to student assessment and evaluation, there are a lot of methods to consider. In some cases, testing is the best way to assess a student’s knowledge, and the answers are either right or wrong. But often, assessing a student’s performance is much less clear-cut. In these situations, a scoring rubric is often the way to go, especially if you’re using standards-based grading . Here’s what you need to know about this useful tool, along with lots of rubric examples to get you started.
What is a scoring rubric?
In the United States, a rubric is a guide that lays out the performance expectations for an assignment. It helps students understand what’s required of them, and guides teachers through the evaluation process. (Note that in other countries, the term “rubric” may instead refer to the set of instructions at the beginning of an exam. To avoid confusion, some people use the term “scoring rubric” instead.)
A rubric generally has three parts:
- Performance criteria: These are the various aspects on which the assignment will be evaluated. They should align with the desired learning outcomes for the assignment.
- Rating scale: This could be a number system (often 1 to 4) or words like “exceeds expectations, meets expectations, below expectations,” etc.
- Indicators: These describe the qualities needed to earn a specific rating for each of the performance criteria. The level of detail may vary depending on the assignment and the purpose of the rubric itself.
Rubrics take more time to develop up front, but they help ensure more consistent assessment, especially when the skills being assessed are more subjective. A well-developed rubric can actually save teachers a lot of time when it comes to grading. What’s more, sharing your scoring rubric with students in advance often helps improve performance . This way, students have a clear picture of what’s expected of them and what they need to do to achieve a specific grade or performance rating.
Learn more about why and how to use a rubric here.
Types of Rubric
There are three basic rubric categories, each with its own purpose.
Holistic Rubric

Source: Cambrian College
This type of rubric combines all the scoring criteria in a single scale. They’re quick to create and use, but they have drawbacks. If a student’s work spans different levels, it can be difficult to decide which score to assign. They also make it harder to provide feedback on specific aspects.
Traditional letter grades are a type of holistic rubric. So are the popular “hamburger rubric” and “ cupcake rubric ” examples. Learn more about holistic rubrics here.
Analytic Rubric
Source: University of Nebraska
Analytic rubrics are much more complex and generally take a great deal more time up front to design. They include specific details of the expected learning outcomes, and descriptions of what criteria are required to meet various performance ratings in each. Each rating is assigned a point value, and the total number of points earned determines the overall grade for the assignment.
Though they’re more time-intensive to create, analytic rubrics actually save time while grading. Teachers can simply circle or highlight any relevant phrases in each rating, and add a comment or two if needed. They also help ensure consistency in grading, and make it much easier for students to understand what’s expected of them.
Learn more about analytic rubrics here.
Developmental Rubric
Source: Deb’s Data Digest
A developmental rubric is a type of analytic rubric, but it’s used to assess progress along the way rather than determining a final score on an assignment. The details in these rubrics help students understand their achievements, as well as highlight the specific skills they still need to improve.
Developmental rubrics are essentially a subset of analytic rubrics. They leave off the point values, though, and focus instead on giving feedback using the criteria and indicators of performance.
Learn how to use developmental rubrics here.
Ready to create your own rubrics? Find general tips on designing rubrics here. Then, check out these examples across all grades and subjects to inspire you.
Elementary School Rubric Examples
These elementary school rubric examples come from real teachers who use them with their students. Adapt them to fit your needs and grade level.
Reading Fluency Rubric
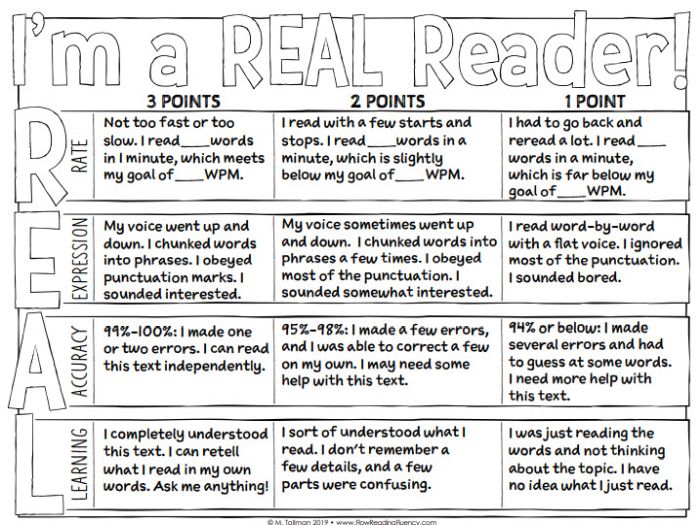
You can use this one as an analytic rubric by counting up points to earn a final score, or just to provide developmental feedback. There’s a second rubric page available specifically to assess prosody (reading with expression).
Learn more: Teacher Thrive
Reading Comprehension Rubric
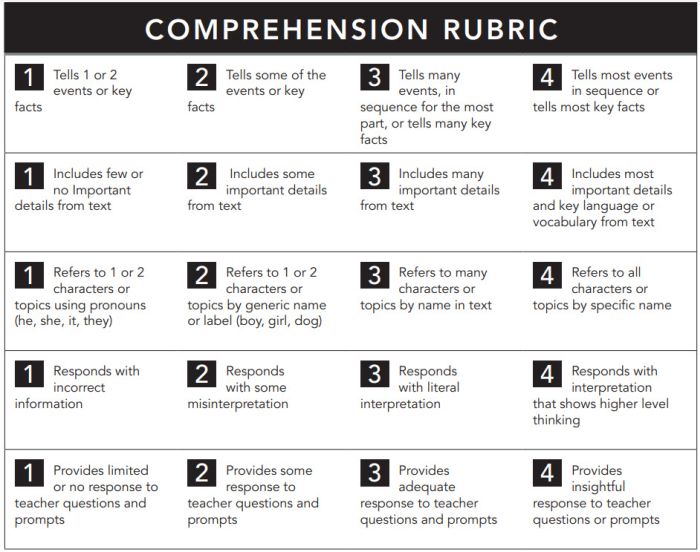
The nice thing about this rubric is that you can use it at any grade level, for any text. If you like this style, you can get a reading fluency rubric here too.
Learn more: Pawprints Resource Center
Written Response Rubric

Rubrics aren’t just for huge projects. They can also help kids work on very specific skills, like this one for improving written responses on assessments.
Learn more: Dianna Radcliffe: Teaching Upper Elementary and More
Interactive Notebook Rubric
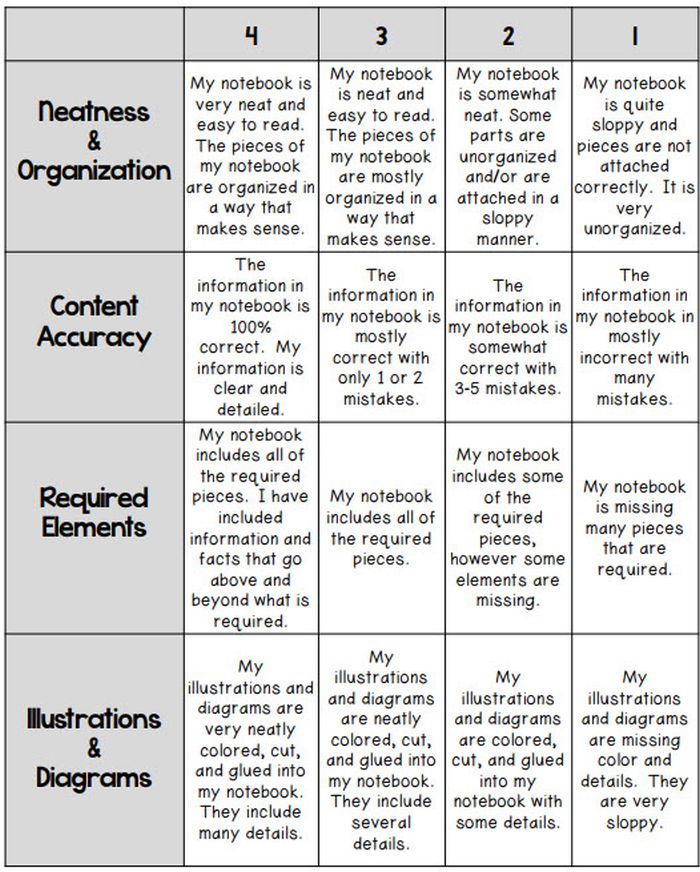
If you use interactive notebooks as a learning tool , this rubric can help kids stay on track and meet your expectations.
Learn more: Classroom Nook
Project Rubric
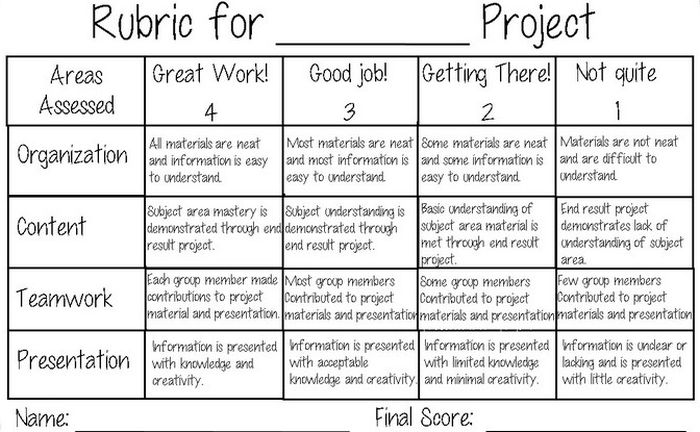
Use this simple rubric as it is, or tweak it to include more specific indicators for the project you have in mind.
Learn more: Tales of a Title One Teacher
Behavior Rubric
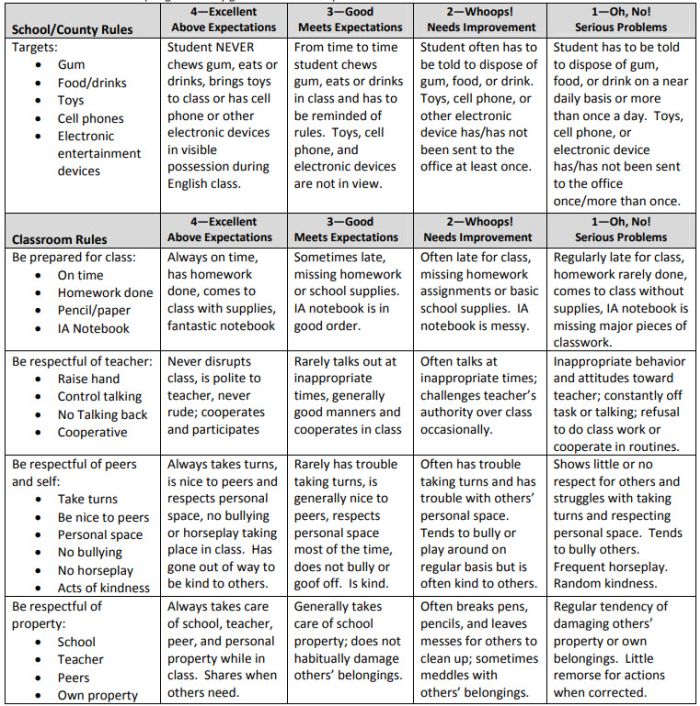
Developmental rubrics are perfect for assessing behavior and helping students identify opportunities for improvement. Send these home regularly to keep parents in the loop.
Learn more: Teachers.net Gazette
Middle School Rubric Examples
In middle school, use rubrics to offer detailed feedback on projects, presentations, and more. Be sure to share them with students in advance, and encourage them to use them as they work so they’ll know if they’re meeting expectations.
Argumentative Writing Rubric
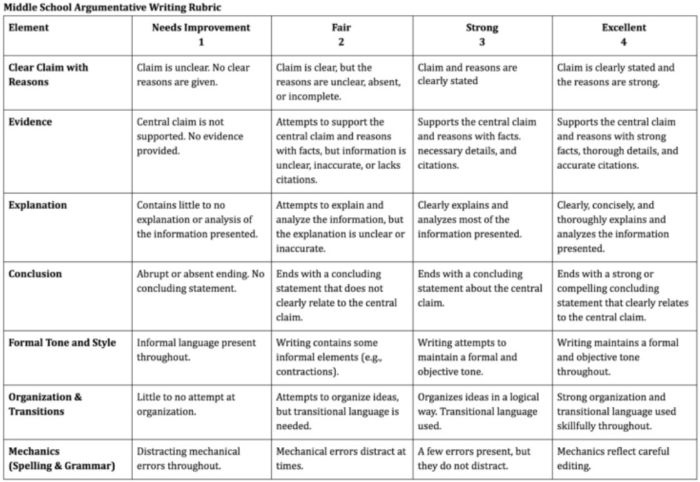
Argumentative writing is a part of language arts, social studies, science, and more. That makes this rubric especially useful.
Learn more: Dr. Caitlyn Tucker
Role-Play Rubric
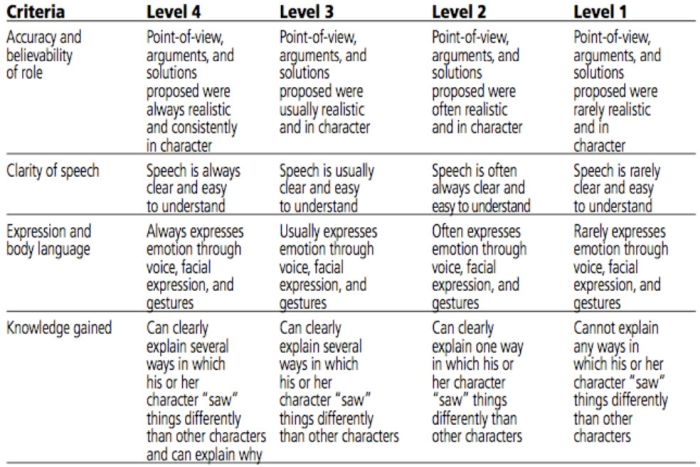
Role-plays can be really useful when teaching social and critical thinking skills, but it’s hard to assess them. Try a rubric like this one to evaluate and provide useful feedback.
Learn more: A Question of Influence
Art Project Rubric
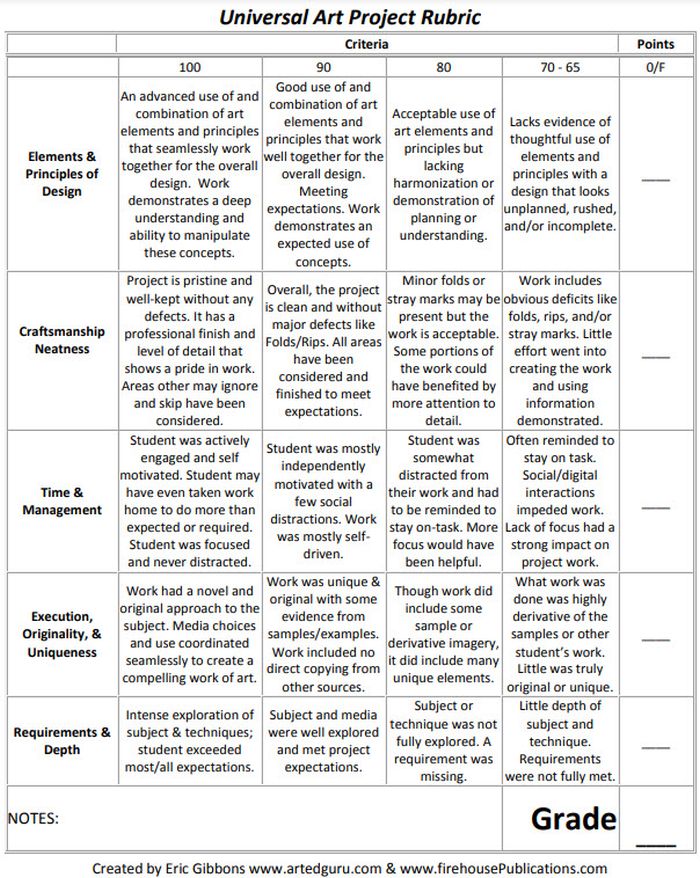
Art is one of those subjects where grading can feel very subjective. Bring some objectivity to the process with a rubric like this.
Source: Art Ed Guru
Diorama Project Rubric
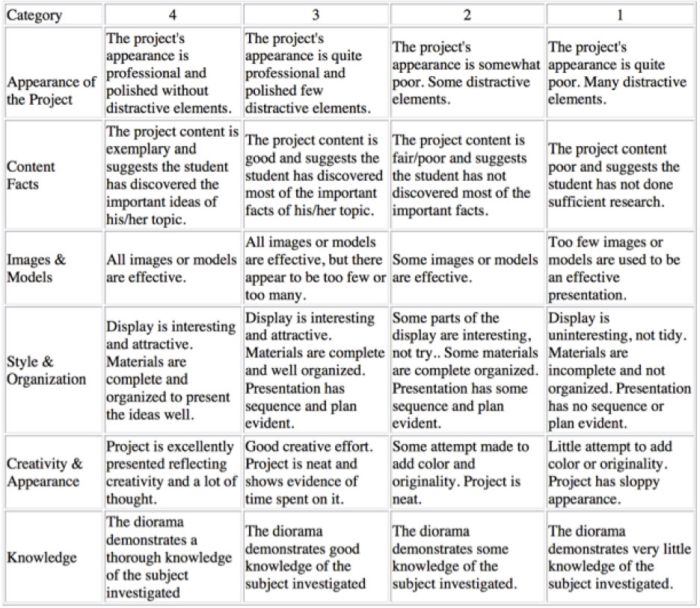
You can use diorama projects in almost any subject, and they’re a great chance to encourage creativity. Simplify the grading process and help kids know how to make their projects shine with this scoring rubric.
Learn more: Historyourstory.com
Oral Presentation Rubric
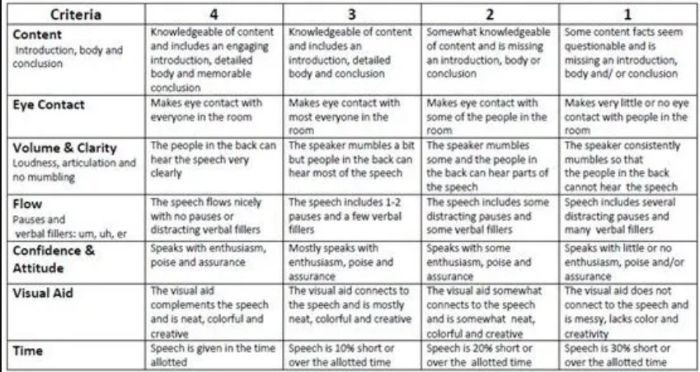
Rubrics are terrific for grading presentations, since you can include a variety of skills and other criteria. Consider letting students use a rubric like this to offer peer feedback too.
Learn more: Bright Hub Education
High School Rubric Examples
In high school, it’s important to include your grading rubrics when you give assignments like presentations, research projects, or essays. Kids who go on to college will definitely encounter rubrics, so helping them become familiar with them now will help in the future.
Presentation Rubric
Analyze a student’s presentation both for content and communication skills with a rubric like this one. If needed, create a separate one for content knowledge with even more criteria and indicators.
Learn more: Michael A. Pena Jr.
Debate Rubric
Debate is a valuable learning tool that encourages critical thinking and oral communication skills. This rubric can help you assess those skills objectively.
Learn more: Education World
Project-Based Learning Rubric
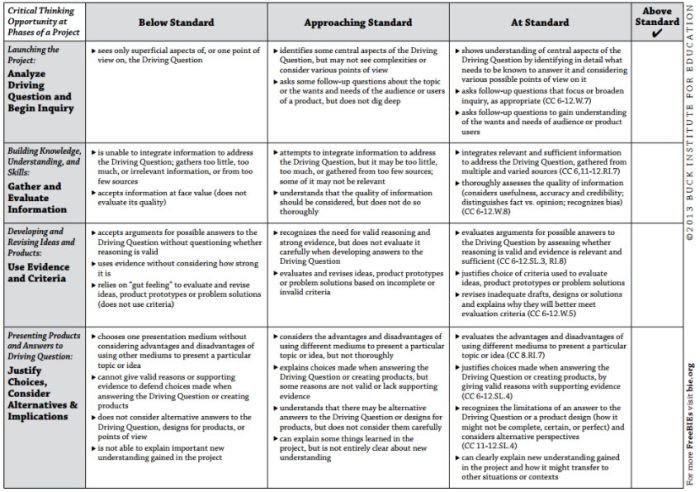
Implementing project-based learning can be time-intensive, but the payoffs are worth it. Try this rubric to make student expectations clear and end-of-project assessment easier.
Learn more: Free Technology for Teachers
100-Point Essay Rubric
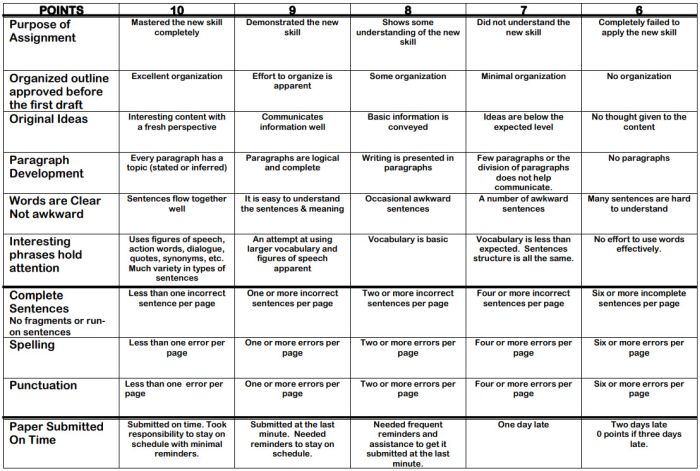
Need an easy way to convert a scoring rubric to a letter grade? This example for essay writing earns students a final score out of 100 points.
Learn more: Learn for Your Life
Drama Performance Rubric
If you’re unsure how to grade a student’s participation and performance in drama class, consider this example. It offers lots of objective criteria and indicators to evaluate.
Learn more: Chase March
How do you use rubrics in your classroom? Come share your thoughts and exchange ideas in the WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook .
Plus, 25 of the best alternative assessment ideas ..

You Might Also Like

25 Formative Assessment Options Your Students Will Actually Enjoy
Get them excited to show you what they know! Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256

- Basics for GSIs
- Advancing Your Skills
Examples of Rubric Creation
Creating a rubric takes time and requires thought and experimentation. Here you can see the steps used to create two kinds of rubric: one for problems in a physics exam for a small, upper-division physics course, and another for an essay assignment in a large, lower-division sociology course.
Physics Problems
In STEM disciplines (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics), assignments tend to be analytical and problem-based. Holistic rubrics can be an efficient, consistent, and fair way to grade a problem set. An analytical rubric often gives a more clear picture of what a student should direct their future learning efforts on. Since holistic rubrics try to label overall understanding, they can lead to more regrade requests when compared to analytical rubric with more explicit criteria. When starting to grade a problem, it is important to think about the relevant conceptual ingredients in the solution. Then look at a sample of student work to get a feel for student mistakes. Decide what rubric you will use (e.g., holistic or analytic, and how many points). Apply the holistic rubric by marking comments and sorting the students’ assignments into stacks (e.g., five stacks if using a five-point scale). Finally, check the stacks for consistency and mark the scores. The following is a sample homework problem from a UC Berkeley Physics Department undergraduate course in mechanics.
Homework Problem
Learning objective.
Solve for position and speed along a projectile’s trajectory.
Desired Traits: Conceptual Elements Needed for the Solution
- Decompose motion into vertical and horizontal axes.
- Identify that the maximum height occurs when the vertical velocity is 0.
- Apply kinematics equation with g as the acceleration to solve for the time and height.
- Evaluate the numerical expression.
A note on analytic rubrics: If you decide you feel more comfortable grading with an analytic rubric, you can assign a point value to each concept. The drawback to this method is that it can sometimes unfairly penalize a student who has a good understanding of the problem but makes a lot of minor errors. Because the analytic method tends to have many more parts, the method can take quite a bit more time to apply. In the end, your analytic rubric should give results that agree with the common-sense assessment of how well the student understood the problem. This sense is well captured by the holistic method.
Holistic Rubric
A holistic rubric, closely based on a rubric by Bruce Birkett and Andrew Elby:
| The student clearly understands how to solve the problem. Minor mistakes and careless errors can appear insofar as they do not indicate a conceptual misunderstanding. | |
| The student understands the main concepts and problem-solving techniques, but has some minor yet non-trivial gaps in their reasoning. | |
| The student has partially understood the problem. The student is not completely lost, but requires tutoring in some of the basic concepts. The student may have started out correctly, but gone on a tangent or not finished the problem. | |
| The student has a poor understanding of the problem. The student may have gone in a not-entirely-wrong but unproductive direction, or attempted to solve the problem using pattern matching or by rote. | |
| The student did not understand the problem. They may have written some appropriate formulas or diagrams, but nothing further. Or they may have done something entirely wrong. | |
| The student wrote nothing or almost nothing. |
[a] This policy especially makes sense on exam problems, for which students are under time pressure and are more likely to make harmless algebraic mistakes. It would also be reasonable to have stricter standards for homework problems.
Analytic Rubric
The following is an analytic rubric that takes the desired traits of the solution and assigns point values to each of the components. Note that the relative point values should reflect the importance in the overall problem. For example, the steps of the problem solving should be worth more than the final numerical value of the solution. This rubric also provides clarity for where students are lacking in their current understanding of the problem.
| Student decomposes the velocity (a vector quantity) into its vertical component | |
| Student realizes that the motion should be decomposed, but does not arrive at the correct expression for | |
| No attempt at decomposing the 2D motion into its vertical component. | |
| Student successfully translates the physical question (the highest point of the ball) to an equation that can be used to help solve the motion ( ). | |
| Student identifies the maximum height condition with minor mistakes. | |
| Incorrect or missing identification of maximum height condition. | |
| Applies the kinematic equations to yield a correct expression for the height in terms of the given variables. Solution uses the fact that the vertical motion has a constant downward acceleration due to gravity. The sequence of steps clearly demonstrates the thought process. Most likely, the solution includes solving for the time it takes to reach the top and then uses that time to see how far up the ball traveled. | |
| Mostly correct application with minor error (e.g. algebraic mistakes or incorporating extraneous equations). | |
| Equations include relevant parameters from the problem, but the student does not isolate relevant variables being solved for (such as time or distance). | |
| Some kinematics formulas are written down but they are not connected with the information in the problem. | |
| No attempt. | |
| Correct numerical answer with appropriate units. | |
| Mostly correct answer but with a few minor errors. Still physically sensible answer (e.g. units and numerical values are reasonable). | |
| No attempt or physically unreasonable answer (e.g. a negative maximum height or reporting the height in units of seconds). | |
Try to avoid penalizing multiple times for the same mistake by choosing your evaluation criteria to be related to distinct learning outcomes. In designing your rubric, you can decide how finely to evaluate each component. Having more possible point values on your rubric can give more detailed feedback on a student’s performance, though it typically takes more time for the grader to assess.
Of course, problems can, and often do, feature the use of multiple learning outcomes in tandem. When a mistake could be assigned to multiple criteria, it is advisable to check that the overall problem grade is reasonable with the student’s mastery of the problem. Not having to decide how particular mistakes should be deducted from the analytic rubric is one advantage of the holistic rubric. When designing problems, it can be very beneficial for students not to have problems with several subparts that rely on prior answers. These tend to disproportionately skew the grades of students who miss an ingredient early on. When possible, consider making independent problems for testing different learning outcomes.
Sociology Research Paper
An introductory-level, large-lecture course is a difficult setting for managing a student research assignment. With the assistance of an instructional support team that included a GSI teaching consultant and a UC Berkeley librarian [b] , sociology lecturer Mary Kelsey developed the following assignment:
This was a lengthy and complex assignment worth a substantial portion of the course grade. Since the class was very large, the instructor wanted to minimize the effort it would take her GSIs to grade the papers in a manner consistent with the assignment’s learning objectives. For these reasons Dr. Kelsey and the instructional team gave a lot of forethought to crafting a detailed grading rubric.
Desired Traits
- Use and interpretation of data
- Reflection on personal experiences
- Application of course readings and materials
- Organization, writing, and mechanics
For this assignment, the instructional team decided to grade each trait individually because there seemed to be too many independent variables to grade holistically. They could have used a five-point scale, a three-point scale, or a descriptive analytic scale. The choice depended on the complexity of the assignment and the kind of information they wanted to convey to students about their work.
Below are three of the analytic rubrics they considered for the Argument trait and a holistic rubric for all the traits together. Lastly you will find the entire analytic rubric, for all five desired traits, that was finally used for the assignment. Which would you choose, and why?
Five-Point Scale
| 5 | Argument pertains to relationship between social factors and educational opportunity and is clearly stated and defensible. |
| 4 | Argument pertains to relationship between social factors and educational opportunity and is defensible, but it is not clearly stated. |
| 3 | Argument pertains to relationship between social factors and educational opportunity but is not defensible using the evidence available. |
| 2 | Argument is presented, but it does not pertain to relationship between social factors and educational opportunity. |
| 1 | Social factors and educational opportunity are discussed, but no argument is presented. |
Three-Point Scale
| Argument pertains to relationship between social factors and educational opportunity and is clearly stated and defensible. | |
| Argument pertains to relationship between social factors and educational opportunity but may not be clear or sufficiently narrow in scope. | |
| Social factors and educational opportunity are discussed, but no argument is presented. |
Simplified Three-Point Scale, numbers replaced with descriptive terms
| Argument pertains to relationship between social factors and educational opportunity and is clearly stated and defensible |
For some assignments, you may choose to use a holistic rubric, or one scale for the whole assignment. This type of rubric is particularly useful when the variables you want to assess just cannot be usefully separated. We chose not to use a holistic rubric for this assignment because we wanted to be able to grade each trait separately, but we’ve completed a holistic version here for comparative purposes.
| The paper is driven by a clearly stated, defensible argument about the relationship between social factors and educational opportunity. Sufficient data is used to defend the argument, and the data is accurately interpreted to identify each school’s position within a larger social structure. Personal educational experiences are examined thoughtfully and critically to identify significance of external social factors and support the main argument. Paper reflects solid understanding of the major themes of the course, using course readings to accurately define sociological concepts and to place the argument within a broader discussion of the relationship between social status and individual opportunity. Paper is clearly organized (with an introduction, transition sentences to connect major ideas, and conclusion) and has few or no grammar or spelling errors. Scholarly ideas are cited correctly using the ASA style guide. | |
| The paper is driven by a defensible argument about the relationship between social factors and public school quality, but it may not be stated as clearly and consistently throughout the essay as in an “A” paper. The argument is defended using sufficient data, reflection on personal experiences, and course readings, but the use of this evidence does not always demonstrate a clear understanding of how to locate the school or community within a larger class structure, how social factors influence personal experience, or the broader significance of course concepts. Essay is clearly organized, but might benefit from more careful attention to transitional sentences. Scholarly ideas are cited accurately, using the ASA style sheet, and the writing is polished, with few grammar or spelling errors. | |
| The paper contains an argument about the relationship between social factors and public school quality, but the argument may not be defensible using the evidence available. Data, course readings, and personal experiences are used to defend the argument, but in a perfunctory way, without demonstrating an understanding of how social factors are identified or how they shape personal experience. Scholarly ideas are cited accurately, using the ASA style sheet. Essay may have either significant organizational or proofreading errors, but not both. | |
| The paper does not have an argument, or is missing a major component of the evidence requested (data, course readings, or personal experiences). Alternatively, or in addition, the paper suffers from significant organizational and proofreading errors. Scholarly ideas are cited, but without following ASA guidelines. | |
| The paper does not provide an argument and contains only one component of the evidence requested, if any. The paper suffers from significant organizational and proofreading errors. If scholarly ideas are not cited, paper receives an automatic “F.” |
Final Analytic Rubric
This is the rubric the instructor finally decided to use. It rates five major traits, each on a five-point scale. This allowed for fine but clear distinctions in evaluating the students’ final papers.
| Argument pertains to relationship between social factors and educational opportunity and is clearly stated and defensible. | |
| Argument pertains to relationship between social factors and educational opportunity and is defensible, but it is not clearly stated. | |
| Argument pertains to relationship between social factors and educational opportunity but is not defensible using the evidence available. | |
| Argument is presented, but it does not pertain to relationship between social factors and educational opportunity. | |
| Social factors and educational opportunity are discussed, but no argument is presented. | |
| The data is accurately interpreted to identify each school’s position within a larger social structure, and sufficient data is used to defend the main argument. | |
| The data is accurately interpreted to identify each school’s position within a larger social structure, and data is used to defend the main argument, but it might not be sufficient. | |
| Data is used to defend the main argument, but it is not accurately interpreted to identify each school’s position within a larger social structure, and it might not be sufficient. | |
| Data is used to defend the main argument, but it is insufficient, and no effort is made to identify the school’s position within a larger social structure. | |
| Data is provided, but it is not used to defend the main argument. | |
| Personal educational experiences are examined thoughtfully and critically to identify significance of external social factors and support the main argument. | |
| Personal educational experiences are examined thoughtfully and critically to identify significance of external social factors, but relation to the main argument may not be clear. | |
| Personal educational experiences are examined, but not in a way that reflects understanding of the external factors shaping individual opportunity. Relation to the main argument also may not be clear. | |
| Personal educational experiences are discussed, but not in a way that reflects understanding of the external factors shaping individual opportunity. No effort is made to relate experiences back to the main argument. | |
| Personal educational experiences are mentioned, but in a perfunctory way. | |
| Demonstrates solid understanding of the major themes of the course, using course readings to accurately define sociological concepts and to place the argument within a broader discussion of the relationship between social status and individual opportunity. | |
| Uses course readings to define sociological concepts and place the argument within a broader framework, but does not always demonstrate solid understanding of the major themes. | |
| Uses course readings to place the argument within a broader framework, but sociological concepts are poorly defined or not defined at all. The data is not all accurately interpreted to identify each school’s position within a larger social structure, and it might not be sufficient. | |
| Course readings are used, but paper does not place the argument within a broader framework or define sociological concepts. | |
| Course readings are only mentioned, with no clear understanding of the relationship between the paper and course themes. | |
| Clear organization and natural “flow” (with an introduction, transition sentences to connect major ideas, and conclusion) with few or no grammar or spelling errors. Scholarly ideas are cited correctly using the ASA style guide. | |
| Clear organization (introduction, transition sentences to connect major ideas, and conclusion), but writing might not always be fluid, and might contain some grammar or spelling errors. Scholarly ideas are cited correctly using the ASA style guide. | |
| Organization unclear or the paper is marred by significant grammar or spelling errors (but not both). Scholarly ideas are cited correctly using the ASA style guide. | |
| Organization unclear and the paper is marred by significant grammar and spelling errors. Scholarly ideas are cited correctly using the ASA style guide. | |
| Effort to cite is made, but the scholarly ideas are not cited correctly. (Automatic “F” if ideas are not cited at all.) | |
[b] These materials were developed during UC Berkeley’s 2005–2006 Mellon Library/Faculty Fellowship for Undergraduate Research program. Members of the instructional team who worked with Lecturer Kelsey in developing the grading rubric included Susan Haskell-Khan, a GSI Center teaching consultant and doctoral candidate in history, and Sarah McDaniel, a teaching librarian with the Doe/Moffitt Libraries.
- Faculty and Staff
Assessment and Curriculum Support Center
Creating and using rubrics.
Last Updated: 4 March 2024. Click here to view archived versions of this page.
On this page:
- What is a rubric?
- Why use a rubric?
- What are the parts of a rubric?
- Developing a rubric
- Sample rubrics
- Scoring rubric group orientation and calibration
- Suggestions for using rubrics in courses
- Equity-minded considerations for rubric development
- Tips for developing a rubric
- Additional resources & sources consulted
Note: The information and resources contained here serve only as a primers to the exciting and diverse perspectives in the field today. This page will be continually updated to reflect shared understandings of equity-minded theory and practice in learning assessment.
1. What is a rubric?
A rubric is an assessment tool often shaped like a matrix, which describes levels of achievement in a specific area of performance, understanding, or behavior.
There are two main types of rubrics:
Analytic Rubric : An analytic rubric specifies at least two characteristics to be assessed at each performance level and provides a separate score for each characteristic (e.g., a score on “formatting” and a score on “content development”).
- Advantages: provides more detailed feedback on student performance; promotes consistent scoring across students and between raters
- Disadvantages: more time consuming than applying a holistic rubric
- You want to see strengths and weaknesses.
- You want detailed feedback about student performance.
Holistic Rubric: A holistic rubrics provide a single score based on an overall impression of a student’s performance on a task.
- Advantages: quick scoring; provides an overview of student achievement; efficient for large group scoring
- Disadvantages: does not provided detailed information; not diagnostic; may be difficult for scorers to decide on one overall score
- You want a quick snapshot of achievement.
- A single dimension is adequate to define quality.
2. Why use a rubric?
- A rubric creates a common framework and language for assessment.
- Complex products or behaviors can be examined efficiently.
- Well-trained reviewers apply the same criteria and standards.
- Rubrics are criterion-referenced, rather than norm-referenced. Raters ask, “Did the student meet the criteria for level 5 of the rubric?” rather than “How well did this student do compared to other students?”
- Using rubrics can lead to substantive conversations among faculty.
- When faculty members collaborate to develop a rubric, it promotes shared expectations and grading practices.
Faculty members can use rubrics for program assessment. Examples:
The English Department collected essays from students in all sections of English 100. A random sample of essays was selected. A team of faculty members evaluated the essays by applying an analytic scoring rubric. Before applying the rubric, they “normed”–that is, they agreed on how to apply the rubric by scoring the same set of essays and discussing them until consensus was reached (see below: “6. Scoring rubric group orientation and calibration”). Biology laboratory instructors agreed to use a “Biology Lab Report Rubric” to grade students’ lab reports in all Biology lab sections, from 100- to 400-level. At the beginning of each semester, instructors met and discussed sample lab reports. They agreed on how to apply the rubric and their expectations for an “A,” “B,” “C,” etc., report in 100-level, 200-level, and 300- and 400-level lab sections. Every other year, a random sample of students’ lab reports are selected from 300- and 400-level sections. Each of those reports are then scored by a Biology professor. The score given by the course instructor is compared to the score given by the Biology professor. In addition, the scores are reported as part of the program’s assessment report. In this way, the program determines how well it is meeting its outcome, “Students will be able to write biology laboratory reports.”
3. What are the parts of a rubric?
Rubrics are composed of four basic parts. In its simplest form, the rubric includes:
- A task description . The outcome being assessed or instructions students received for an assignment.
- The characteristics to be rated (rows) . The skills, knowledge, and/or behavior to be demonstrated.
- Beginning, approaching, meeting, exceeding
- Emerging, developing, proficient, exemplary
- Novice, intermediate, intermediate high, advanced
- Beginning, striving, succeeding, soaring
- Also called a “performance description.” Explains what a student will have done to demonstrate they are at a given level of mastery for a given characteristic.
4. Developing a rubric
Step 1: Identify what you want to assess
Step 2: Identify the characteristics to be rated (rows). These are also called “dimensions.”
- Specify the skills, knowledge, and/or behaviors that you will be looking for.
- Limit the characteristics to those that are most important to the assessment.
Step 3: Identify the levels of mastery/scale (columns).
Tip: Aim for an even number (4 or 6) because when an odd number is used, the middle tends to become the “catch-all” category.
Step 4: Describe each level of mastery for each characteristic/dimension (cells).
- Describe the best work you could expect using these characteristics. This describes the top category.
- Describe an unacceptable product. This describes the lowest category.
- Develop descriptions of intermediate-level products for intermediate categories.
Important: Each description and each characteristic should be mutually exclusive.
Step 5: Test rubric.
- Apply the rubric to an assignment.
- Share with colleagues.
Tip: Faculty members often find it useful to establish the minimum score needed for the student work to be deemed passable. For example, faculty members may decided that a “1” or “2” on a 4-point scale (4=exemplary, 3=proficient, 2=marginal, 1=unacceptable), does not meet the minimum quality expectations. We encourage a standard setting session to set the score needed to meet expectations (also called a “cutscore”). Monica has posted materials from standard setting workshops, one offered on campus and the other at a national conference (includes speaker notes with the presentation slides). They may set their criteria for success as 90% of the students must score 3 or higher. If assessment study results fall short, action will need to be taken.
Step 6: Discuss with colleagues. Review feedback and revise.
Important: When developing a rubric for program assessment, enlist the help of colleagues. Rubrics promote shared expectations and consistent grading practices which benefit faculty members and students in the program.
5. Sample rubrics
Rubrics are on our Rubric Bank page and in our Rubric Repository (Graduate Degree Programs) . More are available at the Assessment and Curriculum Support Center in Crawford Hall (hard copy).
These open as Word documents and are examples from outside UH.
- Group Participation (analytic rubric)
- Participation (holistic rubric)
- Design Project (analytic rubric)
- Critical Thinking (analytic rubric)
- Media and Design Elements (analytic rubric; portfolio)
- Writing (holistic rubric; portfolio)
6. Scoring rubric group orientation and calibration
When using a rubric for program assessment purposes, faculty members apply the rubric to pieces of student work (e.g., reports, oral presentations, design projects). To produce dependable scores, each faculty member needs to interpret the rubric in the same way. The process of training faculty members to apply the rubric is called “norming.” It’s a way to calibrate the faculty members so that scores are accurate and consistent across the faculty. Below are directions for an assessment coordinator carrying out this process.
Suggested materials for a scoring session:
- Copies of the rubric
- Copies of the “anchors”: pieces of student work that illustrate each level of mastery. Suggestion: have 6 anchor pieces (2 low, 2 middle, 2 high)
- Score sheets
- Extra pens, tape, post-its, paper clips, stapler, rubber bands, etc.
Hold the scoring session in a room that:
- Allows the scorers to spread out as they rate the student pieces
- Has a chalk or white board, smart board, or flip chart
- Describe the purpose of the activity, stressing how it fits into program assessment plans. Explain that the purpose is to assess the program, not individual students or faculty, and describe ethical guidelines, including respect for confidentiality and privacy.
- Describe the nature of the products that will be reviewed, briefly summarizing how they were obtained.
- Describe the scoring rubric and its categories. Explain how it was developed.
- Analytic: Explain that readers should rate each dimension of an analytic rubric separately, and they should apply the criteria without concern for how often each score (level of mastery) is used. Holistic: Explain that readers should assign the score or level of mastery that best describes the whole piece; some aspects of the piece may not appear in that score and that is okay. They should apply the criteria without concern for how often each score is used.
- Give each scorer a copy of several student products that are exemplars of different levels of performance. Ask each scorer to independently apply the rubric to each of these products, writing their ratings on a scrap sheet of paper.
- Once everyone is done, collect everyone’s ratings and display them so everyone can see the degree of agreement. This is often done on a blackboard, with each person in turn announcing his/her ratings as they are entered on the board. Alternatively, the facilitator could ask raters to raise their hands when their rating category is announced, making the extent of agreement very clear to everyone and making it very easy to identify raters who routinely give unusually high or low ratings.
- Guide the group in a discussion of their ratings. There will be differences. This discussion is important to establish standards. Attempt to reach consensus on the most appropriate rating for each of the products being examined by inviting people who gave different ratings to explain their judgments. Raters should be encouraged to explain by making explicit references to the rubric. Usually consensus is possible, but sometimes a split decision is developed, e.g., the group may agree that a product is a “3-4” split because it has elements of both categories. This is usually not a problem. You might allow the group to revise the rubric to clarify its use but avoid allowing the group to drift away from the rubric and learning outcome(s) being assessed.
- Once the group is comfortable with how the rubric is applied, the rating begins. Explain how to record ratings using the score sheet and explain the procedures. Reviewers begin scoring.
- Are results sufficiently reliable?
- What do the results mean? Are we satisfied with the extent of students’ learning?
- Who needs to know the results?
- What are the implications of the results for curriculum, pedagogy, or student support services?
- How might the assessment process, itself, be improved?
7. Suggestions for using rubrics in courses
- Use the rubric to grade student work. Hand out the rubric with the assignment so students will know your expectations and how they’ll be graded. This should help students master your learning outcomes by guiding their work in appropriate directions.
- Use a rubric for grading student work and return the rubric with the grading on it. Faculty save time writing extensive comments; they just circle or highlight relevant segments of the rubric. Some faculty members include room for additional comments on the rubric page, either within each section or at the end.
- Develop a rubric with your students for an assignment or group project. Students can the monitor themselves and their peers using agreed-upon criteria that they helped develop. Many faculty members find that students will create higher standards for themselves than faculty members would impose on them.
- Have students apply your rubric to sample products before they create their own. Faculty members report that students are quite accurate when doing this, and this process should help them evaluate their own projects as they are being developed. The ability to evaluate, edit, and improve draft documents is an important skill.
- Have students exchange paper drafts and give peer feedback using the rubric. Then, give students a few days to revise before submitting the final draft to you. You might also require that they turn in the draft and peer-scored rubric with their final paper.
- Have students self-assess their products using the rubric and hand in their self-assessment with the product; then, faculty members and students can compare self- and faculty-generated evaluations.
8. Equity-minded considerations for rubric development
Ensure transparency by making rubric criteria public, explicit, and accessible
Transparency is a core tenet of equity-minded assessment practice. Students should know and understand how they are being evaluated as early as possible.
- Ensure the rubric is publicly available & easily accessible. We recommend publishing on your program or department website.
- Have course instructors introduce and use the program rubric in their own courses. Instructors should explain to students connections between the rubric criteria and the course and program SLOs.
- Write rubric criteria using student-focused and culturally-relevant language to ensure students understand the rubric’s purpose, the expectations it sets, and how criteria will be applied in assessing their work.
- For example, instructors can provide annotated examples of student work using the rubric language as a resource for students.
Meaningfully involve students and engage multiple perspectives
Rubrics created by faculty alone risk perpetuating unseen biases as the evaluation criteria used will inherently reflect faculty perspectives, values, and assumptions. Including students and other stakeholders in developing criteria helps to ensure performance expectations are aligned between faculty, students, and community members. Additional perspectives to be engaged might include community members, alumni, co-curricular faculty/staff, field supervisors, potential employers, or current professionals. Consider the following strategies to meaningfully involve students and engage multiple perspectives:
- Have students read each evaluation criteria and talk out loud about what they think it means. This will allow you to identify what language is clear and where there is still confusion.
- Ask students to use their language to interpret the rubric and provide a student version of the rubric.
- If you use this strategy, it is essential to create an inclusive environment where students and faculty have equal opportunity to provide input.
- Be sure to incorporate feedback from faculty and instructors who teach diverse courses, levels, and in different sub-disciplinary topics. Faculty and instructors who teach introductory courses have valuable experiences and perspectives that may differ from those who teach higher-level courses.
- Engage multiple perspectives including co-curricular faculty/staff, alumni, potential employers, and community members for feedback on evaluation criteria and rubric language. This will ensure evaluation criteria reflect what is important for all stakeholders.
- Elevate historically silenced voices in discussions on rubric development. Ensure stakeholders from historically underrepresented communities have their voices heard and valued.
Honor students’ strengths in performance descriptions
When describing students’ performance at different levels of mastery, use language that describes what students can do rather than what they cannot do. For example:
- Instead of: Students cannot make coherent arguments consistently.
- Use: Students can make coherent arguments occasionally.
9. Tips for developing a rubric
- Find and adapt an existing rubric! It is rare to find a rubric that is exactly right for your situation, but you can adapt an already existing rubric that has worked well for others and save a great deal of time. A faculty member in your program may already have a good one.
- Evaluate the rubric . Ask yourself: A) Does the rubric relate to the outcome(s) being assessed? (If yes, success!) B) Does it address anything extraneous? (If yes, delete.) C) Is the rubric useful, feasible, manageable, and practical? (If yes, find multiple ways to use the rubric: program assessment, assignment grading, peer review, student self assessment.)
- Collect samples of student work that exemplify each point on the scale or level. A rubric will not be meaningful to students or colleagues until the anchors/benchmarks/exemplars are available.
- Expect to revise.
- When you have a good rubric, SHARE IT!
10. Additional resources & sources consulted:
Rubric examples:
- Rubrics primarily for undergraduate outcomes and programs
- Rubric repository for graduate degree programs
Workshop presentation slides and handouts:
- Workshop handout (Word document)
- How to Use a Rubric for Program Assessment (2010)
- Techniques for Using Rubrics in Program Assessment by guest speaker Dannelle Stevens (2010)
- Rubrics: Save Grading Time & Engage Students in Learning by guest speaker Dannelle Stevens (2009)
- Rubric Library , Institutional Research, Assessment & Planning, California State University-Fresno
- The Basics of Rubrics [PDF], Schreyer Institute, Penn State
- Creating Rubrics , Teaching Methods and Management, TeacherVision
- Allen, Mary – University of Hawai’i at Manoa Spring 2008 Assessment Workshops, May 13-14, 2008 [available at the Assessment and Curriculum Support Center]
- Mertler, Craig A. (2001). Designing scoring rubrics for your classroom. Practical Assessment, Research & Evaluation , 7(25).
- NPEC Sourcebook on Assessment: Definitions and Assessment Methods for Communication, Leadership, Information Literacy, Quantitative Reasoning, and Quantitative Skills . [PDF] (June 2005)
Contributors: Monica Stitt-Bergh, Ph.D., TJ Buckley, Yao Z. Hill Ph.D.
Essay Papers Writing Online
Effective essay writing rubrics to enhance students’ skills and performance.

Essay writing is a fundamental skill that students must master to succeed academically. To help students improve their writing, educators often use rubrics as a tool for assessment and feedback. An essay writing rubric is a set of criteria that outlines what is expected in a well-crafted essay, providing students with clear guidelines for success.
Effective essay writing rubrics not only evaluate the quality of the content but also assess the organization, coherence, language use, and overall structure of an essay. By using a rubric, students can better understand what aspects of their writing need improvement and how to achieve higher grades.
This article will explore the importance of essay writing rubrics in academic success and provide tips on how students can use them to enhance their writing skills. By understanding and mastering the criteria outlined in a rubric, students can not only improve their writing but also excel in their academic endeavors.
Learn the Key Elements
When it comes to effective essay writing, understanding the key elements is essential for academic success. Here are some important elements to keep in mind:
- Thesis Statement: A clear and concise thesis statement that presents the main idea of your essay.
- Structure: A well-organized structure with introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
- Evidence: Use relevant evidence and examples to support your arguments.
- Analysis: Analyze the evidence provided and draw conclusions based on your analysis.
- Clarity and Coherence: Ensure that your essay is clear, coherent, and easy to follow.
By mastering these key elements, you can improve your essay writing skills and achieve academic success.
Elements of Effective Essay Writing
When it comes to writing a successful essay, there are several key elements that you should keep in mind to ensure your work is of high quality. Here are some essential aspects to consider:
| A strong thesis statement is the foundation of a well-written essay. It should clearly state the main argument or position you will be defending in your writing. | |
| Your essay should have a logical flow and be well-organized. Make sure your ideas are presented in a coherent manner, with each paragraph contributing to the overall argument. | |
| Your introduction should grab the reader’s attention and provide context for your argument, while the conclusion should summarize your main points and leave a lasting impression. | |
| To support your argument, use relevant evidence and examples to back up your claims. This will make your essay more persuasive and convincing. | |
| It is important to cite your sources properly to give credit where it is due and avoid plagiarism. Make sure to follow the appropriate citation style required by your academic institution. | |
| Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and coherent. Avoid jargon and convoluted sentences, and make sure your ideas are easy to follow for the reader. |
Understand the Importance
Understanding the importance of essay writing rubrics is crucial for academic success. Rubrics provide clear criteria for evaluating and assessing essays, which helps both students and instructors. They help students understand what is expected of them, leading to more focused and organized writing. Rubrics also provide consistency in grading, ensuring that all students are evaluated fairly and objectively. By using rubrics, students can see where they excel and where they need to improve, making the feedback process more constructive and impactful.
of Clear and Concise Rubrics
One key aspect of effective essay writing rubrics is the clarity and conciseness of the criteria they outline. Clear and concise rubrics provide students with a roadmap for success and make grading more efficient for instructors. When creating rubrics, it is essential to clearly define the expectations for each aspect of the essay, including content, organization, style, and grammar.
By using language that is straightforward and easy to understand, students can easily grasp what is expected of them and how they will be evaluated. Additionally, concise rubrics avoid confusion and ambiguity, which can lead to frustration and misunderstanding among students.
Furthermore, clear and concise rubrics help instructors provide more targeted feedback to students, allowing them to focus on specific areas for improvement. This ultimately leads to better learning outcomes and helps students develop their writing skills more effectively.
Implement Structured Guidelines
Structured guidelines are essential for effective essay writing. These guidelines provide a framework for organizing your thoughts, ideas, and arguments in a logical and coherent manner. By implementing structured guidelines, you can ensure that your essay is well-organized, cohesive, and easy to follow.
One important aspect of structured guidelines is creating an outline before you start writing. An outline helps you plan the structure of your essay, including the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. It also helps you organize your ideas and ensure that your arguments flow logically from one point to the next.
Another important aspect of structured guidelines is using transitions to connect your ideas and arguments. Transitions help readers follow the flow of your essay and understand how one point relates to the next. They also help maintain the coherence and clarity of your writing.
Finally, structured guidelines include formatting requirements such as word count, font size, spacing, and citation style. Adhering to these formatting requirements ensures that your essay meets academic standards and is visually appealing to readers.
for Academic Excellence
When aiming for academic excellence in essay writing, it is essential to adhere to rigorous standards and criteria set by the educational institution. The use of effective essay writing rubrics can greatly enhance the quality of academic work by providing clear guidelines and criteria for assessment.
Academic excellence in essay writing involves demonstrating a deep understanding of the subject matter, presenting a well-structured argument, and showcasing critical thinking skills. Rubrics can help students focus on key elements such as thesis development, evidence analysis, organization, and clarity of expression.
By following a well-designed rubric, students can ensure that their essays meet the desired academic standards and expectations. Feedback provided based on the rubric can also help students identify areas for improvement and guide them towards achieving academic success.
| Key Elements | Criteria |
| Thesis Development | Clear thesis statement that addresses the main argument |
| Evidence Analysis | Use of relevant and credible evidence to support arguments |
| Organization | Logical flow of ideas and effective paragraph structure |
| Clarity of Expression | Clear and concise writing style with proper grammar and punctuation |
Master the Art
Mastering the art of essay writing requires dedication, practice, and attention to detail. To become a proficient essay writer, one must develop strong writing skills, a clear and logical structure, as well as an effective argumentative style. Start by understanding the purpose of your essay and conducting thorough research to gather relevant information and evidence to support your claims.
Furthermore, pay close attention to grammar, punctuation, and spelling to ensure your work is polished and professional. Use essay writing rubrics as a guide to help you stay on track and meet the necessary criteria for academic success. Practice makes perfect, so don’t be afraid to revise and edit your work to improve your writing skills even further.
By mastering the art of essay writing through consistent practice and attention to detail, you can set yourself up for academic success and develop a valuable skill that will benefit you in various aspects of your life.
of Constructing Detailed Evaluations
Constructing detailed evaluations in essay writing rubrics is essential for providing specific feedback to students. When designing a rubric, it is important to consider the criteria that will be assessed and clearly define each level of performance. This involves breaking down the evaluation criteria into smaller, measurable components, which allows for more precise and accurate assessments.
Each criterion in the rubric should have a clear description of what is expected at each level of performance, from basic to proficient to advanced. This helps students understand the expectations and enables them to self-assess their work against the rubric. Additionally, including specific examples or descriptors for each level can further clarify the expectations and provide guidance to students.
Constructing detailed evaluations also involves ensuring that the rubric aligns with the learning objectives of the assignment. By mapping the evaluation criteria to the desired learning outcomes, instructors can ensure that the rubric accurately reflects what students are expected to demonstrate in their essays. This alignment helps students see the relevance of the assessment criteria and encourages them to strive for mastery of the material.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, unlock success with a comprehensive business research paper example guide, unlock your writing potential with writers college – transform your passion into profession, “unlocking the secrets of academic success – navigating the world of research papers in college”, master the art of sociological expression – elevate your writing skills in sociology.

School of Medicine (SOM)
Som academics, admissions & financial aid, som student life, som alumni profiles, som policies, visiting medical students, office of faculty affairs, contact som, som grading policy for phase 1 of md program.
Issue Date : May 30, 2024 Supersedes : Course Grading Policy for Phase 1, dated May 8, 2024 Last Review : May 30, 2024
The purpose of this policy is to provide consistent guidelines for grading courses in the New York Medical College, School of Medicine (NYMC SOM) Phase 1.
It is the policy of NYMC SOM that at the end of each course, each student’s performance is evaluated and recorded. All Phase I courses will be graded as Pass/Fail on the student's transcript. Course grades are composed of summative evaluations in two (2) domains: Medical Knowledge (MK) and Patient Care (PC). Any medical student who fails any domain of a course (MK in any module and/or PC), regardless of the outcome of remediation, will be reviewed and monitored by the Student Academic Success Team (SAST). Any medical student who has two (2) course Conditional Passes (CPs) OR one (1) course Fail (F) regardless of the outcome of remediation in an academic year, will be discussed by the Student Advancement, Performance and Review Committee (SAPRC) to determine the outcome of promotions. See the Policy on Student Promotions for more details. Professional behavior of the students is evaluated throughout the curriculum, separately, and monitored by the Professionalism and Integrity Committee (PIC) and the SAPRC.
This policy applies to all faculty, staff, and instructors who teach and assess, and medical students in Phase 1 of NYMC SOM curriculum.
IV. DEFINITIONS
Competency-based grading: assessment of student achievement using pre-defined standards. Grade abbreviations are as follows:
“INC” =incomplete “F” = Fail “P” = Pass “PR” = Pass with remediation “CP” = Conditional Pass “W” = Withdraw “WF” = Withdraw Failing
SAPRC: Student Advancement, Promotions, and Review Committee SAST: Student Academic Success Team ECC: Education and Curriculum Committee NBME : National Board of Medical Examiners
V. PROCEDURES
- Criteria and assessments utilized for assigning grades are established by faculty members with appropriate knowledge and expertise to set standards of achievement in each required learning experience in the medical education program. Criteria are reviewed and approved by the Education and Curriculum Committee (ECC). All criteria and assessments, as well as the associated grade composition/contribution for each course shall be described in the course syllabus. Course syllabi are made available to all students electronically throughout the duration of the course.
- Phase directors must post final course grades to the learning management system and submit them to the Office of the Registrar within 4 weeks of completion of a course.
- Students will receive regular, timely, and behaviorally specific feedback to help guide their individual learning and progressive development and achievement.
- End of course, and when applicable, mid-course/module written examination (NBME-style, short answer, and short essay)
- Laboratory practical exam (selected courses)
- Summative Clinical Skills Exam
- Final Community Engagement Presentation
- Preceptor Evaluations
- A variety of tools, including but not limited to: written assignments, presentations, written and practical lab exams are used to assess Medical Knowledge.
- The passing standard for this domain of the course grade is an average of “70%” (rounded to the nearest integer) for the entire course, together with a 70% or better for each individual module within the course.
- As an example, 69.5% will be considered meeting the required 70% benchmark for passing Medical Knowledge in a module or course.
- The Patient Care domain is assessed using structured rubrics that evaluate the student’s skills in history taking, physical examination, communication, clinical reasoning, ethics, and/or interprofessional collaboration.
- The passing standard for this domain of the course grade is achieving a minimum competency on pertinent patient care assessments within the course as outlined in the course syllabus.
- Assessments may include but are not limited to: Clinical Skills Exams (CSE), written examinations, written assignments, presentations, observed encounters, reflections, community engagement projects, preceptor evaluations.
- Professionalism: Professionalism is assessed throughout the curriculum using specific tools that evaluate stated SOM objectives for the professionalism competency. Lapses in professional behaviors will be recorded for longitudinal monitoring and, as appropriate, amenable to structured remediation.
- Numeric grades for each performance assessment and the final Medical Knowledge average grade for each module will be posted to the learning management system by module directors. The class average and standard deviation for each assessment will also be provided to the students. Where appropriate (e.g., medical knowledge assessment via electronic assessment platform), medical students will receive individualized Strengths and Opportunity reports.
- Application of letter grades will employ rounding of numerical grades to the nearest integer. As an example, 69.5% will be considered a Pass. The original numerical grade (to the nearest tenth) will be reported to the Registrar.
- A student does not achieve the required benchmark threshold for both the MK AND PC domains in a course OR
- A student does not meet the requirements of a CP as stated below (5a).
- A student does not achieve the required benchmark threshold for ONLY 1 competency domain (MK or PC) in a course AND
- The overall MK grade in the course is 67% AND
- The MK deficiency only involves a single module in the course AND
- The individual MK module deficiency is NOT <64%.
- A “CP” grade must be converted to a final grade (“P” or “F”) within one year of its issuance and prior to any determination regarding the student’s promotion to the next phase. Following receipt of a CP grade and absence of other conflicting performance issues, the student will be provided with an opportunity to remediate the deficiency. Conversion of a CP to P will occur for a medical student who successfully remediates the deficiency to the standards set forth by the module and phase directors. Conversion of a CP to F will occur, however, for a medical student who does not successfully remediate the deficiency on first attempt. Further remediation may be provided based on a decision of the SAPRC; successful remediation in such a circumstance would result in a conversion of the F to a PR (pass with remediation).
- Pass-Remediation (“PR”): A grade of PR will be assigned to a medical student who has failed a course but was subsequently successful in an assigned remediation (i.e., Pass with remediation).
- An “INC” grade must be converted to a final grade (“P” or “F”) prior to any determination regarding the student’s promotion to the next phase. A student may not be eligible to sit for the appropriate USMLE until the “INC” has been resolved.
- Withdrawal (“W”): A W grade will be assigned to a medical student who withdraws from a course which is already in progress.
- Withdrawal due to Failure (“WF”): A WF grade will be assigned to a medical student who is failing a course at the time of withdrawal in accordance with policies established by the Office of the Registrar.
VI. EFFECTIVE DATE
This policy is effective immediately.
VII. POLICY MANAGEMENT
Executive Stakeholder: Dean, School of Medicine Oversight Office: Undergraduate Medical Education
VIII. REFERENCES
LCME Standard 10.3: Policies Regarding Student Selection/Progress and Their Dissemination: The faculty of a medical school establish criteria for student selection and develop and implement effective policies and procedures regarding, and make decisions about, medical student application, selection, admission, assessment, promotion, graduation, and any disciplinary action. The medical school makes available to all interested parties its criteria, standards, policies, and procedures regarding these matters.

Campus Tour

Dean's Message

Financial Aid

Professionalism, Accolade and Incident Reporting (PAIR)

Liaison Committee on Medical Education
Clinical Skills and Simulation Center

NOTICE OF NONDISCRIMINATORY POLICY AS TO STUDENTS The New York Medical College admits students of any race, color, national and ethnic origin to all the rights, privileges, programs, and activities generally accorded or made available to students at the college. It does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national and ethnic origin in administration of its educational policies, admissions policies, scholarship and loan programs, and athletic and other school-administered programs. See full non-discrimination statement with contact info .


IMAGES
COMMENTS
A writing rubric is a clear set of guidelines on what your paper should include, often written as a rating scale that shows the range of scores possible on the assignment and how to earn each one. Professors use writing rubrics to grade the essays they assign, typically scoring on content, organization, mechanics, and overall understanding.
Essay Rubric Directions: Your essay will be graded based on this rubric. Consequently, use this rubric as a guide when writing your essay and check it again before you submit your essay. Traits 4 3 2 1 Focus & Details There is one clear, well-focused topic. Main ideas are clear and are well supported by detailed and accurate information.
You might Google, "Rubric for persuasive essay at the college level" and see if there are any publicly available examples to start from. Ask your colleagues if they have used a rubric for a similar assignment. ... Turnitin Assignments: Rubric or Grading Form; Other resources. DePaul University (n.d.). Rubrics. Gonzalez, J. (2014).
It is a sample rubric that needs to be edited to reflect the specifics of a. particular assignment. Students can self-assess using the rubric as a checklist before. submitting their assignment. This sample rubric can also be found under the Turnitin tool in. Edit the assignment requirements column, performance level descriptions in each box, and.
9-10 pts. -Essay maintains a clear, mostly specific, prompt-appropriate focus that develops a clear main idea throughout the essay. -Essay develops purpose with a clear angle. 8 pts. -Essay's focus is somewhat unclear or off-topic, and/or main idea may meander a bit or contain minor digressions.
YALE COLLEGE ENGL 114: Grading Rubric. The A Essay makes an interesting, complex—even surprising—argument and is thoroughly well-executed. While an A essay is the result of serious effort, the grade is based on the essay's content and presentation. The major claim of the essay is complex, insightful, and unexpected.
Logical, compelling progression of ideas in essay;clear structure which enhances and showcases the central idea or theme and moves the reader through the text. Organization flows so smoothly the reader hardly thinks about it. Effective, mature, graceful transitions exist throughout the essay.
The SAT essay rubric says that the best (that is, 4-scoring) essay uses " relevant, sufficient, and strategically chosen support for claim (s) or point (s) made. " This means you can't just stick to abstract reasoning like this: The author uses analogies to hammer home his point that hot dogs are not sandwiches.
Rubrics are tools for communicating grading criteria and assessing student progress. Rubrics take a variety of forms, from grids to checklists, and measure a range of writing tasks, from conceptual design to sentence-level considerations. As with any assessment tool, a rubric's effectiveness is entirely dependent upon its design and its ...
Grading rubrics can be of great benefit to both you and your students. For you, a rubric saves time and decreases subjectivity. Specific criteria are explicitly stated, facilitating the grading process and increasing your objectivity. For students, the use of grading rubrics helps them to meet or exceed expectations, to view the grading process ...
College-Level Writing Rubric Masterful Skilled Able Developing Novice (Way Off) Focus, Purpose, Thesis (Controlling of the assigned topic. Idea) Engaging and full development of a clear thesis as appropriate to assignment purpose. Competent and well-developed thesis; thesis represents sound and adequate understanding Mostly intelligible ideas;
Rubric for Evaluating Application Essays Criteria Not Grad Level--1 point Acceptable—2 points Exceptional—3 points Content Essential qu estions . addressed adequately Supporting details and/or examples. Clarity of purpose. Questions are missed or inadequately addressed. Details and examples are either lacking or irrelevant.
The essay writing rubric is designed to score students' essays using a 100-point grading scale in three major categories: Organization, Content, and Style & Mechanics. Essay Writing Assignment. Scoring Rubric ( 100 points possible) Organization: ( 20 points possible) I. Essay is easy to read due to clear organization of main points 8-10.
Grading rubrics are also valuable to students. A rubric can help instructors communicate to students the specific requirements and acceptable performance standards of an assignment. When rubrics are given to students with the assignment description, they can help students monitor and assess their progress as they work toward clearly indicated ...
In turn, the length of an essay rubric depends on academic levels, types of papers, and specific requirements, while general guidelines are: High School. Length: 1-2 pages. Word Count: 300-600 words. College. Length: 1-3 pages.
Writing rubrics can help address the concerns of both faculty and students by making writing assessment more efficient, consistent, and public. Whether it is called a grading rubric, a grading sheet, or a scoring guide, a writing assignment rubric lists criteria by which the writing is graded.
Rubrics & Checklists. Grading criteria can be very simple or complex. They can analyze discrete elements of performance or describe general traits that define papers in a given grade range. You can use them to set up a scoring sheet for grading final drafts, and to create revision-oriented checklists to speed up commenting on early drafts of ...
Try this rubric to make student expectations clear and end-of-project assessment easier. Learn more: Free Technology for Teachers. 100-Point Essay Rubric. Need an easy way to convert a scoring rubric to a letter grade? This example for essay writing earns students a final score out of 100 points. Learn more: Learn for Your Life. Drama ...
Examples of Rubric Creation. Creating a rubric takes time and requires thought and experimentation. Here you can see the steps used to create two kinds of rubric: one for problems in a physics exam for a small, upper-division physics course, and another for an essay assignment in a large, lower-division sociology course.
Holistic scoring is a quick method of evaluating a composition based on the reader's general impression of the overall quality of the writing—you can generally read a student's composition and assign a score to it in two or three minutes. Holistic scoring is usually based on a scale of 0-4, 0-5, or 0-6.
A random sample of essays was selected. A team of faculty members evaluated the essays by applying an analytic scoring rubric. Before applying the rubric, they "normed"-that is, they agreed on how to apply the rubric by scoring the same set of essays and discussing them until consensus was reached (see below: "6.
Example 1 - Research Paper Rubric. Characteristics to note in the rubric: Language is descriptive, not evaluative. Labels for degrees of success are descriptive ("Expert" "Proficient", etc.); by avoiding the use of letters representing grades or numbers representing points, there is no implied contract that qualities of the paper will ...
Needs Work. Title, Introduction, Conclusion. Title includes both subject and a hint about the thesis or point of view; engaging introduction that prepares the reader accurately for the body paragraphs; thought-provoking or interesting conclusion that ties everything back together and takes the thesis further. Most but not all of the qualities ...
When it comes to effective essay writing, understanding the key elements is essential for academic success. Here are some important elements to keep in mind: Thesis Statement: A clear and concise thesis statement that presents the main idea of your essay. Structure: A well-organized structure with introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Grading: Each of the summative components of the final course grade are evaluated using a specific rubric. Grades of Pass/Fail are assigned for each component of the final course grade. Students must achieve a Pass in both the Medical Knowledge (MK) AND the Patient Care (PC) course grade domains in order to pass a course as follows: Medical ...
The TEA's more rigorous formula raised the threshold for high schools to earn an "A" in college readiness, which is determined by the percentage of students who score well on Advanced ...